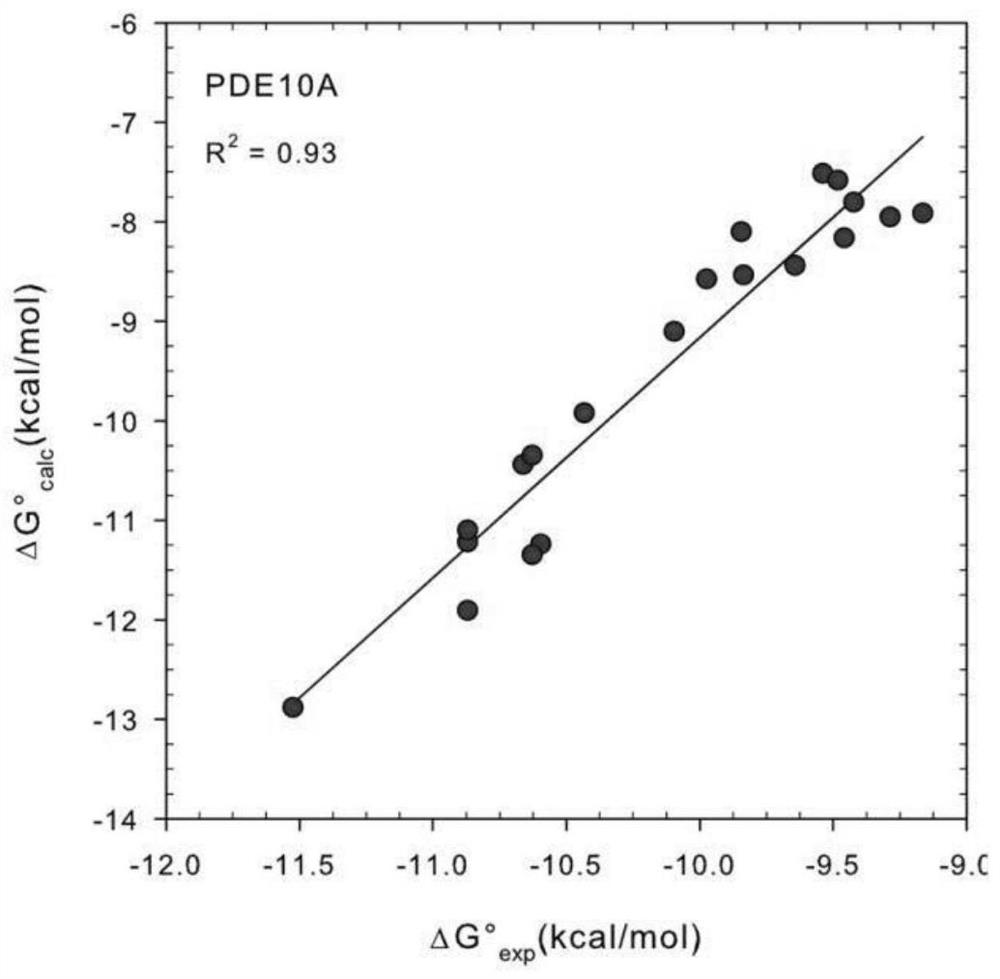
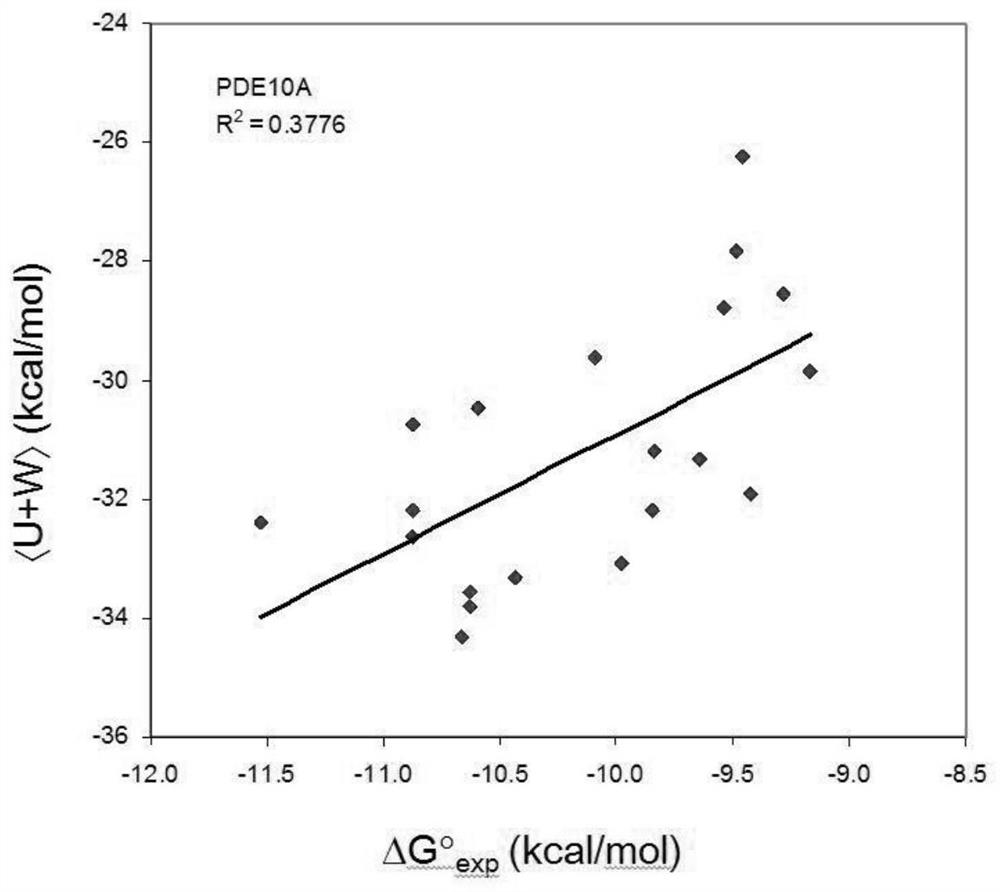
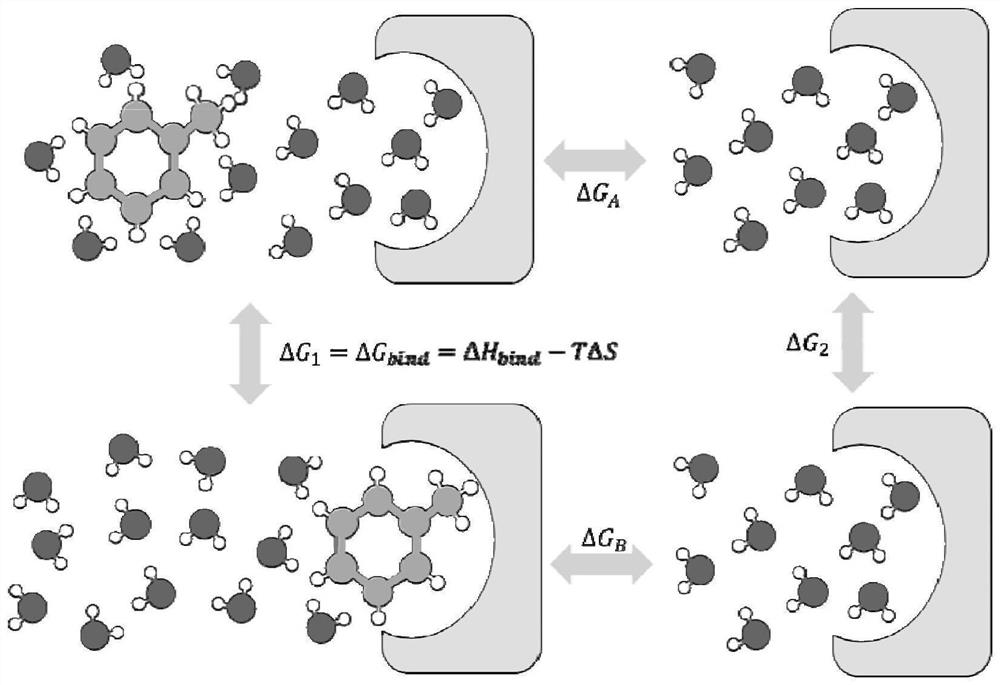
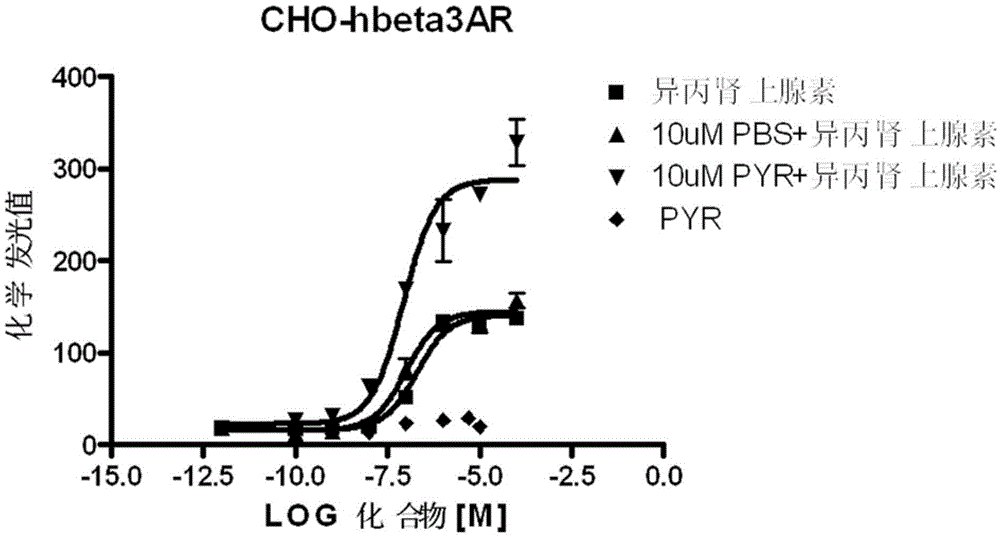
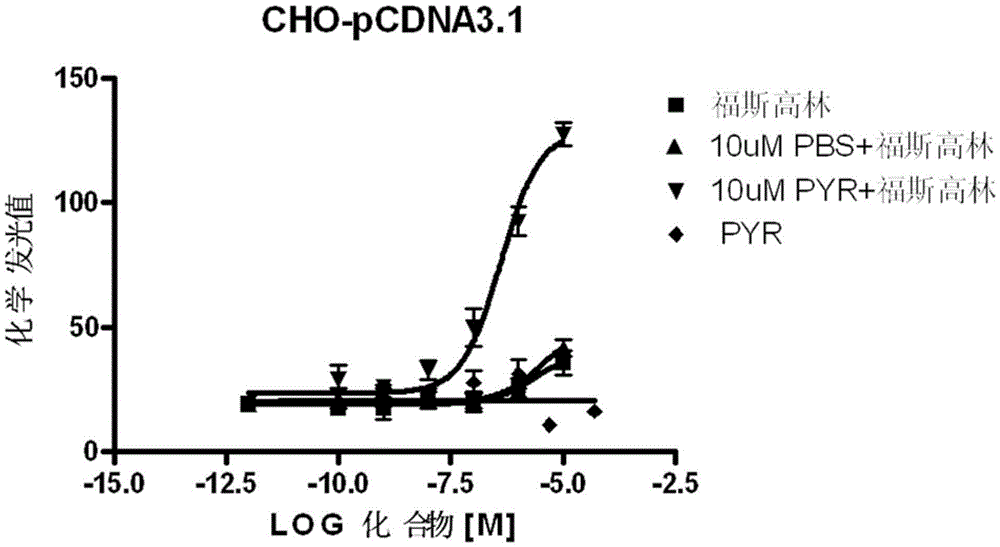
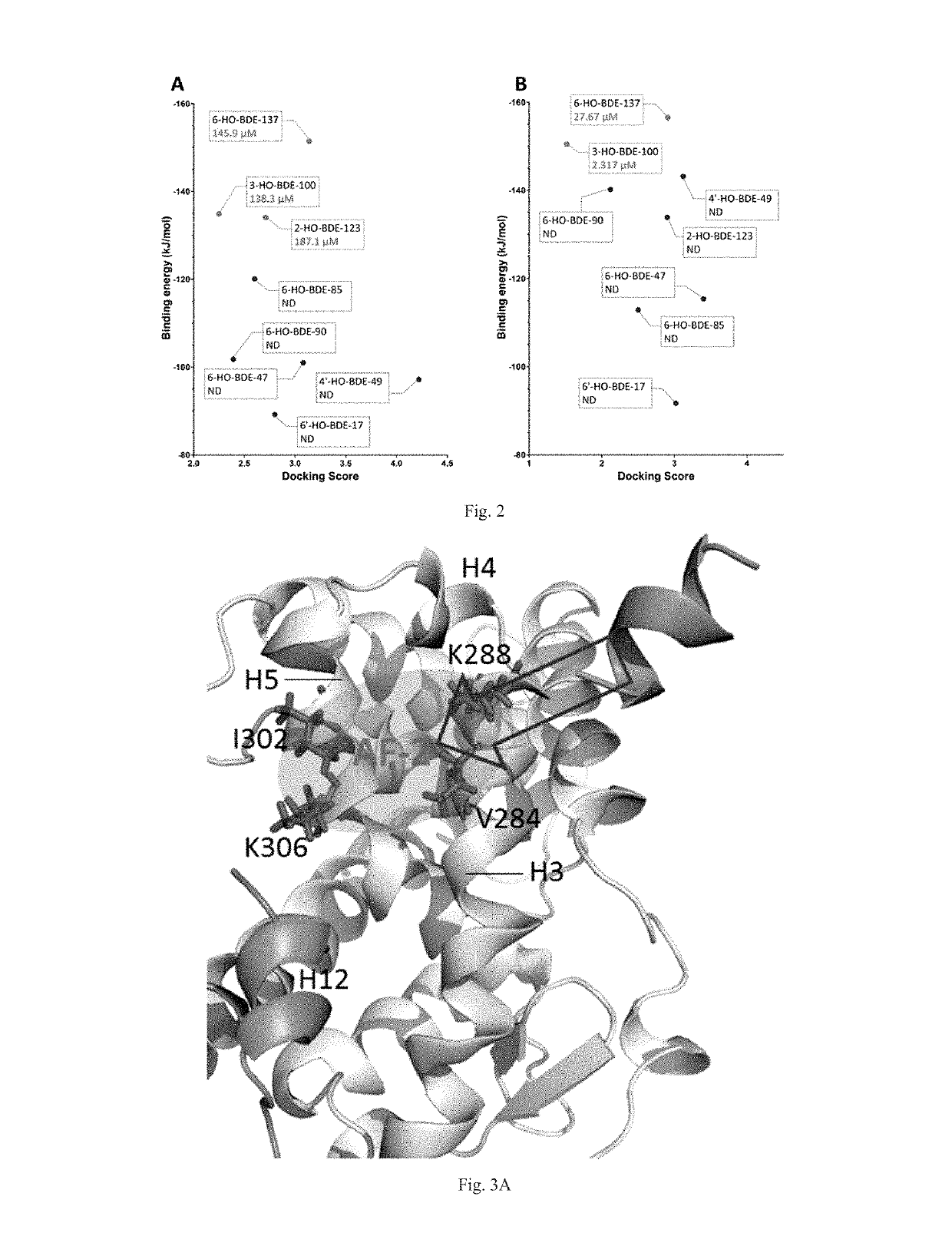
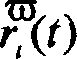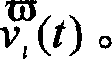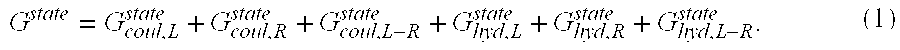Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Binding free energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment or prophylaxis of diseases caused by pilus-forming bacteria
InactiveUS6962791B2Reduce capacityReduce pathogenicityBiocideCompound screeningBacteroidesBinding free energy
Novel methods for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of diseases caused by tissue-adhering bacteria are disclosed. By interacting with periplasmic molecular chaperones it is achieved that the assembly of pili is prevented or inhibited and thereby the infectivity of the bacteria is diminished. Also disclosed are methods for screening for drugs as well as methods for the de novo design of such drugs, methods which rely on novel computer drug modelling methods involving an approximative calculation of binding free energy between macromolecules. Finally, novel pyranosides which are believed to be capable of interacting with periplasmic molecular chaperones are also disclosed.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
Neuregulin mutant, screening method and use
The present invention provides a method of screening NRG mutant for activating ErbB acceptor specifically. The method includes the following steps: establishing 3D model of complex of NRG, ErbB3, ErbB4, NRG / ErbB3 and NRG / ErbB4 in a homogeneous model establishing process; molecular kinetically simulating conformation and stability of NRG / ErbB3 and NRG / ErbB4; MM / PBSA process of calculating the binding free energy between NRG and ErbB3 or ErbB4; scanning and calculating process based on alanine theory to determine the NRG and acceptor affinity change during the mutation from NRG residue to alanine and determining NRG mutant for activating ErbB acceptor specifically. The present invention also provides the NRG mutant and its application and preparation process.
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
Computing method for processing interaction between small molecules and proteins
InactiveCN103049677AIncrease productivityThe key principle of technology is simpleSpecial data processing applicationsCrystallographyBinding site
The invention relates to a computing method for processing interaction between small molecules and proteins. The method includes the following steps that (1) ligand file data of the proteins and the small molecules are read in; (2) atom types in ligands of the proteins and the small molecules are judged; (3) positions and angles of the ligands of the small molecules are randomly initialized; (4) a search protein algorithm is operated, coordinates and angles of the ligands of the small molecules are optimized, and a chemscore formula serves as an evaluation function; (5) the computing is ended after maximum iterative times are achieved; and (6) results such as root mean square deviation (RMSD), binding free energy delta G and coordinates of a binding site are analyzed and output. Compared with computing methods for processing the interaction between the small molecules and the proteins in prior art, the computing method for processing the interaction between the small molecules and the proteins has the advantages that when pollutants and biomacromolecules are interacted can be rapidly determined, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
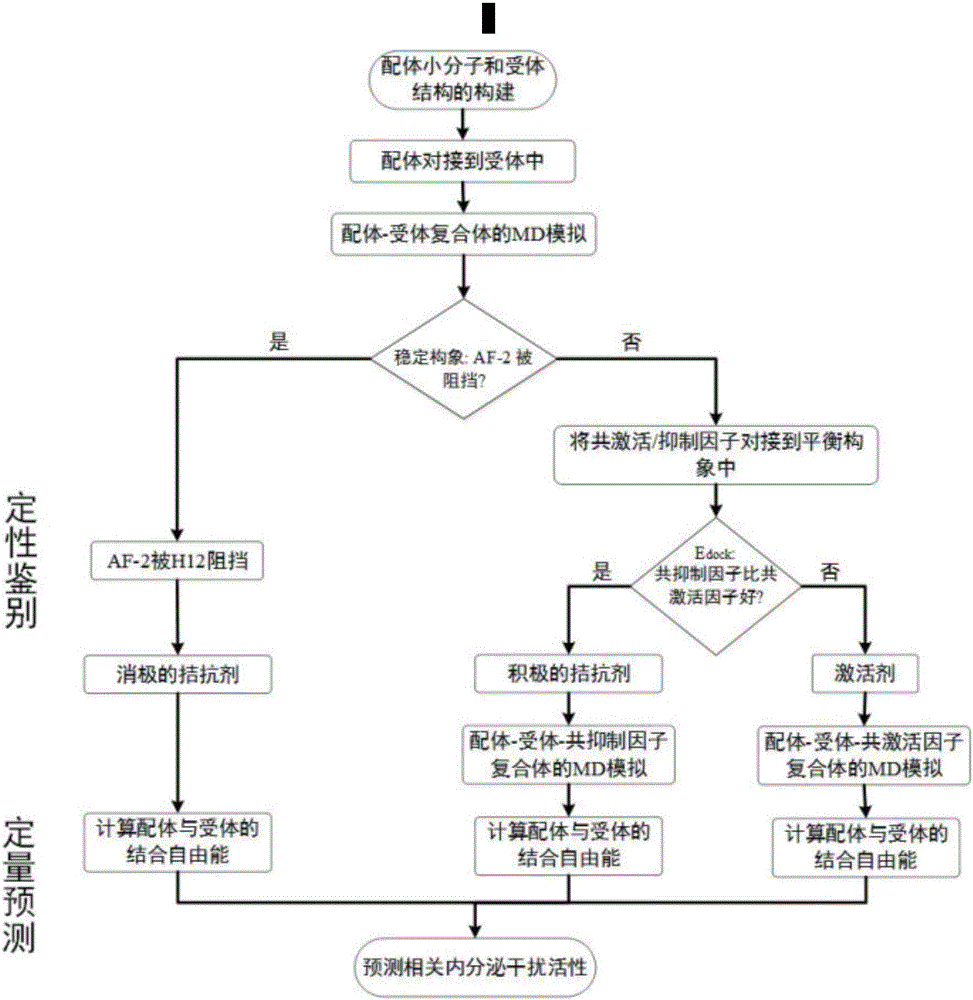
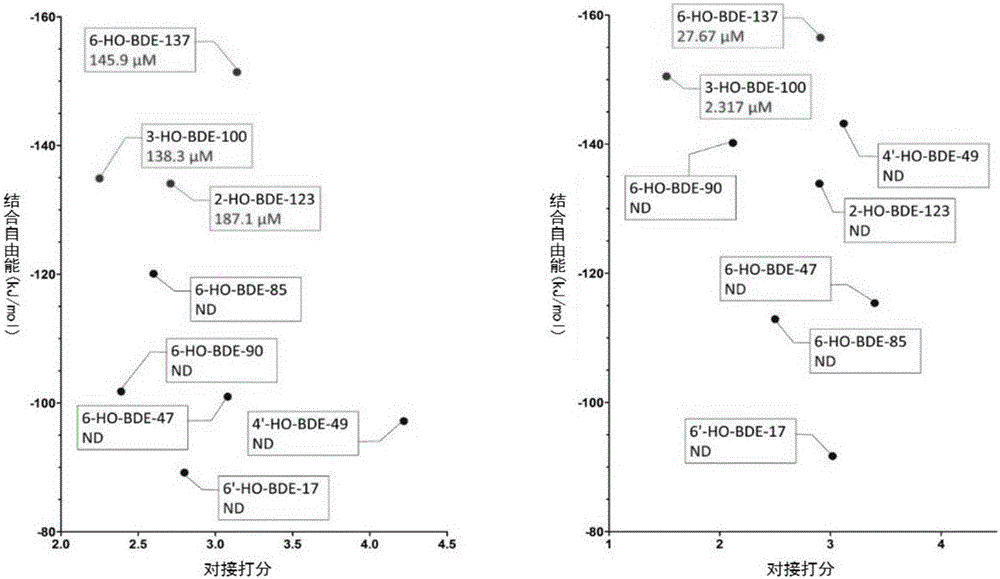
Thyroid hormone disruptor virtual screening and interference activity quantitative calculating method based on nuclear receptor coregulator
ActiveCN105893759ALow costEasy to operateBiological material analysisProteomicsFactor iiScreening method
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Altered antibodies having improved antigen-binding affinity
InactiveUS20070135998A1High affinityUseful and successfulImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProteomicsAntigen bindingSolvent
The invention relates to methods of modulating the antigen-binding affinity of an antibody by determining, using data corresponding to the structure of a complex between the antibody and an antigen in a solvent, a representation of a charge distribution of the CDRs of the antibody which minimizes electrostatic contribution to binding free energy between the antibody and the antigen in a solvent. Guided by these determinations, the antibody is accordingly modified (altered) to improve upon, e.g., antibody / antigen binding by modifying at least one amino acid residue to decrease the binding free energy between the antibody and antigen when bound in a solvent.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Method, system, and device for calculating binding free energy of proteins and drugs, and medium
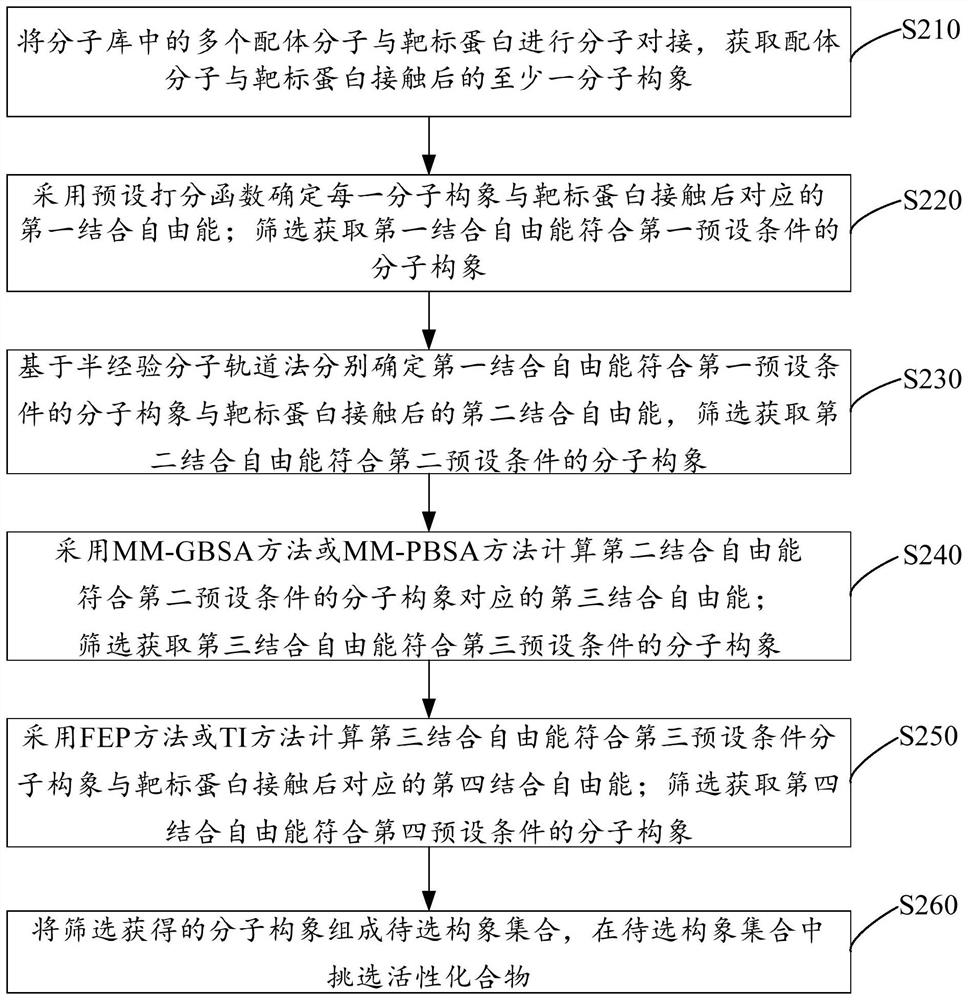
The invention discloses a method, system, and device for calculating binding free energy of proteins and drugs, and a medium. The method includes the steps: constructing a function of the binding freeenergy of proteins and drugs, wherein the function of the binding free energy of the proteins and the drugs is a relationship between the binding free energy of the proteins and the drugs and an electrostatic item, a polar solvation energy item, a van der Waals item, a nonpolar solvation energy item and interaction entropy; collecting each energy item of each protein and each drug complex in a training set, and performing multivariate linear fitting on the function of the binding free energy of proteins and drugs by using each energy item of each protein and each drug complex in the trainingset and the experimental value of each protein and each drug to obtain a function of the binding free energy of the proteins and the drugs; and inputting each energy item of the proteins to be testedand the drug complex into the trained function of the binding free energy of proteins and drugs, and outputting the binding free energy of the proteins and the drugs.
Owner:深圳新锐基因科技有限公司
Protein-ligand binding free energy calculating method based on MM/PBSA model
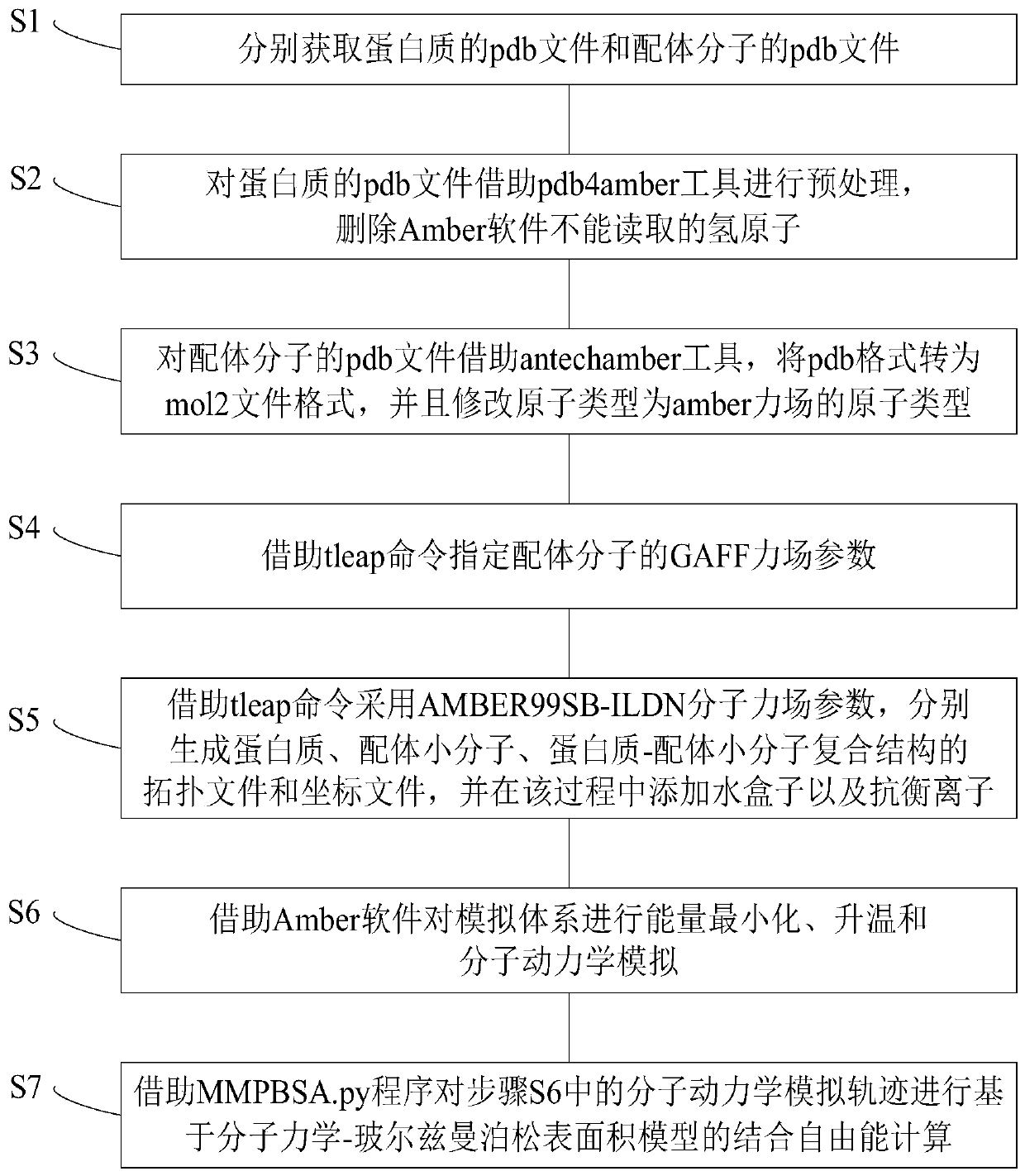
ActiveCN110400598AImprove computing efficiencyImprove calculation accuracyProteomicsGenomicsAntechamberMolecular mechanics
The invention provides a protein-ligand free energy calculating method based on a MM / PBSA model. The method comprises the following steps of respectively acquiring pdb files of a protein and a ligandmolecule; preprocessing the pdb file of the protein by means of a pdb4amber tool, deleting a hydrogen atom which cannot be read by Amber software; for the pdb file of the ligand molecule, converting the pdb format to a mol2 file format by means of an antechamber tool, and correcting the atom type to the atom type of an amber force field; assigning a GAFF force field parameter of the ligand molecule by means of a tleap command; respectively generating a topological file and a coordinate file of the protein, the ligand micromolecule and a protein-ligand micromolecule composite structure by meansof the tleap command through using an AMBER99SB-ILDN molecule force field parameter, and adding a water box and counter ions in the process; performing energy minimizing, heating and molecular dynamics simulation on a simulation system by means of the Amber software; and performing binding free energy calculation based on a molecular dynamics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area model on a molecular dynamics simulating track in a previous step by means of an MMPBSA.py program.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
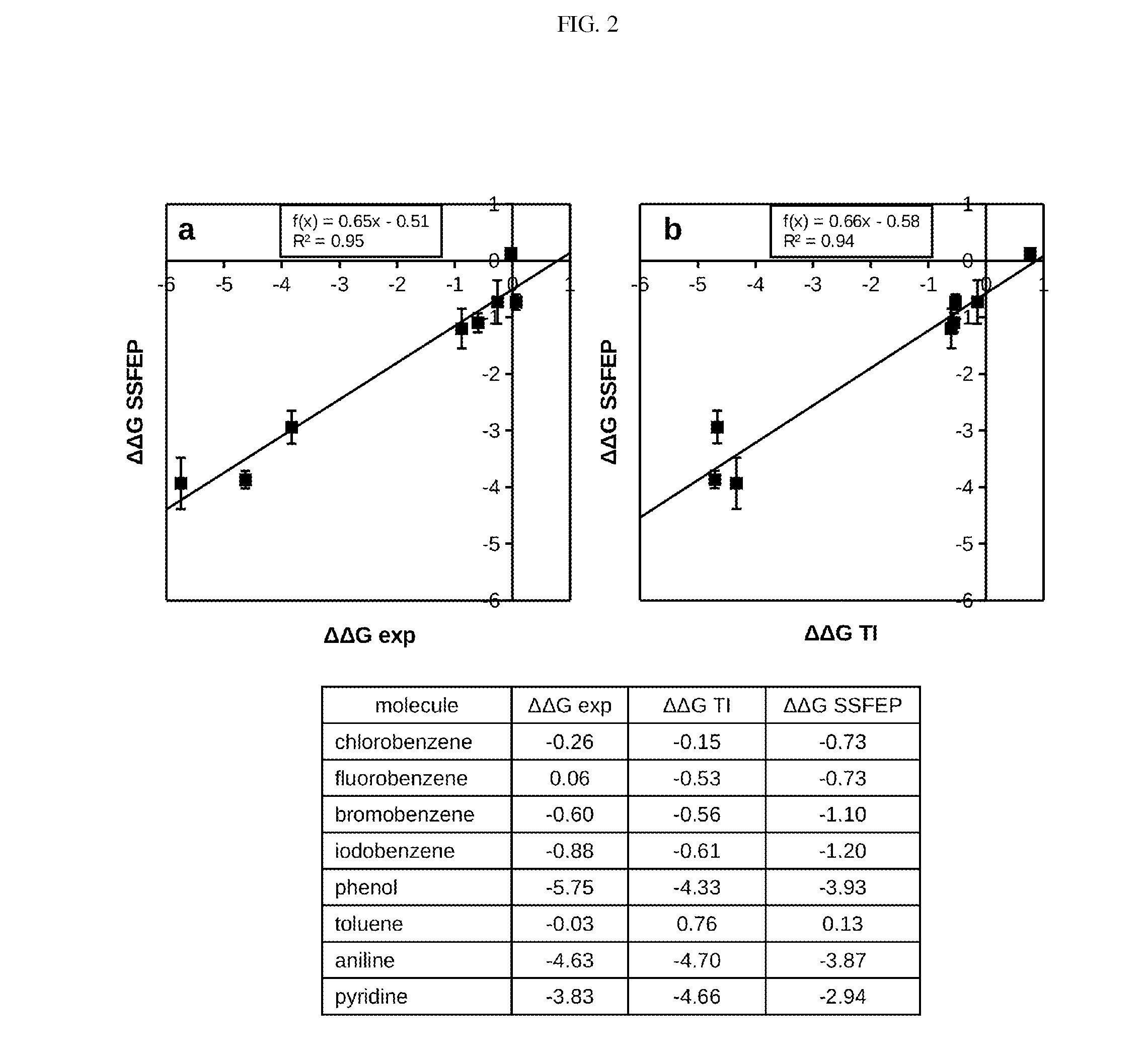
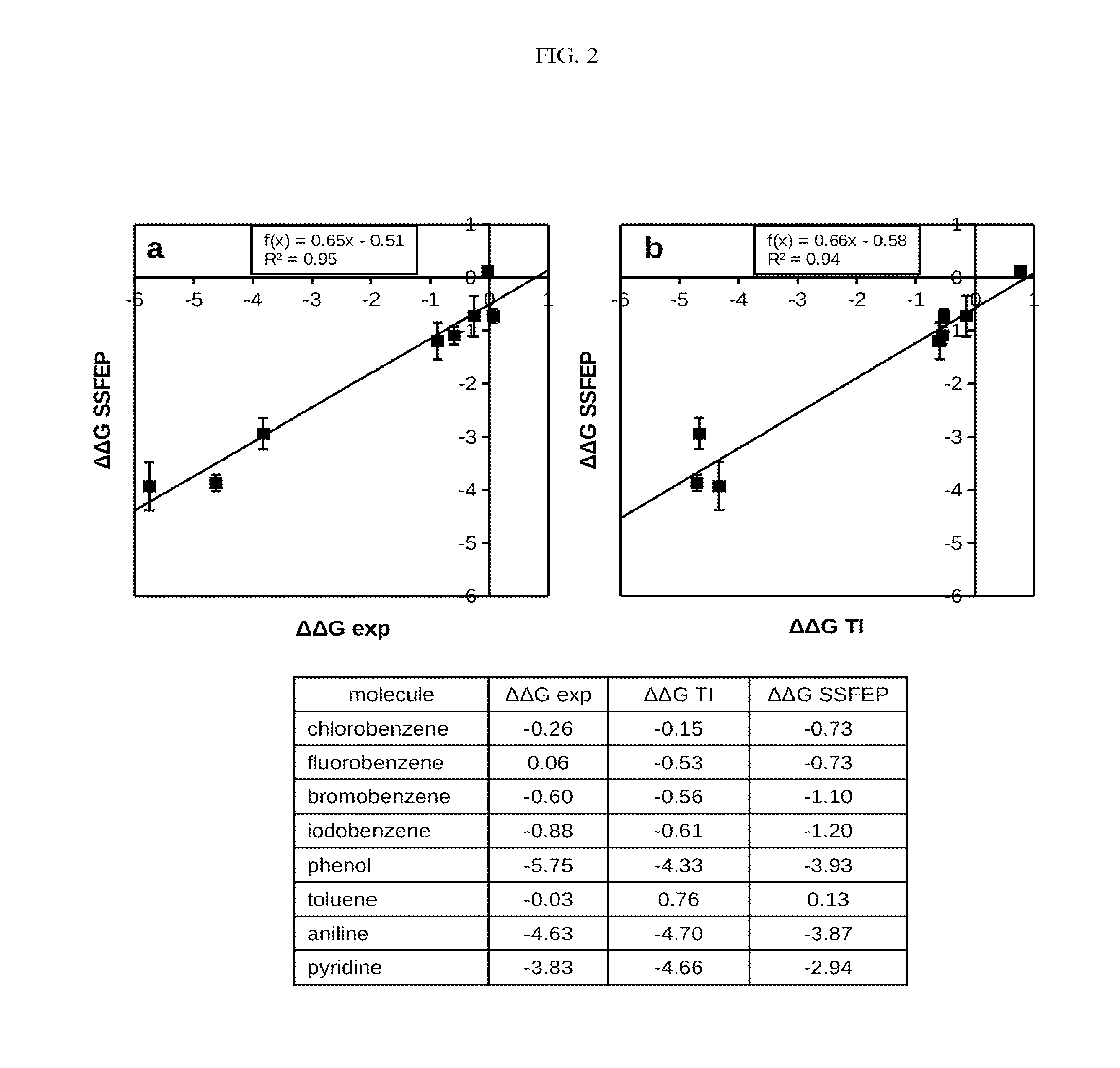
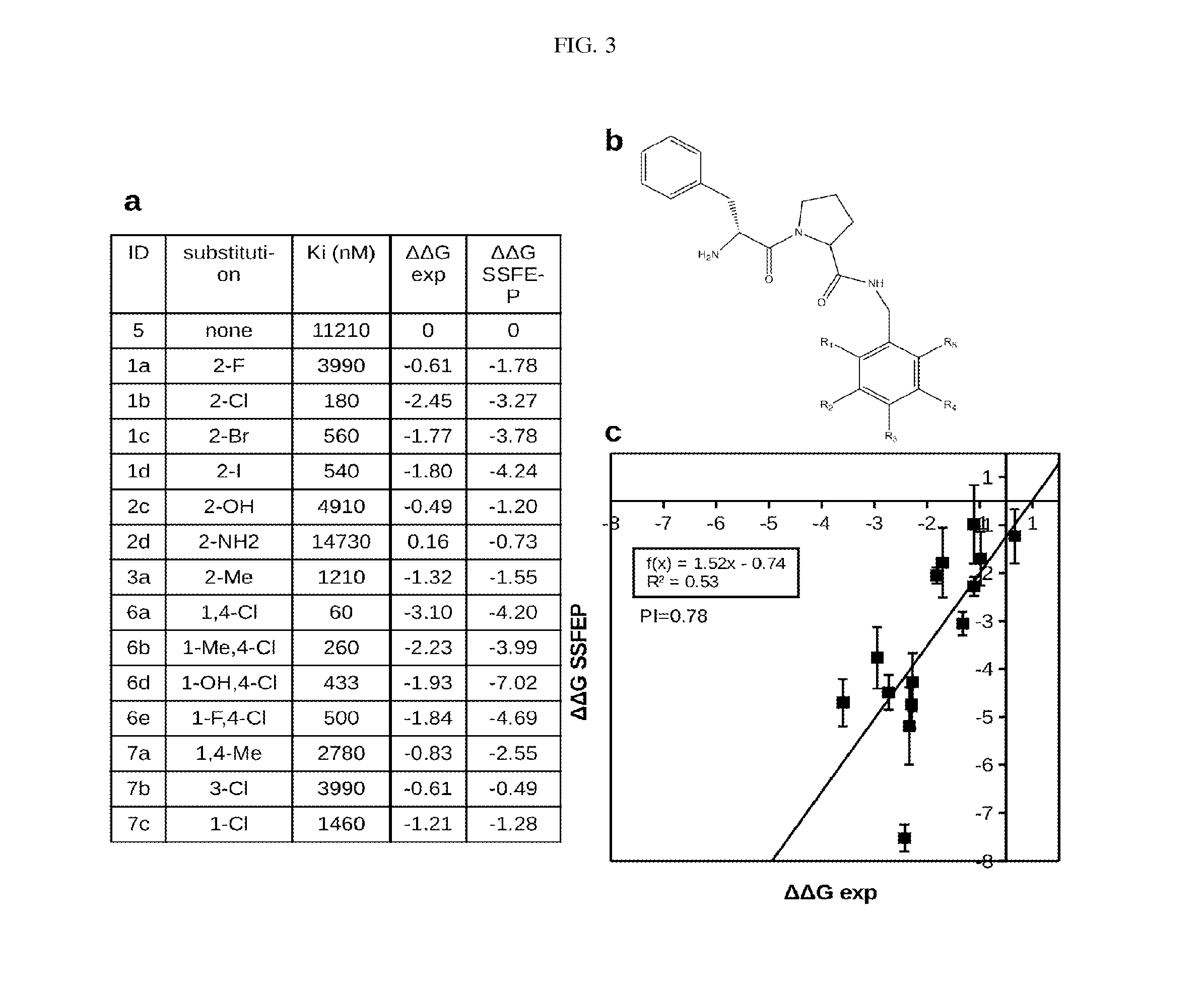
Site-specific fragment identification guided by single-step free energy perturbation calculations
InactiveUS20150095007A1Chemical property predictionMolecular designFree energiesFree energy perturbation
A method and system is disclosed for estimating the difference between binding free energies of molecules.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Algorithm for quickly and accurately calculating free affinity between proteinase and drug molecules
ActiveCN107423570AImprove accuracyShorten the timeMolecular designComputational theoretical chemistryBinding stateSteady state
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmacy and relates to an algorithm for quickly and accurately calculating free affinity between proteinase and drug molecules. The algorithm is characterized in that standard chemical potentials of a ligand and receptor in free state and a standard chemical potential of a receptor-ligand complex in bound state are calculated respectively, and differences among the standard chemical potentials are standard binding free energy; wherein in the calculation of the standard chemical potentials, M most steady-state conformations of the molecules are found first, j refers to energy wells corresponding to the most steady-state conformations, with j equal to 1...N, conformation integral zj of the corresponding energy well j of each most steady-state conformation is calculated, corresponding Boltzmann factor RT is calculated accordingly, and all the conformation integrals are combined to obtain a standard chemical potential for the ligand, the receptor or the receptor-ligand complex in bound state. By replacing experiments via computer simulation, screening and optimizing accuracy for pilot drugs are greatly improved, and time and cost for screening and optimizing are greatly decreased.
Owner:南昌立德生物技术有限公司
Method for measuring clay dispersion average binding free energy and adsorption free energy to cation
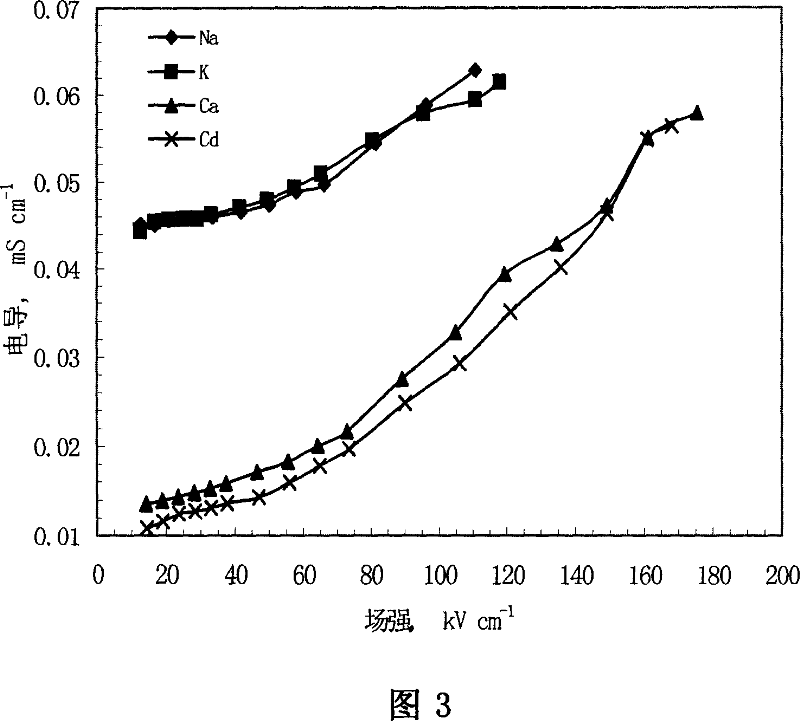
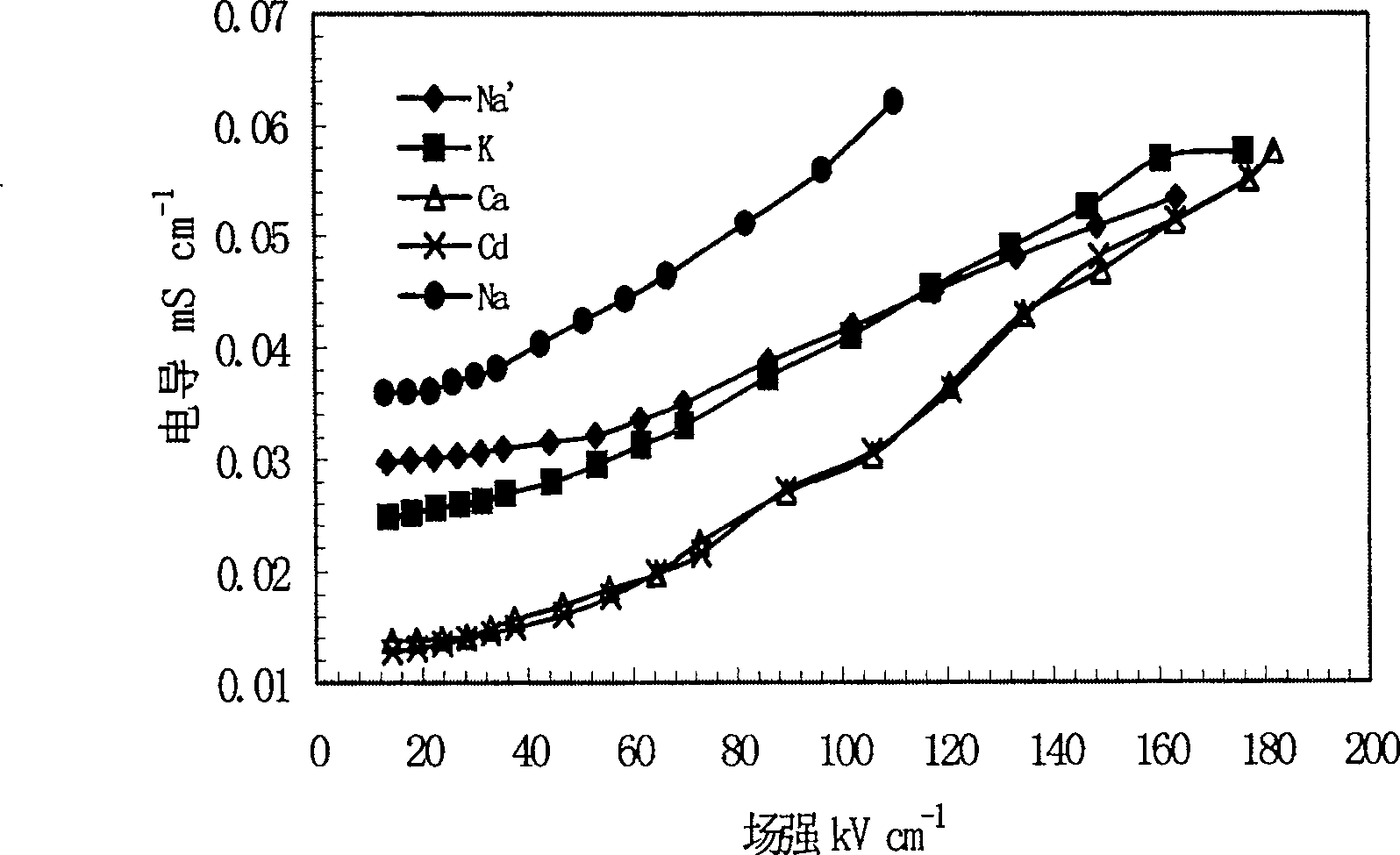
This invention relates to one method to test earth anode ion even combination free energy and absorptive free energy, which comprises the following steps: a, processing the anode saturation earth adhesive particles with radium less than 2 mu m and then using ion remove water or stilled water to match earth hanging liquid; b, putting the earth hanging liquid into field less than 15kV.cm<-1> to gradually form field intensity to test each conductivity rate to get the relation ship curve between earth hanging liquid and field intensity; c, according to math formula to compute particles anode ion even combination free energy and absorptive free energy, wherein, Delta G=RTln(2CEC.Cp.lambada / EC0) (4); Delta G=RTln(EC / EC0) with R for gas constant; T for thermal temperature and CEC for anode ion exchange volume and Cp for particle concentration.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
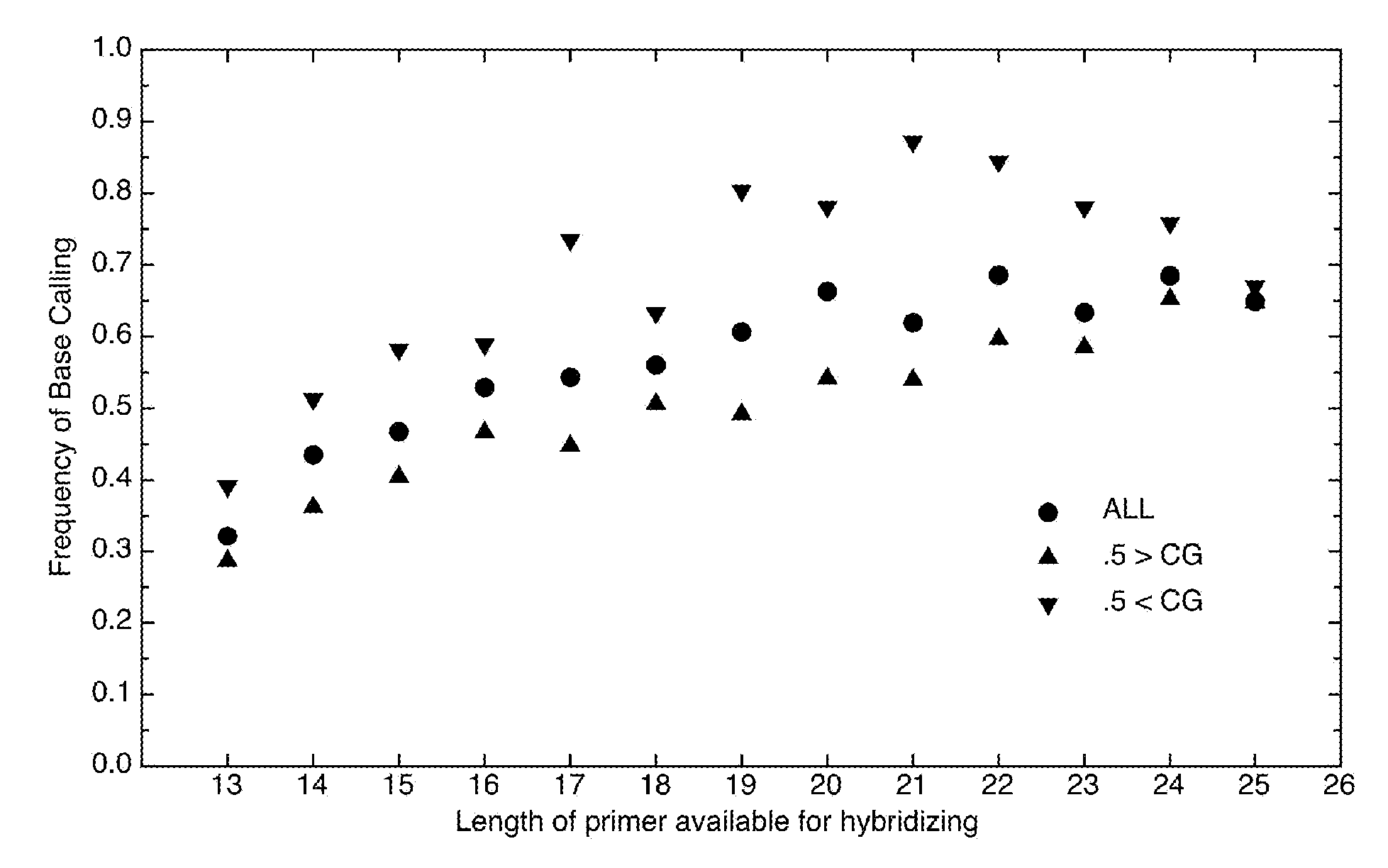
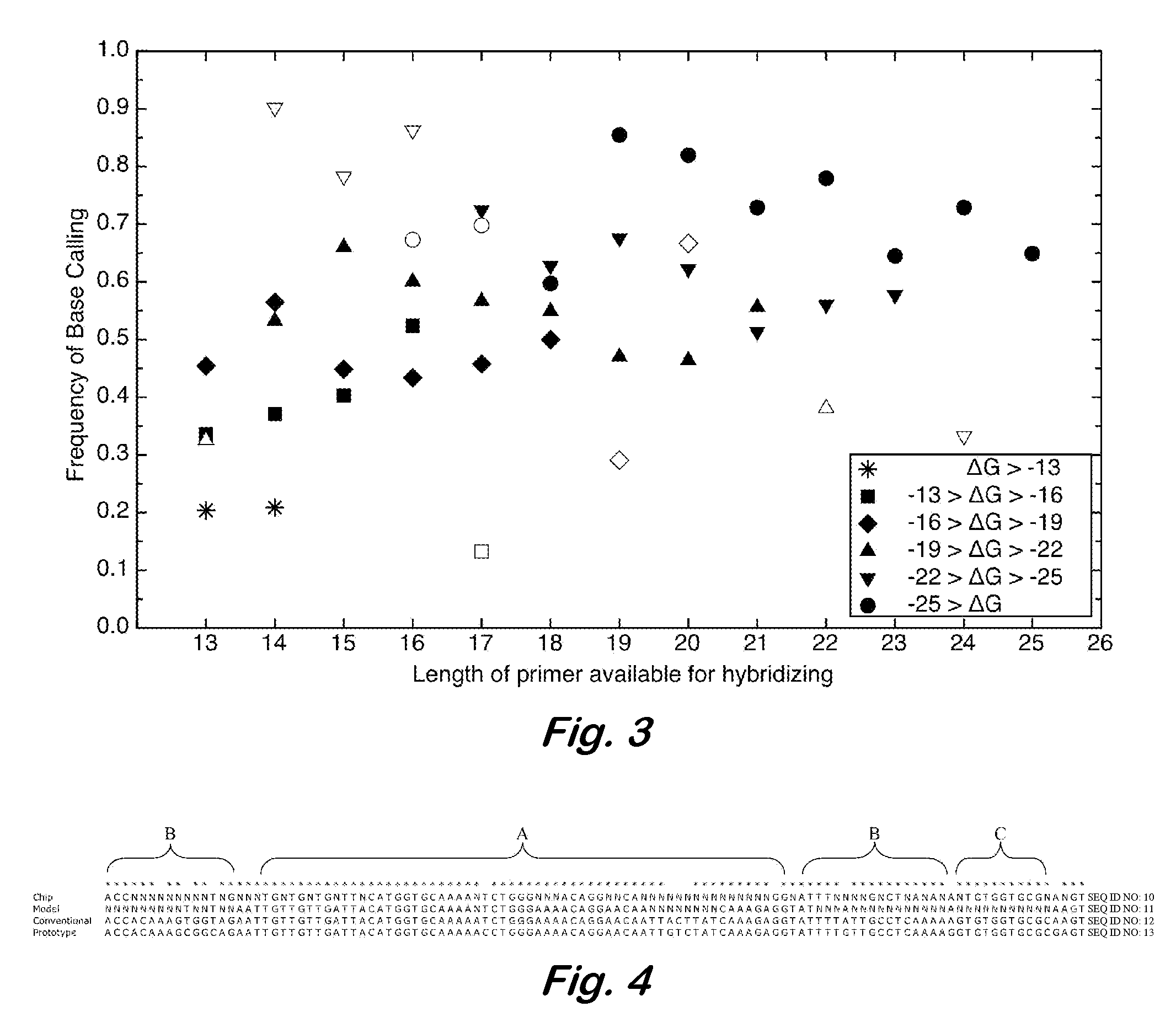
Design and selection of genetic targets for sequence resolved organism detection and identification
InactiveUS7668664B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiochemistry cleaning apparatusBase callingOrganism
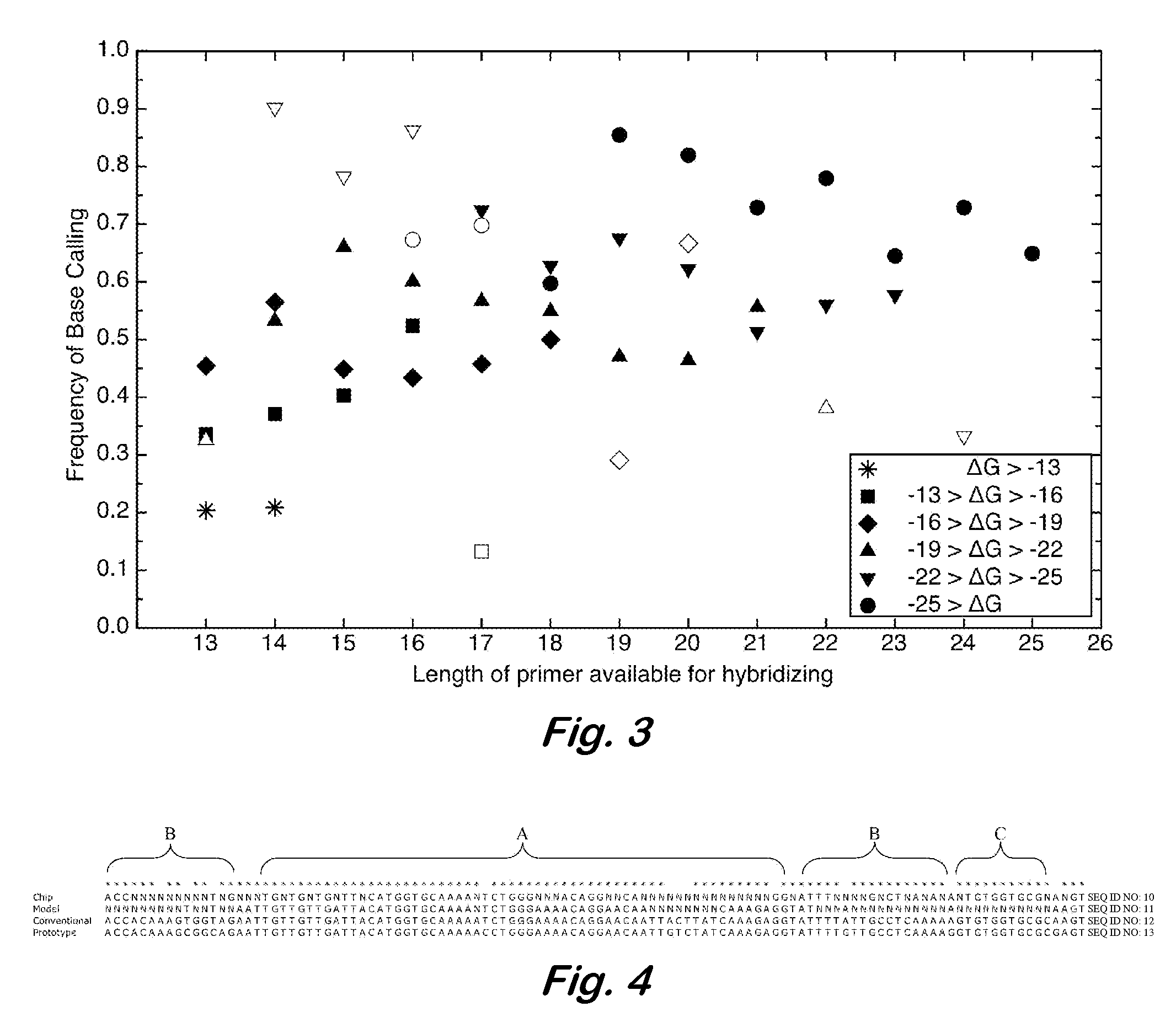
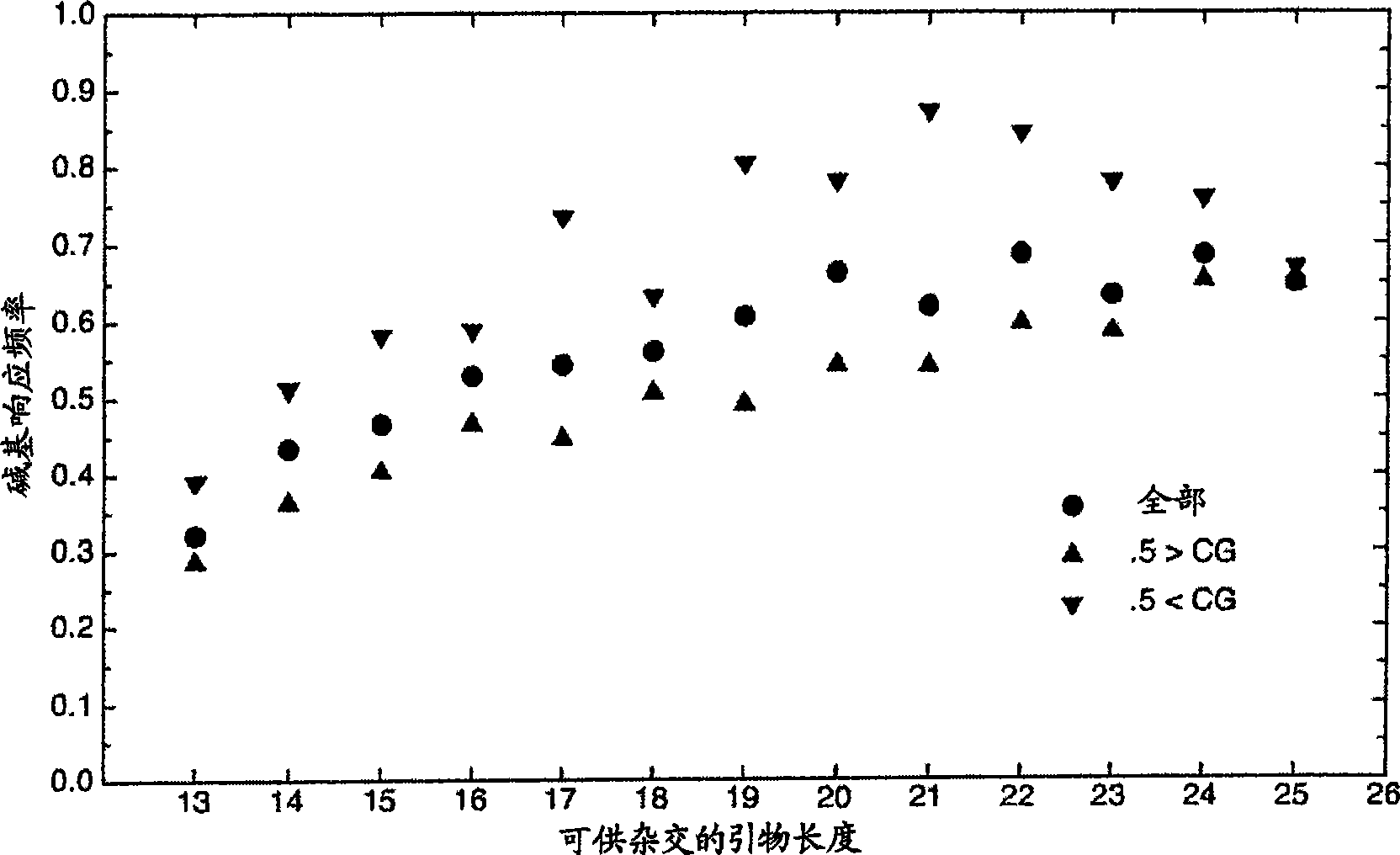
A computer-implemented method as follows. Providing a list of target sequences associated with one or more organisms. Providing a list of candidate prototype sequences suspected of hybridizing to one or more of the target sequences. Generating a collection of probes corresponding to each candidate prototype sequence, each collection of probes having a set of probes for every subsequence. The sets consist of the corresponding subsequence and every variation of the corresponding subsequence formed by varying a center nucleotide of the corresponding subsequence. Generating a set of fragments corresponding to each target sequence. Calculating the binding free energy of each fragment with a perfect complimentary sequence of the fragment. Determining which extended fragments are perfect matches to any of the probes. Assembling a base call sequence corresponding to each candidate prototype sequence.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Computer antibody combination mutation evolution system and method, information data processing terminal
ActiveCN109086568ADesign automationEfficient designSpecial data processing applicationsMutantInformation data
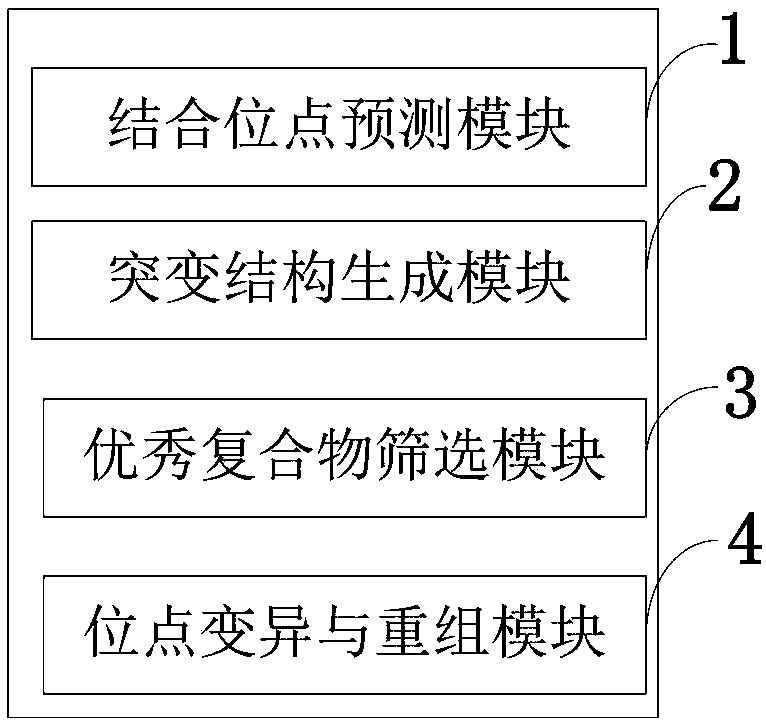
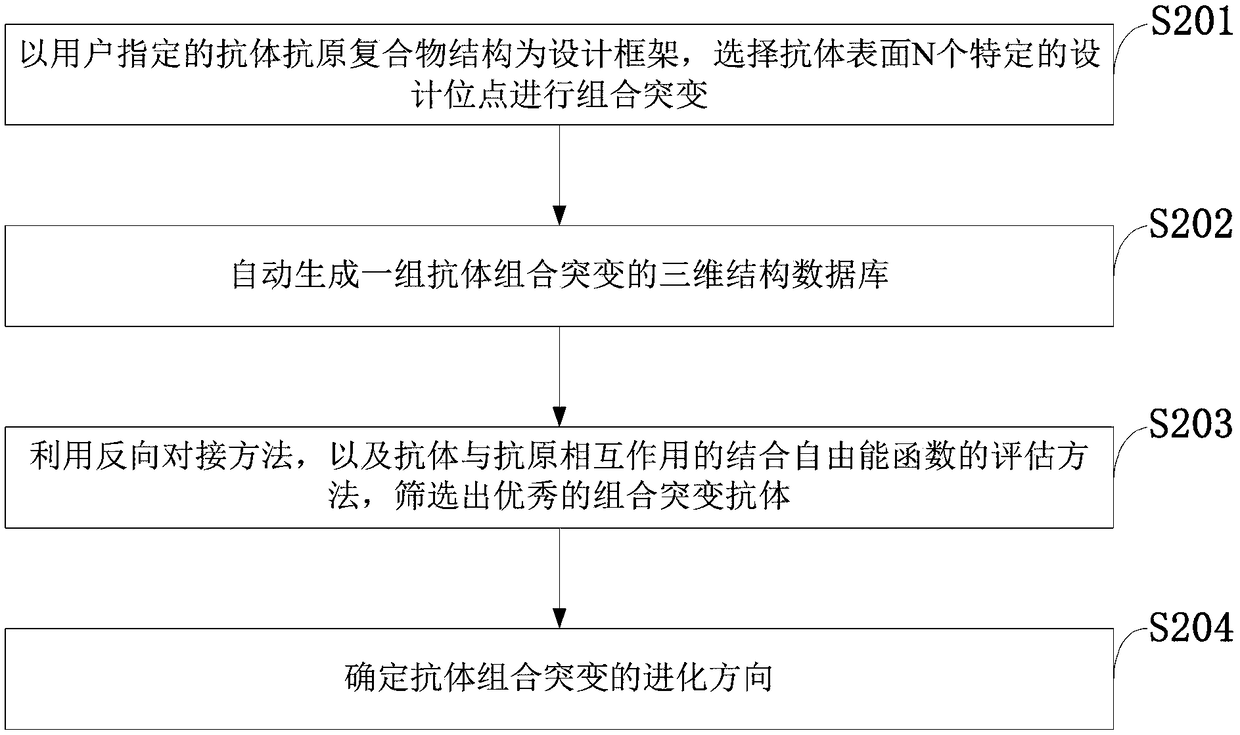
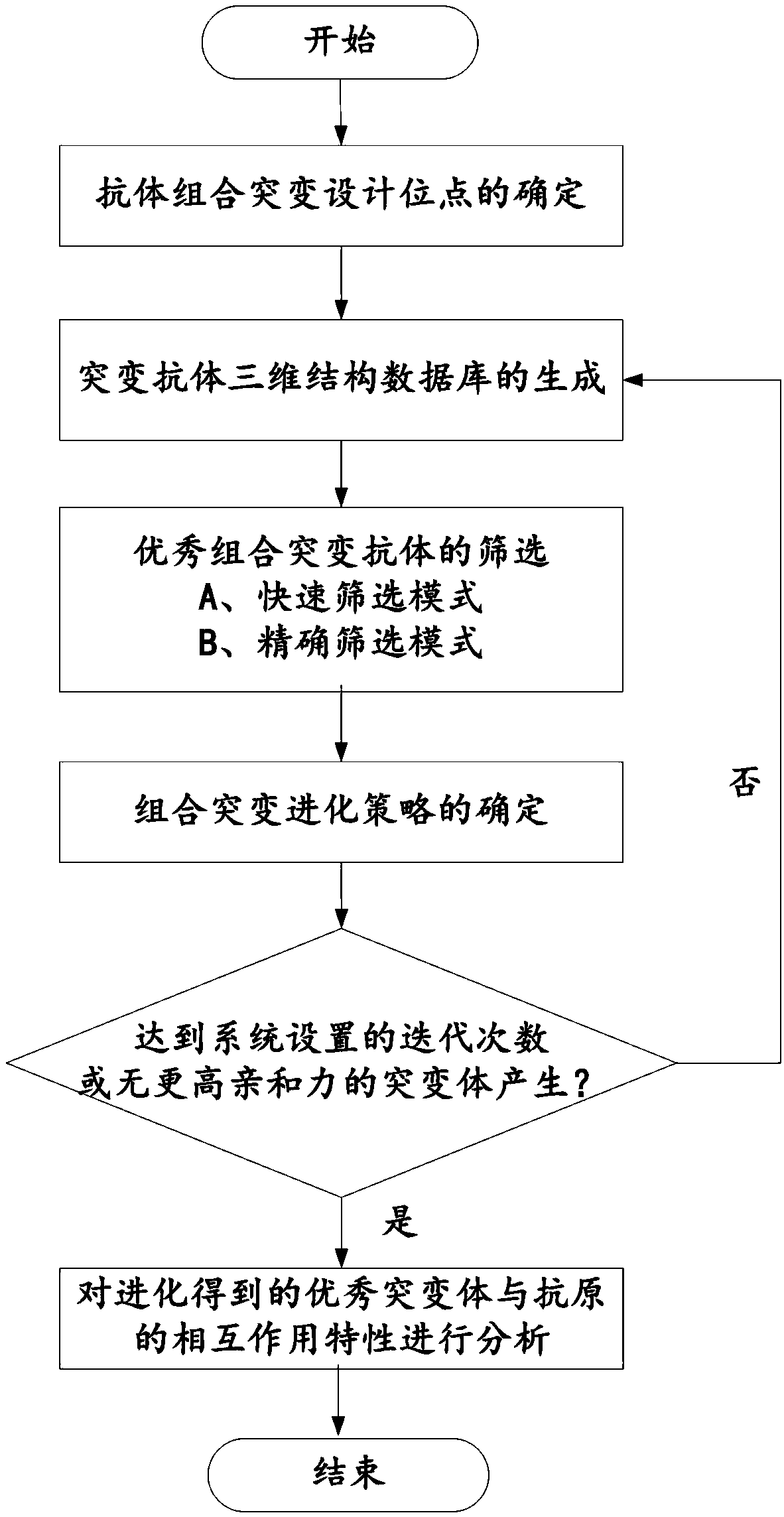
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer software, discloses a system and method for computing antibody combination mutation evolution, an Information Data Processing Terminal. The computer antibody combinatorial mutation evolution method adopts a genetic algorithm searching strategy, and generates a structural database of combinatorial mutants according to a plurality of amino acid sites in an antibody binding pocket through multiple cycles of calculation, and takes a specific binding free energy function as an affinity evaluation method to automatically evolve to obtain a combinatorial mutation antibody. The computer antibody combinatorial mutation evolution method adopts a genetic algorithm searching strategy, and generates a structural database of combinatorial mutantsaccording to a plurality of amino acid sites in an antibody binding pocket through multiple cycles of calculation, and takes a specific binding free energy function as an affinity evaluation method toautomatically evolve to obtain a combinatorial mutation antibody.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for rapidly evaluating binding strength of ultrafiltration membrane and small organic molecular pollutant
The invention relates to a method for predicting the binding strength of an ultrafiltration membrane surface adsorption unit and a small molecular pollutant. The method particularly comprises the steps of firstly, constructing a structure of a system; then calculating a binding free energy curve of a small molecule and the ultrafiltration membrane surface adsorption unit, and on this basis, figuring out a binding constant. A binding mechanism is obtained by analyzing a binding process, and a theoretical direction is provided for the optimization of the adsorption unit. Results indicate that the calculating result obtained by using the method is accurate, the design cost can be effectively reduced, and the design efficiency is remarkably improved. Thus the theoretical method provided by the invention can be used for predicting the binding strength of the ultrafiltration membrane surface adsorption unit and the small molecular pollutant.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Auxiliary prediction method for molecular modification of antibody protein
InactiveCN102222177AAccurate Simulation CalculationsUnique designSpecial data processing applicationsInteraction interfaceBiology
The invention relates to an auxiliary prediction method for molecular modification of antibody protein, which comprises the following steps of: (1) scanning amino acid residuals on a mutual interaction interface of antibodies and antigens; (2) judging microenvironments of the amino acid residuals on the mutual interaction interface of the antibodies and the antigens; (3) determining a candidate reconstruction site, performing virtual mutation to obtain an antigen and mutant antibody complex system, and calculating binding free energy and the change of the binding free energy caused by mutations; and (4) selecting the amino acid residuals possibly having larger impact on affinity and specificity and used as the candidate reconstruction sites according to requirements based on a calculation result of the step (3), and giving a result so as to direct experiments. The method is skillful and unique in design, the statistical rules of the antigen molecular interaction interface are combined, the change of the antigen affinity caused by the mutated antibodies can be predicted qualitatively and quantitatively, the prediction accuracy is greatly improved, and the method is suitable for large-scale promotion and application.
Owner:SHANGHAI CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION TECH
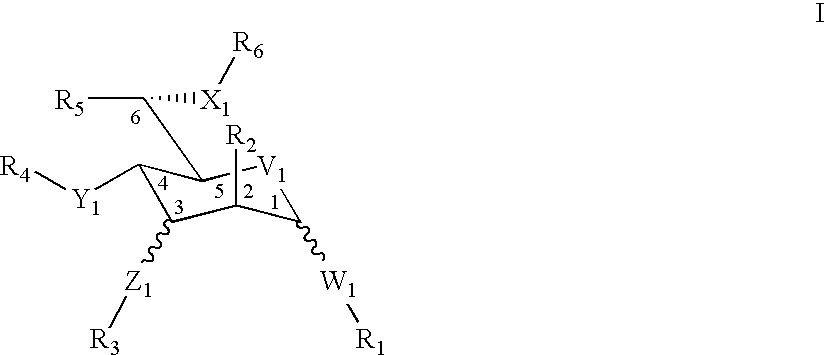
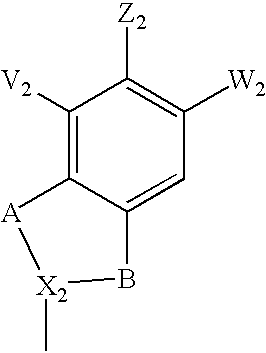
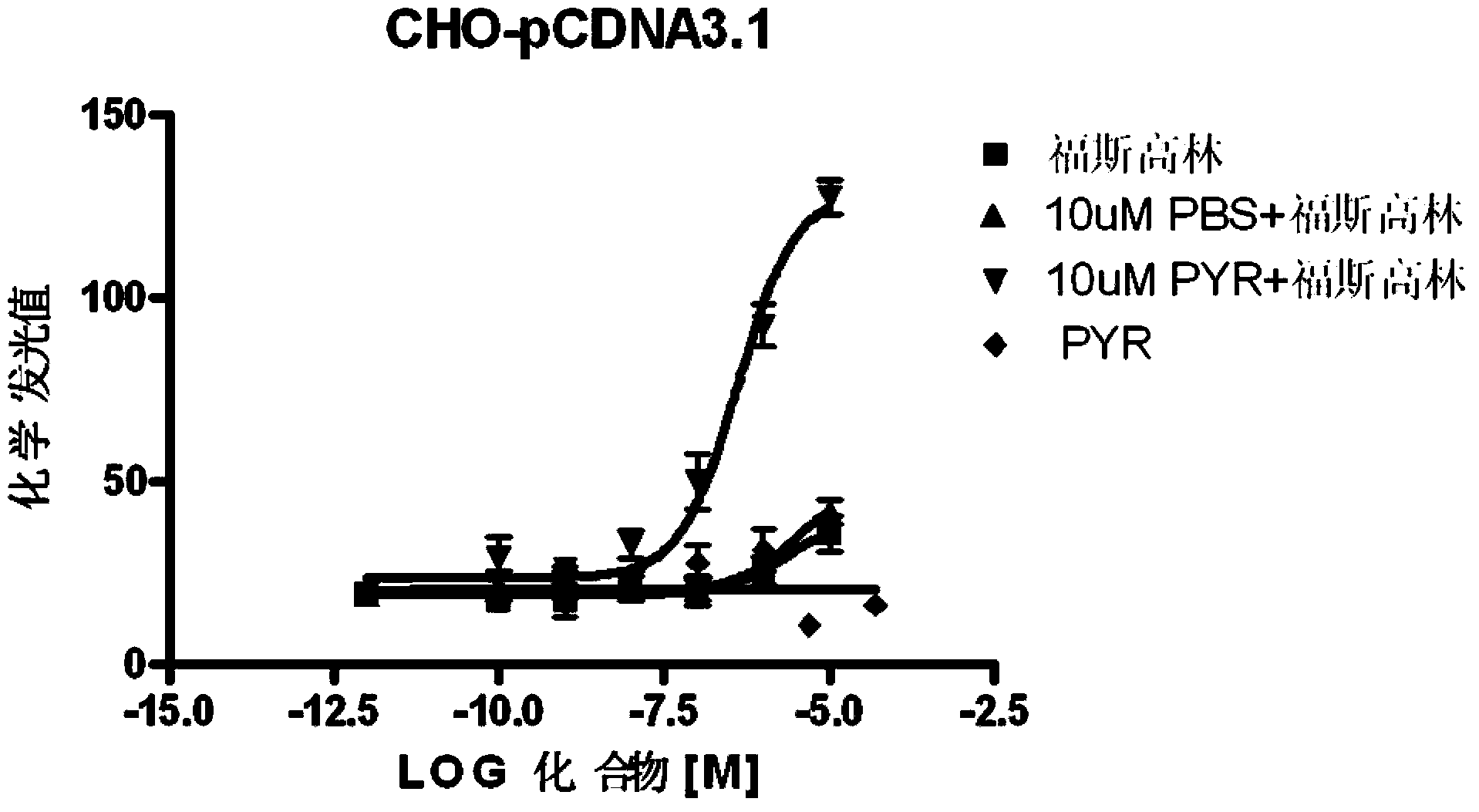
Pyronaridine compounds and applications thereof
InactiveCN103570711AHigh antimalarial activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryIn vivoHigh activity
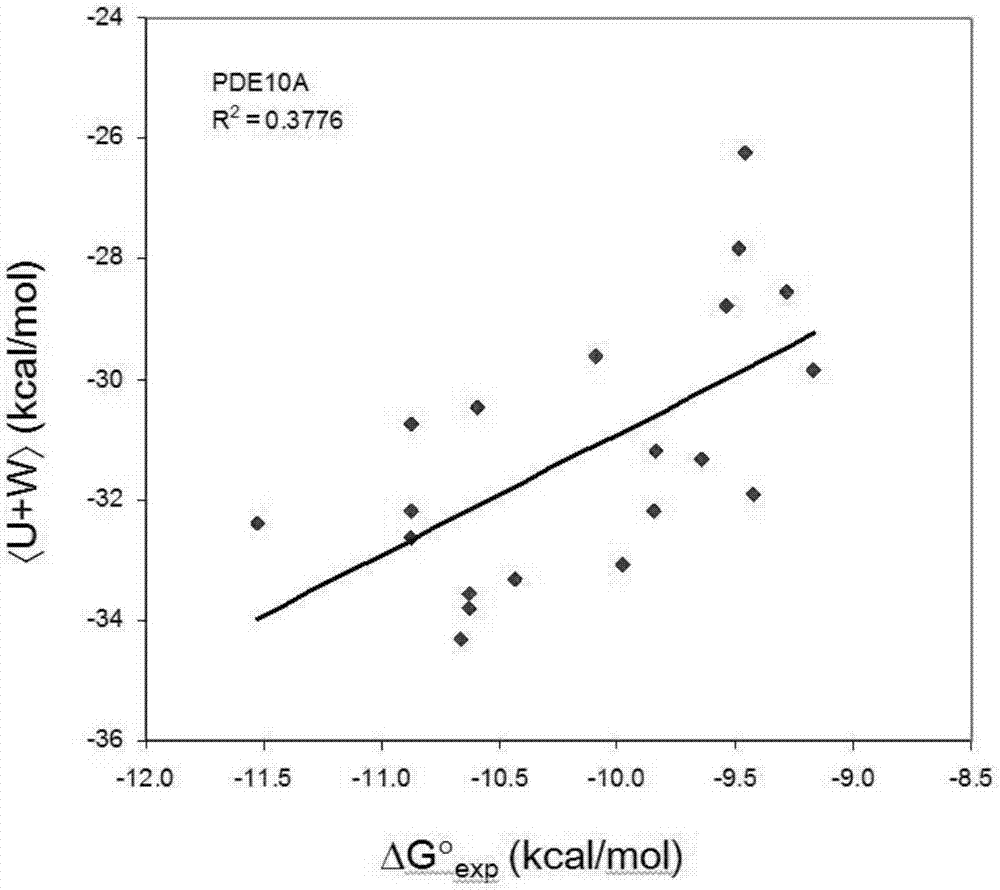
The invention provides pyronaridine compounds and applications thereof. The general formula of the pyronaridine compounds is shown as the formula I, wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are acting sites, and therefore the compounds have activity of inhibiting plasmodium in-vivo PDE. The pyronaridine compounds have a binding free energy lower than pyronaridine, and therefore the pyronaridine compounds have higher activity of inhibiting the plasmodium in-vivo PDE than the pyronaridine, and therefore the pyronaridine compounds have stronger anti-malarial activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
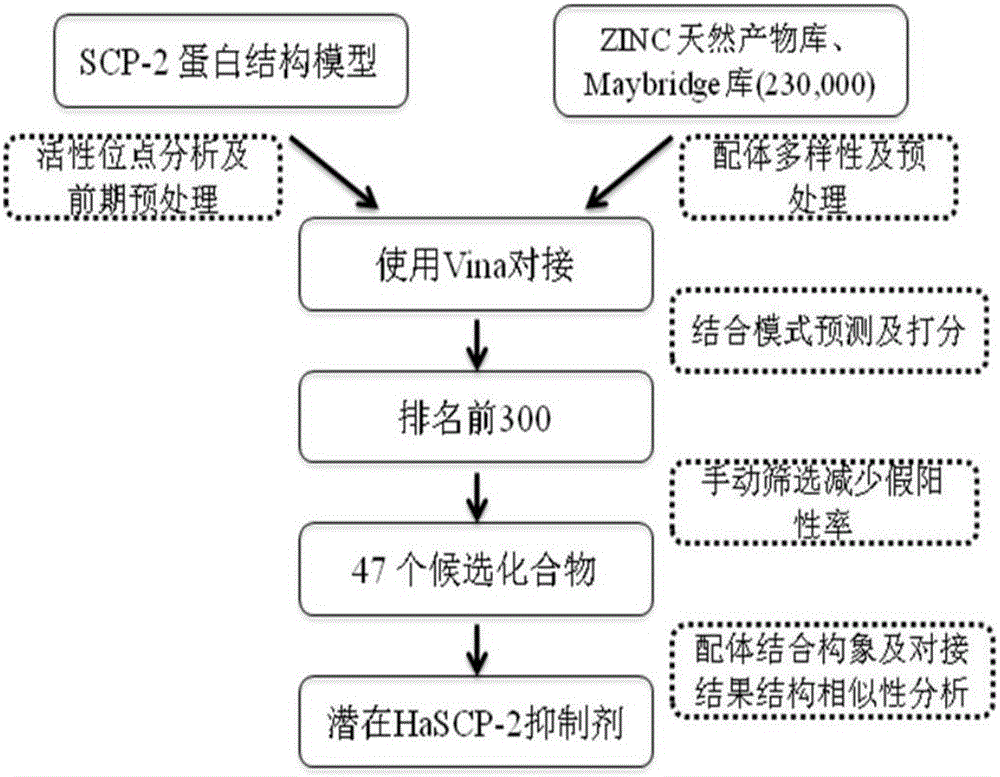
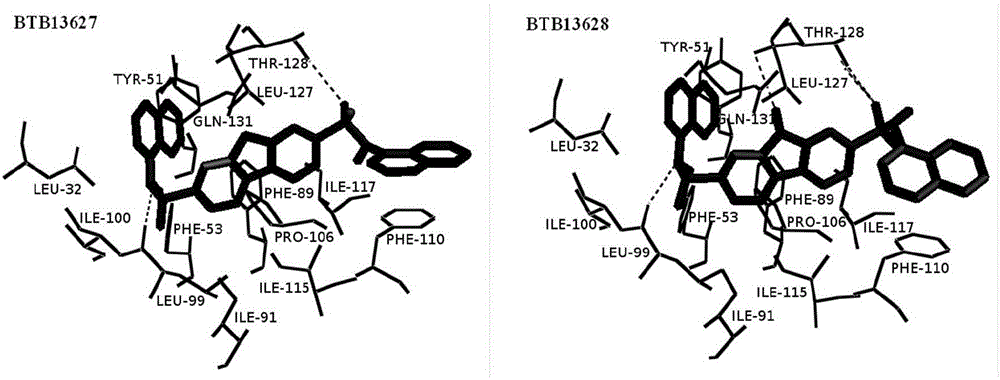
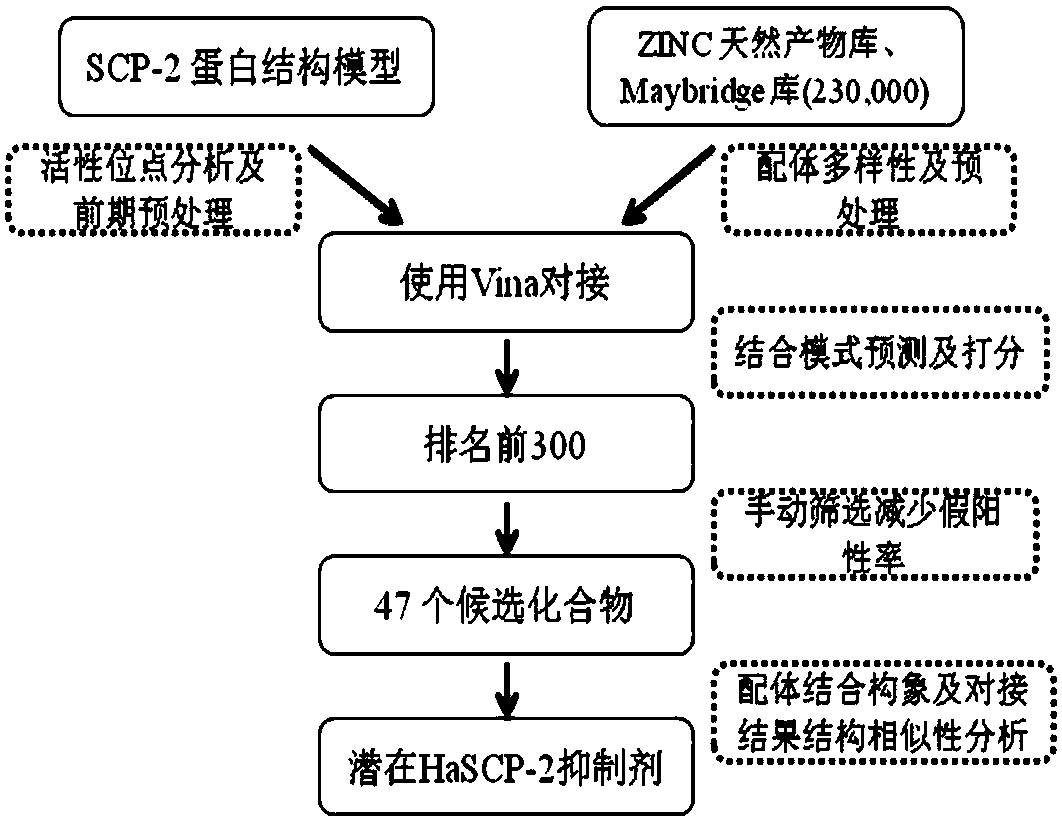
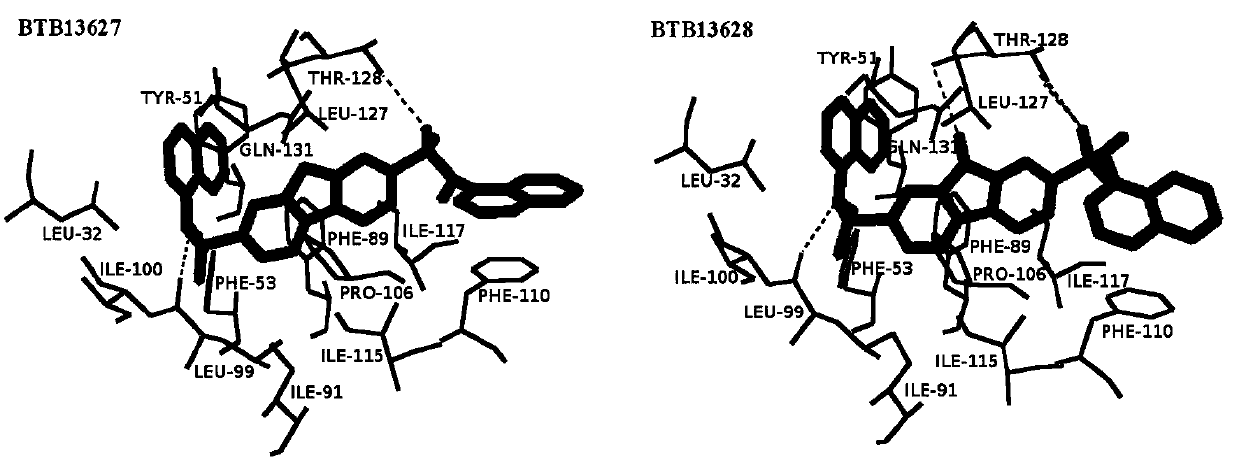
Cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 inhibitor and virtual screening method thereof
InactiveCN106106481AShorten screening timeImprove screening efficiencyChemical property predictionBiocideAgricultural scienceOrder Lepidoptera
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biotechnologies, and relates to establishment of a cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2) small-molecule inhibitor virtual screening method. The method comprises the following steps: according to structural data of cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2), analyzing a key amino acid residue so as to confirm a binding pocket; screening, scoring and calculating binding free energy by using molecular docking software; performing structure clustering and visual analysis on an obtained compound, thereby obtaining a small-molecule inhibitor for SCP-2 protein. The small-molecule inhibitor can be applied to screening, study and development of novel environmental-friendly pesticides for multiple agricultural pests of lepidoptera as the main target.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Design and selection of genetic targets for sequence resolved organism detection and identification
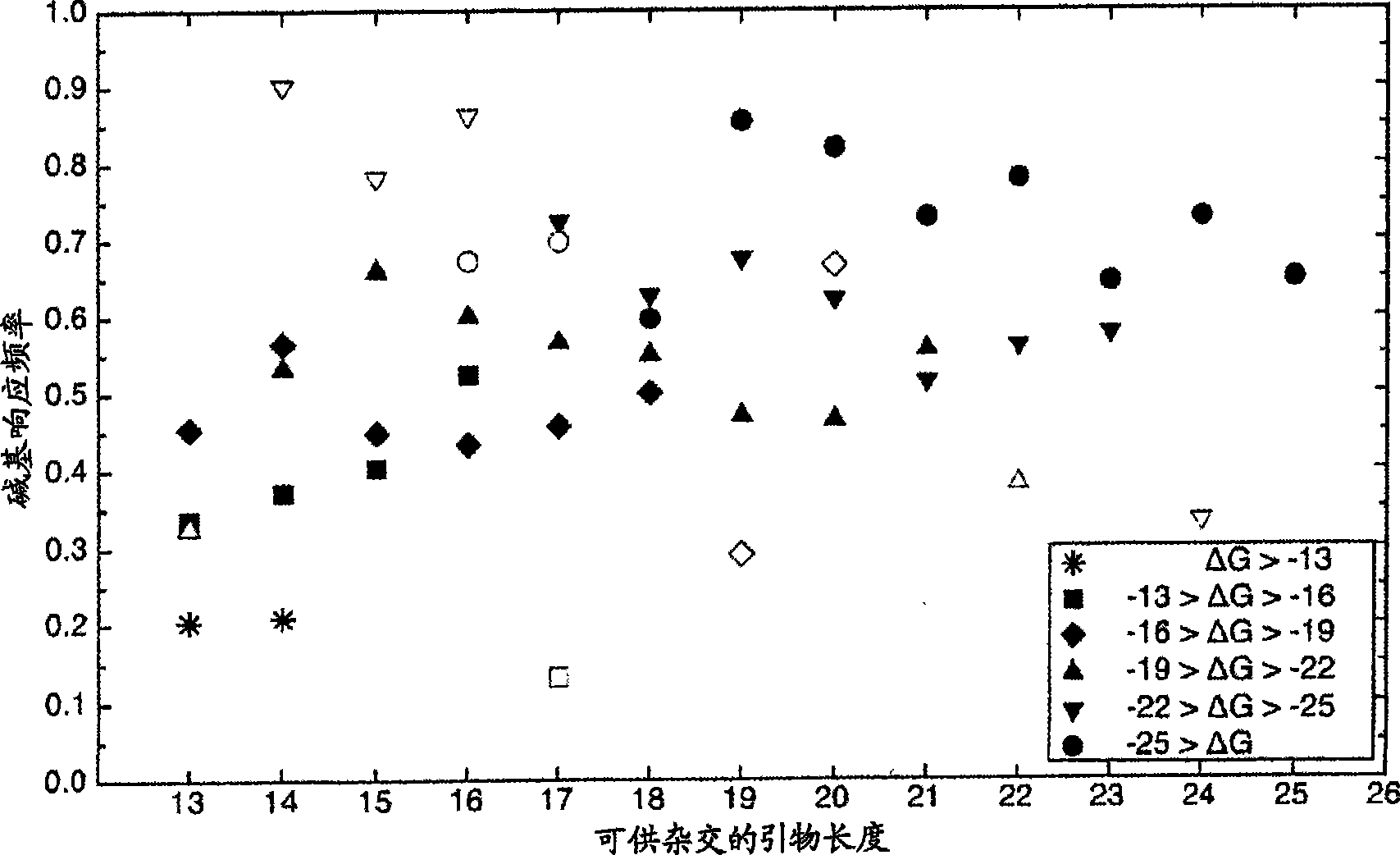
A computer-implemented method as follows. Providing a list of target sequences associated with one or more organisms in a list of organisms. Providing a list of candidate prototype sequences suspected of hybridizing to one or more of the target sequences. Generating a collection of probes corresponding to each candidate prototype sequence, each collection of probes having a set of probes for every subsequence having a predetermined, fixed subsequence length of the corresponding candidate prototype sequence. The sets consist of the corresponding subsequence and every variation of the corresponding subsequence formed by varying a center nucleotide of the corresponding subsequence. Generating a set of fragments corresponding to each target sequence, each set of fragments having every fragment having a predetermined, fixed fragment length of the corresponding target sequence. Calculating the binding free energy of each fragment with a perfect complimentary sequence of the fragment. If any binding free energy is above a predetermined, fixed threshold, the fragment is extended one nucleotide at a time until the binding free energy is below the threshold or the fragment is the same length as the probe, generating a set of extended fragments. Determining which extended fragments are perfect matches to any of the probes. Assembling a base call sequence corresponding to each candidate prototype sequence. The base call sequence has a base call corresponding to the center nucleotide of each probe of the corresponding prototype sequence that is a perfect match to any extended fragment, but for which the other members of the set of probes containing the perfect match probe are not perfect matches to any extended fragment and a non-base call in all other circumstances.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Virtual screening method for micromolecular reversible inhibitor of alkaline metalloproteinase from flavobacterium YS-80-122
InactiveCN103646191AReduce in quantityReduce wasteSpecial data processing applicationsMacromolecular dockingVirtual screening
The invention relates to a virtual screening method for a micromolecular reversible inhibitor of an alkaline metalloproteinase from flavobacterium YS-80-122 and belongs to the field of marine biotechnologies. The virtual screening method comprises the following steps: determining the type of the micromolecular reversible inhibitor according to the known structural data of the alkaline metalloproteinase from the flavobacterium YS-80-122; measuring the inhibition constant of the micromolecular reversible inhibitor of the type to the alkaline metalloproteinase from the flavobacterium YS-80-122, and determining compounds composing a training set; conducting molecular docking on the compounds of the training set and the alkaline metalloproteinase from the flavobacterium YS-80-122; acquiring the theoretical binding free energy and the theoretical reversible inhibition constant of the compounds of the training set and the alkaline metalloproteinase from the flavobacterium YS-80-122; in combination with the measured data, making a screening rule and establishing a screen model; conducting virtual screening. The virtual screening method is high in screening speed, can quickly reduce the quantity of candidate molecules, and reduce waste of time and test materials.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Site-specific fragment identification guided by single-step free energy perturbation calculations
InactiveUS20160267219A1Chemical property predictionMolecular designFree energiesFree energy perturbation
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Design and selection of genetic targets for sequence resolved organism detection and identification
InactiveUS20080033706A1Analogue computers for chemical processesHybridisationBiological bodyBase calling
A computer-implemented method as follows. Providing a list of target sequences associated with one or more organisms in a list of organisms. Providing a list of candidate prototype sequences suspected of hybridizing to one or more of the target sequences. Generating a collection of probes corresponding to each candidate prototype sequence, each collection of probes having a set of probes for every subsequence having a predetermined, fixed subsequence length of the corresponding candidate prototype sequence. The sets consist of the corresponding subsequence and every variation of the corresponding subsequence formed by varying a center nucleotide of the corresponding subsequence. Generating a set of fragments corresponding to each target sequence, each set of fragments having every fragment having a predetermined, fixed fragment length of the corresponding target sequence. Calculating the binding free energy of each fragment with a perfect complimentary sequence of the fragment. If any binding free energy is above a predetermined, fixed threshold, the fragment is extended one nucleotide at a time until the binding free energy is below the threshold or the fragment is the same length as the probe, generating a set of extended fragments. Determining which extended fragments are perfect matches to any of the probes. Assembling a base call sequence corresponding to each candidate prototype sequence. The base call sequence has a base call corresponding to the center nucleotide of each probe of the corresponding prototype sequence that is a perfect match to any extended fragment, but for which the other members of the set of probes containing the perfect match probe are not perfect matches to any extended fragment and a non-base call in all other circumstances.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
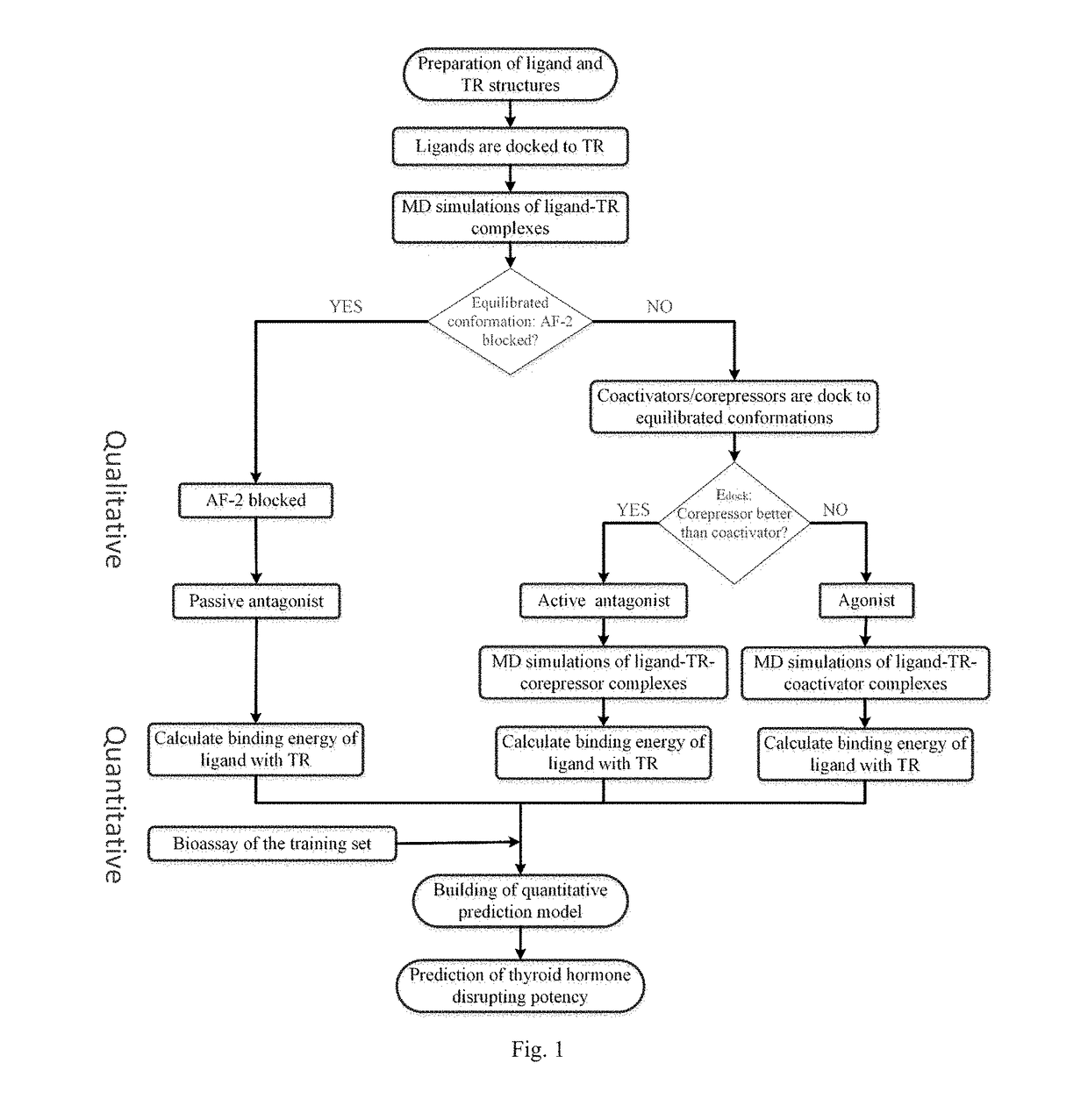
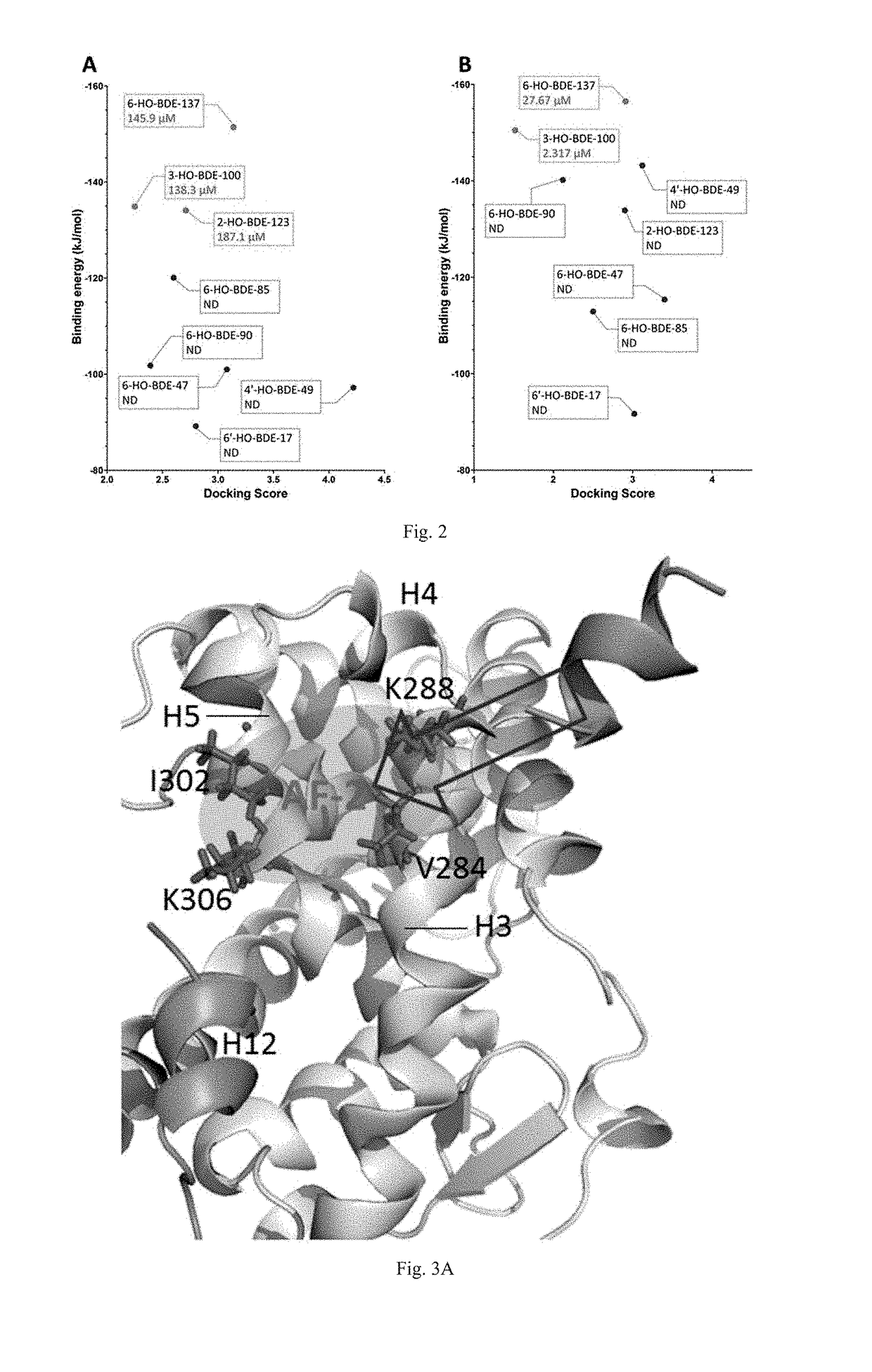
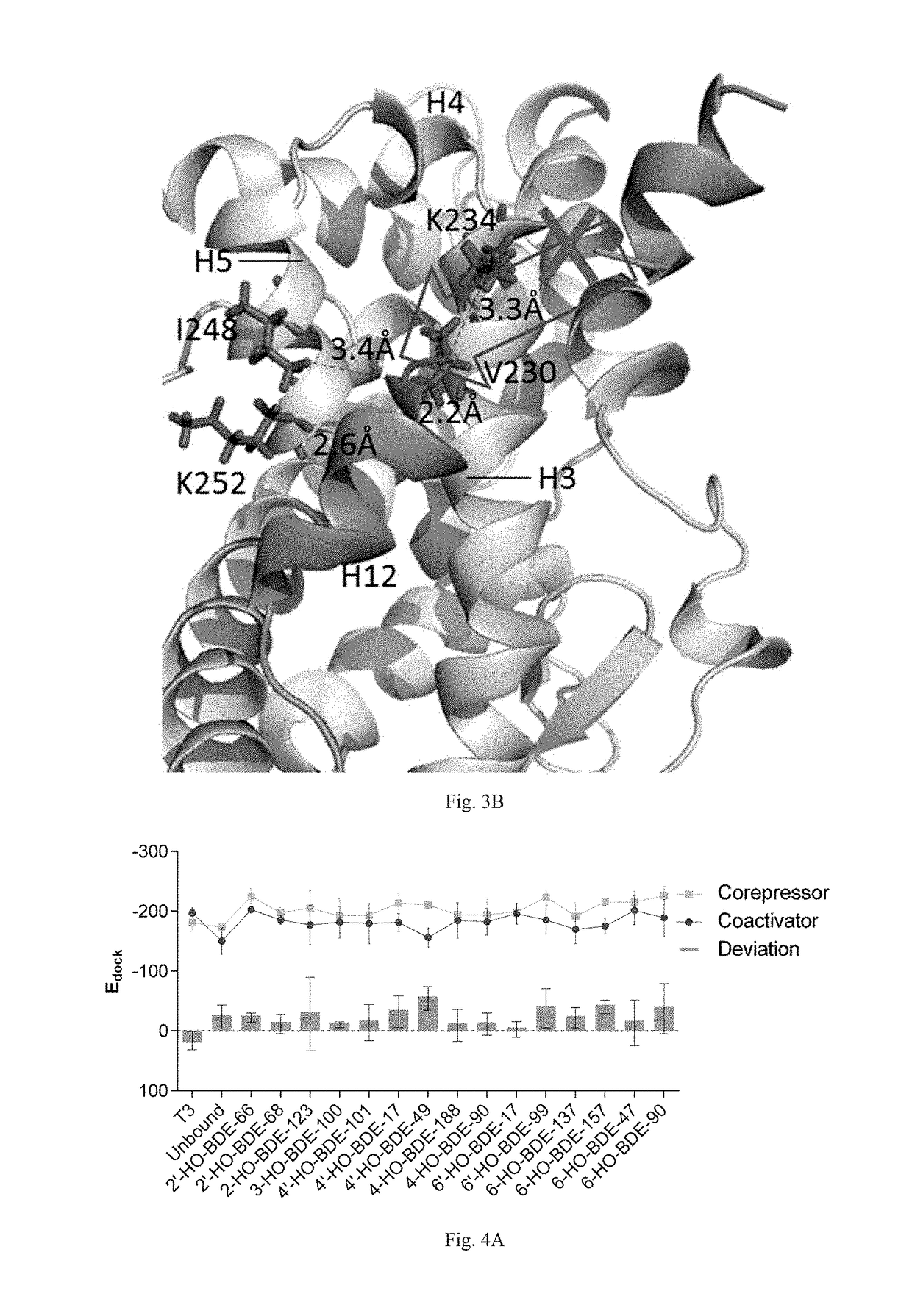
Screening methods for thyroid hormone disruptors based on co-regulator involved simulations
ActiveUS20170285007A1Comprehensive considerationAccurate predictionBiological material analysisProteomicsPerturbateurs endocriniensScreening method
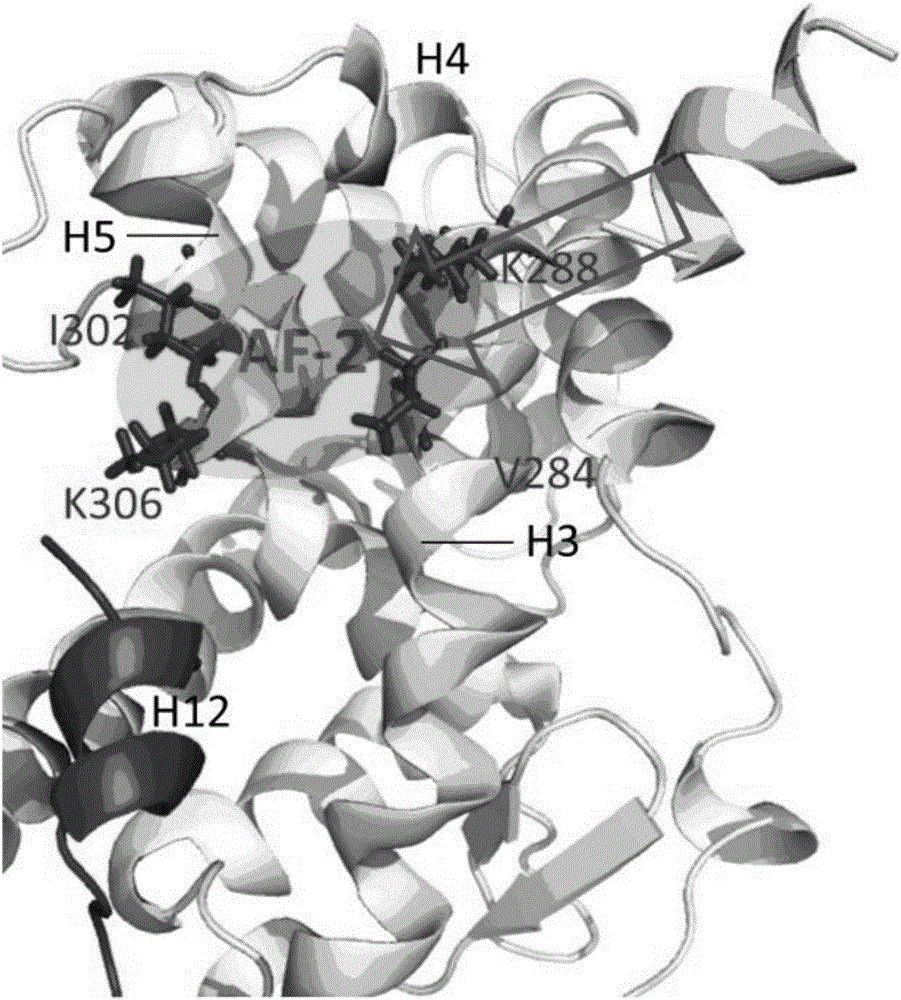
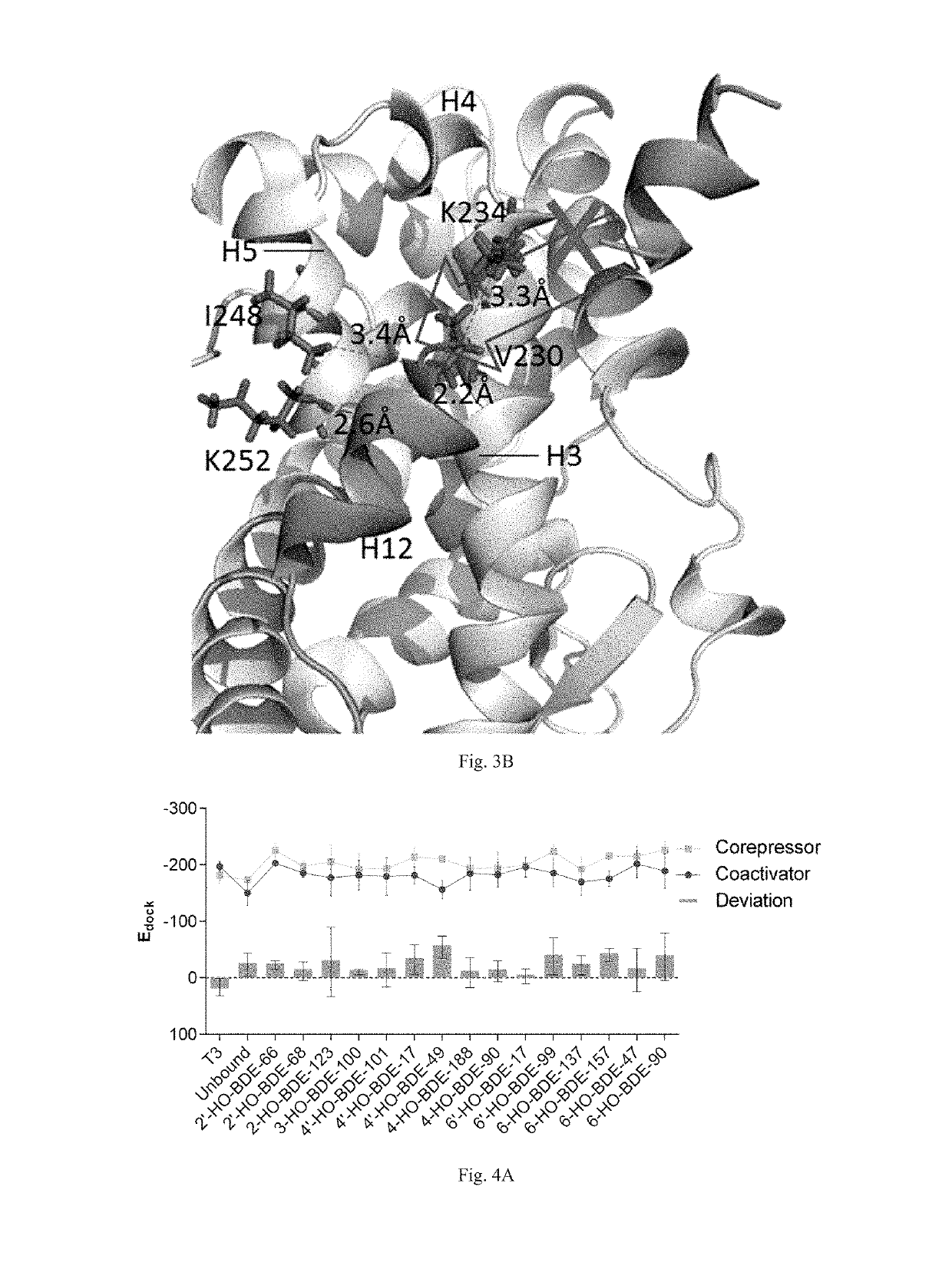
The present patent relates to a method for qualitative identification and quantitative prediction of thyroid hormone disrupting chemicals base on the interaction between thyroid hormone receptor and co-regulators (coactivator and corepressor).The method identifies chemicals as passive antagonists, active antagonists and agonists by means of co-regulator involved molecular dynamics simulations, and predicts the relative disrupting potencies by use of binding free energy, therefore, may be used for screening of thyroid hormone disruptors among environmental pollutants. Upon more comprehensive consideration of the functioning mechanism of thyroid hormone receptor, the present invention is able to sufficiently identify thyroid hormone disruptors as agonists and antagonists, and gives more accurate prediction of the disrupting potency. Further, since nuclear receptors, just as thyroid hormone receptor, are strongly associated with co-regulators, the method may be expanded to the screening of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruptors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for measuring clay dispersion average binding free energy and adsorption free energy to cation
InactiveCN100510727CPreparing sample for investigationMaterial resistanceCation-exchange capacityElectric field
The method for measuring the average binding free energy and average adsorption free energy of soil clay particles to cations includes: a. preparing soil clay particles with a particle size of <2 μm and saturated with cations, and then preparing a soil suspension with deionized water or distilled water; b. Place the soil suspension under an electric field with an initial field strength ≤ 15kV cm-1, and gradually increase the field strength, measure the conductivity of the soil suspension under each field strength, and obtain the conductivity and field strength of the soil suspension c. Calculate the average binding free energy and adsorption free energy of soil clay particles to cations according to the following mathematical formulas: ΔGbo=RTln(2CEC Cp λ / EC0) (4); ΔGad=RTln(EC / EC0 ) (8); in the formula, R is the gas constant; T is the thermodynamic temperature; CEC is the cation exchange capacity, Cp is the concentration of soil clay particles in the suspension; λ is the equivalent conductance of dissociated cations; EC0 is the field strength ≤ 15kV Conductivity of the suspension under an electric field of cm-1; EC is the conductivity of the suspension under an electric field of field strength >15kV·cm-1.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of inhibitor of cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 and its virtual screening method
InactiveCN106106481BShorten screening timeImprove screening efficiencyChemical property predictionBiocideHelicoverpaAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biotechnologies, and relates to establishment of a cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2) small-molecule inhibitor virtual screening method. The method comprises the following steps: according to structural data of cotton bollworm sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2), analyzing a key amino acid residue so as to confirm a binding pocket; screening, scoring and calculating binding free energy by using molecular docking software; performing structure clustering and visual analysis on an obtained compound, thereby obtaining a small-molecule inhibitor for SCP-2 protein. The small-molecule inhibitor can be applied to screening, study and development of novel environmental-friendly pesticides for multiple agricultural pests of lepidoptera as the main target.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
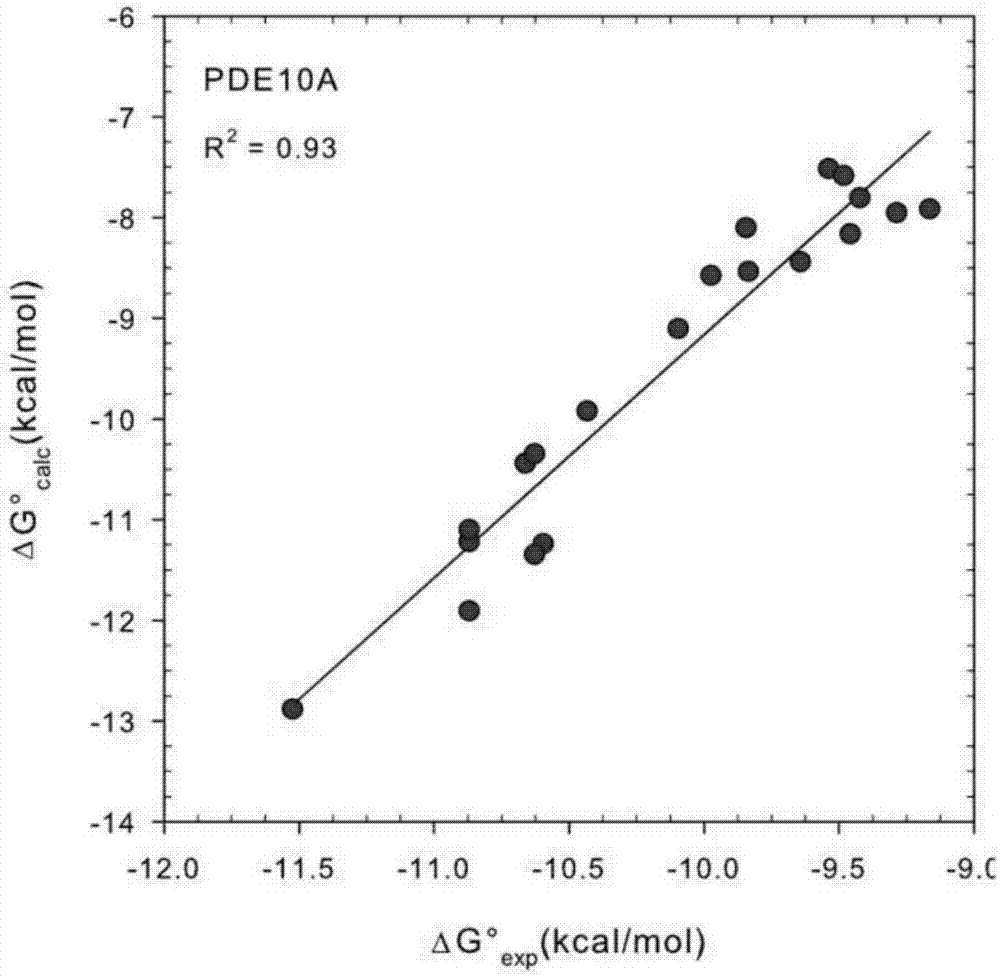
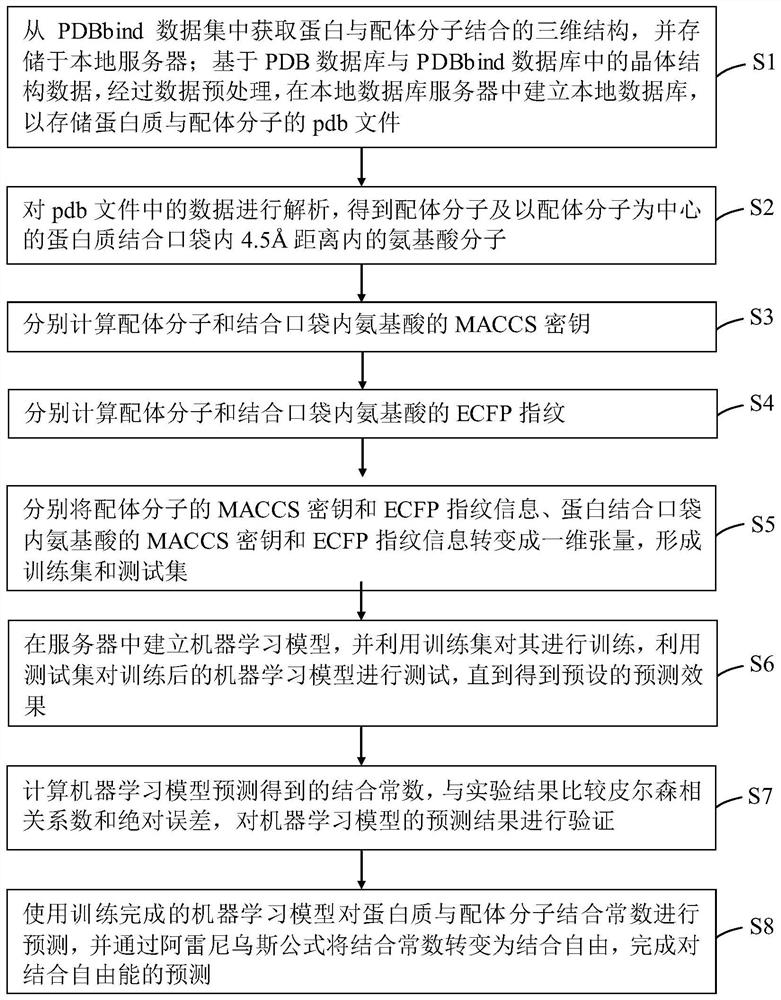
Method and device for predicting binding free energy of protein and ligand molecules
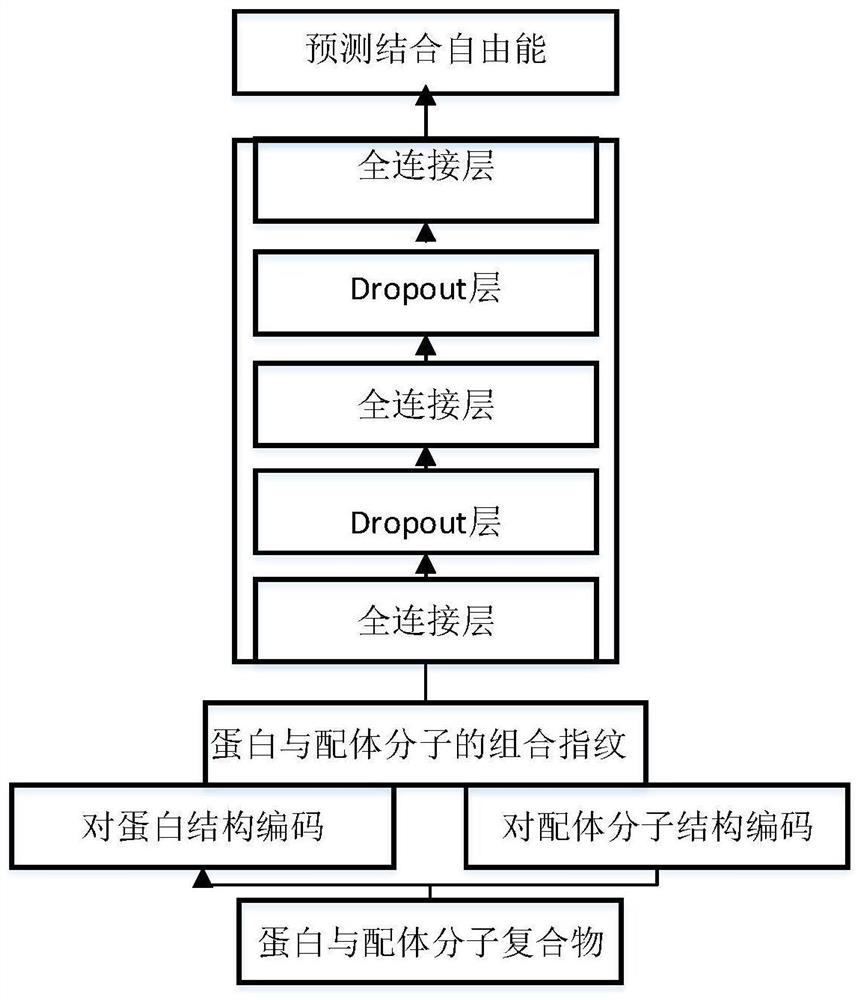
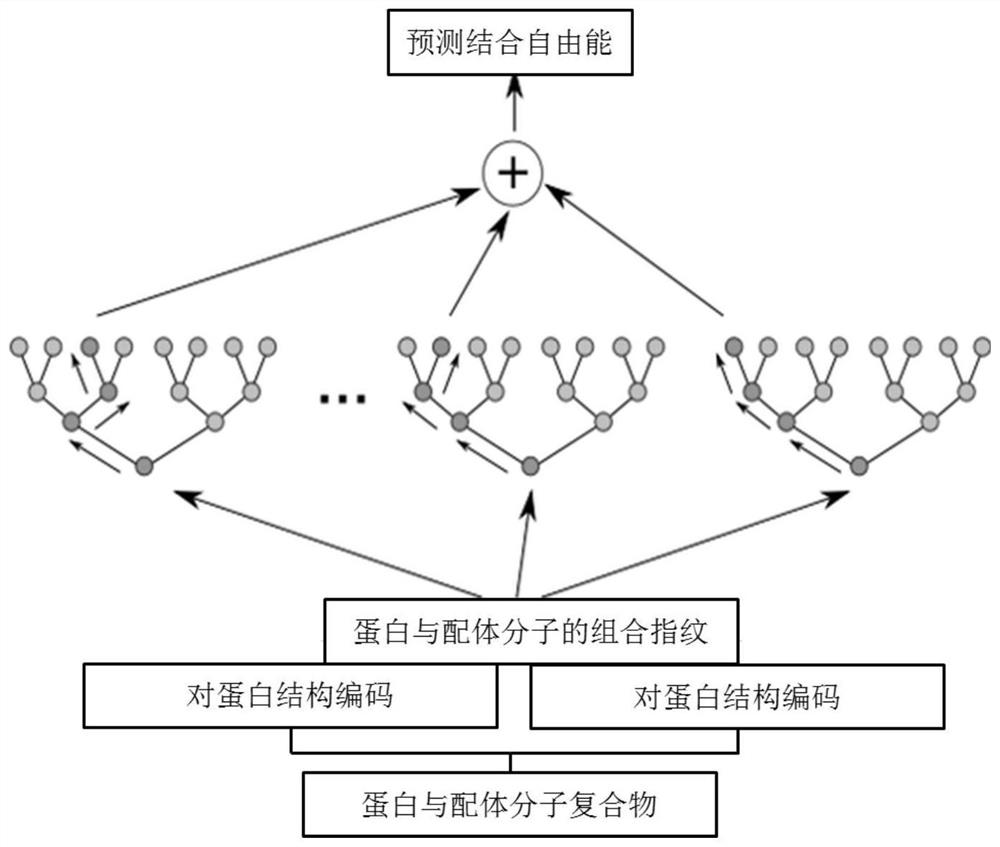
PendingCN112466410AImprove targetingSmall amount of calculationChemical property predictionChemical machine learningCorrelation coefficientBinding constant
The invention provides a method and device for predicting the binding free energy of protein and ligand molecules, and the method comprises the steps: S1, constructing a local database; s2, analyzingthe data to obtain a ligand molecule and an amino acid molecule in a protein binding pocket taking the ligand molecule as a center; s3, calculating the MACCS secret keys of the ligand molecules and the near amino acids; s4, calculating ECFP fingerprints of ligand molecules and near amino acids; s5, converting the MACCS key and ECFP fingerprint information of the ligand molecule and protein into aone-dimensional tensor to form a training set and a test set; s6, establishing a machine learning model, and training the machine learning model; s7, calculating and comparing a Pearson correlation coefficient and an absolute error, and verifying a prediction result of the machine learning model; and S8, predicting the binding constant of the protein and the ligand molecule by using the trained machine learning model, and calculating the binding free energy. Compared with the prediction result of a single fingerprint, the prediction result of the combined fingerprint is obviously better, and the accuracy of free energy prediction is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH +1
A Computational Approach to Handling Small Molecule and Protein Interactions
InactiveCN103049677BIncrease productivityThe key principle of technology is simpleSpecial data processing applicationsCrystallographyBinding site
The invention relates to a computing method for processing interaction between small molecules and proteins. The method includes the following steps that (1) ligand file data of the proteins and the small molecules are read in; (2) atom types in ligands of the proteins and the small molecules are judged; (3) positions and angles of the ligands of the small molecules are randomly initialized; (4) a search protein algorithm is operated, coordinates and angles of the ligands of the small molecules are optimized, and a chemscore formula serves as an evaluation function; (5) the computing is ended after maximum iterative times are achieved; and (6) results such as root mean square deviation (RMSD), binding free energy delta G and coordinates of a binding site are analyzed and output. Compared with computing methods for processing the interaction between the small molecules and the proteins in prior art, the computing method for processing the interaction between the small molecules and the proteins has the advantages that when pollutants and biomacromolecules are interacted can be rapidly determined, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for calculating protein-ligand binding free energy based on cluster model
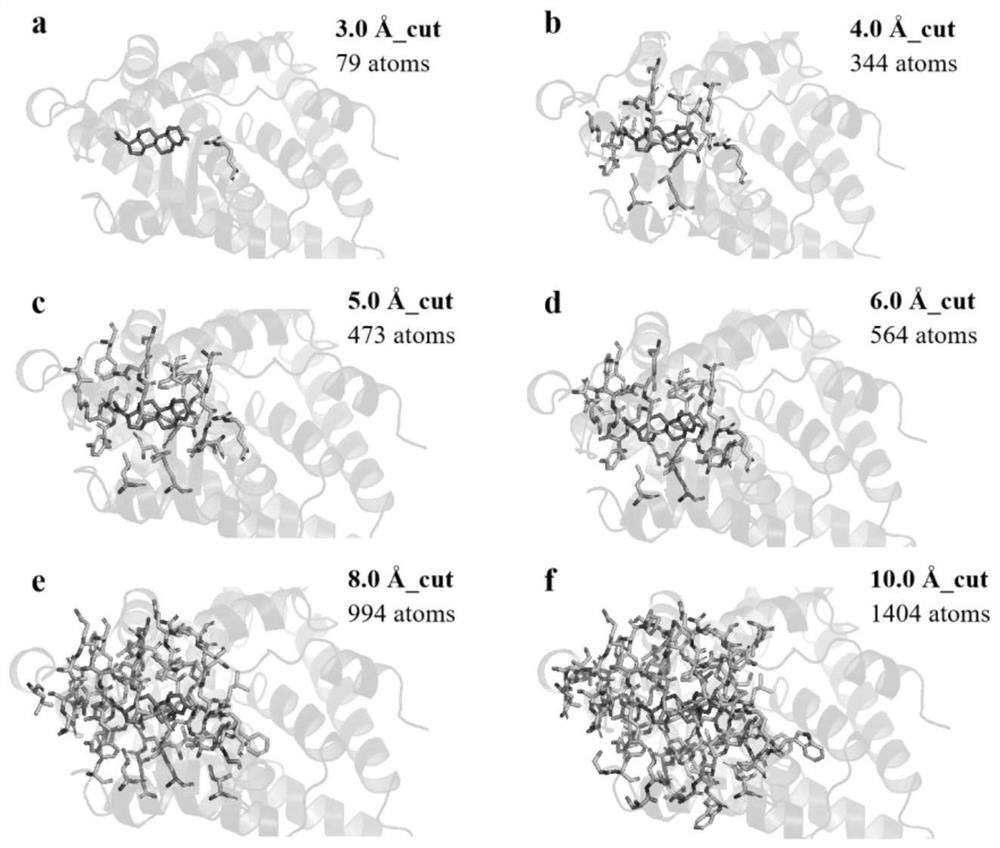
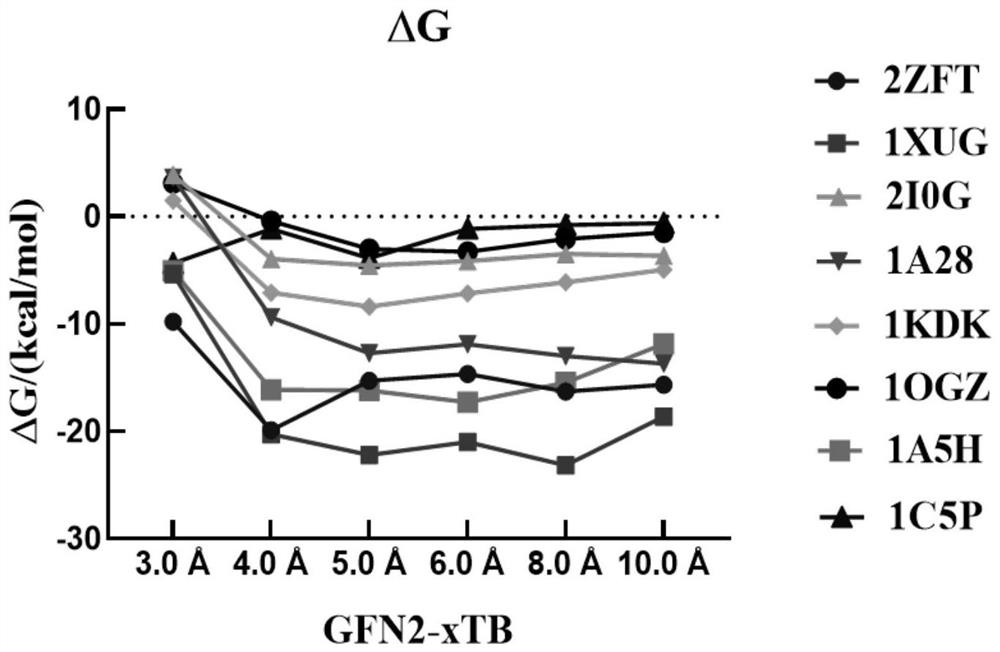
ActiveCN114121148AEasy to useImprove accuracyInstrumentsMolecular structuresFree energiesBiological macromolecule
The invention discloses a method for calculating protein-ligand binding free energy based on a cluster model, compared with other methods for calculating protein-ligand binding free energy, a GFN2-xTB method is easier to use, an input structure can be formed by only needing initial coordinates and element composition, and when the GFN2-xTB method is combined with the cluster model for application, the input structure is more stable. On the premise of ensuring relatively good accuracy, the time cost of calculation is reduced more effectively. The new method based on the cluster model and the GFN2-xTB should have great potential in calculation of combined free energy related to biomacromolecules in the future.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
An Algorithm for Quickly and Accurately Calculating the Free Energy of Affinity Between Protease and Drug Molecules
ActiveCN107423570BReliable determinationReduce computationMolecular designComputational theoretical chemistryReceptorPharmaceutical drug
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmacy and relates to an algorithm for quickly and accurately calculating free affinity between proteinase and drug molecules. The algorithm is characterized in that standard chemical potentials of a ligand and receptor in free state and a standard chemical potential of a receptor-ligand complex in bound state are calculated respectively, and differences among the standard chemical potentials are standard binding free energy; wherein in the calculation of the standard chemical potentials, M most steady-state conformations of the molecules are found first, j refers to energy wells corresponding to the most steady-state conformations, with j equal to 1...N, conformation integral zj of the corresponding energy well j of each most steady-state conformation is calculated, corresponding Boltzmann factor RT is calculated accordingly, and all the conformation integrals are combined to obtain a standard chemical potential for the ligand, the receptor or the receptor-ligand complex in bound state. By replacing experiments via computer simulation, screening and optimizing accuracy for pilot drugs are greatly improved, and time and cost for screening and optimizing are greatly decreased.
Owner:南昌立德生物技术有限公司
Virtual screening method and device and electronic equipment
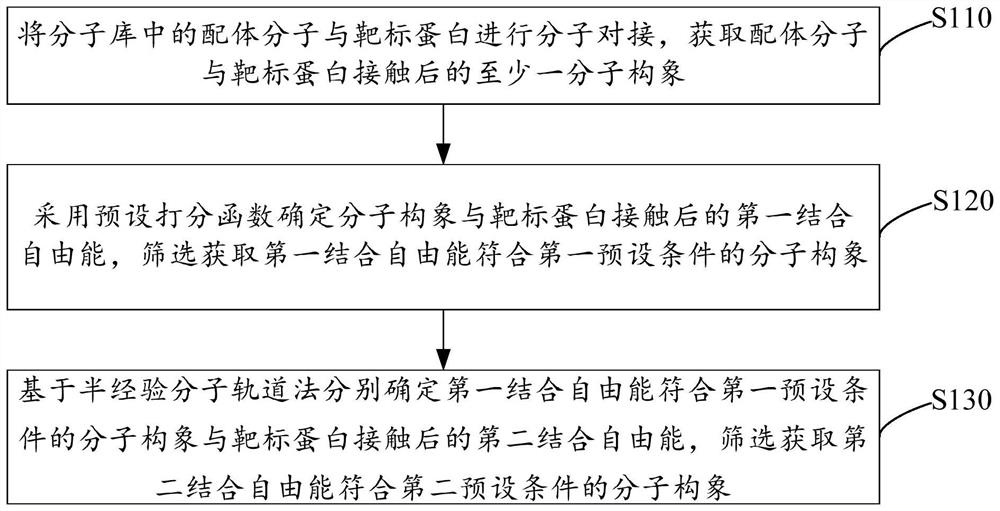
PendingCN114171129AImprove bindingIncrease success rateMolecular designCheminformatics data warehousingProtein targetEngineering
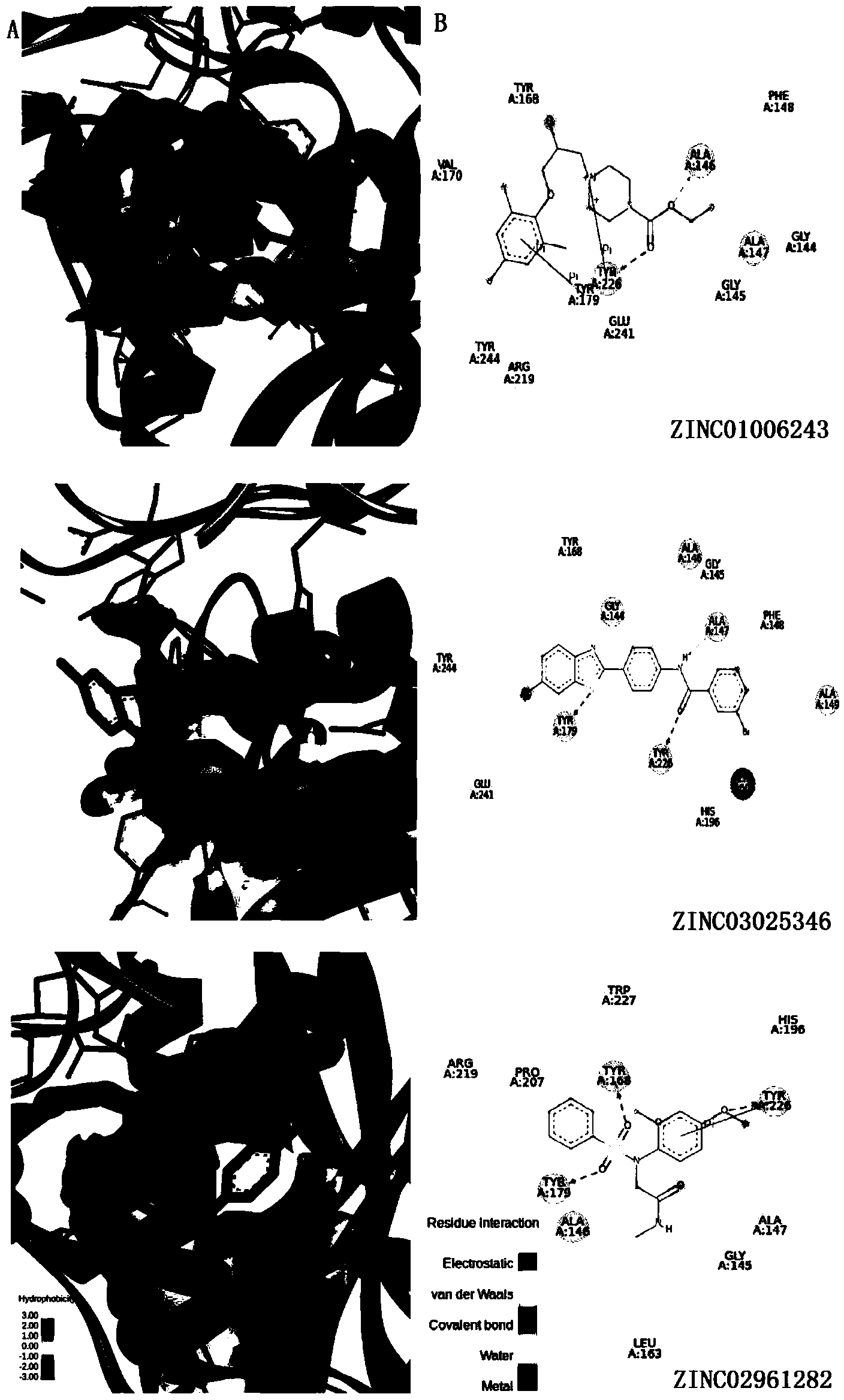
The invention relates to a virtual screening method and device and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out molecular docking on ligand molecules in a molecular library and target protein to obtain at least one molecular conformation after the ligand molecules are contacted with the target protein; determining first binding free energy after the molecular conformation is contacted with the target protein by adopting a preset scoring function, and screening to obtain the molecular conformation of which the first binding free energy meets a first preset condition; based on a semi-empirical molecular orbital method, respectively determining second binding free energy after the molecular conformation with the first binding free energy meeting a first preset condition is contacted with the target protein, and screening to obtain the molecular conformation with the second binding free energy meeting a second preset condition. According to the scheme provided by the invention, the accuracy of the prediction result can be improved while the binding free energy of the molecular conformation can be rapidly predicted, so that the success rate of screening to obtain the active compound is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
A kind of pyronaridine compound and its application
InactiveCN103570711BHigh antimalarial activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical compoundIn vivo
The invention provides pyronaridine compounds and applications thereof. The general formula of the pyronaridine compounds is shown as the formula I, wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are acting sites, and therefore the compounds have activity of inhibiting plasmodium in-vivo PDE. The pyronaridine compounds have a binding free energy lower than pyronaridine, and therefore the pyronaridine compounds have higher activity of inhibiting the plasmodium in-vivo PDE than the pyronaridine, and therefore the pyronaridine compounds have stronger anti-malarial activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Screening methods for thyroid hormone disruptors based on co-regulator involved simulations
ActiveUS10268799B2Comprehensive considerationBiological material analysisProteomicsPerturbateurs endocriniensScreening method
The present patent relates to a method for qualitative identification and quantitative prediction of thyroid hormone disrupting chemicals base on the interaction between thyroid hormone receptor and co-regulators (coactivator and corepressor). The method identifies chemicals as passive antagonists, active antagonists and agonists by means of co-regulator involved molecular dynamics simulations, and predicts the relative disrupting potencies by use of binding free energy, therefore, may be used for screening of thyroid hormone disruptors among environmental pollutants. Upon more comprehensive consideration of the functioning mechanism of thyroid hormone receptor, the present invention is able to sufficiently identify thyroid hormone disruptors as agonists and antagonists, and gives more accurate prediction of the disrupting potency. Further, since nuclear receptors, just as thyroid hormone receptor, are strongly associated with co-regulators, the method may be expanded to the screening of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruptors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com