Strain marker for assisting COVID-19 diagnosis and application thereof
A COVID-19, marker technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, resistance to vector-borne diseases, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as no bacterial species marker reporting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
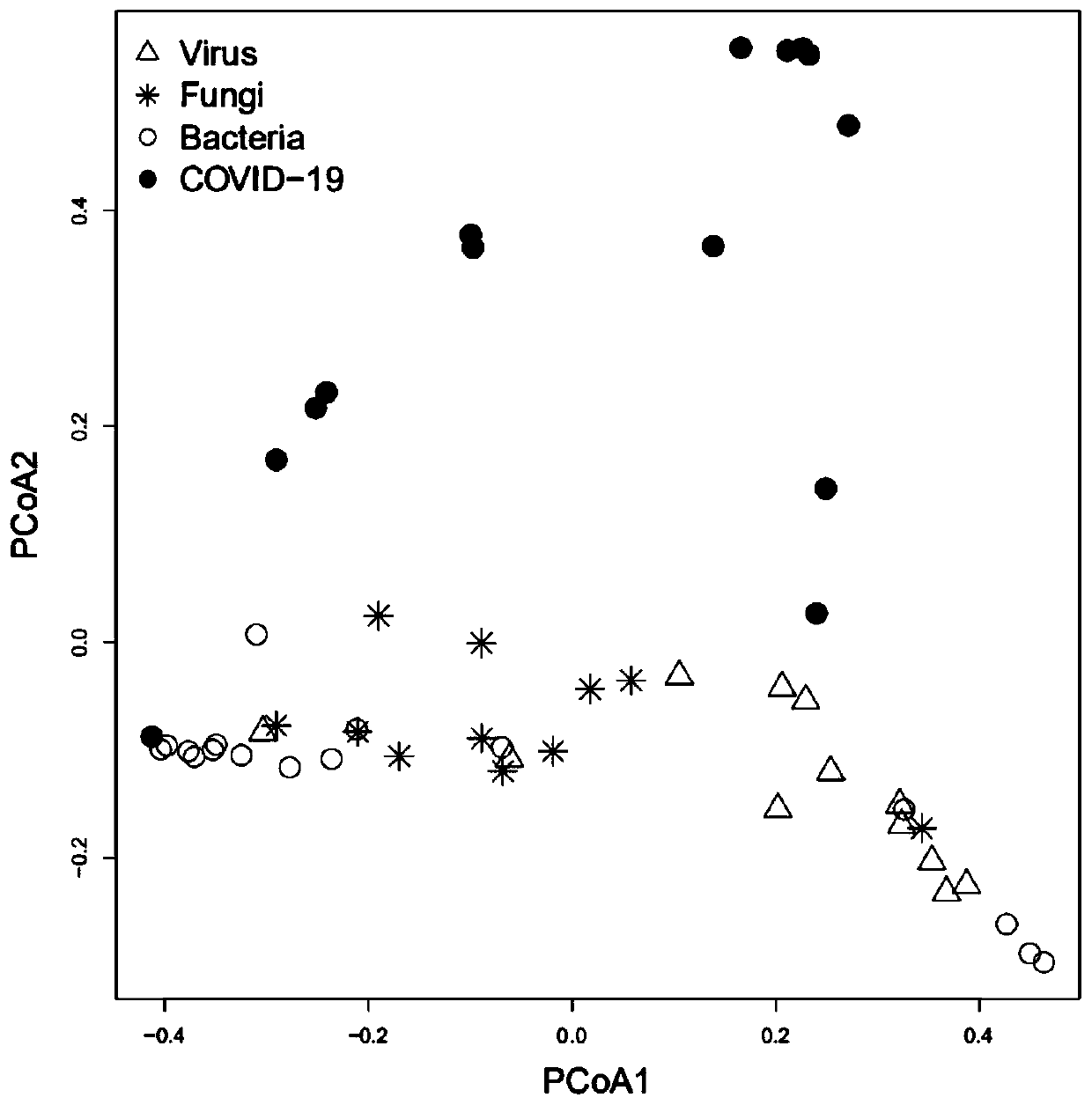
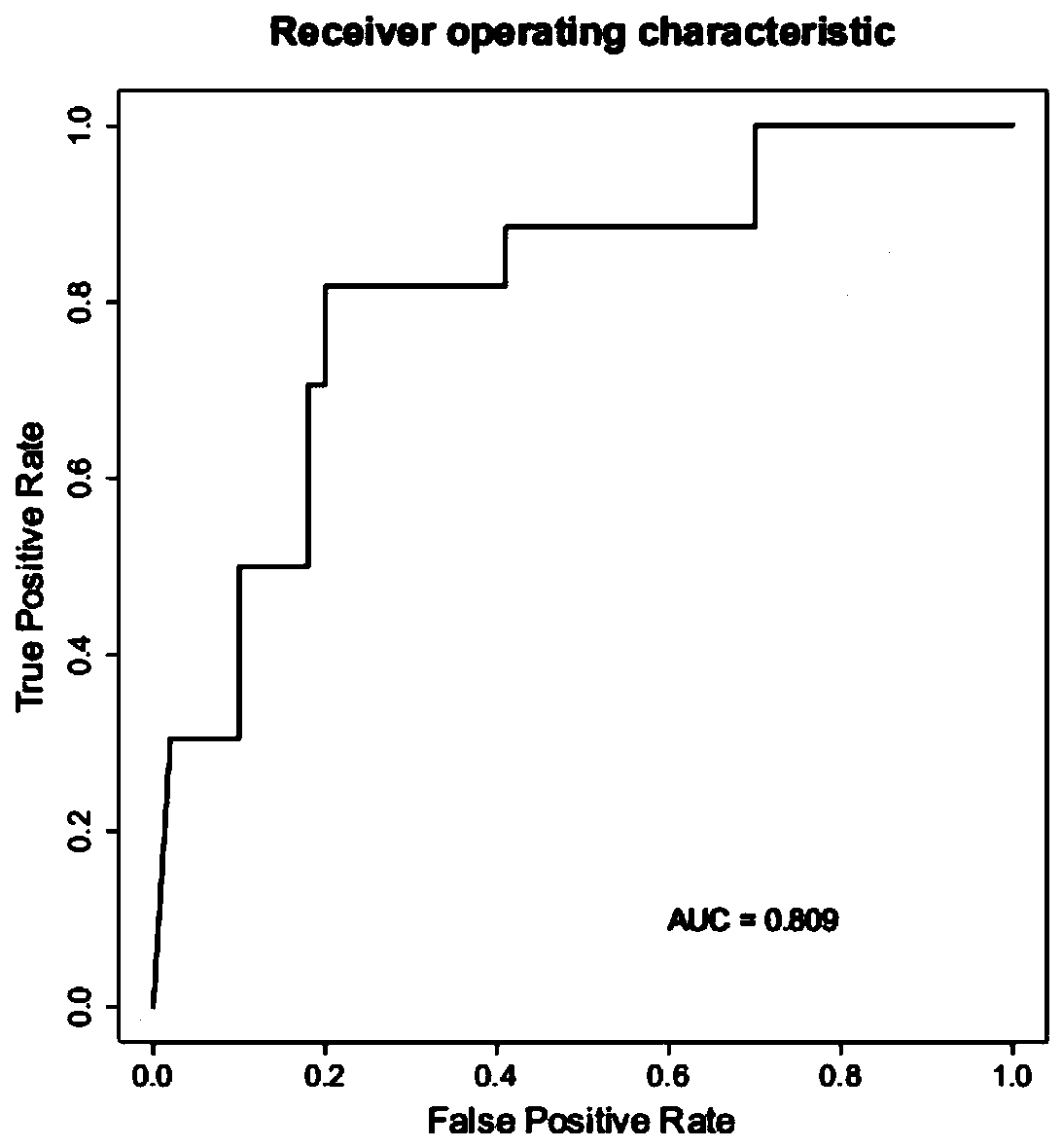
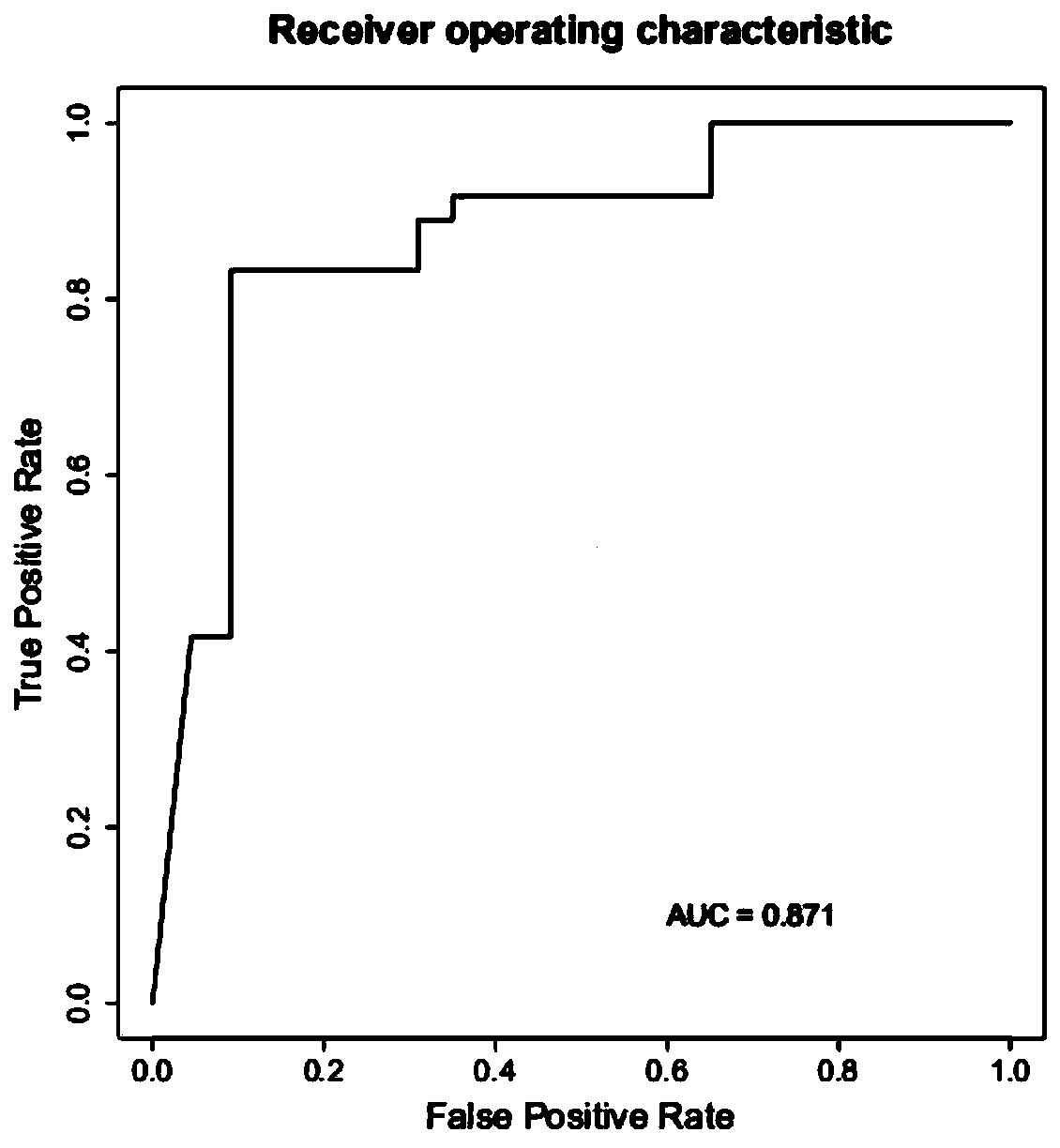
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Sample entry criteria:
[0031] 1. COVID-19 pneumonia group: A sample of suspected 2019-nCoV COVID-19 infection was judged by clinical symptoms and epidemiological history.
[0032] Clinical symptoms: (1) fever and / or respiratory symptoms, (2) chest imaging: early small patchy shadows and interstitial changes, the development of ground glass shadows and invasion shadows in both lungs, severe lung consolidation, pleural effusion (3) The total number of white blood cells is normal or decreased in the early stage of the disease, and the lymphocyte count is normal or decreased.
[0033] 2. Pneumonia group infected by other pathogenic microorganisms: through clinical symptoms, microbial culture, RT-PCR or (and) NGS nucleic acid detection, it is diagnosed as non-SARS-CoV-2 infection, other virus, bacterial or fungal infection.
[0034] 2. Sample collection
[0035] According to the above entry criteria, a total of 14 sputum samples from COVID-19 pneumonia and 39 other pathogenic ...
Embodiment 2
[0085] The bacterial species markers obtained in Example 1 were verified.
[0086] 1. Sample collection
[0087] According to the sample entry criteria of Example 1, 30 samples of confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia and 30 samples of non-COVID-19 pneumonia group were collected as a verification set to verify the results of Example 1.
[0088] 2. Sequencing.
[0089] With reference to the high-throughput sequencing method of Example 1, 60 samples were detected and the relative abundance of each strain of the experimental group and the control group was analyzed.
[0090] 3. Verification of host markers.
[0091] With reference to the difference analysis method in Example 1, 31 different strains in the verification set are obtained. 18 strains whose different strains in the training set of Example 1 and the verification set of this embodiment are intersected with the same up and down direction , As the final candidate strain marker.
[0092] Table 2. Screening results of bacterial species markers...
Embodiment 4
[0099] Feasibility screening of strain markers.
[0100] 1. Sample collection.
[0101] According to the sample entry criteria in Example 1, a total of 1,000 samples including COVID-19 pneumonia and non-COVID-19 pneumonia were collected. 1,000 samples were tested for the macrotranscriptome and the detection stability of 18 candidate markers was analyzed .
[0102] 2. Analysis of detection rate.
[0103] The detection rate of 18 candidate strains in the statistical sample is shown in the following table.
[0104] Table 3. Detection rate of candidate strain markers
[0105]
[0106]
[0107] The combined detection rate of the above 18 strains is greater than 0.95 (ie 95%), and the detection rate of individual strains is less than 0.5, which is caused by the difference of the constant flora of different individuals.
[0108] Among them, Haemophilus_parainfluenzae (Haemophilus parainfluenzae (Haemophilus parainfluenzae, species 1), Propionibacterium_ humerusii (Propionibacterium, species 2),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com