Method for modifying polyester based on Humicola insolens cutinase
A technology of cutinase and polyester, which is applied in the direction of enzyme/microbial biochemical treatment, biochemical fiber treatment, fiber type, etc., can solve the problems of polyester fiber weight and strength loss, low yield of hydrolyzate, poor hydrophilic modification effect, etc. , achieve the effects of mild action, high selectivity and improved catalytic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] A method for modifying polyester based on Humicola insolens cutinase, comprising the steps of:
[0059] (1) Refined fabric of polyester fabric
[0060] Put the polyester fabric in a solution of 5g / L soap flakes and 4g / L sodium carbonate, and treat it at 98°C for 30 minutes for desizing and scouring (bath ratio 1:30); then wash it with water, and dry it in an oven at 105°C ; Finally, place the polyester fabric in a constant temperature and humidity box (21 ± 1 ° C, 65 ± 2%) to balance for at least 24 hours to obtain a refined polyester fabric for use;
[0061] (2) Modification treatment:
[0062] Cut the refined polyester fabric into discs, each weighing 0.4g, put them into the Humicola insolens cutinase solution at a bath ratio of 1:40, and react at pH 8.5 and 60°C for 72 hours. Ultrasonic cleaning with 1% SDS solution for 30 minutes, then ultrasonic cleaning with 20% ethanol solution for 30 minutes, then drying in an oven at 105°C, and finally placing the dried polye...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Adjust the reaction time of step (2) of Example 1 to 6, 24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 h, omit the addition of Trition X-100, and keep the others consistent with Example 1 to obtain a hydrophilic modified polyester fabric.
[0072] The obtained hydrophilic modified polyester fabric is subjected to a performance test, and the test results are as follows:
[0073] The test result of table 2 embodiment 2
[0074]
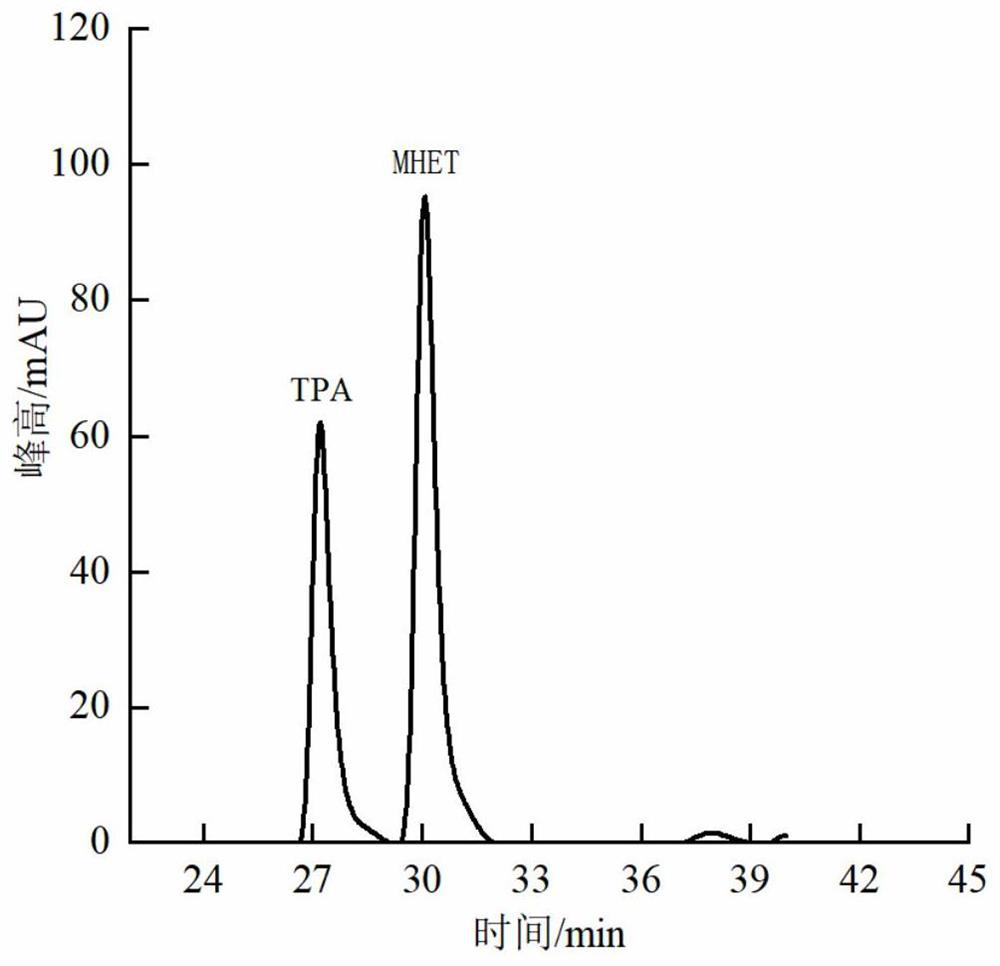
[0075] As can be seen from Table 2: in the initial stage of the reaction, as time goes on, the amount of TPA and its derivatives generated in the reaction raffinate increases rapidly. It has been reported that lipase from Pichia pastoris was used to treat polyester fabrics, and the product production reached saturation at 12.5 mg / L in 7 hours (GAO Aiqin. Hydrophilic modification of polyester fabric by synergetic effect of biological enzymolysis and non-ionic surfactant, and applications in cleaner production[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2017(164):277-287.), and...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Adjust the reaction pH of step (2) of Example 1 to 7.5, 8, 8.5, 9, and the reaction time to 48h, omit the addition of Trition X-100, and keep the others consistent with Example 1 to obtain a hydrophilic modified polyester fabric.
[0078] The obtained hydrophilic modified polyester fabric is subjected to a performance test, and the test results are as follows:
[0079] The test result of table 3 embodiment 3
[0080]
[0081] It can be seen from Table 3 that as the pH value of the reaction solution increases, the amount of the product generated in the reaction residue shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. When the pH value was 8.5, the amount of product generated in the reaction raffinate reached the maximum. The pH value of the reaction system will affect the dissociation degree of the active center group of the enzyme, and also affect the binding and catalysis of the enzyme molecule and the substrate, so the catalytic activity of the enzyme will c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| release amount | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com