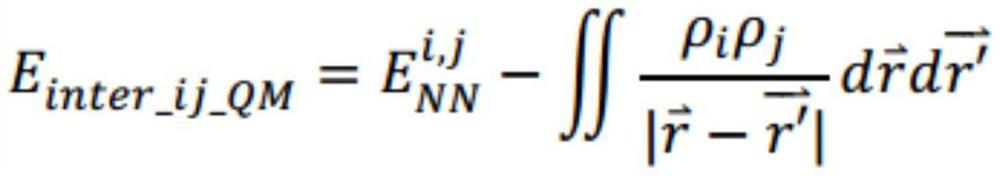Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Molecular mechanics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
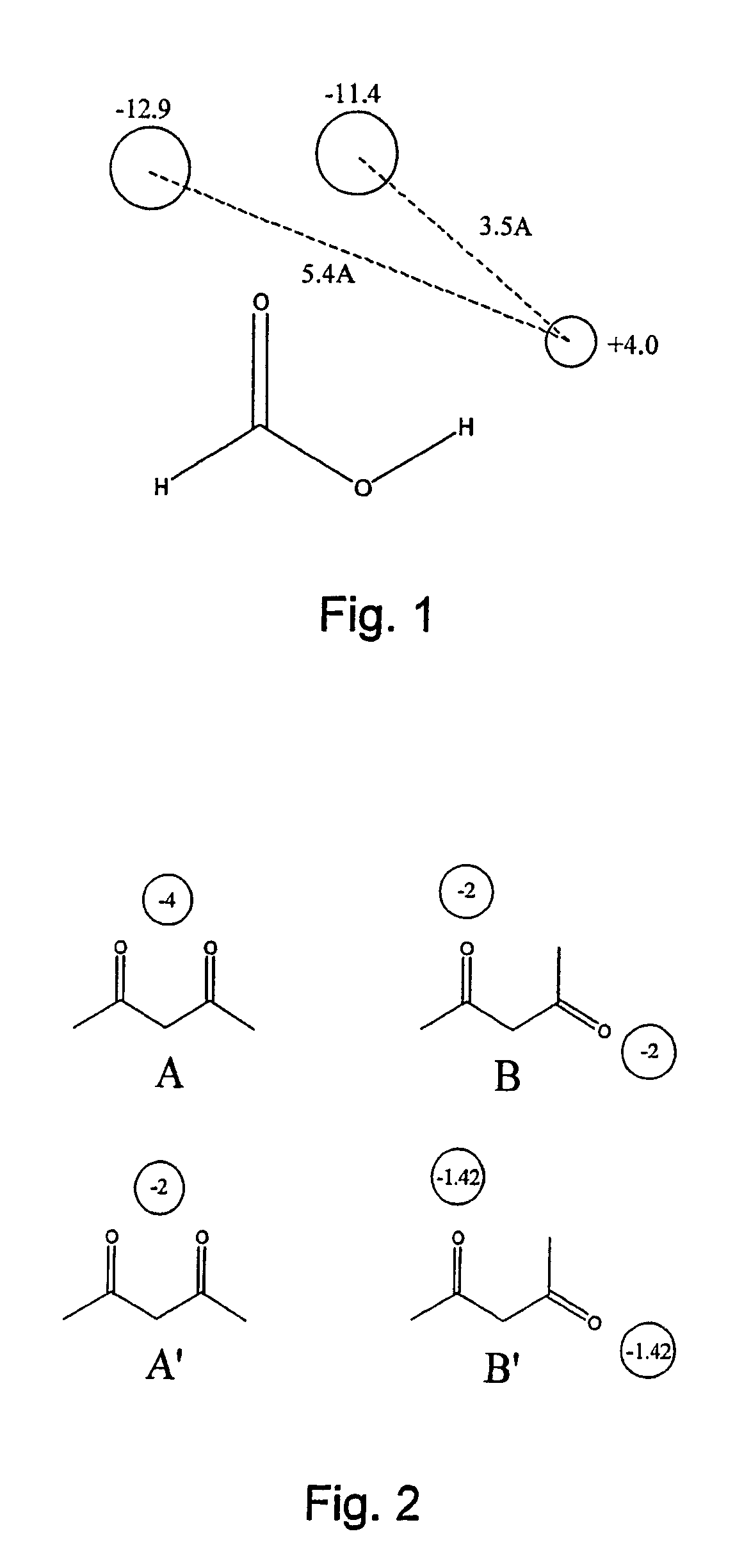
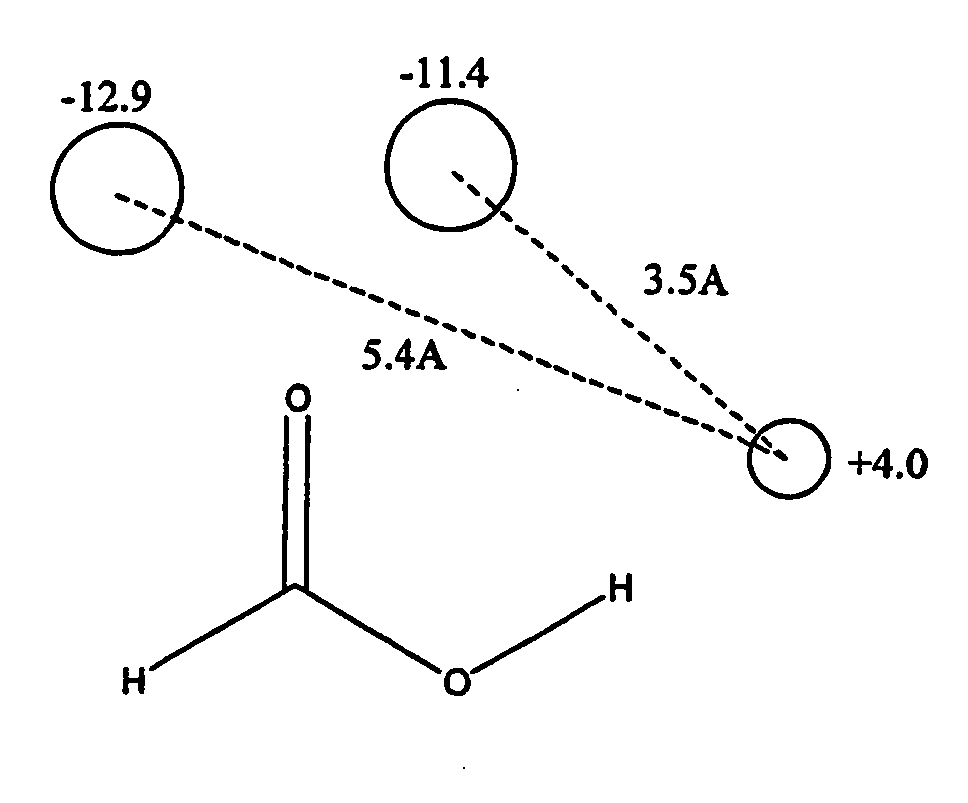
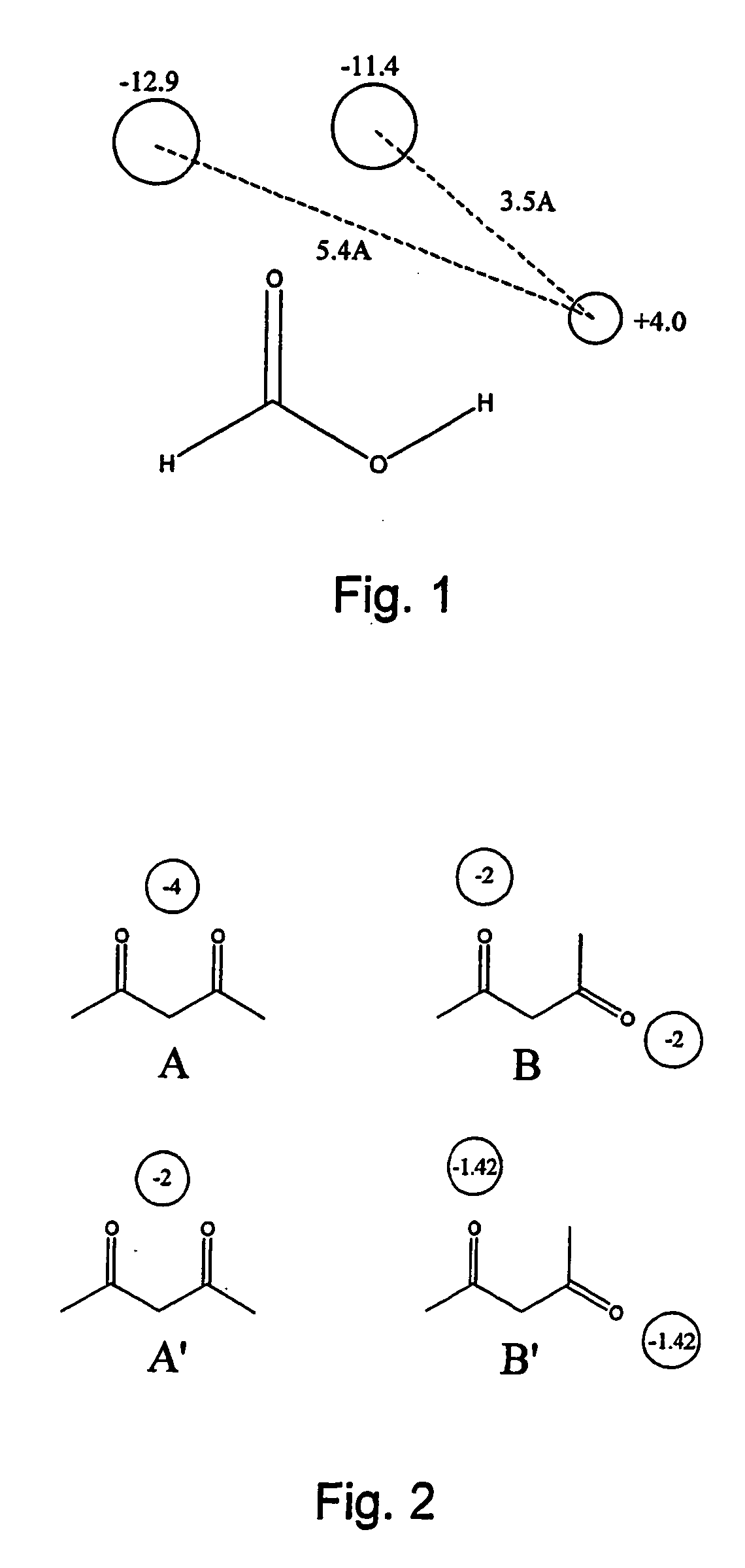
Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms.
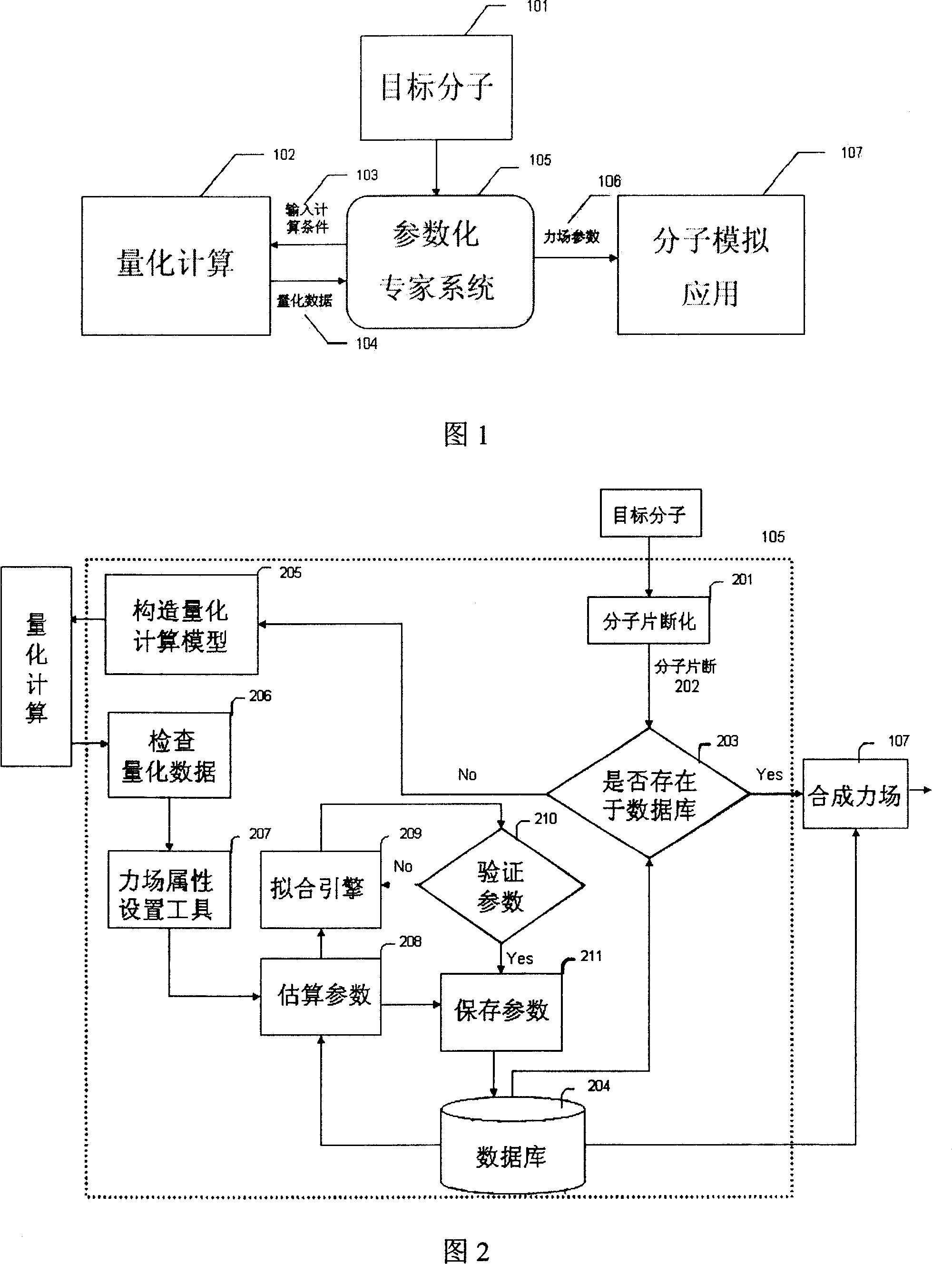
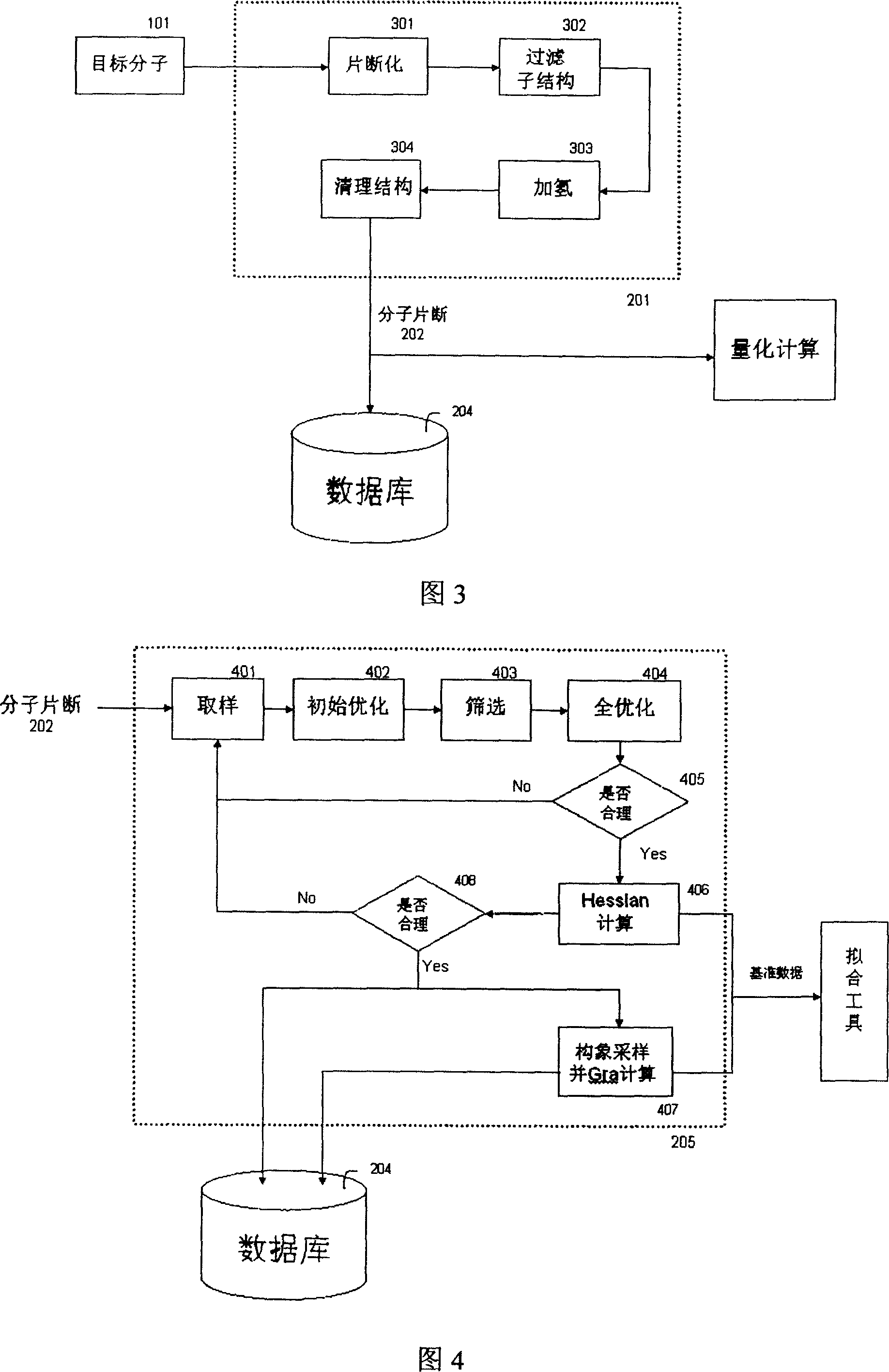
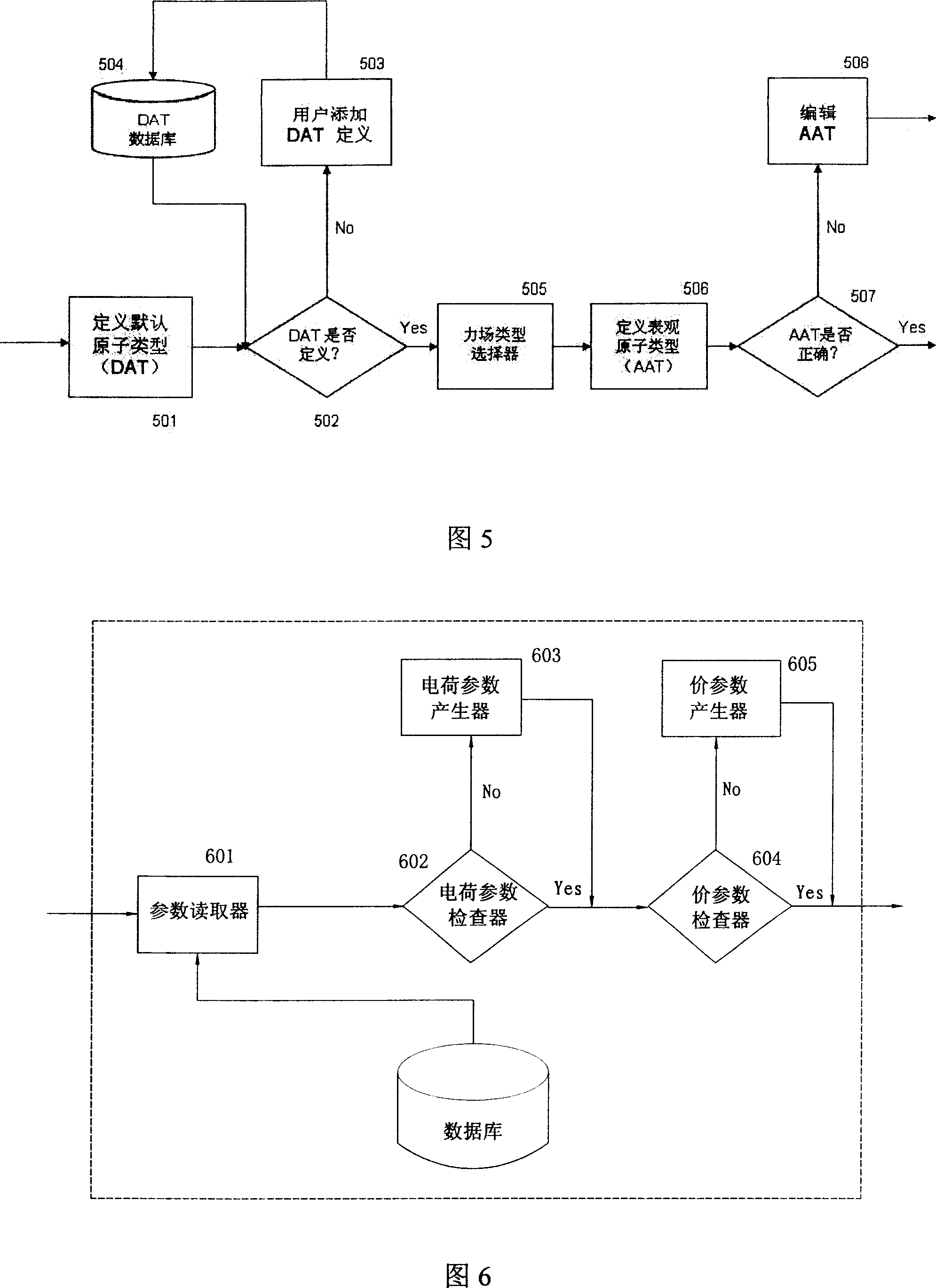
Automatic generating method for force field parameter of molecular mechanics
InactiveCN101131707AAccurate derivationAutomatic derivationComputational theoretical chemistrySpecial data processing applicationsChemical industryBasic research
The invention relates to the automatic generating method of the molecular mechanic field's parameter, including the method to generate automatically the parameter of the molecular mechanic that is required in molecular simulation, and it can be used for basic research such as the materials science, life sciences, medication science, and chemical industry and so on. The main content of the invention are: searching the only molecular-model collection which can be used for generating the molecular field's parameter for the goal molecular; carrying quantum-mechanical calculation on the molecular-model collection to get the reference data that can be used for fitting the molecular mechanics field; fitting automatically a lot of nonlinear data; verifying automatically the fitting results; storing and managing the data and fitting results referred above with database. The invention can solve the bottle-neck problem that lacking perfect and precise force-field in the use of the molecular simulation technique abroad at present. The invention provides a new systematic method which can deduce molecular force field quickly, exactly and automatically.
Owner:YIANG COMPUTATIONAL CHEM SOFTWARE SHANGHAICO
Ricin inhibitors and methods for use thereof
Ricin A-chain is an N-glycosidase that attacks ribosomal RNA at a highly conserved adenine residue. Crystallographic studies show that not only adenine and formycin, but also pterin-based rings can bind in the ricin active site. For a better understanding of the recognition mode between ricin, and adenine-like rings, the interaction energies and geometries were calculated for a number of complexes. Shiga toxin, a compound essentially identical to the protein originally isolated from Shigella dysenteriae, has an active protein chain that is a homologue of the ricin active chain, and catalyzes the same depurination reaction. The present invention is drawn to identifying inhibitors of ricin and Shiga toxin, using methods molecular mechanics and ab initio methods and using the identified inhibitors as antidotes to ricin or Shiga toxin, or to facilitate immunotoxin treatment by controlling non-specific cytotoxicity.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Novel affinity ligand polypeptide library of immunoglobulin G constructed based on protein A affinity model and application of design method
The invention discloses a novel affinity ligand polypeptide library of immunoglobulin G (IgG) constructed based on a protein A affinity model and an application of a design method. According to a molecular mechanics / Poisson-Boltzmann solvent-accessible surface area method, a key residue of protein A with a higher affinity interaction with human IgG is analyzed and obtained based on the available human IgG-protein A compound structure; the simplified protein A affinity model is constructed; the affinity polypeptide molecule library of the IgG is constructed based on the simplified protein A affinity model. On the basis of the peptide library, an amino acid type represented by X is ascertained by further utilizing an amino acid location method. Then, candidate polypeptides are screened gradually by applying molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation means. Finally, polypeptide affinity ligand capable of effectively separating and purifying the IgG is ascertained through an affinity chromatography experimental method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
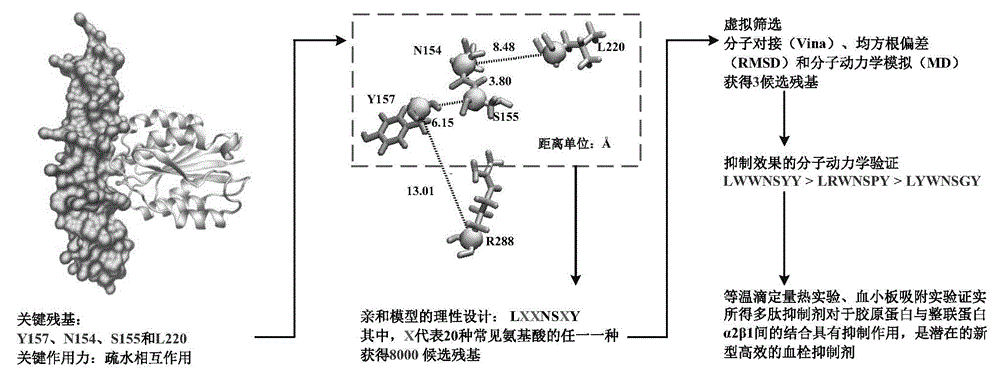
Collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitors and screening method thereof
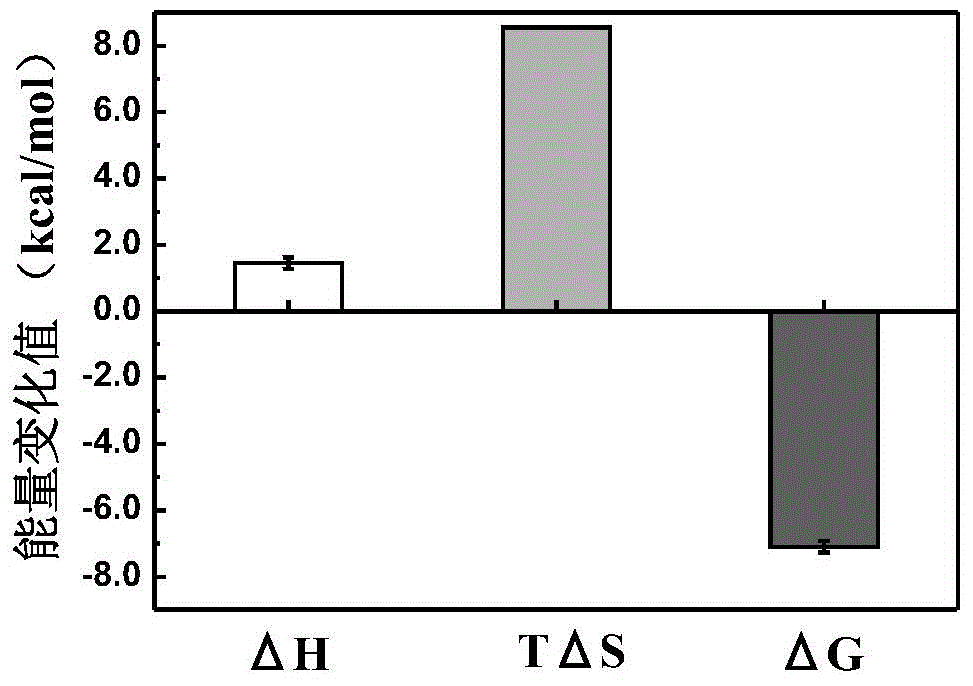
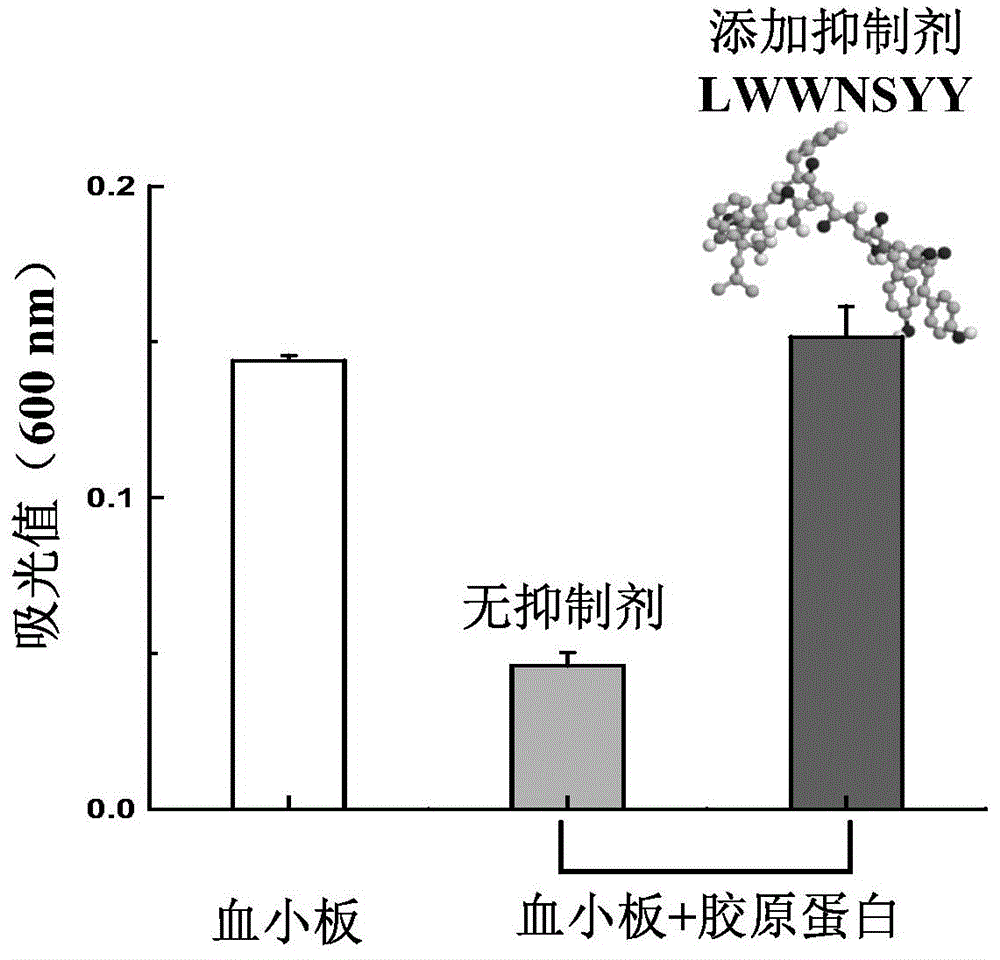
The invention discloses collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitors and a screening method thereof. The collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitors provided for the first time are LWWNSYY, LRWNSPY and LYWNSGY. According to a molecular mechanics-Poisson-Boltzmann solvent accessible surface area analysis method, the interaction between collagen short peptide and integrin alpha2beta1 on the surface of blood platelet is analyzed, so as to obtain a key residue with affinity interaction; therefore, a collagen-integrin alpha2beta1 interacted polypeptide inhibitor library can be constructed, the polypeptide inhibitors having high affinity to collagen can be obtained by screening polypeptides through molecular docking, root mean square deviation comparison and molecular dynamic simulation. Isothermal titration calorimetry experiments and blood platelet adsorption experiments proved that the obtained polypeptide inhibitors can inhibit the bonding between the collagen and integrin alpha2beta1, thus being potential high-efficiency thrombus inhibitors.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
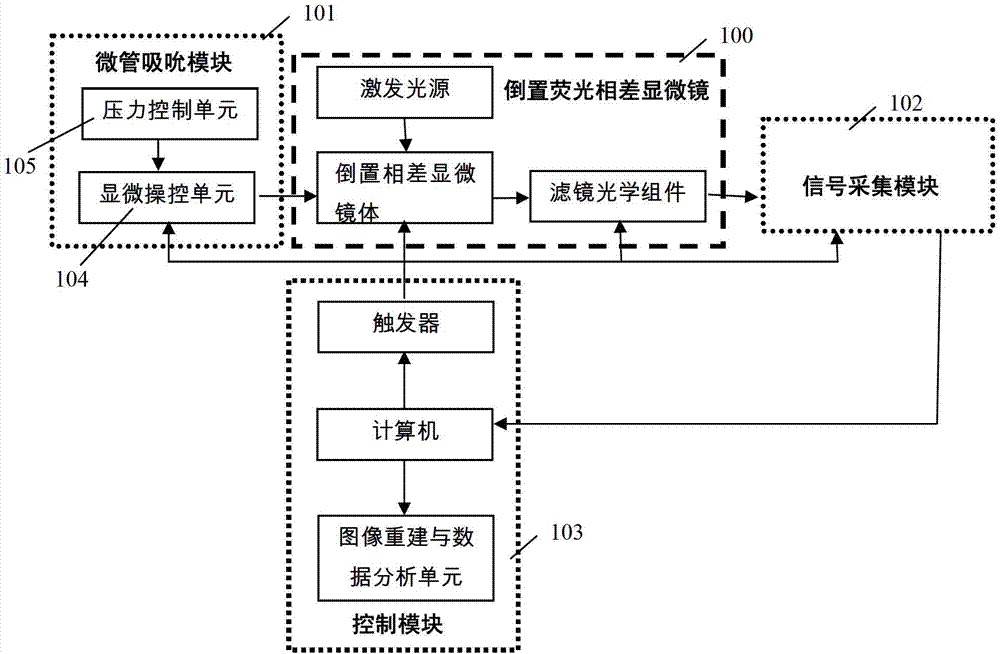
Cytomechanics device capable of synchronously realizing suction loading and fluorescence observation
ActiveCN103205360APerfect mechanical behaviorAchieve mechanical propertiesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiomechanicsFluorescence
The invention discloses a cytomechanics device capable of synchronously realizing suction loading and fluorescence observation. The cytomechanics device comprises a microtubule suction module, an inverted fluorescence phase contrast microscope, a signal acquisition module and a control module, wherein the microtubule suction module is used for capturing, sucking and micro-controlling cells in a sample cell; the inverted fluorescence phase contrast microscope is used for fluorescently exciting the cells; the signal acquisition module is used for acquiring weak fluorescence signals; and the control module is used for synchronously triggering microtubule suction and fluorescence acquisition and conducting data analysis and treatment. The cytomechanics device breaks through the limit of time-space separation of the existing mechanical loading and optical detection method in cell-molecular biomechanics studies, and constructs a molecular-cell dynamics real-time in-situ observation system coupled with microtubule suction mechanical loading and fluorescence observation, thereby improving the platform for studying living cell and molecular mechanical behaviors, and contributing to deep understanding of the mechanics-chemistry and mechanics-biologics coupling rules from the molecular-cell level.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
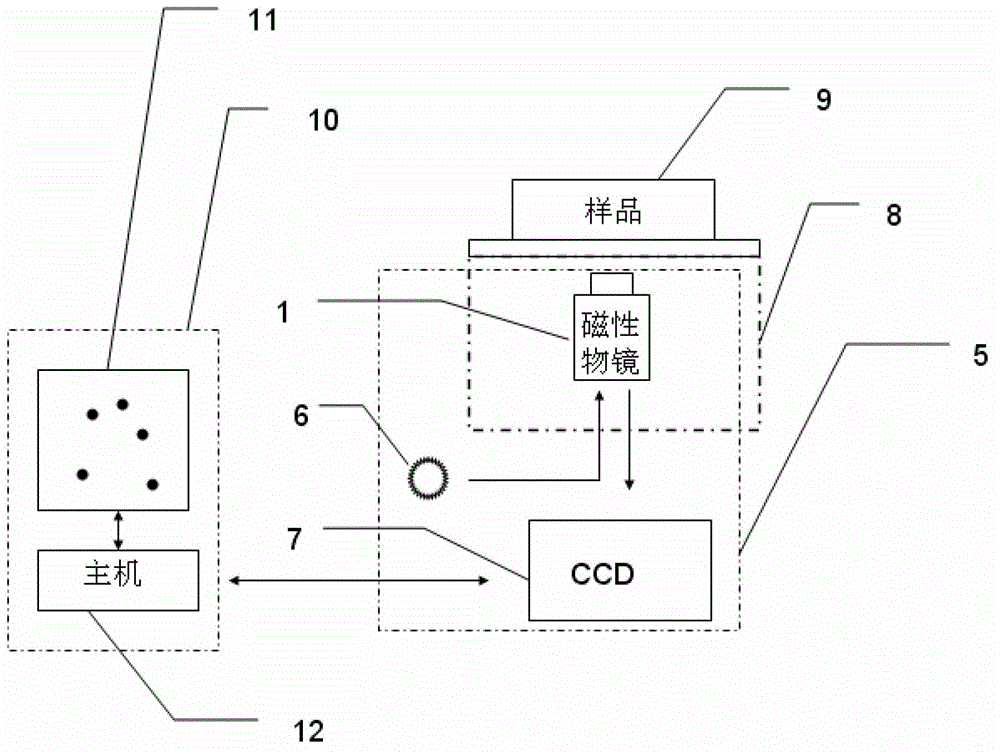
Imaging magnetic tweezers device, and system and method for integrating imaging magnetic tweezers device with single-molecule fluorescence technology
InactiveCN102749441AAchieving single-molecule mechanical manipulationBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceMagnetic field gradientElectricity
The invention discloses an imaging magnetic tweezers device, and a system and a method for integrating imaging magnetic tweezers device with a single-molecule fluorescence technology. The imaging magnetic tweezers device comprises a magnetic object lens with adjustable magnetic field gradient and magnetic field intensity, an illuminating light source and an electric coupling device. The magnetic object lens is combined with the illuminating light source and the electric coupling device to realize superparamagnetic microsphere imaging and conduct single-molecule mechanical control at the same time. On one hand, a magnetic tweezers experiment can be conduct, the magnetic tweezers device can be integrated with various single-molecule fluorescence technologies for application, not only can fluorescence signal detection be conducted to a sample, but also mechanical control can be conducted to the sample, and the fluorescence signal detection and the mechanical control are independent to each other and do not interfere with each other; and on the other hand, the imaging magnetic tweezers device can apply constraints to superparamagnetic microspheres in the sample, the Brownian fluctuation of a single-molecule connecting system can be effectively reduced, an integrated single-molecule fluorescence device can obtain staler fluorescence signals, and the experimental accuracy during single-molecule control measurement is improved.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
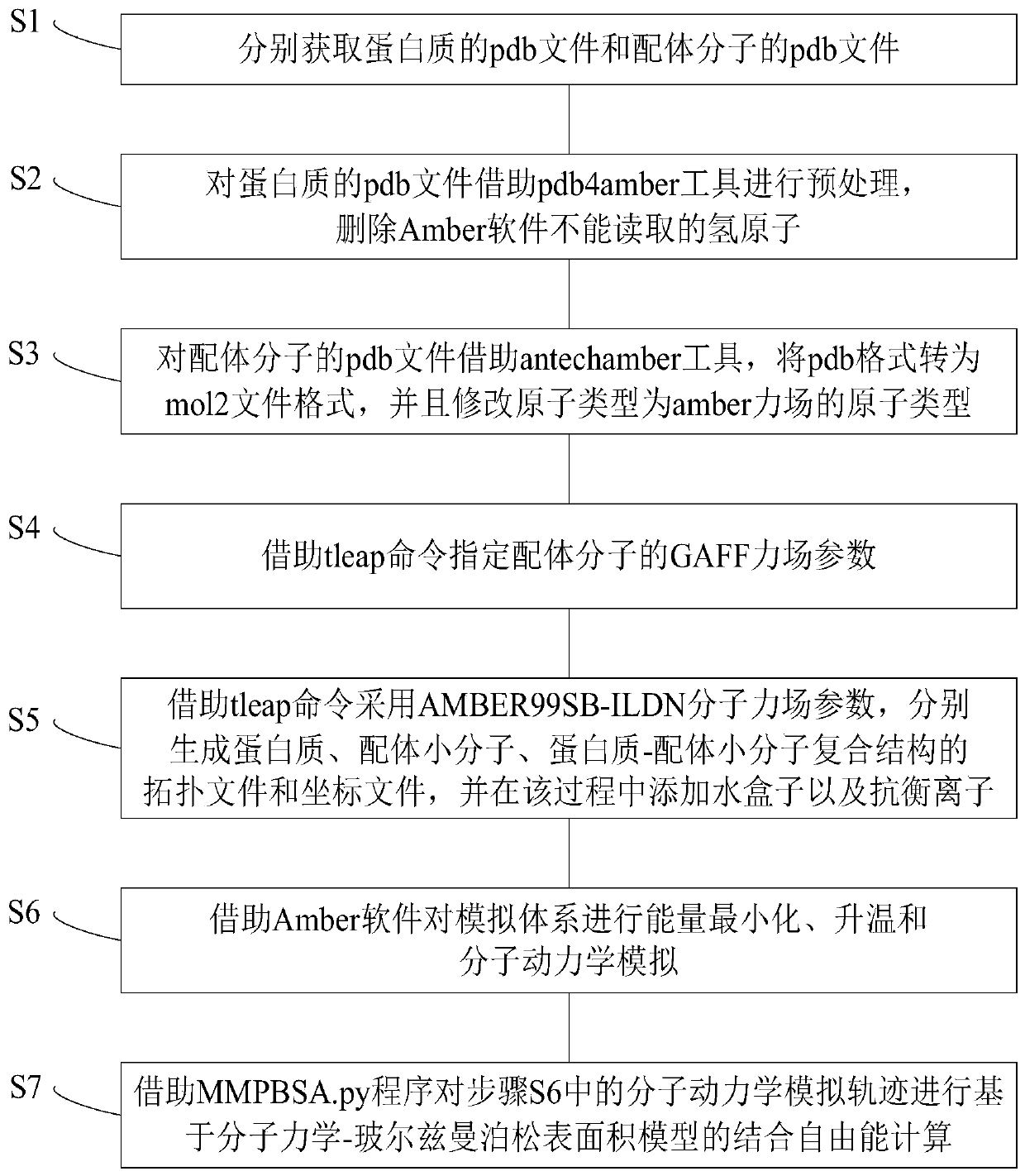
Protein-ligand binding free energy calculating method based on MM/PBSA model
ActiveCN110400598AImprove computing efficiencyImprove calculation accuracyProteomicsGenomicsAntechamberMolecular mechanics
The invention provides a protein-ligand free energy calculating method based on a MM / PBSA model. The method comprises the following steps of respectively acquiring pdb files of a protein and a ligandmolecule; preprocessing the pdb file of the protein by means of a pdb4amber tool, deleting a hydrogen atom which cannot be read by Amber software; for the pdb file of the ligand molecule, converting the pdb format to a mol2 file format by means of an antechamber tool, and correcting the atom type to the atom type of an amber force field; assigning a GAFF force field parameter of the ligand molecule by means of a tleap command; respectively generating a topological file and a coordinate file of the protein, the ligand micromolecule and a protein-ligand micromolecule composite structure by meansof the tleap command through using an AMBER99SB-ILDN molecule force field parameter, and adding a water box and counter ions in the process; performing energy minimizing, heating and molecular dynamics simulation on a simulation system by means of the Amber software; and performing binding free energy calculation based on a molecular dynamics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area model on a molecular dynamics simulating track in a previous step by means of an MMPBSA.py program.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Method for designing flotation reagent molecules based on fragments
ActiveCN108304691AMention the success rate of off-the-shelf medicineMentioned success rateCheminformatics data warehousingCheminformatics programming languagesQuantum chemistryComputer-aided
The invention discloses a method for designing flotation reagent molecules based on fragments. With the help of a computer auxiliary molecule design technique, molecular mechanics and quantum chemistry calculation, the active fragments which are small in molecular weight and high in relative combination efficiency are obtained by sieving through detection, then flotation reagent molecular structures high in activity are obtained after the methods of producing, splicing and fusing are utilized for optimizing the active fragments, and the flotation reagent molecules are obtained through the steps that a fragment molecular compound library is established, active fragment molecules are sieved, and lead compounds are sieved. The dual advantages of high efficiency of the computer auxiliary molecule design technique and the flexibility of a molecule assembly technology are combined; the inspection range for the molecules is scaled to the inspection range for the molecular fragments, in this way, the success rate of reagent formulation is greatly increased for the reagent molecules, the designing efficiency is effectively promoted for the flotation reagent molecules, and the new method isfurther provided for designing flotation reagent.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
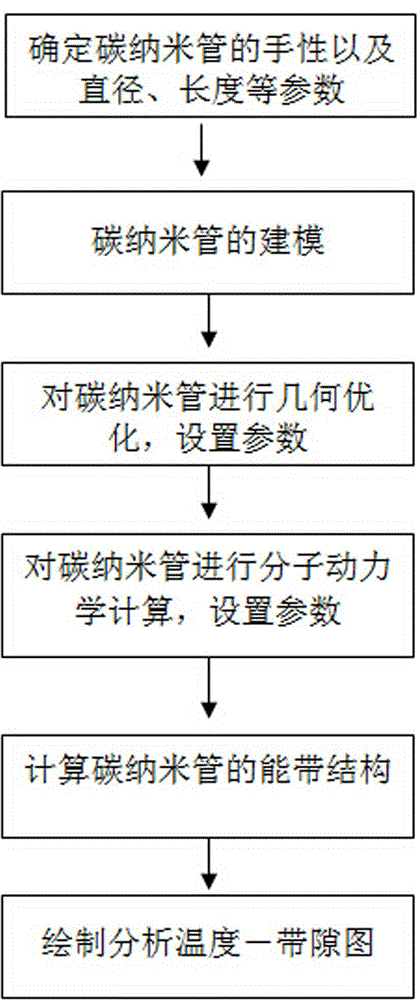
Method for testing temperature characteristic of carbon nanometer pipe
ActiveCN104535859ATest accurateThe result is accurateElectrical testingDensity functional theoryCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a method for testing a temperature characteristic of a carbon nanometer pipe. The method combines quantum mechanics and molecular dynamics and utilizes the theories like the density functional theory, the electrical conductivity of the carbon nanometer pipe at different temperatures is tested from the molecule level to the atom level, and therefore the temperature characteristic of the carbon nanometer pipe is obtained. From the view of quantum mechanics, the method of molecular dynamics is combined, the actual conditions of the structures of molecules in different environments are simulated through the molecular dynamics firstly, time and labor are saved, then the temperature conductivity of the molecules are calculated through the quantum mechanics, the test result can be obtained rapidly and accurately, and the method is simple and effective.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
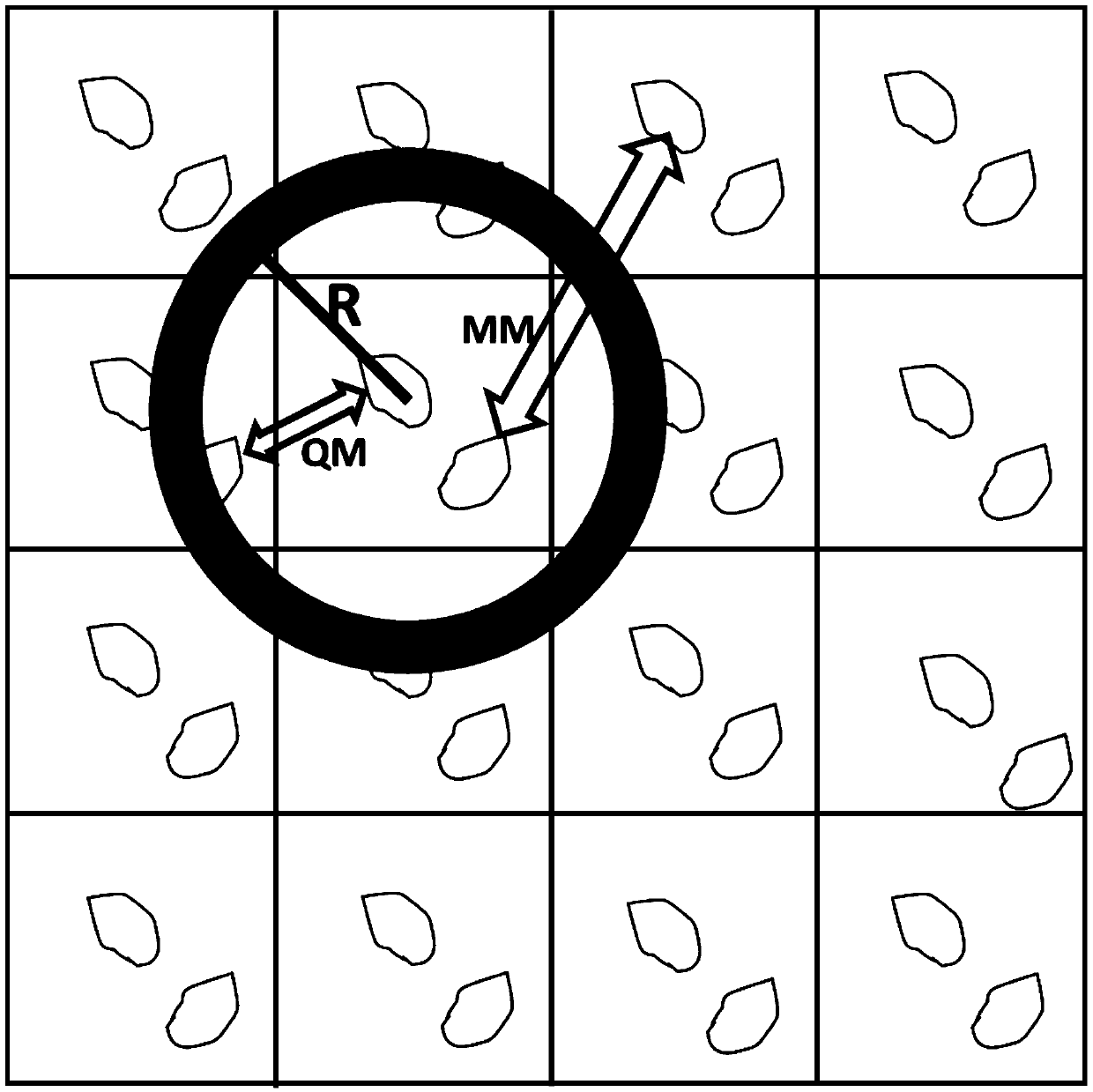
High-precision energy ranking method for organic molecular crystal structure prediction
ActiveCN108959842AImprove Energy Calculation EfficiencyGuaranteed correctnessSpecial data processing applicationsRankingComputational chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic molecular crystal structures and particularly relates to a high-precision energy ranking method for organic molecular crystal structure prediction. The high-precision energy ranking method comprises the steps of determining a quantum mechanics action radius of a center unit cell; in the center unit cell, carrying out energy calculation by adopting a density block interaction algorithm; within a range of a radius R, calculating action energy of molecules outside the center unit cell on the molecules inside the center unit cell at quantum mechanics precision; calculating the action energy of a periodically extended unit cell on the molecules inside the center unit cell outside the range of the radius R under a classical molecular mechanics precision condition; and calculating total energy of crystal, wherein the total energy of the crystal comprises energy in the center unit cell and the energy between the center unit cell and the periodically extended unit cell. According to the high-precision energy ranking method for organic molecular crystal structure prediction, the energy calculation efficiency and accurate energy feedbackin molecular crystal of a drug are improved, and a CSP is guided to look for a true low-energy dominant crystal form in the right direction in the crystal prediction process.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
Construction method for food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model
ActiveCN103714266AGood correlationSpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a construction method and application for a food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model. The method comprises the steps of using a food-borne polypeptide with known activity as a research object, utilizing the three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship technology for establishing the food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model, and adopting the MM+ method the semi-empirical quantum chemistry method AM1, the DFT method and other quantum chemistry technologies to obtain quantum chemistry parameters. According to the construction method, analysis and statistics are carried out on the food-borne polypeptide quantum chemistry parameters, the antioxidant activity sites of the food-borne polypeptide are determined, and quantitative structure-activity model is constructed by utilizing the bond length, charge distribution, frontier molecular orbit energy parameters of the activity sites and food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity values. The constructed model can rapidly and accurately predict the activity value of the food-borne polypeptide with the unknown activity, and the relationship between the antioxidant activity and structural features can be reasonably explained; compared with a traditional high throughput screening technology, the screening efficiency is greatly improved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
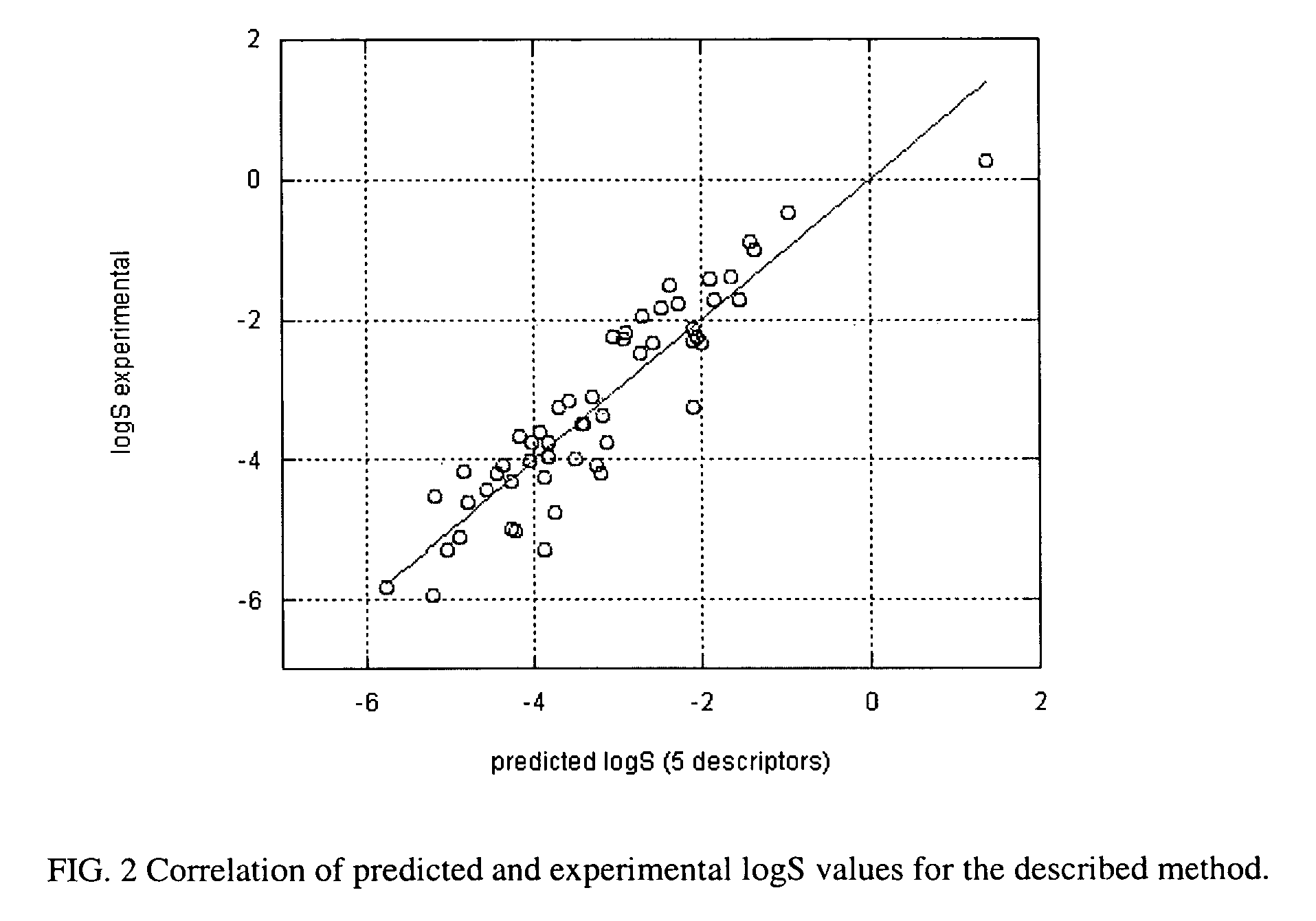
Method of prediction of solubility of chemical compounds
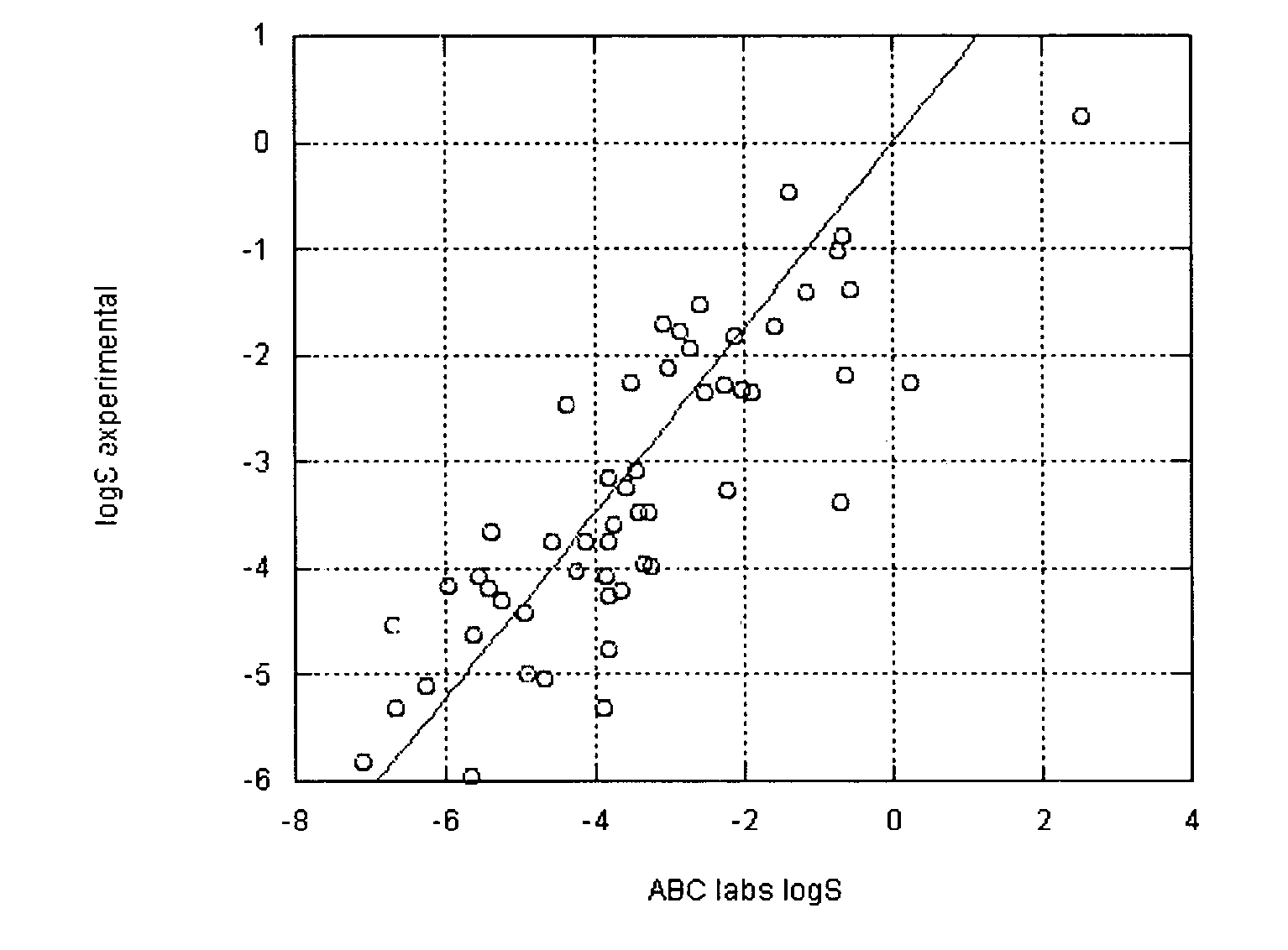
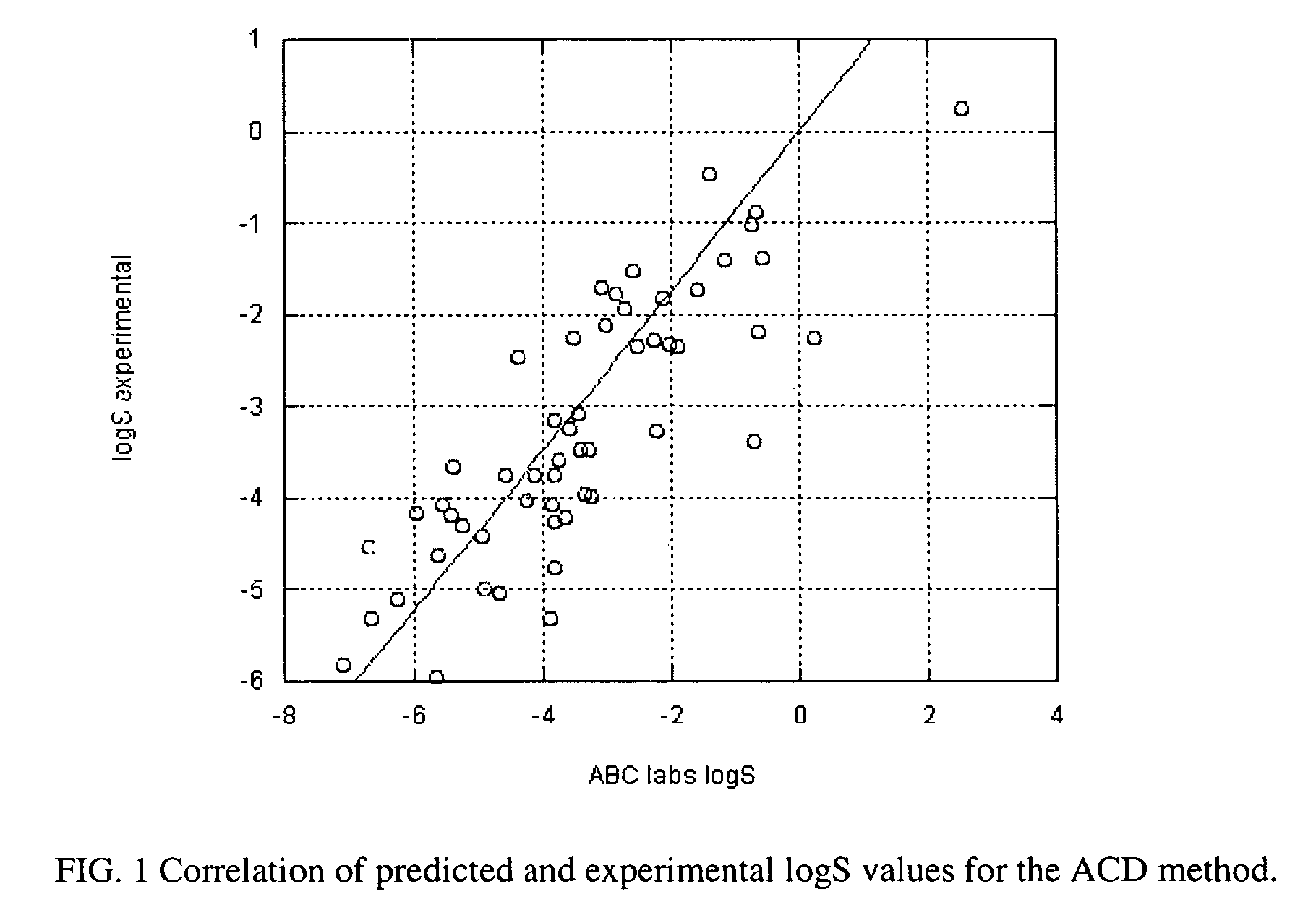
InactiveUS7117102B2Accurate interactionAccurate solubilityChemical property predictionProgram control using stored programsSolubilityChemical compound
Descriptors of cohesive interactions in the solid state are calculated from a computational model of a solid state, i.e. from a small cluster of copies of the molecule of interest assembled using a molecular mechanics method. A model for predicting solubility is built using the cohesive interaction descriptors along with other descriptors useful for this purpose. Predicted solubility is computed for the compound of interest by computing the same descriptors and applying the solubility model. Explicit modeling of solid state allows to more accurately characterize cohesive interactions in solids, hence, more accurately predict solubility.
Owner:FILIKOV ANTON
A method for calculating critical injection pressure of fluid in a nanopore throat
ActiveCN109885954AAvoid bias in resultsSimple and fast operationSpecial data processing applicationsOil phaseUnconventional oil
The invention discloses a method for calculating critical injection pressure of fluid in a nanopore throat. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a nanopore throat structure; 2) constructing a fluid and a push plate; 3) adjusting the size of the model, setting a vacuum area, and finishing model construction; 4) distributing force field and charge parameters; and 5) carrying outmolecular mechanics optimization, balanced molecular dynamics simulation and tensile molecular dynamics simulation, counting and analyzing the stress change process of the oil phase in the nanopore throat filling process, and obtaining the critical injection pressure of the oil phase in the nanopore throat filling process through a formula P = F / S. According to the invention, a computer simulation technology is utilized to obtain the calculation method of the critical injection pressure of the fluid in the nanopore throat; the result deviation caused by ignoring the intermolecular interactionin the mathematical calculation method is avoided, the method can realize the regulation and control of the simulation conditions such as the nanopore throat size and the fluid components, and a convenient and effective way is provided for the research of the critical physical properties of the unconventional oil and gas reservoir.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Comparison of molecules using field points
ActiveUS7805257B2Analogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingField sizeChemical physics
A method of comparing two conformers in which an overlay score is obtained, comprises providing a set of field points representing field extrema of a first molecule, wherein each field point has a position and a field size value; determining at the position of each of the field points of the first molecule the field of a second molecule to obtain a set of field sample values; and combining the field sample values with the field size values to obtain a score indicative of the field similarity of the first molecule to the second molecule. The method overcomes a limitation of conventional pseudo-Coulombic scoring in which a low score is achieved when extrema of large extent overlap but have their minimum points widely separated. The method can be applied to molecular mechanics modeling using atom centered charges (ACCs) and extended electron distributions (XEDs) as well as to quantum mechanics models.
Owner:CRESSET BIOMOLECULAR DISCOVERY
Comparison of molecules using field points
ActiveUS20060129323A1Analogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingLower scoreMolecular mechanics
A method of comparing two conformers in which any score is obtained by determining the field value for molecule A at the coordinates of molecule B's field point. Molecule B's field point does not have to be very close to molecule A's field point to get a good overlay score: it just needs to be in a region where molecule A's field is large. This overcomes a limitation of conventional pseudo-Coulombic scoring in which a low score is achieved when extrema of large extent overlap but have their minimum points widely separated. The method can be applied to molecular mechanics modelling using atom centred charges (ACCs) and extended electron distributions (XEDs) as well as to quantum mechanics models.
Owner:CRESSET BIOMOLECULAR DISCOVERY
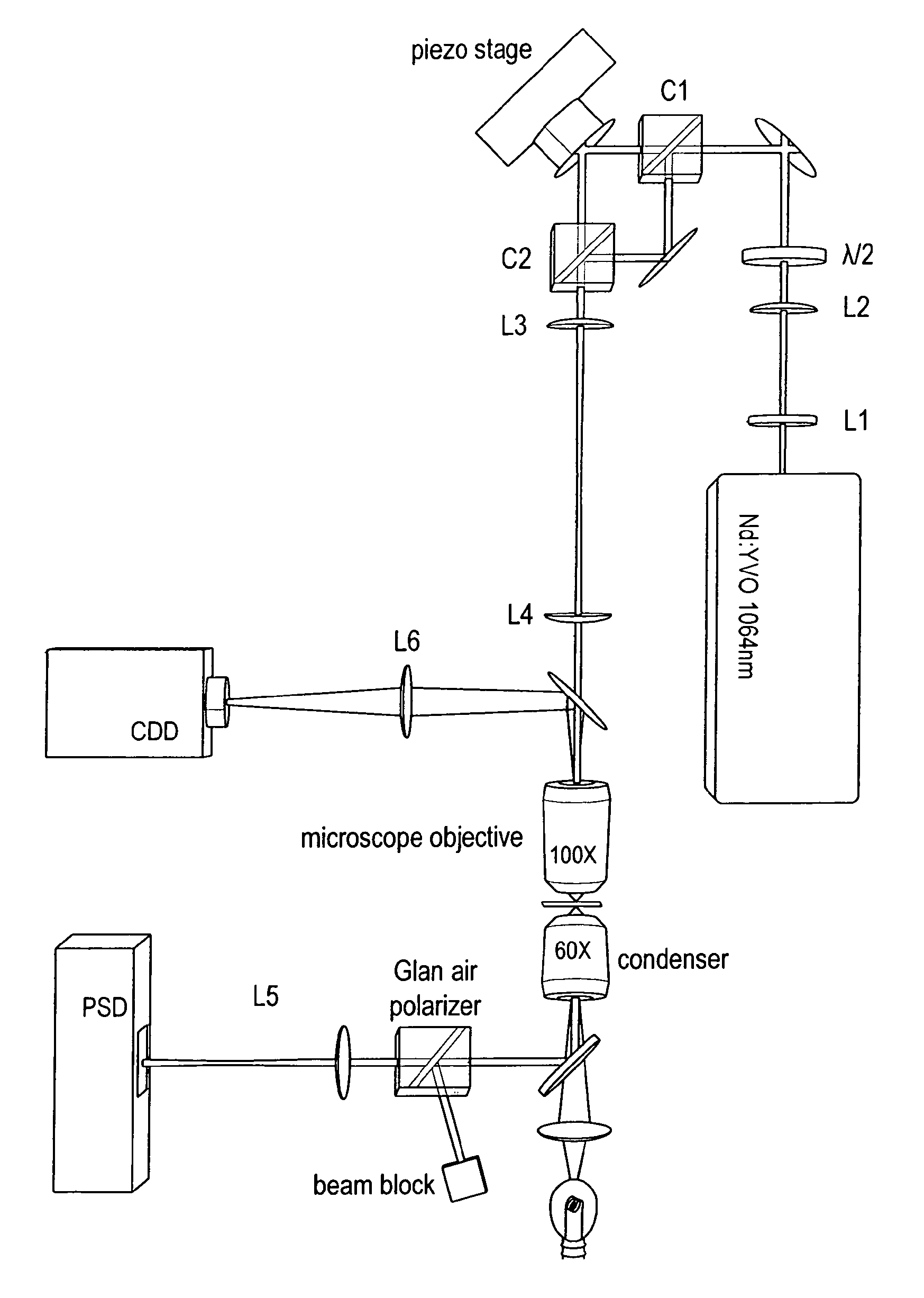
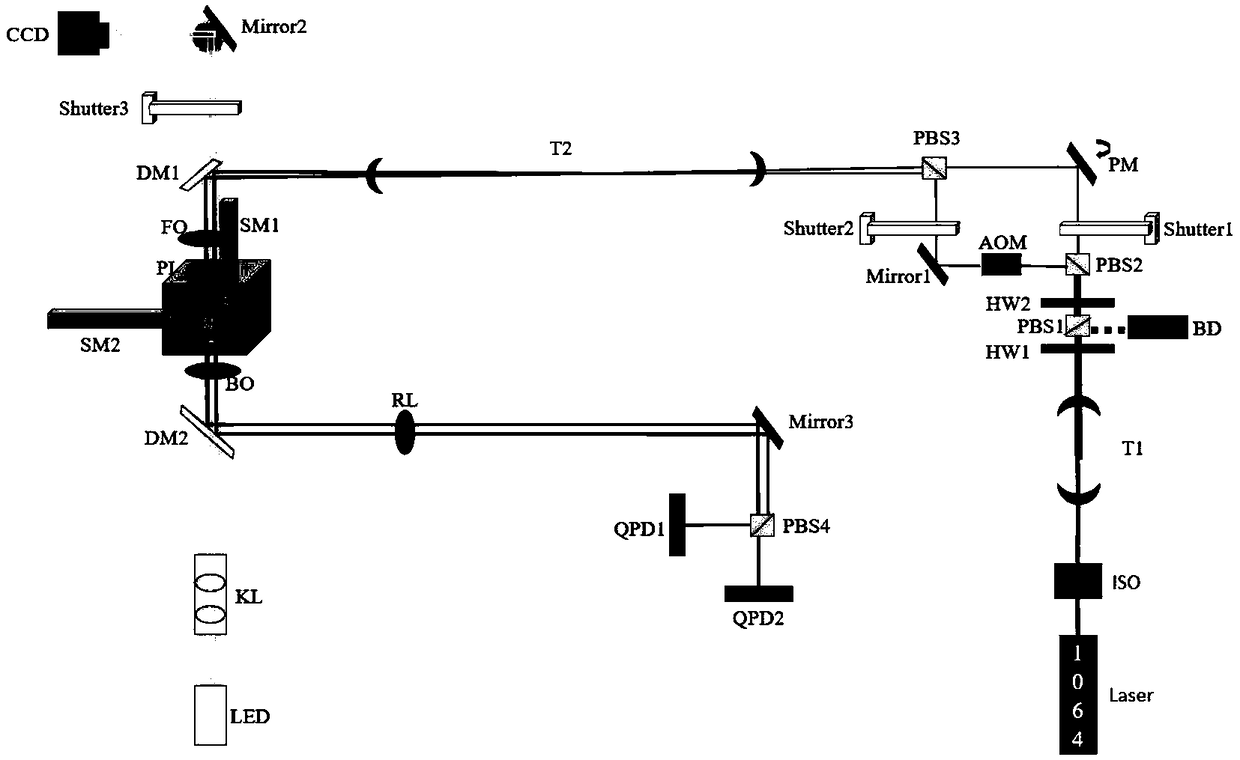
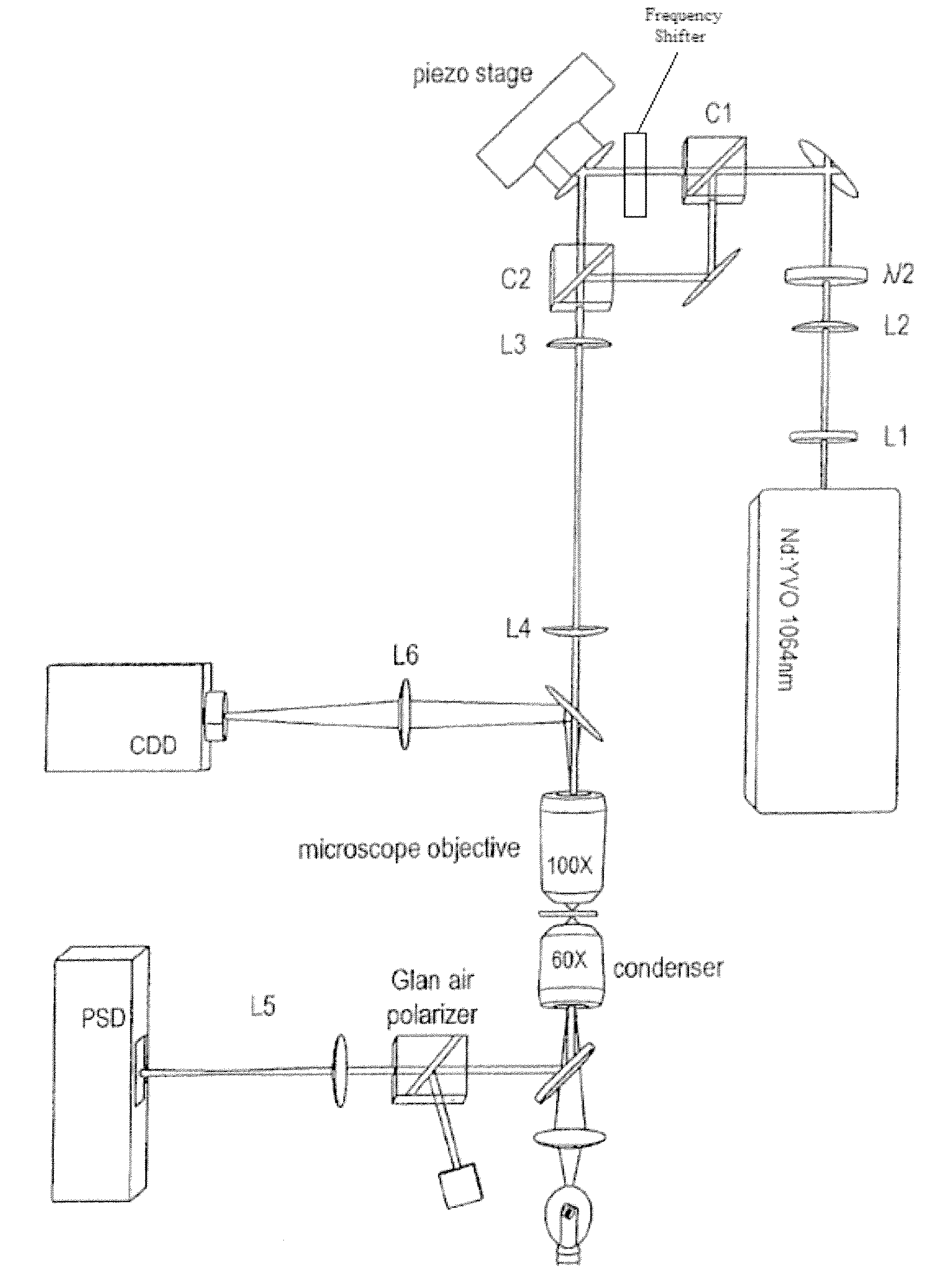
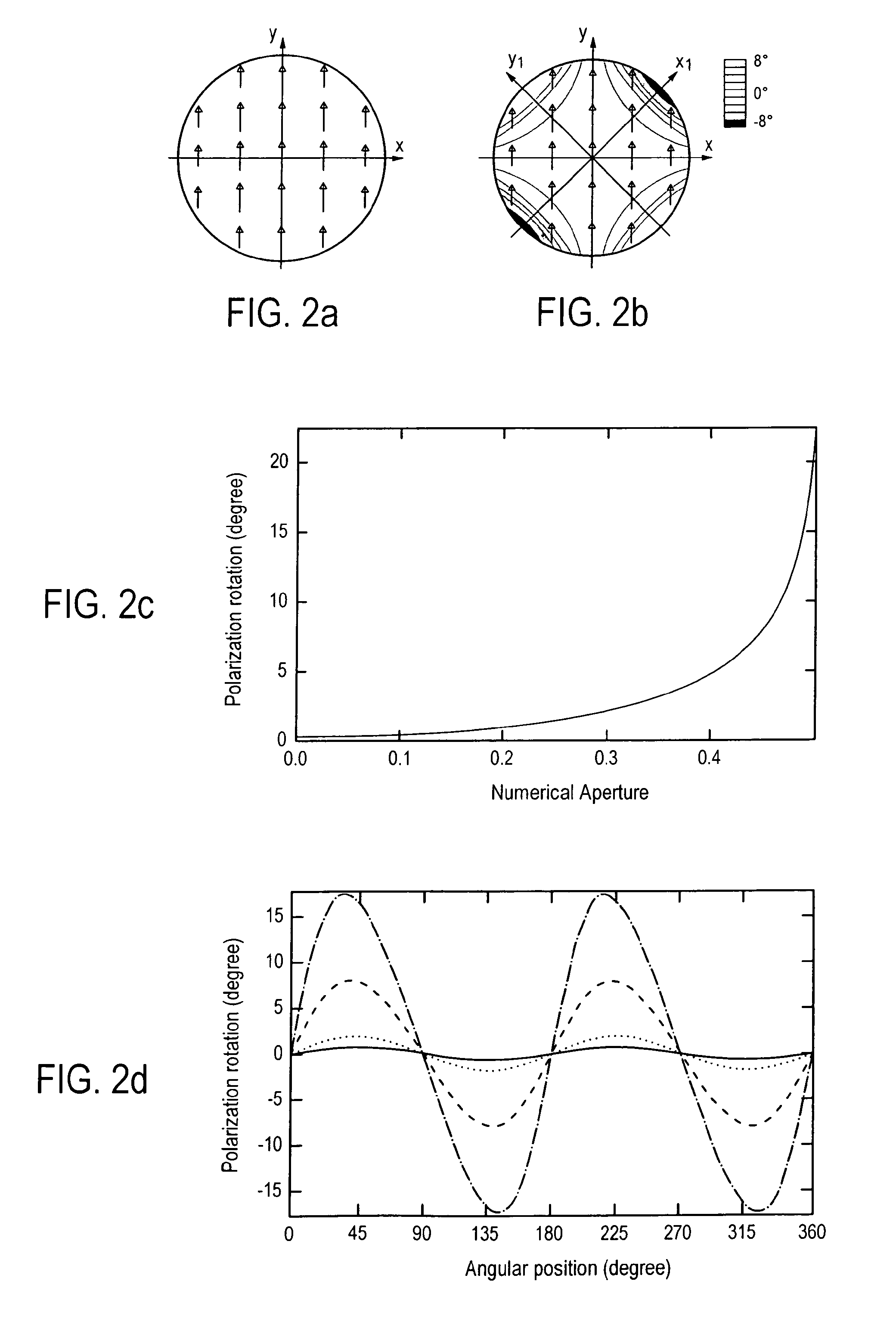
Method for reducing interference and crosstalk in double optical tweezers using a single laser source, and apparatus using the same
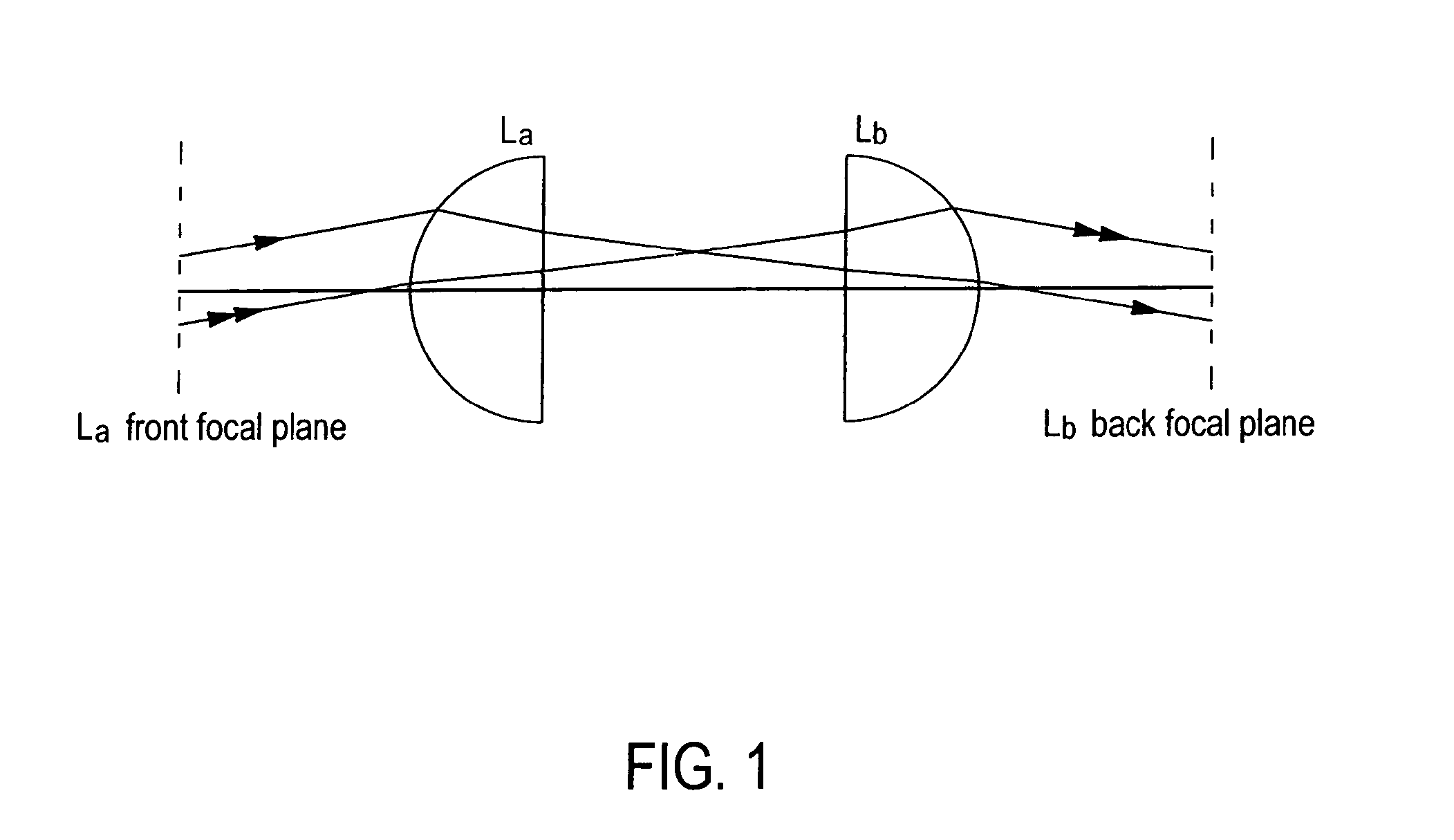
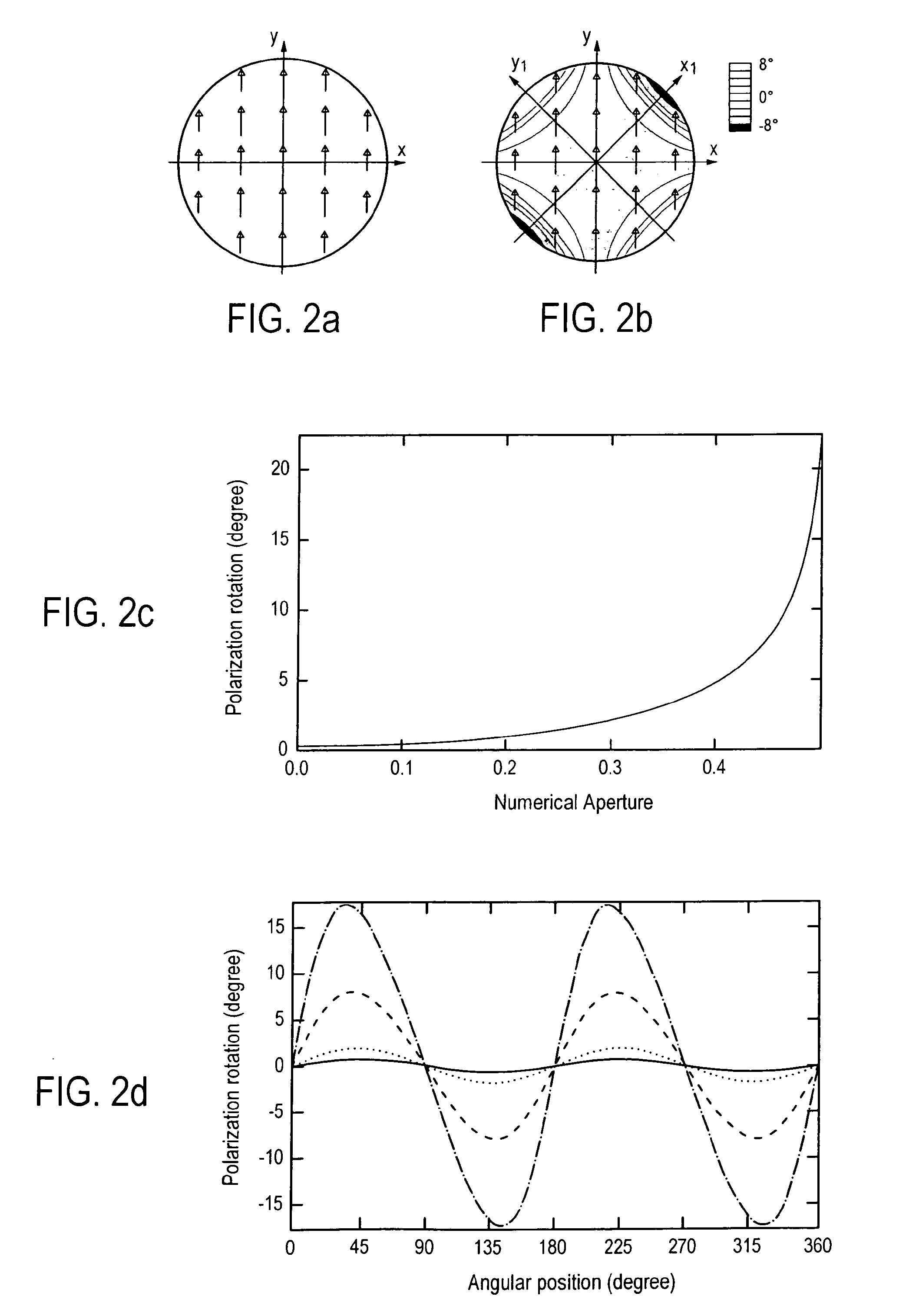
Experimental studies of single molecule mechanics require high force sensitivity and low drift, which can be achieved with optical tweezers through an optical tweezers apparatus for force measurements. A CW infrared laser beam is split by polarization and focused by a high numerical aperture objective to create two traps. The same laser is used to form both traps and to measure the force by back focal plane interferometry. Although the two beams entering the microscope are designed to exhibit orthogonal polarization, interference and a significant parasitic force signal occur. Comparing the experimental results with a ray optics model, the interference patterns are caused by the rotation of polarization on microscope lens surfaces and slides. Two methods for reducing the crosstalk are directed to polarization rectification by passing through the microscope twice and frequency shifting of one of the split laser beams.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
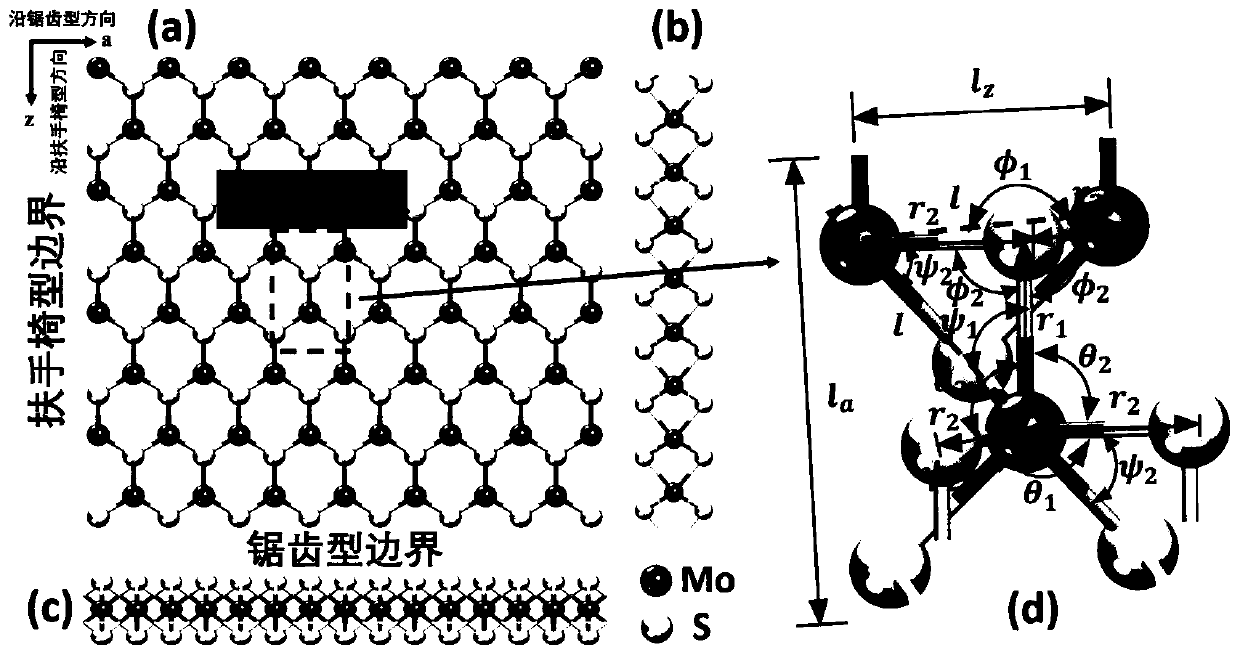
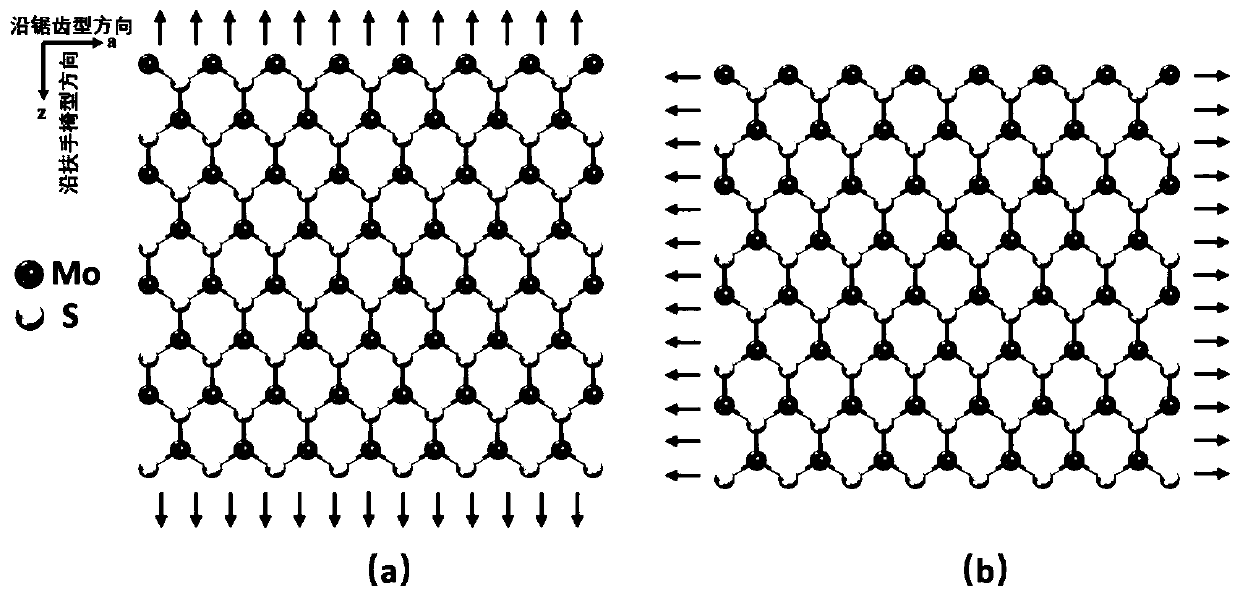
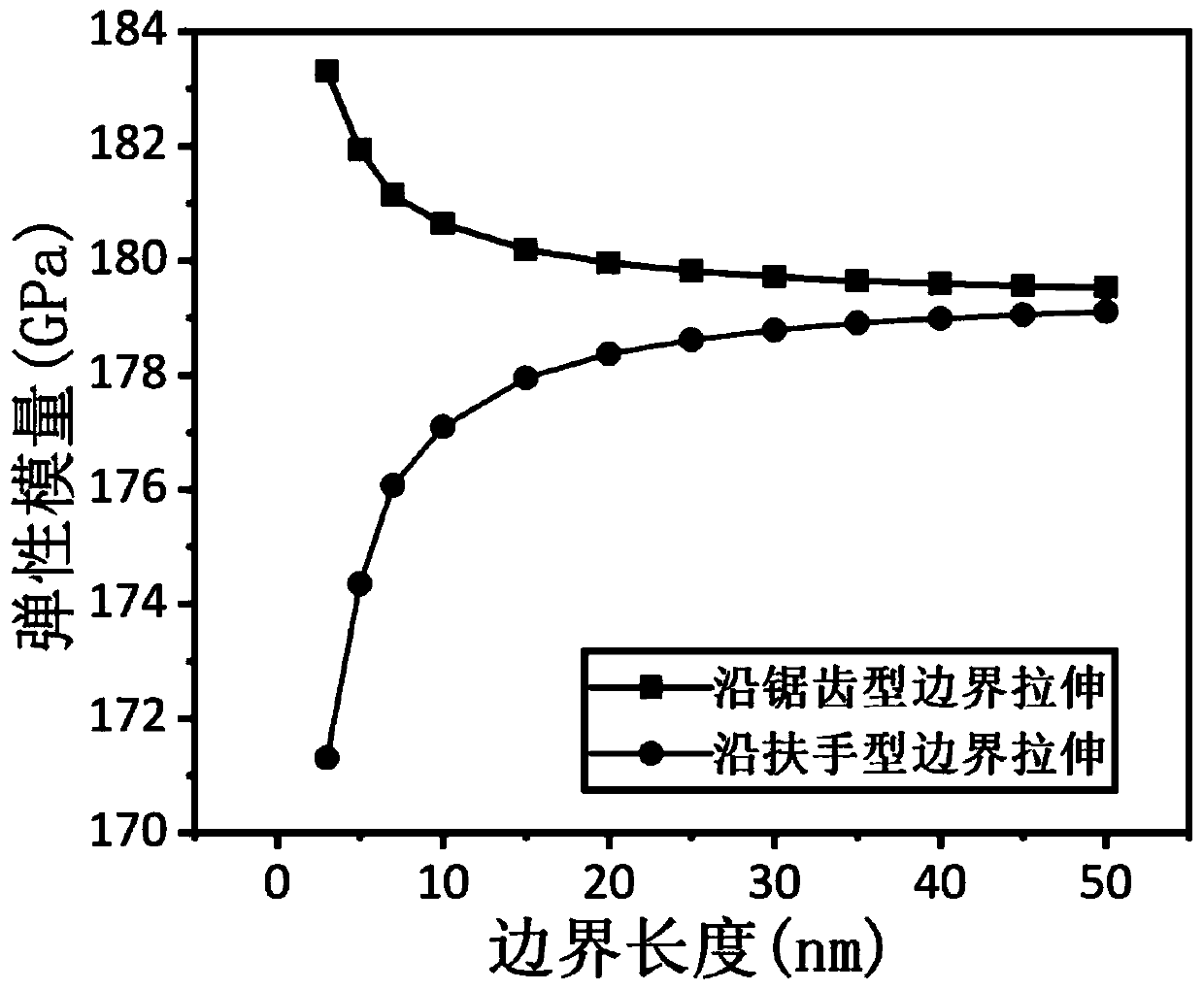
Molecular mechanical method for measuring elasticity modulus and Poisson ratio of monolayer molybdenum disulfide
ActiveCN110020478AQuick and flexibleShortcut Poisson's RatioDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBi-isotropic materialMechanical property
The invention belongs to the technical field of calculation of two-dimensional nano materials, and provides a molecular mechanical method for measuring the elasticity modulus and the Poisson's ratio of monolayer molybdenum disulfide. Related mechanical properties of monolayer molybdenum disulfide are determined through a molecular mechanical method, and the size effect of the material is given. According to the method, firstly, a molecular mechanics theoretical model of the monolayer molybdenum disulfide is established, a projection auxiliary structure model does not need to be established, and an analytical expression capable of representing the elasticity modulus and the Poisson's ratio of the monolayer molybdenum disulfide of any size is directly obtained. According to the method, the elasticity modulus and the Poisson ratio of the monolayer molybdenum disulfide can be effectively measured, high cost caused by experiments is avoided, and the result shows that the monolayer molybdenum disulfide is gradually transited from an anisotropic material to an isotropic material along with increase of the feature size. The method provides important theoretical reference for the application based on the monolayer molybdenum disulfide material.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
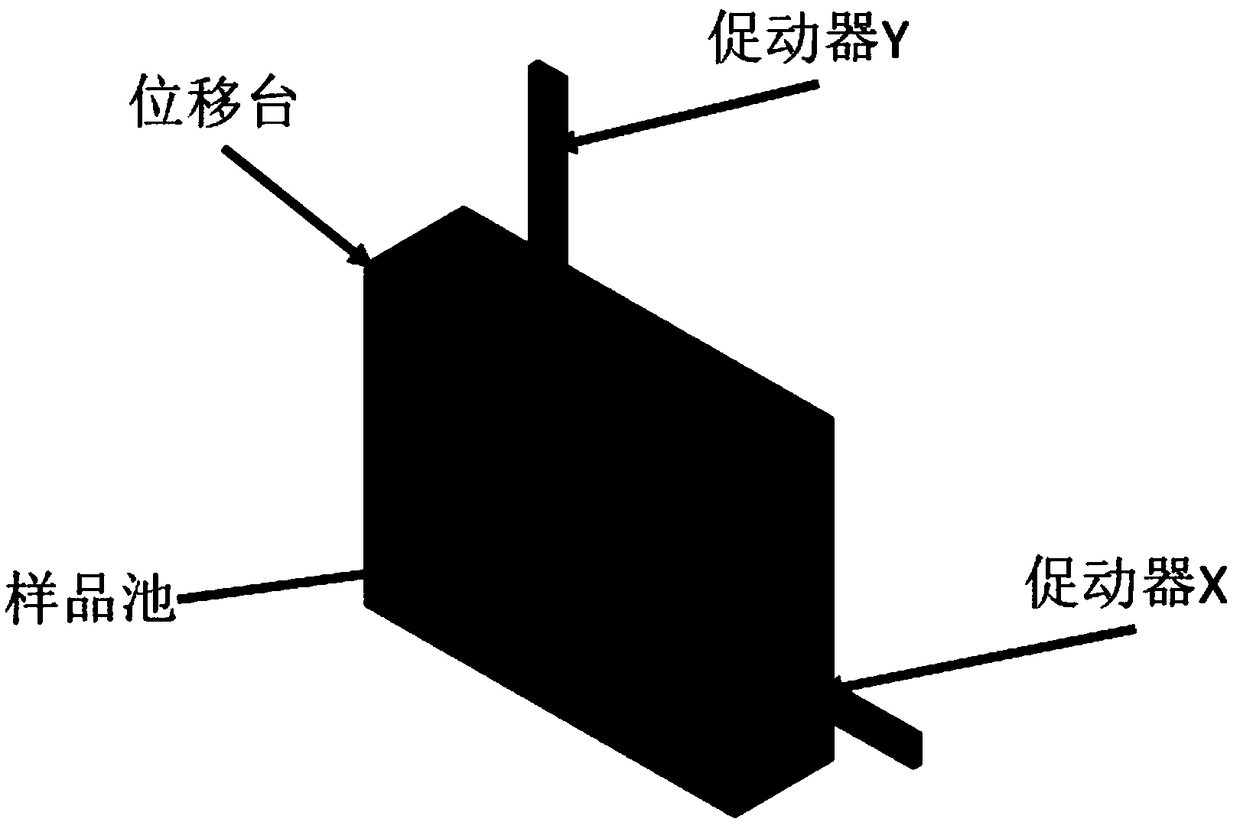
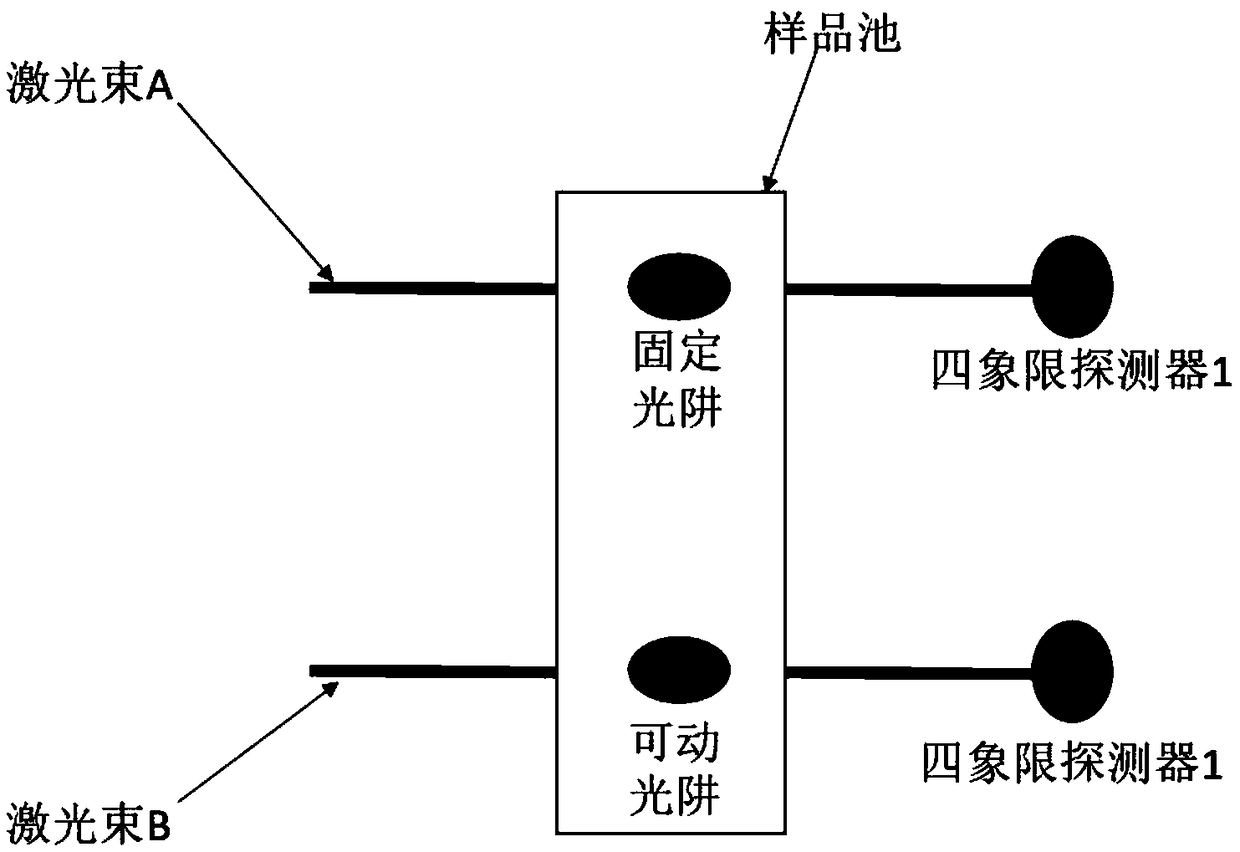
Efficient implementation method of single-molecular mechanical test
The invention relates to an efficient implementation method of single-molecular mechanical test, comprising the steps of enabling a sample cell to move relative to light traps through an actuator, andcapturing microspheres; processing in real time to monitor the double light traps until each light trap contains only single microsphere; stopping the actuator operating, controlling a displacement table to drive the sample cell to do simple harmonic motion in the horizontal direction under certain frequency and amplitude; performing single-molecular mechanical test and storing data; when it is monitored that each light trap contains no single microsphere and if multiple microspheres occur in the light trap, controlling a retaining plate to close and then open to release the microspheres fromthe light traps, controlling a piezoceramic mirror PM to rotate so that the movable light traps are moved to reset positions; if no microspheres occur in the light traps, moving the movable light traps directly to the reset positions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Molecular force field quality control system and control method thereof
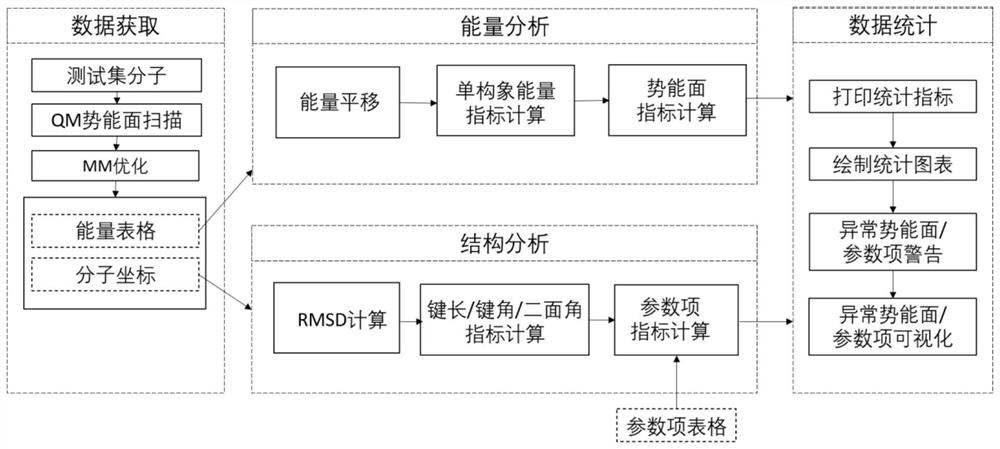
ActiveCN112233733AAccurate identificationBroad handlingComputational theoretical chemistryInstrumentsStructure analysisOriginal data
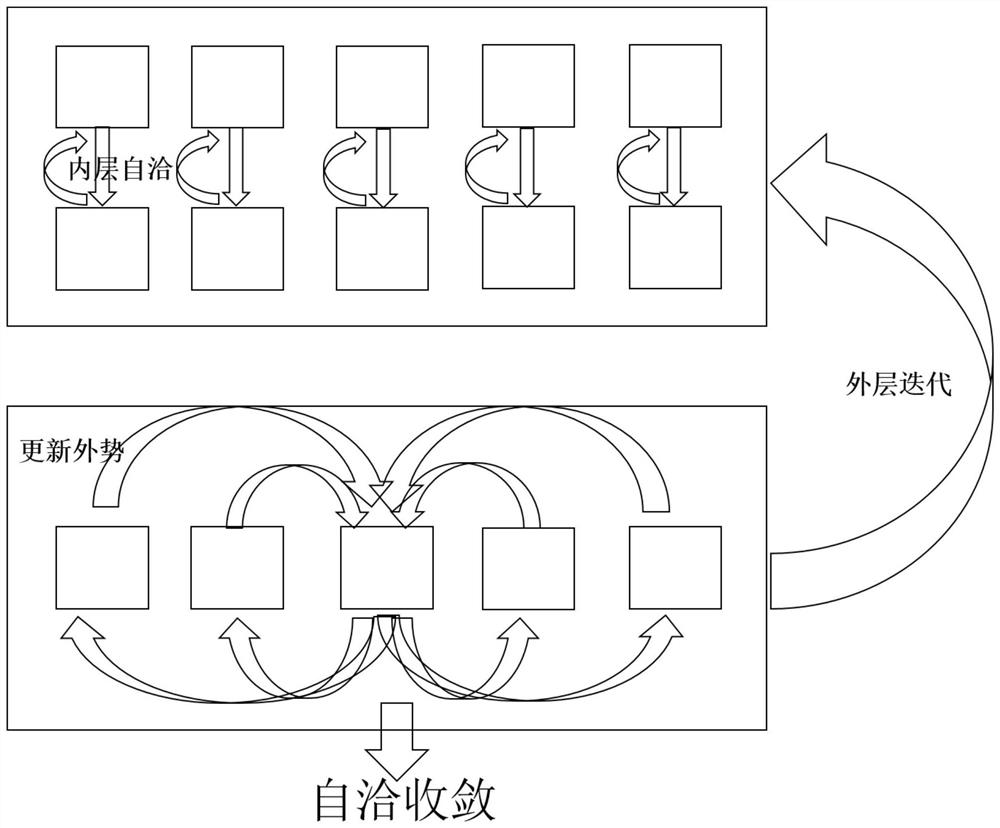
The invention provides a molecular force field quality control system and a control method thereof, wherein the system comprises a data obtaining module, an energy analysis module, a structure analysis module and a data statistics module; the data obtaining module reads quantum mechanics optimization data for benchmarking and molecular mechanics optimization data of a to-be-measured force field, and arranges the data into a data table containing a specified column and a molecular coordinate file; the energy analysis module is used for calculating evaluation indexes related to molecular conformational energy and potential energy surfaces of an index set, calculating an energy analysis index according to two test method parameters, and generating an original data table; the structure analysis module is used for calculating evaluation indexes related to a molecular structure of the index set, calculating a structure analysis index, and generating an original data table; and the data statistics module is used for calculating statistical indexes, printing statistical data and drawing a statistical chart. Force field parameter items are brought into the quality control process, a force field developer can accurately identify the parameter items with poor performance in the test set, and parameter optimization is carried out in a targeted mode.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for molecular mechanics analysis of molecular systems
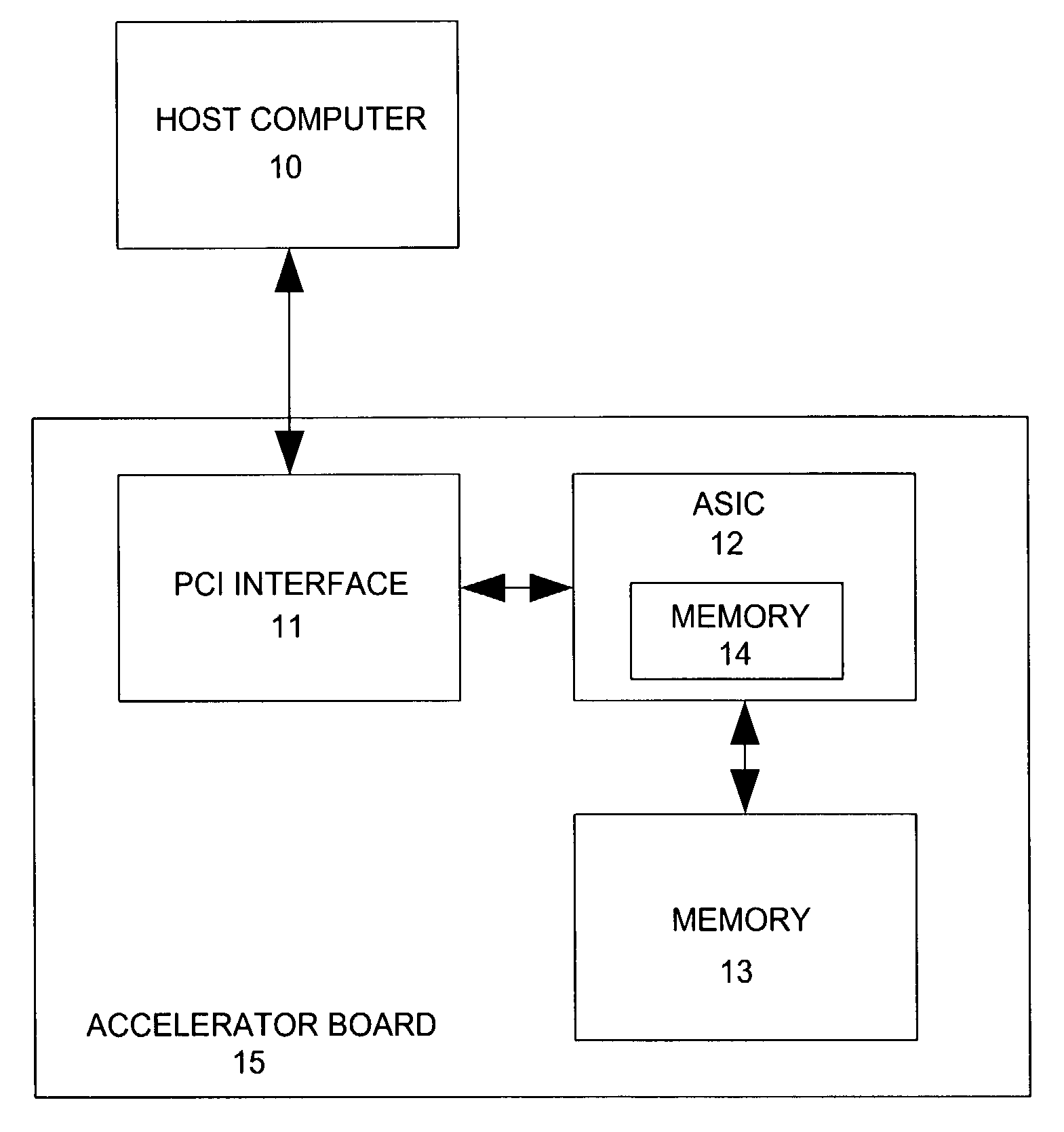
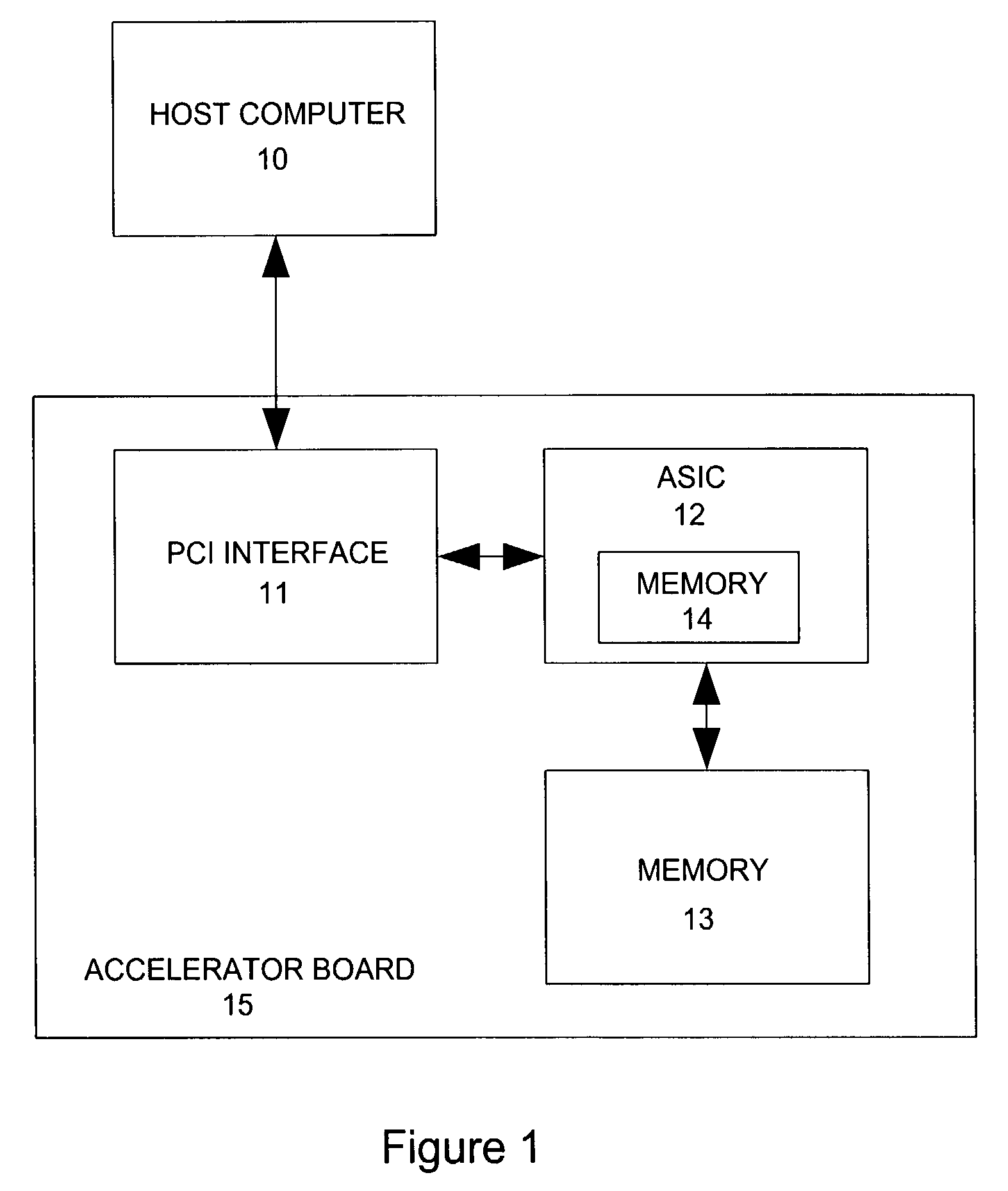
ActiveUS7577553B2Small sizeIncrease computing speedCheminformatics data warehousingComputation using non-denominational number representationProgrammable logic deviceSingle chip
A method and apparatus for analyzing molecular systems with reconfigurable special-purpose hardware is provided. An entire molecular mechanics calculation is implemented on a programmable logic device (PLD) integrated circuit (IC) (“single chip”). This single IC accelerator is achieved by run-time reprogramming of the PLD to handle different terms in the molecular mechanics calculation.
Owner:VALO HEALTH INC
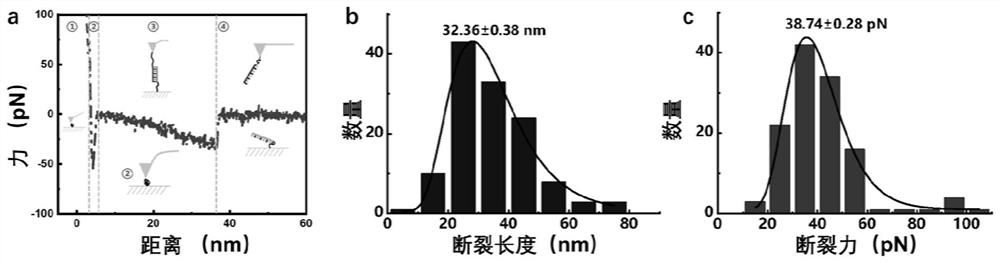
Accurate single-molecule force spectroscopy method with high throughput
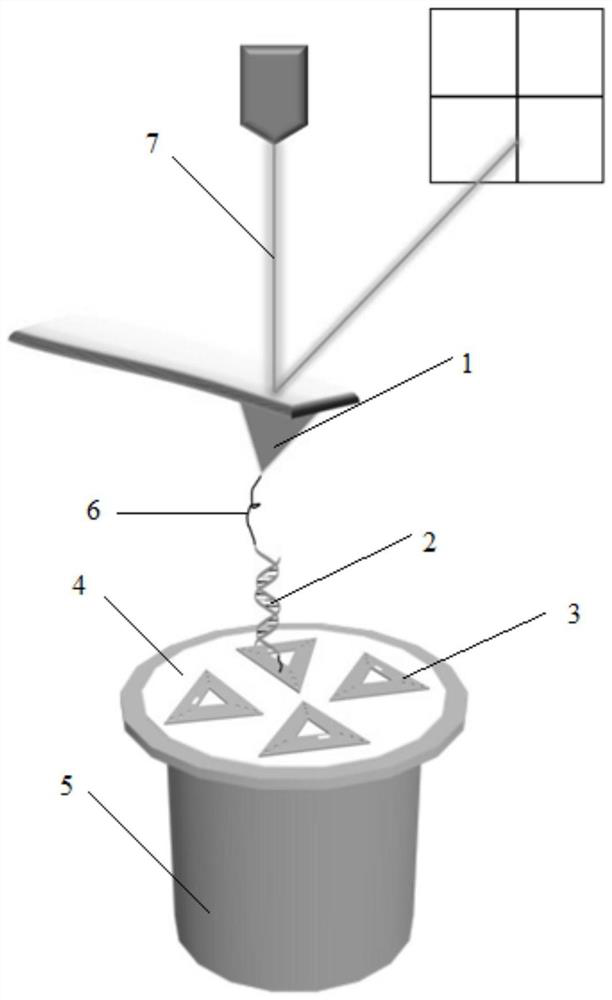
ActiveCN109557341AEasy to analyzeSolve the characteristicsScanning probe microscopyDNA origamiSpecific force
The invention provides an accurate single-molecule force spectroscopy method with high throughput. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) using DNA origami as a substrate, selecting several modification sites on the DNA origami according to the geometry of the DNA origami, and extending a stretch of a target DNA strand at the 5' end of the oligonucleotide strand of the selected modification site, wherein the target DNA strand can be complementary to the DNA strand immobilized on an AFM probe; and 2) measuring the interaction force between two complementary DNA strands located on the DNA origami and the AFM probe by an atomic force microscopy single-molecule force spectroscopy method, and collecting the specific force-distance curve data. According to the accurate single-molecule force spectroscopy method with high throughput, the detection efficiency is high, and the specificity and precision are improved. The simple and efficient single-molecule force spectroscopy method withhigh throughput provides an efficient and accurate measuring method for the quantitative measurement of single molecule mechanics.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-precision energy ranking method for crystal structure prediction of organic molecules
ActiveCN108959842BImprove Energy Calculation EfficiencyGuaranteed correctnessMolecular entity identificationComputational theoretical chemistryChemical physicsMolecular solid
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic molecular crystal structure, and specifically relates to a high-precision energy ranking method used in the prediction of organic molecular crystal structure, including determining the quantum mechanical action radius of the central unit cell; in the central unit cell, the density block interaction algorithm is used to carry out Energy calculation; within the range of radius R, the effect of molecules outside the central unit cell on the molecules in the central unit cell can be calculated under the precision of quantum mechanics; under the condition of classical molecular mechanics precision, outside the range of calculation radius R, the periodically extended unit The action energy of the cell on the molecules in the central unit cell; calculate the total energy of the crystal, which includes the energy in the central unit cell and the energy between the central unit cell and the periodically extended unit cell. The invention improves the energy calculation efficiency in the drug molecular crystal, and the precise energy feedback will guide the CSP to find the real low-energy dominant crystal form in the correct direction during the crystal prediction process.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
A Computer Calculation Method for Activation Energy and Reaction Rate Constant of Aromatic Hydrogenation Reaction
ActiveCN103020413BObvious superiorityWide measurement rangeSpecial data processing applicationsActivation energyHydrogenation reaction
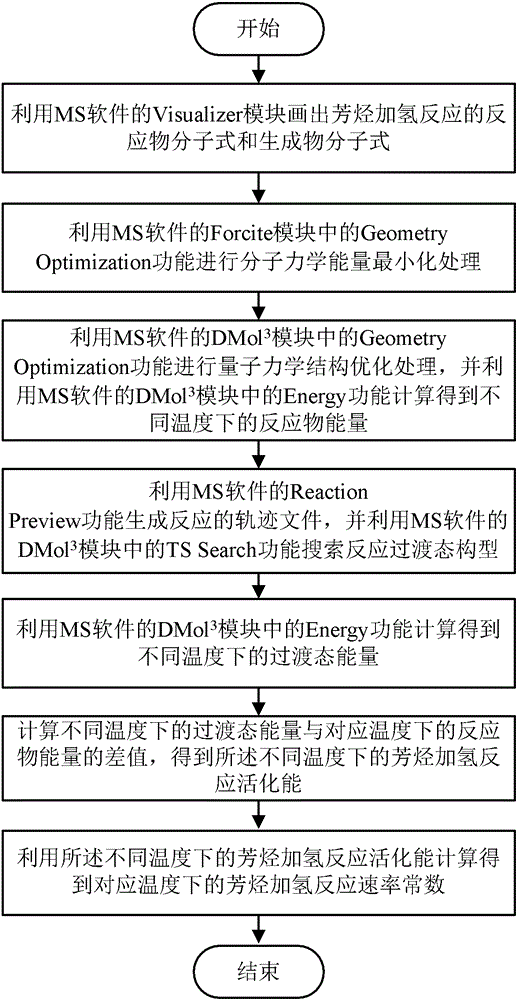
The invention discloses a method for calculating activation energy and a reaction rate constant in arene hydrogenation reaction at different temperatures by a computer. The method comprises the steps of: 1, according to the Visualizer module of MS (Microsoft) software, drawing the molecular formulas of a reactant and a resultant in the arene hydrogenation reaction; 2, according to a Geometry Optimization function in the Forcite module of MS software, carrying out the treatment of molecular mechanical energy minimization; 3, according to the Geometry Optimization function in the DMo13 module of the MS software, carrying out the treatment of quantum mechanical structural optimization, and according to an Energy function in the DMo13 module of the MS software, calculating the reactant energy at different temperatures; 4, according to the Reaction Preview function of the MS software, generating the document of reaction trajectory, and according to a TS Search function in the DMo13 module of the MS software, searching a reaction transition state configuration; 5, according to an Energy function in the DMo13 module of the MS software, calculating the transition state energy at different temperatures; 6, calculating activation energy of arene hydrogenation reaction at different temperatures; and 7, according to the activation energy of arene hydrogenation reaction at different temperatures, calculating the reaction rate constant of arene hydrogenation reaction at corresponding temperatures.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A high-throughput single-molecule force spectroscopy method
ActiveCN109557341BEasy to analyzeImprove detection efficiencyScanning probe microscopyDNA origamiOligonucleotide
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
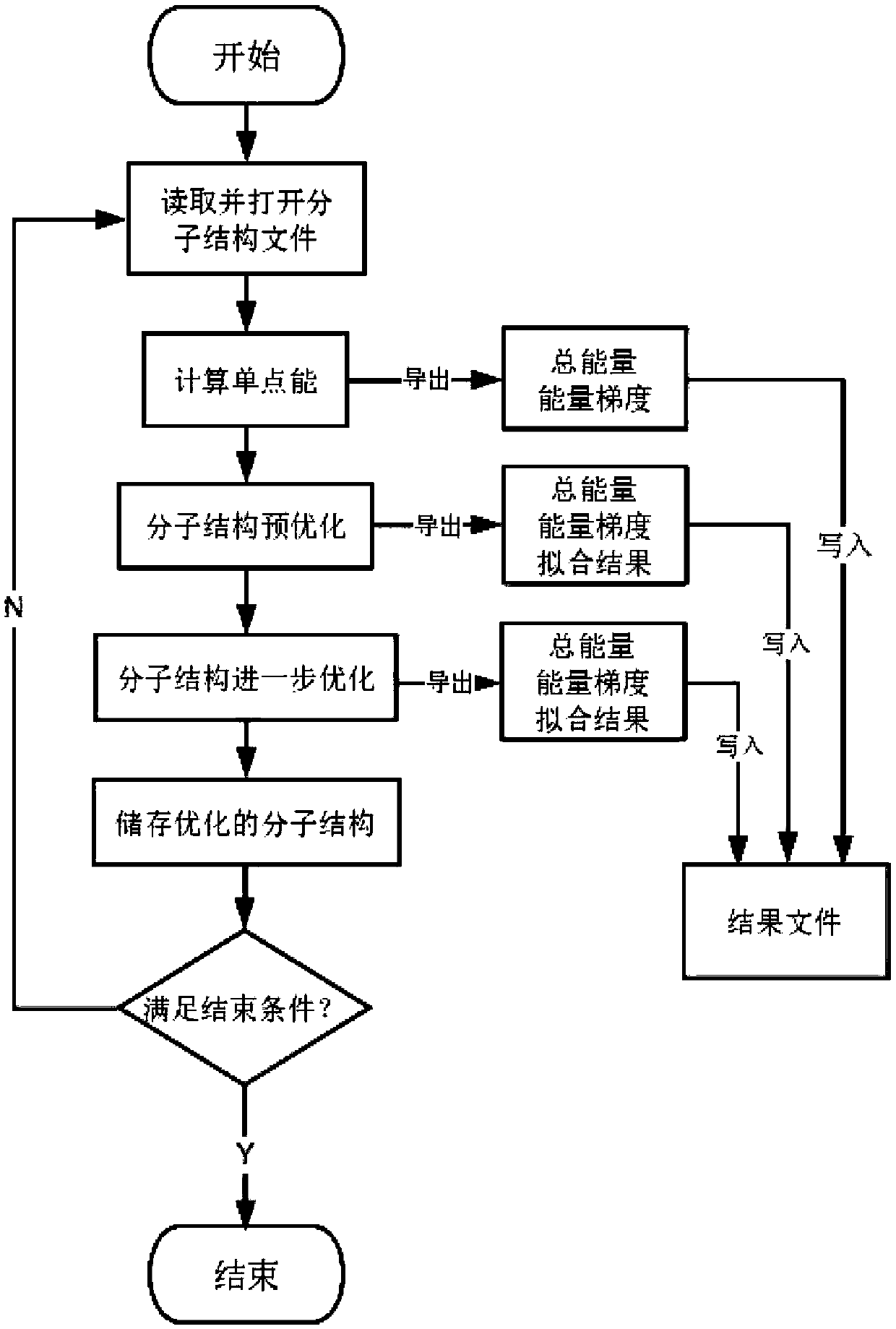
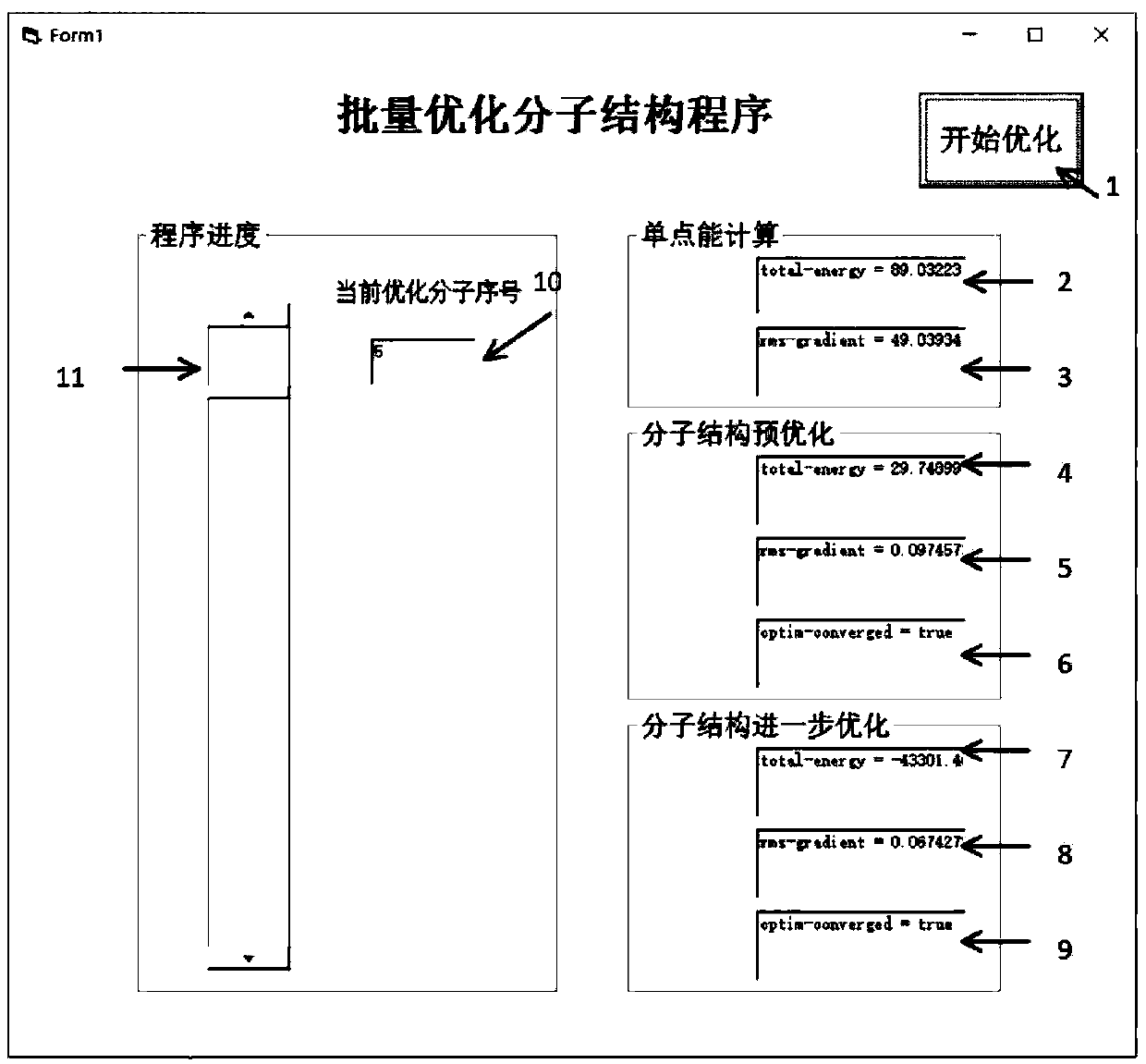
A method for efficiently optimizing molecular structures in batches
ActiveCN110875085ARealize automatic controlImprove work efficiencyMolecular designEnergy gradientAlgorithm
The invention relates to a method for efficiently optimizing molecular structures in batches. The method mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, a large number of optimized molecular structures cannot be rapidly obtained. According to the method for efficiently optimizing the molecular structures in batches, through VB programming, automatic optimization of large-batch molecular structures is completed through one-time operation of a program; one-time program operation is used instead of multiple times of manual optimization calculation, and molecular structure files are read in batches; molecular single-point energy is automatically calculated; pre-optimization is carried out through a molecular mechanics method, and further optimization is carried out through a quantum mechanicssemi-empirical method to make the energy gradient value of the molecular structure reduced to be below 0.05kcal / (mol.Angstrom), and finally, the stable molecular structure is obtained. Such technicalscheme well solves the problems, and the method can be used for optimizing the molecular structure in batches.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Method for reducing interference and crosstalk in double optical tweezers using a single laser source, and apparatus using the same
Experimental studies of single molecule mechanics require high force sensitivity and low drift, which can be achieved with optical tweezers through an optical tweezers apparatus for force measurements. A CW infrared laser beam is split by polarization and focused by a high numerical aperture objective to create two traps. The same laser is used to form both traps and to measure the force by back focal plane interferometry. Although the two beams entering the microscope are designed to exhibit orthogonal polarization, interference and a significant parasitic force signal occur. Comparing the experimental results with a ray optics model, the interference patterns are caused by the rotation of polarization on microscope lens surfaces and slides. Two methods for reducing the crosstalk are directed to polarization rectification by passing through the microscope twice and frequency shifting of one of the split laser beams.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Mutant sugar isomerase with improved activity, derived from e. coli, and production of l-gulose using same
ActiveUS20170191098A1Enzymatic activity is lowEasy to optimizeIsomerasesFermentationEscherichia coliFructose
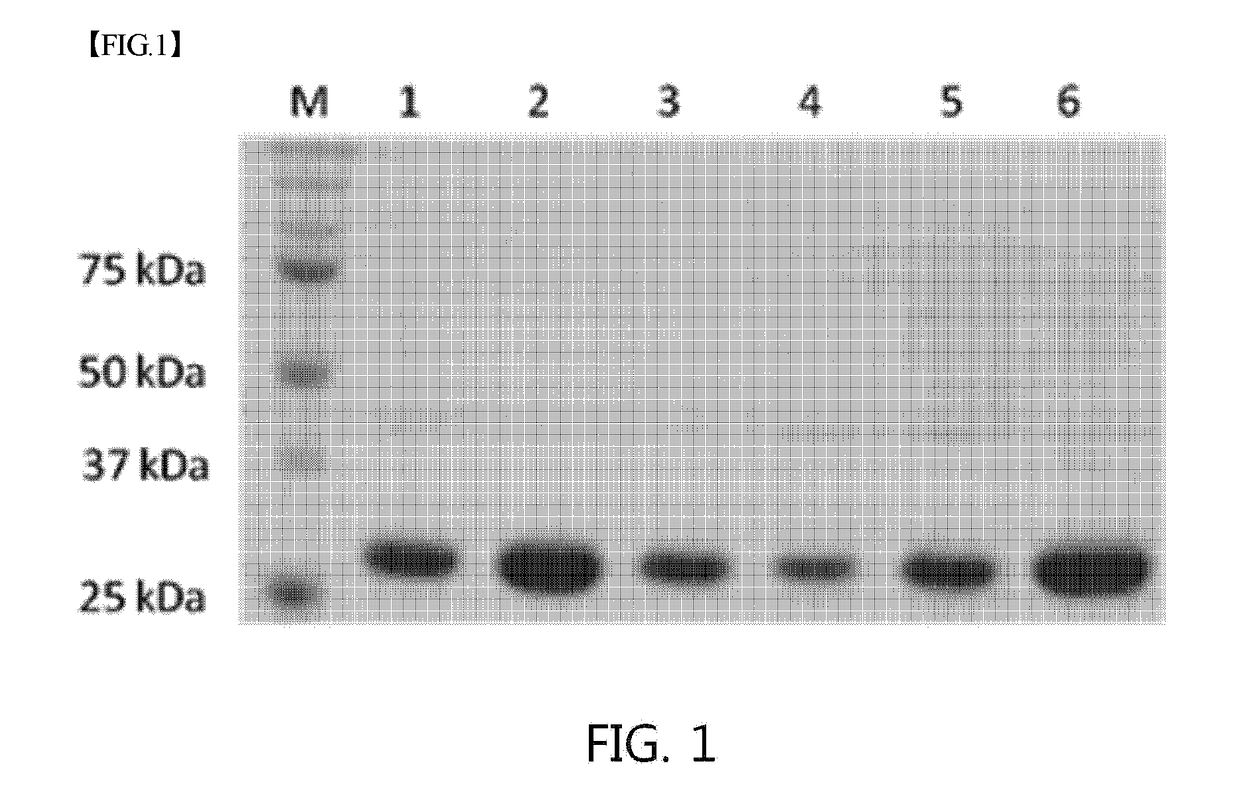
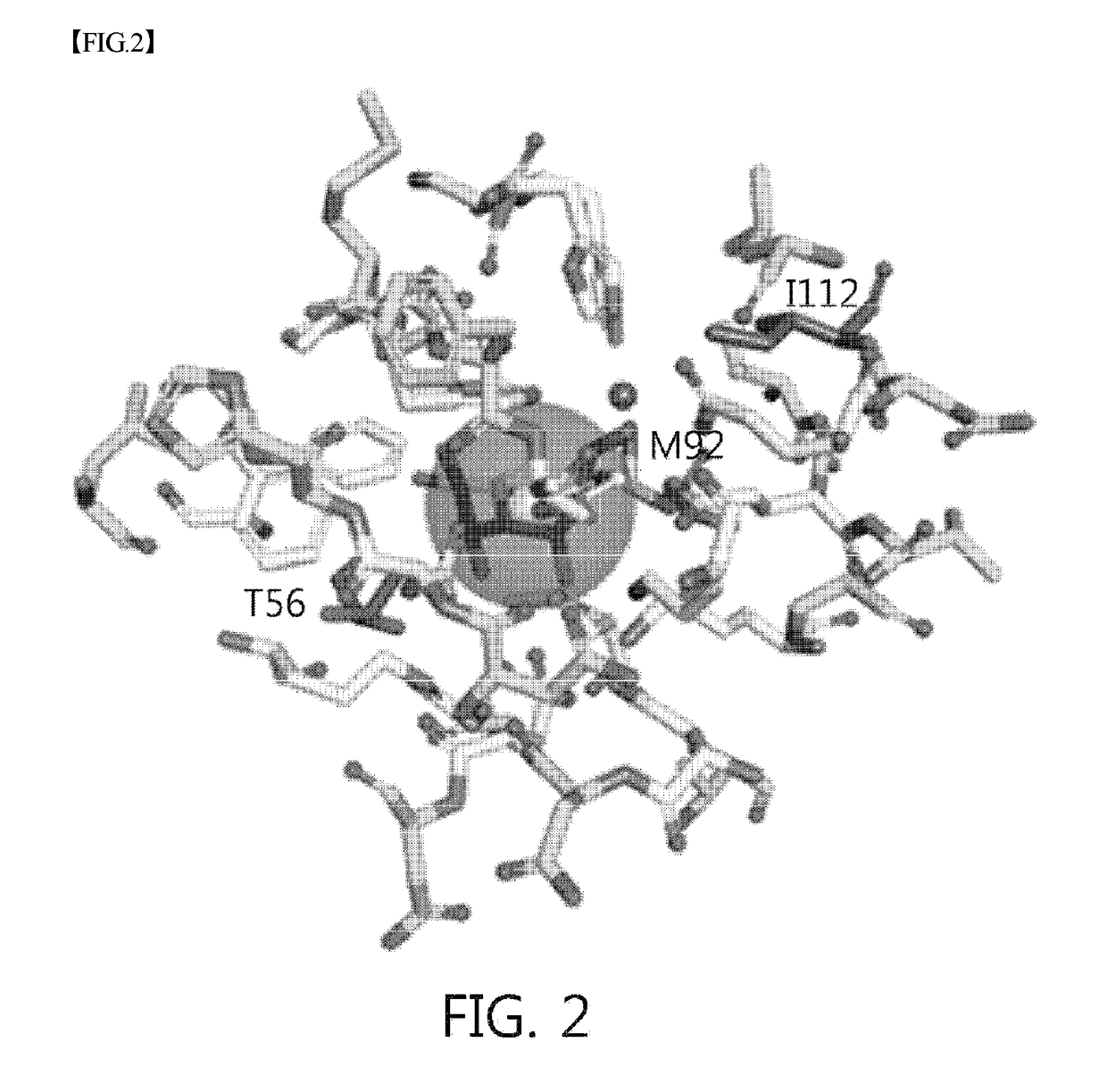
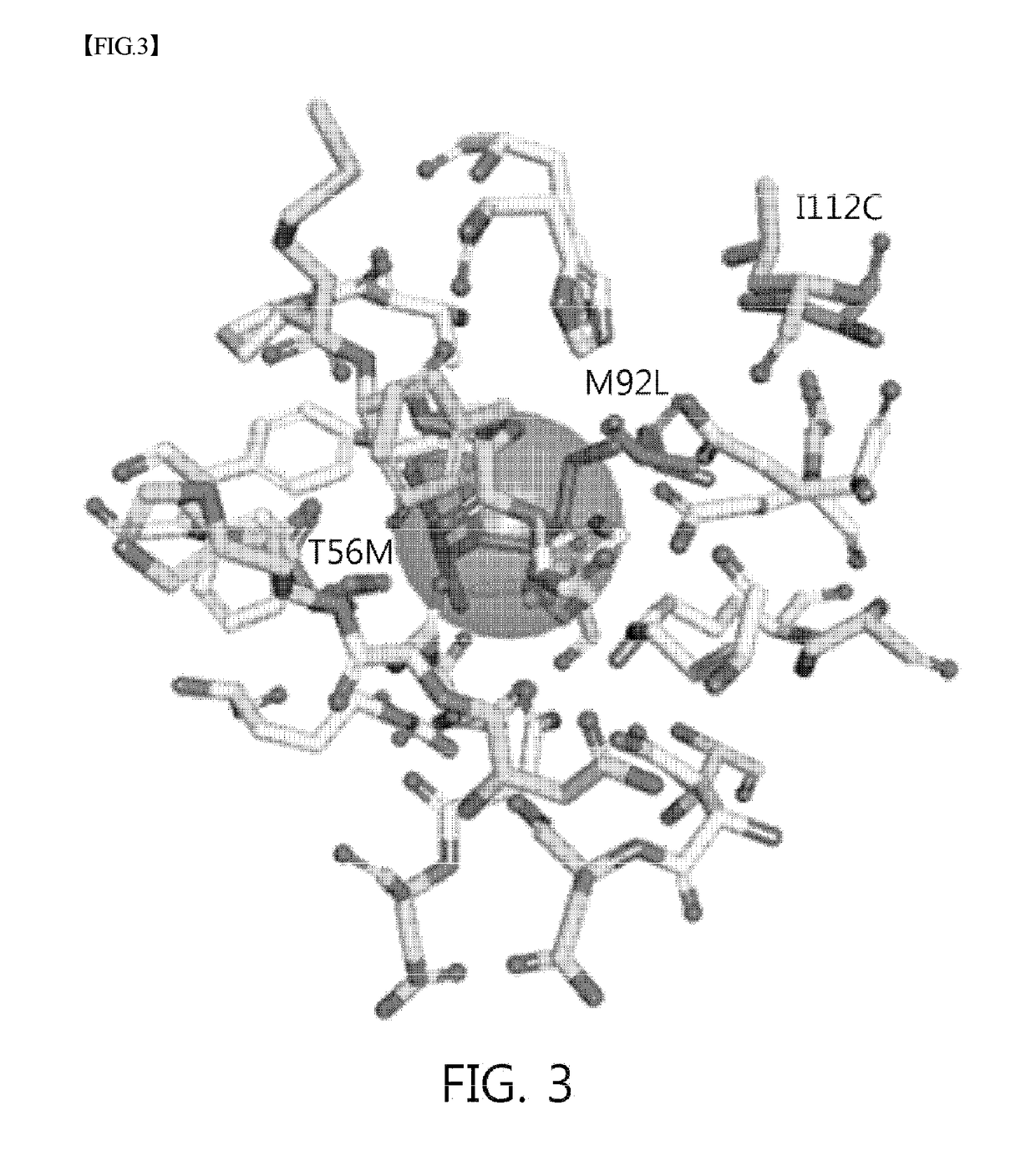
The present invention relates to improving the enzymatic activity of Escherichia coli O157:H7-derived sugar isomerase by molecular mechanics and site-directed mutagenesis. More particularly, the present invention relates to a sugar isomerase having an enzymatic activity improved by mutation, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the same, a vector comprising the nucleic acid molecule, a transformant comprising the vector, a mutant of the sugar isomerase, and a method for producing L-gulose using the improved sugar isomerase.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV IND COOP CORP
Novel affinity ligand polypeptide library of immunoglobulin G constructed based on protein A affinity model and application of design method
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for testing temperature characteristics of carbon nanotubes
ActiveCN104535859BTest accurateThe result is accurateElectrical testingDensity functional theoryCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a method for testing the temperature characteristics of carbon nanotubes. The method combines quantum mechanics and molecular dynamics, and uses density functional theory to test the conductivity of carbon nanotubes under different temperature conditions from the molecular level to the atomic level. , so as to obtain its temperature characteristics. From the perspective of quantum mechanics, combined with the method of molecular dynamics, the present invention first uses molecular mechanics to simulate the real structure of molecules in different environments, saving time and effort, and then uses quantum mechanics to calculate its temperature and conductivity properties, so that it can be quickly and accurately The method is simple and effective to obtain test results.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
A design method for tailoring-induced spontaneous curling of graphene to form carbon nanocones
InactiveCN104401967BEasy to control the lengthLength regulationMaterial nanotechnologyNumerical controlCarbon nanocone
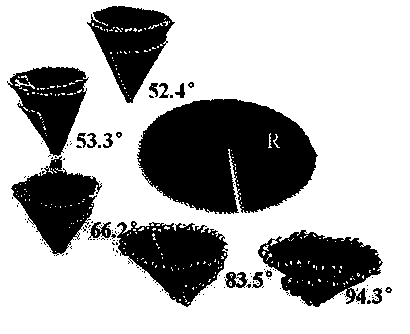
The invention provides a design method for cutting and inducing graphene to spontaneously crimp to form a carbon nanocone. The design method comprises the steps: 1) constructing circular graphene sheets in different semidiameters in MaterialsStudios software, 2) cutting out a gap in each circular graphene sheet from a circle center in any semidiameter direction, and 3) carrying out molecular mechanic optimization and dynamic simulation on the cut graphene with a Discover module in the MaterialsStudios software to form a carbon nanocone configuration finally. The invention provides the design method of change of the graphene sheets to a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) structure via cutting by using a computer simulation technology, regulation and control of structural parameters of the graphene sheets such as a cone angle and length can be achieved; and the provision of the method has important guide significance on experimental preparation of the carbon nanocone.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com