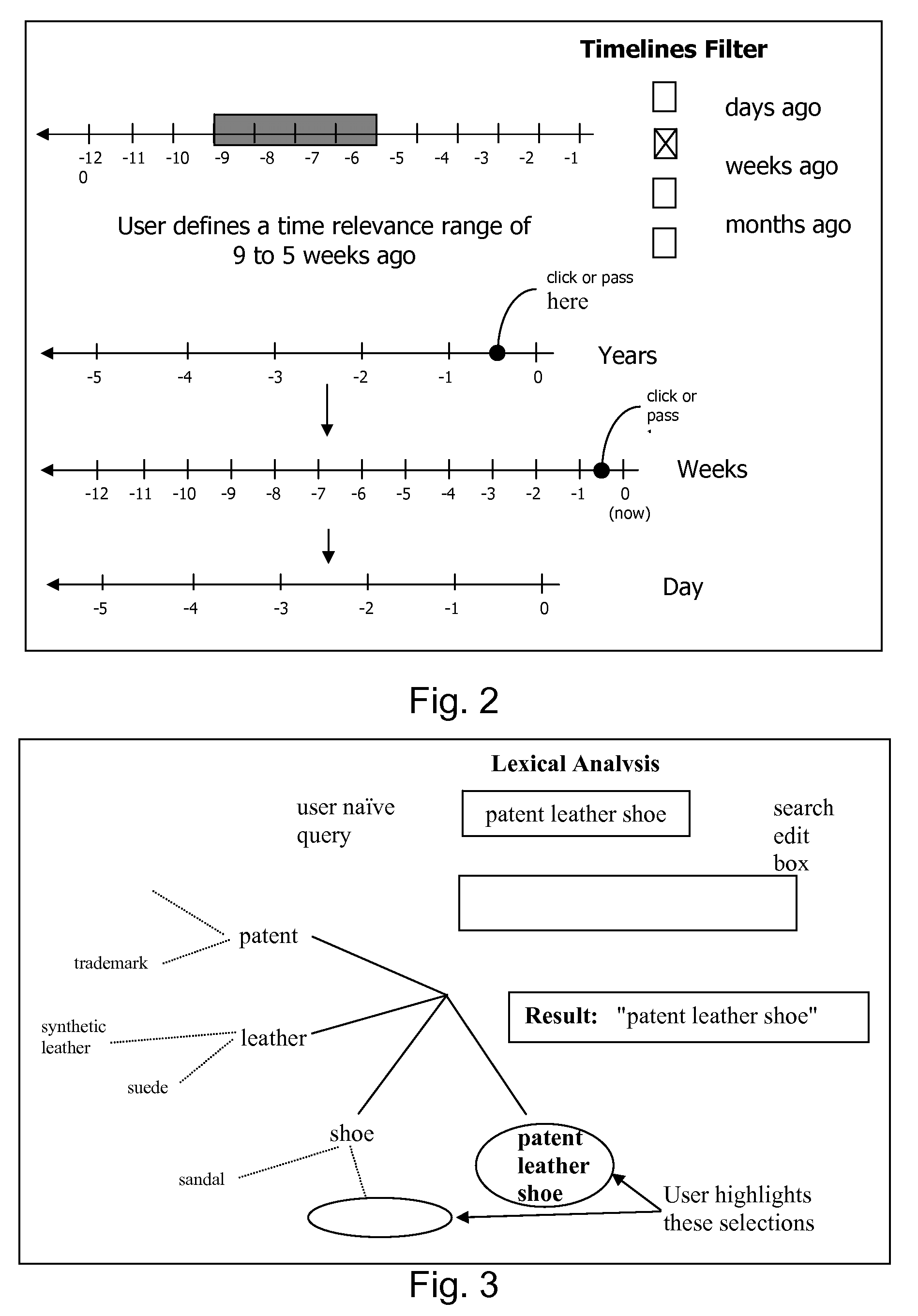
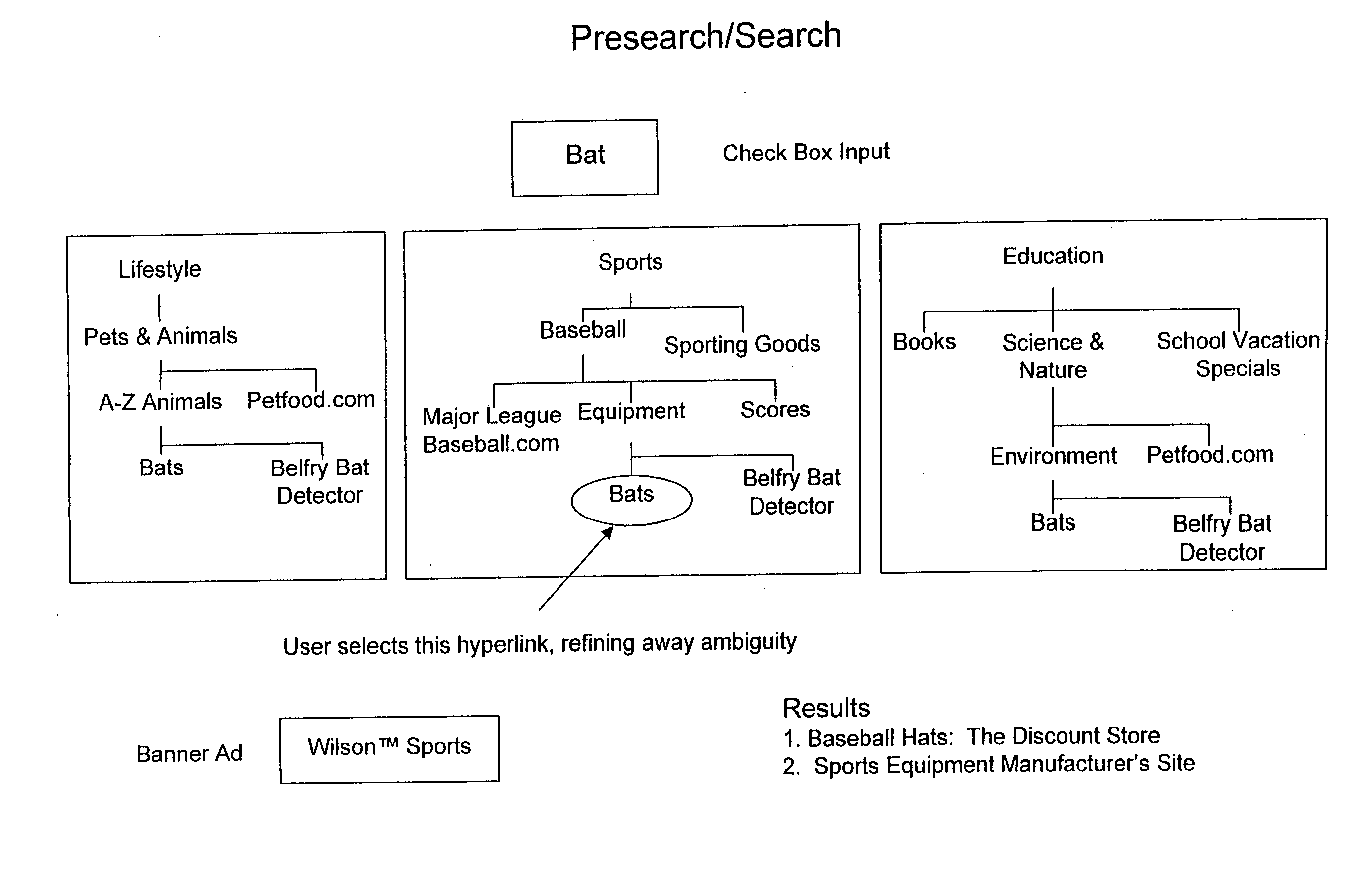
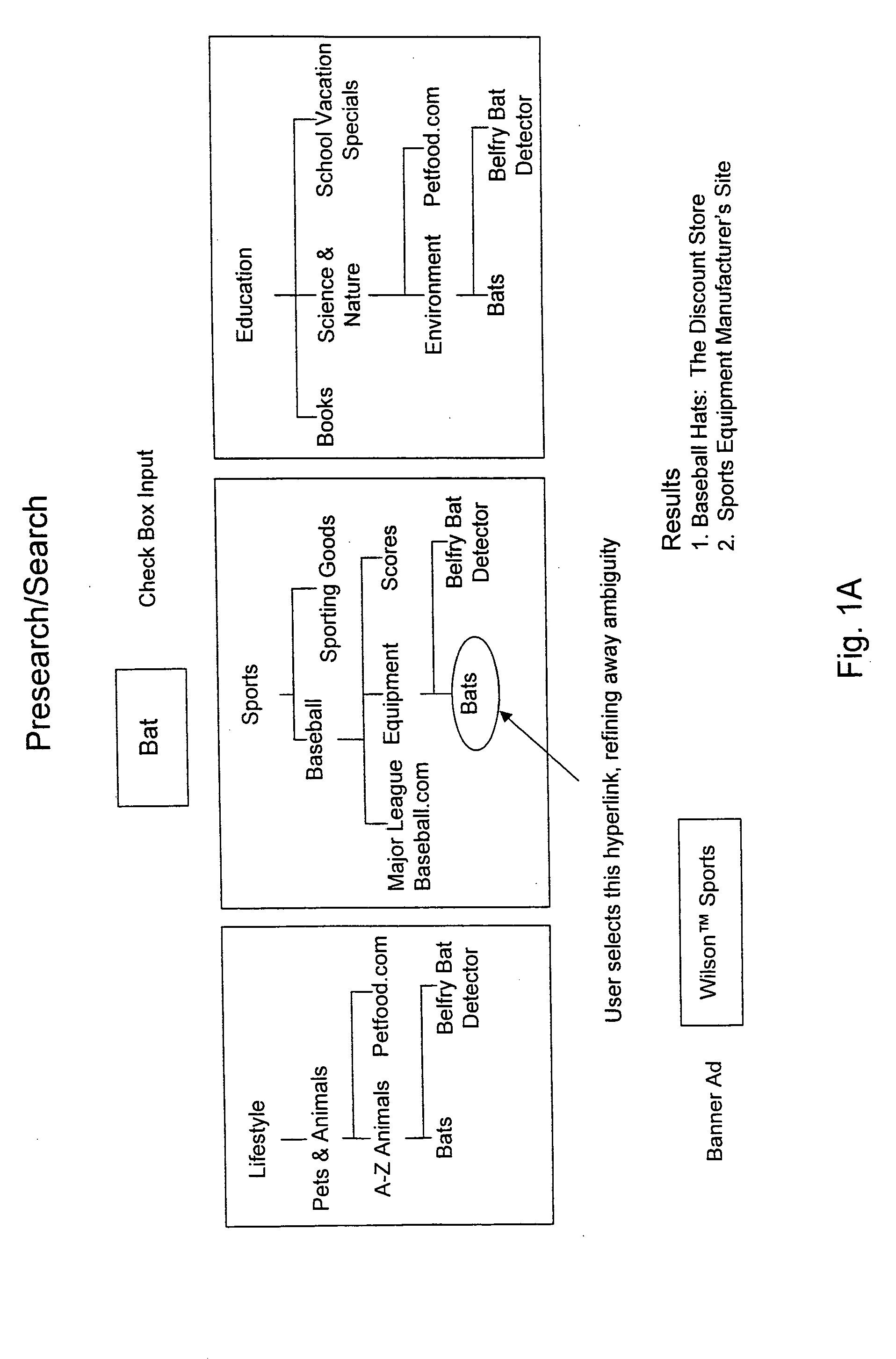
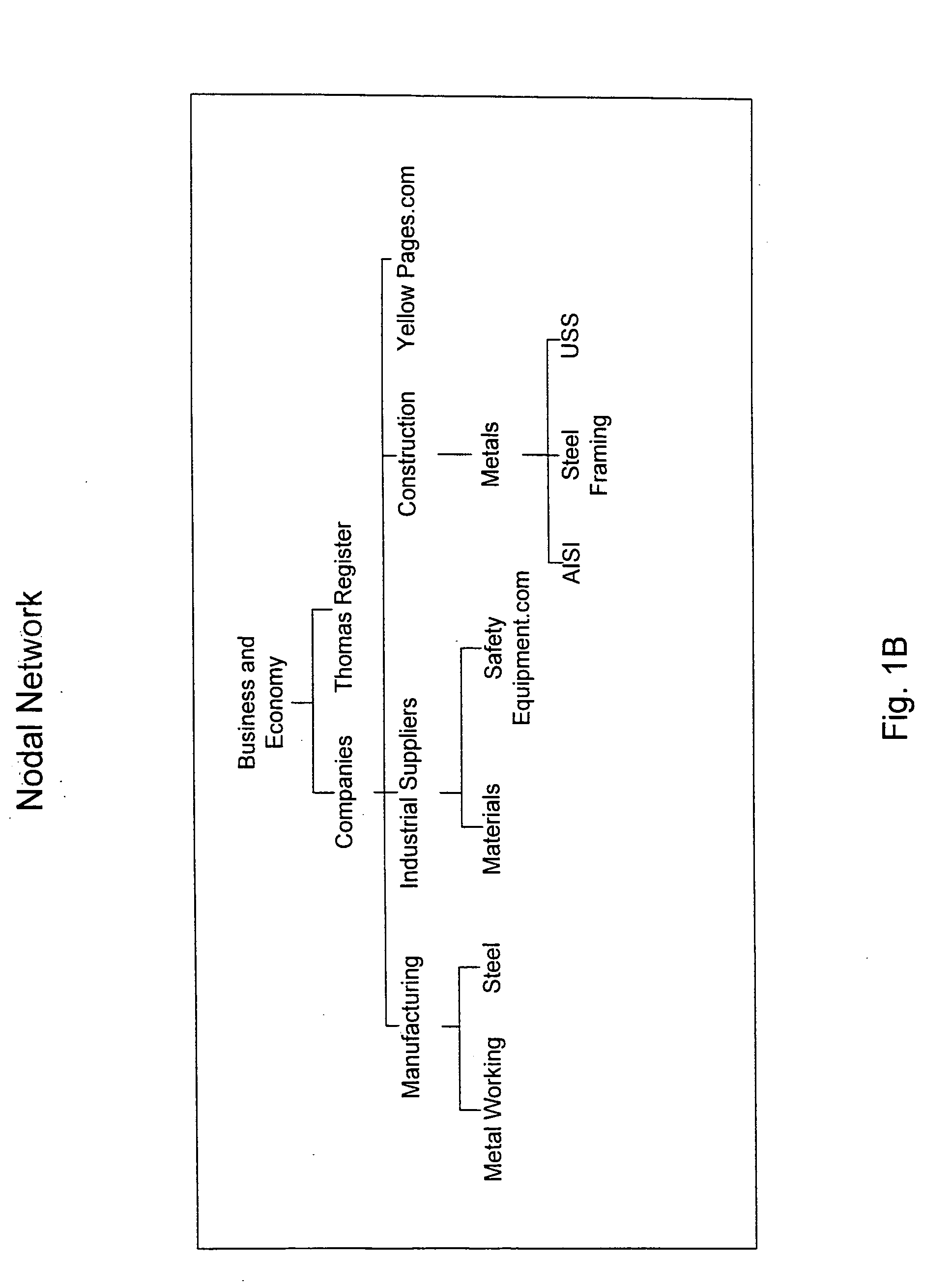
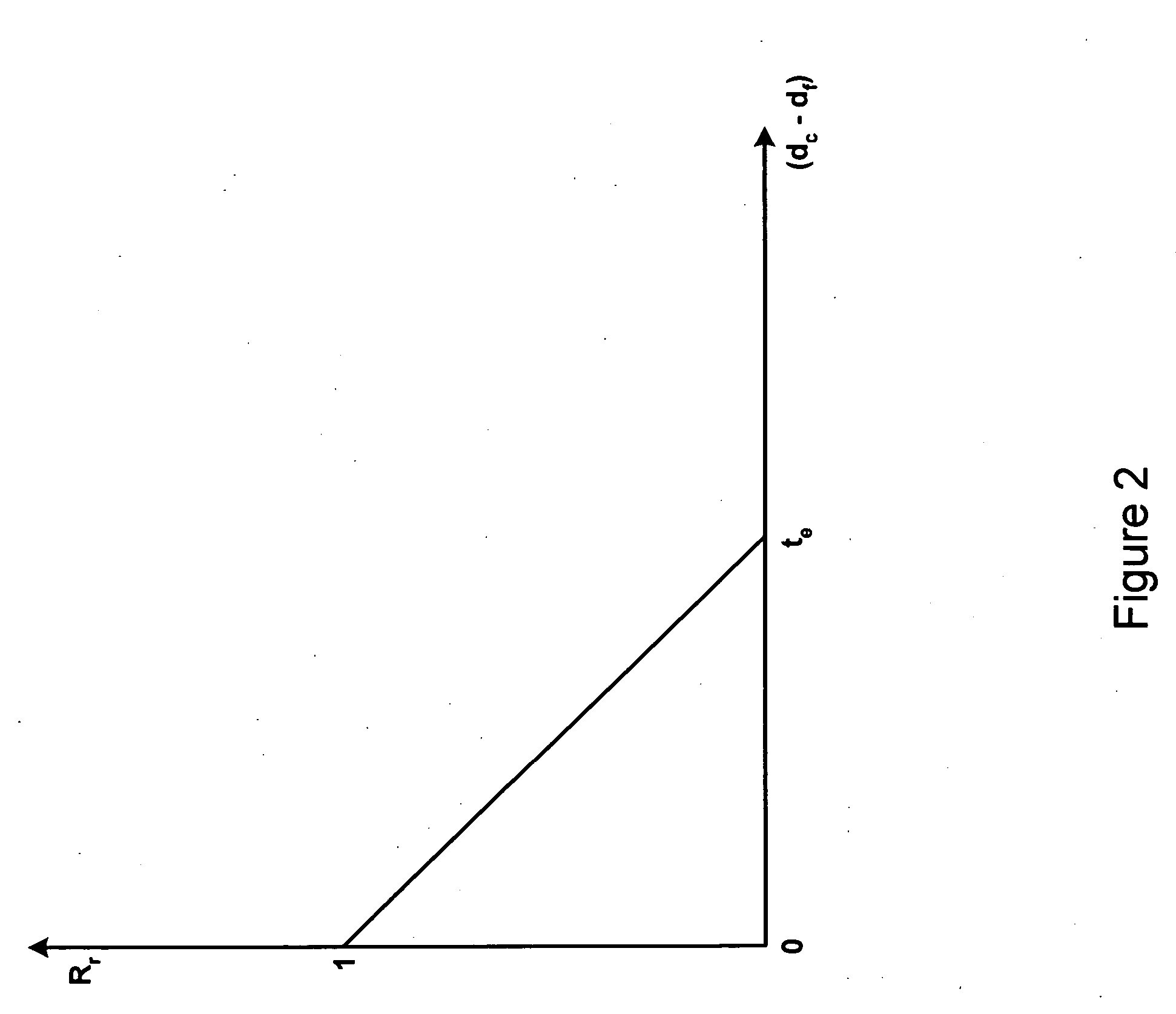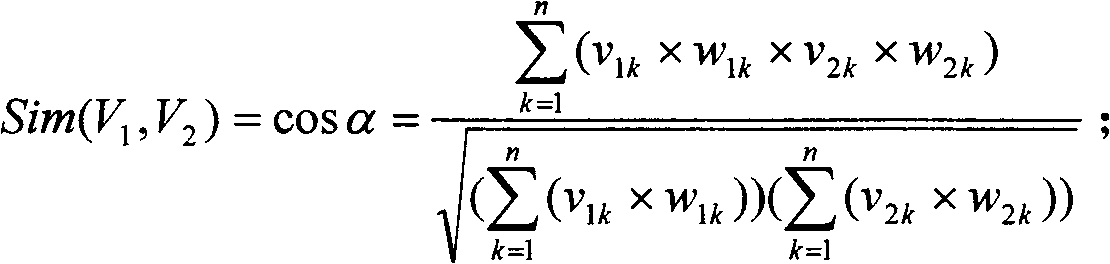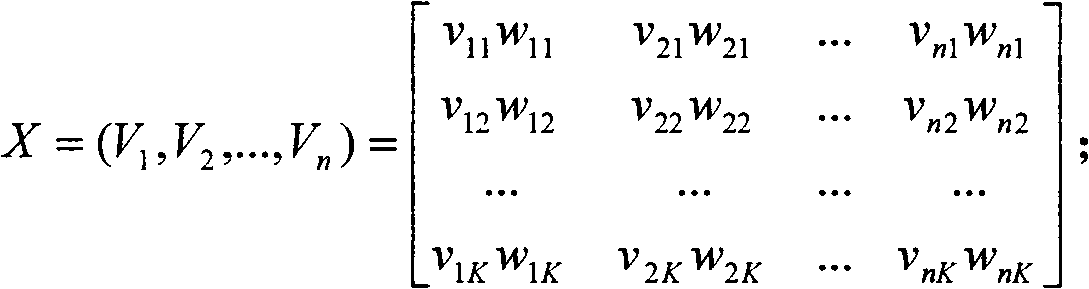Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1303 results about "Collaborative filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Collaborative filtering (CF) is a technique used by recommender systems. Collaborative filtering has two senses, a narrow one and a more general one. In the newer, narrower sense, collaborative filtering is a method of making automatic predictions (filtering) about the interests of a user by collecting preferences or taste information from many users (collaborating). The underlying assumption of the collaborative filtering approach is that if a person A has the same opinion as a person B on an issue, A is more likely to have B's opinion on a different issue than that of a randomly chosen person. For example, a collaborative filtering recommendation system for television tastes could make predictions about which television show a user should like given a partial list of that user's tastes (likes or dislikes). Note that these predictions are specific to the user, but use information gleaned from many users. This differs from the simpler approach of giving an average (non-specific) score for each item of interest, for example based on its number of votes.
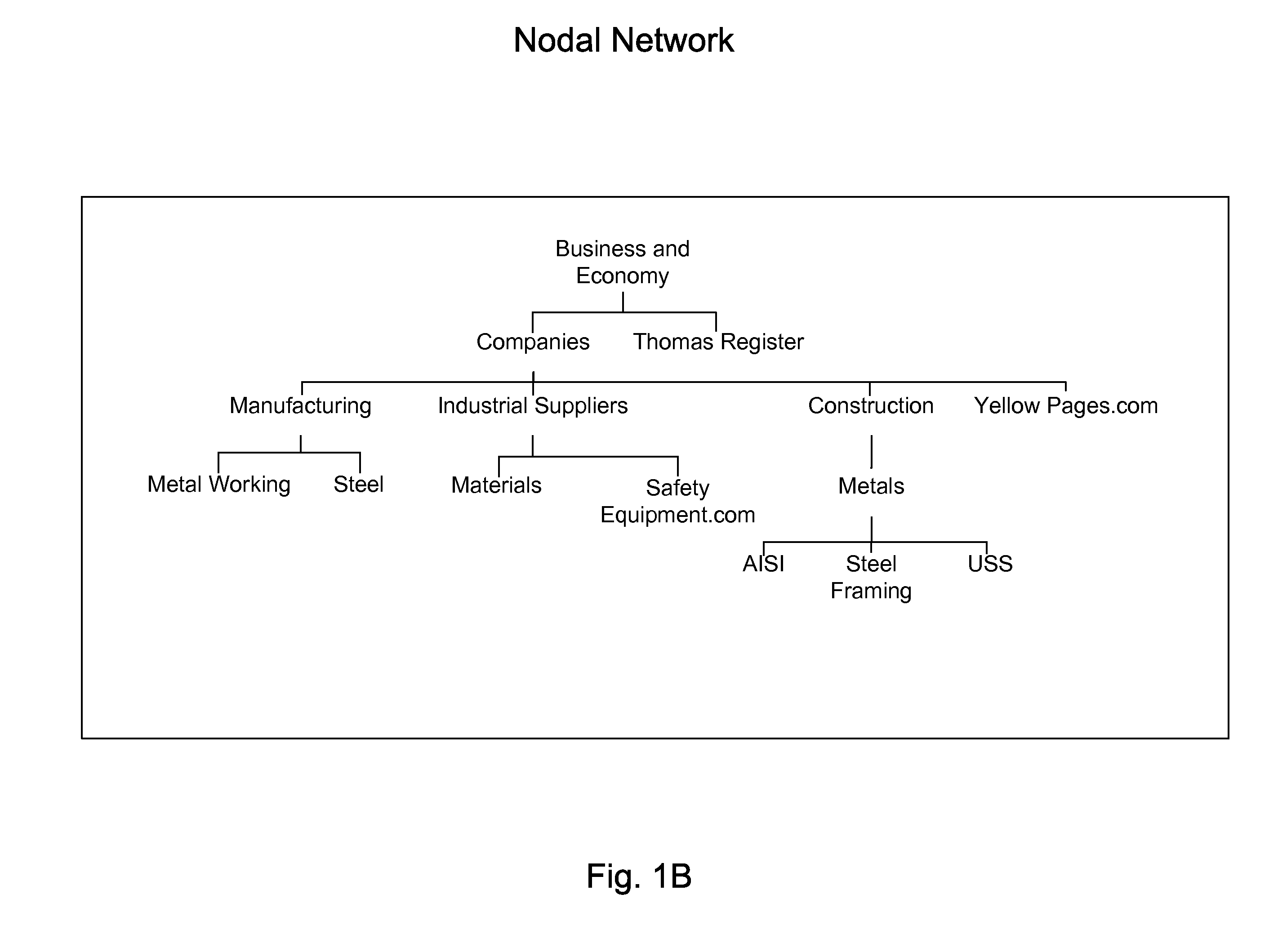
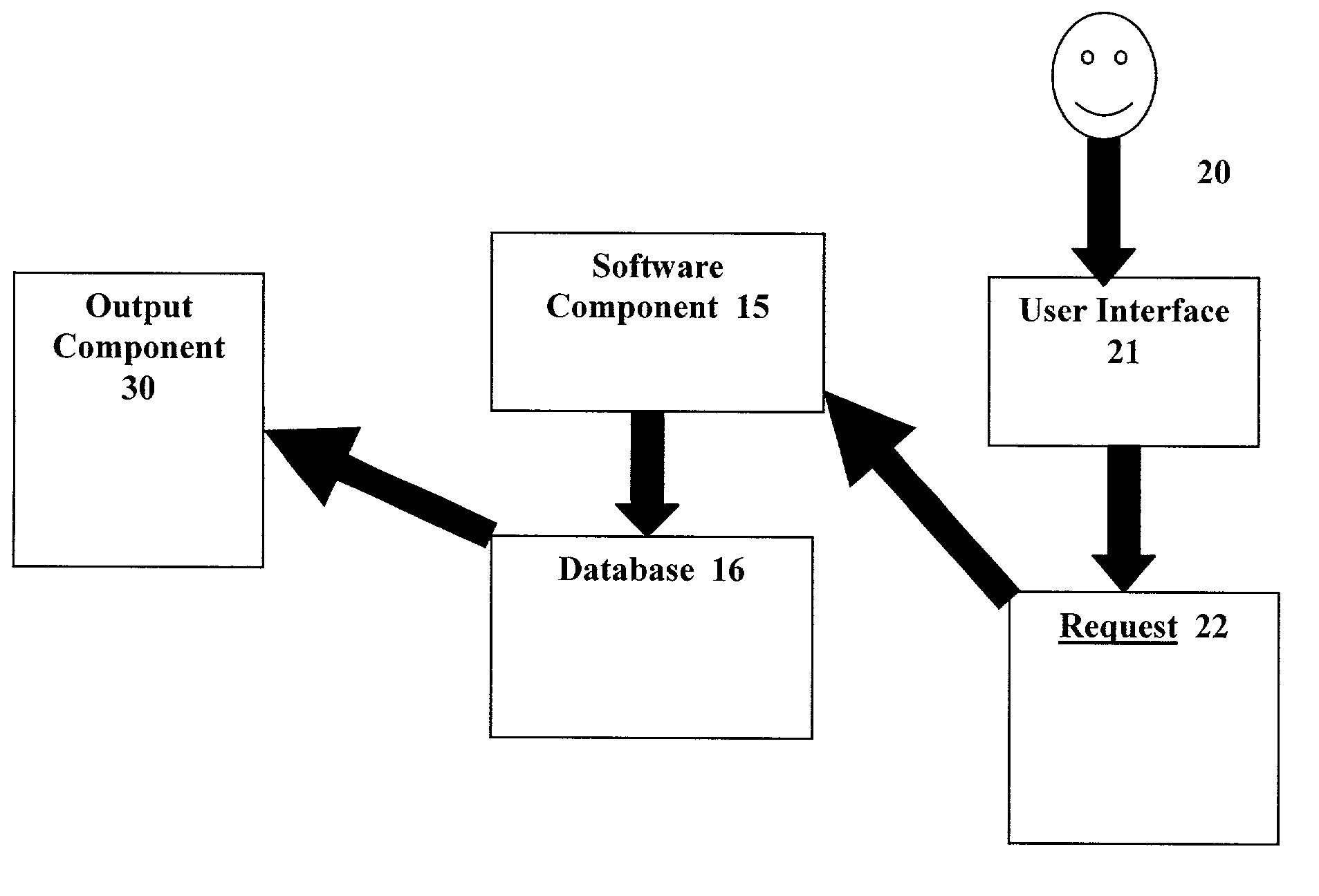
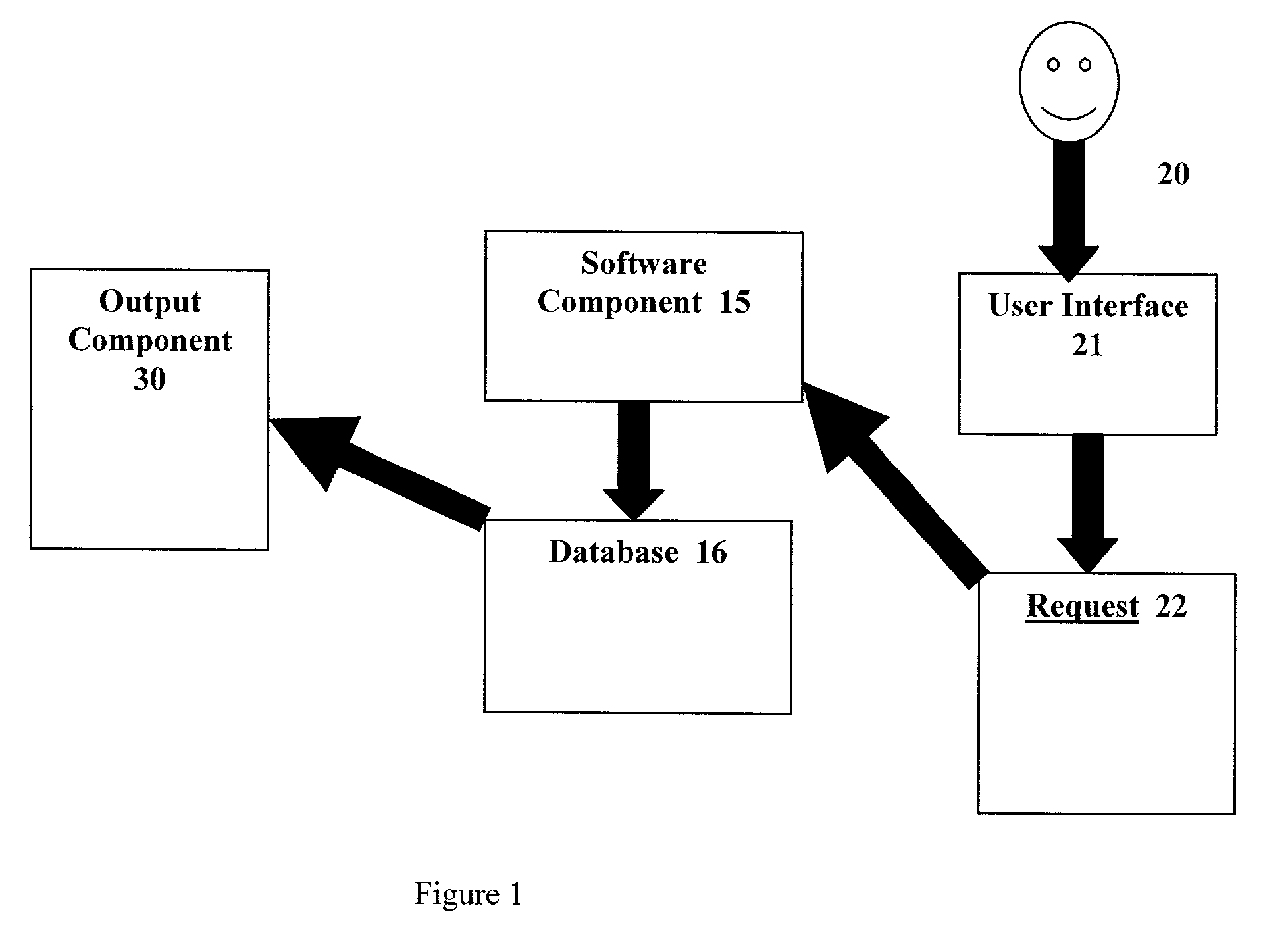
Database access system
ActiveUS7181438B1Increased formationGood user interfaceDigital data information retrievalAdvertisementsAnonymityPopulation statistics
An improved human user computer interface system, wherein a user characteristic or set of characteristics, such as demographic profile or societal “role”, is employed to define a scope or domain of operation. The operation itself may be a database search, to interactively define a taxonomic context for the operation, a business negotiation, or other activity. After retrieval of results, a scoring or ranking may be applied according to user define criteria, which are, for example, commensurate with the relevance to the context, but may be, for example, by date, source, or other secondary criteria. A user profile is preferably stored in a computer accessible form, and may be used to provide a history of use, persistent customization, collaborative filtering and demographic information for the user. Advantageously, user privacy and anonymity is maintained by physical and algorithmic controls over access to the personal profiles, and releasing only aggregate data without personally identifying information or of small groups.
Owner:RELATIVITY DISPLAY LLC
Database access system
InactiveUS20070156677A1Increased formationGood user interfaceDigital data information retrievalAdvertisementsPersonal detailsAnonymity
An improved human user computer interface system, wherein a user characteristic or set of characteristics, such as demographic profile or societal “role”, is employed to define a scope or domain of operation. The operation itself may be a database search, to interactively define a taxonomic context for the operation, a business negotiation, or other activity. After retrieval of results, a scoring or ranking may be applied according to user define criteria, which are, for example, commensurate with the relevance to the context, but may be, for example, by date, source, or other secondary criteria. A user profile is preferably stored in a computer accessible form, and may be used to provide a history of use, persistent customization, collaborative filtering and demographic information for the user. Advantageously, user privacy and anonymity is maintained by physical and algorithmic controls over access to the personal profiles, and releasing only aggregate data without personally identifying information or of small groups.
Owner:RELATIVITY DISPLAY LLC
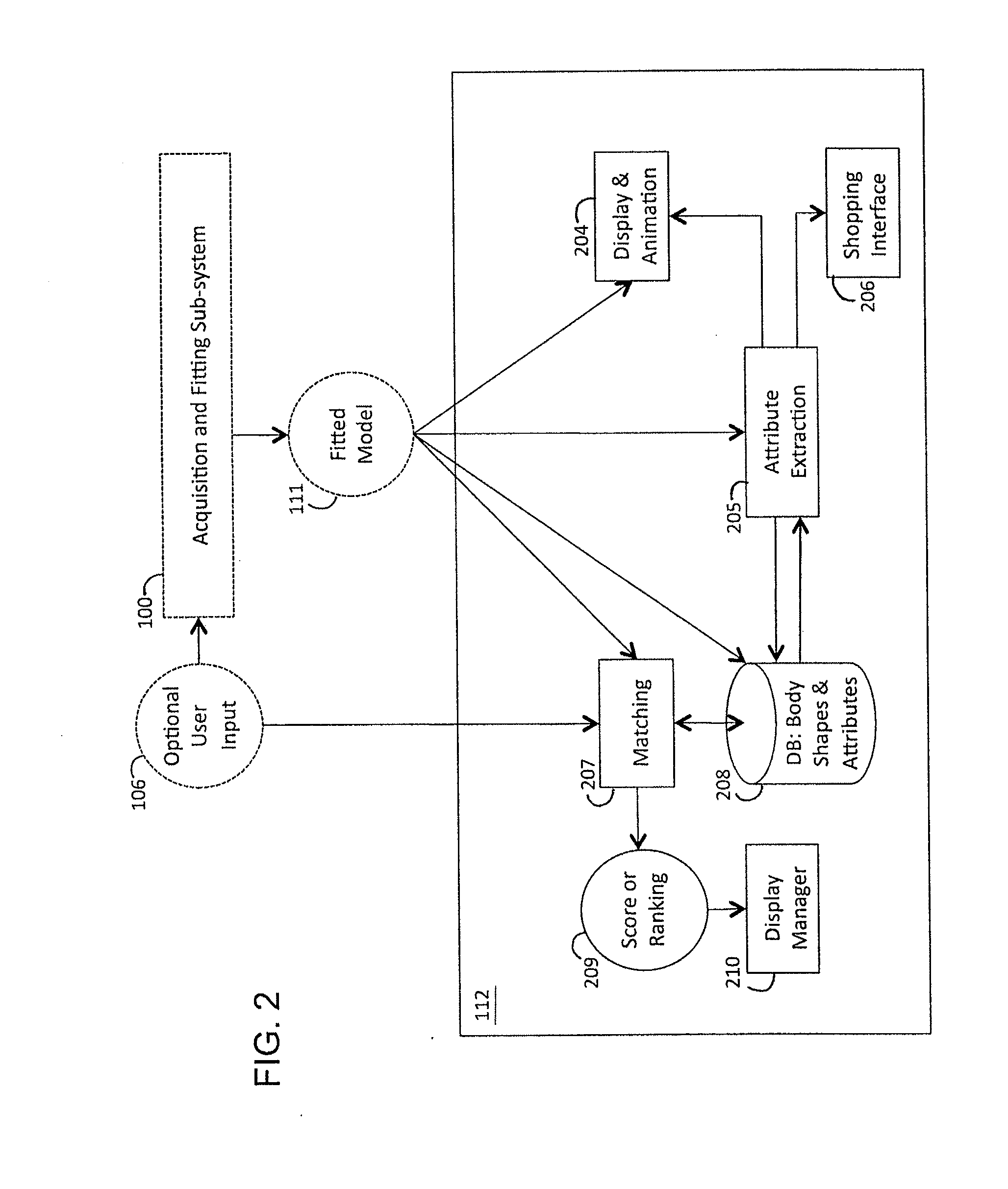
Method and apparatus for estimating body shape
ActiveUS20100111370A1Less-accurate measurementAccurate captureImage enhancementImage analysisBody shapeThe Internet
A system and method of estimating the body shape of an individual from input data such as images or range maps. The body may appear in one or more poses captured at different times and a consistent body shape is computed for all poses. The body may appear in minimal tight-fitting clothing or in normal clothing wherein the described method produces an estimate of the body shape under the clothing. Clothed or bare regions of the body are detected via image classification and the fitting method is adapted to treat each region differently. Body shapes are represented parametrically and are matched to other bodies based on shape similarity and other features. Standard measurements are extracted using parametric or non-parametric functions of body shape. The system components support many applications in body scanning, advertising, social networking, collaborative filtering and Internet clothing shopping.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Computer graphic display visualization system and method
InactiveUS6868525B1Improve compactnessIncrease flexibilityDrawing from basic elementsAdvertisementsGraphicsCollaborative filtering
An improved human user computer interface system, providing a graphic representation of a hierarchy populated with naturally classified objects, having included therein at least one associated object having a distinct classification. Preferably, a collaborative filter is employed to define the appropriate associated object. The associated object preferably comprises a sponsored object, generating a subsidy or revenue.
Owner:RELATIVITY DISPLAY LLC
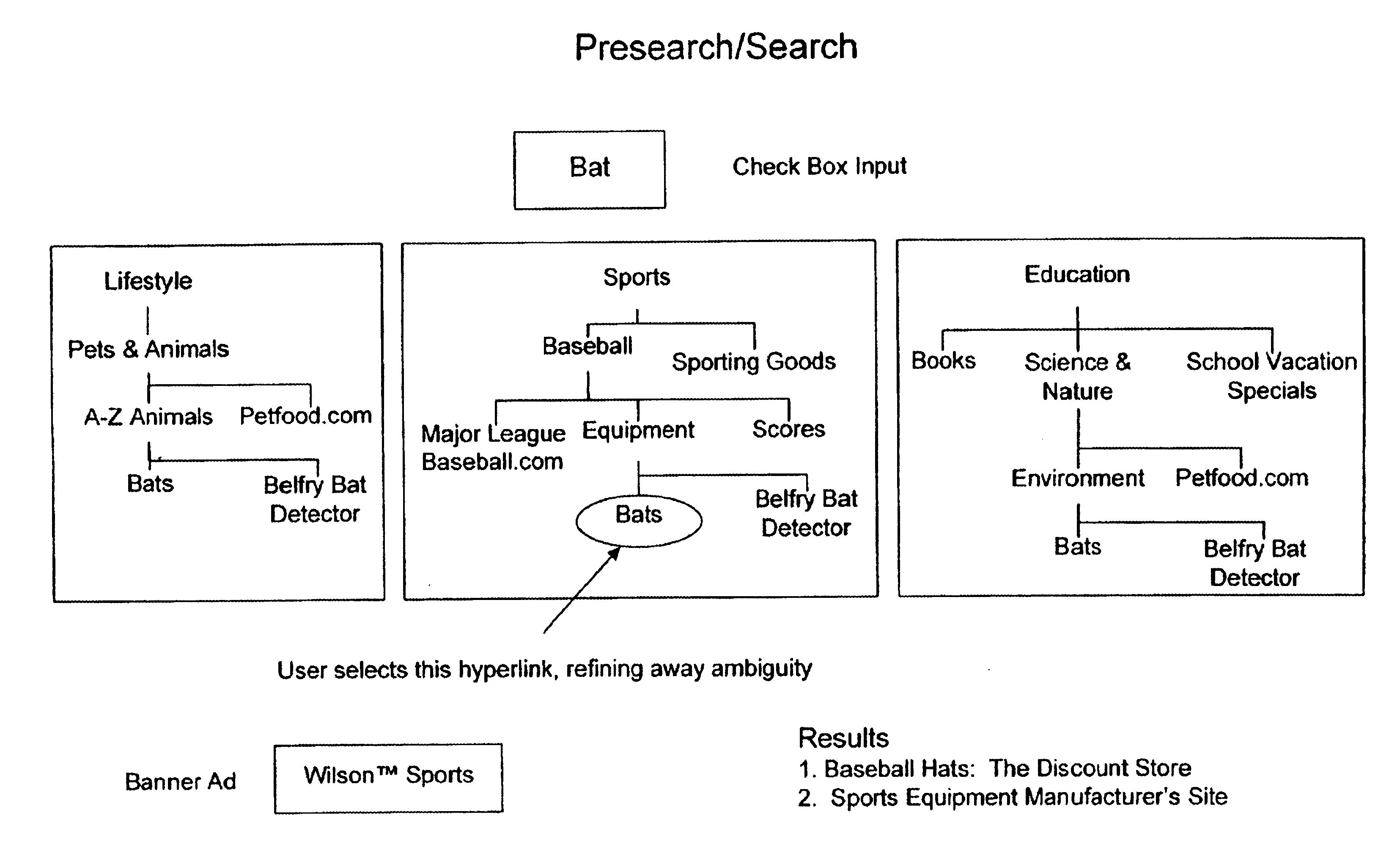
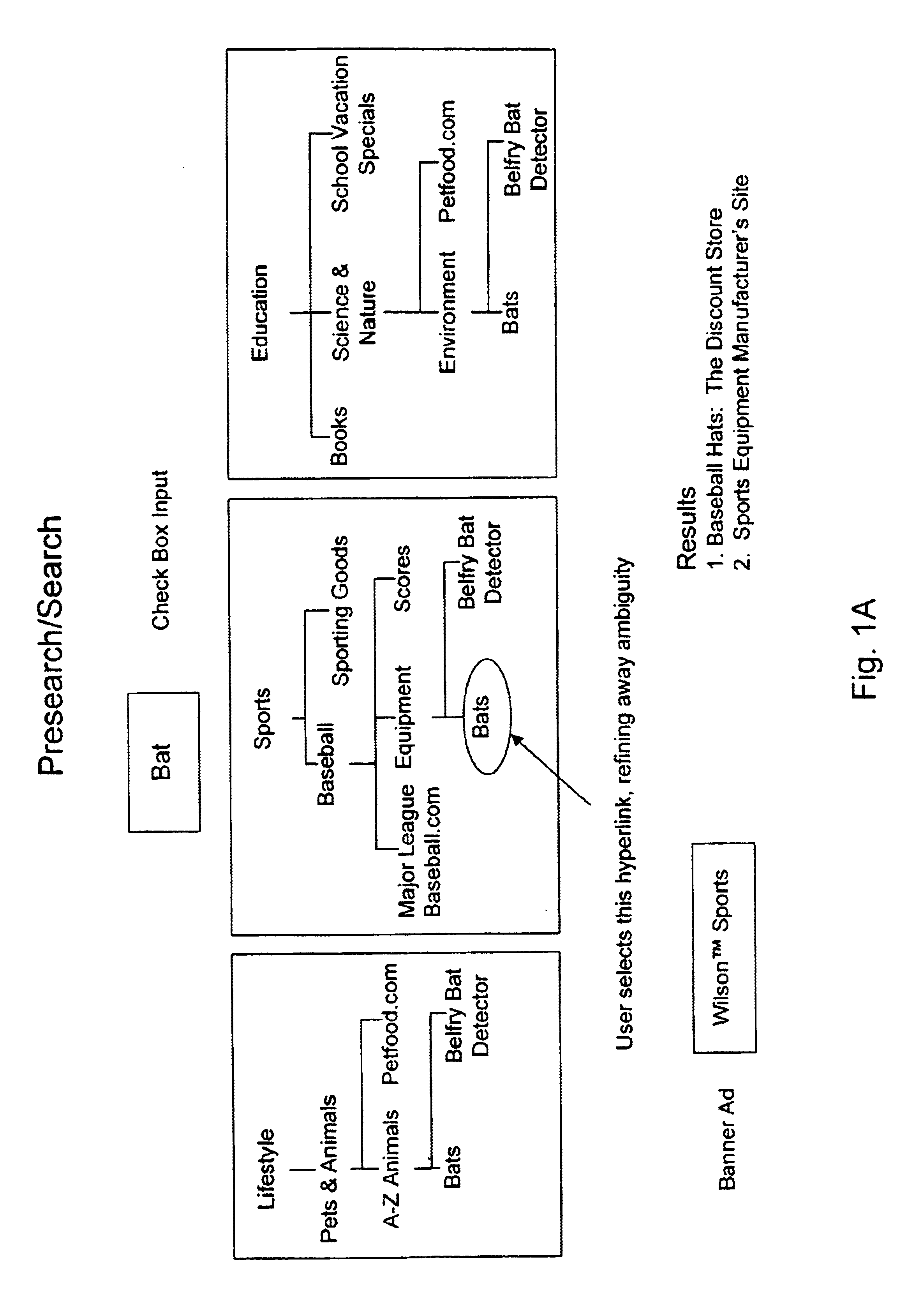
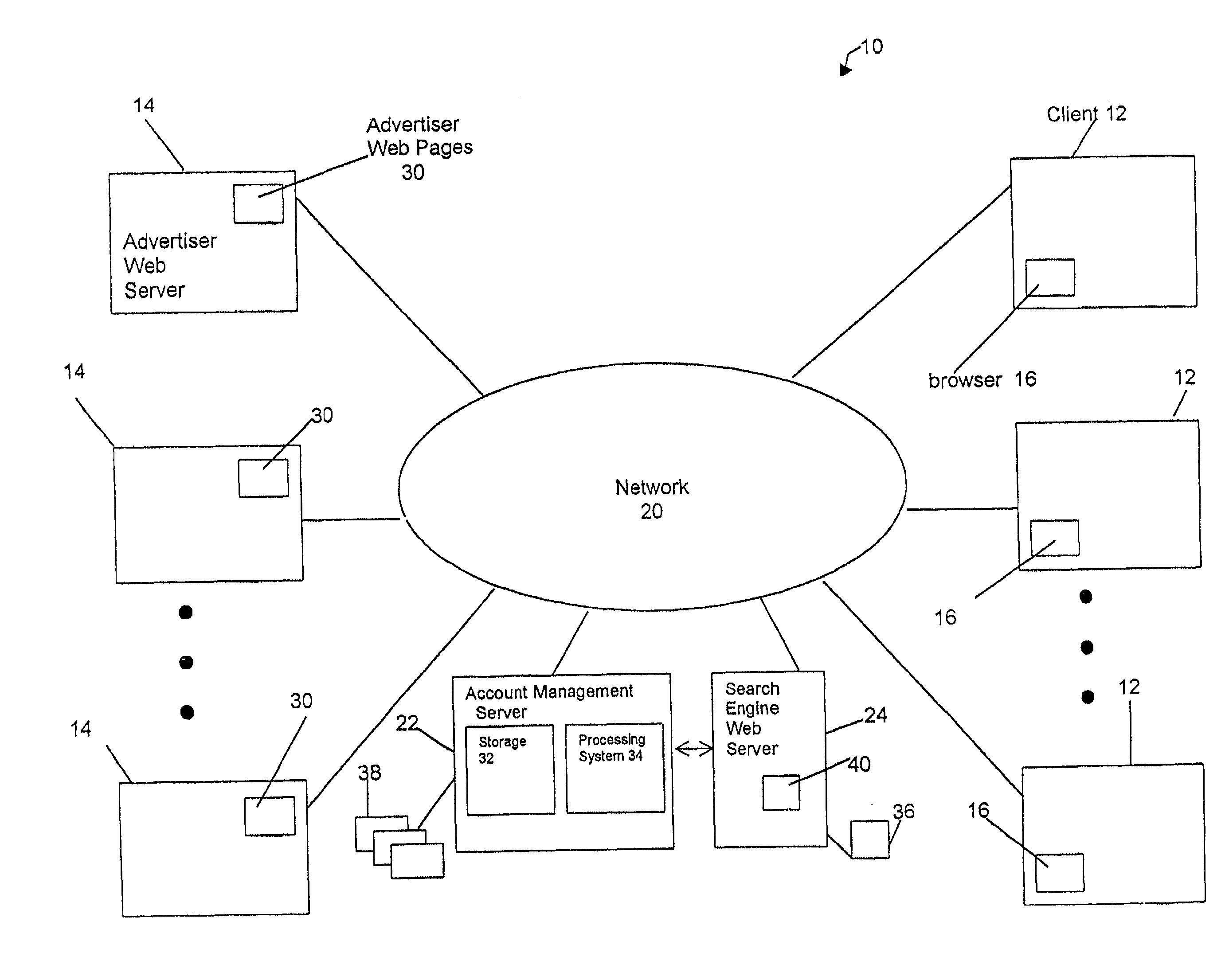
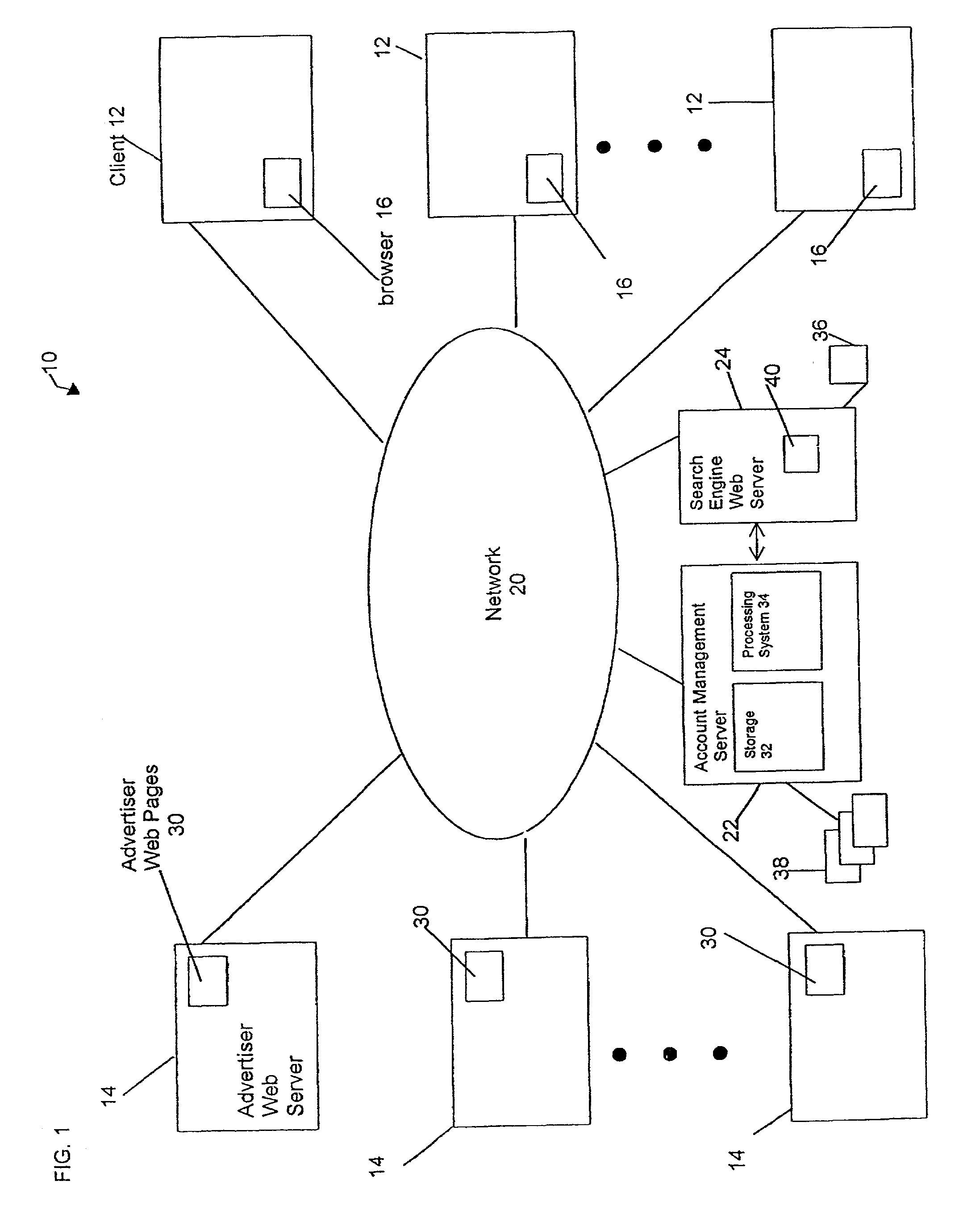
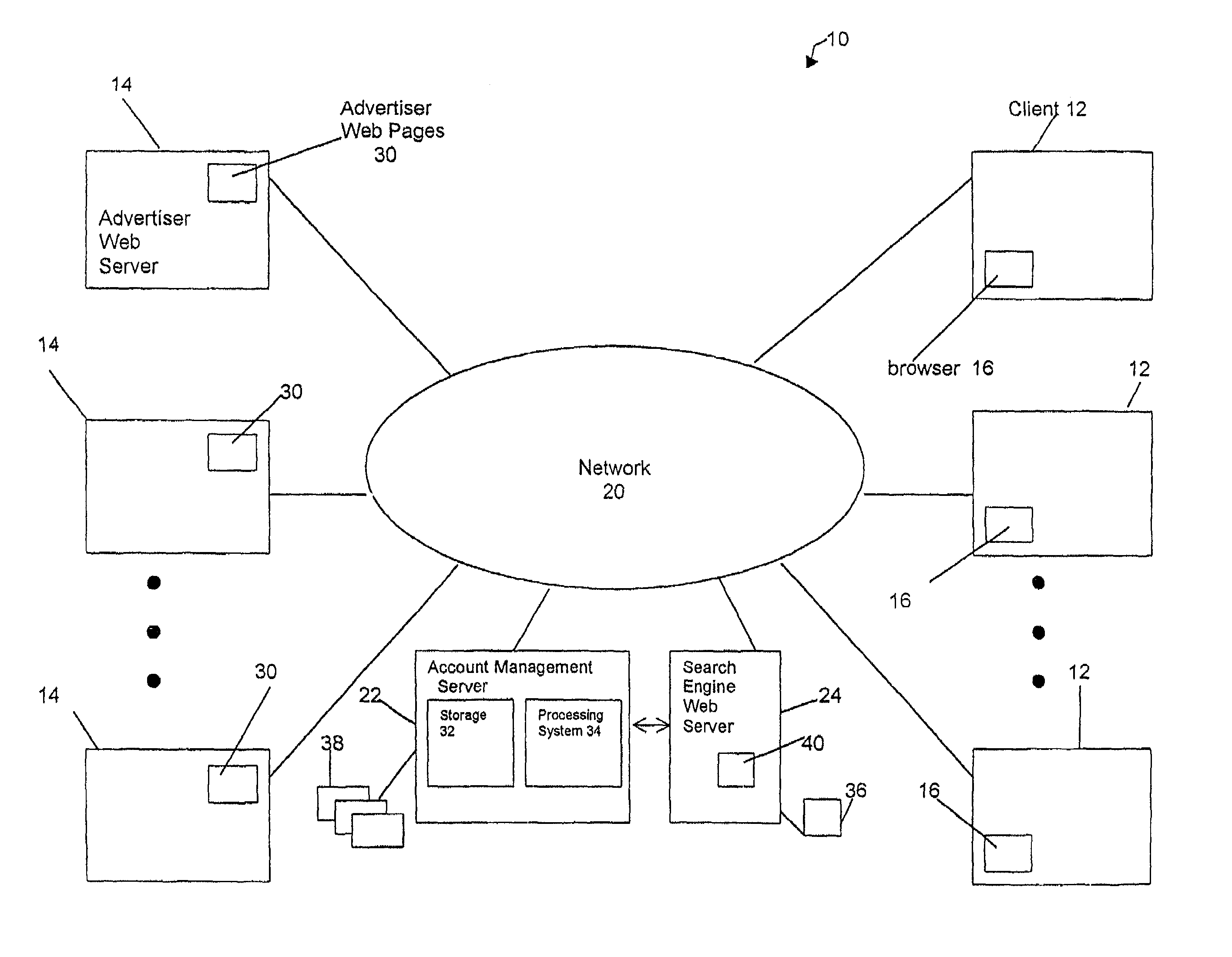
Recommending search terms using collaborative filtering and web spidering
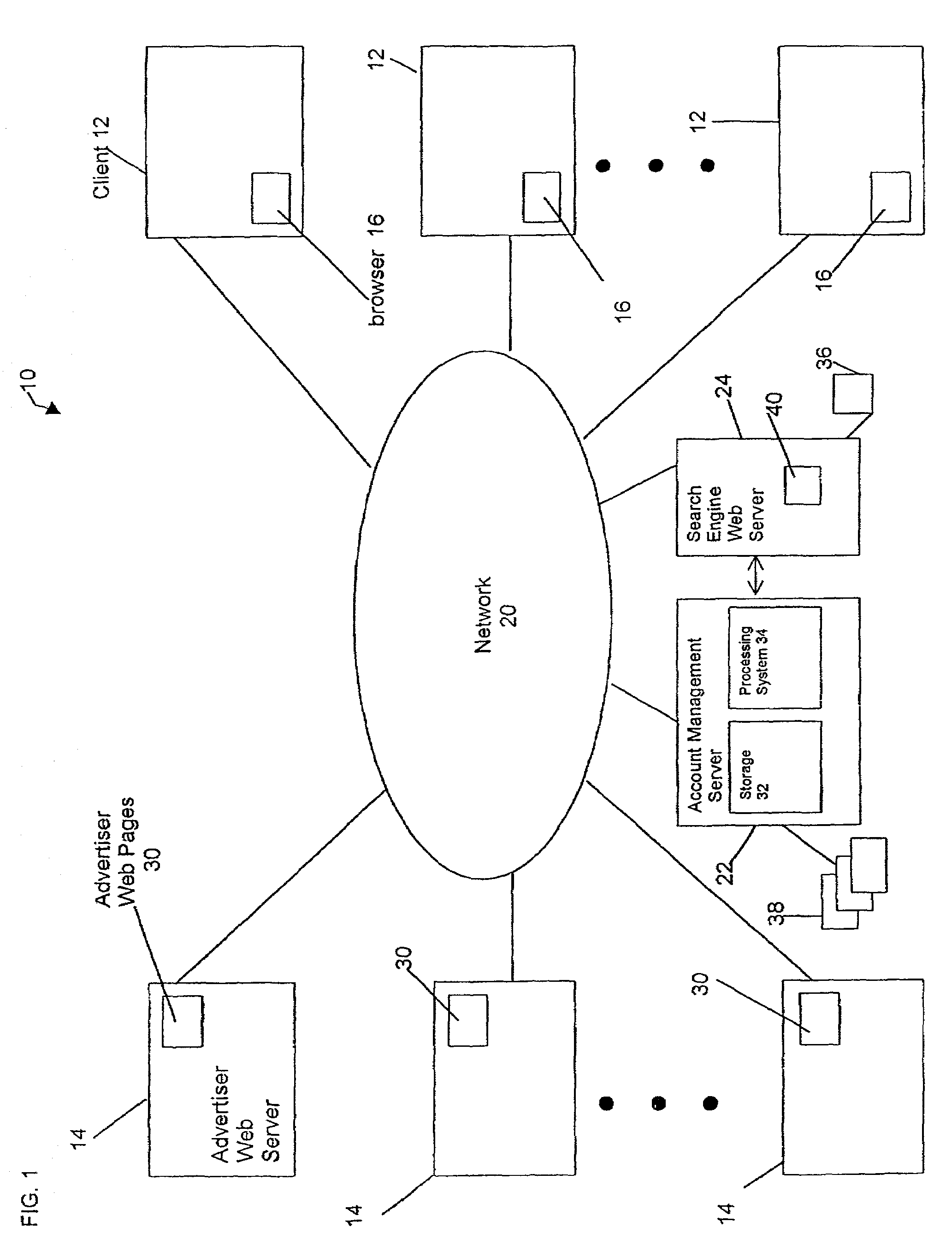
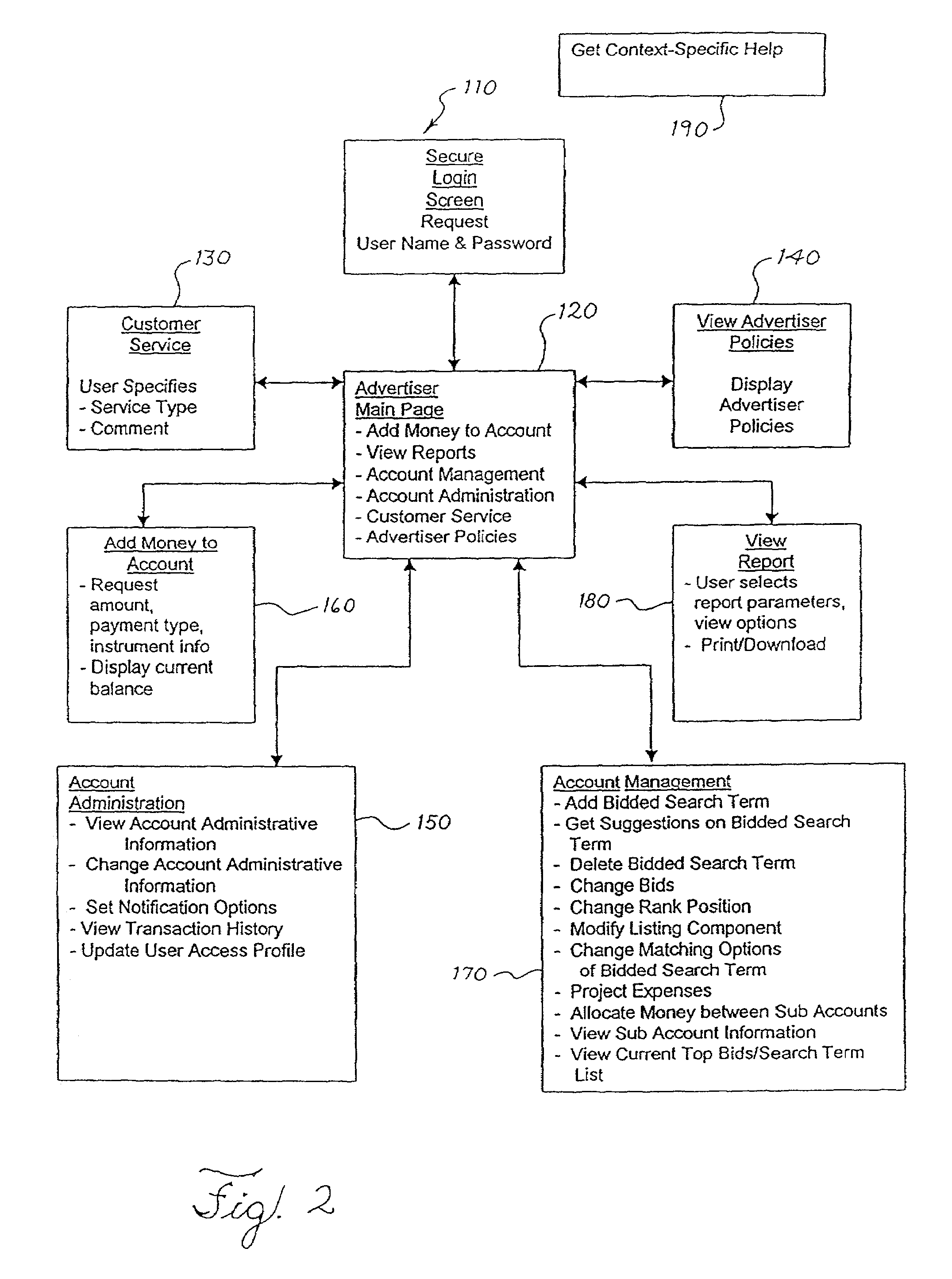
In a pay-for-placement search system, the system makes search term recommendations to advertisers managing their accounts in one or more of two ways. A first technique involves looking for good search terms directly on an advertiser's web site. A second technique involves comparing an advertiser to other, similar advertisers and recommending the search terms the other advertisers have chosen. The first technique is called spidering and the second technique is called collaborative filtering. In the preferred embodiment, the output of the spidering step is used as input to the collaborative filtering step. The final output of search terms from both steps is then interleaved in a natural way.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
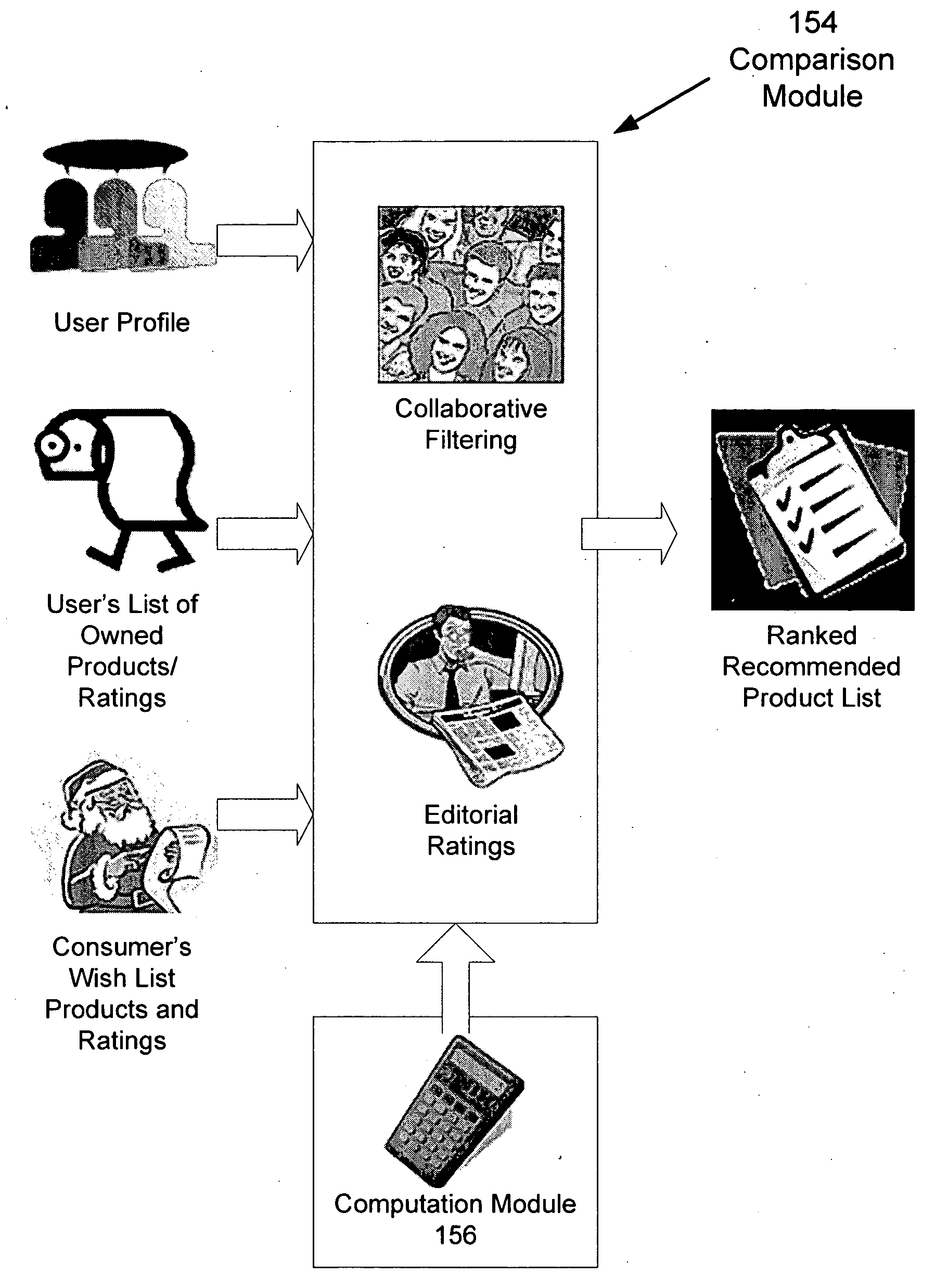
System and method for an electronic product advisor
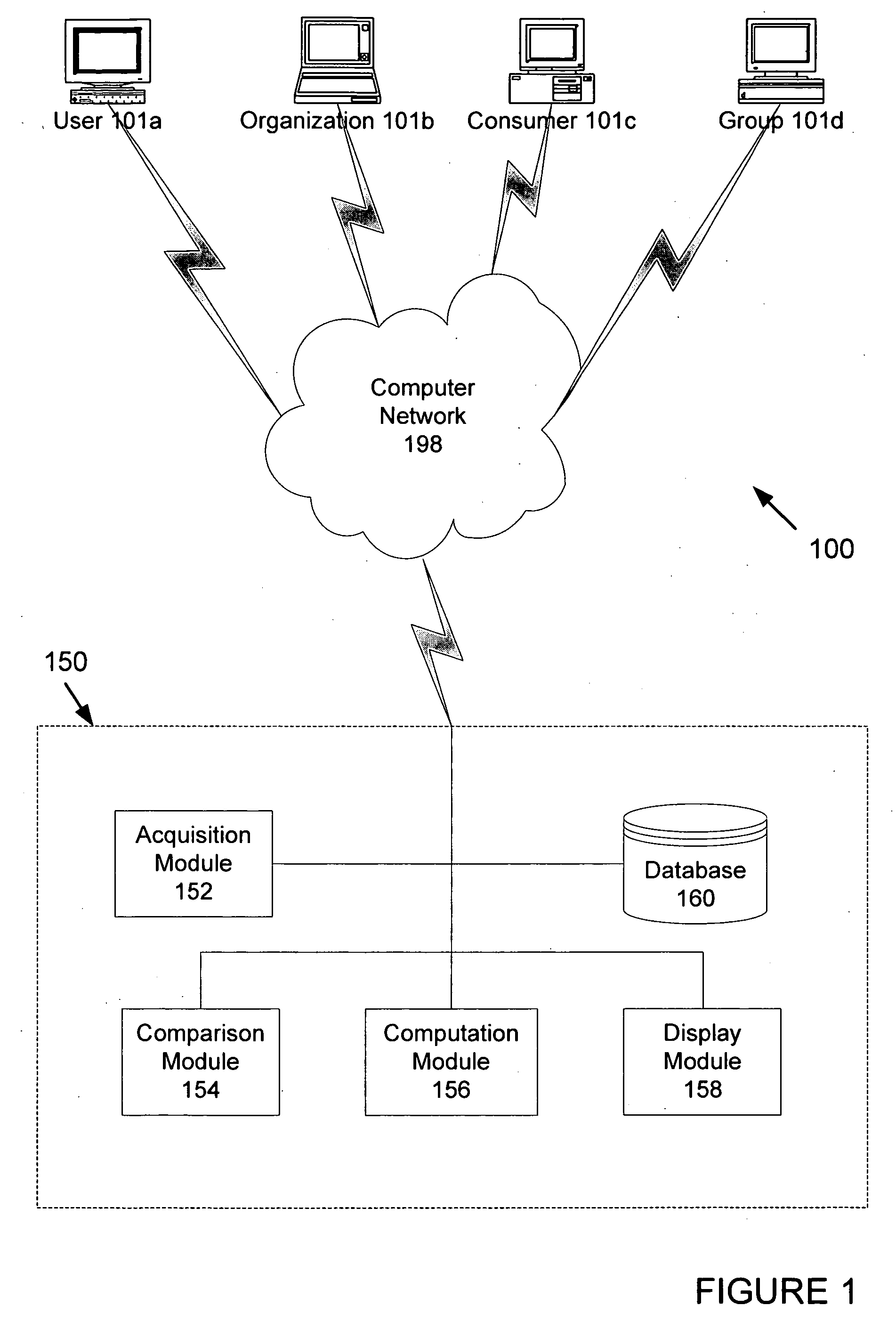
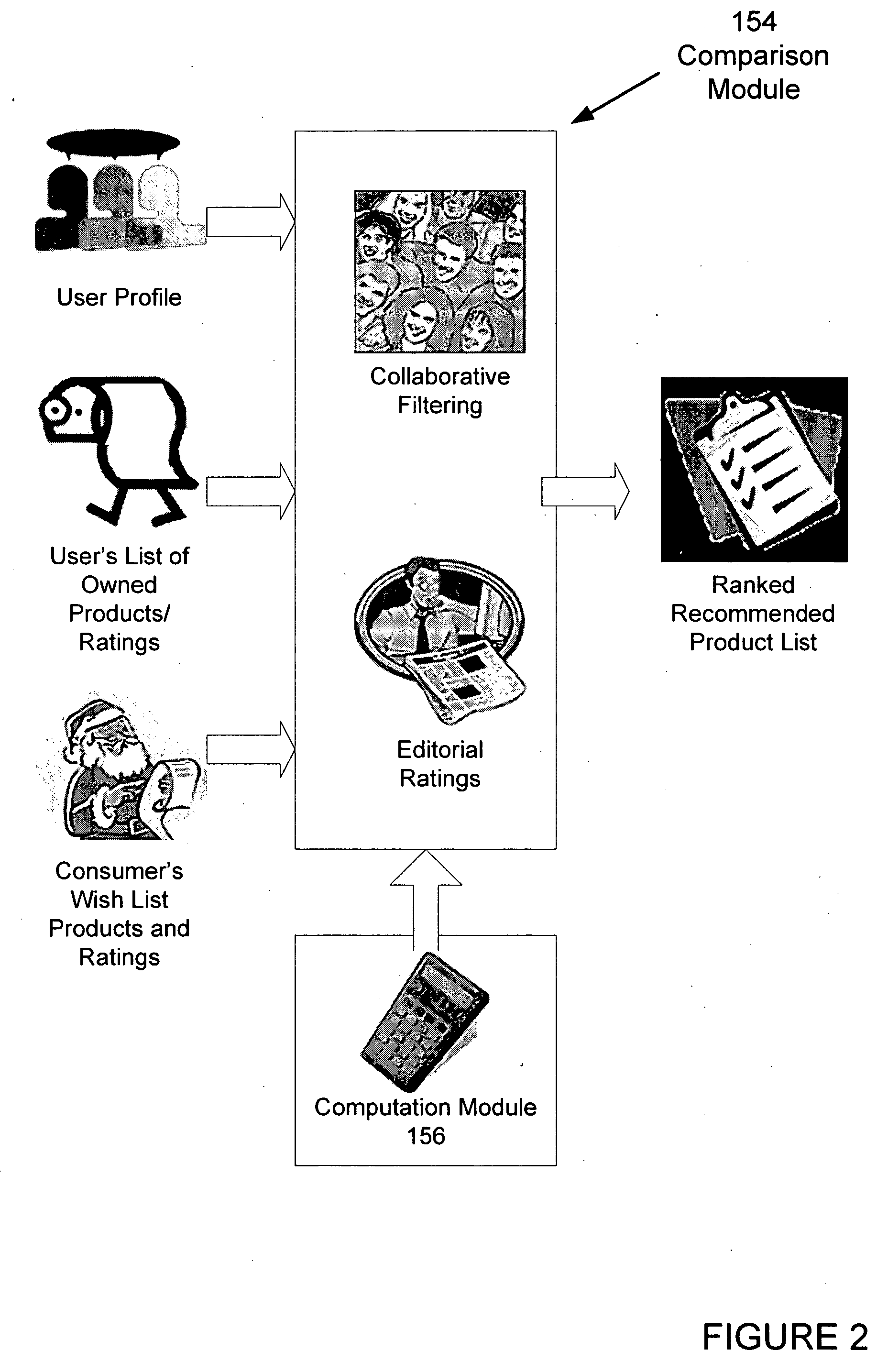
A system and method operates on a client device and acquires a suspect list of user products based on information derived from the client device. The system normalizes the list, and the user confirms the accuracy of the product list. The user product list is sent to a server where the user product list is compared to other lists using collaborative filtering techniques. The collaborative filtering techniques determine products of interest for the use and the level of interest of the user. The system computes a similarity measure based upon the number of similar products that match the user's product list and rankings provided by the user and others. Demographic and behavioral data may also be used in performing the comparison and the similarity measure. The system acquires editorial rankings of products from other users and provides a ranked list of recommended products based upon the editorial rankings.
Owner:CBS INTERACTIVE INC
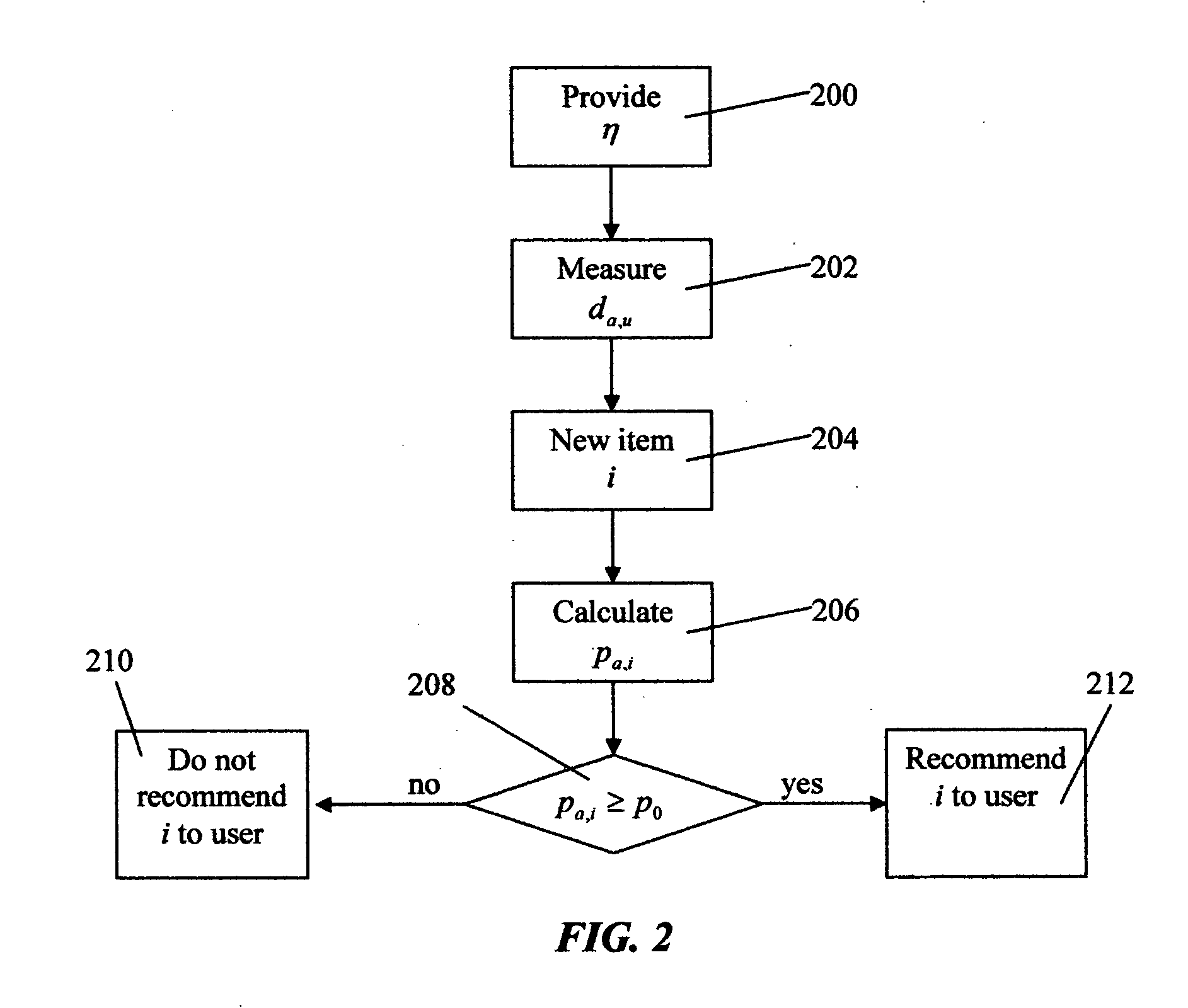
System and method for utilizing social networks for collaborative filtering
InactiveUS20050256756A1Easy to optimizeImprove recommendationsMarket predictionsSelective content distributionFilter systemCollaborative filtering
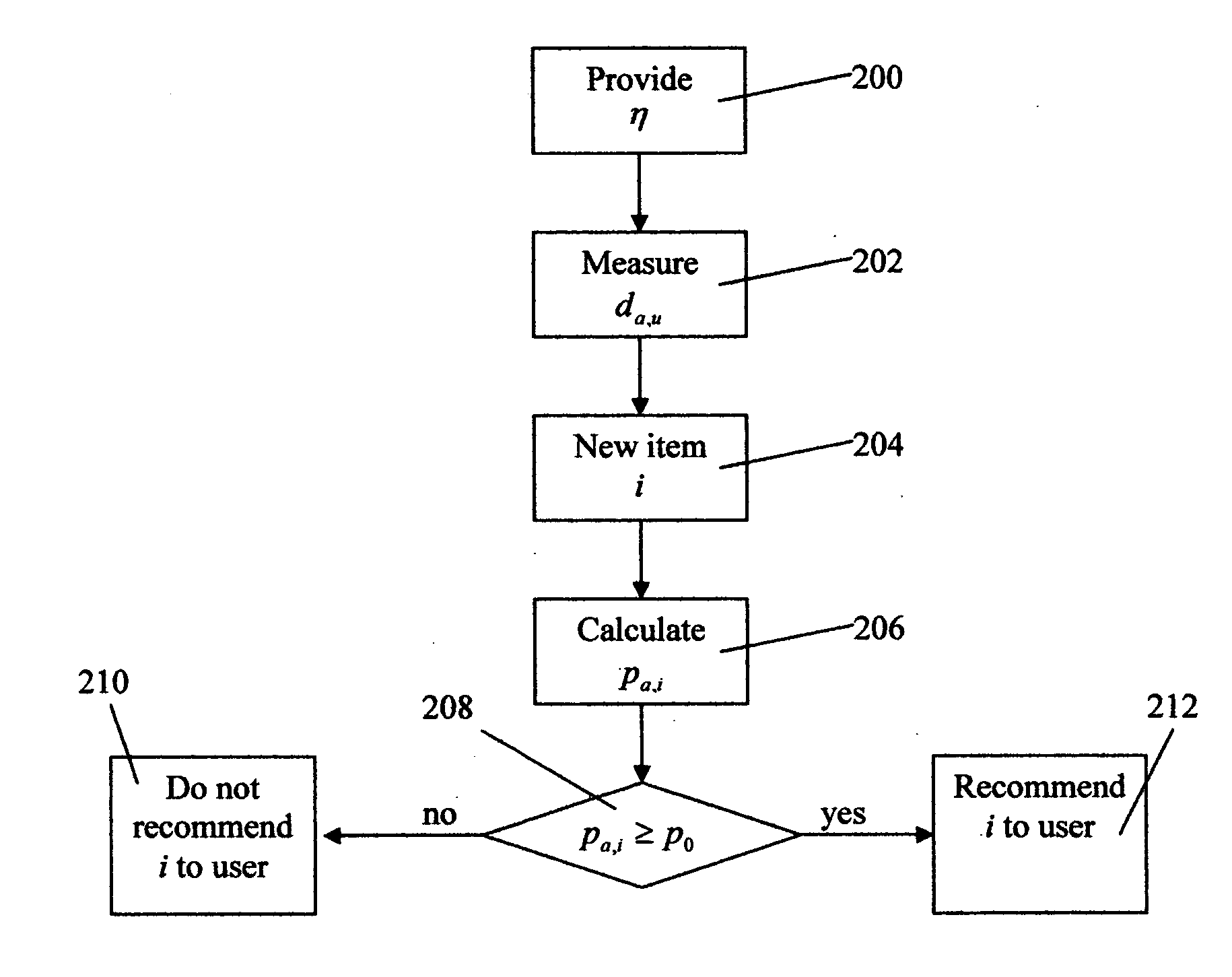
A novel system and method of predicting a user's rating of a new item in a collaborative filtering system is described. The invention incorporates social network information in addition to user ratings to make recommendations. The distance between users in the social network is used to enhance the estimate of user similarities for collaborative filtering. The social network can be constructed explicitly by users or deduced implicitly from observed interaction between users.
Owner:LAM CHUCK P +1
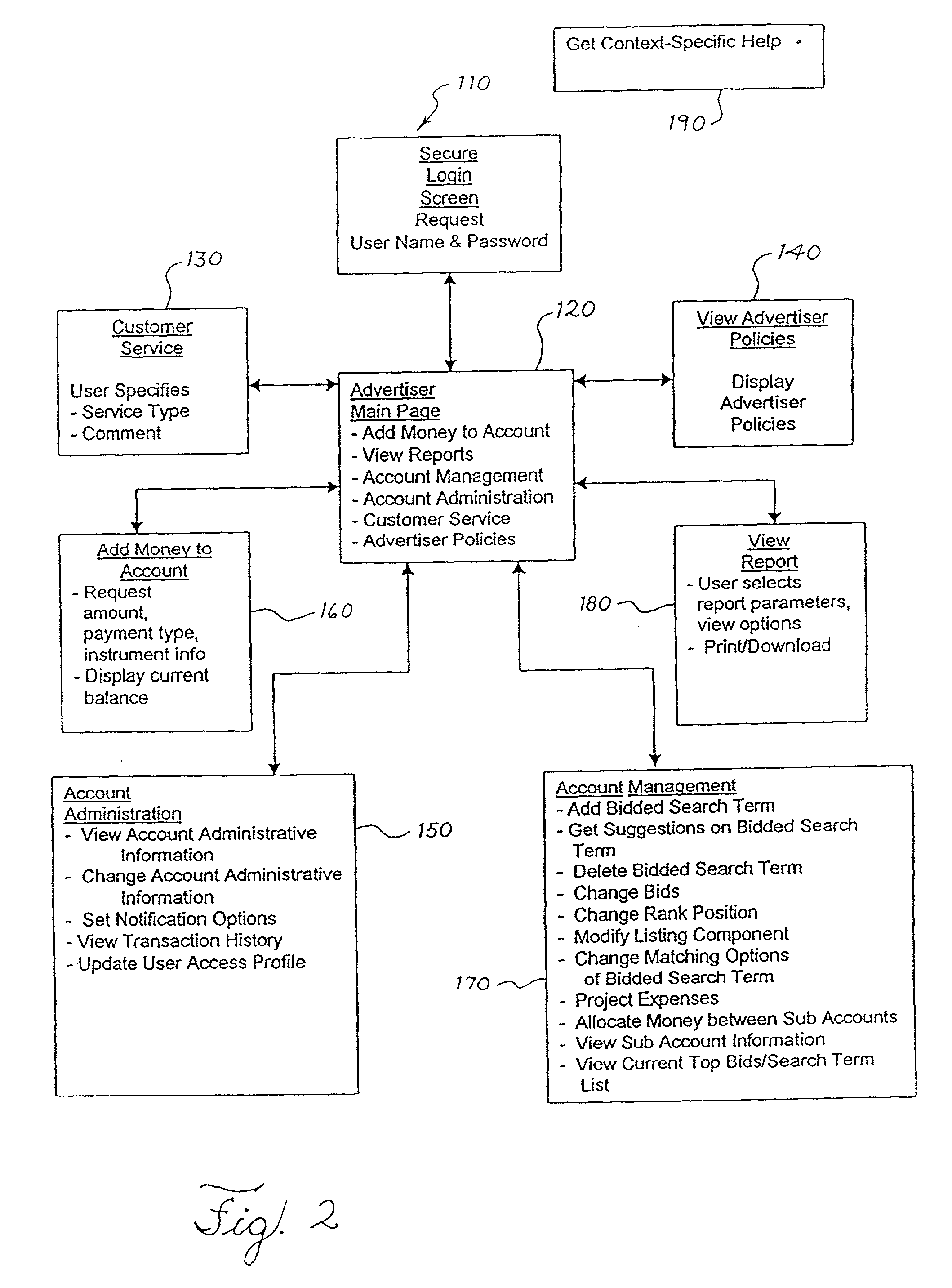
Intelligent web based help system
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
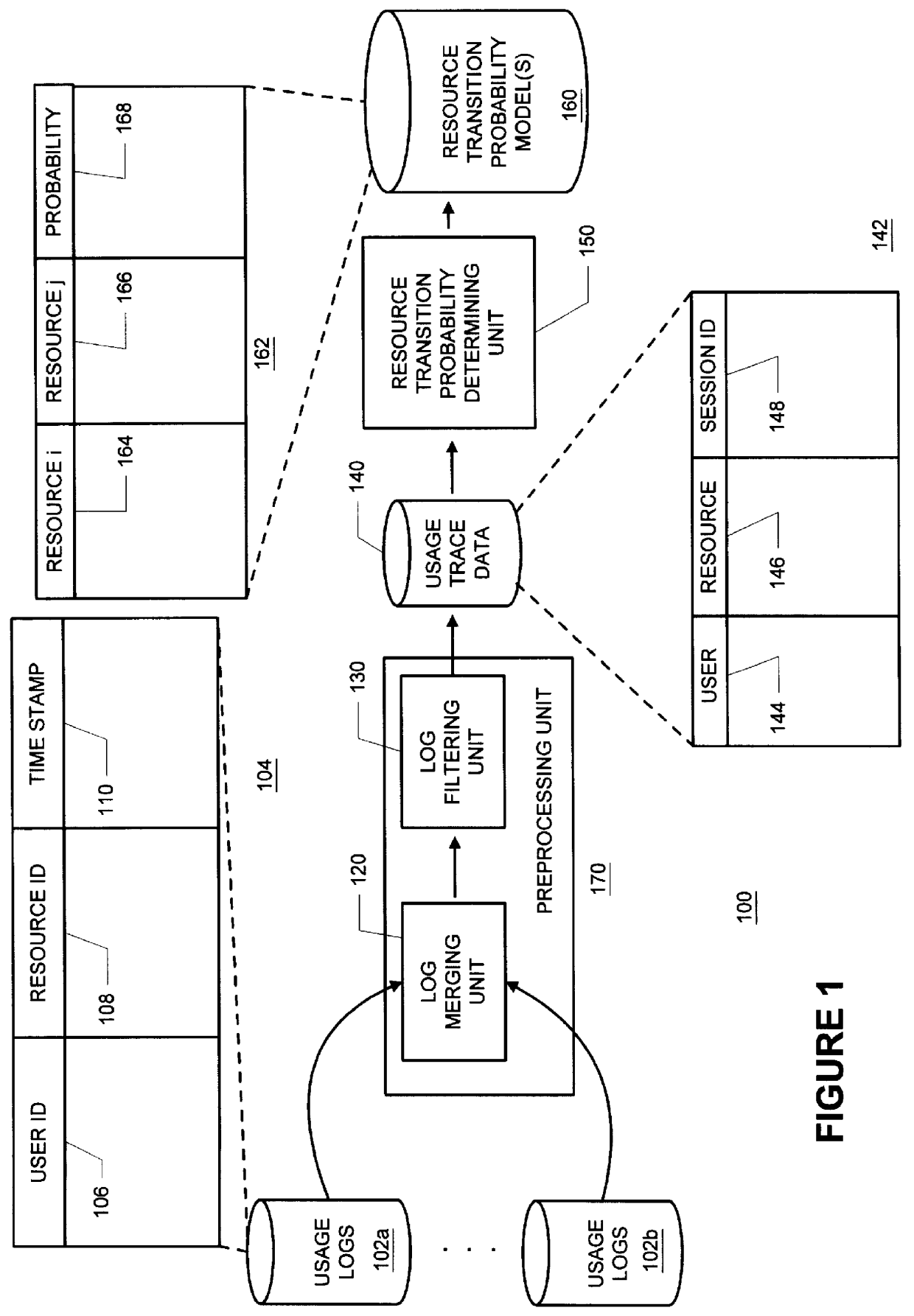
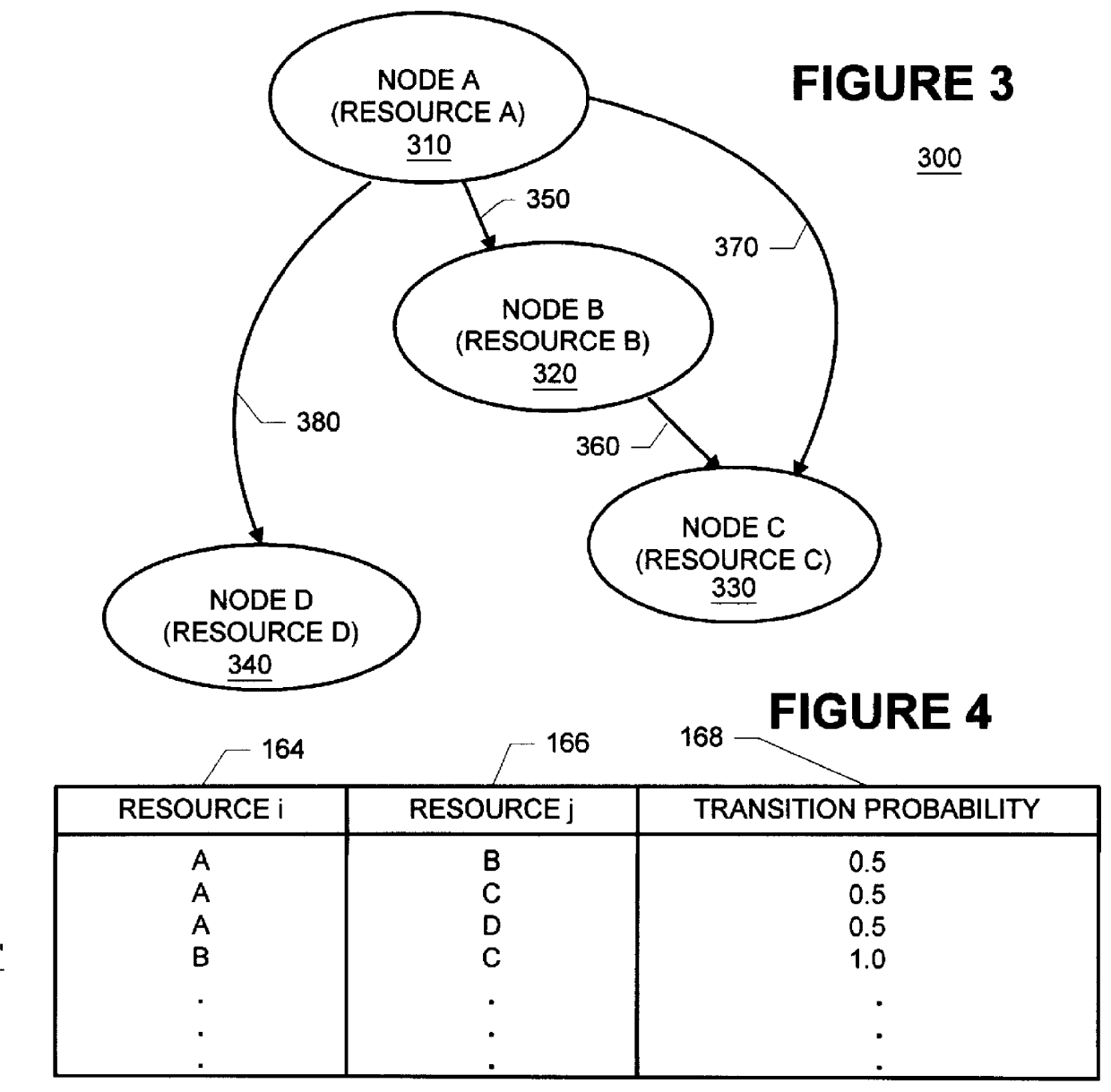
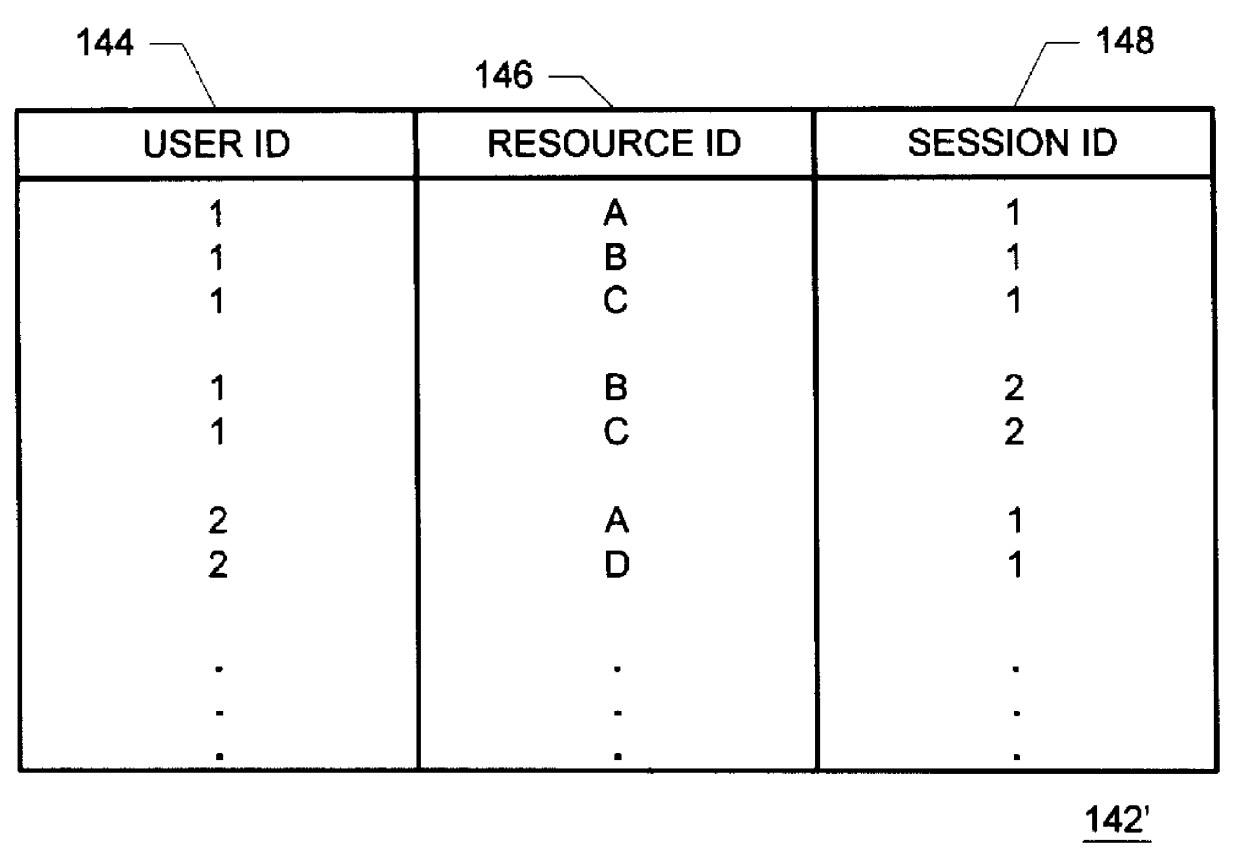
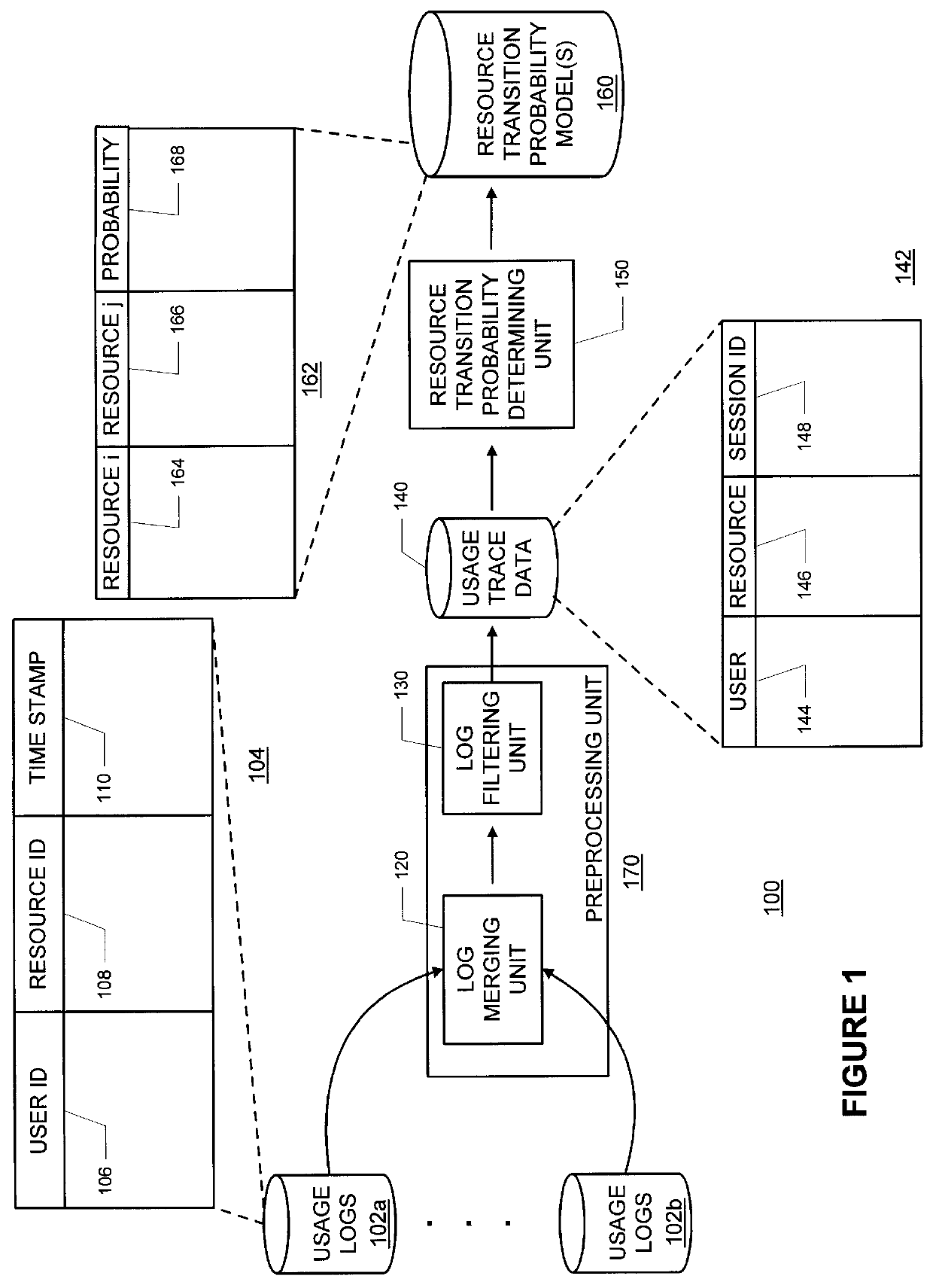
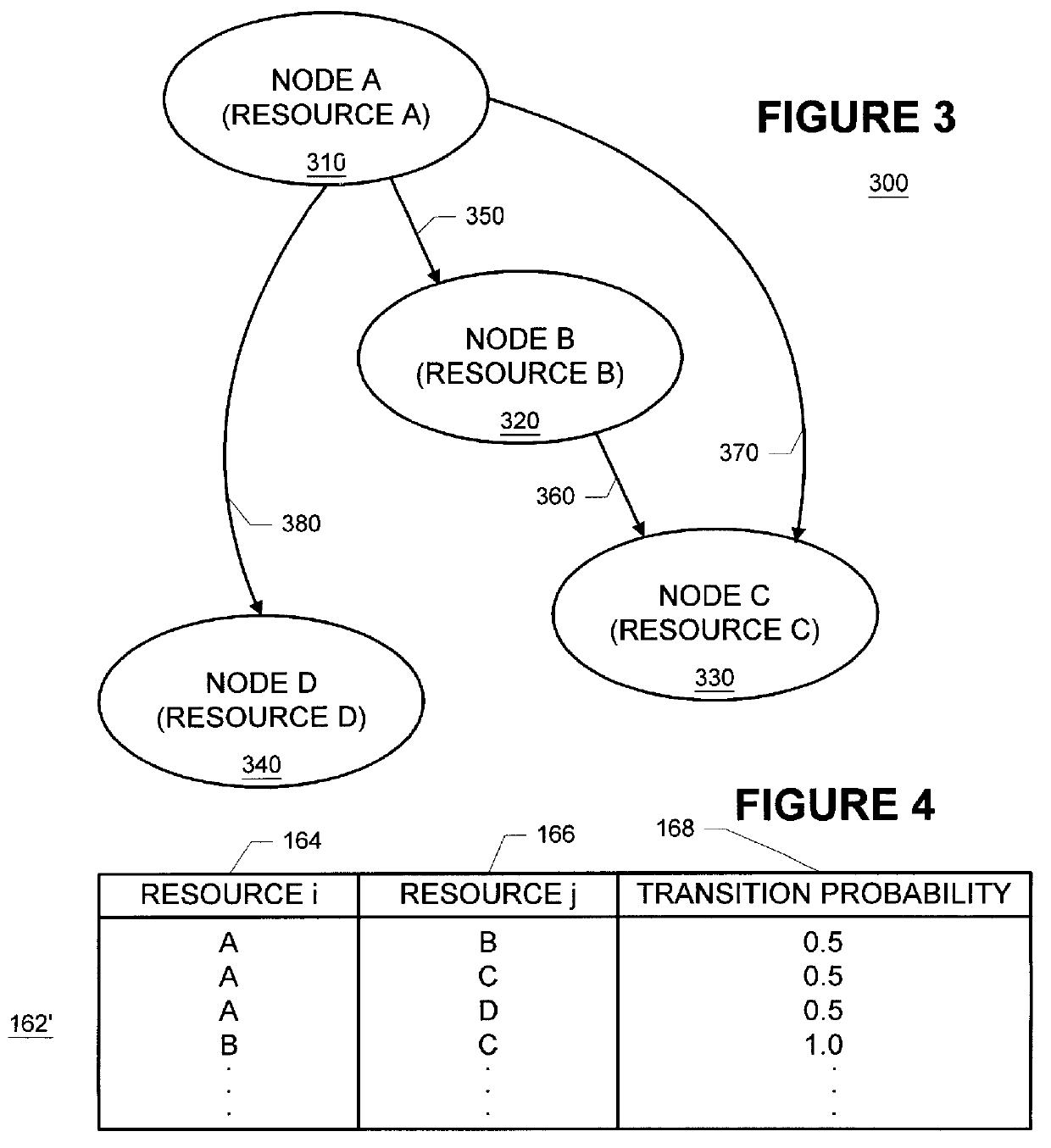
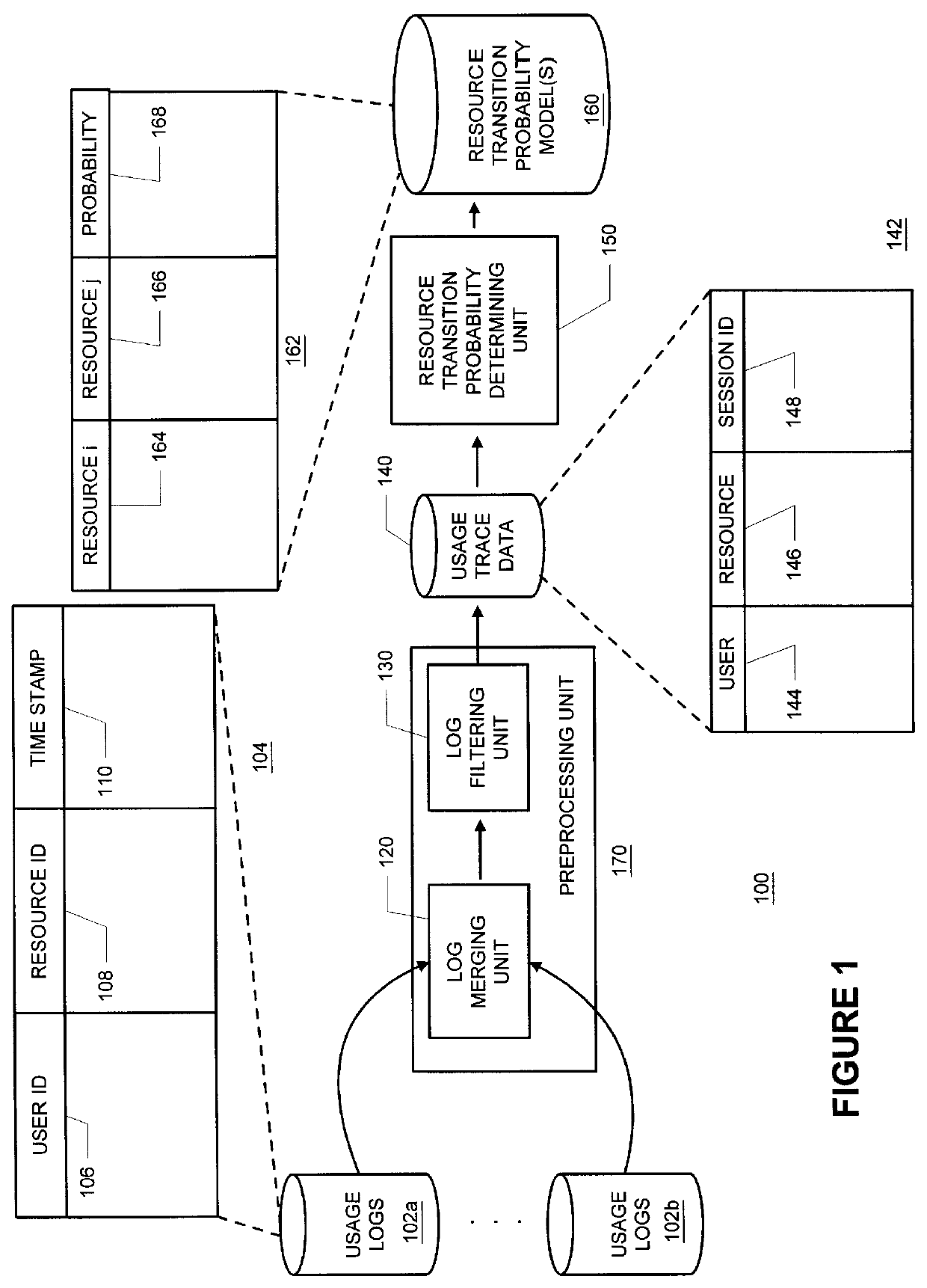
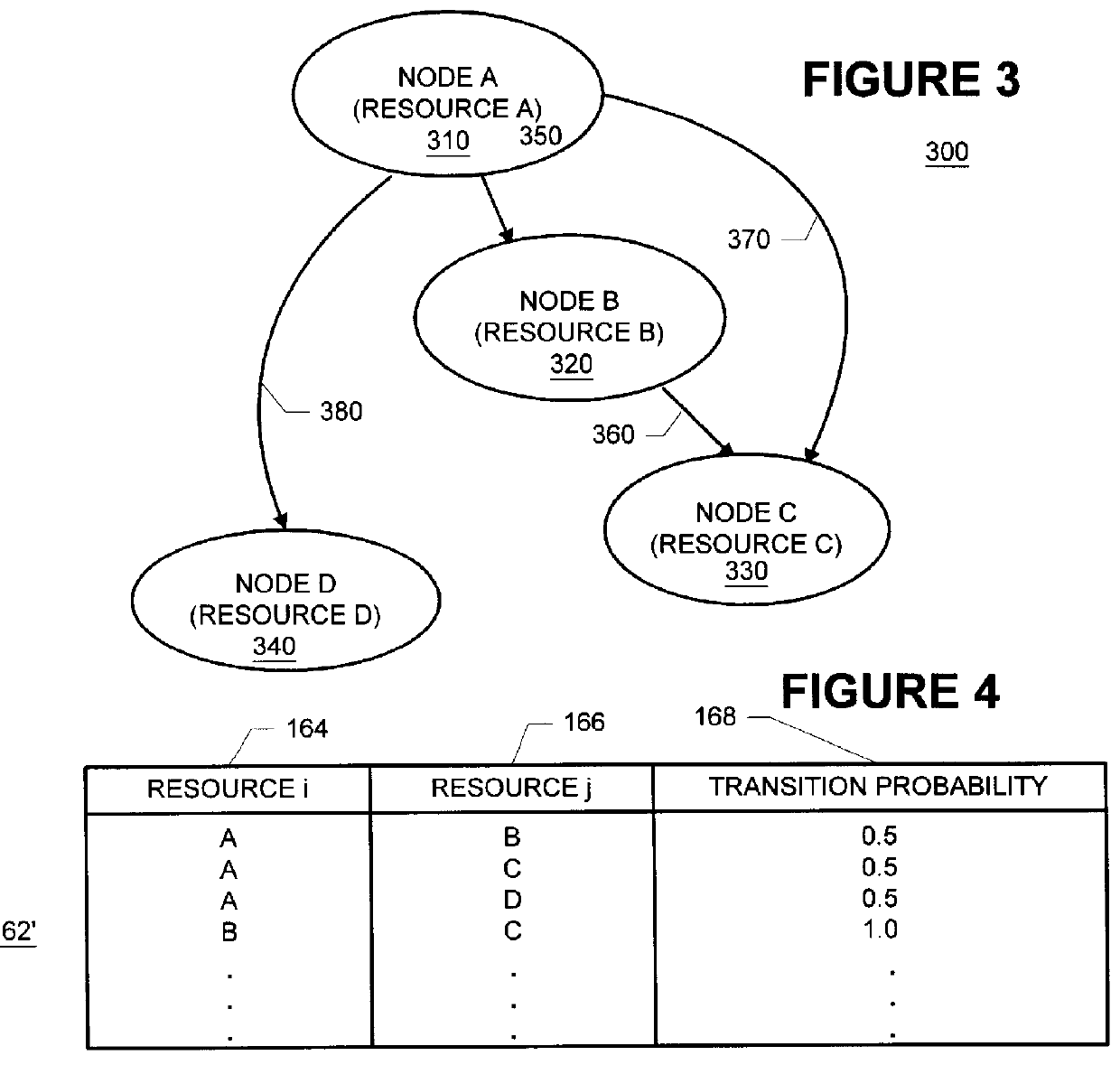
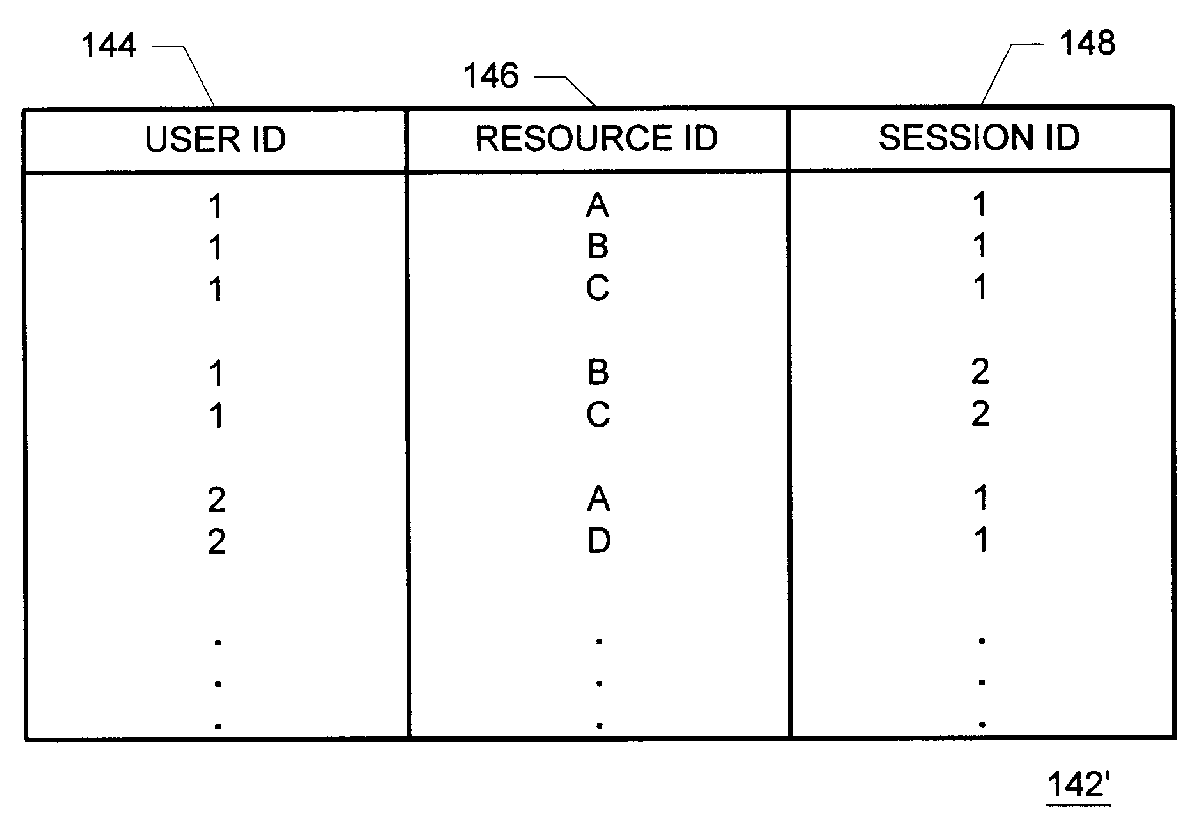
Methods and apparatus for building resource transition probability models for use in pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering
InactiveUS6012052AData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalInternet contentResource transfer
Building resource (e.g., Internet content) and attribute transition probability models and using such models for pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Database access system
InactiveUS7801896B2Increased formationGood user interfaceDigital data information retrievalAdvertisementsAnonymityPopulation statistics
An improved human user computer interface system, wherein a user characteristic or set of characteristics, such as demographic profile or societal “role”, is employed to define a scope or domain of operation. The operation itself may be a database search, to interactively define a taxonomic context for the operation, a business negotiation, or other activity. After retrieval of results, a scoring or ranking may be applied according to user define criteria, which are, for example, commensurate with the relevance to the context, but may be, for example, by date, source, or other secondary criteria. A user profile is preferably stored in a computer accessible form, and may be used to provide a history of use, persistent customization, collaborative filtering and demographic information for the user. Advantageously, user privacy and anonymity is maintained by physical and algorithmic controls over access to the personal profiles, and releasing only aggregate data without personally identifying information or of small groups.
Owner:RELATIVITY DISPLAY LLC
Computer graphic display visualization system and method
InactiveUS20050165766A1Improve compactnessIncrease flexibilityDrawing from basic elementsAdvertisementsGraphicsCollaborative filtering
An improved human user computer interface system, providing a graphic representation of a hierarchy populated with naturally classified objects, having included therein at least one associated object having a distinct classification. Preferably, a collaborative filter is employed to define the appropriate associated object. The associated object preferably comprises a sponsored object, generating a subsidy or revenue.
Owner:RELATIVITY DISPLAY LLC
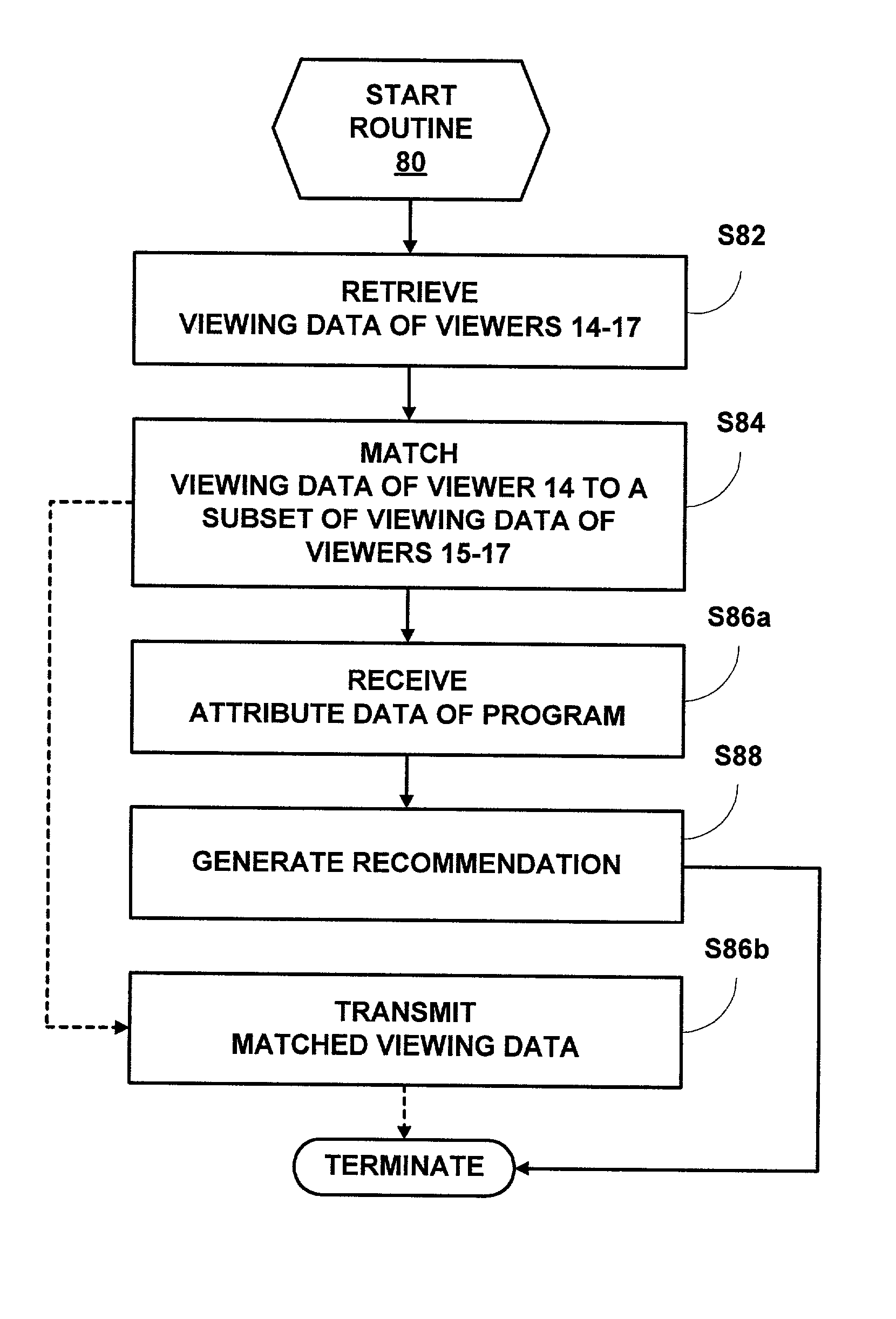
Four-way recommendation method and system including collaborative filtering
A system employing an automated collaborative filtering process for recommending an item to a viewer based upon feedback data, implicit data, and / or explicit data corresponding to a primary viewer as well as secondary viewers is disclosed. A first act of the automated collaborative filtering process is to match data indicative of a viewing of a first group of items by the primary viewer to data indicative of a viewing of a second group of items by the secondary viewers. A second act of the automated collaborative filtering process is to generate a recommendation of the item by the primary viewer as a function of data indicative of one or more attributes of the item as compared to the data matching accomplished in the first act.
Owner:PACE MICRO TECH
Method and system for creating and distributing collaborative multi-user three-dimensional websites for a computer system (3D Net Architecture)
InactiveUS7107549B2Easy accessImage data processingWeb data navigationHuman–machine interfaceFile size
The present invention is a new 3D graphical user interface (3D GUI) technology that seamlessly integrates personal computer (PC) desktop, web portal, and data visualization functions in an intuitive 3D environment. This new paradigm in human computer interfaces provides a seamless and intuitive ability to create a 3D website, “walk” or navigate from one 3D website to another, and allows multiple users to collaborate and interact with each other and the website. The invention dynamically creates a customized 3D environment that allows intuitive access to complicated websites as well as seamless multi-user collaboration and interaction. —In a preferred embodiment of the invention—The 3D GUI installs as the active desktop on a PC, replacing the user's “wallpaper” with the 3D GUI. —In another embodiment—The 3D GUI is accessed via a standard web browser window (i.e. using Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer). —In either of these embodiments—, The user can simply “walk” from one 3D website to another, see and communicate with other users that are also at that website, access website information and share information with other users currently visiting the website. The invention also provides a method for reducing the file size normally associated with transmitting all the content in a 3D website.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Computer graphic display visualization system and method
InactiveUS20060288023A1Improve compactnessIncrease flexibilityDrawing from basic elementsAdvertisementsGraphicsCollaborative filtering
An improved human user computer interface system, providing a graphic representation of a hierarchy populated with naturally classified objects, having included therein at least one associated object having a distinct classification. Preferably, a collaborative filter is employed to define the appropriate associated object. The associated object preferably comprises a sponsored object, generating a subsidy or revenue.
Owner:RELATIVITY DISPLAY LLC
System, method and computer program for automated collaborative filtering of user data
InactiveUS20020065797A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetEngineering
A system and method for collaborative filtering of data, such that accurate real time recommendations can be provided to users, without prior rating by users. The invention's main purpose is to discover the purchasing patterns of the users (customers) of a particular vendor (this includes stores or other points of sale, such as service businesses), whether they are virtual places on the Internet or conventional offline places. The present invention operates in two stages: In the preliminary stage the system reads the previous sales transactions, and makes various queries on previously collected user data, deriving rules. In the second phase, a user making a new request sends the request to the software component, where it is processed in relation to the rules. The result of this processing is a derivation of predictions and alerts concerning the users' information or purchase requests. The system also checks user baskets in order to predict if there are preferred items that have not been included, or determine whether there are unexpected items that may indicate buying mistakes or security warnings. The best modes of the invention are for use in online virtual stores and offline conventional stores. Such stores may be shops, vendors or service providers.
Owner:WIZSOFT
Recommending search terms using collaborative filtering and web spidering
In a pay-for-placement search system, the system makes search term recommendations to advertisers managing their accounts in one or more of two ways. A first technique involves looking for good search terms directly on an advertiser's web site. A second technique involves comparing an advertiser to other, similar advertisers and recommending the search terms the other advertisers have chosen. The first technique is called spidering and the second technique is called collaborative filtering. In the preferred embodiment, the output of the spidering step is used as input to the collaborative filtering step. The final output of search terms from both steps is then interleaved in a natural way.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
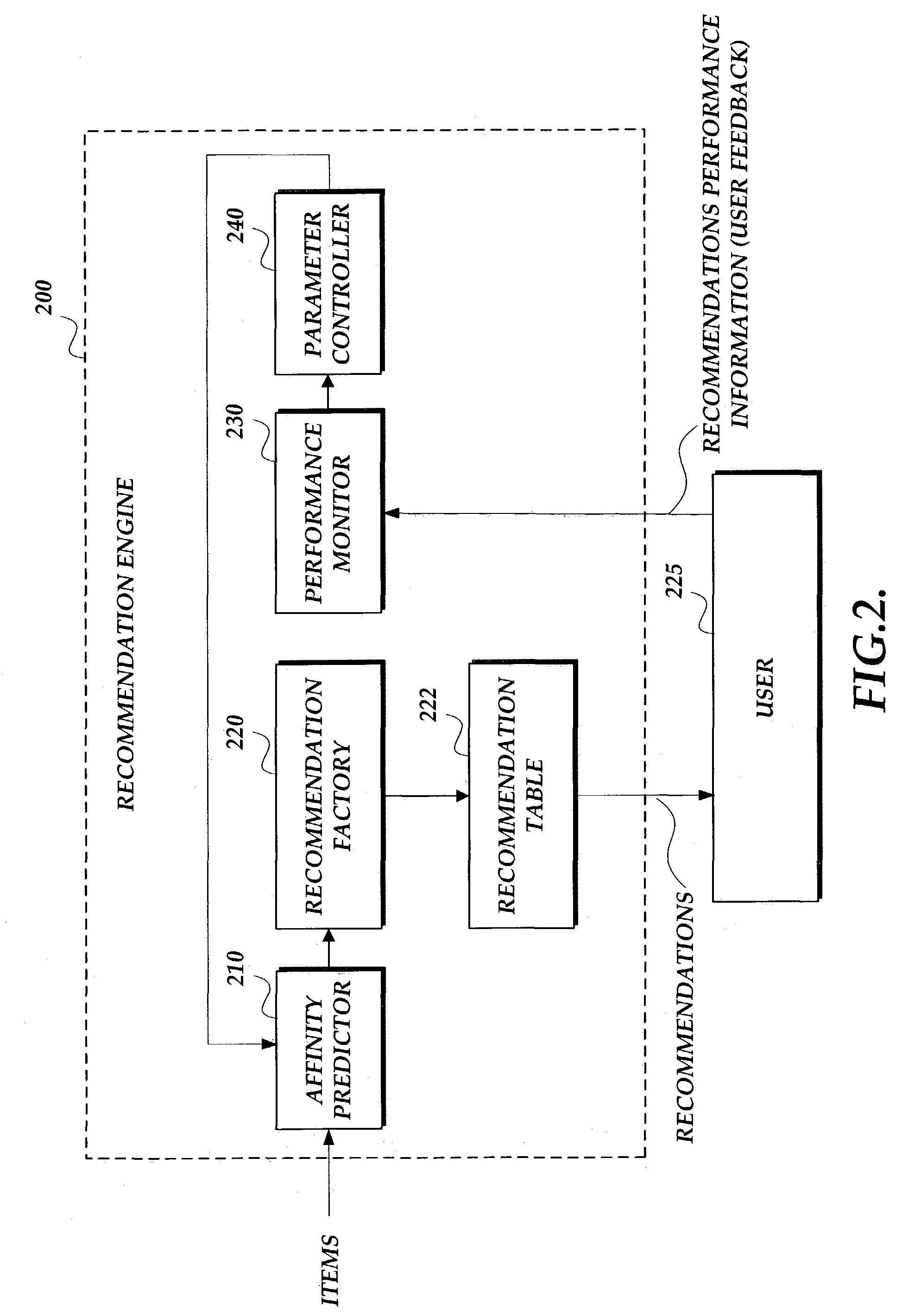
System for delivering recommendations
InactiveUS7013238B1Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital computer detailsComputer scienceCollaborative filtering
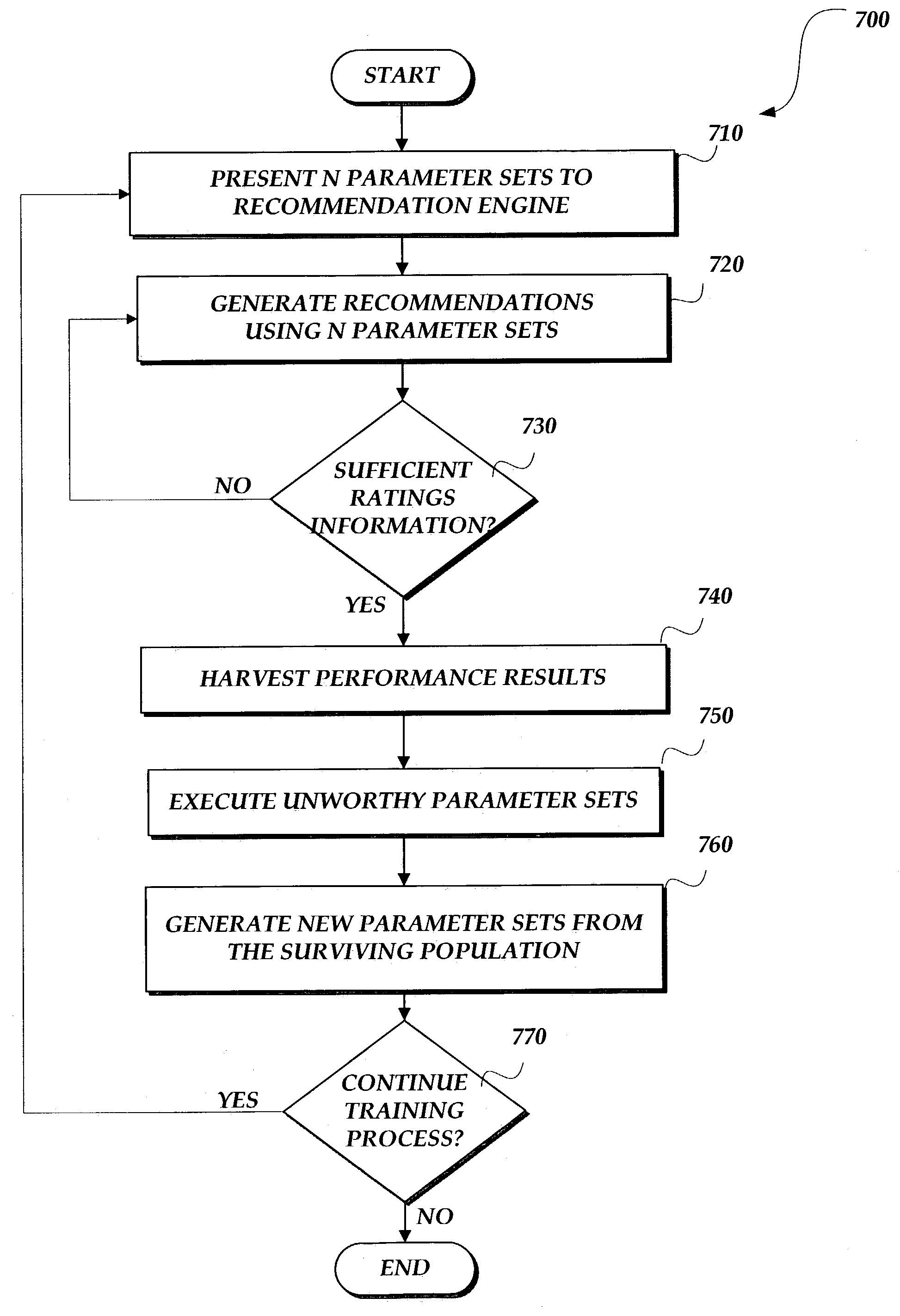
A system for generating recommendations which automatically optimizes over time without human intervention is disclosed. While known recommendation systems tended to be either attribute based or collaborative filtering based, the present system adjusts its internal parameters in response to the measured performance of the recommendations as determined by user behavior. In one embodiment, the user provides feedback in the form of ratings for the recommendations. This feedback is processed and then utilized to adjust the internal parameters of the system. Over time, the system settles on optimal parameter values.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and apparatus for using resource transition probability models for pre-fetching resources
InactiveUS6088718AQuickly renderedDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsInternet contentResource transfer
Building resource (e.g., Internet content) and attribute transition probability models and using such models for pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Recommender system for on-line articles and documents
InactiveUS20090300547A1Increase engagementIncrease the number ofKnowledge representationMachine learningDocumentationUser interface
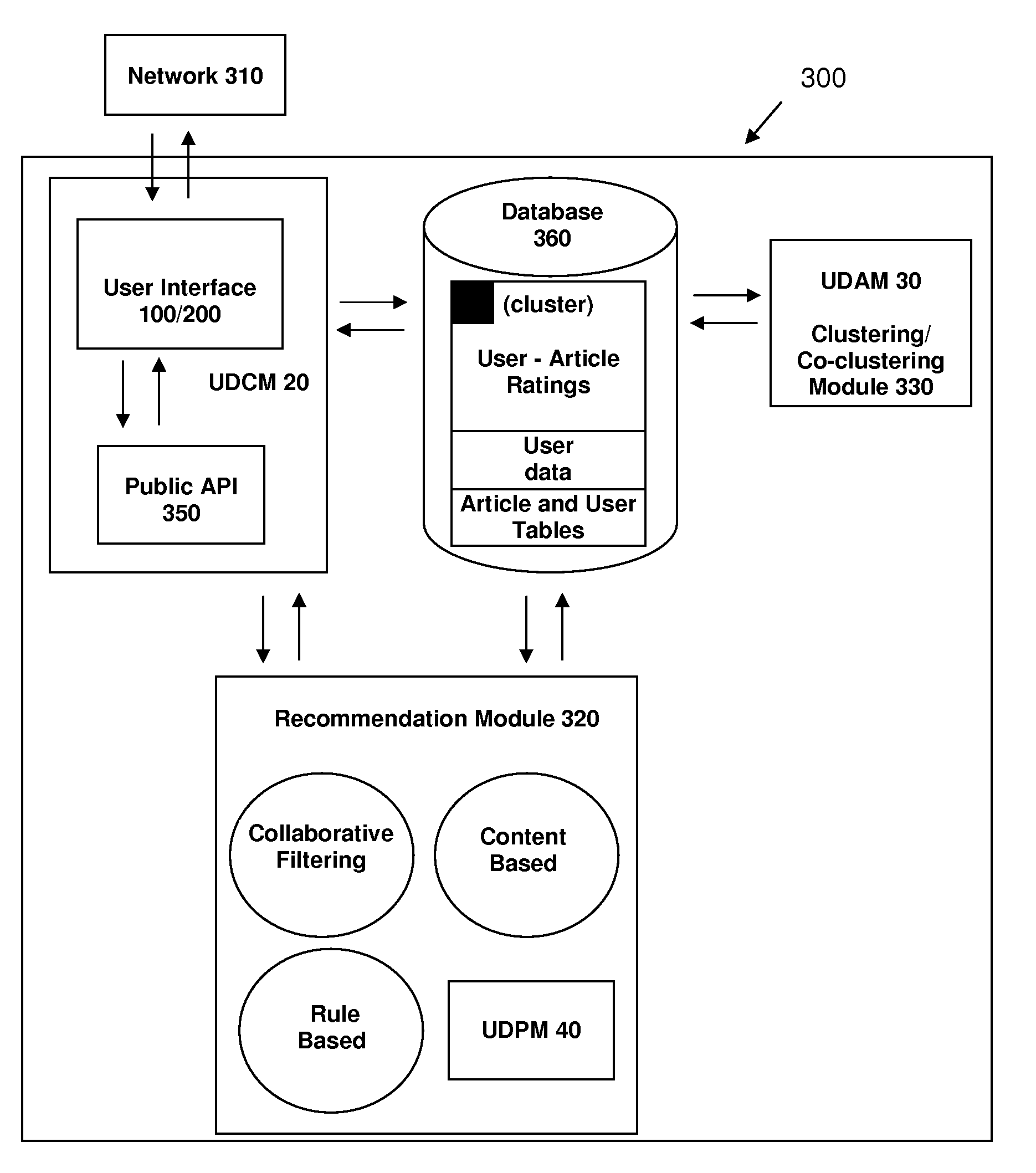
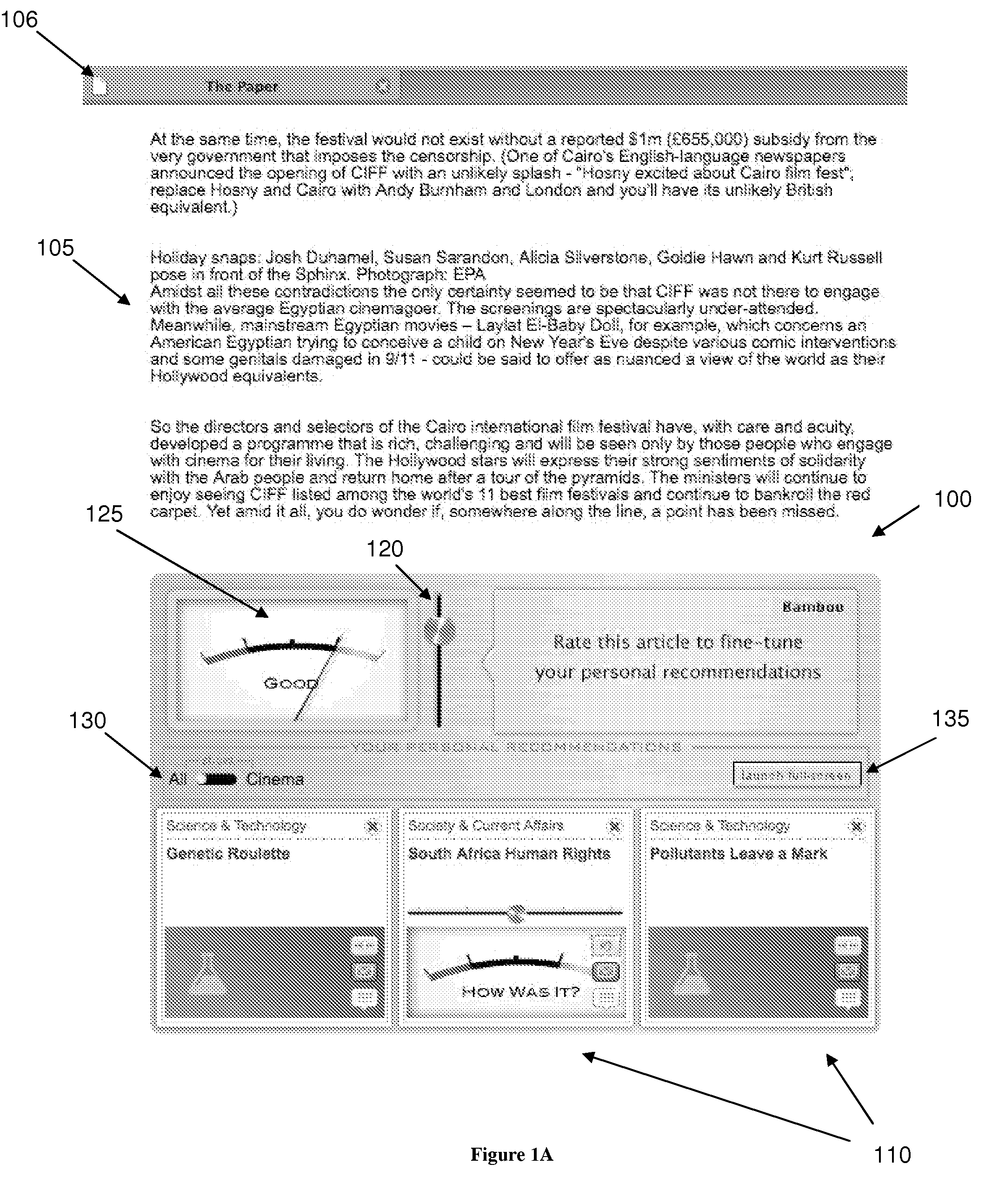
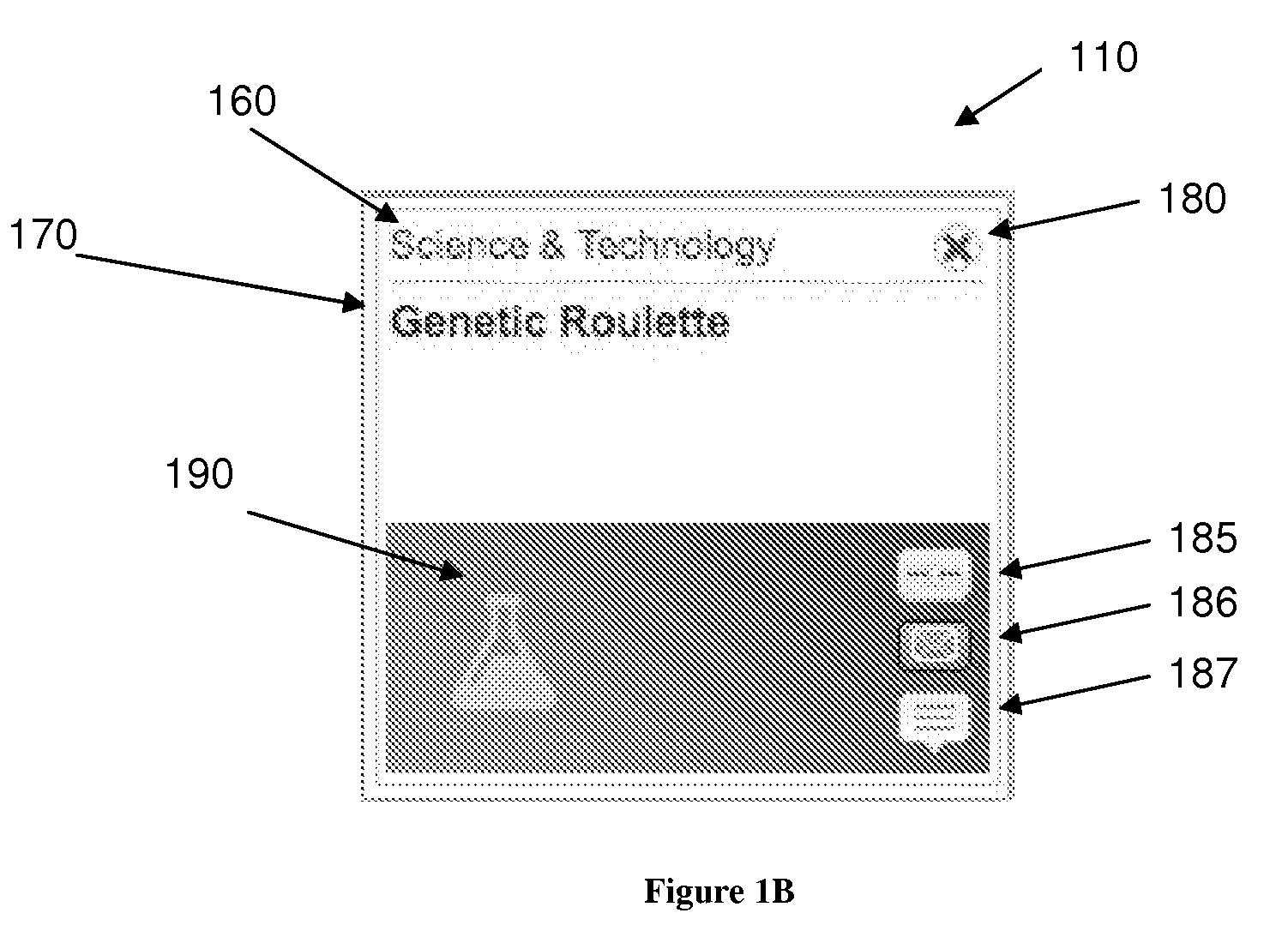
A system and method for recommending on-line articles and documents to users is disclosed. The method provides an article widget user interface and a full-screen widget user interfaces to allow a user to rate articles, to preview articles, to filter articles based on category, article length, or other characteristics. A recommender system is configured to provide a continually refreshing list of recommended articles to the user via the user interfaces. The system comprises a module configured to monitor the user's explicit and implicit interactions with the user interfaces, and provides a refreshed list of recommended articles accordingly. The recommender system may be configured to use a package of approaches including rule-based, content-based or collaborative filtering approaches including Slope, Co-Visitation, Mwinnow and Clustering / Co-clustering.
Owner:KIBBOKO
Methods and apparatus for using attribute transition probability models for pre-fetching resources
InactiveUS6154767AQuickly renderedDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet contentDistributed computing
Building resource (e.g., Internet content) and attribute transition probability models and using such models for pre-fetching resources, editing resource link topology, building resource link topology templates, and collaborative filtering.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for a ranking engine
ActiveUS20060218141A1Highly targeted search resultImprove accuracyData processing applicationsWeb data indexingOrganizational documentFile allocation
A computer-implemented method is provided for ranking files from an Internet search. In one embodiment, the method comprises assigning a score to each file based on at least one of the following factors: recency, editorial popularity, clickthru popularity, favorites metadata, or favorites collaborative filtering. The files may be organized based on the assigned scores to provide users with more accurate search results.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
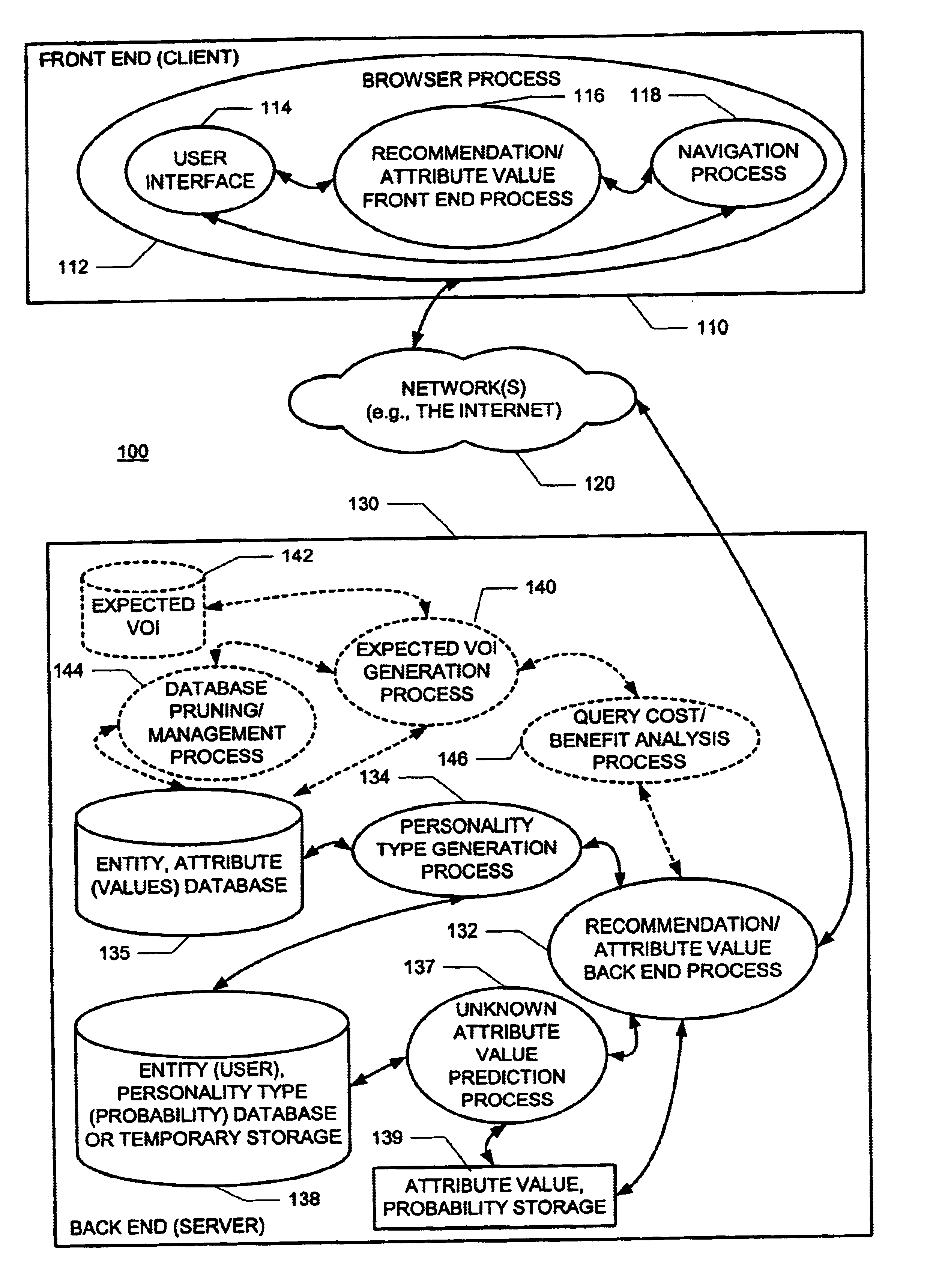
Methods and apparatus for predicting and selectively collecting preferences based on personality diagnosis
InactiveUS20040076936A1Minimal effectCumbersome processMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProbabilistic semanticsValue of information
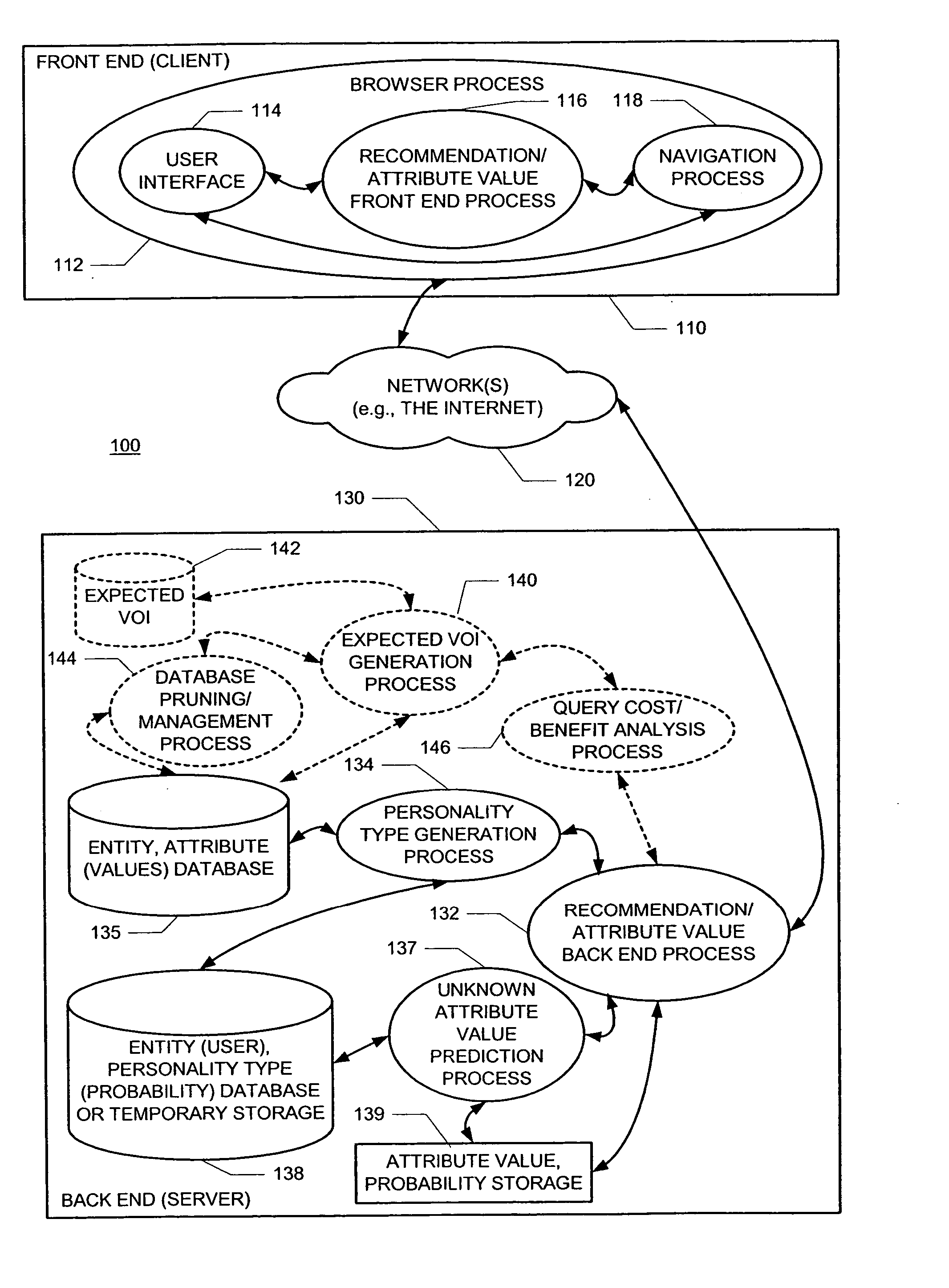
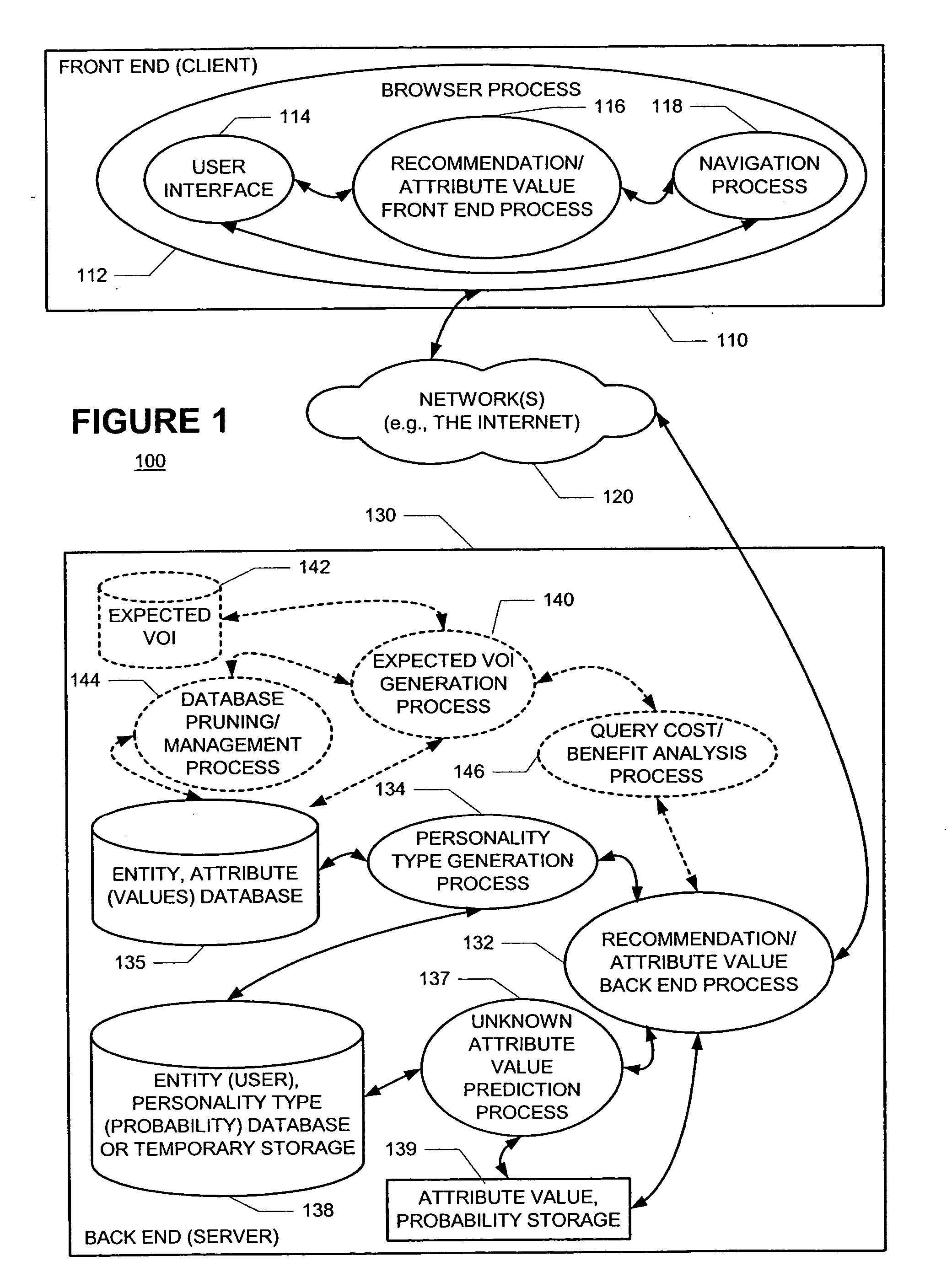
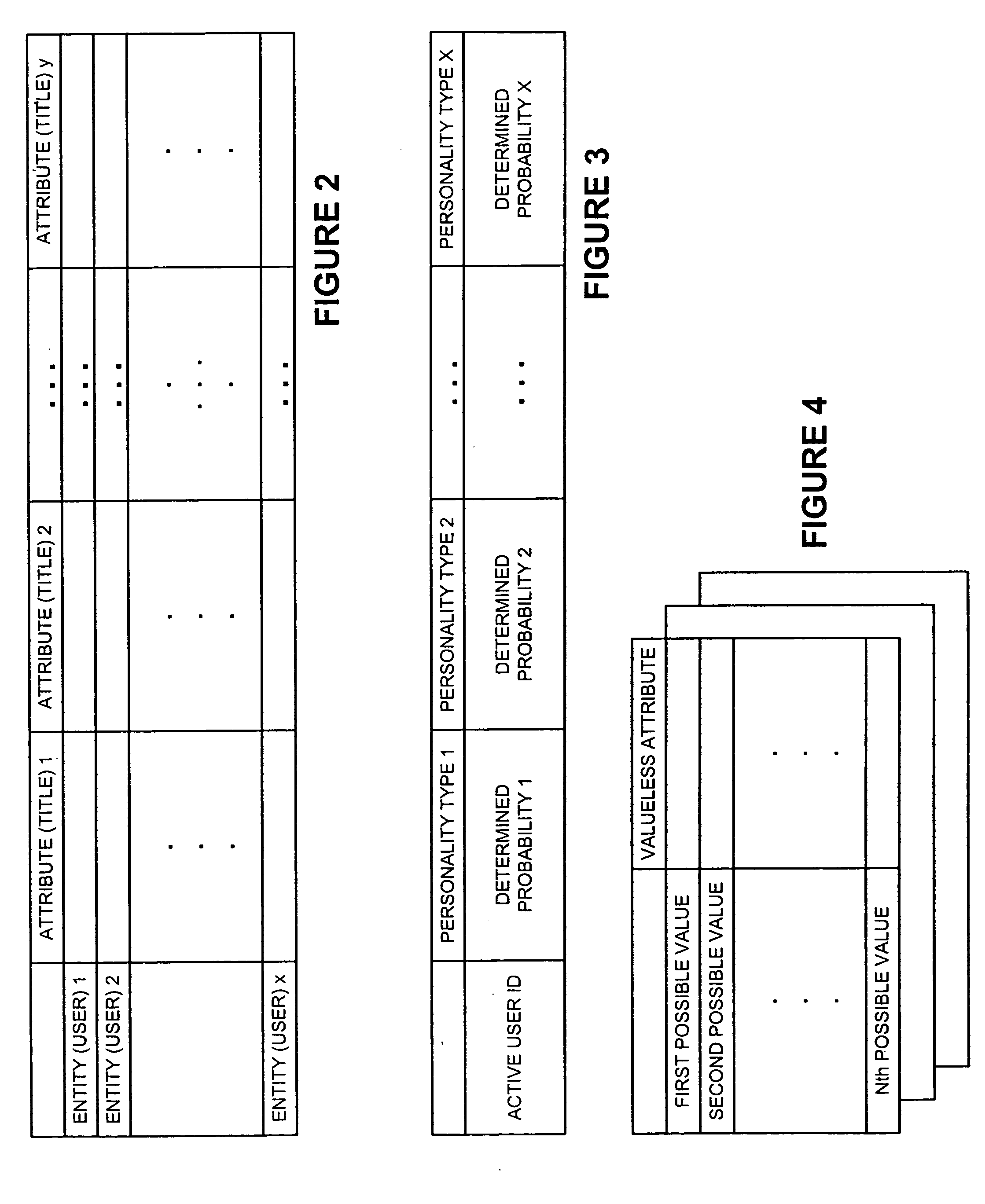
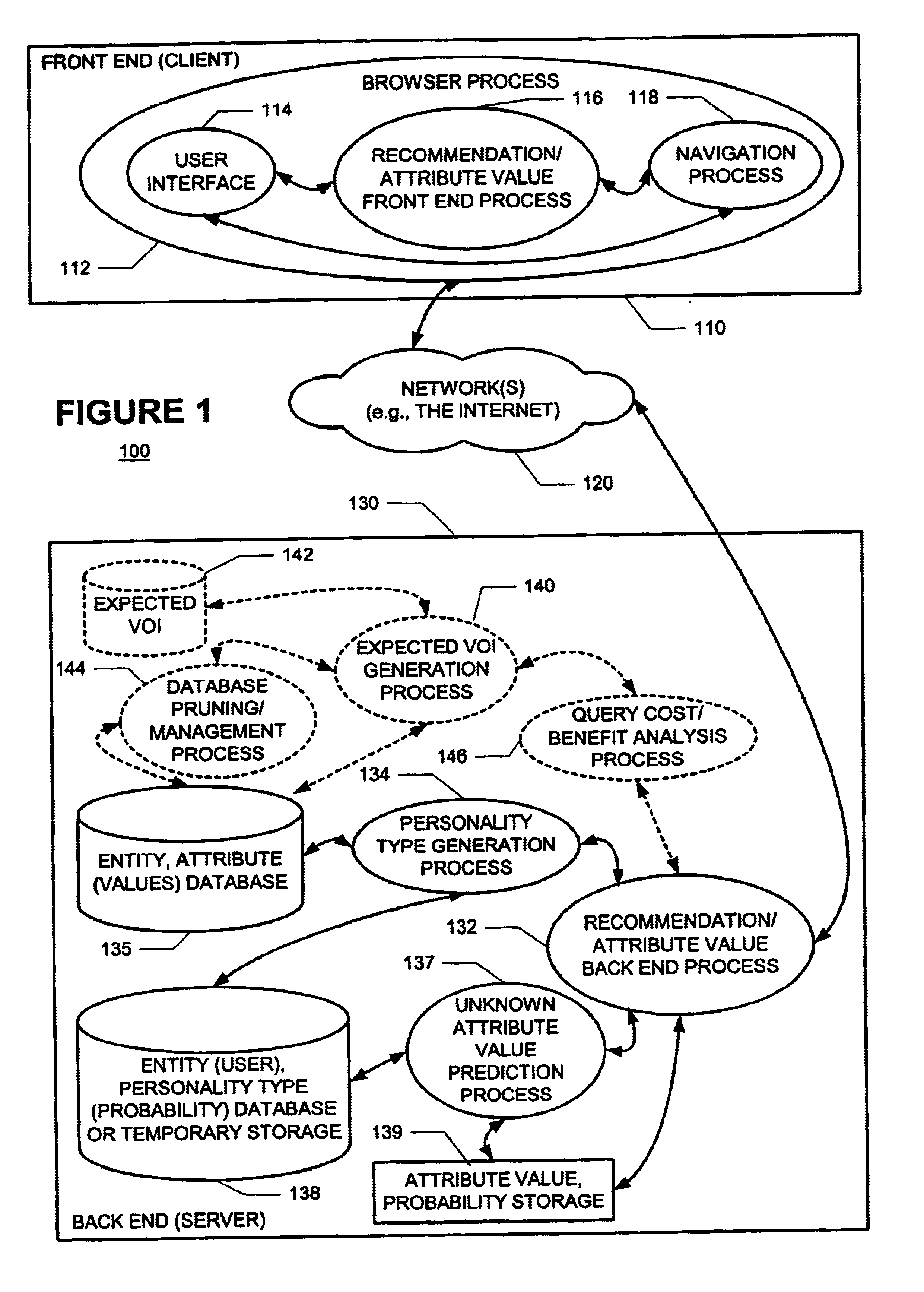
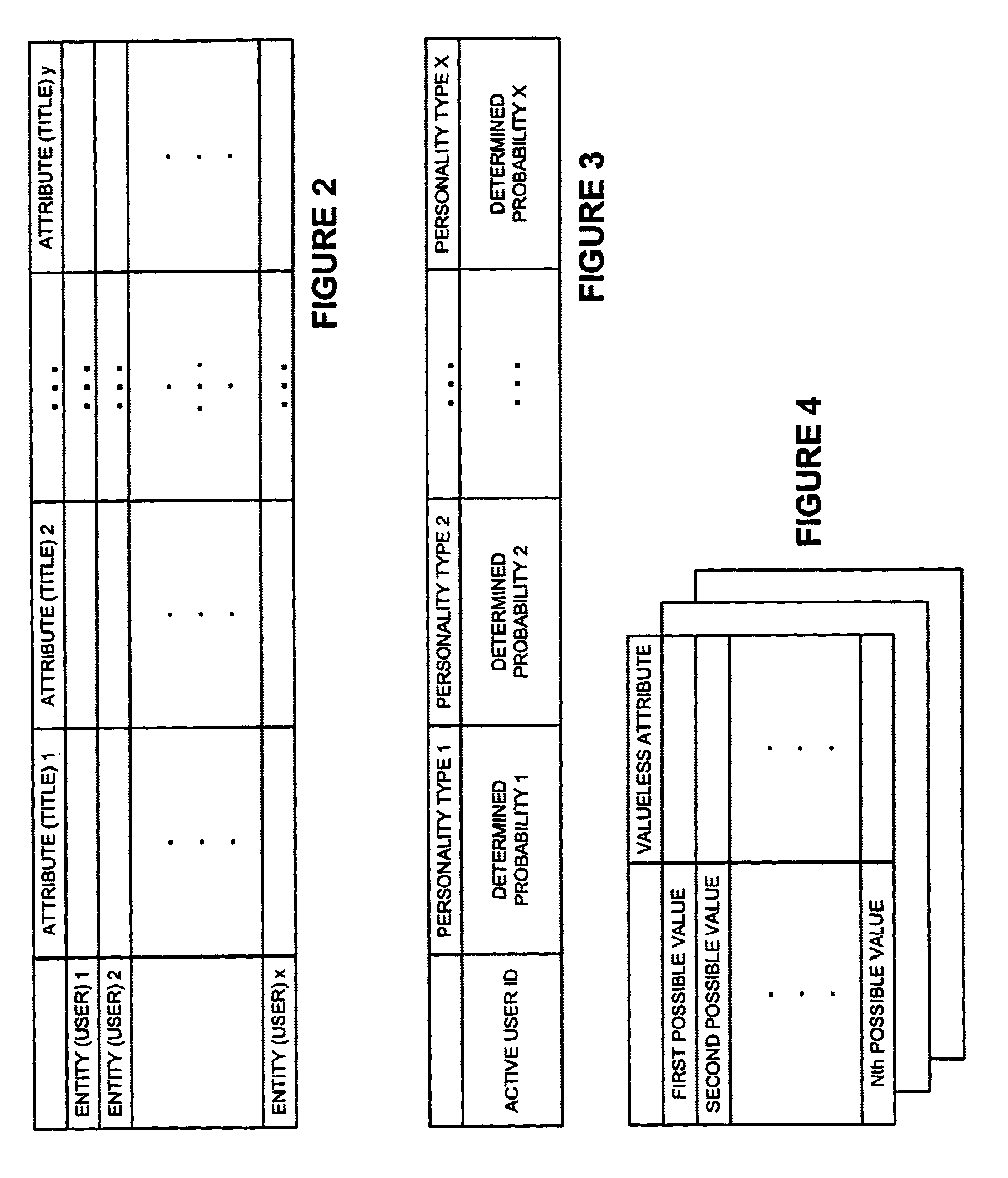
A new recommendation technique, referred to as "personality diagnosis", that can be seen as a hybrid between memory-based and model-based collaborative filtering techniques, is described. Using personality diagnosis, all data may be maintained throughout the processes, new data can be added incrementally, and predictions have meaningful probabilistic semantics. Each entity's (e.g., user's) reported attributes (e.g., item ratings or preferences) may be interpreted as a manifestation of their underlying personality type. Personality type may be encoded simply as a vector of the entity's (e.g., user's) "true" values (e.g., ratings) for attributes (e.g., items) in the database. It may be assumed that entities (e.g., users) report values (e.g., ratings) with a distributed (e.g., Gaussian) error. Given an active entity's (e.g., user's) known attribute values (e.g., item ratings), the probability that they have the same personality type as every other entity (e.g., user) may be determined. Then, the probability that they will have a given value (e.g., rating) for a valueless (e.g., unrated) attribute (e.g., item) may then be determined based on the entity's (e.g., user's) personality type. The probabilistic determinations may be used to determine expected value of information. Such an expected value of information could be used in at least two ways. First, an interactive recommender could use expected value of information to favorably order queries for attribute values (e.g., item ratings), thereby mollifying what could otherwise be a tedious and frustrating process. Second, expected value of information could be used to determine which entries of a database to prune or ignore-that is, which entries, which if removed, would have a minimal effect of the accuracy of recommendations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
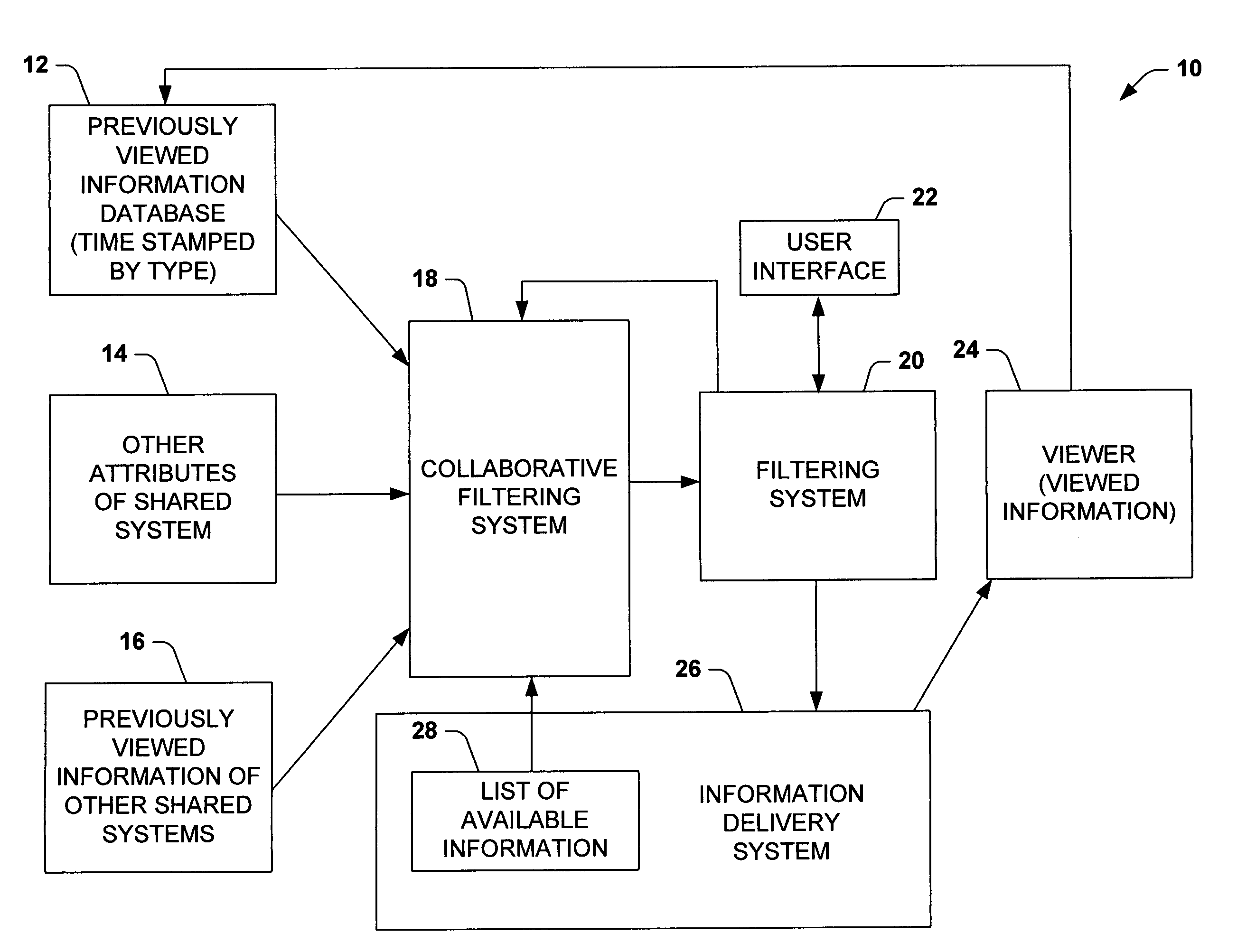
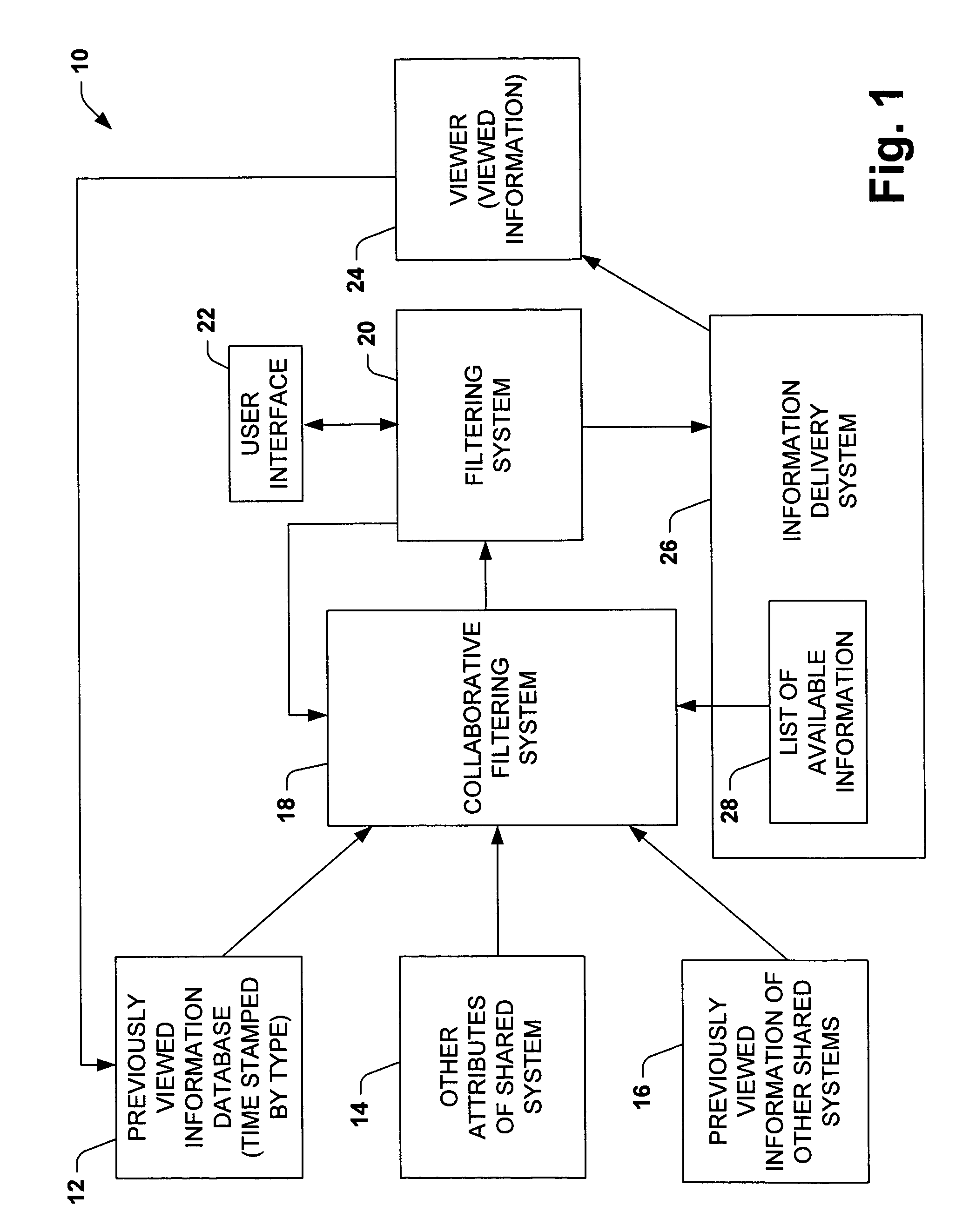
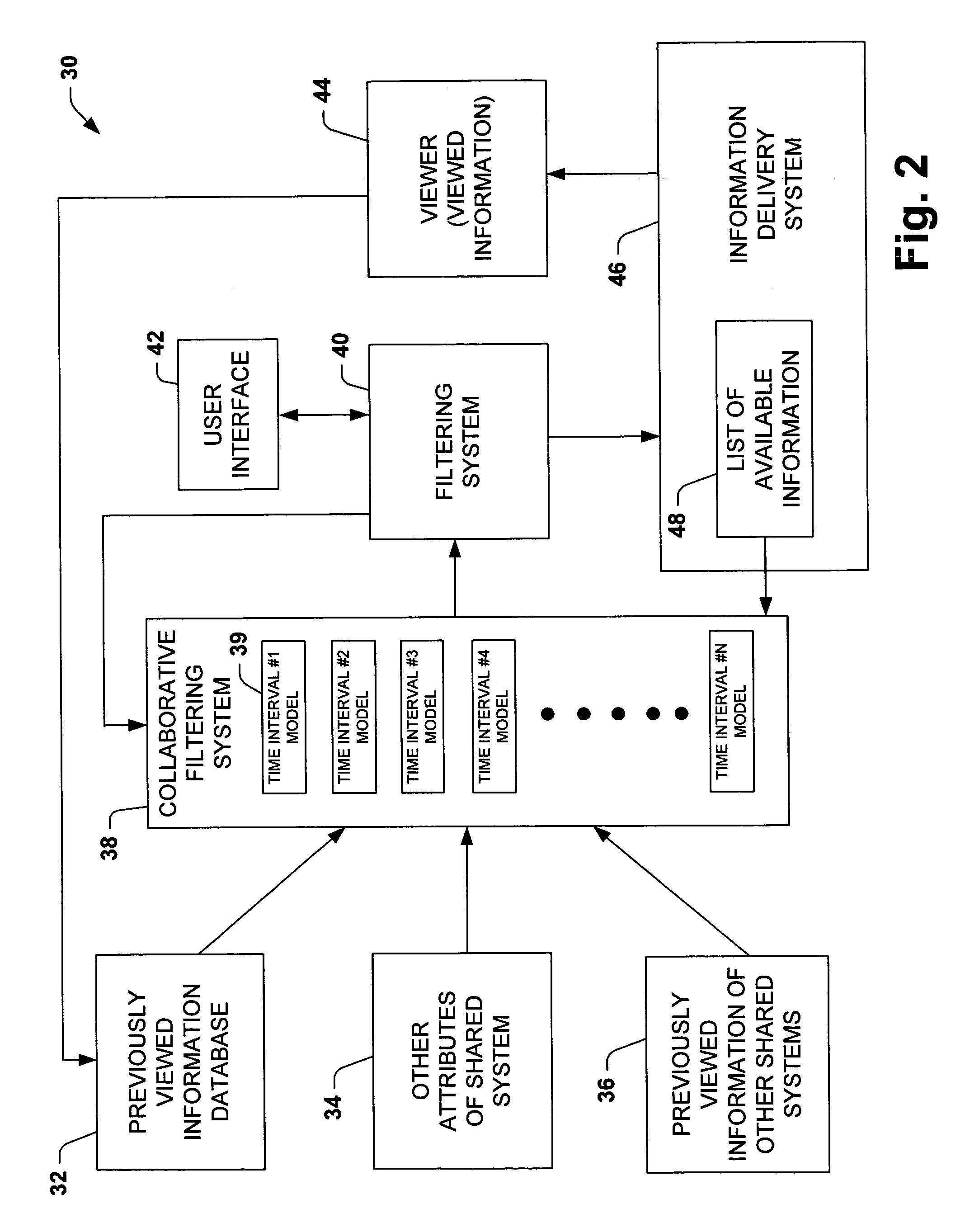
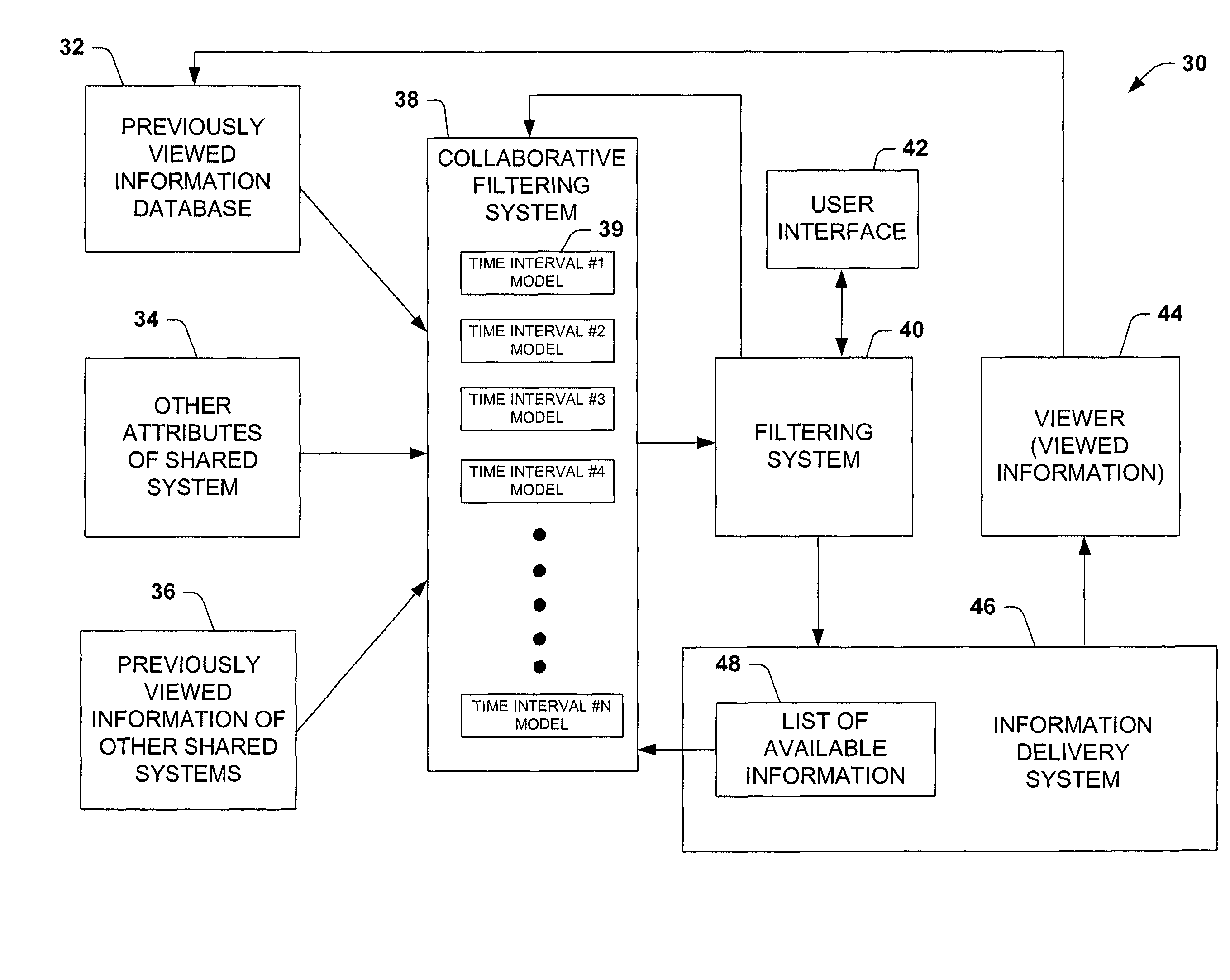
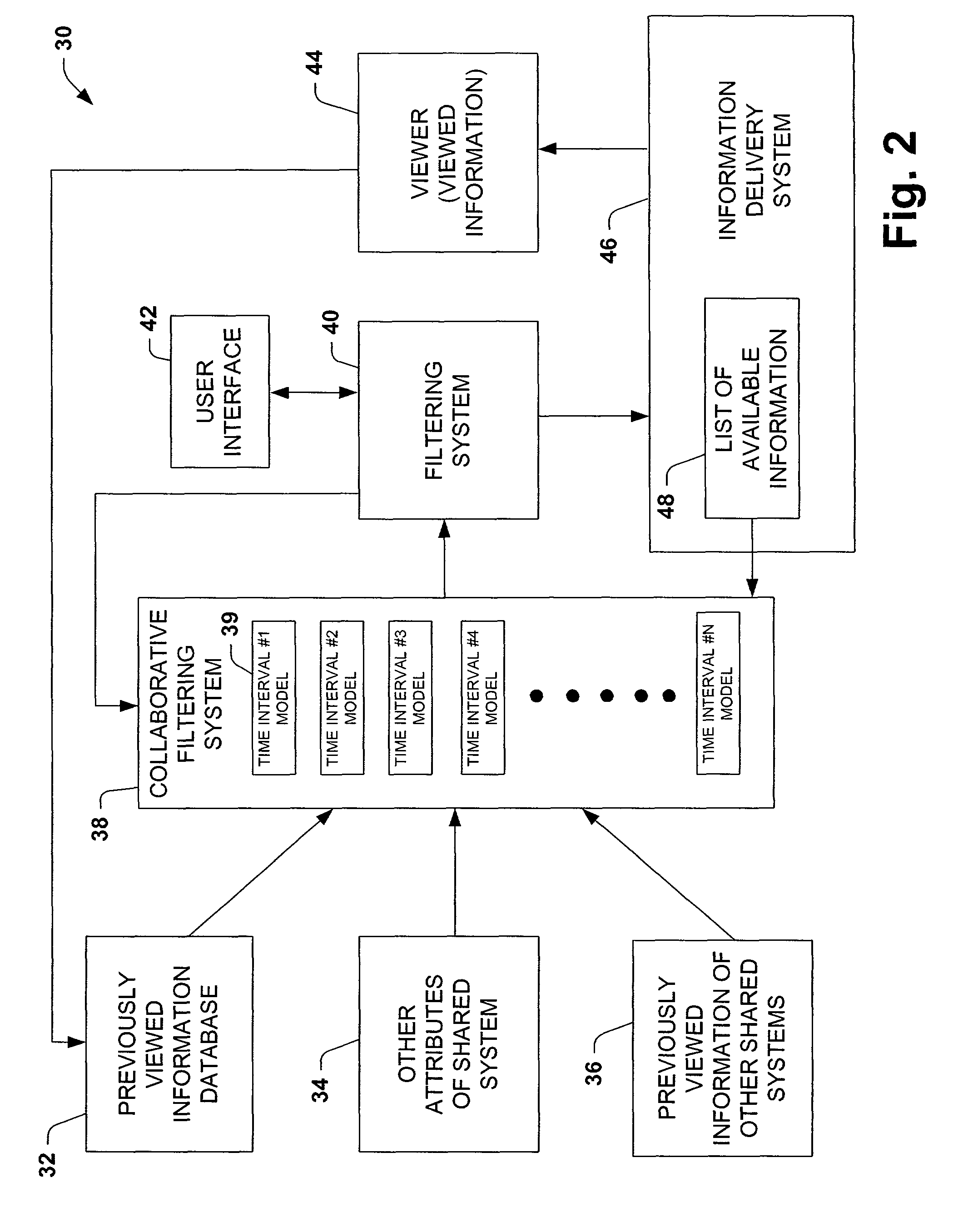
Time-centric training, interference and user interface for personalized media program guides
InactiveUS7644427B1Improved probability predictionIncrease probabilityTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsPersonalizationTime segment
The present invention is related to a system and method of considering time segments or intervals in a collaborative filtering model. The present invention extends collaborative filtering approaches by integrating considerations of temporality into the training and / or vote input associated with the usage of collaborative filtering models. The present invention also applies filtering to the output with temporal models, so as to view a most appropriate subset of recommended content, centering on content that may be available at a target time. The present invention applies time to a collaborative filtering model by allowing weight to be associated with selections within a current time segment, selections historically watched within the current time segment by the user and selections historically watched within the current time segment by a large group of users.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and apparatus for predicting and selectively collecting preferences based on personality diagnosis
InactiveUS6655963B1Cumbersome processMinimal effectMarket predictionsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProbabilistic semanticsData mining
A new recommendation technique, referred to as "personality diagnosis", can be seen as a hybrid between memory-based and model-based collaborative filtering techniques. Using personality diagnosis, all data can be maintained throughout the processes, new data can be added incrementally, and predictions have meaningful probabilistic semantics. Each entity's reported attributes can be interpreted as a manifestation of their underlying personality type. Personality type can be encoded simply as a vector of the entity's "true" values for attributes in the database. Given an active entity's known attribute values, the probability that they have the same personality type as every other entity can be determined. Then, the probability that they will have a given value for a valueless attribute can then be determined based on the entity's personality type. The probabilistic determinations can be used to determine expected value of information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
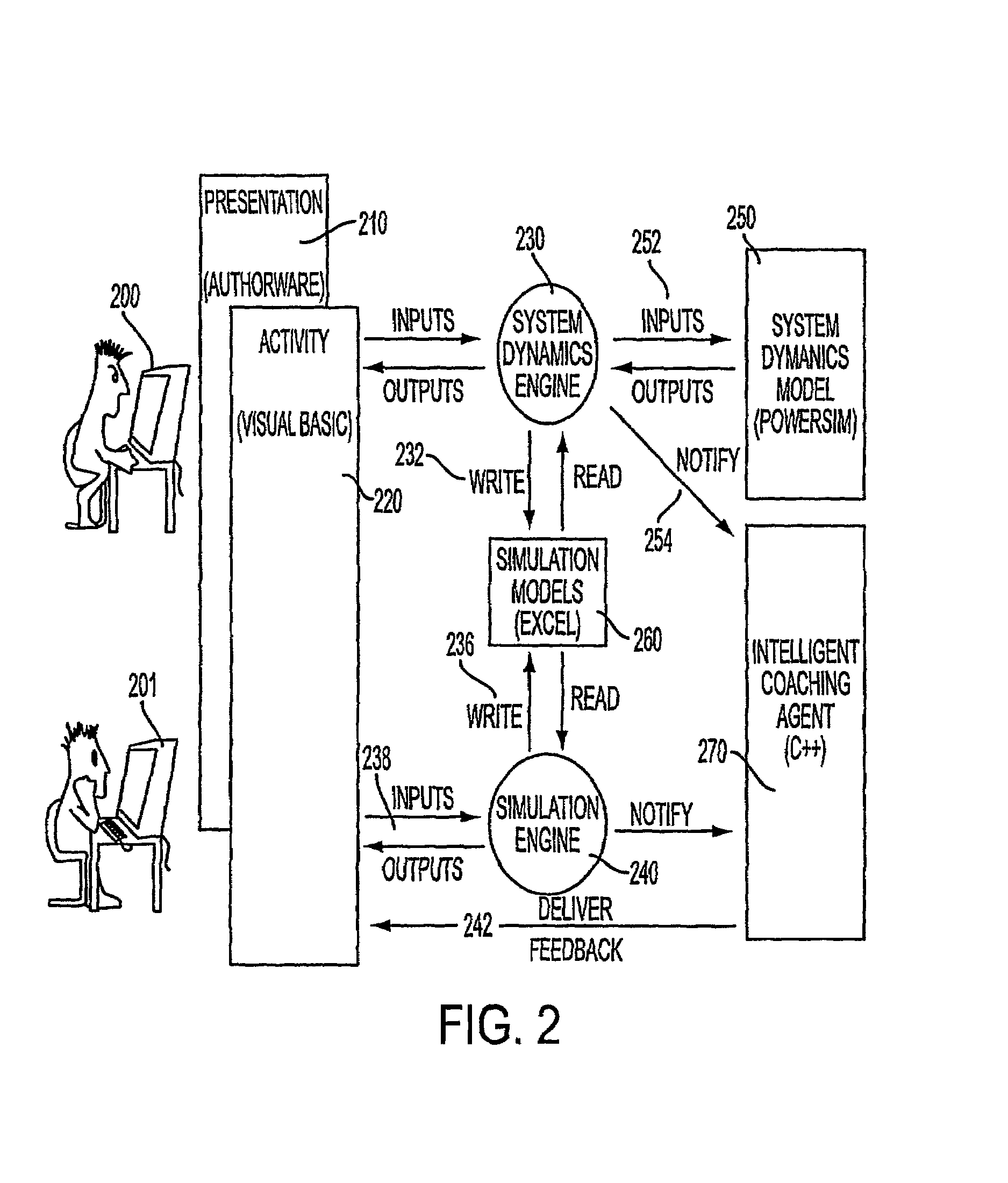
Creating collaborative simulations for creating collaborative simulations with multiple roles for a single student
A system is disclosed that provides a goal based learning system utilizing a rule based expert training system to provide a cognitive educational experience. The system provides the user with a simulated environment that presents a training opportunity to understand and solve optimally. Mistakes are noted and remedial educational material presented dynamically to build the necessary skills that a user requires for success in the business endeavor. The system utilizes an artificial intelligence engine driving individualized and dynamic feedback with synchronized audio, video, graphics and animation used to simulate real-world environment and interactions. Multiple “correct” answers are integrated into the learning system to allow individualized learning experiences in which navigation through the system is at a pace controlled by the learner. Multiple “roles” are also available for the student to learn from each simulated environment from multiple viewpoints. A robust business model provides support for realistic activities and allows a user to experience real world consequences for their actions and decisions and entails realtime decision-making and synthesis of the educational material. A dynamic feedback system is utilized that narrowly tailors feedback and focuses it based on the performance and characteristics of the student to assist the student in reaching a predefined goal.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
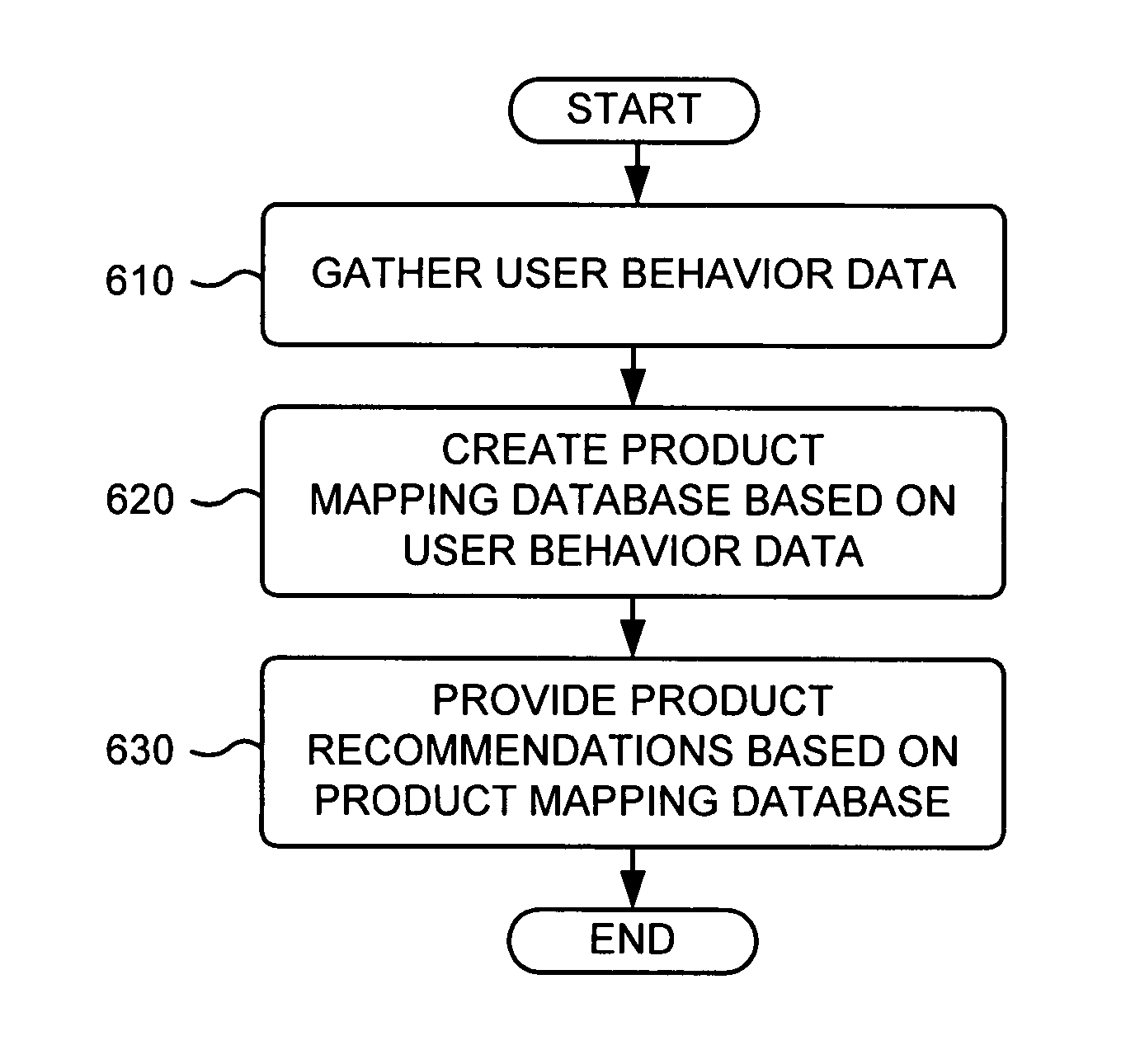
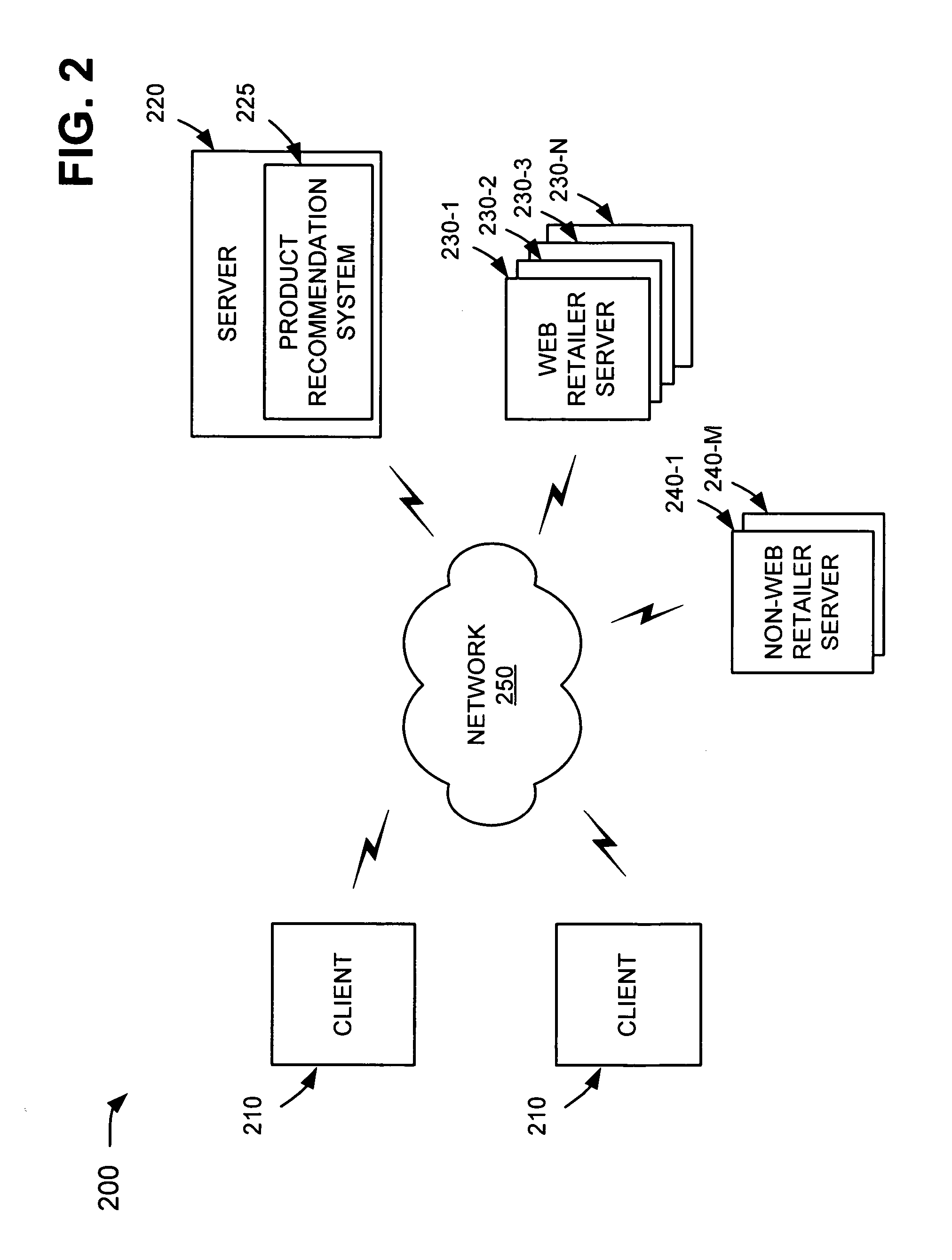
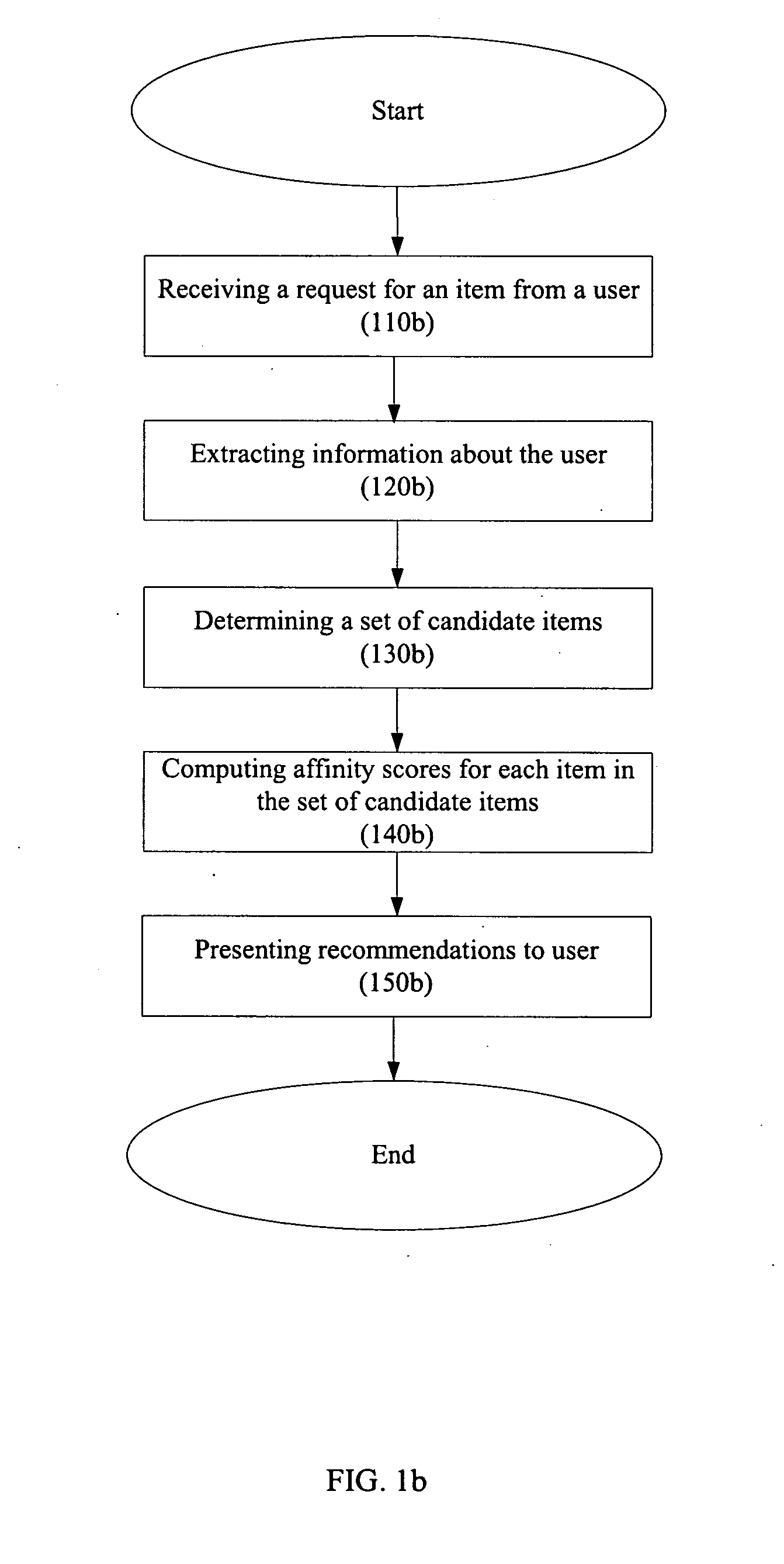
Product recommendations based on collaborative filtering of user data
ActiveUS20070005437A1Other databases browsing/visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsBehavioral dataWorld Wide Web
A system gathers user behavior data from a group of web retailers and / or non-web retailers, analyzes the user behavior data to identify product recommendations for products offered by the web retailers, and provides one of the identified product recommendations in connection with a product page associated with one of the web retailers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
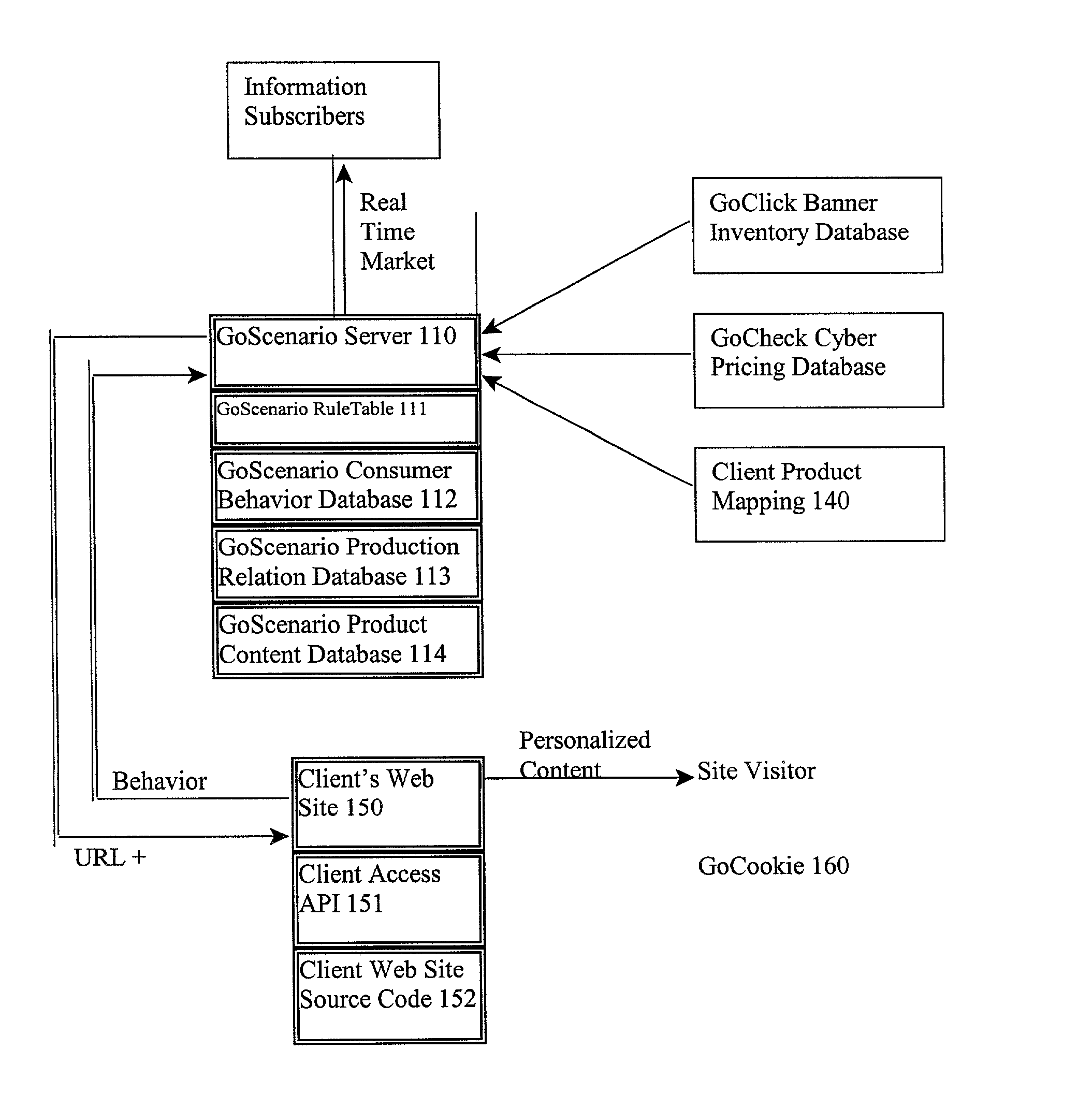
Knowledge by go business model
InactiveUS20020178166A1Digital data processing detailsWebsite content managementCustomer relationship managementField analysis
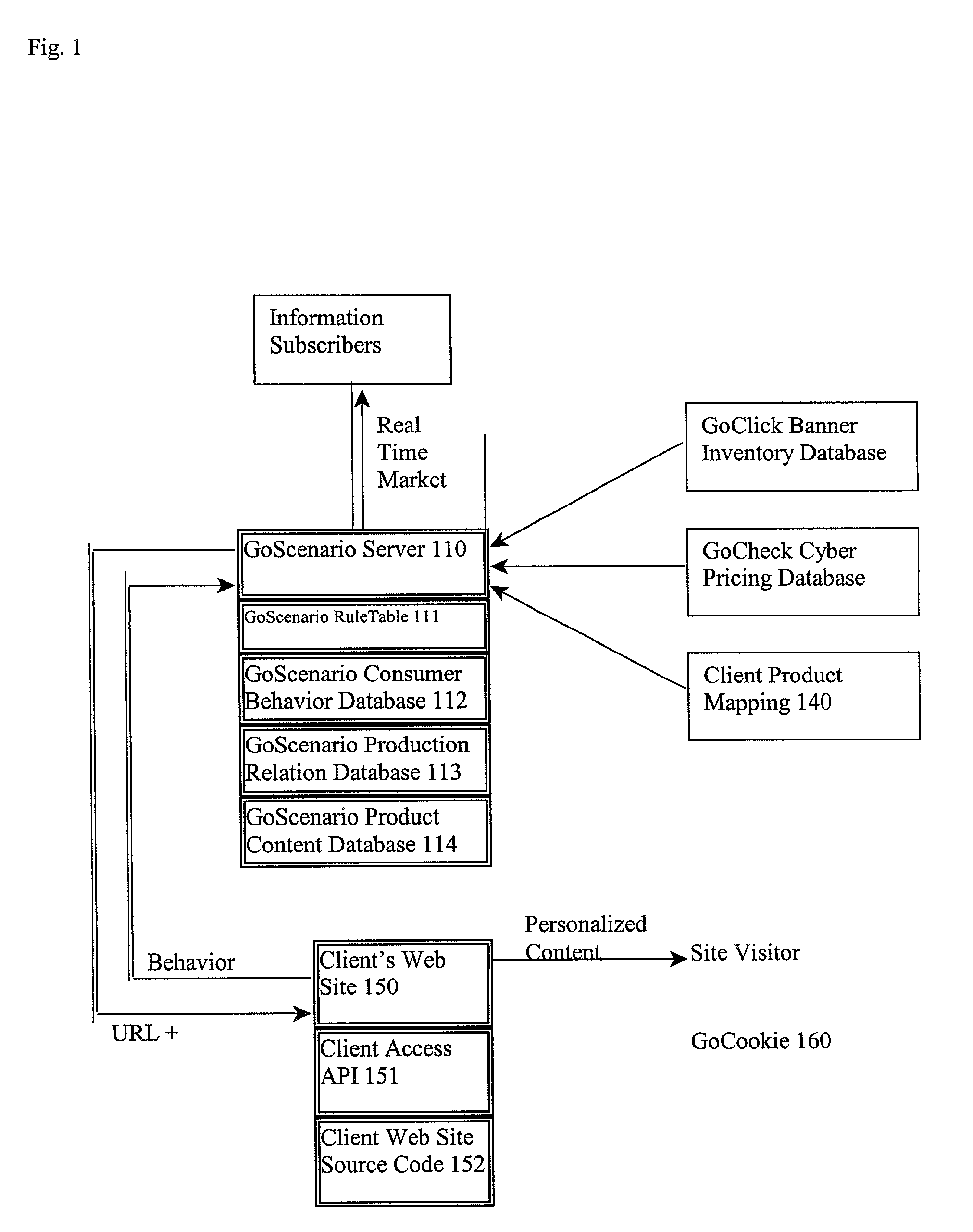
KnowledgeByGo is a knowledge based Internet application service provider system (ASP), that tracks and analyzes browser behavior in real-time. Data analysis is delivered to the website owner or marketing agent to decide if a real time response or off line campaign needs to be initiated. KnowledgeByGo allows real-time behavioral tracking and prediction; customer relation management; one-to-one banner manager; site analysis reporting service; industry wide marketing research reports; product management; order processing; secure payment system; and customer contact manager. Subscribers get the immediate benefits of: collaborative filtering; real-time behavioral prediction; up-selling and / or cross-sell selling; banner advertisement income; Customer Relation Management (CRM); one-to-one banner management; site analysis reporting server; network-wide sales and marketing reports; product content and online pricing spidering; site management, backend product management, backend order processing, RMA processing, secured payment system, customer contact manager, price-search engine utility, and consolidated participation purchasing.
Owner:DIRECT411 COM
Determining User Preference of Items Based on User Ratings and User Features
ActiveUS20100250556A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNear neighborCollaborative filtering
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
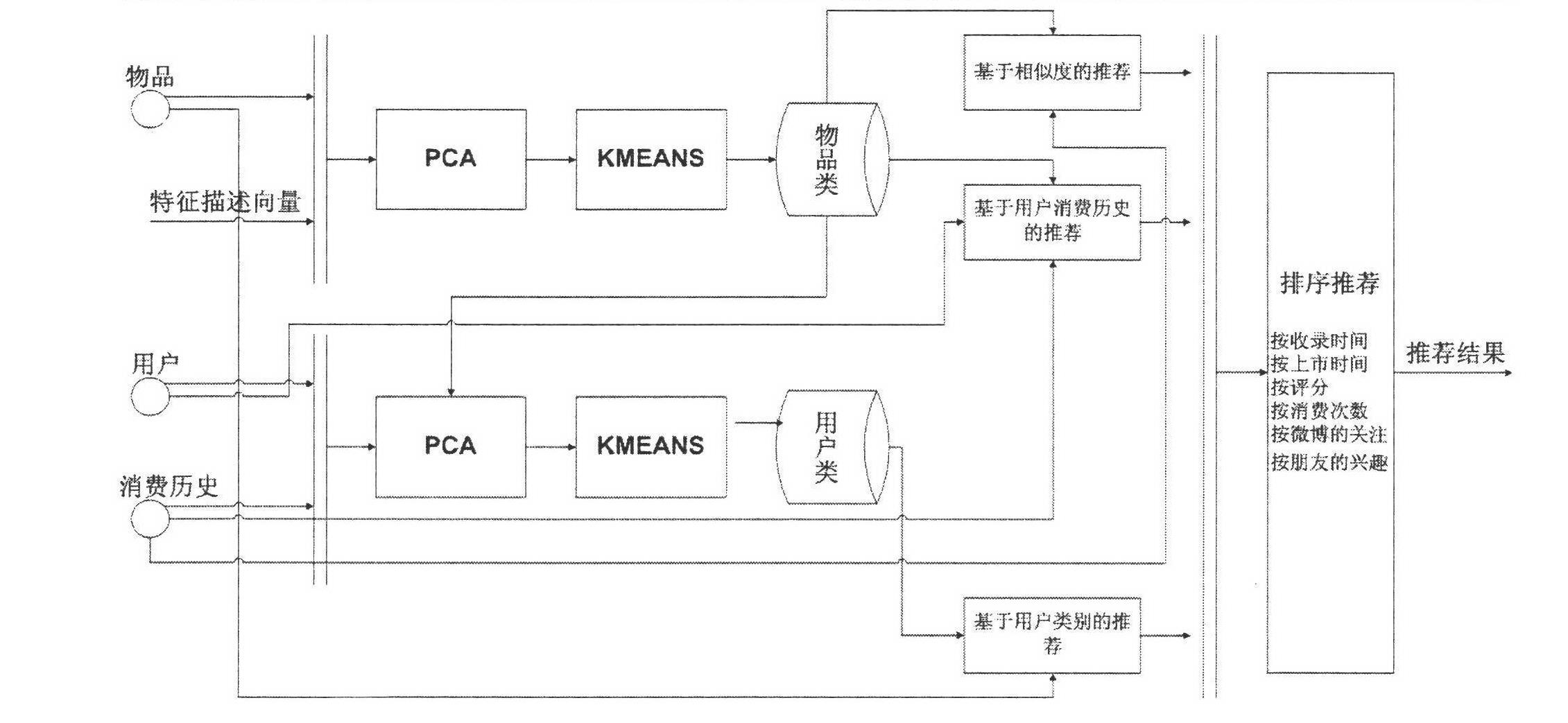
Collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on article sorting and user sorting
ActiveCN102609523ASimple methodImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsExtensibilityCollaborative filtering
The invention relates to a collaborative filtering algorithm, in particular to a collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on article sorting and user sorting, which is characterized by including steps: A, article clustering and sorting; B, user clustering and sorting; C, integration of article clustering and user clustering; and D, sorting recommendation. Compared with the prior art, collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm has the advantages that the data clustering is completed by means of modified KMEANS algorithm, the method is simple, and extensibility is improved while the problems of sparsity and cold boot are solved.
Owner:上海视畅信息科技有限公司
Time-centric training, inference and user interface for personalized media program guides
InactiveUS7757250B1Increase probabilityTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsPersonalizationTime segment
The present invention is related to a system and method of considering time segments or intervals in a collaborative filtering model. The present invention extends collaborative filtering approaches by integrating considerations of temporality into the training and / or vote input associated with the usage of collaborative filtering models. The present invention also applies filtering to the output with temporal models, so as to view a most appropriate subset of recommended content, centering on content that may be available at a target time. The present invention applies time to a collaborative filtering model by allowing weight to be associated with selections within a current time segment, selections historically watched within the current time segment by the user and selections historically watched within the current time segment by a large group of users.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com