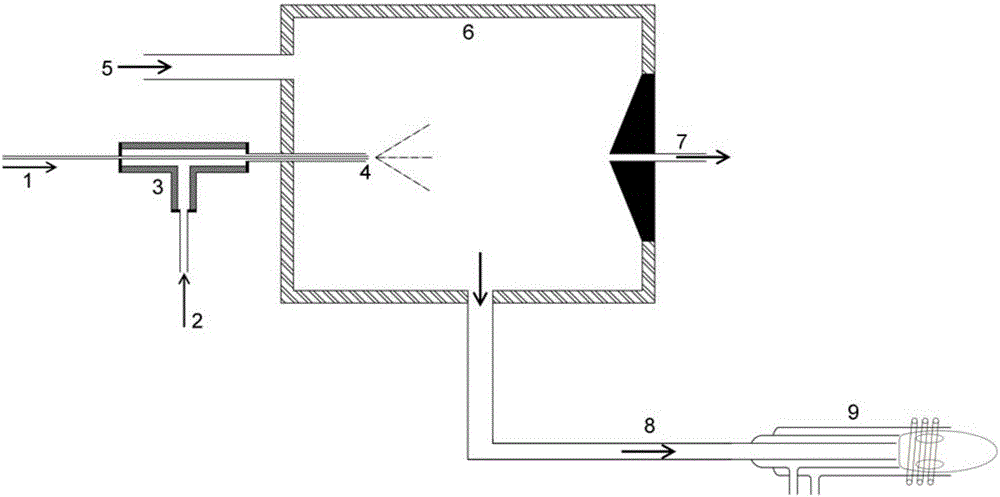
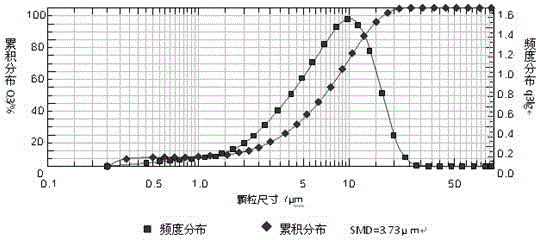
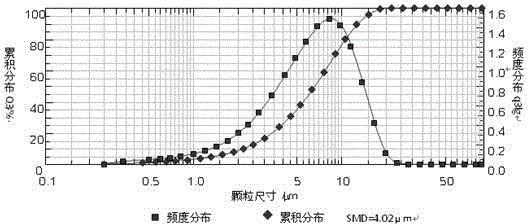
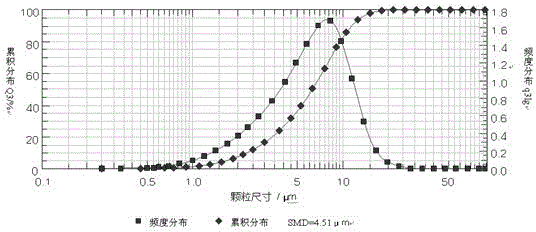
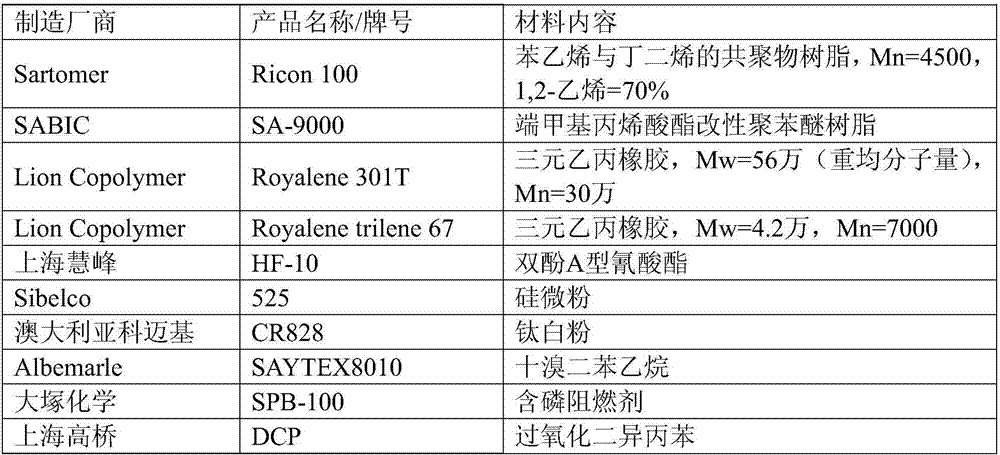
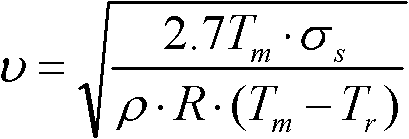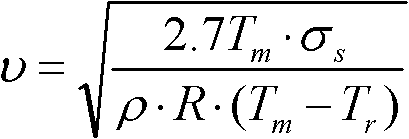Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
341 results about "Element composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
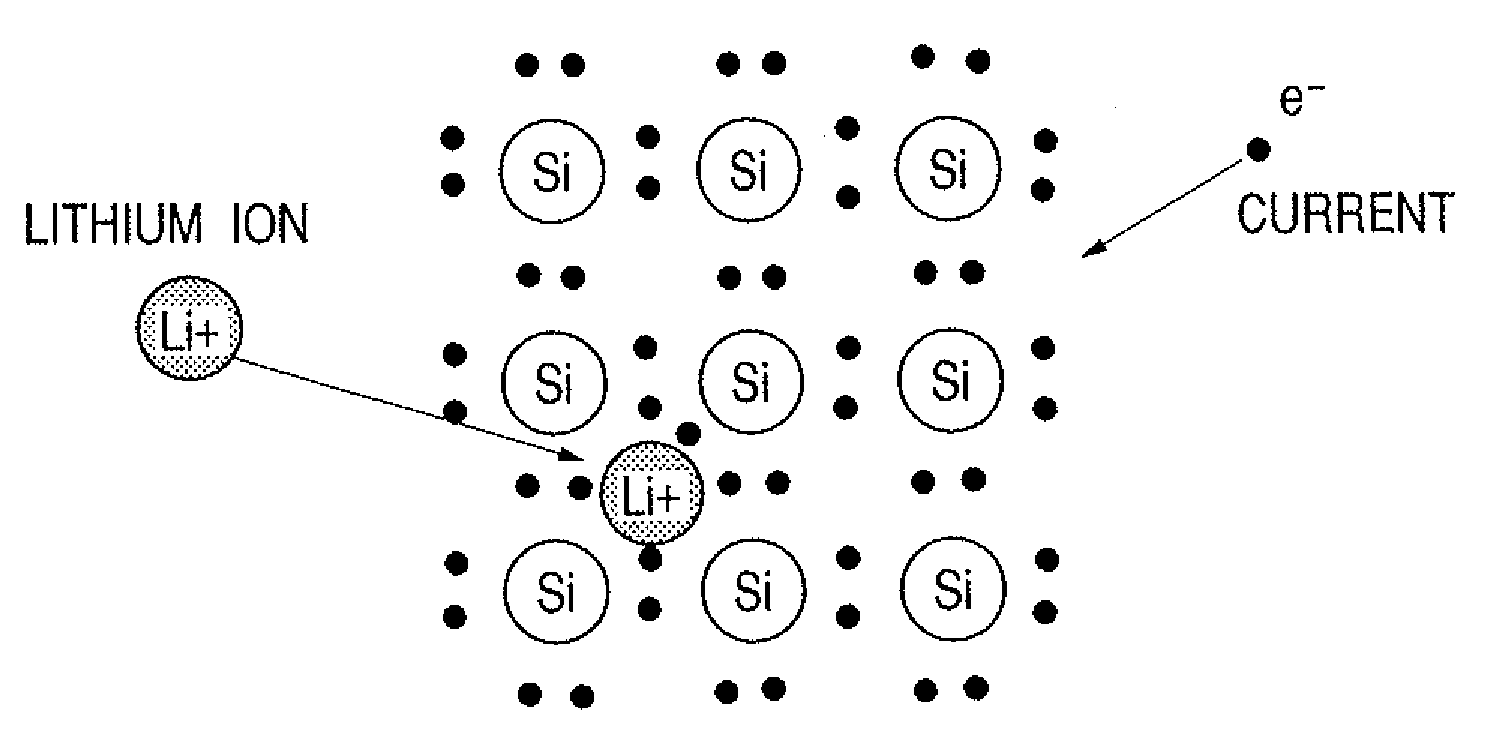
Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element that retains all the characteristics of the element. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, which is composed of the basic building blocks of mater, leptons and quarks. .
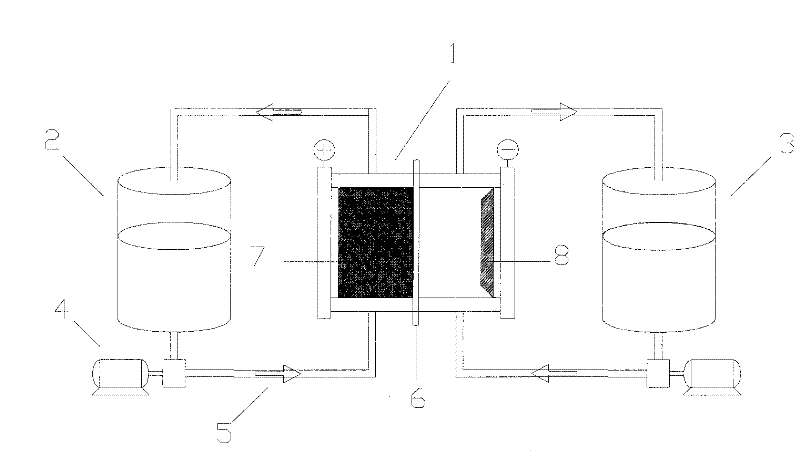
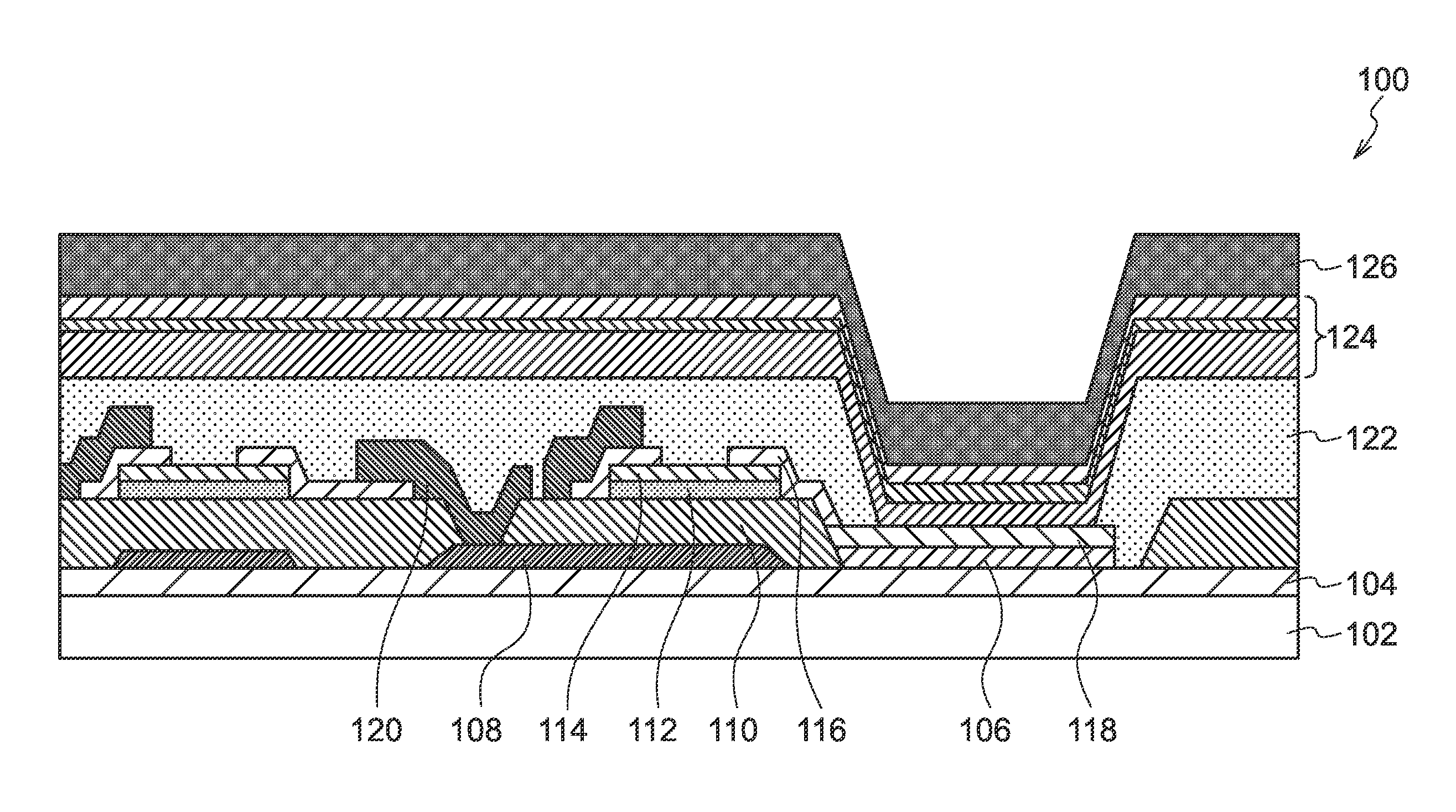
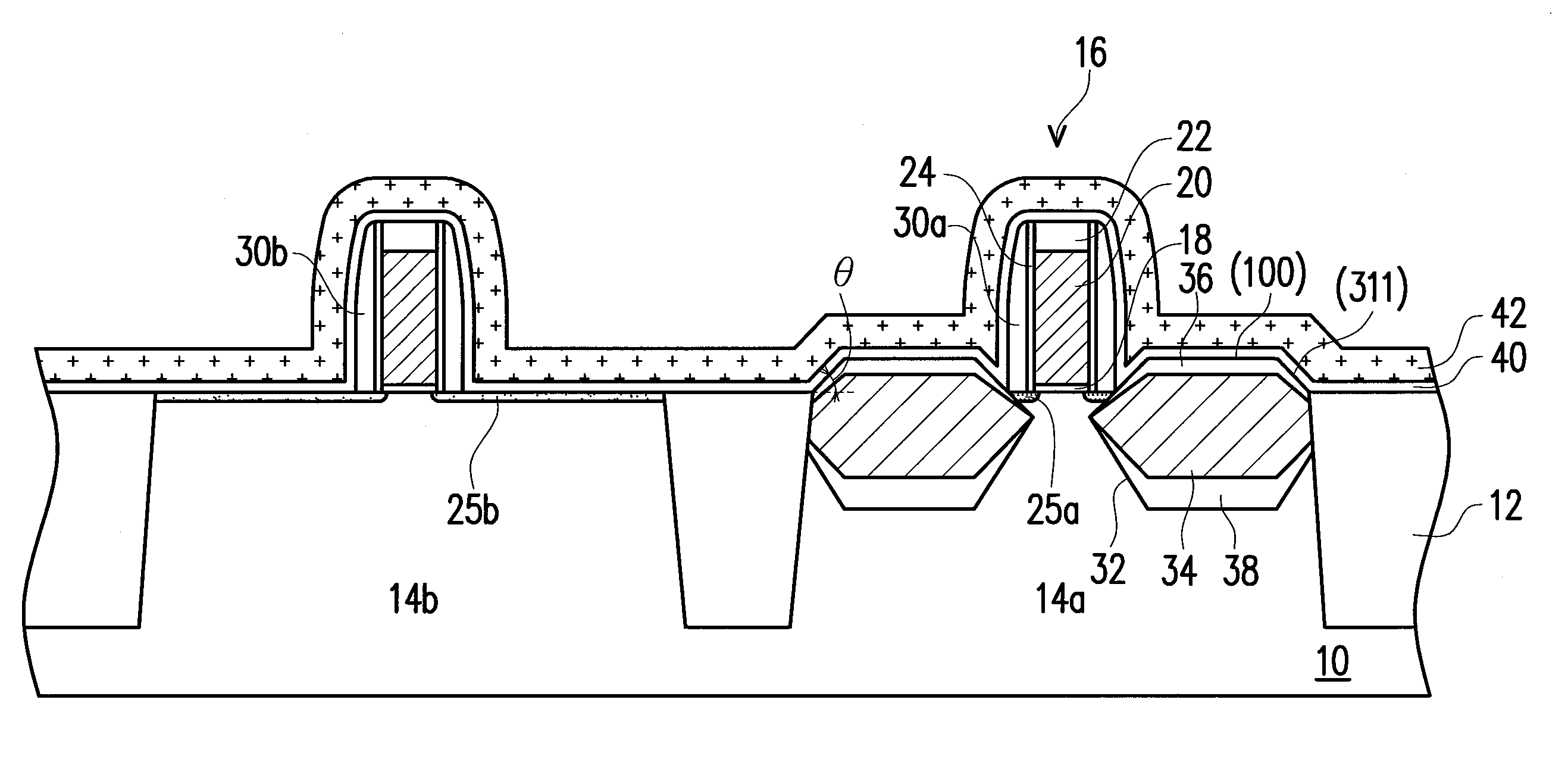
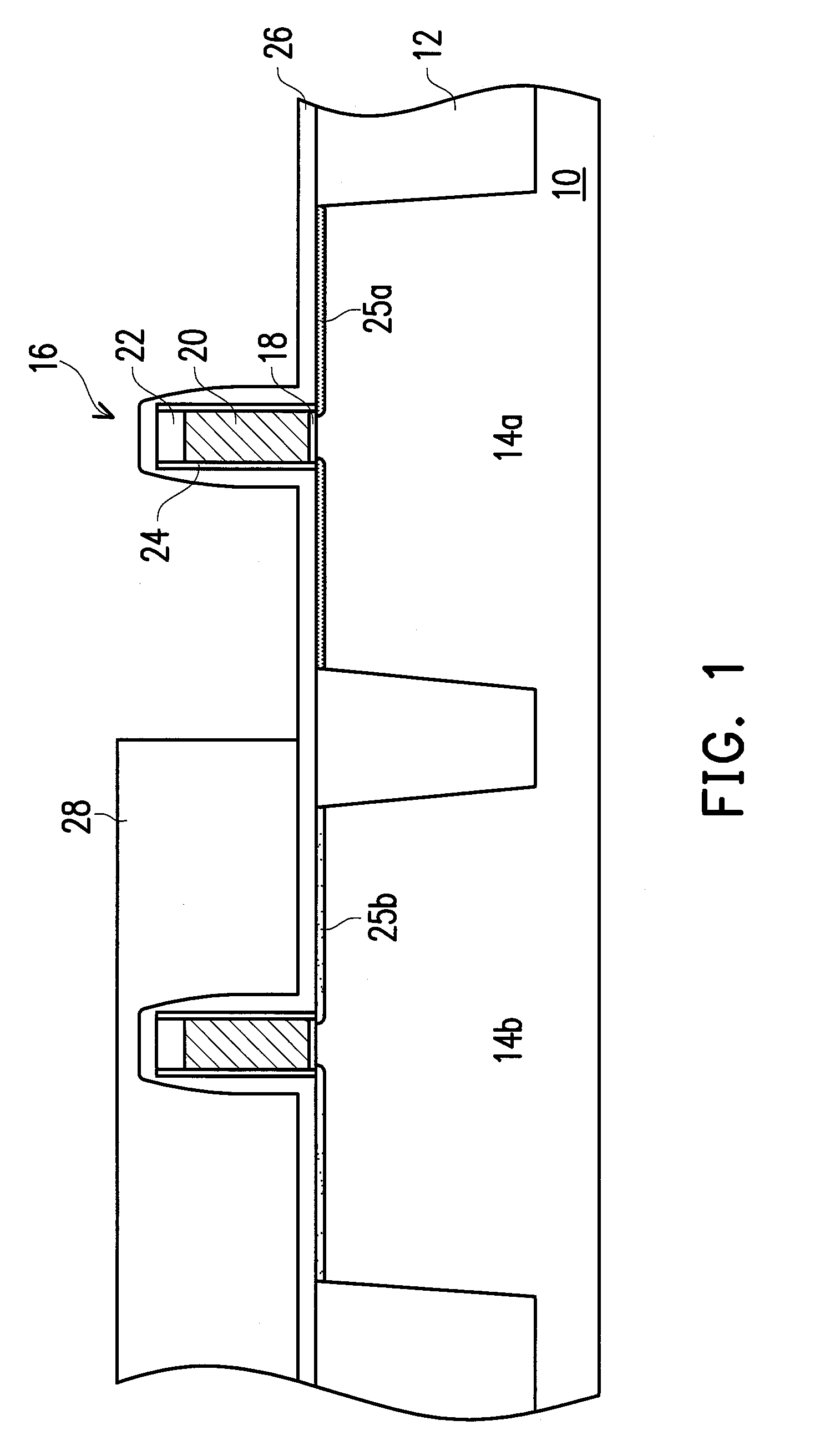
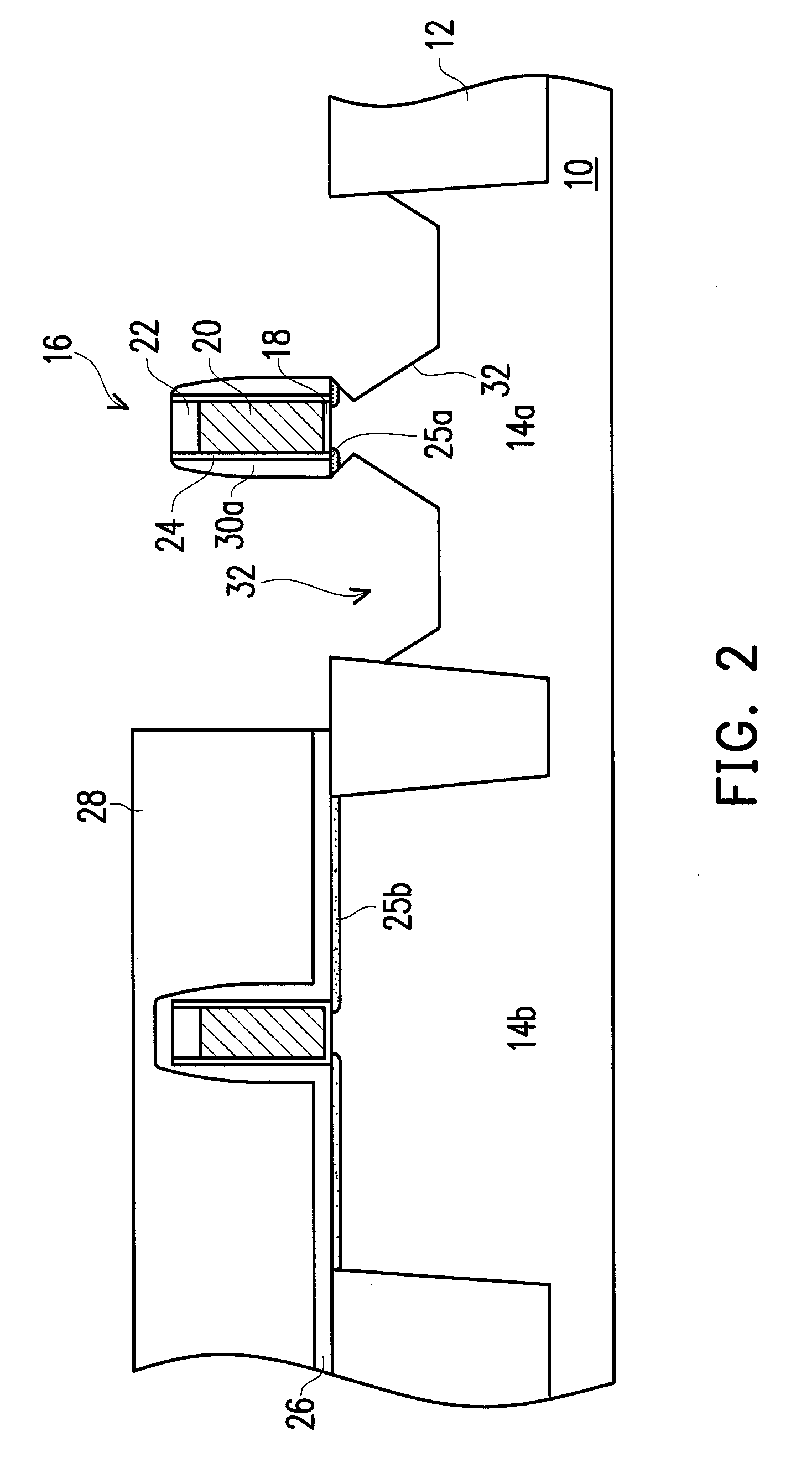
Electrode material for lithium secondary battery and electrode structure having the electrode material
InactiveUS20060040182A1Reduce conductivityImprove conductivityLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithiumLiquid state
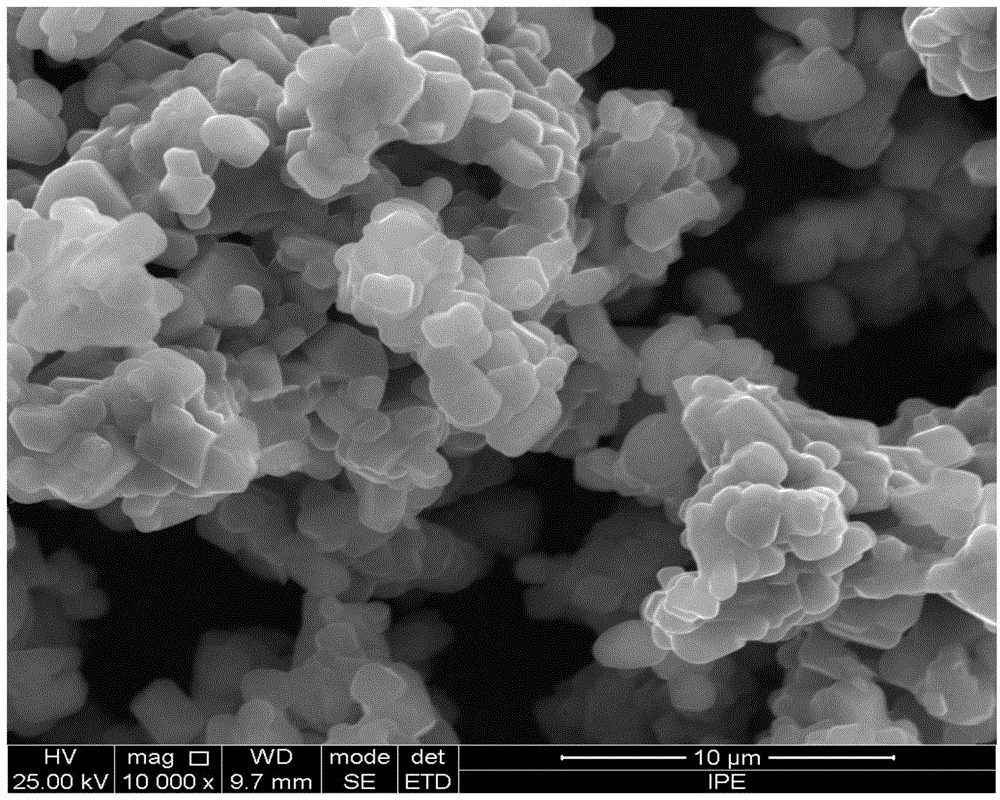
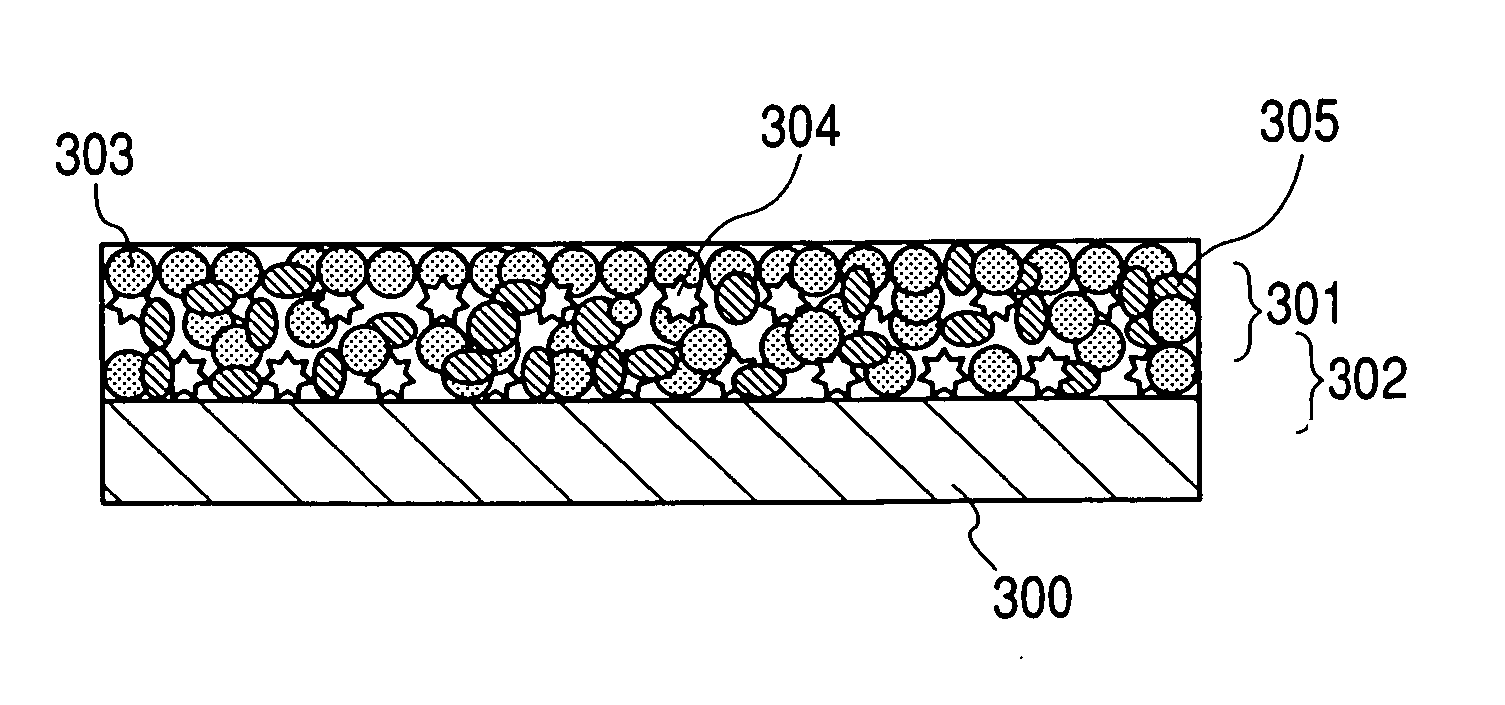
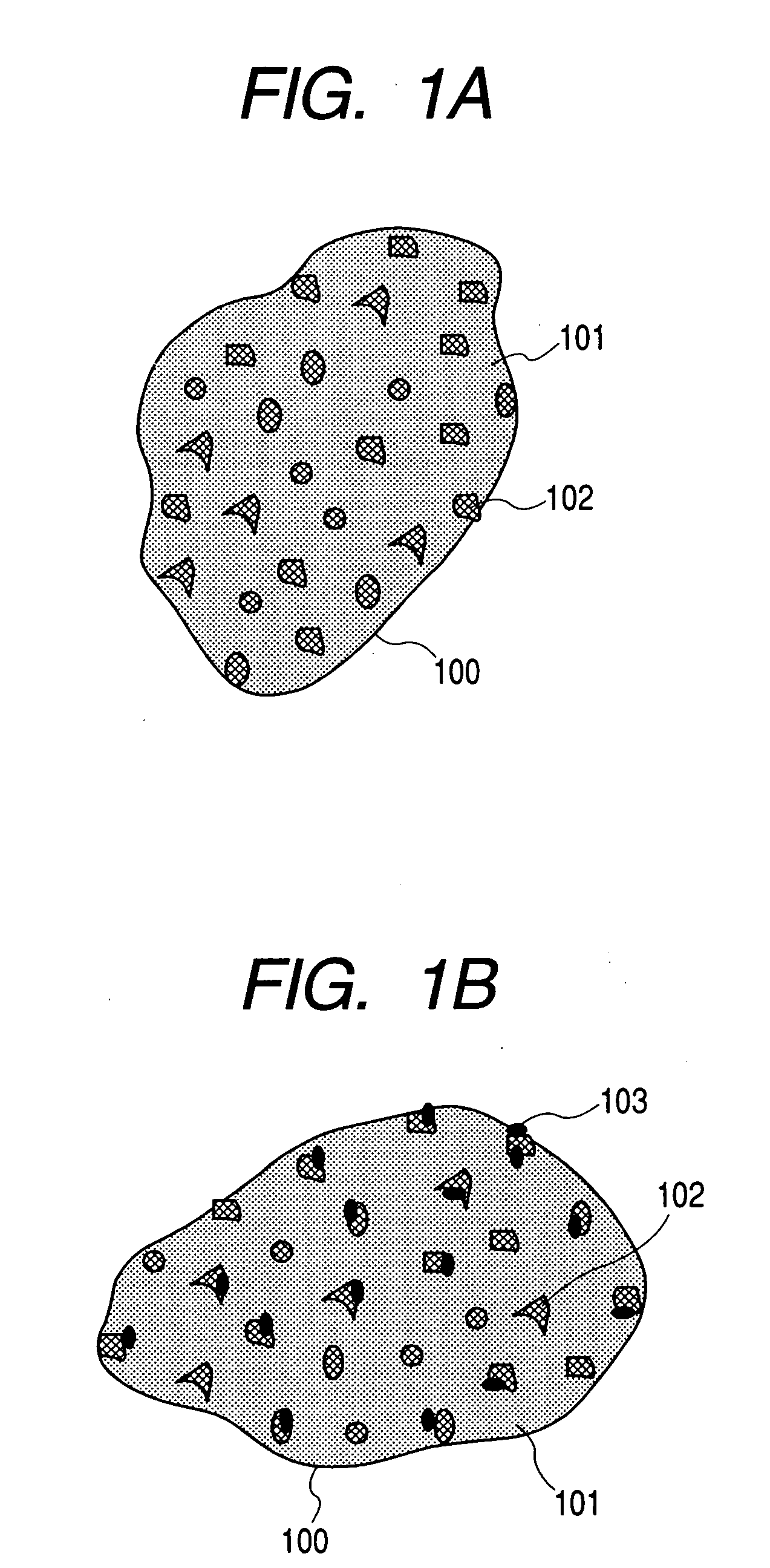
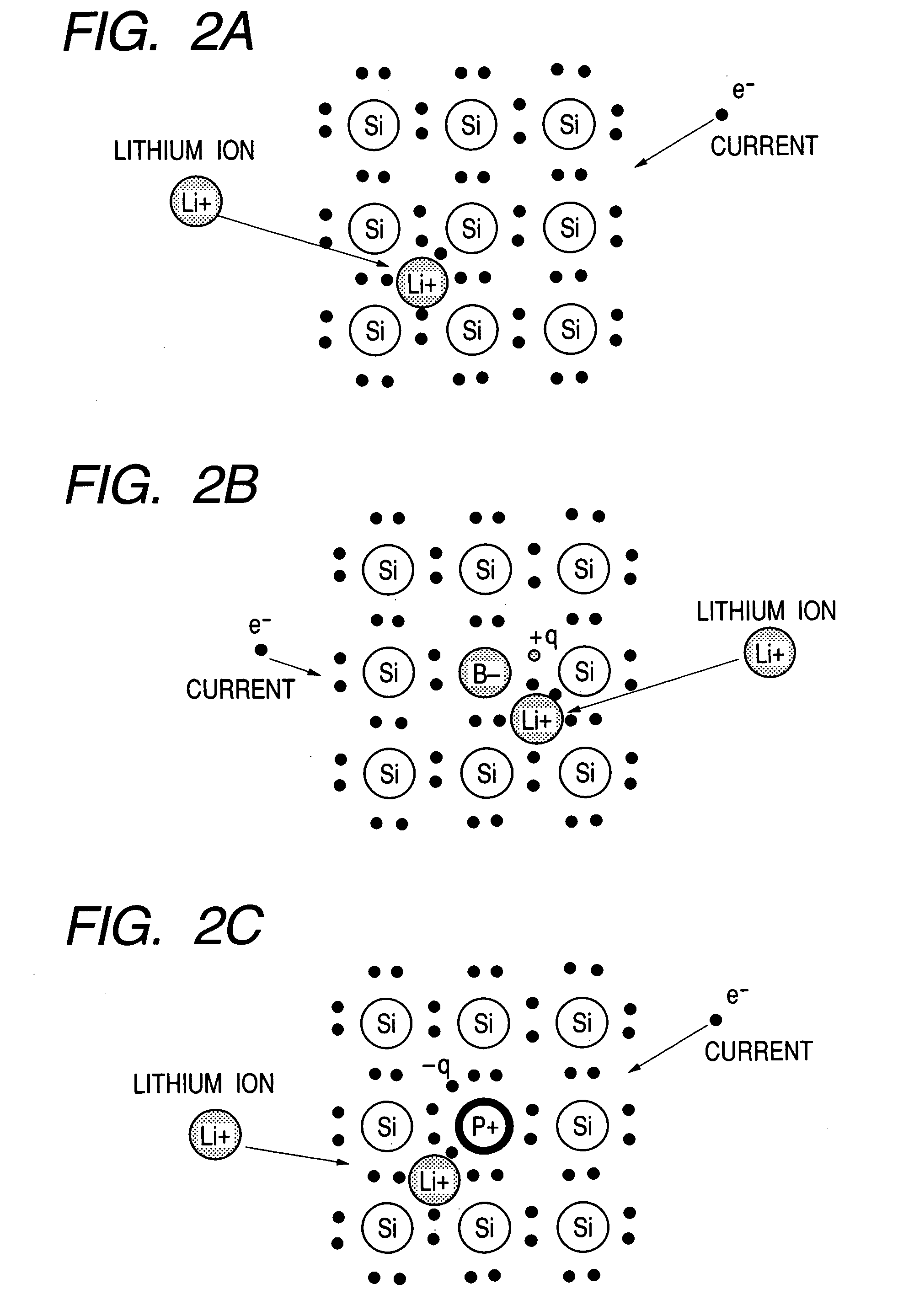
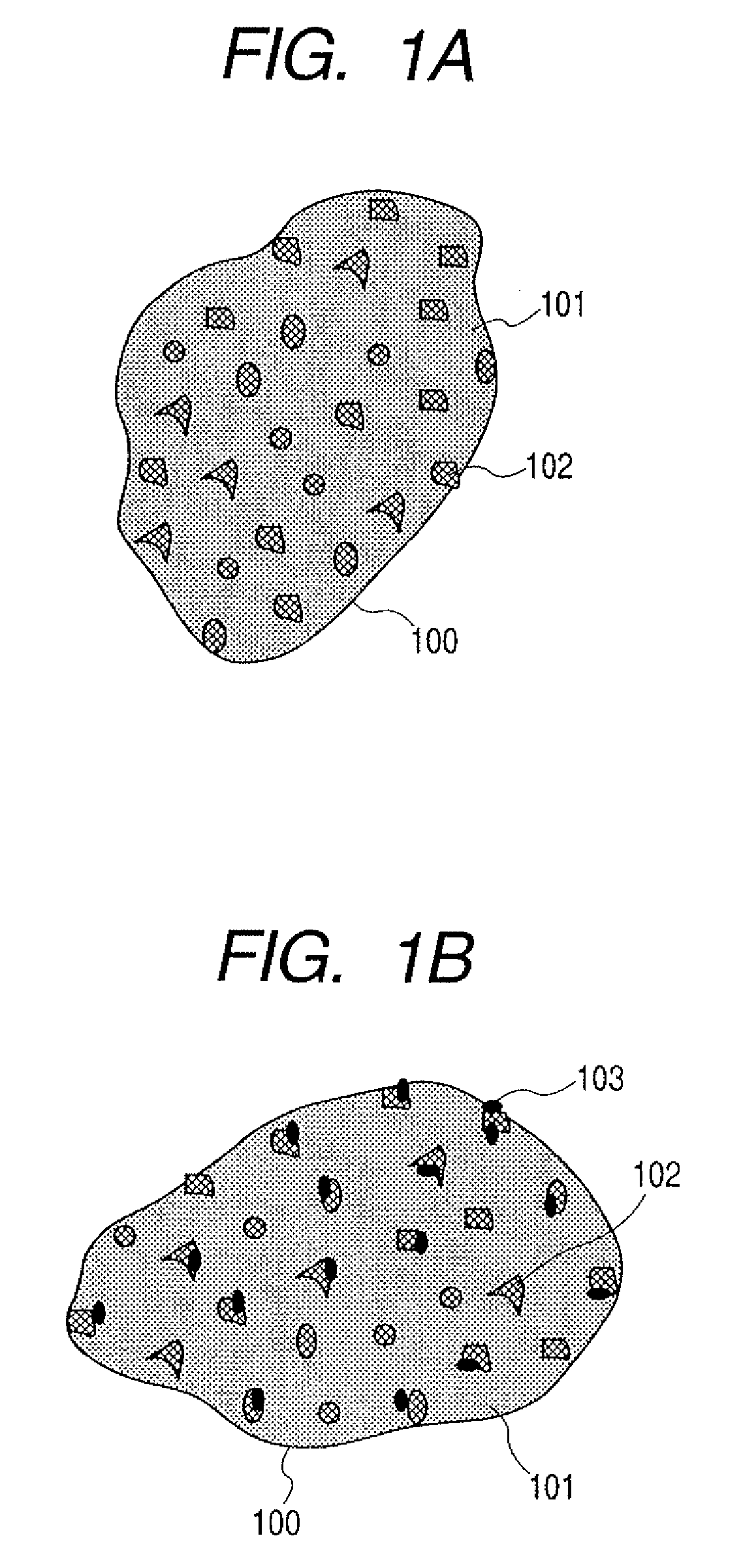
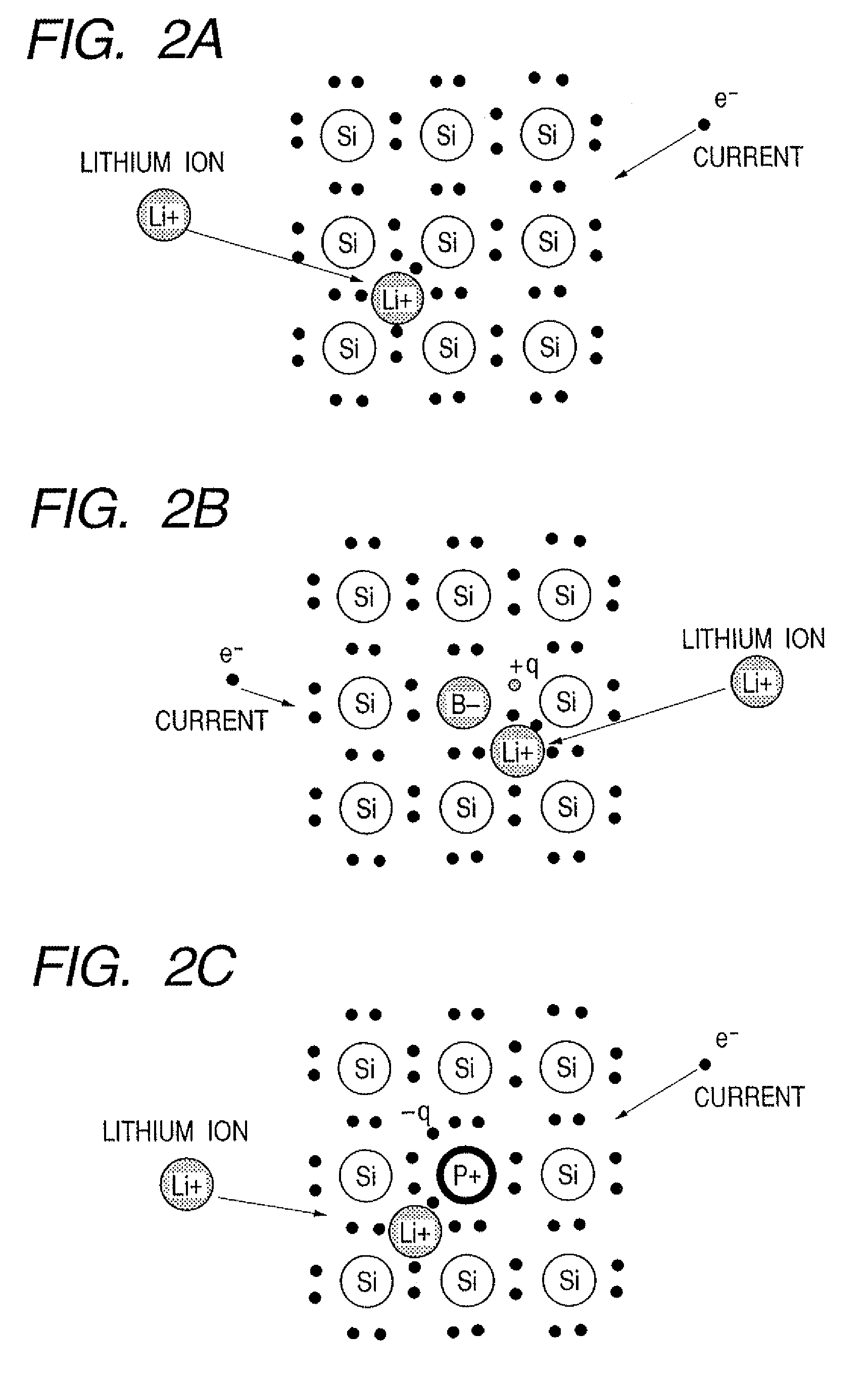
The electrode material for a lithium secondary battery according to the present invention includes particles of a solid state alloy having silicon as a main component, wherein the particles of the solid state alloy have a microcrystal or amorphous material including an element other than silicon, dispersed in microcrystalline silicon or amorphized silicon. The solid state alloy preferably contains a pure metal or a solid solution. The composition of the alloy preferably has an element composition in which the alloy is completely mixed in a melted liquid state, whereby the alloy has a single phase in a melted liquid state without presence of two or more phases. The element composition can be determined by the kind of elements constituting the alloy and an atomic ratio of the elements.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for preparing fuel element for smoking article
The invention provides a method for making a fuel element for a smoking article including the steps of mixing a metal-containing catalyst precursor with a filler material or graphite or a combination thereof to form a pre-treated fuel element component; optionally calcining the pre-treated fuel element component in order to convert the catalyst precursor to a catalytic metal compound; after the optional calcining step, combining the pre-treated fuel element component with a carbonaceous material and a binder to produce a fuel element composition; and forming the fuel element composition into a fuel element adapted for use in a smoking article. Examples of metal-containing catalyst precursors include iron nitrate, copper nitrate, cerium nitrate, cerium ammonium nitrate, manganese nitrate, magnesium nitrate, and zinc nitrate. Fuel elements treated according to the invention, and smoking articles including such fuel elements, are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Injection molded vaso-occlusive elements
Compositions comprising injection-molded vaso-occlusive elements are described. Thus, one or more injection-molded elements are formed into a desired three-dimensional configuration. Each injection-molded element of the device may have a different shape, for example, ovoid, spherical, cylindral or pyramidal. The devices described herein may also be detachable linked to pusher element for placement in a body cavity. Also described are methods of making and using these elements.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Monomers and polymers for optical elements
ActiveUS20060052547A1Inhibition of polymerizationSpectales/gogglesThin material handlingPolyesterEpoxy
Compositions comprising a matrix polymer and a mixture of monomers are used for making polymer mixtures containing the matrix polymer and a second polymer formed from the monomer mixture. Preferably, the matrix polymer comprises a polyester, polystyrene, polyacrylate, thiol-cured epoxy polymer, thiol-cured isocyanate polymer, or mixtures thereof. Preferably, the monomer mixture comprises a thiol monomer and at least one second monomer selected from the group consisting of ene monomer and yne monomer. The compositions may be used to fabricate optical elements such as lenses.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Ambient temperature, rechargeable cells with metal salt-based electrodes and a system of cell component materials for use therein
InactiveUS6187479B1Improve battery performanceImprove performanceLead-acid accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsHalogenRechargeable cell
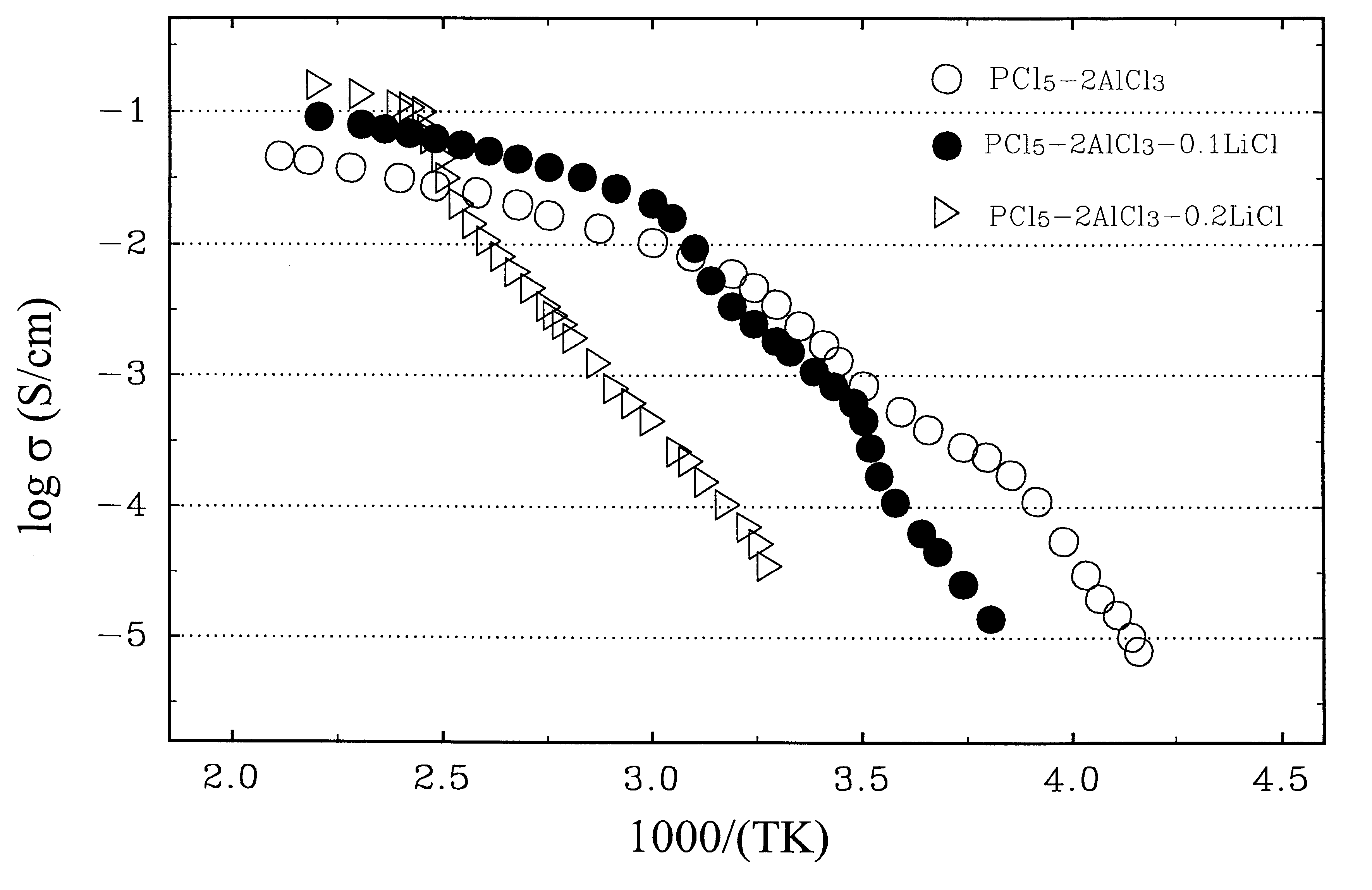
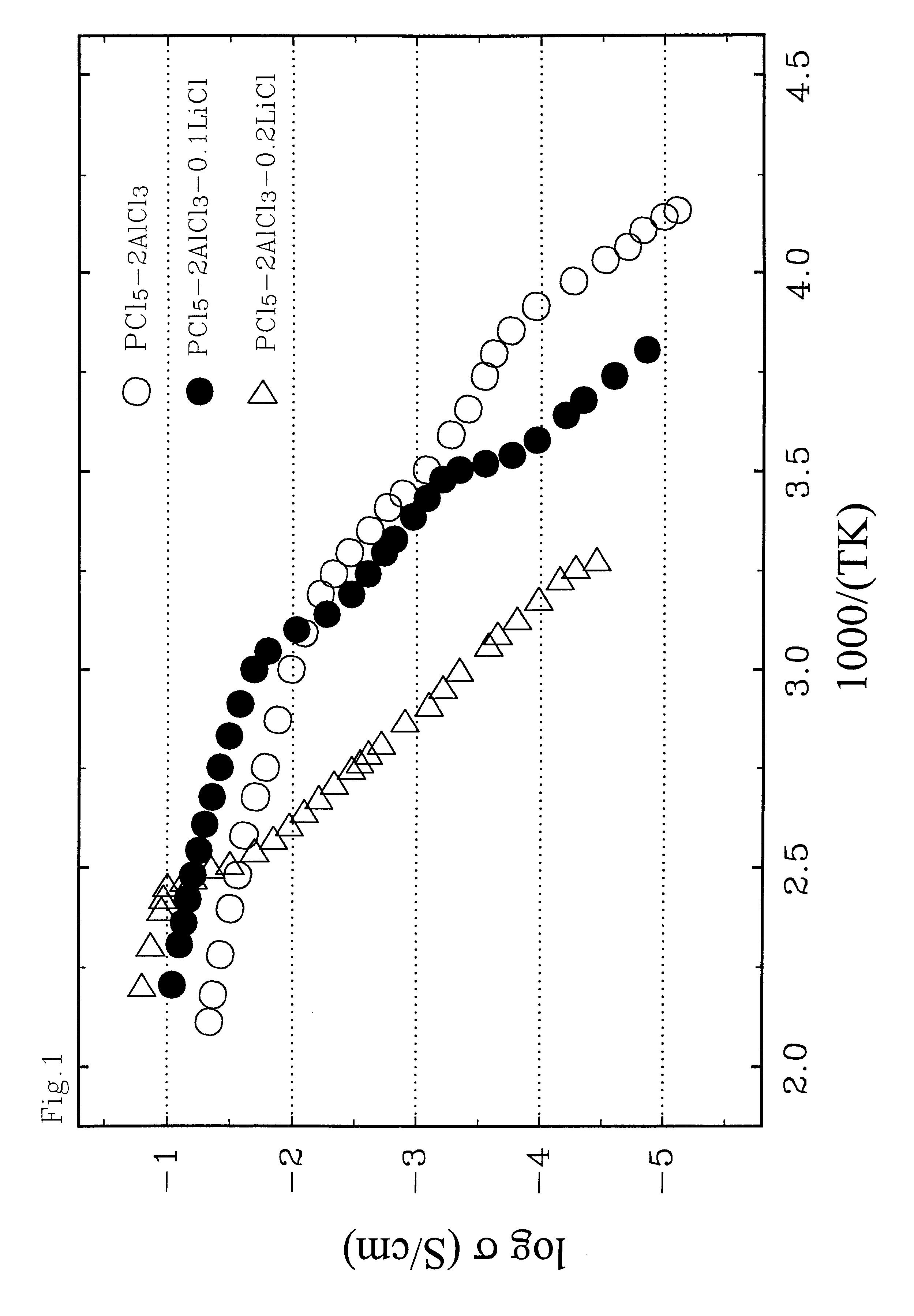
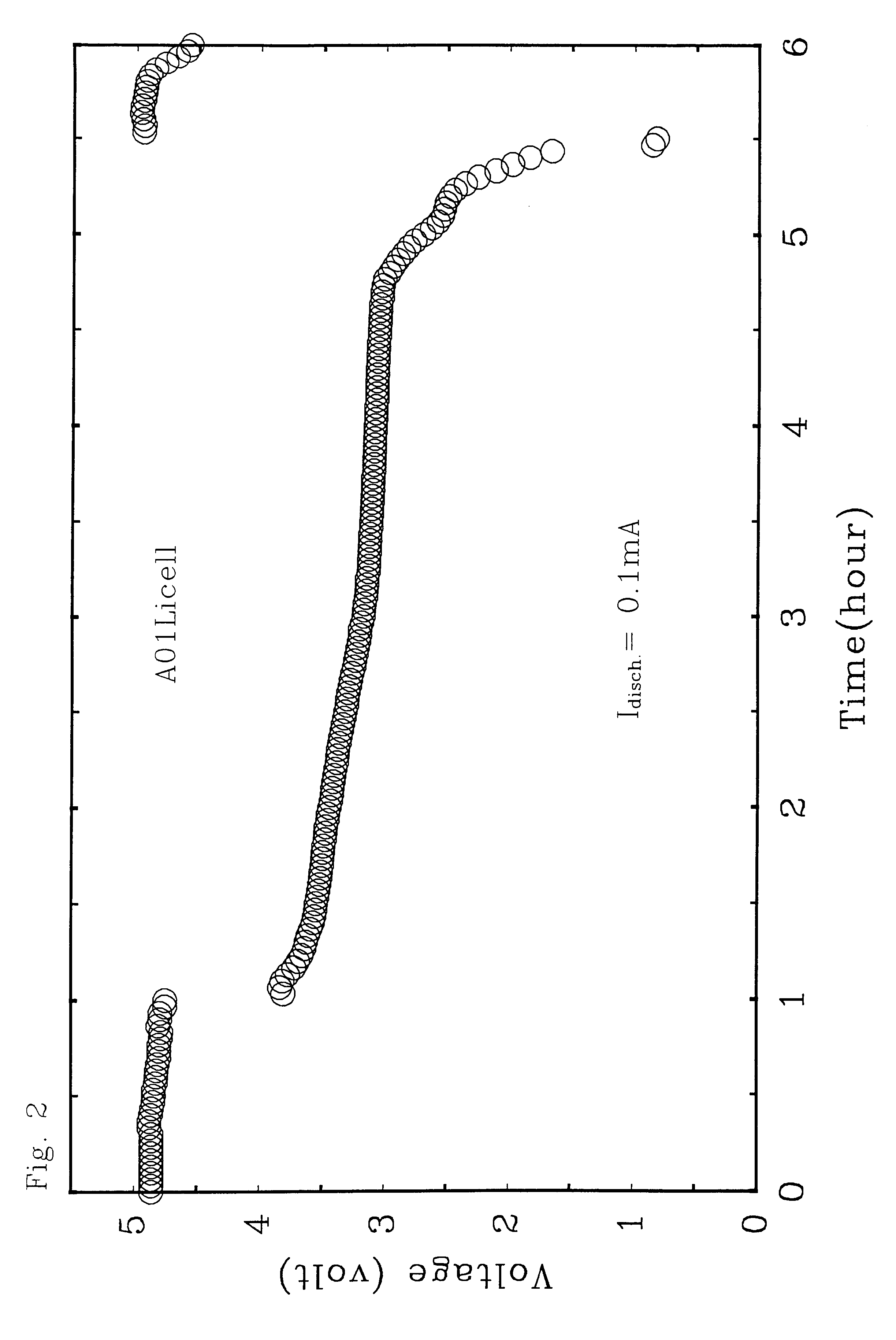
A rechargeable battery or cell is disclosed in which the electrode active material consists of at least one nonmetallic compound or salt of the electropositive species on which the cell is based, and the electrolyte or electrolyte solvent consists predominantly of a halogen-bearing or chalcogen-bearing covalent compound such as SOCl2 or SO2Cl2. Also disclosed are cell component materials which include electrodes that consist primarily of salts of the cell electropositive species and chemically compatible electrolytes. These latter electrolytes include several newly discovered ambient temperature molten salt systems based on the AlCl3-PCl5 binary and the AlCl3-PCl5-PCl3 ternaries.
Owner:LIU CHANGLE
Electrode material for lithium secondary battery and electrode structure having the electrode material
InactiveUS20090061322A1Increase capacityImprove efficiencyNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLi-accumulatorsAlloyMicrocrystalline silicon
The electrode material for a lithium secondary battery according to the present invention includes particles of a solid state alloy having silicon as a main component, wherein the particles of the solid state alloy have a microcrystal or amorphous material including an element other than silicon, dispersed in microcrystalline silicon or amorphized silicon. The solid state alloy preferably contains a pure metal or a solid solution. The composition of the alloy preferably has an element composition in which the alloy is completely mixed in a melted liquid state, whereby the alloy has a single phase in a melted liquid state without presence of two or more phases. The element composition can be determined by the kind of elements constituting the alloy and an atomic ratio of the elements.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for preparing fuel element for smoking article
The invention provides a method for making a fuel element for a smoking article including the steps of mixing a metal-containing catalyst precursor with a filler material or graphite or a combination thereof to form a pre-treated fuel element component; optionally calcining the pre-treated fuel element component in order to convert the catalyst precursor to a catalytic metal compound; after the optional calcining step, combining the pre-treated fuel element component with a carbonaceous material and a binder to produce a fuel element composition; and forming the fuel element composition into a fuel element adapted for use in a smoking article. Examples of metal-containing catalyst precursors include iron nitrate, copper nitrate, cerium nitrate, cerium ammonium nitrate, manganese nitrate, magnesium nitrate, and zinc nitrate. Fuel elements treated according to the invention, and smoking articles including such fuel elements, are also provided.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
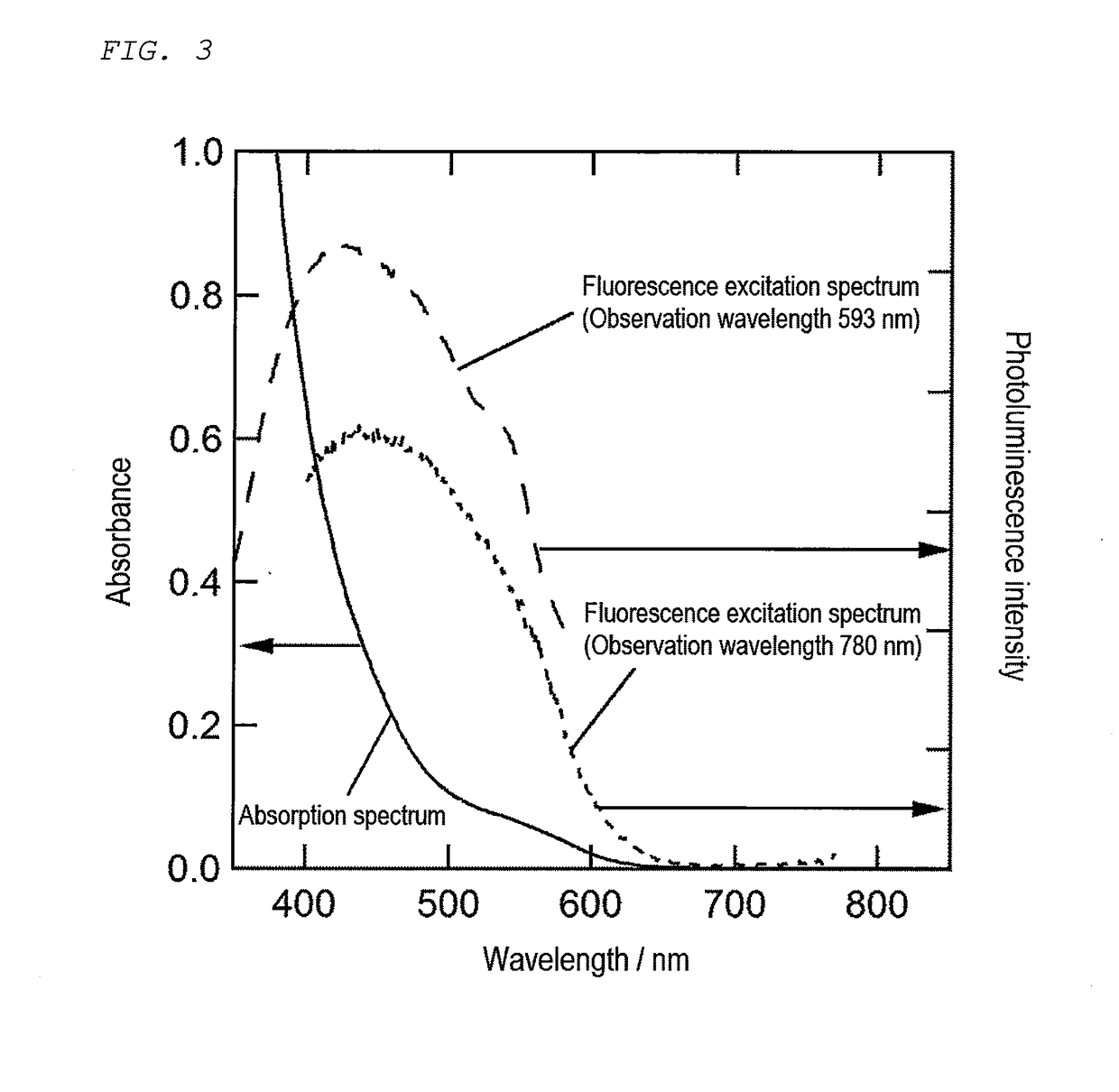
Phosphor And Production Process Of Same
InactiveUS20080277625A1Low toxicLow toxicityLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesIndiumChalcopyrite
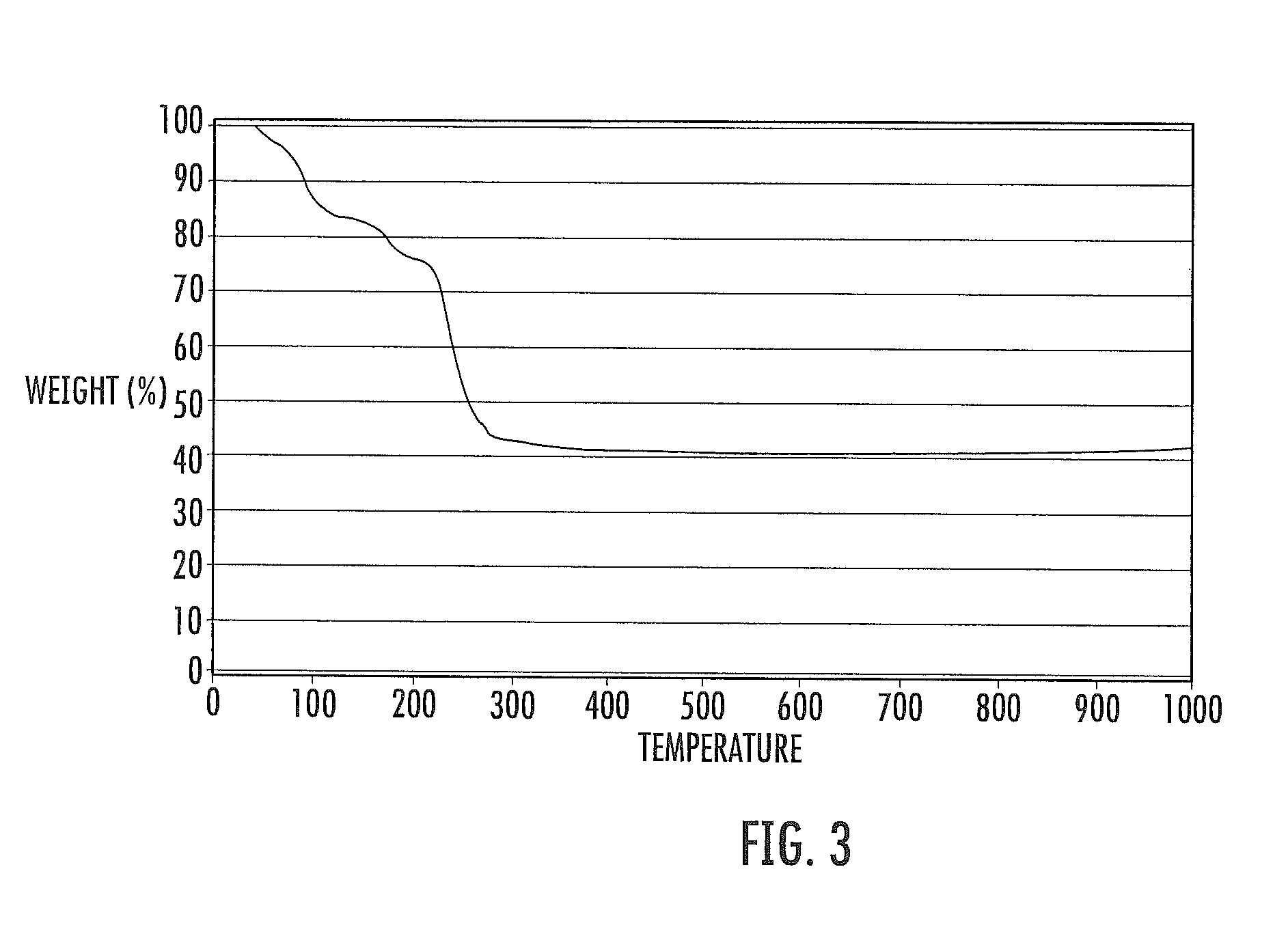
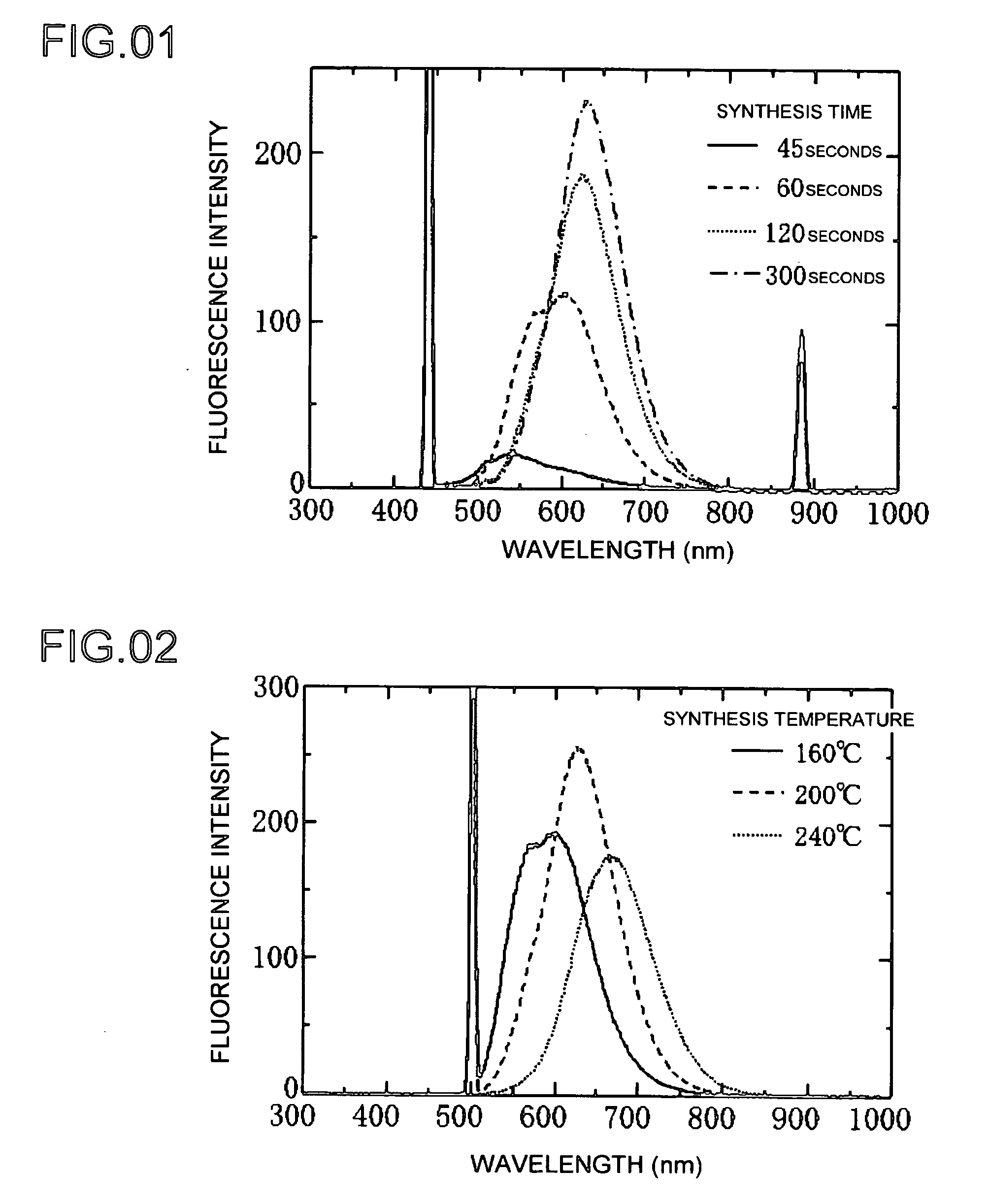
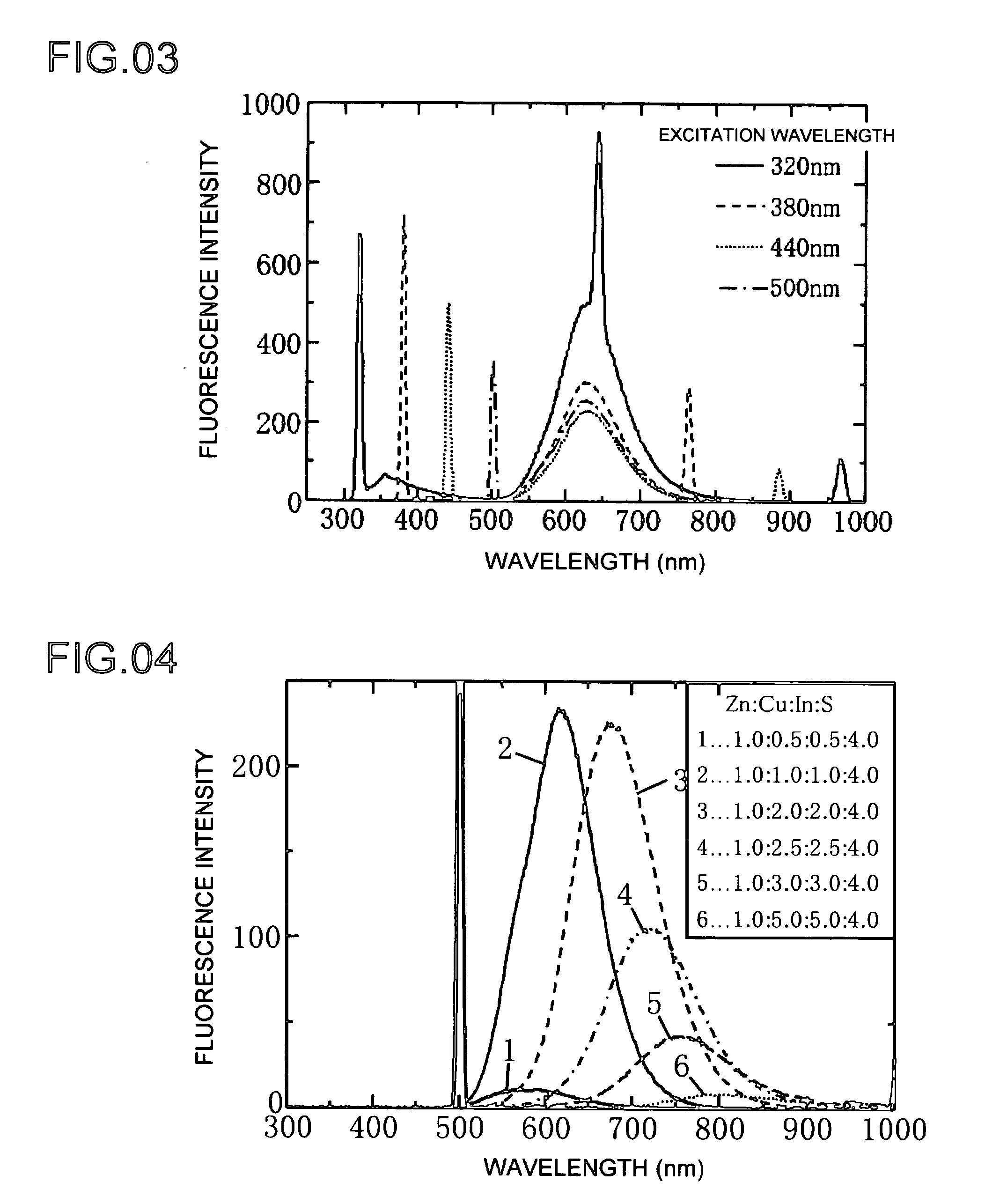
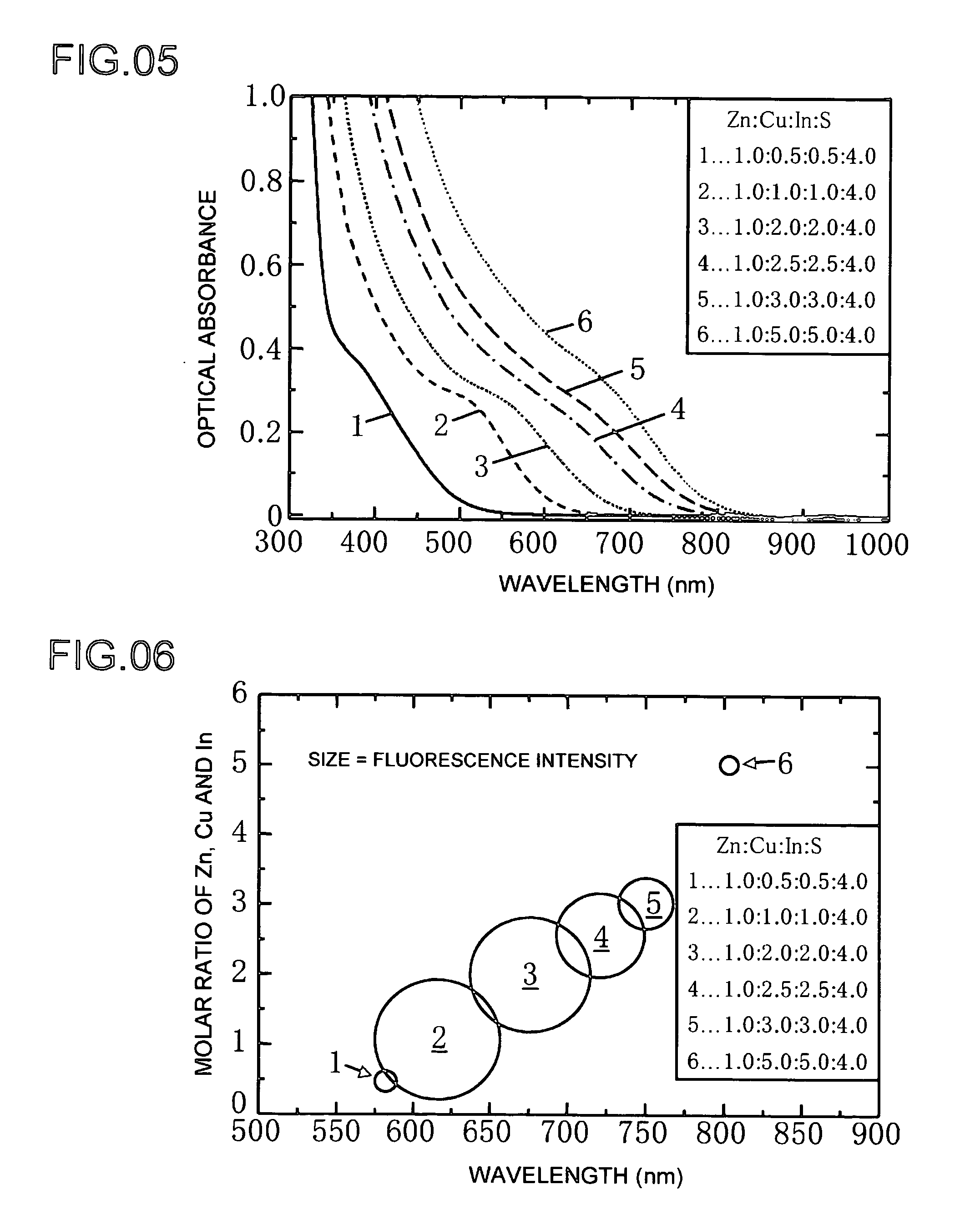
The present invention provides a lowly toxic phosphor and a production process thereof, and more particularly, the synthesis of nanoparticles having a chalcopyrite structure, a phosphor by compounding with a metal chalcogenite, and a production process thereof. The phosphor is a first compound composed of elements of groups I, III and VI having a chalcopyrite structure, or composite particles or composite compound containing the first compound, and the particle diameter of the first compound, or the composite particles or composite compound, is 0.5 to 20.0 nm. The phosphor is produced by mixing a first solution (Solution A), in which one or more of copper (I), copper (II), silver (I), indium (III), gallium (III) and aluminum (III) are respectively dissolved and mixed in a solution to which has been added a complexing agent, and a second solution (Solution C), in which a chalcogenite compound has been dissolved, followed by heat-treating under pre-determined synthesis conditions.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Zinc / polyhalide energy storage cell
InactiveCN102479968AEasy to moveIncrease energy densityRegenerative fuel cellsZinc bromideHigh energy
The invention discloses a zinc / polyhalide energy storage cell. An electrode of conductive inert material and an electrolyte solution of zinc chloride solution and zinc bromide solution are used to form a zinc / polyhalide energy storage cell. The zinc / polyhalide energy storage cell employs zinc and polyhalide with small electrochemical equivalent and high hydrogen evolution overpotential are used as active substances of the cell. Anode and cathode electric pair has high potential difference, and the two together decide that the cell technology has high energy density and power density. Compared with a zinc bromine liquid flow cell, a new system energy storage cell has energy density increased by 30%, power density increased by 10%, obviously enhanced removability and reduced cost of the cell system. The anode and the cathode of the cell employ electrolytes with a same element composition to avoid negative influence on cell performance and life caused by crossed contamination of electrolytes; the cell of the invention has advantages of long cycling life, low cost and good mobility and can be widely applied to fields of energy electric power, transportation and information communication, etc.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
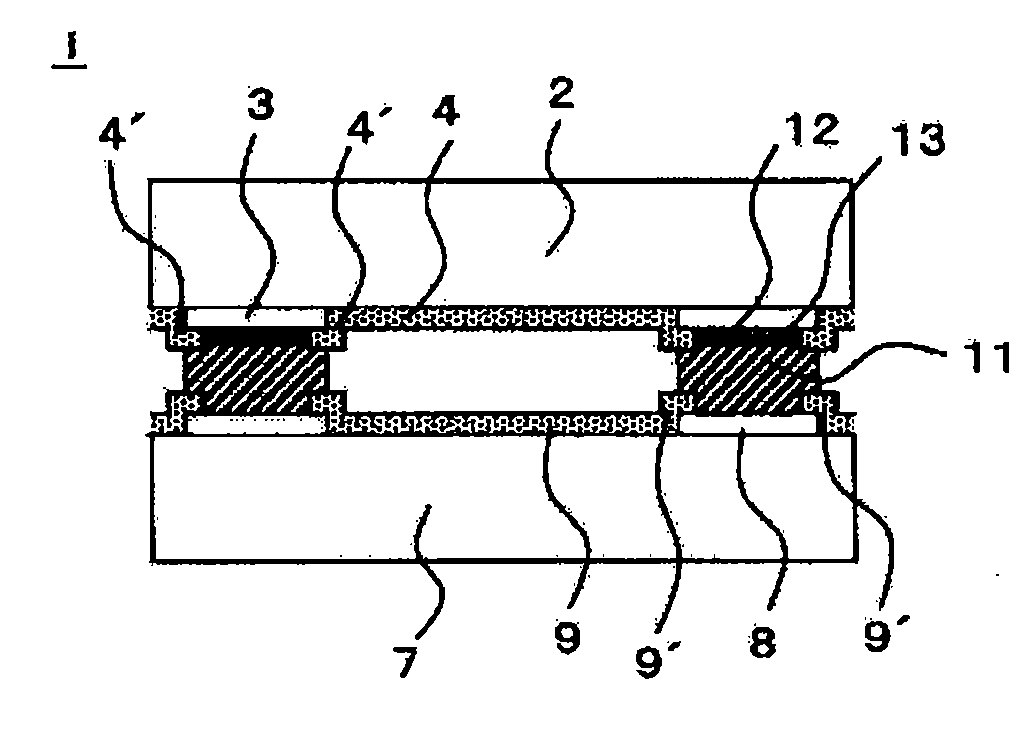
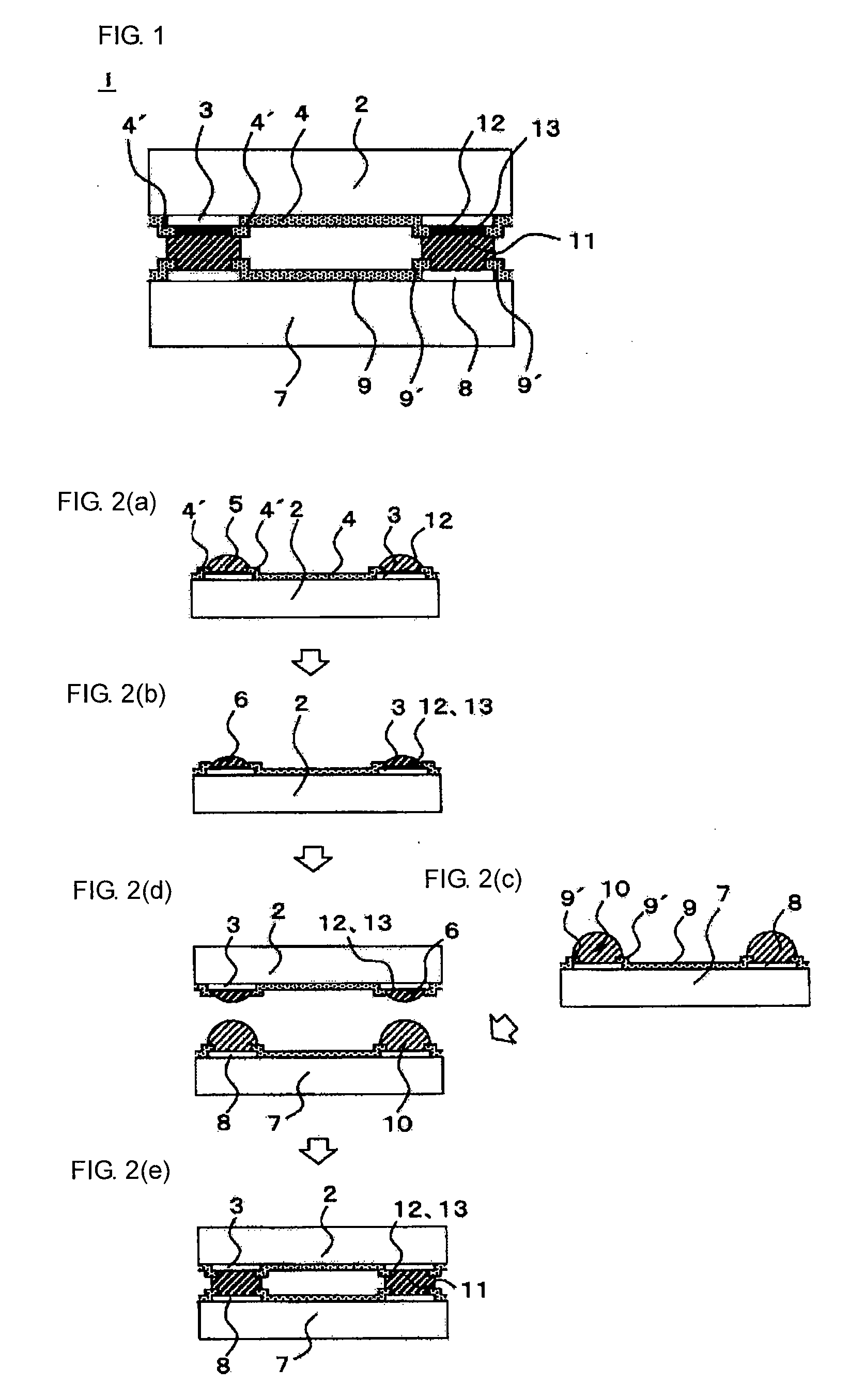
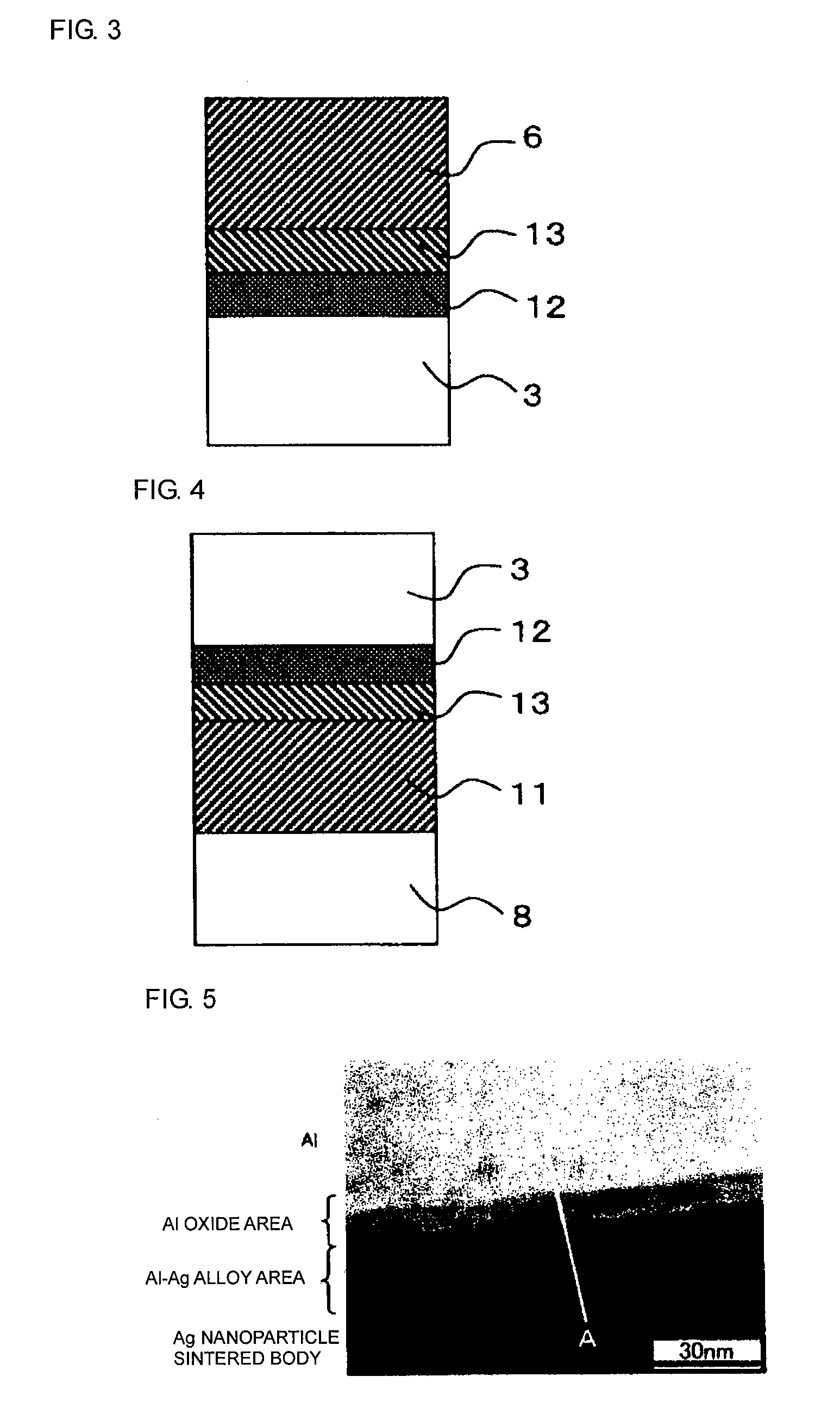
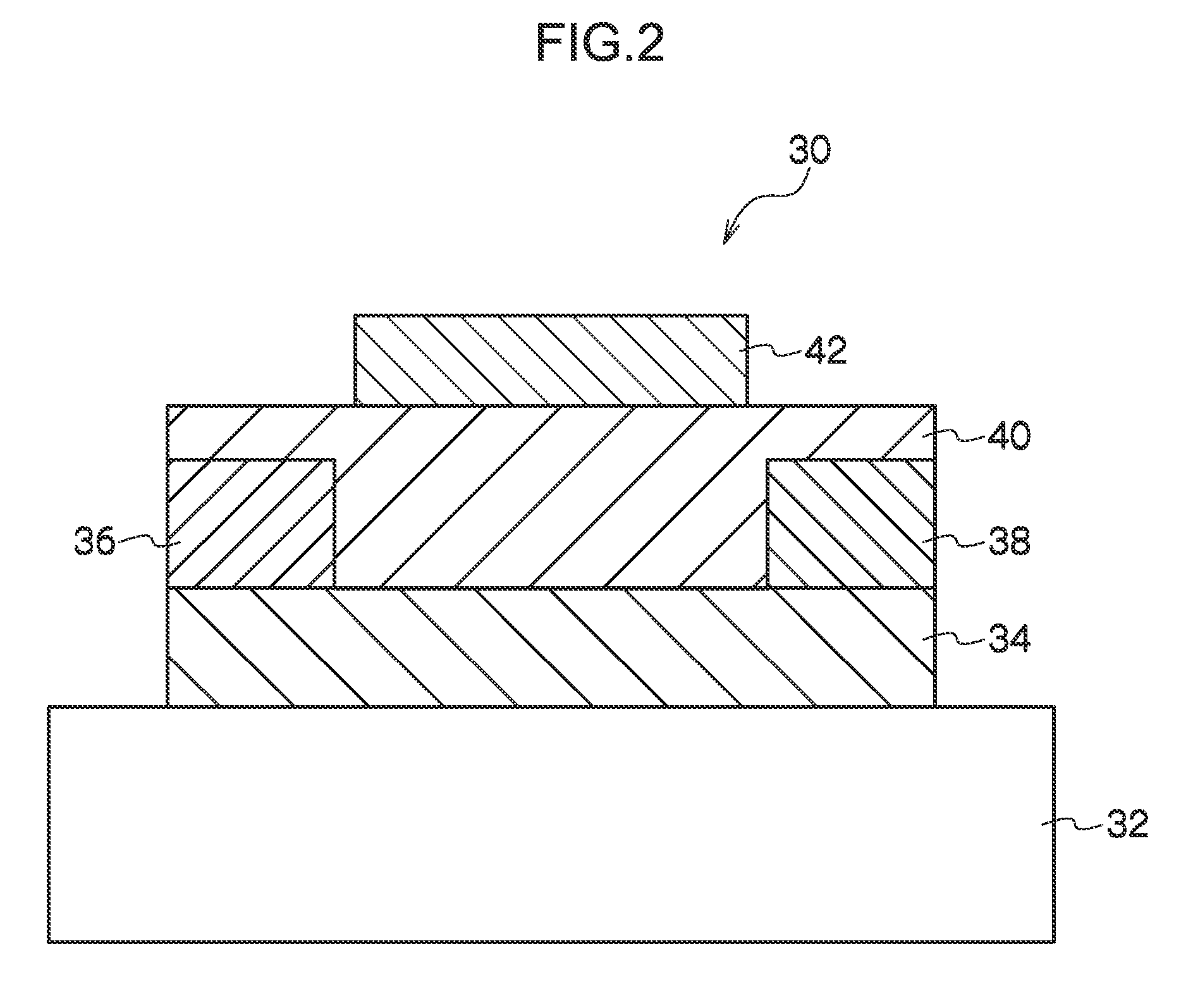
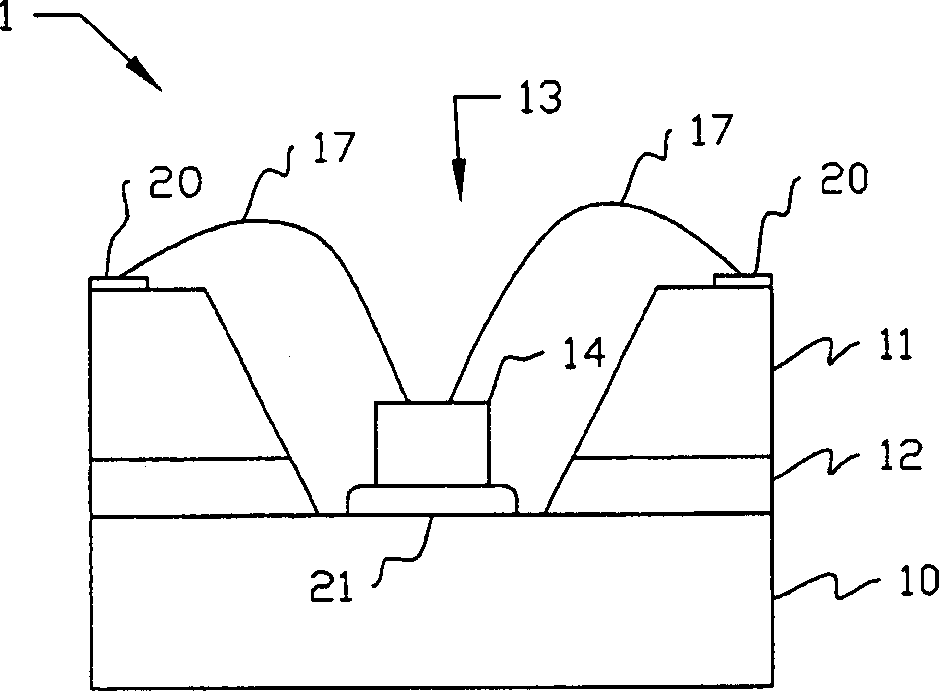
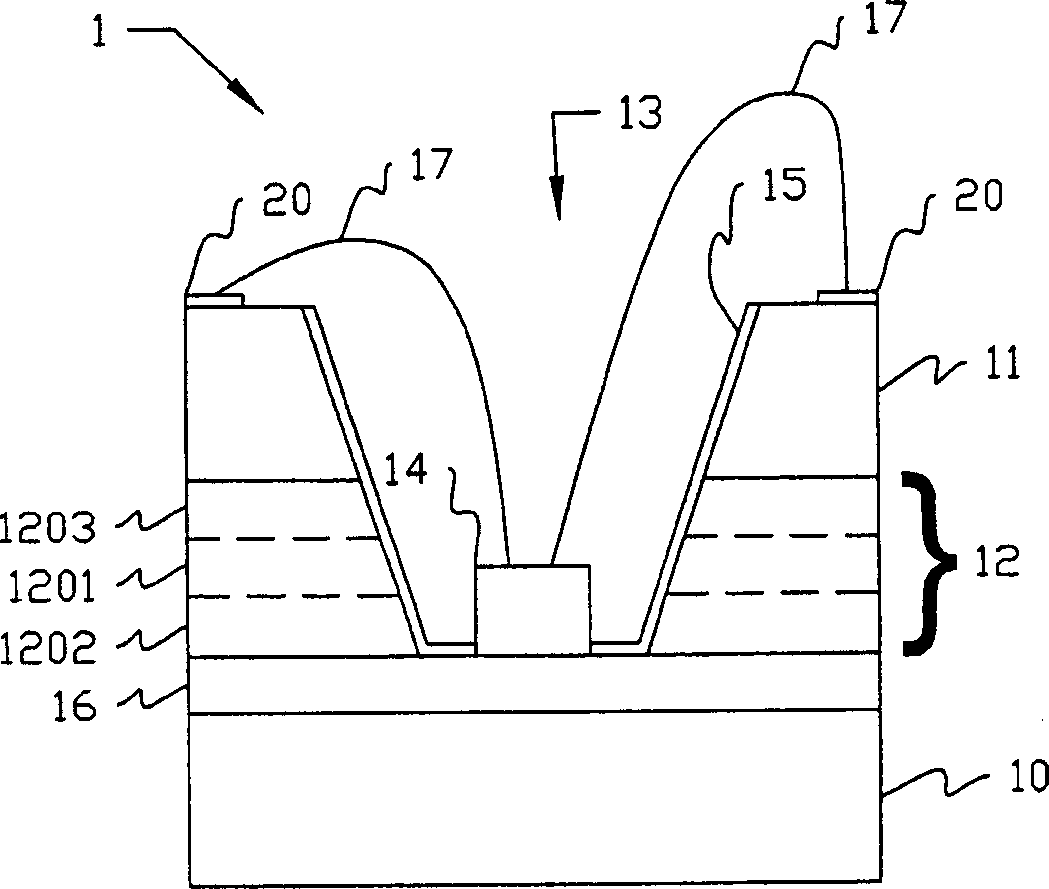
Electronic Element, Electronic Element Device Using the Same, and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090039507A1Bonding reliability can be stablyAvoid insufficient thicknessNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBond interfaceElement composition
An electronic element including an electronic element base and electrodes each of which has a first electrode having a surface composed of at least Al or an Al alloy and a second electrode composed of a metal nanoparticle sintered body and bonded to the first electrode. A bonding interface between the first electrode and the second electrode has a multilayer structure including, from the side of the first electrode to the side of the second electrode, (a) a first layer primarily composed of Al, (b) a second layer primarily composed of an Al oxide, (c) a third layer primarily composed of an alloy of Al and a constituent element of metal nanoparticles, and (d) a fourth layer primarily composed of the constituent element of the metal nanoparticles.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Amorphous oxide semiconductor material, field-effect transistor, and display device
ActiveUS20110042668A1Reduce absorptionTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceElement composition
There is provided an amorphous oxide semiconductor material including an amorphous oxide semiconductor including In, Ga and Zn, wherein when In:Ga:Zn=a:b:c denotes an element composition ratio of the oxide semiconductor, the element composition ratio is defined by the range of a+b=2 and b<2 and c<4b−3.2 and c>−5b+8 and 1≦c≦2.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
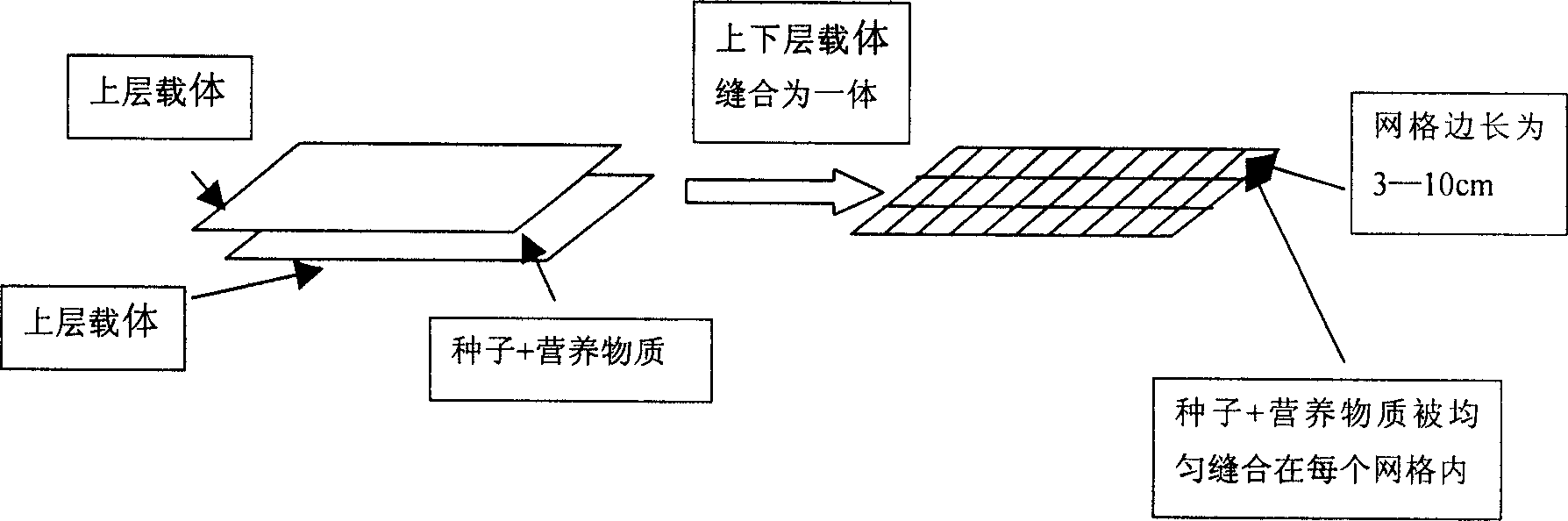
Lawn seed nursery belt sewn with household wastes and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN1732730AImprove performanceImprove folding resistanceCultivating equipmentsSeed arrangmentsPlanting seedElement composition
The invention relates to a stitched domestic waste lawn seeded strip and the producing method, which applies the domestic waste as raw material to make carrier with up and low layer, lawn plant seed and nutriment element composition, the said lawn plant seed and nutriment element is distributed in the up and low layer homogeneously, the said carrier is made up of waste newspaper, waste cotton fabric, gaze and face tissues. The productive technology of the invention is very simple, the resistance to folding and transport endurance are improved significantly, realizing 100% weeds controlling, with the cost dropping above 100%, promoting the city ecological construction and realizing the target of sustainable development with highly effective uniformity of the environment and economy.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Titanium alloy used for aviation fastener and manufacturing method
InactiveCN102011026AIncreased heterogeneous nucleation coreGrain refinementNiobiumElement composition
The invention discloses a titanium alloy used for an aviation fastener and a manufacturing method, and relates to a titanium base alloy. The titanium alloy comprises the following elements in percentage by mass: 5 to 9 percent of aluminum (Al), 1 to 6 percent of vanadium (V), 8 percent of molybdenum (Mo), 11 to 15 percent of niobium (Nb), 1 percent of zirconium (Zr), 0.1 to 2 percent of chromium (Cr) and the balance of Ti, wherein an amorphous titanium alloy inoculant is added in a melting process of the titanium alloy. The titanium alloy used for the aviation fastener has more reasonable new element compositions; the amorphous titanium alloy inoculant is added into the melting process; a heterogeneous nucleation core when the titanium alloy is solidified is added; the crystal size of an as-cast titanium alloy is refined; the tensile strength of a titanium alloy product used for the aviation fastener manufactured by the manufacturing method for the titanium alloy used for the aviation fastener can reach 1,370 MPa; the elongation rate can reach 11.6 percent; and the titanium alloy has both strength and flexibility and can be widely used for fasteners for manufacturing a civil aviation aircraft.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Mass spectrum feeding device and mass spectrum detection equipment
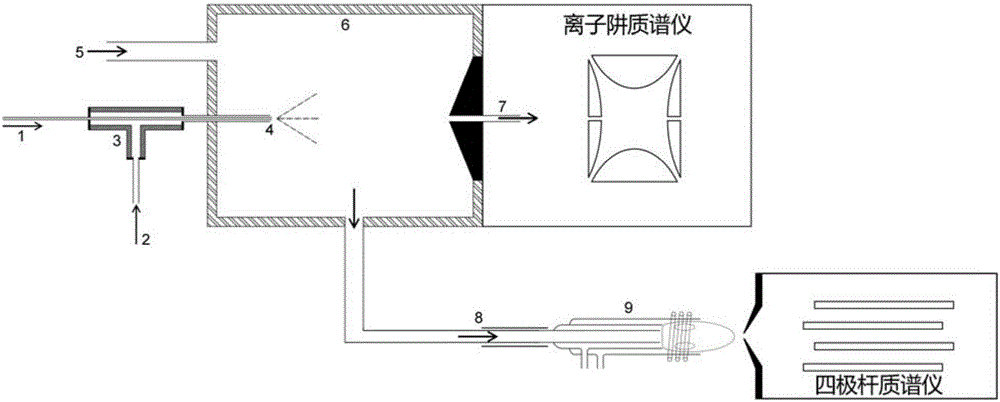
InactiveCN106198707AReasonable designSimple structureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElement compositionMass analyzer
The invention provides a mass spectrum feeding device and mass spectrum detection equipment with the mass spectrum feeding device. The device comprises a spraying device, a sealed cavity, a carrier gas pipeline, a transmission pipeline and an inductive coupling plasma source, wherein the spraying device comprises a feeding pipe, an auxiliary gas pathway and a nozzle, and the nozzle is formed in the sealed cavity; a carrier gas input opening connected with the carrier gas pipeline, an organic mass spectrum sampling interface and an inorganic mass spectrum sampling interface are formed in the sealed cavity; a to-be-detected liquid sample is atomized and ionized under the action of an electric field and an auxiliary airflow, the generated ions are analyzed and detected in a mass spectrometer through the organic mass spectrum sampling interface, and carrier gas input from the carrier gas input opening is used for sending out the sample remained in the sealed cavity through the inorganic mass spectrum sampling interface; and the sample is brought to the inductive coupling plasma source through the transmission pipeline, is atomized and ionized, and is subjected to element composition analysis through a mass spectrometer or a spectrometer. The feeding device can be used for detecting inorganic mass spectrum and organic mass spectrum in parallel.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Non-noble element catalysts and methods for making
ActiveUS20170354953A1Produced economicallyFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesNitrogenElement composition
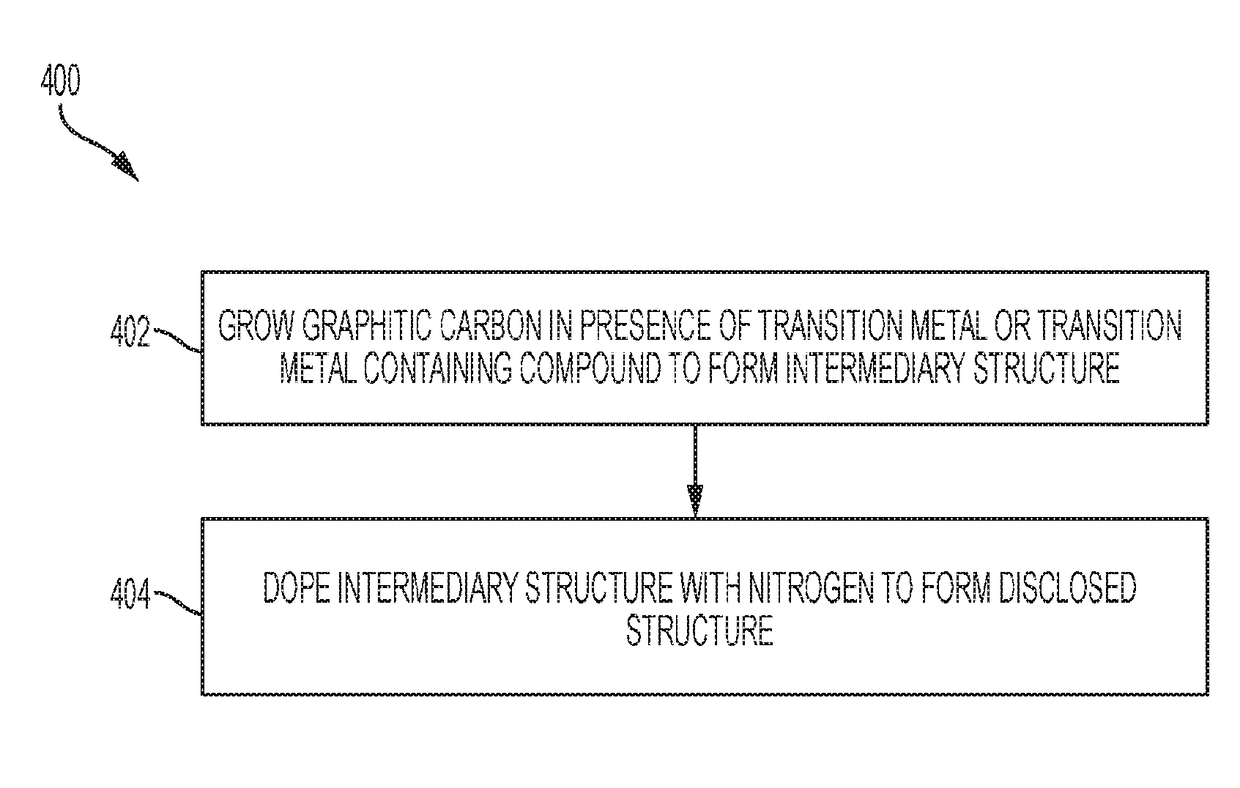
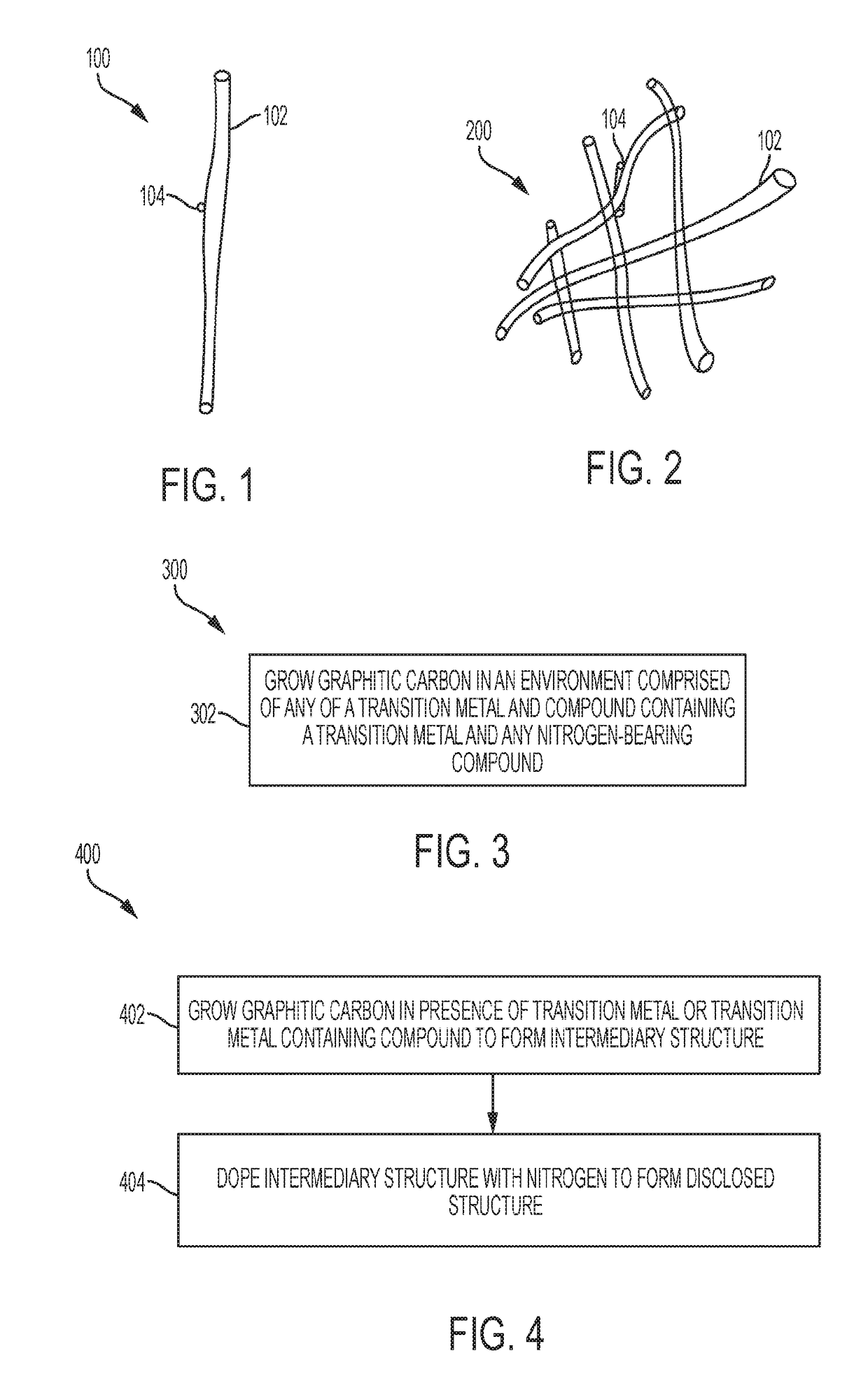
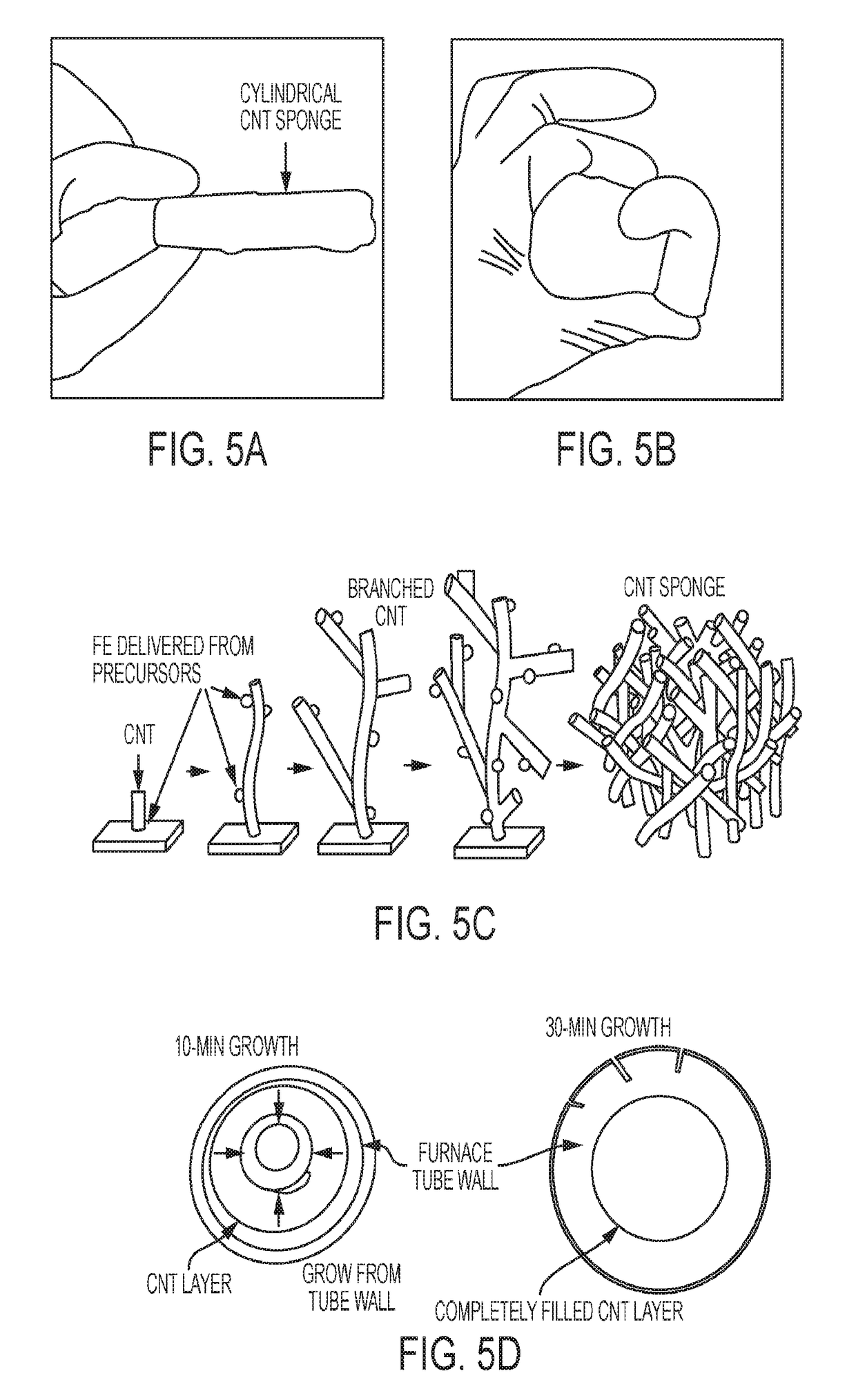
Disclosed are non-noble element compositions of matter, structures, and methods for producing the catalysts that can catalyze oxygen reduction reactions (ORR). The disclosed composition of matter can be comprised of graphitic carbon doped with nitrogen and associated with one or two kinds of transition metals. The disclosed structure is a three dimensional, porous structure comprised of a plurality of the disclosed compositions of matter. The disclosed structure can be fashioned into an electrode of an electrochemical cell to serve as a diffusion layer and also to catalyze an ORR. Two methods are disclosed for producing the disclosed composition of matter and structure. The first method is comprised of two steps, and the second method is comprised of a single step.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Metal doping LiMn(1-x-y)NixCoyO2 compounded by lithium ion battery positive electrode waste, as well as preparation method and application of metal doping LiMn(1-x-y)NixCoyO2
ActiveCN104953199AImprove electrochemical performanceShort processCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingElement compositionLithium-ion battery
The invention provides metal doping LiMn(1-x-y)NixCoyO2 compounded by lithium ion battery positive electrode waste, as well as a preparation method and an application of the metal doping LiMn(1-x-y)NixCoyO2. The method comprises the steps: removing a binder and a conductive agent from the lithium ion battery positive electrode waste so as to obtain a positive electrode active material; determining the element composition of the positive electrode active material; adjusting the content / contents of one or more of Ni, Co, Mn and M in the positive electrode active material, so as to enable a molar ratio to accord with the molar ratio of Ni to Co to Mn to M in the molecular formula LiNixMnyCo(1-x-y-z)MzO2 so as to obtain positive electrode active material precursor powder; and adding a lithium source, and performing high-temperature solid-phase reaction so as to obtain metal doping LiMn(1-x-y)NixCoyO2. The method is wide in application range, easy to operate, low in cost and capable of avoiding secondary pollution, and achieving the short-range cleaning circulation of the positive electrode active material in a waste lithium ion battery. The prepared metal doping LiMn(1-x-y)NixCoyO2 is excellent in electrochemical performance.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
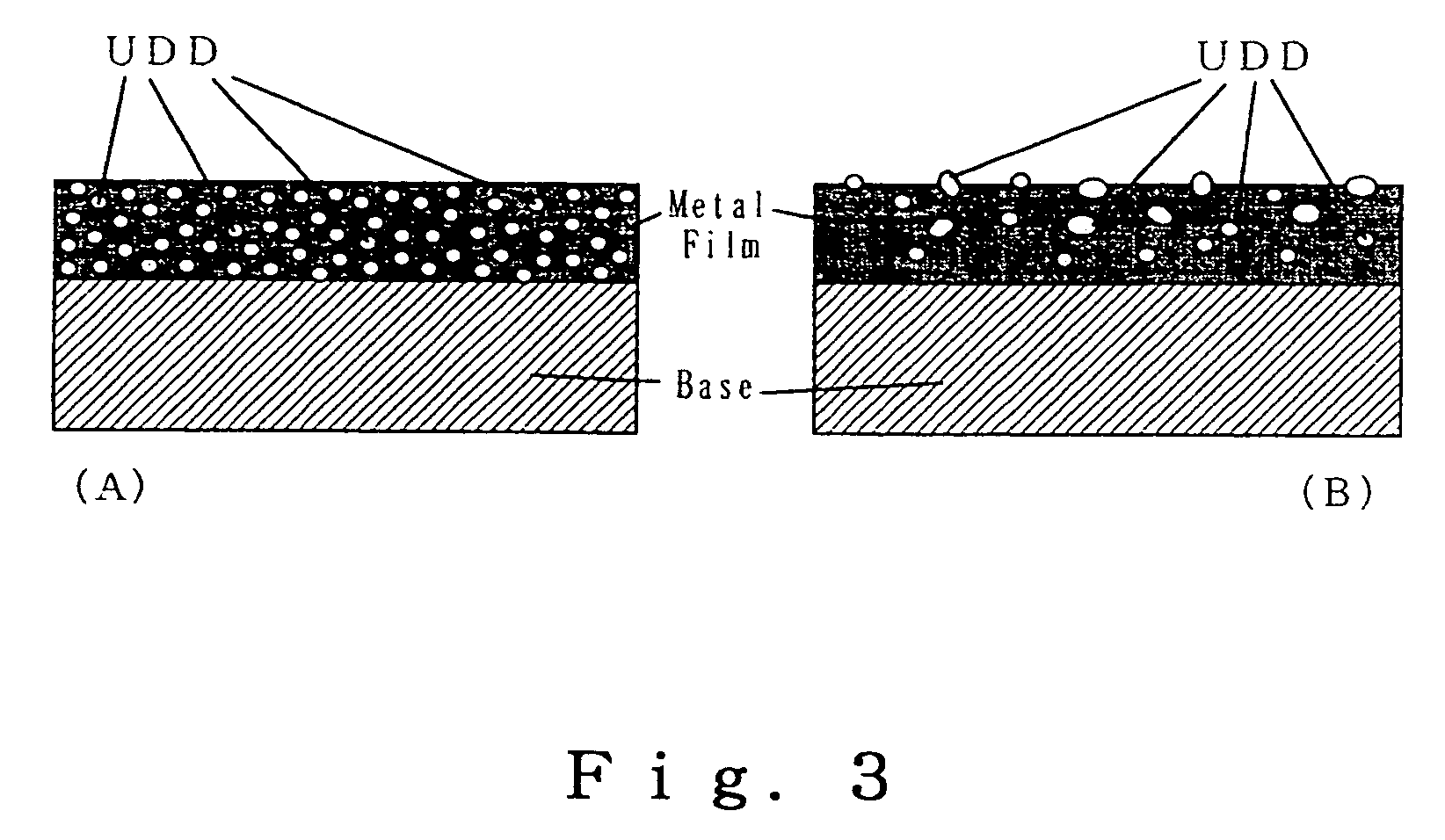
Stable aqueous suspension liquid of finely divided diamond particles, metallic film containing diamond particles and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20060147644A1High activityGood dispersionFrom gel stateHot-dipping/immersion processesX-rayOxygen
An aqueous suspension liquid of finely divided diamond particles comprising 0.05 to 160 parts by weight of a finely divided diamond particles in 1000 parts of water, wherein; (i) the finely divided diamond particles have an element composition consisting mainly of 72 to 89.5% by weight of carbon, 0.8 to 1.5% of hydrogen, 1.5 to 2.5% of nitrogen, and 10.5 to 25.0% of oxygen; (ii) and, almost all of said diamond particles are in the range of 2 nm to 50 nm in diameters thereof (80% or more by number average, 70% or more by weight average), (iii) and, said finely divided diamond particles exhibit a strongest peak of the intensity of the Bragg angle at 43.9° (2θ±2°), strong and characteristic peaks at 73.5° (2θ±2°)and 95° (2θ±2°), a warped halo at 17° (2θ±2°), and no peak at 26.5°, by X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrum analysis using Cu—Kα radiation when dried, (iv) and, specific surface area of said diamond particles when dry state powder is not smaller than 1.50×105 m2 / kg, and substantially all the surface carbon atoms of said particles are bonded with hetero atoms, and the total absorption space of said powder is 0.5 m3 / kg or more, when dried. The diamond particles are very active and dispersible in aqueous liquid in stable, and have essentially same mechanical properties as that of usual diamonds.
Owner:NICCA CHEM COMPANY
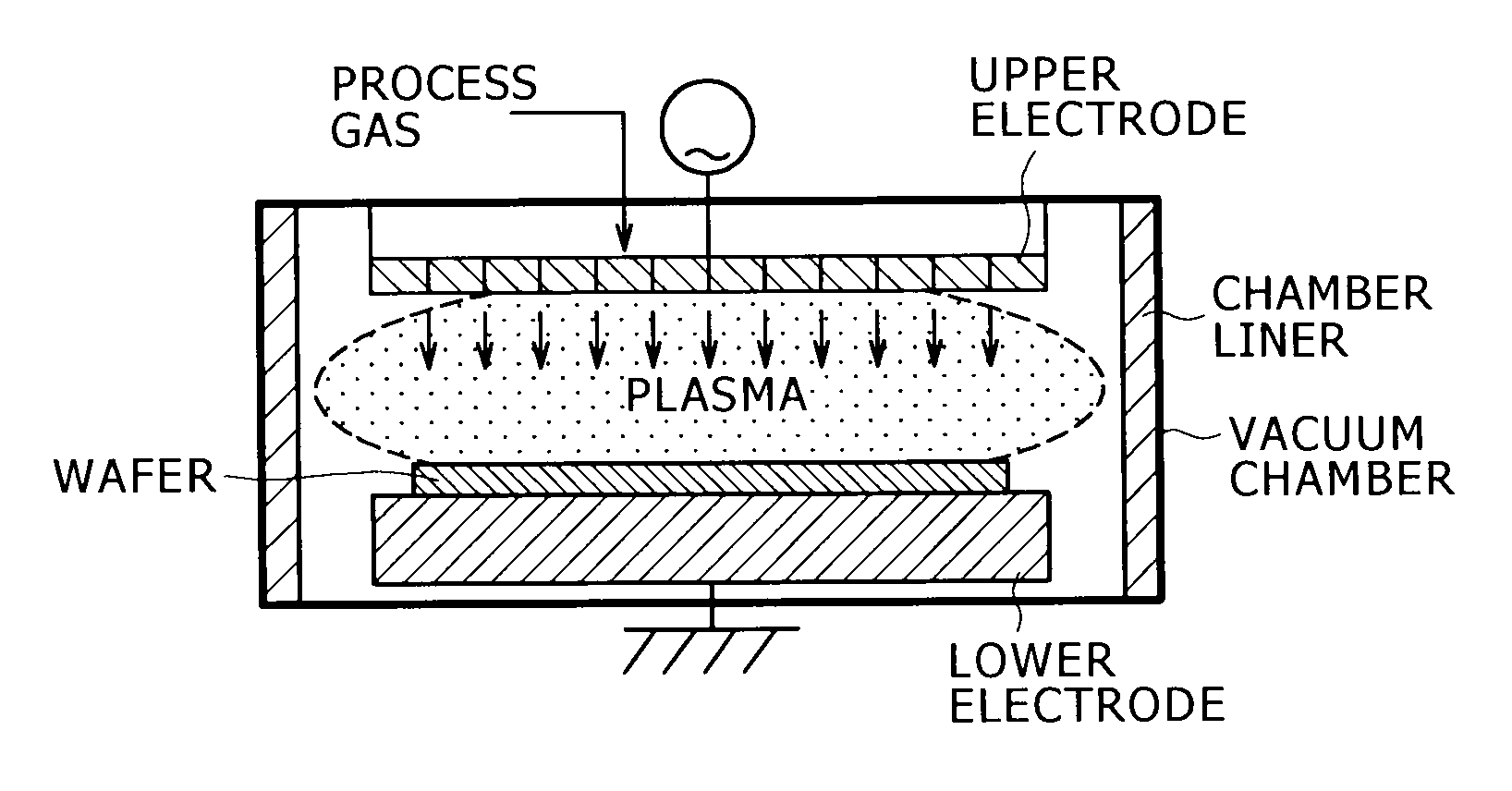
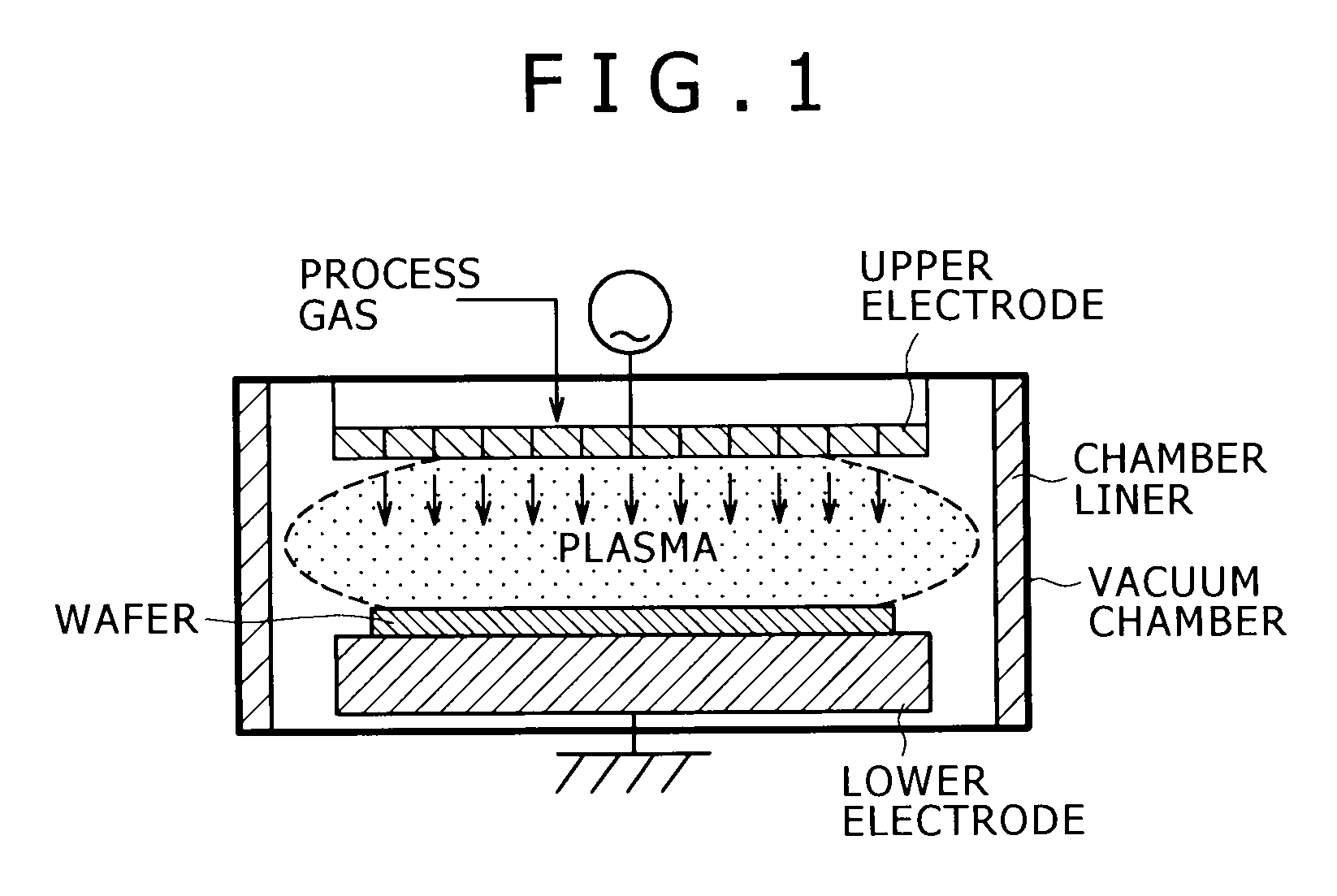
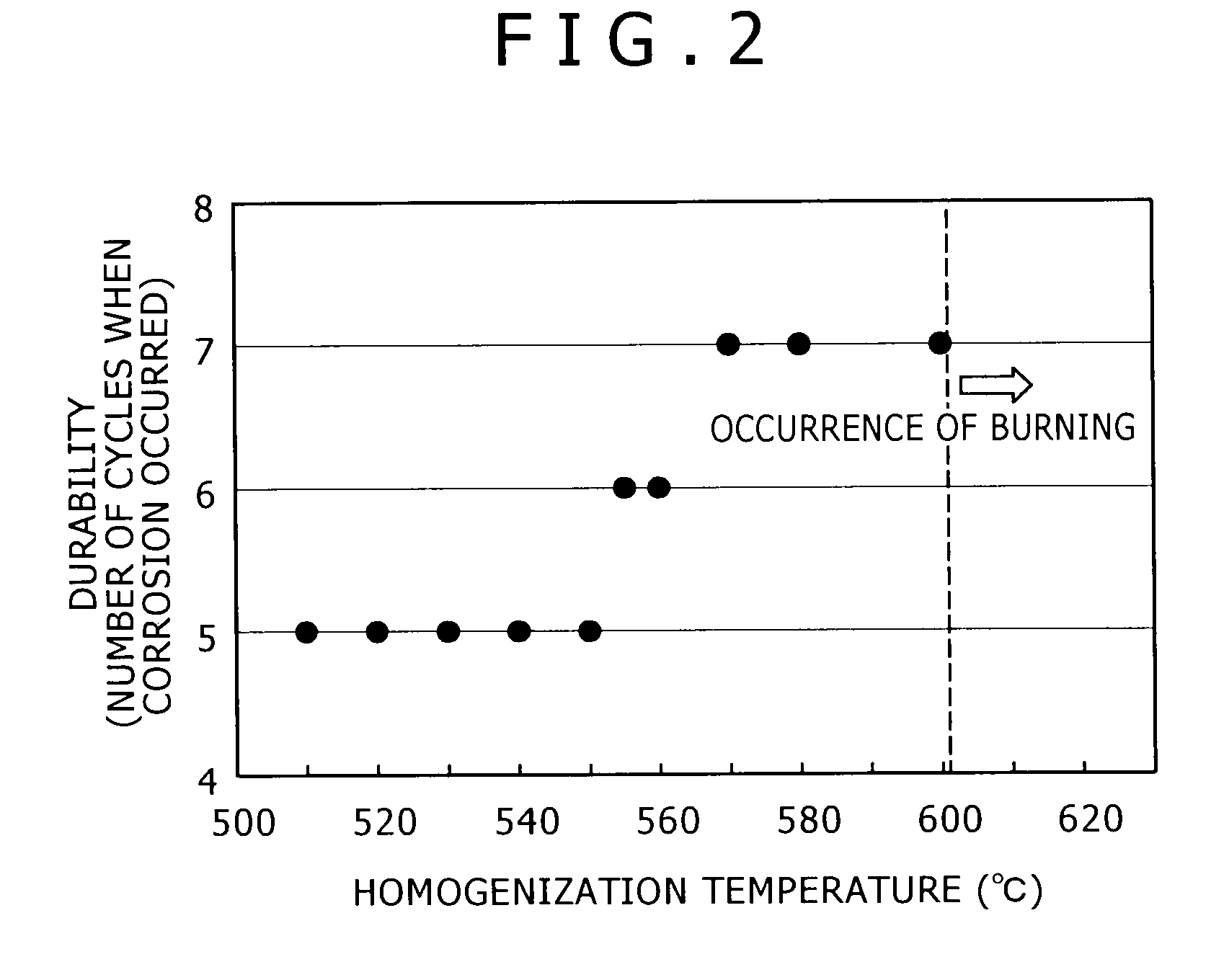
Aluminum alloy for anodizing having durability, contamination resistance and productivity, method for producing the same, aluminum alloy member having anodic oxide coating, and plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100018617A1Increased durabilityIncrease resistanceAnodisationChemical vapor deposition coatingProduction rateElement composition
The aluminum alloy for anodic oxidation treatment directed to the present invention comprises as alloy elements 0.1 to 2.0% Mg, 0.1 to 2.0% Si, and 0.1 to 2.0% Mn, wherein each content of Fe, Cr, and Cu is limited to 0.03 mass % or less, and wherein the remainder is composed of Al and inevitable impurities. An aluminum alloy more excellent in the durability can be obtained by subjecting the aluminum alloy ingot having the above element composition to a homogenization treatment at a temperature of more than 550° C. to 600° C. or less. An aluminum alloy member can be obtained by forming an anodic oxidation coating on the surface of the aluminum alloy.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method for directly casting and rolling aluminum plate base for PS plate with electrolytic aluminium liquid
ActiveCN101318288AQuality assuranceQuality improvementTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsSocial benefitsFiltration
The invention relates to a method for cast-rolling to produce aluminum substrates used in PS plates directly by electrolytic aluminum liquid; the main steps are as follows: electrolyzing the aluminum liquid under the high temperature, smelter hearth, adjusting element compositions, refining, conducting the furnace, adjusting the temperature to 740 DEG C to 750 DEG C, adding Al-Ti-B refiners to carry out the grain refinement, degassing, filtering, cast-rolling coils of strip, cool rolling, stretch bending and straightening, and producing finished products; various steps of the invention are synthesized to optimize technique parameters; the prepared aluminum substrates used in the PS plates is high in tensile strength and elongation, and the quality of the prepared aluminum substrates are better than that of similar products, thus omitting the remelting process when aluminum ingots are used, saving resources, reducing the production cost and increasing the economic and social benefits.
Owner:登电集团铝加工有限公司
Samarium and cobalt sintered permanent magnet material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104637642ASpeed up coolingIntegrity guaranteedInorganic material magnetismCobaltCritical magnetic field
A samarium and cobalt sintered permanent magnet material comprises, in weight percent, 25-27%wt of samarium, 49-51%wt of cobalt, 5-6.5%wt of copper, 3-3.5%wt of zirconium and 15-18%wt of iron. A preparation method includes the steps: smelting; casting an ingot; absorbing hydrogen for the cast ingot; making powder; performing orientation forming and sintering. In the smelting process, the thickness of a casting mould cavity is decreased, cooling water is filled into the wall of the mould cavity, cooling of the cast ingot is accelerated, element composition segregation is decreased, the production process is stabilized, a dendrite crystal is restrained by adding a zirconium element, hydrogen absorbing is performed for the cast ingot in the smelting process, production steps are saved, and energy consumption is reduced. In the subsequent milling process, the cast ingot absorbed hydrogen is crystallized into particles, the particles fracture along crystal boundaries in the milling process of airflow, the integrality of crystal particles is ensured, the anisotropy of the crystal particles is improved, magnetic powder particles are obtained, particle size distribution is concentrated with the range of 3.5-4.5 micrometers, the sintering temperature needed by the magnetic powder particle of each point of a blank is the same in the later sintering process, the sizes of the sintered crystal particles are the same and uniform, and the performances, particularly, such as residual magnetism Br, maximum magnetic energy product (BH) max and critical magnetic field Hk of a sintered permanent magnet are improved.
Owner:NINGBO NINGGANG PERMANENT MAGNETIC MATERIALS
Alkyl phenyl sulfonate surfactant, its preparation and application in tertiary oil extraction
An alkyl phenylsufonate (equivalent at 400-470) as surfactant suitable for weak alkali is prepared from the heavy alkyl phenyl group (between C10 and C24) through sulfonating reaction and compounding with alcohol (5-25%). Its advantages are easily available raw materials, low cost and high stability of product. It can be used to prepare a three-element composition for displacing petroleum with high recovey rate increased by 20% or more.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD
Composite material, high frequency circuit substrate prepared from composite material, and preparation of composite material
ActiveCN106867173AImproved long-term thermo-oxidative aging performanceExcellent solvent solubilityPrinted circuit aspectsHigh frequency circuit adaptationsSolubilityDielectric
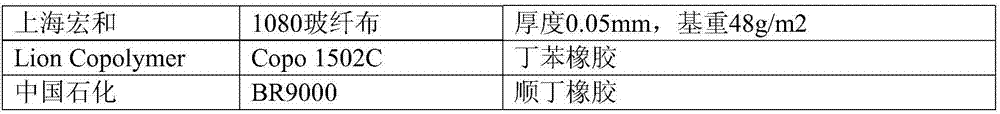
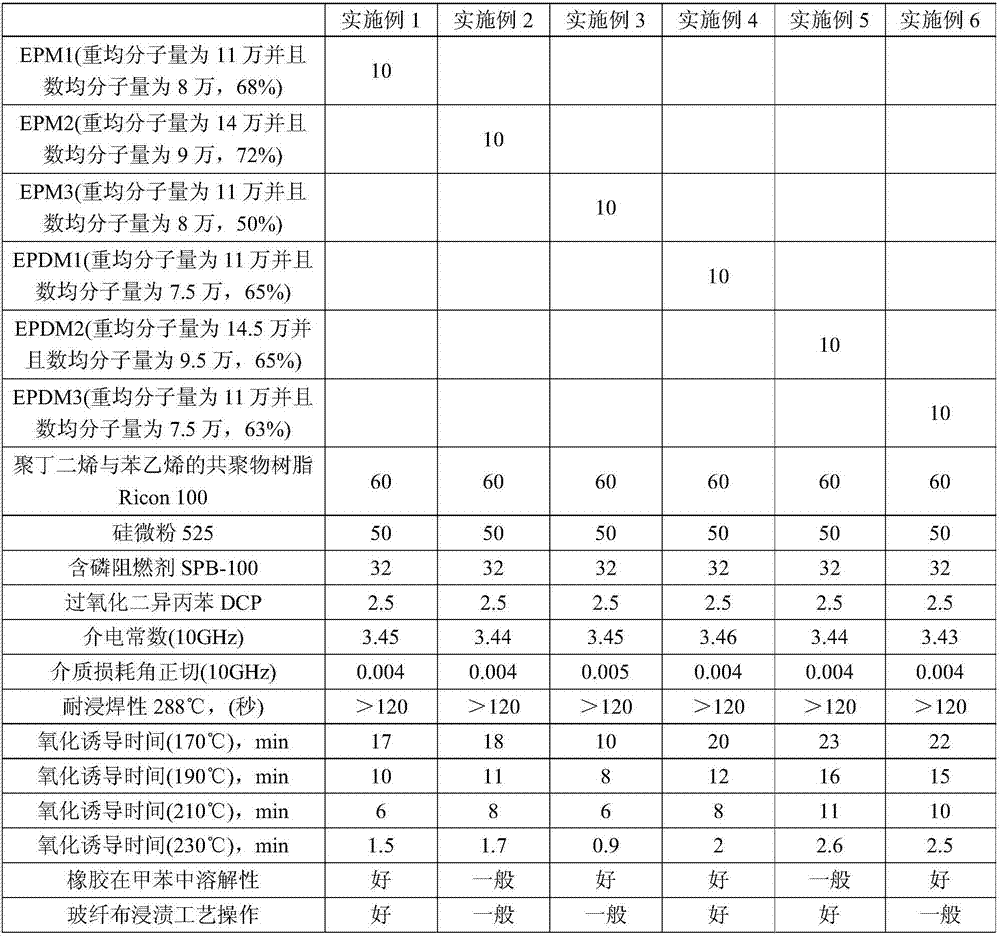
The invention relates to a composite material, a high frequency circuit substrate prepared from the composite material, and a preparation of the composite material. The composite material comprises 20 to 70 parts of a thermosetting mixture, 10 to 60 parts of glass fibre cloth, 0 to 70 parts of a powder filling material, and 1 to 3 parts of a curing initiator; the thermosetting mixture is composed of a thermosetting resin and an ethylene propylene rubber; the thermosetting resin is a polybutadiene or a copolymer of the polybutadiene with styrene, wherein the molecular weight of the polybutadiene is lower than 11000Da, the polybutadiene is composed of C and H, and contains more than 60% vinyl; the weight average molecular weight of the ethylene propylene rubber is larger than 100kDa, and lower than 150kDa, the number-average molecular weight of the ethylene propylene rubber is larger than 60kDa, and lower than 100kDa, and the ethylene propylene rubber is a solid material at room temperature. The composite material possesses excellent solvent solubility, and is excellent in operability; the high frequency circuit substrate prepared from the composite material possesses excellent high frequency dielectric properties and better thermal-oxidative aging properties.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYI SCI TECH
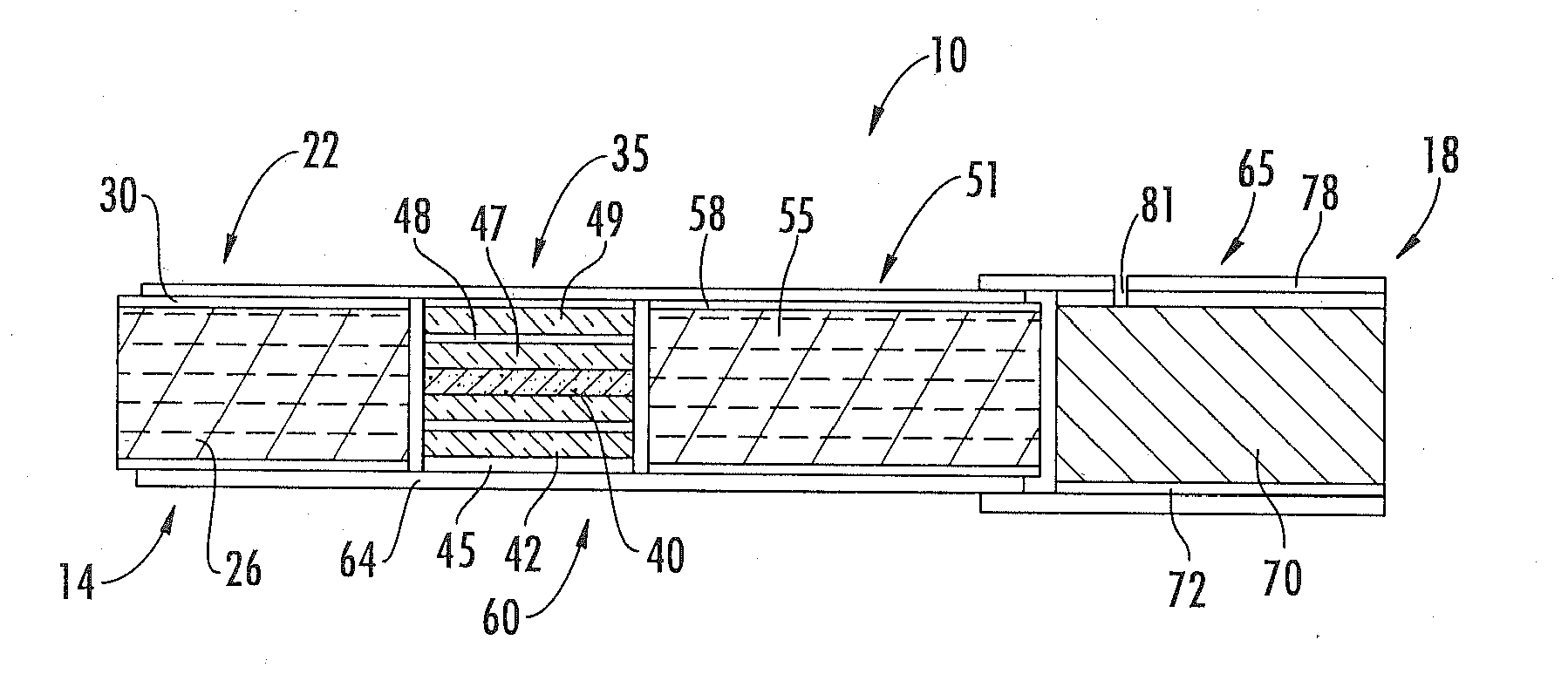
Thin film capacitor element composition, high permittivity insulation film, thin film capacitor element, thin film multilayer capacitor, and method of production of thin film capacitor element
ActiveUS7580241B2Easy to produceLow pour pointThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricRare-earth elementElement composition
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
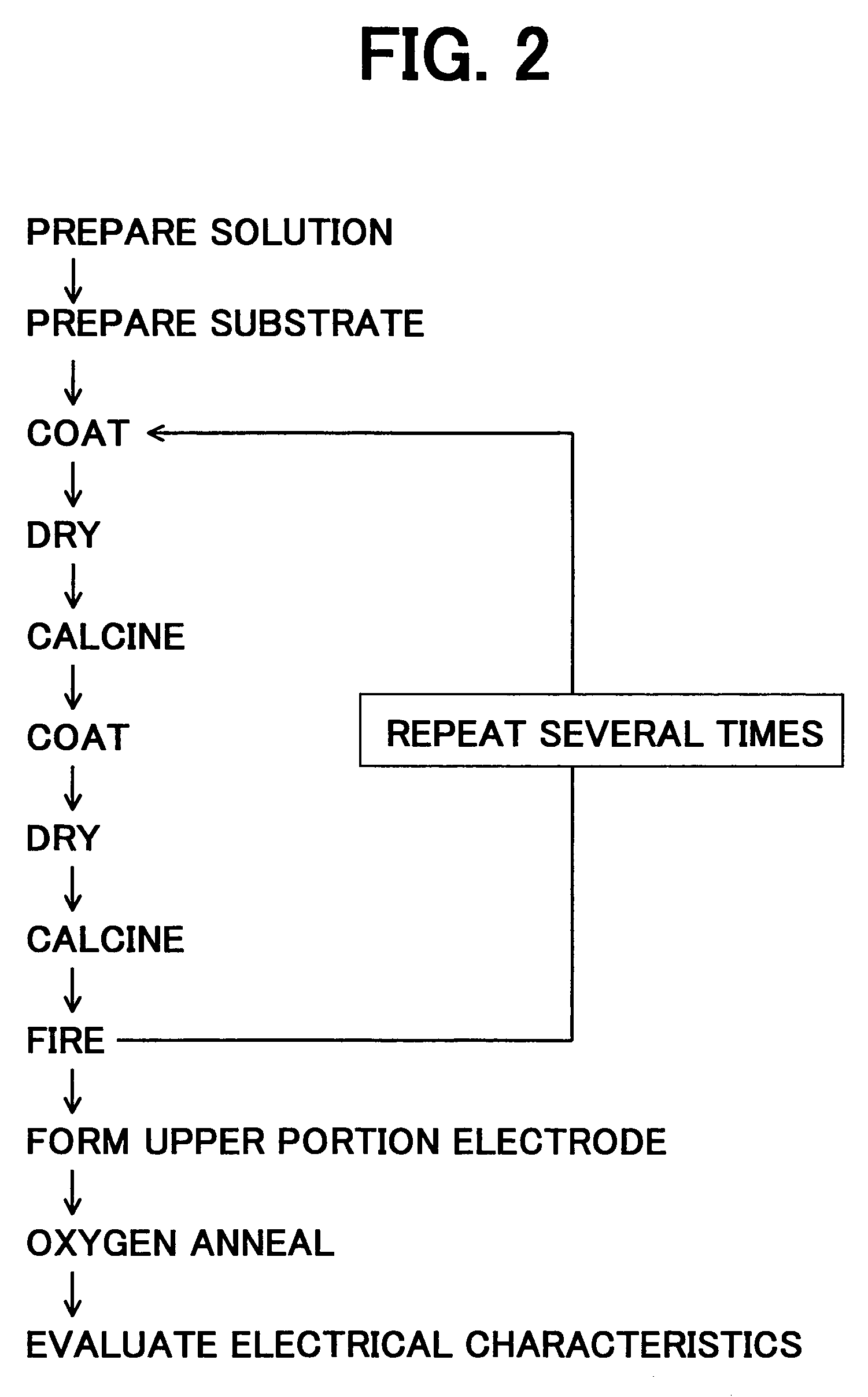
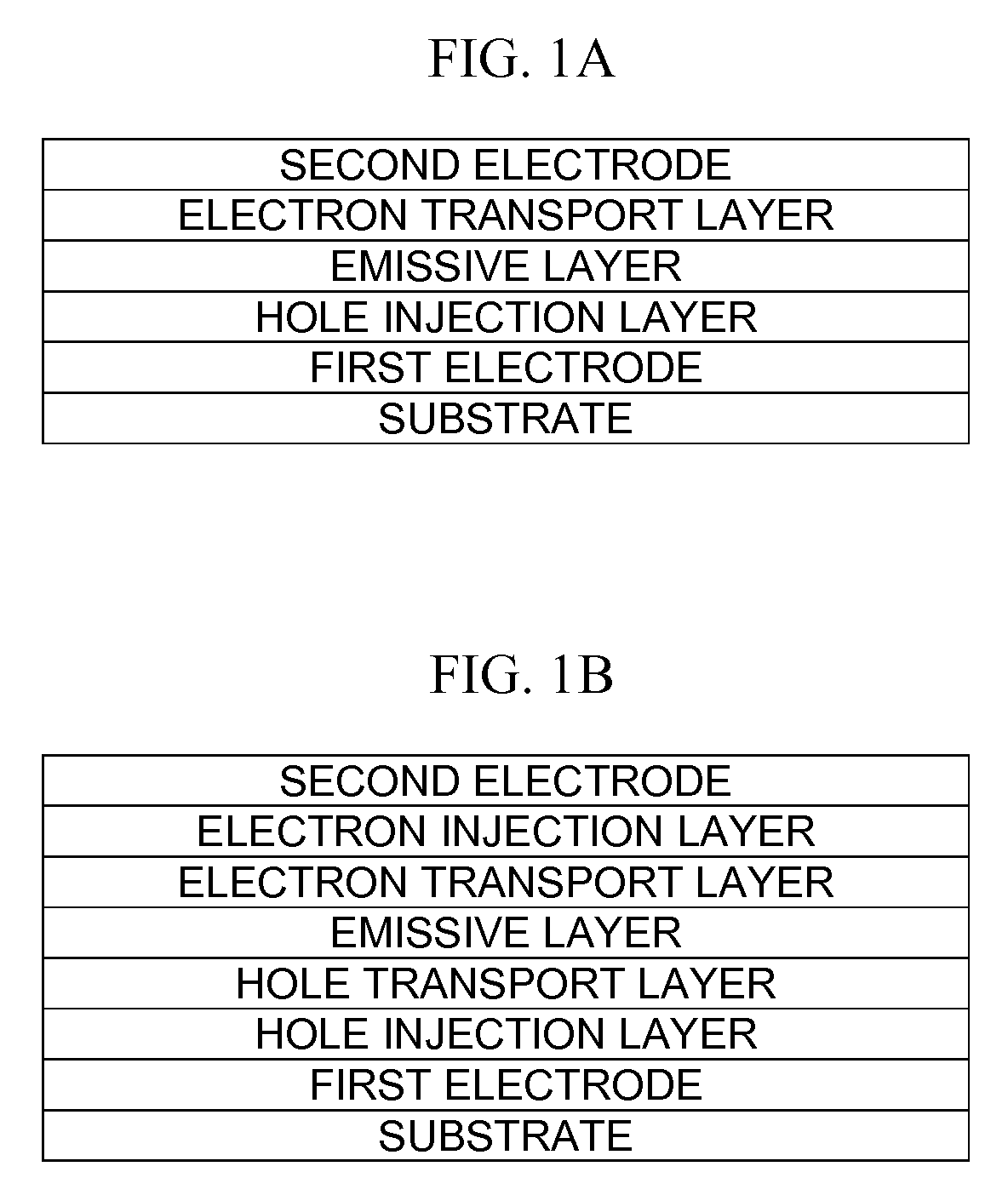
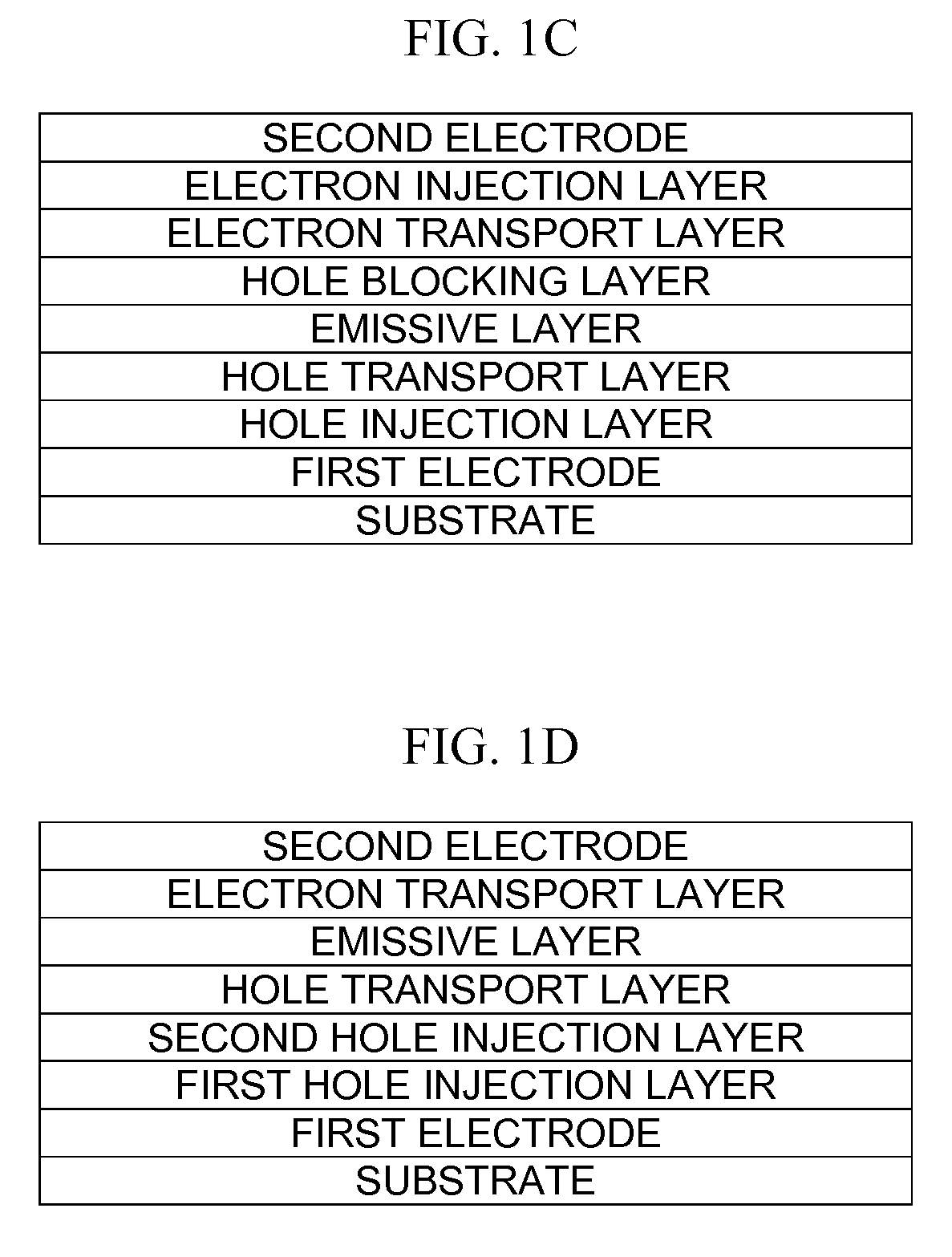
Organic light emitting device
ActiveUS20090160319A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesMetalElement composition
An organic light emitting device includes a first electrode; a second electrode; an emissive layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode; a hole injection layer disposed between the first electrode and the emissive layer; and an electron transport layer disposed between the emissive layer and the second electrode. The hole injection layer includes a hole injecting material and a first compound made up of an element selected from the group consisting of Mo, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and B and an element selected from the group consisting of O, F, S, Cl, Se, Br, and I. The electron transport layer includes an electron transporting material and a second compound, wherein the second compound is represented by Formula 1:XaYb <Formula 1>X is an alkali metal, an alkali earth metal, or a transition metal,Y is a group 7 element, or a C1-C20 organic group,a is a number in the range of 1 to 3, andb is a number in the range of 1 to 3.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor luminescent element composition
ActiveCN1825640AImprove cooling effectPrinted circuit detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorComposite substrate
The invention discloses a semiconductor luminous component, comprising a composite substrate, a circuit layout carrier, an adhesive structure, a sunk space and a semiconductor luminous component, where the adhesive structure is used to bond the composite substrate with the circuit layout carrier, the sunk space is formed on the circuit layout carrier and extends to the composite substrate , and the semiconductor luminous component is arranged in the sunk space and connected to the circuit layout carrier.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
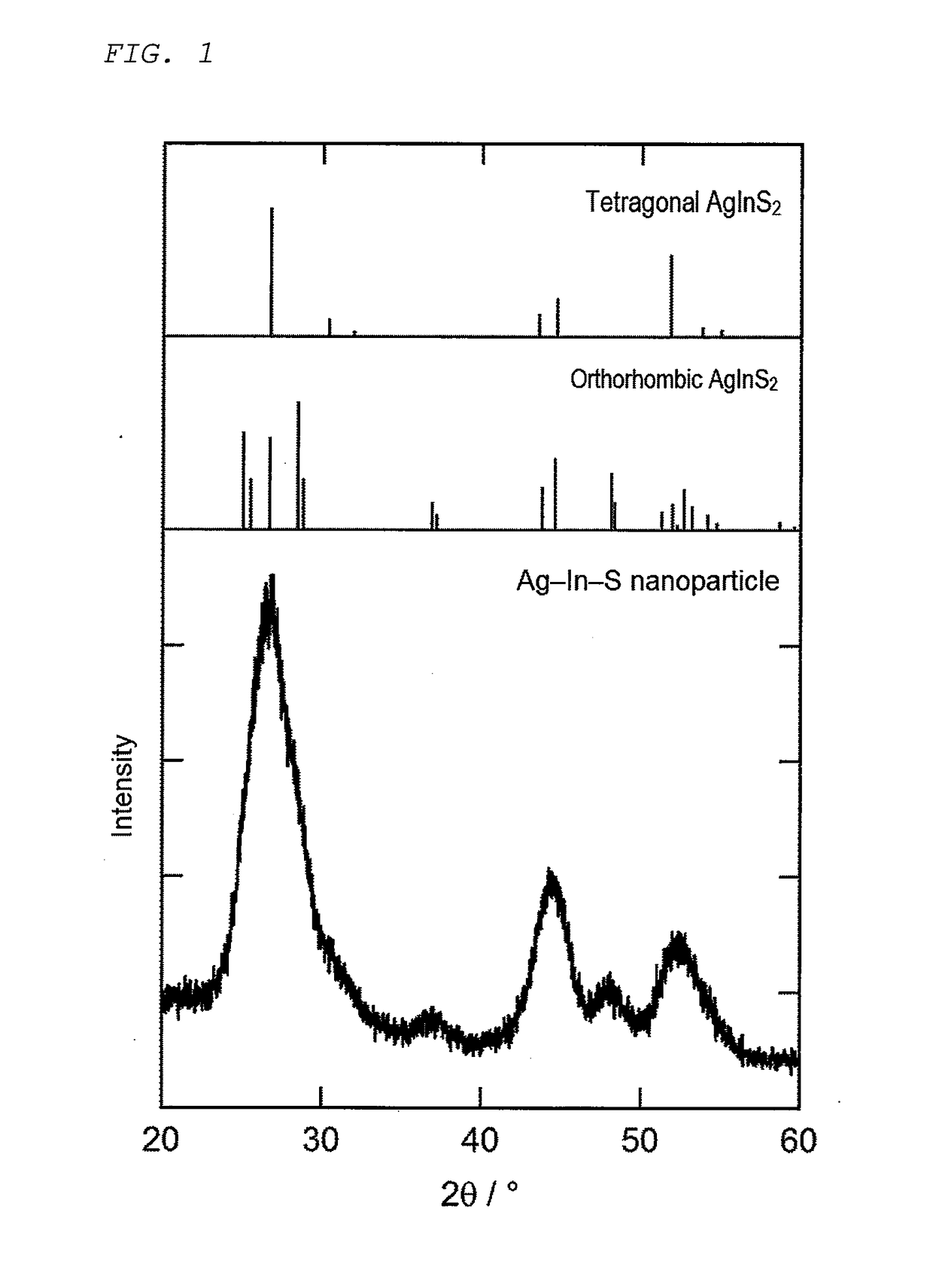
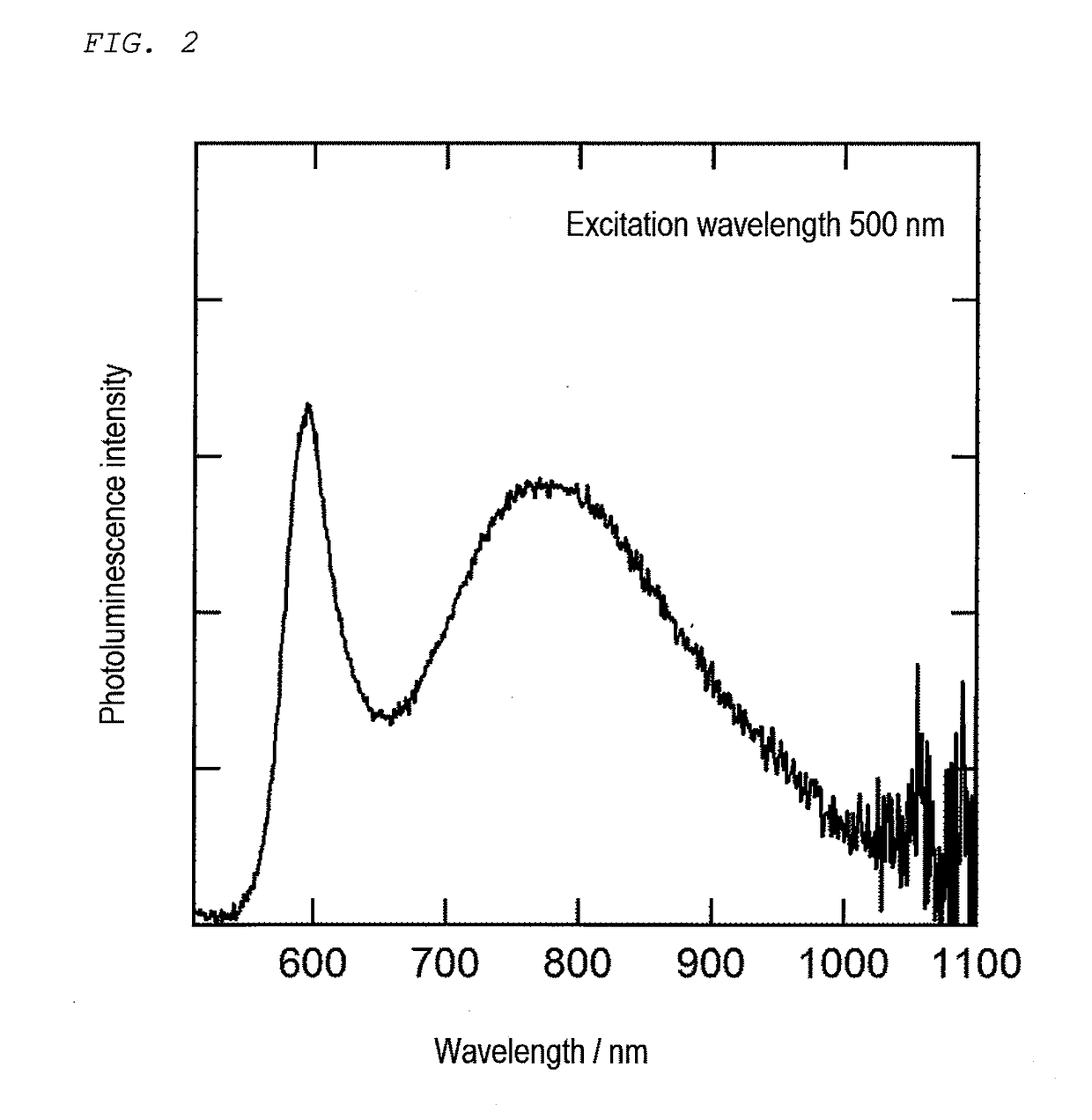
Semiconductor nanoparticles and method of producing semiconductor nanoparticles
ActiveUS20170267924A1Large bandgap energyUse of materialMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic dyesHeterojunctionElement composition
A semiconductor nanoparticle includes a core and a shell covering a surface of the core. The shell has a larger bandgap energy than the core and is in heterojunction with the core. The semiconductor nanoparticle emits light when irradiated with light. The core is made of a semiconductor that contains M1, M2, and Z. M1 is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ag, Cu, and Au. M2 is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, Ga, In and Tl. Z is at least one element selected from the group consisting of S, Se, and Te. The shell is made of a semiconductor that consists essentially of a Group 13 element and a Group 16 element.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +2
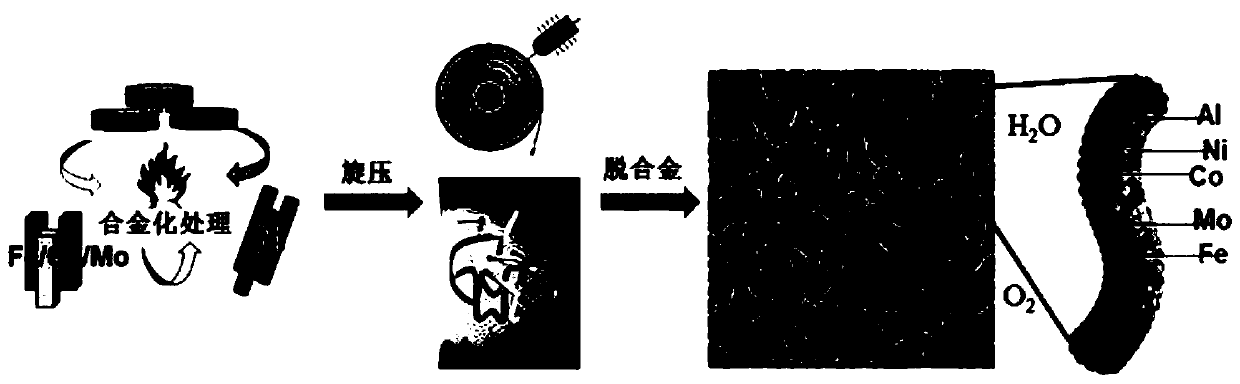
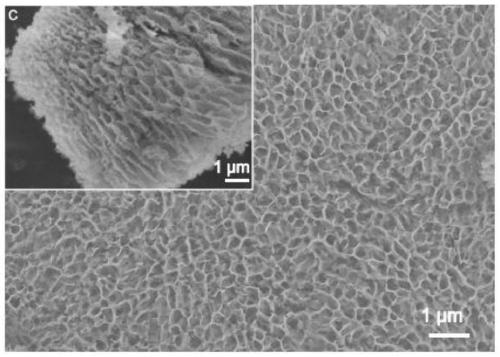
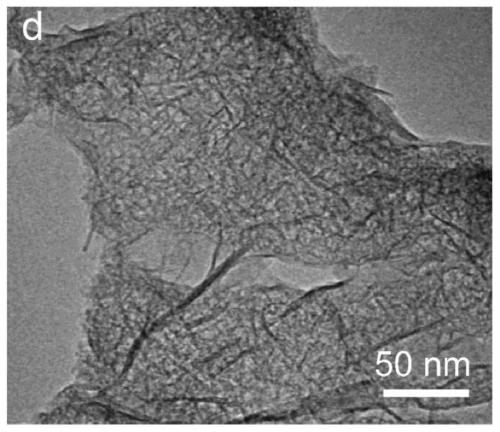
Nano-porous high-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110484764AImprove electrochemical durabilityEasy to prepareHigh entropy alloysSynthesis methods
The invention relates to the field of high-entropy alloy materials, and provides a non-noble metal nano-porous high-entropy alloy and a preparation method thereof. The element composition of the nano-porous high-entropy alloy is AlNiCoFeX, wherein X is one or more of Mo, Cu, Mn, Cr, V, Zr and Nb; the nano-porous high-entropy alloy is of a layered nano porous structure and is provided with a macro-hole channel layer and a thin-wall layer; the macro-hole channel layer comprises first nano-pores; the thin-wall layer comprises second nano-pores; and the size of the first nano-pores is 20-30 timesthat of the second nano-pores. The preparation method of the non-noble metal nano-porous high-entropy alloy is simple; and the highly-controllable top-to-bottom synthesis method is developed by combining traditional metallurgy, rapid cooling and dealloying, the overall synthesis concept is ingenious, and the requirements for high-precision control over the process and the high technical level of operators are reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
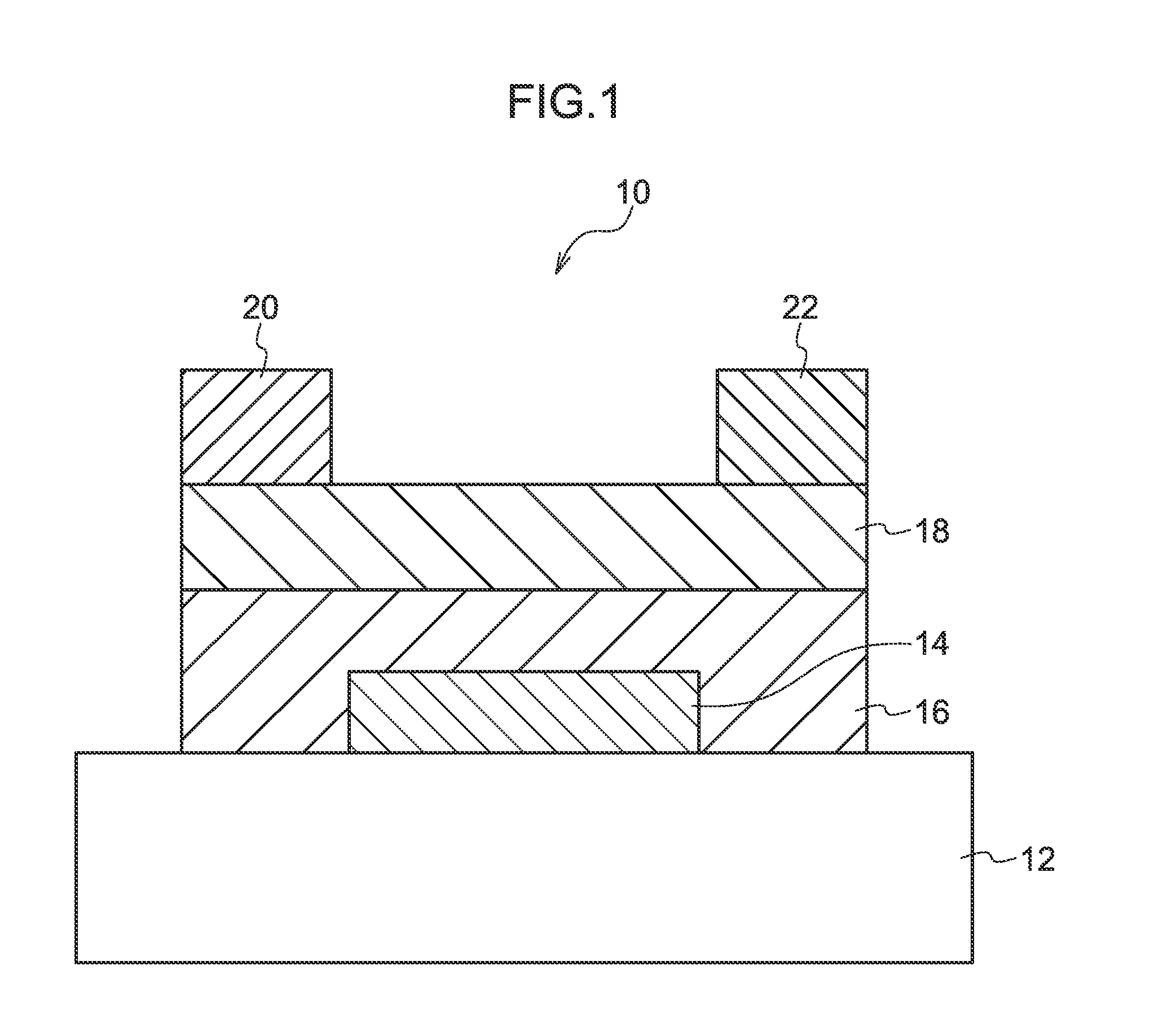
Method for fabricating first and second epitaxial cap layers
ActiveUS8647953B2Increase currentTotal current dropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElement compositionSemiconductor
A method for fabricating a metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) device is described, including following steps. Two recesses are formed in a substrate. A first epitaxy growth process is performed, so as to form a first semiconductor compound layer in each of the recesses. A second epitaxy growth process is performed with an epitaxial temperature lower than 700° C., so as to form a cap layer on each of the first semiconductor compound layers. Each of the cap layers includes a second semiconductor compound layer protruding from a surface of the substrate. The first and the second semiconductor compound layers are composed of a first Group IV element and a second Group IV element, wherein the second Group IV element is a nonsilicon element. The content of the second Group IV element in the second semiconductor compound layers is less than that in the first semiconductor compound layers.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Manufacturing method of ultra-fine grain high-temperature alloy plate blanks
ActiveCN103008659AExcellent high temperature strengthExcellent fatigue resistanceUltra fineSuperalloy
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of ultra-fine grain high-temperature alloy plate blanks. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of 1, preparation of high-temperature alloy powder; 2, heat treatment of the high-temperature alloy powder; 3, selection of a high-temperature alloy core tube; 4, high-temperature spray deposition and composite recrystallization of plate blanks; and 5, heat treatment of the plate blanks, and finally forming the high-temperature alloy plate blanks in ultra-fine microstructures. According to the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, the high-temperature alloy powder is prepared by adopting a gas atomization technology, and the obtaining of an oxygen-free and segregation-free well-closed formation is controlled through a heat treatment system; the element composition is controlled by selecting the high-temperature alloy core tube, and the real-time control for the temperature during a forming process is controlled; and the forming of high-temperature alloy is carried out on the outer surface of the high-temperature alloy core tube by adopting the high-temperature spray deposition technology, the composite recrystallization is synchronously carried out, the growth of grains in the microstructure is controlled as a large temperature gradient is simultaneously formed, and the high-temperature alloy plate blanks in the ultra-fine microstructures are finally formed through the heat treatment. According to the manufacturing method disclosed by the invention, the microstructure of the plate blanks is compact, the size is large, and most of all, a forging machine or an extrusion device in large tonnage is not needed.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Preparation method of ferroalloy calibration samples for X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis
InactiveCN102818722ASolving No Standard SamplesSolve the problem of insufficient standard samplesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationX-rayAlloy
The invention discloses a preparation method of ferroalloy calibration samples for X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis. The preparation method is characterized in that firstly, high-pure metal and / or standard reagents are weighed according to the alloy proportioning, then, the high-pure metal and / or standard reagents are dissolved into solution by solvents, next, the solution is quantificationally transferred into a platinum yellow crucible and is melted after being mixed with lithium borate, oxidants and release agents, the cooling is carried out, and a ferroalloy calibration sample glass fuse piece is obtained. The method has the advantages that the ferroalloy calibration samples to be measured are compounded by reference or standard substances with similar element composition and content range, and the problem of no ferroalloy standard sample to be measured or standard sample insufficiency is solved. The ferroalloy calibration sample glass fuse piece obtained by the method is used for the X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis, the result is accurate and reliable, and the application range of an X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis method is expanded.
Owner:HBIS COMPANY LIMITED HANDAN BRANCH COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com