Cytomechanics device capable of synchronously realizing suction loading and fluorescence observation
A cell and fluorescence technology, applied in biochemical cleaning devices, enzymology/microbiology devices, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem that mechanical loading cannot be performed in situ, test results are difficult to quantify, and real-time dynamic detection cannot be realized, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
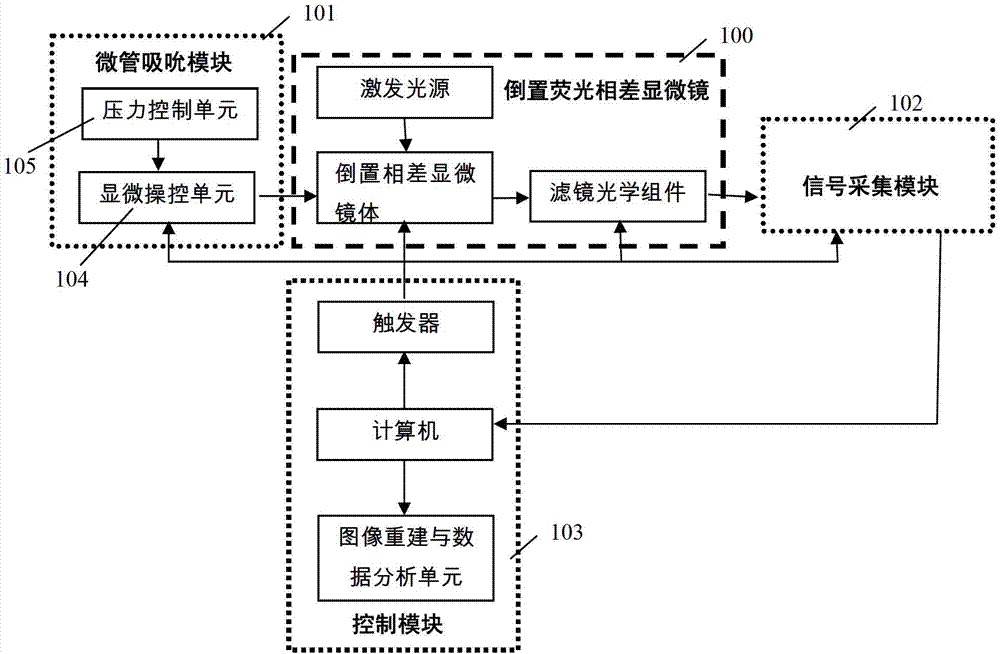
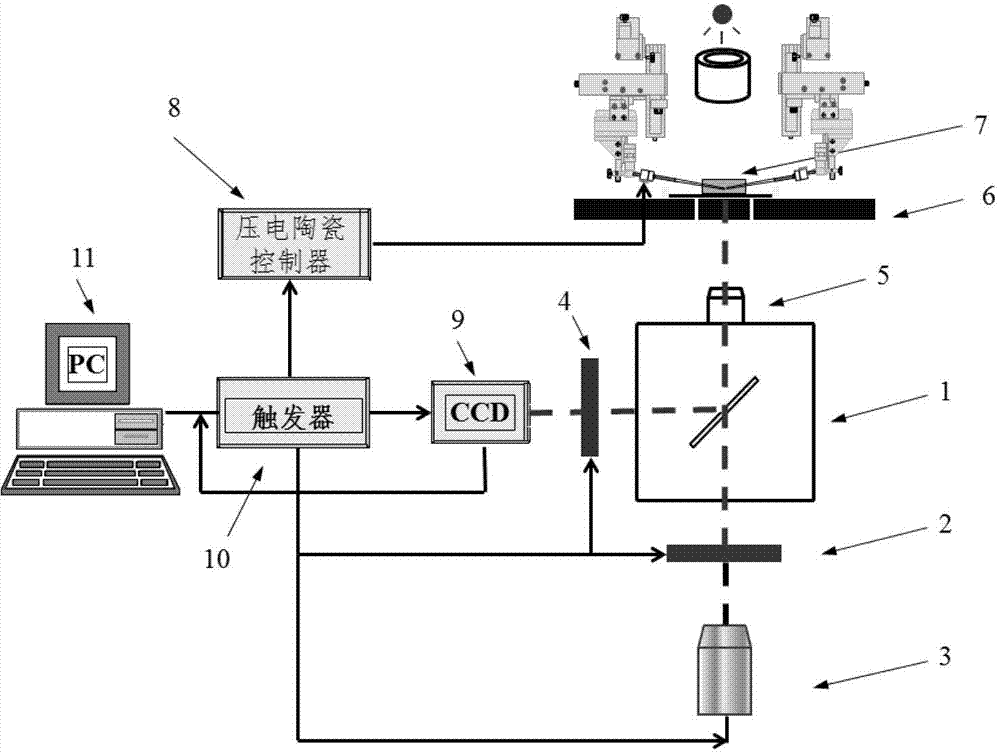
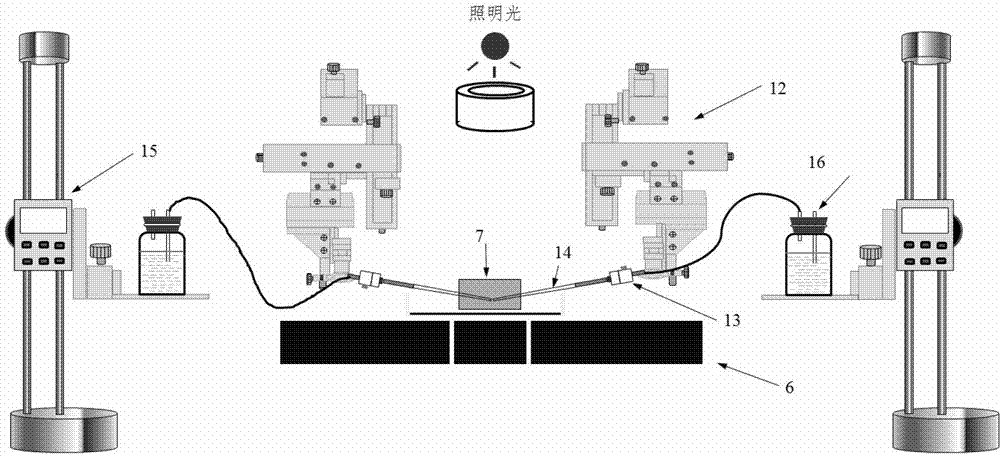
[0031] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown in , 3 , a cell mechanical device capable of sucking and fluorescence observation of the present invention is composed of an inverted fluorescence phase contrast microscope 100 , a microtube sucking module 101 , a signal acquisition module 102 and a control module 103 .
[0032] The inverted fluorescence phase contrast microscope 100 includes a microscope body 1 , an excitation filter 2 , an excitation light source 3 , an emission filter 4 , an objective lens 5 and a stage 6 . In this embodiment, the microscope body 1 adopts an Olympus IX71 inverted microscope, and the working lens is a 100 times oil lens (NA1.30). In this example, the sample cells are labeled with CFP (Cyan Fluorescence Protein, cyan fluorescent protein) (433 / 475nm excitation / emission); the excitation light source 3 is a mercury lamp (100W), and a band-pass excitation filter 4 is placed in front of the mercury lamp (420 / 20nm), allowing light with a wavelength in the rang...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com