Raw trichoderma asperellum strain, bactericide and application of raw trichoderma asperellum strain and bactericide in treatment of organic waste
A technology of Trichoderma aculeatus and Trichoderma, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as inability to achieve decomposition effects and complex material components, and achieve the effects of reducing soil-borne diseases, low preparation costs, and reducing cellulose content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: the acquisition of Trichoderma aculeatus T-1
[0038] The Trichoderma aculeatus strain involved in the present invention is isolated from soil by carboxymethyl cellulose plate and dilution coating method, and is determined to be an efficient cellulose degrading bacteria by Congo red staining and filter paper strip decomposition test, and then undergoes physiological Characteristic analysis and ITS rDNA identification confirmed that it was Trichoderma aculeatus, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0039]1. Separation: Weigh 10g of the soil sample, put it into a triangular flask filled with 90ml of sterile water, shake it for about 20 minutes, that is, the soil solution with a dilution of 10-1, use a pipette to draw 1ml of the soil suspension into it In a test tube containing 9ml of sterile water, blow and suck three times, try to mix thoroughly, that is, a soil solution with a dilution of 10-2, then draw 1ml of the solution from the test tube and inje...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: the plate antagonism experiment of Trichoderma aculeatus T-1
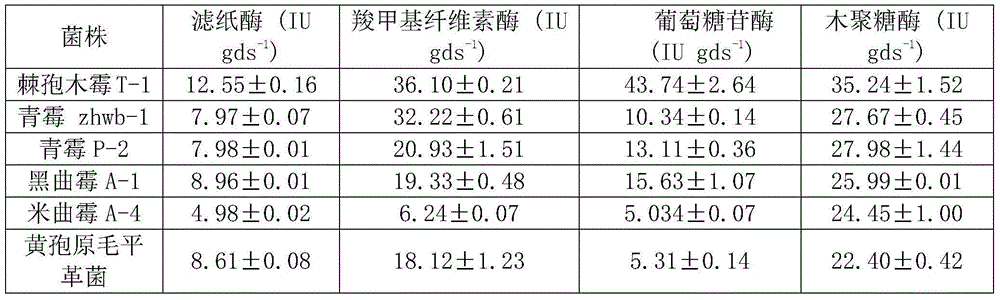
[0045] Use the confrontation culture method to prepare a PDA plate, use a puncher to punch a small piece of bacterial cake at the edge of Trichoderma aculeatus and the bacteria to be antagonistic, inoculate it into the center of the opposite sides of the new PDA shield, culture at 28°C, and observe the Aechinospora Action of Trichoderma against antagonistic bacteria. The results showed that Trichoderma aculeatus T-1 could inhibit the growth of plant pathogens Fusarium oxysporum and Fusarium solani.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3: the preparation of Trichoderma aculeatus T-1 microbial bacterial agent
[0047] Using crop straw as the main substrate, Trichoderma aculeatus T-1 is cultivated by solid-state fermentation to prepare microbial inoculum. The specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0048] Strain activation culture, inoculate the slant preservation of Trichoderma aculeatus T-1 strain on a PDA plate, and culture it at 25°C-30°C for 3-5 days until a large number of spores are formed;
[0049] To prepare a solid medium, mix the straw with a crushed particle size of 20-40 mesh and bran according to the ratio of solid amount of 3:1, and then add Mandel culture solution, autoclaved at 121°C for 20 minutes, cooled as a solid medium for Trichoderma aculeatus T-1, in which Mandel culture solution contains NaNO 3 2g, KH 2 PO 4 1.5g, CaCl 2 0.3g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.005g, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.0016g, ZnSO 4 ·H 2 O0.0014g, CoCl 2 0.0005g, water 1000ml, pH 6; ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com