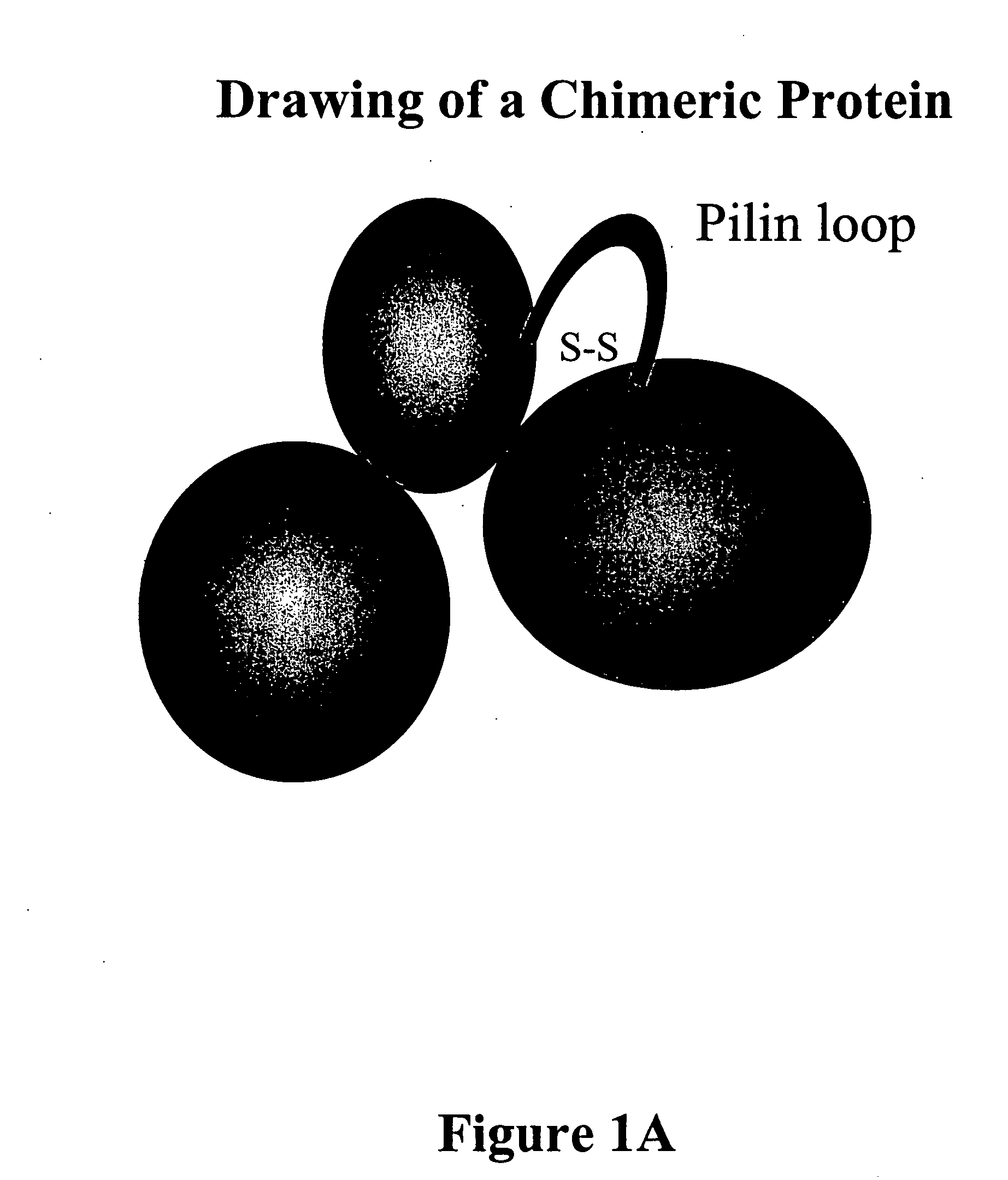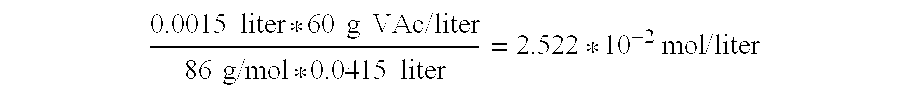Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
166 results about "Genus Pseudomonas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
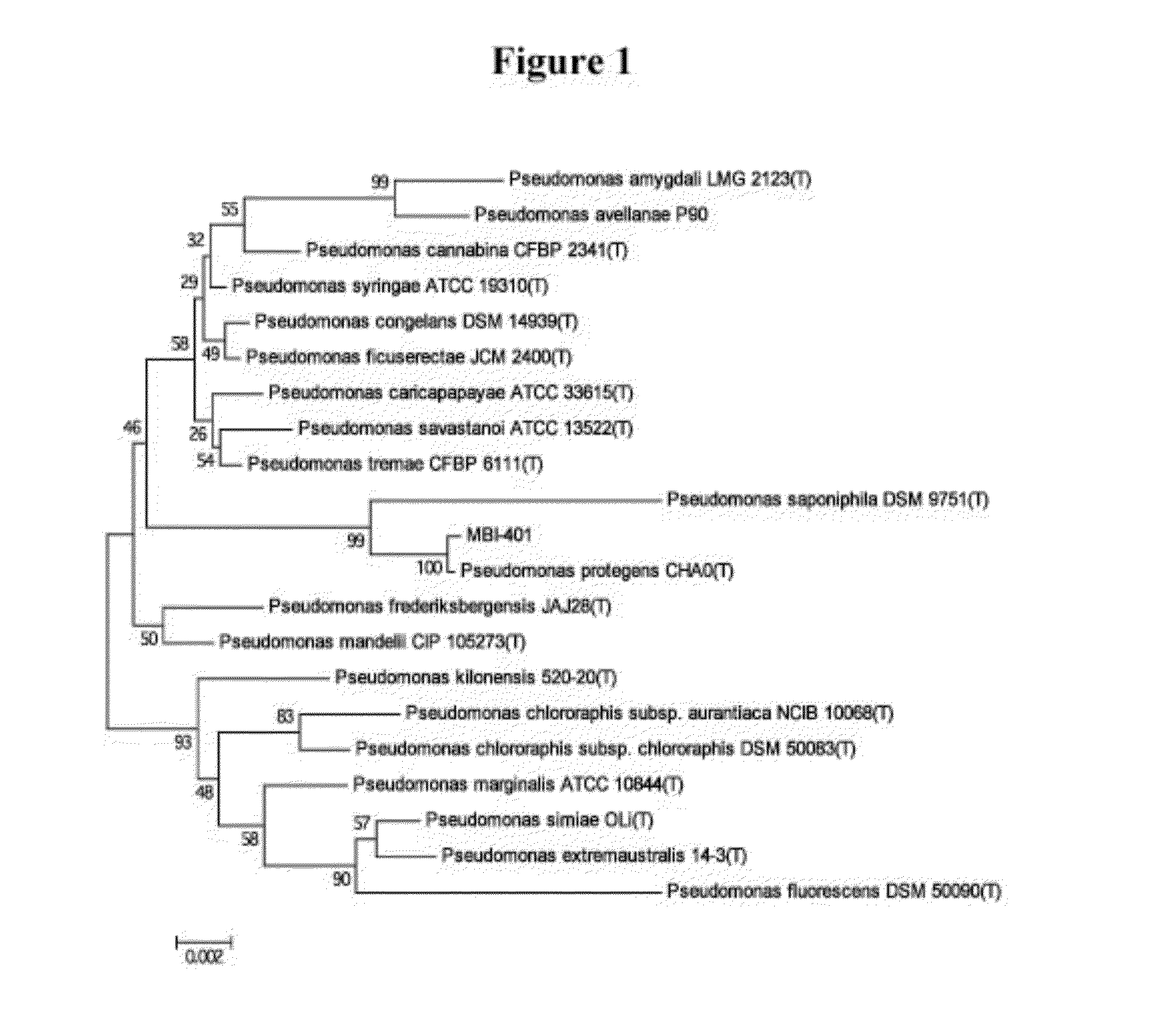
Freebase(0.00 / 0 votes)Rate this definition: Pseudomonas. Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative aerobic gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae containing 191 validly described species. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is increasingly recognized as an emerging opportunistic pathogen of clinical relevance.
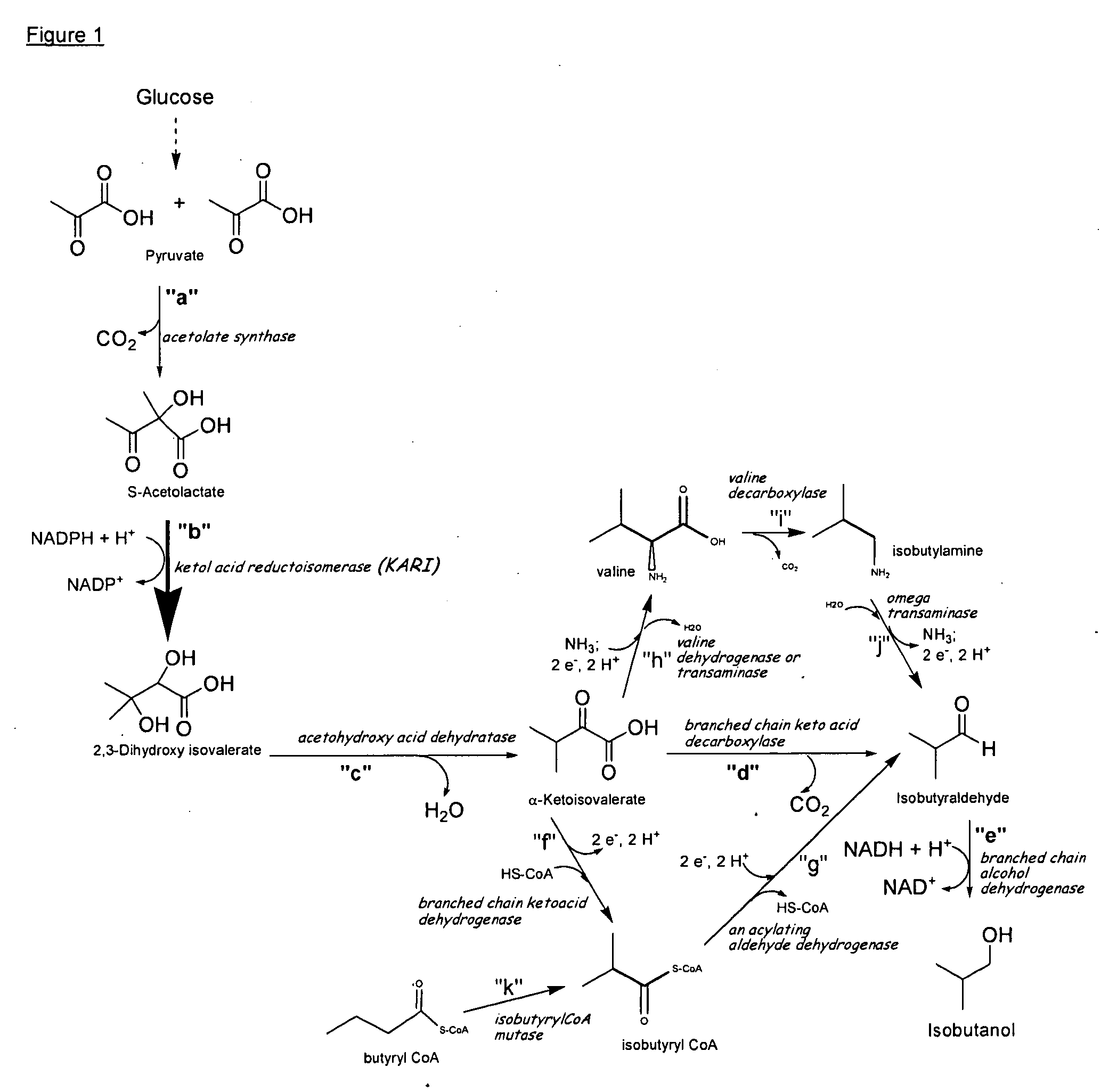
Ketol-acid reductoisomerase using nadh
Owner:GEVO INC
Systems for treating pulmonary infections
Provided herein are systems for treating a subject with a pulmonary infection, for example, a nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary infection, a Burkholderia pulmonary infection, a pulmonary infection associated with bronchiectasis, or a Pseudomonas pulmonary infection. The system includes a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a liposomal aminoglycoside dispersion, and the lipid component of the liposomes consist essentially of electrically neutral lipids. The system also includes a nebulizer which generates an aerosol of the pharmaceutical formulation at a rate greater than about 0.53 gram per minute. The aerosol is delivered to the subject via inhalation for the treatment of the pulmonary infection.
Owner:INSMED INC
Pseudomonas Bacterium
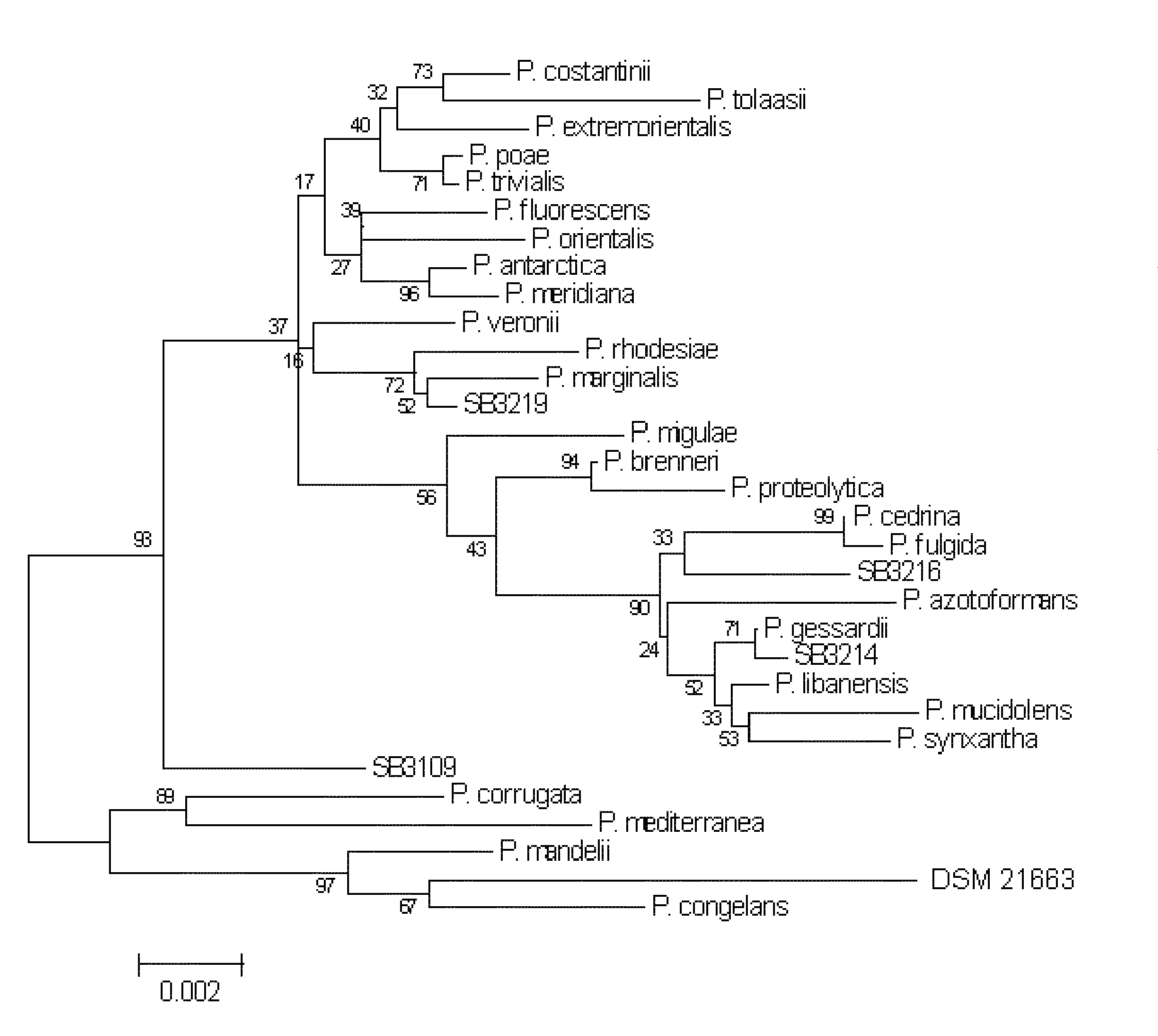
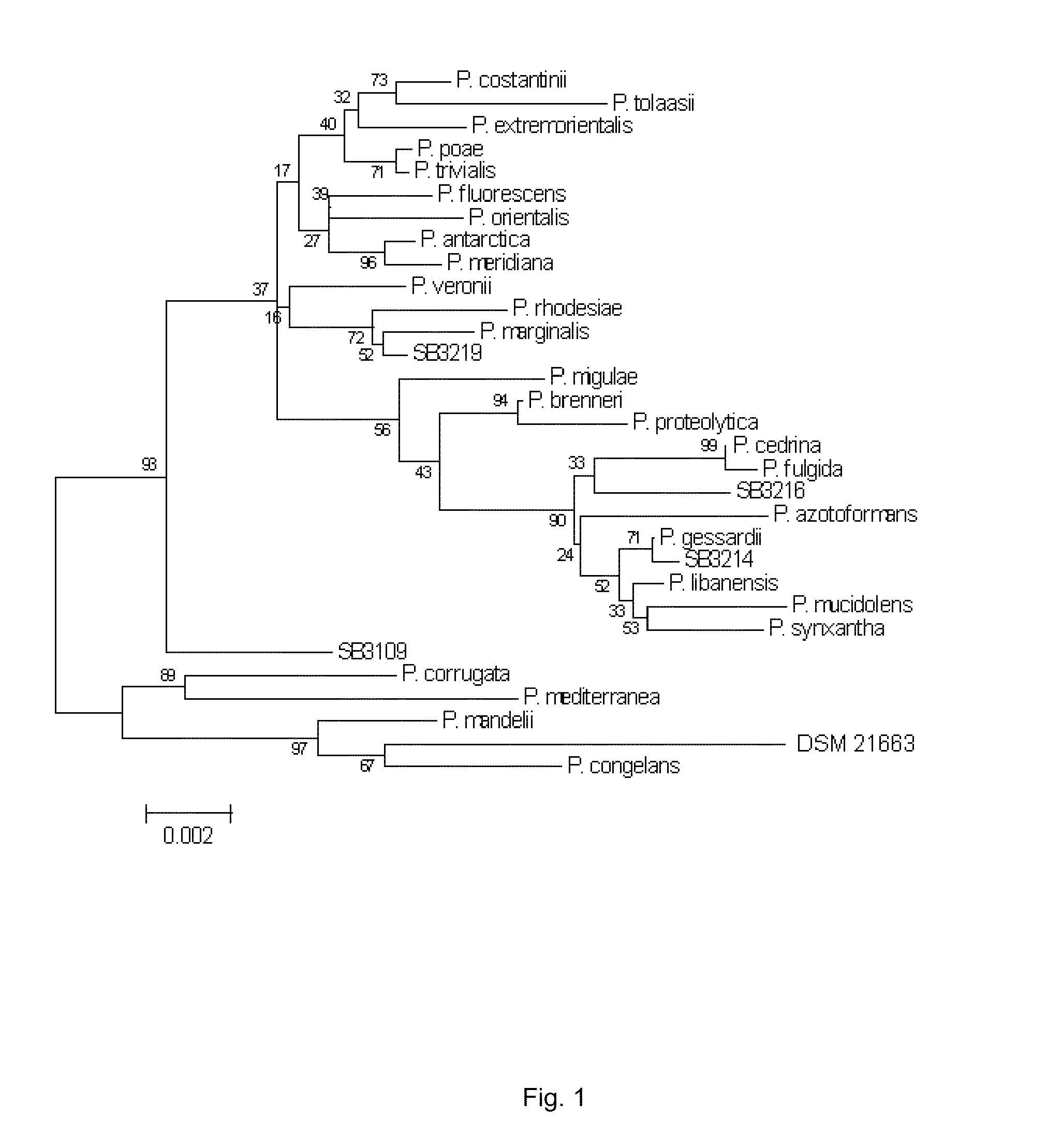
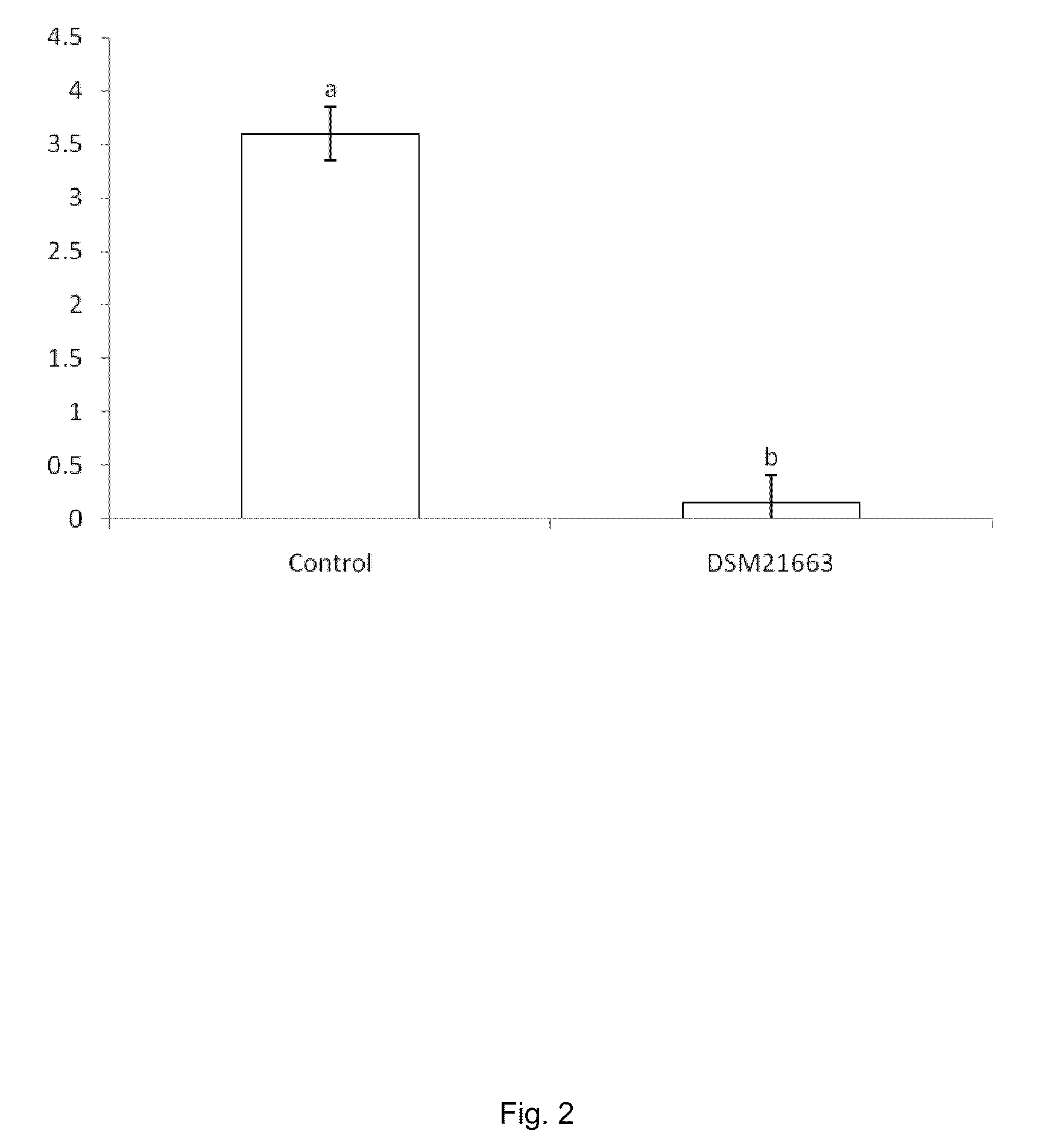
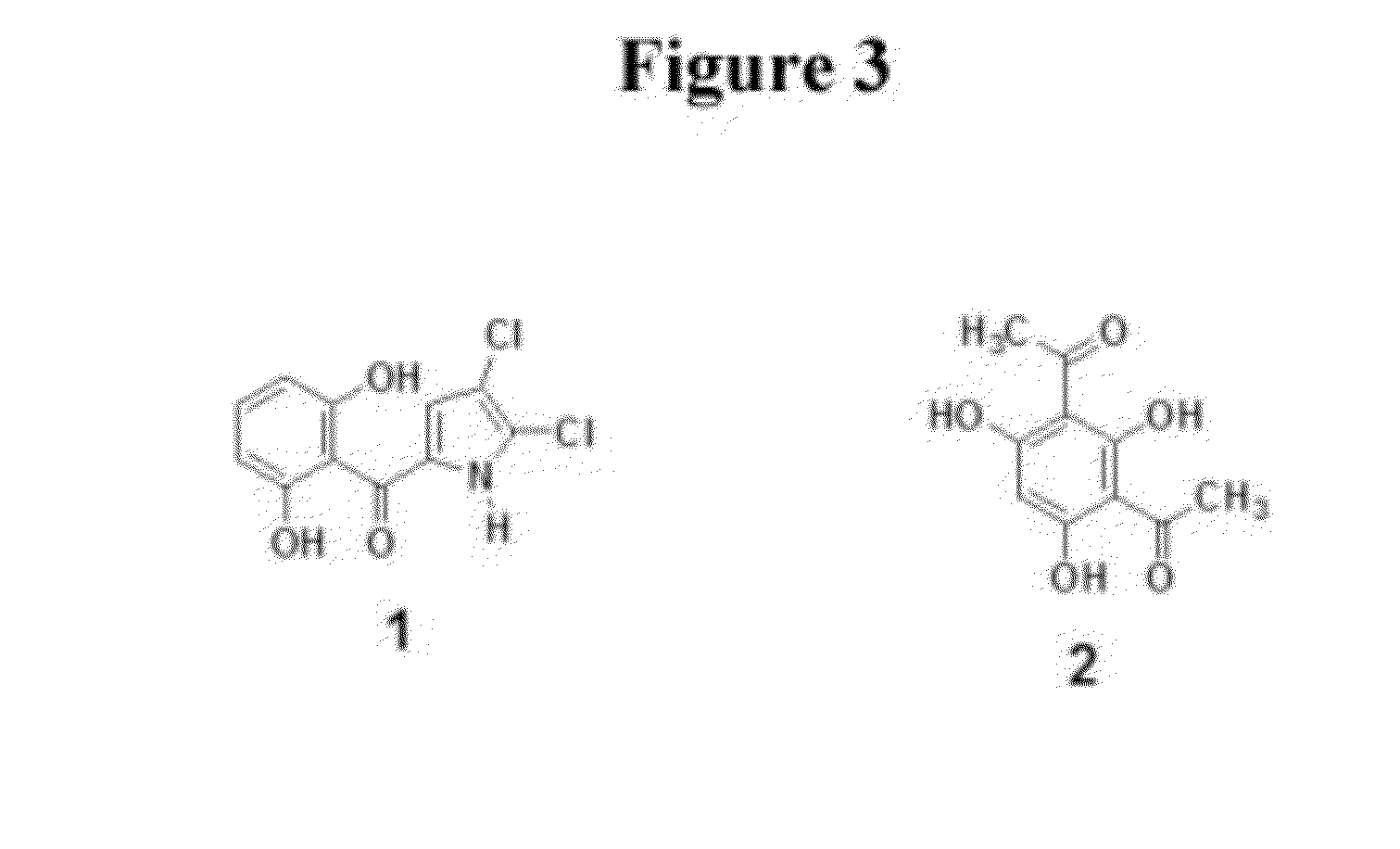
According to the present invention a new isolate of a Pseudomonas spp, DSM 21663, has been shown to possess unique properties. This Pseudomonas is a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR). Among its modes of action involved in plant growth-promotion are anti-biotic production (2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol, (DAPG); pyrrolnitrin, PRN and others), indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) production and phosphate solubilization, and production of unique volatiles. The strain is fluorescent, oxidase-positive, and has the ability to suppress soil-borne root and foliar pathogens of both fungal and bacterial origin.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Fusion antigen used as vaccine
InactiveUS7595054B2SsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsBacterial exotoxinReticulum cell
Fusion antigen used as vaccine. The invention relates to a fusion antigen specific for a target cell. The fusion antigen contains a ligand moiety, a Pseudomonas exotoxin A translocation domain II, an antigenic moiety, and a carboxyl terminal moiety. The ligand moiety is capable of reacting, recognizing or binding to receptors on the target cell. The carboxyl terminal moiety permits retention and processing of the fusion antigen in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane of the target cell. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of inducing an immune response using the same are also disclosed.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Chemical and biological agents for the control of molluscs
ActiveUS20130196013A1Good curative effectNo less efficacyBiocideOrganic chemistryCarbamateCarboxylic acid
Compositions and methods for controlling molluscs, members of the Gastropoda and Bivalvia classes which includes but is not limited to lactones, lactams, carbamates, amides, and / or carboxylic acid containing compounds as active ingredients and / or compounds derived from Pseudomonas and / or Erwinia. Also provided are methods and compositions for increasing the efficacy of chemical and biological control for invasive molluscs in open waters, power plants, and drinking water treatment facilities under coldwater conditions.
Owner:MARRONE BIO INNOVATIONS
Air purifying material of microorganism absorption degradation, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101554485AGood purification effectHigh viability of immobilized cellsMicroorganism based processesDeodrantsAir cleaningPollutant
The invention discloses an air purifying material of microorganism absorption degradation, a preparation method and applications thereof. The air purifying material of microorganism absorption degradation is obtained by embedding biological grains with 2 to 4mm grain diameter of pseudomonades or acinetobacter which are cultured and acclimatized in a crosswise way in calcium alginate gel. The air purifying material of microorganism absorption degradation can be used in the long time purification of formaldehyde and benzene series pollution in rooms with obvious effect. The product has the advantages of high activity of immobilized cells, good stability, effectively reducing the content of chemical pollution of formaldehyde and benzene series pollution in rooms, being beneficial for realizing the recycling, regenerating and reusing of biocatalysts, and seriously avoiding the pollution to room environment by microorganisms. The raw material has low cost, the preparation process is simple, easy and convenient in operation, and product can be applied in different reactors.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
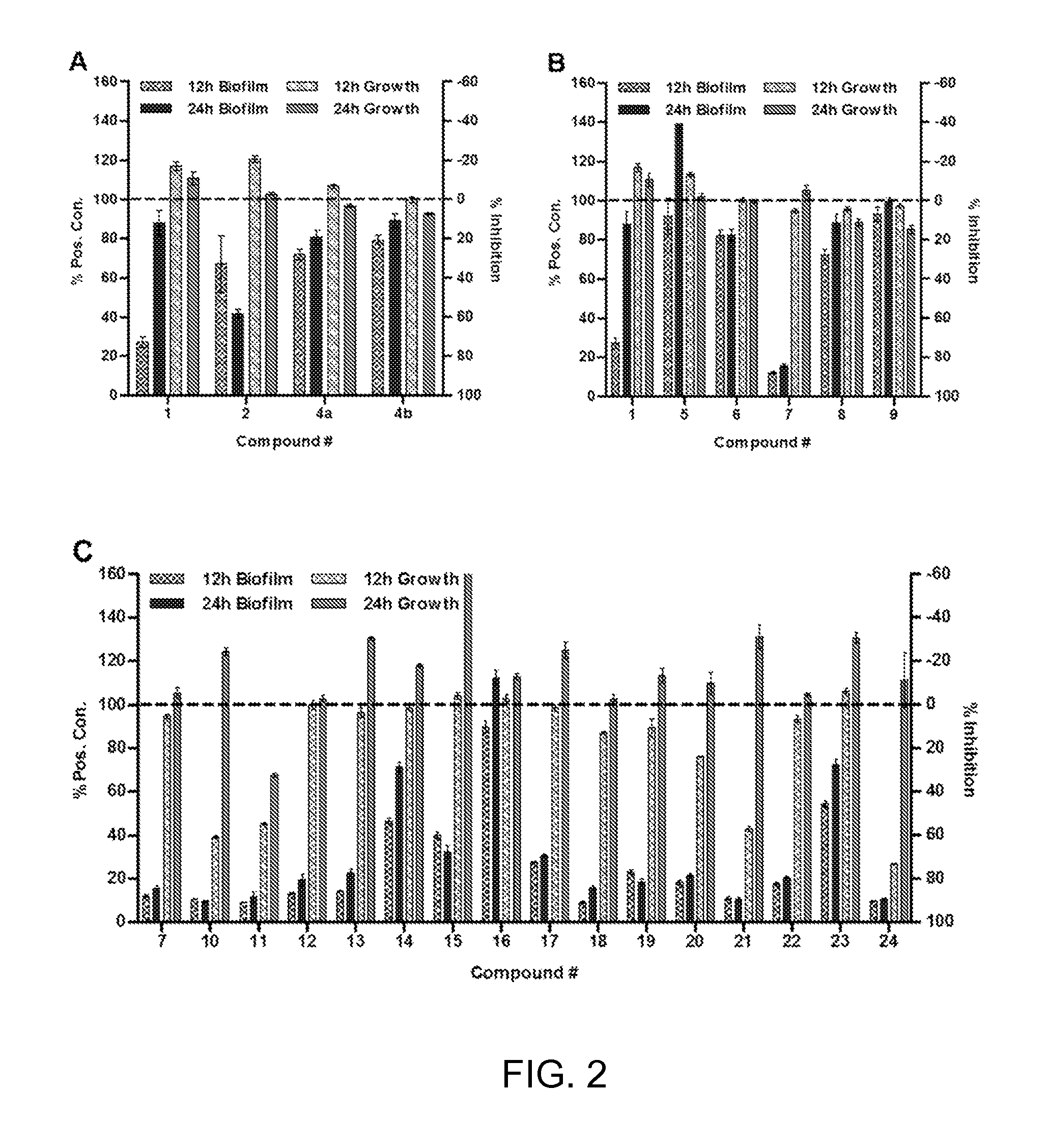
Inhibition and Dispersion of Bacterial Biofilms with 2-Aminobenzimidazole Derivatives
InactiveUS20130136782A1Reducing bacterial virulenceIncreased susceptibilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideControlled release2-aminobenzimidazole
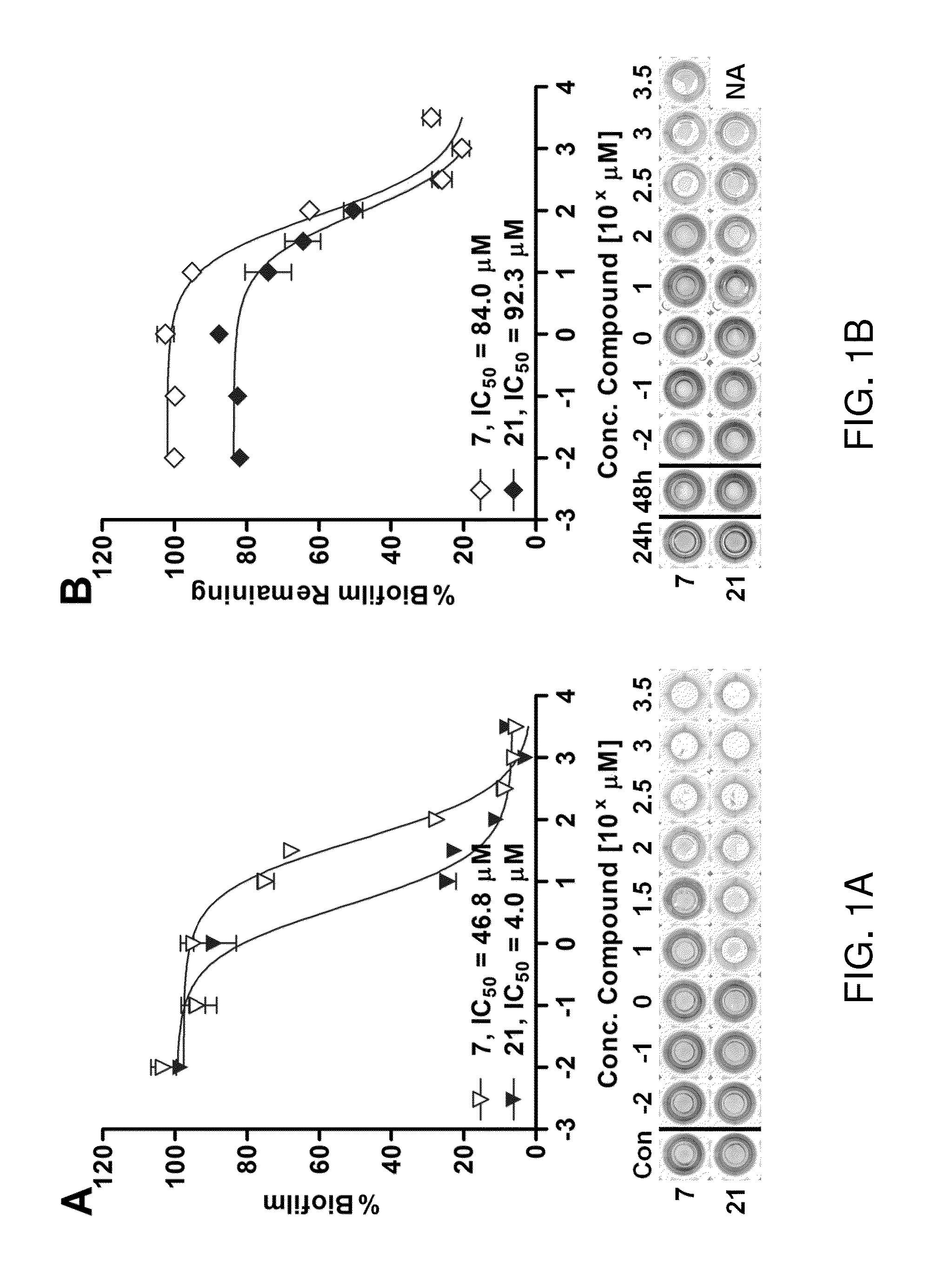
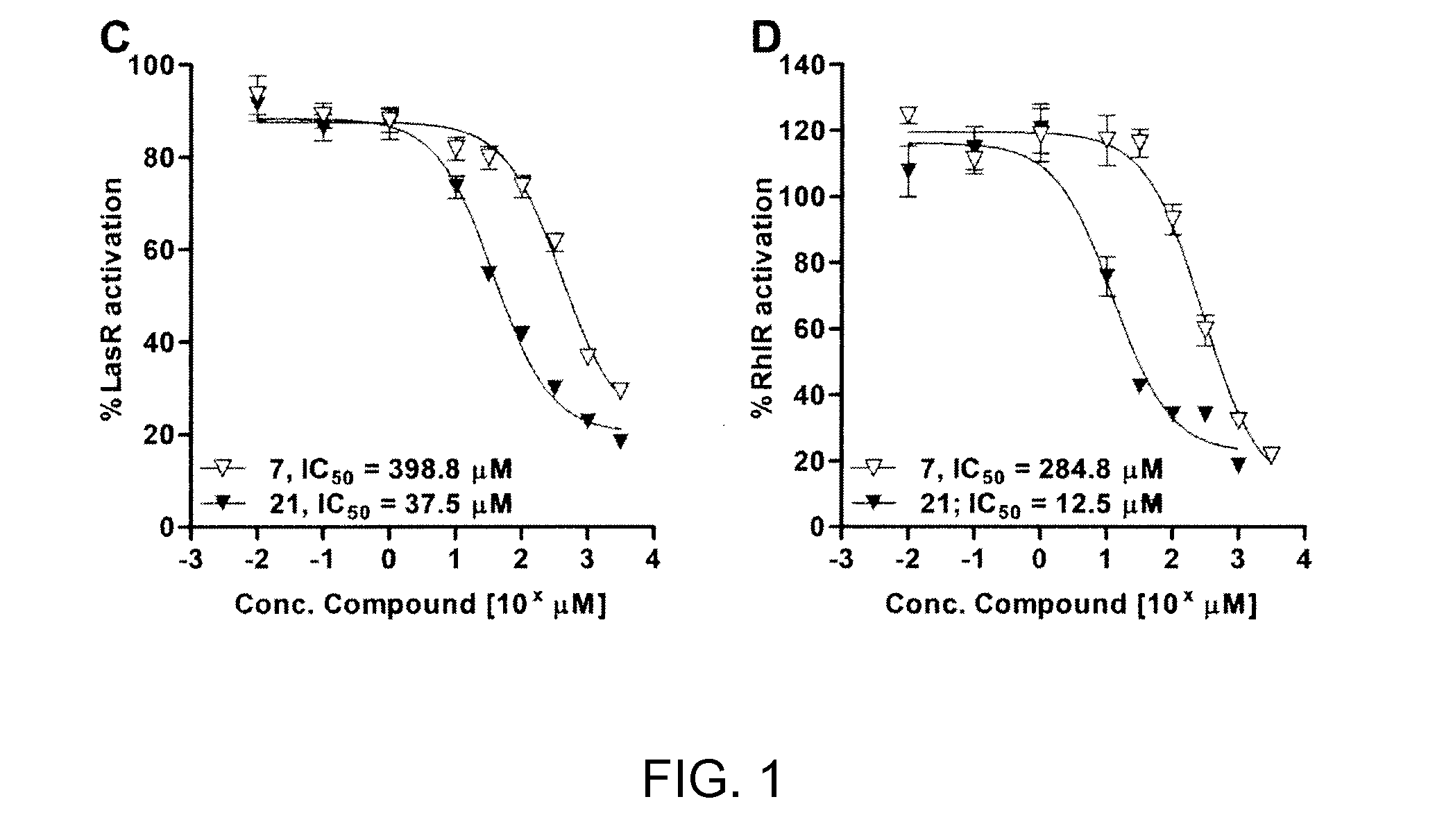
Compounds described herein inhibit biofilm formation or disperse pre-formed biofilms of Gram-negative bacteria. Biofilm-inhibitory compounds can be encapsulated or contained in a polymer matrix for controlled release. Coatings, films, multilayer films, hydrogels, microspheres and nanospheres as well as pharmaceutical compositions and disinfecting compositions containing biofilm-inhibitory compounds are also provided. Methods for inhibiting formation of biofilms or dispersing already formed biofilms are provided. Methods for treating infections of gram-negative bacteria which form biofilms, particularly those of Pseudomonas and more particularly P. aeruginosa.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Microbial-based composition and method of use
A microbial-based composition provides a co-cultured microorganism consortium in culture medium that includes one or more Acetobacter sp., Bacillus sp., Bifidobacterium sp., Enter ococus sp., Gluconacetobacter sp., Lactobacillus sp., Rhodopseudomonas sp., Saccharomyces sp., Pichia sp., and Trichoderma sp., as well as a carbon source and chlorine-free water. In some embodiments, the microbial-based composition is useful in the agricultural industry as a plant growth promoting and silage-enhancing agent. For plant growth promotion applications, the microbial-based composition may be applied to the foliar surface of a plant or to the plant growth medium, such as soil or hydroponic solution, surrounding the plant. In silage operations, the microbial-based composition may be applied to a cut plant product during one or more stages in the silage process.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITY DEV LLC
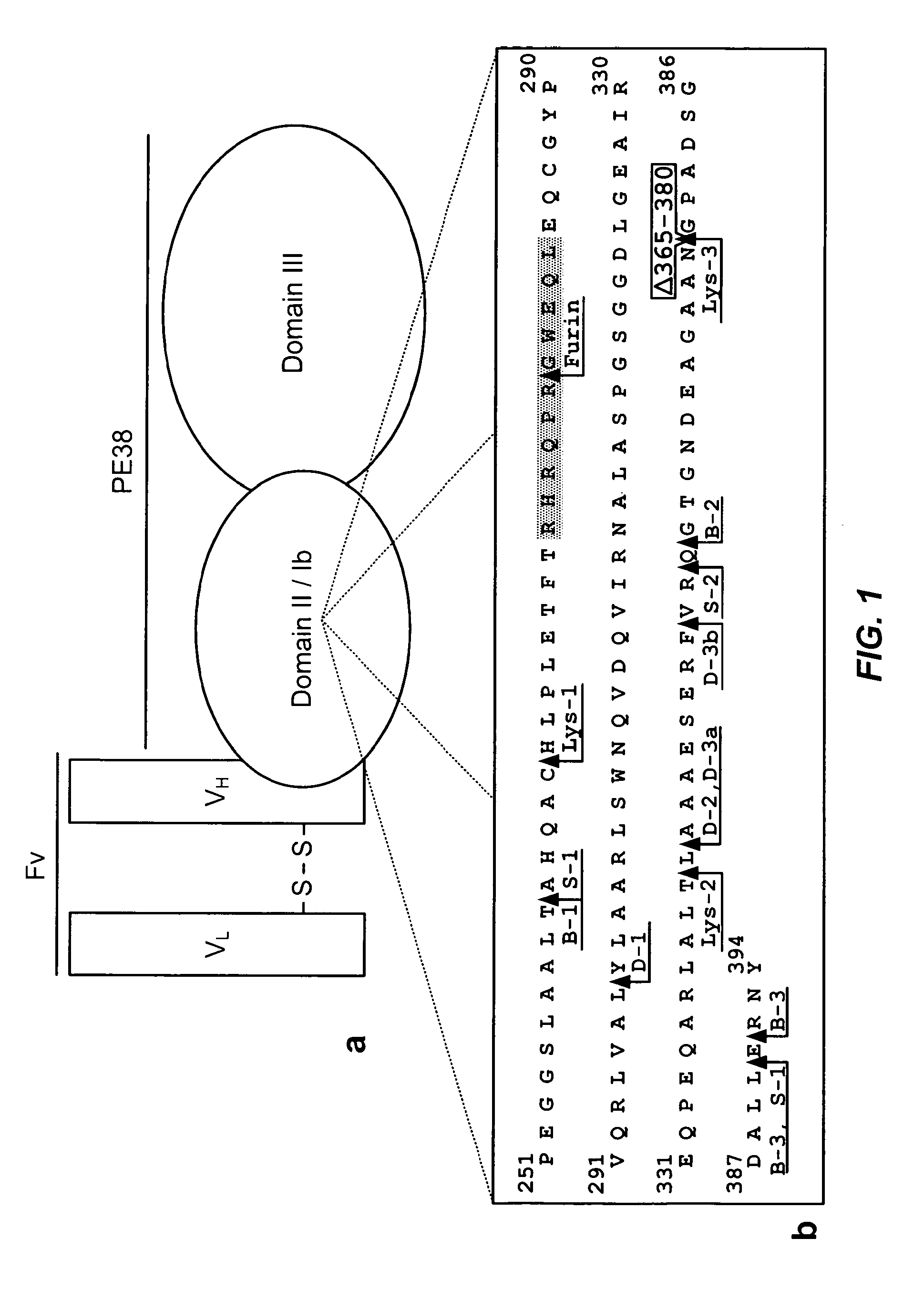
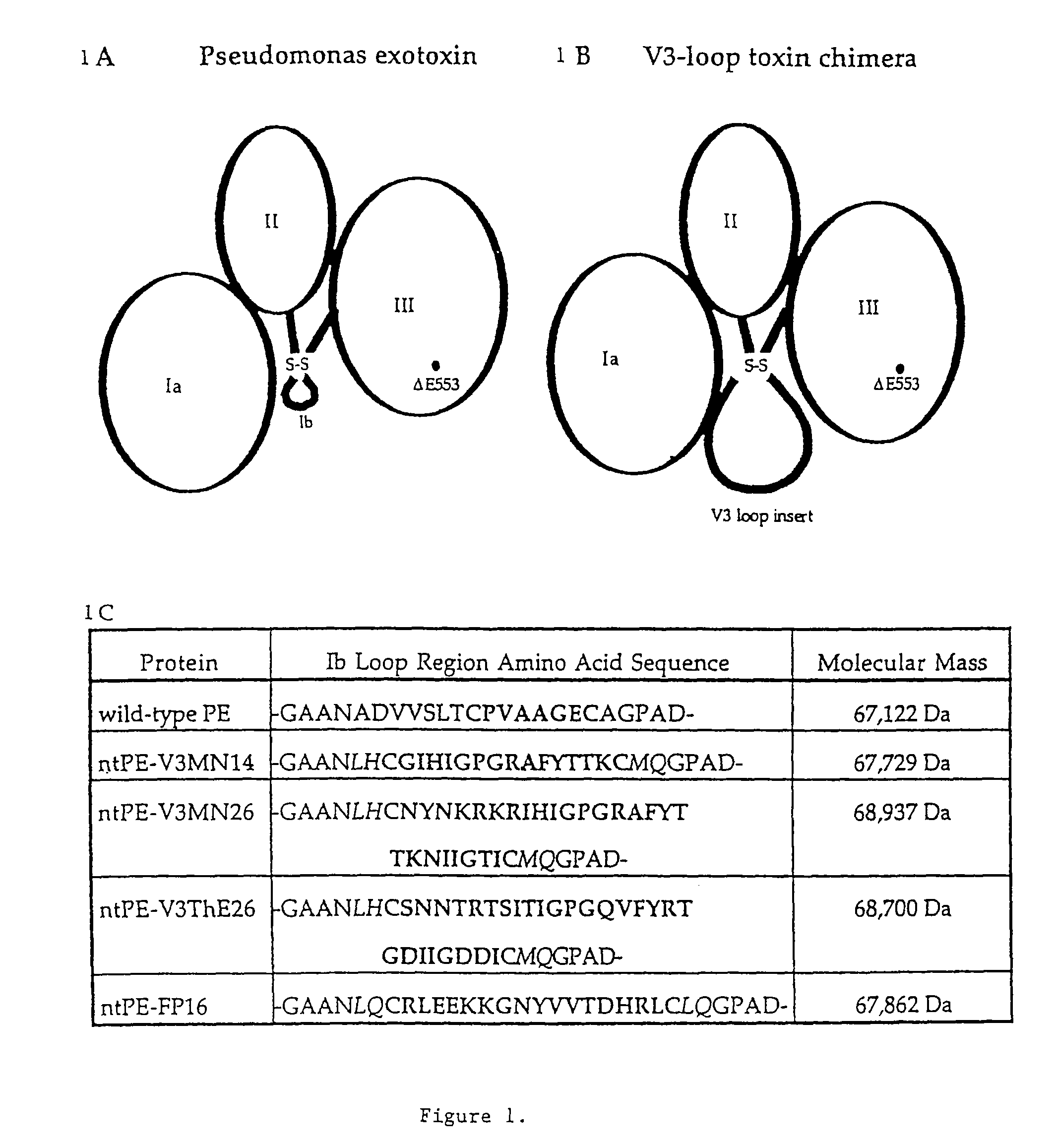
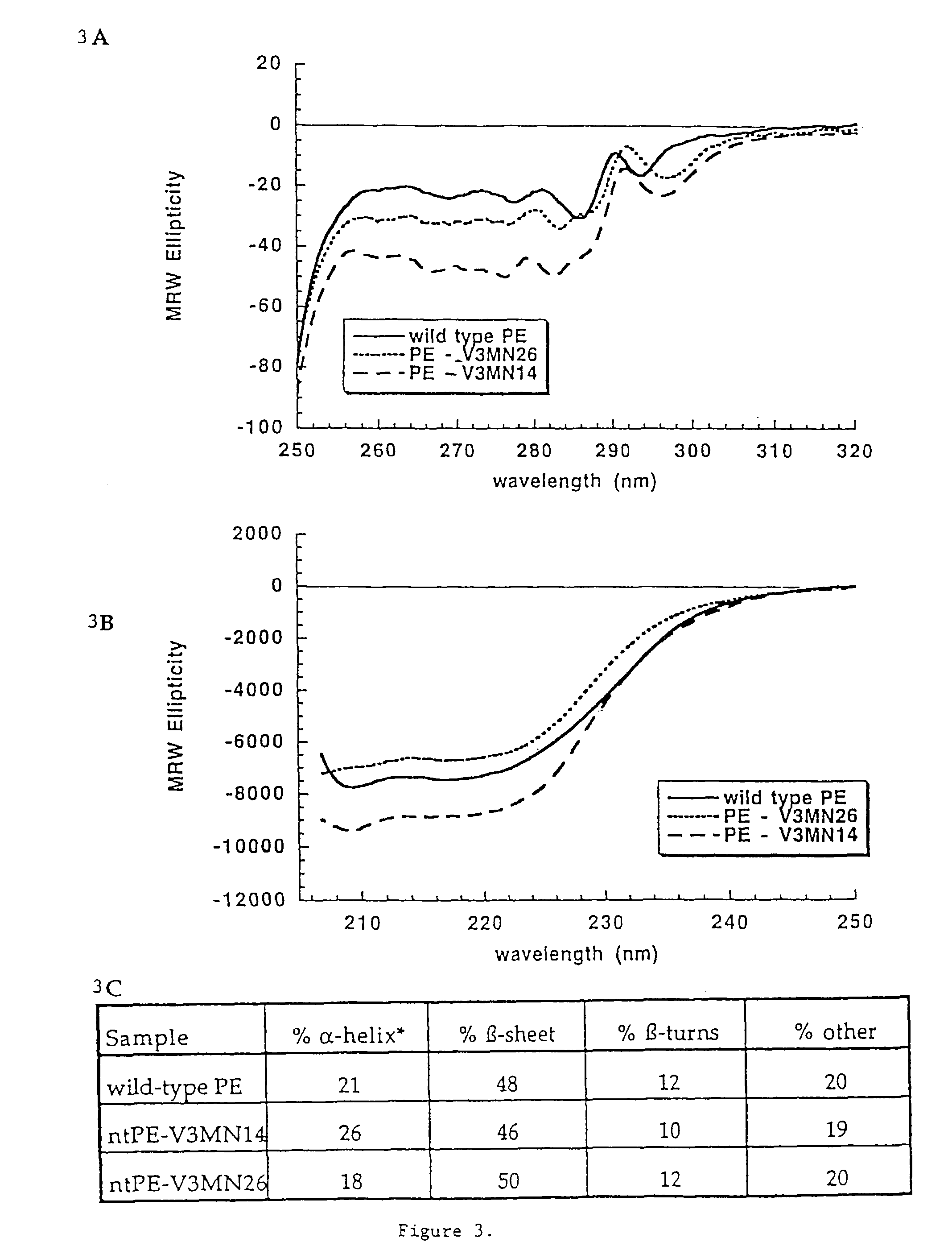
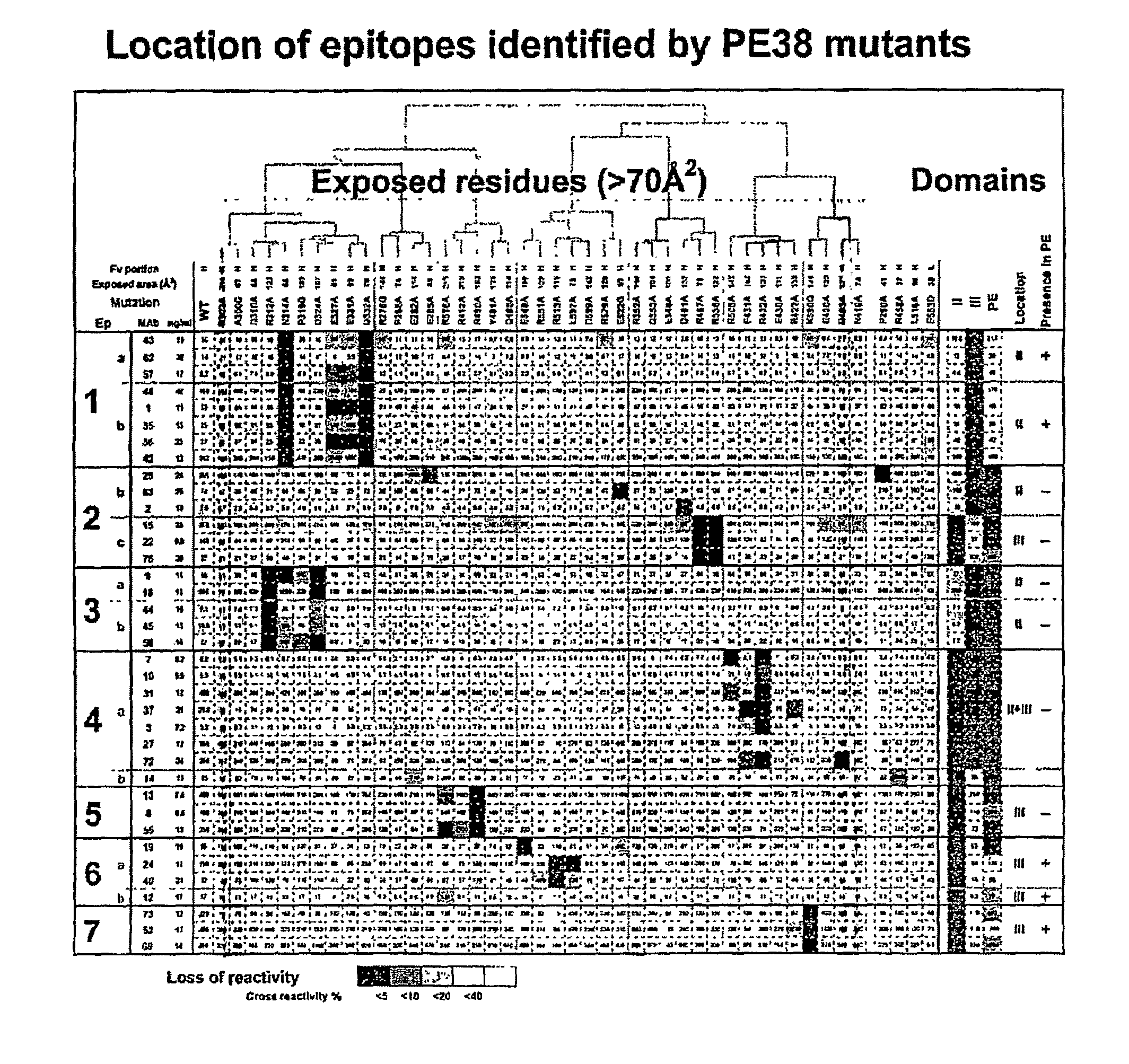
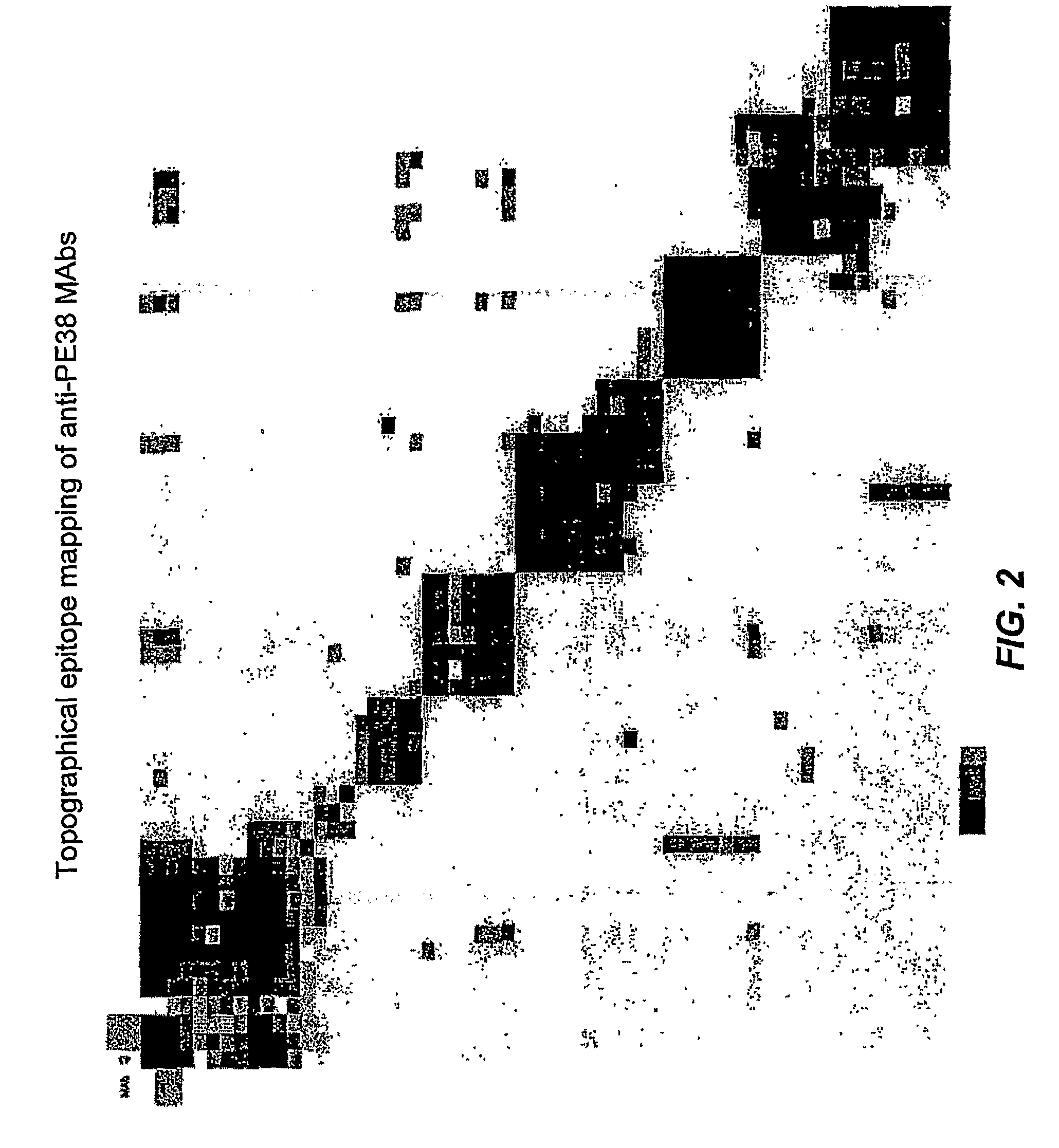
Deletions in domain ii of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS20100215656A1Maintain immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
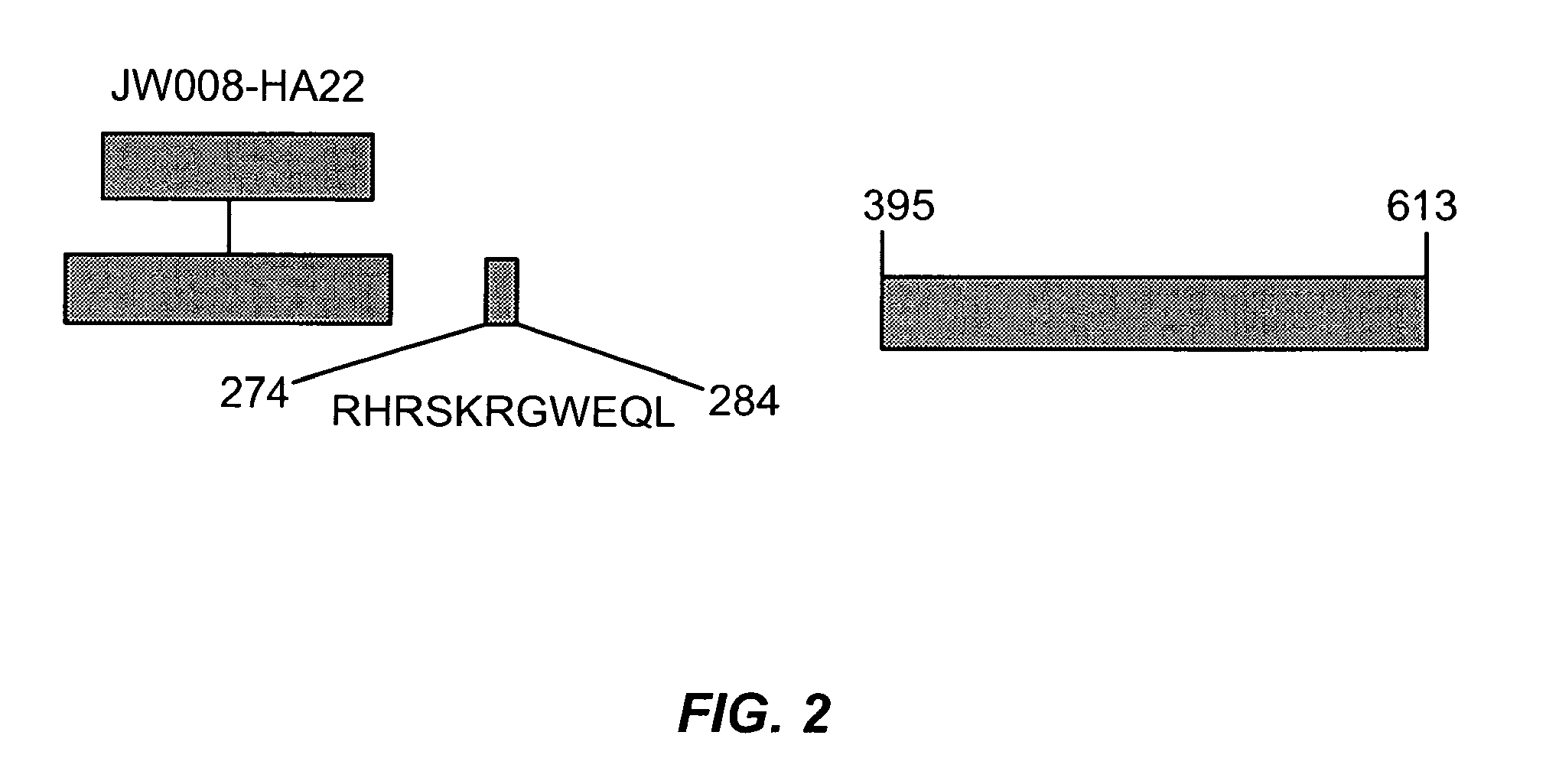
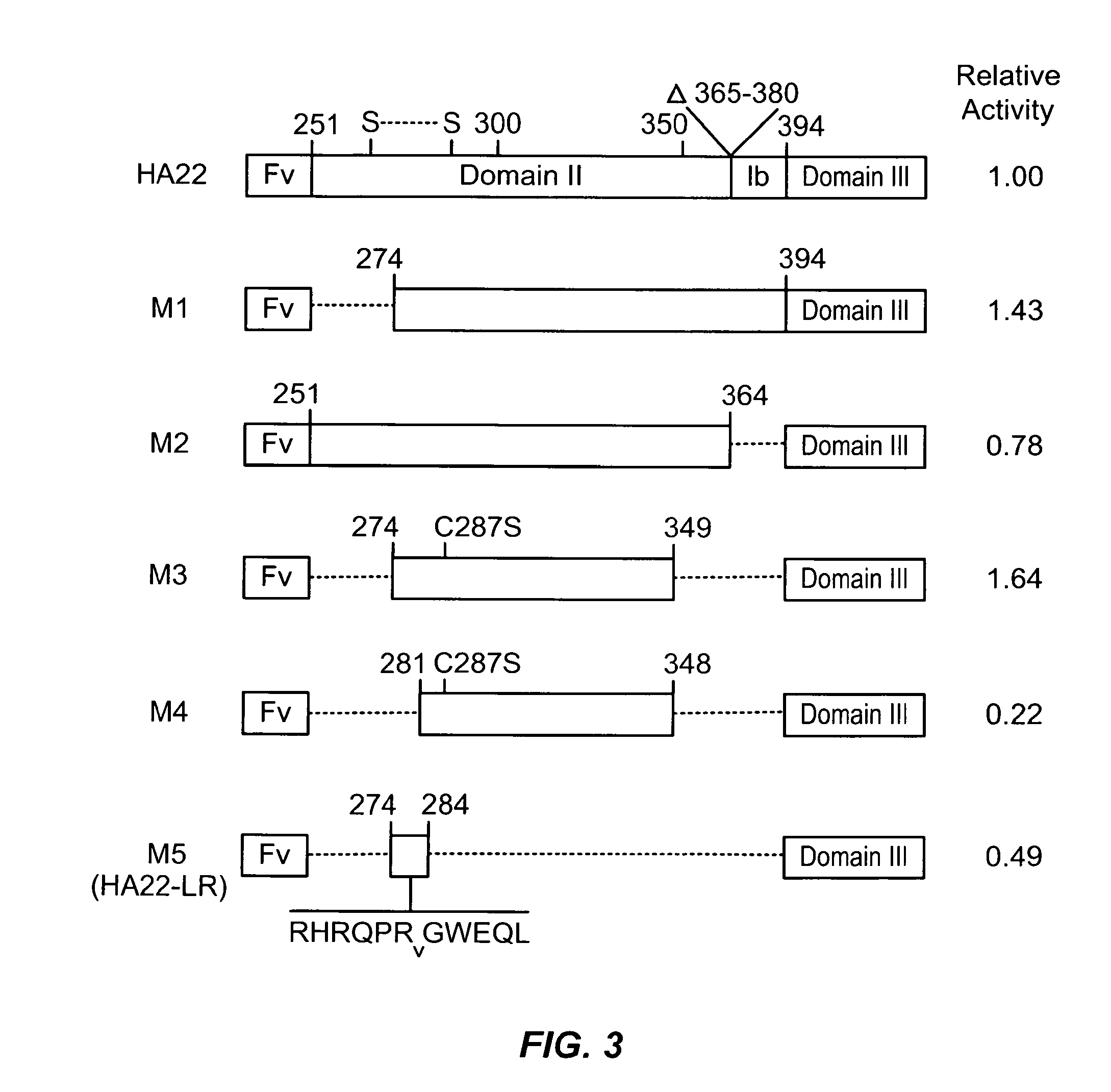
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
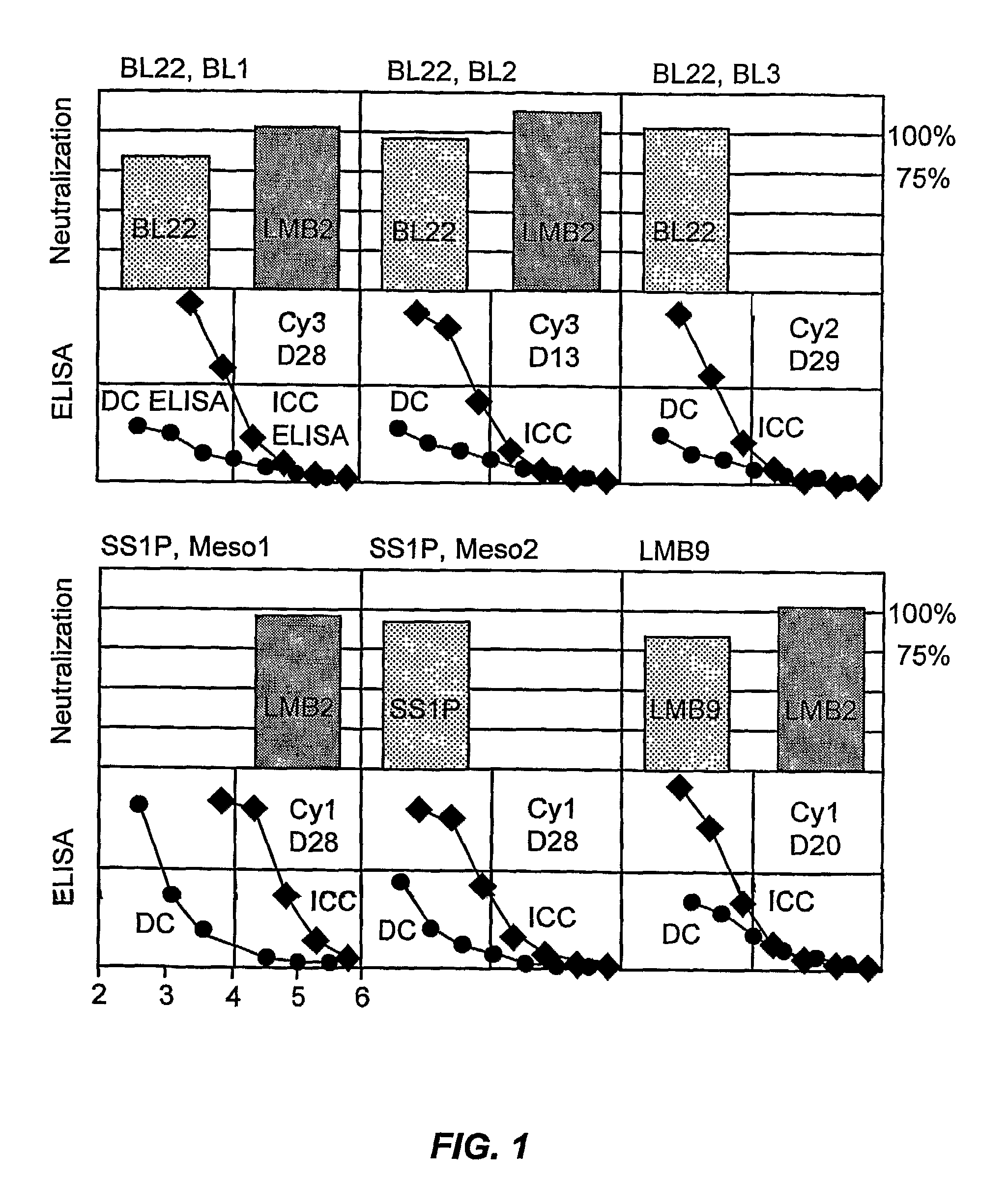
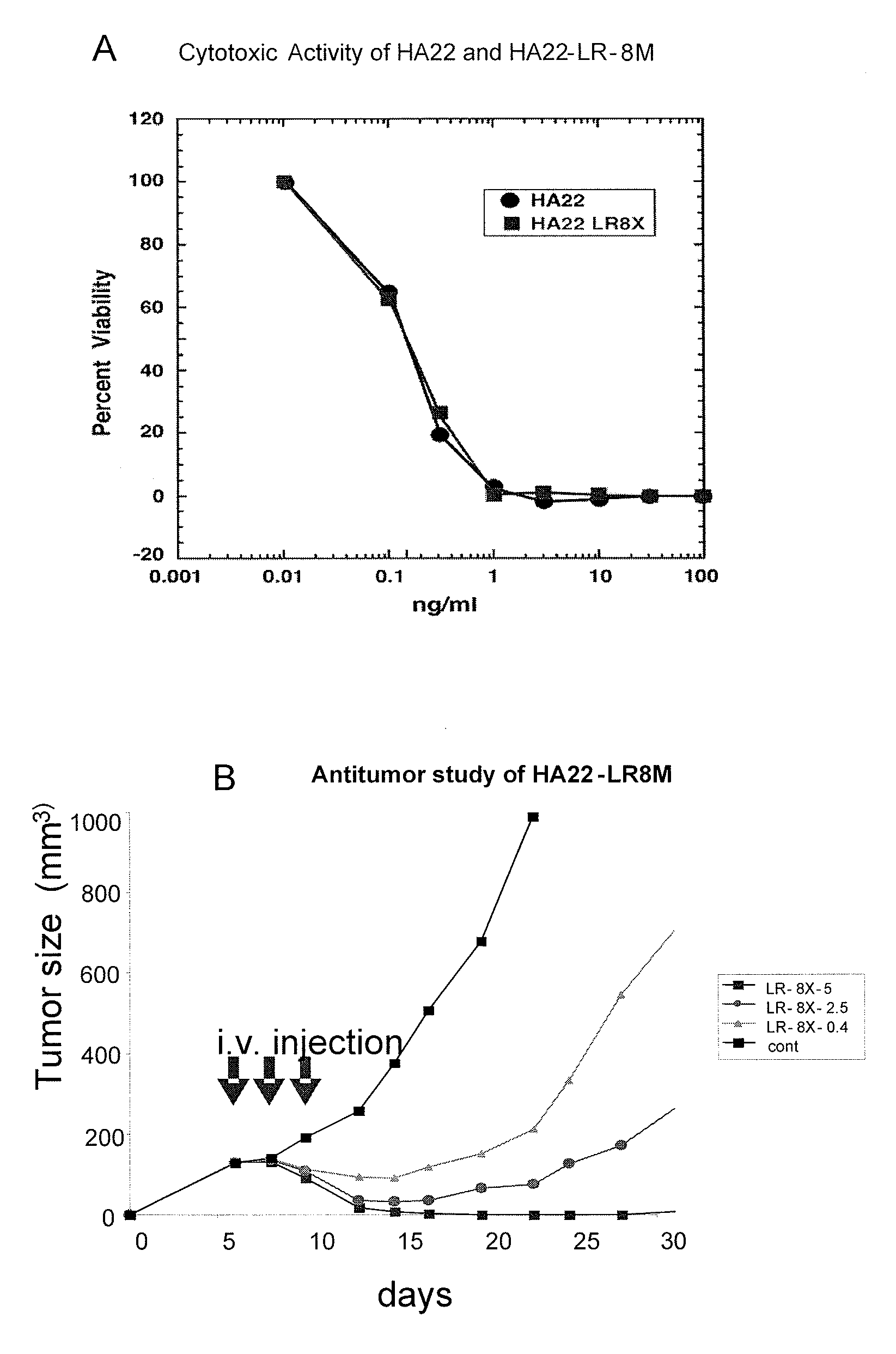
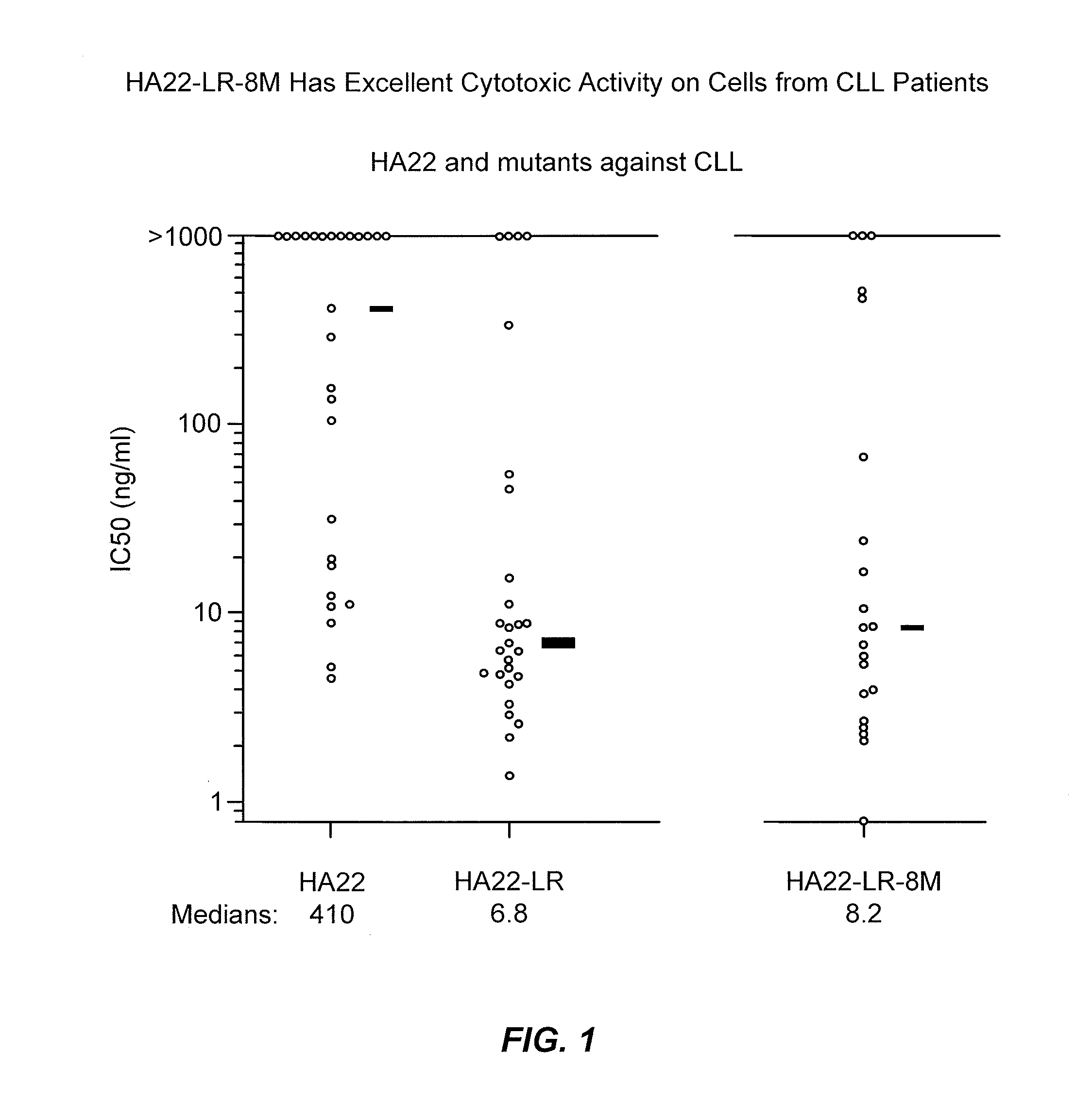
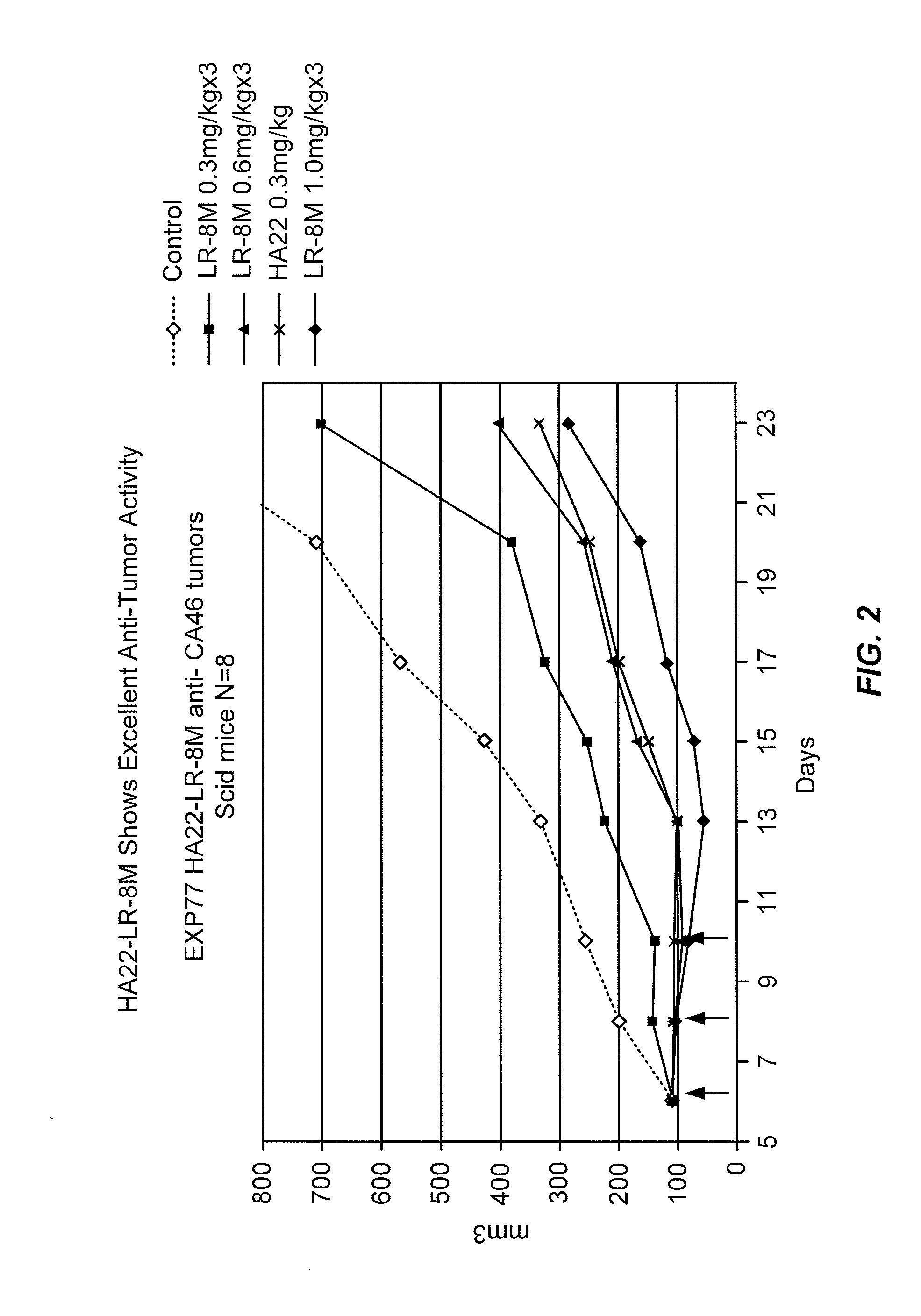
Recombinant antibodies and immunoconjugates targeted to cd-22 bearing cells and tumors
InactiveUS20090305411A1BacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
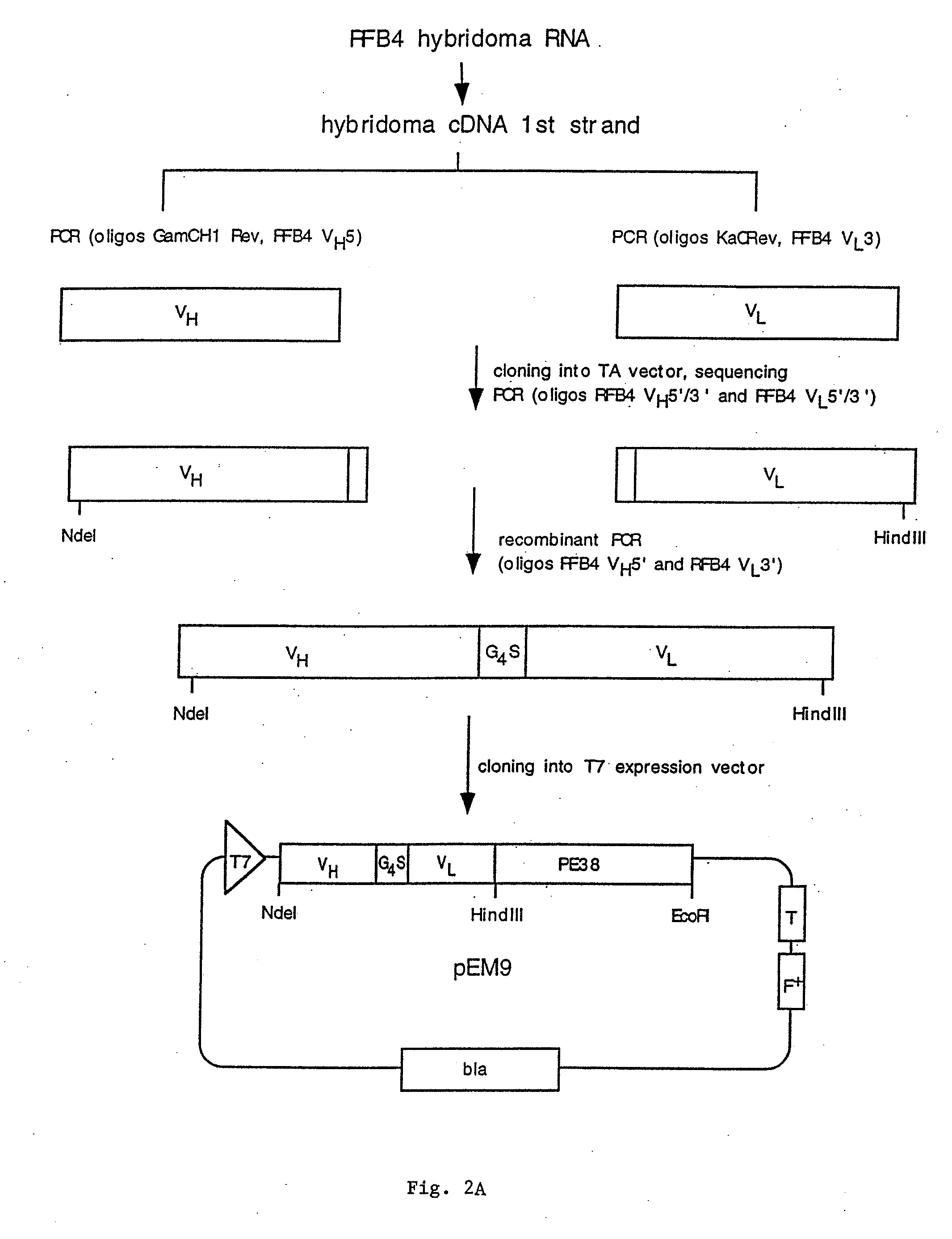
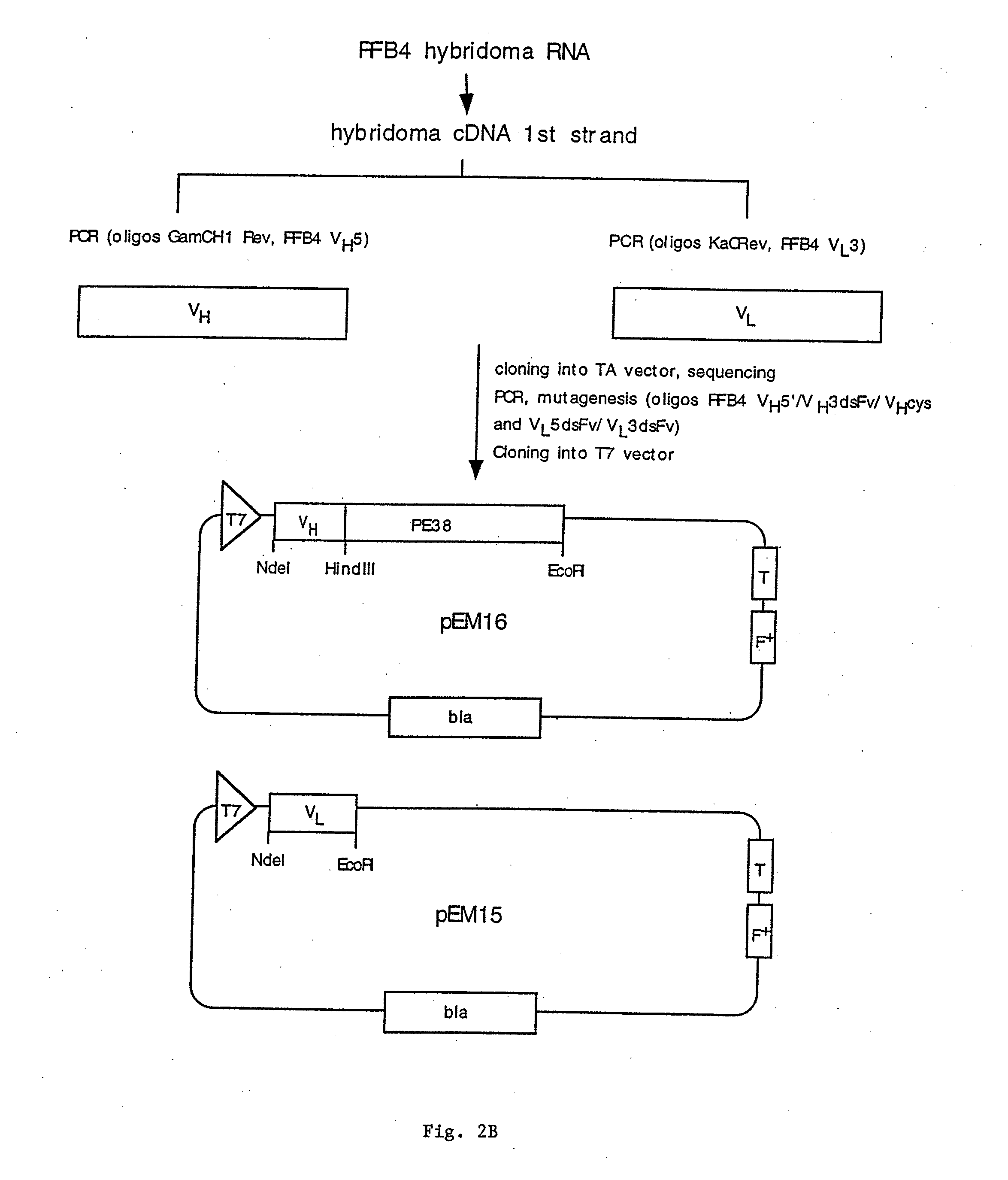
Methods and compositions relating to anti-CD22 antibodies with high binding affinity, and immunoconjugates comprising the anti-CD22 antibody linked to a therapeutic agent such as a Pseudomonas exotoxin or a detectable label. The invention provides diagnostic methods, and means to inhibit the growth of malignant B cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
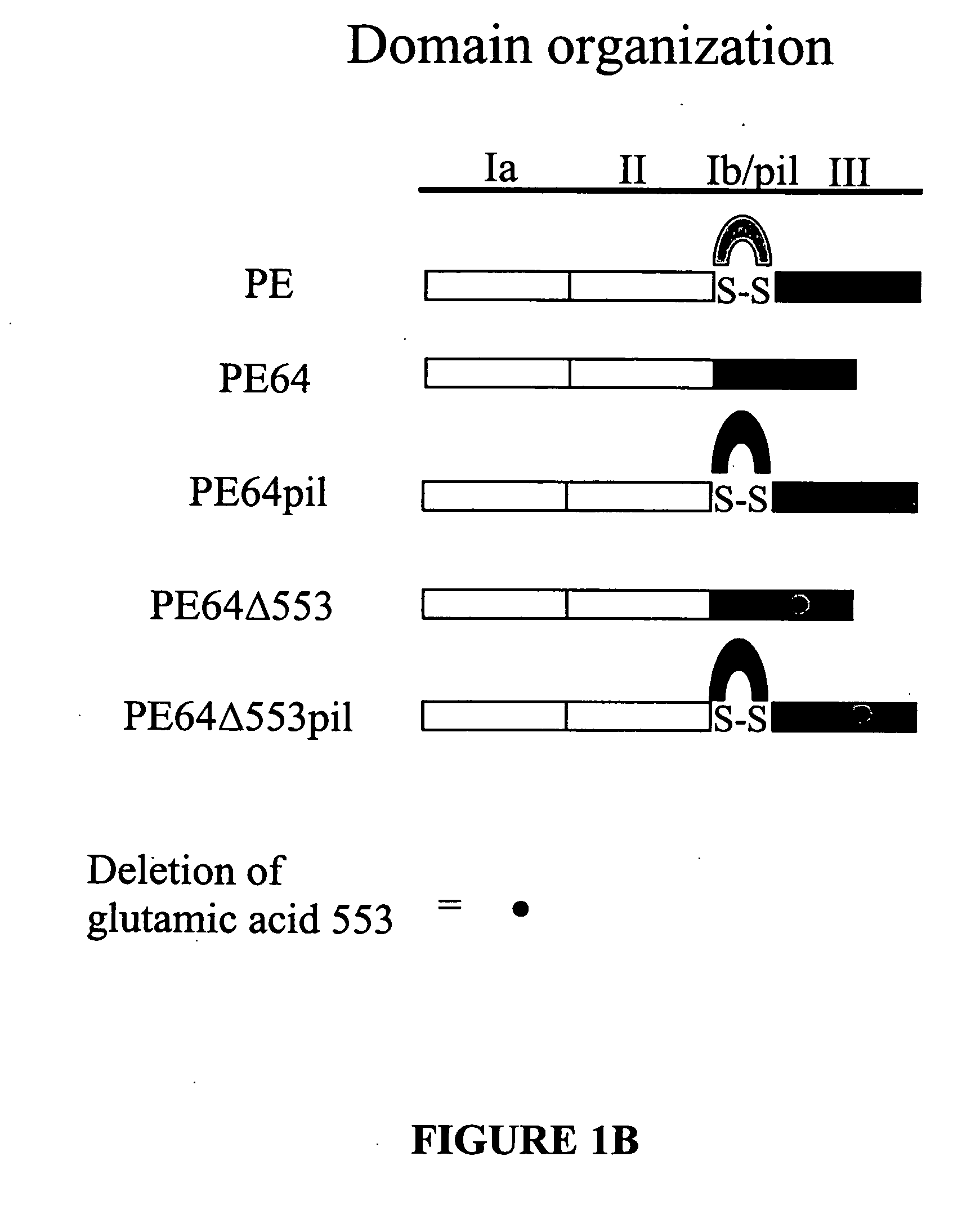
Chimeric protein comprising non-toxic pseudomonas exotoxin and type IV pilin sequences
InactiveUS20070003578A1Reduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ABacterial exotoxin
The invention provides chimeric proteins comprising a non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A sequence and a Type IV pilin loop sequence, wherein the Type IV loop sequence is inserted within the non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A. The invention also provides polynucleotides encoding the chimeric proteins, and compositions comprising the polynucleotides or the chimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods for using the chimeric proteins, polynucleotides and compositions of the invention.
Owner:THE GOV OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEP OF HEALTH & HUAMN SERVICES
Pseudomonas and microbial agent as well as applications thereof
InactiveCN102250798APromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismGenus Pseudomonas
The invention provides pseudomonas with the collection number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.4793, a microbial agent containing the pseudomonas, and applications of the pseudomonas or the microbial agent in petroleum hydrocarbon degradation, petroleum pollution bioremediation, petroleum polluted soil bioremediation and petroleum polluted water bioremediation. The pseudomonas with the collection number of CGMCC No.4793 and the microbial agent containing the pseudomonas have strong degrading capability for the petroleum hydrocarbon, can be widely applied to petroleum hydrocarbon degradation and petroleum pollution renovation, petroleum polluted soil renovation, petroleum polluted water renovation and the like.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method of controlling fungal pathogens, and agents useful for same
A method of preventing or treating infection by a range of fungal pathogens in an animal or plant or stored plant product comprising administering an effective amount of a sugar acid, in particular mannonic acid, gluconic acid or galacturonic. The sugar acid can be delivered by a biocontrol that can manufacture the sugar acid. An exemplified biocontrol is Pseudomonas strain AN5, which is characterized by the capacity to convert aldose to sugar acid. Also disclosed are nucleotide sequences from enzymes in the Pseudomonas PQQ enzyme pathway which may be used to transform microorganisms and plants so that they produce sugar acids at levels sufficient to control the growth or viability of pathogens.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Recombinant fusion protein and polynucleotide construct for immunotoxin production
The present invention relates to a polynucleotide construct encoding a fusion protein consisting of a domain which binds the immunoglobulin Fc region, genetically fused to a truncated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE). In particular, the invention discloses the fusion protein, ZZ-PE38, and further provides immunotoxins, formed from complexes of the fusion protein with antibodies for targeted cell killing.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Pseudomonas exotoxin A-like chimeric immunogens
InactiveUS8092809B2Eliminate needAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitopeGenus Pseudomonas
This invention provides Pseudomonas exotoxin A-like chimeric immunogens that include a non-native epitope in the Ib domain of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Methods of eliciting an immune response using these immunogens also are provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
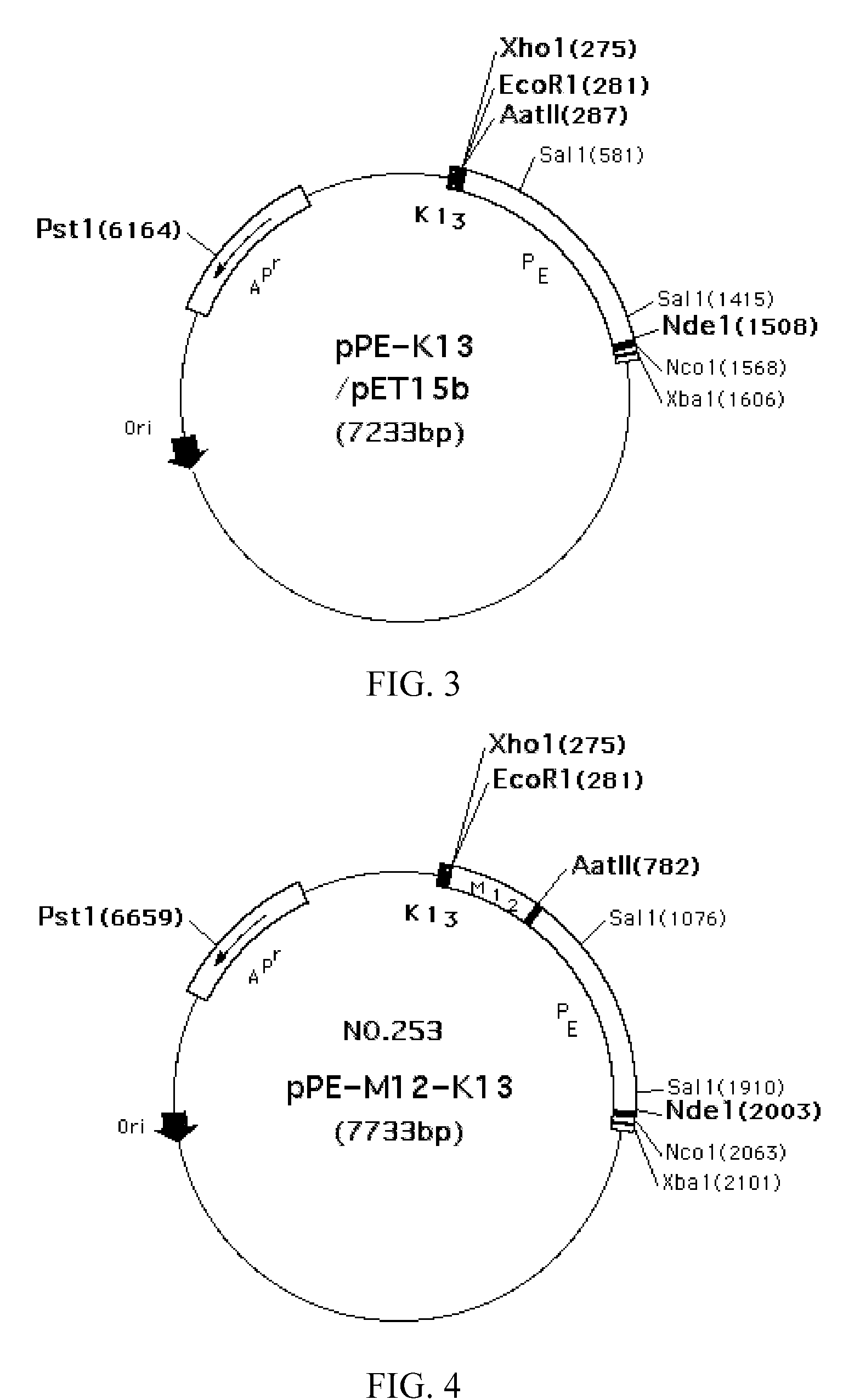
Novel plasmid, bearing the plasmid, and method of producing an enzyme using the transformant
InactiveUS20020076751A1Promote safe productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesGenus Pseudomonas
The invention relates to a plasmid characterized in that the plasmid comprises a DNA fragment containing a gene coding for an enzyme taking PQQ as the prosthetic group as cloned in a broad-host-range vector defected of conjugative transfer function beforehand and that the plasmid is capable of being expressed in bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
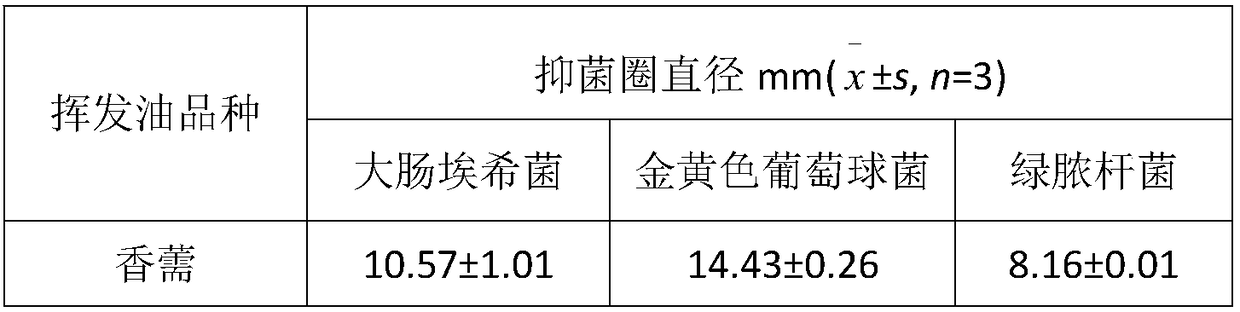
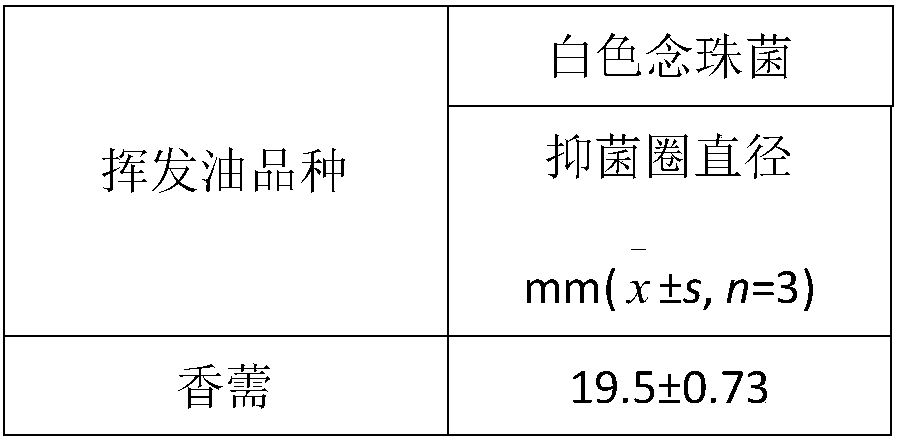
Application of elsholtzia volatile oil in sterilizing and/or anti-bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses application of elsholtzia volatile oil in anti-bacteria and antibiotic resistant bacteria. The elsholtzia volatile oil is extracted by steam distillation. The elsholtzia volatile oil has certain functions of killing and / or inhibiting growth on bacteria of staphylococcus, escherichia coli, candida, pseudomonas, enterobacter, streptococcus and the like and fungi. The elsholtzia volatile oil has certain functions of killing and / or inhibiting growth on bacteria of drug-resistant staphylococcus, drug-resistant escherichia coli, drug-resistant enterobacter, drug-resistant klebsiella, drug-resistant pseudomonas, drug-resistant acinetobacter, drug-resistant streptococcus, and drug-resistant enterococcus and the like. The elsholtzia volatile oil can be used in industries offood, medicine, health care products, cosmetics and the like and can be used for preparing various forms of products with antibacterial and antibiotic resistant bacteria functions, and belongs to thenew application field of the elsholtzia volatile oil.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
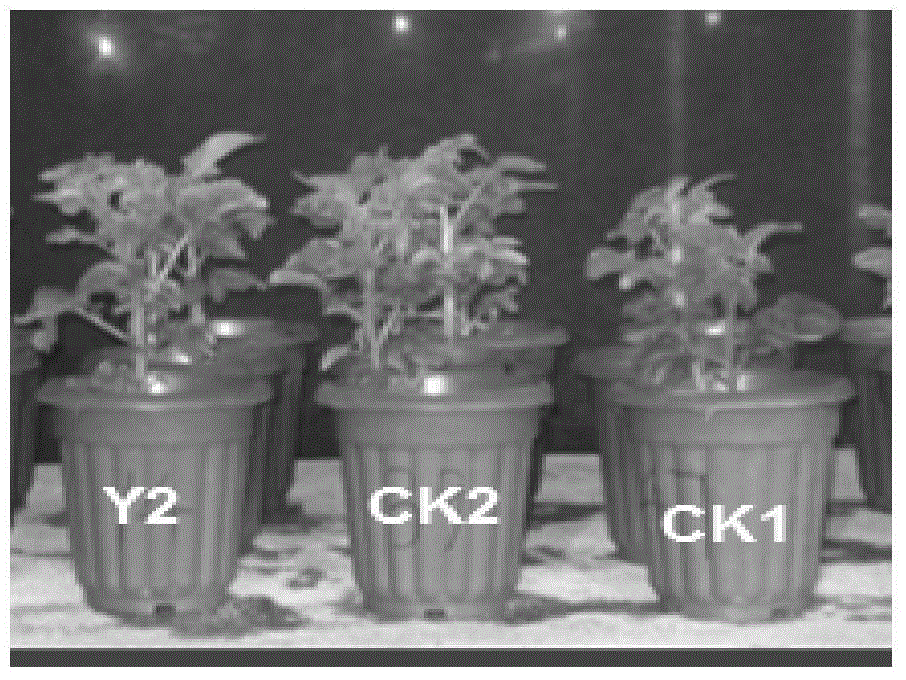
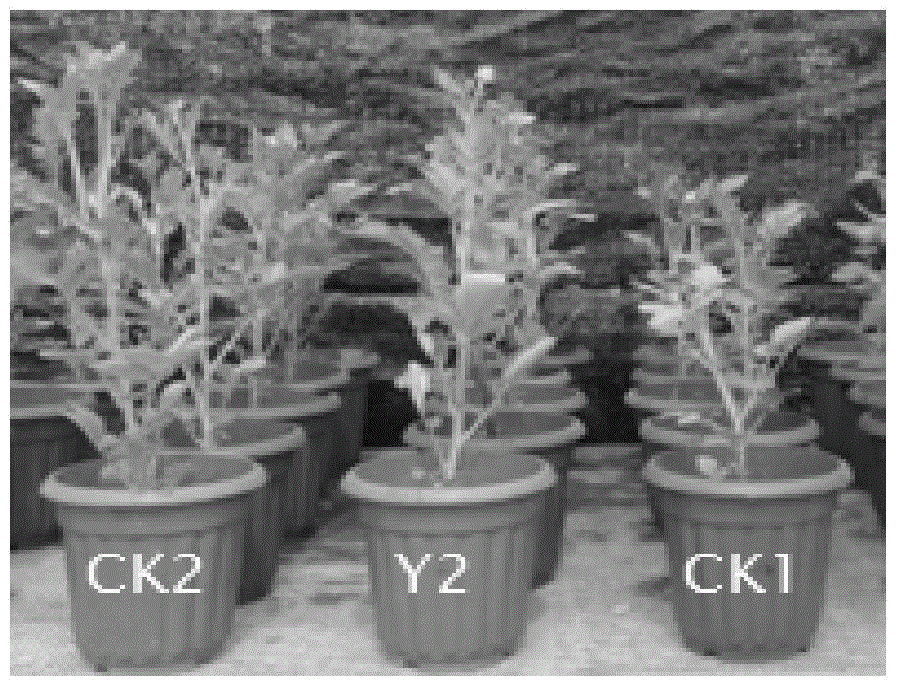
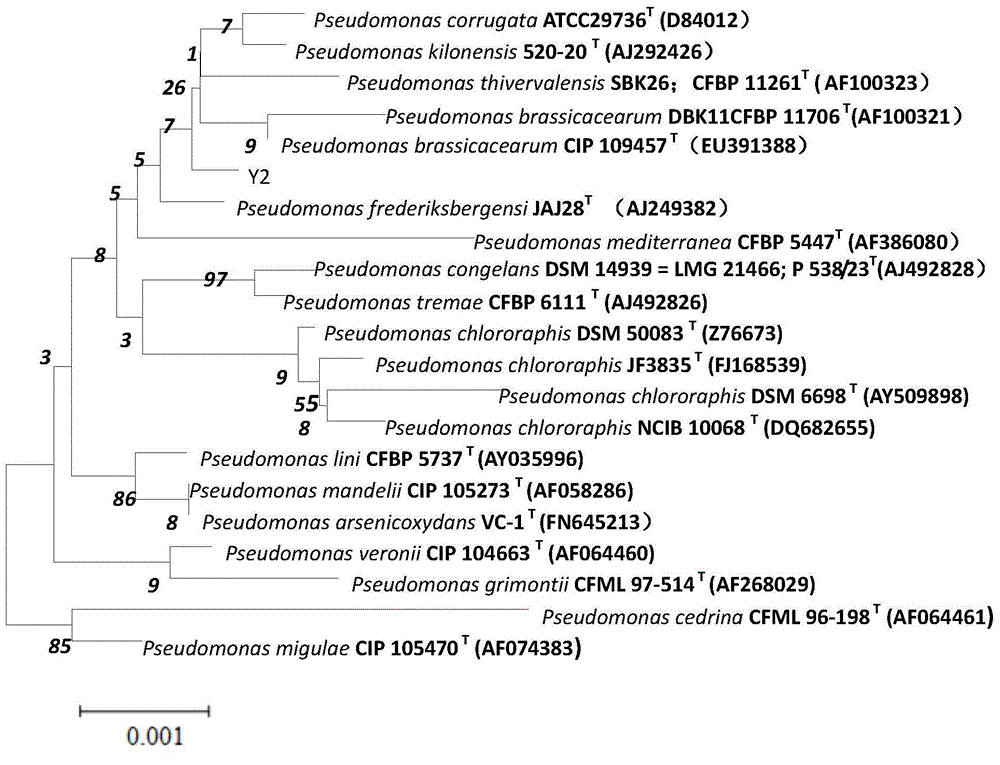
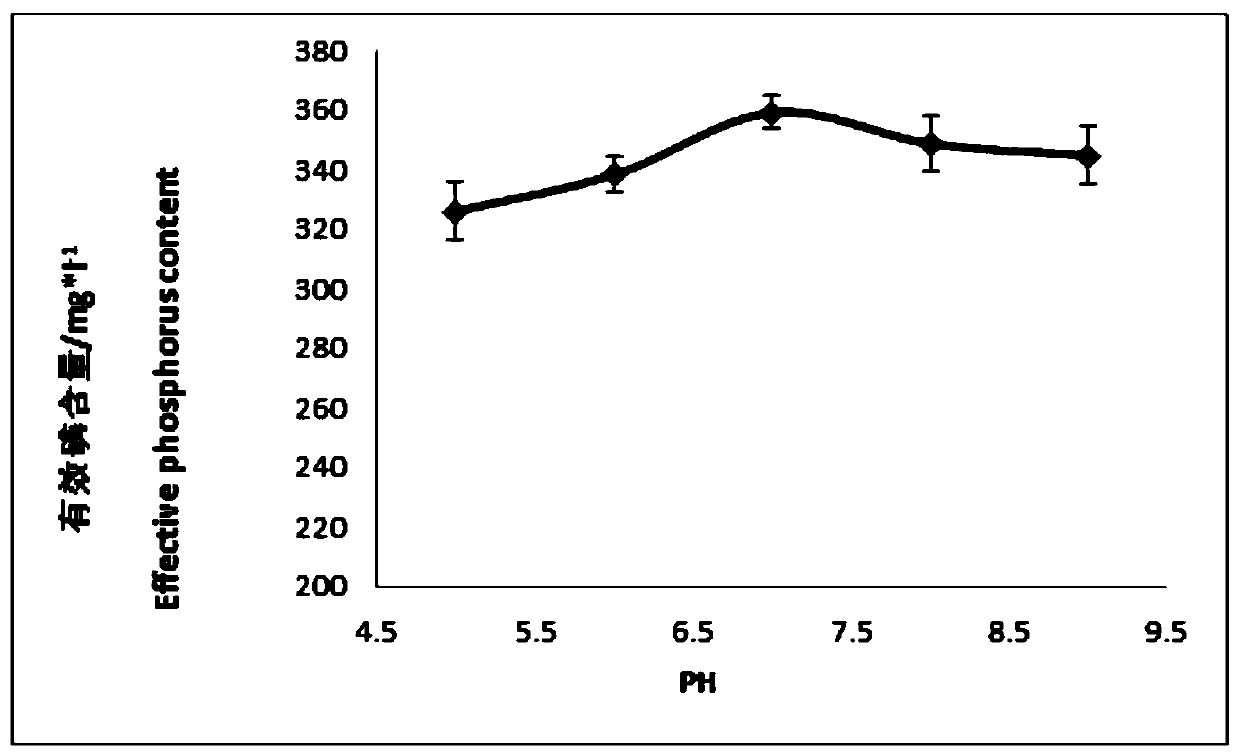
Pseudomonas phosphate dissolving bacterium Y2, bioorganic fertilizer prepared through using bacterium, and application of fertilizer
ActiveCN105112319APromote growthSuitable for large area useBiocidePlant growth regulatorsNicotiana tabacumPhosphate
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas phosphate dissolving bacterium Y2, a bioorganic fertilizer prepared through using the bacterium, and an application of the fertilizer. The above bacterium strain is separated from potato rhizosphere, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on Dec. 25, 2014 with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.10242. A result of rocking bottle experiments show that the bacterium strain can effectively reduce the pH value of a solution and dissolve insoluble phosphate in the solution; and a result of bacterium filled pot test shows that the bacterium strain can effectively promote growth of potato, corn and tobacco plants, and can massively colonize at the rhizosphere of the plants to realize a growth promotion effect. The granular bioorganic fertilizer developed through using the bacterium strain, decomposed chicken manure and rapeseed meal can be applied to substantially promote the growth of the corn plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Enzymatic hydrolysis of a polymer comprising vinyl acetate monomer
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Mutated Pseudomonas exotoxins with reduced antigenicity
The invention provides mutated Pseudomonas exotoxins (PE) that have reduced immunogenicity compared to PEs containing the native sequence. The PEs of the invention have one or more individual mutations of positions of the native sequence of PE that reduce antibody binding to one or more PE epitopes. Nucleic acids encoding the mutated PEs, chimeric molecules comprising them, compositions comprising the chimeric molecules and methods of using them, are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
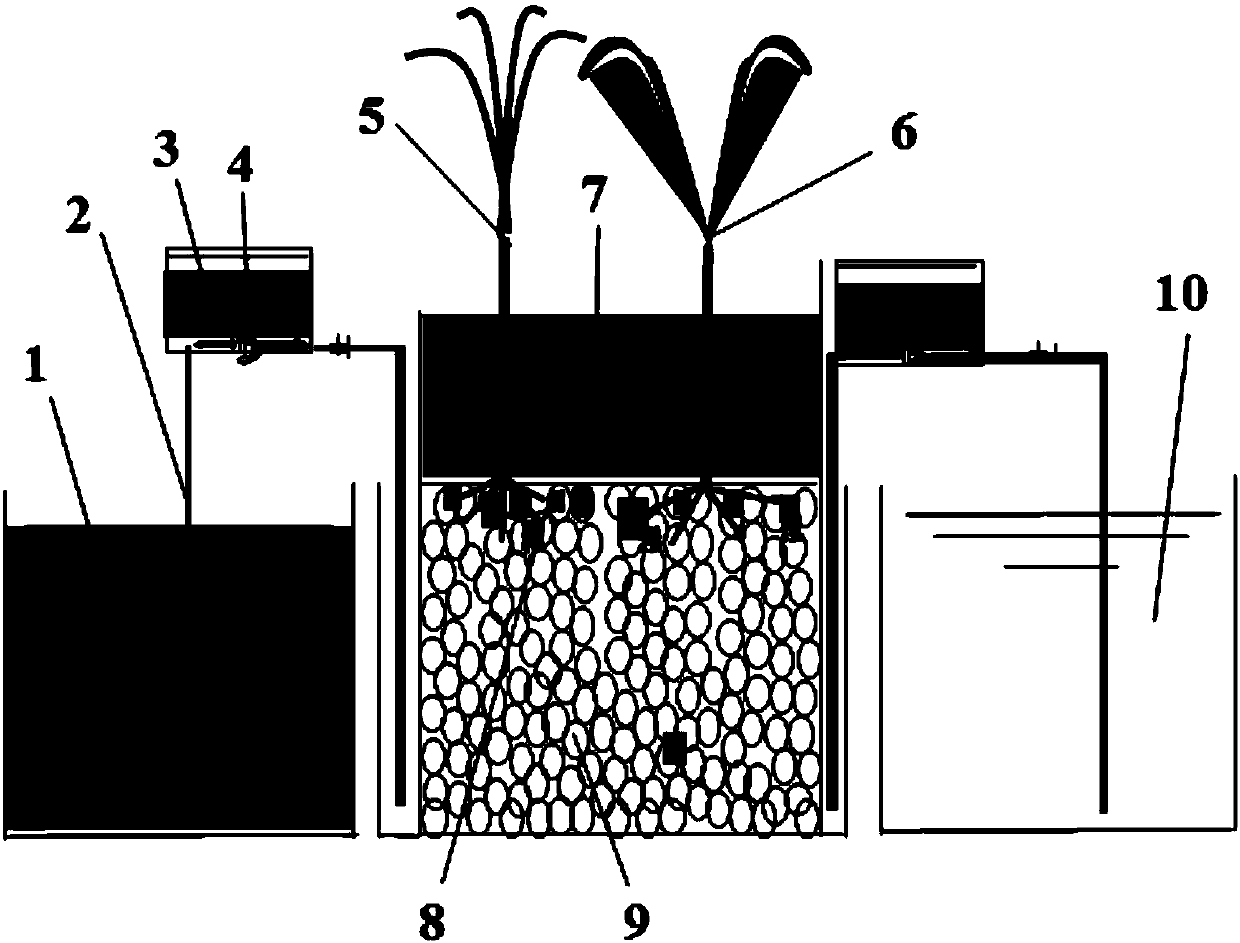
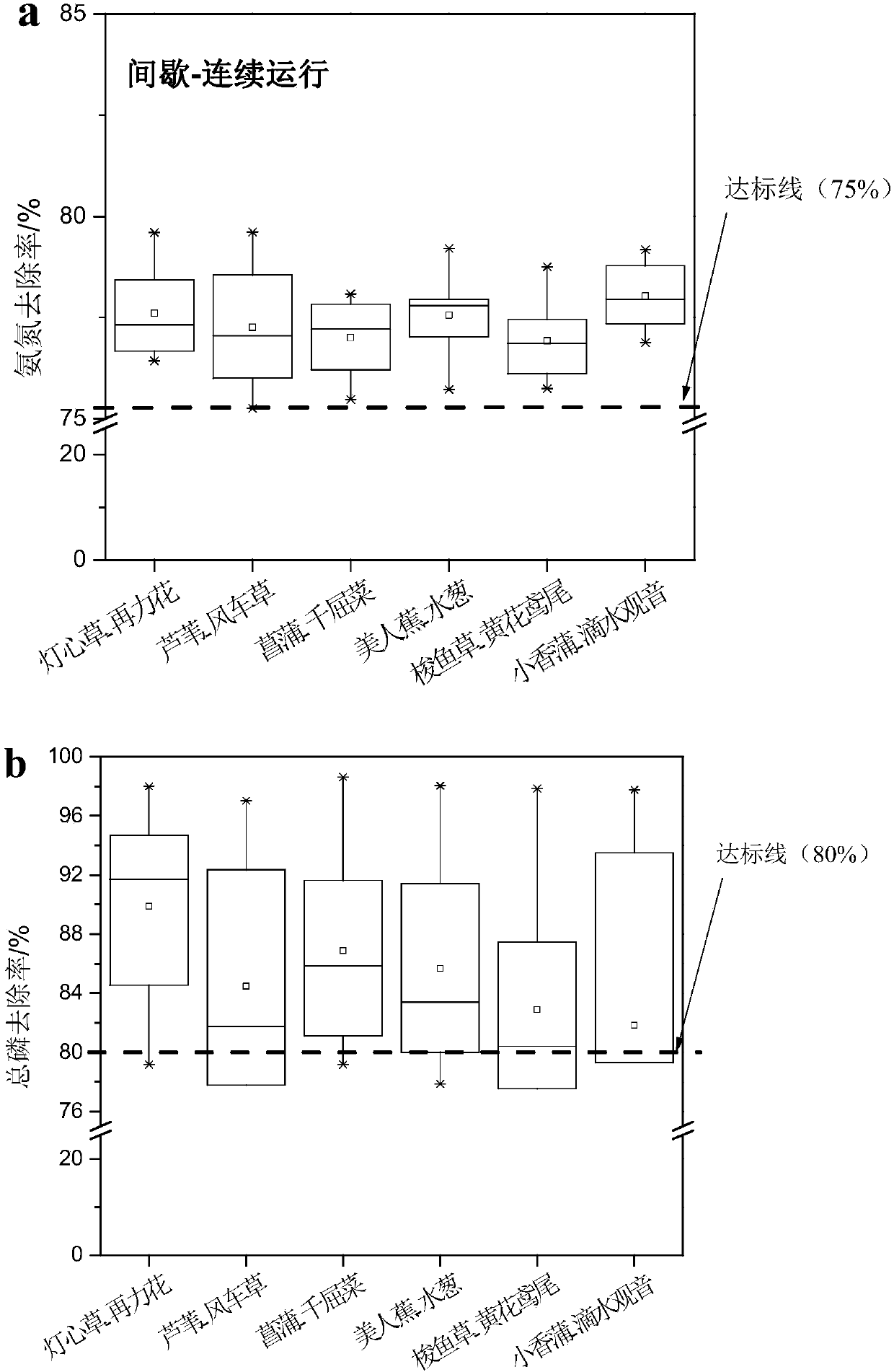
Underflow constructed wetland ecological system for disposing rural domestic waste and disposing method
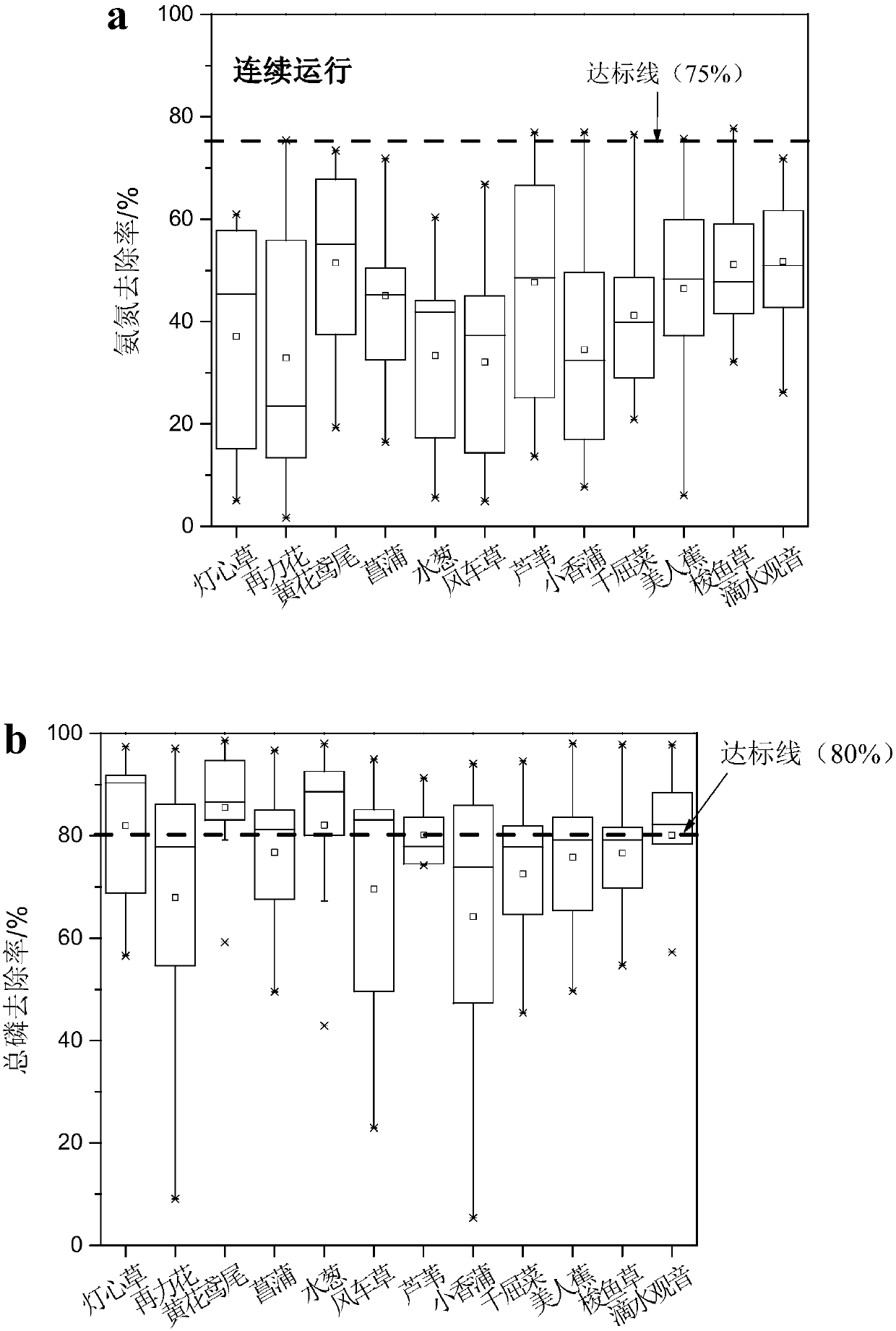
ActiveCN107686167AGuaranteed denitrification efficiencyMaintain stable operationWater contaminantsBiological treatment apparatusRoot systemEcosystem
The invention discloses an underflow constructed wetland ecological system for disposing rural domestic waste and a disposing method. By adding root advantageous microorganisms in a canna water planting system, ratio of Alkaligenes, flavobacterium, lysobacter, Pseudomonas and other advantageous germs can be rapidly increased, the abundance of dioxygenase, dehydrogenase, phosphate dehydrogenase, urease, nitrate reductase, and dehydrogenase gene in catalase gene in the constructed wetland can be improved; two kinds of wetland plants can be planted in an intersecting manner, thus the different plant root secreta can be generated and a rich root microbial community structure is formed; the underflow constructed wetland ecological system can remove COD, ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus atthe same time. Then the method of alternatively running continuous water feeding-intermittent water feeding is applied, thus the nitrogen removal efficiency is promoted while the system is stably operated. The method fully applies the advantages of the constructed wetland, strengthens the rapid construction of the constructed wetland ecological system, and optimizes the wetland running mode; the underflow constructed wetland ecological system is significant in environment, economic and social values.
Owner:ZHEJIANG METALLURGICAL RES INST +1
Cadmium-resistant bacteria and method for inhibiting heavy metal cadmium absorption of paddy rice
InactiveCN103952333AImprove patienceEasy to cultivateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationResistant bacteriaSoil science
The invention relates to cadmium-resistant bacteria and a method for inhibiting heavy metal cadmium absorption of paddy rice, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural and environmental pollution treatment. The cadmium-resistant bacteria are (Pseudomonas sp.) TCd-1, is preserved in the China center for type culture collection of Wuhan university on December 11, 2013 and has the accession number of CCTCC M2013649. An identification result shows that the bacterial strain TCd-1 is Pseudomonas sp., has resistance to a plurality of heavy metals, and has cadmium, lead and nickel resistance concentrations of 900mg.L<-1>, 800mg.L<-1> and 600mg.L<-1>. A ratio of the number ratio active live bacteria in the bacterial liquid is 1.85-1.87*10<9> per milliliter. Through use of 2mL of the bacterial liquid in each kg of heavy metal cadmium-polluted wet soil, cadmium-caused paddy rice growth inhibition is overcome, cadmium content of all parts of the paddy rice is effectively reduced and especially, cadmium content of brown rice is reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Process for producing theanine
InactiveCN1688705AEfficient preparationEasy to produceMicroorganism based processesFermentationGenus PseudomonasPseudomonas tolaasii
It is intended to provide a novel process for efficiently producing theanine, thereby enabling convenient and industrially advantageous production of theanine. Pseudomonas citronellosis GEA, which has been newly isolated from soil in nature and selected, is a theanine-producing strain belonging to the species citronellosis of the genus Pseudomonas and showing a gamma-glutamyl transfer reaction. Theanine can be highly efficiently produced, compared with the existing methods, by using glutaminase originating in the above strain in a mixture of glutamine with ethylamine at pH 9 to 12.
Owner:TAIYO KAGAKU CO LTD
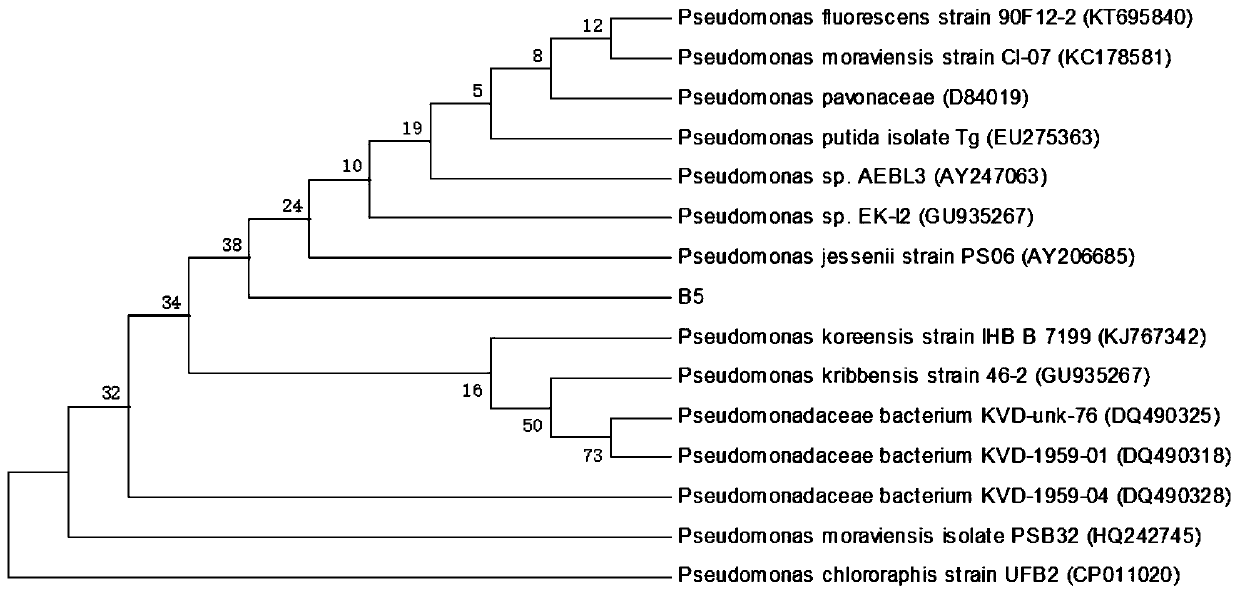
Phosphate solubilizing bacterium and extraction method thereof
InactiveCN110669696AAbundant resourcesPhosphorus dissolving ability is strongBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySucrose
The invention discloses a phosphate solubilizing bacterium and an extraction method thereof. The phosphate solubilizing bacterium is named a strain B5, the strain B5 is a pseudomonas bacterium, determination results of biochemical criterion are gram staining is negative, a methyl red test is negative, a V-P reaction is negative, an indole test is negative, an oxidase test is negative, the strain B5 can use citrate as a carbon source to produce extracellular enzyme-gelatinase liquidation gelatin, catalase and indole are produced, and H2S is generated; the order of the phosphate solubilizing ability of the strain B5 from high to low under different carbon sources is that glucose is greater than galactose, the galactose is greater than lactose, the lactose is greater than sucrose, and the sucrose is greater than soluble phosphate starch, and the order of the phosphate solubilizing ability under different nitrogen sources is that ammonium sulfate is greater than ammonium chloride, the ammonium chloride is greater than urea, and the urea is greater than potassium nitrate; and the optimum growth temperature of the strain B5 is 28-32 DEG C, and the optimum growth pH of the strain B5 is 7-9.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Pseudomonas exotoxin a with reduced immunogenicity
ActiveUS20120263674A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ACytotoxicity
The present invention provides improved Pseudomonas Exotoxin A (PE) molecules with high cytotoxicity and reduced immunogenicity, compositions containing the improved (PE), and methods of use.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
Microbial prepn for promoting germination of ephedra seed
The present invention relates to microbial preparation for promoting germination of ephedra seed. Two kinds of known bacteria, i.e., yellow pseudomonads and Bacillus subtilis, are separated and screened form rhizospheric soil of wild ephedra and through culture in medium and other steps, the microbial preparation for soaking ephedra seed is prepared. When it is used in soaking ephedra seed, the seedling stage can be 4-5 days brought forward and the seedling rate may be 13-19% raised. When it is used for processing ephedra seedling before being transplanted, it can promote the taking root and tillering and transplanted ephedra seedling.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for culturing Rhodopseudomonas photosynthetic bacteria by using cyanobacterial bloom
ActiveCN105543148AEasy accessLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenus Pseudomonas
The invention discloses a method for culturing high-density Rhodopseudomonas photosynthetic bacteria by using cyanobacterial bloom, which comprises the following steps: acquiring cyanobacterial bloom from a cyanobacterial bloom generating water body, and concentrating properly until the total nitrogen concentration in the concentrated cyanobacterial bloom system is 230-2010 mg / L and the total phosphorus concentration is 35-350 mg / L; and putting in an open transparent container in a light environment, and continuously aerating while keeping the concentrated cyanobacterial bloom system at 20-42 DEG C to form an coexistence of an aerobic region and an anaerobic region until the high-density photosynthetic bacteria are generated. The method can be used for converting the cyanobacterial bloom into the Rhodopseudomonas photosynthetic bacteria, is capable of promoting the innocent treatment and utilization of water body nutrient substances and accelerating the conversion of the water body nutrient substances, and can be directly used for treating the cyanobacterial bloom; and the formed photosynthetic bacteria can be directly used for breeding industry or sewage purification.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Pseudomonas sp. and a preparation method and application of bifunctional enzyme preparation of pseudomonas sp.
ActiveUS20190376153A1Remarkable degradation activityEfficiently degrading polychlorinated biphenyl and atrazineBacteriaCulture processPolychlorinated biphenylPseudomonas sp. BT1
A Pseudomonas sp. ECO-1 strain was preserved at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Mar. 31, 2017, with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 13960. The Pseudomonas sp. ECO-1 strain was separated from POPs (Persistent Organic Pollutants) polluted soil for the first time. The bifunctional enzyme preparation capable of efficiently degrading polychlorinated biphenyl and atrazine was prepared by utilizing the strain for the first time; especially, the bifunctional enzyme preparation has remarkable degradation activity on the polychlorinated biphenyl which is difficult to degrade under an aerobic condition, which is completely different from functions of existing known Pseudomonas sp. and enzyme preparations thereof.
Owner:ECOLOGY INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Pseudomonadaceae petroleum degrading bacterium L-1, microbial mixed agent of Pseudomonadaceae petroleum degrading bacterium L-1 and in-situ remediation method of petroleum-contaminated soil
InactiveCN109482638AReduce contentRealize harmless disposalContaminated soil reclamationContaminated soilsPseudomonadaceae
The invention provides a Pseudomonadaceae petroleum degrading bacterium L-1, a microbial mixed agent of the Pseudomonadaceae petroleum degrading bacterium L-1 and an in-situ remediation method of petroleum-contaminated soil. The preservation number of the Pseudomonadaceae petroleum degrading bacterium is CGMCC NO.16557. The microbial mixed agent contains the Pseudomonadaceae petroleum degrading bacteria in the preservation number being CGMCC NO.16557 and indigenous bacteria. By the aid of the method, the content of petroleum hydrocarbon and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in petroleum-containing sludge can be reduced effectively, harmless treatment of the petroleum-containing sludge can be realized, harms caused by the contaminated soil to human bodies can be eliminated, and ecological functions of the soil can be restored. Thus, degradation of the petroleum hydrocarbon is used as a starting point, microbes having the obvious degrading effect on soil petroleum are separated and cultivated, and the specific implementation measure of an on-site petroleum-contaminated soil microbial in-situ remediation technology is further provided. The petroleum-contaminated soil with the concentration being 3% can be degraded by 77% after 30 days.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Low temperature resistant cellulose degradation bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN103361282AEfficient degradationLow costBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseCellulose degradation
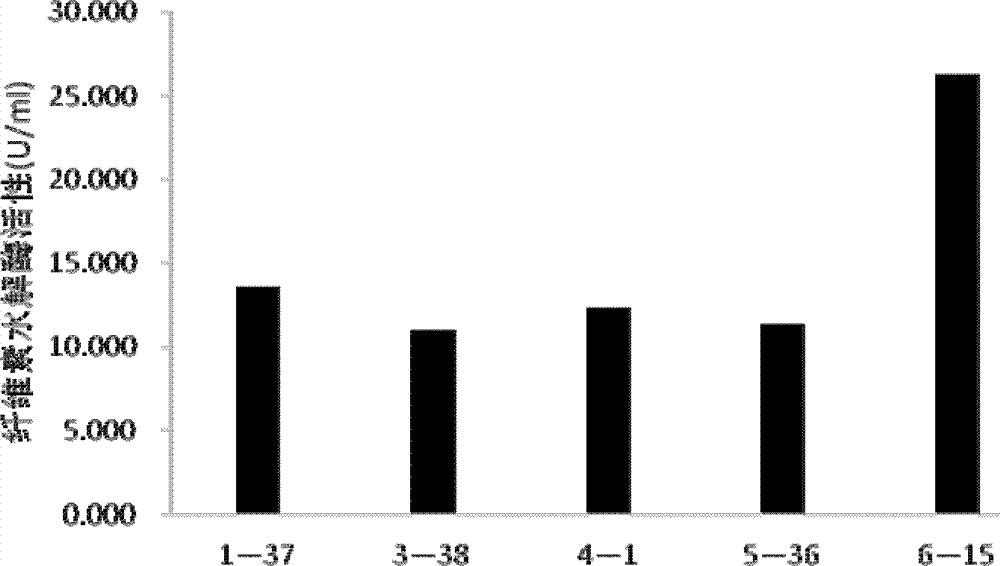
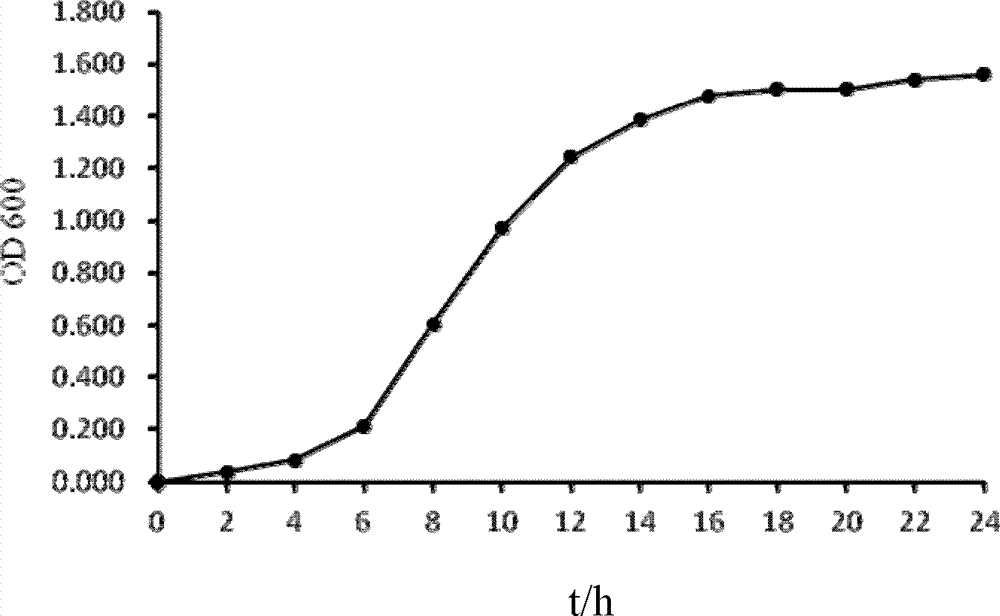
The invention provides low temperature resistant cellulose degradation bacteria, which are pseudomonas (Pseudomonas sp.) bacterial strains B6-15, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC NO.5851. By adopting the bacteria, the cellulose can be efficiently degraded in a low-temperature condition (15-20 DEG C); and a new microbial resource and a technical support are provided for facilitating rise of compost temperature by degrading the cellulose in the composting process in a low-temperature environment.
Owner:北京沃土天地生物科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com