An Algorithm for Quickly and Accurately Calculating the Free Energy of Affinity Between Protease and Drug Molecules
An accurate calculation and drug molecule technology, applied in molecular design, computational theoretical chemistry, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of accuracy and speed limitation in the primary selection stage of lead drugs, and achieve the effect of reducing time and cost and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be described in further detail below.
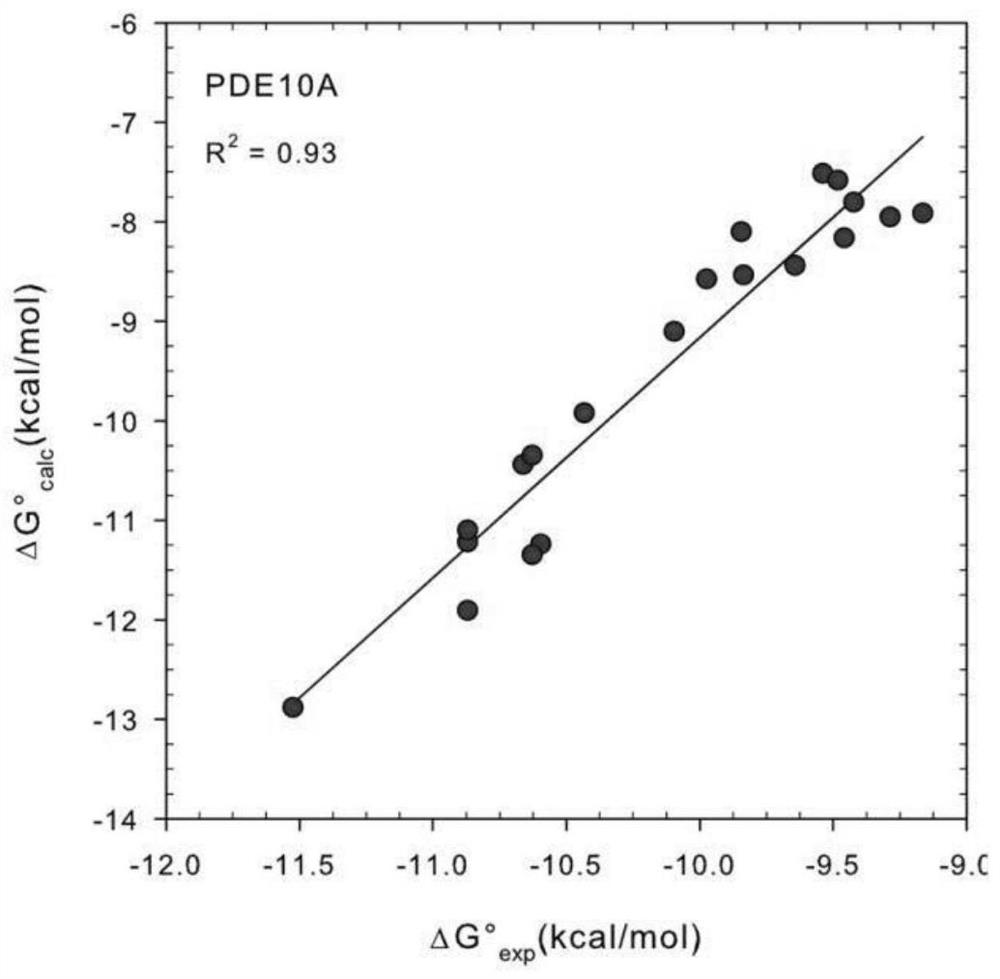
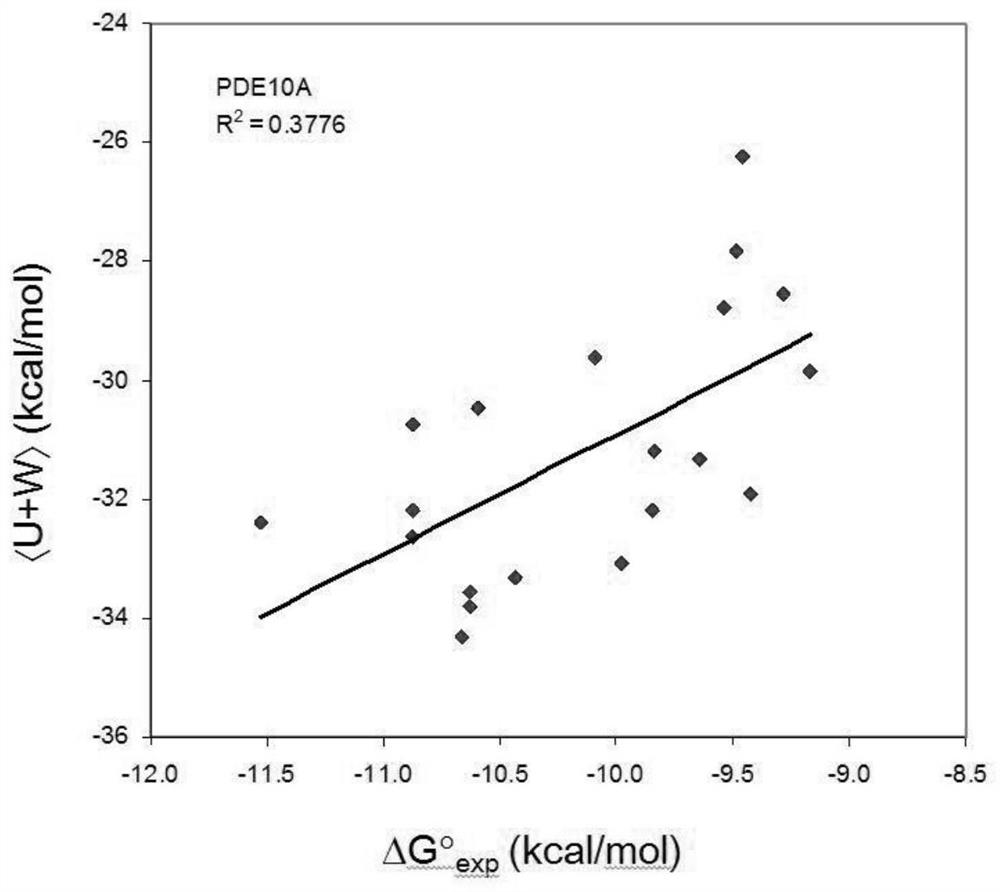
[0019] A fast and accurate algorithm for calculating the affinity free energy between proteases and drug molecules, which calculates the standard chemical potentials of the free-state ligand, receptor, and the bound state receptor-ligand complex, and the relationship between them The difference is the standard binding free energy:
[0020]
[0021] In the above formula, R represents the receptor, L represents the ligand, and RL represents the receptor-ligand complex in the bound state, represents the standard chemical potential of the acceptor, represents the standard chemical potential of the ligand, represents the standard chemical potential of the receptor-ligand complex in the bound state, ΔG 0 represents the standard binding free energy.
[0022] Each standard chemical potential in the above formula is calculated by the following method. We first find the N most stable conformations of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com