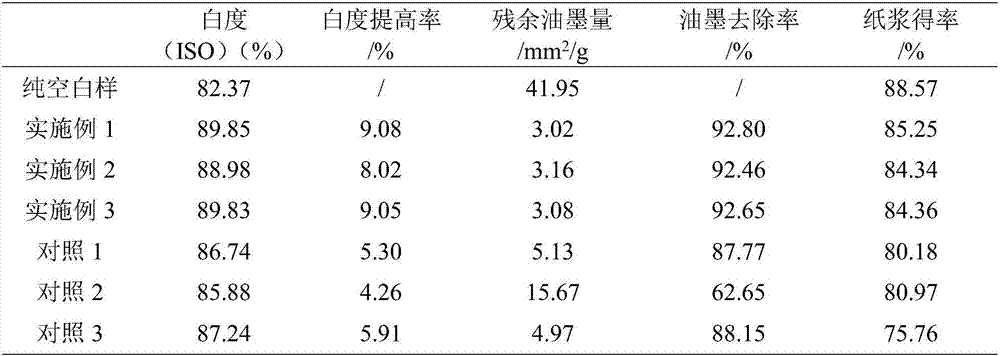
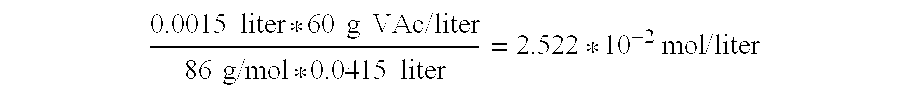Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138 results about "Cutinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
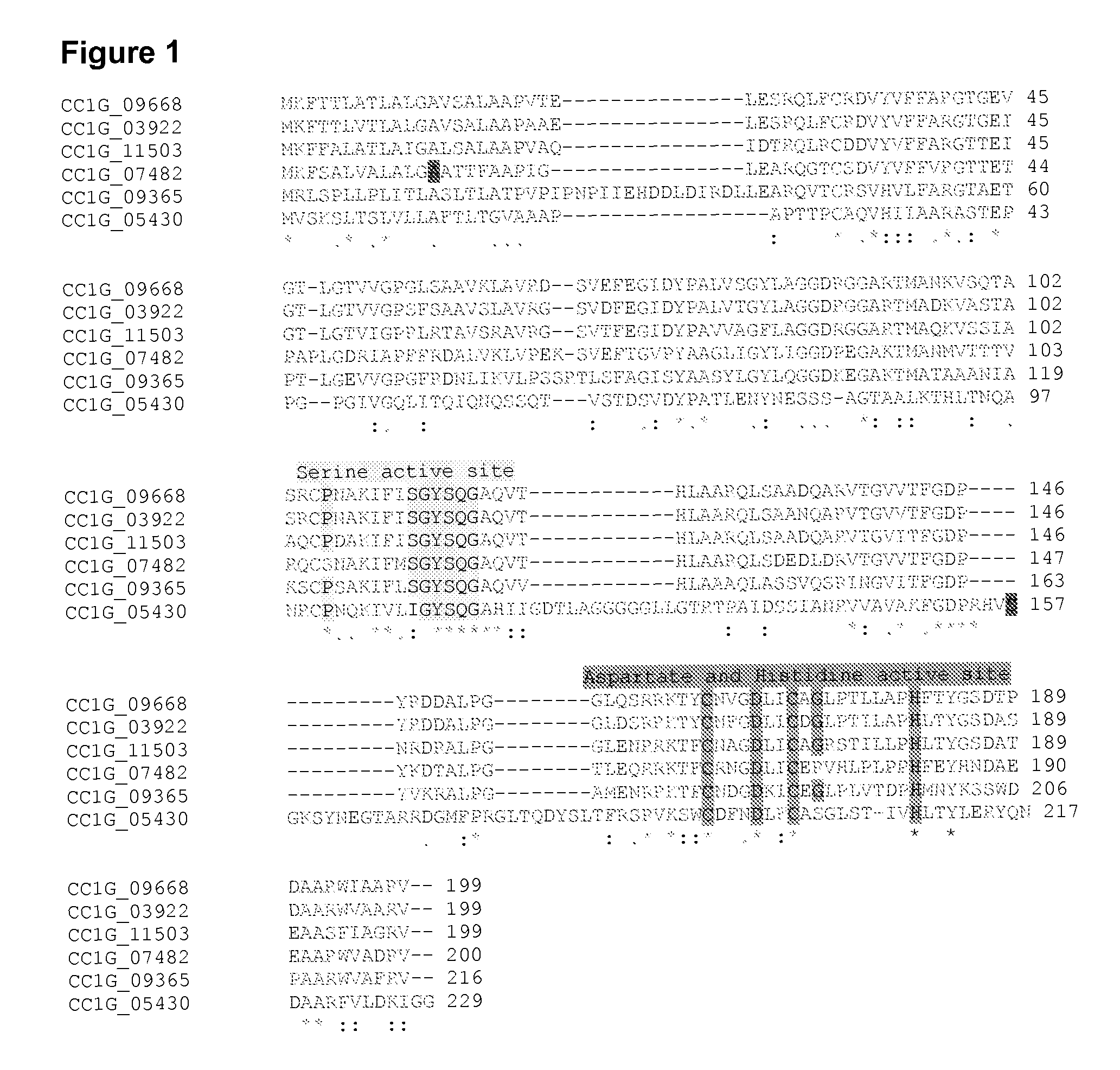
A cutinase (EC 3.1.1.74) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction cutin + H₂O ⇌ cutin monomers Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are cutin and H₂O, whereas its product is cutin monomer. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on carboxylic ester bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is cutin hydrolase. Aerial plant organs are protected by a cuticle composed of an insoluble polymeric structural compound, cutin, which is a polyester composed of hydroxy and hydroxyepoxy fatty acids.
Esterases and their use
The present invention relates to polyesterases having cutinase and / or suberinase activity obtainable from Coprinus and Trichoderma. The invention further relates to a method for producing the polyesterases, and to polynucleotides, vectors and host cells used therein. The enzymes are useful in hydrolysing cutin, suberin and other polyesters for example in treating agricultural or food raw materials, or wood raw materials, pulp and paper products and waste, and in modifying polyester fibers, or in laundry and dish applications.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase and method for constructing same
ActiveCN101792729AIncrease productionReduce pollutionBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
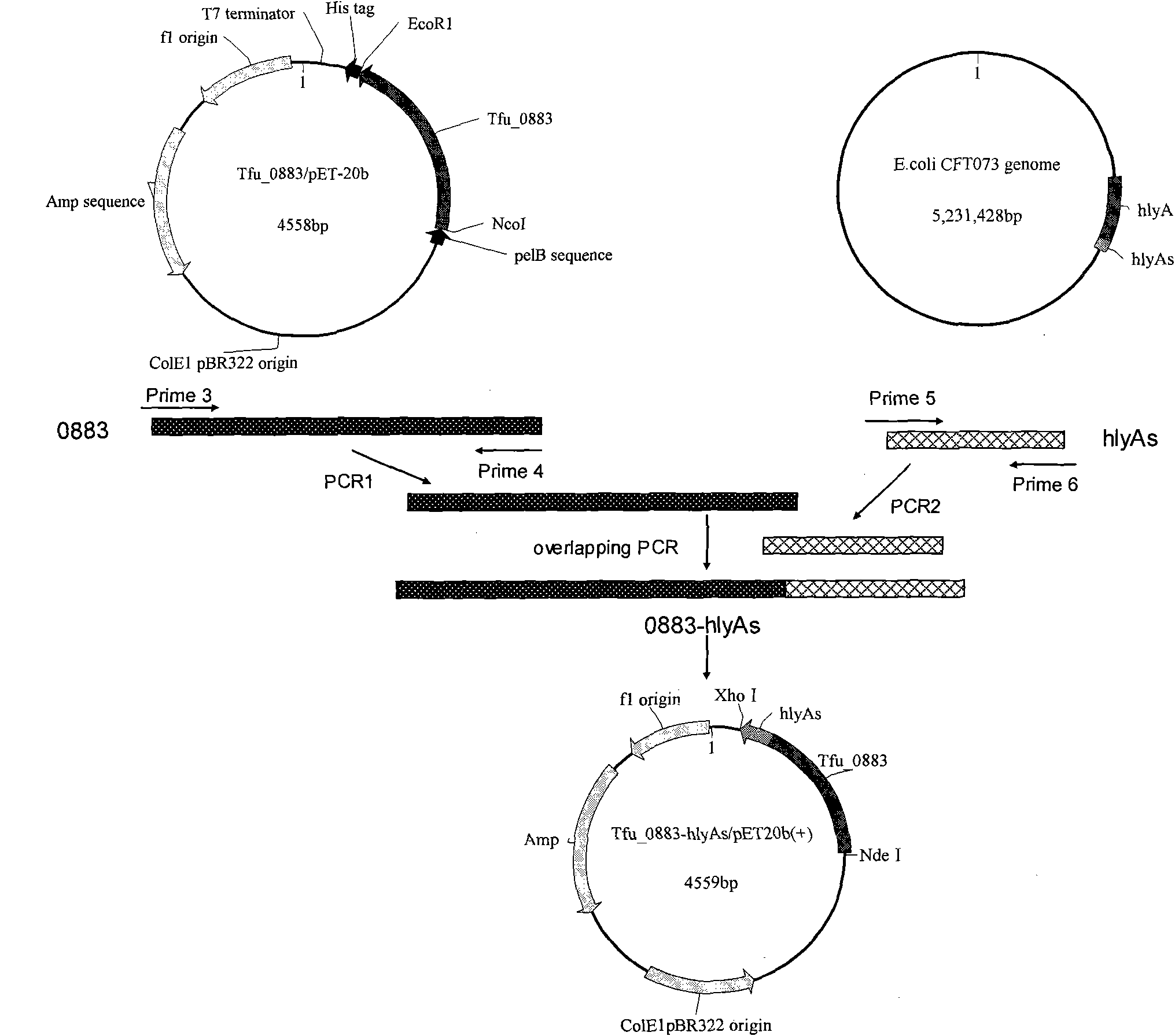
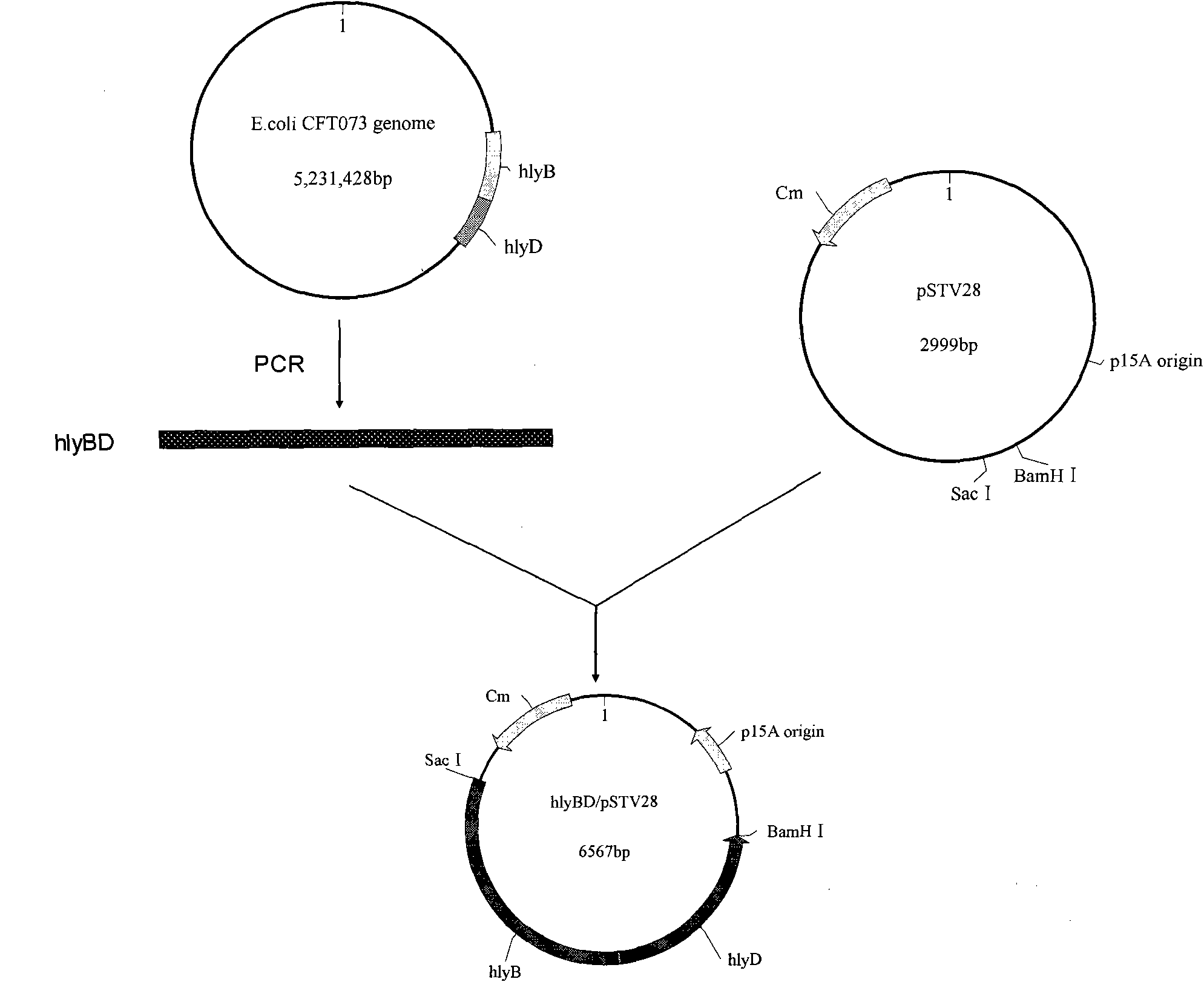
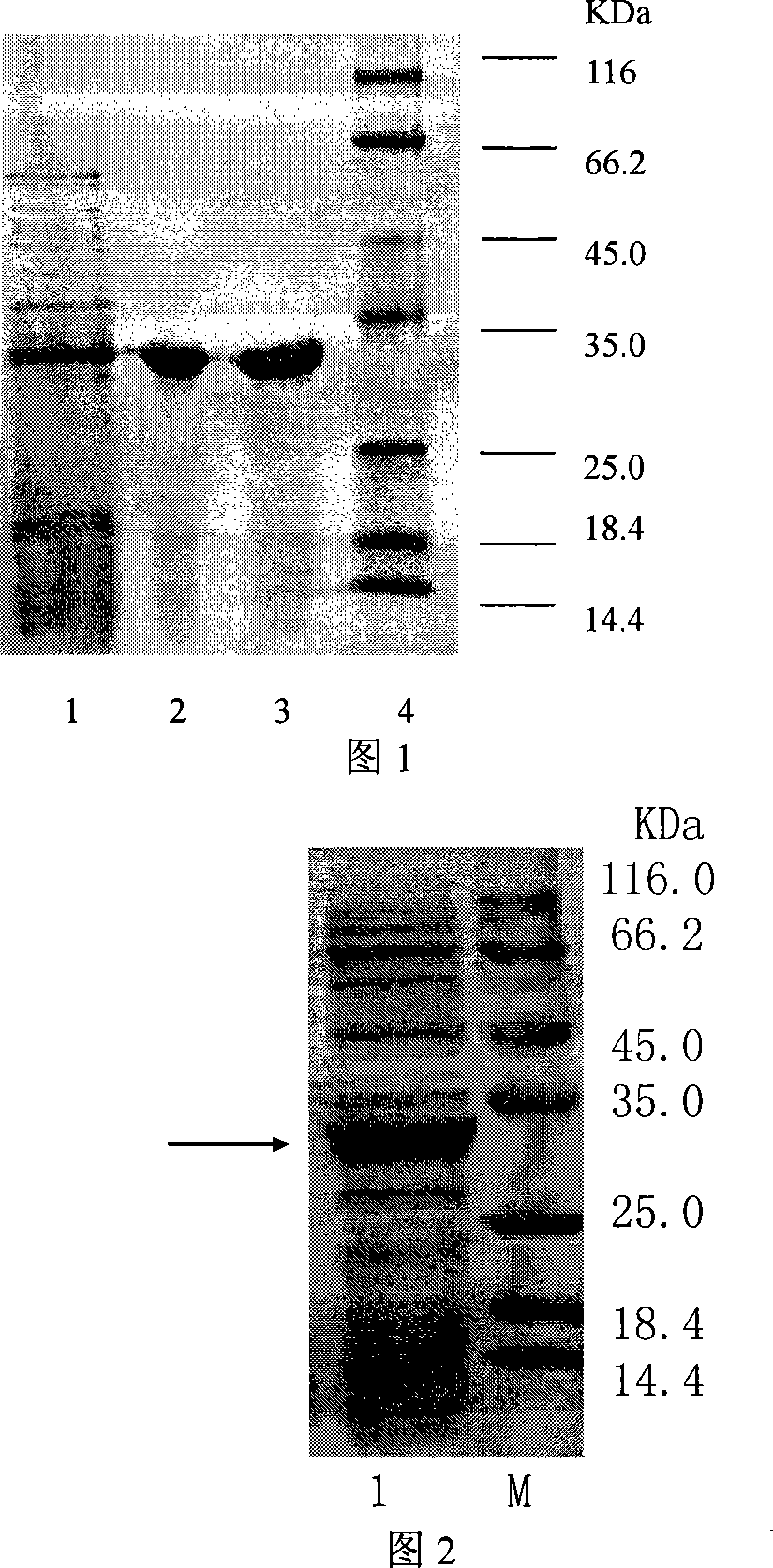
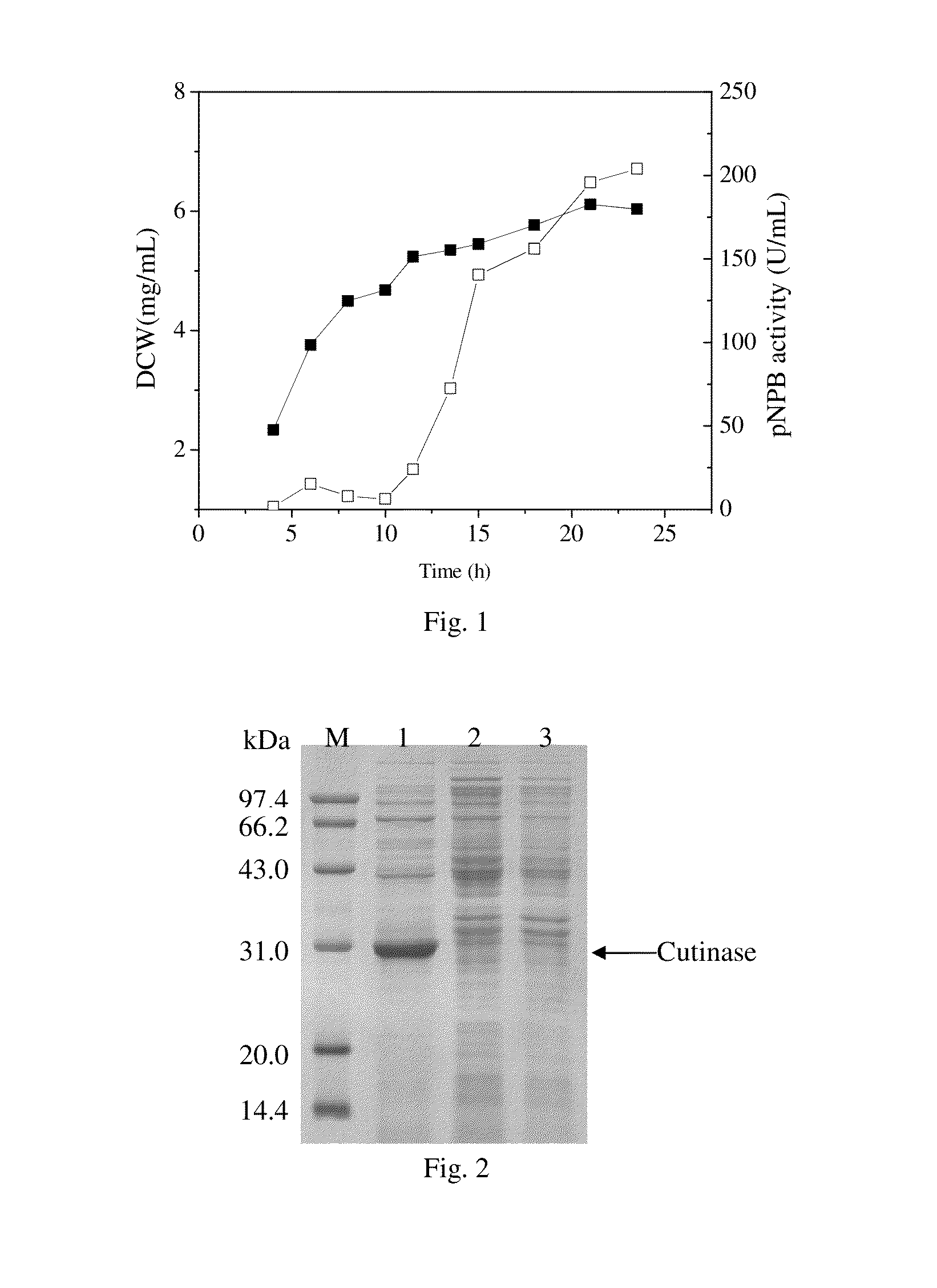
The invention relates to genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase and a method for constructing the same, belonging to the field of the bioengineering technology. The genetically engineered bacteria are escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) which carry two recombinant plasmids, and the recombinant plasmids are respectively plasmid pSTV28 carrying the specific genes in the Alpha-hemolysin A (hly A) pathway and plasmid pET20b(+) containing the cutinase-hly As genes. The method for constructing the genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase comprises the following steps: constructing two key recombinant plasmids and transforming the constructed recombinant plasmids in the escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain the genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently secreting, expressing and reconstructing cutinase. The cutinase is produced by using the genetically engineered bacteria through culturing liquid and inducing and expressing the cutinase. The cutinase Tfu_0883 for thermophilic monospore bacteria of Thermobifida Fusca WSH03-11 is used as the report protein. The shaking flask fermentation shows that the extracellular output of the cutinase is 306U / mL which is 1.7 times of the output of the cutinase which adopts the II-type secreting pathway in the preliminary working process in the research laboratory. The cutinase is secreted and expressed efficiently.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Wool-fabric protease anti-felting method based on weak oxidation and cutinase pretreatment
InactiveCN101565902AShort wetting timeLower contact angleBiochemical fibre treatmentAnimal fibresFiberCutinase
The invention provides a wool-fabric protease anti-felting method based on weak oxidation and cutinase pretreatment, which belongs to the technical field of dyeing and finishing of wool fabric in the wool-spinning industry. The method aims to overcome the defects that the chlorination-process for wool-felting prevention seriously pollutes environment and the single protease-method treatment is poor in fabric wettability and high in felting rate in order to achieve the aim of optimizing the protease treatment effect of the wool fabric. All-wool grey fabric is extracted in a chloroform-methanol or carbon tetrachloride-methanol solution to remove free oily impurities, is pretreated with hydrogen peroxide and cutinase in turn to improve the hydrophilicity of the fiber surface, and then is subjected to reduction processing in a protease solution so as to realize biological processing combined with wool enzyme reduction. The method makes the prior chlorination-process felting prevention replaced with a biological-method wool-felting prevention process, and the method not only can effectively improve the reduction rate and anti-felting effect of the wool fabric, and promote the improvement of fabric wettability, but also can effectively increase the dyeing depth of fabric, and reduce fiber damage in reduction processing, and is favorable for protecting ecological environment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
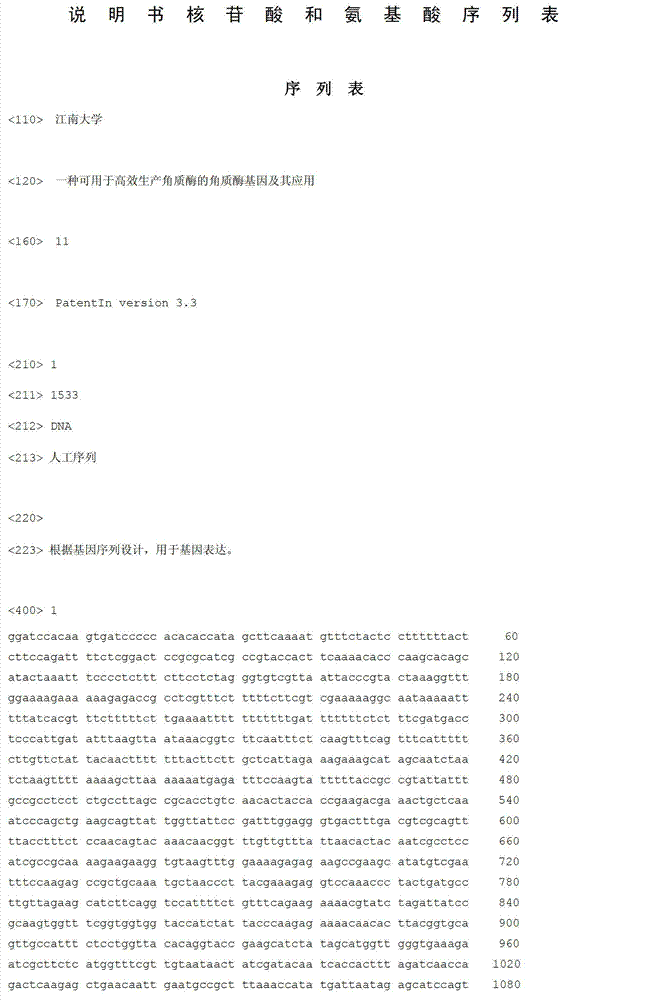
Heat resistance cutinase and its coding gene and expression
A heat-resistant cutinase and its coding gene and expression belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The present invention provides a bacterial cutinase different from fungal cutinase, its encoding gene and expression system, including extracting the total DNA of Thermobifida fusca WSH03-11, designing primers, and PCR amplification to obtain the gene encoding heat-resistant cutinase, It has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the full length is 906 nucleotides, and it encodes 301 amino acids. The plasmid pET20b(+) is used as the expression vector, and E.coli BL21 Rosetta(DE3)PlysS is used as the expression vector. The host can realize the high-efficiency expression of the heat-resistant cutinase gene. This cutinase has good thermal stability and has a good hydrolysis effect on cutin, triglyceride and various soluble synthetic esters, and can be widely used in textile, detergent and other industries.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cutinase producing gene engineering bacteria and use thereof
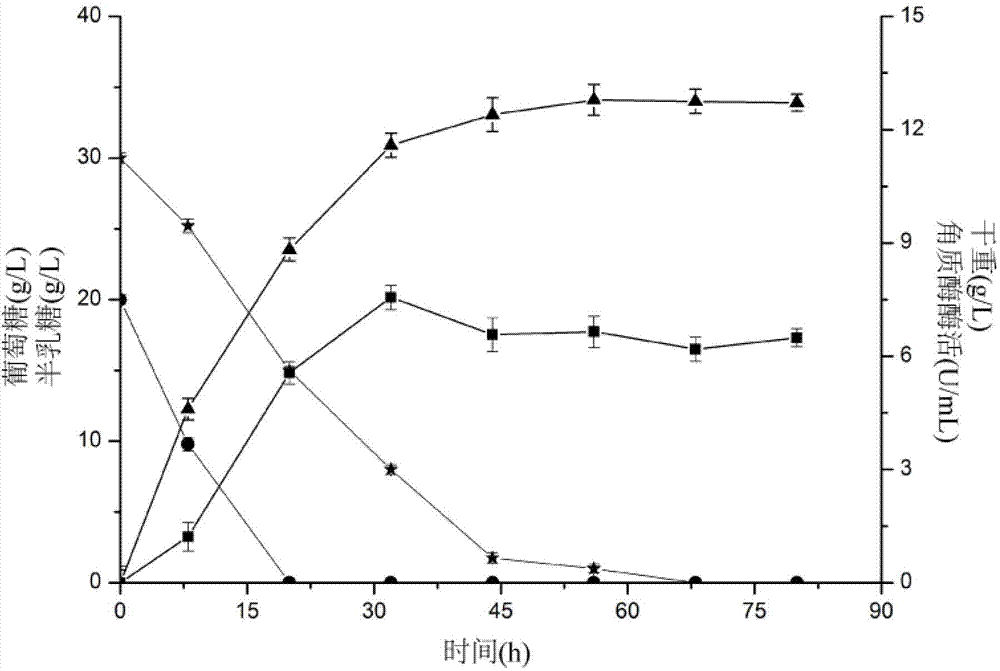
The invention discloses a cutinase producing gene engineering bacteria and use thereof and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Recombinant plasmid Tfu-0883-hlyAs / pET20b(+) is constructed, Escherichia coli E.coliBL21(DE3) is converted to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli Tfu-0883-hlyAs / pET20b(+) / E.coliBL21(DE3). A certain specific growth speed is controlled in a feed supplement batch fermentation manner, fermentation culture is performed for 30 to 34 hours, and the enzyme survival rate in fermentation supernate reaches 700 to 750U / Ml. In the invention, glycerol is used as a main raw material, a semisynthetic culture medium is adopted, and the cutinase producing gene engineering bacteria have the advantages of stability, convenient regulation and the like and are suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Oxidizing enzymes in the manufacture of paper materials
InactiveCN1575363AHave a bleaching effectWith deinking effectNon-fibrous pulp additionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpAmylaseAdjuvant
The use of fatty acid oxidizing enzymes in the manufacture of paper materials, such as paper, linerboard, corrugated paperboard, tissue, towels, corrugated containers and boxes. Examples of fatty acid oxidizing enzymes are oxygenases classified as EC 1.13.11. including any of the sub-classes thereof, such as lipoxygenase, EC 1.13.11.12. The effect of these enzymes is that the deposition of pitch is reduced, and bleaching and de-inking effects are also observed on the paper pulp and the resulting paper material. The fatty acid oxidizing enzyme can be used in combination with a substrate, with proteases, lipases, xylanases, cutinases, oxidoreductases, cellulases, endoglucanases amylases, mannanases, steryl esterases, and / or cholesterol esterases; or with surfactants and other adjuvants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Wool-fabric biological anti-felting method based on cutinase, keratinase and protease treatment
InactiveCN101565901AShort wetting timeLower contact angleBiochemical fibre treatmentAnimal fibresFiberCutinase
The invention provides a wool-fabric biological anti-felting method based on cutinase, keratinase and protease treatment, which belongs to the technical field of application of dyeing and finishing of wool fabric in the wool-spinning industry. The method aims to overcome the defects that the chlorination-process for wool-felting prevention seriously pollutes the environment and the single protease-method treatment is poor in fabric wettability and high in felting rate in order to achieve the aim of optimizing the protease treatment effect of the wool fabric. After all-wool grey fabric is extracted to remove free oily impurities, the all-wool grey fabric is sequentially pretreated with cutinase and keratinase solutions so as to improve the surface hydrophilicity of fiber scales and the accessibility of protease molecules, and then the wool fabric is subjected to reduction processing in a protease solution, thus biological processing combined with wool enzyme reduction is realized. The method makes the prior chlorination-process felting prevention replaced with a biological-method wool-felting prevention process, and the method not only effectively improve the reduction rate and anti-felting effect of the wool fabric, and promote the improvement of fabric wettability, but also can effectively increase the dyeing depth of fabric, and reduce fiber damage in reduction processing, and is favorable for protecting ecological environment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cutinase gene capable of efficiently producing cutinase and application thereof
The invention discloses a cutinase gene capable of efficiently producing cutinase and an application thereof, and particularly relates to an artificial encoding gene of the cutinase gene and an application thereof. The encoded cutinase gene is synthetically optimized to obtain tfu, and alpha-factor signal peptide and a kozark sequence are artificially added to an N end. Expression of the artificial cutinase gene in saccharomyces cerevisiae is successfully achieved by the invention. In addition, engineering bacteria with good enzyme production and performance are built by combining with the optimization of a promoter in a recombinant strain expression system; and a certain theoretical basis is established for industrial production of subsequent cutinase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
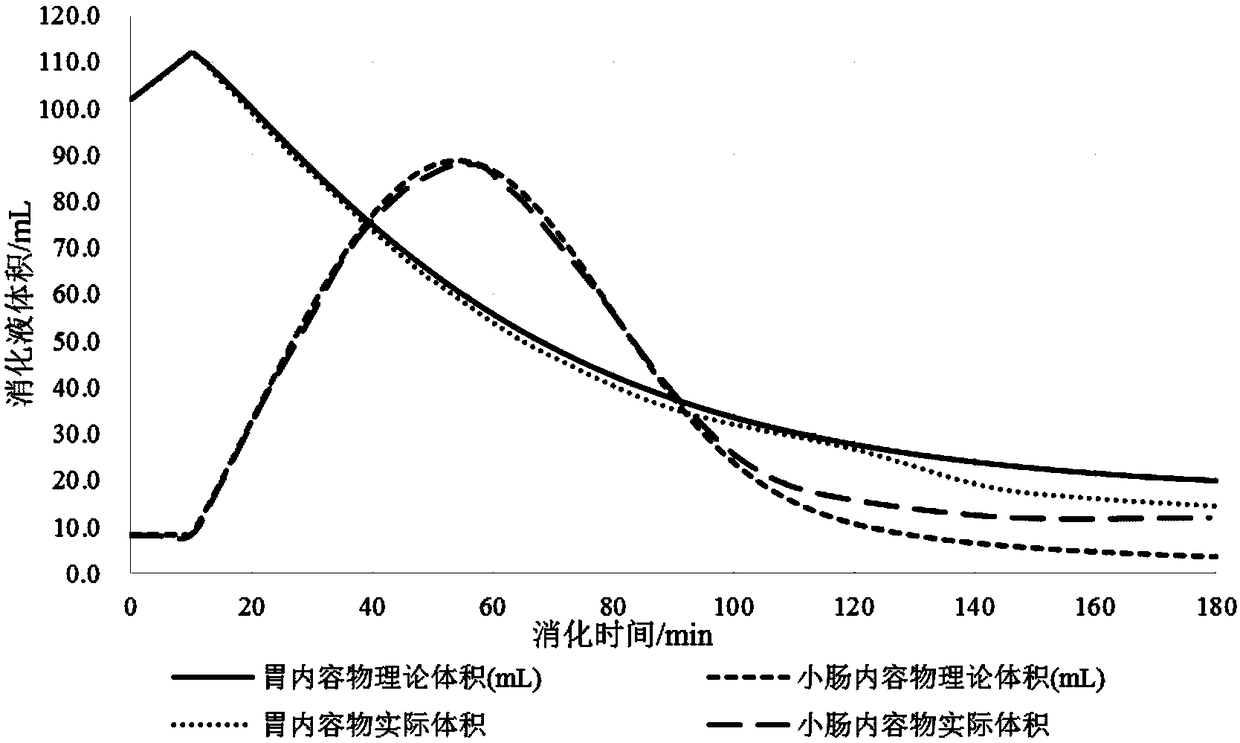
Human body stomach-small intestine digestion simulation method and device
ActiveCN108364553ARealize real-time dynamic regulationReal-time streamingEducational modelsHuman bodyCutinase
The invention discloses a human body stomach-small intestine digestion simulation method and device. According to the invention, real time dynamic control over pH values of the stomach and a small intestine digestion chamber is realized and pH dynamic curve can be output at the same time. Through regulating stomach emptying speed and intestine transport speed in real time, real time flow of food between different digestive tracts is realized. Human body stomach-small intestine digestion state and environment are simulated more truly and more comprehensively. According to the invention, simulation of an external digestion process of different people such as premature infants, term infants, adults and aged people can be realized. Rabbit gastric lipase or cutinase are used in simulated gastric fluid, so that human gastric lipase is simulated more truly.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Wool product two-bath process anti-felting treatment technology based on composite bio-enzyme
InactiveCN102965958AUnpacking dense structuresInfluence efficiencyBiochemical fibre treatmentAnimal fibresCutinaseDecomposition
The invention discloses a wool product two-bath process anti-felting treatment technology based on composite bio-enzyme, belonging to the technical field of wool fabric dyeing and finishing, which is aimed at solving the shortcomings that a wool chlorination anti-felting method causes serious environmental pollution, a single protease method has low wettability and high felting rate in treating fabric, a cutinase, keratinase and protease three-step method has low treatment efficiency, a cutinase, keratinase and protease one-step method requires inconsistent optimal action conditions in treating the three enzymes and the protease possibly decomposes the rest two enzymes in a one-bath method so as to realize an effect of optimizing wool fabric protease treatment. A wool sample is pretreated in a solution containing certain concentration of cutinase and keratinase to remove hydrophobic lipoids on the surface of wool and decompose the dense structure of wool scales; then, the wool sample is treated in the protease solution; and through the synergistic effect of the three-enzyme two-bath method, the acting efficiency of the protease is improved. The technology disclosed by the invention can replace the traditional chlorination anti-felting method, and improve the anti-felting performance of a wool product.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compound enzyme preparation for deep processing of olive and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing and provides a compound enzyme preparation for deep processing of olive and a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound enzyme preparation can comprise the following mixed components according to parts by weight: 15-25 parts of starch, 15-20 parts of pectinase, 10-15 parts of complex cellulases, 5-8 parts of cutinase and 3-6 parts of pH buffer. The compound biological enzyme preparation provided by the invention can completely peel fresh olive fruits within a shorter period by combining enzymolysis technology with mechanical stirring. The compound enzyme preparation provided by the invention is prepared by a mixing method. The compound enzyme preparation provided by the invention is low in method cost, good in peeling effect, high in efficiency and simple in operation method, and the product is free of enzyme flavor and is good in taste.
Owner:FUZHOU DASHIJIE OLIVE
Enzymatic hydrolysis of a polymer comprising vinyl acetate monomer
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Flammulina velutipes fungus chaff feed and production method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of reuse of waste fungus chaff after edible fungi cultivation and particularly relates to flammulina velutipes fungus chaff feed and a production method and an application thereof. The flammulina velutipes fungus chaff feed comprises a mixture a and a mixture b, wherein the mass ratio of the mixture a to the mixture b is (1000:1)-(1000:10); the mixture a consists of the following raw materials: flammulina velutipes fungus chaff powder, sweet potato dreg powder, rice bran, wheat flour, soya bean meal, fish meal or meat and bone meal and table salt; and the mixture b consists of the following raw materials: cellulase, hemicellulase, aspergillus niger, ligninase, cutinase, feruloyl esterase and brown sugar. The production method of the flammulina velutipes fungus chaff feed is simple. The flammulina velutipes fungus chaff feed is used for culturing barley pests, the time required by culturing the barley pests is short, the weights of the barley pests are heavy, and a plurality of eggs can be laid by the barley pests. The cultured barley pests are added into the conventional feed and are used for feeding beasts and birds, crabs, fishes, turtles, eels, finless eels or batrachia, the growth of a fed animal is obviously accelerated, the increase production is remarkable, and the effect is good.
Owner:SERICULTURE & AGRI FOOD RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI +3
Bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation containing Stenotrophomonas pavanii and application of bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation
ActiveCN111826310AGood synergistic degradation effectPromote degradationBacteriaHydrolasesStenotrophomonas pavaniiMicroorganism
The invention relates to a bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation containing Stenotrophomonas pavanii and application of the bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation, and belongs to the technical fieldof microorganisms. The invention provides a novel method for degrading polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and a PET intermediate. By combining a specific strain and a specific biological enzyme, the bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation with specific degradation application is prepared, and the mixed preparation is a compound of Stenotrophomonas pavanii and cutinase; the bacterium and enzyme mixedpreparation provided by the invention is used to degrade PET and BHET intermediate, the degradation ability of the bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation is far better than that of using bacteria or enzymes alone. The bacterium and enzyme mixed preparation has a significant synergistic effect on high-crystallinity PET and the intermediate BHET in the degradation process, and has good promotion andapplication value in the field of the plastic degradation technology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cutinase, keratinase and protease one-bath process anti-felting technology
InactiveCN102965955AAvoid damageImprove wettabilityBiochemical fibre treatmentAnimal fibresFiberEcological environment
The invention discloses a wool biological process anti-felting finishing method based on a cutinase, keratinase and protease one-bath process, belonging to the technical field of wool fabric dyeing and finishing, which aims to solve the shortcomings that a wool chlorination anti-felting method causes serious environmental pollution, a single protease method has poor wettability and high felting rate in treating fabric and a cutinase, keratinase and protease three-step method has low treatment efficiency to realize an effect of optimizing wool fabric protease treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting a wool sample to remove free oily impurities; and performing one-bath process treatment in a solution containing cutinase, keratinase and protease of certain concentration, wherein through the synergistic effect of the three enzymes, the hydrophilicity of the fiber scale surface and the acting efficiency of the keratinase and protease in the treatment bath, the removal effect of a scale layer on the wool surface and the anti-felting performance of the wool fabric are improved, and the treatment time is shortened. According to the invention, the biological process anti-felting method can replace the traditional chlorination method, the quality of the wool anti-felting finishing is improved, and protection on ecological environment is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production technology for extracting berberine from cortex phellodendri and coptidis rhizoma through complex enzyme method
The invention discloses a production technology for extracting berberine from cortex phellodendri and coptidis rhizoma through a complex enzyme method.The production technology comprises the following steps that1, the medicinal material cortex phellodendri or coptidis rhizoma is smashed, and water is added to the powder for soaking; 2, beta-dextranase, xylanase, phytase and cutinase are added into the mixture, the pH is adjusted with diluted hydrochloric acid, enzymolysis and boiling are conducted, enzymes are subjected to inactivation, and enzymatic hydrolysate is obtained; 3, water is added, the pH is adjusted with diluted hydrochloric acid, extraction is conducted, hot filtration is conducted, and filtrate is collected; 4, ethyl alcohol is added into filter residues, and digestion is conducted; 5, filtrates are combined, concentration is conducted, the pH is adjusted with diluted hydrochloric acid, cooling is conducted, a saturated NaCl solution is added, overnight preservation is conducted at 4 DEG C, suction filtration is conducted, drying is conducted, and berberine is obtained.The production technology for extracting berberine from cortex phellodendri and coptidis rhizoma through the complex enzyme method is simple in method, high in product yield and purity, low in cost and free of environmental pollution.
Owner:天津尚美化妆品有限公司
Recombinant escherichia coli engineering bacterium realizing high yield of cutinase and fermentation process thereof
InactiveCN108753671AWide variety of sourcesIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
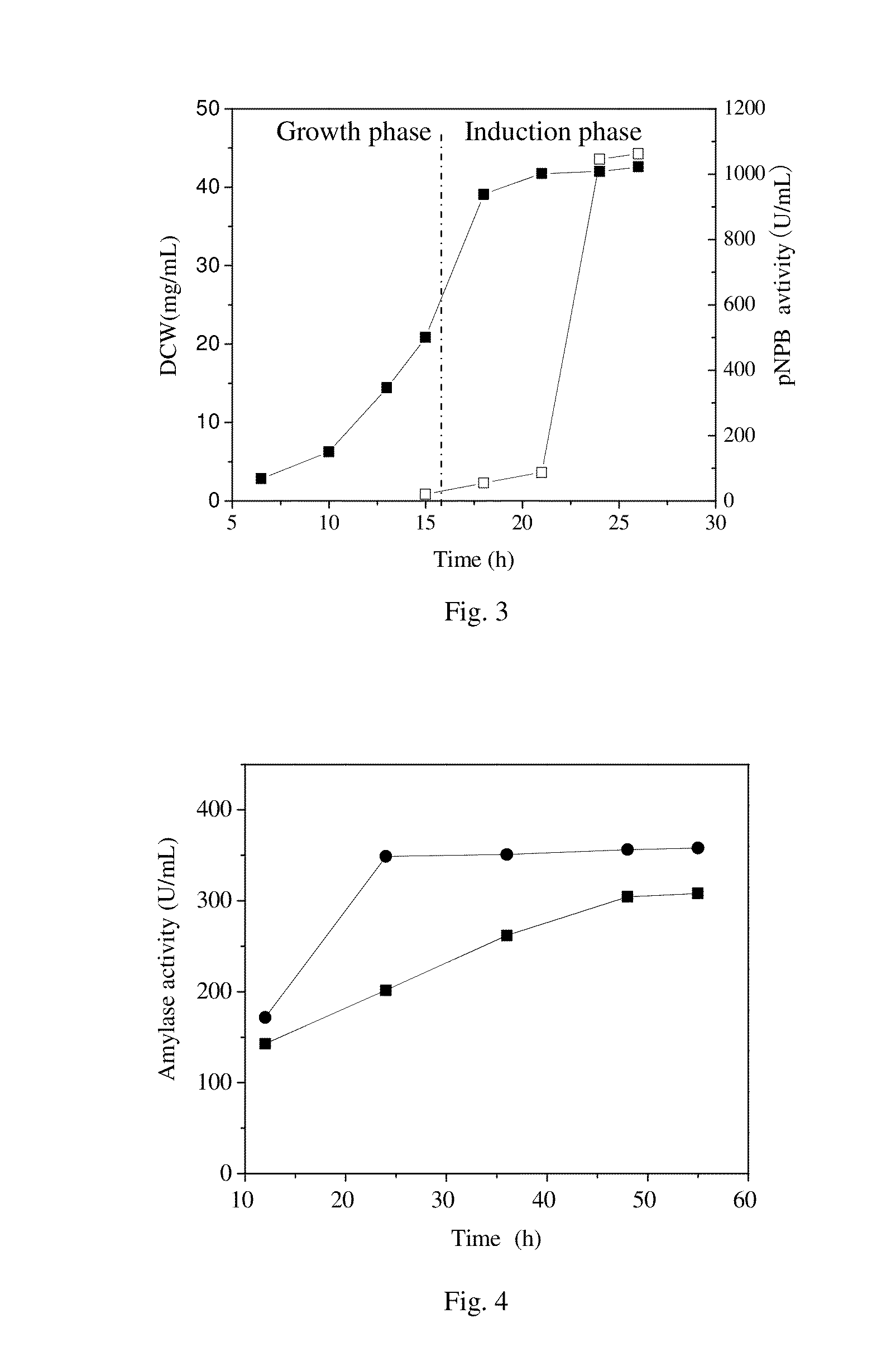
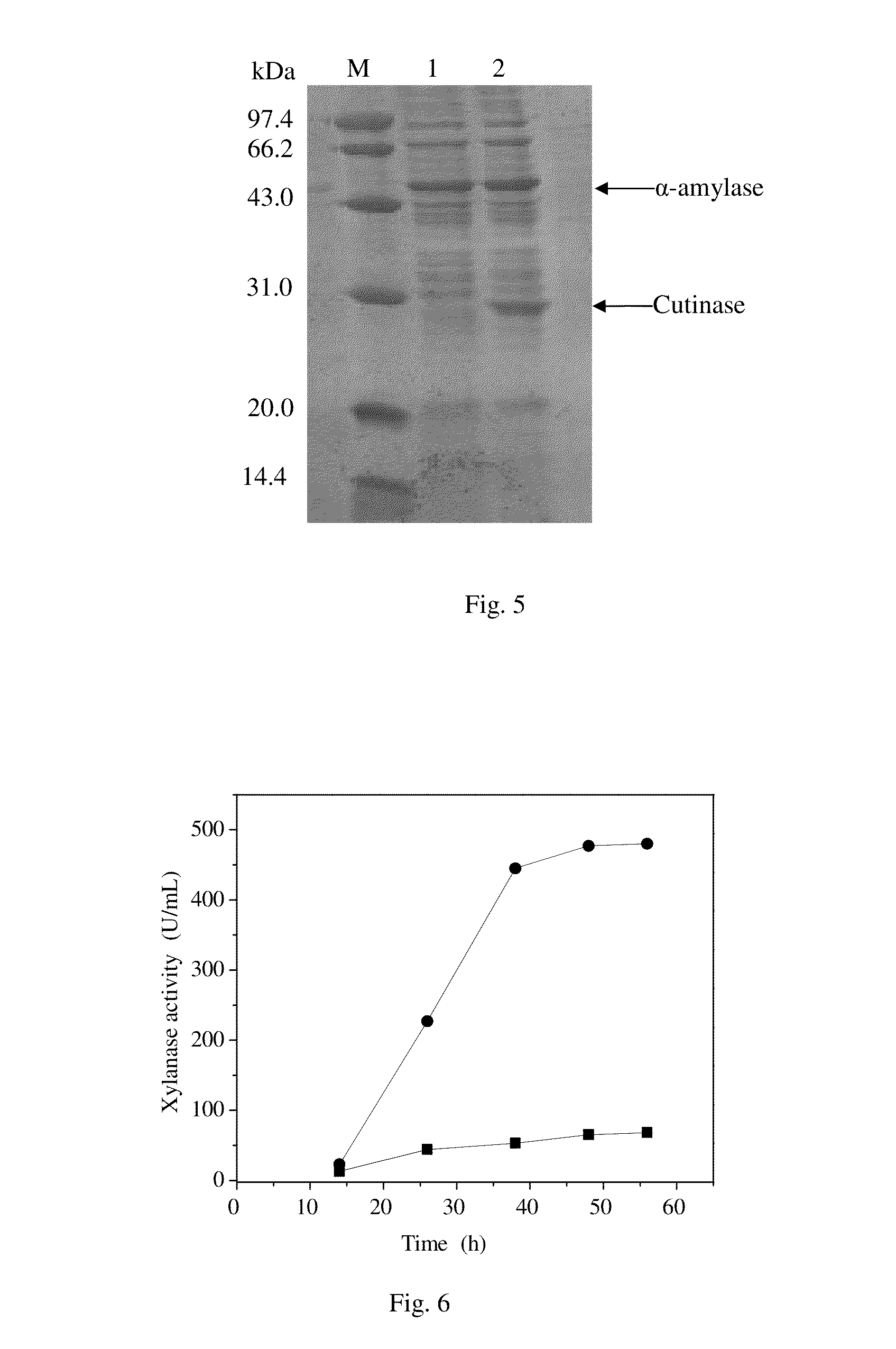
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli engineering bacterium realizing high yield of cutinase and a fermentation process thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineeringand fermentation engineering. Humicola isnolens sourced cutinase gene is used as a target gene; pET-20b(+) is used as an expression vector; E.coli BL21(DE3) is used as an expression vector; a gene engineering bacterium E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-20b(+) / hic capable of realizing efficient active expression of the cutinase is successfully built; meanwhile, the recombinant escherichia coli engineering bacterium E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-20b(+) / hic is creatively used as a production strain; a production process of combining a two-stage temperature control process, a constant dissolved oxygen control process,a pH control process, a supplemented material batch fermentation process, and a high induction thallus concentration combined high induction intensity induction control process is used for producingthe cutinase; the advantages of high yield, wide raw material sources, low production cost and the like are realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
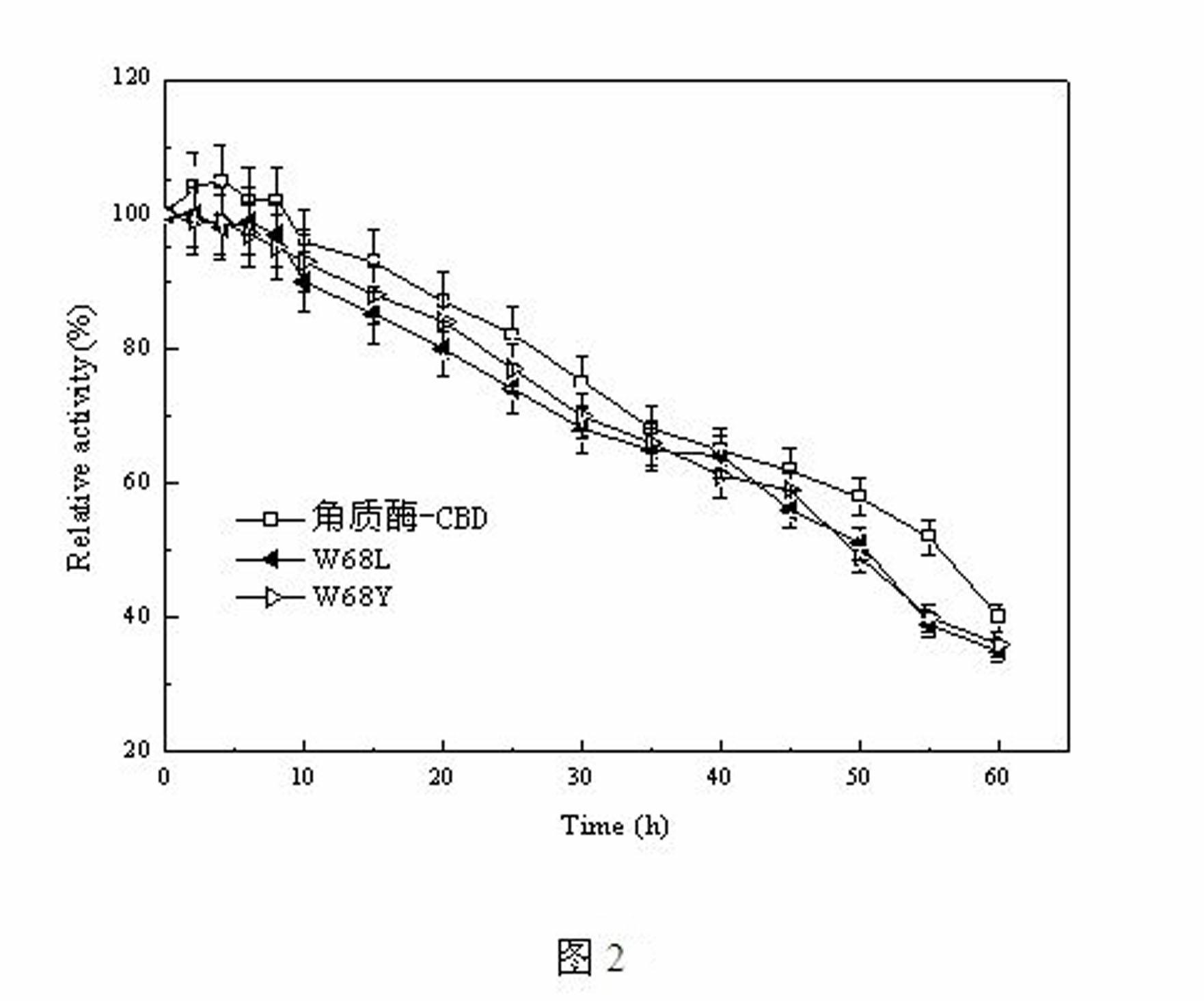
Heat-resistant cutinase-CBD (cellulose-binding domain) fusion enzyme, its mutants and application
ActiveCN102358896AImprove adsorption efficiencyBiochemical fibre treatmentFibre typesCellulosePolyester
Belonging to the genetic engineering and enzyme engineering fields, the invention discloses a heat-resistant cutinase-CBD fusion enzyme, its mutants and application in polyester fiber modification. The invention provides a preparation method of a Thermobifidafusca cutinase-CBD fusion enzyme and its mutants. The mutants comprise a substitute at a binding site on the CBD of the Thermobifidafusca cutinase-CBD fusion enzyme. Adsorption efficiency of mutants W68L and W68Y for polyester fiber are enhanced by 14% and 17% respectively compared with the cutinase-CBD fusion enzyme, while the hydrolysisabilities of the mutants for polyester fiber is 1.4 and 1.5 times of the hydrolysis ability of the cutinase-CBD fusion enzyme. And the two mutants of the cutinase-CBD fusion enzyme are more suitable for application in polyester fiber modification.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fusion protein and application of fusion protein in degrading polymers
ActiveCN112159478AImprove degradation rateIncrease contentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesCutinaseCutin
The invention discloses a fusion protein and application of the fusion protein in degrading polymers, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention provides the fusion protein capable of degrading polymers such as polyethylene glycol terephthalate with good degradation effect. The fusion protein is formed by sequentially connecting a cutinase, a connecting peptide and a carbohydratebinding assembly, and when the fusion protein is used for degrading a PET film for 4 d, the content of phthalic acid (TPA) in a PET degradation product can reach up to 116.83 mg / L. When an unfused cutinase with the equal enzyme activity is used for degrading the PET film under the same condition, no phthalic acid (TPA) is detected in the degradation product, and the degradation rate of polyacrylate degraded by the fusion protein is improved by 36% compared with the degradation rate of the unfused cutinase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of laundering a fabric
ActiveUS20140230157A1Increase depositionDetergent dyesNon-surface-active detergent compositionsCutinaseLaundry detergent
A method of laundering a fabric comprising the steps of; (i) contacting the fabric with a cutinase, (ii) contacting the fabric from step (i) with a soil; (iii) contacting the fabric from step (ii) with a laundry detergent composition, wherein the laundry detergent composition comprises a hueing agent.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for scouring and bleaching cotton fabric with composite enzyme preparation in one bath
InactiveUS20100192308A1Increase consumptionHigh high pollutionBleaching apparatusBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsEthylenediamineCellulose
A method for scouring and bleaching cotton fabric with composite enzyme preparation in one bath is provided. The method relates to the application of composite alkaline enzyme preparation in scouring and bleaching processes of cotton fabric. The enzyme preparation for scouring and bleaching cotton fabric is compounded from cutinase, alkaline pectase, alkaline xylanase, alkaline cellulose, and carbohydrate oxidase. The method includes: scouring the cotton fabric by adding the composite enzyme preparation, glucose, oxidation bleaching stabilizer RB-3, penetrant JFC, and Triton X-100 in a treating bath at 55-70° C. and pH 8-10, and then bleaching the cotton fabric for 30 min by directly adding tetraacetyl ethylenediamine (TAED) in the scouring bath to activate hydrogen peroxide. After being treated by the method of the present invention, the cotton fabric has high impurity removal ratio, favorable wettability, and high whiteness. The present invention has the advantages of low power consumption, short process flow, and being environment friendly, and may be used to replace conventional chemical treatment process under the condition of concentrated alkali and high temperature.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for treating papermaking white water by utilizing cutinase
The invention discloses a method for treating papermaking white water by utilizing cutinase and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The method disclosed by the invention adopts efficient and stable cutinase for carrying out enzyme catalytic decomposition on lipids such as glycerol trioleate and polyvinyl acetate, high temperature heating or vigorous stirring does not need to be carried out, reaction conditions are mild, and degradation rate can reach 83.5%, thereby being environment-friendly. Production of cutinase required by reaction is simple, and production efficiency is improved. Meanwhile, compared with other physical treatment, enzymatic method treatment is simple in steps, and in the actual white water treatment process, when the dose of cutinase is 0.5-1U per g substrate, better treatment effect also can be obtained, and turbidity difference reaches more than 95%. The white water treated by cutinase can be directly reused and partially or completely replaces cleaning water, so that closed circulation of papermaking system water is realized, and zero discharge in real sense is achieved. The advantages become especially important in the modern society with environmental protection taken seriously increasingly.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Wool worsted fabric compound enzyme padding-steaming stacking anti-felting finishing technology
InactiveCN102965956AImproves felting resistanceShort wetting timePhysical treatmentBiochemical fibre treatmentCutinaseWorsted
The invention discloses a pure-wool worsted fabric compound bio-enzyme padding-steaming stacking anti-felting finishing technology, belonging to the technical field of wool fabric dyeing and finishing in the wool spinning industry. A continuous padding-steaming stacking method adopted by the invention comprises the following steps of: padding the pure-wool worsted fabric in a compound bio-enzyme solution consisting of different combinations of cutinase, keratinase and protease; performing steaming stacking at certain temperature for certain time; performing hot water washing (as well as enzyme deactivation); sufficiently washing with cold water to remove various enzyme decomposition products, deactivated enzyme and impurities on the wool fabric; and finally drying. Through the technology disclosed by the invention, the acting efficiency of the keratinase and protease and the anti-felting effect of the wool fabric can be obviously improved; and the technology also has the advantages of obvious reduction in water consumption, obvious reduction in wastewater discharge, obvious improvement of production efficiency and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cotton fabric bio-enzyme and method for performing co-bath scouring and bleaching on cotton fabric
ActiveCN103374823AAvoid damageMild treatment conditionsBiochemical fibre treatmentBleaching apparatusPectinaseCutinase
The invention discloses a cotton fabric bio-enzyme and a method for performing co-bath scouring and bleaching on a cotton fabric. The cotton fabric bio-enzyme comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of cutinase, 5-10 parts of protease, 5-10 parts of alkaline pectinase, 20-30 parts of alkaline xylanase, 5-10 parts of B-1, 4-glucan glucano-hydrolase, 10-20 parts of glucose oxidase and 15-25 parts of laccase. The cotton fabric bio-enzyme disclosed by the invention is adopted for performing co-bath scouring and bleaching on the cotton fabric, the treatment conditions are mild, the damages to the fabric are small, an environment is friendly, the process flow is short, and the energy consumption is saved.
Owner:南通市第三毛巾厂有限公司
Method for Enhancing Extracellular Secretion of Recombinant Proteins in Escherichia coli by Co-expressing Thermobifida Fusca Cutinase
The present invention provides a method of increasing extracellular secretion of secretory proteins by co-expressing the secretory proteins with a mature cutinase. Cutinase can improve the permeability of E. coli cell membrane without destroying the membrane, and thus facilitate cross-membrane transfer of the secretory proteins co-expressed in E. coli. Increased extracellular secretion of target proteins can shorten cell culture time, reduce the formation of inclusion bodies and increase production of target proteins.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enzyme quantitative detection method of textile fiber content
ActiveCN103543084ASolve poor specificityProcess greenWeighing by removing componentTextile fiberCutinase
The invention relates to an enzyme quantitative detection method of textile fiber content. The enzyme quantitative detection method of the textile fiber content has the characteristics of high accuracy, environmental friendliness and harmlessness. According to the technical scheme, the enzyme quantitative detection method of the textile fiber content sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out qualitative identification on fiber components of textiles; (2) dyeing the textiles by adopting a direct dye, a reactive dye, an insolubility azo pigment or a cationic dye which has great influence on the enzymatic activity, and pretreating by using an oxidation-reduction enzyme so as to remove the dye; (3) respectively selecting corresponding cellulase or / protease or / A enzyme for carrying out selective separate degradation treatment on the plurality of textiles treated in the step (2) one by one according to the qualitative identification result in the step (1), or selecting corresponding cellulase or / protease or / A enzyme for sequentially carrying out selective degradation treatment on the textiles treated in the step (2) according to the qualitative identification result in the step (1), wherein the A enzyme is lipase or cutinase.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
Rhodotorula mucilaginosa strain ZZR-1# and method using strain to produce cutinase
A Rhodotorula mucilaginosa strain ZZR-1# is named as Rhodotorula mucilaginosa, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.8890. The method using Rhodotorula mucilaginosa ZZR-1# to produce cutinase comprises the following steps: carrying out slant culturing on the Rhodotorula mucilaginosa by a slant culture medium, carrying out shaking seed culture, enlarged culture, enlarged culture and fermentation tank culture, filtering the obtained fermentation liquid by a gauze, and centrifuging the obtained filtrate at 4DEG C under a rotating speed of 5500rpm for 30min to obtain a supernatant which is a crude cutinase liquid; and concentrating the crude cutinase liquid, and purifying to obtain cutinase. The method using the Rhodotorula mucilaginosa ZZR-1# to produce cutinase is designed against the characteristics of the strain, and has the advantages of reasonability, simplicity, low cost, high enzyme activity in the crude cutinase liquid, high cutinase output, and good application prospect.
Owner:HENAN HENGRUIYUAN IND
Environment-friendly and efficient waste paper deinking method
ActiveCN107313277AHigh whitenessLittle loss of strengthPaper recyclingCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesFiberCutinase
The invention discloses an environment-friendly and efficient waste paper deinking method, and belongs to the technical field of papermaking. The invention adopts a combined technology of bioenzymes, environment-friendly surfactants, ultrasonic treatment, adsorption and flotation. In the deinking process, connection between fiber and ink is cut off by adding a complex enzyme of cutinase, amylase, lipase, cellulase, hemicellulase, laccase and other bioenzymes, and in combination with the surfactants with good biodegradability, namely cardanol polyoxyethylene ether, cardanol sulfonate and fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sulfate, the ink is emulsified and dispersed. By the combined method, the production cost and the subsequent wastewater treatment cost are reduced and the environment pollution is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Immobilized biological adsorption degradable material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103752283ASimple processEasy to operateOther chemical processesOn/in inorganic carrierCutinaseCutin
The invention relates to an immobilized biological adsorption degradable material, a preparation method and application thereof. With a porous gold nanometer material as a carrier and a polyethyleneimine as a modifying agent, the immobilized biological adsorption degradable material is fixed with cutinase. The preparation method of the immobilized biological adsorption degradable material comprises the following steps: placing the porous gold nanometer material in a lipoic acid solution; after the reaction is completed, adding a surface carboxylation material obtained by the reaction to pyridine and dimethylformamide, heating, adding epoxy chloropropane, after the reaction is completed, adding a surface chlorine group-containing material obtained through the reaction to a polyethyleneimine-containing organic solution, reacting, and washing to obtain a polyethyleneimine modified porous gold nanometer material, crosslinking the polyethyleneimine modified porous gold nanometer with the cutinase chemically to obtain the immobilized biological adsorption degradable material. The immobilized biological adsorption degradable material is high in adsorption efficiency and large in adsorption amount, can be repeatedly used, is simple in preparation process, is capable of effectively removing phthalic acid ester materials in a water body, and is free from secondary pollution.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
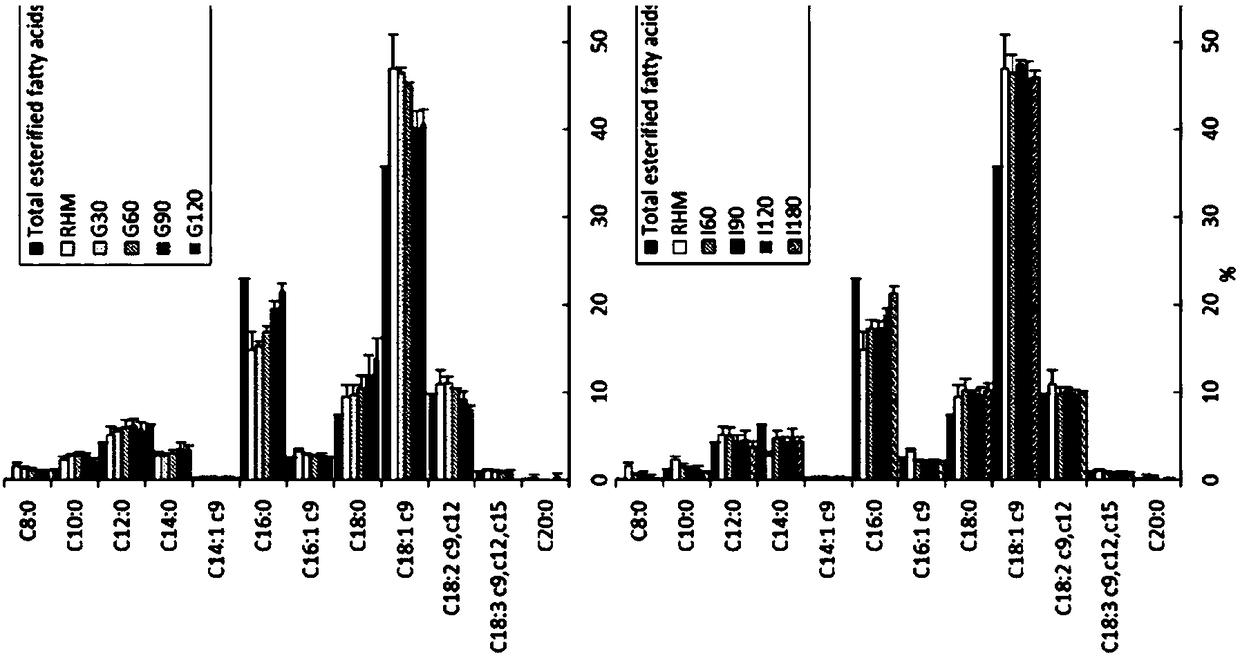
Method for modifying polyester based on Humicola insolens cutinase
InactiveCN113338044AAchieve the effect of hydrophilic modificationImprove adsorption capacityFibre typesBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsHydrophilizationPolymer science
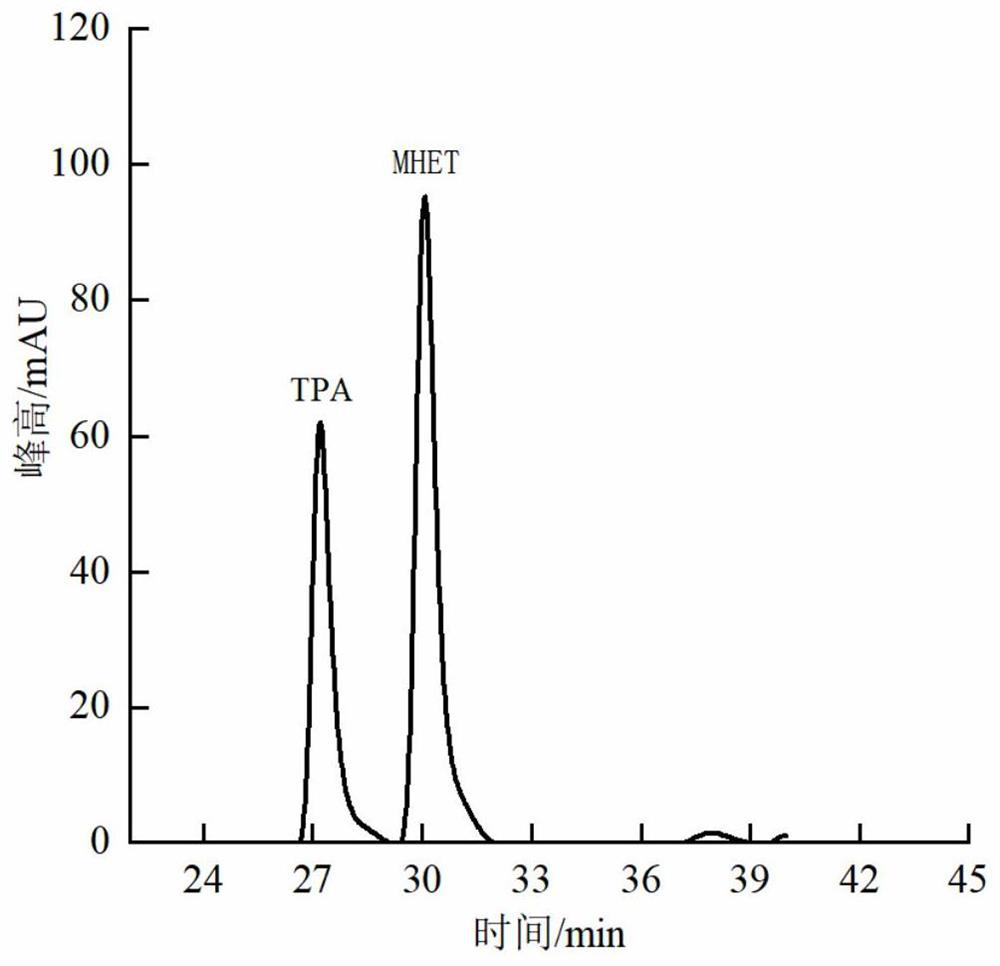
The invention discloses a method for modifying polyester based on Humicola insolens cutinase, and belongs to the technical field of terylene surface modification. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of putting a refined polyester fabric into a Humicolainsolens cutinase solution, reacting at 45-65 DEG C for 48-72 hours, washing, and drying to obtain a hydrophilic modified polyester fabric, wherein the Humicola insolens cutinase solution is prepared from Humicola insolens cutinase, a Tris-HCl buffer solution and a non-ionic surface active agent; and the concentration of the Humicola insolens cutinase is 20 to 120 U / mL, and the concentration of the non-ionic surface active agent is 0.5 to 2 g / L. According to the method, the adopted Humicola insolens cutinase can catalyze hydrolysis of ester bonds on the surface of the polyester to generate hydrophilic groups, namely hydroxyl and carboxyl, and meanwhile, hydrolysis products are generated; the main hydrolysis products are terephthalic acid (TPA) and mono (2-hydroxyethyl terephthalate) (MHET), and the hydrophilic modification effect is achieved on the basis that the advantages and properties of the polyester are kept unchanged.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com