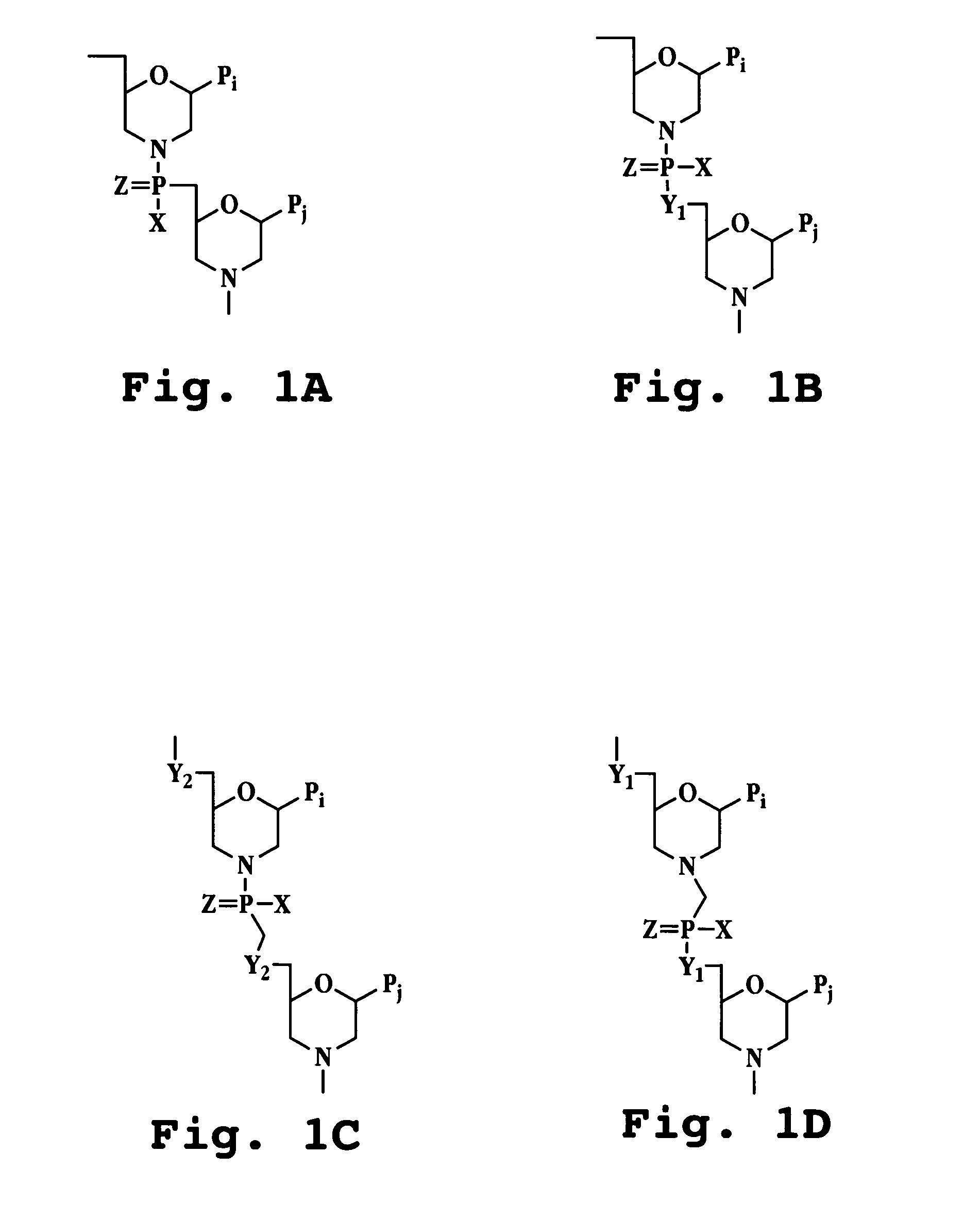
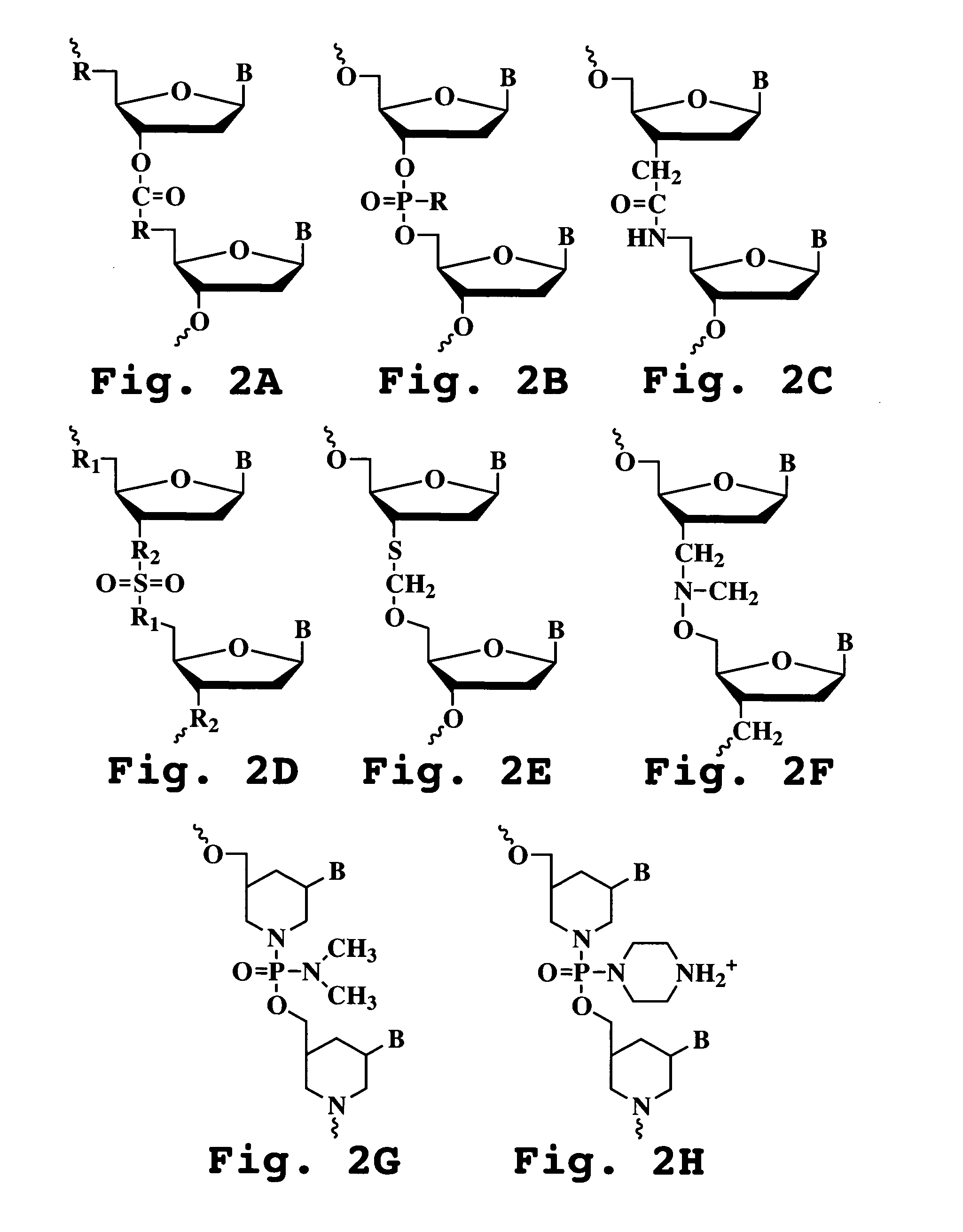
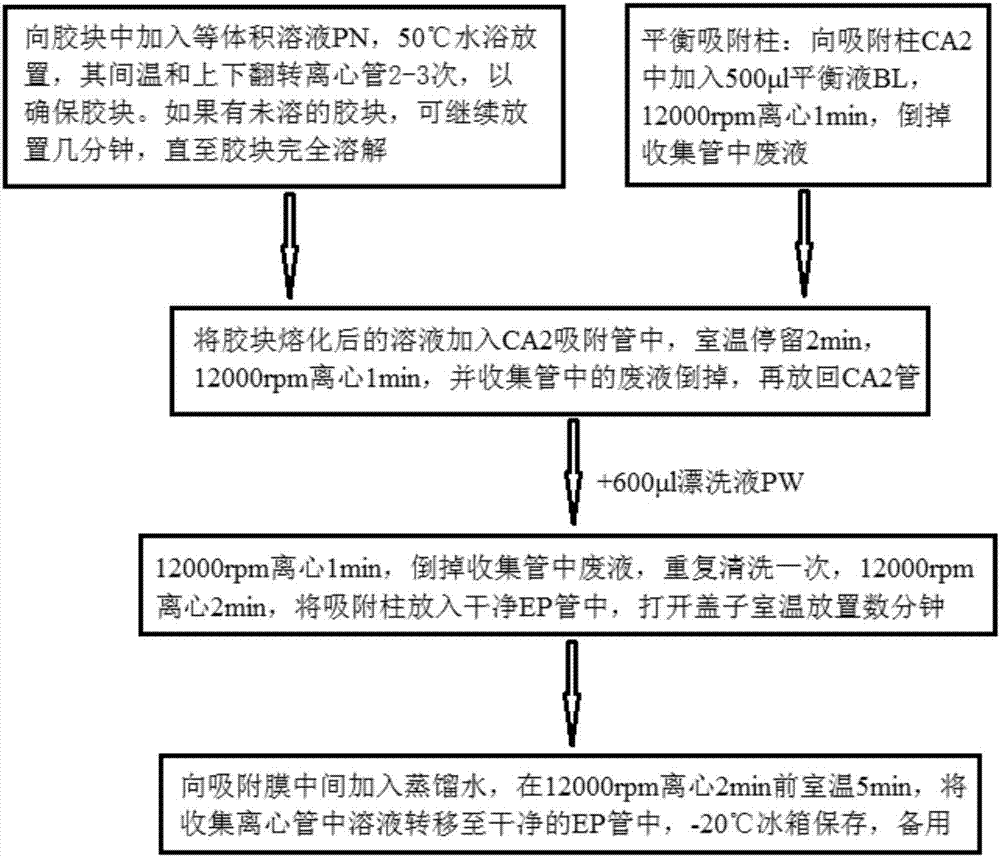
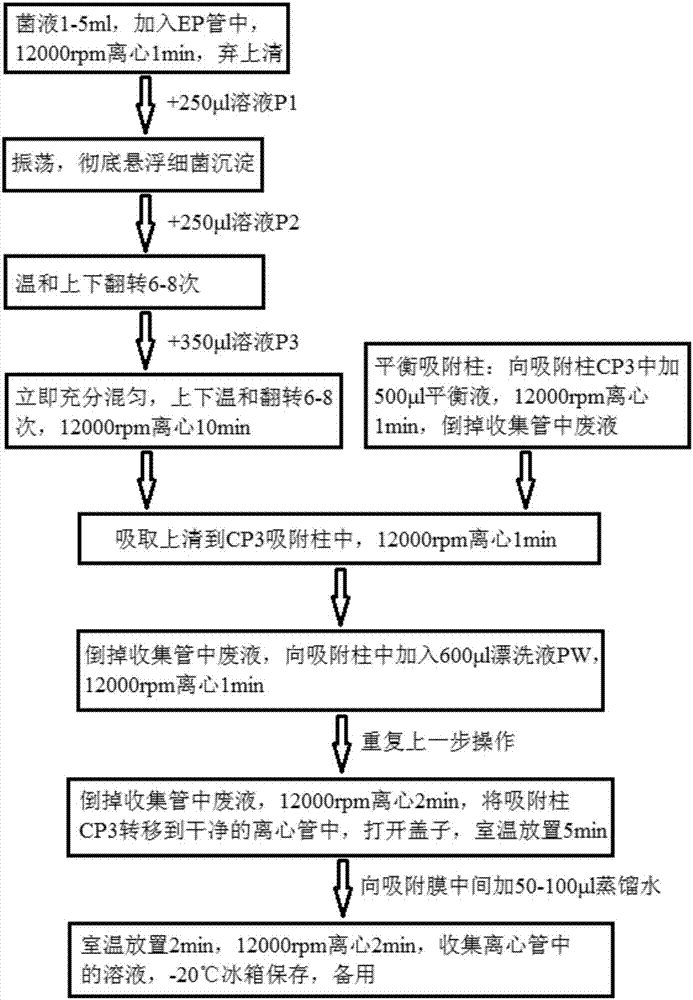
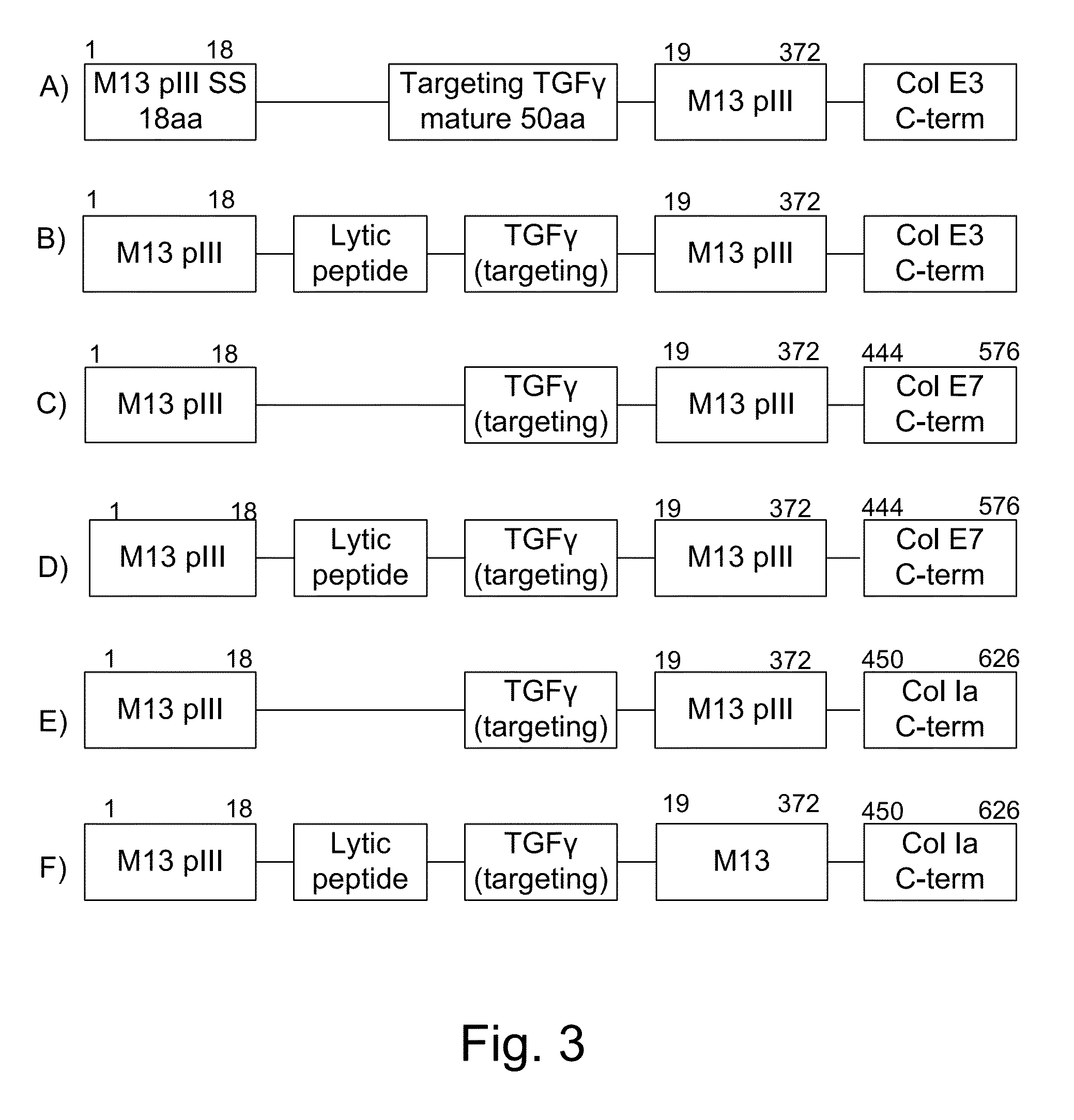
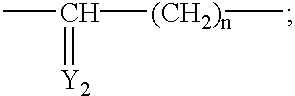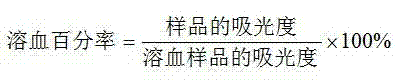Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
455 results about "Unclassified Bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
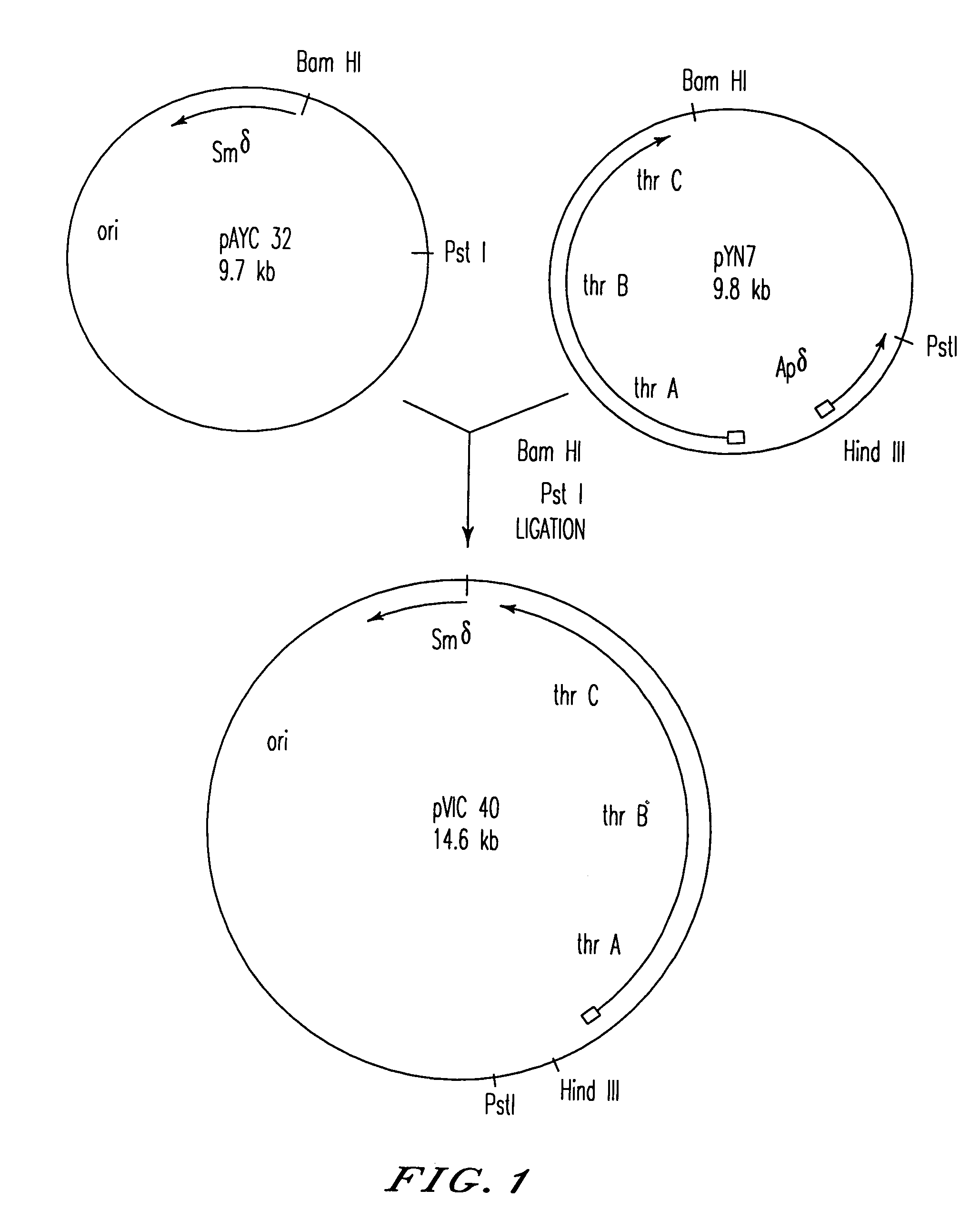
Bacterial strain of Escherichia coli BKIIM B-3996 as the producer of L-threonine
InactiveUS7138266B2High yieldHigh plasmid stabilityBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacilliThreonine dehydrogenase activity
A bacterial strain of Escherichia coli is described which produces L-threonine, and is obtained by a process comprising transduction by bacteriophage P1 which bears a transposon which inactivates threonine dehydrogenase activity, and isolation of a transductant lacking threonine dehydrogenase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
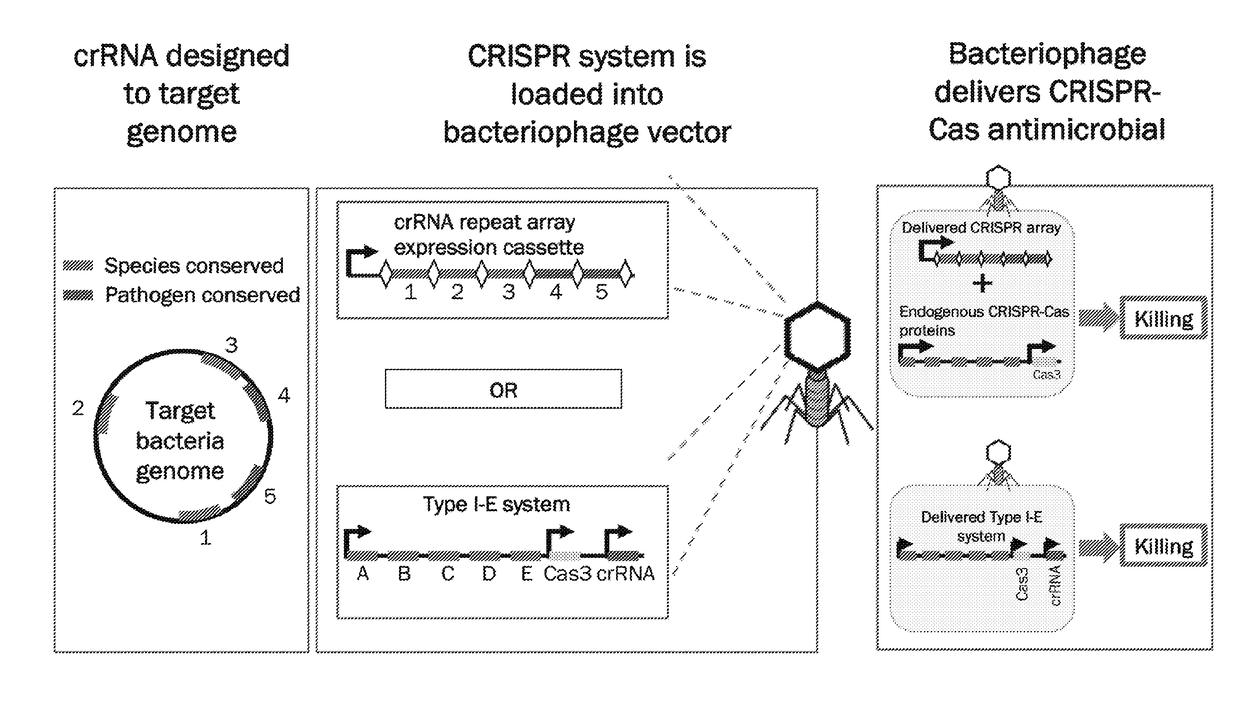
Methods and compositions for efficient delivery of nucleic acids and rna-based antimicrobials
ActiveUS20180155729A1Improve efficiencyAlters activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobial agentAntimicrobial
The invention relates to the methods for modifying the methylation pattern of bacteriophage DNA and phagemid DNA and to methods for selective killing of bacteria using lysogenic bacteriophages comprising bacteriophage DNA or phagemid DNA comprising components of an engineered CRISPR-Cas system.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Bacteriophages for reducing toxicity of bacteria
A genetically modified bacteriophage is disclosed which comprises:(i) an exogenous polynucleotide which encodes an agent which reduces the toxicity of a bacterium; and(ii) an exogenous polynucleotide which encodes a selectable marker.Uses thereof and kits comprising same are also disclosed.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
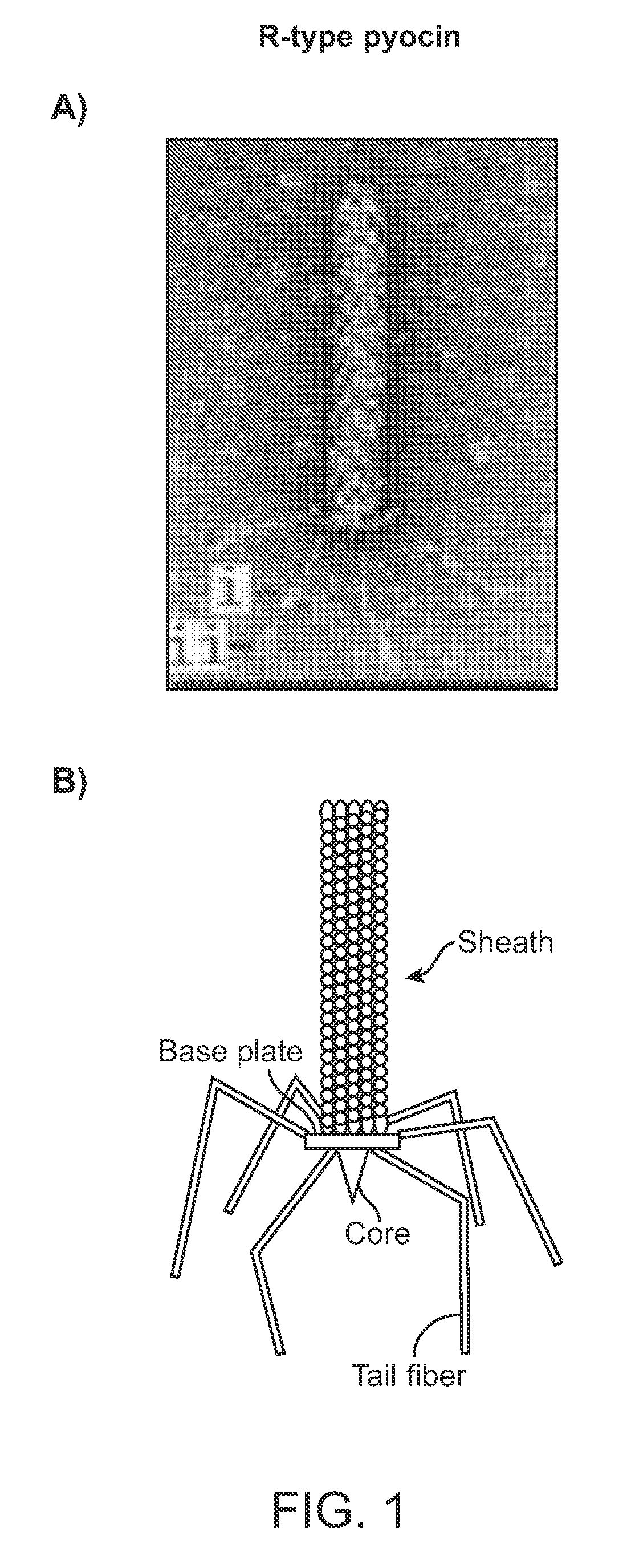
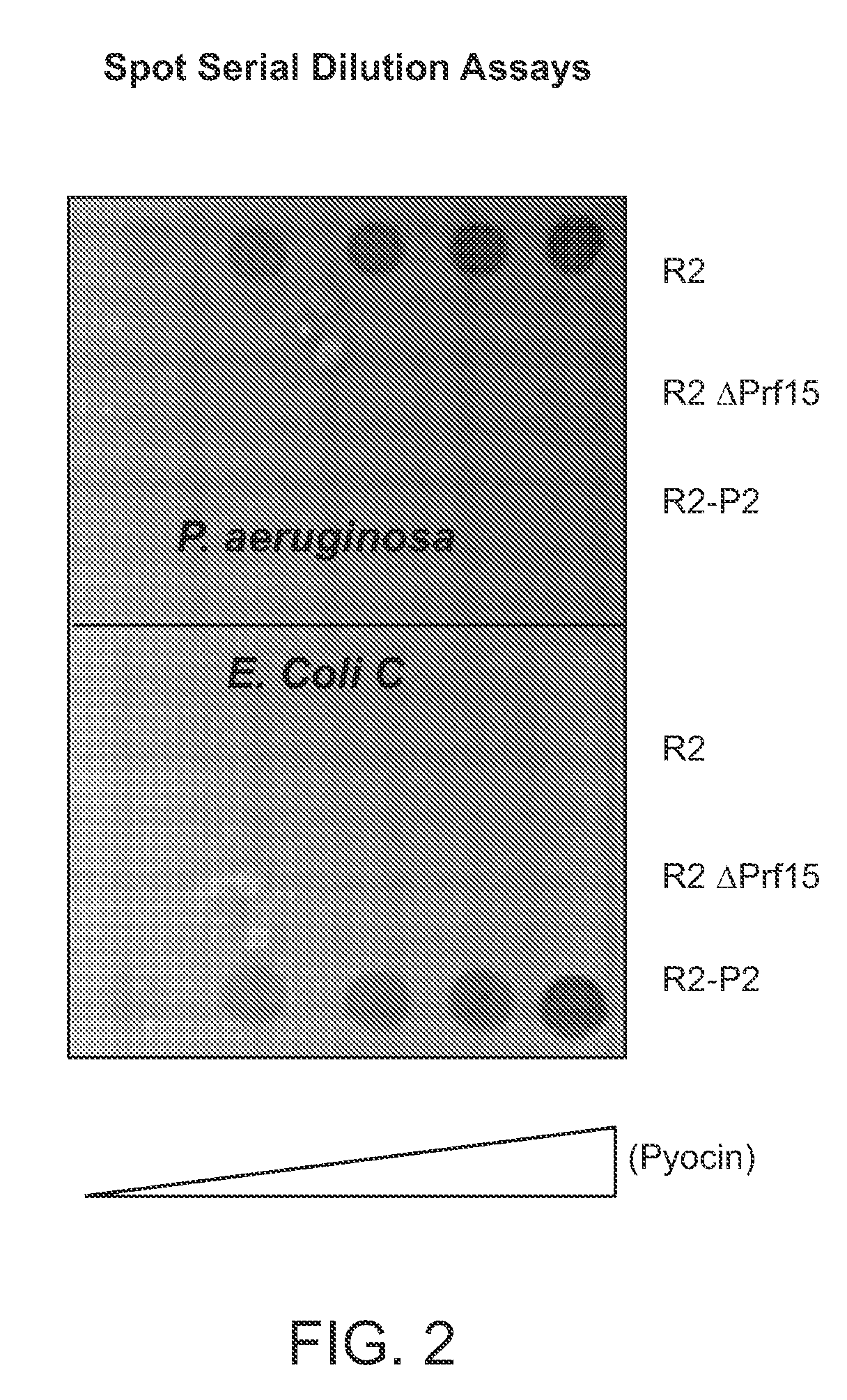
Recombinant bacteriophage and methods for their use
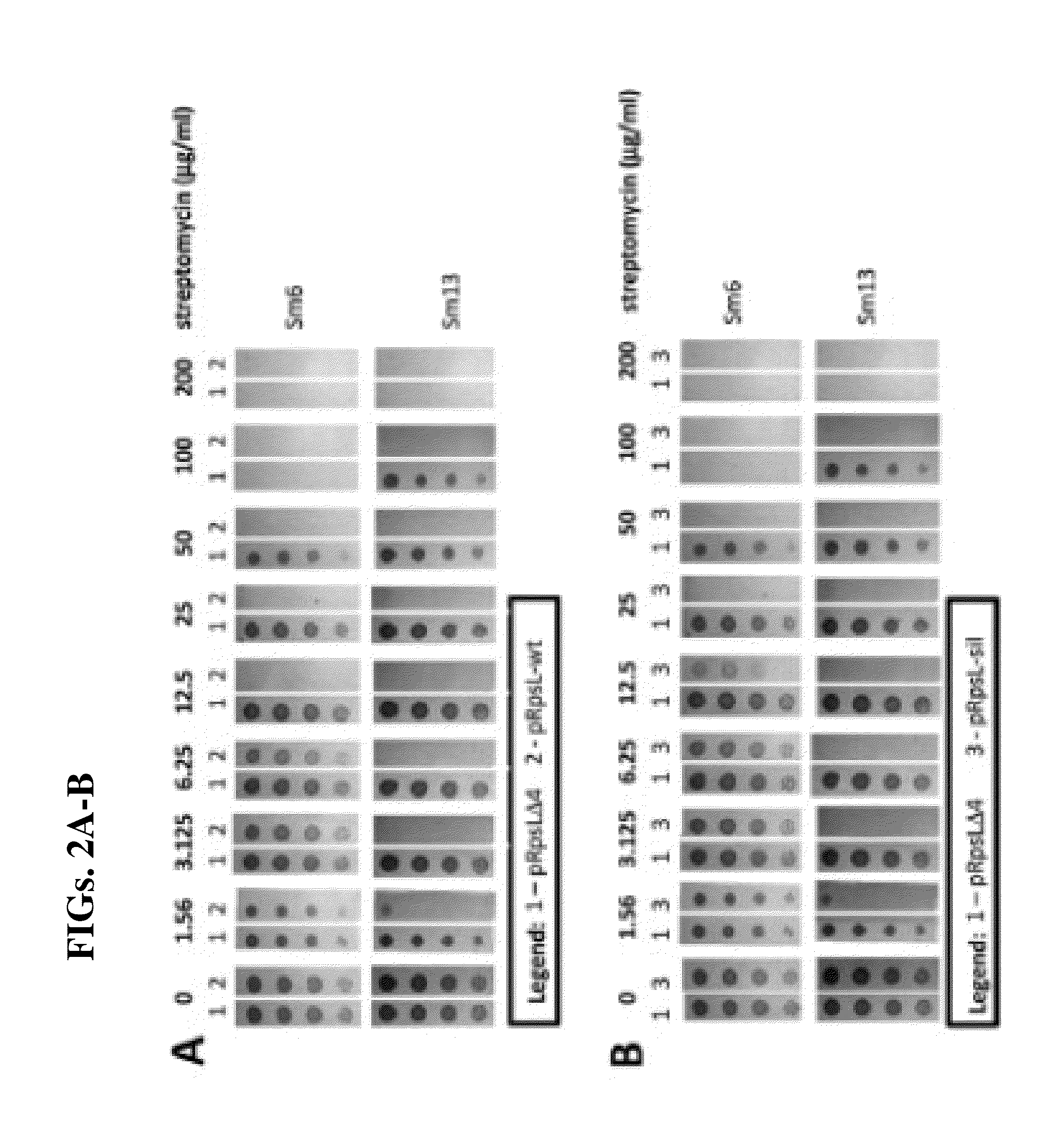
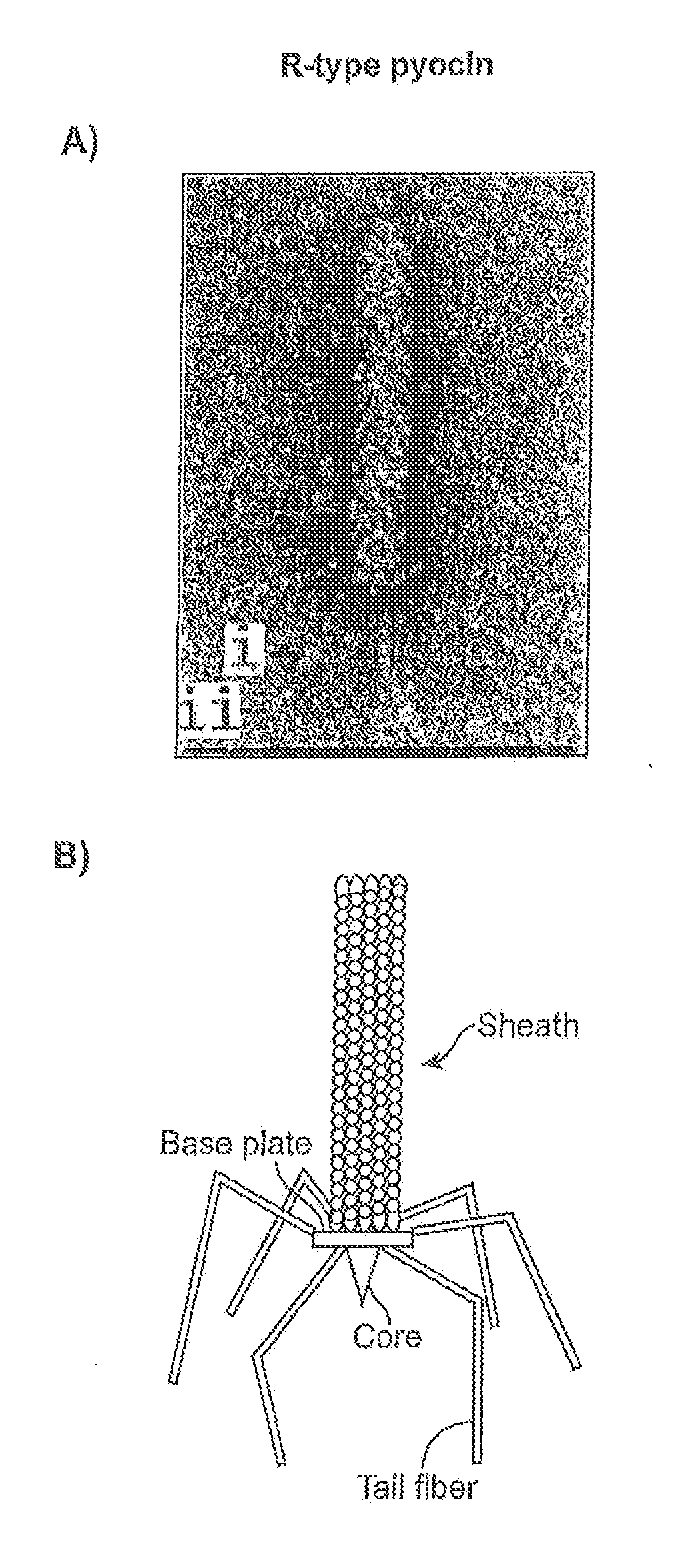
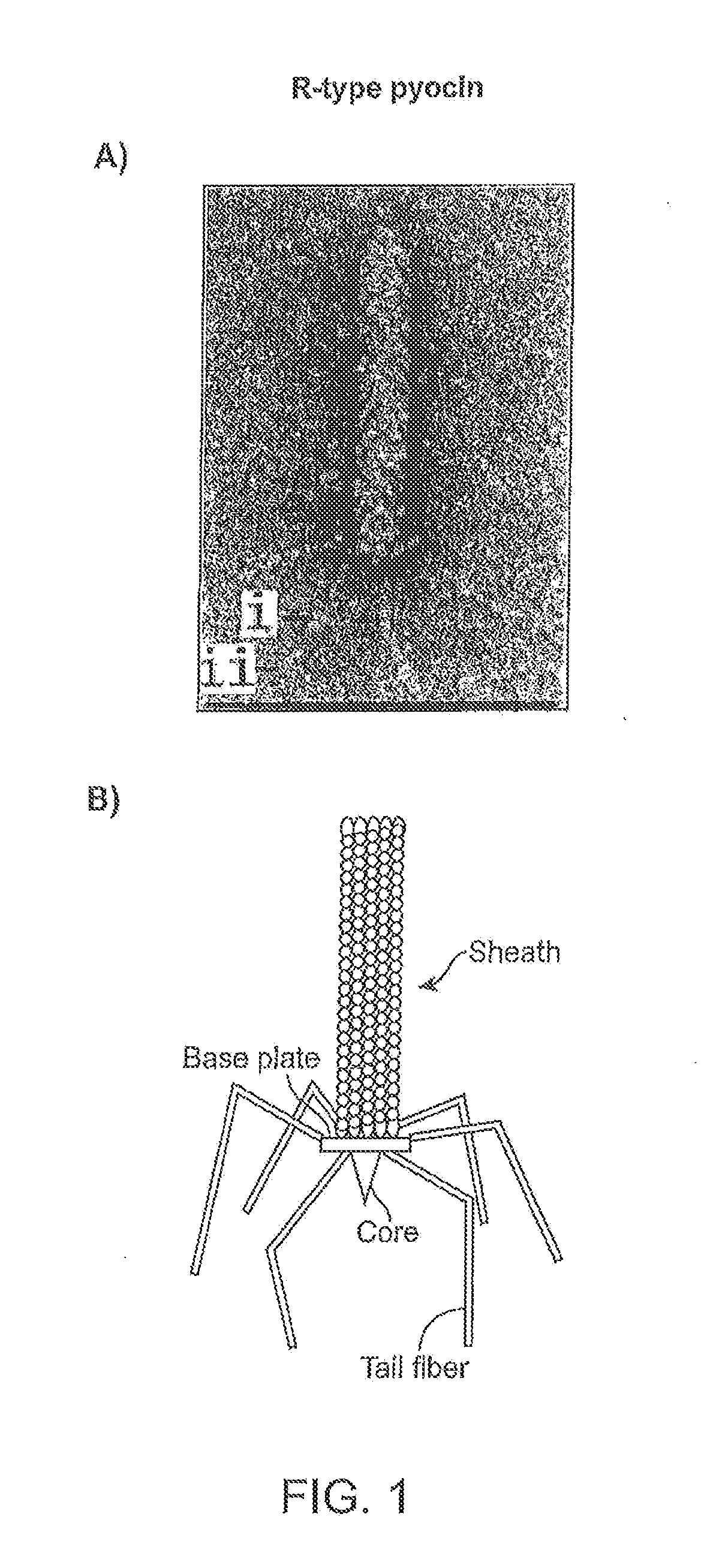
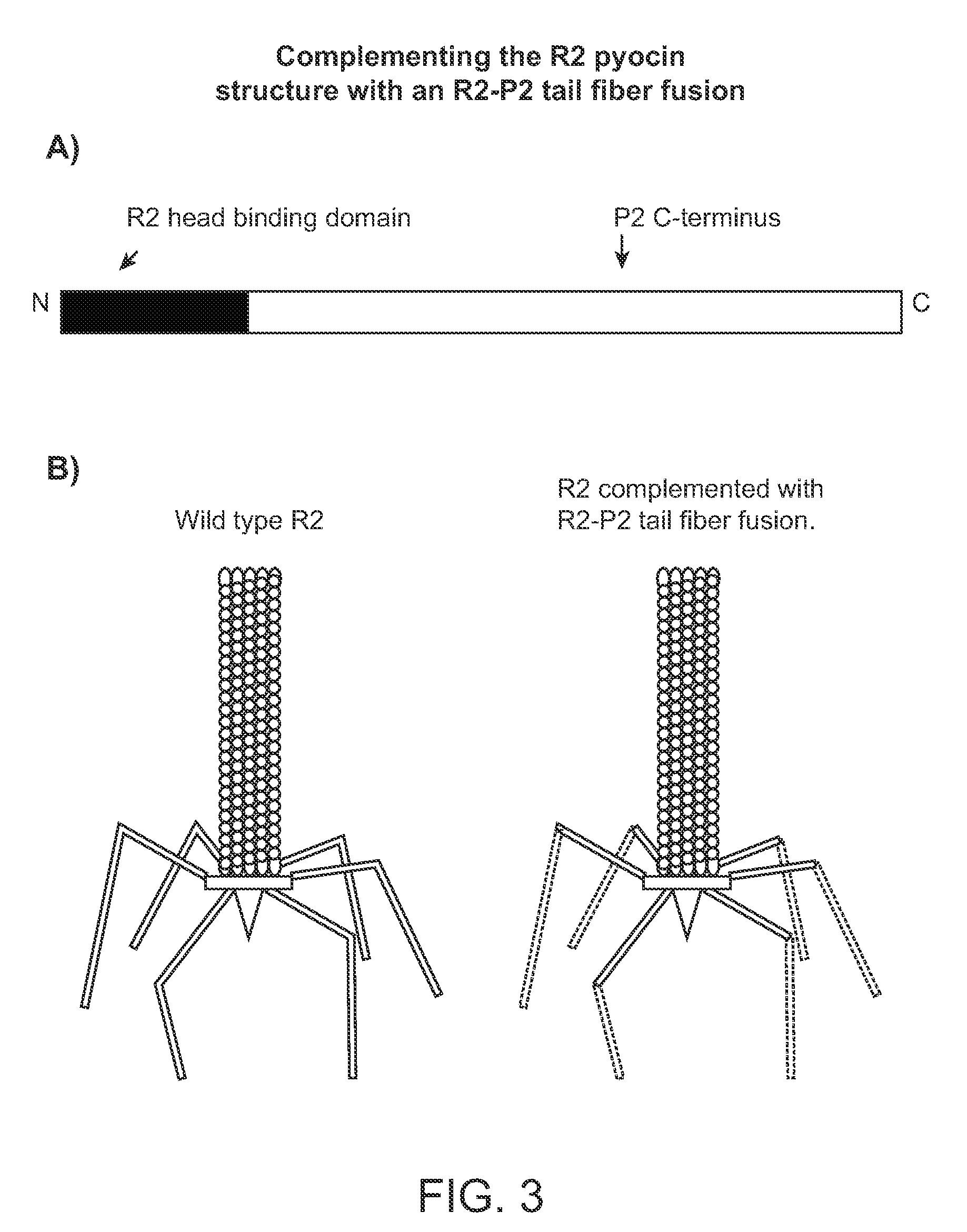
Modified forms of naturally occurring bacteriocins, such as the R-type pyocins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are disclosed as are methods for producing them in GRAS organisms. The bacteriocins are modified at the ends of their tail fibers in a region responsible for binding specificity and affinity to their cognate binding partners, or receptors, such as those on the surface of bacteria. Methods for the use of the modified bacteriocins, such as to bind receptors, including virulence or fitness factors, on the surfaces of bacteria, are also described.
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Treatment or prophylaxis of diseases caused by pilus-forming bacteria
InactiveUS6962791B2Reduce capacityReduce pathogenicityBiocideCompound screeningBacteroidesBinding free energy
Novel methods for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of diseases caused by tissue-adhering bacteria are disclosed. By interacting with periplasmic molecular chaperones it is achieved that the assembly of pili is prevented or inhibited and thereby the infectivity of the bacteria is diminished. Also disclosed are methods for screening for drugs as well as methods for the de novo design of such drugs, methods which rely on novel computer drug modelling methods involving an approximative calculation of binding free energy between macromolecules. Finally, novel pyranosides which are believed to be capable of interacting with periplasmic molecular chaperones are also disclosed.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
ActiveUS20070135333A1Inhibition of replicationSimple designAntibacterial agentsBiocideArginineNucleotide
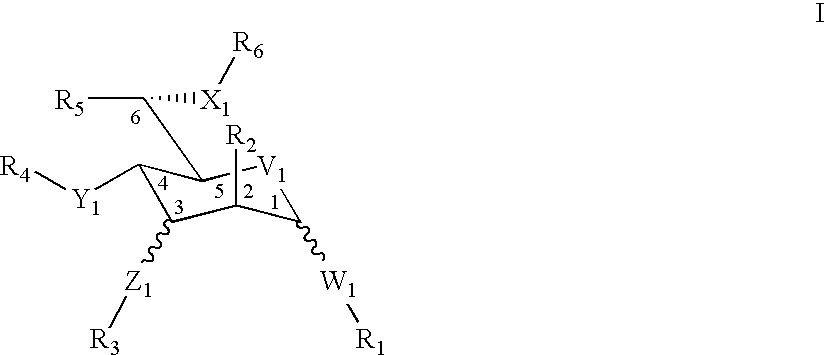
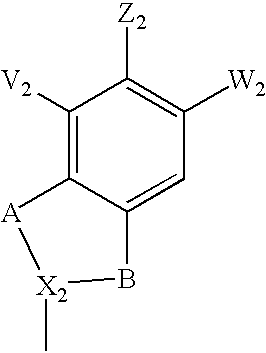
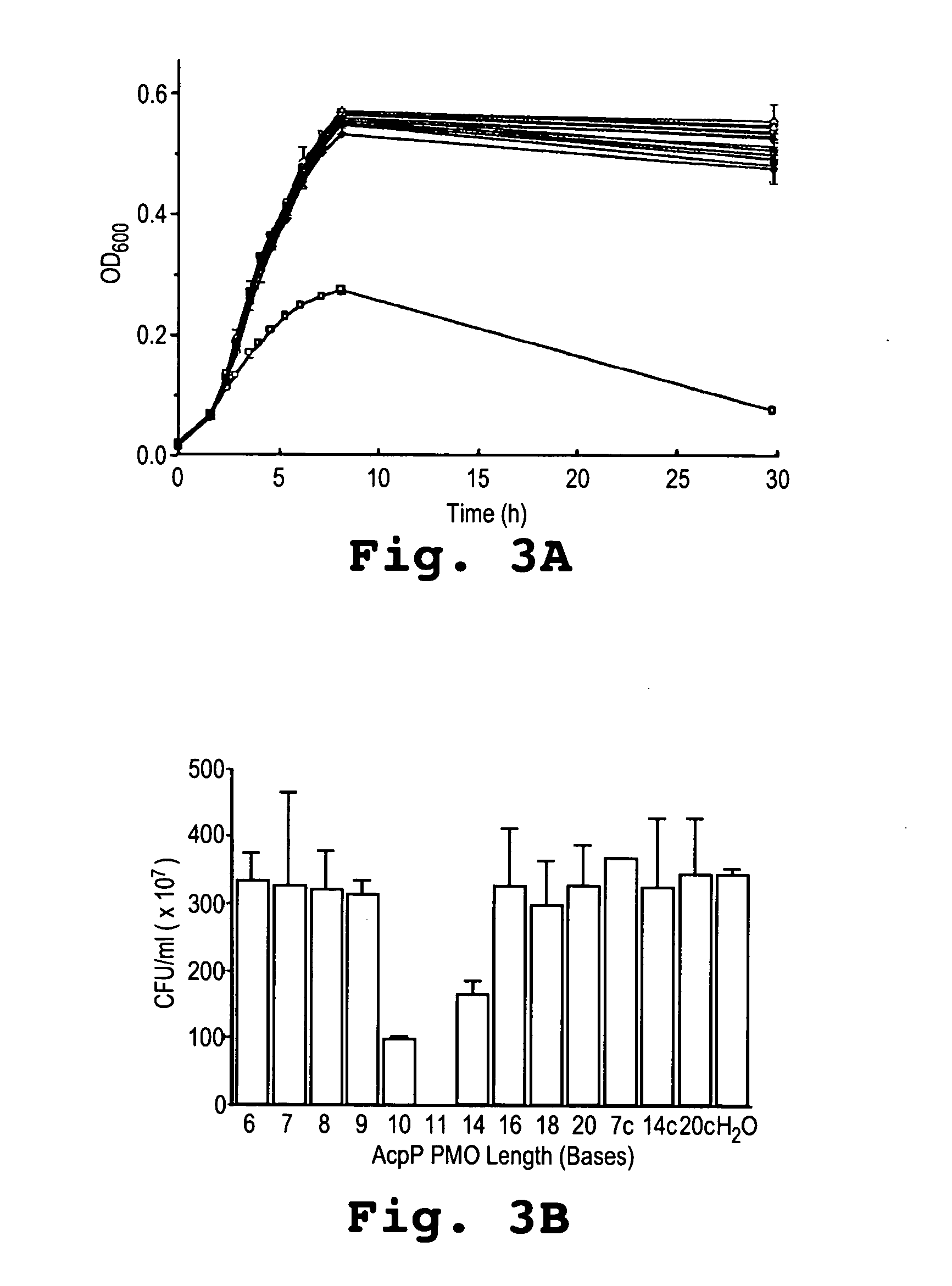
An antibacterial antisense conjugate and method of using the same for treating a bacterial infection in a mammalian host are disclosed. The conjugate includes an antisense oligonucleotide conjugated to a carrier peptide that significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the oligonucleotide. The antisense oligonucleotide contains 10-20 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication, where the compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The carrier peptide is an arginine-rich peptide containing between 6 and 12 amino acids.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107338315AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria. The kit can detect streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, baumanii, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, enterobacter cloacae, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, burkholderia cepacia, legionella pneumophila and chlamydia pneumoniae which cover clinically common pneumonia pathogenic bacteria difficult to culture. 16S rDNA and specific gene sequences corresponding to the pneumonia pathogenic bacteria are detected by combining gene chips with multiple asymmetric PCR reactions, and the categories of the bacteria in a to-be-detected sample are identified in genus and species. The kit makes up for the defect that current clinical detection of pneumonia pathogenic bacteria is not in time or comprehensive and a novel detection means for early diagnosis and early treatment of patients suffering from pneumonia is provided.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
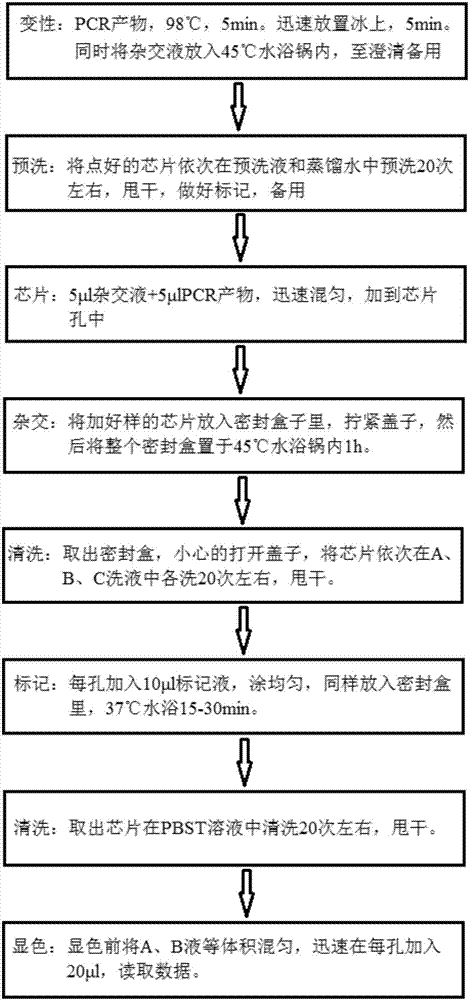
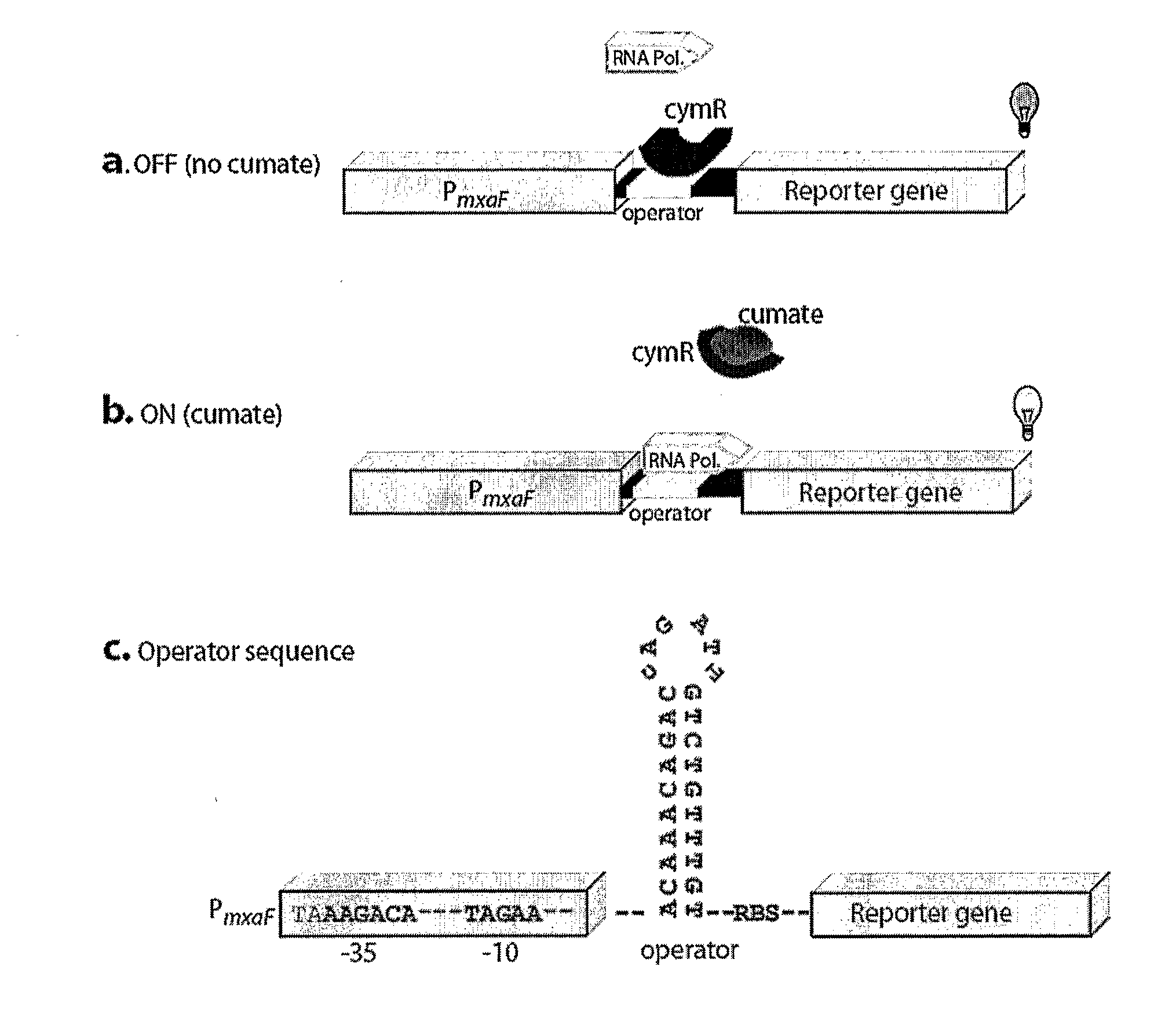
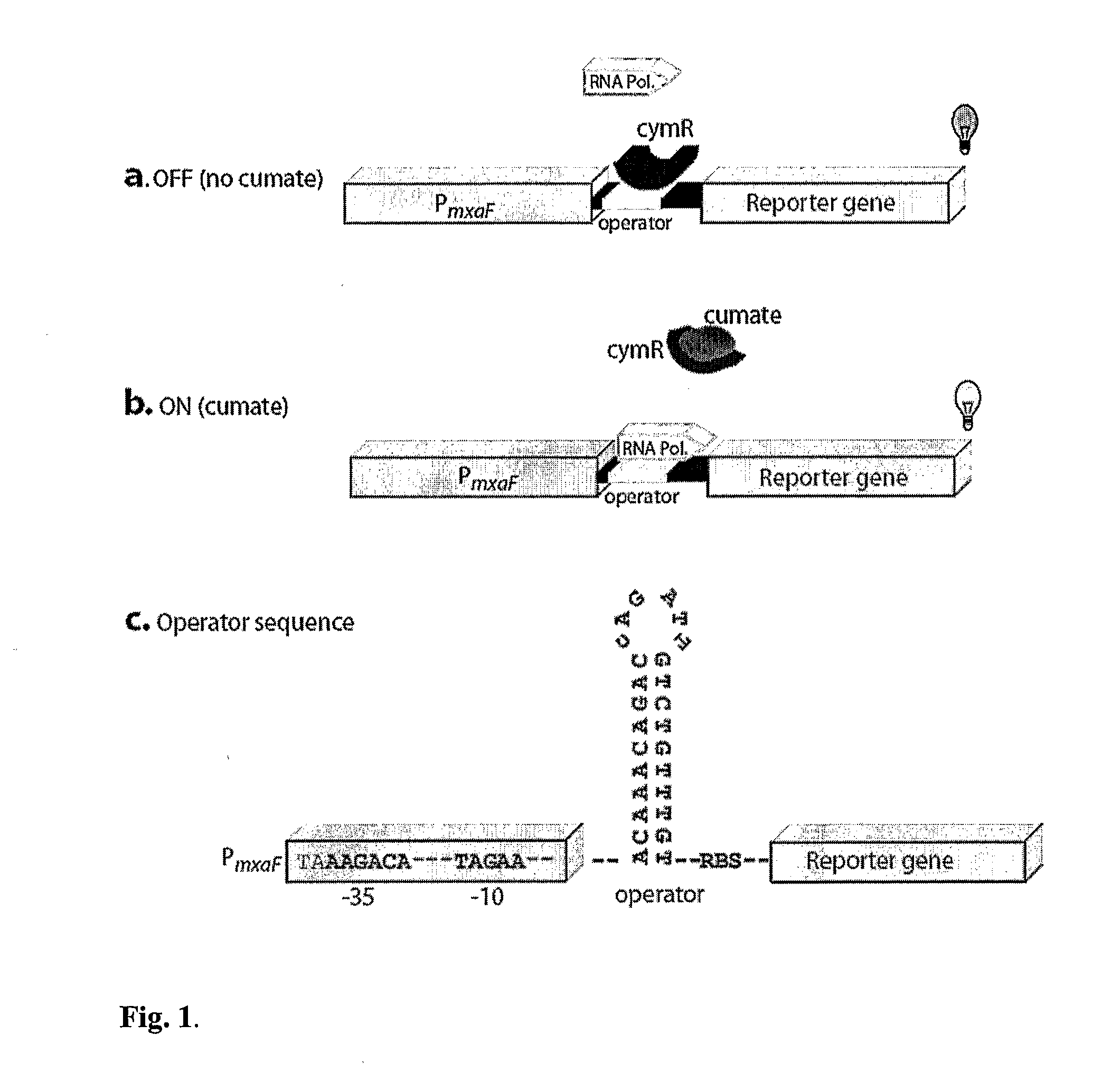
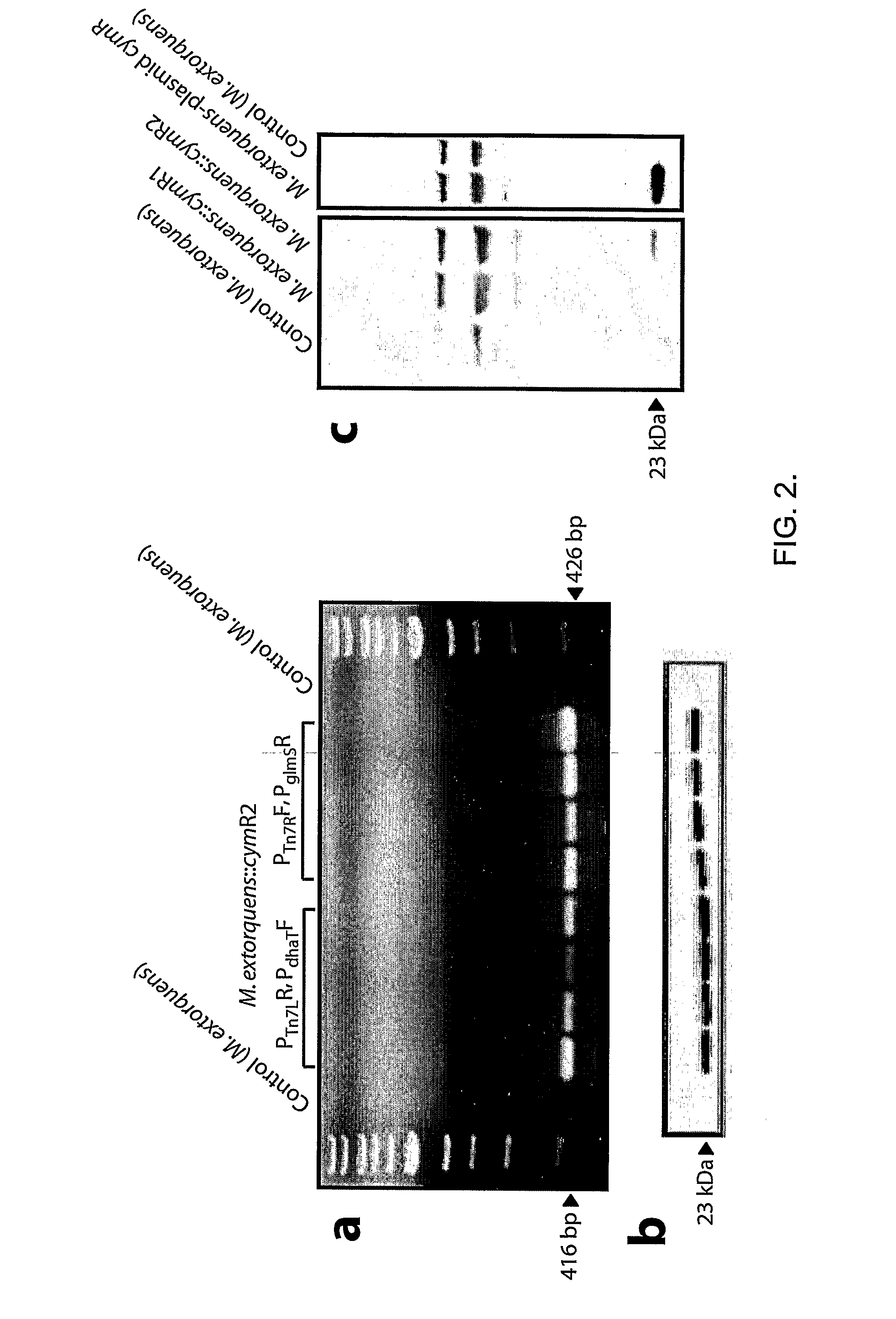
Regulation of heterologous recombinant protein expression in methylotrophic and methanotrophic bacteria
Methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria such as Methylobacterium are transformed with a gene of interest, and expression of the gene is regulated by means of a cumate repressor protein and an operator sequence which is operatively linked to the gene of interest, and the addition of an external agent. Specifically, the cymR repressor and cmt operator from Pseudomonas putida may serve to regulate gene expression in methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria with the addition of cumate.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Bacillus subtilis LFB112 as well as bacteriocin produced by same and application thereof
ActiveCN102071162ABenign sustainable developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibacterial activityBacterial strain
The invention provides bacillus subtilis LFB112 with the collection number of CGMCC No.2996. The bacterial strain has relatively high antibacterial activity and has antibacterial effect on various animal pathogenic bacteria and food pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides bacteriocin produced by the bacterial strain, wherein the bacteriocin is relatively stable against heat and acid and has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect without inhibiting beneficial bacteria. Experiments indicate that the bacterial strain LFB112 provided by the invention and the bacteriocin produced by the same can be used for improving the clinical symptoms of chicken and increasing the growth speed and feed price, and can be used in biological veterinary medicaments or feed additives.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
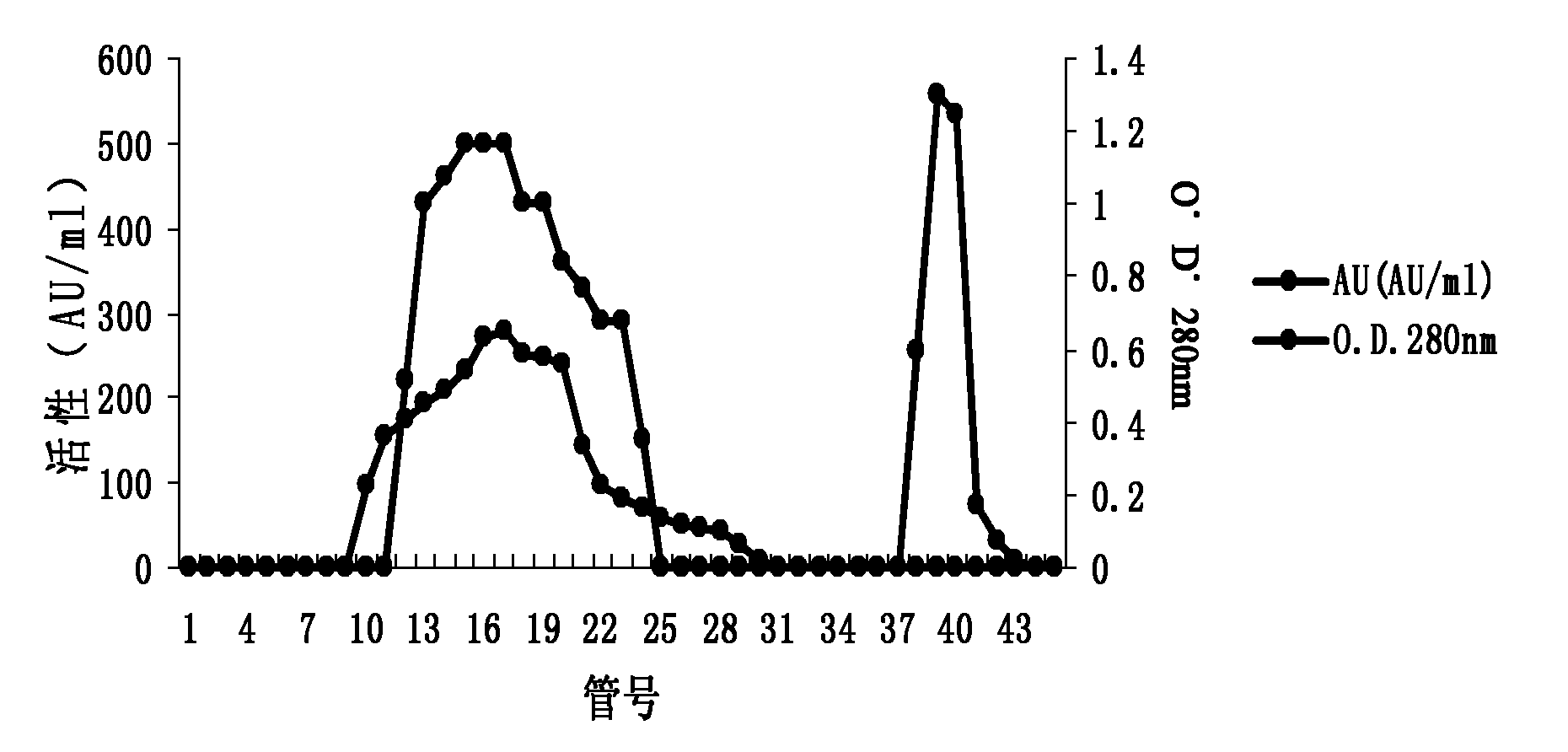
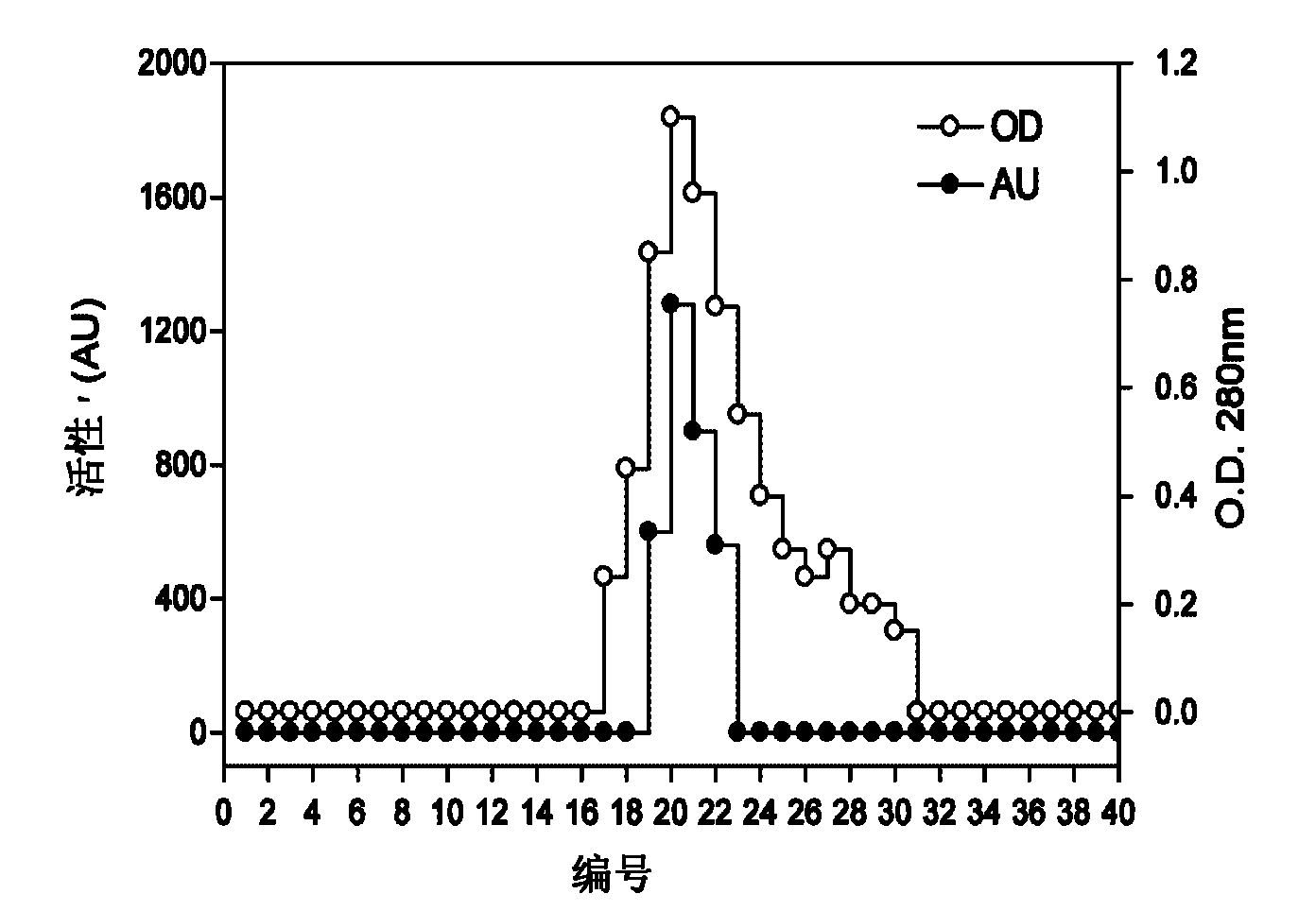
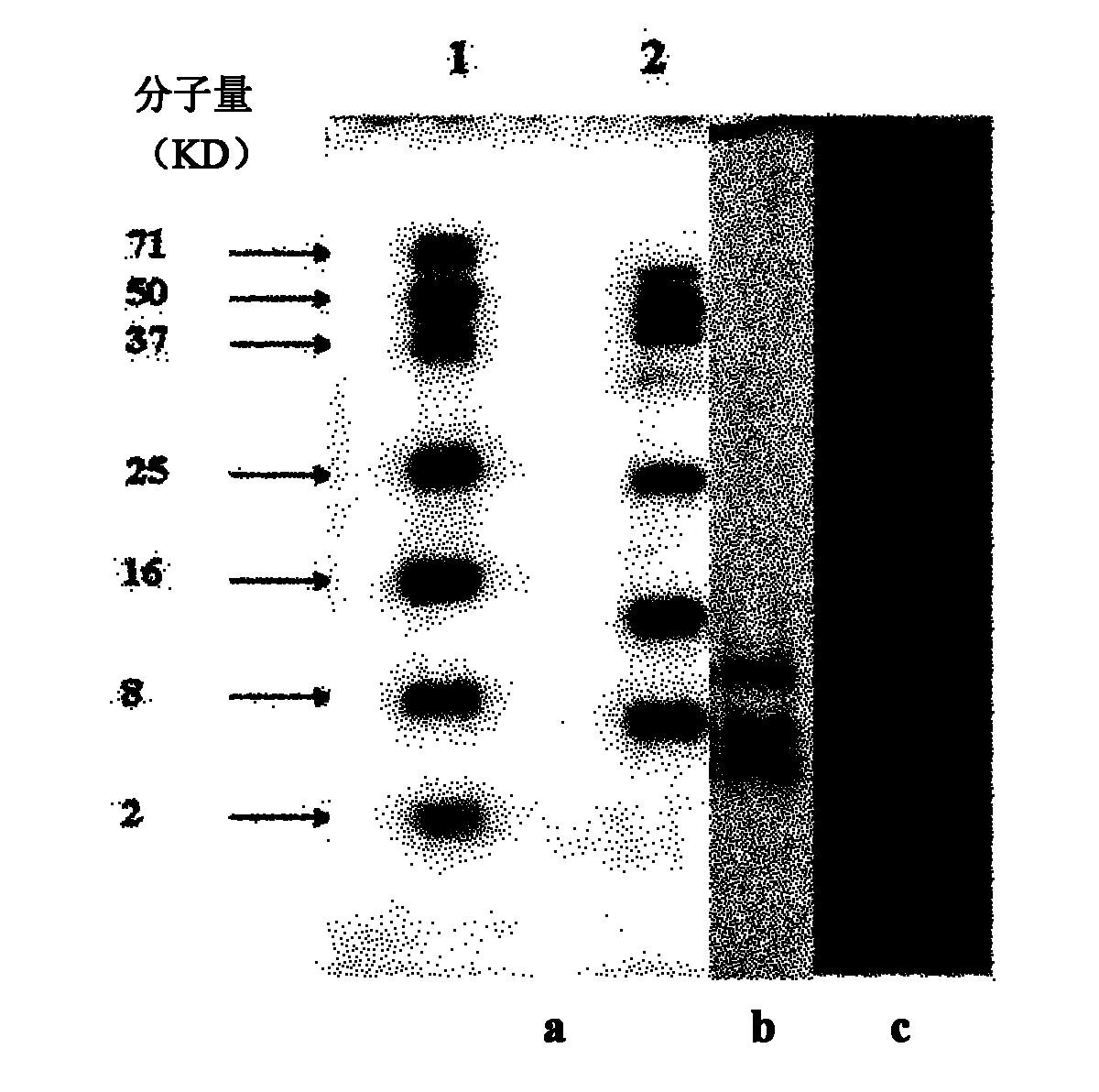
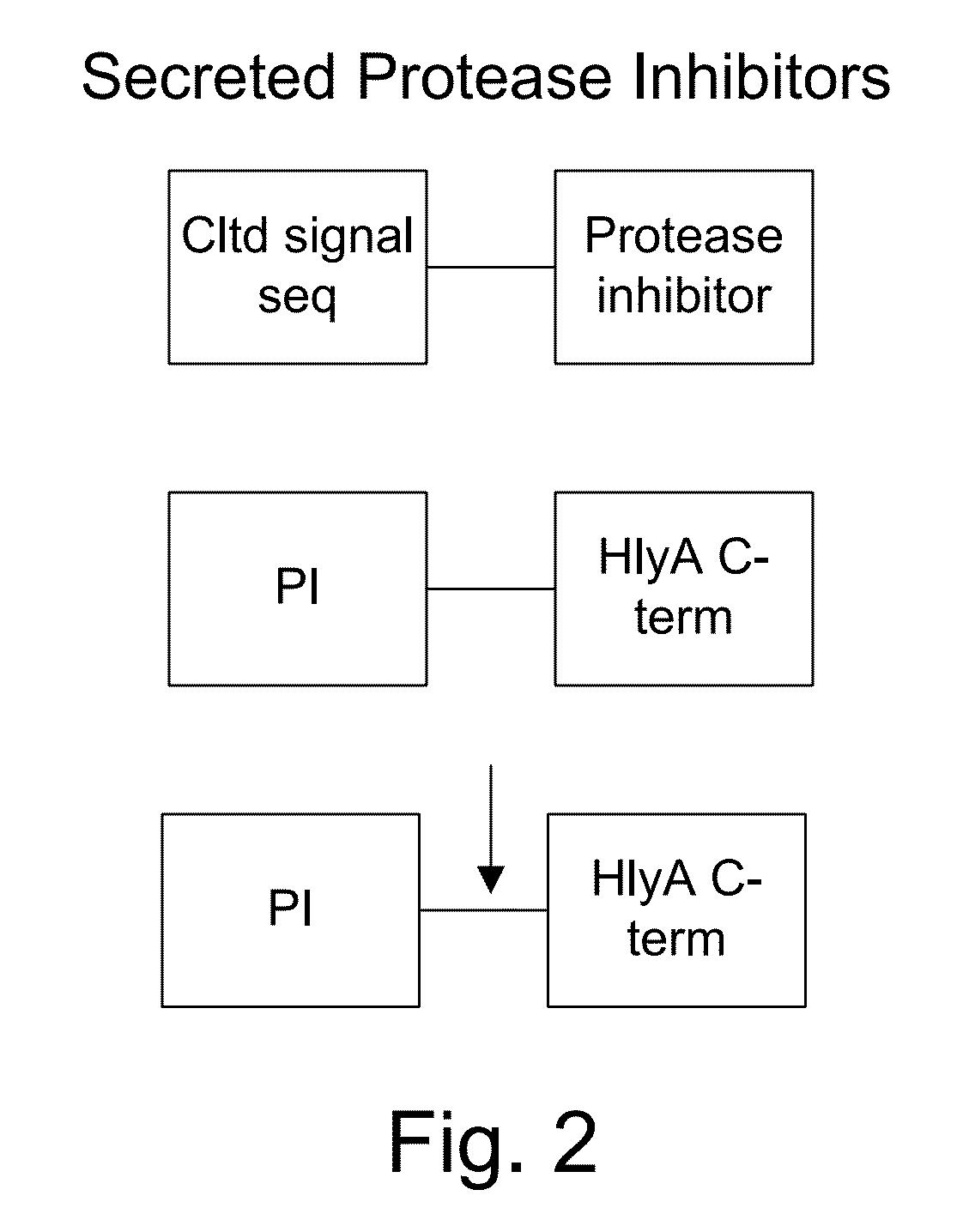
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system and method improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins and phage and phagemids delivered by bacteria
The present invention uses co-expression of protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents that results in their localized production within the target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. Inactivation is also accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic construct for proteases, preferably those that are under-expressed within the target tissue yet present in non-target tissues within the body, resulting in therapeutic activity within the target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria are also described. The chimeric proteins include chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells and cells of the immune system. Novel combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria capable of delivering phage / phagemids expression cassettes for DNA and RNA-based therapeutics are also described.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Melittin and use thereof
InactiveCN1704431AInhibition of death protectionSuppression of respiratory burstAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMelittinAmino acid
The invention discloses Melittin, a micro-molecular polypeptide of amino acid type antibacterial / mAb with the formula of INLKAIAALAKKLL-NH2. The invention can be applied for the preparation of medicaments for eradicating bacteria and treating pyaemia.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
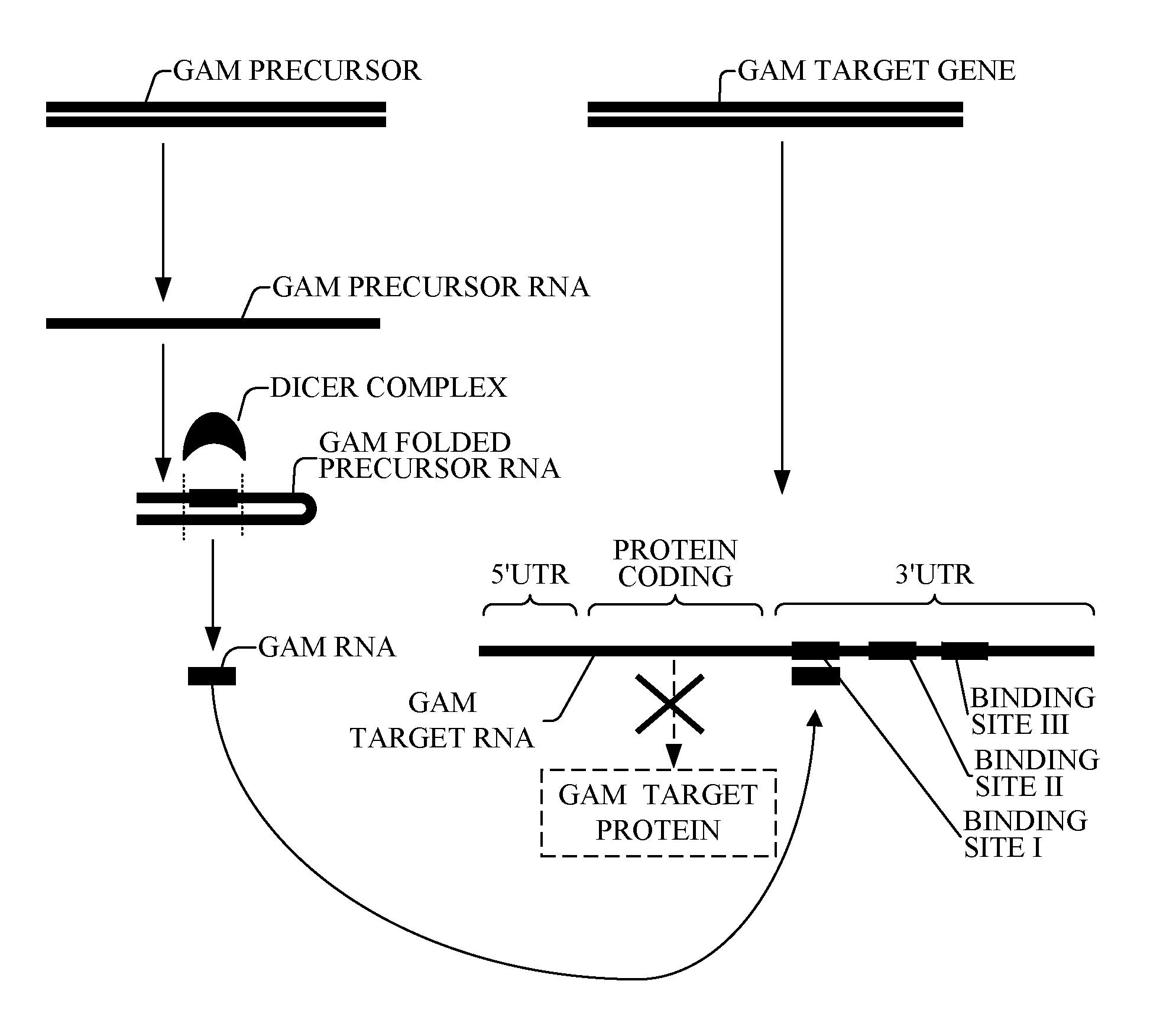
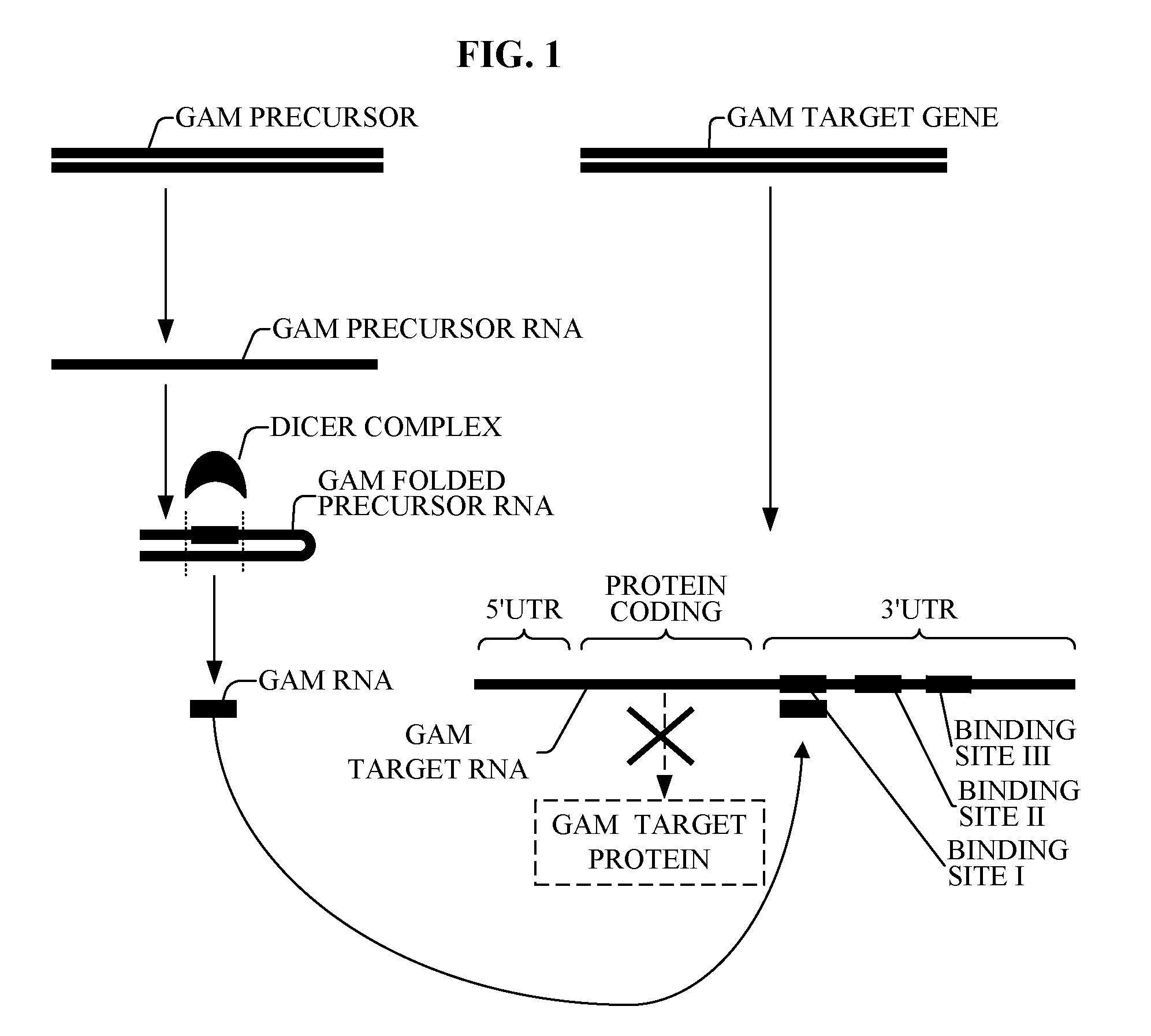
Bioinformatically detectable group of novel regulatory bacterial and bacterial associated oligonucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070042982A1Preventing and treating bacterial diseasesSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideBacterial disease
The present invention relates to a first group of novel bacterial and human associated oligonucleotides, here identified as Genomic Address Messenger or GAM oligonucleotide, and a second group of novel operon-like bacterial and human polynucleotides, here identified as Genomic Record or GR polynucleotide. GAM oligonucleotides selectively inhibit translation of known ‘target’ genes, many of which are known to be involved in various bacterial diseases. Nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding 6444 GAM precursors oligonucleotides, and 726 GR polynucleotides, as are vectors and probes both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides and specific functions and utilities thereof, for detecting expression of GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides, and for selectively enhancing and selectively inhibiting translation of the respective target genes thereof.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
ActiveUS20070021362A1Growth inhibitionSimple designAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCompound aStart codon
A method and antisense compound for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacterial cells are disclosed. The compound contains no more than 12 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence of no fewer than 10 bases in length that is complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication. The compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The relatively short antisense compounds are substantially more active than conventional antisense compounds having a targeting base sequence of 15 or more bases.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Composition and method of treating mastitis
InactiveUS20070077235A1Improve purification effectPromote sportsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLyaseMastitis
A composition and method for treating bacterial infections by the use of an effective amount of at least one lytic specific for the bacteria causing specific. The lytic enzyme is genetically coded for by a bacteriophage which may be specific for said bacteria. The enzyme may be at least one lytic protein or peptides in a natural or modified form.
Owner:LOOMIS LAWRENCE +1
L-amino acid producing bacterium and method of producing l-amino acid
ActiveUS20090258401A1Efficient productionEasy to useSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyAmino acid
L-amino acid is produced by culturing a bacterium belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family which has L-amino acid-producing ability and is modified so that expression of the nhaA gene, nhaB gene, nhaR gene, chaA gene, mdfA gene, or combinations thereof is enhanced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
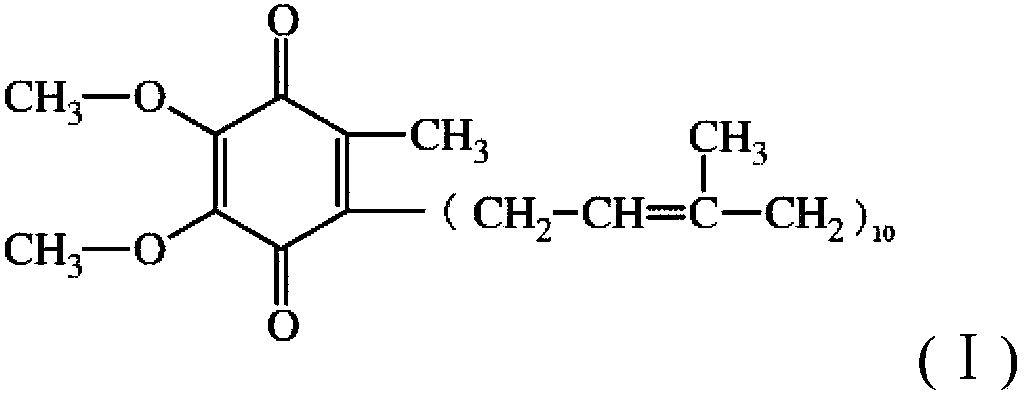
Coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and application thereof
ActiveCN103509816AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps that: a, total genomic DNA is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides cacterial liquid; b, UbiG gene is obtained by amplification with a polymerase chain reaction; c, the amplified UbiG gene is connected with broad-host plasmid, such that recombinant vector is constructed; d, the recombinant vector is transferred to Escherichia coli S17-1; and e, the Escherichia coli S17-1 is subjected to conjugal transfer with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides, such that the engineered bacteria are obtained. According to the method provided by the invention for improving coenzyme Q10 yield through regulating Rhodobacter sphaeroides aromatic ring modification pathway, the operation is simple, and coenzyme Q10 synthesis capacity can be improved by higher than 30%. The method is suitable for coenzyme Q10 large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
Primers and method of detecting bacteria
InactiveUS20050176001A1Rapidly and easily detectingEasily and rapidly presence and absenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacilliSalmonella
The first primer of the invention is a primer which, when used in PCR under appropriate conditions, serves to detectably amplify 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs of bacteria of the Escherichia, Salmonella and Vibrio genera, but when used in PCR under the same conditions, does not serve to detectably amplify either chloroplast 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs or mitochondrial 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs. The second primer of the invention is a primer which, when used in PCR under appropriate conditions, serves to detectably amplify 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs of Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus, but when used in PCR under the same conditions, does not serve to detectably amplify either chloroplast 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs or mitochondrial 16S rRNA-encoding DNAs.
Owner:NISSIN YORK
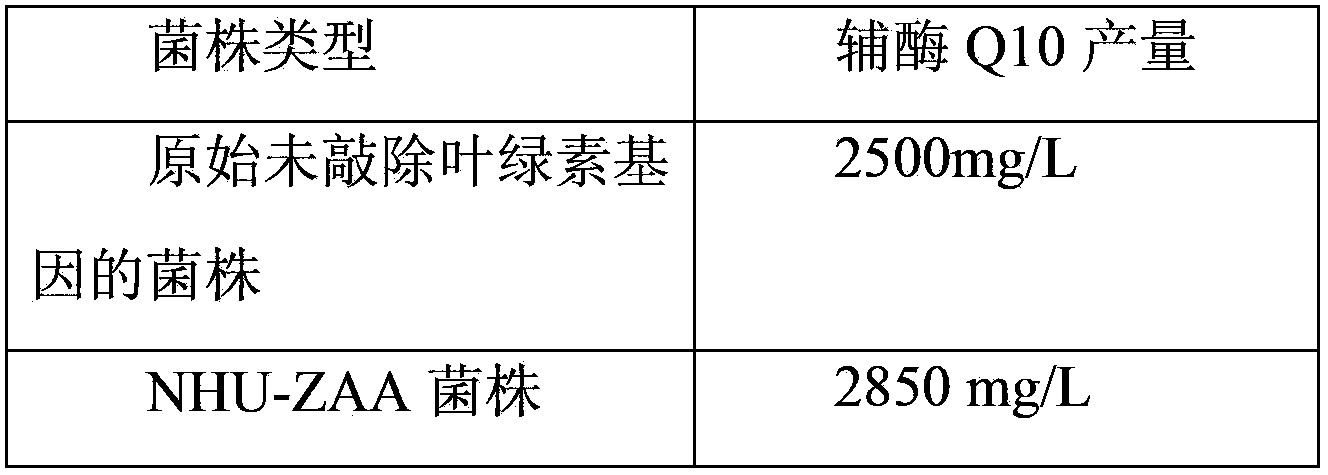
Coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and application thereof
ActiveCN103509728ALarge amount of synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGenomic DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps that: a, total genomic DNA is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides cacterial liquid; b, bchG homologous gene is obtained by amplification with a polymerase chain reaction; c, the amplified homologous gene is connected with broad-host plasmid, such that recombinant vector is constructed; d, the recombinant vector is transferred to Escherichia coli S17-1; and e, the Escherichia coli S17-1 is subjected to conjugal transfer with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides, such that the engineered bacteria with chlorophyll synthesis gene bchG knocked out are obtained. According to the method provided by the invention for improving coenzyme Q10 yield through knocking out Rhodobacter sphaeroides chlorophyll synthesis gene, coenzyme Q10 synthesis capacity can be improved by higher than approximately 15%. The method is suitable for coenzyme Q10 large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
Modified bacteriocins and methods for their use
Owner:PYLUM BIOSCI INC
Attenuated bacteria useful in vaccines
InactiveUS20050054075A1Improve protectionReliable and rapid isolationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacterial strainImmunogenicity
The invention provides strains of bacteria, especially enterotoxigenic E. coli, attenuated by mutations in the genes encoding enterotoxins (LT, ST, EAST1) and optionally further attenuated by deletion of additional chromosomal genes. In addition the invention provides strains of attenuated bacteria expressing immunogenic but non-toxic variants of one or more of these enterotoxins. These bacteria are useful as a vaccine against diarrhoeal disease.
Owner:ACAMBIS RES LTD
Acid-proof and high-temperature resistant alpha-amylase and production thereof
A fire-resistant and acid-proof alpha-amylase and its production are disclosed. The process is carried out by separating precursor-alpha-amylase gene from lichenized bacillosporin, mutating for L134 and S320 amino acid residues and high-efficient expressing alpha-amylase mutant in bacterium. It achieves better safety, expression and acid stability, and more yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
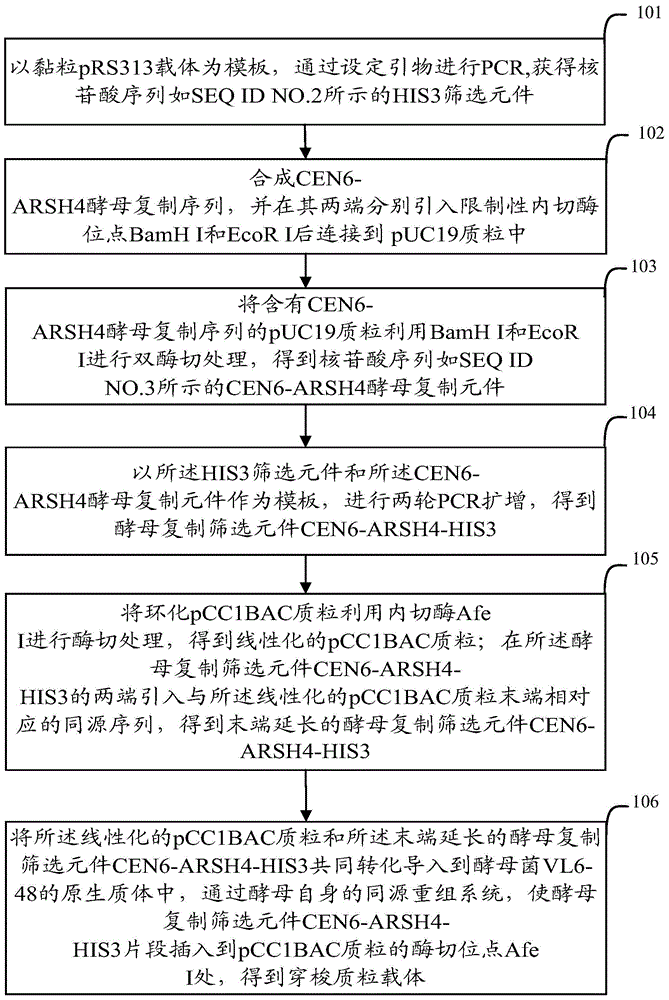
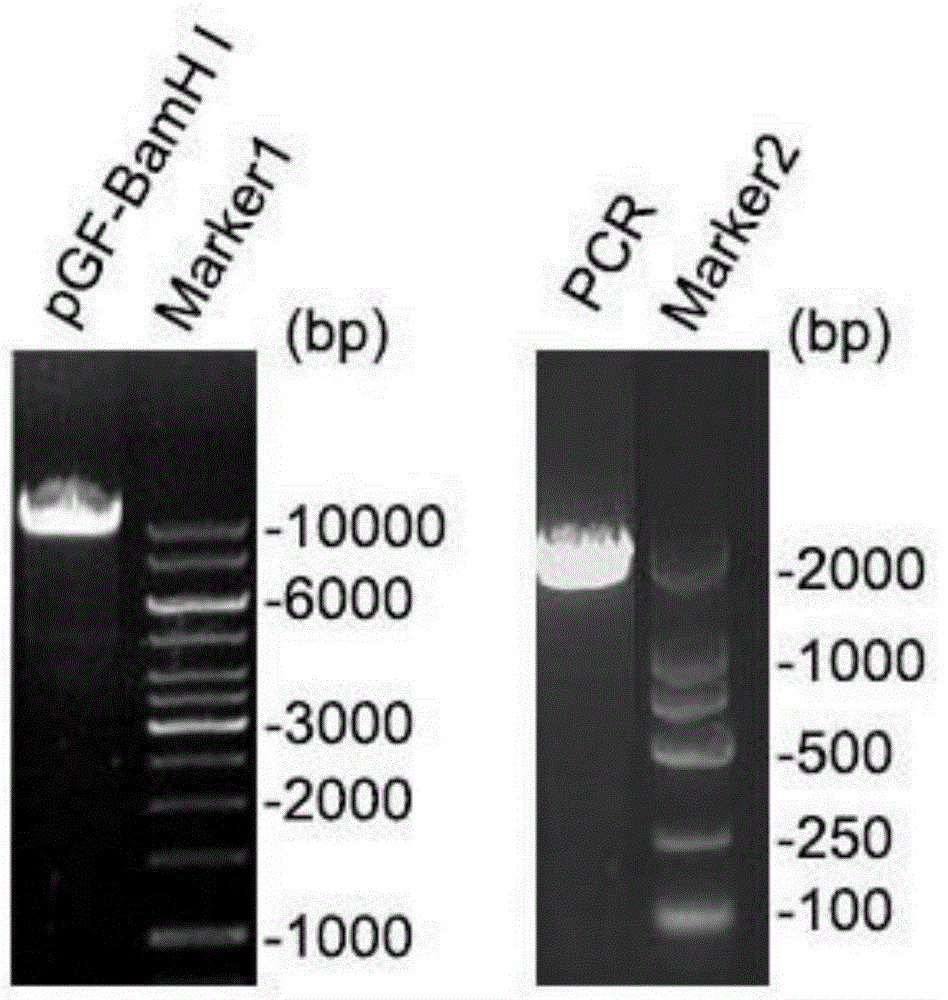
Shuttle plasmid vector, as well as construction method and applications thereof
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a shuttle plasmid vector, as well as a construction method and applications thereof. The shuttle plasmid vector can shuttle in yeast and Escherichia coli, and the nucleotide sequence of the shuttle plasmid vector is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Compared with the prior art, he shuttle plasmid vector realizes the shuttling in yeast and bacteria, and has the capabilities of homologous recombination cloning, self replication and recombinant screening in yeast, as well as the characteristics of being stable in replication and maintenance and convenient for DNA purification and separation in bacteria.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Truncated-form streptococcus hemolyticus bacteriolysin O and detection kit using same
ActiveCN102964435ASpecific immunogenicityIncrease productionDepsipeptidesBiological testingEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention provides a truncated-form streptococcus hemolyticus bacteriolysin O gene and an ASO detection kit. According to the invention, part of SLO gene fragments are cloned, and the part of SLO genes are cloned into an expression vector of escherichia coli and the like so as to realize mass expression and facilitate purification. In particular, the invention provides a DNA sequence which has a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the invention, the truncated-form SLO sequence can greatly improve the yield of SLO protein; more than 150 mg of SLO protein can be obtained through purification of one liter of bacterial culture, and the purity is more than 90%; immunological tests prove that the sectionally expressed SLO still maintains the specific immunogenicity.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
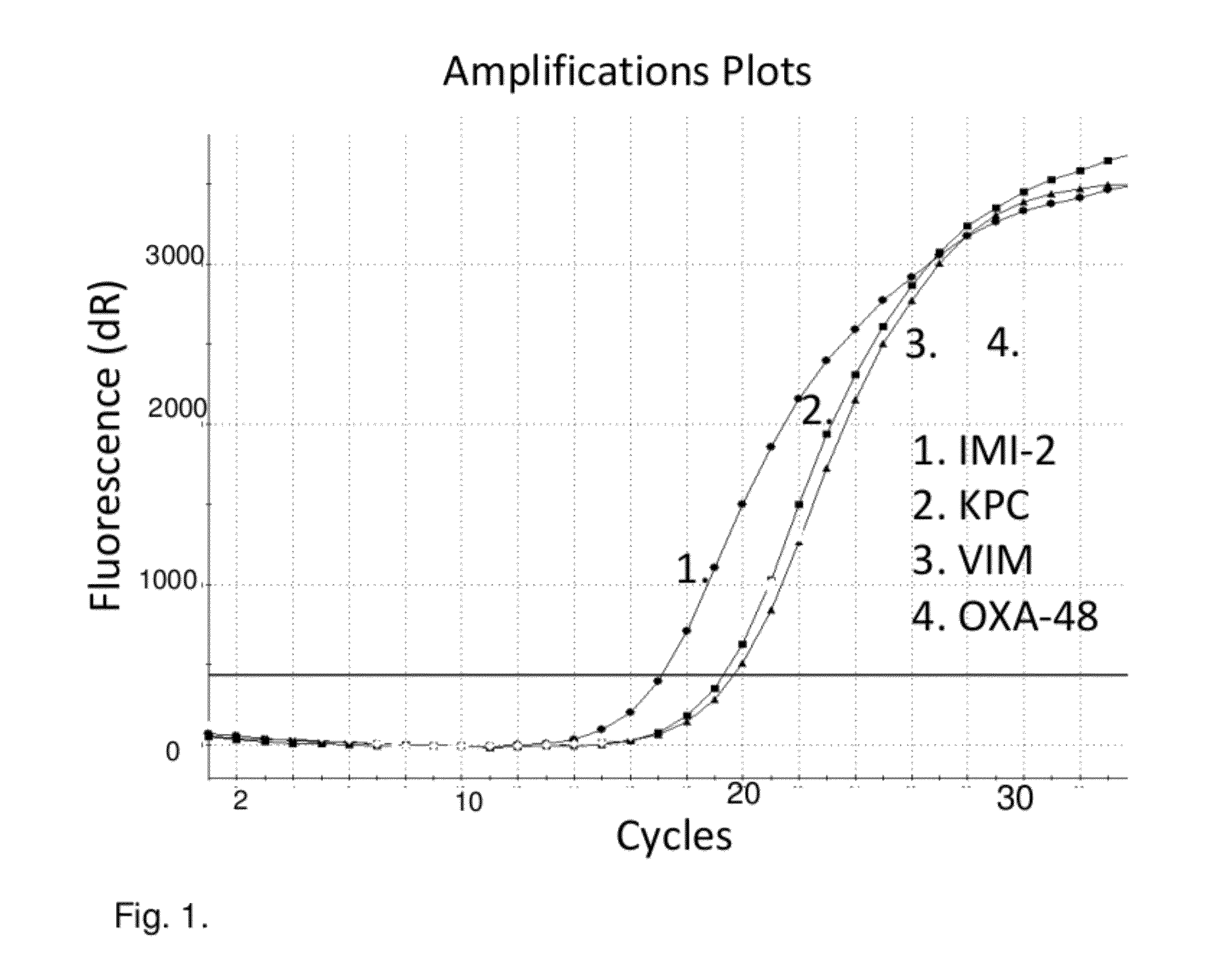
Method and A Kit for Detecting Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
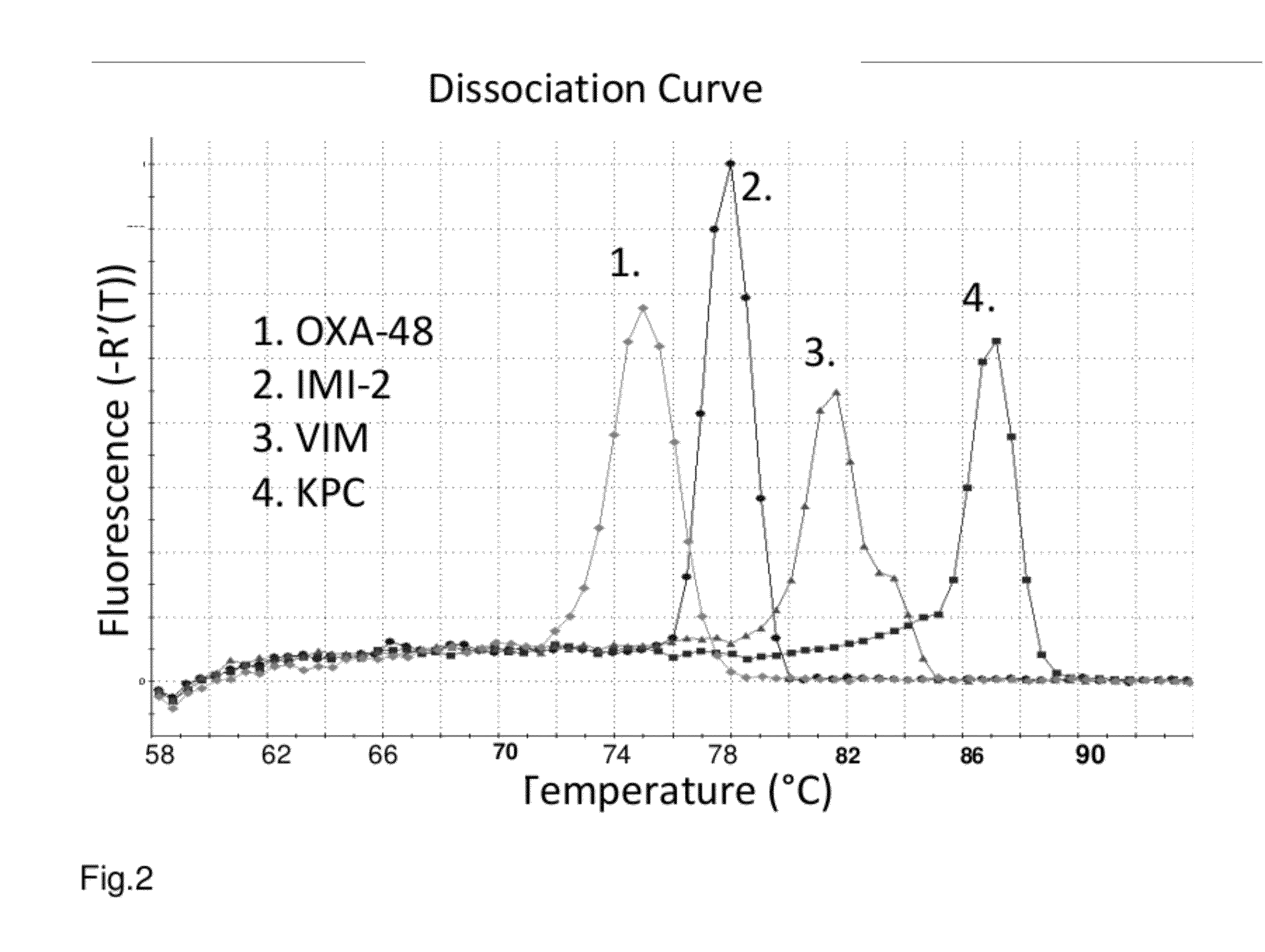
ActiveUS20120129180A1Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBacilliCarbapenem resistance
The present invention relates to a method and kit for detecting carbapenemase resistance genes causing carbapenem resistance in bacteria. The invention provides oligonucleotide primers, which can be used in the detection. The method can be used to detect OXA-48, SME, GIM-1, VIM 1-22, SPM, GES 1-10, KPC 1-7, IMI 1-3 / NMC-A, IMP 1-24 within a single reaction and OXA-23 group, OXA-24 group, OXA-51 group with ISabal promoter, OXA-55, OXA-58, OXA-60, OXA-62, CMY 1, -10, -11 SFC-1, NDM-1, and SIM-1 within another single reaction.
Owner:MOBIDIAG OY
Process for the production of L-amino acids by fermentation using coryneform bacteria
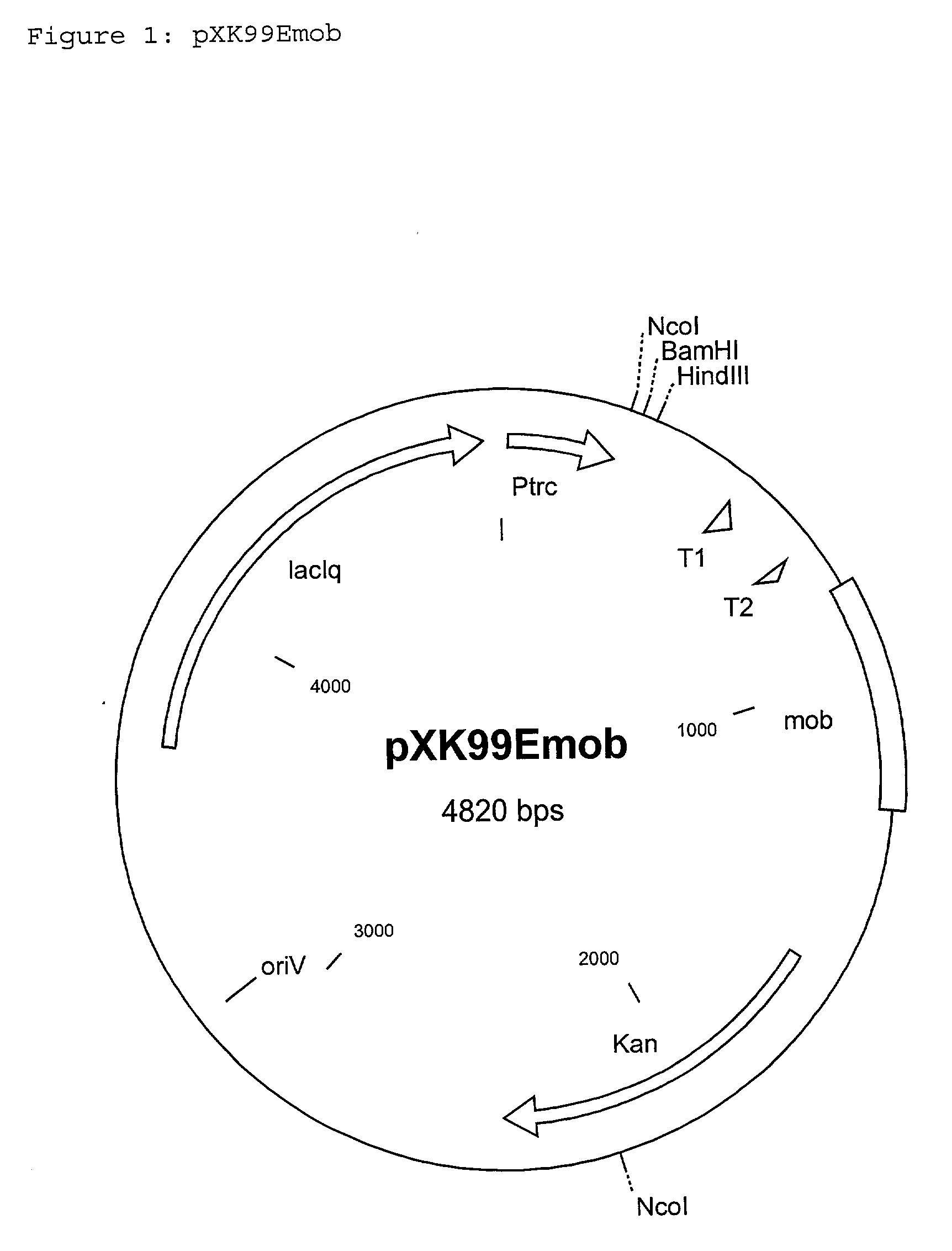
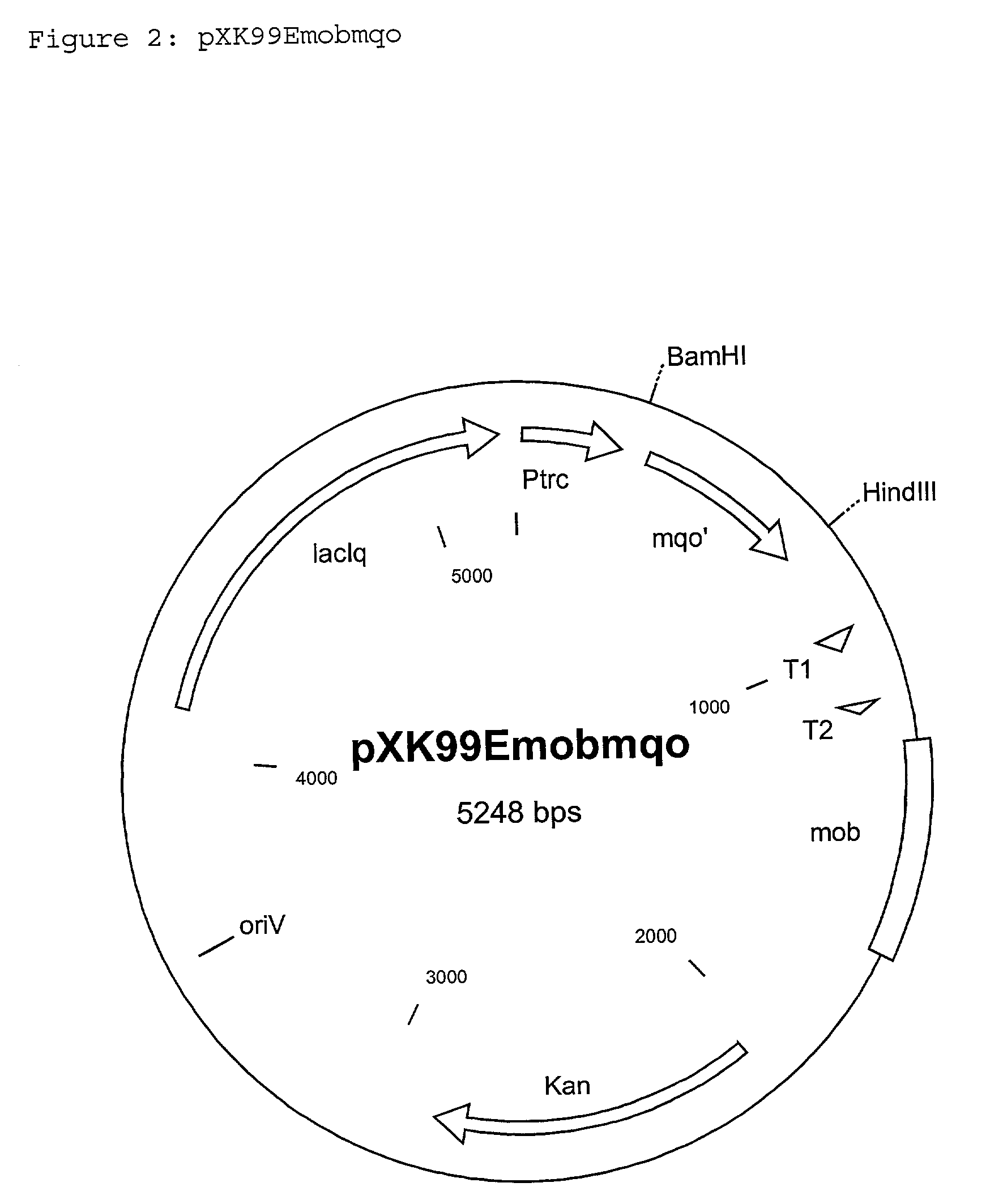
The invention relates to a process for the production of L-amino acids, in which the following steps are carried out: a) fermentation of the coryneform bacteria producing the desired L-amino acid, in which at least the mqo gene is attenuated, b) concentration of the desired L-amino acid in the medium or in the cells of the bacteria, and c) isolation of the L-amino acid, and, optionally, bacteria are used in which further genes of the biosynthesis pathway of the desired L-amino acid are additionally enhanced, or bacteria are used in which at least some of the metabolic pathways reducing formation of the desired L-amino acid are excluded.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for detecting enteritis pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN102154450AAvoid damageCause drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacteria, in particular to a method for detecting enteritis pathogenic bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of one or more bacteria samples; (2) amplifying full length of 16S rDNA (ribosomal DNA) of a sample by using a primer of 16S rDNA of bacteria; (3) breaking an amplified PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) product; (4) repairing ends of the broken product from each bacteria sample and connecting deoxyadenosine at the end 3' of the product, and then connecting different PCR-free joints; (5) sequencing a connection product by using a second-generation sequencing technology to obtain a sequence of the connection product; and (6) comparing the sequence with 16S rDNA reference sequences of all existing bacteria to determine types of bacteria existing in each sample.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司
Antibacterial peptides and application of antibacterial peptides to preparation of medicament resisting drug-resistant bacteria
InactiveCN102807610ANo residueHigh activity against drug-resistant bacteriaAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsResistant bacteriaHemolysis
The invention discloses antibacterial peptides and application of the antibacterial peptides to preparation of a medicament resisting drug-resistant bacteria. The antibacterial peptides consist of 21 amino acids, wherein the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQIDNO.1. The in-vivo and in-vitro research shows that six kinds of antibacterial peptides have a strong inhibiting and killing action for the mostly clinically-separated drug-resistant bacteria and can remarkably reduce the mortality of a septicemia model caused by the drug-resistant bacteria; and a hemolytic test and an acute local stimulus test results show that six kinds of derivates have no hemolytic test or acute toxic stimulus reaction when the concentration is 2.5mg / mL.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Novel plasmid, bearing the plasmid, and method of producing an enzyme using the transformant
InactiveUS20020076751A1Promote safe productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesGenus Pseudomonas
The invention relates to a plasmid characterized in that the plasmid comprises a DNA fragment containing a gene coding for an enzyme taking PQQ as the prosthetic group as cloned in a broad-host-range vector defected of conjugative transfer function beforehand and that the plasmid is capable of being expressed in bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Recombinant bacteria having the ability to metabolize sucrose
Recombinant bacteria capable of metabolizing sucrose are described. The recombinant bacteria comprise in their genome or on at least one recombinant construct: a nucleotide sequence from Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf5 (ATCC® BAA-477) encoding a polypeptide having sucrose transporter activity and a nucleotide sequence from Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf5 (ATCC® BAA-477) encoding a polypeptide having sucrose hydrolase activity. These nucleotide sequences are each operably linked to the same or a different promoter. Recombinant bacteria capable of metabolizing sucrose to produce glycerol and / or glycerol-derived products such as 1,3-propanediol and 3-hydroxypropionic acid are also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com