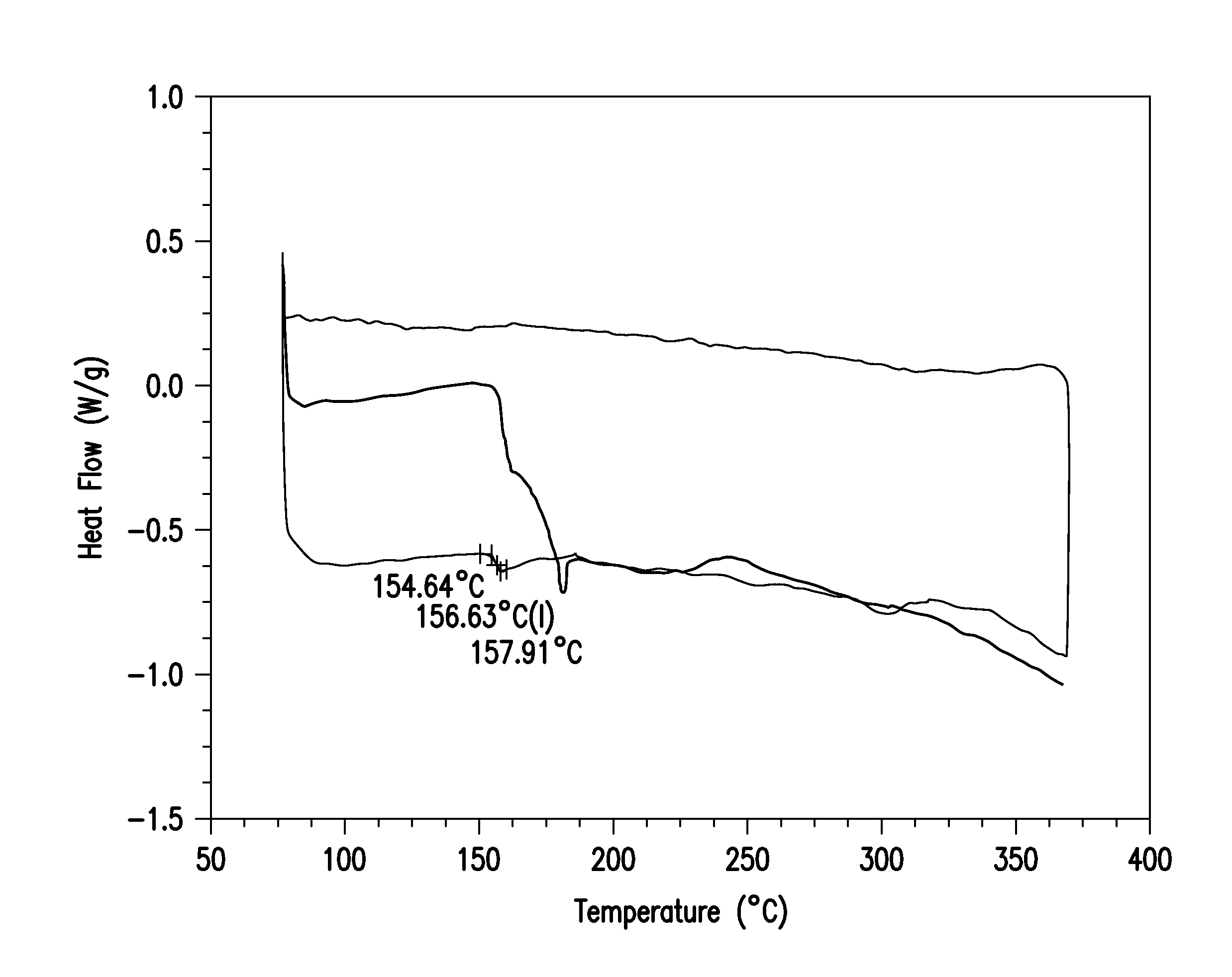
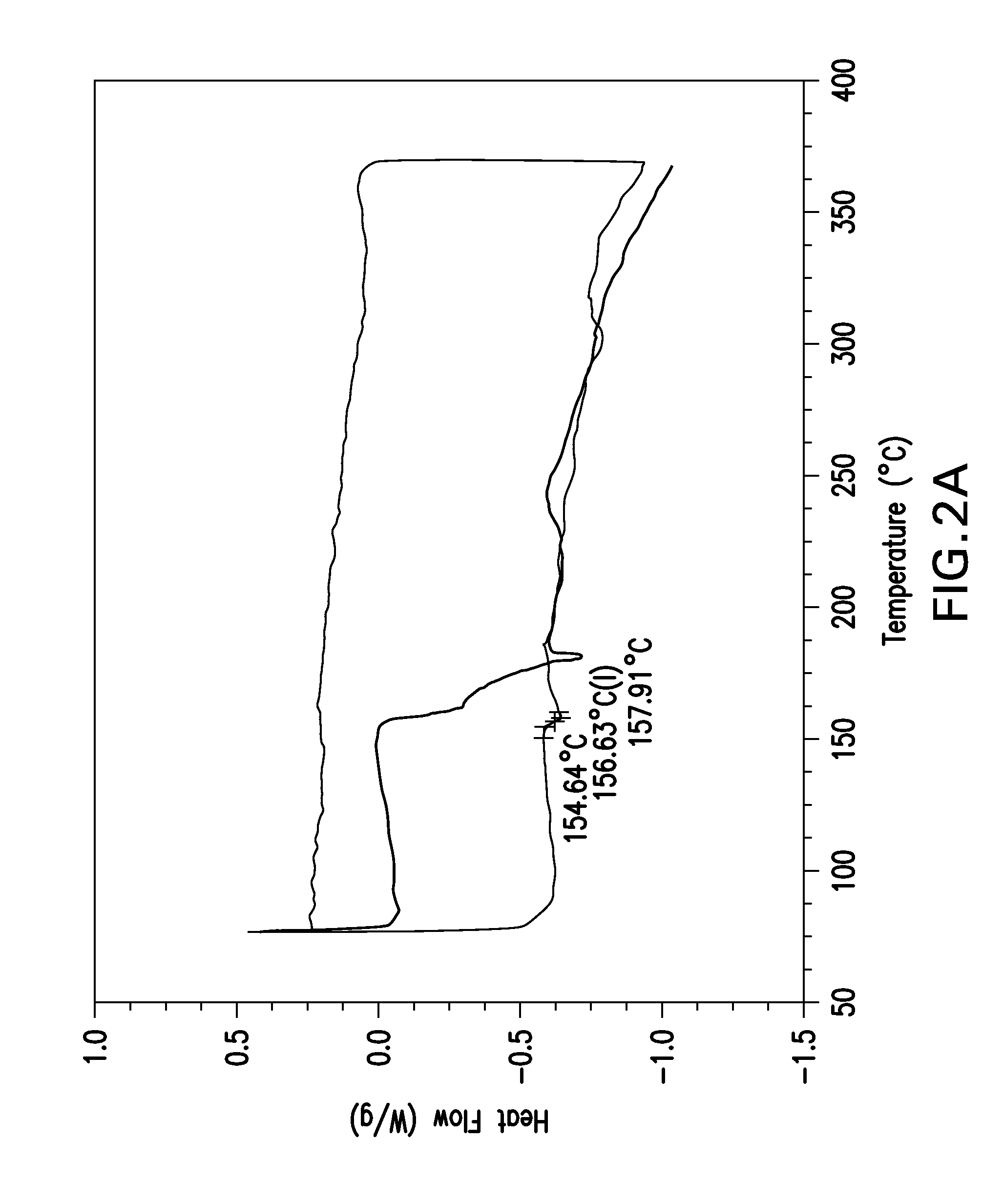
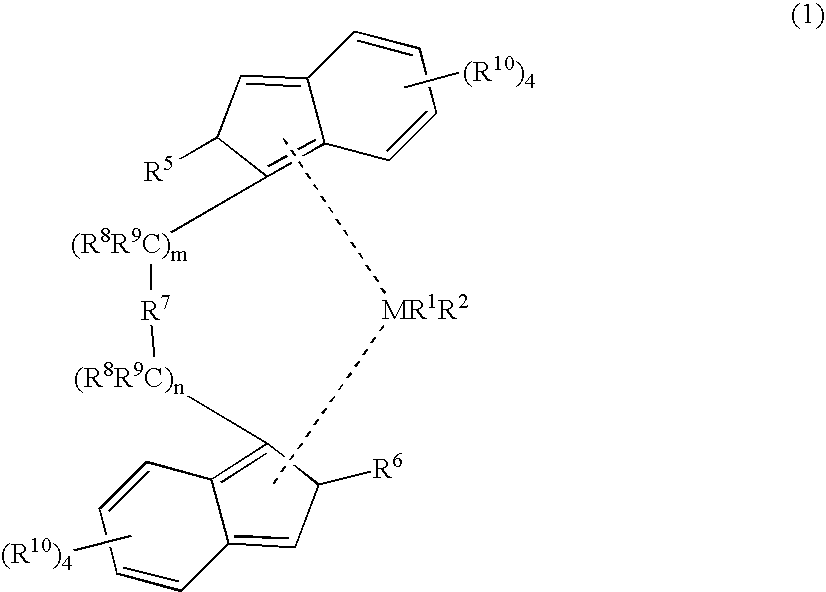
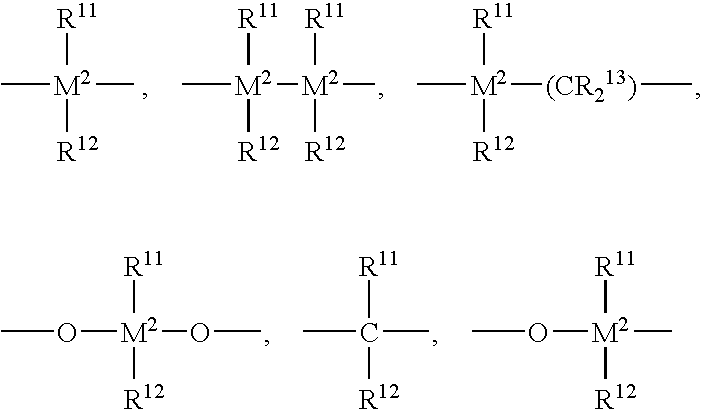
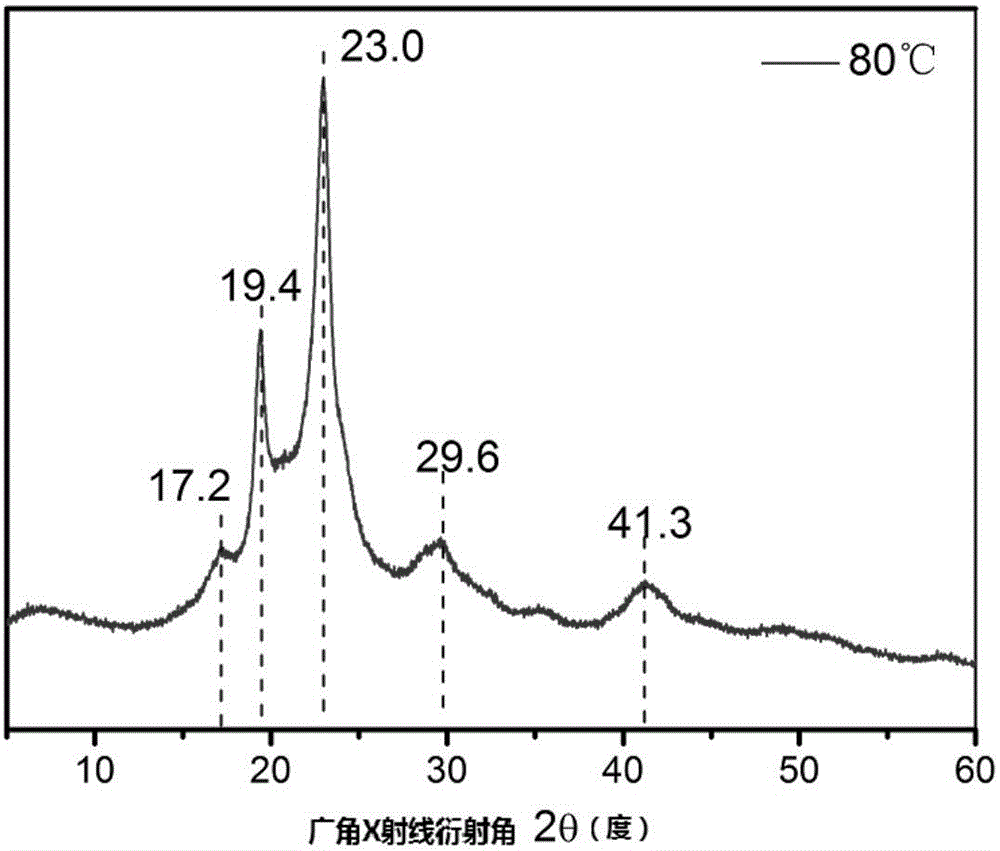
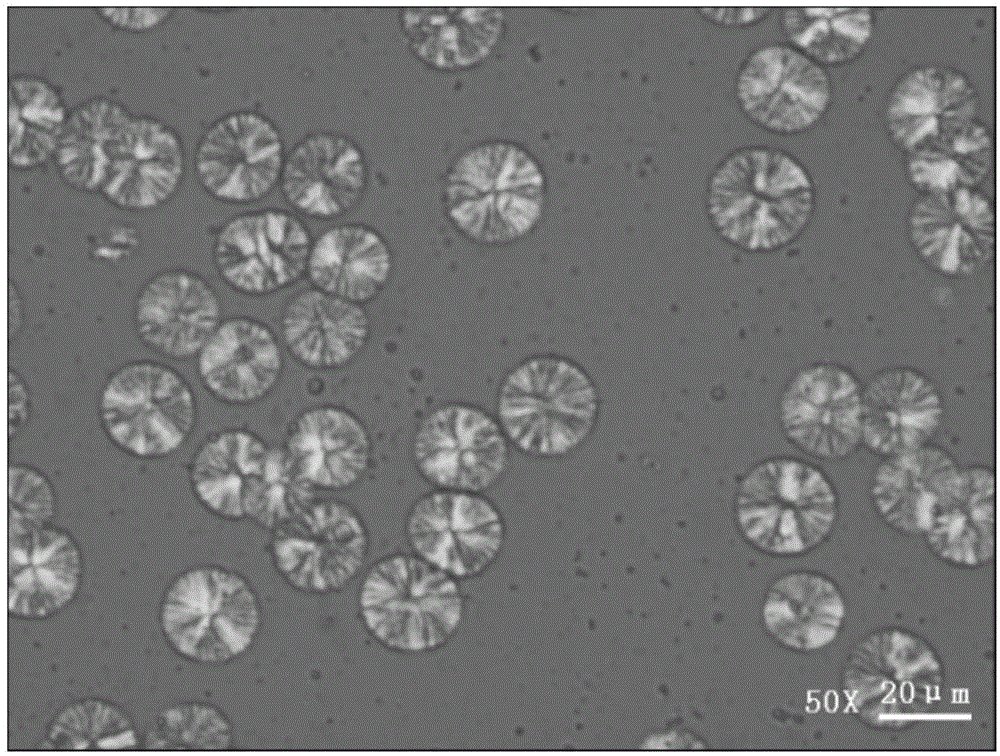
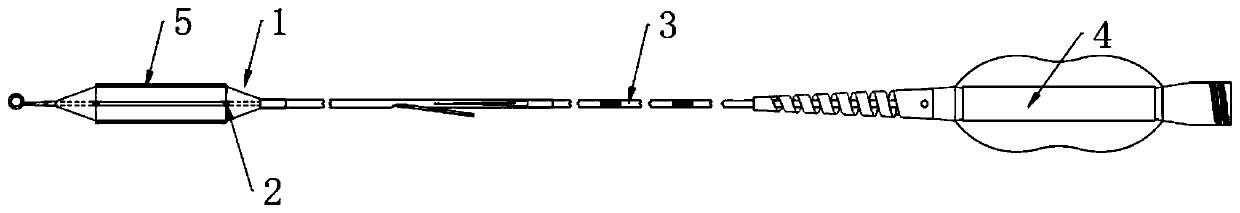
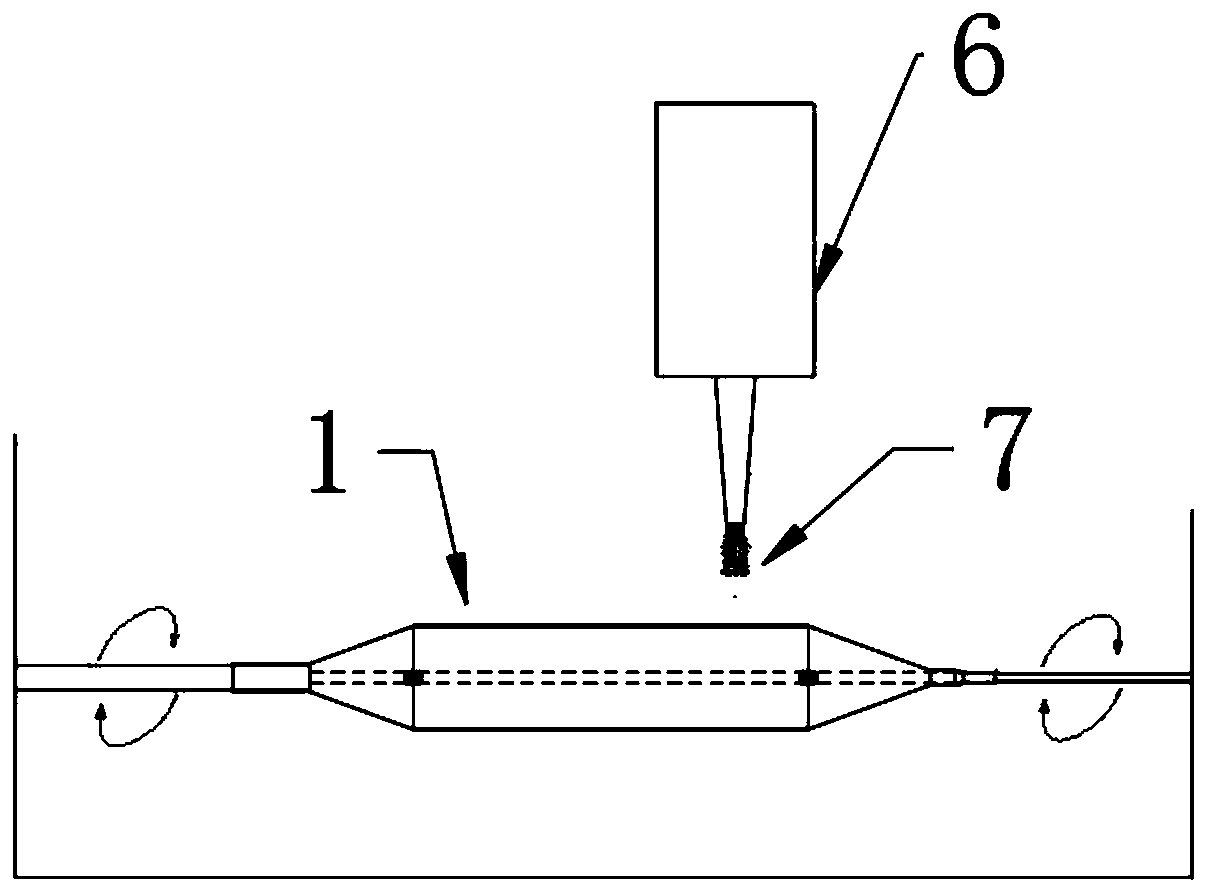
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
286results about How to "Crystallize fast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
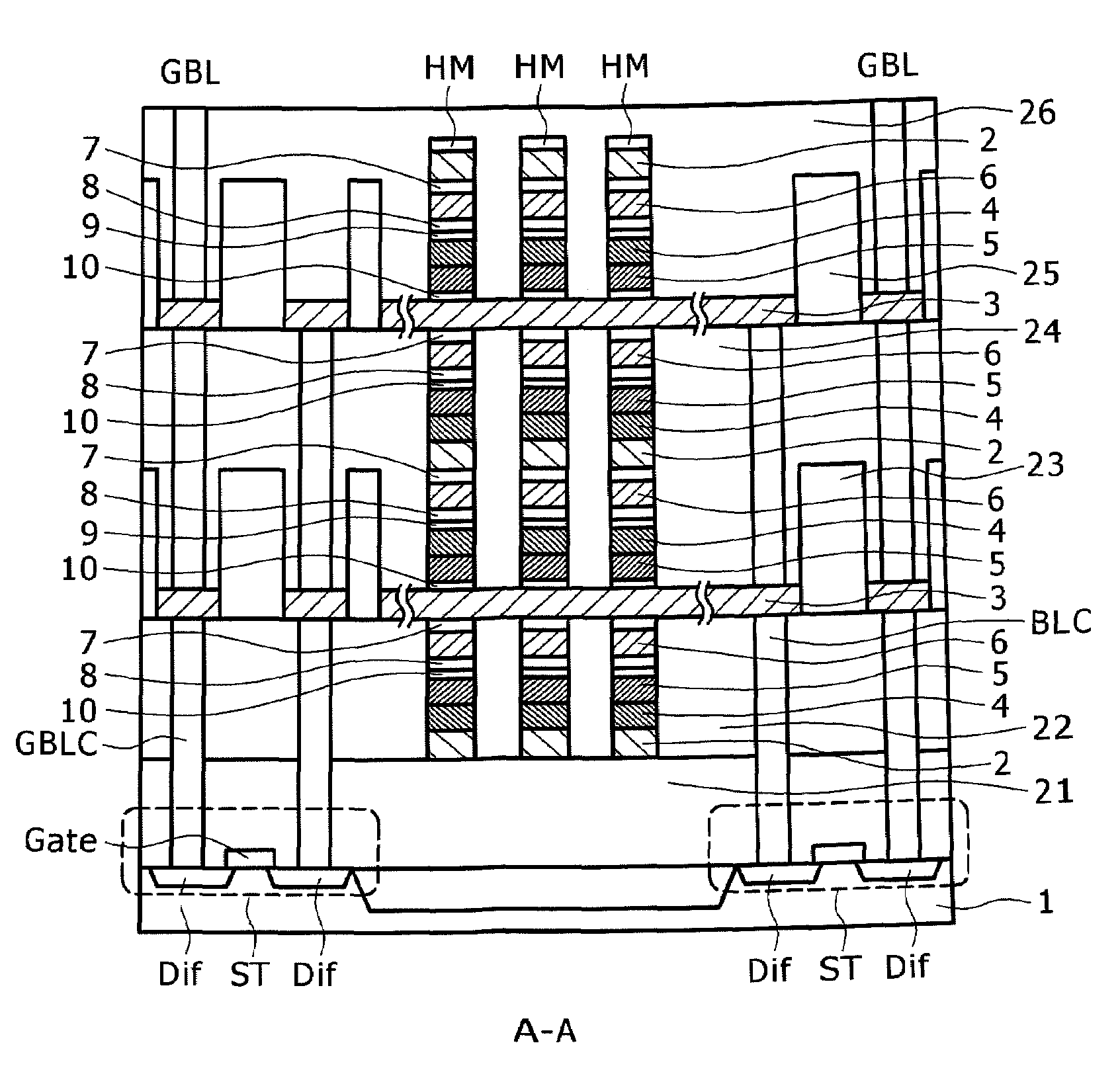
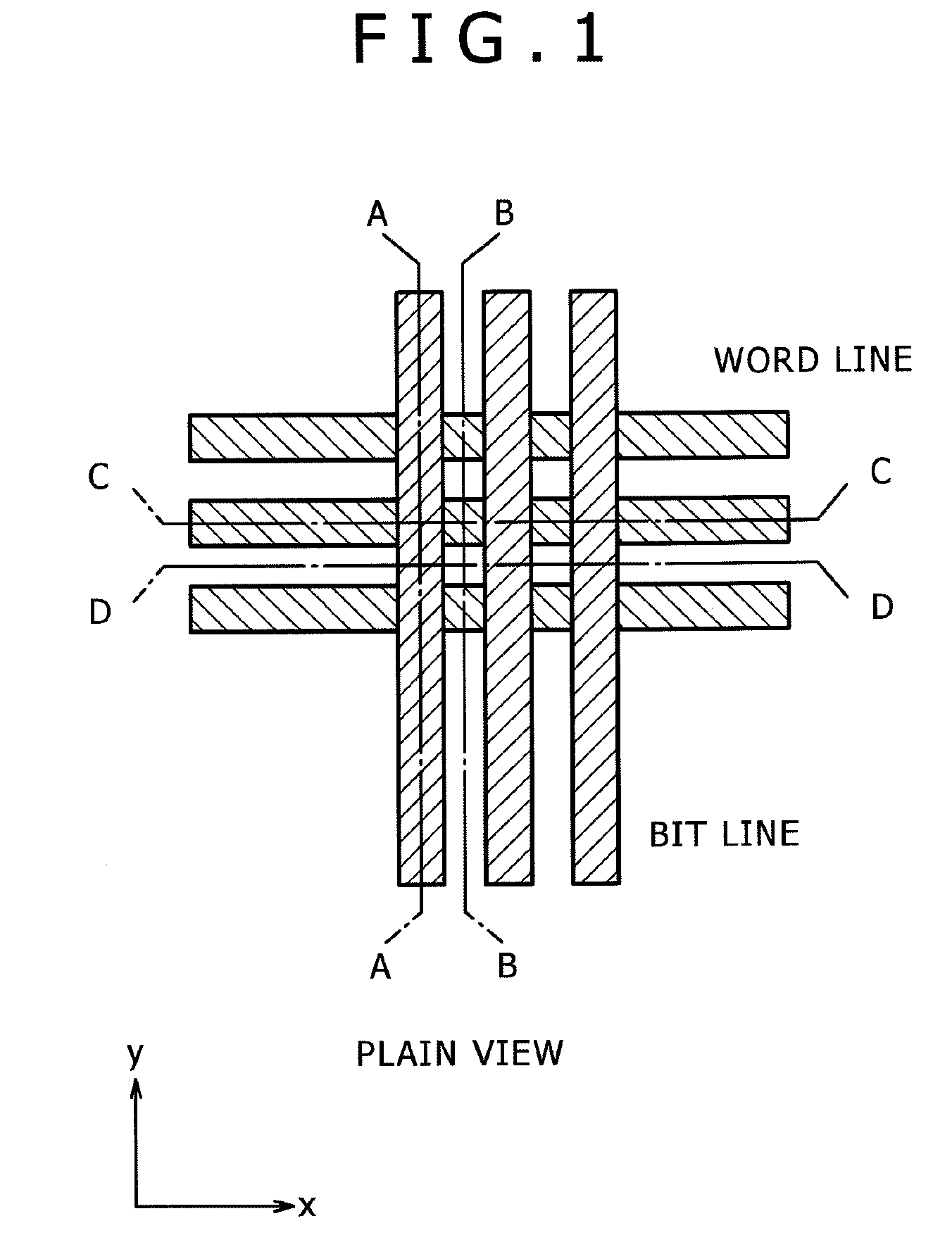
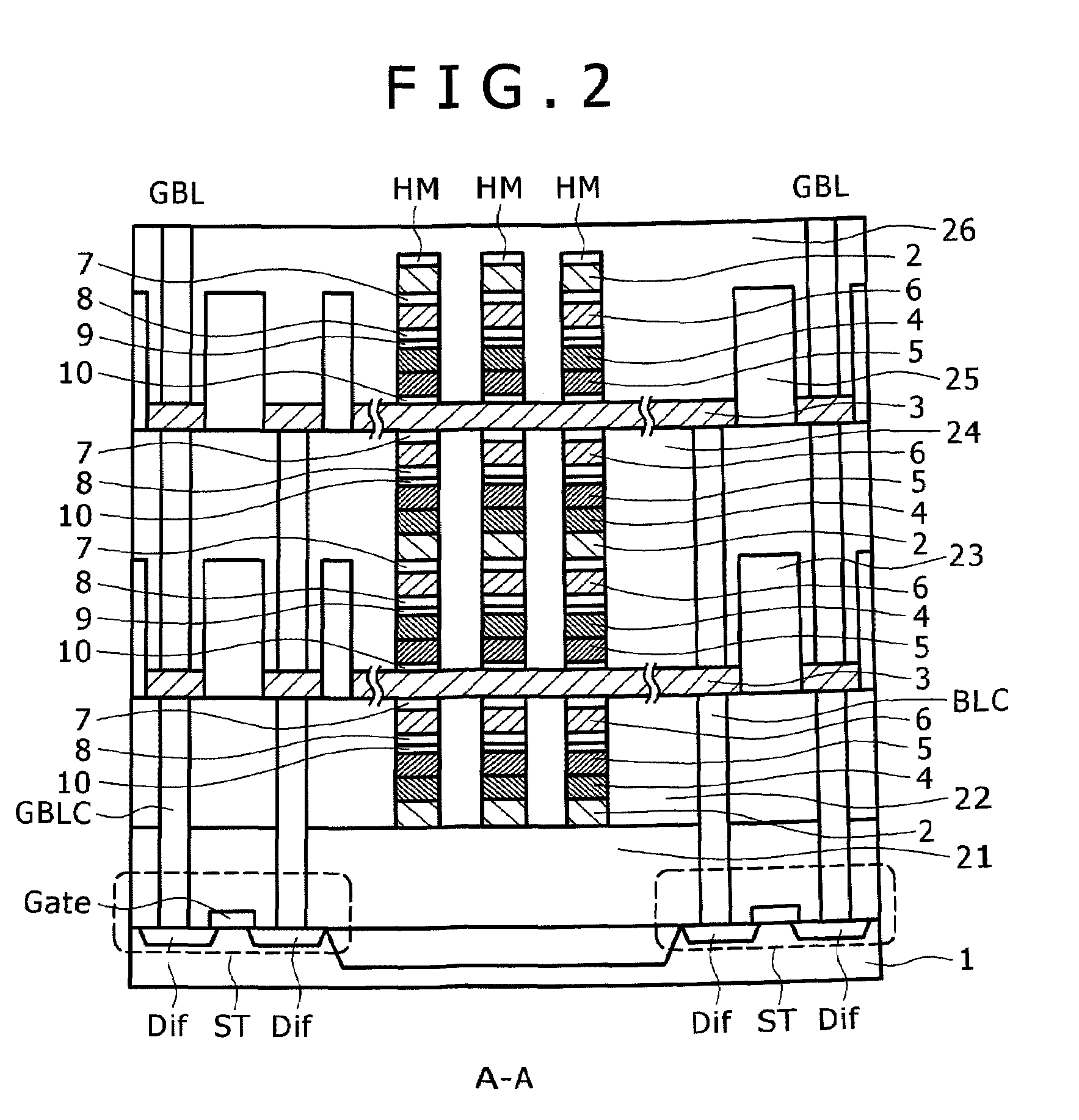
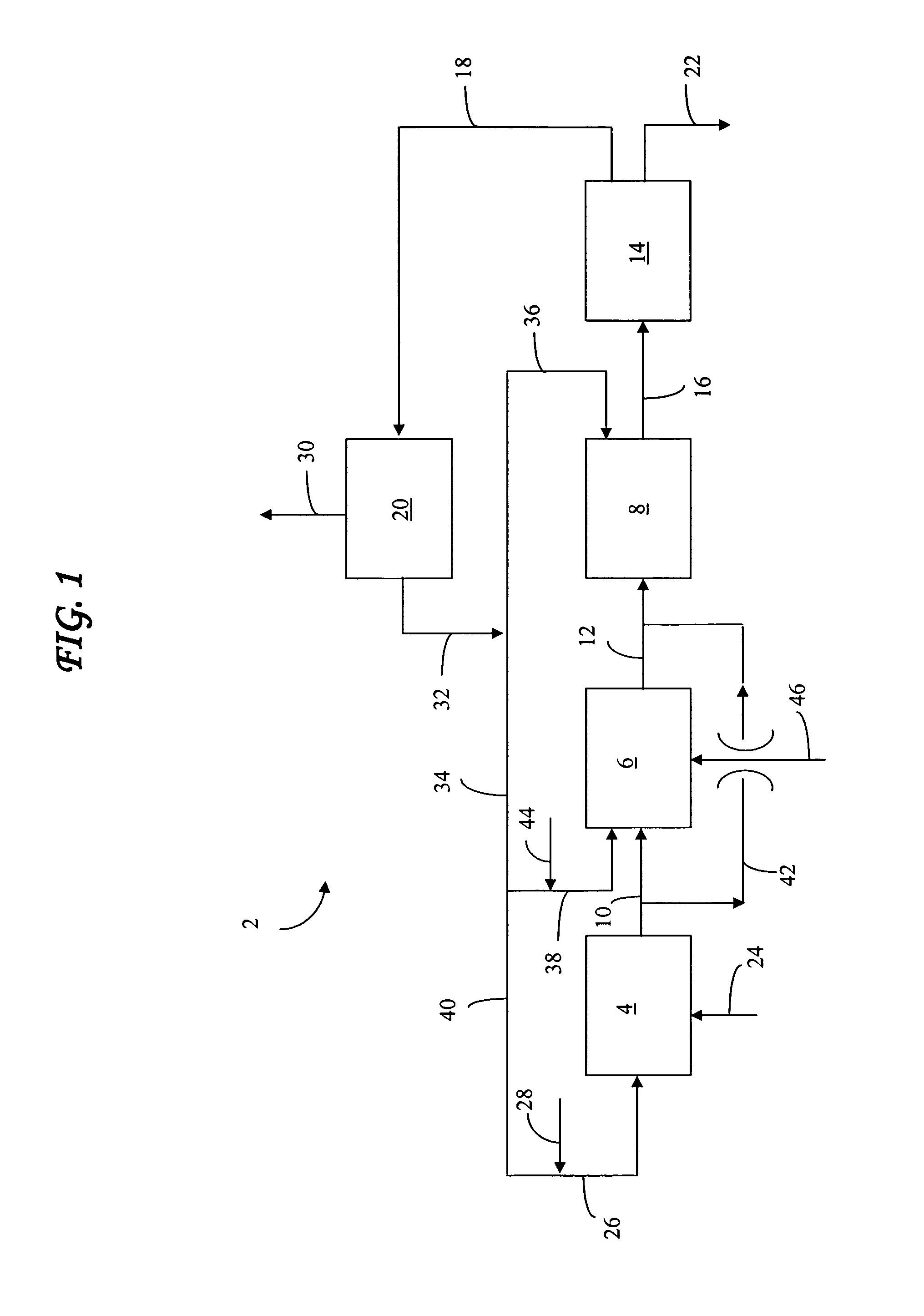
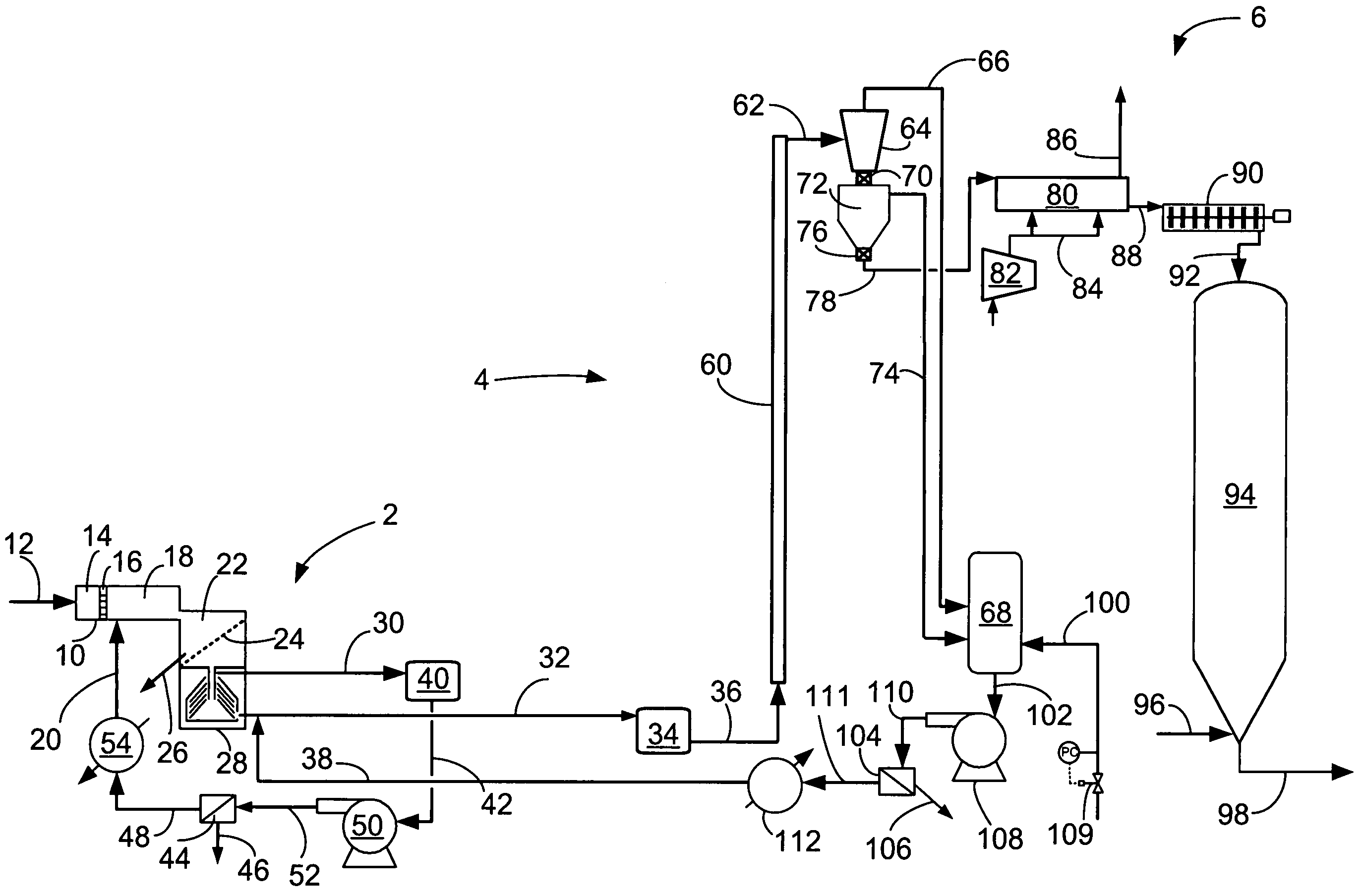
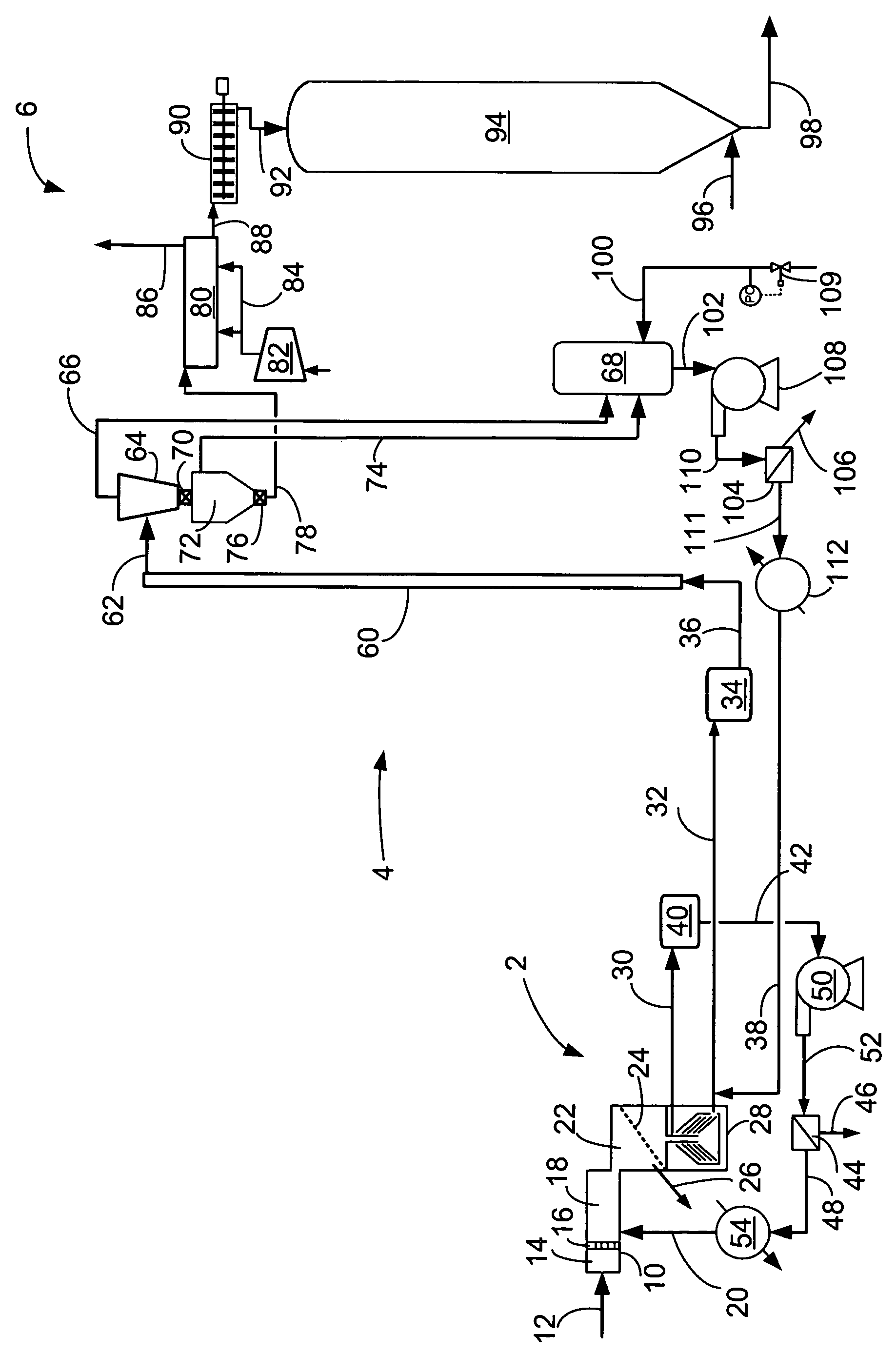
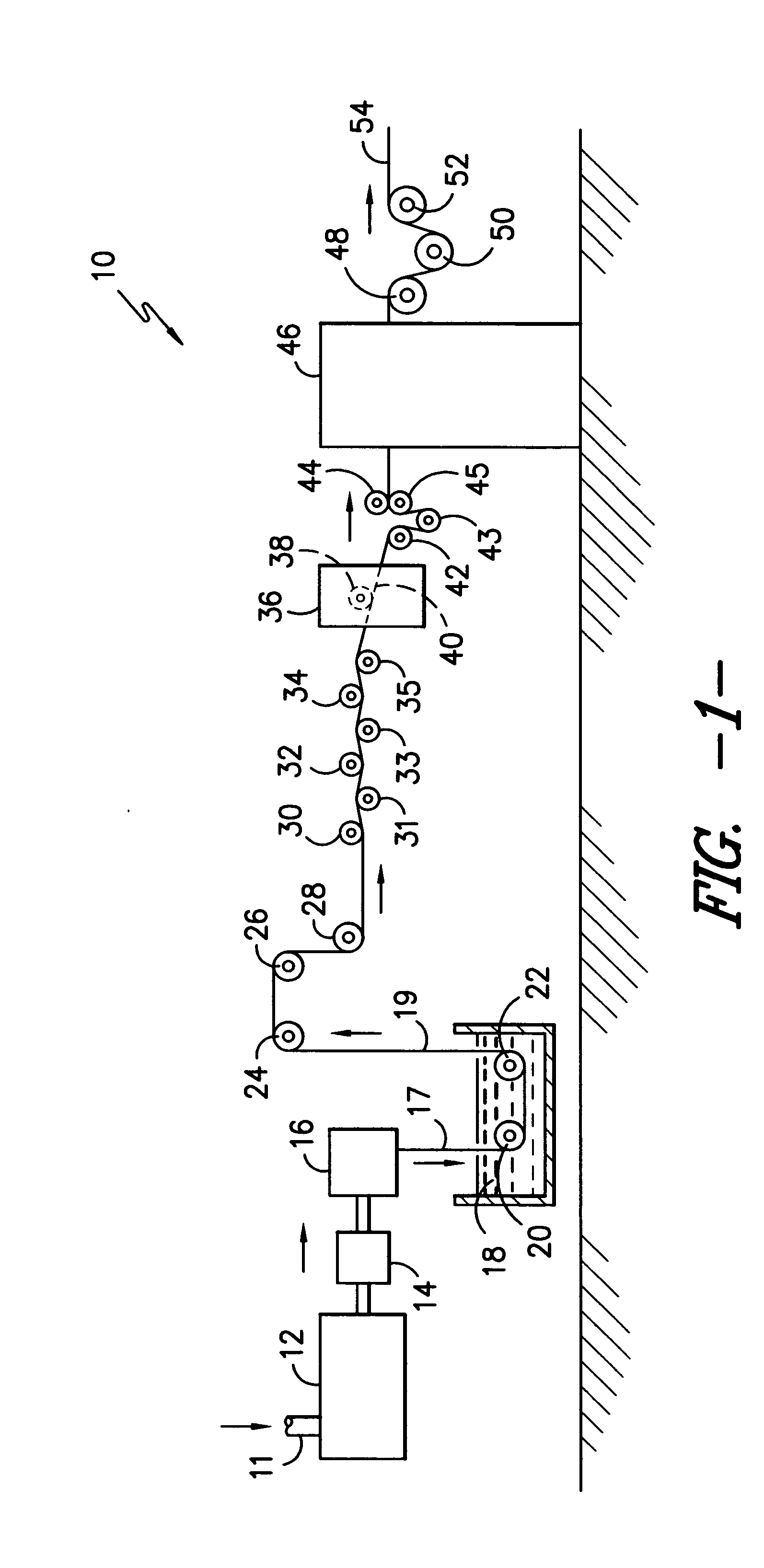
Semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090267047A1Large capacityImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryDevice material
The present invention can promote the large capacity, high performance and high reliability of a semiconductor memory device by realizing high-performance of both the semiconductor device and a memory device when the semiconductor memory device is manufactured by stacking a memory device such as ReRAM or the phase change memory and the semiconductor device. After a polysilicon forming a selection device is deposited in an amorphous state at a low temperature, the crystallization of the polysilicon and the activation of impurities are briefly performed with heat treatment by laser annealing. When laser annealing is performed, the recording material located below the silicon subjected to the crystallization is completely covered with a metal film or with the metal film and an insulating film, thereby making it possible to suppress a temperature increase at the time of performing the annealing and to reduce the thermal load of the recording material.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Polymer blends and pellets and methods of producing same
Blends of at least two polymers incorporating propylene-derived units and processes for producing such blends are provided. The first polymer of the blend is a low crystallinity polymer including propylene-derived units. The second polymer is a high crystallinity polymer including propylene-derived units. The polymer blends exhibit the beneficial performance characteristics of low crystallinity propylene polymers while minimizing certain processing and handling problems associated with low crystallinity propylene polymers. Low crystallinity propylene polymer pellets often exhibit a tendency to agglomerate because of the softness of such particles. Agglomeration of the pellets creates problems in handling and processing the particles. The polymer blends disclosed reduce the tendency of polymer pellets to agglomerate while maintaining the desirable physical properties, such as elastomeric properties, exhibited by low crystallinity propylene polymers. Various processes for producing the polymer blends are also provided.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Thermoplastic monofilament fibers exhibiting low-shrink, high tenacity, and extremely high modulus levels
InactiveUS6759124B2High tensile strengthLow shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingThermoplasticYarn
Unique thermoplastic monofilament fibers and yarns that exhibit heretofore unattained physical properties are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the extrusion of thermoplastic resins that include a certain class of nucleating agent therein, and are able to be drawn at high ratios with such nucleating agents present that the tenacity and modulus strength are much higher than any other previously produced thermoplastic fibers, particularly those that also simultaneously exhibit extremely low shrinkage rates. Thus, such fibers require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target thermoplastic (for example, polypropylene), particularly after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target thermoplastic after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and allowing such an oriented polymer to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target thermoplastic without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the "rigidifying" nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for thermoplastic crystal growth. The preferred "rigidifying" compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as [2.2.1]heptane-bicyclodicarboxylic acid, otherwise known as HPN-68, sodium benzoate, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts [such as sodium 2,2'-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11]. Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive thermoplastic fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Polymer blends and pellets and methods of producing same
Blends of at least two polymers incorporating propylene-derived units and processes for producing such blends are provided. The first polymer of the blend is a low crystallinity polymer including propylene-derived units. The second polymer is a high crystallinity polymer including propylene-derived units. The polymer blends exhibit the beneficial performance characteristics of low crystallinity propylene polymers while minimizing certain processing and handling problems associated with low crystallinity propylene polymers. Low crystallinity propylene polymer pellets often exhibit a tendency to agglomerate because of the softness of such particles. Agglomeration of the pellets creates problems in handling and processing the particles. The polymer blends disclosed reduce the tendency of polymer pellets to agglomerate while maintaining the desirable physical properties, such as elastomeric properties, exhibited by low crystallinity propylene polymers. Various processes for producing the polymer blends are also provided.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
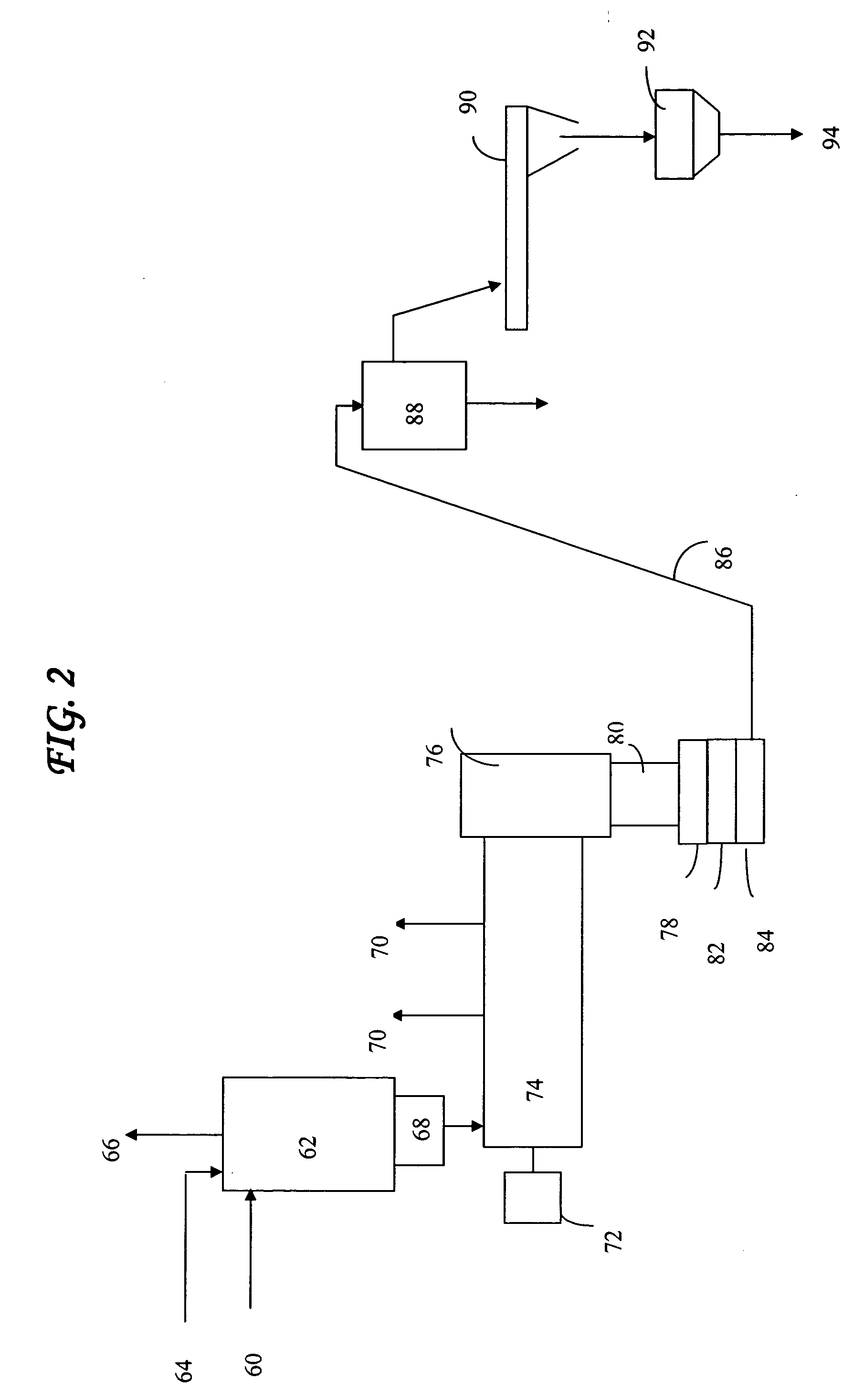
Method and apparatus for crystallizing polymer particles
ActiveUS7250486B1Save heatEfficiently formedChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPolymer scienceShell molding
The present invention is a process and apparatus for conserving loss of heat while forming and crystallizing polymer particles in a liquid. The cooling liquid quenches the polymer during particle molding to facilitate shaping. The cooling liquid cools the polymer particles not below a temperature that allows adequate crystallization to occur. Cooling liquid is quickly switched with a warming liquid, so the temperature of the polymer is in the crystallization range and the heat of crystallization self-heats the polymer to a higher temperature.
Owner:UOP LLC
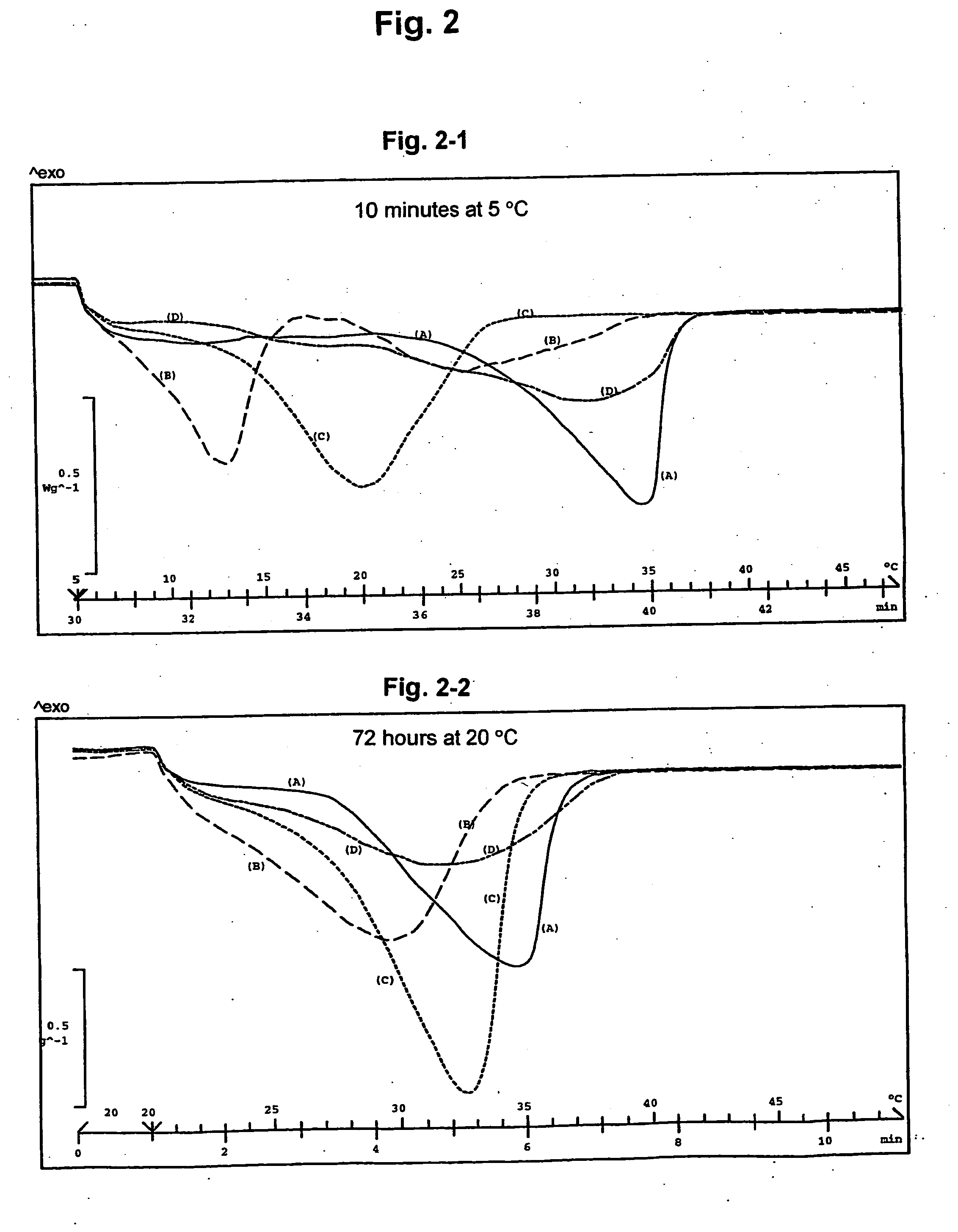
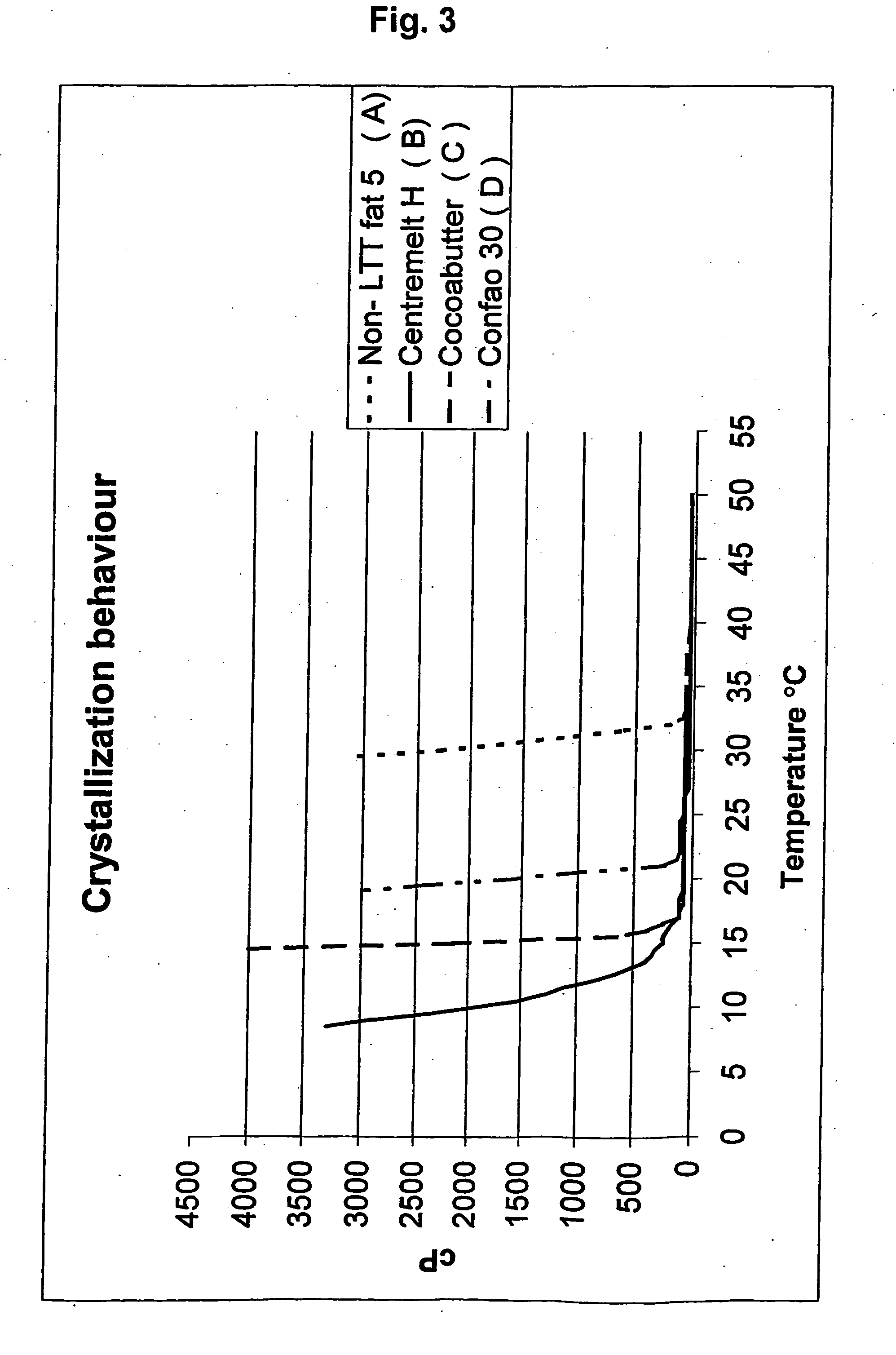
Non-lauric, non-trans, non-temper fat compositions
InactiveUS20050142275A1Crystallize fastDiversify rangeCosmetic preparationsDough treatmentArachidic acidTriglyceride
A non-lauric, non-trans, non-temper (Non-LTT) fat composition comprising a fraction obtained from a randomised triglyceride mixture in which min. 90% by weight of the constituent fatty acids are: palmitic (C16:0), stearic (C18:0), arachidic (C20:0) behenic (C22:0), oleic (C18:1) and linoleic (C18:2) acid and the total content of arachidic and behenic acid is 3-40% by weight and the total content of palmitic and stearic acids is 25-60% by weight, said fraction having the following physical and chemical properties: (1) slip melting point measured according to AOCS Cc 3-25: below 36° C. and solid fat content (SFC) measured according to IUPAC 2.150 mod. (stabilised at 20° C. for 24 h): above 25% by weight at 20° C.; (2) total content of saturated fatty acids measured according to IUPAC 2.301 and 2.304: 40-75% by weight, preferably 45-70% by weight; (3) total content of arachidic and behenic acids: 3-40% by weight, preferably 5-35% by weight, and total content of palmitic and stearic acids: 25-60% by weight, preferably 25-50% by weight, both measured according to IUPAC 2.301 and 2.304; (4) total content of triglycerides having triglyceride composition (TGC) of C56-C60 measured by number of total carbon atoms of constituent fatty acids according to IUPAC 2.323: min. 9% by weight, preferably min. 15% by weight; (5) total content of S2U-type triglycerides: min. 25% by weight, preferably min. 35% by weight, where S=saturated fatty acids and U=unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:AAK DENMARK
Preparation method of lodging-resistant multi-difference polyester low-elastic filament
ActiveCN106400179AImprove heat resistanceEasy to processMelt spinning methodsMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lodging-resistant multi-difference polyester low elastic filament. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing nano sepiolite fibers, organic magnesium hydroxide whisker, organic barium sulfate nano powder, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, p-hydroxybenzoic acid and sodium germanate to obtain a high-modulus composite alcohol solution; secondly, mixing organic wollastonite nano needle-like fibers, mica powder, polyethylene glycol, the propylene glycol, an antioxidant 1010, ethylene glycol antimony and protonated agent phosphoric acid to obtain a high-modulus composite promoter; thirdly, co-polycondensing the high-modulus composite multifunctional alcohol solution and the high-modulus composite promoter with purified terephthalic acid and the ethylene glycol to obtain high-modulus modified polyester; a melt of the high-modulus modified polyester is sprayed from a T-shaped spinneret orifice in a spinneret plate; the lodging-resistant multi-difference polyester low elastic filament is prepared by a special cooling mode and a low-temperature texturing process. The fiber prepared by the preparation method has multiple different properties of different crystallization, different orientation and different shrinkage; after different shrinkage, the appearance is good, and a brushed fabric prepared from the lodging-resistant multi-difference polyester low elastic filament is not easy to lodge.
Owner:荣翔化纤有限公司
Thermoplastic Composites and Methods of Making and Using Same
ActiveUS20110097575A1Crystallize fastReduce manufacturing costLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceSurface layer
Thermoplastic composites having a core composite layer including a fibrous substrate and one or more high performance polymer, and a surface layer polymer applied to at least one surface of the core composite layer, which forms a polymer blend with the high performance polymer thereby imparting improved toughness and processing times, and methods for making and using same, are provided herein.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Polypropylene fibers and fabrics
InactiveUS7081299B2Improve featuresShot levelFixed capacitor dielectricSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceNon-coordinating anion
The present invention is a meltblown fiber and a fabric manufactured from the fiber comprising reactor grade polypropylene having a melt flow rate of from 100 to 5000 and having less than 50 stereo defects per 1000 units. Further, the polypropylene is typically produced from a metallocene catalyzed process, the metallocene being at least one bridged 2,4 di-substituted indenyl metallocene in one embodiment, and a bridged 4-phenyl indenyl metallocene in another embodiment. The metallocene is part of a system that can include a fluorided support and a non-coordinating anion activator.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Polypropylene monofilament and tape fibers exhibiting certain creep-strain characteristics and corresponding crystalline configurations
InactiveUS6863976B2High tensile strengthLow shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingYarnThermoplastic
Unique thermoplastic (polypropylene, specifically) monofilament and / or tape fibers and yarns that exhibit heretofore unattained physical properties are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the extrusion of thermoplastic resins that include a certain class of nucleating agent therein, and are able to be drawn at high ratios with such nucleating agents present, that the tenacity and modulus strength are much higher than other previously produced thermoplastic fibers (particularly those produced under commercial conditions), particularly those that also simultaneously exhibit extremely low shrinkage rates. Thus, such fibers require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target thermoplastic (for example, polypropylene), particularly after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target thermoplastic after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and allowing such an oriented polymer to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target thermoplastic without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the “rigidifying” nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for thermoplastic crystal growth. The preferred “rigidifying” compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as [2.2.1]heptane-bicyclodicarboxylic acid, otherwise known as HPN-68, sodium benzoate, talc, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts [such as sodium 2,2′-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11]. Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive thermoplastic fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
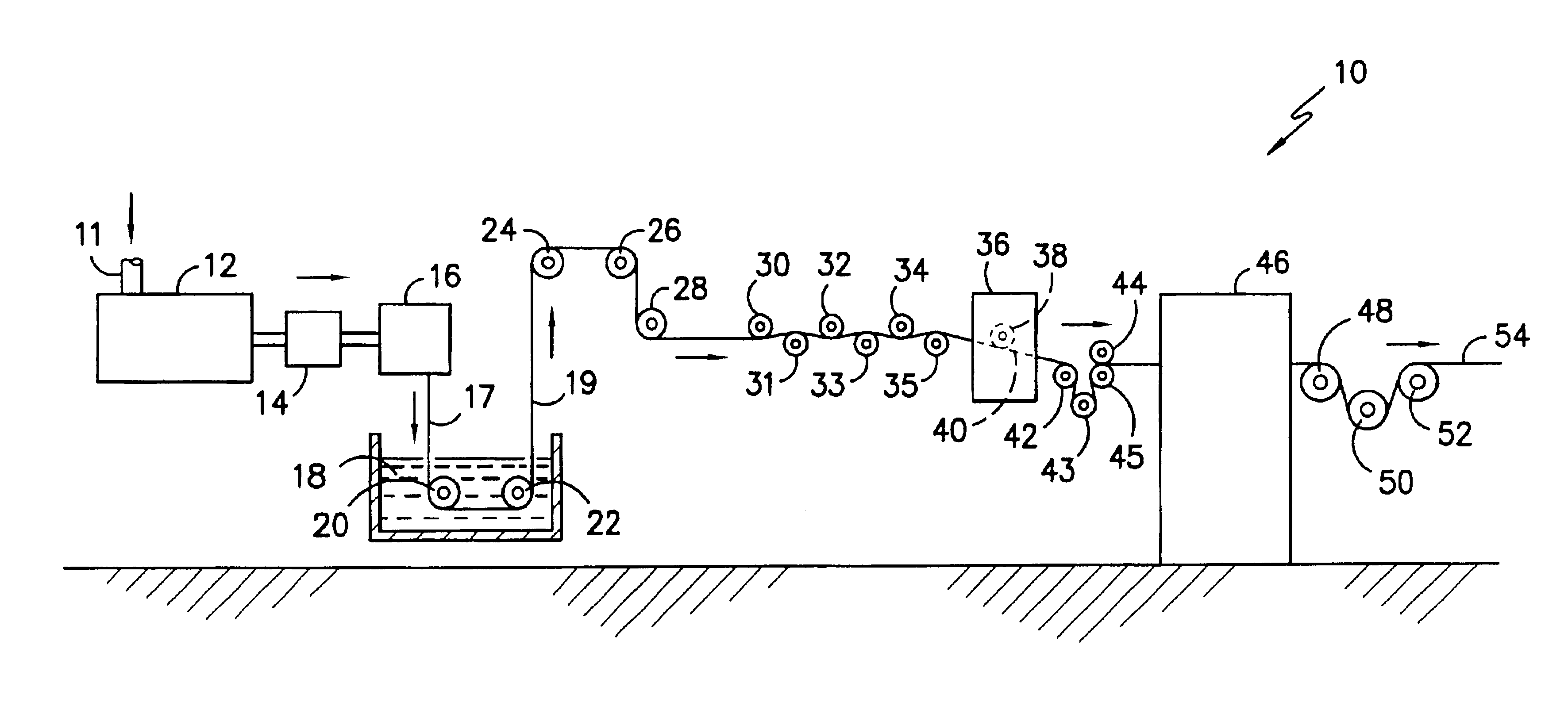
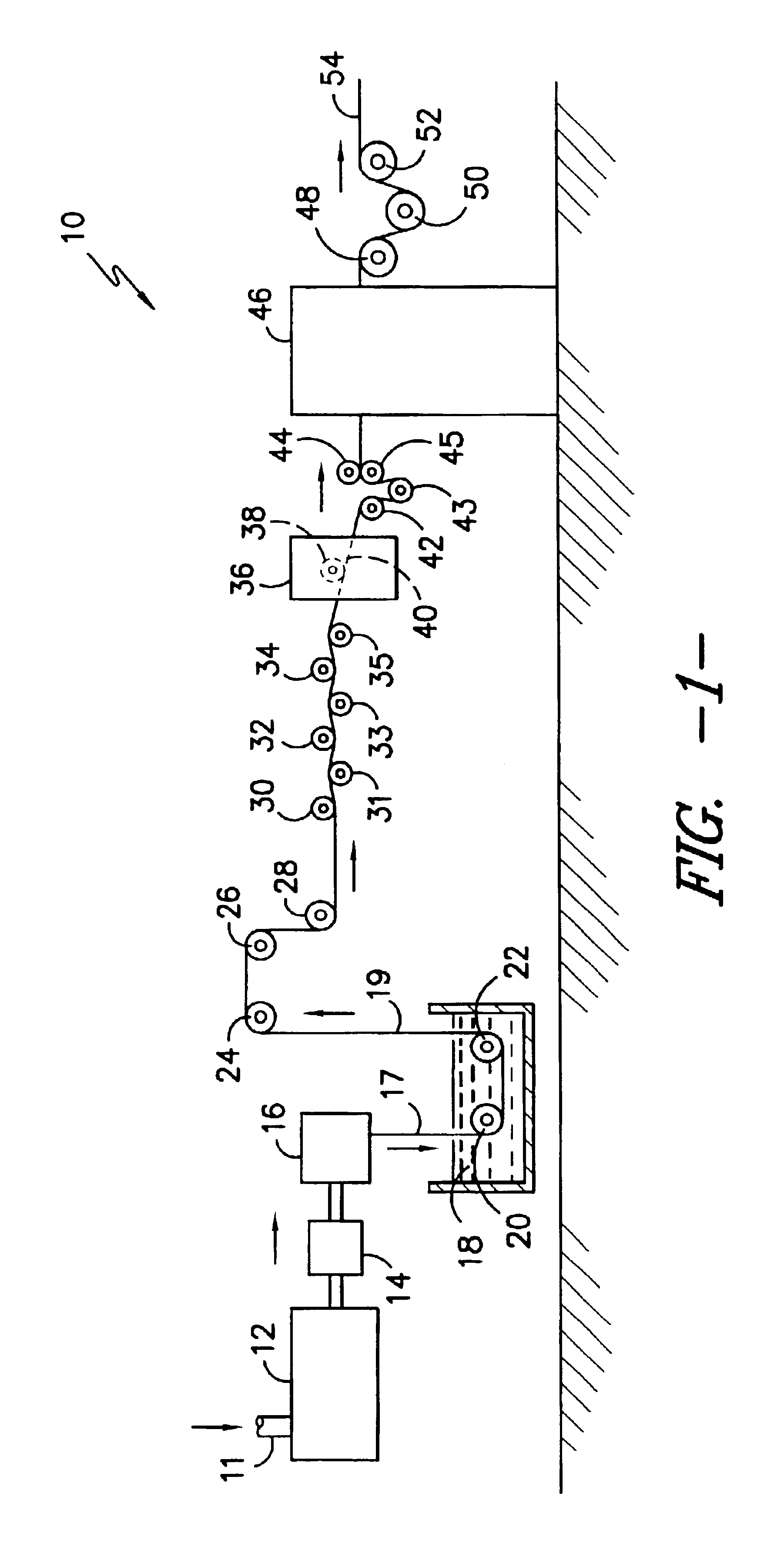
Apparatus for preparing a gypsum wallboard core
InactiveUS20040131714A1Reduce the possibilityAccelerates setting reactionFrozen sweetsConfectioneryActive agentMining engineering
A gypsum wallboard core, and methods and apparatus for making the same are disclosed. Methods of making a gypsum wallboard core include extruding a gypsum slurry containing water, gypsum, slip agents, water-reducing agents, surfactants and, optional additives, through a die and onto a substantially flat, smooth, moving surface. The die has provisions at its outer sides for the introduction of slip agents into the slurry, and provisions at its lateral outer edges for the introduction of a strength-enhancing agent. Once extruded onto the conveyor belt, the slurry is chemically-activated to set and form a hardened board core which then may be easily removed from the conveyor belt and dried.
Owner:GOLD BOND BUILDING PROD LLC
Water-soluble polyester for textile size and preparation method of water-soluble polyester
The invention relates to a water-soluble polyester for textile size and a preparation method of the water-soluble polyester. The water-soluble polyester disclosed by the invention uses terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol to constitute a main repeating unit, namely ethylene terephthalate, and contains phthalate-5-sulphonate or a derivative thereof accounting for 8-20% of the mole number of the terephthalic acid, and calculated by the weight of the terephthalic acid, 3-20% of polyethylene glycol, 0.03-0.3% of acetate and 0.001-0.03% of inorganic nanoparticles are added. The intrinsic viscosity of the water-soluble polyester is 0.25-52dL / g, and the glass transition temperature is 35-55 DEG C. The water-soluble polyester can prevent adhesion during crushing and meet the requirements of continuous production; and the obtained product can be sized under moist environmental conditions in summer, and sized fiber fabric can be desized thoroughly.
Owner:山东巨业精细化工有限公司
Thermoplastic composites and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS8158245B2Crystallize fastReduce manufacturing costSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationPolymer scienceThermoplastic composites
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
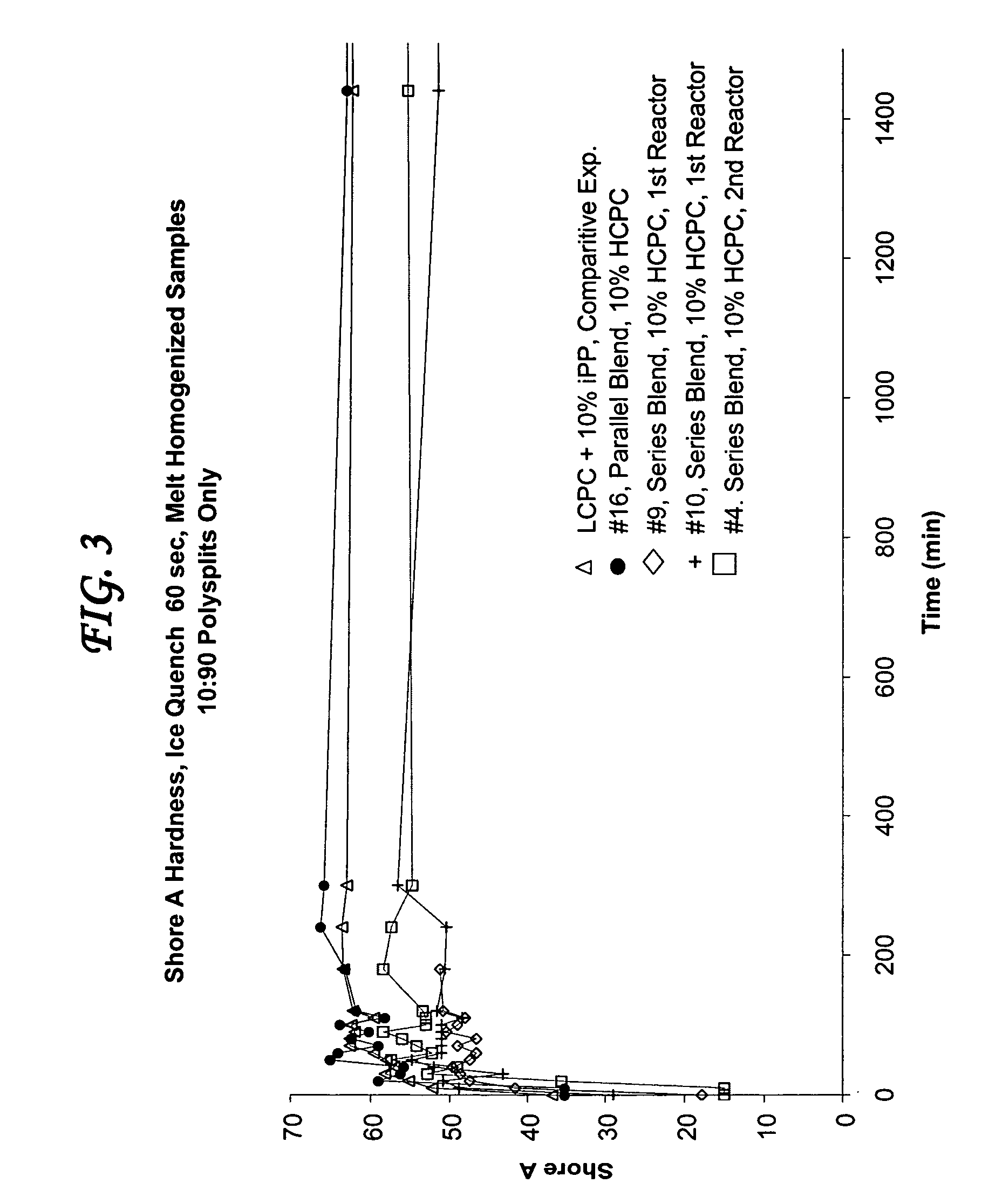
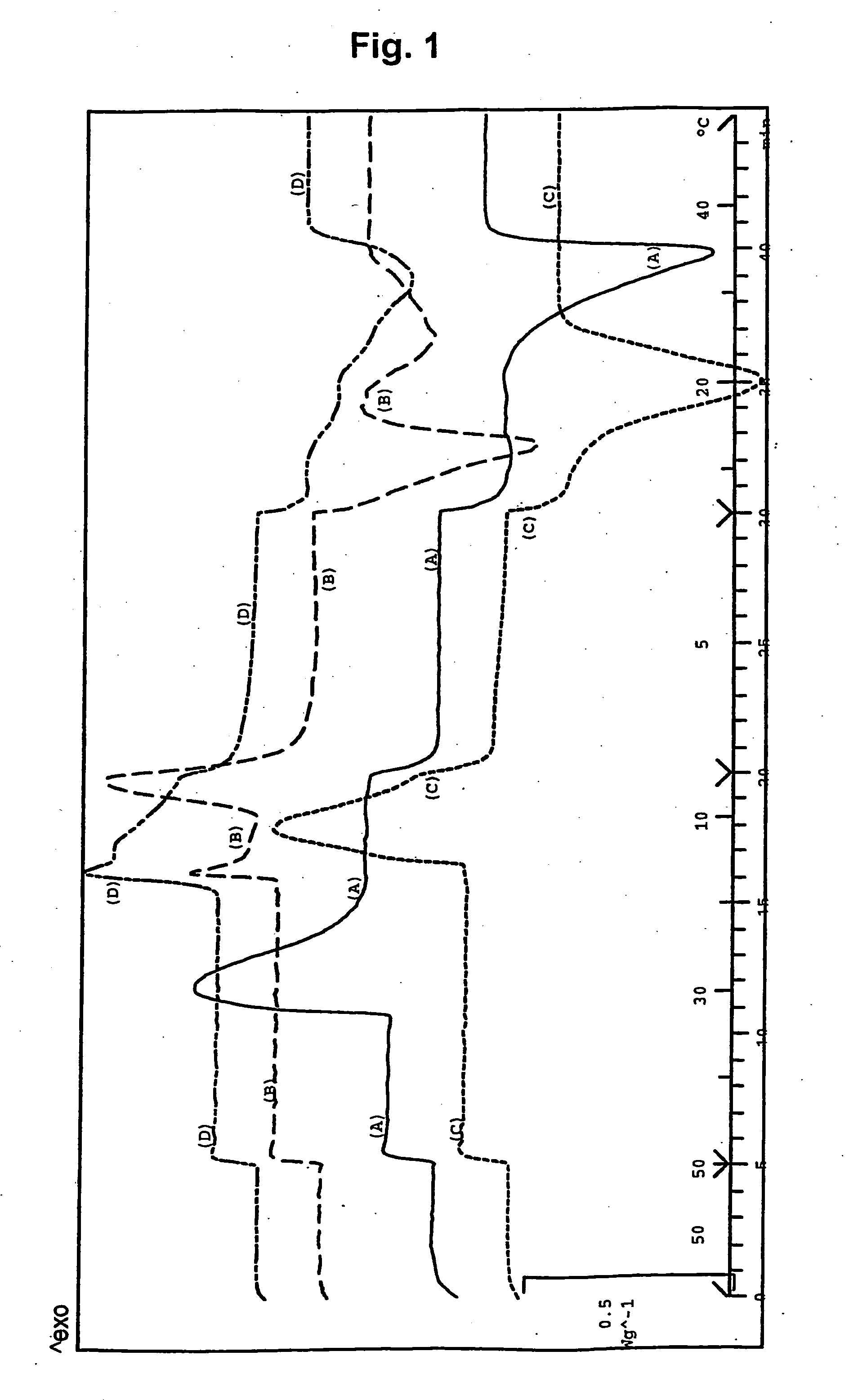
Methods and apparatus for rapid crystallization of biomolecules
InactiveUS7459021B2Crystallize fastQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionIsoelectric point
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for promoting rapid formation of biomolecule crystals from a solution of biomolecules, preferably proteins, wherein the protein solution undergoes rapid concentration according to its isoelectric point in an electric field. Protein crystallization according to the methods of the present invention takes place within a period of hours or less.
Owner:BUKSHPAN SHMUEL
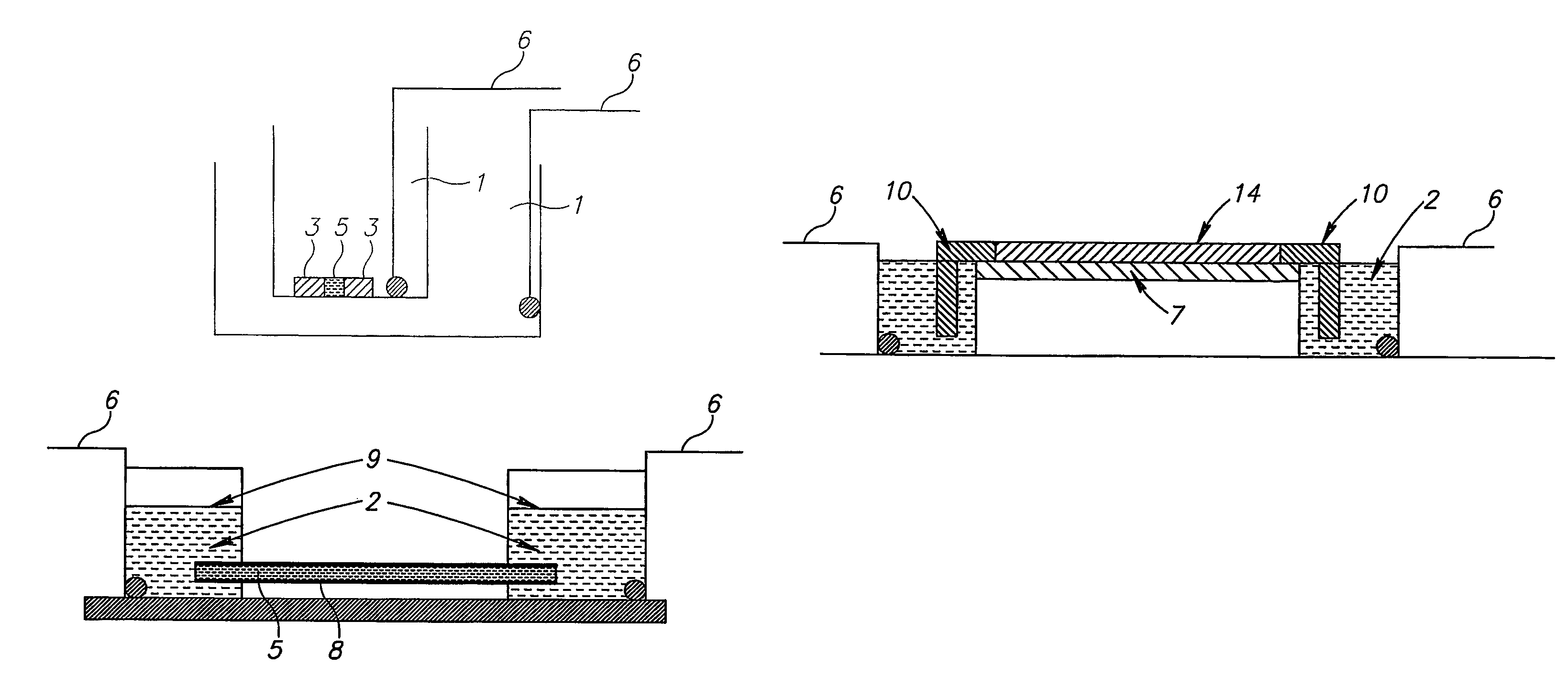
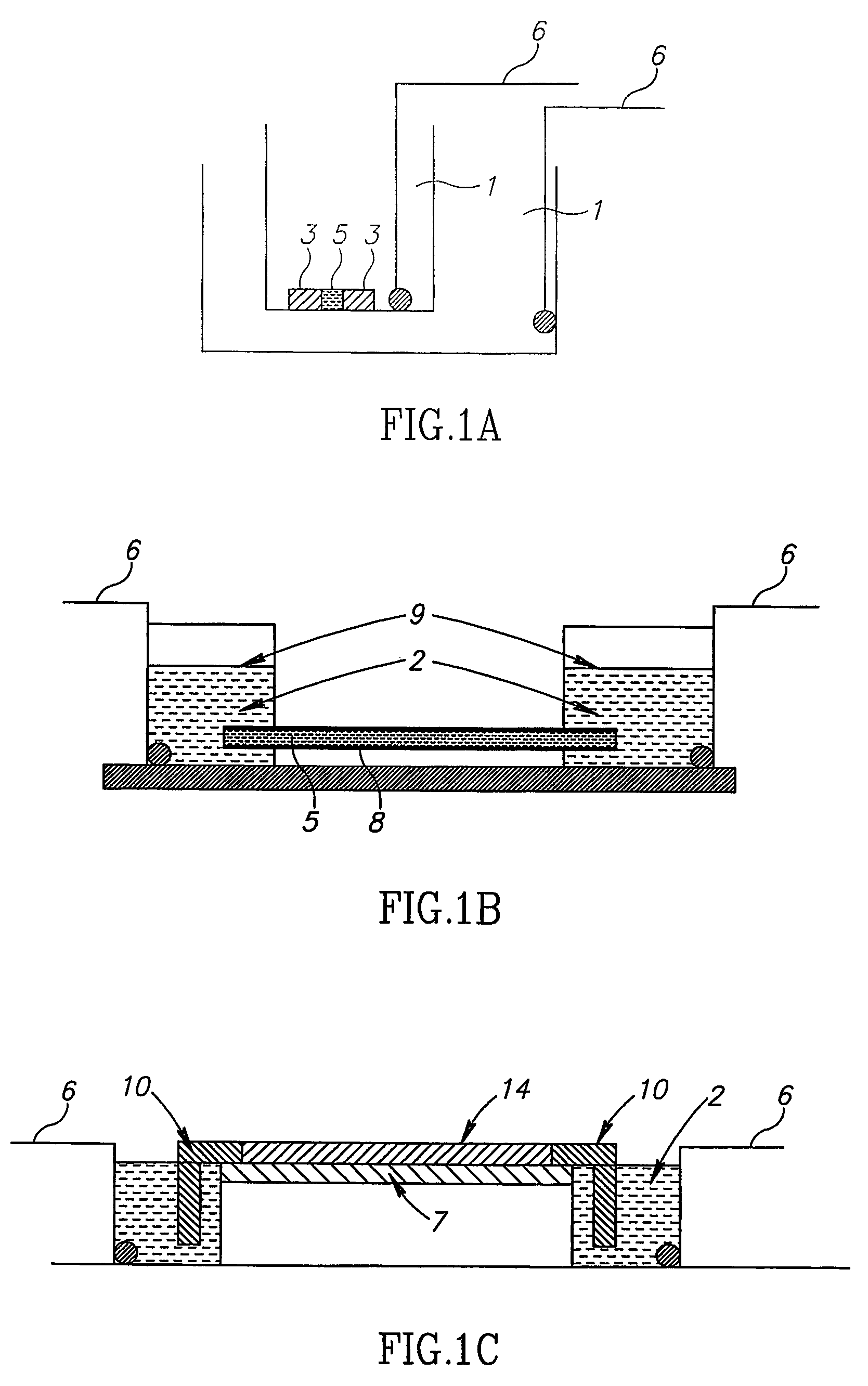
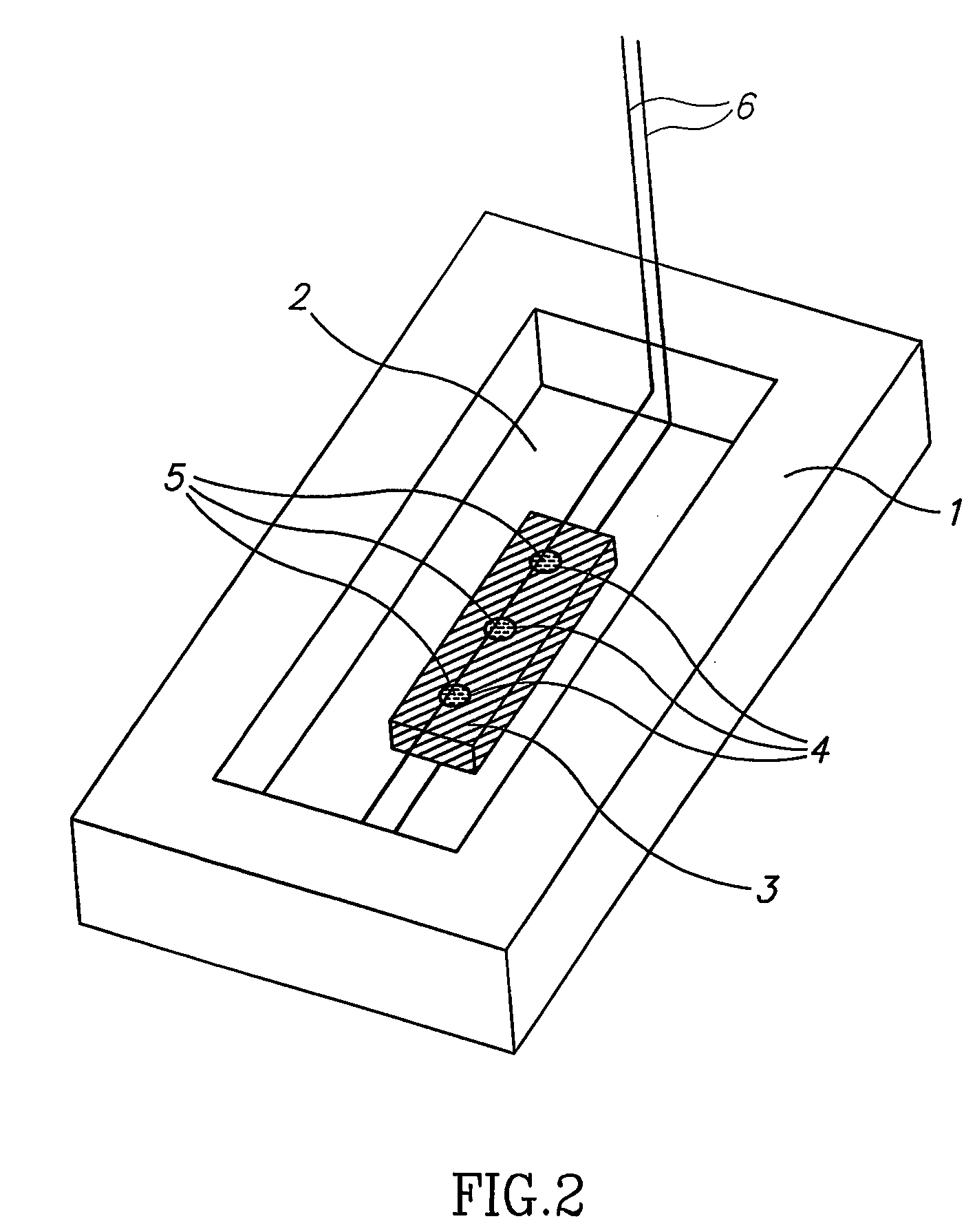
Aqueous ink, image recorded using said aqueous ink and method for forming said image
InactiveUS7267716B2Satisfactorily obtainedCrystallize fastMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsWater dispersibleWater soluble
Owner:CANON KK
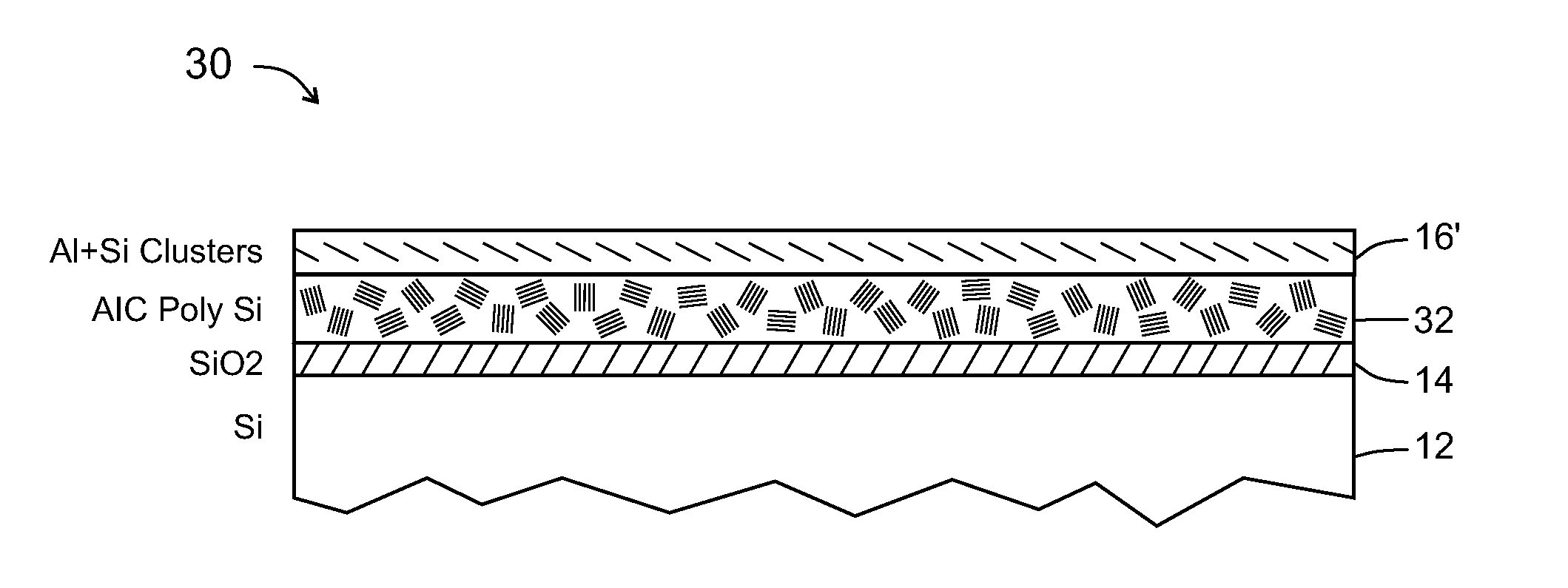
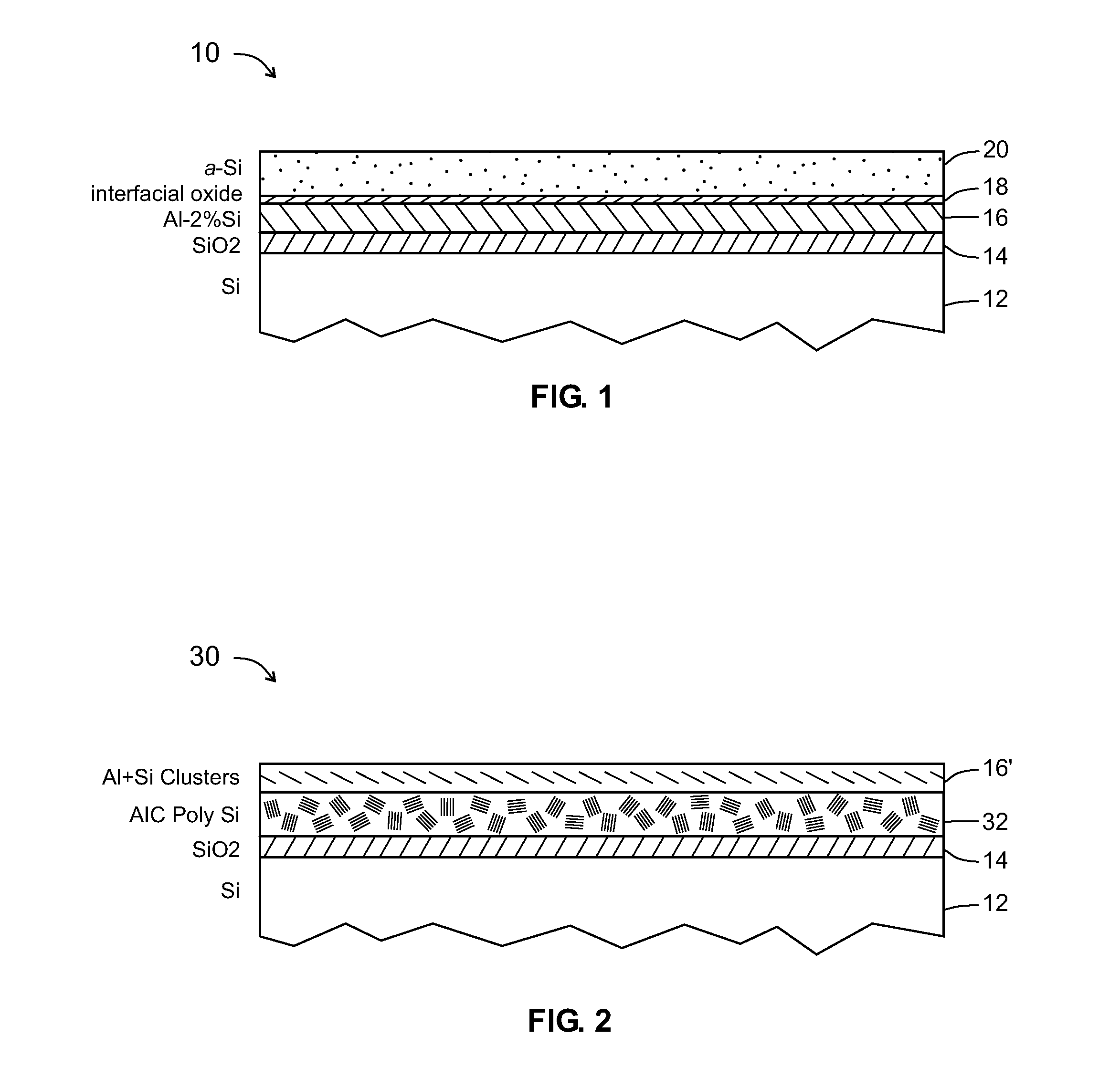
Low-temperature formation of polycrystalline semiconductor films via enhanced metal-induced crystallization
ActiveUS20100184276A1Enhance formationLow temperaturePolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateMetal-induced crystallizationAmorphous semiconductors
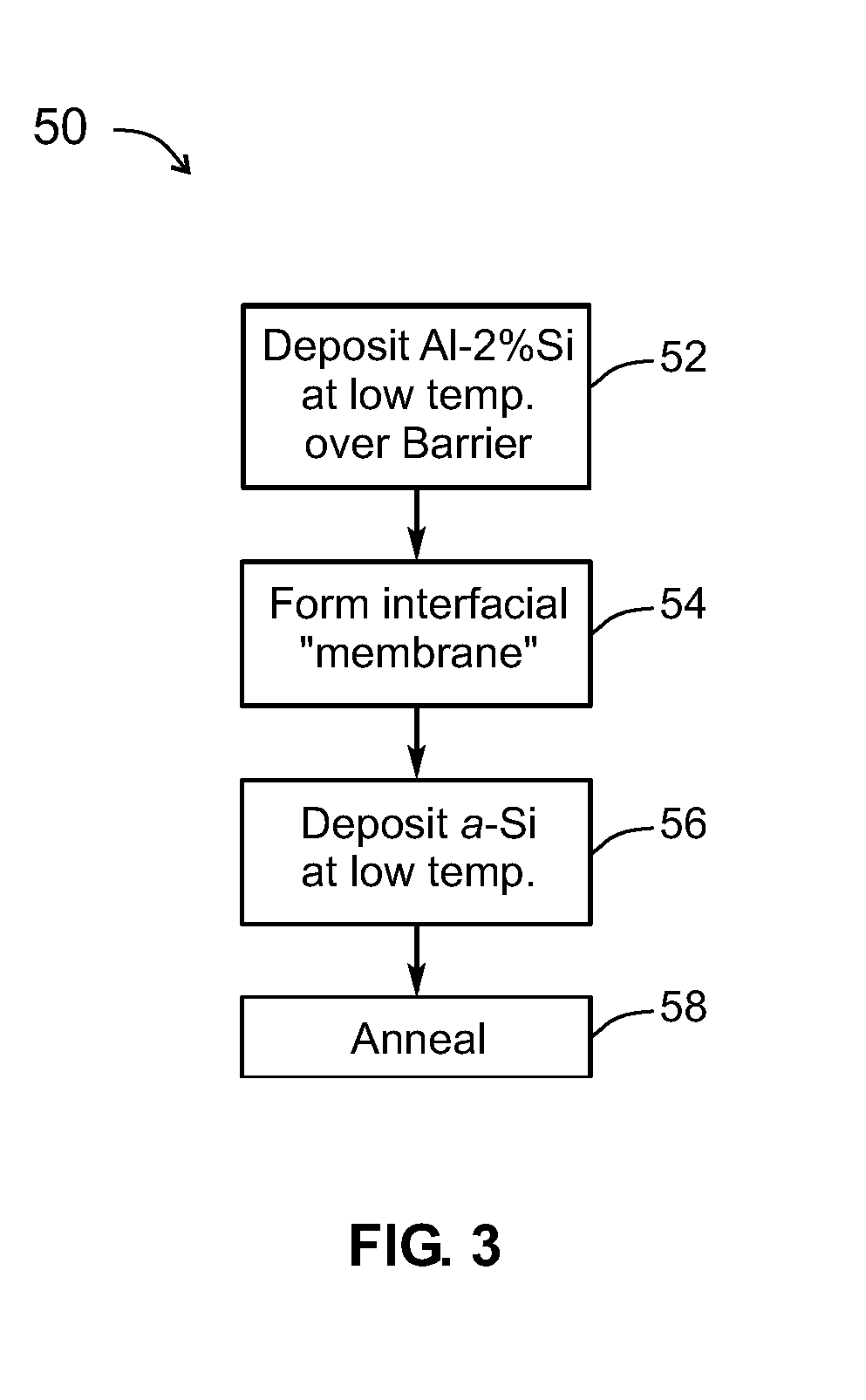
A method for forming polycrystalline semiconductor film from amorphous semiconductor film at reduced temperatures and / or accelerated rates. The inclusion of a small percentage of semiconductor material, such as 2% within the metal layer, reduces the temperatures required for crystallization of the amorphous semiconductor by at least 50° C. in comparison to the use of the metal layer without the small percentage of semiconductor material. During a low temperature isothermal annealing process adjacent Al-2% Si and a-Si films undergo a layer exchange resulting in formation of a continuous polycrystalline silicon film having good physical and electrical properties. Formation of polycrystalline-semiconductor in this manner is suitable for use with low temperature substrates (e.g., glass, plastic) as well as with numerous integrated circuit and MEMs fabrication devices and practices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Aqueous ink, image recorded using said aqueous ink and method for forming said image
InactiveUS20060021545A1Good effectHigh image densityMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsWater dispersibleWater soluble
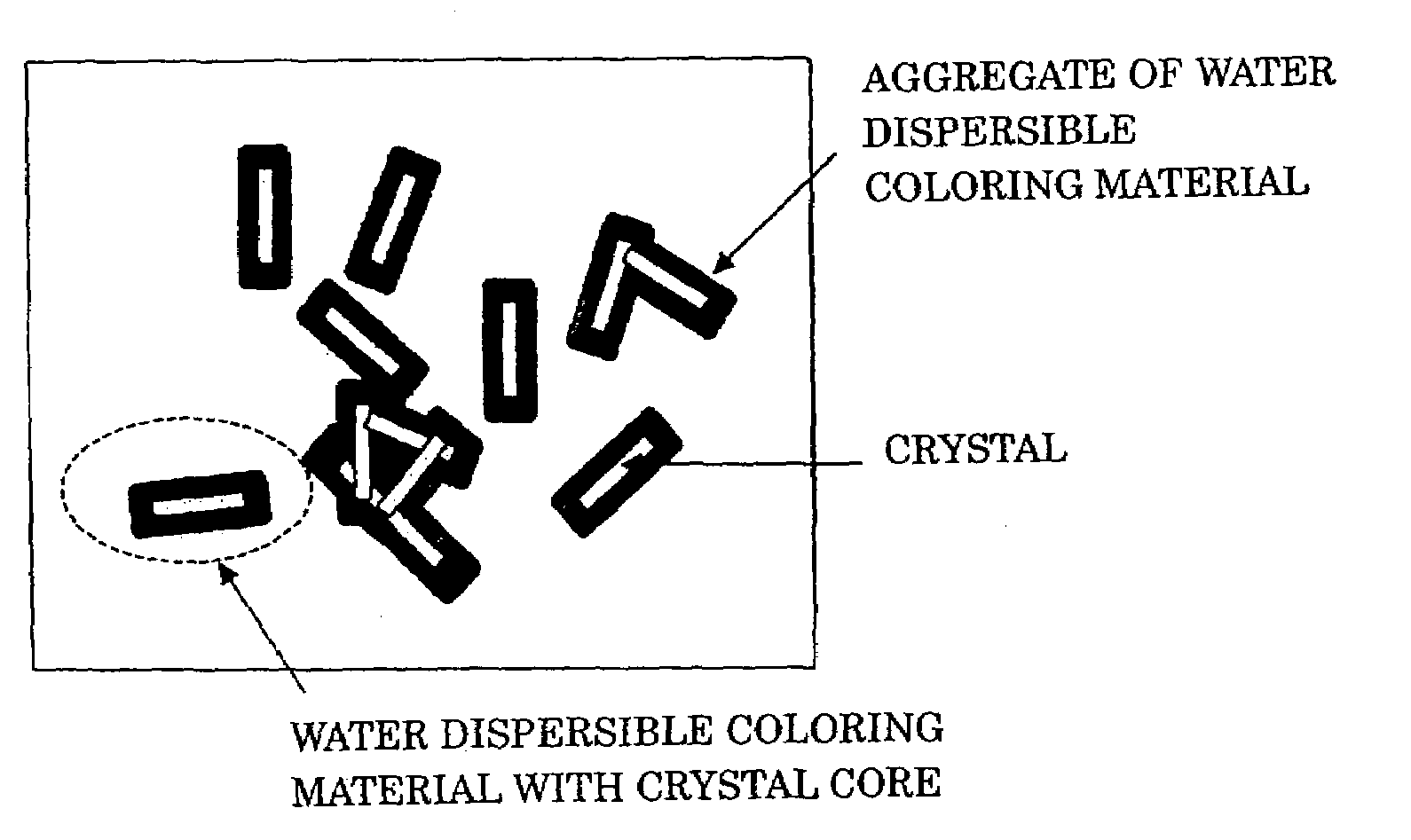
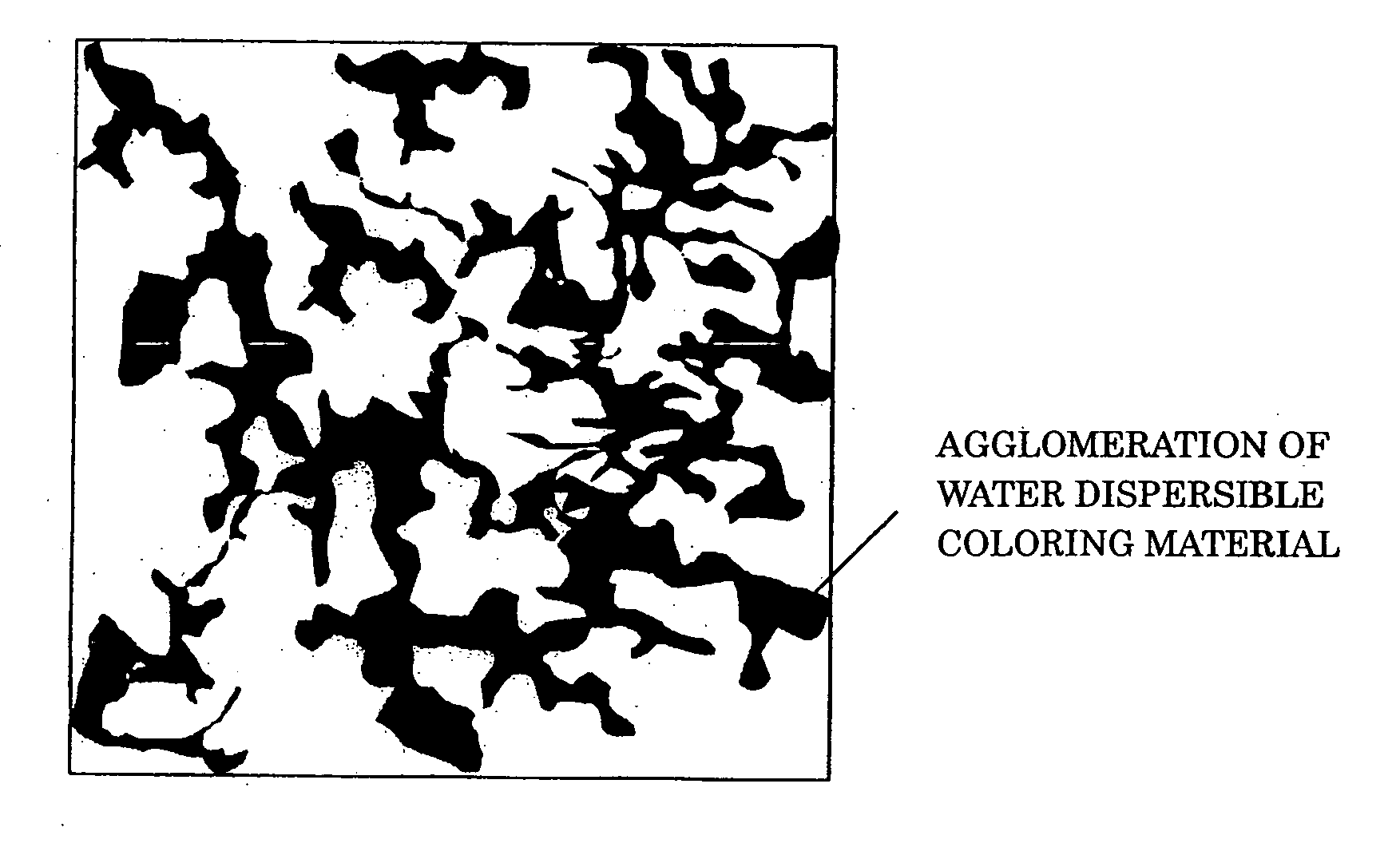
An aqueous ink containing at least a water-dispersible coloring material and a water-soluble crystalline component, characterized in that the water-dispersible coloring material forms an aggregate around a crystal of the crystalline component formed as the content of the aqueous ink decreases, which ink may further contain a water-soluble coloring material.
Owner:CANON KK
High glaze polypropylene material and preparation method thereof
A high-lustre polypropylene material and its production are disclosed. The material consists of polypropylene resin 100 proportion, filler nanometer calcium carbonate 25-35 proportion, dispersant 0.5-1.5 proportion, cross-linking agent diisopropylzene 0.1-0.5 proportion, beta-crystal nucleation agent 0.1-0.5 proportion, and antioxidant 0.1-0.5 proportion. It costs low, has better toughness and surface brightness on surface.
Owner:SHENZHEN KEJU NEW MATERIAL
Method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by ammonia method using electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues
ActiveCN102863007AGrowth inhibitionSmall particle sizeZinc oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologyElectrolysisZno nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by an ammonia method using electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues. The method comprises the following steps of: adding slaked lime being 1-5% of the mass of electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues before a leaching step to perform activation, then leaching with ammonia-ammonium bicarbonate solution, adding 0.3-0.5kg of sodium fluorosilicate to per cubic meter of ammonia-ammonium bicarbonate solution, and refining after performing purification and impurity removal. According to the method for producing high-purity nano-zinc oxide by ammonia method using electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues, the electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues can be leached efficiently, the high-purity nano-zinc oxide with the purity up to above 99.7% can be obtained, and the high-purity nano-zinc oxide has high practical value and economic value; all the valuable and harmful heavy metals in the electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues are leached and utilized, so that the obtained final leaching residues are converted from electrolytic zinc acid-leaching residues as high hazard wastes into ordinary solid wastes, the environment is protected, and the resources are rationally utilized.
Owner:SICHUAN JUHONG TECH
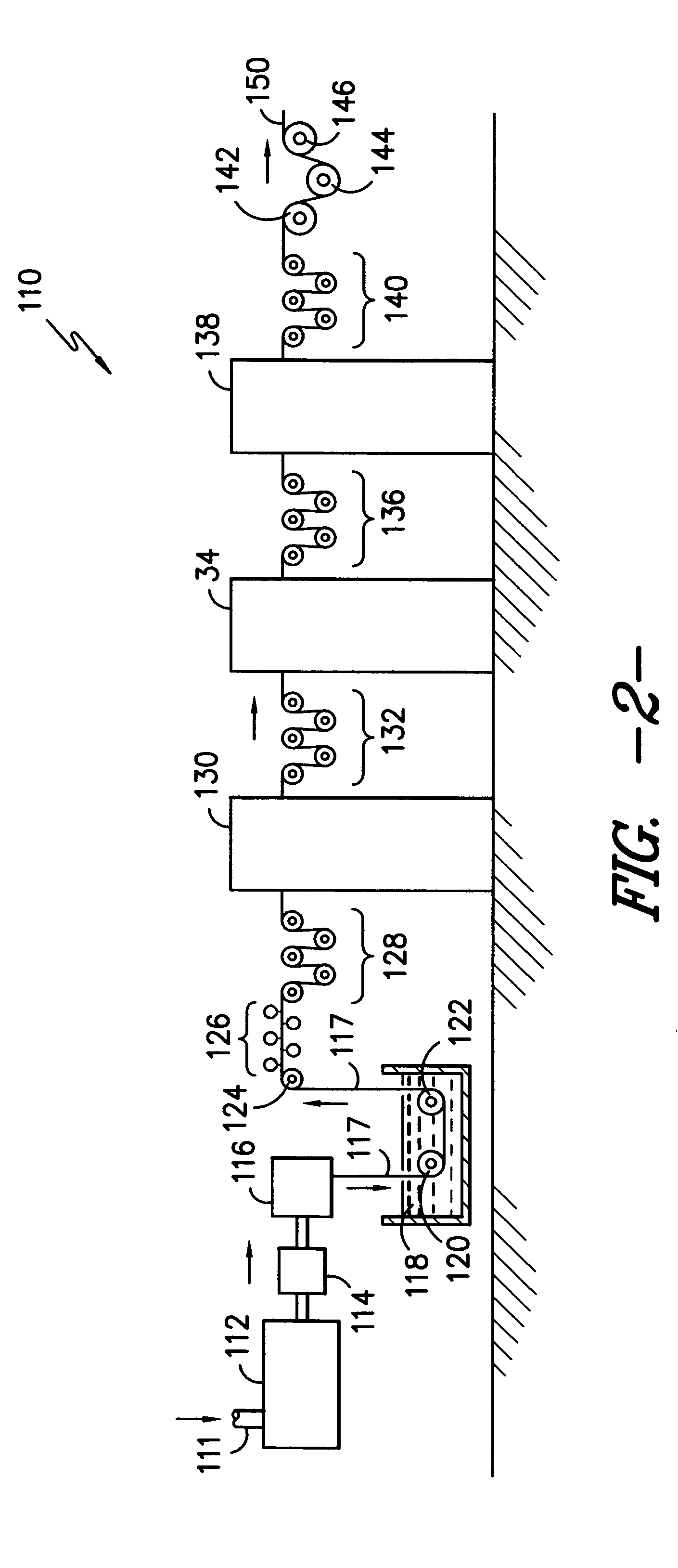
Method for annealing silicon thin films and polycrystalline silicon thin films prepared therefrom
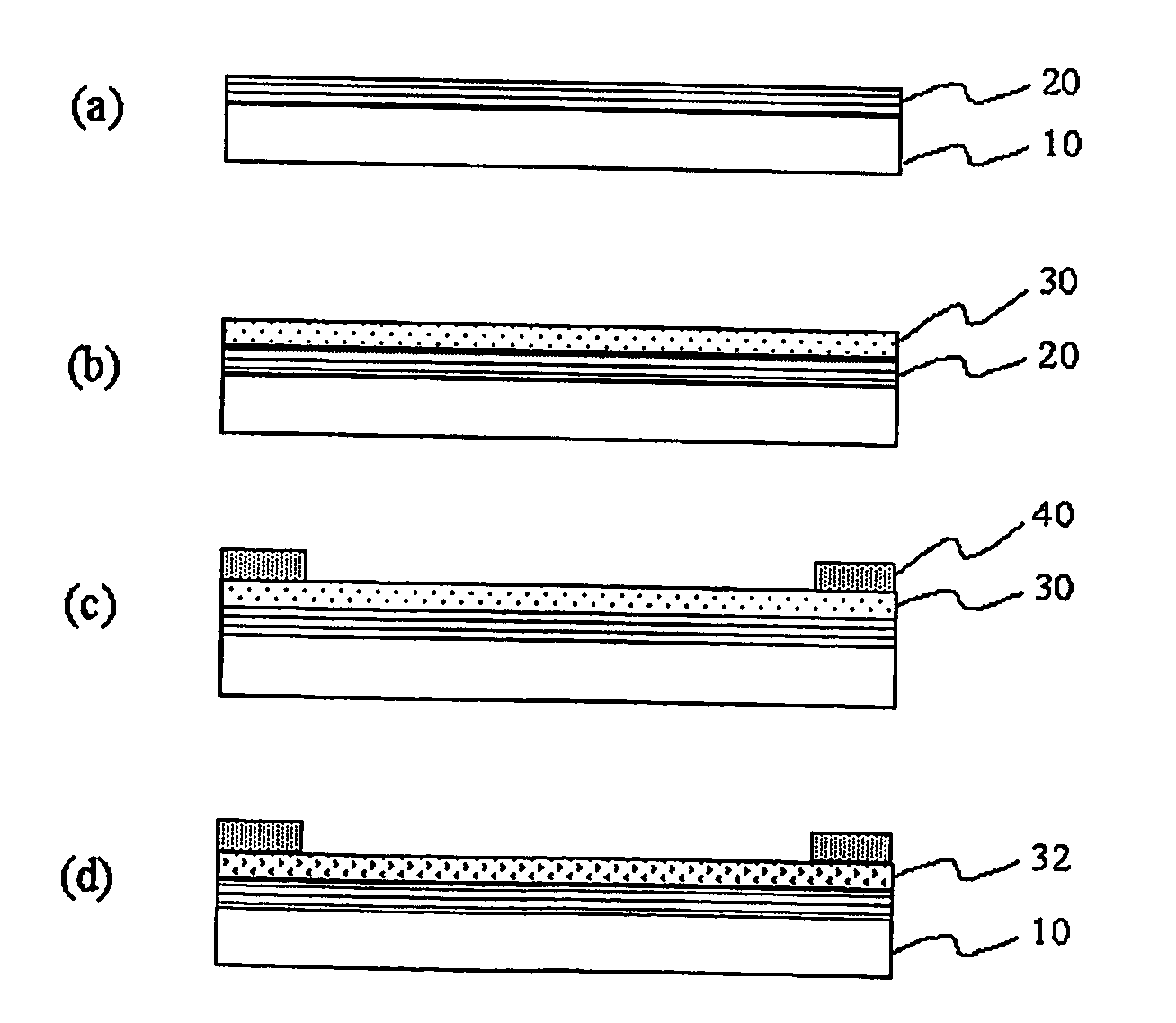
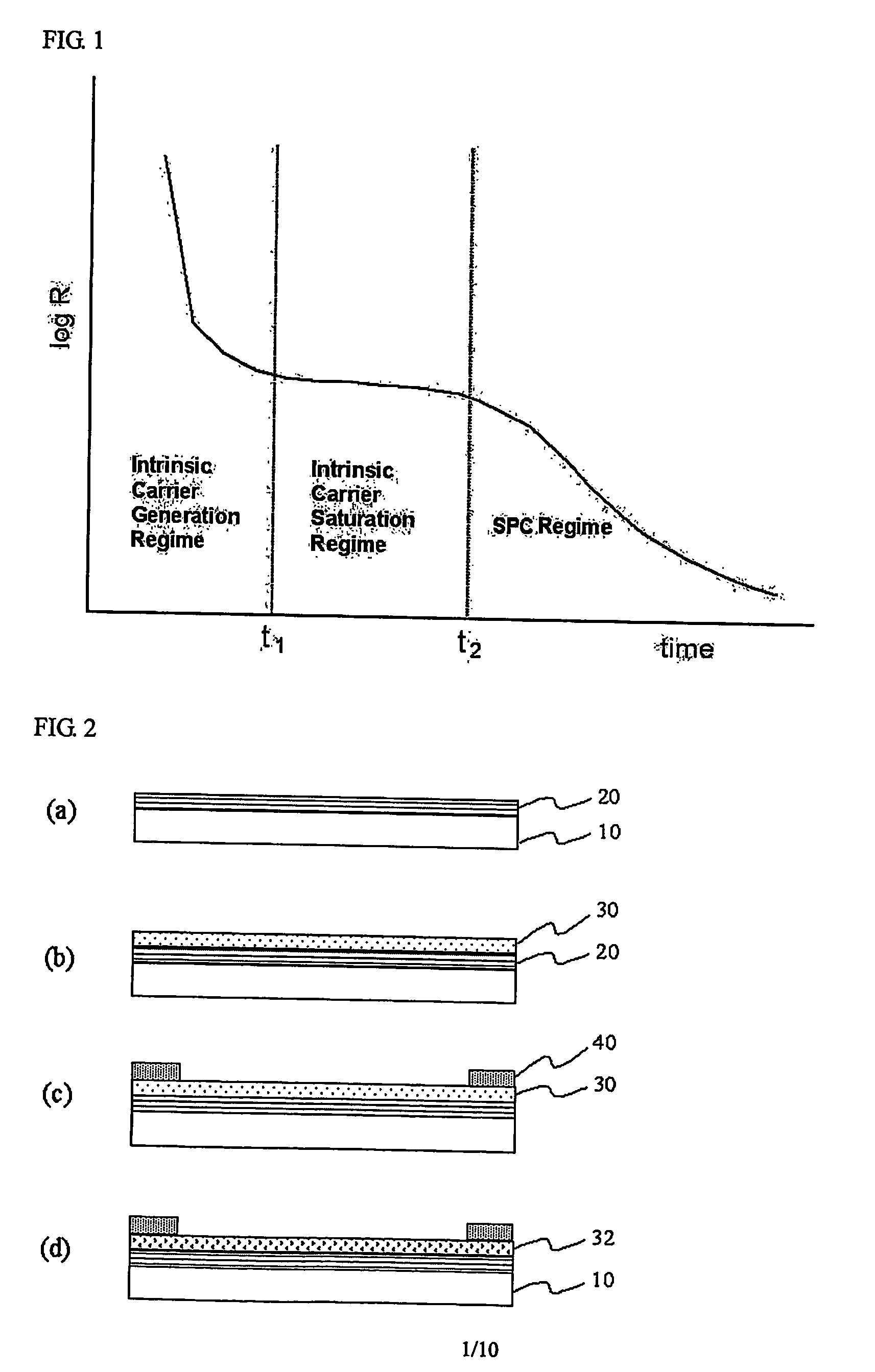
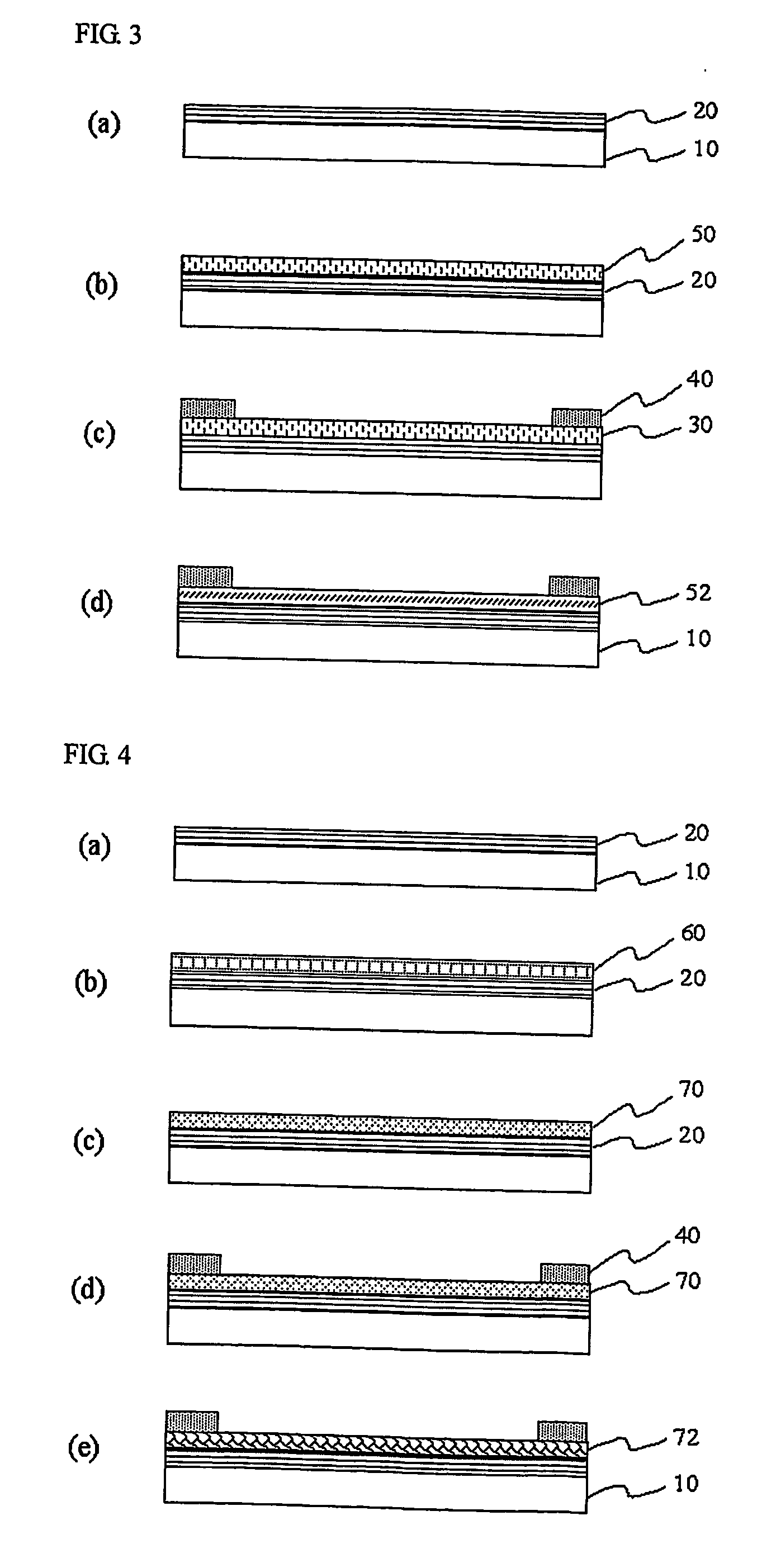
InactiveUS20070099352A1Simple processReduce defectsTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerCrystallographic defect
Disclosed is a method for annealing a silicon thin film in a substrate in which an insulation layer and the silicon thin film are subsequently formed. The method includes heating or preheating the silicon thin film within a temperature range at which the substrate is not transformed during the process so as to generate an intrinsic carrier therein, thereby lowering a resistance to a value at which Joule heating is possible; and applying an electric field to the preheated silicon thin film so as to induce Joule heating by means of movement of the carrier, thereby conducting crystallization, eliminating crystal defects, and ensuring crystal growth. When using the method, Joule heating is selectively induced to a-Si thin film, a-Si / Poly-Si thin film or a Poly-Si thin film according to the preheating condition, thereby making a Poly-Si thin film of good quality within a very short time without damaging the substrate.
Owner:ENSIL TECH CO LTD
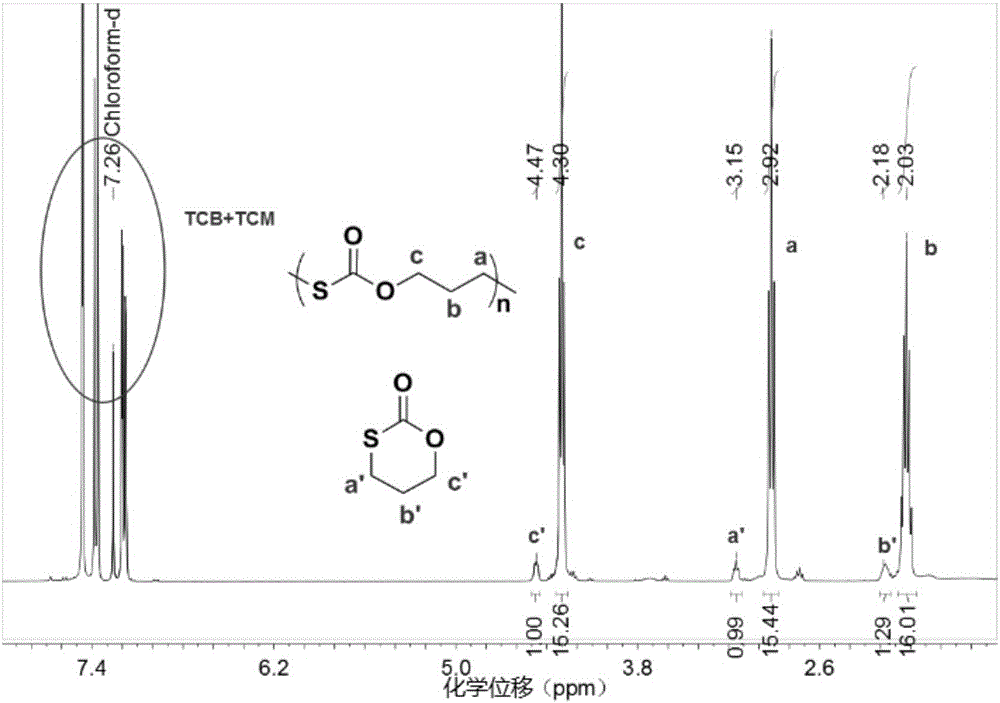
Poly(monothiocarbonic ester) containing crystals and preparation method of poly(monothiocarbonic ester)
The invention discloses poly(monothiocarbonic ester) containing crystals and a preparation method of poly(monothiocarbonic ester), and belongs to the field of polymer materials. The method includes the steps of adding carbon oxysulfide, oxetane, third monomer, chain transfer agent, catalyst and promoter into a dry high-pressure reaction still, conducting copolymerization reaction for 0.5-24 hours on a body or a solution under the self-generated pressure at a temperature of 0-150 DEG C, and conducting purifying and drying to obtain poly(monothiocarbonic ester) containing crystals. Prepared poly(monothiocarbonic ester) containing crystals contains sphero-crystal structures in the crystals and has the crystallinity of 13-85%, the crystallization temperature of 60-110 DEG C, the melting temperature of 100-135 DEG C and the melting enthalpy value of 4-90 J / g. By means of the method, oxygen-sulfur exchange reaction is completely restrained at high polymerization temperature, poly(monothiocarbonic ester) clear in structure and adjustable in crystallization property is obtained, and poly(monothiocarbonic ester) has a degradable thiocarbonic ester structure, can crystallize like high density polyethylene, has a wide processing window and has high strength and toughness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Medicine coating balloon, preparation method and medicine coating balloon dilatation catheter
InactiveCN111298272AAvoid the risk of microembolismStrong penetrating powerBalloon catheterMedical devicesBalloon dilatation catheterPharmacy medicine
The invention discloses a medicine coating balloon. The medicine coating balloon comprises a balloon body and a medicine coating covering the surface of the balloon body, wherein the medicine coatingis formed by spraying a medicine spraying solution to the surface of the balloon body; and the medicine spraying solution is obtained by dissolving medicine, a fat-soluble excipient and a hydrophilicexcipient in a solvent. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the medicine coating balloon and a medicine coating balloon dilatation catheter. According to the medicine coating balloon, the firmness of the medicine coating is higher, the granularity of the medicine is small, the medicine loss can be greatly reduced in the medicine balloon crossing and dilatation process, the tissue absorption rate is high, and the medicine utilization rate is increased.
Owner:KOSSEL MEDTECH SUZHOU
Polypropylene monofilament and tape fibers exhibiting certain creep-strain characteristics and corresponding crystalline configurations
InactiveUS20050019565A1High tensile strengthLow shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingYarnThermoplastic
Unique thermoplastic (polypropylene, specifically) monofilament and / or tape fibers and yarns that exhibit heretofore unattained physical properties are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the extrusion of thermoplastic resins that include a certain class of nucleating agent therein, and are able to be drawn at high ratios with such nucleating agents present, that the tenacity and modulus strength are much higher than other previously produced thermoplastic fibers (particularly those produced under commercial conditions), particularly those that also simultaneously exhibit extremely low shrinkage rates. Thus, such fibers require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target thermoplastic (for example, polypropylene), particularly after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target thermoplastic after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and allowing such an oriented polymer to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target thermoplastic without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the “rigidifying” nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for thermoplastic crystal growth. The preferred “rigidifying” compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as [2.2.1]heptane-bicyclodicarboxylic acid, otherwise known as HPN-68, sodium benzoate, talc, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts [such as sodium 2,2′-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11]. Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive thermoplastic fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Flame-retardant glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material for manufacturing coil frame and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a flame-retardant glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material for manufacturing a coil frame and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is mainly prepared from polypropylene, glass fiber, a fire retardant, a compatilizer, a nucleating agent, a dispersing agent and an antioxidant serving as raw materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) uniformly mixing the polypropylene, the fire retardant, the compatilizer, the nucleating agent, the dispersing agent and the antioxidant; and (2) performing melt extrusion on the mixed raw materials obtained by the step (1) and the glass fiber in a melt extruder and pelleting to obtain a product. The invention provides the flame-retardant glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material for manufacturing the coil frame and the preparation method thereof.
Owner:ANHUI KEJU NEW MATERIALS
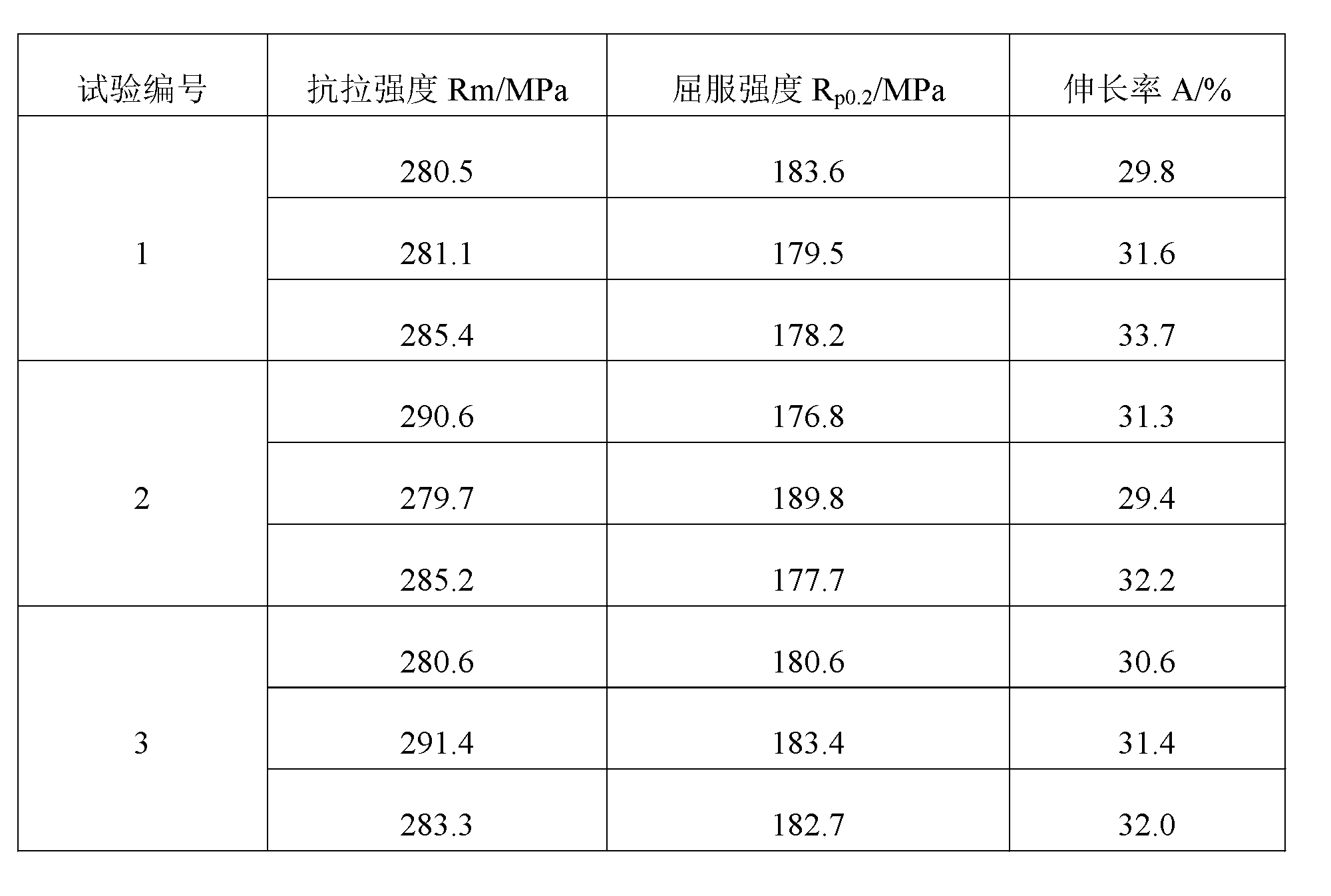
Rare earth magnesium-lithium alloy sheet and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a rare earth magnesium-lithium alloy sheet and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of metal processing. The rare earth magnesium-lithium alloy sheet is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 11-15% of Li, 0.5-2% of Y, 0.5-2% of Gd, 0.1-1% of Sc, 7-9% of Al and the balance of magnesium. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: melting magnesium and intermediate alloy by using an industrial medium-frequency or line-frequency induction melting furnace, adjusting the furnace temperature for heat preservation treatment, sampling from the furnace and carrying out rapid on-the-spot sample analysis after the heat preservation time is reached, and detecting whether the components are qualified; and hot rolling and cold rolling a pouring and rolling sheet, carrying out T6 treatment, then, making a mechanical sample, and measuring the mechanical property. By using the rare earth magnesium-lithium alloy sheet and the preparation method thereof, the strength of magnesium-lithium alloy is ensured, the plastic deformation capability of the magnesium-lithium alloy is also greatly enhanced, the production difficulty of the deformed magnesium-lithium alloy sheet is lowered, and the production efficiency is increased. The alloy smelting process is simple, convenient and reliable, convenient to operate and free of special processing process and alloy adding methods. A cast ingot is fine and uniform in tissue, free of meshy and thick sheet-like Mg17Al12 phase and uniform in precipitated phase. The rolling process is simple, convenient, reliable and feasible, and the sheet has favorable comprehensive mechanical property.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA 52 SPECIAL MATERIAL ENG TECH RES CENT
Method for preparing PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) engineering plastic particle of attapulgite fast crystallization
ActiveCN101899201ACrystallize fastReduce the impact of other performancePigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsPolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention relates to a method for preparing a PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) engineering plastic particle of attapulgite fast crystallization. The particle is applied to various industries such as aviation, trains, other traffic and transportation systems and the like. The method comprises the following technical steps of: (1) modifying the surface of attapulgite; (2) adding the modified attapulgite in the step (1) to ethylene glycol, stirring, dispersing, adding terephthalic acid, the modified attapulgite and the ethylene glycol dispersion liquid into an esterification kettle for esterification, adding ethylene glycol antimony as a catalyst, mixing, stirring, introducing the mixture into a polycondensation kettle, reacting and discharging to obtain an attapulgite / PET fast crystallization particle; and adding the attapulgite / PET fast crystallization particle into a twin-screw extruder, simultaneously drying and introducing glass fiber into the twin-screw extruder, cooling with water after extrusion, and granulating. The invention has simple technology and low additive addition quantity, a fast crystallization nucleating agent is evenly distributed over a polyester PET macromolecule by a copolymerization mode, and the product performance is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGYIN JIHUA NEW MATERIAL
Methods and apparatus for rapid crystallization of biomolecules
InactiveUS20060137603A1Crystallize fastQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProtein solutionIsoelectric point
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for promoting rapid formation of biomolecule crystals from a solution of biomolecules, preferably proteins, wherein the protein solution undergoes rapid concentration according to its isoelectric point in an electric field. Protein crystallization according to the methods of the present invention takes place within a period of hours or less.
Owner:BUKSHPAN SHMUEL
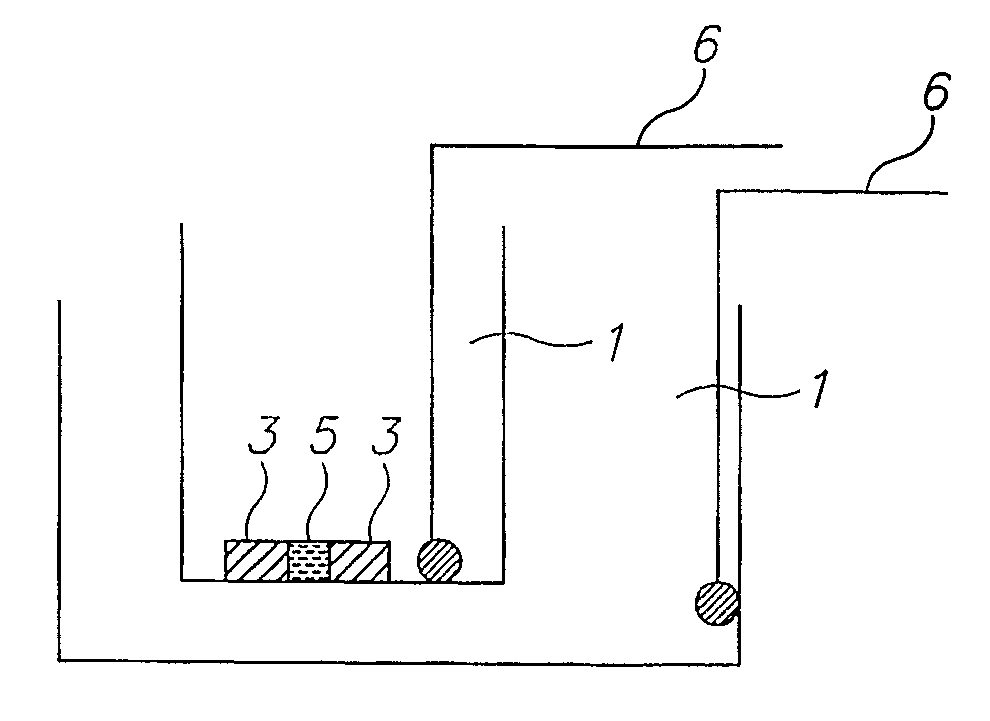
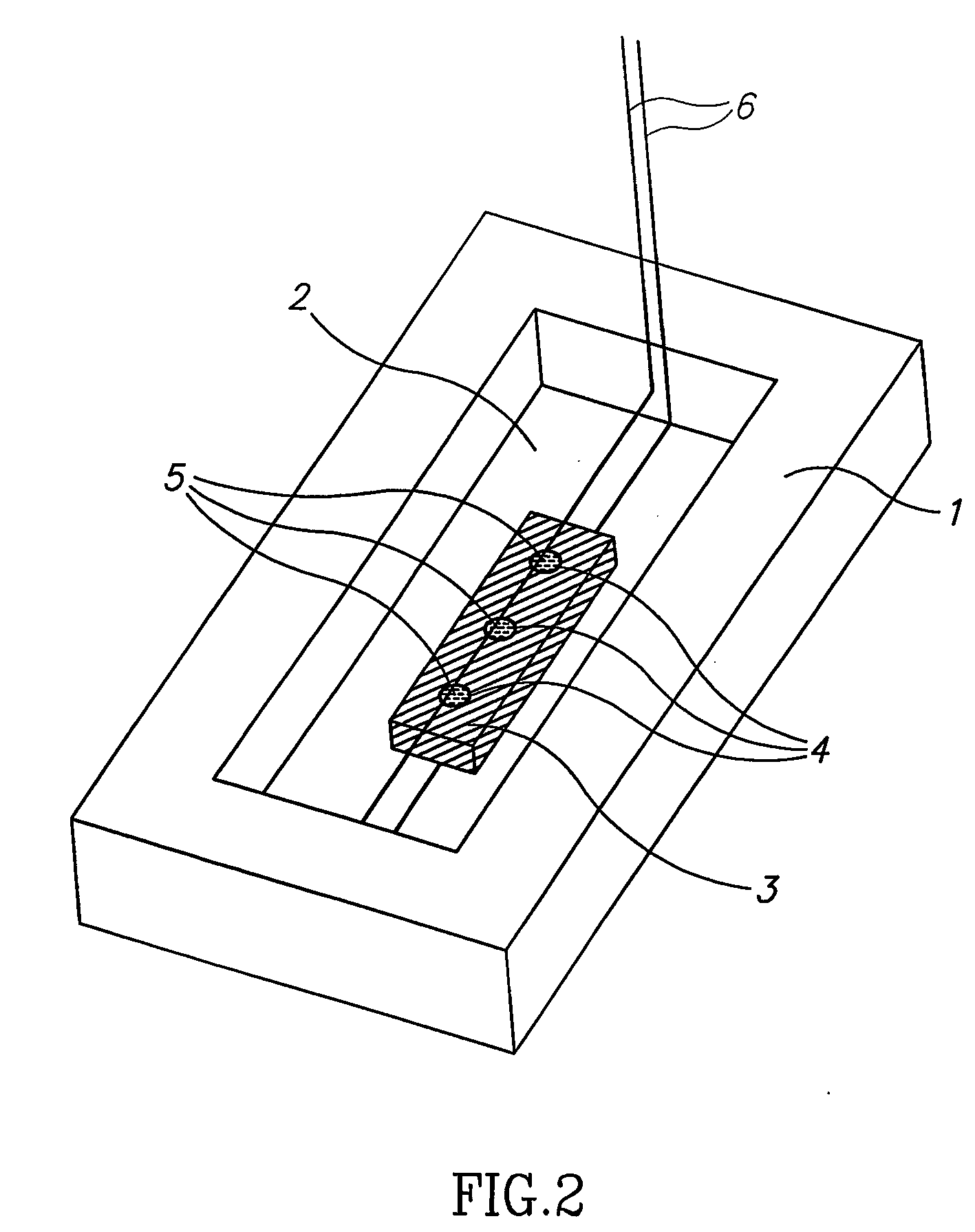
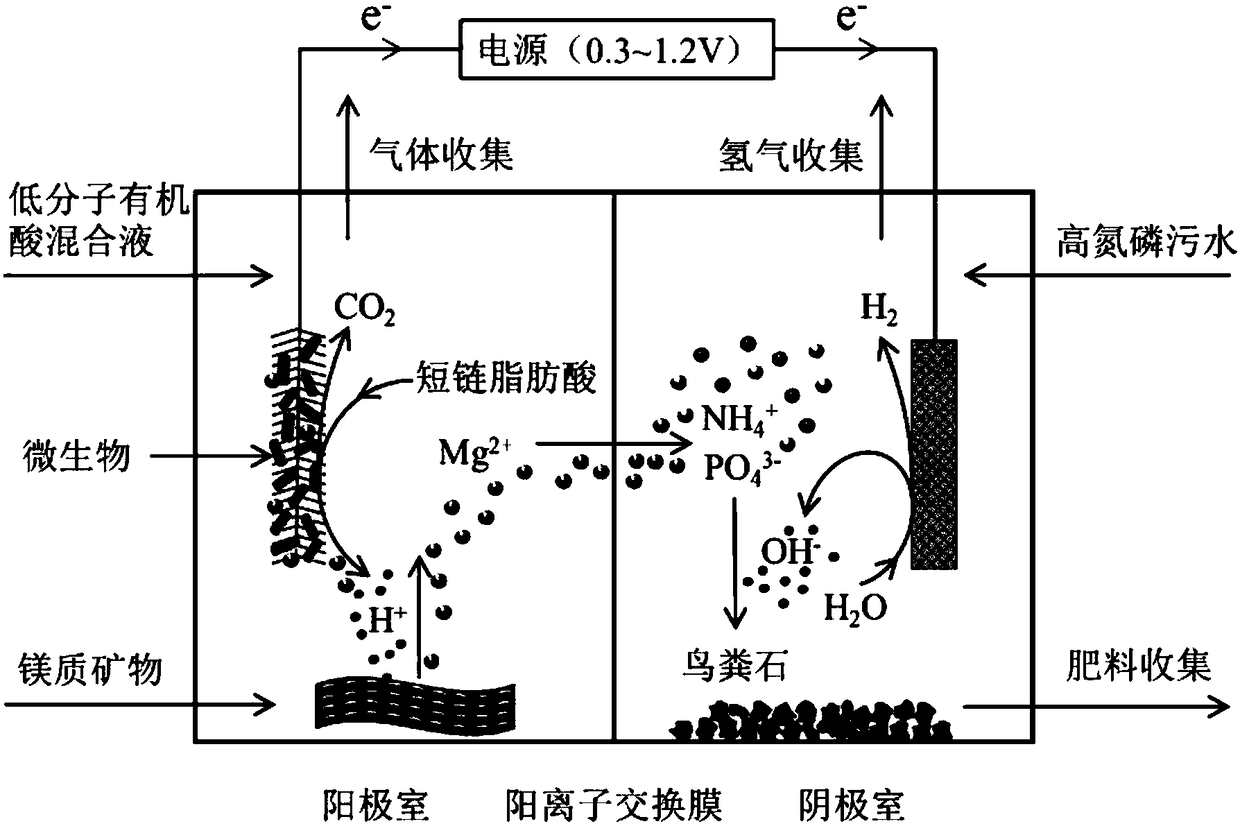
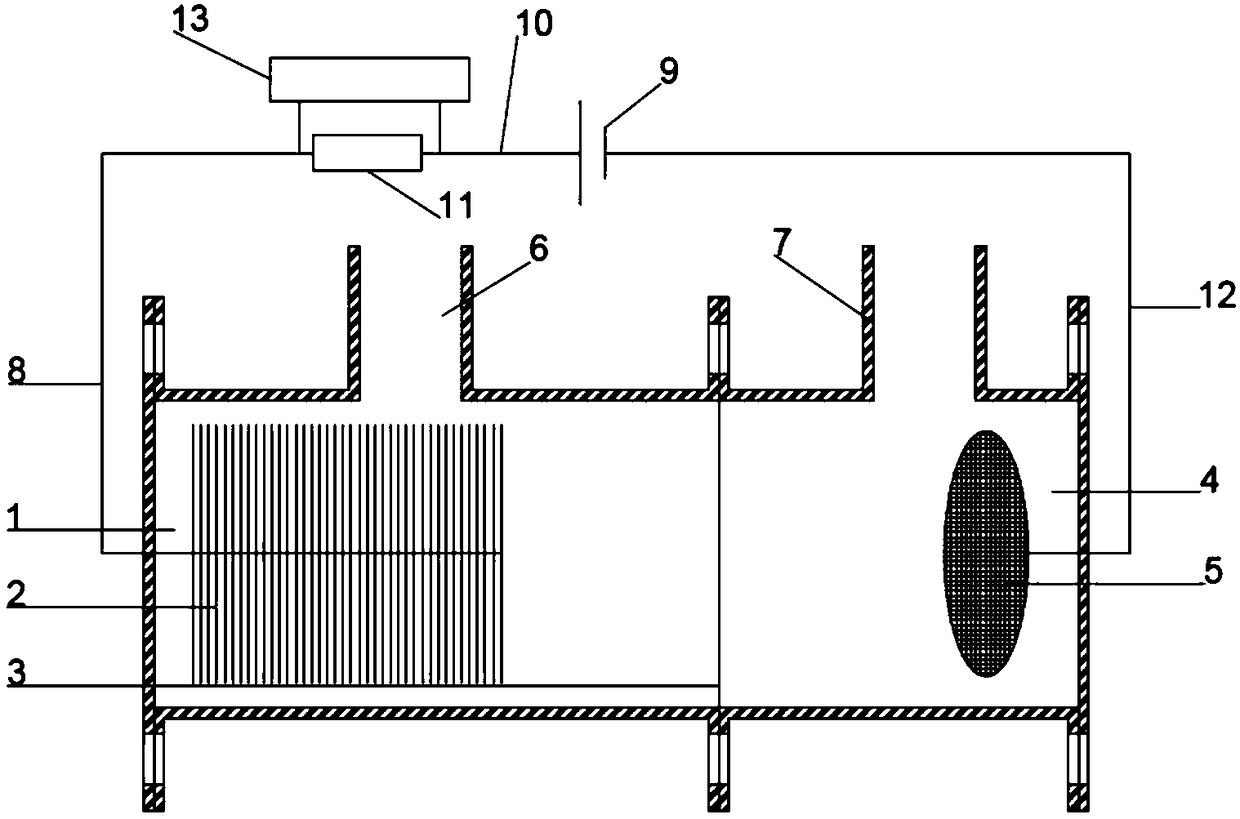
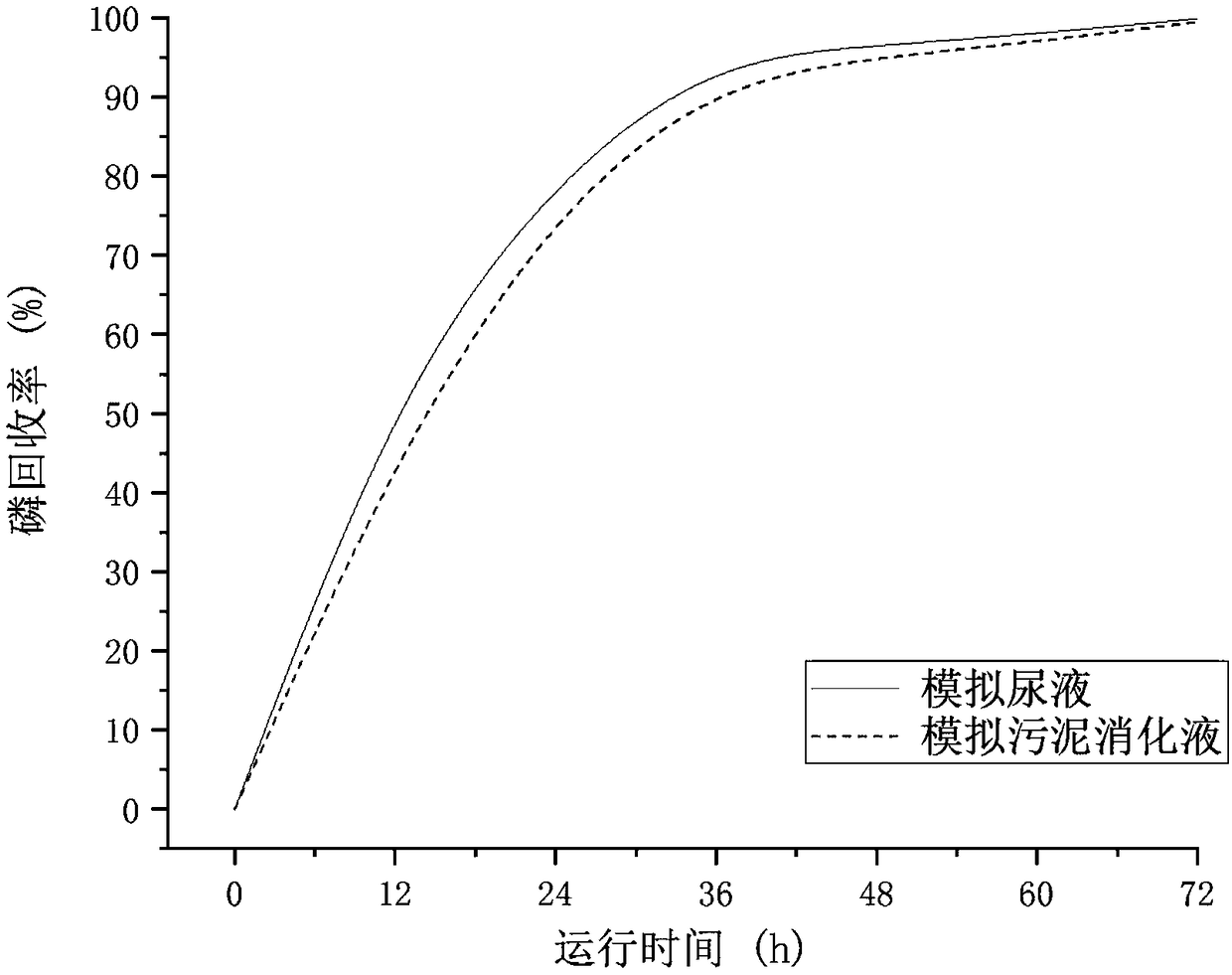
Method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization
ActiveCN108660475APromote acidolysisCrystallize fastCellsTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesOverpotentialMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for recycling phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization. The method aims to solve the problems that in existing recycling of phosphorus from sewage through bioelectrochemical struvite crystallization, an anode liquid is acidized, the overpotential is large, the magnesium source cost is high, and the like. Cheap magnesium ores are subjected to acidolysis in the anode liquid, acidification of the anode liquid is prevented, the overpotential is remarkably reduced, and the magnesium source cost is lowered. According to the method, based on a bichamber microbial electrolysis pool, under an extremely low externally applied voltage (0.3-1.2 V), an electrode reaction is performed to form conditions for acidification of the anode liquid and acidification of a cathode liquid; the crushed magnesium ores are added to an anode chamber, acidification of the anode liquid is prevented, the pH of the anode liquid is stabilized, and microorganisms are promoted to continuously degrade organic matter to generate power; and magnesium ions released through acidolysis of the magnesian cores move to an cathode through a cation exchange membrane under the drive of the electric filed force and has a crystallization reaction with ammonium radials and phosphate radicals under an alkaline condition, struvite deposits are formed, the pH of the cathode liquid is stabilized, and the purposes of removing and recycling the phosphorus from sewage are realized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cadmium-free silver filler containing lithium and niobium and production method thereof
ActiveCN101524793AImprove wettabilityGood spreadabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaNiobiumMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the field of welding material, in particular relating to a cadmium-free silver filler containing lithium and niobium and a production method thereof; the chemical composition of the cadmium-free silver filler is as follows according to mass percent: 35.0%-40.0% of Cu, 42.0%-52.0% of Zn, 4.0%-6.0% of Sn, 0.001%-0.1% of Li, 0.001%-0.1% of Nb, and the balancing of Ag. In the invention, Nb and Li are added in sequence, so that the purity of the tissue of the silver filler can be obviously improved, thus improving the wettability and spreadability of the silver filler. The invention has low silver content, excellent braze welding performance, no toxic cadmium in the welded parts during welding or after welding, can replace Bag35CuZnCd brazing filler and Bag25CuZn brazing filler, and is applicable to braze welding for metal materials such as copper, brass, carbon steel, stainless steel, and nickel base alloy, etc.
Owner:JINHUA SANHUAN WELDING MATERIALS
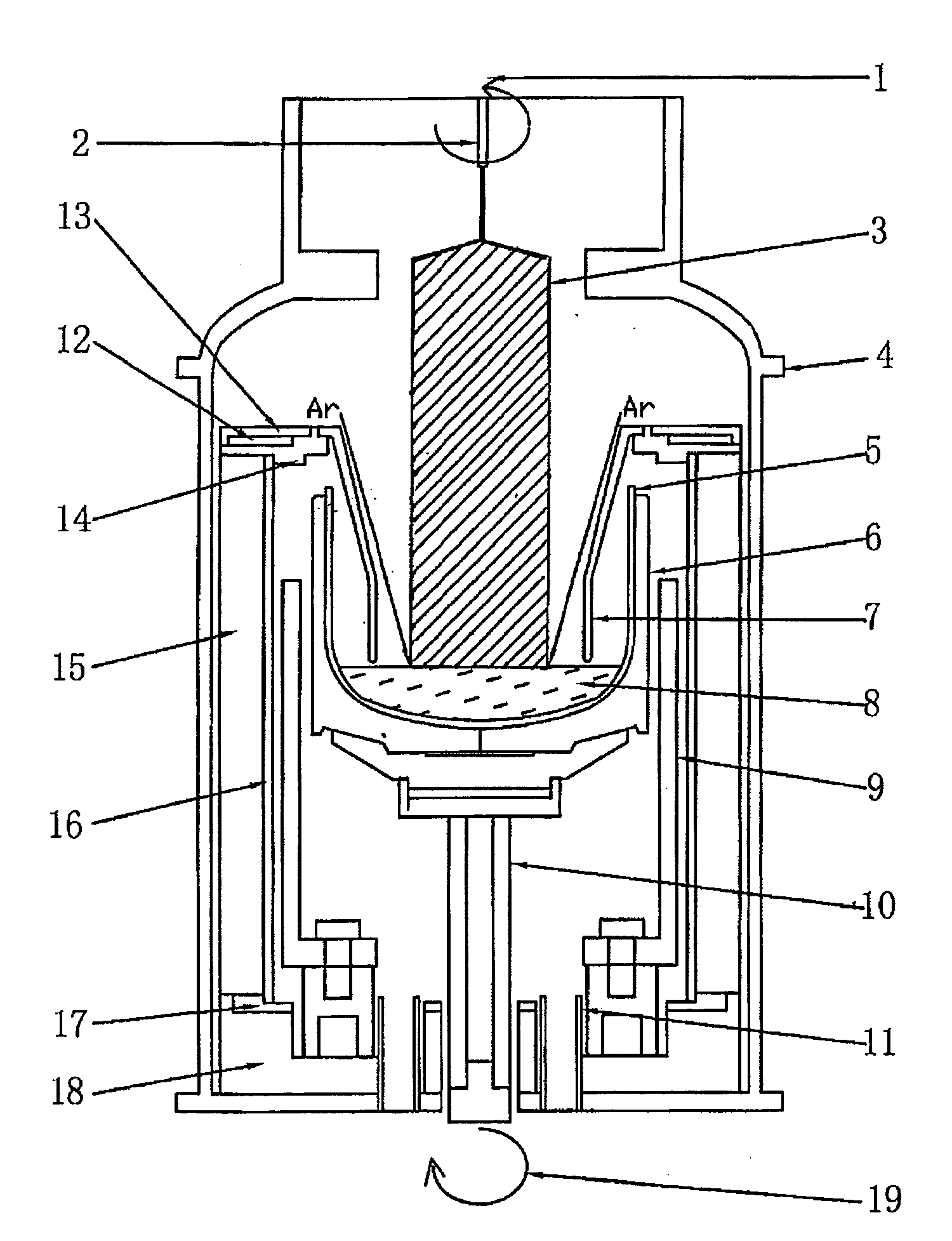
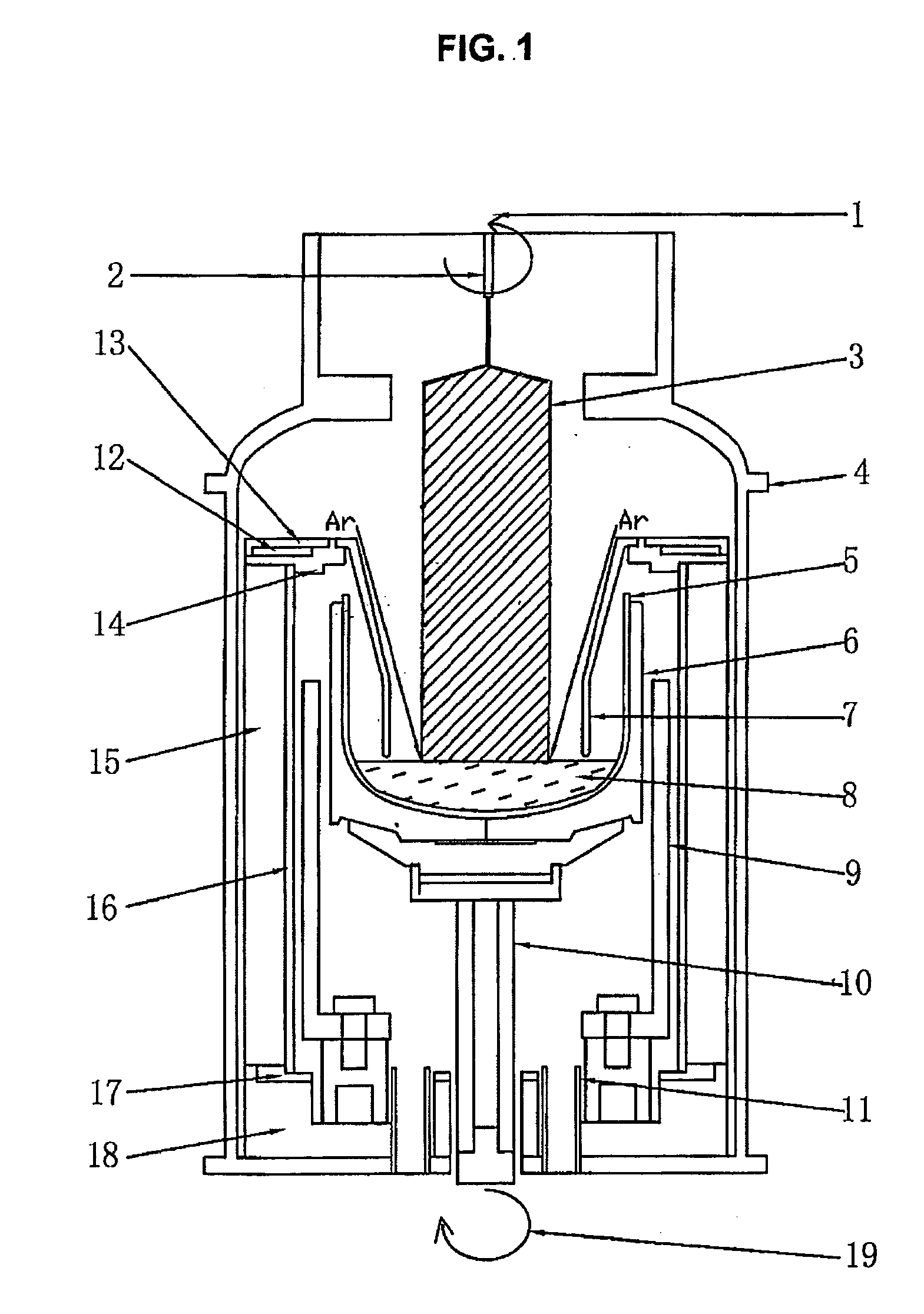
Device and process for growing ga-doped single silicon crystals suitable for making solar cells
InactiveUS20090072202A1Simple procedureLow production costPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltMetallurgySolar cell
A device and method for producing Ga doped silicone single crystal with a diameter between 150 and 165 mm and a narrow resistivity distribution range (from 3 Ω·cm to 0.5 Ω·cm). The device is characterized by the use of a shorter heater and a funnel shaped gas flow guide capable of blowing an inert gas such as Ar straight to the crystallization frontier at the interface between outer surface of the nascent single crystal ingot and the surface of the melt of polycrystalline silicone raw materials in a quartz crucible.
Owner:REN BING YAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com