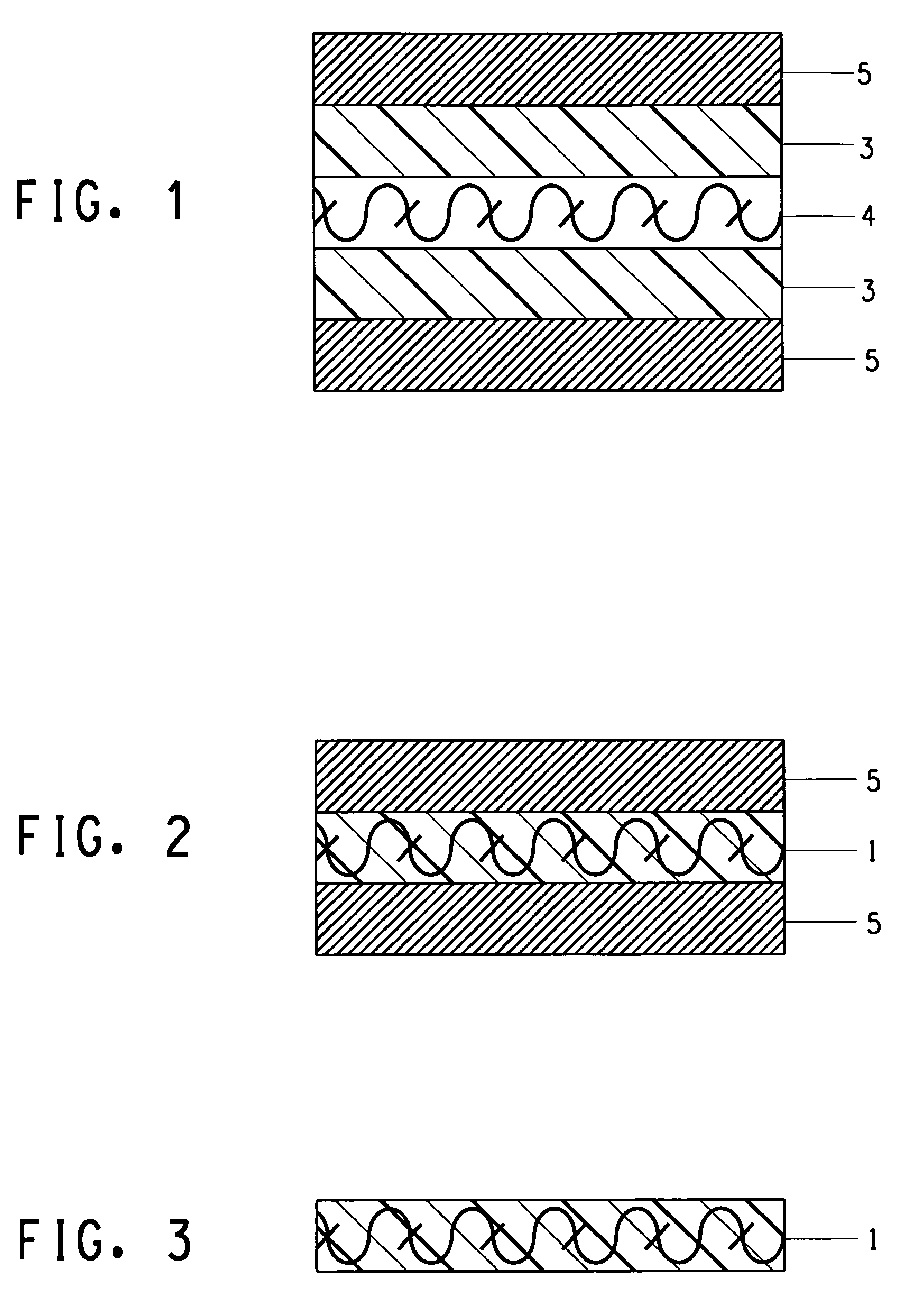
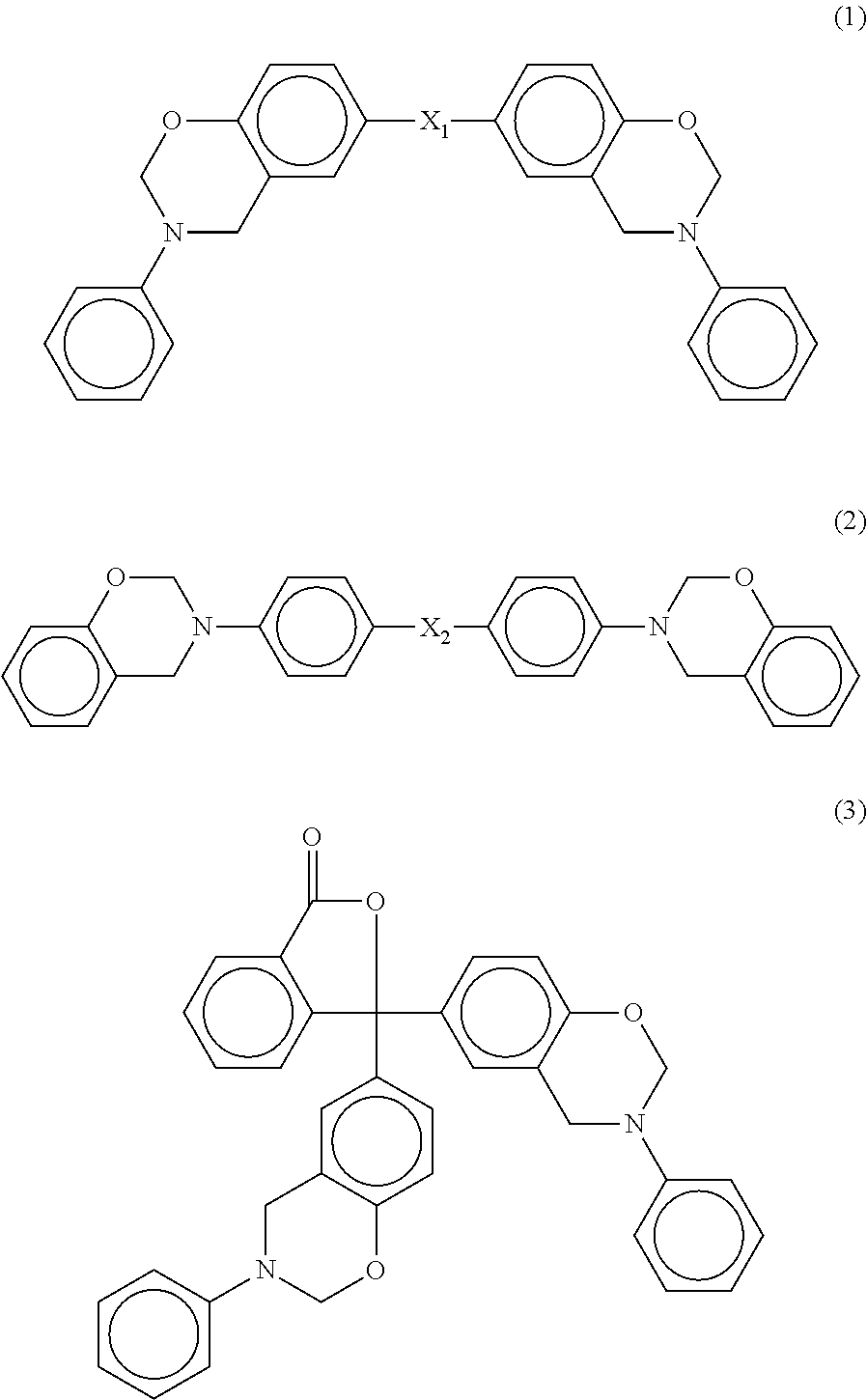
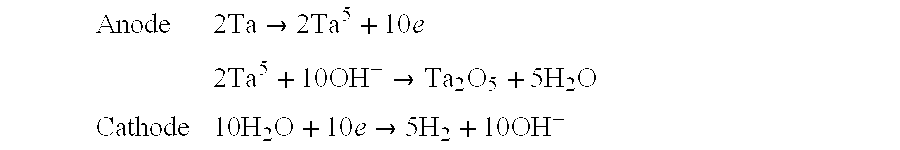Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
171results about How to "Low dissipation factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
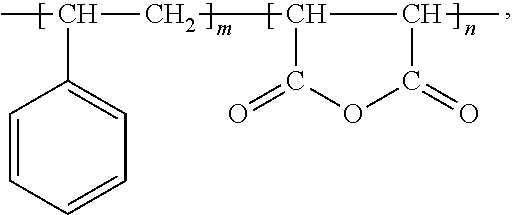
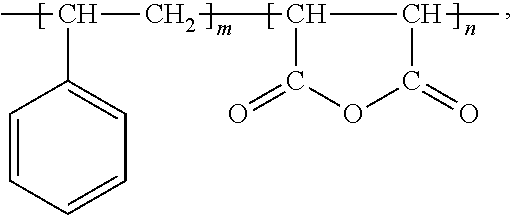
Halogen-free resin composition and its application for copper clad laminate and printed circuit board
ActiveUS20130161080A1Low dielectric constantImprove heat resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsEpoxyLow dissipation
A halogen-free resin composition includes (A) 100 parts per hundred resin of epoxy resin; (B) 1 to 100 parts per hundred resin of benzoxazine resin; (C) 1 to 100 parts per hundred resin of styrene-maleic anhydride; (D) 0.5 to 30 parts per hundred resin of amine curing agent; and (E) 5 to 150 parts per hundred resin of halogen-free flame retardant. The composition obtains properties of low dielectric constant, low dissipation factor, high heat resistance and flame retardancy by specific composition and ratio. Thus, a prepreg or a resin film, which can be applied to a copper clad laminate and a printed circuit board, is formed.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
Halogen-free resin composition and copper clad laminate and printed circuit board using same
ActiveUS20130075138A1Low dissipation factorHigh heat resistancePrinted circuit aspectsSynthetic resin layered productsLow dissipationStyrene maleic anhydride
The halogen-free resin composition comprises (A)100 parts by weight of cyanate ester resin; (B) 5 to 50 parts by weight of styrene-maleic anhydride; (C) 5 to 100 parts by weight of polyphenylene oxide resin; (D) 5 to 100 parts by weight of maleimide; (E) 10 to 150 parts by weight of phosphazene; and (F) 10 to 1000 parts by weight of inorganic filler. By using specific components at specific proportions, the halogen-free resin composition of the invention offers the features of low dielectric constant, low dissipation factor, high heat resistance and high flame retardancy, and can be made into prepreg or resin film, and thereby used in copper clad laminate or printed circuit board.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
Protective coating for electrolytic capacitors
InactiveUS6864147B1Low dissipation factorLow leakage currentSolid electrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingShellacElectrolysis
A solid electrolytic capacitor that comprises an anode that contains a valve-action metal (e.g., tantalum, niobium, and the like) and a dielectric film overlying the anode is provided. The capacitor also comprises a protective coating overlying the dielectric film, wherein the protective coating contains a relatively insulative, resinous material. For example, in one embodiment, the resinous material can be a drying oil, such as olive oil, linseed oil, tung oil, castor oil, soybean oil, shellac, and derivatives thereof. The capacitor also comprises a conductive polymer coating overlying the protective coating. As a result of the present invention, it has been discovered that a capacitor can be formed that can have a relatively low leakage current, dissipation factor, and equivalents series resistance.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
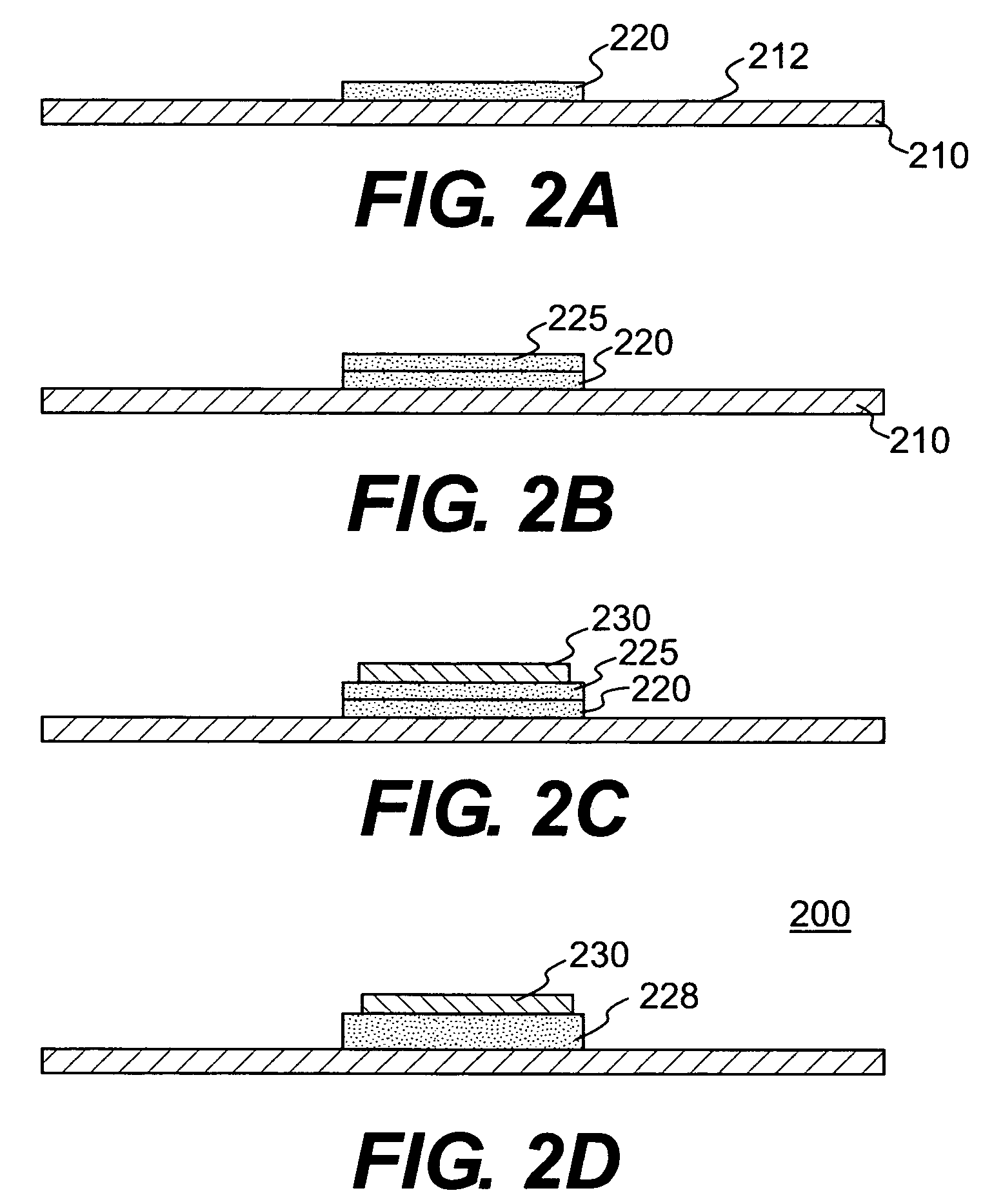
Composite dielectric material, composite dielectric substrate, prepreg, coated metal foil, molded sheet, composite magnetic substrate, substrate, double side metal foil-clad substrate, flame retardant substrate, polyvinylbenzyl ether resin composition, thermosettin
InactiveUS6908960B2Low dielectric constantMinimized of constantShielding materialsPrinted capacitor incorporationShell moldingMetal foil
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Resin composition for insulation film
ActiveUS20130245161A1Low dielectric constantLow DfDomestic articlesThin material handlingPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
A resin composition includes (A) 100 parts by weight of epoxy resin; (B) 20 to 100 parts by weight of polybutadiene styrene divinylbenzene graft terpolymer resin; (C) 2 to 20 parts by weight of di-tert-butylhydroquinone (DTBHQ); (D) 5 to 50 parts by weight of polyphenyl ether modified cyanate ester resin; and at least one of (E) inorganic filler, (F) chain extending sealing agent, and (G) catalyst. The resin composition is characterized by specific ingredients and proportions thereof to attain high heat resistance, low dielectric constant Dk, and low dielectric dissipation factor Df, and being halogen-free, and therefore is applicable to protective film of printed circuit boards, insulating protective film of electronic components, and resin insulation film of leadframes.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
Low dielectric constant, low dielectric dissipation factor coatings, films and adhesives
Curable functionalized imide-linked polyimides compounds have been synthesized that have been found to possess very low dielectric constant and extremely low dissipation factor. These compounds also have a range of high to low modulus, extremely low moisture uptake and are very thermally stable. The combination of these materials in formulation along with functionalized polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutadiens have been found to be ideal for forming films and coatings for the microelectronic applications, multiplayer capacitors and interconnects, and high power cables and wire coatings. The addition of perfluorinated hydrocarbons, and POSS nanoparticles to the formulations have decreased the dielectric constant and dielectric dissipation factor further, and have also improved the flammability of the compositions.
Owner:MIZORI FARHAD G +1
Resin composition
ActiveUS20170166729A1Low thermal expansionImprove heat resistanceFireproof paintsDielectric materialsThermal expansionCopper
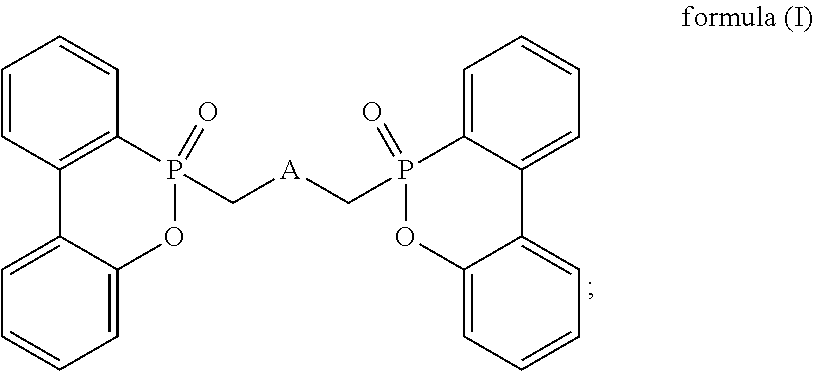
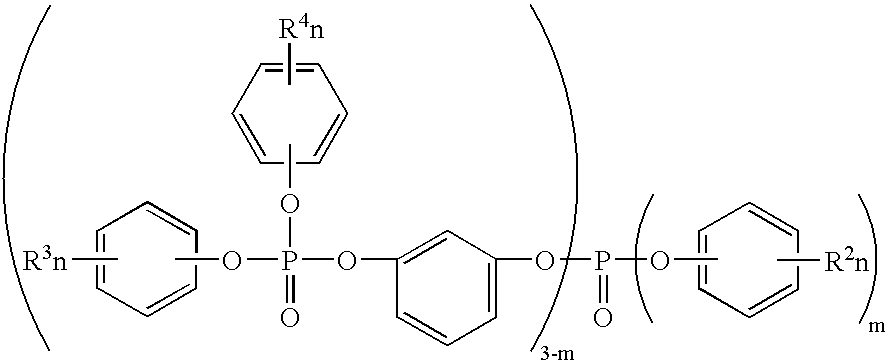
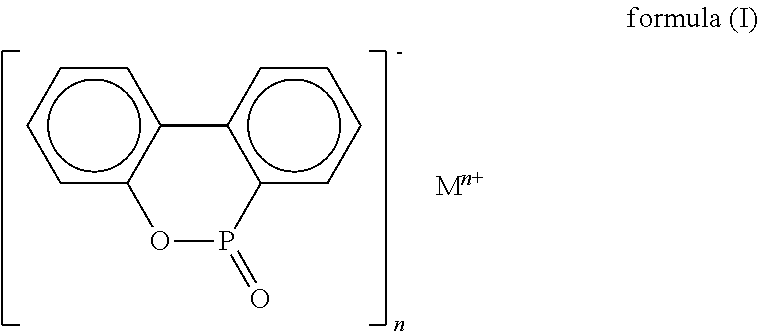
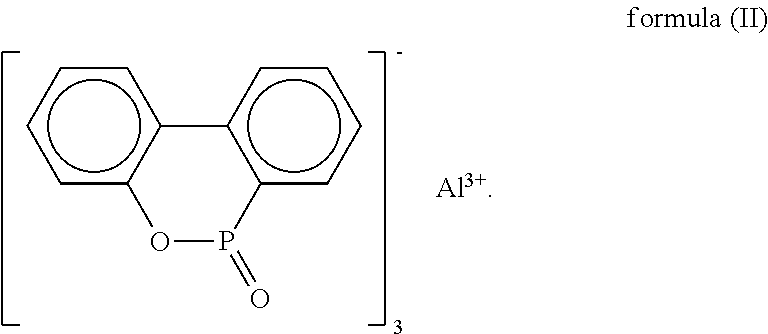
The present invention relates to resin composite materials, and more particularly, to low-dielectric resin composition and prepreg, resin film, resin coated copper, laminate and printed circuit board formed therefrom. The low-dielectric resin composition includes a phosphorus-containing flame retardant as shown in formula (I) and a resin with an active unsaturated bond. The low-dielectric resin composition may further be manufactured as a prepreg, a resin film, a resin coated copper, a laminate, or a printed circuit board, having a high glass transition temperature, low dielectric property, halogen-free flame retardancy and low percent of thermal expansion of laminate.
Owner:ELITE ELECTRONICS MATERIAL ZHONGSHAN
Laminates having a low dielectric constant, low disapation factor bond core and method of making same
InactiveUS20050121226A1Improve bindingLow dissipation factorInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementDielectric materialsLow dissipationPolyetherimide
Laminates have at least one resin-system layer, a low dielectric, low dissipation factor bond core having at least one surface that is treated for adhesion, such as by etching, plasma or Corona discharge or mechanical roughing to facilitate bonding to the at least one resin system layer and a conductive metal cladding on the at least one resin system layer. The bond core can be a fluoropolymer film or a fluoropolymer prepreg, having at least one etched or Corona discharge treated surface. Alternately, the bond core can be a polyetherimide film or a polyetherimide prepreg, having at least one etched or Corona discharge treated surface. The laminates are used, for example, high performance, low loss printed circuit boards. The laminates have the desired dielectric properties inherent to fluoropolymer materials and can be produced using conventional printed circuit board manufacturing processes, materials, and equipment. Methods of producing laminates are disclosed.
Owner:PARK ELECTROCHEMICAL CORP
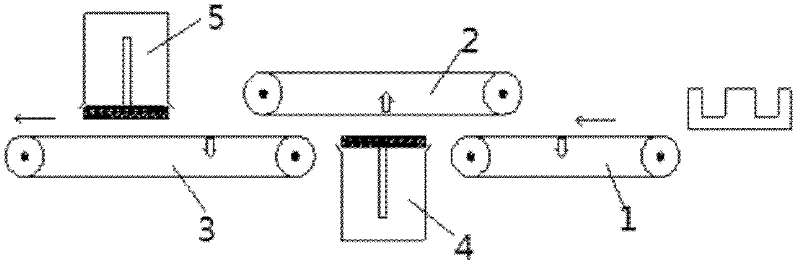
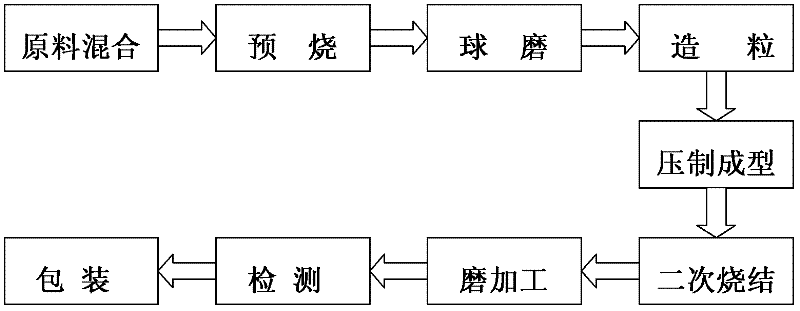
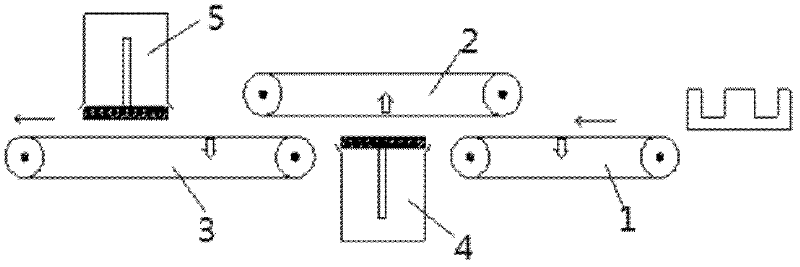
Method for producing soft magnetic ferrite core
InactiveCN102643083AImprove permeabilityLow dissipation factorEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesInitial permeabilitySoft magnet
The invention discloses a method for producing a soft magnetic ferrite core. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing of raw materials, pre-sintering, ball milling, compression moulding, secondary sintering, grinding and detection, wherein an integral magnetic-attraction double-sided grinding machine is adopted in the grinding process. The magnetic core produced by the method has high magnetic conductivity and low loss factor, and energy sources can be saved; the magnetic core has uniform color, flat end surface and bright and clean surface; the ball milling as well as the uniformity and sphericity of the mixed material are improved; a low-temperature sintering technology is adopted, the heating rate and cooling rate of each stage are adjusted, the ferrite transformation of the material is promoted, and the grain size can be effectively controlled; and the initial permeability and temperature characteristic are improved.
Owner:ANHUI TAIDE ELECTRONICS TECH
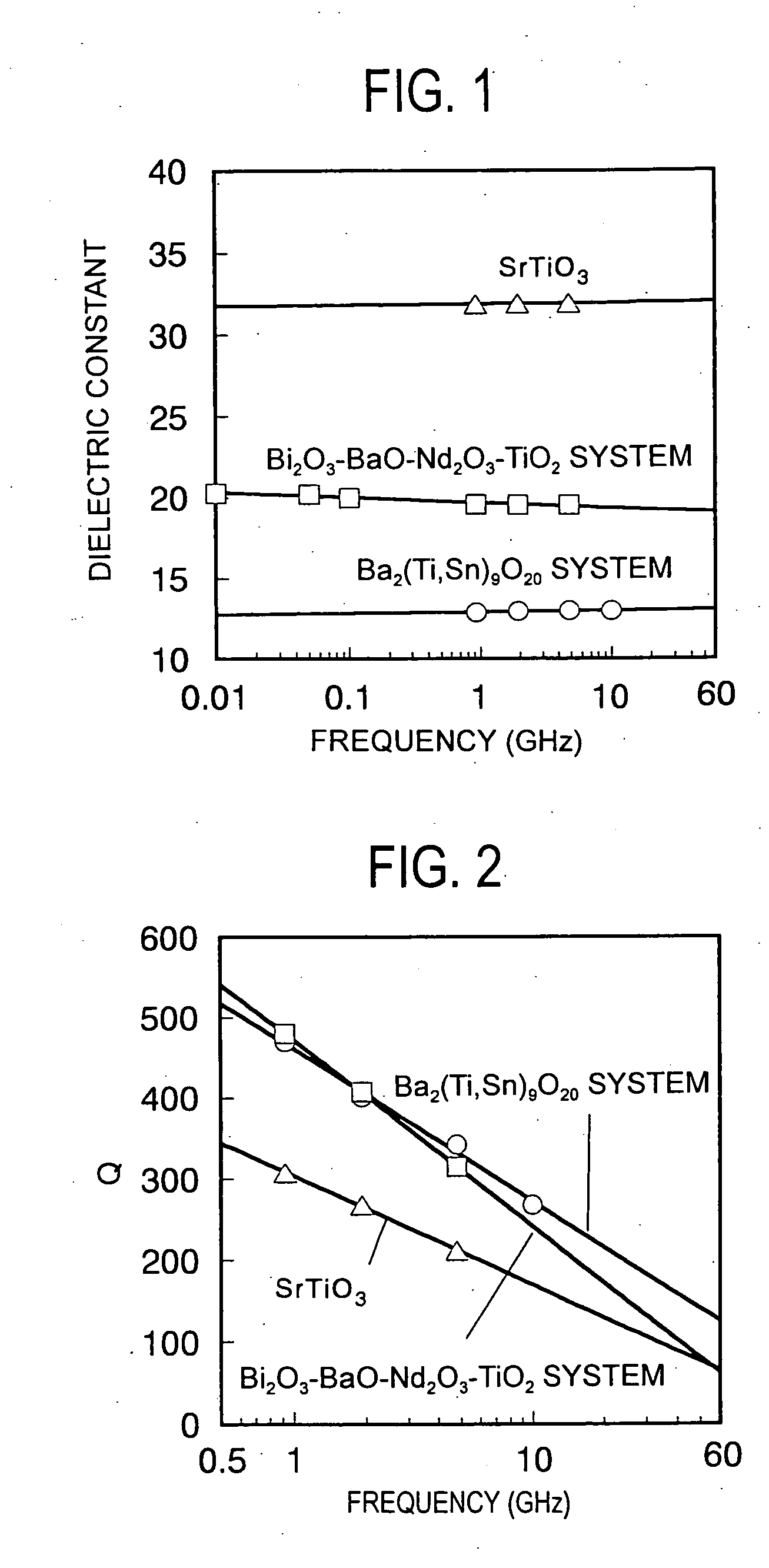
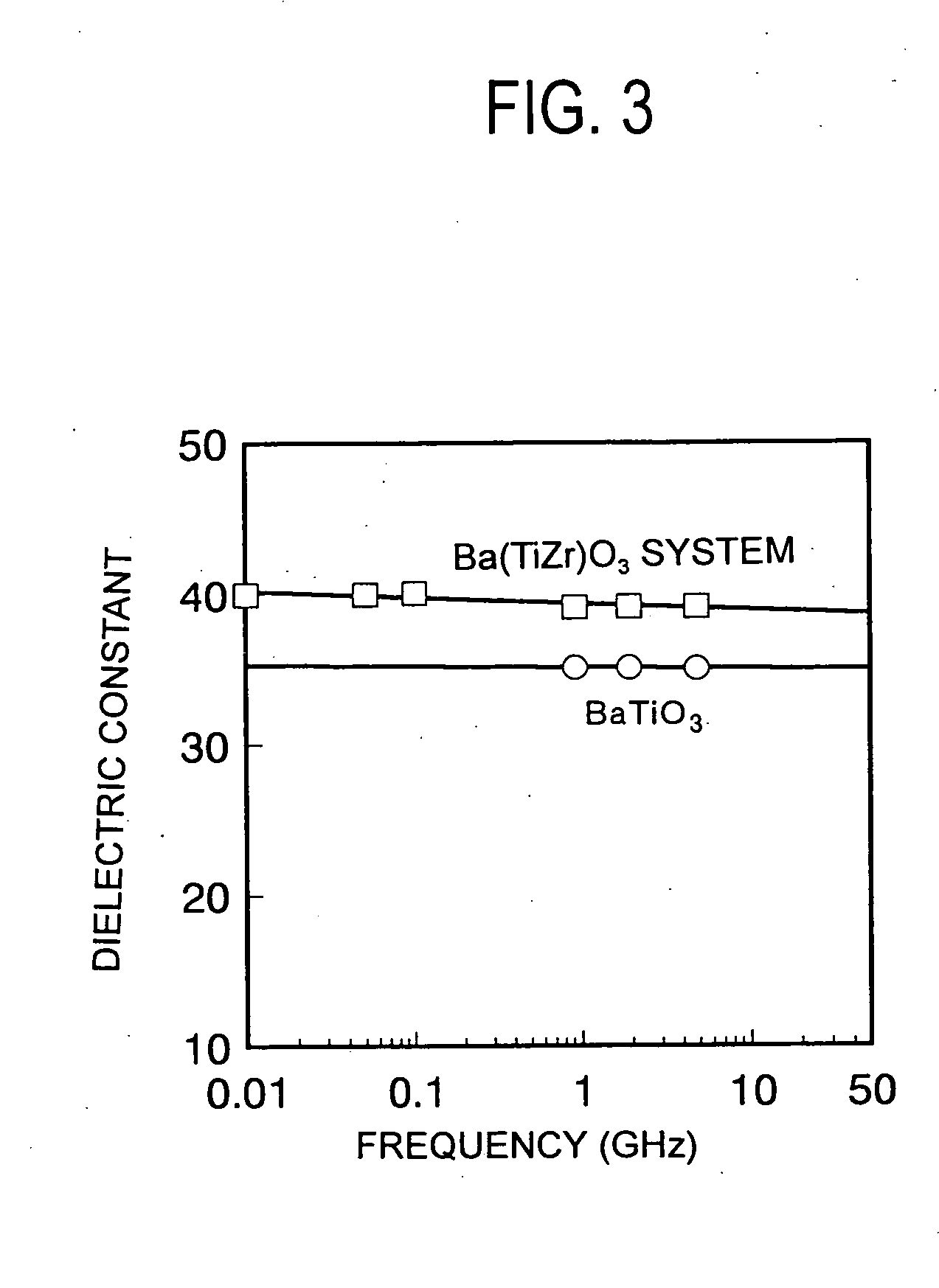
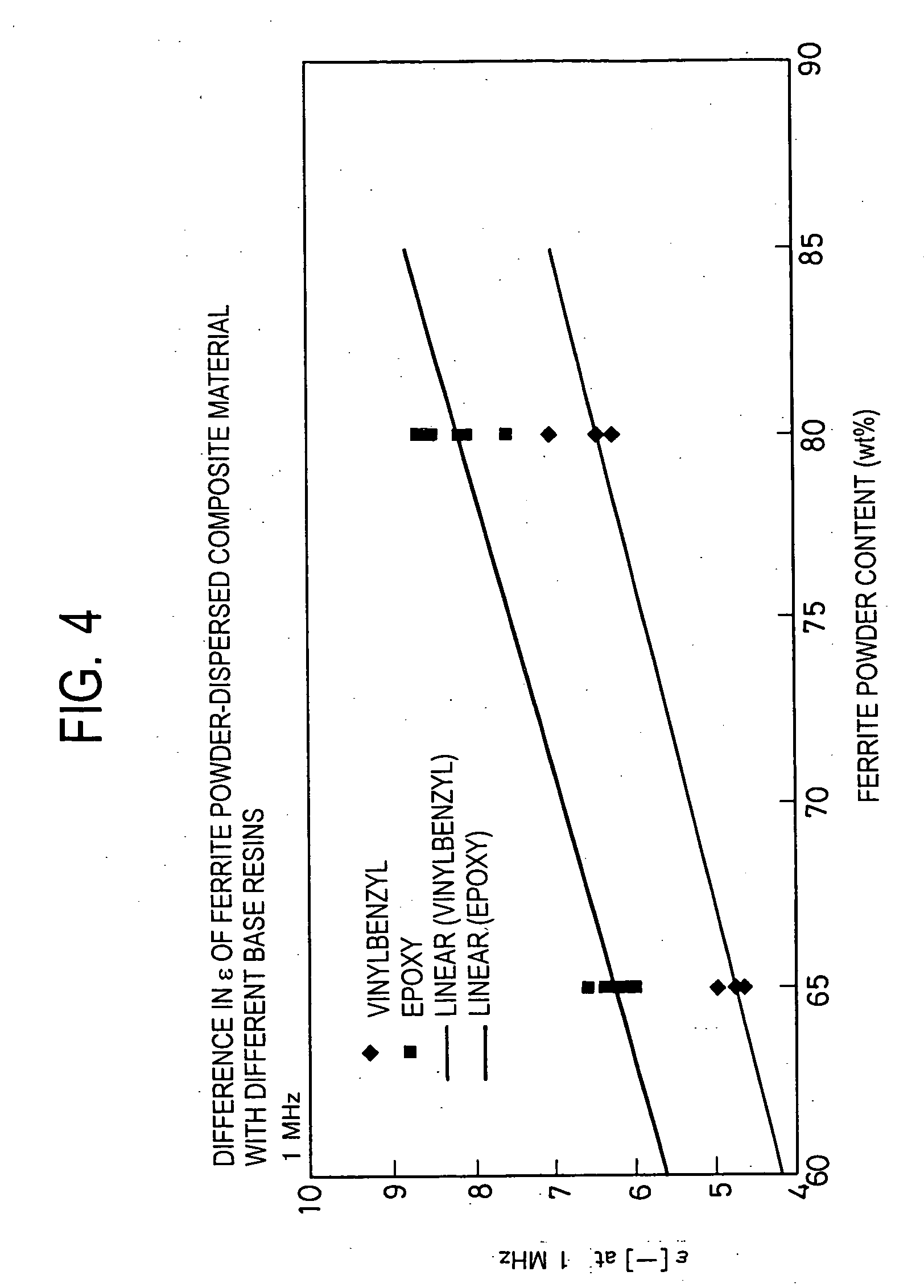
Composite dielectric, composite dielectric sheet, composite dielectric paste, metal-layered composite dielectric, wiring board and multilayer wiring board
InactiveUS7247590B2Excellent dielectric propertiesHigh-frequency regionLiquid crystal compositionsPhotosensitive materialsPolyesterPolymer science
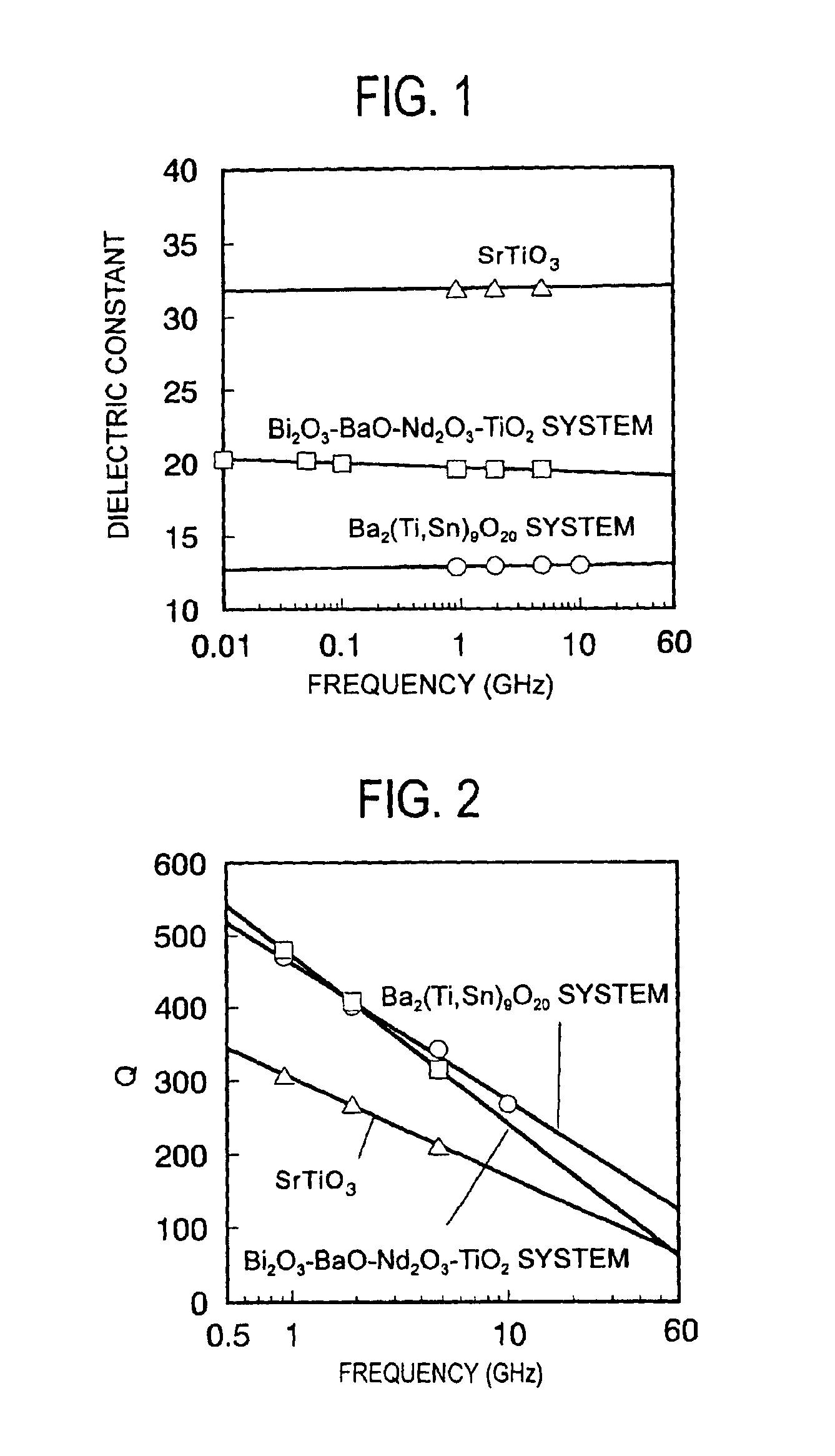
The composite dielectric of the present invention contains an aromatic liquid crystal polyester and a dielectric ceramic powder arranged in the aromatic liquid crystal polyester, wherein the dielectric ceramic powder exhibits a Q value greater than 650 at a frequency of 1 GHz by perturbation. A wiring board comprising a composite dielectric sheet made of a composite dielectric having such a characteristic exhibits a high dielectric constant and a low dielectric dissipation factor, thereby yielding less transmission loss, and thus can favorably be used in electronic instruments driven in high-frequency regions.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Low-dielectric resin composition and copper-clad laminate and printed circuit board using the same
ActiveUS20150044485A1Low dissipation factorHigh frequencySynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsLow dissipationPrinted circuit board
The present invention provides a resin composition useful for a copper-clad laminate and a printed circuit board, wherein the resin composition comprises the following components: (A) 100 parts by weight of vinyl-containing polyphenylene ether resin; (B) 5 to 50 parts by weight of maleimide; (C) 10 to 100 parts by weight of styrene-butadiene copolymer; and (D) 5 to 30 parts by weight of cyanate ester resin. The present invention also provides a resin composition and an article made therefrom having low dissipation factor at high frequency and excellent thermal resistance and peeling strength and being useful for a copper-clad laminate and a printed circuit board.
Owner:ELITE ELECTRONICS MATERIAL KUNSHAN
Halogen-free resin composition
ActiveUS20130316155A1Low dielectric constantImprove heat resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsEpoxyDielectric loss factor
A halogen-free resin composition includes 100 parts by weight of epoxy resin; 10 to 100 parts by weight of benzoxazine resin; 10 to 100 parts by weight of styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer; and 10 to 90 parts by weight of dicyclopentadiene phenol novolac resin. The halogen-free resin composition features specific ingredients and proportions thereof to attain low dielectric constant (Dk), low dielectric dissipation factor, high heat resistance and high non-flammability and produce prepregs or resin film, and is thus applicable to copper clad laminates and printed circuit boards.
Owner:ELITE ELECTRONICS MATERIAL ZHONGSHAN
Thermosetting resin composition, and prepreg, laminated board for wiring board and printed wiring board using the same
InactiveUS20060008632A1Low dissipation factorHigh modulusSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingBenzoxazolePolymer science
The present invention discloses a thermosetting resin composition which comprises (A) 35 to 75 parts by weight of a thermosetting resin comprising a compound having a hydrobenzoxazine ring as a main component, (B) 10 to 25 parts by weight of a polycondensation product of a phenol, a compound having a triazine ring and an aldehyde, and (C) 10 to 45 parts by weight of an epoxy resin, based on 100 parts by weight of the total amount of organic solid components of Components (A), (B) and (C), and (i) a bisphenol F epoxy resin having a weight-average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,000, or (ii) a mixed epoxy resin of bisphenol F epoxy resin and bisphenol A epoxy resin having a weight average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,000, is contained in Component (C) in an amount of 0 to 100% by weight of Component (C); and a prepreg, a laminated board for a wiring board and a wiring board using the same.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Thermoplastic resin composition, adhesive film and wiring film using the same
InactiveUS20120037410A1Simple methodImproved adhesive forceOrganic chemistryFilm/foil adhesivesChemical structureIsocyanate compound
A thermoplastic resin composition including a polyphenylene ether-based polymer having hydroxyl groups in its chemical structure and having 2,6-dimethylphenylene ether as a repeating unit, an isocyanate compound having a plurality of isocyanate groups in its structure; or a reaction product of the polyphenylene ether-based polymer having 2,6-dimethylphenylene ether as a repeating unit and the isocyanate compound having a plurality of isocyanate groups in its structure; and a hydrogenated styrene-based elastomer, and an adhesive film and a wiring film using the same are disclosed.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Low dielectric resin composition, and resin film, prepreg, printed circuit board made thereby
ActiveUS20150353730A1Easy to storeExtension of timePrinted circuit aspectsCircuit susbtrate materialsLow dissipationHeat resistance
A resin composition, including (A) a polyimide resin; (B) a pre-polymerised maleimide resin; (C) a thermosetting resin; and (D) a flame retardant. The reactants for use in synthesizing the polyimide resin include an acid anhydride and a diamine, with the diamine including 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane and its analogous compounds and polyetherdiamines. The resin composition has the following advantages, a resin film or a prepreg is manufactured from the resin composition comprises a polyimide resin synthesized from a diamine of a specific structure and a pre-polymerised maleimide resin, so as to achieve satisfactory characteristics of circuit laminates, such as a low dielectric constant, a low dissipation factor, high heat resistance, and high adhesiveness, so as to be for use in the manufacturing of metal clad laminates and printed circuit boards.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
Halogen-free resin composition with high frequency dielectric property, and prepreg and laminate made therefrom
ActiveUS20110053447A1Improve propertiesIncrease resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsDielectric loss factorStyrene maleic anhydride
The present invention relates to a halogen-free resin composition with high frequency dielectric property, and a prepreg and a laminate made therefrom. The halogen-free resin composition with high frequency dielectric property comprises, calculating according to the parts by weight of organic solids: (A) 10-50 parts by weight of copolymer of styrene-maleic anhydride; (B) 10-50 parts by weight of at least one compound having dihydrobenzoxazine ring; (C) 10-50 parts by weight of at least one polyepoxide; (D) 5-30 parts by weight of at least one phosphorus-containing flame retardant. Prepregs and laminates made from the resin composition have low dielectric constant, low dielectric dissipation factor, high glass transition temperature, high heat resistance, low moisture adsorption, and the technological operation is simple.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYI SCI TECH
Fluoropolymer-coated conductor, a coaxial cable using it, and methods of producing them
InactiveUS20060121288A1Lowered dielectric lossLow dielectric constantCoaxial cables/analogue cablesSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceCoaxial cable
A fluoropolymer-coated conductor, in which a central conductor is coated with a mixture of at least two fluoropolymers, each having different melting points, one of which is polymers is PTFE, a coaxial cable using the coated conductor, and a method for producing a fluoropolymer-coated conductor in which a central conductor is coated with a mixture obtained by mixing at least two kinds of fluoropolymers, each having different melting points, one of which polymers is PTFE, and heating these at a temperature above the melting point of the lowest melting fluoropolymer and below the melting point of the highest melting fluoropolymer.
Owner:DUPONT MITSUI FLUOROCHEMICALS CO LTD
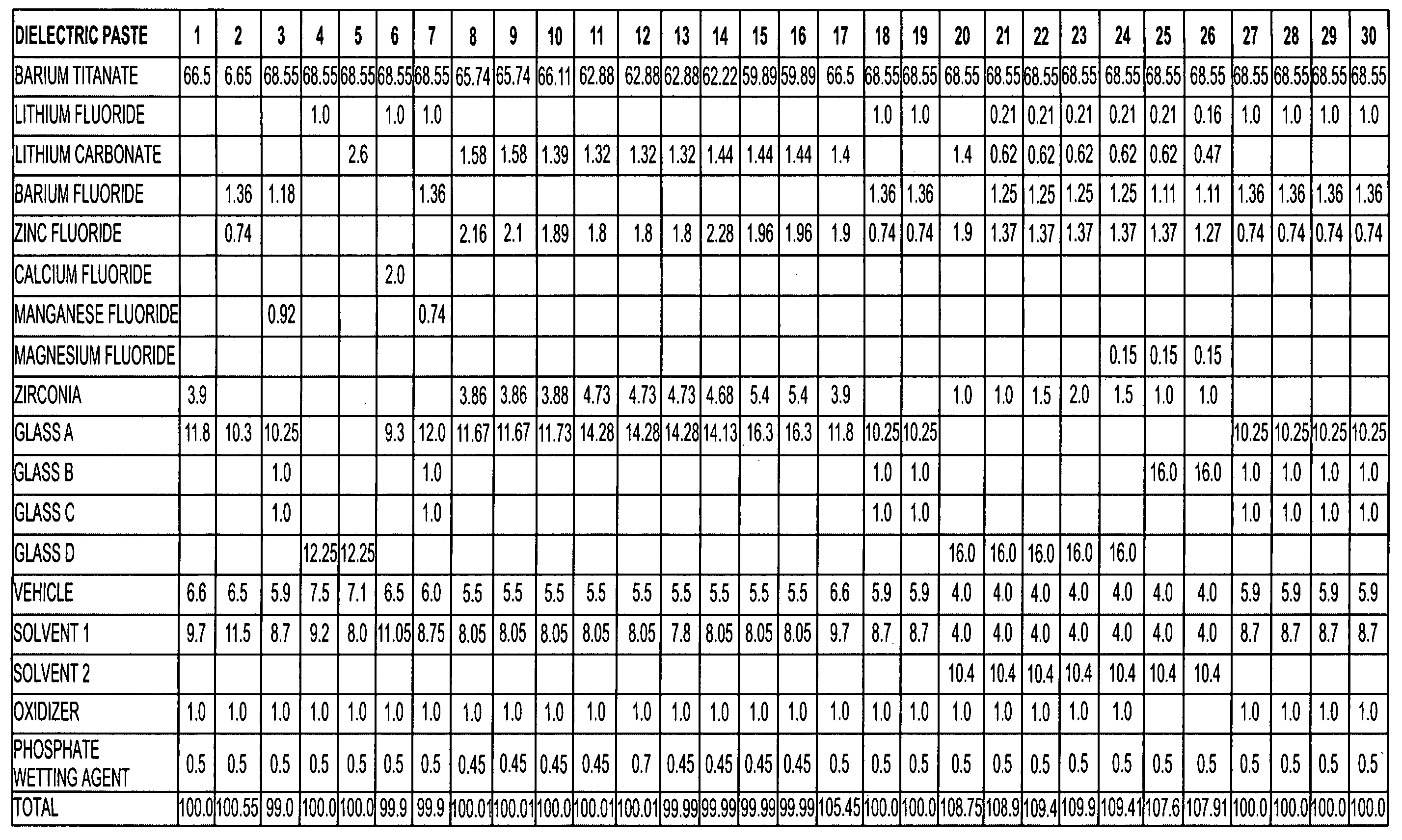
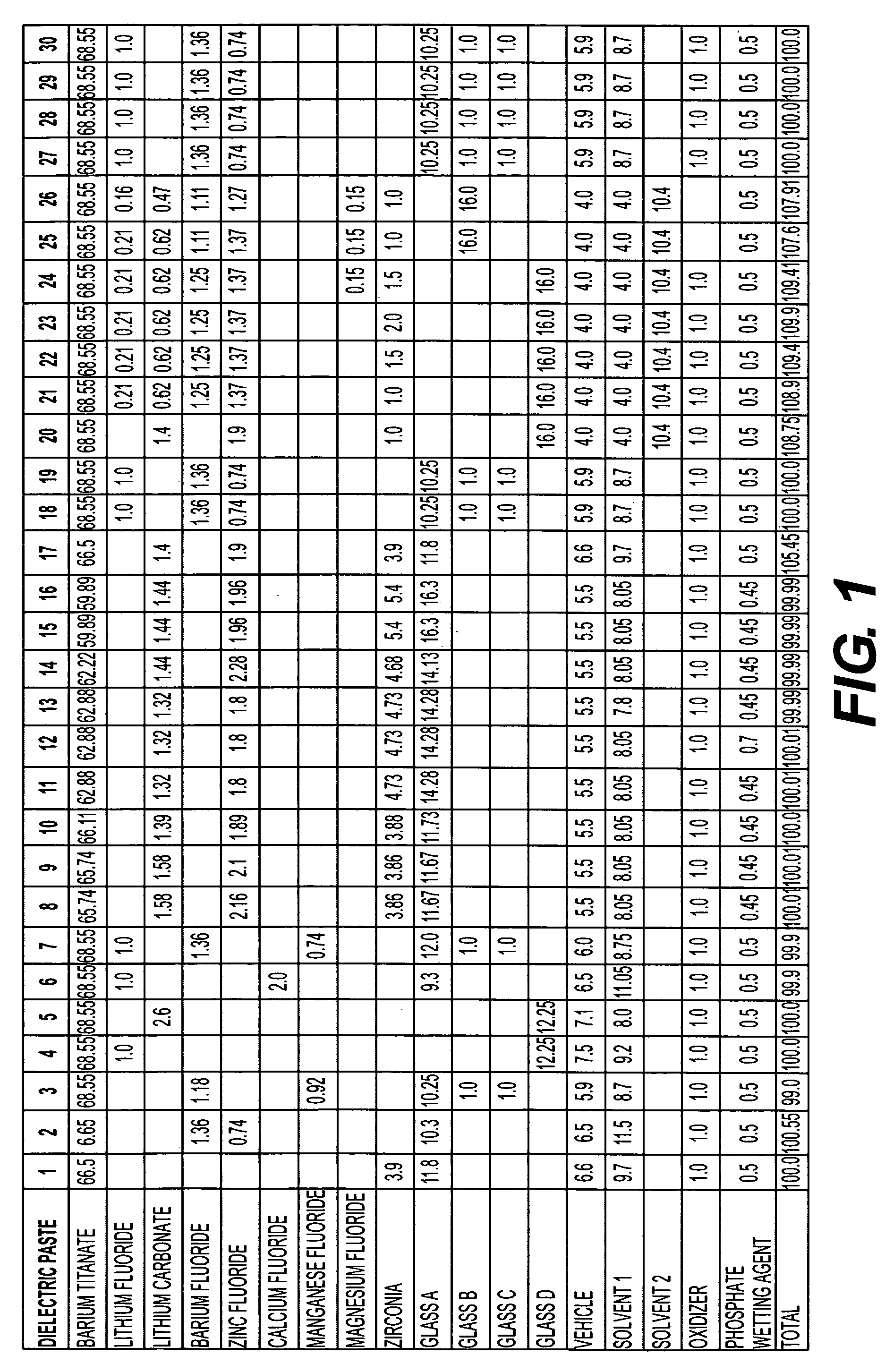
Thick-film dielectric and conductive compositions
InactiveUS20050204864A1High dielectric constantLow dissipation factorFixed capacitor electrodesDielectric materialsHigh dielectric permittivityDielectric
Conductive powder and paste compositions are formed having desirable electrical and physical properties. The conductive powder and paste compositions may be used in combination with dielectric powder and thick-film paste compositions, which are formed having high dielectric constants, low loss tangents, and other desirable electrical and physical properties, to form capacitors and other fired-on-foil passive circuit components.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
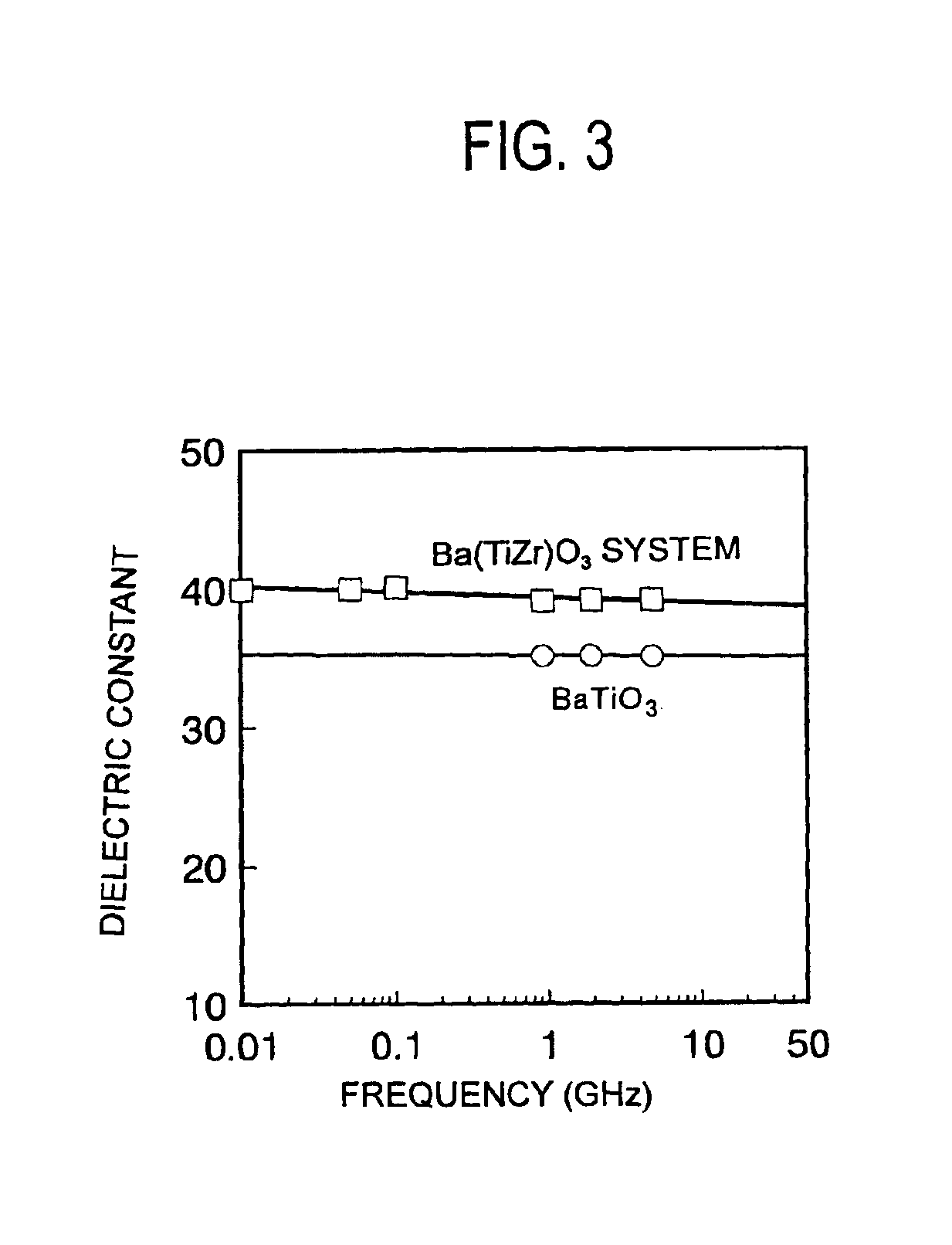
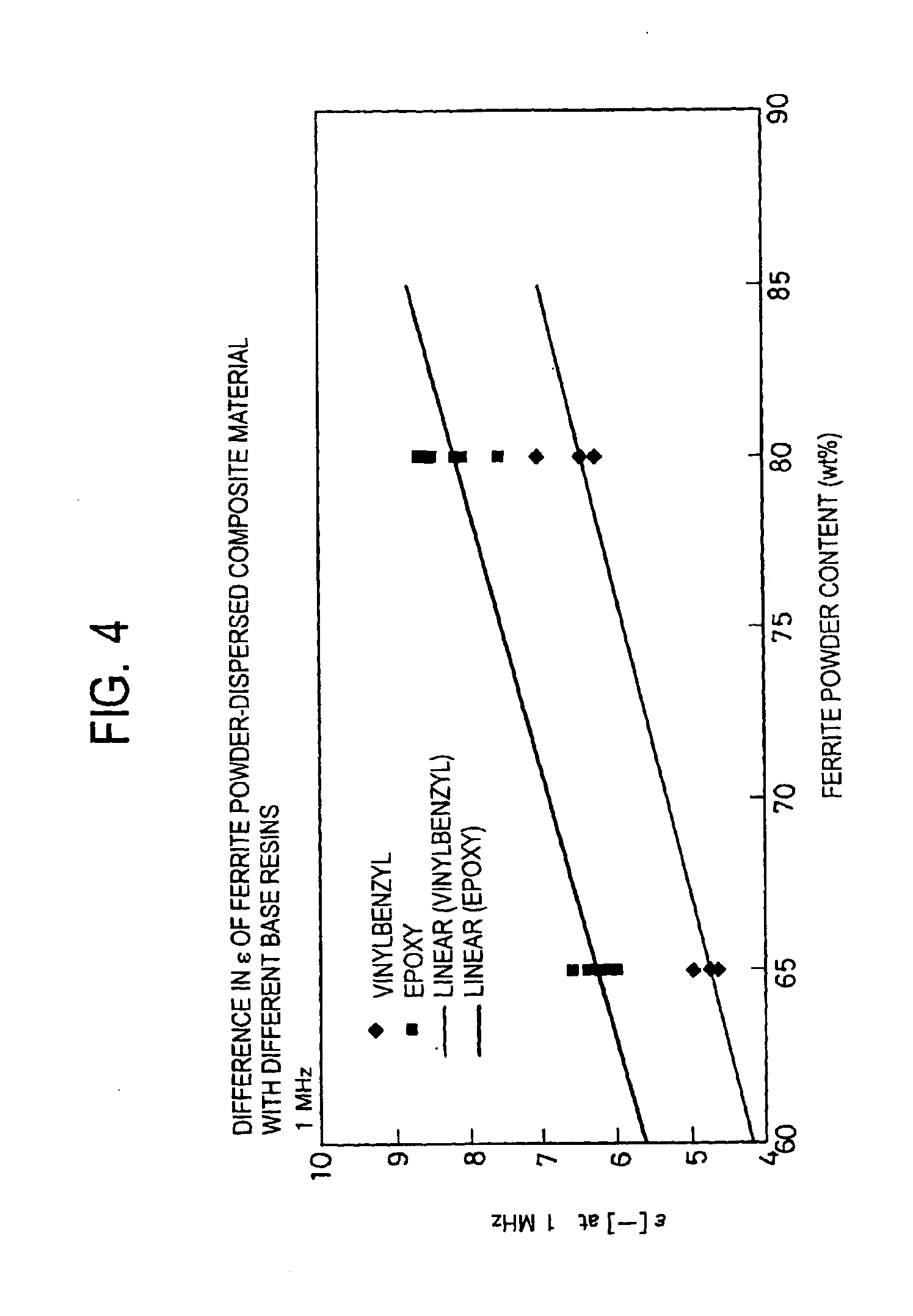
Composite dielectric material, composite dielectric substrate, prepreg, coated metal foil, molded sheet, composite magnetic substrate, substrate, double side metal foil-clad substrate, flame retardant substrate, polyvinylbenzyl ether resin composition, thermosetting polyvinylbenzyl ether resin composition, and method for preparing thermosetting polyvinylbenzyl ether resin composition
InactiveUS20050154110A1Low dielectric constantMinimized of constantShielding materialsRadiating elements structural formsMetal foilEther
A composite dielectric material comprising a resin resulting from a polyvinylbenzyl ether compound and a dielectric, ceramic powder dispersed therein is useful in the high-frequency region. A composite magnetic material comprising a polyvinylbenzyl ether compound and a magnetic powder is also provided as well as a flame retardant material comprising a polyvinylbenzyl ether compound and a flame retardant. These materials may be used in the fabrication of substrates, prepreg sheets, coated metal foils, molded items, and metal foil-clad substrates.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Printed circuit board having embedded capacitors using hybrid material and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070125574A1Capacitance varyEmission minimizationPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufactureHybrid materialDielectric layer
The present invention is related to a printed circuit board having embedded capacitors using a hybrid material and a method of manufacturing the same. This invention provides a printed circuit board having embedded capacitors using a material for a hybrid dielectric layer including liquid crystal polymer and ceramic powder, and a method of manufacturing such a printed circuit board.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Resin composition for copper foil-clad base plate in high-frequency and high-speed field and application thereof
ActiveCN106589748AImprove performanceLow dielectric constantLaminationLamination apparatusCopper foilBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
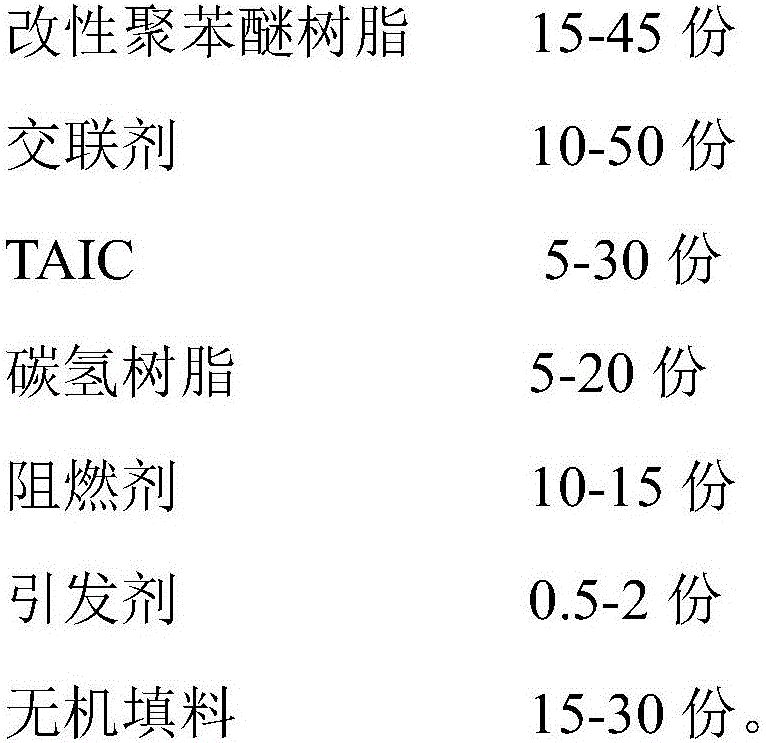
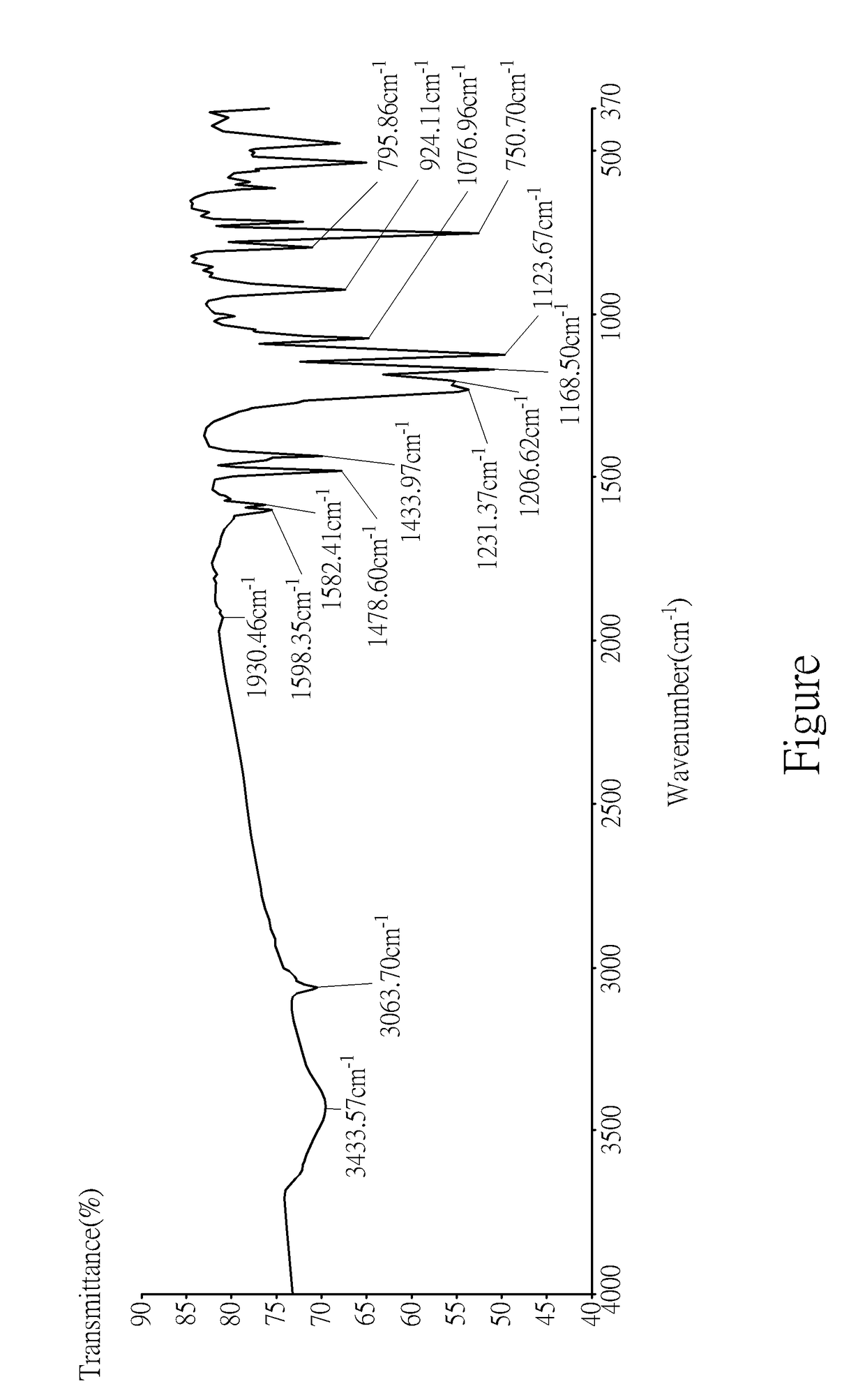
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer composite materials, and particularly relates to a resin composition for a copper foil-clad base plate in the high-frequency and high-speed field and application thereof. The resin composition is prepared from 55 to 70 weight percent of active ingredients and 30 to 45 weight percent of solvents, wherein the active ingredients comprise the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15 to 45 parts of modified polyphenyl ether resin, 10 to 50 parts of cross-linking agents, 5 to 30 parts of TAIC, 5 to 20 parts of hydrocarbon resin, 10 to 15 parts of fire retardants, 0.5 to 2 parts of initiators and 15 to 30 parts of inorganic fillers. The obtained resin composite with various excellent properties can be applied to the preparation of high-performance copper-clad plates; and the copper-clad plates have the excellent dielectric property and high temperature-resistant performance, soldering-tin-resistant performance, heat-resistant performance and high glass transition temperature.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION
Resin composition, copper-clad laminate using the same, and printed circuit board using the same
ActiveUS20170260364A1Improve heat resistanceImprove flame retardant performancePrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufactureHeat resistanceEther
A resin composition, a copper-clad laminate using the same, and a printed circuit board using the same are introduced. The resin composition comprises a specific phosphorus-containing salt and a prepolymer of vinyl-containing polyphenylene ether. The resin composition features specific ingredients and proportion to thereby achieve satisfactory properties of prepreg made from the resin composition, and attain satisfactory laminate properties, such as high degree of heat resistance and satisfactory dielectric properties, and thus is suitable for producing a prepreg or a resin film to thereby be applicable to copper-clad laminates and printed circuit boards.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
Fabric reinforcement using modified cyclic olefin copolymer and resin substrate for printed circuit board
InactiveUS20060246284A1Improve material performanceLow dielectric constantEngine sealsPrinted circuit aspectsPolymer scienceCyclic olefin copolymer
The present invention is related to a fabric reinforcement using a modified cyclic olefin copolymer and a resin substrate for a printed circuit board. Specifically, the current invention provides a fabric reinforcement using a modified cyclic olefin copolymer, which is prepared from filaments obtained by melting the modified cyclic olefin copolymer including a cyclic olefin copolymer backbone grafted with a monomer having at least one unsaturated carboxylic group, and a resin substrate for a printed circuit board.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Magnetic material antenna and ferrite sintered body
ActiveUS8154464B2Suitable for useHigh strengthLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorFerric
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Miniature patch antenna with increased gain
ActiveUS7460072B1Process controlReduce dissipationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric permittivityGround plate
The present invention, relates to the preparation of a patch antenna with a specific effective dielectric constant; and a reduced dissipation factor. In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, size requirements and the desired resonant signal frequency dictate the permittivity value of the dielectric material to be used between the patch plate and the ground plate. Instead of using a dielectric material with the calculated permittivity value and its given dissipation factors a two layer dielectric of the same size with an effective dielectric constant that is equal to the desired dielectric constant, is used to replace the dielectric material and reduce the dissipation factor.
Owner:ORIGIN GPS LTD
Fluoropolymer-glass fabric for circuit substrates
ActiveUS20070049146A1Improve adhesionMaintain good propertiesDielectric materialsSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringFluoropolymer
An improved circuit substrate is provided wherein glass cloth is completely embedded within fluoropolymer by thermocompression to form a composite structure, which when containing an adhesive agent such as the combination of functional groups and liquid crystal polymer is self-adhering to a metal layer such as of copper.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC +1
RF tags
InactiveUS7683785B2Costly stepsTime costlyWave amplification devicesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalLow dissipationElectricity
A single sided RF tag suitable for use for electronic article surveillance comprises a tuned circuit formed on one side of a substrate. Provided by a deposited first conducting layer which comprises an inductive coil, which behaves as an antenna and is electrically connected to a first capacitor plate and a connection means to connect to a second conducting layer. A low dissipation factor dielectric layer is deposited onto said first conducting layer. A second conducting layer comprising at least one capacitor and a connection means to electrically connect to the first conducting layer is deposited on the dielectric layer. The second capacitor plate is substantially co-located above the first capacitor plate, to form the capacitor. The capacitor and coil together form a resonant circuit. The circuit pattern for the first and second layer may be formed by known metal printing techniques, such as, for example the use of a catalytic seed layer which is deposited by a pattern transfer mechanism into the circuit pattern. Alternatively the circuit pattern may be formed by standard photo-lithography etch techniques to reveal a circuit pattern from a metallised surface. The tag will preferably incorporate known methods of fusing to deactivate or detune the tag, to permit removal of articles from an enclosed area. The substrate may further include a second RF tag tuned to an alternative frequency on the opposite side of the substrate. Alternatively a plurality of tags may be built up in successive layers on one or both sides of the tag.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
High dielectric film
InactiveUS20150368413A1Low dissipation factorHigh dielectric constantFixed capacitor dielectricSolid ballsTetrafluoroethyleneLow dissipation
The present invention aims to provide a film having a high dielectric constant and a low dissipation factor. The high dielectric film of the present invention includes a vinylidene fluoride / tetrafluoroethylene copolymer (A) with a mole ratio (vinylidene fluoride) / (tetrafluoroethylene) of 95 / 5 to 80 / 20. The film includes an β-crystal structure and a β-crystal structure. The ratio of the β-crystal structure is 50% or more.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Fluoropolymer-glass fabric for circuit substrates
ActiveUS7439200B2Improve adhesionMaintain good propertiesWeft knittingDielectric materialsEngineeringFluoropolymer
An improved circuit substrate is provided wherein glass cloth is completely embedded within fluoropolymer by thermocompression to form a composite structure, which when containing an adhesive agent such as the combination of functional groups and liquid crystal polymer is self-adhering to a metal layer such as of copper.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC +1
Resin composition, copper-clad laminate and printed circuit board for use therewith
ActiveUS20140178696A1Low dielectric propertyLow hygroscopicityOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsChemistryDielectric loss factor
A resin composition includes (A) an epoxy resin; (B) a benzoxazine (BZ) resin; (C) a styrene maleic anhydride (SMA) copolymer; and (D) a polyester. The resin composition includes specific ingredients of a polyester and is characterized by specific proportions thereof so as to achieve a low delta Tg value of copper clad laminates manufactured in accordance with the resin composition and attain a low dielectric constant, a low dielectric dissipation factor, high heat resistance, and high fire retardation of the copper clad laminates and printed circuit boards manufactured in accordance with the resin composition.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com