Method for measuring clay dispersion average binding free energy and adsorption free energy to cation
A metal cation and soil technology, which is applied in the field of measuring the average binding free energy and average adsorption free energy of soil clay particles to cations, and can solve the problems that the experimental determination of the energy relationship between soil and ions has not really solved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example.
[0047] Preparation of soil samples and suspensions
[0048] The soil clay particles with a particle size of -1 (if the concentration is 10g L -1 ) suspension, after ultrasonic dispersion, vibrate at constant temperature 1-2 times a day, and measure the Wien effect after 7-10 days of equilibrium.
[0049] measuring device
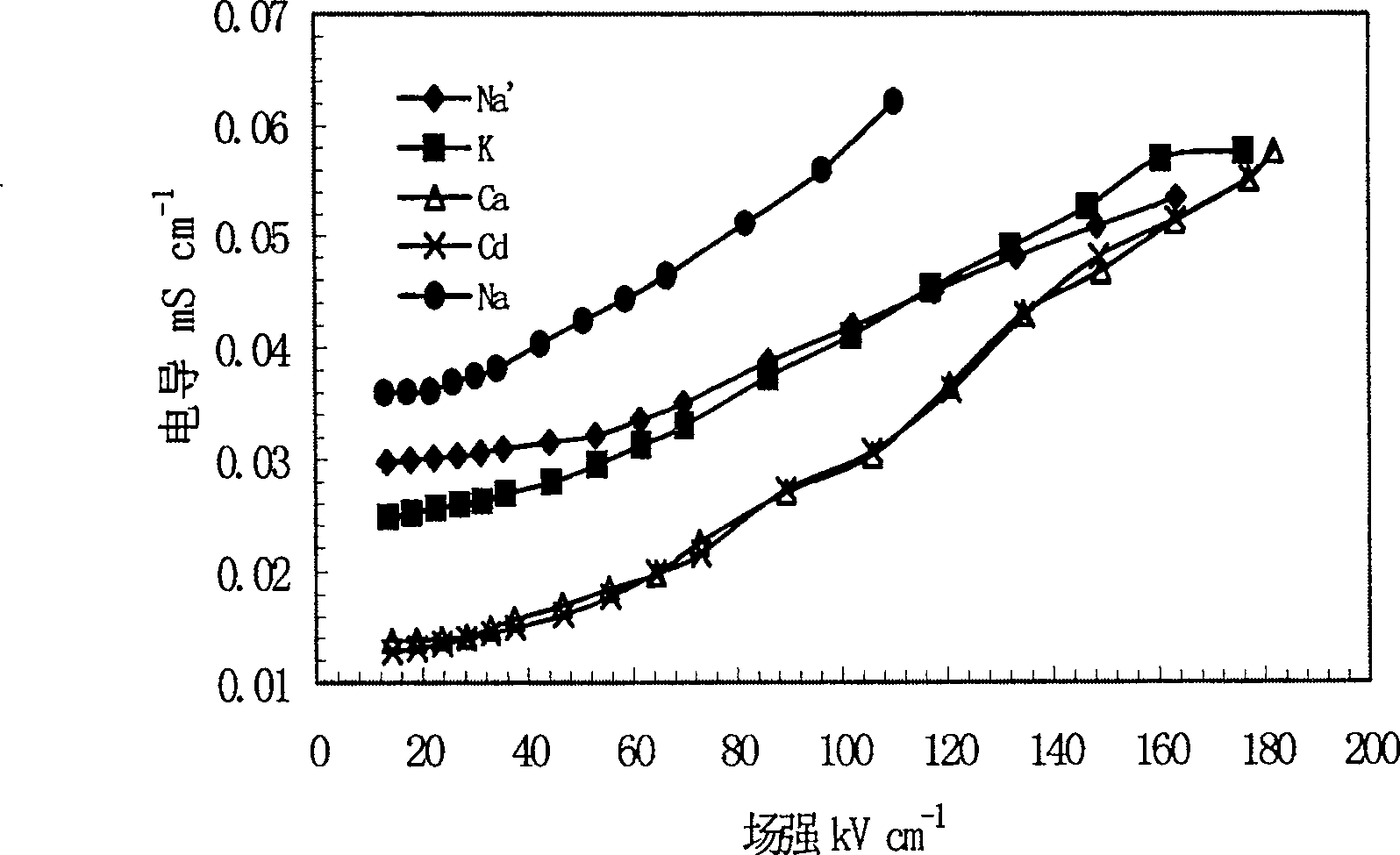
[0050] The device used to measure the Wien effect in soil suspension consists of a pulse variable high-voltage DC power supply and a conductivity cell, the output DC voltage is as high as 30kV; the pulse width is several μS to tens of μS; the resistance of the conductivity cell can be measured in the range of 1~20kΩ.
[0051] Measurement methods
[0052] Put the measuring device in a constant temperature room, pour the balanced soil suspension into the conductivity cell at a constant temperature (25°C), start from the lowest applied voltag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com