Low temperature resistant cellulose degradation bacteria and application thereof
A technology of cellulose-degrading bacteria and low-temperature resistance, applied in the field of microorganisms and biodegradation, can solve the problems of high cost and low efficiency of cellulose degradation, and achieve the effect of easy operation control and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 Isolation of low temperature resistant cellulose degrading bacteria
[0020] Humus soil samples were collected from Shuangfeng Forest Farm in Mudanjiang City, Heilongjiang Province. Add 10 g of the collected sample to 90 mL of sterile water, shake it fully, and let the supernatant liquid be added to the beef extract peptone liquid medium, and acclimate and cultivate through a temperature gradient of 5 °C, 7 °C, and 10 °C, 3d is a cycle .
[0021] After acclimation and culture, take 1 mL of cultured bacterial solution and dilute it with sterile water to 10 -5 , 10 -6 , 10 -7 , respectively, take 0.1 mL of coated plates, and then pick a single colony for isolation and purification after constant temperature incubation at 4 °C. The single colony obtained after purification was transferred to the plate for preservation.
[0022] The purified strains obtained from the primary screening were spotted on the cellulose-degrading bacteria screening medium, and afte...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2 Enzyme activity assay of low temperature resistant cellulose degrading bacteria
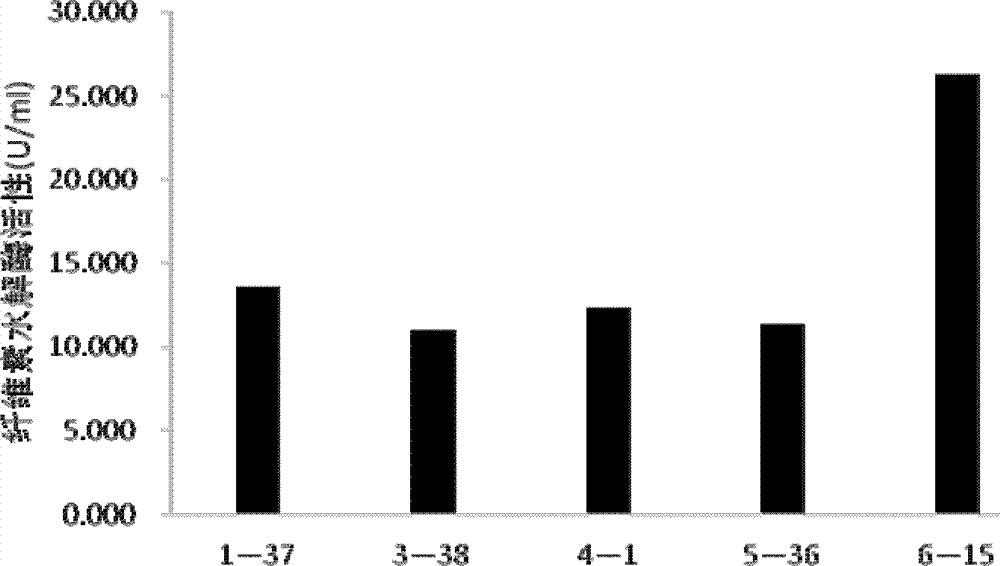
[0026] The 5 strains of degrading bacteria screened in Example 1 were picked and placed into the beef extract peptone liquid medium for 24 hours at 15°C to make seed liquid, and then inserted into the shake flask cellulose fermentation medium at 15°C. Cellulase activity was measured after 3 days of culture.
[0027] Wherein, shake flask cellulose fermentation medium: NaCl 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, CMC-Na 5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 1g / L, 1000mL deionized water, sterilized for use.
[0028] When measuring cellulase activity, filter paper was used as substrate to measure cellulase activity by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method, and absorbance value was measured at 540nm. The amount of enzyme required to hydrolyze cellulose to produce 1 μg of glucose per minute was defined as 1 unit of enzyme activity (U).
[0029] The result is as figure 1 As shown, strain B6-15 (Deposi...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 Morphological identification and growth curve of low temperature resistant cellulose degrading bacteria
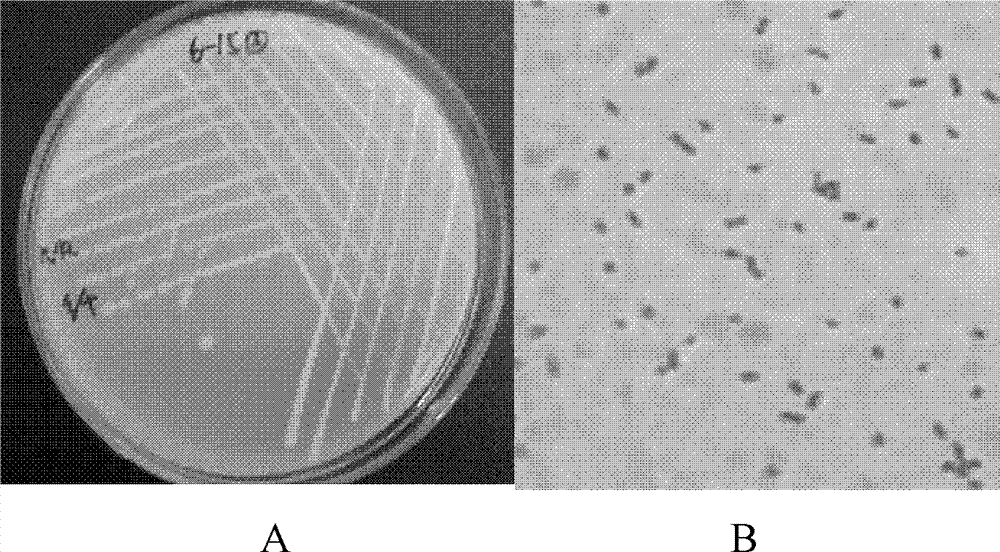
[0031] The typical strain B6-15 selected in Example 2 was taken as the research object. First, the strains were inoculated on the plate, and after culturing at 15°C for 24 hours, the colony morphology on the plate was observed; then simple staining, Gram staining and spore staining were performed, and the morphology of single cells was observed using a light microscope.
[0032] The result is as figure 2 As shown, the colony is round, light yellow, 2-3mm in diameter, the surface is moist, the center is more prominent, the edge is neat, opaque; the single cell is short rod-shaped, Gram-negative, without spores, with capsule.
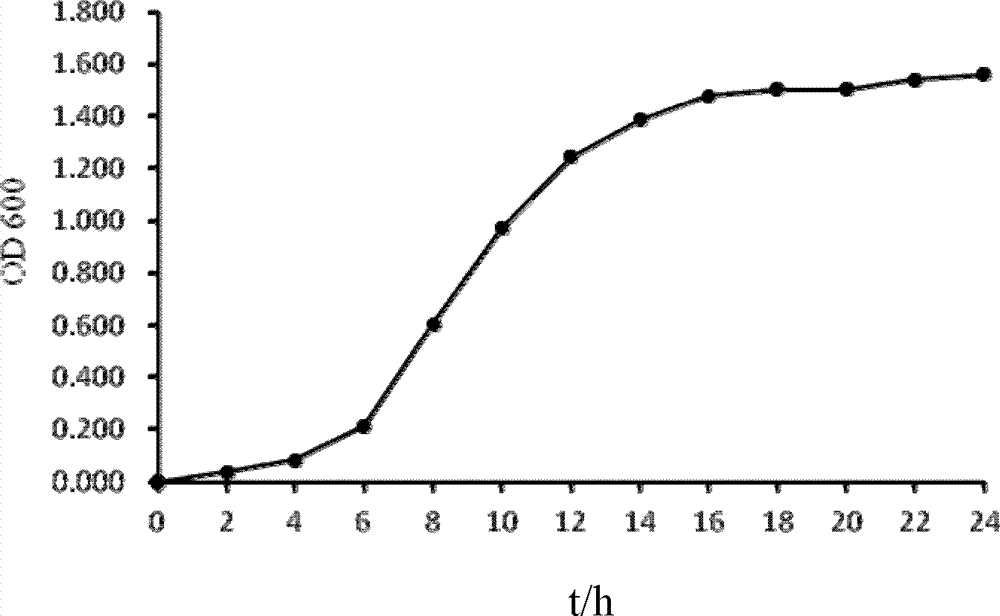
[0033] The strains were inserted into the liquid medium, in a shaker at 15°C, the rotation speed was 160r / min, and cultivated for 24 hours to prepare a bacterial liquid, and then 1ml of the above bacterial liquid was taken into a fr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com