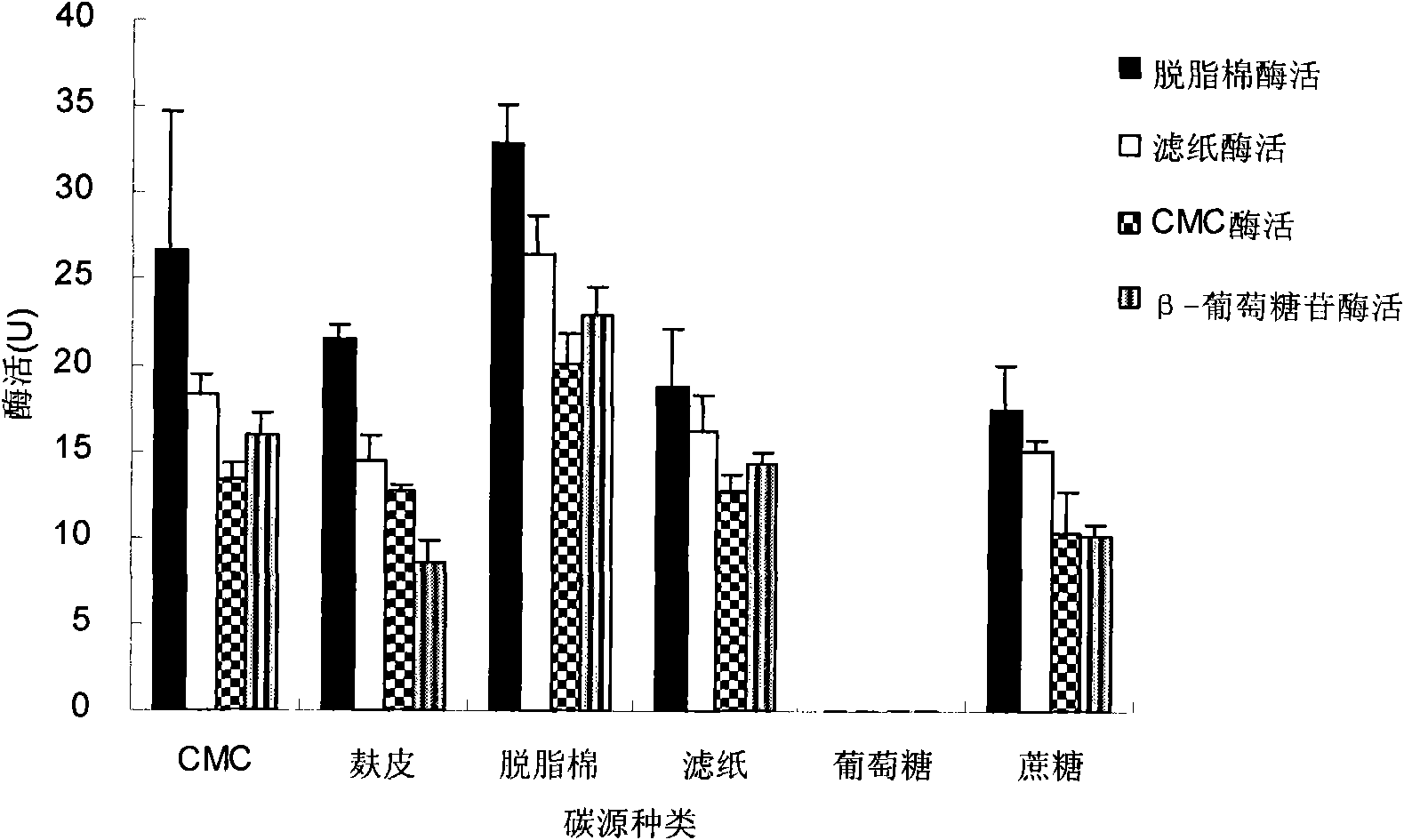
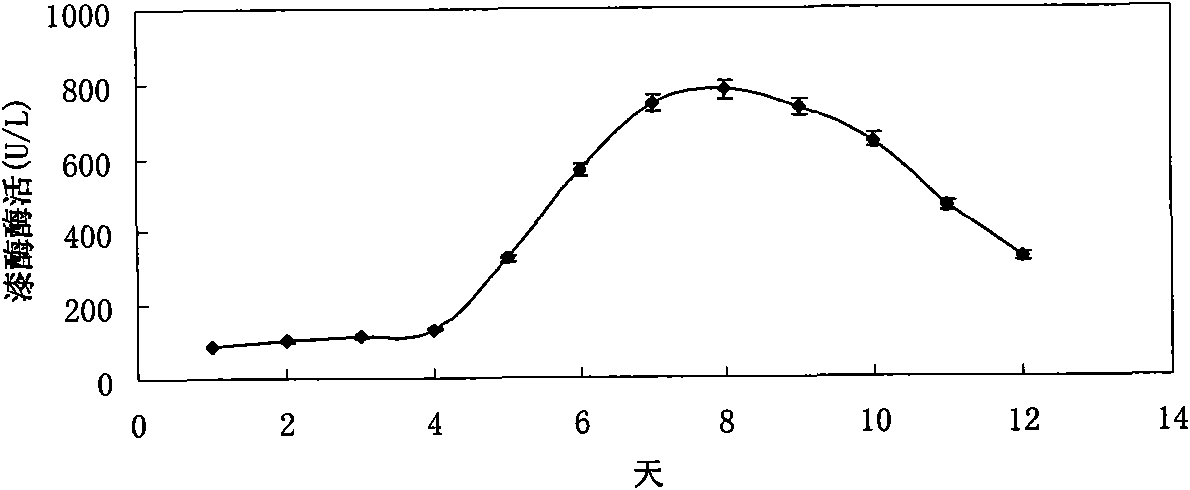
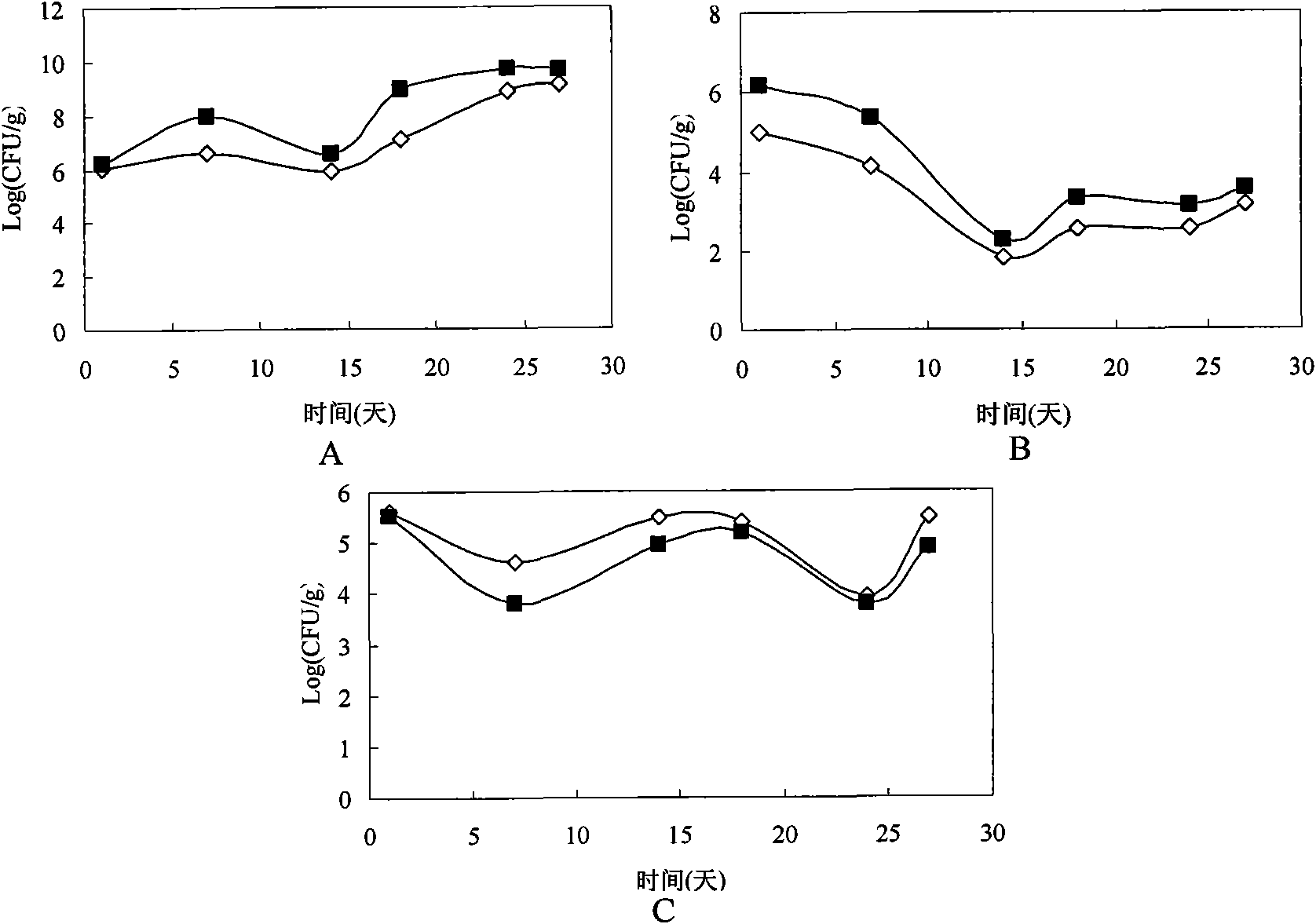
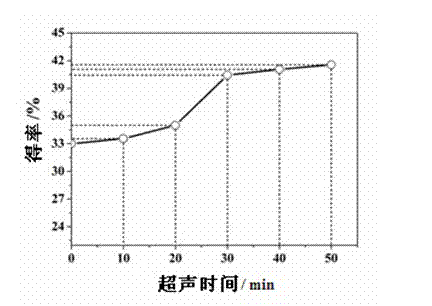
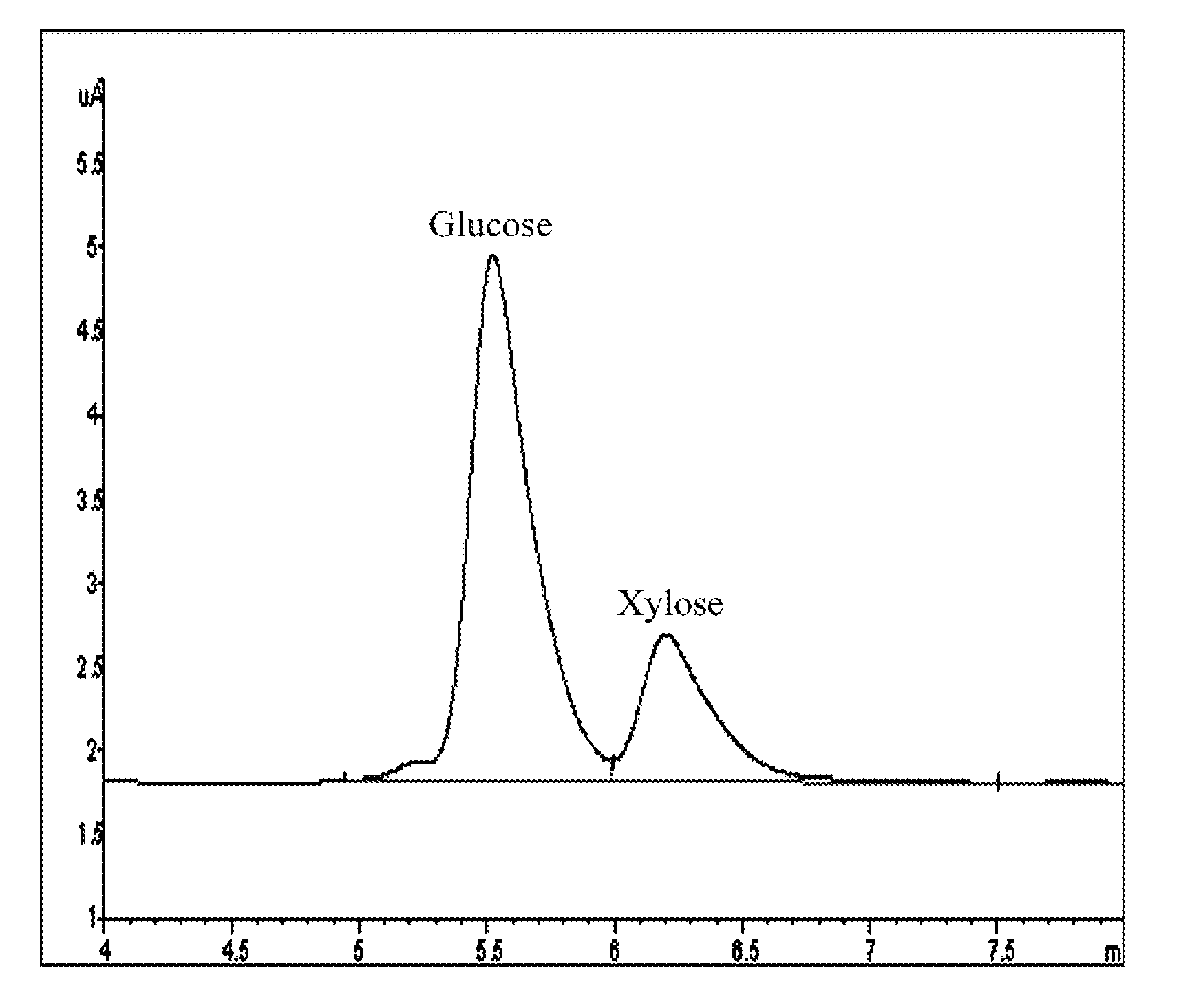
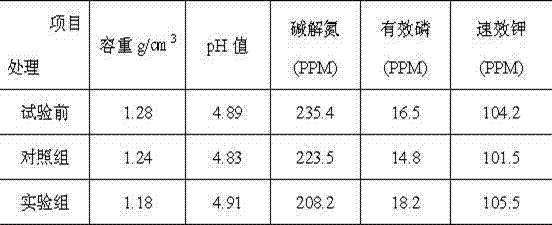
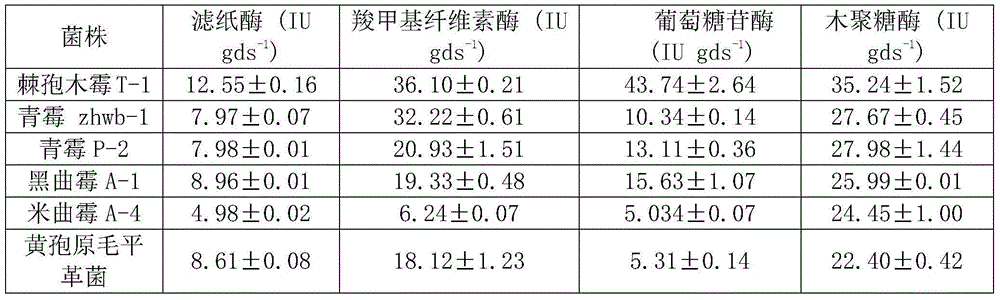
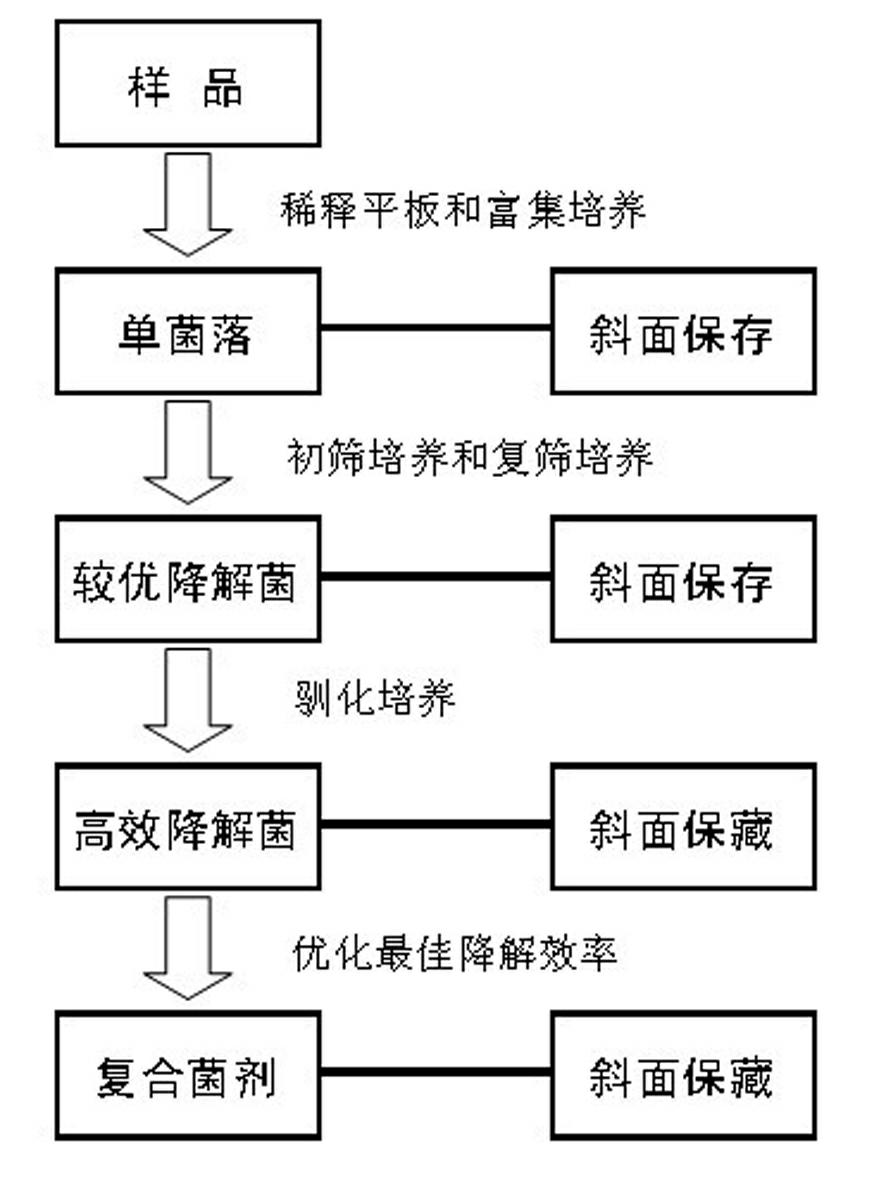
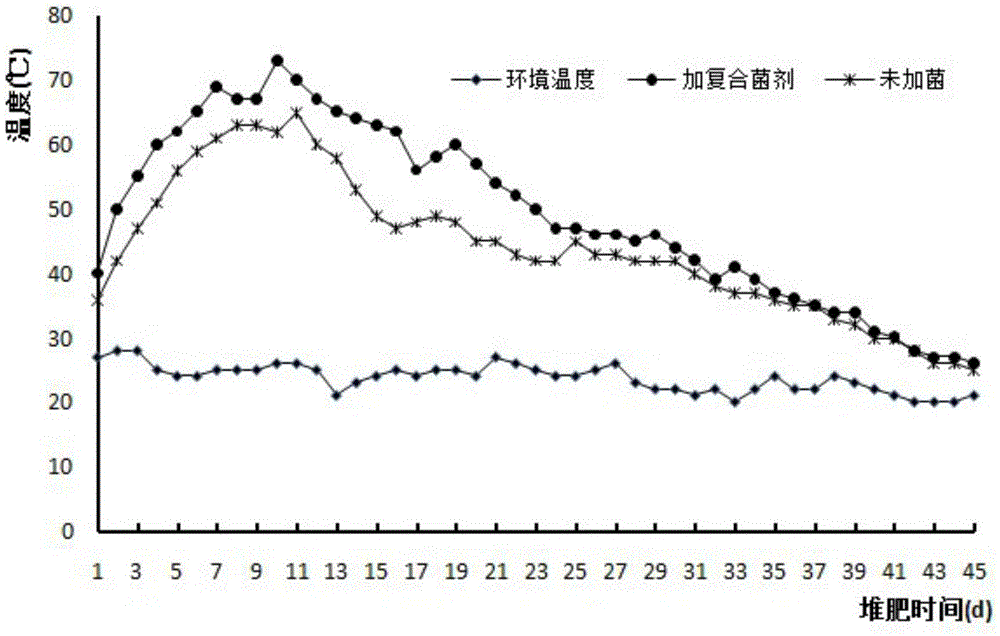
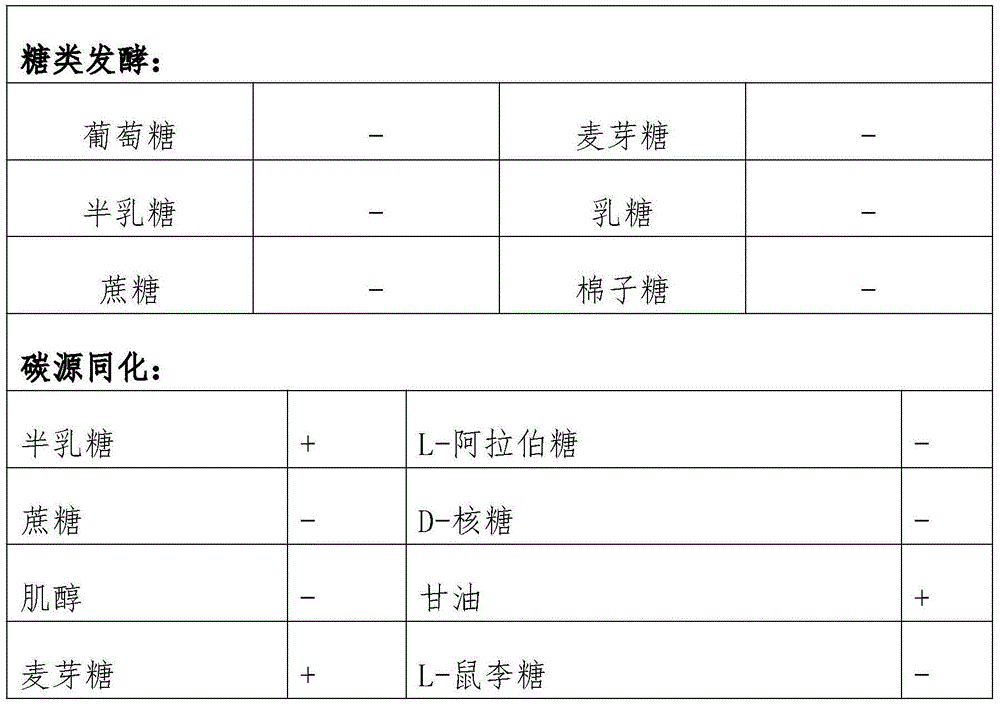
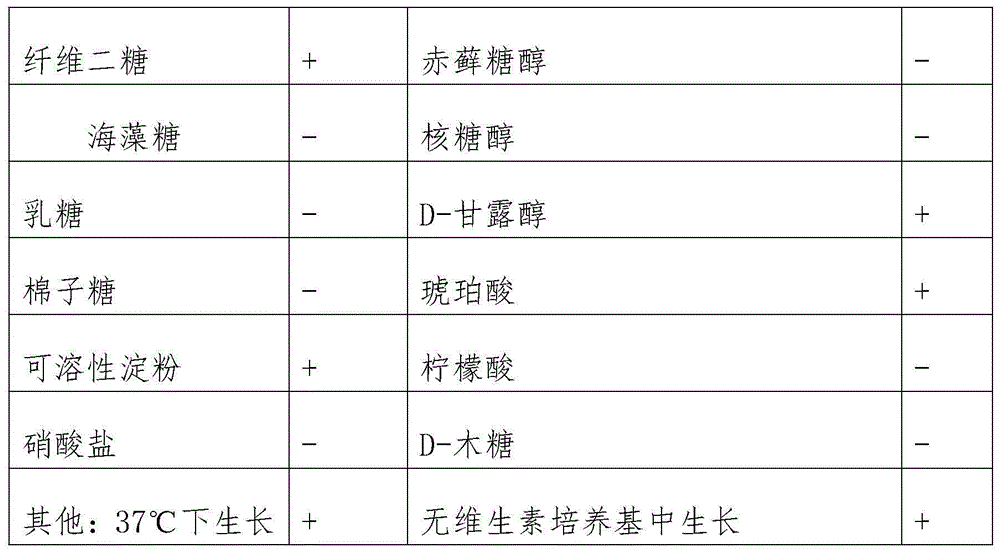
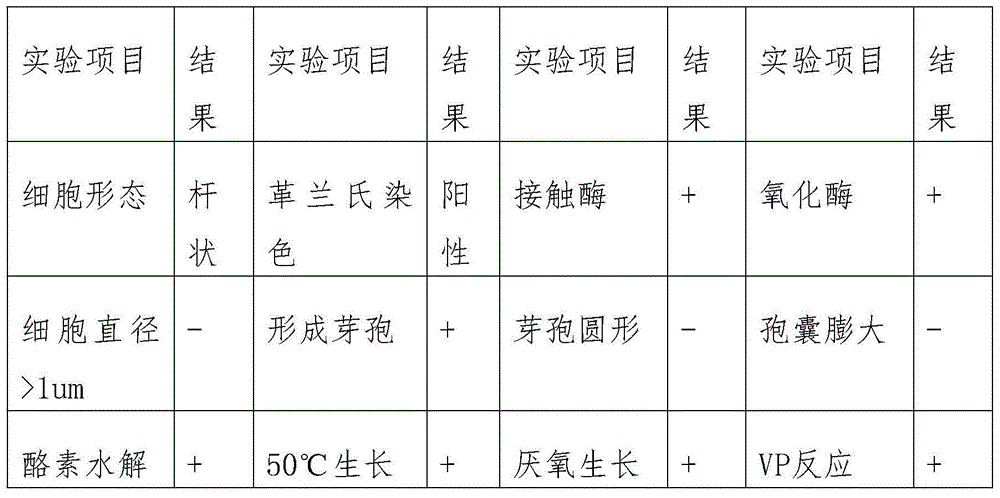
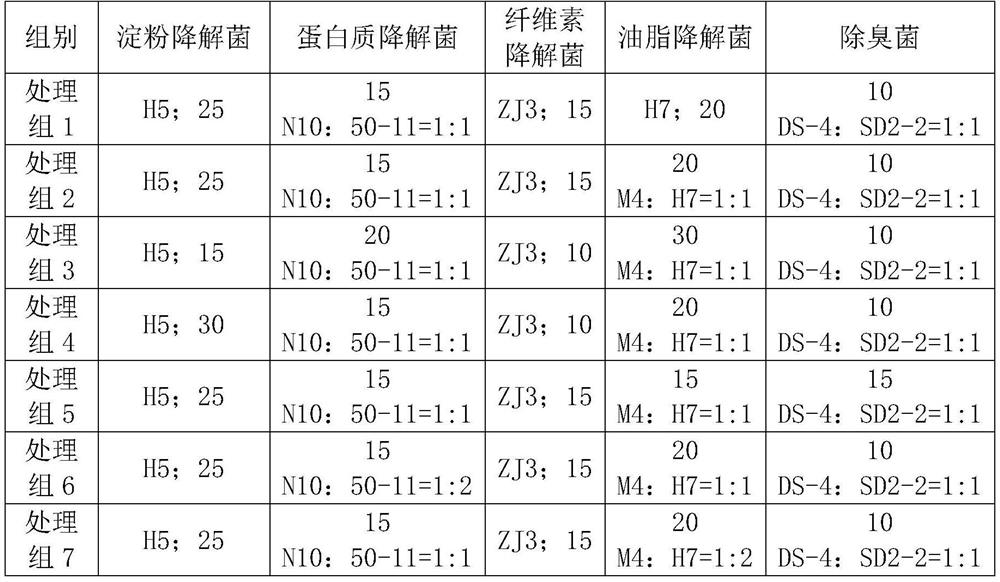
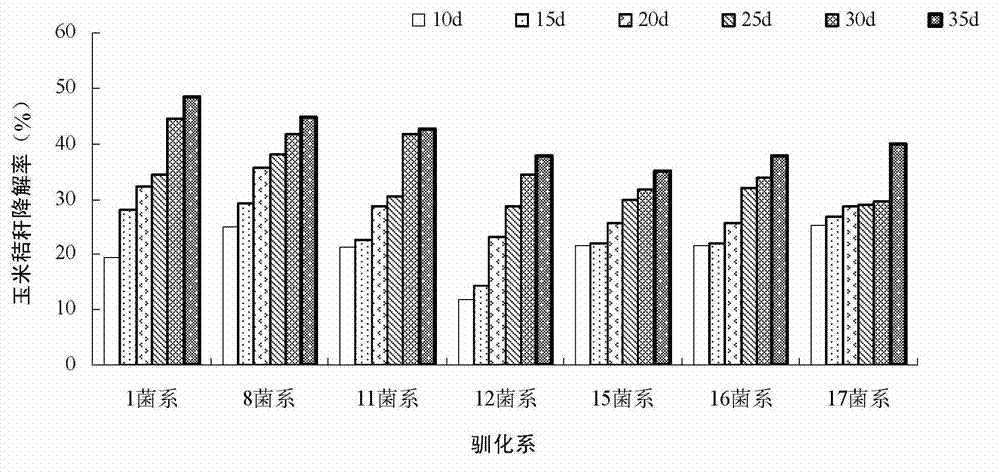
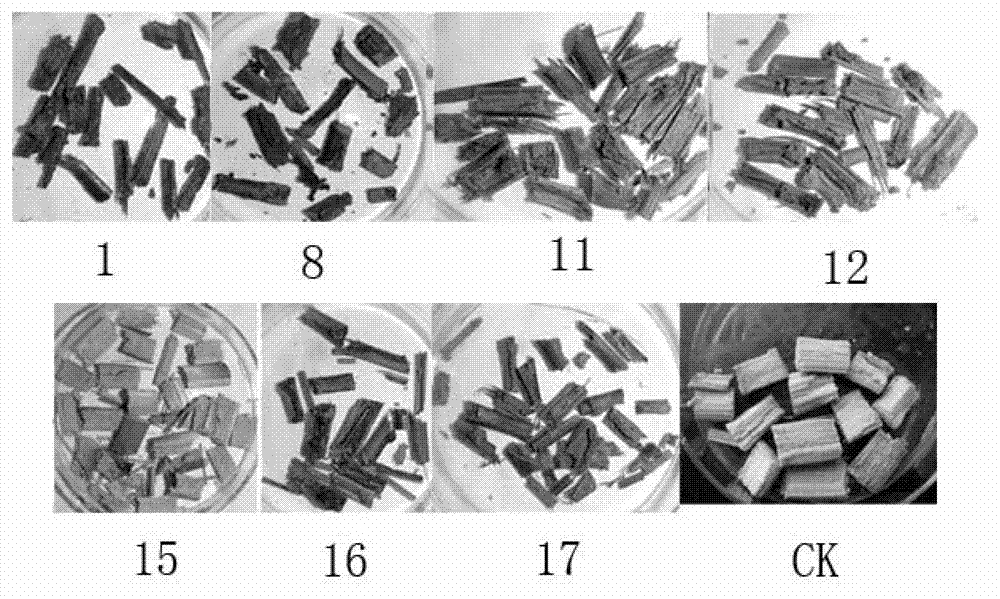
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
611 results about "Cellulose degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A molecular-level understanding of the resistance of cellulose to degradation is a key step toward overcoming the fundamental barrier to making biofuels cost-competitive. However, significant questions remain with respect to cellulose's structure, particularly its surface layers and crystalline core.
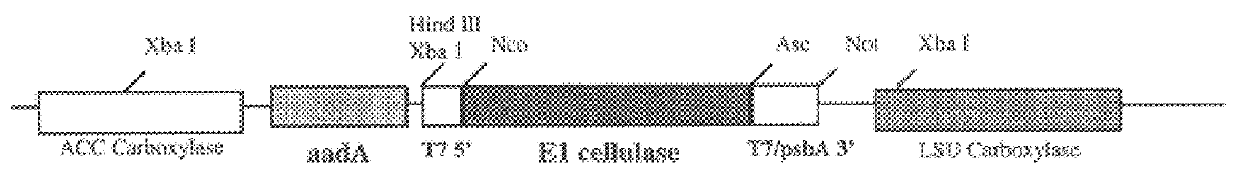
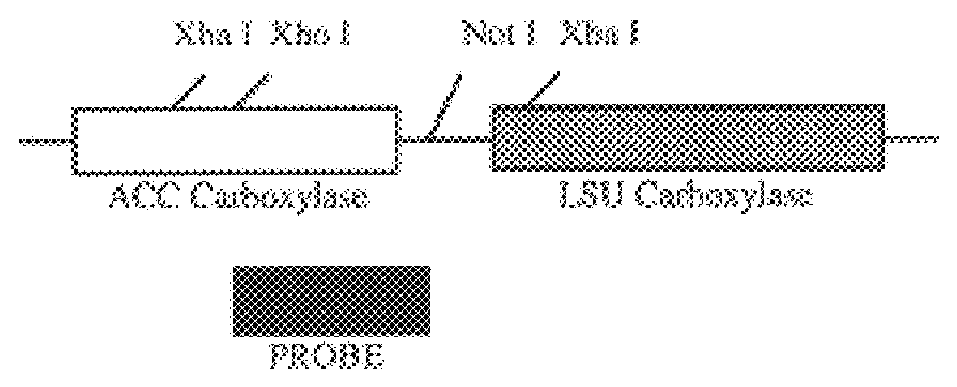
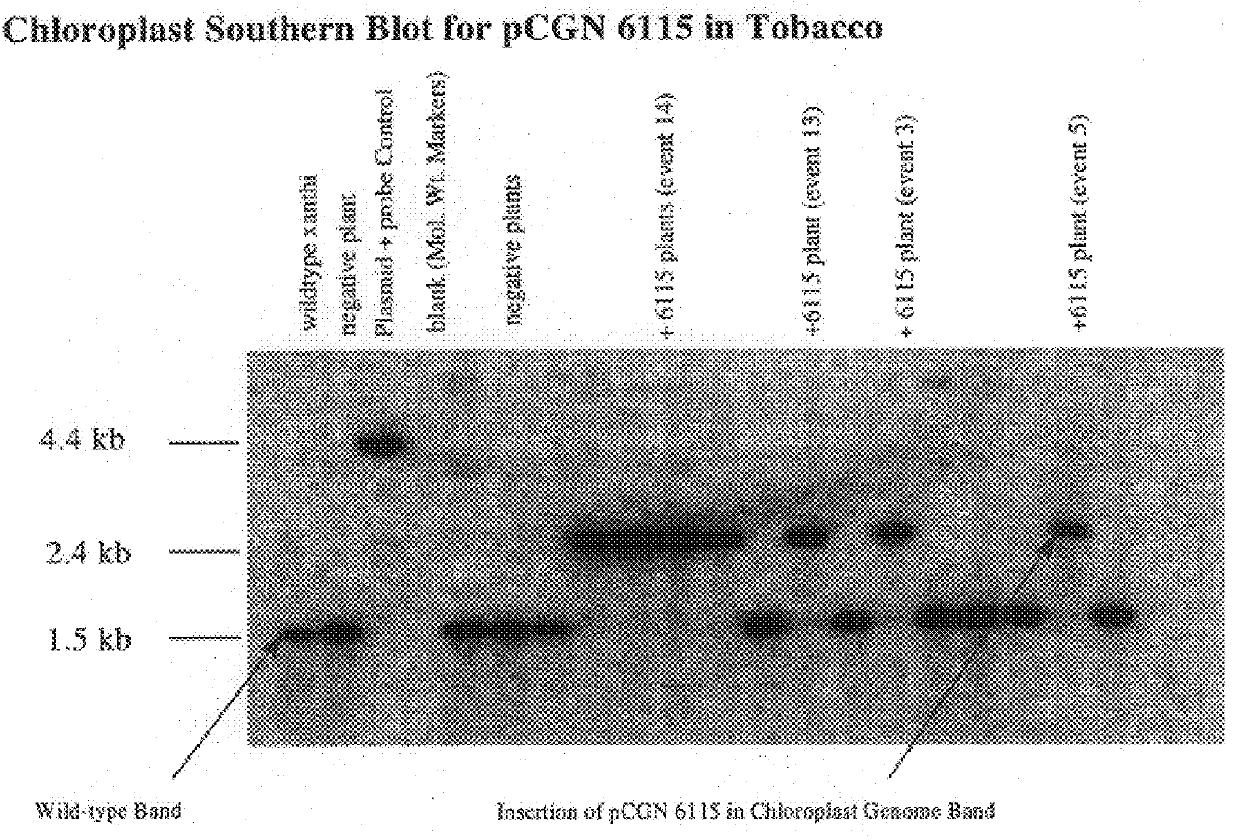
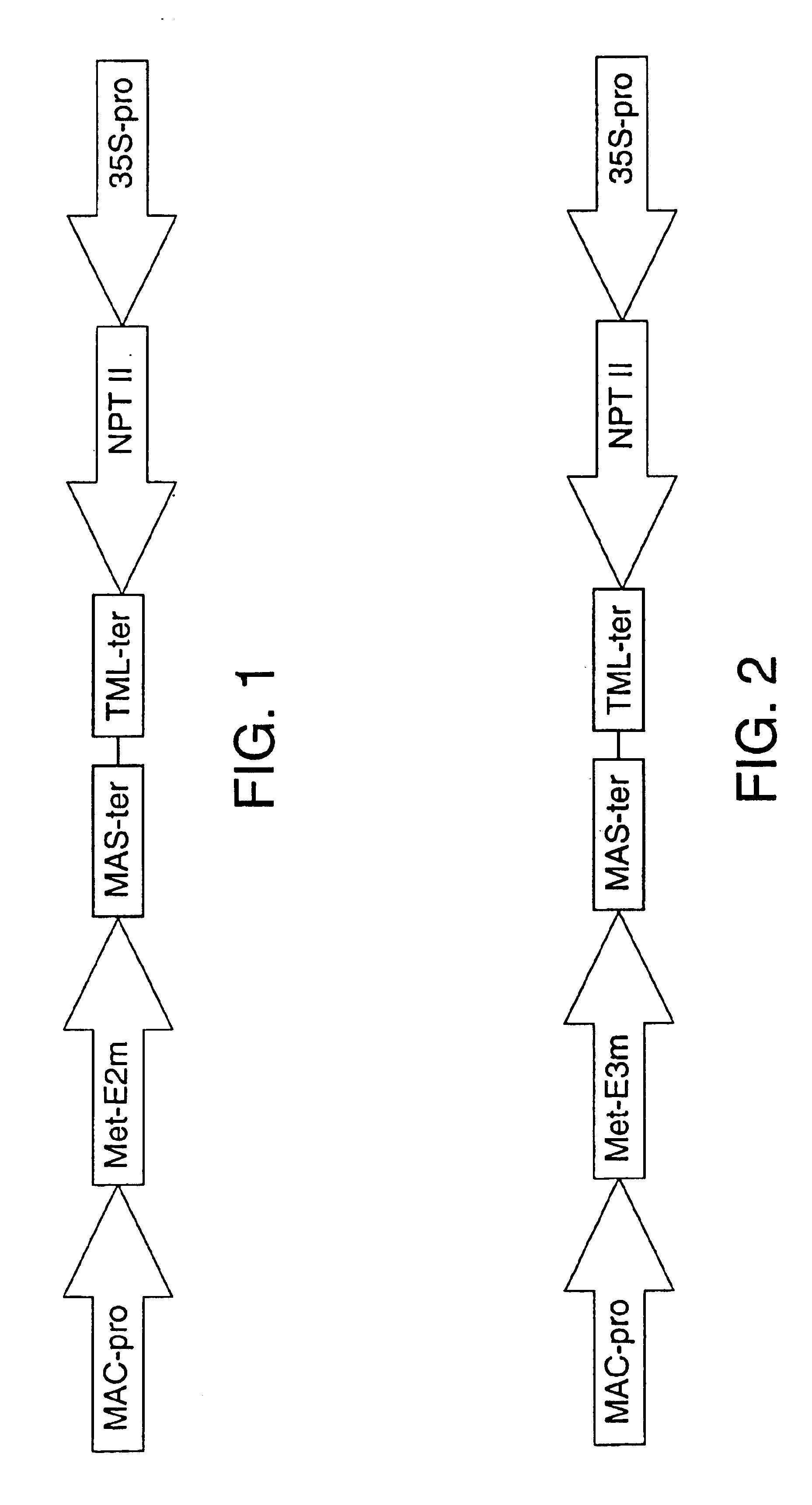
Transgenic plants as an alternative source of lignocellulosic-degrading enzymes
InactiveUS6818803B1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesCelluloseCellulose degradation
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Hydrolytic swelling feed and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101461443ALow costSlow release of ammoniaFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberDigestion
The invention discloses an hydrolyzed puffing forage and preparation method thereof. The method comprises: choosing the plants with high wood-fiber content such as straw, cereal shell, corn core, coconut cover, palm leaf, wood / bamboo scraps, bagasse, herbage rhizome and weed, performing hydrolysis and puffing treatment for destroying the encapsulation effect of lignin to hemicellulose and cellulose, degrading the hemicellulose and cellulose into small molecule soluble sugar, and continuously extruding and puffing by force. The continuous forced feeding and discharging technology realizes stable transitions between different pressures. The invention increases digestion rate greatly, can substitute part of corn and wheat bran, and can be prepared into complete feeds for different birds or animals in different growth stages by adding protein forage, salt, vitamin, mineral elements and aminating agent. The hydrolyzed puffing forage of the present invention has similar digestion rate with the conventional grain forage and sweeter taste, reduces cost greatly, alleviates the grain shortage difficulty, and is suitable for pig, cattle, sheep, chicken, duck, goose, rabbit and specially raised pets.
Owner:邢志强
Compound microbial agent as well as processing method and application thereof
ActiveCN103756941AGood decomposition effectImprove decomposition effectBacteriaSolid waste disposalFiberProtein Degradations
The invention relates to a compound microbial agent which comprises compound bacteria for decomposing kitchen wastes and auxiliary materials for solid fermentation, wherein the compound bacteria comprise 10-15 parts of cellulose degradation bacteria, 15-30 parts of starch degradation bacteria, 15-20 parts of protein degradation bacteria, 15-20 parts of grease degradation bacteria, 10-15 parts of bacillus subtilis and 5-15 parts of pseudomonas aeruginosa; the auxiliary materials comprise 50-60 kg of wheat bran, 15-20 kg of bean pulp, 0.4-0.6 kg of magnesium sulfate, 0.4-0.6 kg of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1-0.2 kg of disodium hydrogen phosphate and 8-10 kg of glucose. The inoculation amount of the compound bacteria in the auxiliary materials is 0.8%-1%, and the compound bacteria is subjected to solid fermentation to obtain the compound microbial agent. The compound microbial agent has a good decomposing effect on greases, proteins and fiber substances and can be tolerant to salt with a certain concentration; optimally, the degradation rate can reach more than 90%.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Method for preparing biological feed by taking manioc residues as raw materials
The invention provides a method for preparing a biological feed by taking manioc residues as raw materials. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing fermentation strains and fermentation mother cultures from aspergillus, bacillaceae, lievito and lactobacillus, and performing mixed fermentation by taking the manioc residues as the raw materials to obtain a biological feed crude product; and mixing uniformly, crushing, sieving, drying and packaging to obtain a biological feed finished product. According to the method, the manioc residues are used as the raw materials, so the biological feed is low in cost and wide in source, industrial waste residues are recycled, and the problem of the pollution of the manioc residues is solved. Simultaneously, the strains which are high in cellulose degradation effect and high in yield of mycoprotein are selected, so that cellulose in the manioc residues is degraded fully, the protein content of the feed is improved, a large number of enzymes, beneficial viable bacteria and organic acids are added.
Owner:广西九通王环保生物工程有限公司
Enzyme and microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101560488AImprove degradation rateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroides xylanisolvensFlavobacterium aquatile
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose and application thereof. The active component of the microbial inoculum consists of Alcaligenes faecalis, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, Clostridium xylanolyticum, Clostridium lentocellum, Flavobacterium aquatile, and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Experiments prove that the microbial inoculum has high degradation rate to the lignocellulose, and the degradation rate can reach between 60 and 70 percent. The microbial inoculum has low cost and simple preparation, breaks through the limitation that a purification bacterium and a clastic enzyme thereof cannot decompose the lignocellulose efficiently, provides a key technique for decomposing, saccharifying biomass containing cellulose and converting the biomass into an energy source, and has extensive application prospect in the field of decomposing the lignocellulose.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of activated carbon
The invention provides a method for preparing activated carbon by degraded residues of straw-type lignocellulose, which comprises the following steps: 1) processing straw-type lignocellulose by an alkali method; 2) processing the residues obtained in step 1) by enzyme hydrolysis; and 3) performing activation to the enzyme hydrolyzed residues obtained in step 2) by a chemical activator under a high temperature condition to prepare an activated carbon product. In the method provided by the invention, the sugar solution obtained after the pretreatment of the lignocellulose raw material by the alkali method and the enzyme hydrolysis is applicable to the preparations of bio-fermentation products such as alcohol, citric acid, xylitol, and the like; the enzyme hydrolyzed residues is applicable to the preparation of activated carbon; the utilization ratio of the raw material is increased, and the method has considerable economic and social benefits.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Microbial bacterium agent for degrading Chinese kitchen refuses and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a microbial bacterium agent for degrading Chinese kitchen refuses, which contains the components by mass ratio: protein degrading bacteria: starch degrading bacteria: fat degrading bacteria: cellulose degrading bacteria= (1-2):(1-2): (1-2):(2-3). Simultaneously, the invention further discloses a preparing method of the microbial bacterium agent. Aiming at components of refuses in domestic kitchens, the corresponding microbial bacteria are adopted for gradual degrading, finally the purpose of completely degrading the refuses is achieved, not thorough degrading and long time consumption of the traditional land filling mode and large secondary pollution and high energy consumption of the burning mode are avoided, and the microbial bacterium agent for degrading Chinese kitchen refuses and the preparing method of the microbial bacterium agent can meet the present low carbon, environmental protection and energy saving requirements.
Owner:田兴军 +1
Bacillus licheniformis and application thereof in promotion of cellulose degradation
InactiveCN101892182APromote degradationHigh nutritional valueBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBacillus licheniformisNutritive values
The invention discloses bacillus licheniformis and application thereof in the promotion of cellulose degradation. The invention provides the bacillus licheniformis J15CGMCC No.3905. Fermentation liquor obtained by fermenting the bacillus licheniformis J15 is the cellulose degradation enzymic preparation of the invention. The bacillus licheniformis J15 can be used for degrading cellulose and preparing compost. By degrading straws with cellulose decomposition bacteria, the bacillus licheniformis has the advantages of improving the nutritive value and the utilization value of the straw, along with high nutritive value, reproducibility, environmental friendliness, less energy consumption and the like. By inoculating the cellulose decomposition bacteria to the high temperature compost, cellulase content in the composting process can be obviously increased, the degradation of the cellulose and the decomposition of the compost can be promoted and the quality of the compost can be improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Production of alcohol from mixed bacterial population degradable fermented bastose substance
InactiveCN1896254AReduce degradationShorten the fermentation cycleBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesAlcohol productionCellulose degradation
Production of alcohol from mixed microbial pool degradable and fermented lignocellulose substance is carried out by crushing lignocellulose substance, soaking with H2SO4, bursting by steam, solid-liquid separating, adding nutritive liquid into solid-phase substance, sterilizing, adding distiller's yeast and cellulose degrading microbe into saccharifying fermentative substrate, degradation saccharifying-fermenting synchronously, distilling and rectifying to obtain final product. It is simple, has short saccharifying and fermenting period, higher raw material utilization rate and more alcohol yield and no feedback inhibition function.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Industrial fermentation ramee rapid extraction technique for Erwinia
ActiveCN101235357AReduce technical difficultyImprove activation process parametersBacteriaMutant preparationAnimal ForagingHigh pressure
The invention discloses a technique for rapidly extracting ramie hemp erwinia bacterium factory production fermentation, the technique comprises preprocessing material, immersing or sprinkling and inoculating, immersing or fermenting, deactivating with hot water, and the procedure of circulation washing, water dressing and fiber finish, erwinia bacterium which has broad-spectrum and high effective to degumming, pulping and saccharifying of herb fiber material, and bacterial agent preparation and activated technical parameter. The erwinia bacterium addicts the mannose, the peak for secreting non-cellulose to degrade key enzyme (pectic enzyme, beta-mannase and xylanase) can be achieved through purely culturing for 7h to 9h. Bacterial agent is inoculated on herb fiber material such as ramie and the like for activating the bacterial agent for 5h-6h, fermentation forage fodder turns to blue after fermenting for 5h-6h, pectine, hemicellulose and partial lignin which are partially degraded and associated in fiber cell are stripped, non-cellulose residues which are absorbed on fiber can be removed by means of the flushing of high-pressure flushing, and the purpose of extracting net fiber can be reached.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Lignocellulose degrading bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN101974436AReduce biotransformation timeImprove qualityBio-organic fraction processingFungiFungicidePenicillium bilaiae
The invention discloses lignocellulose degrading bacteria and application thereof. The lignocellulose degrading bacteria is expanded penicillium W4 with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) No.4077. The stain can generate cellulose and laccase and degrade straw lignocellulose, can be used as a main effective component of microbial fungicides of a mushroom culture medium and has the effects of shortening the biological transformation time of the mushroom culture medium and improving the quality of the mushroom culture medium. Particularly for the biological transformation of a small quantity of packed mushroom culture media of a family workshop, the lignocellulose degrading bacteria has obvious advantage in environment with lower temperature.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing nanometer microcrystalline cellulose by combining acid hydrolysis and ultrasonic treatment
ActiveCN103174046AImprove visibilityImprove chemical reactivityPaper material treatmentFreeze-dryingAcid hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing nanometer microcrystalline cellulose by combining acid hydrolysis and ultrasonic treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a sulfuric acid solution with certain concentration; slowly adding tonnor EM100 powder, which is provided by Shanghai Tonnor Material Science Co., Ltd, to the sulfuric acid solution while stirring; ultrasonically treating for certain time after the tonnor EM 100 powder is completely dissolved; adding a certain amount of distilled water to stop the reaction after the ultrasonic treatment; carrying out centrifugal separation onto the obtained mixed solution; dialyzing the collected nanometer microcrystalline cellulose colloid until the collected nanometer microcrystalline cellulose colloid is neutral; and finally refrigerating and freeze-drying the dialyzed nanometer microcrystalline cellulose colloid to obtain the nanometer microcrystalline cellulose powder. The method for preparing nanometer microcrystalline cellulose by combining acid hydrolysis and ultrasonic treatment is simple to operate, free of damages to the cellulose degradation and easy to control; and more importantly, the environment pollution can be reduced in comparison with the pure acid hydrolysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONNOR MATERIAL SCI
Microbial degrading agent for decomposing cassava stalks and preparation method
InactiveCN102174400APromote degradationEffective decomposing and fermentationMicroorganismsBiofuelsMicroorganismCellulose degradation
The invention discloses a microbial degrading agent for decomposing cassava stalks and a preparation method. The microbial degrading agent for decomposing the cassava stalks is characterized in that: microbial strains of the microbial degrading agent consist of the following components in percentage by taking bacterial biomass as a counting unit: 10 to 50 percent of lignin degradation flora, 10 to 50 percent of hemicellulose degradation flora and 10 to 50 percent of cellulose degradation flora, wherein each strain is purified, rejuvenated, propagated and cultivated; each cultivated strain is compounded according to the proportion; a microbial adsorbent is added; and the components are uniformly mixed to prepare a solid microbial degrading agent. The microbial degrading agent has high efficiency and pertinence; the cassava stalks can be quickly degraded; environmental pollution caused by piling, incineration and the like is avoided; the cassava stalks which are decomposed by the microbial degradation bacteria are changed into things of value to prepare a fertilizer so as to increase both production and income; the microbial degrading agent is easy to operate and is low in using cost; and positive effects of improving soil structure, reducing environmental pollution and the like are achieved when the degrading agent is popularized and applied at cassava planting areas.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method for producing feed by fermenting and ammoniating straws
InactiveCN102178045AImprove degradation efficiencyHigh in nutrientsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffCellulosePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for producing feed by fermenting and ammoniating straws, which relates to the field of environmental science. The method comprises the steps of: (1) after pulverizing the straws, carrying out ammoniation processing and drying for later use; (2) preparing mixed fermenting bacterium liquid No.1, uniformly mixing the mixed fermenting bacterium liquid No.1 with materials, adding a composite trace element and a phosphoric acid solution and fermenting for two to three days; (3) preparing mixed fermenting bacterium liquid No.2, uniformly mixing with the fermented materials and fermenting for three to five days; and (4) drying hydrous fermented materials to obtain straw vinasse mixed feed. In the method, the ammoniated straws are adopted, and the mixed fermenting bacterium No.1, namely efficient cellulose degrading bacteria, is added, so that the cellulose degrading rate can be improved; the mixed fermenting bacterium No.2 can improve the nutrition content of the feed; and the fermented mixed feed has the crude protein content of 14-19 percent, contains various amino acids, and has certain acid flavor and improved palatability. The fermenting process is simple in operation, and the fermenting time is 5-8 days.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Raw trichoderma asperellum strain, bactericide and application of raw trichoderma asperellum strain and bactericide in treatment of organic waste
ActiveCN104450530AGrow fastStrong sporulation abilityBiocideBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a biocontrol strain, namely trichoderma asperellum T-1, for highly producing composite cellulose degrading enzyme. The trichoderma asperellum T-1 is preserved at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 24, 2014; and the preservation number is CGMCC 9722. The invention also provides a waste composting bactericide prepared from the trichoderma asperellum T-1 and an application of the waste composting bactericide in treatment of the organic waste. The trichoderma asperellum T-1 provided by the invention is rapid in growth, high in spore-producing ability, and high pH tolerance; a plurality of cellulose materials can be taken as substrates; and the trichoderma asperellum T-1 is a member of biocontrol bacteria, and can be applied to planting of crops to prevent diseases. By adding the trichoderma asperellum T-1 provided by the invention to the organic waste, the penetrating fluid generated by waste composting can be reduced; the degradation efficiency of the cellulose materials in the waste can be improved; and the quality of the waste composting product is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Composite bacterial agent for efficiently degrading kitchen garbage, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102533718ARich in nutrientsSolve the smell problemWaste based fuelOn/in organic carrierMicroorganismCellulose
The invention discloses a composite bacterial agent for efficiently degrading kitchen garbage, and a preparation method and application thereof. The efficiently degrading kitchen garbage, and preparation method and application thereof consists of a starch-degrading strain, an oil-degrading strain, a protein-degrading strain, a cellulose-degrading strain and a vector; and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing enrichment culture on each single strain, screening, and preparing the vector; and mixing a high-quality composite bacterial agent with the vector. The synergism of various microorganisms in the natural world is fully utilized, a microorganism-based control method is established, and the composite bacterial agent is utilized for coupled fermentation of the kitchen garbage to accelerate the biogas fermentation progress, improve the traditional fermentation process and improve the biogas yield.
Owner:无锡丰陆环保科技有限公司
Methods to enhance the activity of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes
Methods for hydrolyzing lignocellulose are provided, comprising contacting the lignocellulose with at least one chemical treatment. Methods for pretreating a lignocellulosic material comprising contacting the material with at least one chemical are also provided. Methods for liberating a substance such as an enzyme, a pharmaceutical, or a nutraceutical from plant material are also provided. These methods are more efficient, more economical, and less toxic than current methods.
Owner:ATHENIX
Method for producing L-lactic acid through biomass fermentation
ActiveCN102174602AReduce alkali consumptionImprove efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationWater dischargeWastewater
The invention discloses a method for producing L-lactic acid through biomass fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: after the biomass is subjected to alkaline liquid heat treatment, performing solid-liquid separation to obtain a liquid I and residues II; adding a culture medium containing the residues II into a saccharification fermentation tank, adding a cellulose degradation enzyme and performing a hydrolysis reaction for 0.5-6 hours at 50-55 DEG C; keeping the temperature of the saccharification fermentation tank at 50-55 DEG C; adjusting the pH value of the culture medium to 6.0-6.5 by using the liquid I; inoculating bacillus coagulans into the saccharification fermentation tank; and performing synchronous saccharification fermentation on the residues II for 48-96 hours in an anaerobic condition to produce L-lactic acid, and adding the liquid I in flow to keep the pH value of the fermentation liquid at 5.2-5.8. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention not only can improve the comprehensive efficiency of converting cellulose and hemicellulose into lactic acid, and adopts an alkaline waste liquid to neutralize lactic acid in the fermentation process so as to reduce alkali consumption and waste water discharge in the lactic acid production industry.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for pre-processing corn stalks through physical-chemical-biological method
InactiveCN105255953AImprove degradation rateImprove availabilityFood processingBiofuelsChrysosporium speciesFermentation
The invention relates to a method for pre-processing corn stalks through a physical-chemical-biological method. The corn stalks are firstly smashed and physically processed, then the corn stalks are chemically processed through dilute alkali, and finally, the corn stalks are biologically processed through phanerochaete chrysosporium and cellulose degradation bacteria. Lignin removal is facilitated due to dilute alkali processing, the corn stalks can be fully degraded easily because of mixed fermentation, the utilizing rate is increased, and microorganisms producing ethyl alcohol are inoculated into the pre-processed stalks to produce ethyl alcohol, or feeding yeast is inoculated to produce protein feed. The method is simple in technology and convenient to implement.
Owner:刘云平
Bacillus amyloliquefacien and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103275907AImprove antibacterial propertiesIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyCellulose
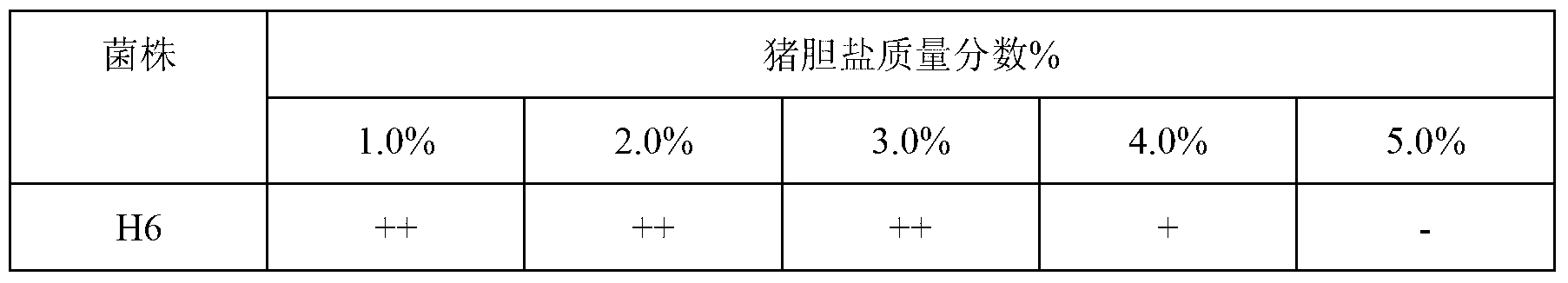
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefacien and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the bacillus amyloliquefacien and the preparation method and the application thereof, the culture collection number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens H6 is CCTCC No: M2013249; the bacillus amyloliquefaciens has obvious growth inhibition effect for gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria, strong degradation ability for starch, albumen, and cellulose, strong environment tolerance, and excellent effect for preventing diarrhea and promoting growing, and can not produce adverse effect with large doses of feeding; and the rear condition is simple, the cost is low, and the development and application prospect is excellent.
Owner:WUHAN KEQIAN BIOLOGY CO LTD
A microbial mixed flora that enhances the flavor of liquor brewing
The invention relates to a microbial mixed colony capable of enhancing flavor of brewed white liquor, which comprises live brevibacillus borstelesis, clostridium.sp, bacillus subtilis, paenibacillus, clostridium thermo succinogene and brevibacillus brevis and can be used for brewing white liquor with strong aromatic flavor. The mixed colony is used in the fermentation process in brewing of the white liquor of the strong aromatic flavor to help a saccharifying starter improve the flavor of raw liquor. The mixed colony is capable of degrading cellulose, and can improve the utilization rate of liquor brewing raw materials and increase yield of white liquor. Meanwhile, the mixed colony is proved to have the characteristics of producing beneficial metabolins such as protease, amylase, organic acids, lipase and vitamins, along with ethanol resistance and heat resistance, and therefore enjoys a great advantageous in the brewing environment; and the metabolins are benefit for enhancing the flavor of the white liquor and increasing the nutrients in the white liquor.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Composite conditioner for preparing sludge compost and application thereof
InactiveCN101913920APromote degradationShorten the fermentation cycleBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationCelluloseSludge compost
The invention discloses a composite conditioner for preparing a sludge compost and application thereof. The composite conditioner for preparing the sludge compost is combined by an agricultural waste fermentation product and non-metallic ore powder in a volume ratio of 1-10:5-1, wherein the agricultural waste fermentation product is prepared by performing direct pile fermentation on one or a mixture of more of sawdust, barks, rice hulls, straw and bagasse or adding zymophyte for aerobic fermentation; and the non-metallic ore powder is one or more of pearlite, vermiculite, zeolite, medical stone and sepiolite with the grain size of smaller than 0.5cm. The composite conditioner can quickly degrade cellulose, shorten the sludge fermentation period to 7-15 days, improve the C / N ratio of the sludge and reduce the diffused odor, also can adjust the pH value of mixed materials, is more favorable for the growth of microorganisms, and can improve fertilizer efficiency and improve the soil.
Owner:娄底市裕德科技有限公司
Method for improving forage nutritional value of cottonseed meal through microbial fermentation
InactiveCN104186957AImprove the nutritional value of feedHigh protein contentAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention utilizes a microbial fermentation technology to improve the forage nutritional value of the cottonseed meal, so as to improve the forage quality of the cottonseed meal, increase the addition proportion in the forage and realize the promotion of the protein nutritional value and the feeding value of the cottonseed meal, aiming at the disadvantages that cottonseed meal is rich in antinutritional factors of free gossypol, cellulose, oligosaccharide, phytic acid and the like, the protein quality is relatively poor and the content of essential amino acids of methionine and the like is low and unbalanced, so that the large-scale forage of cottonseed meal is restricted. The method for improving forage nutritional value of cottonseed meal through the microbial fermentation adopts the technology of 'composite enzymatic hydrolysis and multi-strain three-step solid-state fermentation', so as to prepare the fermented cottonseed meal product that is high in the free gossypol, cellulose degradation degree and the protein content; the cottonseed meal product is rich in nutritional ingredients of probiotics, vitamins, enzyme, amino acid, short peptide, high-grade protein and the like; the method for improving the forage nutritional value of cottonseed meal through the microbial fermentation has the advantages of prompting growth and development, improving the utilization ratio of the forage, enhancing immunization, improving intestinal micro ecology, preventing diseases and the like. The method for improving forage nutritional value of cottonseed meal through the microbial fermentation adopts the solid-state fermentation; the manufacturing technology is simple; the energy consumption is low; zero environmental pollution is generated; and the investment is small. Therefore, mass production is easy.
Owner:QINGDAO JIARUI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Biodegradable plastic and production method thereof
The invention discloses a biodegradable plastic. The biodegradable plastic is characterized in that lignocelluloses and zeolite powder are scattered in polyethylene resin, and cellulose degradation enzymes are arranged in pores of the polyethylene resin. The biodegradable plastic is prepared by steps: adding biodegradable enzymes into ethanol and stirring; mixing the zeolite powder with ethanol solution at the step one, and removing the ethanol; mixing the lignocelluloses, the polyethylene resin and the zeolite powder; and using a granulator for granulating. Compared with starch type biodegradable plastics, the biodegradable plastic has the advantages of high strength and easiness in degradation.
Owner:BIJIE SHANGKUN PLASTIC PROD CO LTD
Preparation and application of garden waste compound degrading microbial agent
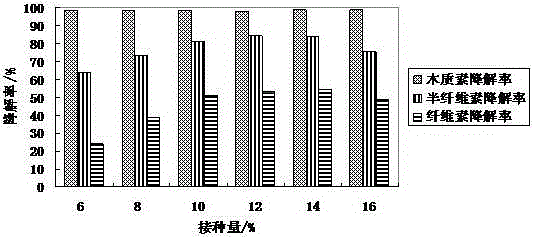
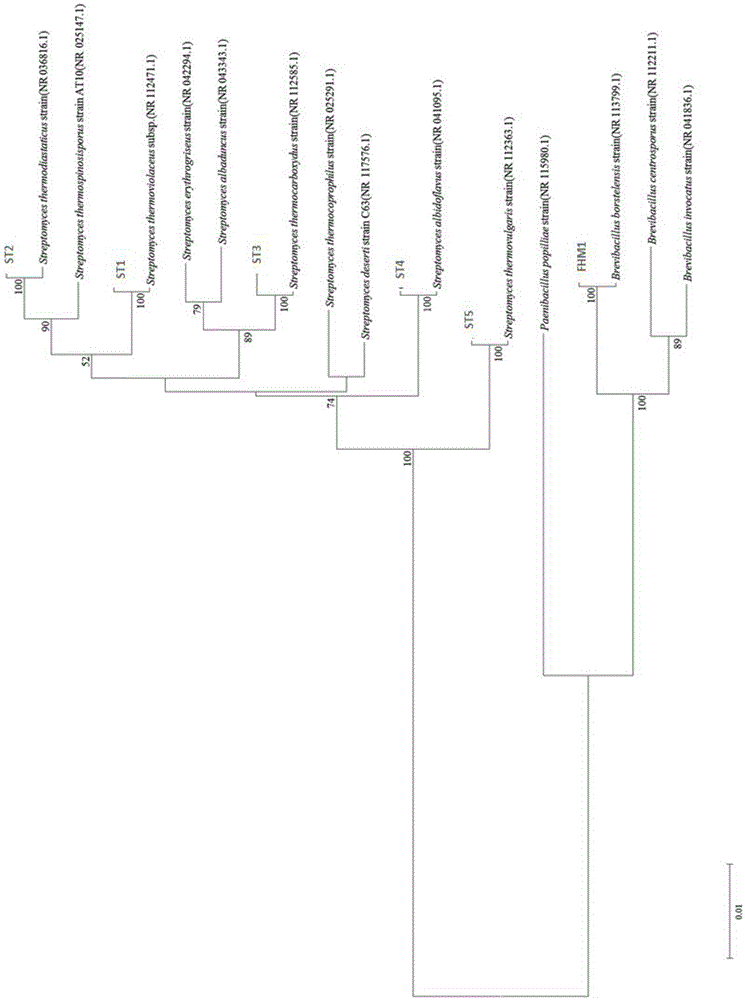
ActiveCN105567612AEfficient and stable degradation abilityAccelerates the composting processBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseStreptomyces thermocarboxydus
The invention discloses a compound microbial agent with a function of effectively degrading cellulose at high temperature. The compound microbial agent contains five actinomycetes: Streptomyces thermoviolaceus, Streptomyces thermodiastaticus, Streptomyces thermocarboxydus, Streptomyces albidoflavus and Streptomyces thermovulgaris, and one bacteria: Brevibacillus borstelensis. The compound microbial agent solves the problem of slow composting and long cycle of garden waste due to the limitation in cellulose degradation difficulty, accelerates cellulose degradation in the composting process, shortens the fermentation period, and improves the conversion efficiency, thereby having a broad application prospect in the aspects such as the application of composting treatment and resource utilization of garden waste, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Cellulose degradation bacteria agent and raw material strain, and preparation methods and application of cellulose degradation bacteria agent and raw material strain
ActiveCN104059862AAccelerated ripeningPromote maturityBio-organic fraction processingFungiCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to the technical field of a biological agent, and particularly relates to a cellulose degradation bacteria agent and a raw material strain, and preparation methods and applications of the cellulose degradation bacteria agent and raw material strain. The compound bacteria agent for degrading cellulose mainly comprises a paecilomyces varioti MM2 strain, an aspergillus fumigates MM6 strain, a candida rugosa MJ4 strain, and a bacillus licheniformis MX8 strain. The cellulose can be efficiently degraded and utilized by the compound bacteria agent disclosed by the invention, the compound bacteria agent can be used as a detonating agent and an enhancer of wine sediment compost, the compost process can be accelerated, the compost rotten degree is improved, an organic fertilizer is fabricated, and the cellulose degradation bacteria agent is especially applicable to resourceful treatment of lignocelluloses solid waste and production of the organic fertilizer by using the wine sediment.
Owner:KWEICHOW MOUTAI COMPANY
Kitchen garbage bio-drying and stabilizing microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111662853AReduce moisture contentIncrease the low calorific valueBacteriaClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a kitchen garbage bio-drying and stabilizing microbial agent as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. According to the technical scheme, pseudomonas aeruginosa is conserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) with the conservation number being CGMCC No.17868.By means of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, microbial composition including starch degrading bacteria, protein degrading bacteria, cellulose degrading bacteria, oil degrading bacteria and deodorization bacteria is provided; and the oil degrading bacteria comprise pseudomonas aeruginosa. The microbial composition can treat kitchen garbage in a targeted manner and achieve the purposes of dewatering, drying, reduction and recycling of the kitchen waste.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Screening and domesticating method of composite microbial system for low-temperature degradation of straws
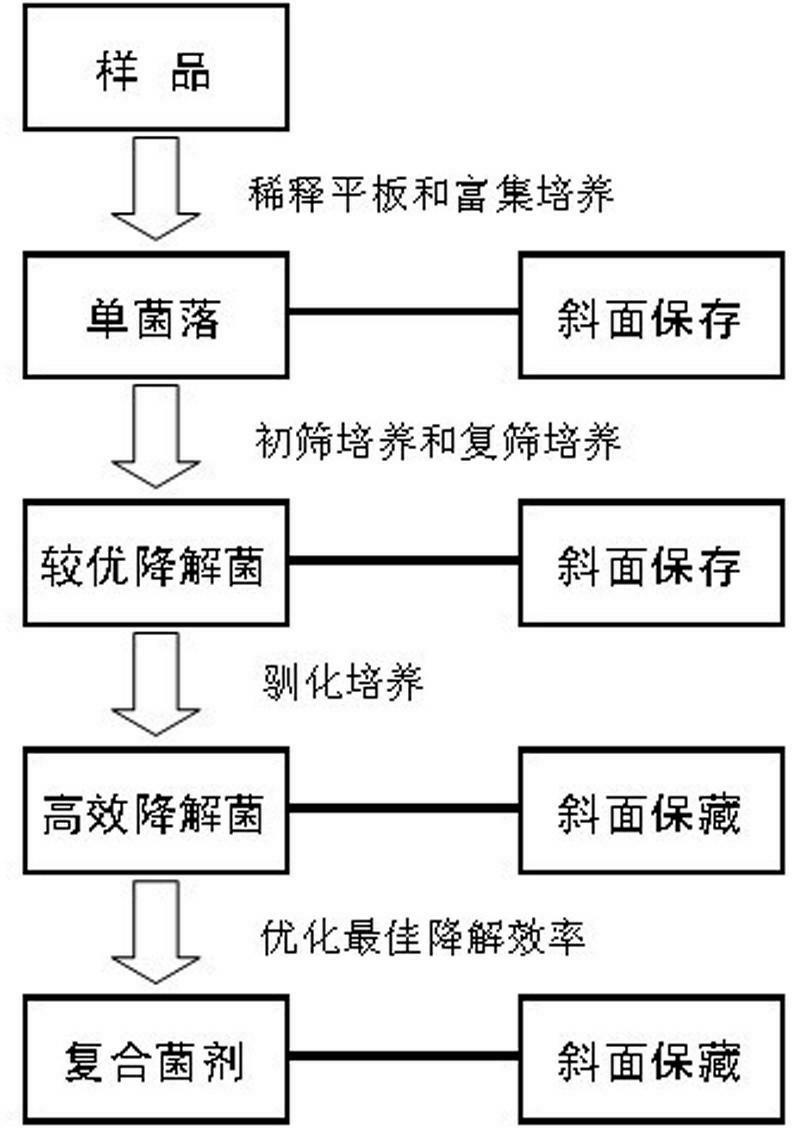
InactiveCN103087973AEfficient degradationEfficient constructionMicroorganism separationMicrobiology processesCellulose degradationEnrichment culture
The invention discloses a screening and domesticating method of a composite microbial system for low-temperature degradation of straws. The screening and domesticating method comprises the steps of acquiring a natural material sample rich in cellulose in an alpine area in which the annual average temperature is -0.6-8 DEG C, carrying out enrichment culture on a cellulose degradation microbial system, then carrying out restrictive subculture preliminary screening, low-temperature gradient induced domestication and cellulase enzyme activity re-screening, and then carrying out low-temperature multi-generation restrictive carbon source subculture domestication to obtain the composite microbial system for low-temperature degradation of straws. The screening and domesticating method can be used for screening and domesticating the composite microbial system for high-efficiency degradation of straws at low temperature and has an important meaning in field returning and utilization of straw resources in the northern area.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com