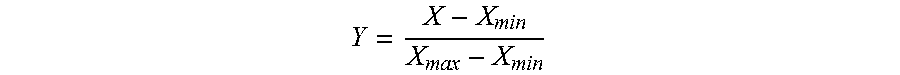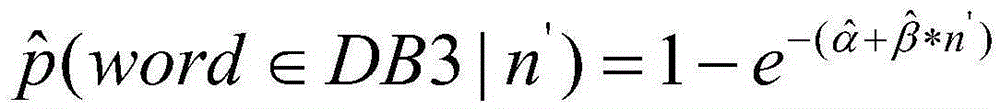Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
111 results about "Geographical feature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
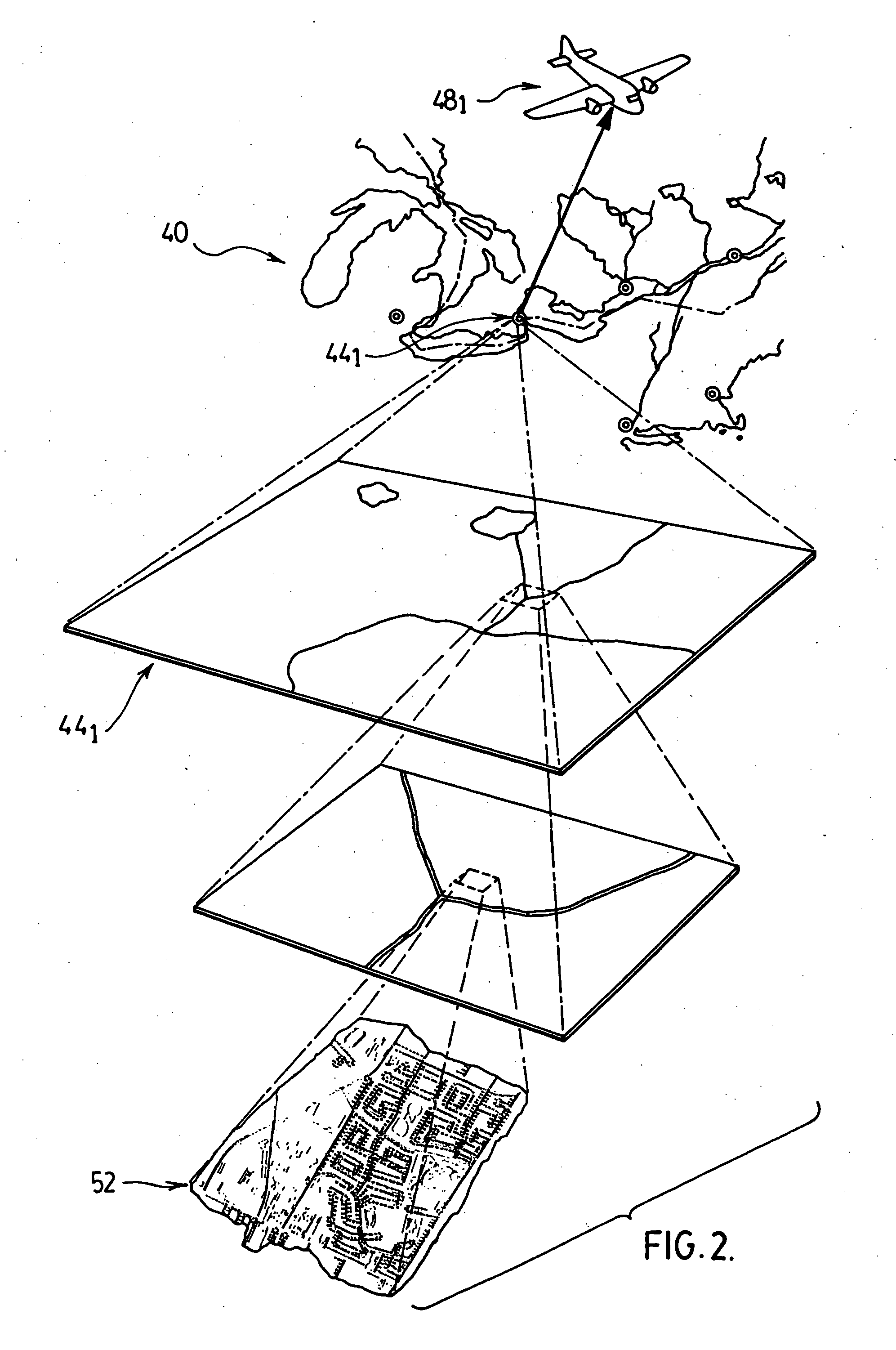
Geographical features are naturally-created features of the Earth. Natural geographical features consist of landforms and ecosystems. For example, terrain types, (physical factors of the environment) are natural geographical features. Conversely, human settlements or other engineered forms are considered types of artificial geographical features.
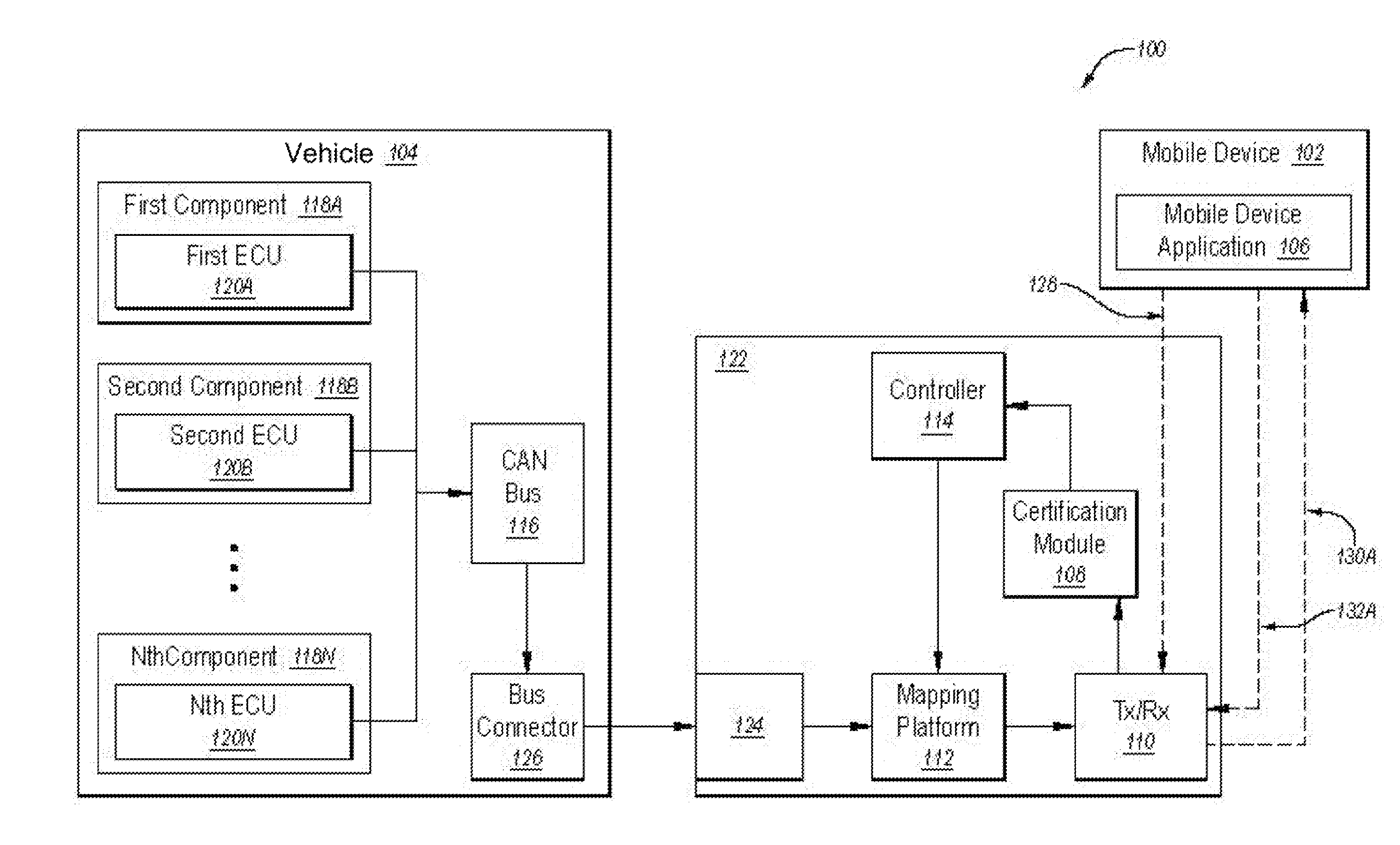
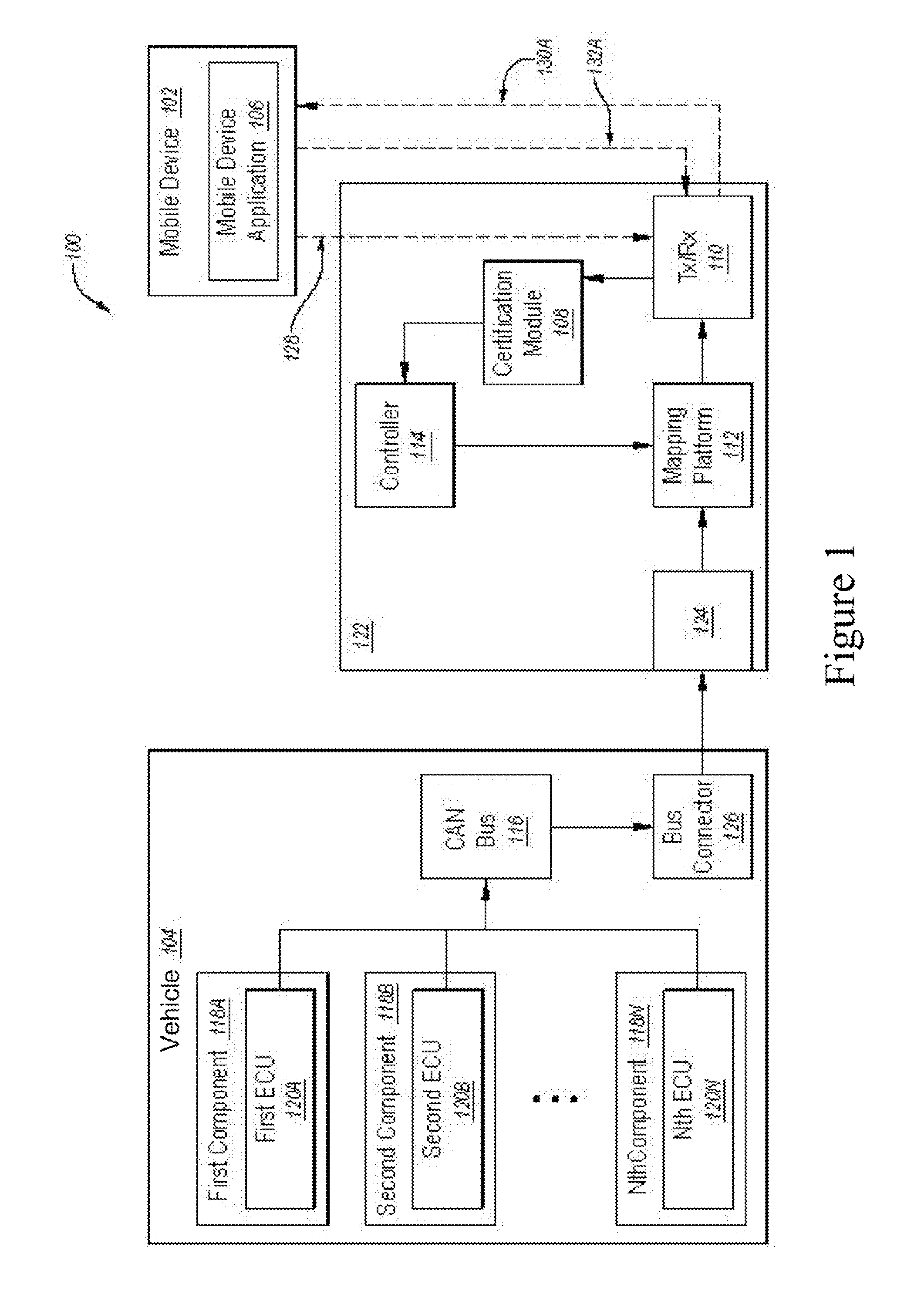
Charging system
InactiveUS20020049630A1Small data amountLow accuracyInstruments for road network navigationTicket-issuing apparatusGeographical featureEngineering
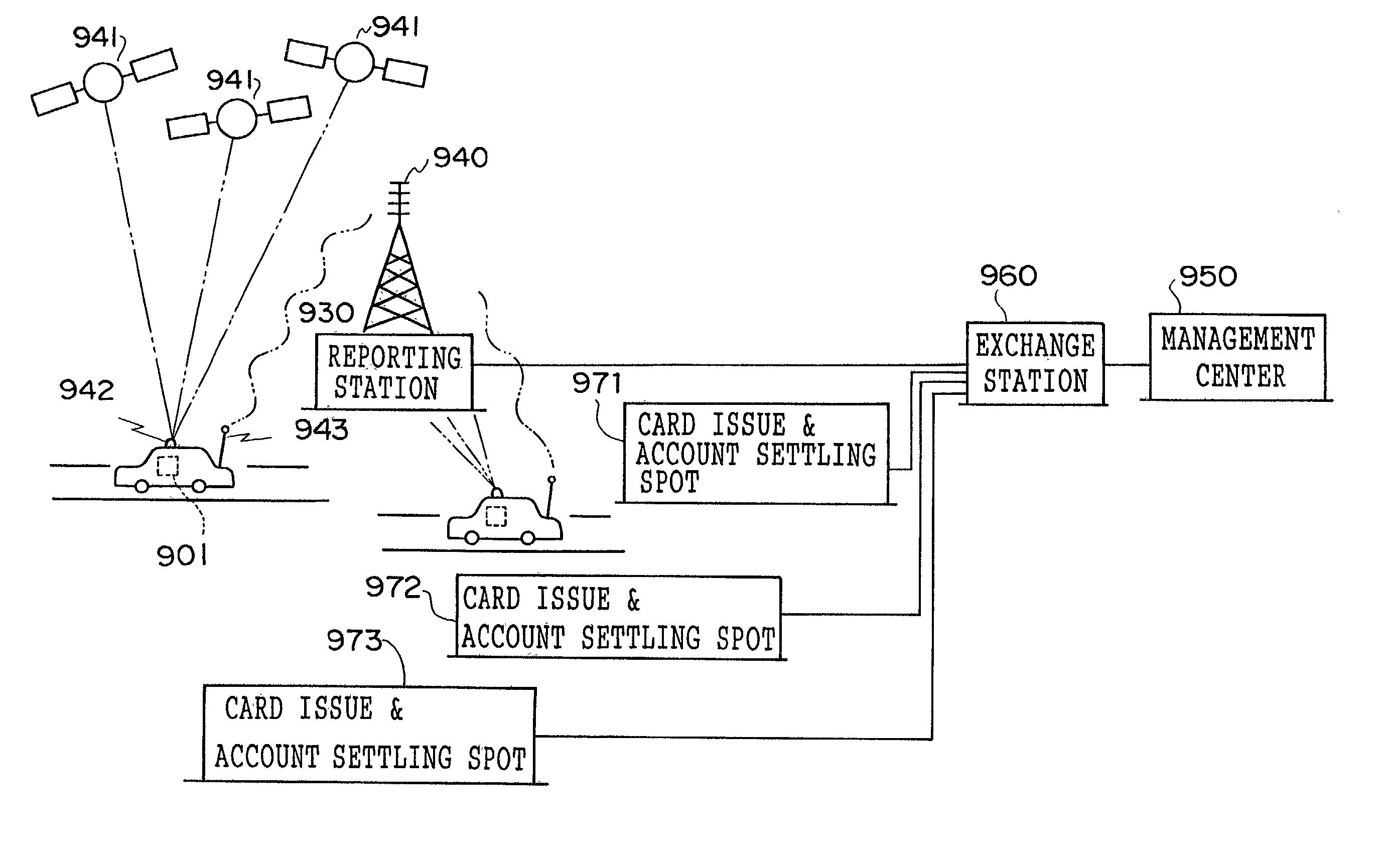
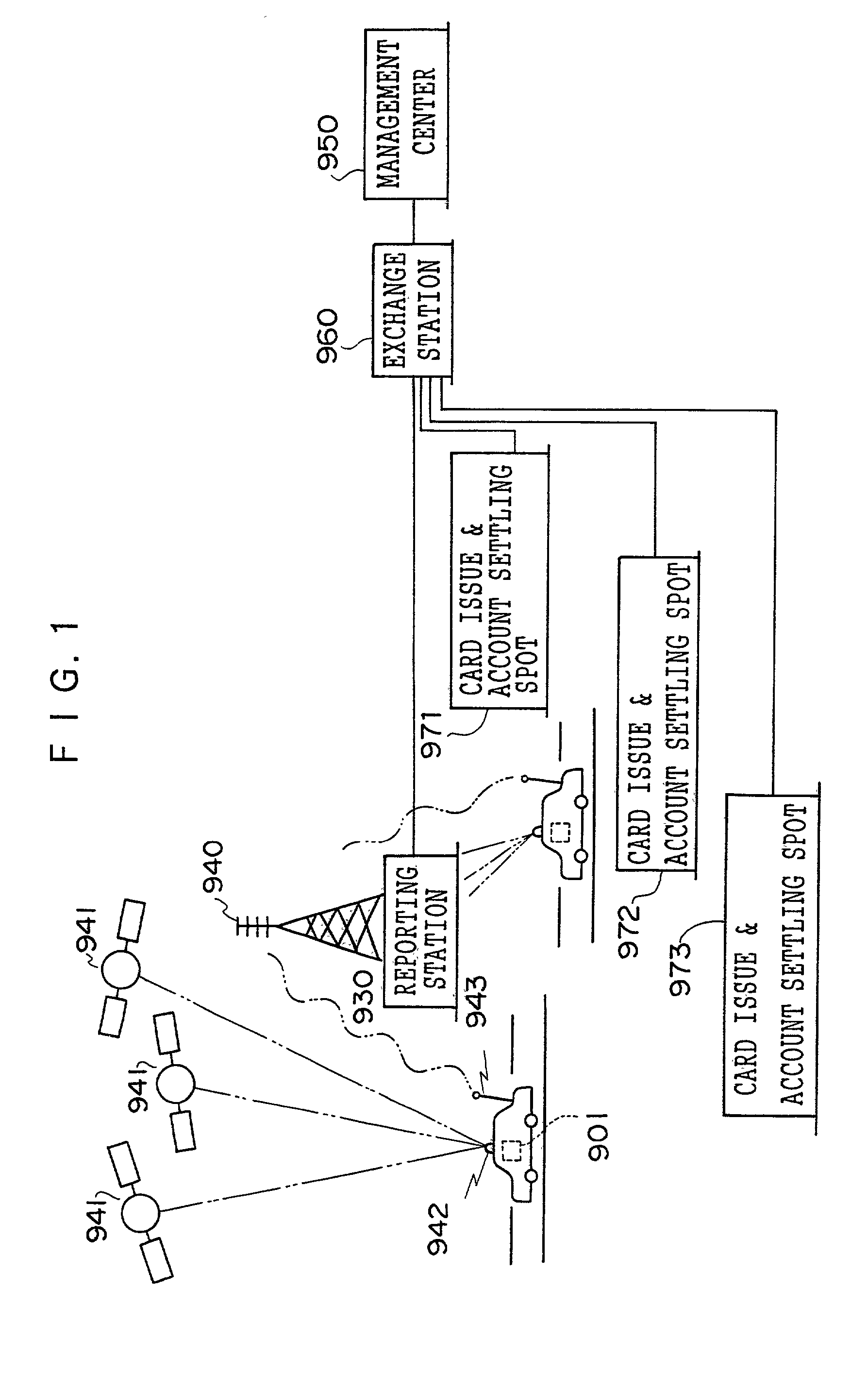
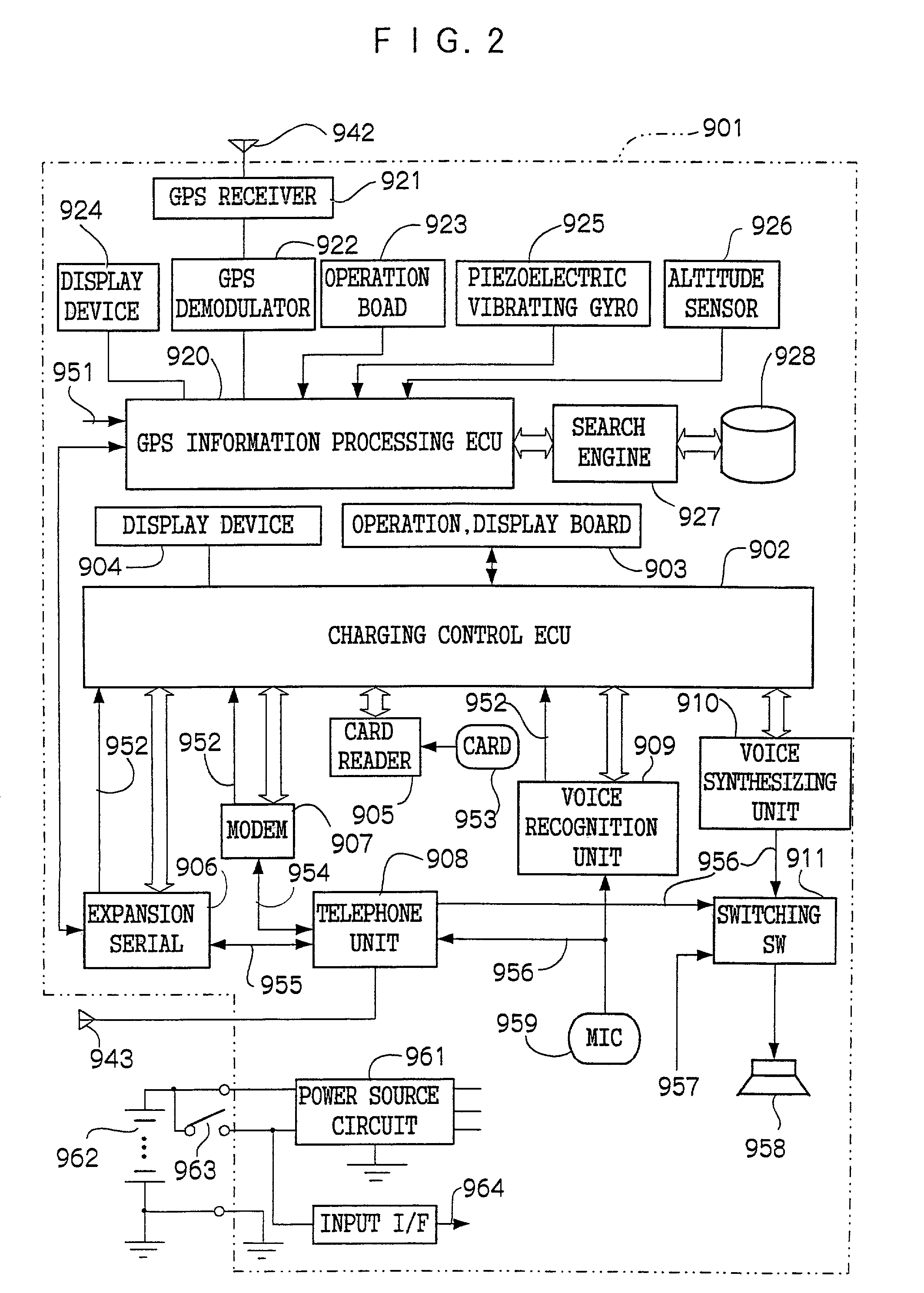
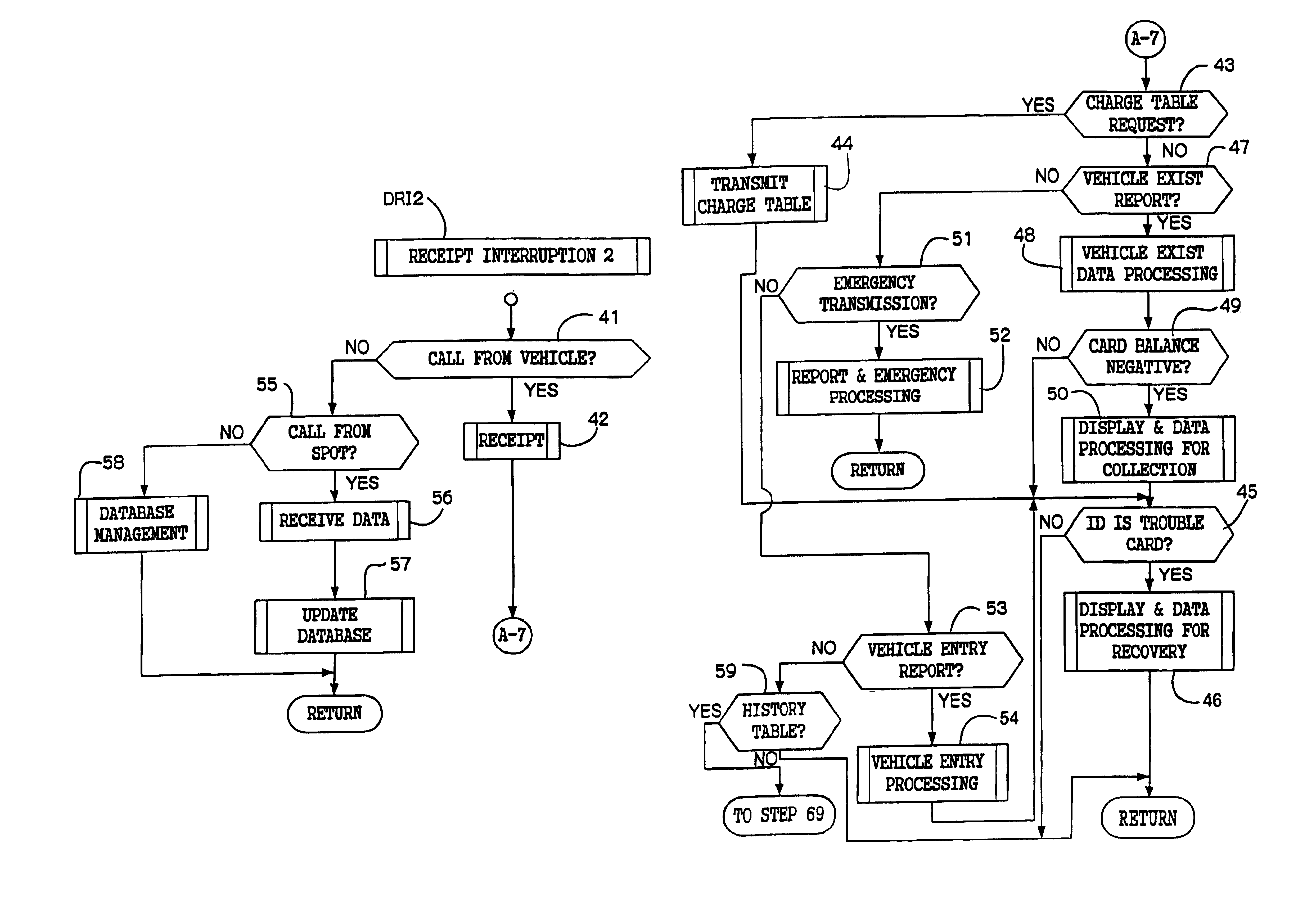
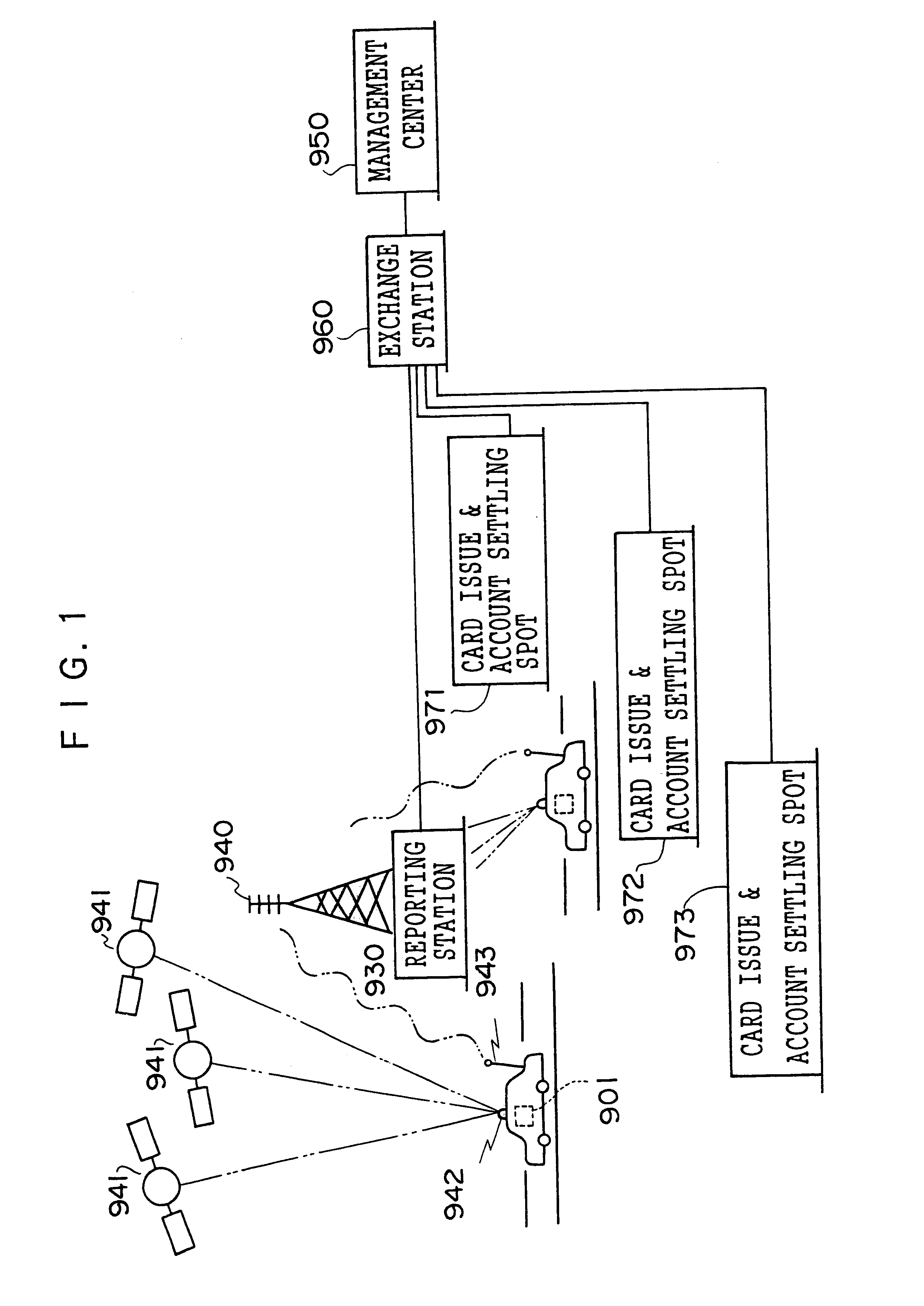
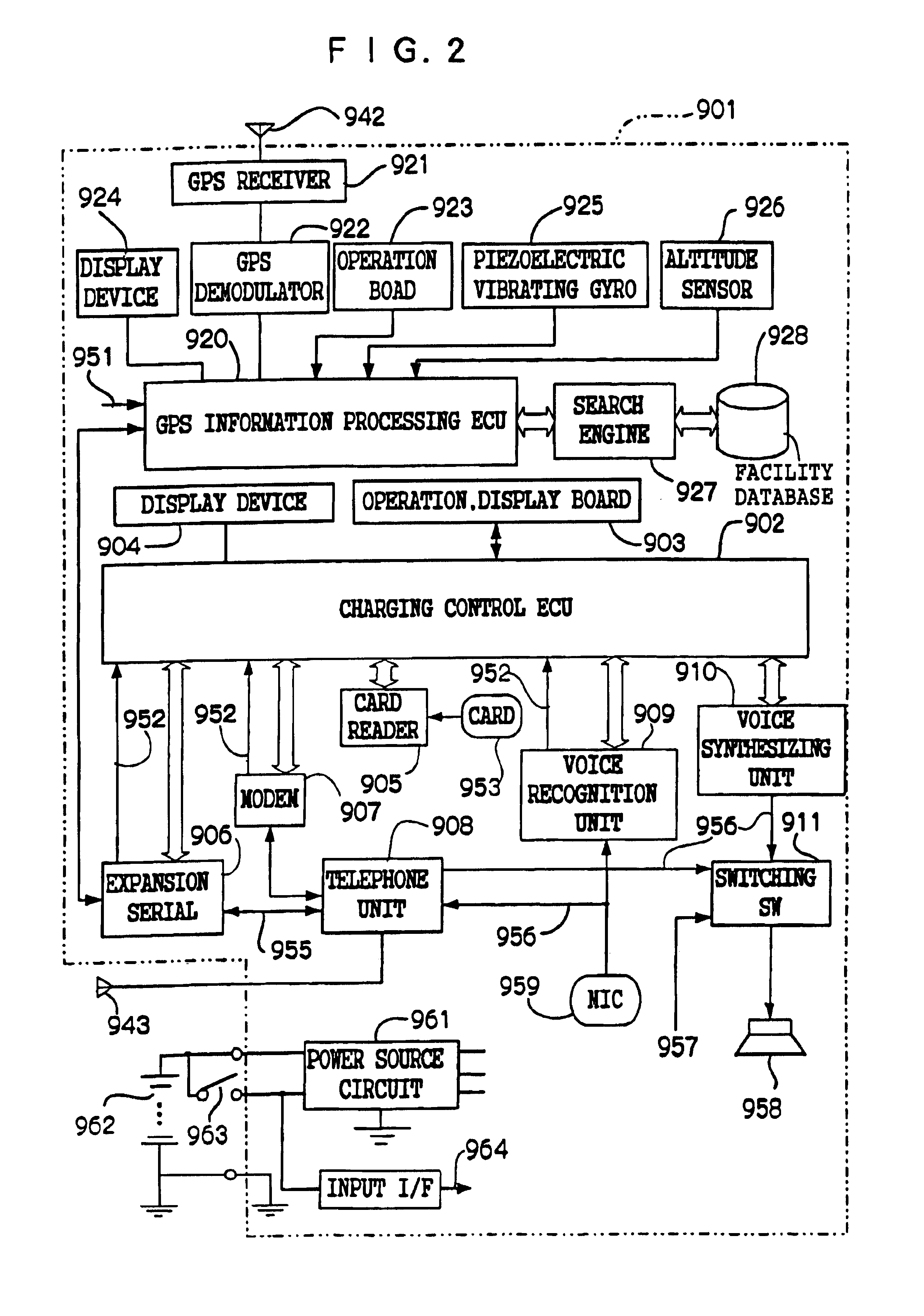
An object of the present invention is to provide a charging system which carries out position confirmation of a moving body at a place where there is a radio wave blocked facility, and which carries out automatic detection of GPS antenna blockage for avoiding charging. In a charging system including a GPS positioning device 921 for recognizing a vehicle position, a vehicle speed pulse measuring device 920 for dead reckoning navigating, a monitor device 920, 927, 928 which generates information expressing a current position by using these, and a charging processing 902 which judges whether or not a recognized current position is within a charge area and which carries out data processing for charging, the monitor 920 includes a simple map database 928 which includes positions of facilities or geographical features at which GPS positioning is impossible, and when GPS positioning is impossible, the facility or geographical feature corresponding to the current position is detected, and that position is made to be a current position.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Efficient pre-computing of simplified vector data for rendering at multiple zoom levels
InactiveUS20120206469A1Reduce in quantitySimplify workInstruments for road network navigationGeometric image transformationGeographical featureComputer graphics (images)
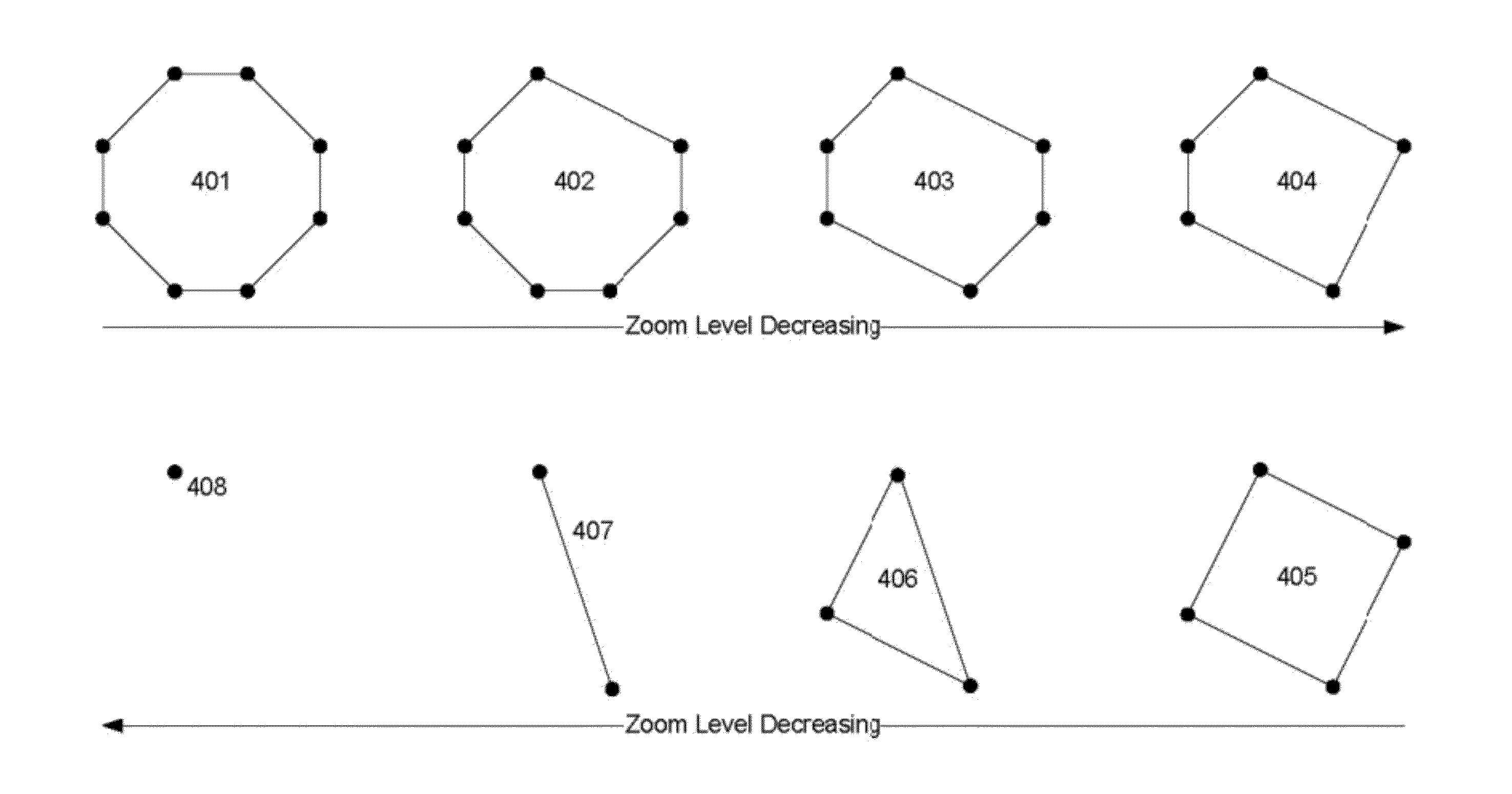
Aspects of the invention relate generally to accessing, storing, and processing vector data to represent various geographical features such as roads, rivers, lakes, countries, continents, and oceans on one or more maps. More specifically, the vector data may be pre-simplified for rendering at different zoom levels. The simplification process is based on removing vertices from vector data in order to reduce the number of points in a given polygon or line. As this process is very expensive in terms of time and processing power, the system and method allow for estimation of the proportion of vertices which that would be removed from the original geometry. Based on this estimation, one may decide whether or not the simplification is worth the effort to compute and store the simplified data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
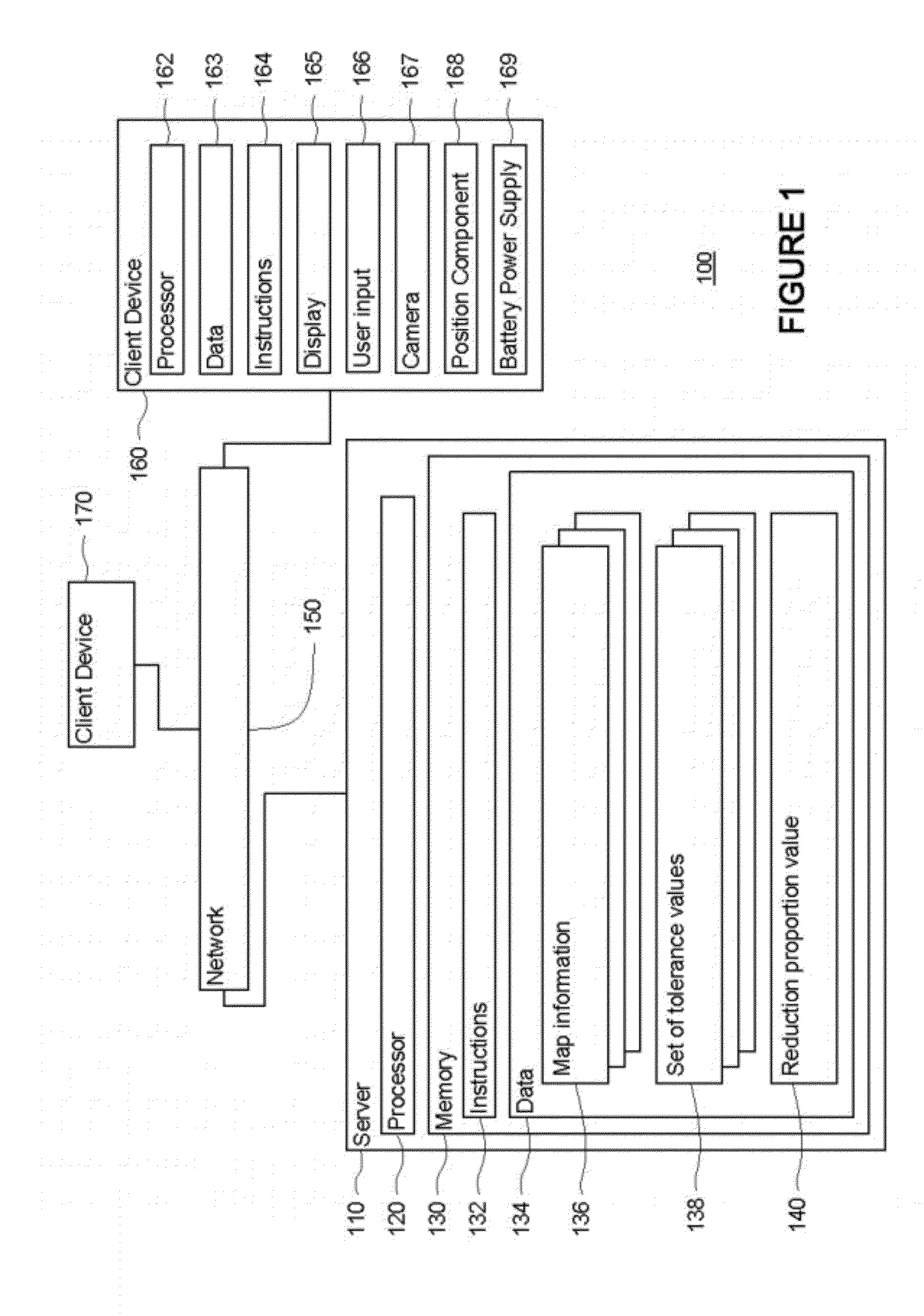
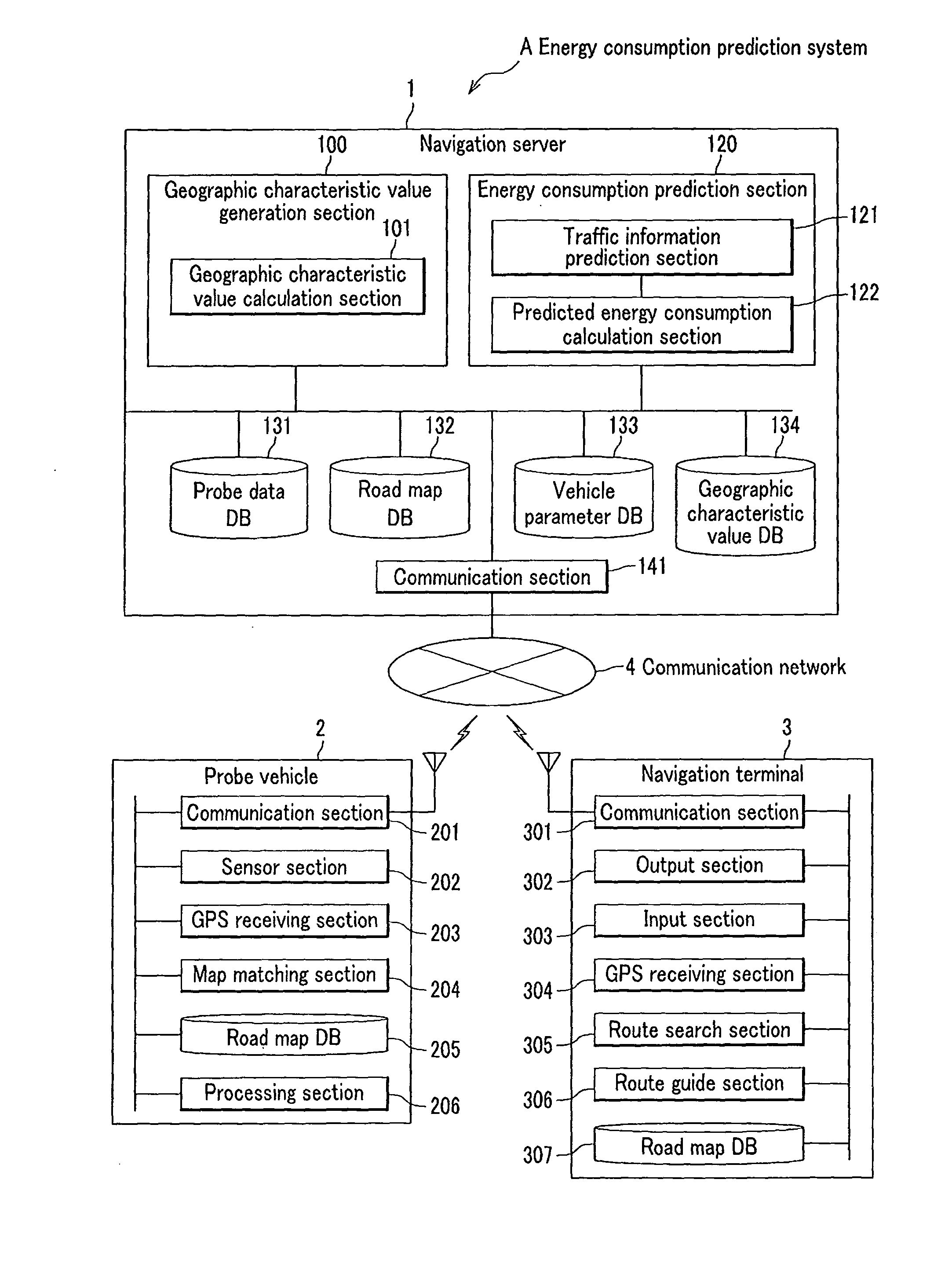
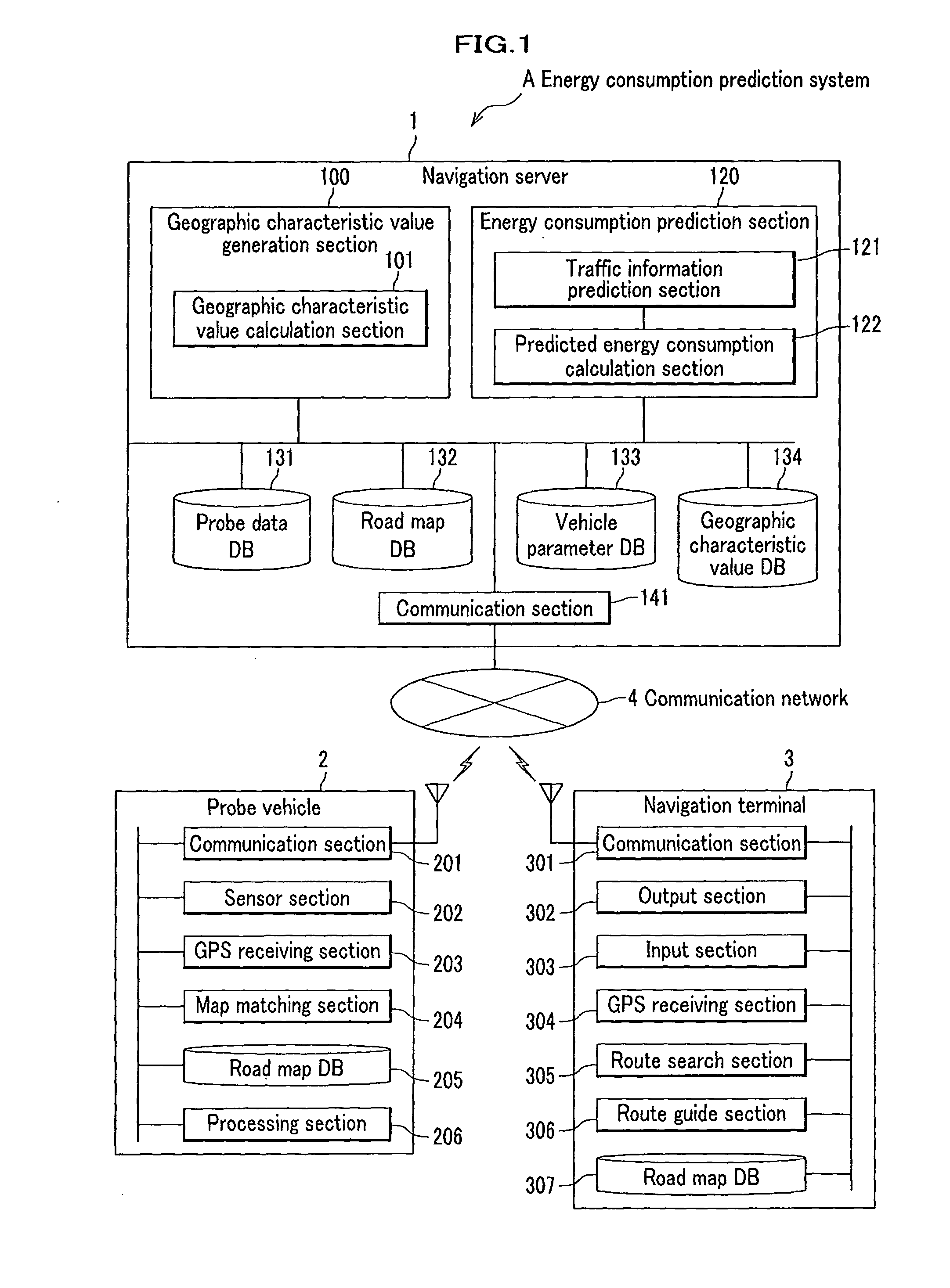
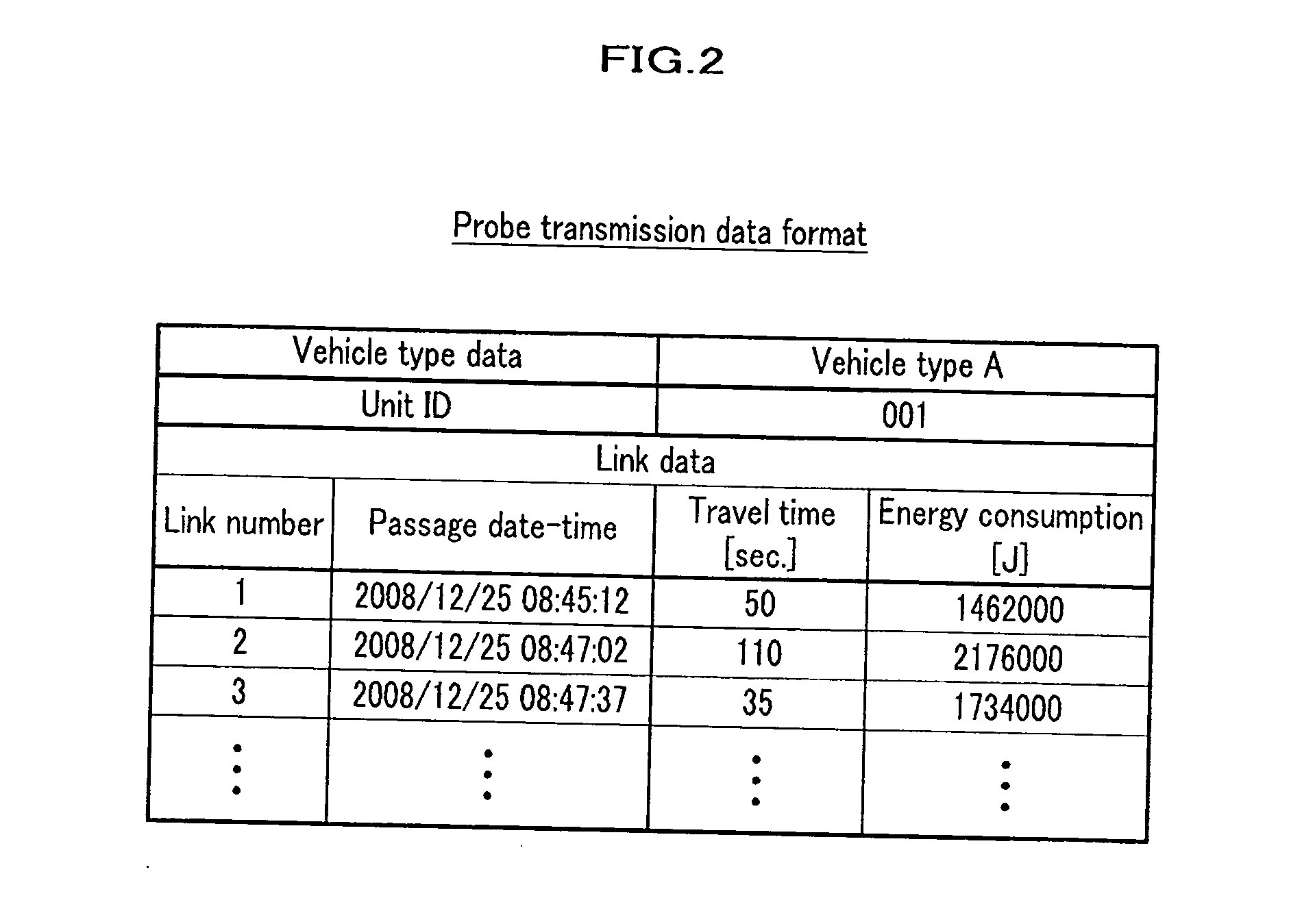
Method of predicting energy consumption, apparatus for predicting energy consumption, and terminal apparatus
ActiveUS20110060495A1Low accuracyDegrades accuracy of predictionVehicle testingInstruments for road network navigationGeographical featureTerminal equipment
An object of the invention is to predict energy consumptions of a vehicle, using geographic characteristic values which are independent from particular driving patterns and vehicle parameters and unique to respective links. A navigation server predicts energies which are consumed when a vehicle runs on links. The navigation server calculates geographic characteristic values of respective links, the geography of the each link affecting the consumption energy with the geographic characteristic values, the calculation being based on energy consumptions collected from probe vehicles, and calculates predicted energy consumption of each link selected as a processing target, based on the geographic characteristic values. A navigation terminal obtains these predicted energy consumptions and performs route search with the obtained predicted energy consumptions as costs.
Owner:CLARION CO LTD
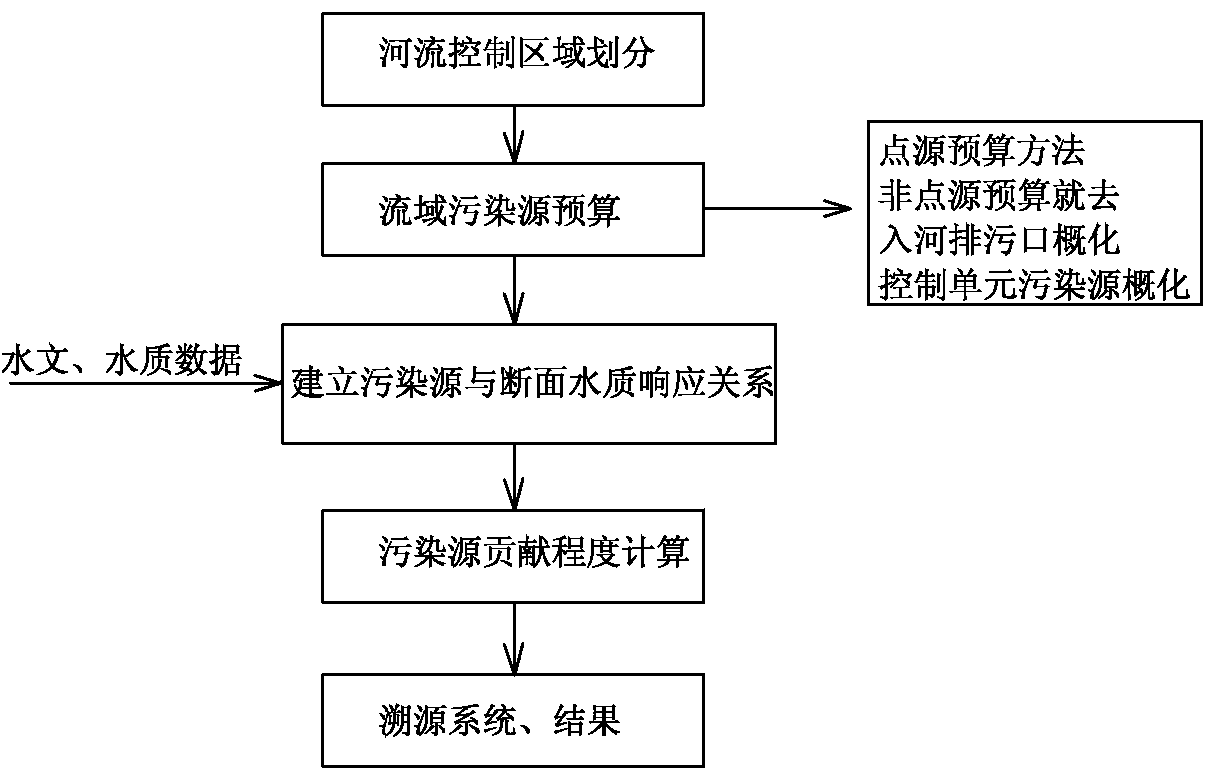
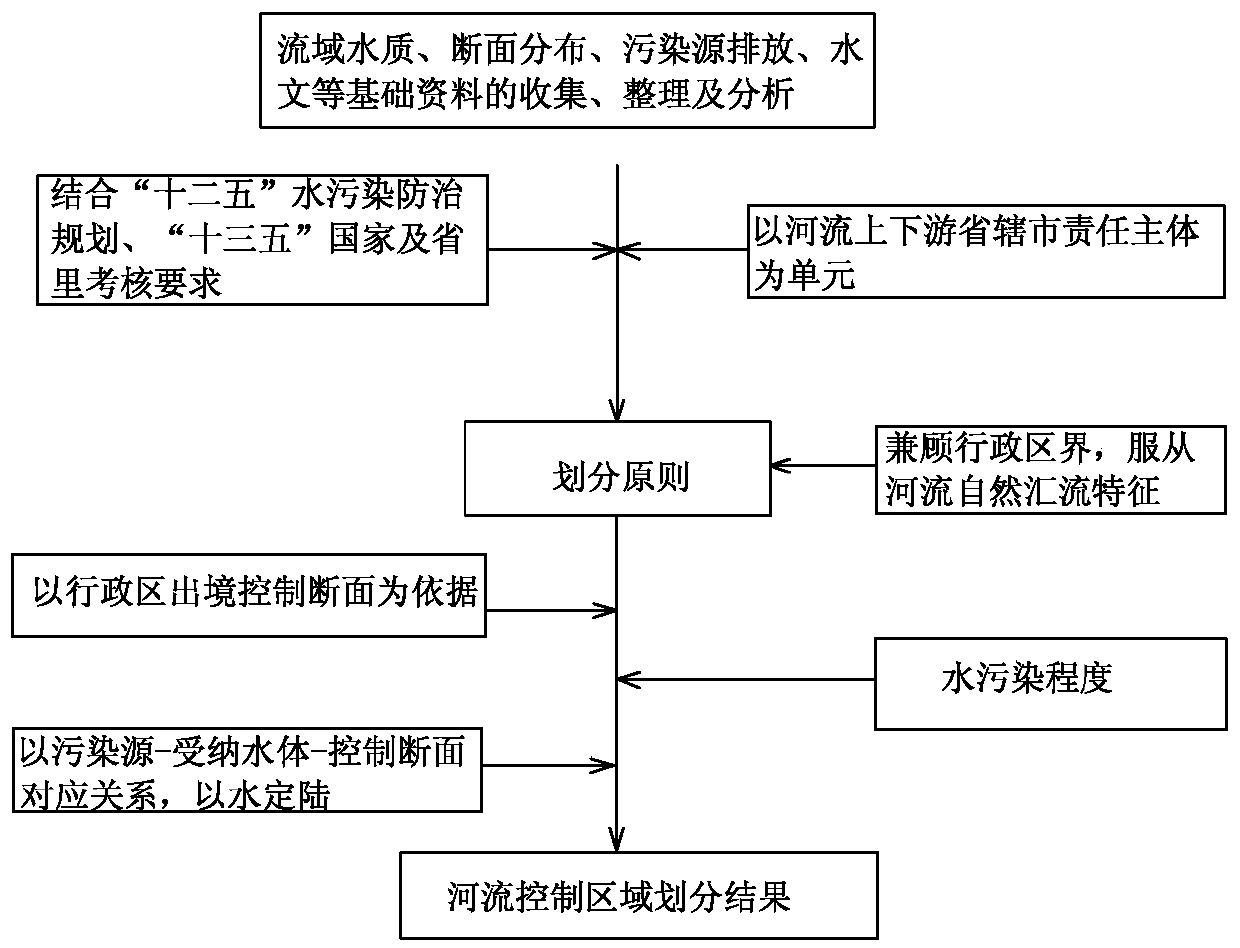
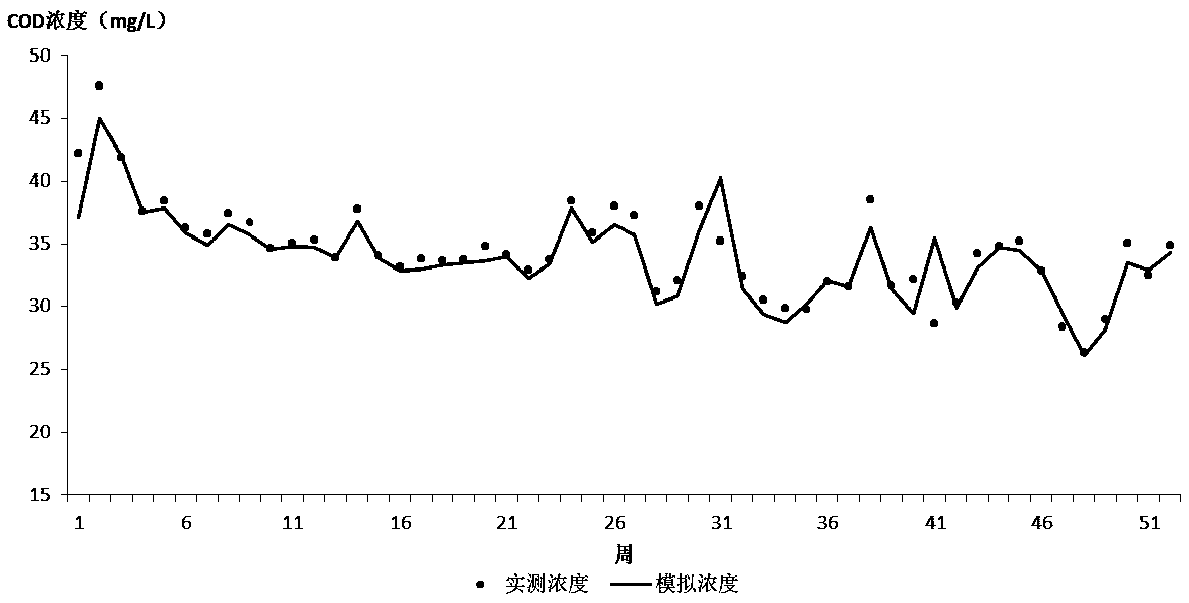
Method for calculating tracing contribution of sudden accidental water pollution source at a point source
InactiveCN107563139AEffective protectionEfficient governanceGeneral water supply conservationSpecial data processing applicationsWater qualityFluvial
The invention relates to a method for calculating the tracing contribution of a sudden accidental water pollution source at a point source, which is effective in rapid tracing of a river basin and environmental management and protection of the river basin. The method includes: according to the natural geographical features of the river basin, determining the control area corresponding to the control section of the river basin; using the monitoring data of the pollution source and the statistical data of the pollution source to budget regarding the pollution source in the river basin; using a one-dimensional unsteady water quality model to establish the relationship between pollution source and water quality of the section; using the relationship between pollution source and water quality of the section to calculate the contribution coefficient of the pollution source within the river basin and characterizing the contribution of pollution sources. The method is novel and unique, easy tooperate and use, accurate in calculation, and high in efficiency, makes full use of the basic information of the existing pollution source, quickly feeds back the state of the pollution source in theriver control section in a short time, locks the pollution source which has relatively greater contribution to the river water quality in the river basin, provides the support for the pollution tracing of the river basin, and is effectively used for the environmental protection and treatment of the river.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
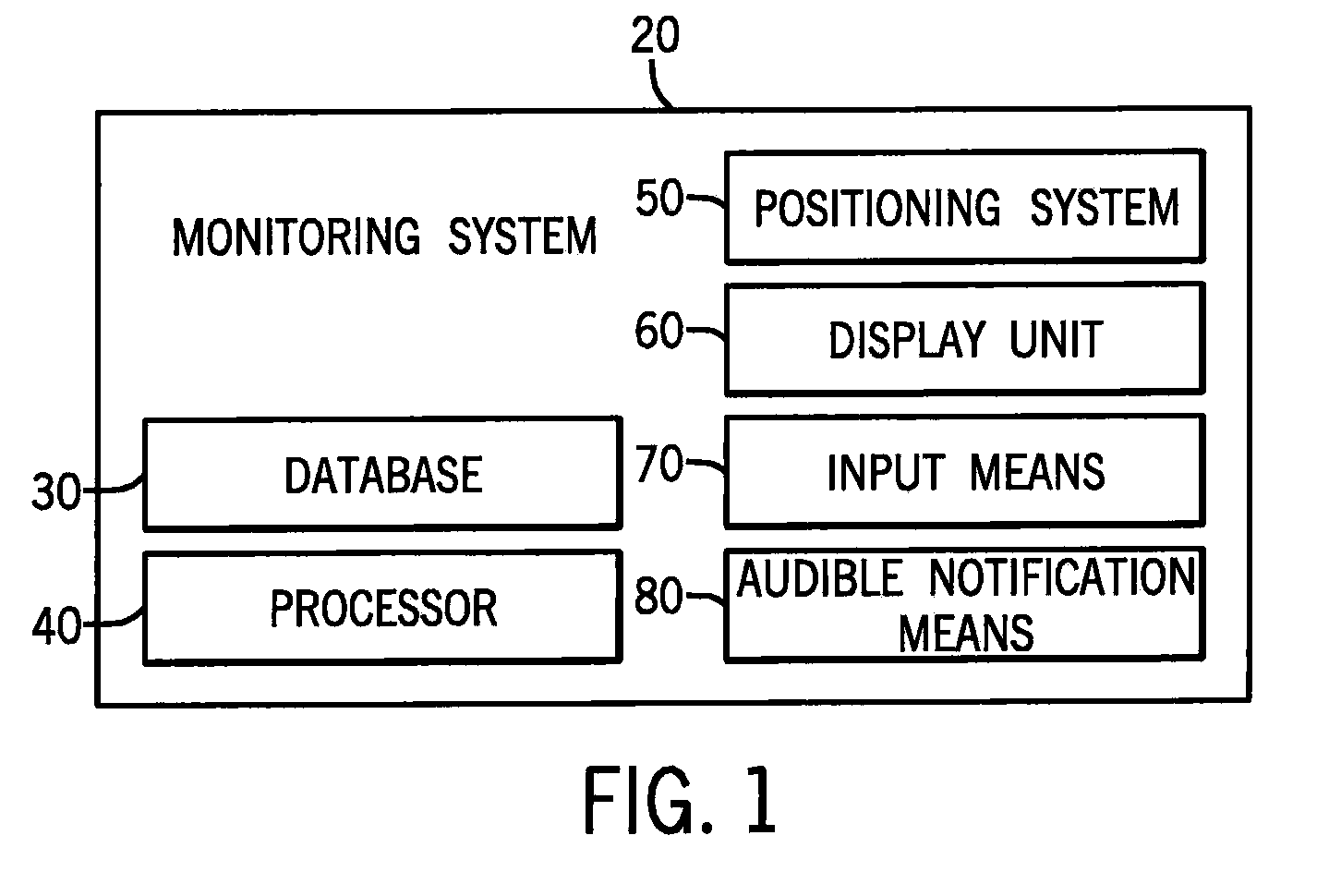
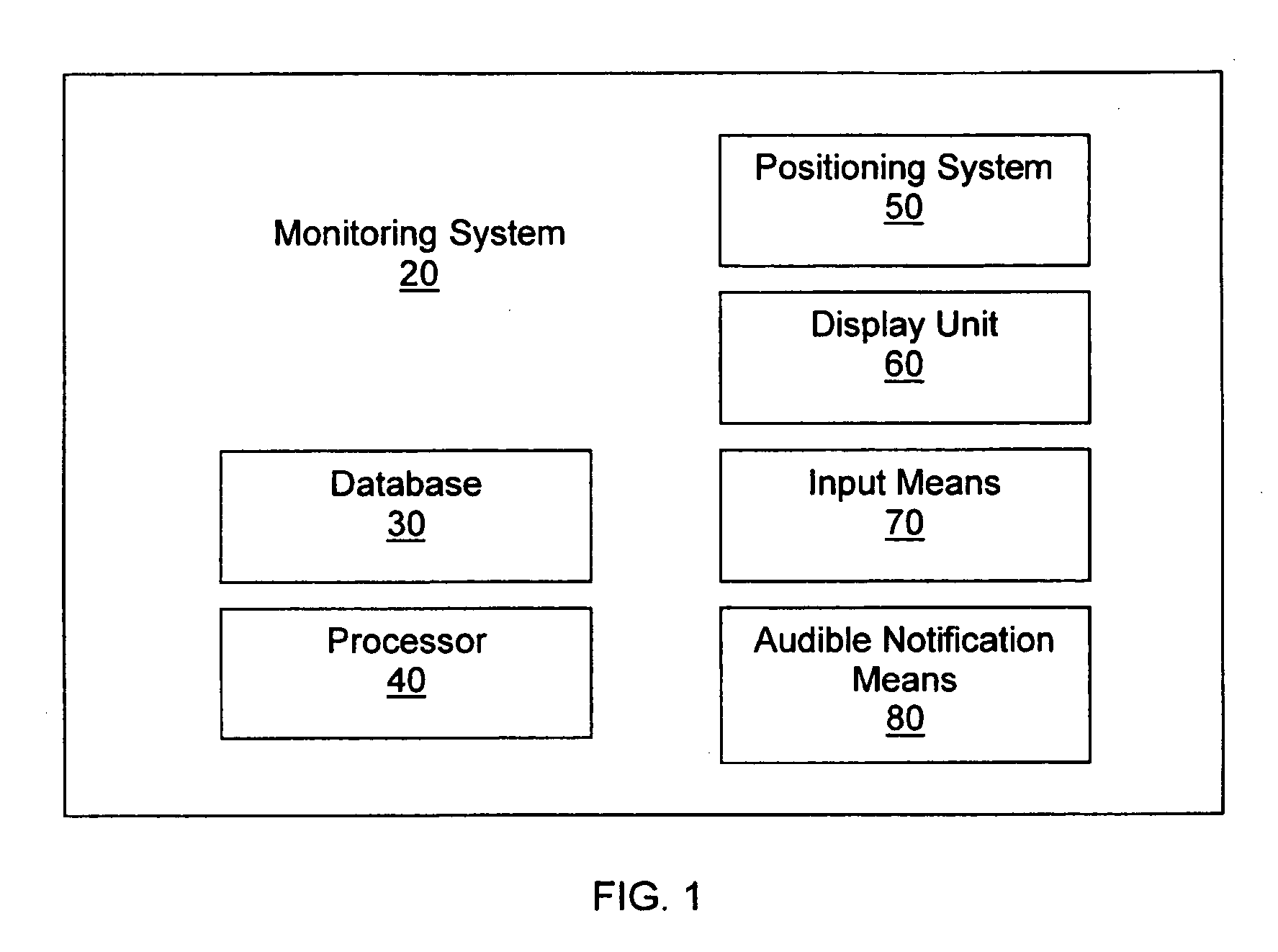
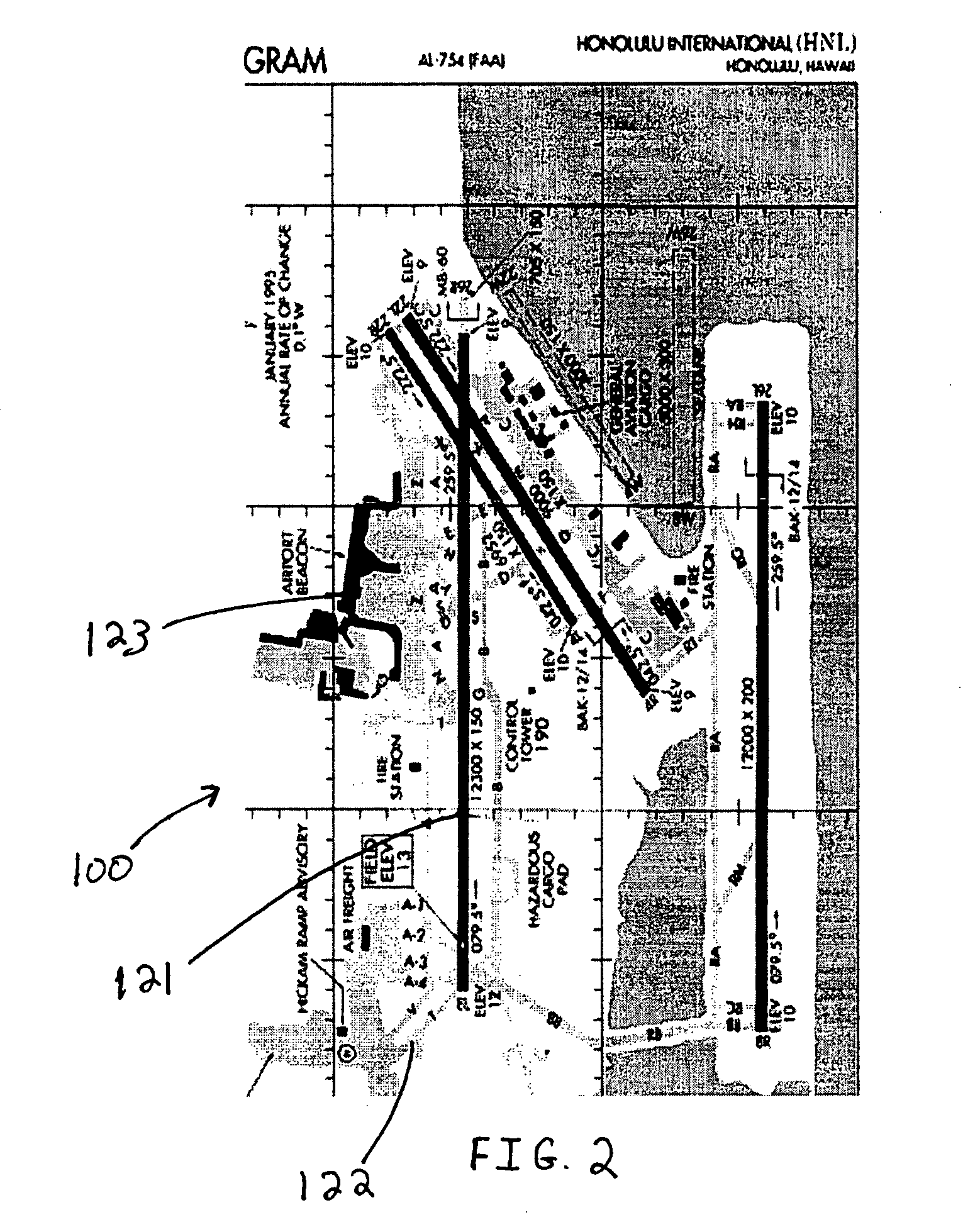
Aircraft-centered ground maneuvering monitoring and alerting system
A monitoring system for alerting operators of aircraft or other vehicles when they are approaching a geographical feature of interest, such as a runway, taxiway or other aircraft. The system includes a database having at least one geo-referenced chart, a processor, a positioning system configured to identify a number of aircraft or other vehicle operational parameters and transmit that data to the processor, and a display unit configured to display the present position of the aircraft on the geo-referenced chart. After receiving the operational parameters, the processor identifies a virtual containment zone centered about the aircraft or vehicle. The processor further monitors the position of the aircraft or other vehicle relative to any geographical features of interest and determines whether at least a portion of a geographical feature is located within the containment area. If such a condition is detected, a notification is generated and presented to the operator who may respond accordingly.
Owner:UNIVERSAL AVIONICS SYST
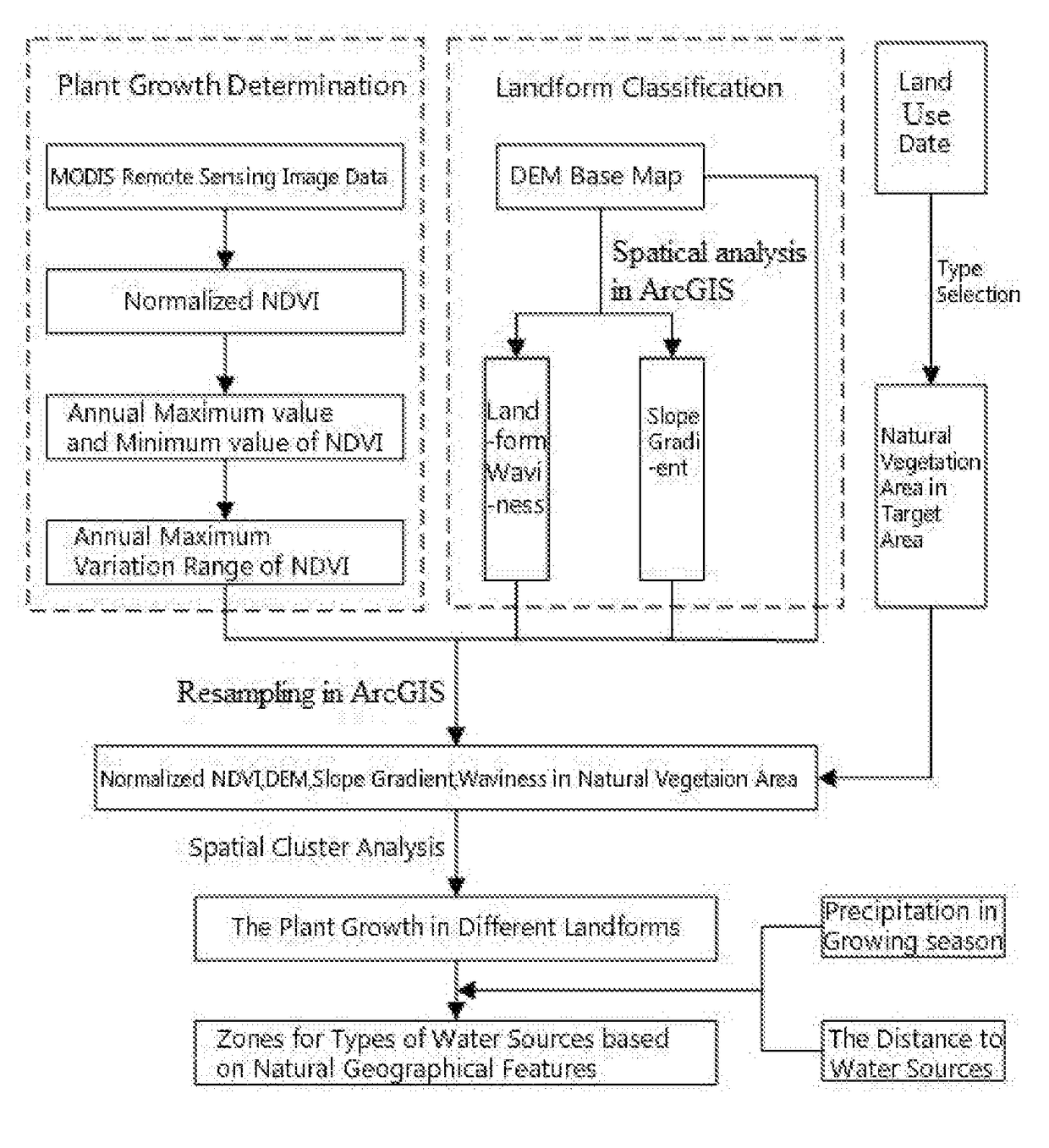
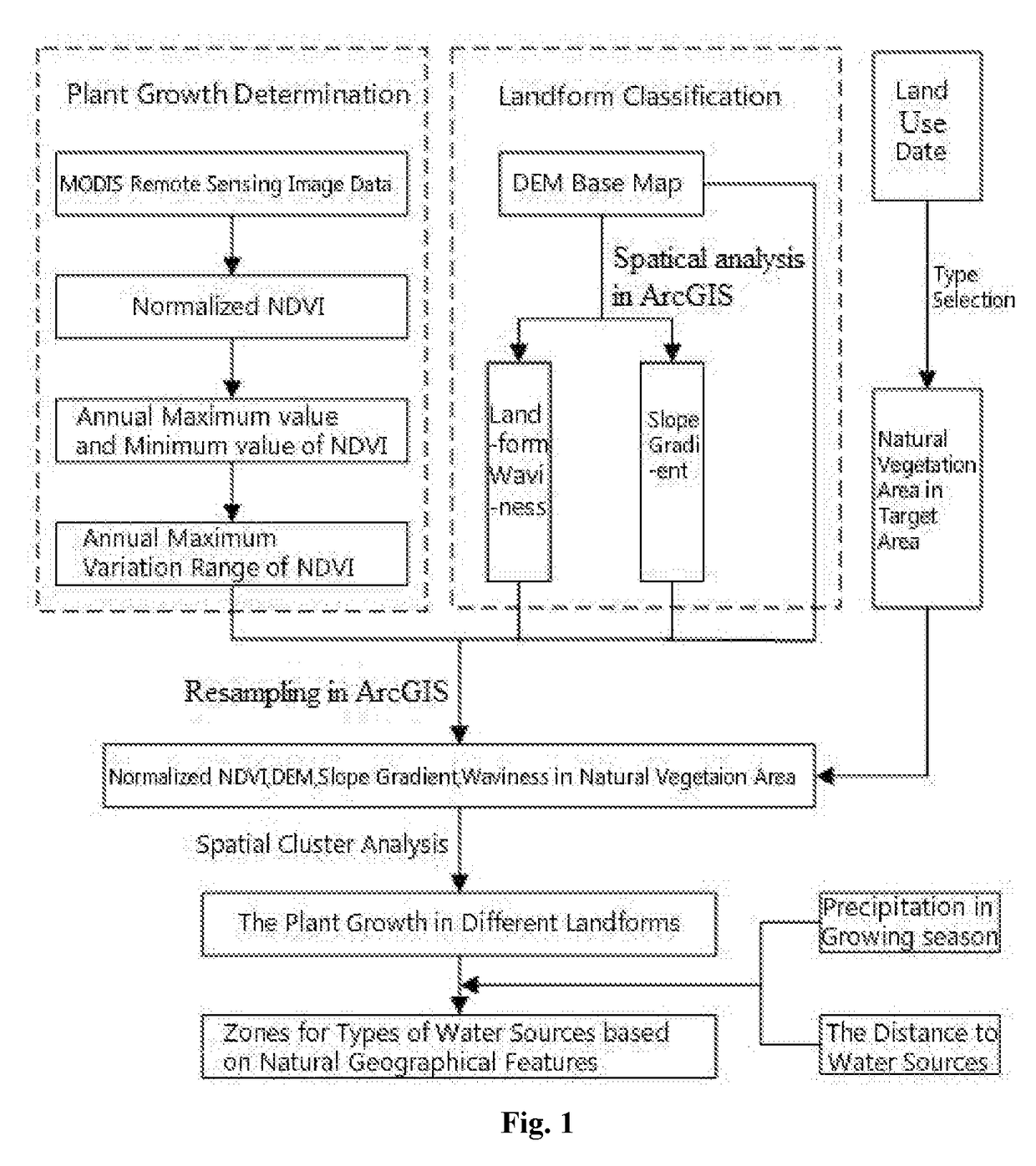
Method for analyzing the types of water sources based on natural geographical features
A method for analyzing types of water sources based on natural geographical feature, the method includes: collecting and processing remote sensing image data of target area, and obtaining maximum and minimum value of an annual vegetation index; subtracting the minimum value from the maximum value to obtain maximum variation range of annual vegetation index; extracting topography factors from a digital elevation model in target area; obtaining a natural vegetation area in target area; carrying out a normalization processing for the maximum variation range and the topography factors in this natural regions, and obtaining landform zones and situation of plant growth of different zones in the natural vegetation area by spatial cluster analysis in ArcGIS; obtaining a precipitation of landform zones in the growing season and the distances between the landform zones and the water sources, and obtaining the zones for the types of water sources based on natural geographical features.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Method for organizing map data
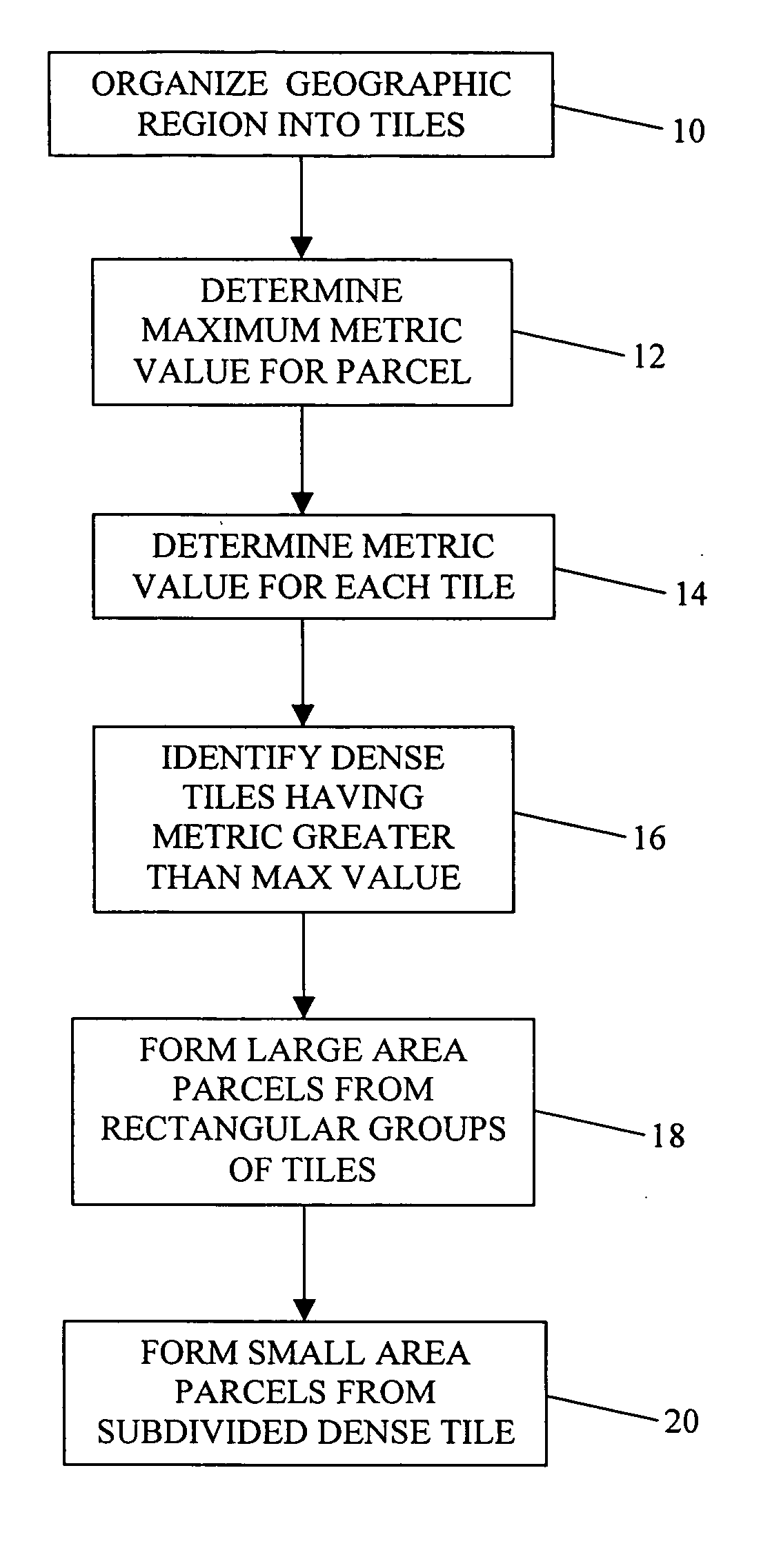
InactiveUS20050027445A1Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsGeographic regionsGeographic feature
A method of organizing map data on a physical storage medium is disclosed. The map data represents geographic features located in a geographic region. The method identifies at least one dense area in the geographic region. The map data representing the geographic features within the dense area have a data size exceeding a predetermined maximum size for a predetermined sized geographic area of the region. The method subdivides the map data representing the geographic features within the dense area into parcels so that the portion of map data contained in the parcel is close to a predetermined parcel size. The method subdivides the map data less the map data representing the dense area into parcels so that the portion of map data contained in the parcel is close to the predetermined parcel size. Additionally, the method locates the map data in each parcel together on the physical storage medium.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Charging system which carries out data processing for fee payment
InactiveUS6845362B2Improve reliabilitySmall data amountInstruments for road network navigationTicket-issuing apparatusPaymentGeographical feature
A charging system which carries out position confirmation of a moving body at a place where there is a radio wave blocked facility, and which carries out automatic detection of GPS antenna blockage for avoiding charging. The charging system includes a GPS positioning device for recognizing a vehicle position, a vehicle speed pulse measuring device for dead reckoning navigating, a monitor device which generates information expressing a current position by using these, and a charging processing which judges whether or not a recognized current position is within a charge area and which carries out data processing for charging. The monitor includes a simple map database which includes positions of facilities or geographical features at which GPS positioning is impossible, and when GPS positioning is impossible, the facility or geographical feature corresponding to the current position is detected, and that position is made to be a current position.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
System, apparatus and method for mapping
InactiveUS20060136126A1Instruments for road network navigationDrawing from basic elementsUrban regionGeographical feature
The present invention provides a novel apparatus and method for mapping of urban regions. An apparatus includes the remote sensing equipment that is connected to a computer processor. The remote sensing equipment gathers imaging data about an urban region. The computer processor interprets the imaging data to generate a map of the urban region comprising representations that identify a first set of indicia representing physiographic characteristics, a second set of indicia representing different types of built forms, and a third set of indicia representing patterns of human activity associated with both the physiographic characteristics and the built forms. The map can also include a fourth set of indicia representing an intensity level that at least one of the other types of indicia occurs.
Owner:1626628 ONTARIO LTD
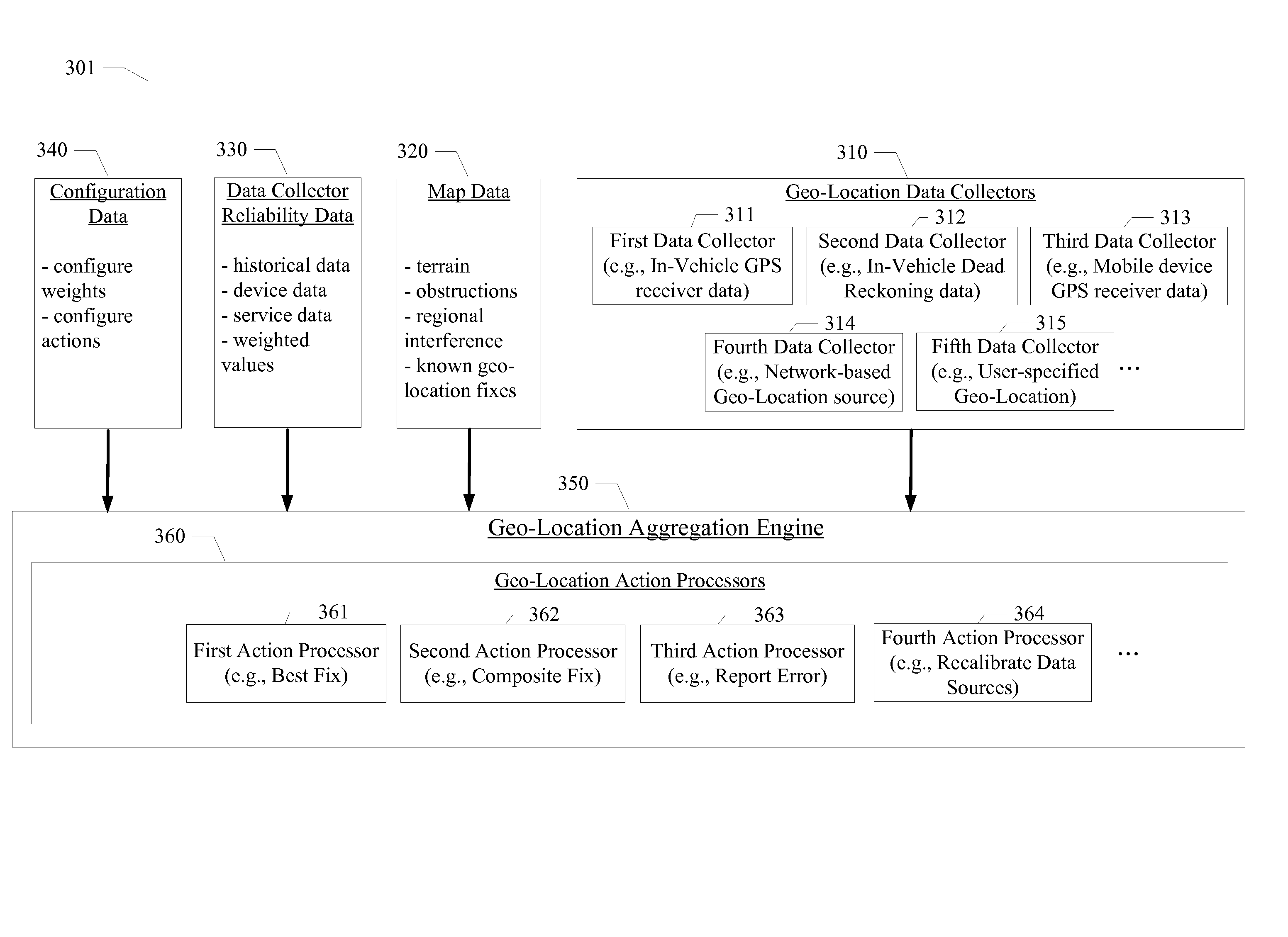
Geographical location aggregation from multiple sources
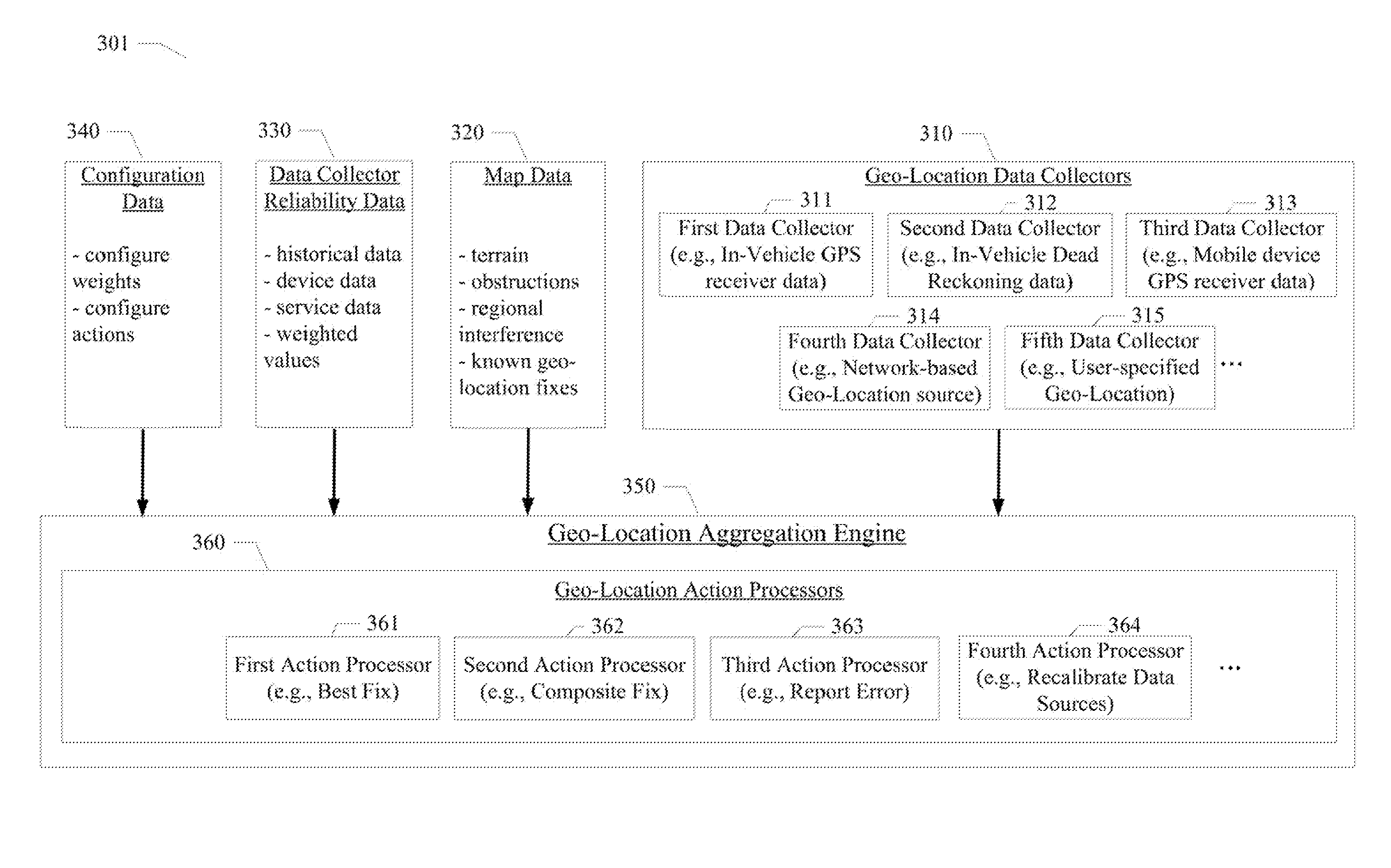
InactiveUS20140149032A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographic siteGeographical feature
Systems and methods for obtaining geographical location data from multiple sources and aggregating the geographical location data are disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving geo-location data from a plurality of geo-location data collectors, at least one of the plurality of geo-location data collectors being in data communication with an in-vehicle geo-location data source, at least one of the plurality of geo-location data collectors being in data communication with a geo-location data source in a mobile device; collecting reliability data corresponding to one or more of a plurality of geo-location data sources corresponding to the plurality of geo-location data collectors; collecting map data including information related to geographical features associated with the geo-location data; and aggregating, by use of a data processor, the geo-location data from the plurality of geo-location data collectors based on the reliability data and the map data to produce a resulting geo-location fix.
Owner:LENNY INSURANCE LTD
System, apparatus and method for mapping
InactiveUS7856312B2Instruments for road network navigationDrawing from basic elementsUrban regionGeographical feature
The present invention provides a novel apparatus and method for mapping of urban regions. An apparatus includes the remote sensing equipment that is connected to a computer processor. The remote sensing equipment gathers imaging data about an urban region. The computer processor interprets the imaging data to generate a map of the urban region comprising representations that identify a first set of indicia representing physiographic characteristics, a second set of indicia representing different types of built forms, and a third set of indicia representing patterns of human activity associated with both the physiographic characteristics and the built forms. The map can also include a fourth set of indicia representing an intensity level that at least one of the other types of indicia occurs.
Owner:1626628 ONTARIO LTD
System and method of displaying position information including an image in a navigation system
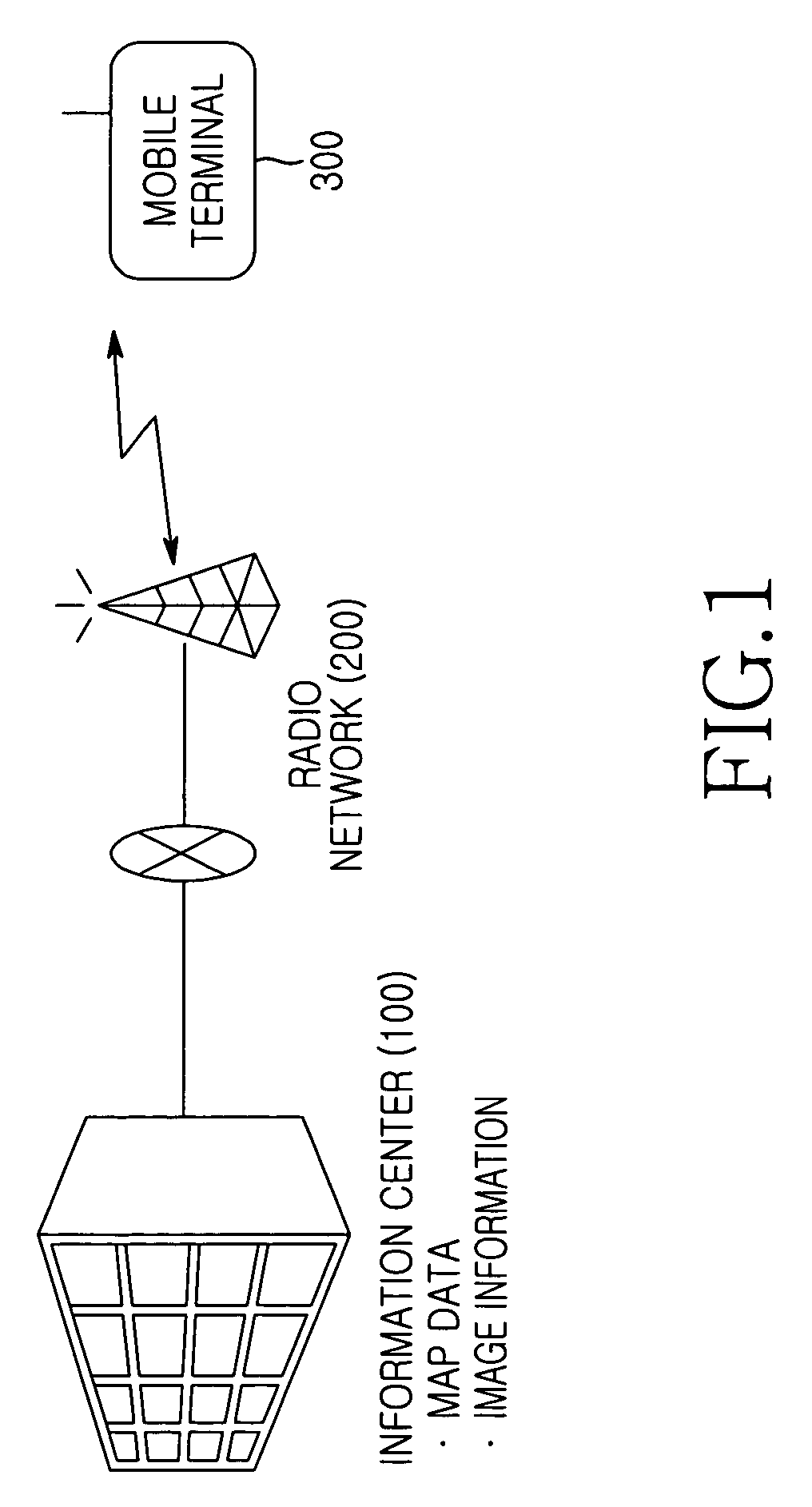
ActiveUS7383123B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographical featureNavigation system
A system and method of displaying position information including an image in a navigation system are disclosed. The navigation system has an information center and a mobile terminal. The information center includes a database for storing a node message with node image information about the geographical features of a node and a database for storing map data. The node image information is divided into image segments corresponding to directions. The information center sets a route according to a current position and a destination of the mobile terminal, generates map data including the route and nodes in the route, and transmits it to the mobile terminal. The mobile terminal selects nodes for which to receive node messages in the map data. The information center transmits a node message for the next node each time the mobile terminal reaches each of the selected nodes. The mobile terminal reproduces the node message.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
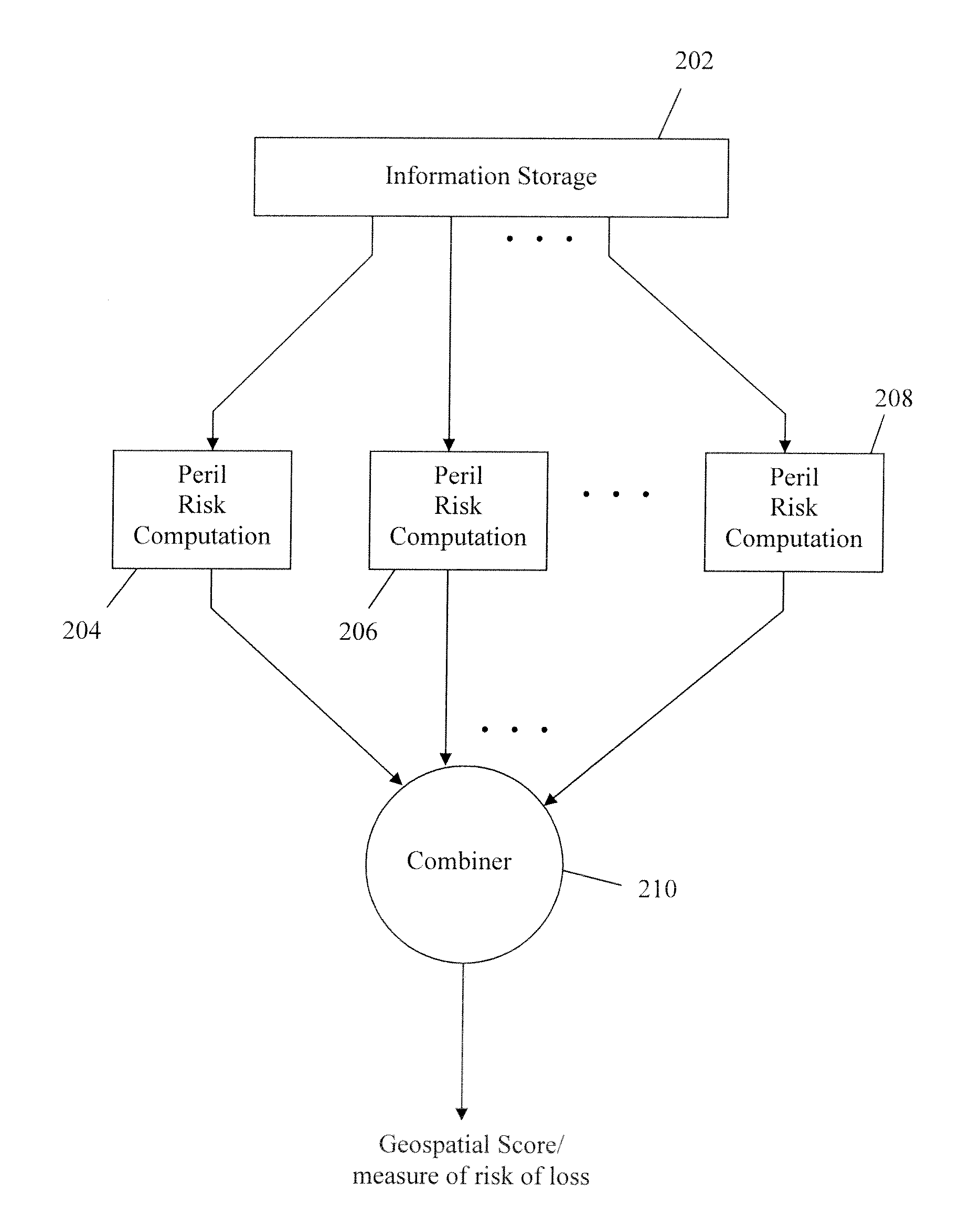
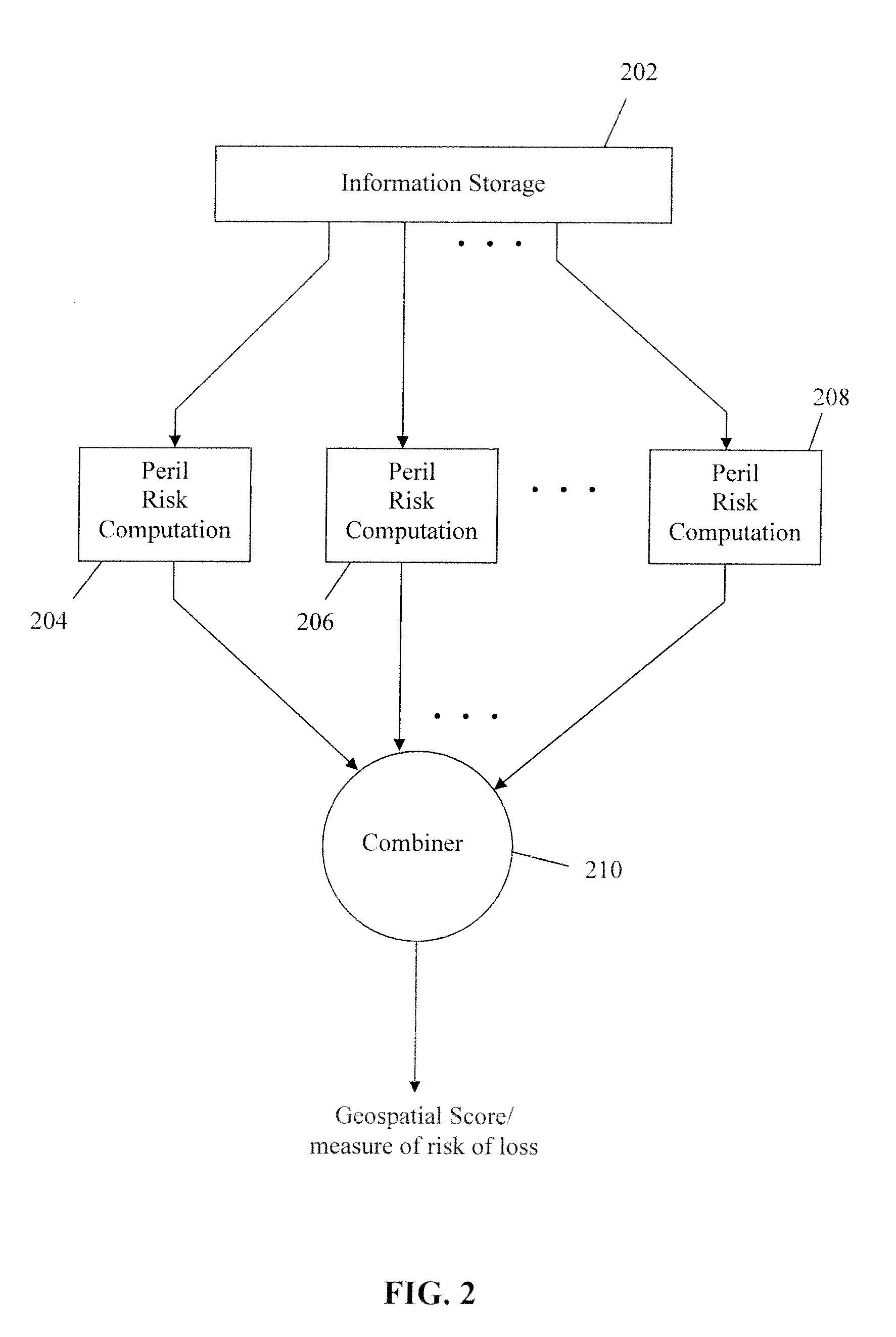
Method and System for Assessing Insurance Risk
The disclosed technology provides systems and methods for estimating the risk of loss for a location. A computer implemented method in accordance with the disclosed technology accesses one or more geographical characteristics associated with a geographical address, considers a plurality of perils and for each peril, computes a corresponding measure of peril that indicates a risk of loss at the geographical address from that peril. The corresponding measure of peril is computed based on the geographical characteristic(s) associated with the geographical address. The individual measures of peril are combined to form a combined measure that indicates a combined risk of loss at the geographical address from the plurality of perils. In one embodiment, the combined measure is used to compute an insurance premium for property at the geographical address. The disclosed technology also includes a computer executing software, wherein the executed software causes the computer to perform the steps above.
Owner:METROPOLITAN PROPERTY & CASUALTY INSURANCE
Process for preserving three dimensional orientation to allow registering histopathological diagnoses of tissue to images of that tissue
InactiveUS20100093023A1Keep the distanceAccurately determinePreparing sample for investigationBiological testingPathology diagnosisFixed Specimen
A process for maintaining 3 dimensional orientation between a tissue specimen and images of the area of investigation, to register histopathologic diagnoses of multiple locations within the specimen with corresponding locations on the surface of said area of investigation, by marking at least two fiduciary lines on the area of investigation; acquiring a fiduciary image of the tissue with the fiduciary lines; excising the tissue to form a tissue specimen; inserting at least two parallel needles through said specimen; acquiring a specimen image of the specimen with inserted needles over an alignment grid; fixing the specimen by immersing the specimen; acquiring a fixed image of the fixed specimen with the inserted needles over the alignment grid; forming a paraffin mold containing the fixed specimen and inserted needles; injecting different colored inks through the needles while withdrawing them from the fixed specimen, so that different colored needle tracks are formed in the specimen; sectioning the specimen to create specimen blocks having different colored needle tracks; further sectioning the specimen to cut the specimen blocks into specimen slices having different colored ink dots corresponding to the different colored needle tracks; forming pathology images from the specimen slices; performing histopathology analyses on the pathology images; annotating the pathology images with histopathology annotations; aligning the annotations with the fixed image using the colored ink dots; determining shrinkage between the fixed image and the annotations by using the grid to compare the distance between the needles in the fixed image with the distance between the ink dots on the specimen slices; registering the fixed image to the specimen image to account for shrinkage caused by fixation, using locations of the needles in both of the images as landmarks; registering the specimen image to the fiduciary image to account for tissue translation and soft tissue movement using the fiduciary lines and geographical features of said area of investigation as landmarks; registering the fiduciary image to the reference image to account for tissue translation and soft tissue movement using said geographical features; whereby annotations of histopathologic diagnoses are provided for multiple locations on or under the surface of the specimen that are registered to images of the specimen.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
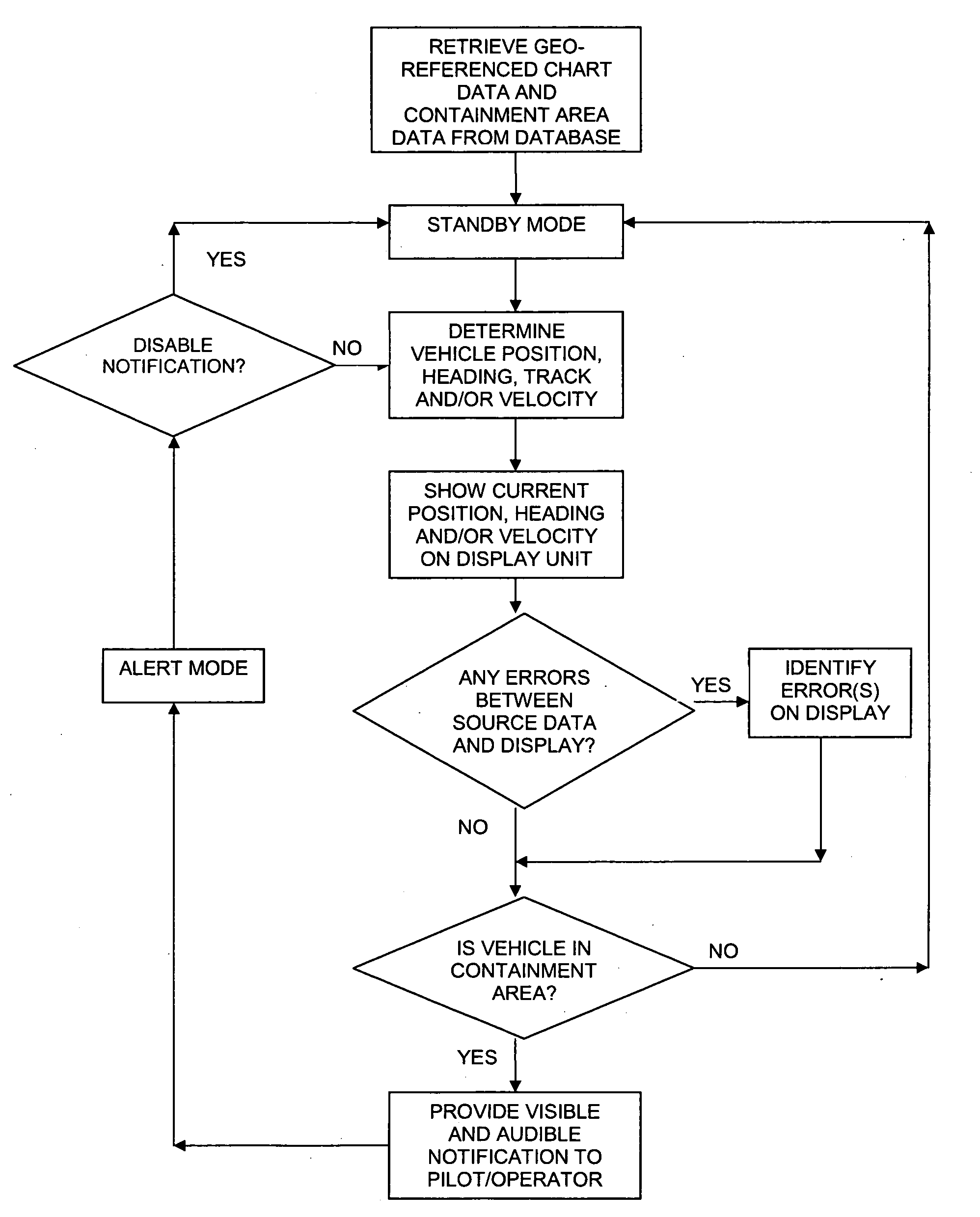
Aircraft ground maneuvering monitoring system
ActiveUS20080140269A1Aircraft componentsDigital data processing detailsGeographical featureMonitoring system
A monitoring system for alerting pilots of aircraft or operators of vehicles when the aircraft or vehicle is approaching a geographical feature of interest, such as a runway, includes a database including at least one geo-referenced chart; a processor; a positioning system configured to identify at least one of the position, heading, track and velocity of the vehicle, and transmit such data to the processor; and a display unit configured to display the present position of the aircraft on the at least one geo-referenced chart. After receiving the position, heading, track and / or velocity data, the processor determines whether the aircraft has entered a containment area associated with a geographical feature of interest, and if so, provides a visible notification to the pilot or operator, which may comprise a change in display of the geographical feature of interest.
Owner:UNIVERSAL AVIONICS SYST
Geographical location aggregation from multiple sources
InactiveUS20150073697A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographical featureGeographic site
Systems and methods for obtaining geographical location data from multiple sources and aggregating the geographical location data are disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving geo-location data from a plurality of geo-location data collectors, at least one of the plurality of geo-location data collectors being in data communication with an in-vehicle geo-location data source, at least one of the plurality of geo-location data collectors being in data communication with a geo-location data source in a mobile device; collecting reliability data corresponding to one or more of a plurality of geo-location data sources corresponding to the plurality of geo-location data collectors; collecting map data including information related to geographical features associated with the geo-location data; and aggregating, by use of a data processor, the geo-location data from the plurality of geo-location data collectors based on the reliability data and the map data to produce a resulting geo-location fix.
Owner:LENNY INSURANCE LTD
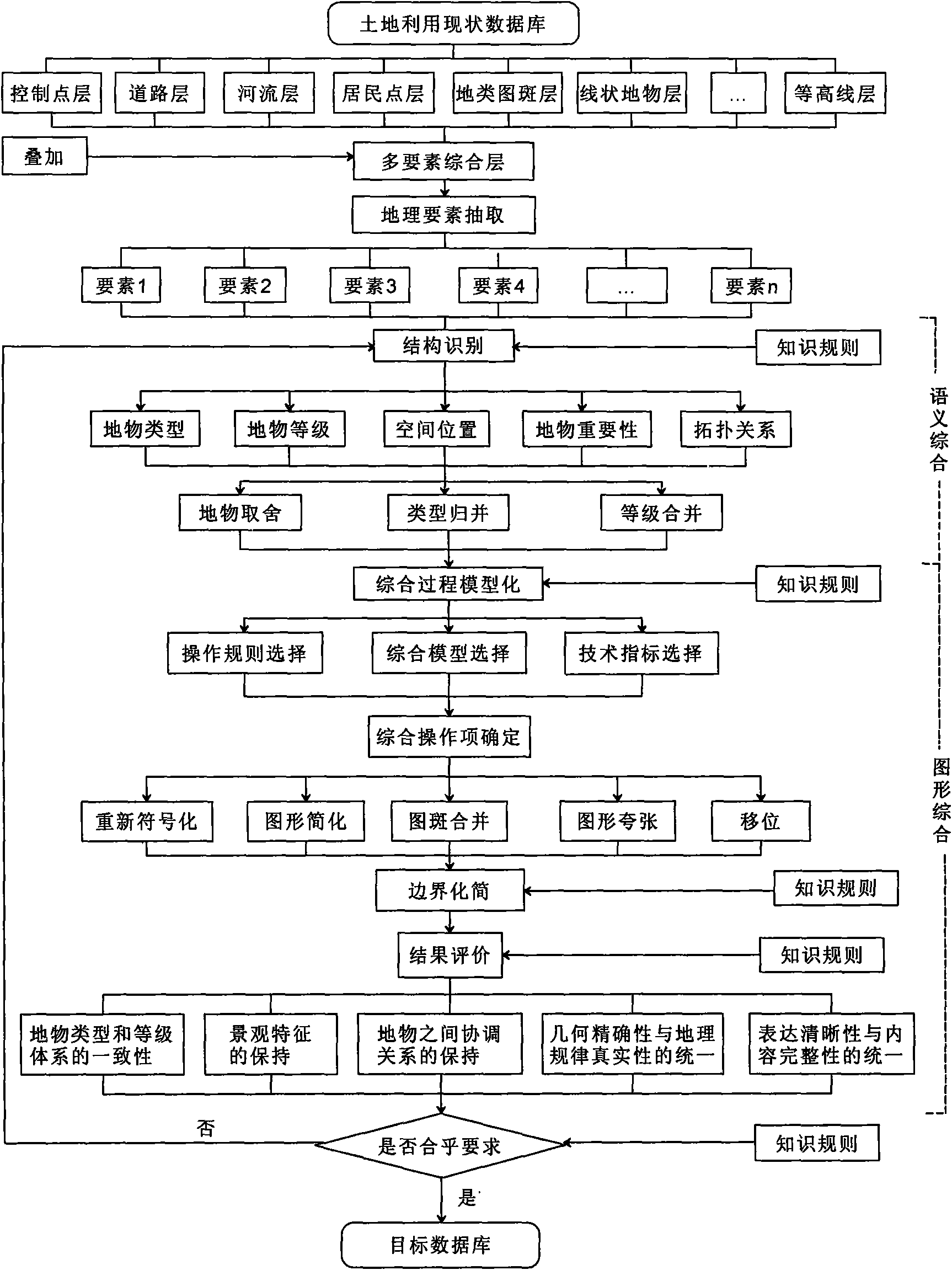
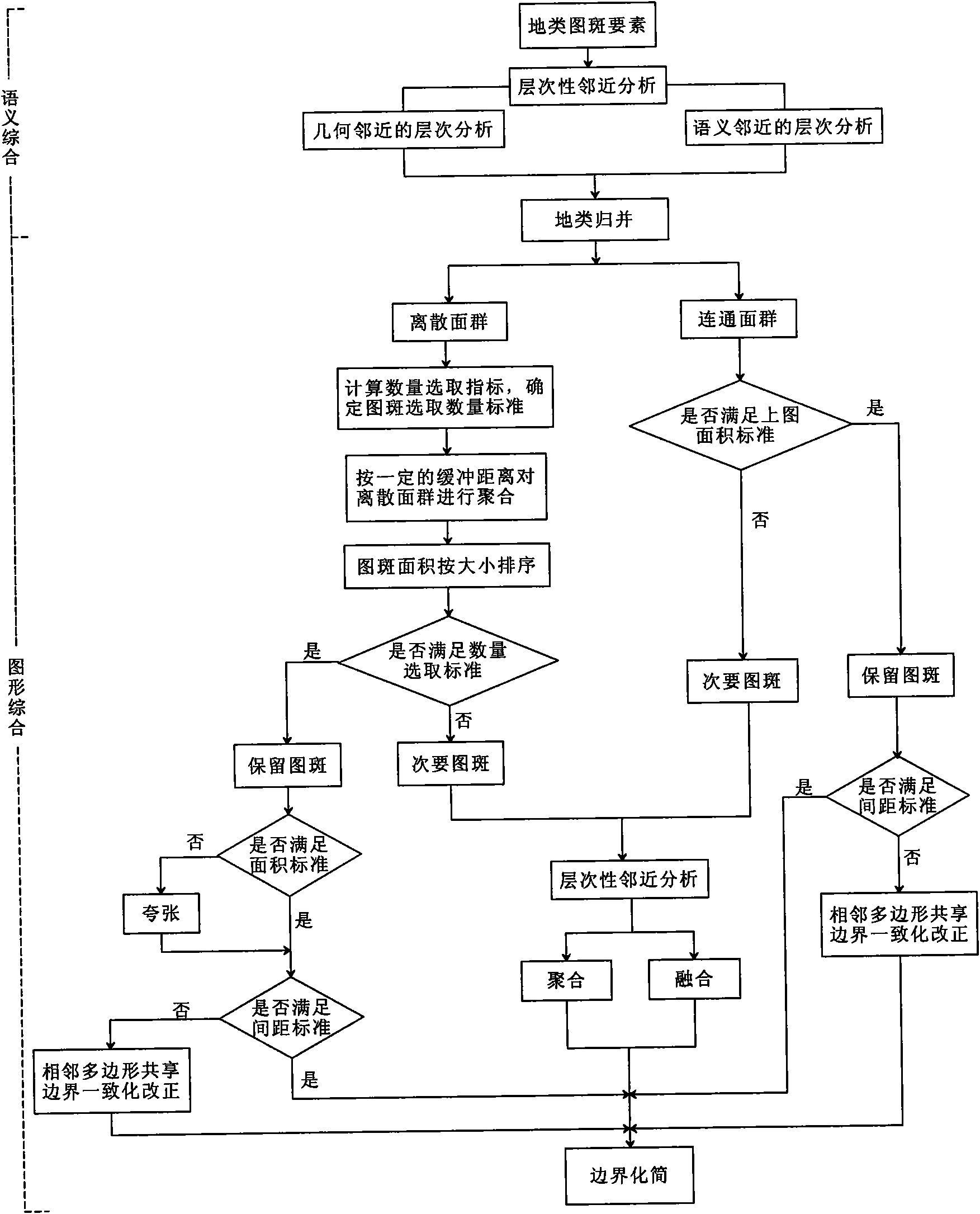
Spatial database synthesis method in land utilization information multi-scale expression
InactiveCN101599070ARealize dynamic associationIncrease the content of semantic synthesisData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsSynthesis methodsSpatial database
The invention discloses a spatial database synthesis method in land utilization information multi-scale expression; a spatial database in the land utilization information multi-scale expression is synthetically divided into two steps: semantics synthesis and graphics synthesis, wherein, the process of the semantics synthesis is synthesis constraint based on a thematic data base, under the control and guidance of knowledge inference, the geographic characteristics of land features in the database is judged, comprising the steps of identifying the spatial relation of land feature types, land feature grades, spatial position and other land features and determining the importance of the land features, therefore, the process is structural identification. The graphics synthesis is the synthesis of point features, line features and surface features under the guidance of cartography theory. The synthesis model based on the database is built, the standardization of database synthesis is realized, and the disadvantages that the traditional cartography synthesis only concerns graphics synthesis and neglects special semantics synthesis are overcome.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
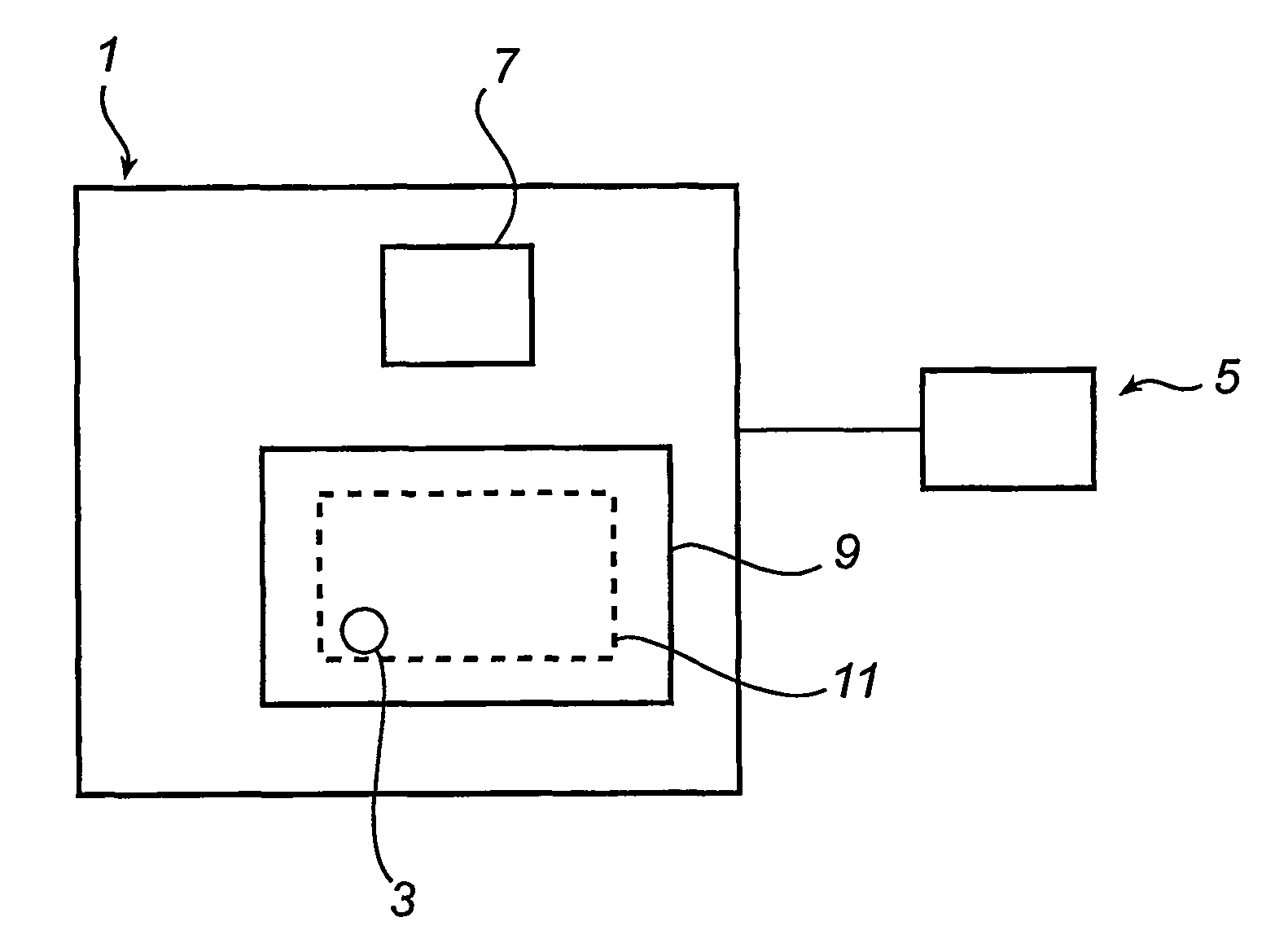
Device and carrier of map information data
InactiveUS20050165548A1Increase speedLow costInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographical featureImage resolution
Device (1) and carrier for providing map information data (3) interactively to a display unit (5). The device (1) comprises a processor (7) and a memory (9) comprising a map information database (11) comprising map information data (3) representing geographical features, the map information data (3) being based on aggregations of at least one of nodes (15), links (17) and rings (19), each one of which corresponding to geographic features. The map information data (3) of a higher resolution level comprises additional map information data, resulting in more detailed map information (3) presented on the display unit (5), compared to the map information data (3) of a lower resolution level. The map information data (3) of a higher resolution level is generated by enhancement of the map information data (3) of a lower resolution level combined with the additional data, the enhancement being based on disaggregation of nodes (15), links (17) and rings (19). The processor (7) is configured for receiving a request for map information data (3); and providing map information data (3). Also, a device for providing map information data to a planning apparatus (33) for planning at least one of locations of society facility and travel routes is disclosed.
Owner:IDEVIO
GSM mobile communication network terminal positioning method
InactiveCN102264097AEasy to calculateRealization of geographic operation and maintenanceWireless communicationGeographical featureHigh probability
The invention discloses a method for positioning a GSM (global system for mobile communication) mobile communication network terminal. The method comprises the following steps: a. dividing grids for a region covered by a mobile communication network according to the established sizes, and numbering each grid; b. establishing an initial radio broadcasting model of the grid according to a geographical feature and a radio broadcasting feature of each grid; c. generating feature data of the radio broadcasting model of each grip according to DT (drive test) data; d. acquiring a signaling data from the mobile communication network, screening out each conversation in the signaling data, extracting a test report in the conversation, and screening the test report; e. analyzing the matching degree of the screened test report and the feature data of each grip one by one, and calculating a probability value; and f. finding centers of the grids with the highest probabilities, namely the positions of the mobile communication network terminal of the conversation. The positioning method has the characteristics of fast positioning speed and easiness of implementation.
Owner:北京维泽瑞科技有限公司
Method for extracting altered mineral at vegetation-covered areas by hyperspectral remote sensing
ActiveCN103383348AColor/spectral properties measurementsGeographical featureReflectance spectroscopy
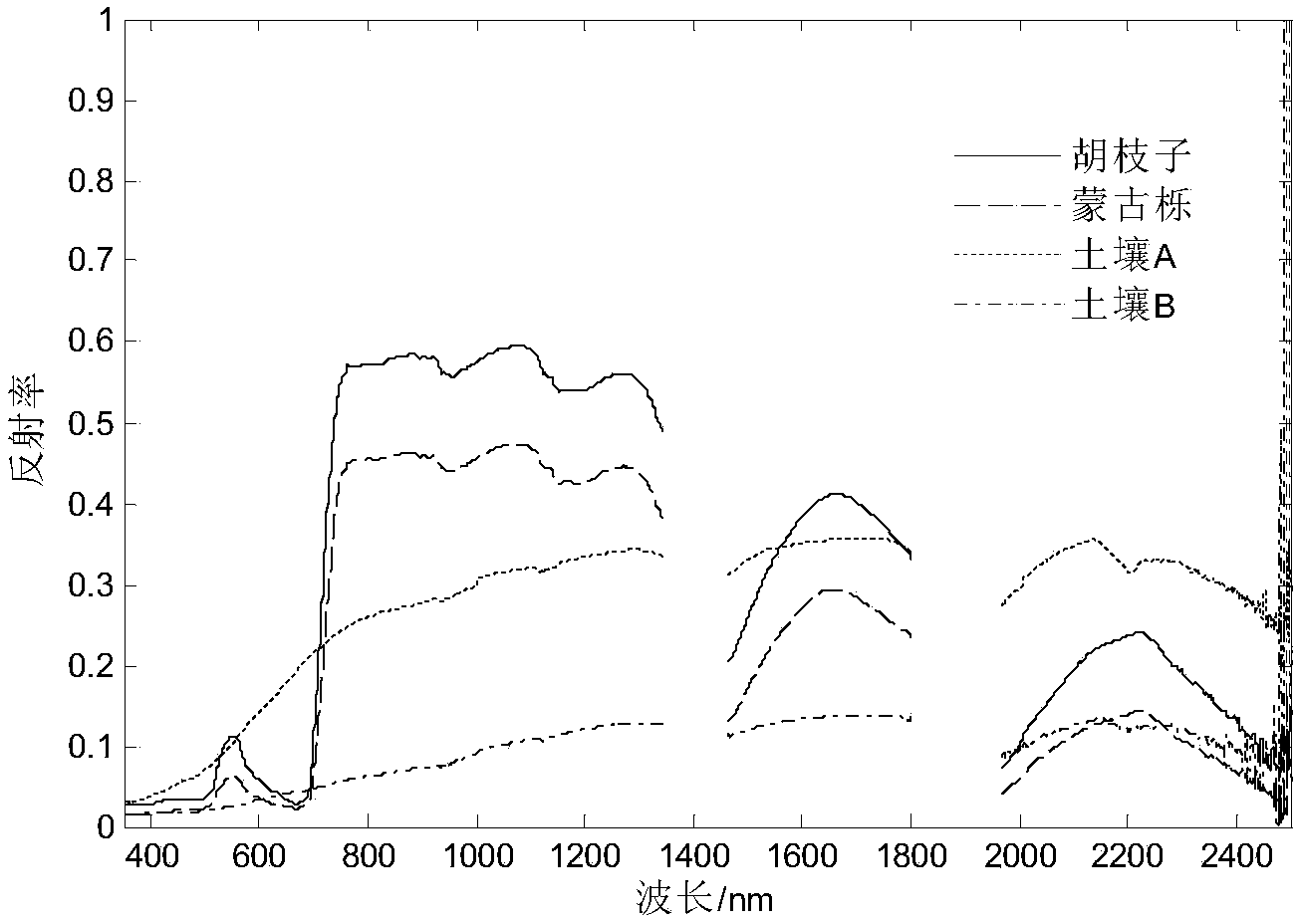
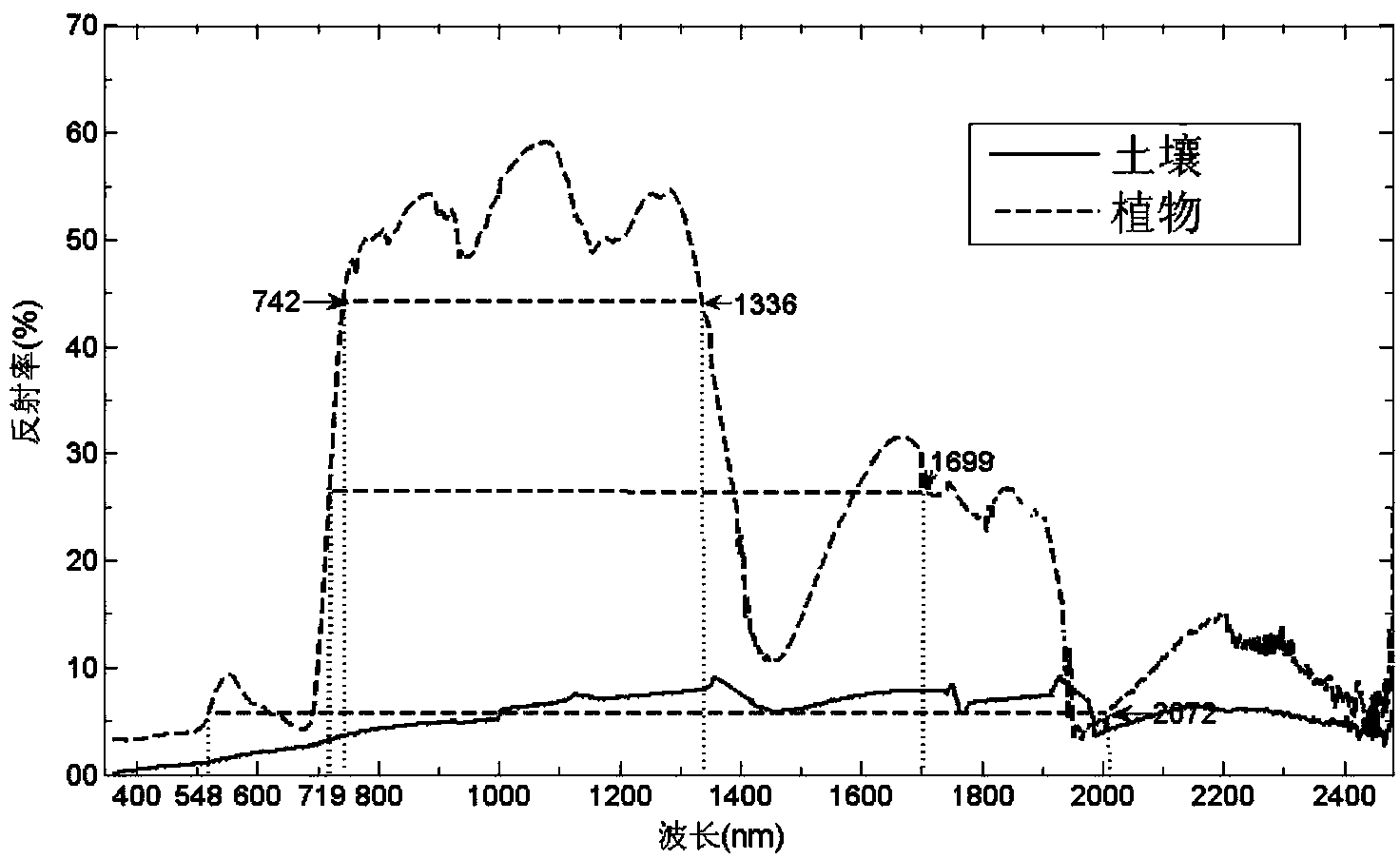
The invention relates to a method for extracting altered mineral at vegetation-covered areas by hyperspectral remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps: a detection gun is directed at leaves of broadleaved plants to directly measure reflectance spectrum of leaves, measures reflectance spectrum of herbaceous plant canopy and measure reflectance spectrum of fresh surface of soil; uncalibrated and steam-influeced waveband removal, absolute radiation value conversion, bad wire restoration and atmospheric correction are carried out on Hyperion data; two principal components which have large absolute values but are opposite in sign are found according to principal component analysis characteristic value and a 2-D point diagram is made according to the two principal components; and abnormity is delineated according to the point diagram. Through the comparison of spectral feature fitting method and mineral extraction model, multilayer information separation of background, interference and abnormal information is adopted, and the key is to select the best waveband for spatial feature analysis. Through analysis of hyperspectral data characteristics and vegetation-covered area geographical features and the best waveband selection used during spatial feature optimization, vegetation information is better inhibited, and alteration information characteristics are enhanced.
Owner:吉林高分遥感应用研究院有限公司
Method for matching place name and address in news event based on geographical feature hierarchical segmented words
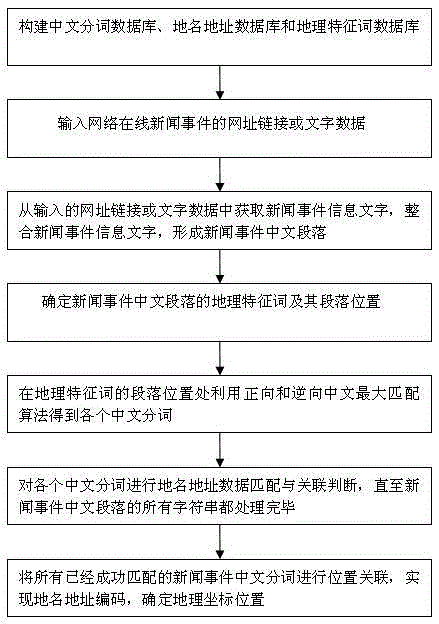
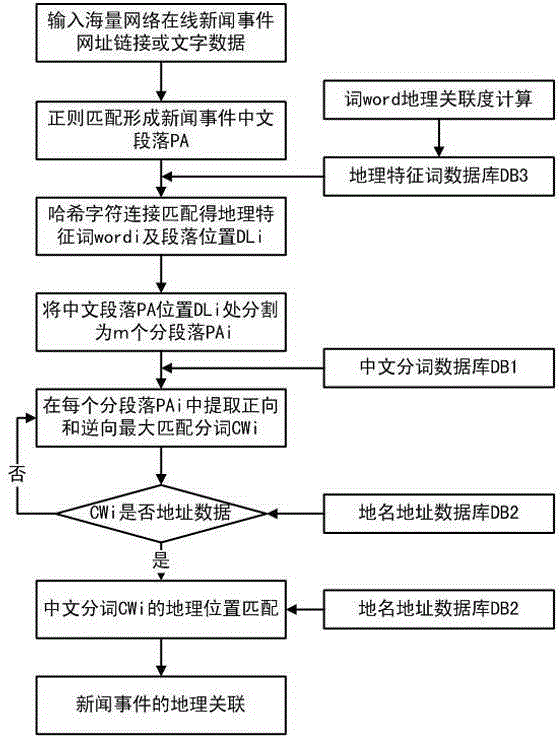
ActiveCN105404686AGet visual imageHigh precisionGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsGeographical featureData matching
The present invention discloses a method for matching a place name and an address in a news event based on geographical feature hierarchical segmented words. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a Chinese segmented word database, a place name and address database and a geographical feature word database; acquiring a geographical feature word of a Chinese paragraph of the news event and a paragraph position of the geographical feature word; performing place name and address data matching and correlative judgement on Chinese segmented words in the paragraph position of the geographical feature word; and performing position association on the successfully matched Chinese segmented words of the news event, implementing place name and address coding, and determining a geographical coordinate position. According to the method, in combination with a geographical information system and a place name and address matching algorithm, the display and geographical association of the news event in a map are implemented; and the news event is converted from a one-dimensional text to a two-dimensional geographical space position, thereby acquiring news information more visually and vividly, and implementing automatic, accurate and fast matching and association of the place name and the address in the news event.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
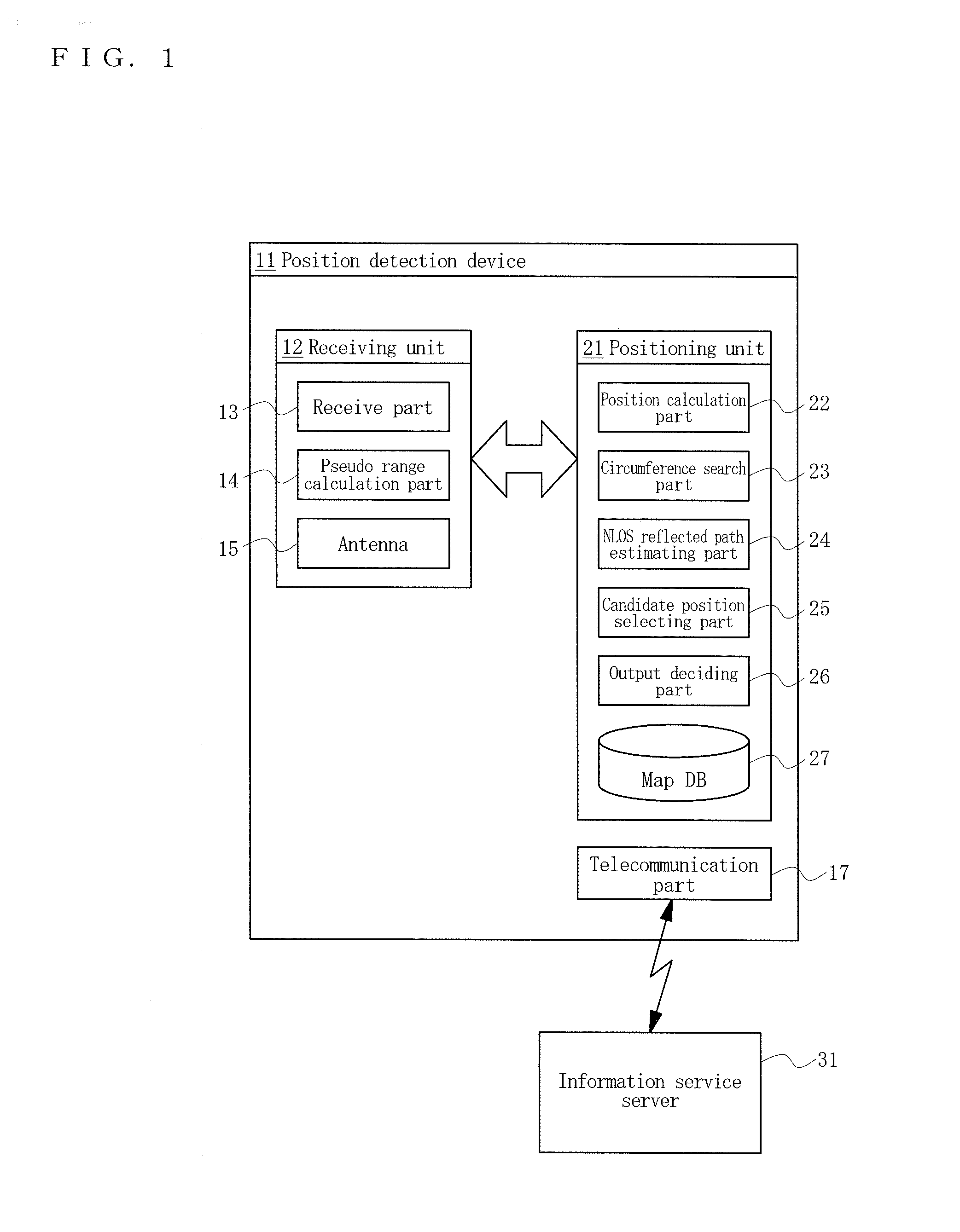
Position detection device, position detection system, and position detection method
InactiveUS20160146945A1Low costShort timeSatellite radio beaconingGeographical featureLocation detection
An object is to make it possible to determine and output an accurate current position reliably in a short time and at a low cost, even in environments where signals from positioning satellites are complicatedly affected by structures, geographical features, etc. Therefore, the present invention provides a position detection device comprising: a receiving unit receiving signals from a positioning satellite, and calculating a pseudo range to the positioning satellite based on the signals, and a positioning unit calculating an initial position based on the pseudo range calculated by the receiving unit, calculating the pseudo range to the positioning satellite at plural positions around the initial position using a three-dimensional map data and a ray-tracing method, selecting candidate positions from the plural positions based on the pseudo range, and deciding a current position based on the candidate positions within such a short distance from the initial position that predetermined conditions are satisfied.
Owner:THE FOUND FOR THE PROMOTION OF IND SCI
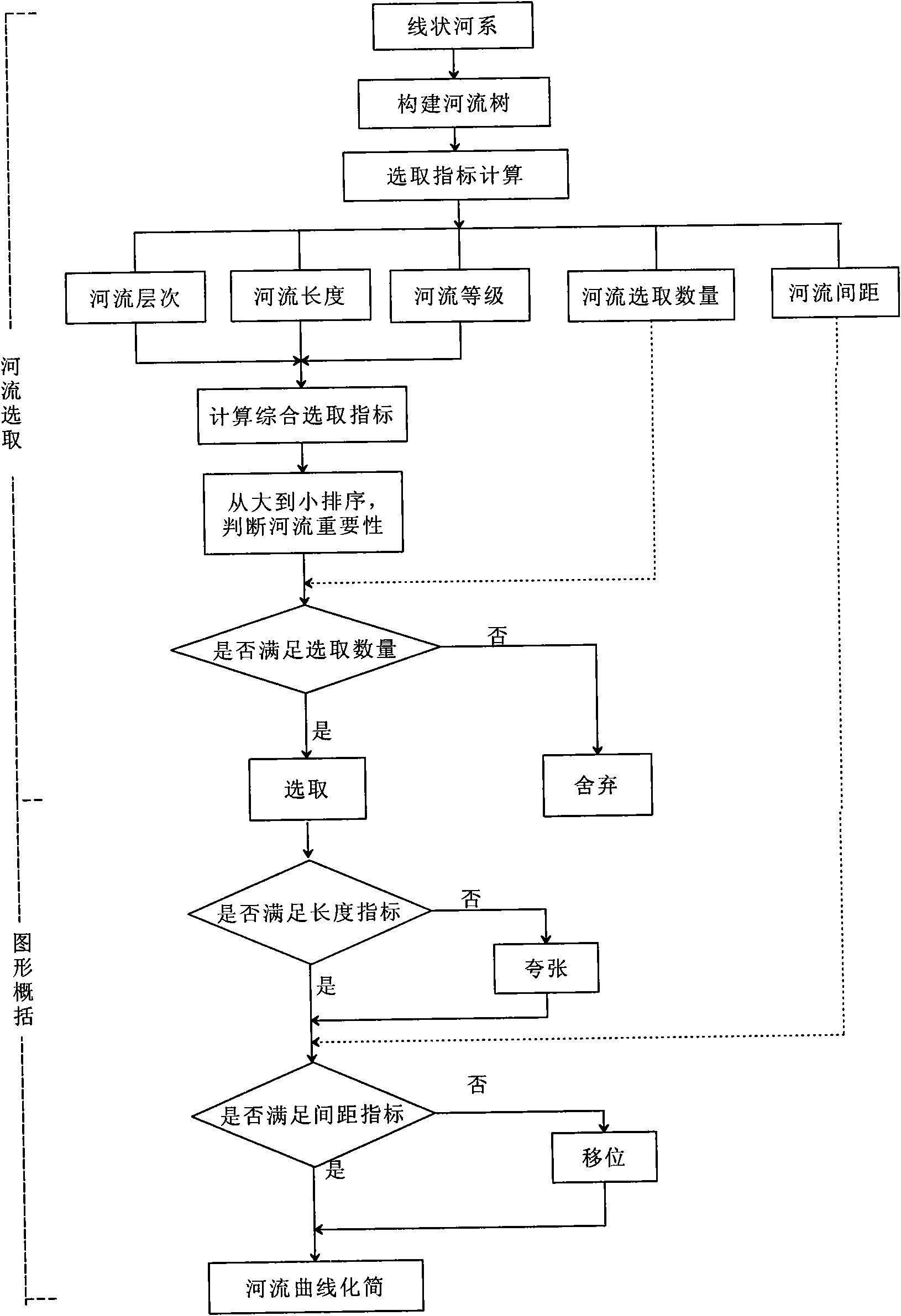
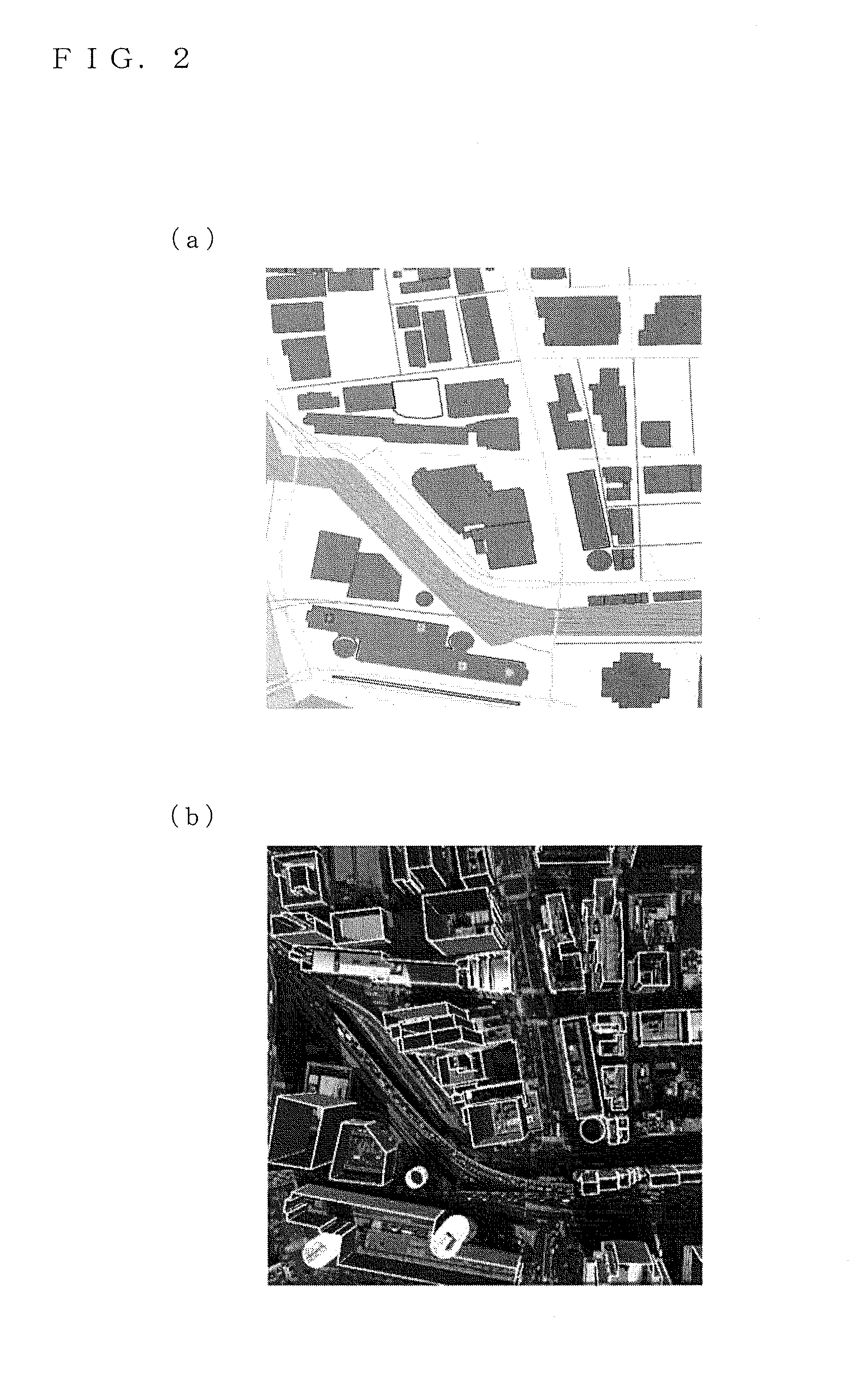
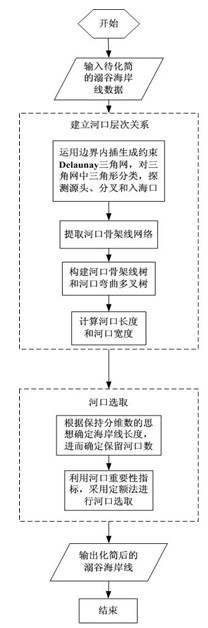
Method for simplifying shoreline of drowned valley by taking geographical features into account
InactiveCN102609898AEnsure consistencyEnsure safetyGeometric image transformationRiver mouthGeographical feature
The invention relates to a method for simplifying a shoreline of a drowned valley, in particular to a method for simplifying the shoreline of the drowned valley by taking geographical features into account. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a hierarchical relationship of river mouths of the shoreline of the drowned valley based on a Delaunay triangular network, and calculating the length and width of the river mouth; and (2) designing an important index of the river mouth based on this basis, deducing the number of selected river mouths without changing the shoreline fractal dimension, and selecting the river mouths by adopting a quota method so as to realize shoreline simplification through the river mouth selection. According to the method for simplifying the shoreline of the drowned valley by taking geographical features into account, the important geographical characteristics, such as a tree-shaped structure, a river mouth hierarchical structure and gradual changes of the individual width of the river mouth of the shoreline of the drowned valley and the like can be maintained, and the topological consistency of the simplifying result and the sailing safety are guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
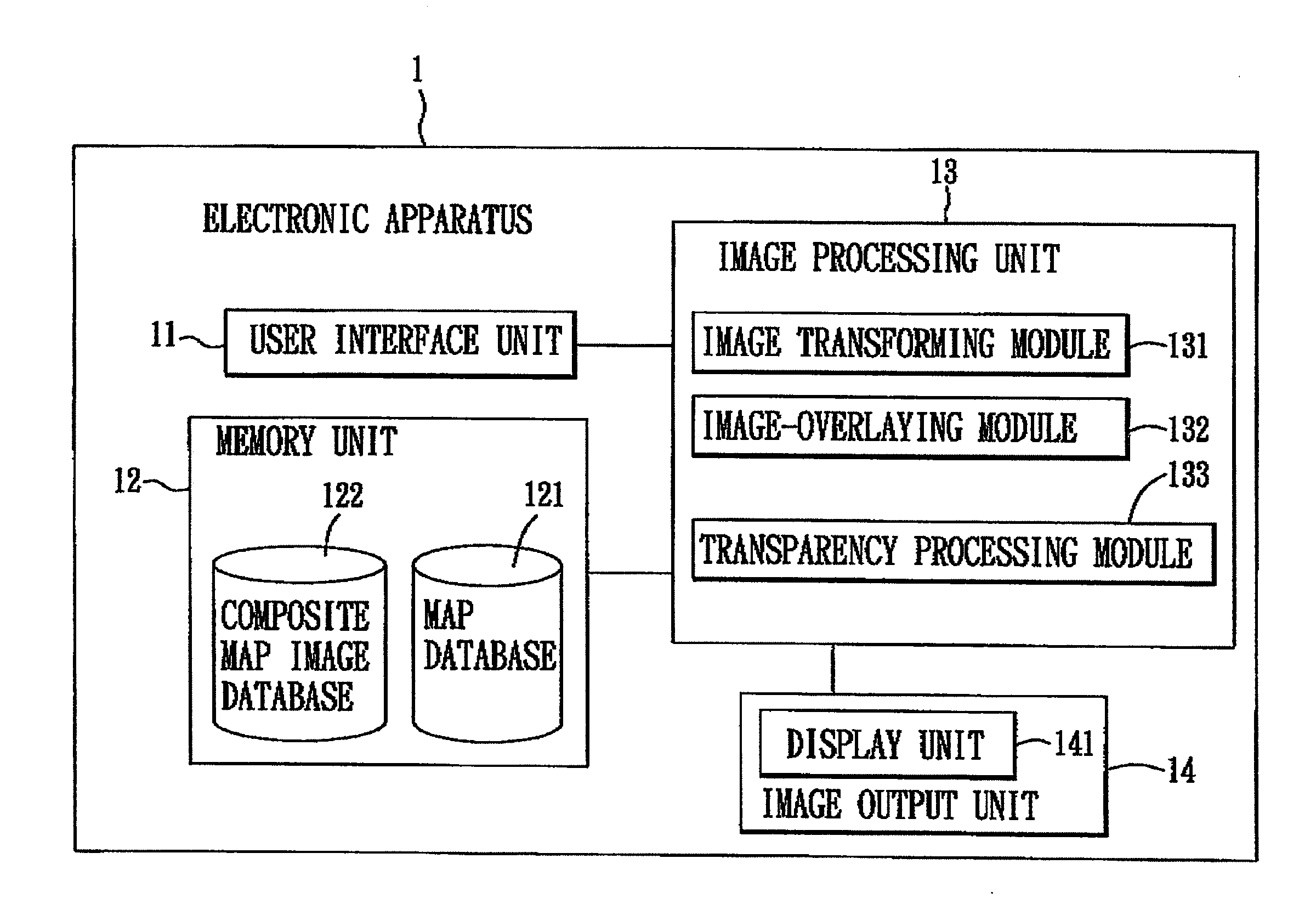
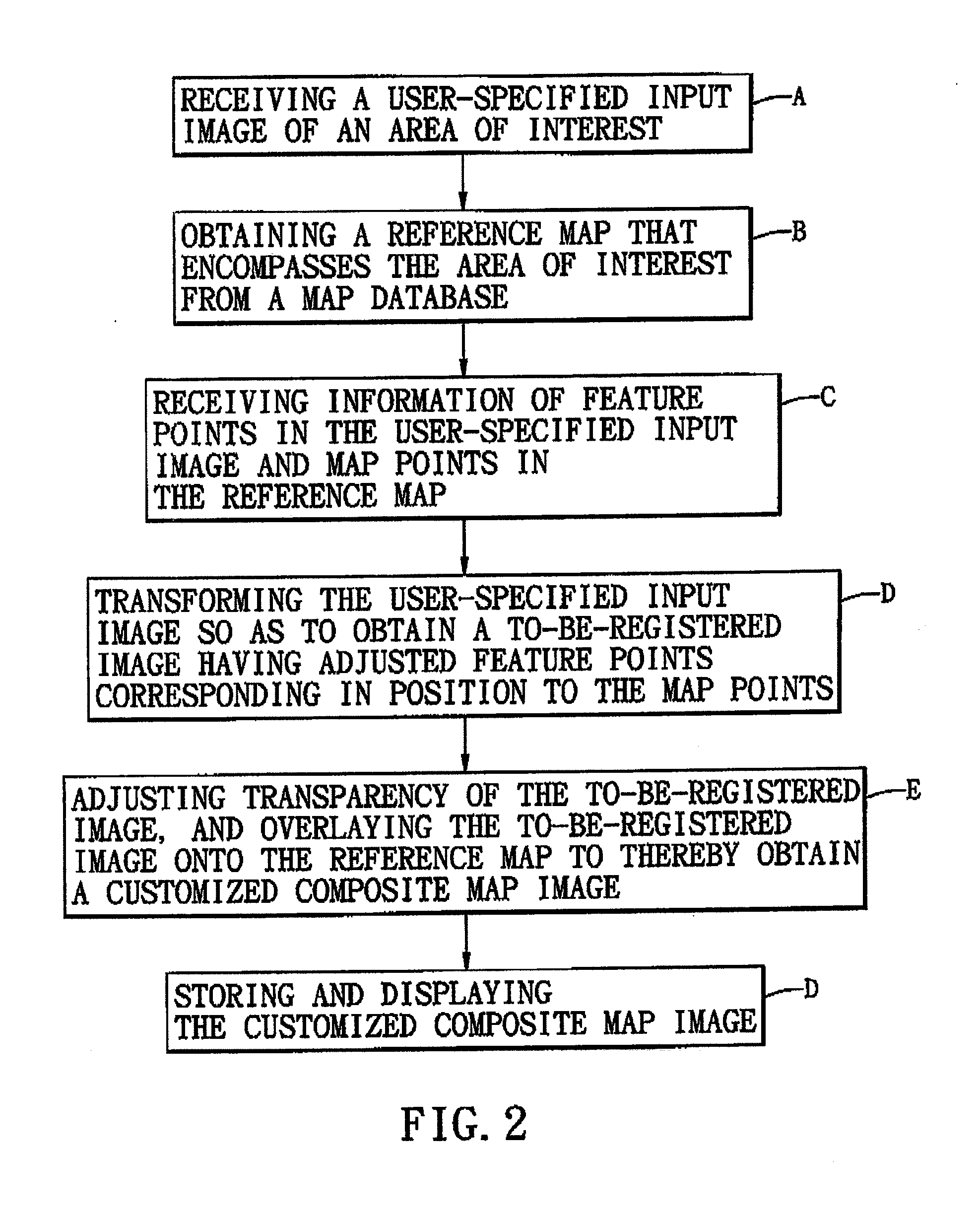
Method for generating a customized composite map image and electronic apparatus for implementing the same
ActiveUS20110181620A1Instruments for road network navigationCathode-ray tube indicatorsReference mapGeographical feature
A method is to be implemented by an electronic apparatus having a map database established therein, and includes the steps of: receiving a user-specified input image of an area of interest, and obtaining from the map database a reference map that encompasses the area of interest; selecting a set of feature points in the user-specified input image, and a set of map points in the reference map that correspond in geographical features to the feature points; transforming the user-specified input image according to positional differences between the feature points and the corresponding map points to thereby obtain a to-be-registered image having adjusted feature points corresponding in position to the map points; overlaying the to-be-registered image onto the reference map to thereby obtain a customized composite map image; and outputting the customized composite map image.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
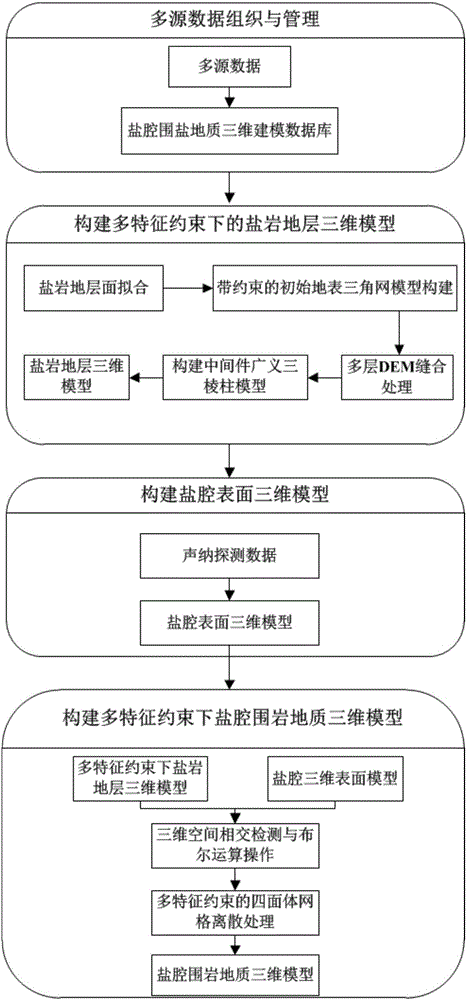
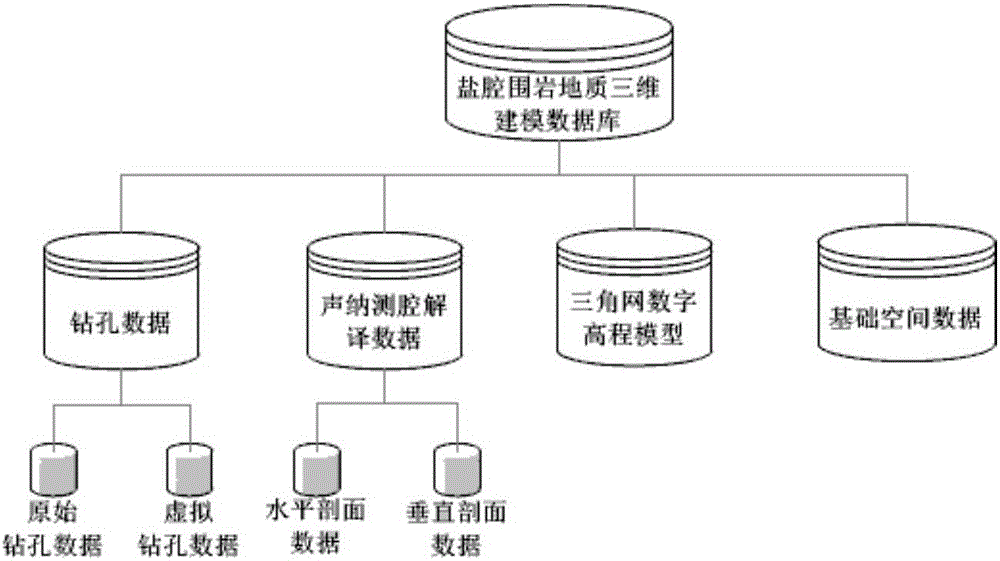
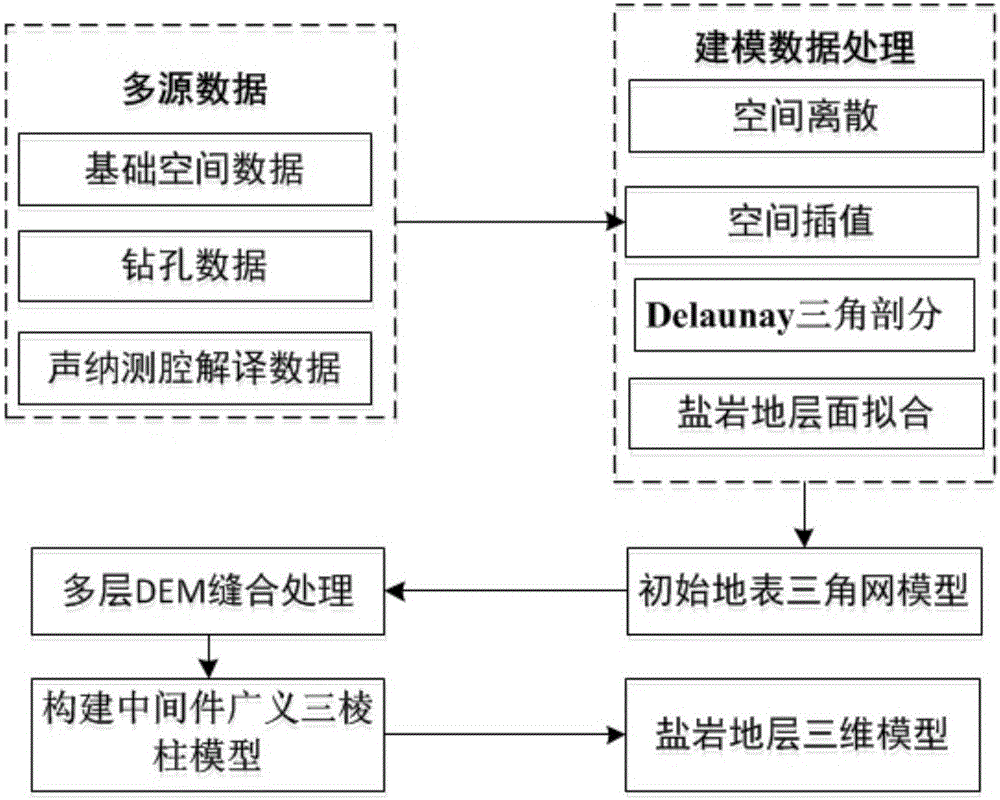
Salt cavity surrounding rock geological three-dimensional modeling method under multiple feature constraints
The invention discloses a salt cavity surrounding rock geological three-dimensional modeling method under multiple feature constraints. According to the method, in a three-dimensional modeling process of a saline stratum by use of multi-source data, engineering geographical boring, triangular net digital high-elevation model, a mining area boundary, a mudstone interlayer and the like are taken as important feature constraint conditions, the three-dimensional modeling process of the saline stratum of a real geographical environment is constructed by full use of landform, geomorphy and geographical features revealed by the multi-source data; and by use of sonar detection data, a salt cavity surface three-dimensional model is constructed and is taken as an internal hole constraint, and by use of such space analysis operation as a three-dimensional space Boolean operation, grid dispersing and the like, salt cavity surrounding rock geological three-dimensional modeling is realized under the multiple feature constraints. The method provided by the invention can construct a salt cavity surrounding rock geological three-dimensional model reflecting a true three-dimensional geometric form, provides an effective calculation model for salt cavity surrounding rock creep deformation characteristic value simulation and analysis, and improves the safety of energy reservation by use of a salt cavity.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
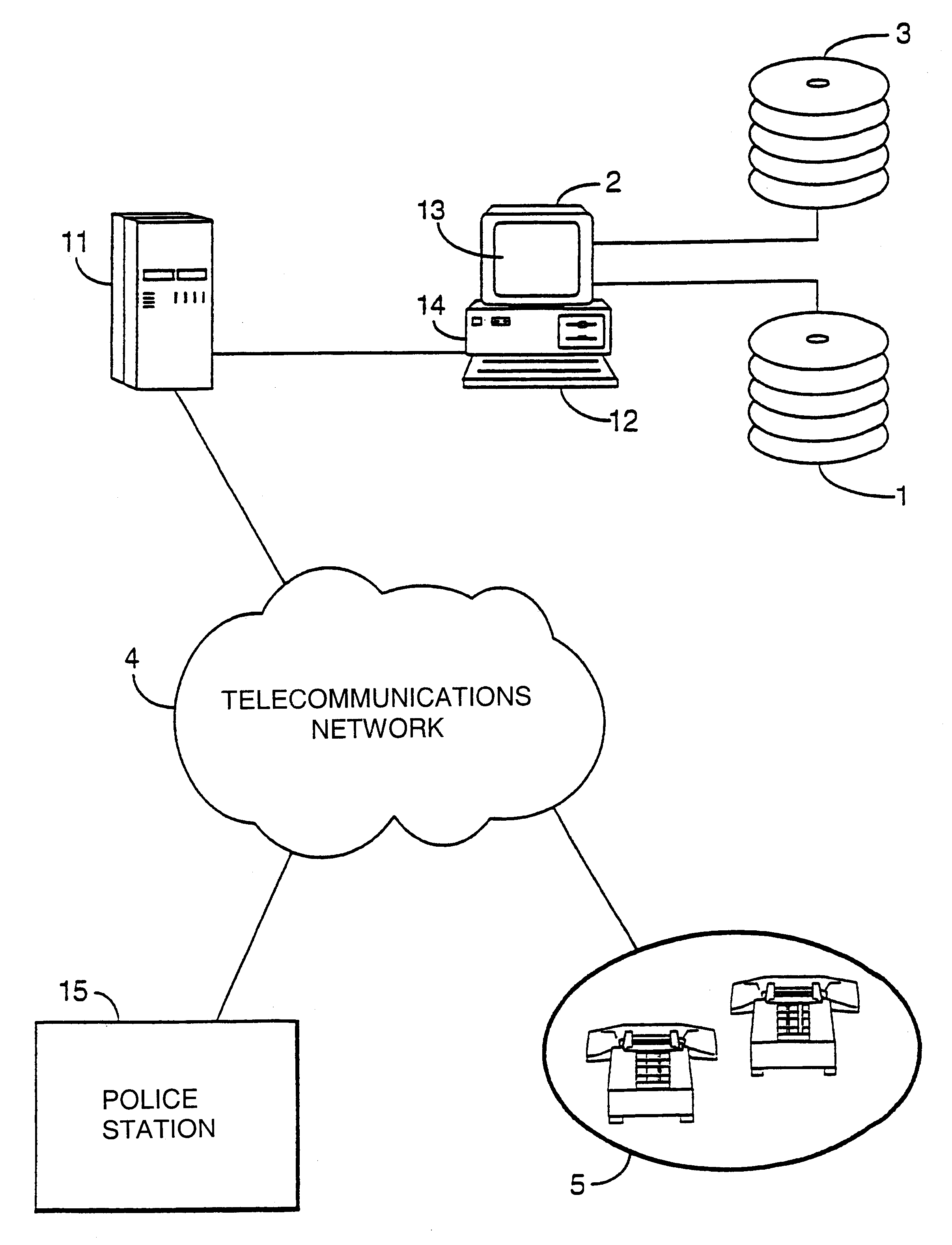
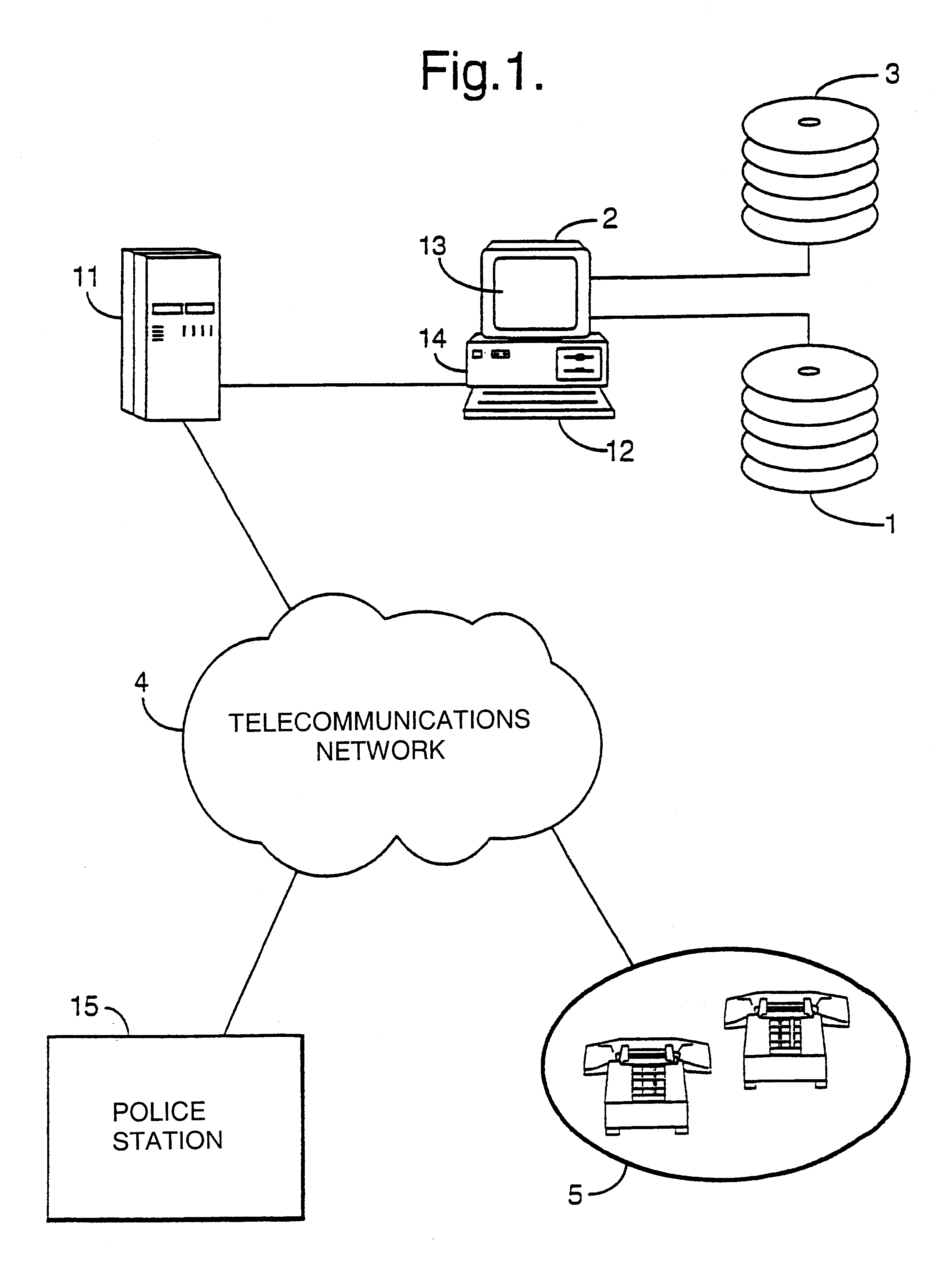
Communications system
InactiveUS6912270B1Reduce congestionSpread quicklyAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingGeographical featureCommunications system
A message distribution system for distributing a message via a telecommunications network to a plurality of communications terminals comprises: a message unit for contacting each of the terminals and sending the message, memory for storing, for a plurality of said terminals, corresponding terminal address data, and storing also a plurality of geographical element data linking geographical features of a portion of the Earth with location data; input for accepting an input control signal to initiate message distribution; area designation unit to designate a geographical area within the portion of the Earth; terminal derivation unit for outputting the terminal address data of terminals for outputting the terminal address data of terminals recorded as being geographically within the area and supplying the addresses for use by the message unit.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Geographical location aggregation from multiple sources
InactiveUS8898002B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographical featureGeographic site
Systems and methods for obtaining geographical location data from multiple sources and aggregating the geographical location data are disclosed. A particular embodiment includes: receiving geo-location data from a plurality of geo-location data collectors, at least one of the plurality of geo-location data collectors being in data communication with an in-vehicle geo-location data source, at least one of the plurality of geo-location data collectors being in data communication with a geo-location data source in a mobile device; collecting reliability data corresponding to one or more of a plurality of geo-location data sources corresponding to the plurality of geo-location data collectors; collecting map data including information related to geographical features associated with the geo-location data; and aggregating, by use of a data processor, the geo-location data from the plurality of geo-location data collectors based on the reliability data and the map data to produce a resulting geo-location fix.
Owner:LENNY INSURANCE LTD
Individual position recommending system related to geographical features
ActiveCN105718576ARealize location recommendationReduce sparsitySpecial data processing applicationsGeographical featurePersonalization
The invention discloses an individual position recommending system related to geographical features, and mainly aims to overcome the defects that the conventional collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm is poor in performance in a data sparseness scene. According to the technical scheme, different functional modules are coordinated with one another to achieve recommendation: a database acquiring module is adopted to acquire target information; a user database module is adopted to save target information in a user database; a user preference digging module is adopted to acquire a candidate position recommending list which is ordered according to user preference from a user database; a geographical database module is adopted to store the target information in a geographical database; a geographical feature digging module is adopted to acquire the candidate position recommending list which is ordered according to geographical features from the geographical database; a recommending module is adopted to acquire recommendation results by using the recommending list ordered according to user preference and the recommending list ordered according to geographical feature influence. As geographical features are taken into account, the problem of data sparseness is alleviated, and the individual position recommending system can be used in site push service based on a position social network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
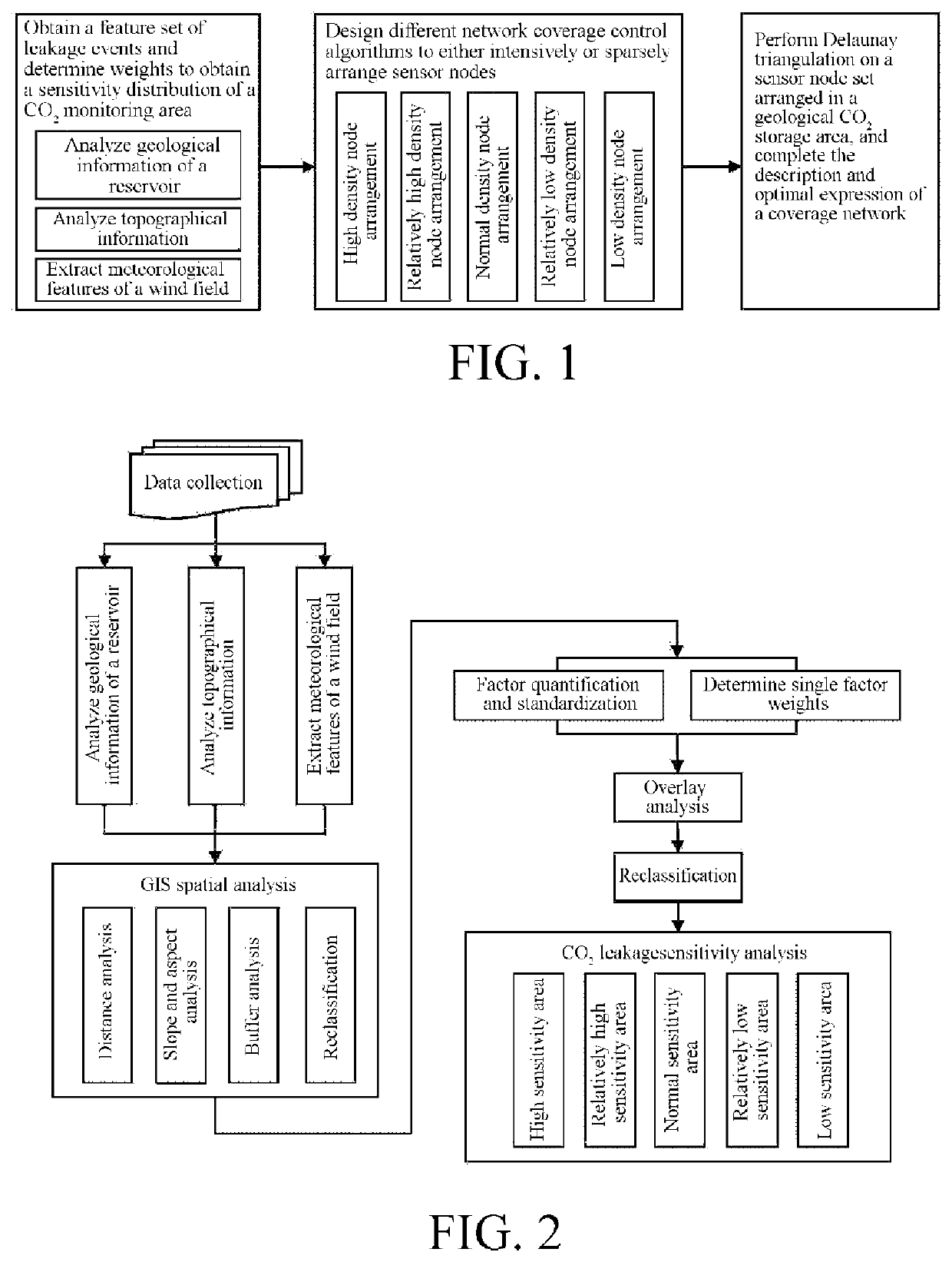
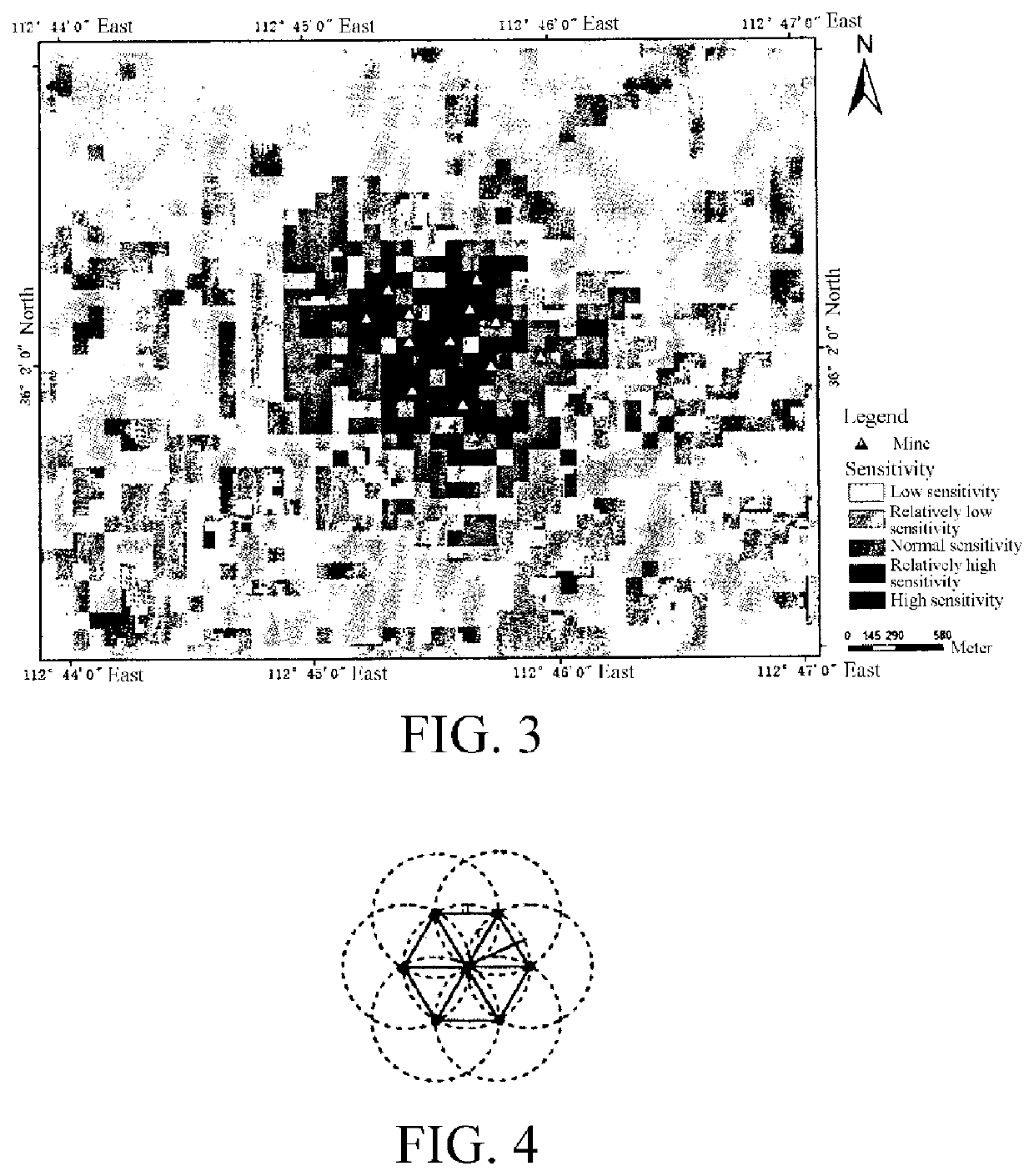
Method for Optimizing Sensor Network Node Location in Geological CO2 Storage Area
ActiveUS20200024930A1Improve monitoring qualityStrong coverageNetwork topologiesPosition fixationCo2 storageDynamic monitoring
The present invention discloses a method for optimizing sensor network node location in a geological CO2 storage area. In the method, by analyzing data in a monitoring area, such as geological data, geographical data, and meteorological data, analyzing influence factors of a CO2 leakage event and determining a sensitivity partition, designing different coverage control schemes of monitoring sensor network nodes, or intensively or sparsely arranging sensor monitoring nodes, a coverage network is described and optimally expressed on the basis of Delaunay triangulation. In the method for optimizing sensor network node location in a geological carbon dioxide storage area, the arrangement density of wireless sensor network nodes can be dynamically adjusted according to geological and geographical features of a detection area, and the arrangement optimization of a dynamic monitoring sensor network for coal seam carbon dioxide injection area leakage can be realized. The method reduces node redundancy and communication overheads as much as possible, and has strong network coverage and network connectivity.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +3
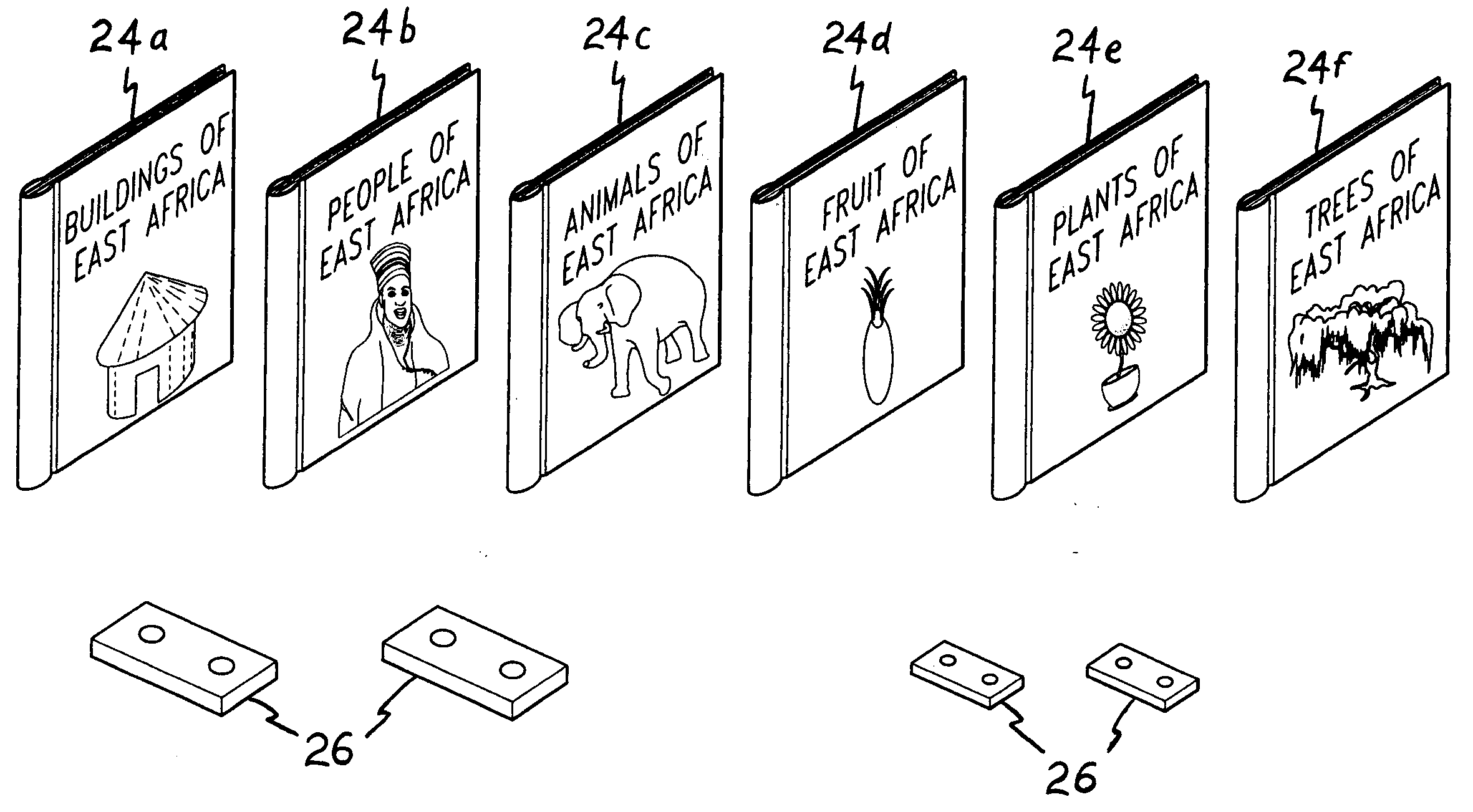
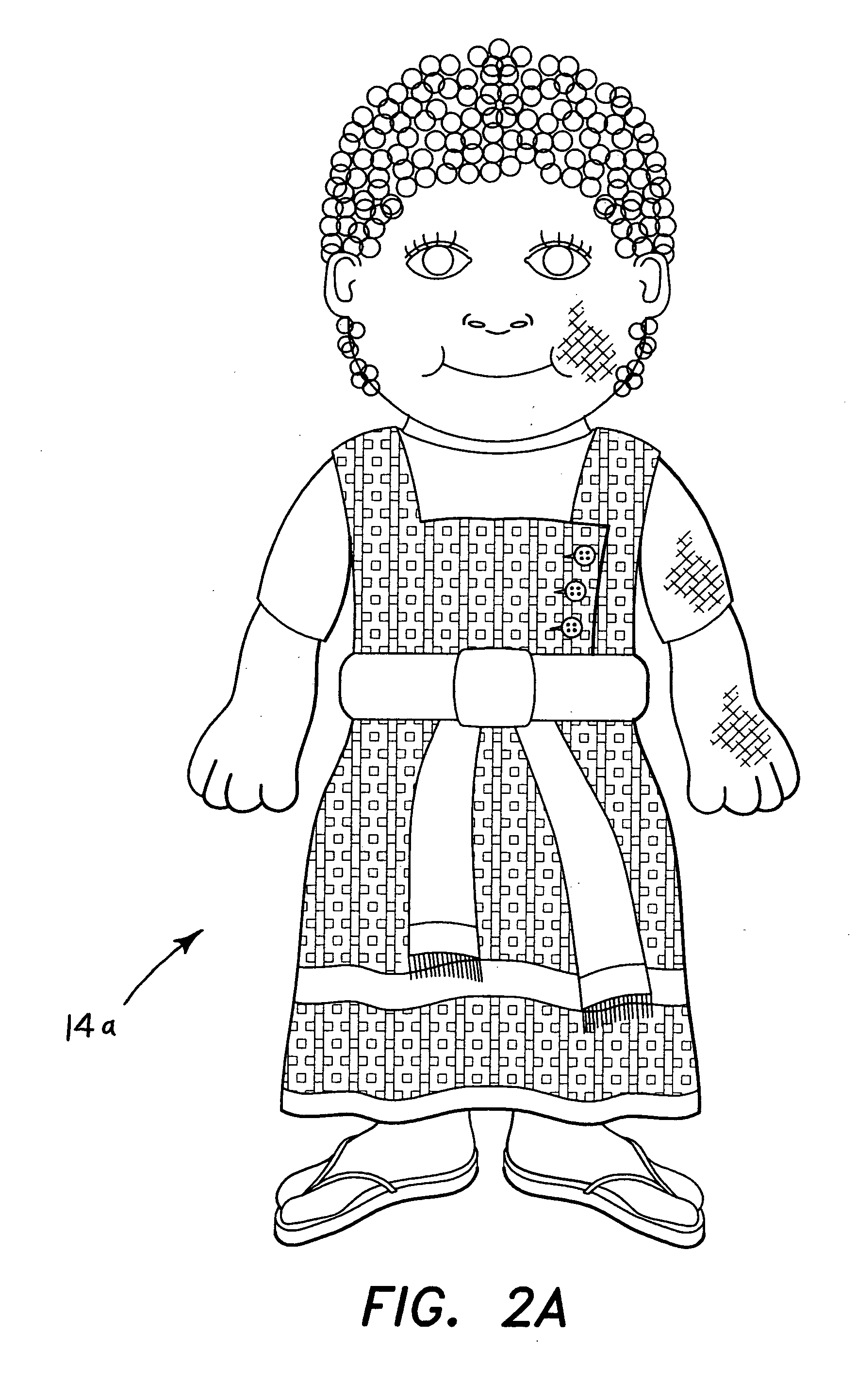
Multicultural educational kit
The multicultural educational kit includes a series of components relating to one or more specific cultural, ethnic, racial, national, or other population groups, for teaching young children about such different groups throughout the world and eliminating the development of early prejudices toward peoples different from one's own. The present kit preferably contains a costumed doll representing a child native to the group being studied, a video presentation describing a typical day in the life of a child of the culture, a series of finger puppets representing a family of the group being studied, a series of small picture books and corresponding audio presentations discussing various subject areas of the culture or group being studied, an activity book relating to the culture or group being studied, a regional map, and a series of flash cards having various terms or words for colors, numbers, family members, geographical features, etc.
Owner:PERKINS CHERYL E +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com