Plant flavonoid synthesis regulation gene and its application
A technology of flavonoids and genes, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering and biology, can solve the problems of very little research on the synthesis of effective ingredients flavonoids and the molecular mechanism of regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: the isolated clone of EsMYBA1 gene
[0042] The EsMYBA1 gene was isolated from Epimedium sagittatum by homologous cloning combined with RACE technology, and the process was as follows:
[0043] First, total RNA was extracted from the young leaves of Epimedium sagittatum according to the operating instructions of the RNAiso plus reagent (Takara company, the same below). The specific method is as follows: Take 50-100mg of fresh tissue or frozen tissue, fully grind it in liquid nitrogen, transfer the powder to a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, add 1mL RNAiso plus reagent to fully lyse, and go through chloroform layering, isopropanol precipitation and ethanol Wash and finally dissolve in 50uL of RNase-free ddH 2 O middle. The quality and yield of the RNA solution was detected by gel electrophoresis and UV spectrophotometer Nanodrop2000c (ThermoFisher scientific company, the same below), which met the requirements of reverse transcription, and then stored at -20oC for...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: subcellular localization
[0050] First, the complete ORF of the EsMYBA1 gene was transferred to the cloning vector pBI221-GFP containing the GFP reporter gene by enzyme-cut ligation, and then the onion epidermal cells were bombarded with a gene gun, observed and photographed under a confocal laser microscope. The vector construction process for subcellular localization analysis is as follows: design a pair of GSP (forward primer: GC GGATCC ATGAAGCCAGATTTTAGTGAGAT, underlined BamHI restriction site; reverse primer: 5'CG GTC GAC TTCAAAATTCCAAAAGTTCAAG, the underlined SalI restriction site), using the recombinant plasmid pMD19-T containing the full-length sequence of EsMYBA1 as a template, amplified its ORF with high-fidelity PrimeStar DNA polymerase, and the PCR system was as described in Example 1. Direct PCR product recovery, BamHI and SalI double digestion, the target fragment recovered after digestion was connected to the cloning vector pBI221-GFP (c...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: yeast two-hybrid
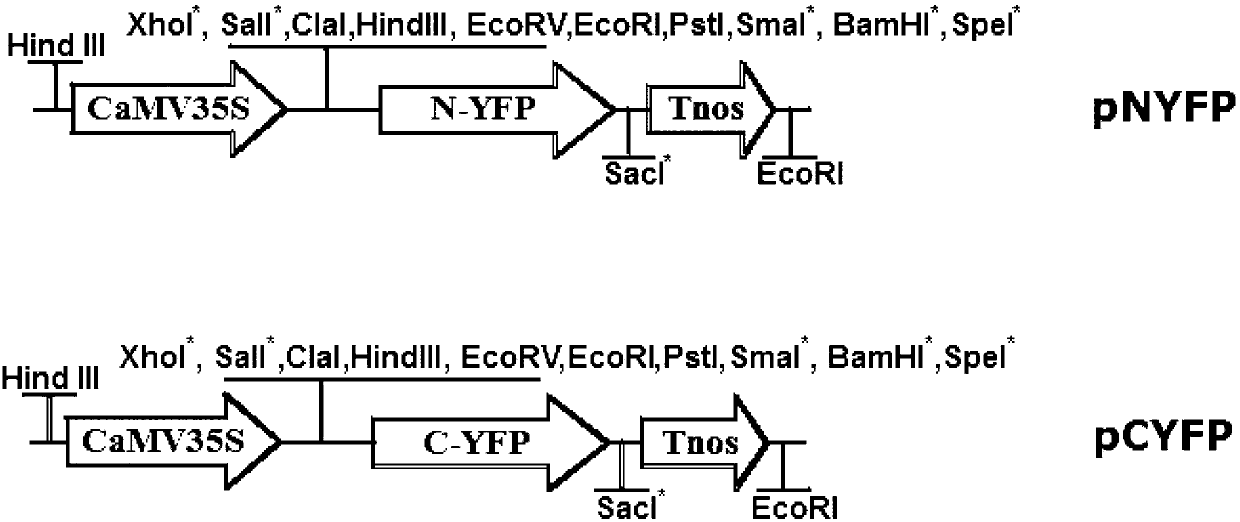
[0052] In order to verify whether EsMYBA1 has the ability to interact with other bHLH TFs that regulate flavonoid synthesis, we used yeast two hybrid assay (yeast two hybrid) for analysis. The yeast two-hybrid vectors used are pAD-GAL4-2.1 and pBD-GAL4Cam (Stratagene, abbreviated as pAD and pBD, the same below), which contain the AD (activating domain) and BD (binding domain) of the GAL4 protein, respectively. , binding domain), all located under the ADH1 (alcohol dehydrogenase 1, alcohol dehydrogenase 1) promoter. Firstly, the ORF of EsMYBA1 was cloned into pAD and pBD vectors by double enzyme digestion EcoRI / SalI to obtain recombinant vectors pAD-EsMYBA1 and pBD-EsMYBA1, and the recombinant plasmids were digested, identified by PCR and sequencing. The primers used to amplify the ORF of EsMYBA1 are GC GAATTC ATGA AGCCAGATTTTAGTGAGAT (underlined EcoRI restriction site) and CG GTC GAC TTCAAAAATTCCAAAAGTTCAAG (the underline is the Sal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com