Probes and primers for detection of malaria
A probe and malaria technology, applied in the field of detection and quantification of malaria infection caused by Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium vivax, can solve laborious and time-consuming problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] DNA was isolated from a sample plate consisting of 10 P. falciparum positive blood samples and 10 uninfected blood samples. Similarly, DNA was isolated from 10 P. vivax positive blood samples and 10 uninfected blood samples using a commercial DNA isolation kit. The purified DNA was subjected to real-time PCR using the probe of SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 4 or 10 and 7, or the probe of SEQ ID No. 2 and SEQ ID No. 5 and 8 to detect Plasmodium falciparum. Similarly, SEQ ID No. 3 was used together with SEQ ID No. 6 and 9 for the detection of Plasmodium vivax. The same concentrations of real-time PCR reagents, templates and primers were used in all cases, and cycling conditions were kept constant for all reactions. The composition and PCR conditions of the PCR mixture are shown in Table 4&5.
[0065] Table 4: Real-time PCR using Takara master mix
[0066]
[0067] Table 5: Real-time PCR cycling conditions
[0068]
[0069] Repeat steps 2 and 3 40 times
[0070...
Embodiment 2
[0077] In another study, DNA was isolated from a double-blind sample plate consisting of 25 infected blood samples. The efficacy of SEQ ID Nos. 1, 2 and 3 to detect malaria from infected blood samples was then tested by real-time PCR. The results obtained were then compared with other commercial techniques for detecting malaria, namely microscopy and rapid diagnostic tests (RDT).
[0078] The results obtained showed that SEQ ID No. 1, 2 and 3 even selected cases of mixed infections, which were revealed as single infections by the other two techniques. If we look at the Ct values for the mixed infection case, the Ct of the obtained P. vivax infection is delayed and the Ct is loaded with parasites of about 3-5 parasites / μl, which is a very low number. Microscopic examination and RDT tests cannot detect such low levels of parasites, so the infection reported by these two tests is a single infection. A few samples were not detected by the other two tests and were shown as not ...
Embodiment 3
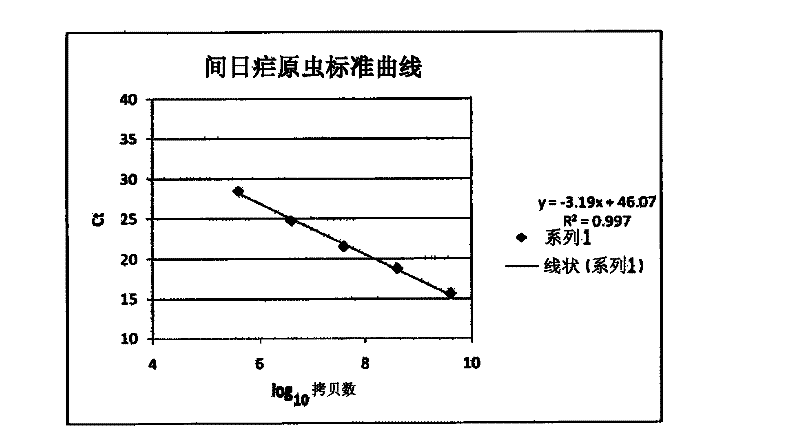
[0082] It is also possible to quantify the parasite load of infected samples by comparing the Ct values obtained from the standard curve ( figure 1 , 2 ) and (Table 9, 10).
[0083] Copy Number Calculation Method
[0084] By using a traditional PCR machine, about 25 microliters of malaria DNA (P. falciparum or P. vivax) was mixed with SEQ ID No.4 or 10 and SEQ ID No.7 primers for P. PCR was performed together with the primers of SEQ ID No.6 and SEQ ID No.9. After PCR, amplified samples were run on an agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. Amplicon bands were then excised from the gel and purified using a Qiaquick gel extraction kit. Absorbance at 260 nm was estimated using a spectrophotometer nanodrop (2 μl DNA). The absorbance coefficient of DNA was calculated by summing the respective base coefficients.
[0085] Calculate the nanomolar number of amplicons using the following equation:
[0086]
[0087] Use this formula to calculate copy number:
[0088...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com