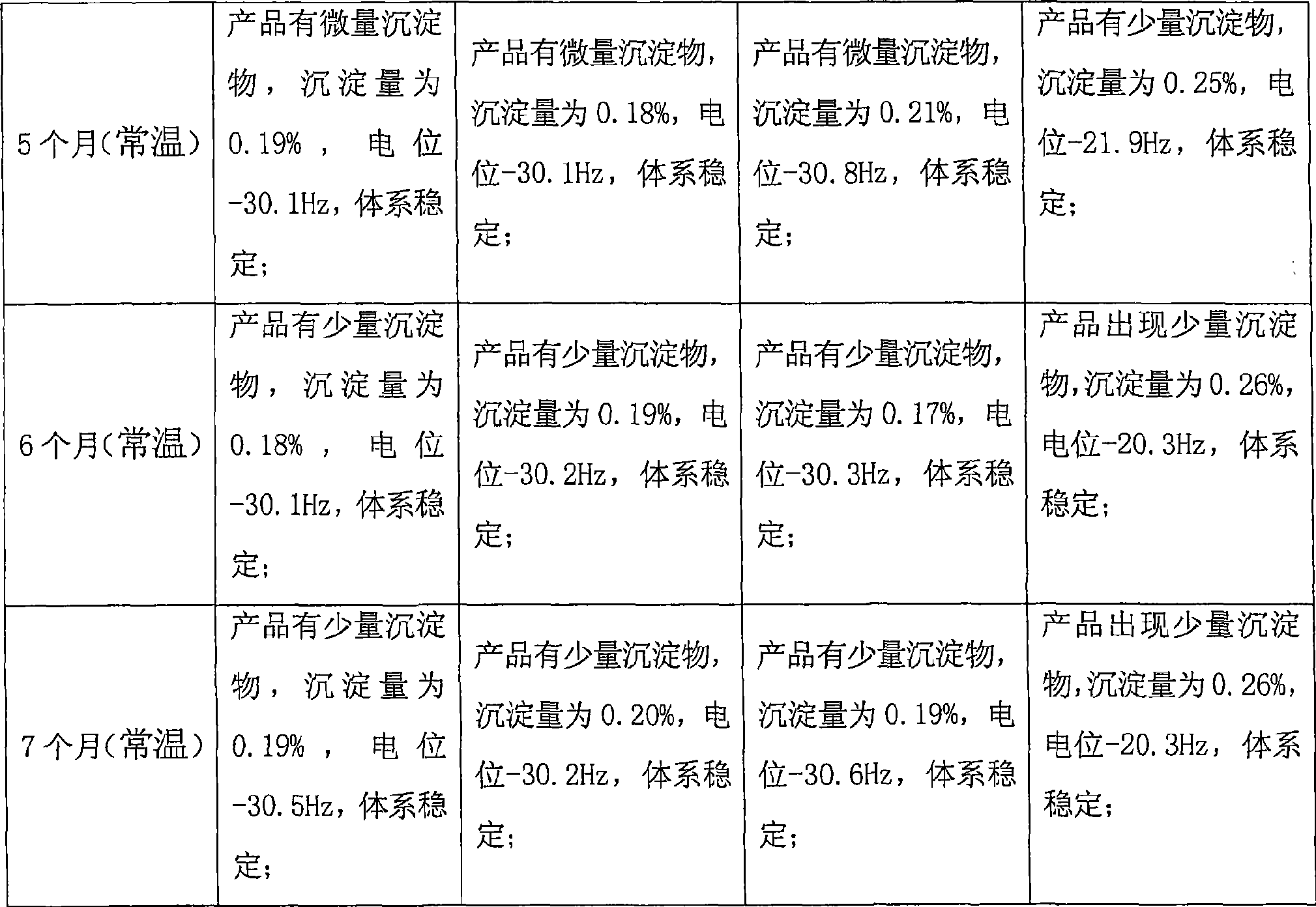
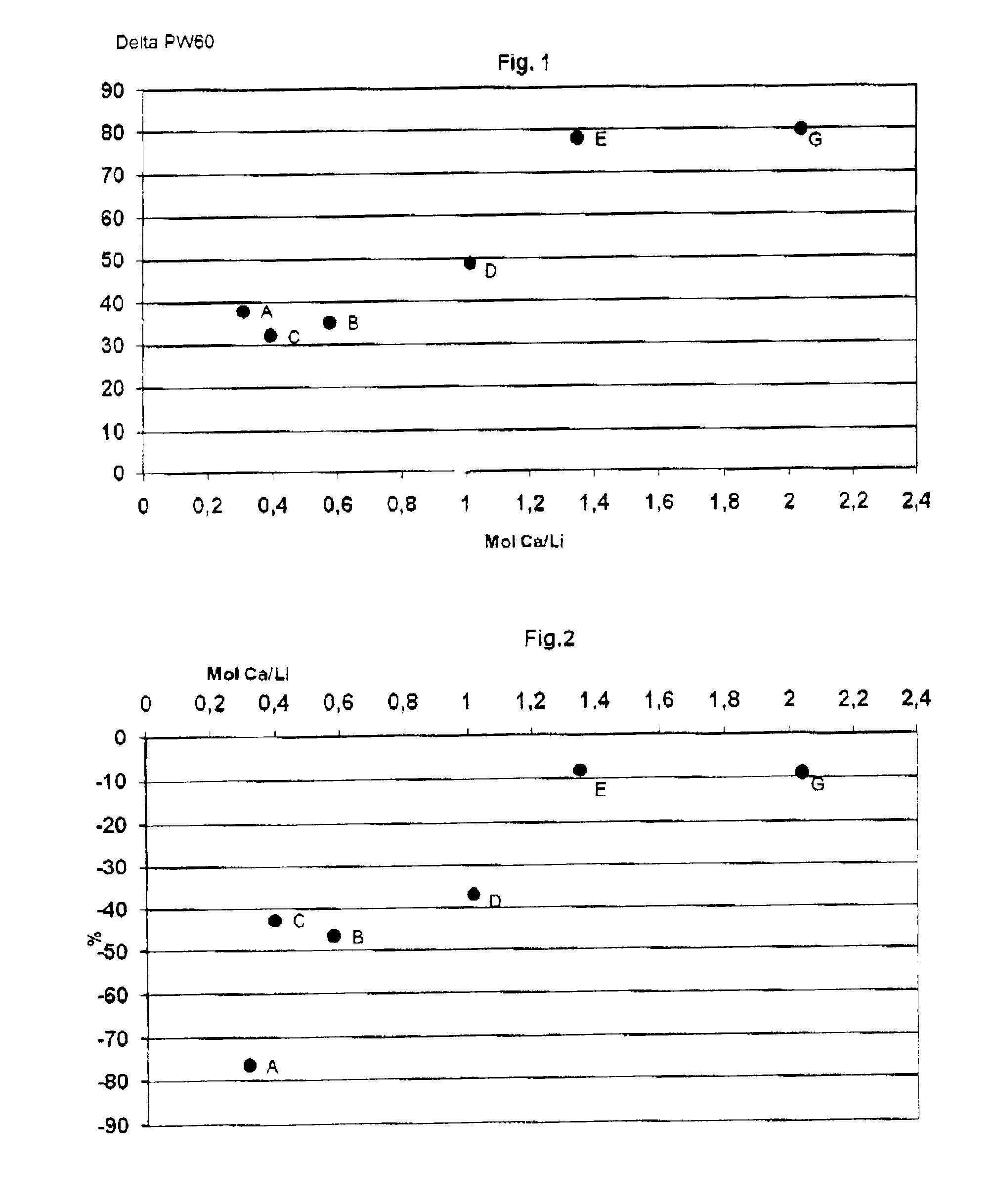
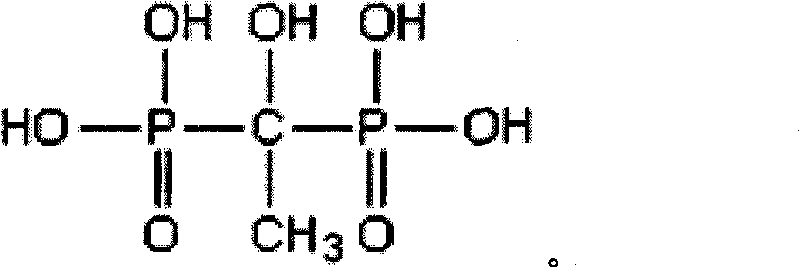
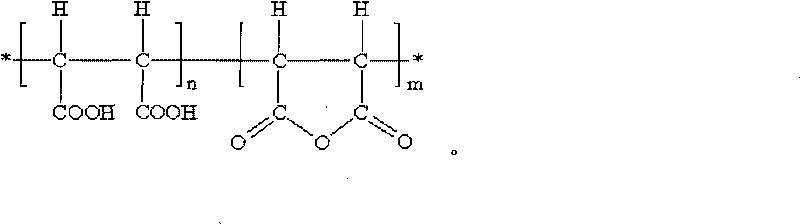
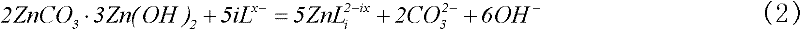Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1728 results about "High calcium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Calcification vanadium slag sintering method
InactiveCN101161831AEasy temperature controlShorten roasting timeProcess efficiency improvementSlagCalcification
The invention discloses a method of vanadium slag direct entering high temperature roasting furnace calcify roasting, that is, high calcium vanadium slag or ordinary vanadium slag and lime or limestone are mixed uniformly without the gradual heating up process from low temperature to high temperature, the mixture enters into the roasting furnace of more than 600 DEG C for calcified roasting., the vanadium of the vanadium slag is changed into vanadium acid calcium, vanadium of the roasting clinker is dissolved into the solution under the leaching function of sulphuric acid solution, vanadium oxide and the like vanadium products are further made. The invention needs no gradual heating up process from low temperature to high temperature of the prior sodium treatment roasting, thereby reducing roasting time, improving productivity of unit and reducing production cost.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Non-phosphorus compound scale and corrosion inhibitor for treatment of circulating cooling water
ActiveCN1621362AEasy to useIncrease the concentration factorScale removal and water softeningPhosphateTungstate
The composite phosphate-free scale inhibiting corrosion inhibitor for treating circular cooling water consists of scale inhibitor and corrosion inhibitor. The scale inhibitor consists of one or several of PASP, PVA, oxidized starch, polyacrylic acid, acrylic acid / acrylate copolymer and acrylic acid / acrylate copolymer with sulfo radical. The corrosion inhibitor consists of one or several of sodium salt / potassium salt / ammonium salt of organic salt, sodium / potassium / ammonium borate, nitrous organic matter, soluble molybdenate, soluble tungstate, soluble nitrate, soluble nitrite and soluble zinc salt. The composite scale inhibiting corrosion inhibitor has excellent scale inhibiting and corrosion inhibiting performance, is environment friendly, and is especially the treatment of hard circulation water with high calcium and high alkali content.
Owner:BEIJING YANHUA XINGYE TECH DEV +1
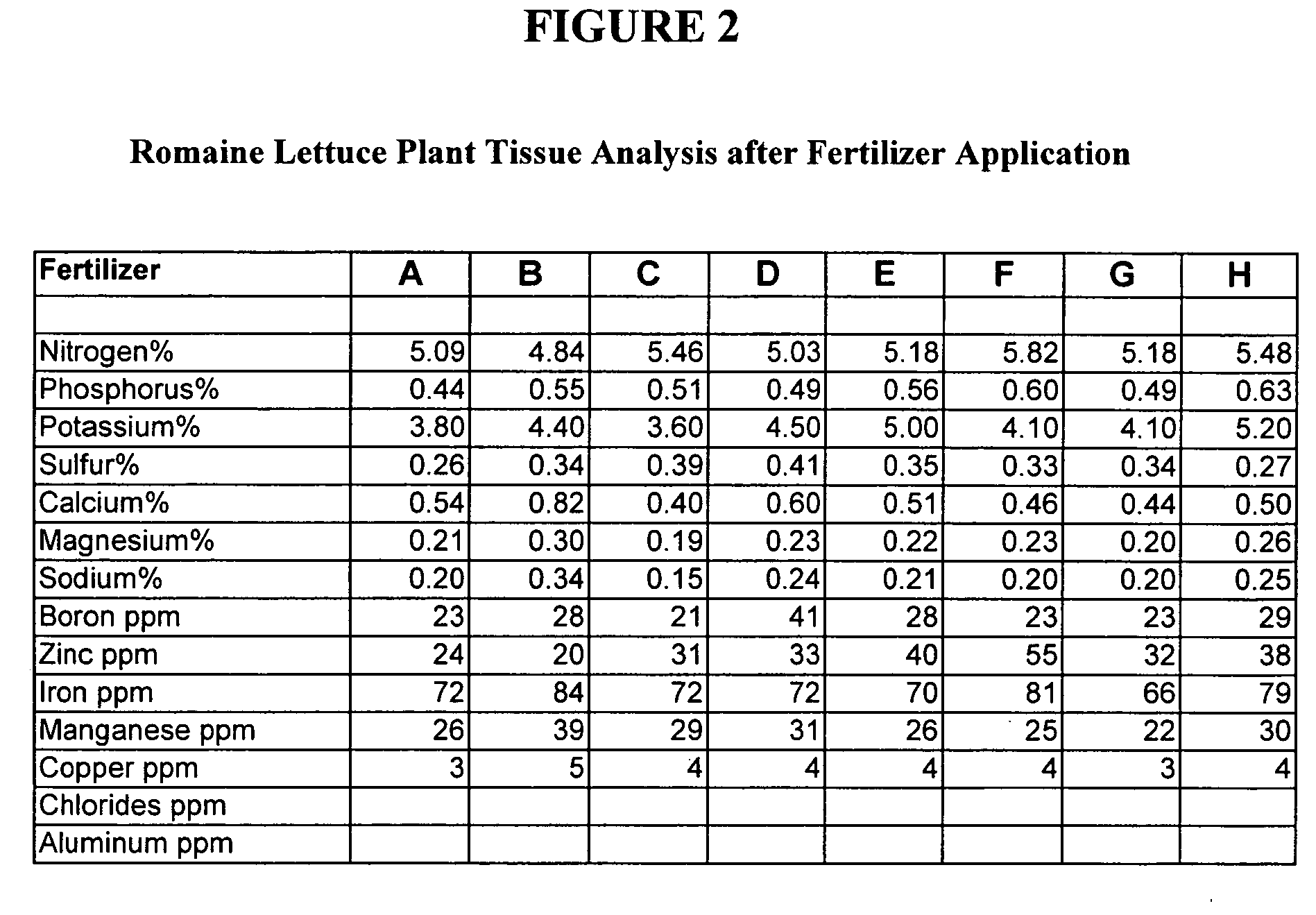
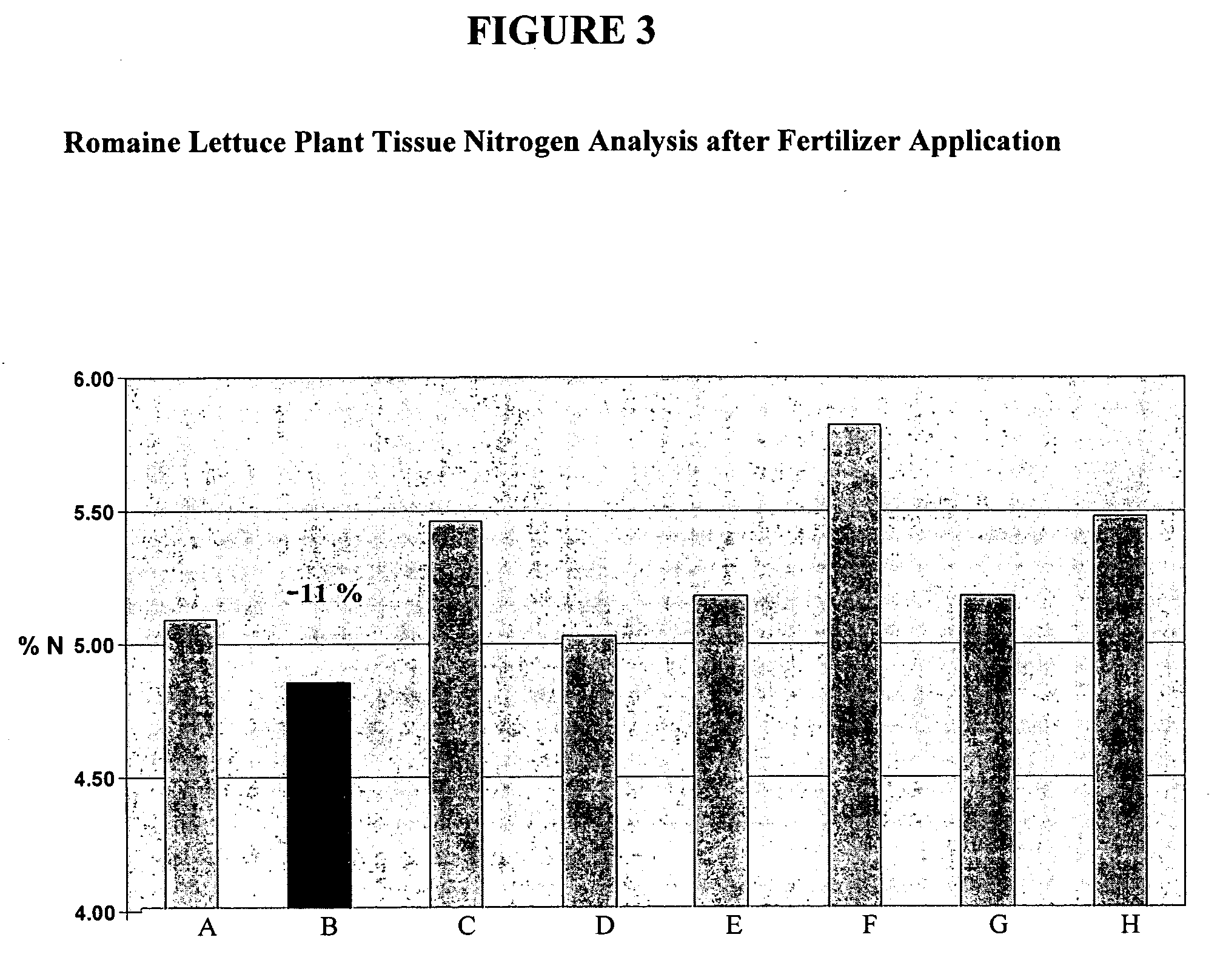
High calcium fertilizer composition
Calcium phosphite containing fertilizers, as well as methods of making and methods of using these fertilizers, are disclosed.
Owner:VERDESIAN LIFE SCI
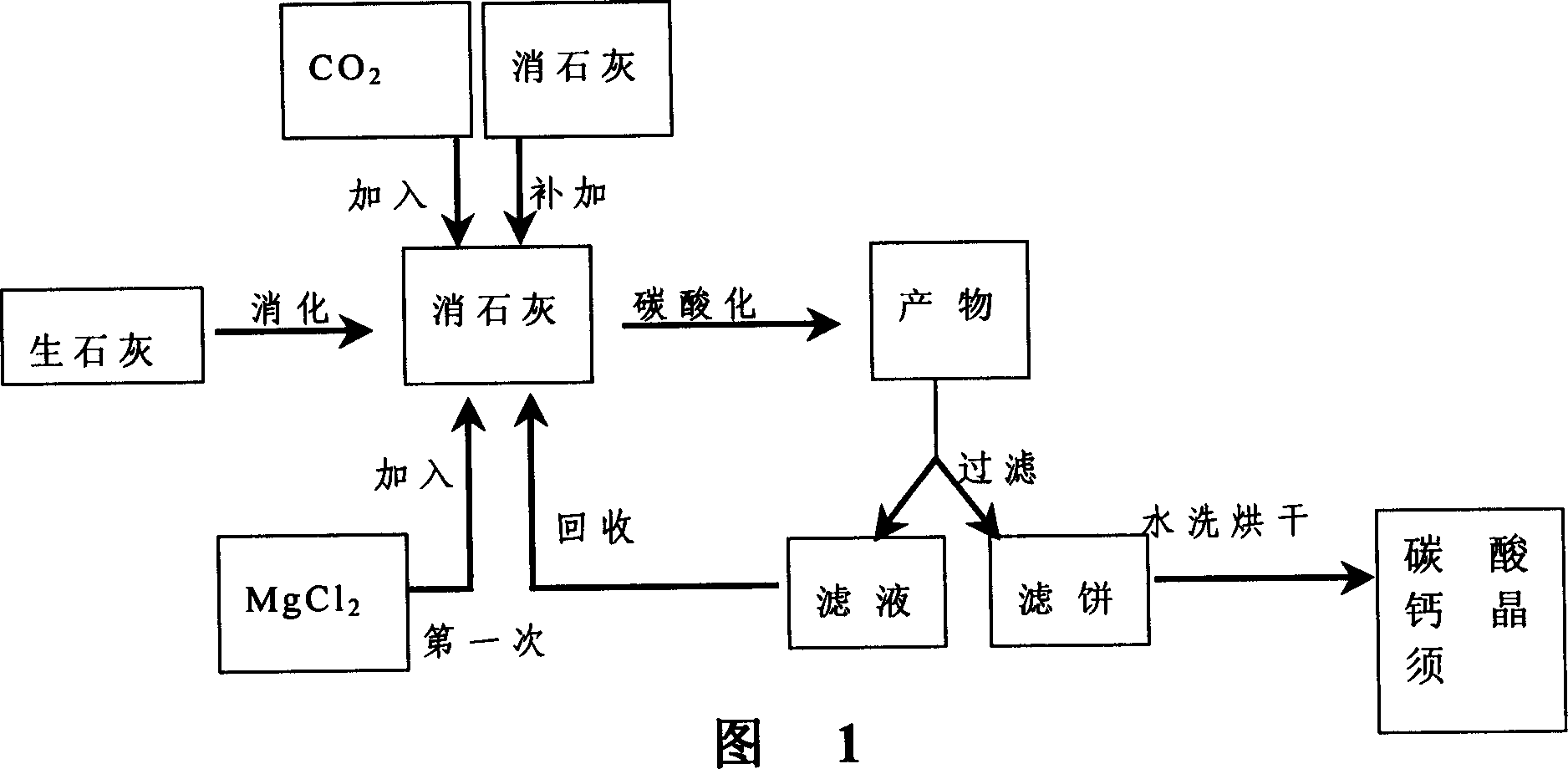
Method for preparing aragonite type calcium carbonate whisker
InactiveCN1641077AReduce manufacturing costReduce qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPolycrystalline material growthMagnesium saltDiameter ratio
The present invention relates to the preparation process of high purity aragonite type calcium carbonate whisker. The present invention prepares aragonite type calcium carbonate whisker with lime or slaked lime as main material and magnesium salt as crystal salt controlling agent and through a CO2 carbonating process. The process features the repeated use of the magnesium salt solution and the homogeneous replenishment of lime slurry during carbonating reaction. The process has low production cost, less environmental pollution and high calcium carbonate whisker yield, and the prepared calcium carbonate whisker has high purity and high length / diameter ratio. The process is suitable for industrial production of calcium carbonate whisker.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
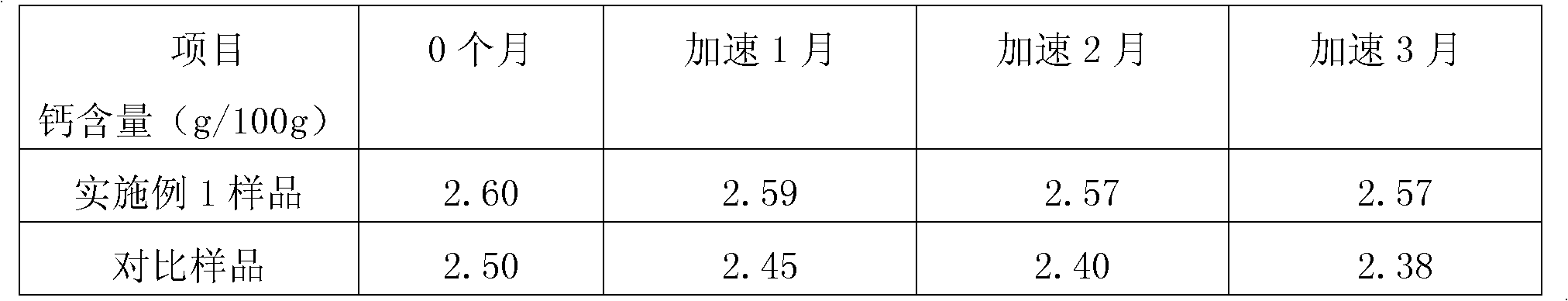
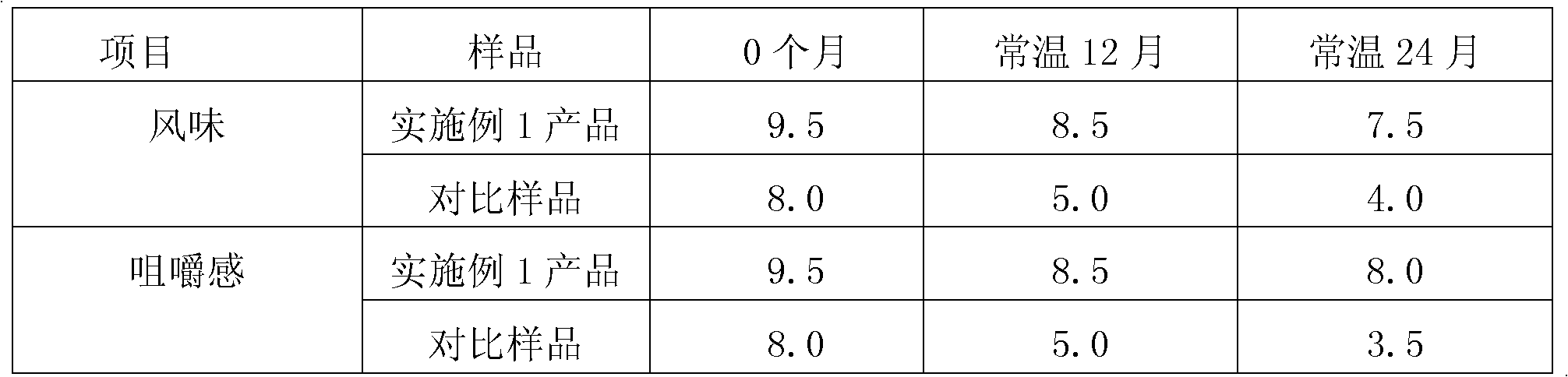
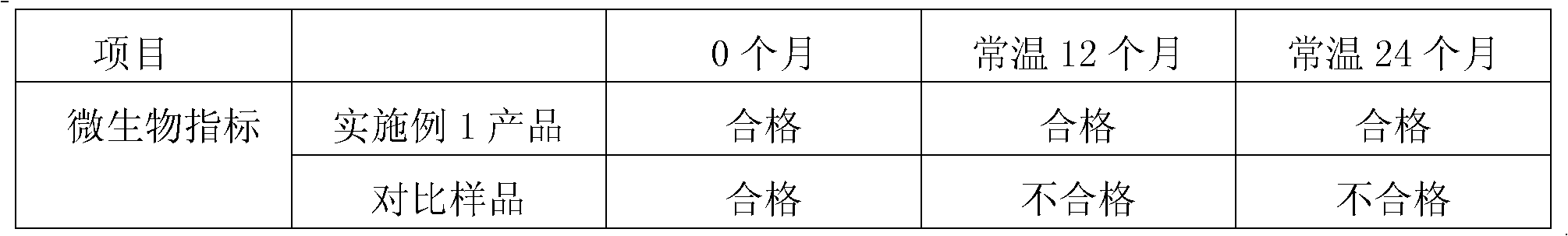
High-calcium soft candy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102511603ALess frequent consumptionHigh in calciumConfectionerySweetmeatsFood additiveCalcium content
The invention discloses a high-calcium soft candy which comprises the following raw materials by weight portion: 1 to 16.6 parts of candyeners, 1.3 to 14.2 parts of edible calcium-containing compounds, 0.1 to 1.6 parts of gels, 0 to 1 part of vitamin and 0 to 1 part of food additive, wherein, the content of calcium in the high-calcium soft candy is 2.6 g to 20.0 g / 100 g. The high-calcium soft candy has the benefits as follows: firstly, the calcium content is high, so that the eating frequency of people taking calcium supplements is decreased; secondly, the soft candy has a good taste and can be accepted by a majority of people easily, particularly by children; and thirdly, the soft candy has a better stability, the calcium content, taste and microbial index conform to standards within theguarantee period, and the guarantee period is twelve months.
Owner:SIRIO HEALTHCARE ANHUI CO LTD
Bearing cleaning composition and method of use
ActiveUS7241723B2Easy to distinguishHigh in calciumRotary combination bearingsBearing componentsSulfonateEngineering
A composition for cleaning bearings in rotating equipment and industrial machinery that contains powdered limestone having a high calcium content dispersed in a calcium sulfonate grease, together with a colorant that readily enables a user to differentiate between contaminated grease, cleaning composition and fresh grease. A method is also disclosed that enables a user to clean and re-lubricate bearings without the need for removing the bearings from service or for shutting down the associated equipment or machinery.
Owner:NCH CORP
Geopolymer grouting material
InactiveCN101712546AImprove early strengthImprove liquiditySolid waste managementCement productionSlagGeopolymer
The invention discloses a geopolymer grouting material, which is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10-30 parts of waste concrete powder, 5-15 parts of desulfurization gypsum, 10-20 parts of steel slag powder, 20-40 parts of scoria powder, 3-8 parts of high calcium fly ash, 20-50parts of coal ash and 5-10 parts of alkali-activator. The geopolymer grouting material has the advantages of high early strength, good flowing property, low production cost, and the like; moreover, the geopolymer grouting material has self-hardening property, can react with soil, and enable soil bodies to become a plate-shaped structure, thereby improving the bearing capacity of a soil roadbed.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Milk powder
The milk powder is prepared with the materials including: fresh milk or milk powder, defatted milk powder or defatted milk, lactase, desalted whey powder, whey protein powder and / or soybean protein powder, vegetable oil, phospholipid, oligose, honey, calcium lactase, CPP, wolfberry fruit, vitamins and minerals. The product may avoid lactose intolerance, has the effects of resisting fatigue, resisting senility, raising memory and improving gastrointestinal tract function, and has the advantages of no cane sugar, high calcium content and low lactose content.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Geopolymer soil consolidation grouting material
InactiveCN101250034AImprove liquidityConvenient slurrySolid waste managementCement productionSlagGeopolymer
The invention relates to a soil consolidation grouting material of geopolymer, which is composed of fly ash, slag, steel slag, high-calcium fly ash, alkali-activator, nonpolar alkaline surface active agent and water, wherein the nonpolar alkaline surface active agent is obtained by reacting curled hair of human or animal with sodium hydroxide, and the pH value of the water is larger than 6.5. The soil consolidation grouting material of geopolymer of the invention is high in initial strength, fine in water stability, liquidity, frost-resisting property and service durability and the like, simultaneously, the soil consolidation grouting material of geopolymer has the characteristic of low manufacturing cost and reducing environmental pollution.
Owner:芮志平 +1
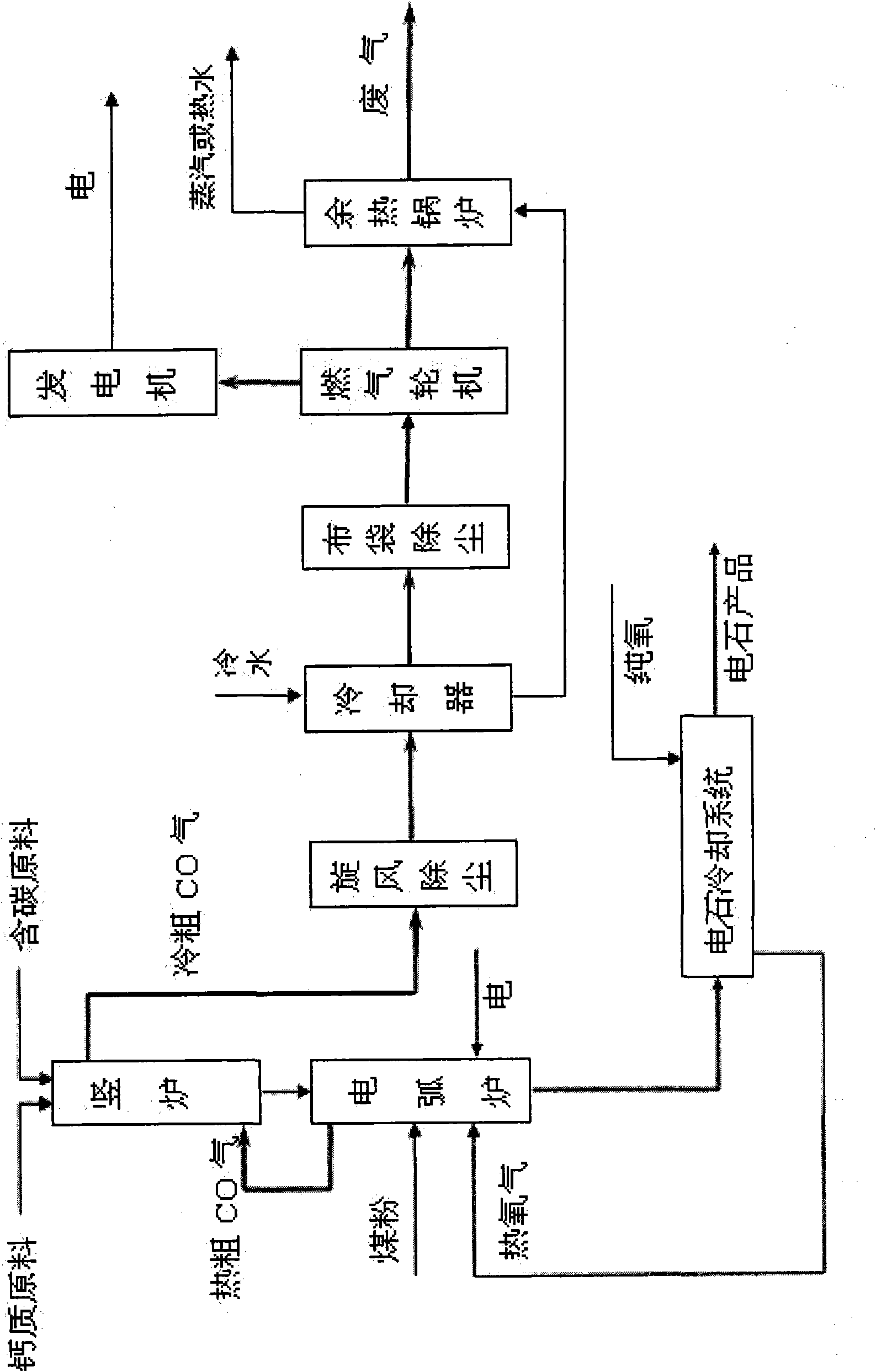
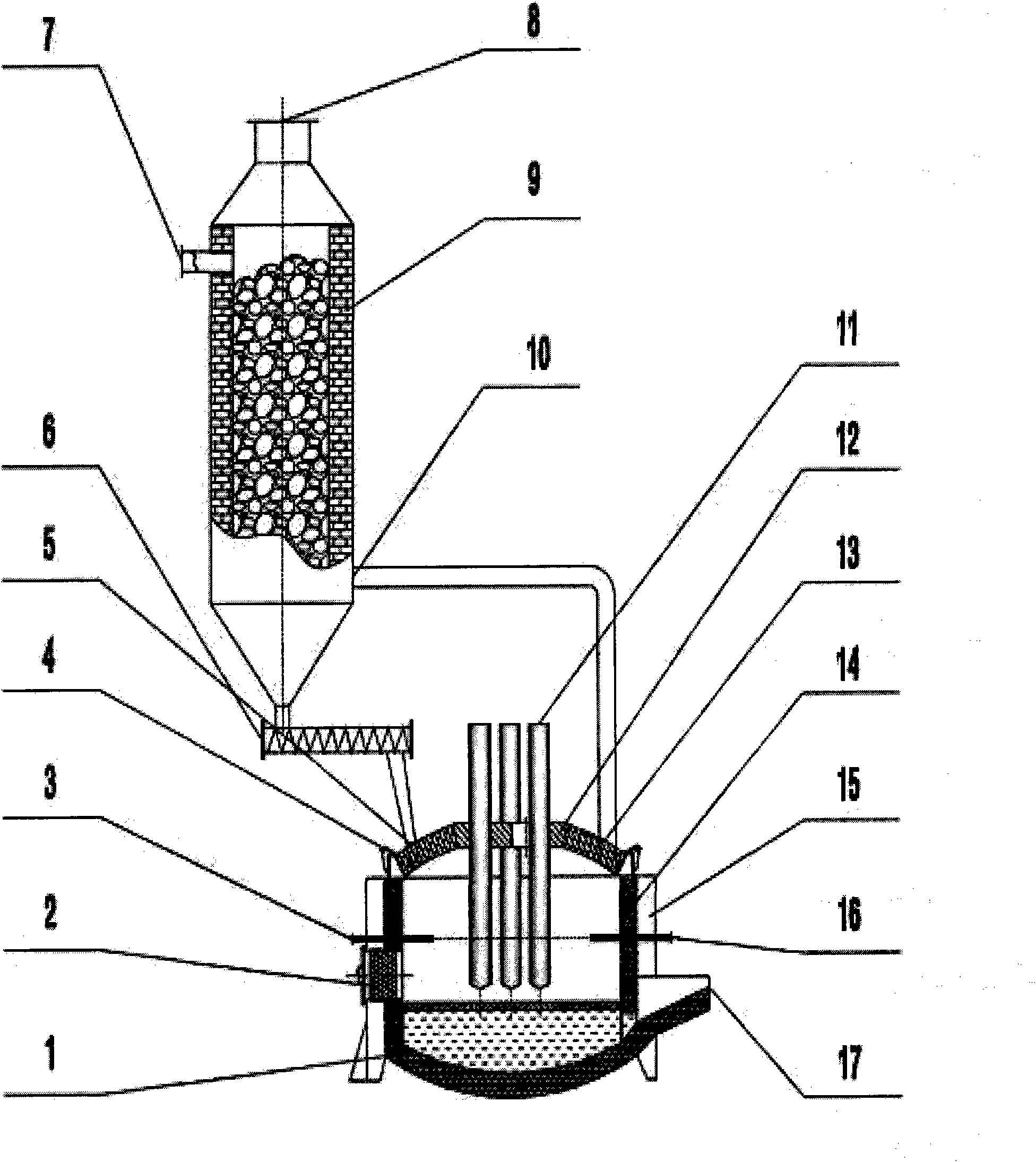
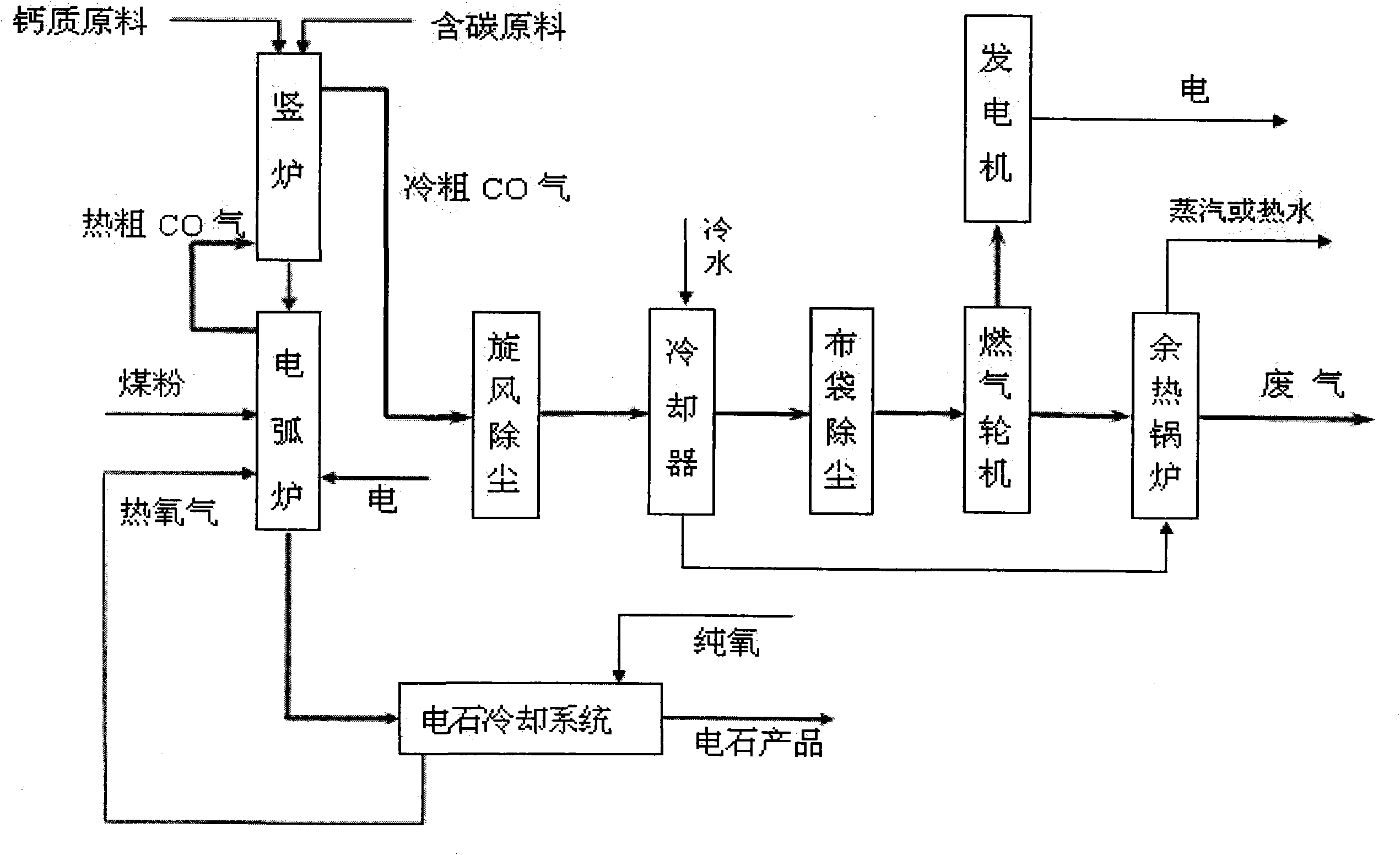
Technique for producing calcium carbide and cogeneration by two-stage method and device thereof
InactiveCN101830464AQuality assuranceReduce consumptionEnergy inputCalcium carbideElectric arc furnaceCogeneration
The invention relates to a technique for producing calcium carbide and cogeneration by a two-stage method and a device thereof. The technique comprises the following steps: after being preheated at a shaft furnace at the upper section, massive carbonous raw material and massive calcic raw material enter an arc furnace at the lower section; while blowing oxygen and coal powder and supplying heat by the electrode in the arc furnace, the raw materials react to produce calcium carbide; and the produced calcium carbide furnace gas is dedusted and combusted by a gas turbine so as to drive the generator to generate power, and sensible heat of exhaust gas is recycled by an exhaust-heat boiler, thereby centrally supplying heat to cities and towns. The invention has the advantages of capability of continuous production, high yield, low investment, low energy consumption, high calcium carbide grade, energy saving, high efficiency and investment saving, and realizes coordinated development of economy, environment and energy sources.
Owner:山西亿众公用事业有限公司
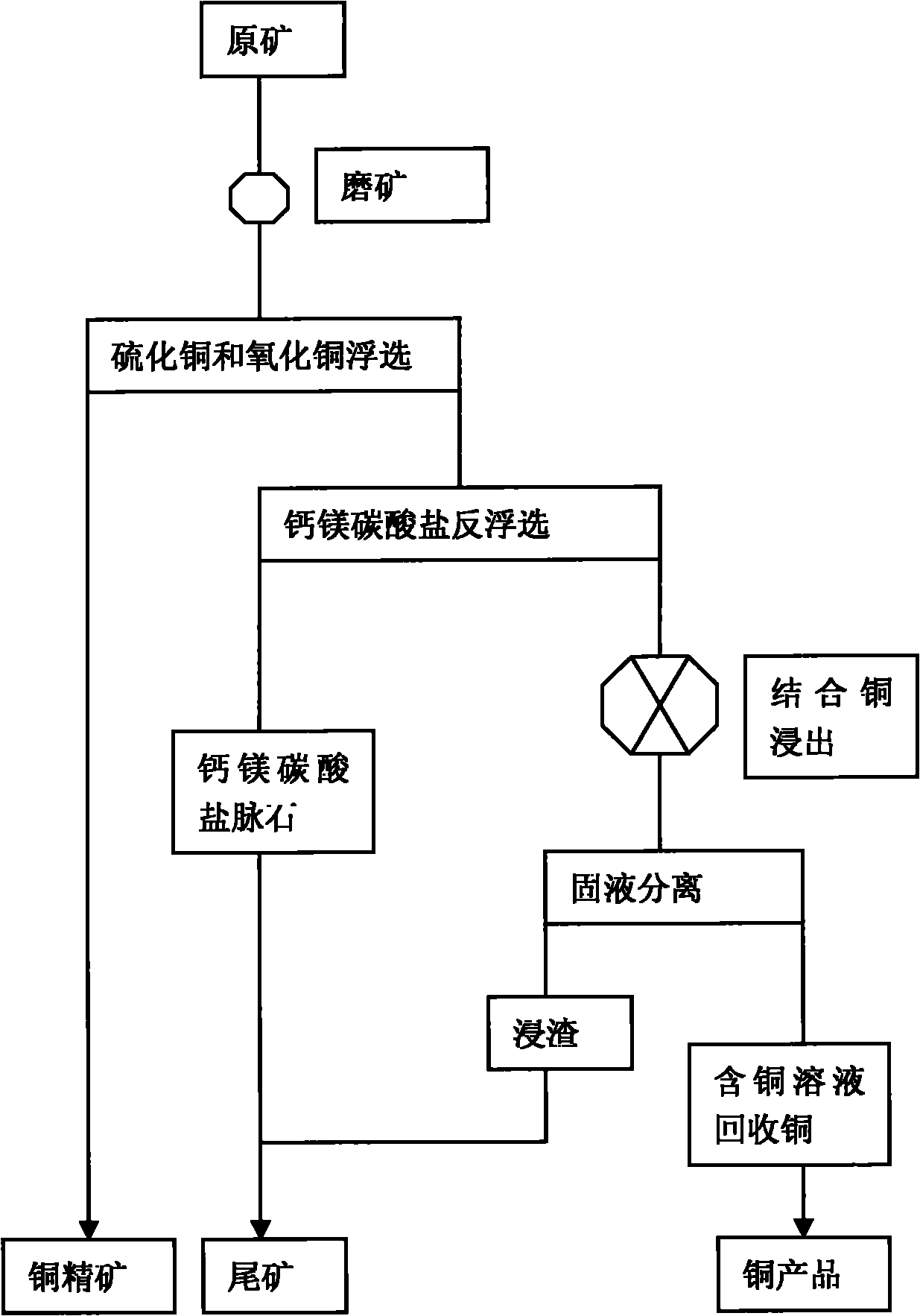
Flotation and metallurgy method of high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore
ActiveCN101831559AAvoid lostReduce consumptionFlotationProcess efficiency improvementCopper oxideOxygen
The invention relates to a flotation and metallurgy method of high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore. The flotation and metallurgy method comprises the following steps of: firstly, recovering copper sulfide minerals and free copper oxide minerals in the high-bonding-ratio oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore with high calcium-magnesium carbonate gangue mineral content by flotation; carrying out reverse flotation on calcium-magnesium carbonate ore in tailings obtained after floatation with fatty acid to obtain middlings containing combined copper and less calcium-magnesium carbonate minerals; then, adding sulphuric acid and stirring to leach out combined copper; and processing a copper-contained solution obtained after solid-liquid separation to obtain a copper product by a metallurgy method. The method combines the flotation and the metallurgy for complementary advantages, efficiently recovers and utilizes high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore resources incapable of being processed at present, lessens the emission of castoff, such as carbon dioxide, magnesium calcium sulfate, and the like and has favorable economic benefits and environmental benefits.
Owner:YUNNAN TIEFENG MINING CHEM NEW TECH CO LTD
Method for processing marinated beef with bean fragrance and marinated beef with bean fragrance
The invention provides a method for processing marinated beef with bean fragrance. The method comprises the following working procedures of marinating beef, cooking beans, mixing the beef and the beans, packaging in vacuum, sterilizing and putting a finished product into a storehouse. The marinated beef with the bean fragrance has rich nutrition; the meat is soft, tender and matured; the fragrance is rich; the taste is proper; the flavor is unique; the meat has high protein, low fat and high calcium; the marinated beef with the bean fragrance has the health protection effects of tonifying the spleen, stimulating the appetite, moistening the lung, reducing the lip, promoting the sleeping and the like and also has the effects of nourishing the body, complementing the calcium, expelling the toxin, beautifying and eliminating acne; the processing technology is scientific; and nitrite is eliminated.
Owner:ANHUI GUANGZHENG FOOD
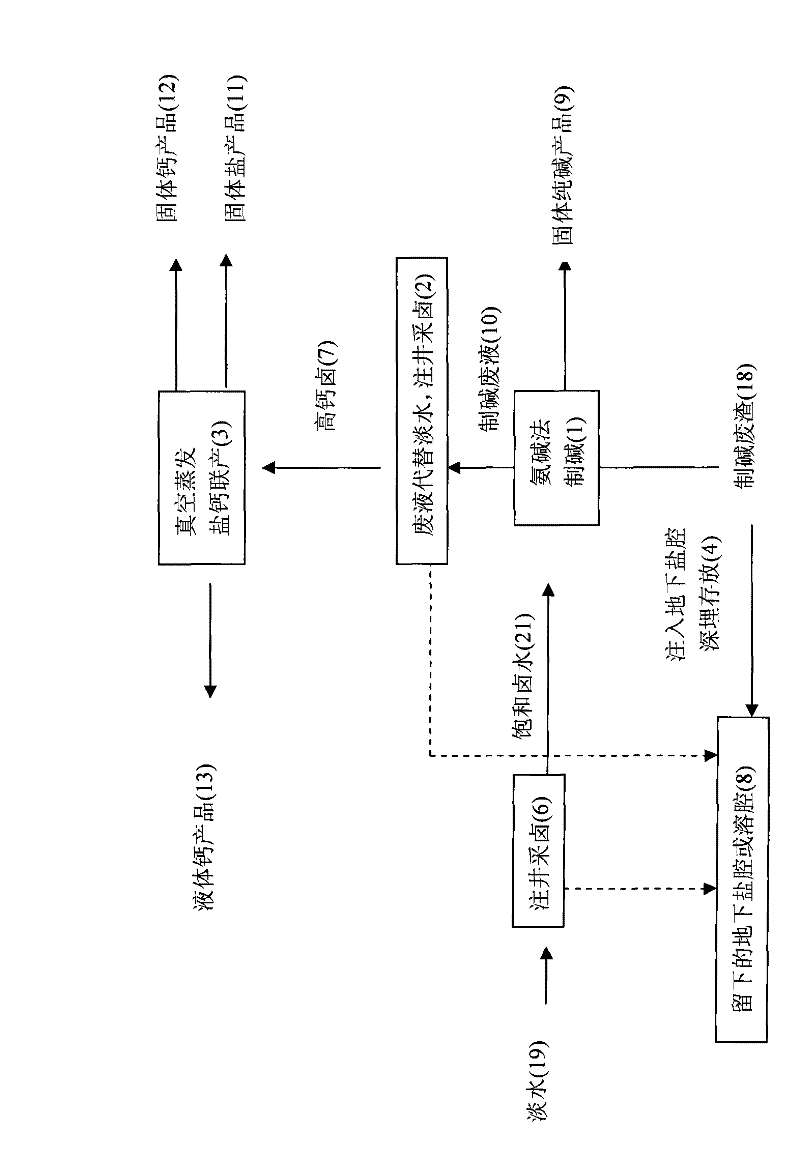
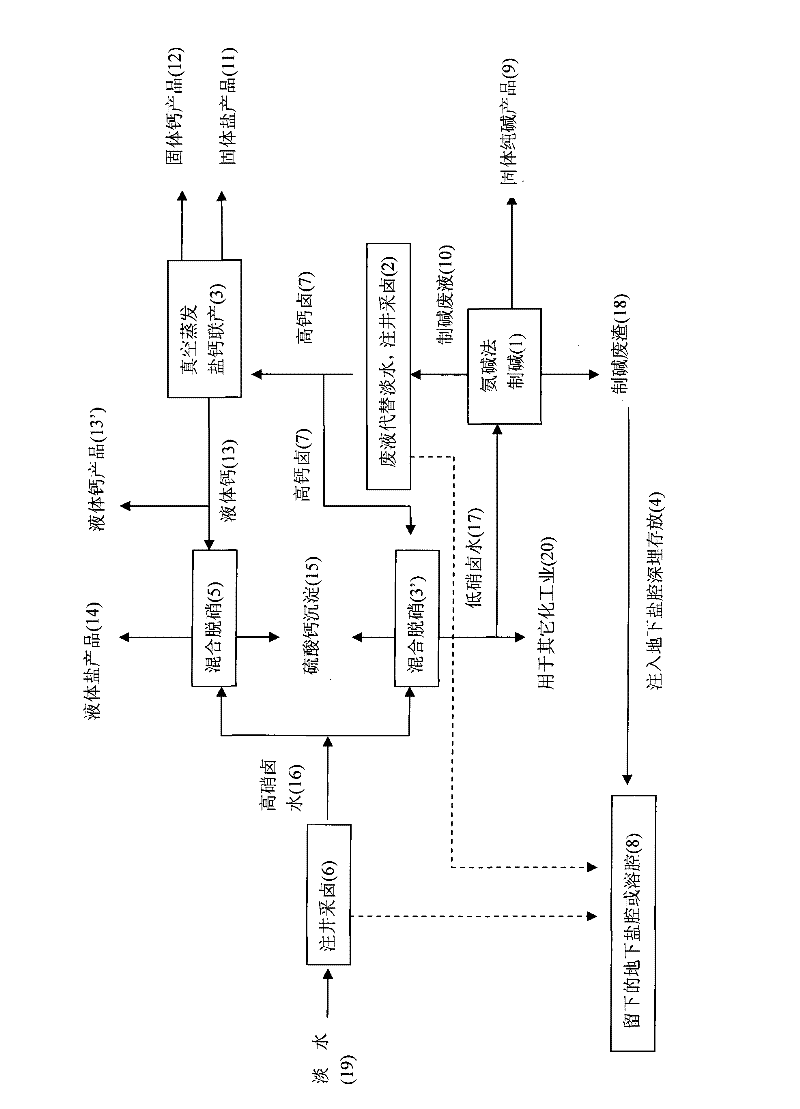
Salt, alkali and calcium combined cycle production technology by the use of well mineral salt
ActiveCN102205979ASolve processing problemsRealize energy saving and consumption reductionCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesAlkali metal chloridesDissolutionCalcium EDTA
The invention relates to a salt, alkali and calcium combined cycle production technology by the use of well mineral salt. Based on the exploitation of brine from well mineral salt, the salt, alkali and calcium combined cycle production technology by the use of well mineral salt is a cycle production technology, which focuses on the technology for making alkali from brine by the ammonia-soda process and takes account of the vacuum salt-making (including the brine refinement) and calcium-making technologies. Alkali-making wastewater replaces most fresh water to be injected into a salt mine well to collect brine, and the obtained high-calcium brine is taken as the raw material of the salt and calcium (including liquid calcium) co-production as well as the raw material for preparing alkali and other chemical production raw materials, wherein the liquid calcium can be used to produce liquid salt; alkali-making waste residues are injected into an underground dissolution cavern, namely a salt cavern which is formed by the exploitation of brine from well mineral salt, thus accomplishing the combined cycle production technology in which alkali-making and salt-making technologies are closely related with materials. The produced wastes are used as resources or undergo a harmless treatment, thus protecting the environment. In addition, the utilization rate of sodium chloride in rock salt reaches 100%, achieving maximum efficiency.
Owner:江苏苏盐井神股份有限公司 +1
High calcium carbonate filled herd polyvinyl chloride material
A hard polyvinyl chloride material filled by more calcium carbonate is prepared from nano (or micron)-class calcium carbonate as filler, polyvinyl chloride resin, thermal stabilizer, lubricant, impact modifier, and titanium oxide powder through fusing, mixing and extruding out. Its advantages are high tension strength, elongation for break, impact strength and vicat softening point.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Technology of animal high-calcium powder, chondrine and collagen by composite enzyme method
InactiveCN1896262AReduce pollution indexReduce acid and alkali consumptionFermentationFiltrationCollagen VI
The present invention relates to a biological fermentative production technology of extracting high-calcium powder, chondroitin sulfate and collagen from animal cartilage which includes the following steps: the animal cartilage is simply broken into 5-20mm fragments, mixed with 1-4 times weight of water in the reaction kettle, heated to 100DEG C and kept for 1-2 hours to denature the proteins, then cold water is passed over into the kettle jacket to cool down the kettle to 40-50DEG C, compound enzyme in mass ratio of 1:0.001 which is mainly collagenase is then added, the mixture is stirred and hydrolyzed for 8-12 hours under the condition of 40-50DEG C, pH 7-8, bone residue that contains calcium phosphate is obtained after simple filtration through 100-meshed sieves; the filtrate is clarificated after fine filtration with filter press, then ethanol is added to the final concentration of 60-70%, chondroitin will be sedimentated, while remaining liquid is the mixture of collagen and ethanol. The sedimentated calcium phosphate is washed and dried and becomes calcium phosphate powder. The crystal sediment of chondroitin is purified by ethanol-washing. Collagen is separated after the mixture of collagen and ethanol goes through the ethanol regenerating column. This technology can produce different products with high purity from animal cartilage and solves the problems of pollution and single product of traditional technology.
Owner:郭秀明
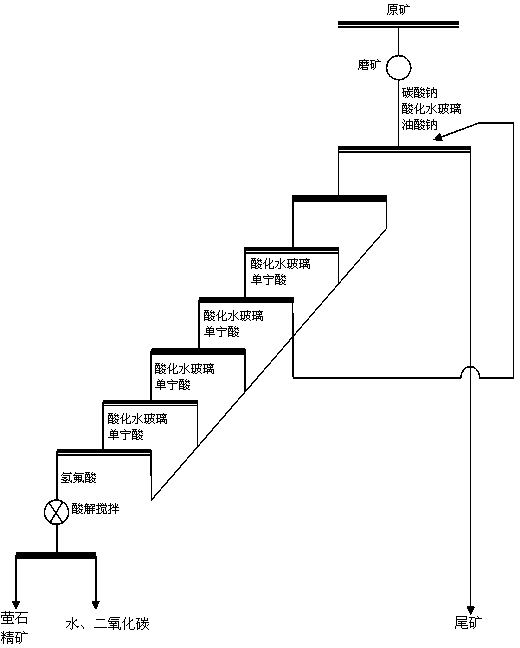
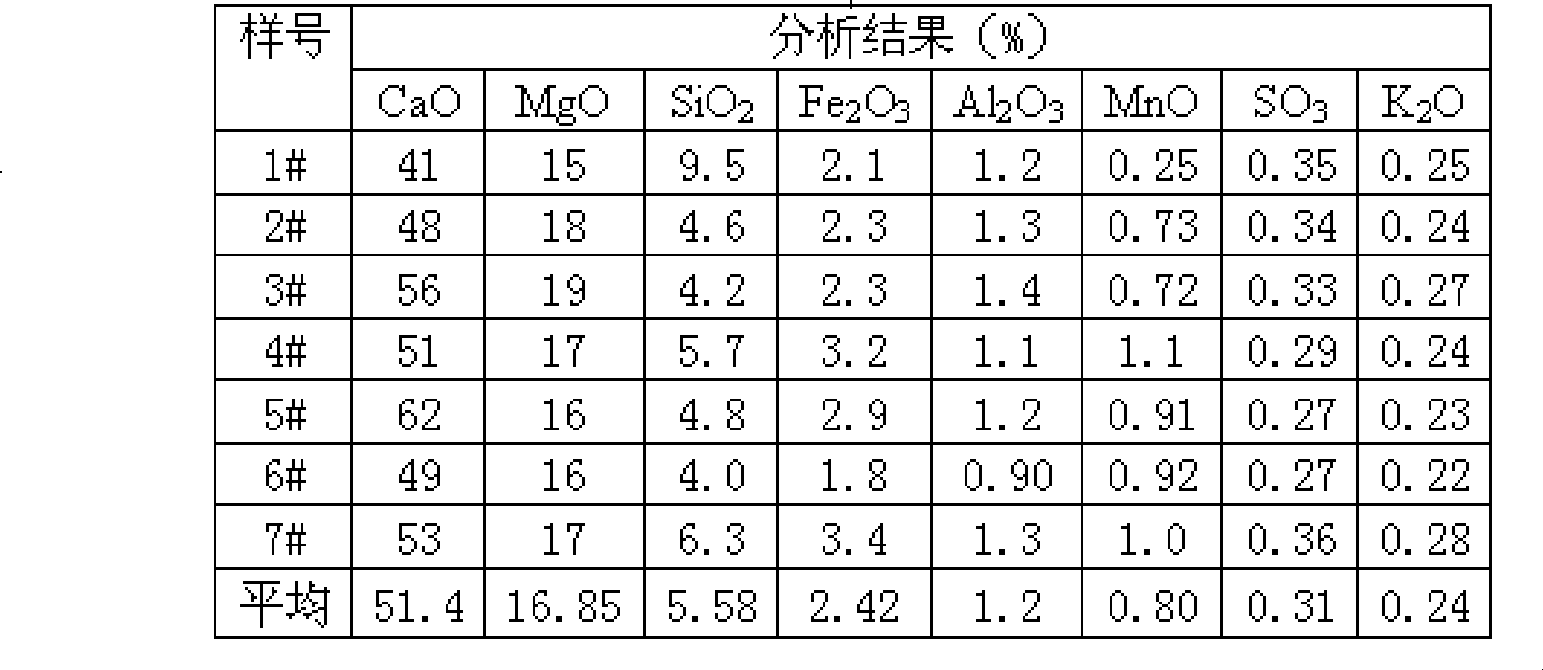
Beneficiation method of high calcium carbonate content type fluorite ore
The invention relates to a beneficiation method of high calcium carbonate content type fluorite ore and belongs to the field of beneficiation. The beneficiation method comprises the steps of conducting flotation, wherein ore grinding is conducted on the high calcium carbonate content type fluorite ore until the fluorite ore with the granularity smaller than 74 microns accounts for 78%-92% firstly, secondly, sodium carbonate serving as a pulp regulator, acidized sodium silicate serving as a gangue inhibitor and sodium oleate serving as a catching agent are added in sequence, and then a fluorite rough concentrate is obtained; conducting concentration six times, wherein concentration is conducted on the fluorite rough concentrate obtained through the last step six times, acidized sodium silicate serving as a gangue inhibitor and tannin are added in sequence every time concentration is conducted from the third time to the sixth time, and a fluorite concentrate pulp is obtained after concentration is conducted six times; conducting acid leaching, wherein the fluorite concentrate pulp obtained from the last step is concentrated, hydrofluoric acid is added, the fluorite concentrate pulp and the hydrofluoric acid are evenly mixed, leaching is conducted, and a high-grade fluorite concentrate can be obtained after liquid-solid separation. By the adoption of the beneficiation method, the beneficiation effect is good and the recovery rate of fluorite is high.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Steel-smelting regulator and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101413043AReduce TFe contentAvoid pollutionManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingHigh calcium
The invention belongs to the ironmaking and steelmaking field, and provides a steelmaking regulator with settled dust as a main material and a method for preparing the same. The invention aims at solving the problem existing in prior art that discharged settled dust causes environmental pollution. The steelmaking regulator is prepared from the following materials in weight percentage: 67 to 73 percent of settled dust, 7 to 13 percent of silicon carbide material, 15 to 20 percent of magnesium material, and bonding agent which accounts for 5 to 10 percent of the total weight of the settled dust, the silicon carbide material and the magnesium material. The steelmaking regulator can completely replace the prior technique of adding modifier and furnace protecting material, has good slag regulating and slag thickening effect, has better slag splashing furnace protection effect compared with the prior product, reducing TFe in slag, obviously lowering production cost of steelmaking, thoroughly eliminating environmental pollution caused by the emission of steelmaking high calcium settled dust and realizing the recovery and the reutilization of resources.
Owner:PANZHIHUA GANGCHENG GROUP
Method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage by zeolite synthesized by coal ash
ActiveCN102219233ARealize resourcesHigh removal rateOther chemical processesAluminium silicatesSludgeMixing ratio
The invention provides a method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage by zeolite synthesized by coal ash. Low-calcium coal ash and high-calcium coal ash are respectively used as raw materials so as to synthesize zeolite with different removing effects by alkali fusion method. The zeolite synthesized by the low-calcium coal ash is adopted for processing ammonia nitrogen-contained sewage, the zeolite synthesized by the high-calcium coal ash is adopted for processing phosphorus-contained sewage, and the zeolite synthesized by the low-calcium ash coal and high-calcium ash coal with different mixing ratios is adopted for processing mixture sewage with different nitrogen and phosphorus ratios. In the invention, the prepared zeolite has high purity, different types of zeolite can be adopted according to sewage properties, the pollutant absorbing amount is large, and the solid adding amount in the practical application is reduced effectively. After absorbing nitrogen and phosphorus, the sludge can be used as fertilizer, so that not only the environmental pollution problems caused by waste solid coal ash, nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage and the like are solved, but also the reclamation in the pollutant is realized. According to the technology, the operation is simple, the running cost is low, and the method can be applied to industrial point source, plane source and nitrogen and phosphorus treatment in tail water of sewage treatment plants in cities and towns.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for preparing vanadium oxide
InactiveCN103146930AAchieve recyclingReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementHigh phosphateSlag
The invention provides a method for preparing vanadium oxide, which comprises the following steps of: mixing vanadium slag with calcium oxide or limestone to form a mixed material; roasting the mixed material to obtain calcified clinker; leaching the calcified clinker by using C2O4<2-> and 35-70 g / L of oxalate solution at 80-95 DEG C; after leaching, carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain vanadium-containing leachate and residues; removing silicon from the vanadium-containing leachate, so that the silicon concentration in the vanadium-containing leachate is less than 0.1 g / L, then adding ammonium oxalate into the vanadium-containing leachate, adjusting the mol ratio of NH4<+> to TV to 2-3.5, precipitating ammonium metavanadate, and filtering to obtain ammonium metavanadate and vanadium precipitation wastewater; and oxidizing, roasting and deaminizing ammonium metavanadate to prepare vanadium pentoxide or reducing to prepare vanadium trioxide. According to the invention, on the premise of satisfying environment-friendly requirements, preparation of vanadium oxide from ordinary vanadium slag and high-calcium and high-phosphate vanadium slag is realized; furthermore, consumption of reagents can also be reduced; and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method of producing yeast protein feed with leftovers from kitchen
InactiveCN1416718ASolve environmental pollutionSolve pollutionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyYeast
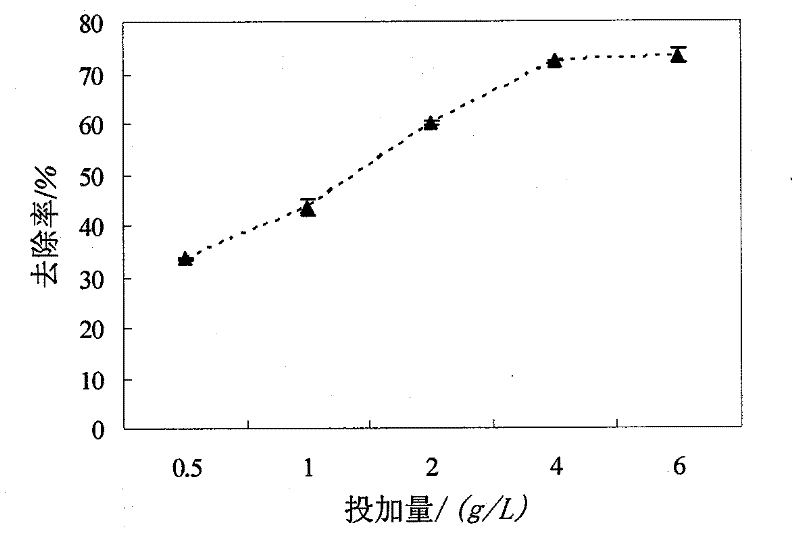
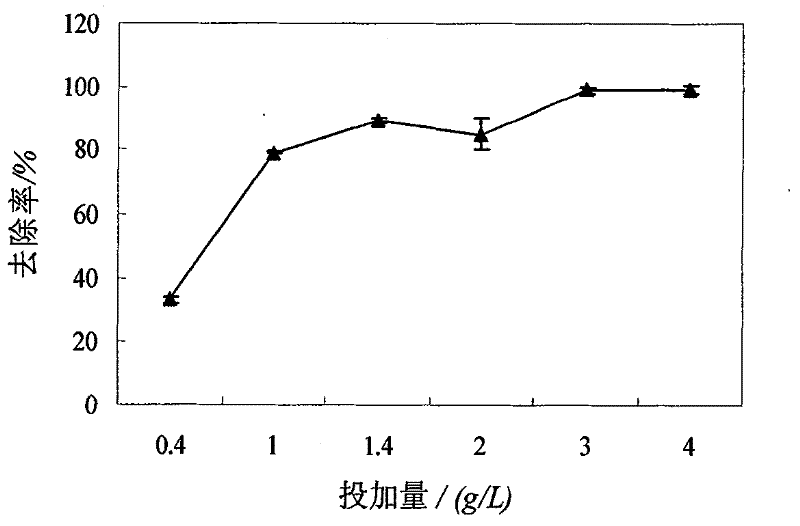
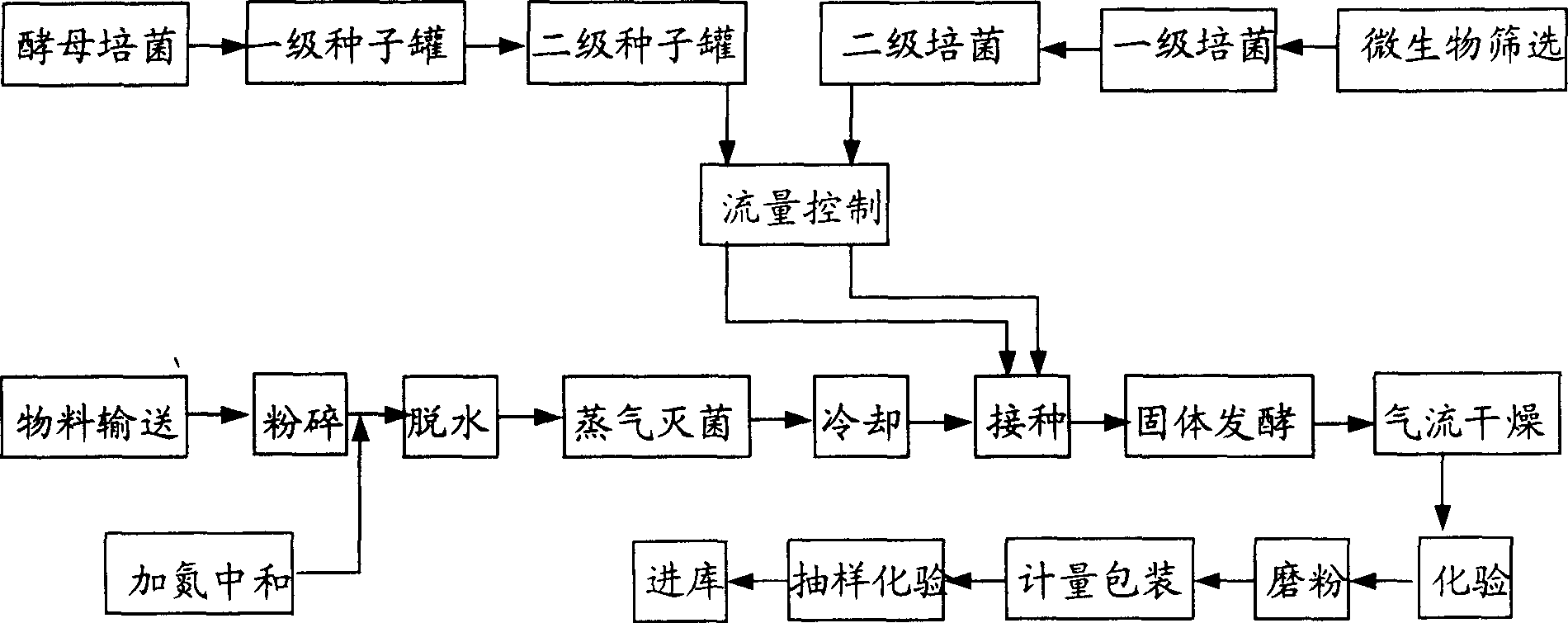
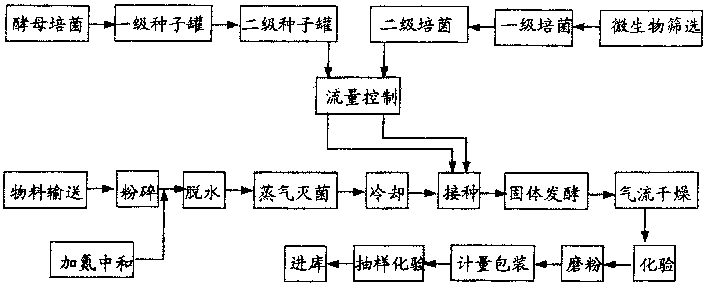
The present invention discloses a method of producing yeast protein feed with leftovers from kitchen. The production process of high-calcium multivitamin yeast protein feed includes crushing, dewatering, adding nitrogen to neutralize, disinfection, inoculation of yeast and microbial bacteria, solid fermentation under control of computer, drying, milling, assaying and packing. It makes it possible to change waste leftovers into high-quality high-calcium multivatamin yeast protein feed.
Owner:陈建乐
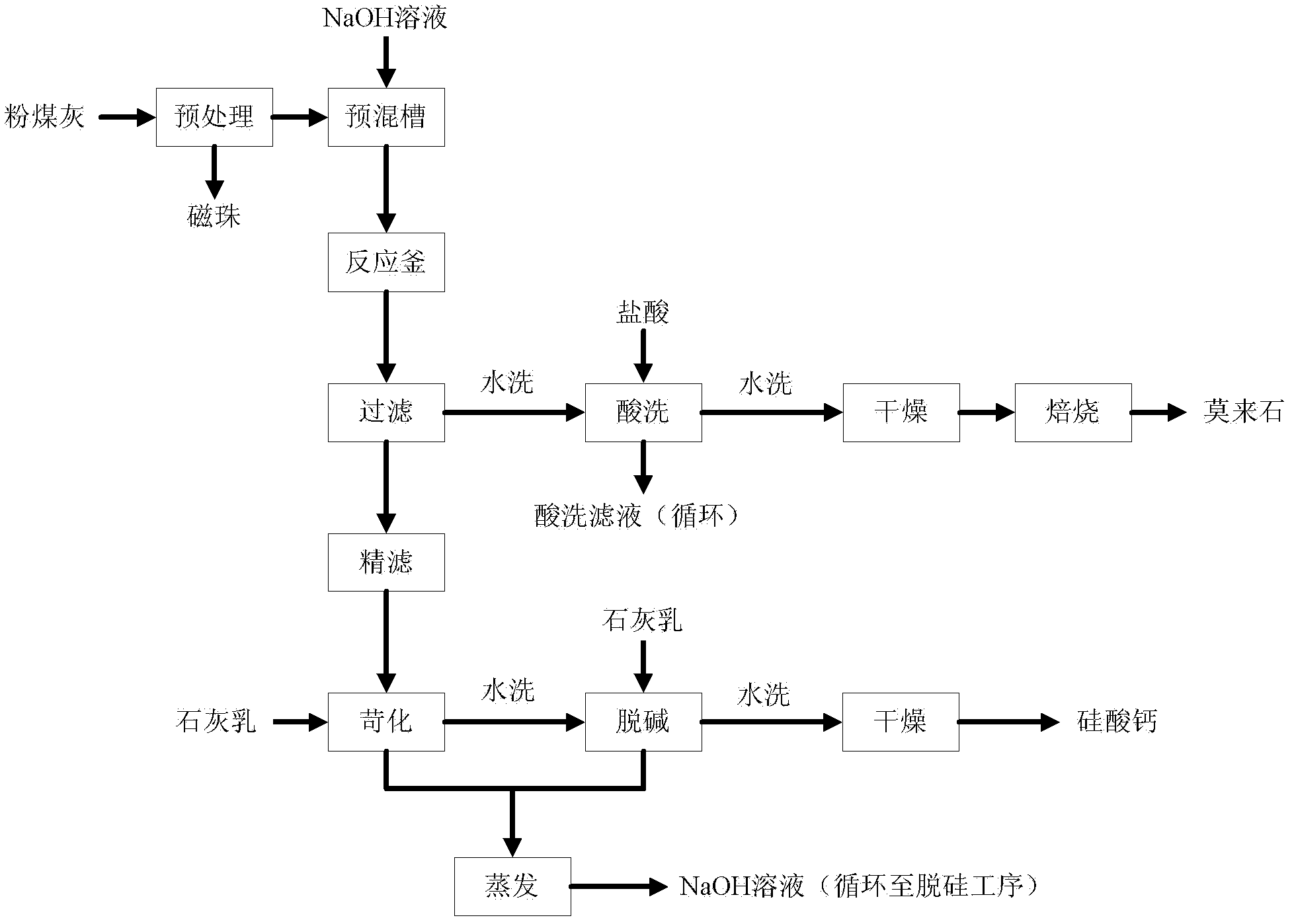
Method for producing mullite and calcium silicate by using high-alumina fly ash
ActiveCN102583409ARealize resource utilizationReduce manufacturing costAluminium silicatesAlkaline-earth metal silicatesCalcium silicateAcid washing
The invention relates to a method for producing mullite and calcium silicate by using high-alumina fly ash, and relates to the technical field of solid waste comprehensive utilization and the synthesis of fire-resisting and filling materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing ball milling on a rejected material, namely the high-alumina fly ash of an electric power plant, which is used as a raw material, and then performing desilication reaction on the raw material and a sodium hydroxide solution; and performing water washing, acid washing, drying and baking on a solid phase to obtain a mullite product, and performing causticization, water washing and drying on a liquid phase to obtain a calcium silicate product. Compared with the prior art, the method has the characteristics of wide source of raw materials, low production cost, low energy consumption, high mullite yield and high calcium silicate quality, aluminum oxide is not required to be added, and the economical and environmental benefits are remarkable.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
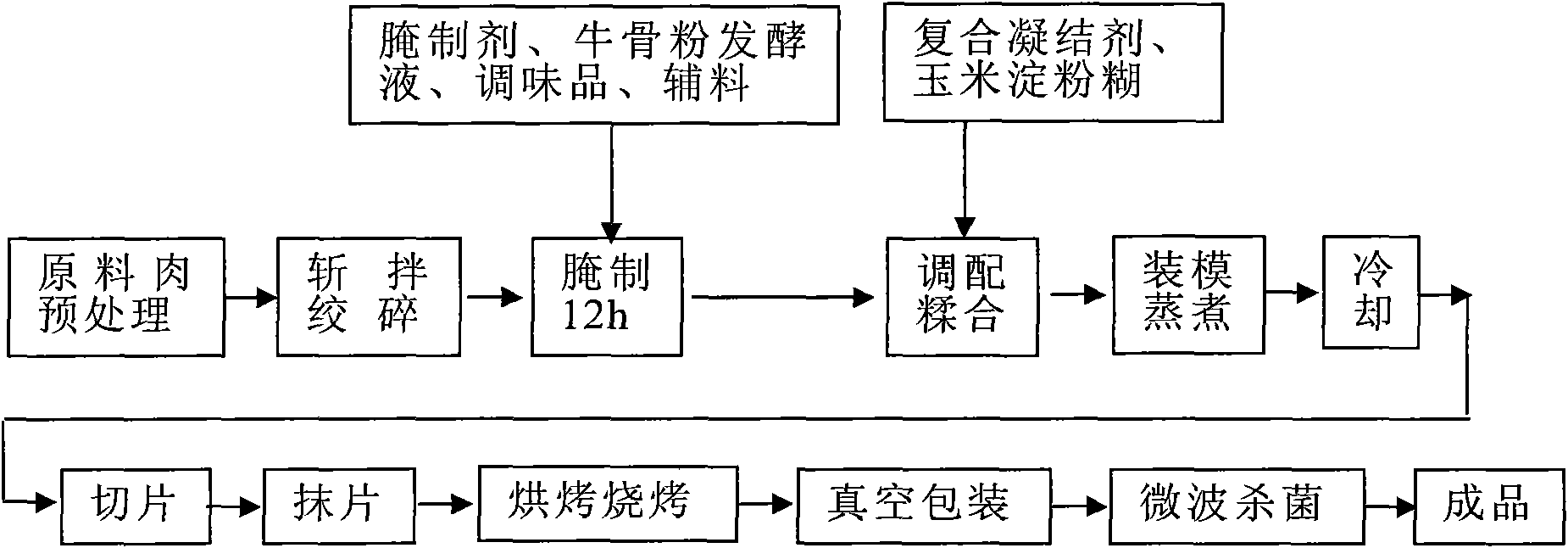
Nutritional beef dried meat with high bone calcium and making method thereof
The invention relates to nutritional beef dried meat with high bone calcium and a making method thereof, belonging to a nutritional food and a processing technology thereof. The nutritional beef dried meat is formed by preparing and processing raw materials comprising ground beef, a curing agent, cattle bone powder fermentation liquid, corn starch paste, a compound coagulant, a flavoring agent and auxiliary materials according to a certain mixture ratio and a certain production technology. The product contains high calcium, high protein, abundant nutrition, delicate mouth feel, moderate rigidity, no residue after being chewed, special flavor, good and savory taste and thick aftertaste and adds a new variety of beef dried meat.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
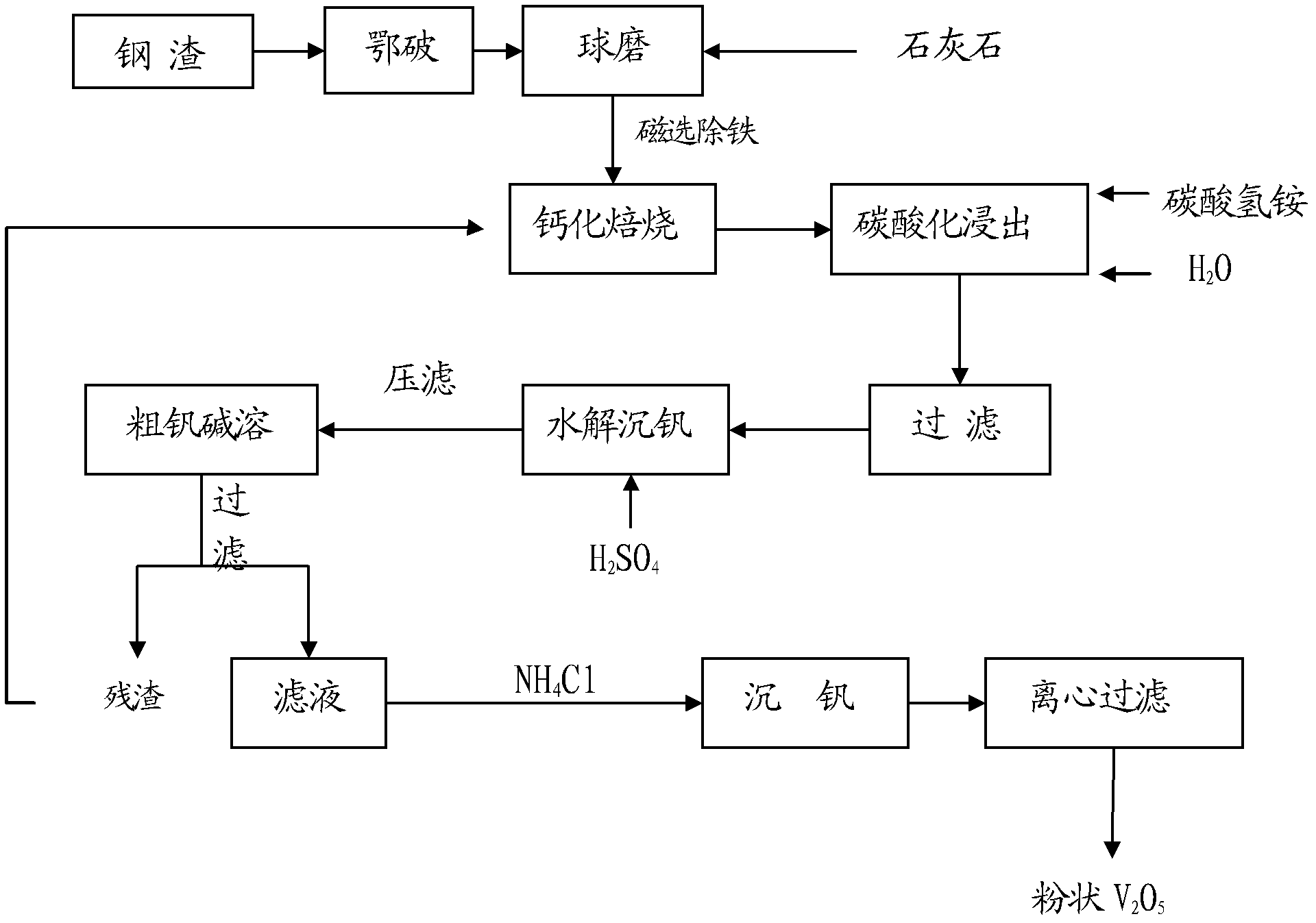
Vanadium extraction technology of low-grade high-calcium vanadium-containing steel slag
InactiveCN102534233AEfficient use ofEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingCalcification
The invention discloses a vanadium extraction technology of low-grade high-calcium vanadium-containing steel slag. The technology comprises the following steps of: a, performing pretreatment of the low-grade high-calcium vanadium-containing steel slag; b, performing oxidation calcification roasting of the low-grade high-calcium vanadium-containing steel slag; c, performing carbonation leaching treatment of the vanadium-containing steel slag after the roasting to obtain vanadium-containing leachate; d, adding an acid to the vanadium-containing leachate to precipitate vanadium, and filtering to obtain coarse vanadium; e, performing alkaline solution treatment of the coarse vanadium, and filtering to obtain V<5+>-containing filtrate; and f, adding NH4Cl into the V<5+>-containing filtrate, reacting to generate NH4VO3, and performing deamination to obtain V2O5 finally. Through the vanadium extraction technology disclosed by the invention, the requirement on calcium content is reduced; high-purity vanadium pentoxide is produced from low-grade high-calcium vanadium-containing steel slag; and the vanadium resource in the vanadium-titanium magnetite is effectively recycled and utilized. The invention provides conditions for the vanadium extraction of a converter single-link method; and the vanadium-containing molten iron is directly used for steelmaking, the vanadium enters the low-grade high-calcium steel slag, and an additional converter for vanadium extraction is not needed, thereby avoiding the interference and influence on the steelmaking caused by the additional vanadium extraction converter for vanadium extraction.
Owner:SICHUAN DAZHOU IRON & STEEL GROUP
Sorbent composition to reduce emissions from the burning of carbonaceous fuels
InactiveUS20070140943A1Efficient sulfur captureHarmful emissionGas treatmentOther chemical processesCombustionFlue gas
Sulfur emissions from combustion of coal and other fuels are reduced by using sugar beet lime as a sorbent during the coal burning process. In various embodiments, the sugar beet lime is added onto the coal before combustion, along with the coal into the furnace, is injected directly into the fire coal, or is added into the flue gases downstream of the furnace. The relatively high calcium content of the sugar beet lime leads to efficient sulfur capture at suitably low treat levels. Excess ash is avoided in the process.
Owner:COMRIE DOUGLAS C
Neutral liquid high calcium milk and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101543245AMeet calcium needsPromote robustnessMilk preparationFood preparationPhosphopeptideCow milk
The invention provides product compositions and a preparation method of neutral liquid high calcium milk. Every 100 weight portions of the neutral liquid high calcium milk comprises the following compositions in portion by weight: 97.50 to 99.05 portions of milk, 0.40 to 0.80 portion of milk calcium, 0.10 to 0.50 portion of hydrolyzed collagen, 0.05 to 0.30 portion of casein phosphopeptides (CPP), 0.20 to 0.60 portion of stabilizing agent and 0.10 to 1.00 portion of dietary fiber. The neutral liquid high calcium milk has high safety and nutrition, good taste, high calcium content and balanced calcium-phosphor proportion, and is easy to be digested and absorbed by human body; moreover, the high calcium milk can meet the requirements of consumers of different age groups on calcium supplementation and is favorable for strengthening bone and articular cartilage.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Fluidized bed technology and fluidized bed system for directly capturing CO2 in mineralized flue gas
ActiveCN104759203ASimple processReduce usageDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementSlagFresh gas flow
The invention discloses a fluidized bed technology for directly capturing CO2 in mineralized flue gas. In the technology, a high-calcium waste, such as fly ash, carbide slag, steel slag, waste cement and the like, as a raw material. A by-pass is formed on a flue gas discharge pipeline to feed a flue gas flow of which the humidity and the temperature are regulated by a temperature and humidity regulator. In a fluidized bed reactor, the flue gas flow, of which the humidity and the temperature are regulated, is contacted with the high-calcium waste in a co-current flow manner to generate calcium carbonate. After the reaction, a dust-containing gas flow discharged out from the fluidized bed reactor is fed into a cyclone separator for gas-solid separation to obtain a gas flow, wherein the gas flow is fed into the original flue gas discharge pipeline and then is fed into the chimney for being discharged. The invention also provides a fluidized bed system for directly capturing CO2 in the mineralized flue gas. The technology can not only effectively increase the utilization rate of fly ash but also reduce CO2 emission of a power plant, is simple in processes, is convenient to continuously operate, is high in device processing capacity, is small in size and less in occupied area and can be combined with the existing system conveniently. Meanwhile, the decarbonized fly ash does not influence the original use approach of the fly ash from the power plant, thereby achieving a lower decarbonization cost.
Owner:HUANENG POWER INTERNATIONAL +1
High-calcium fish ball and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN102551108ASolve the problem of eating fishSolve the problem of fear of fishboneFood preparationGARLIC POWDERPre treatment
The invention discloses a high-calcium fish ball and a manufacture method thereof. The fish ball is made of minced fillet, fishbone paste, egg white, refined salt, monosodium glutamate, white ground pepper, garlic powder and the like according to fixed proportion. The manufacture method comprises the steps of 1 pretreating fish heads or fish bones, rinsing fresh chub heads or fish bones with ozone water, and washing the fresh chub heads or the fish bones with tap water; 2 manufacturing bone paste with the fish heads or the fish bones, and sequentially grinding the washed fish heads or the washed fish bones with a bone paste machine to obtain fish bone paste of certain particle diameter; 3 chopping and stirring, and placing weighted raw materials in a chopping and stirring machine to be chopped and stirred, continuously adding icy water to control temperature; 4 forming, and placing the chopped and stirred materials in a ball machine to be stirred to be formed; 5 heating to form, placed formed fish balls in water, and fishing the fish balls in tap water to be cooled when the fish balls float up; and 6 refrigerating, freezing the cooled fish balls with a double spiral quick freezer, and placing the fish balls in a refrigerator to be refrigerated. The high-calcium fish ball and the manufacture method are reasonable in formula, the raw materials are easy to obtain, production cost is low, and the manufacture method is easy to use, convenient to operate and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:武汉梁子湖水产品加工有限公司
Calcium/Lithium Complex Greases and Encapsulated Constant Velocity Joint Containing the Grease and Method for their Production
ActiveUS20100048436A1Loss of efficiency and lifetime in joint shaftsThickenersAdditivesLithium soapHigh calcium
Embodiments of the invention include compositions of calcium / lithium complex greases containing calcium / lithium soaps having a high calcium fraction and complexing agents, encapsulated constant velocity shafts containing such lubricating greases and the use of the lubricating greases in encapsulated shafts of constant velocity shafts.
Owner:FUCHS PETROLUB SE
Composite scale inhibitor
InactiveCN101700937AGood anti-scaling effectDoes not accelerate corrosionScale removal and water softeningWastewaterHardness
The invention discloses a composite scale inhibitor which is applicable to high-hardness high-alkali industrial circulating water, and the scale inhibitor consists of HEDP, polyaspartic acid, polymaleic anhydride, polyacrylic acid dispersant and the like. Wherein, the polyacrylic acid dispersant can be one or more of polyacrylic acid ternary dispersants or quaternary dispersants. The composite scale inhibitor has excellent scale inhibition performance and very low formation rate of calcium carbonate scale during the using process, the discharged waste water under the use of the formula can not cause the nutrition-rich pollution to the environment, thereby belonging to environment-friendly products and being particularly applicable to processing the circulating water with high calcium hardness and high alkaline hardness. The cost of using the formula for processing the industrial circulating water is very low, and the cost of a medicament added for processing each ton of water is less than 0.7 yuan, thereby having very high economic value.
Owner:SHENZHEN NANFENG WATER TREATMENT SERVICE
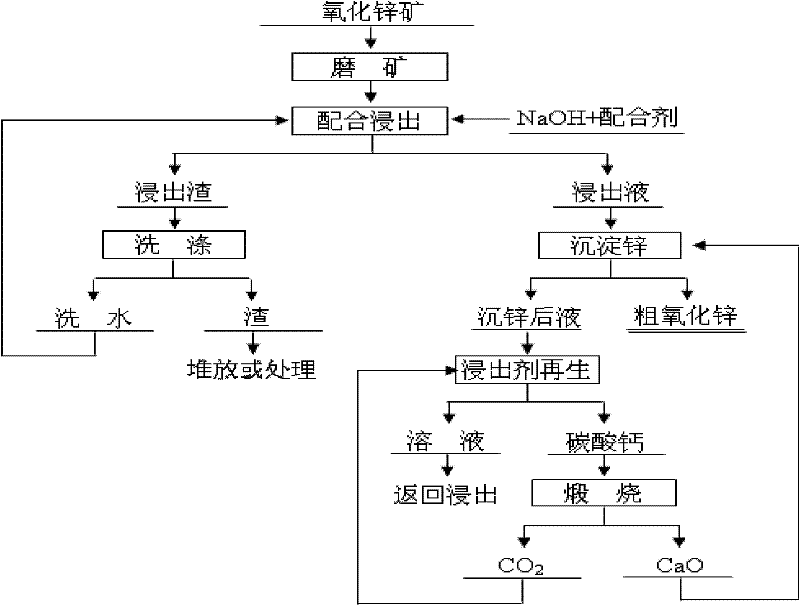
Method for treating low-grade zinc oxide ore by using weakly alkaline amino acid salt system
InactiveCN102242262AImprove leaching effectSmall side effectsProcess efficiency improvementCadmium CationChemistry
The invention discloses a method for treating a low-grade zinc oxide ore by using a weakly alkaline amino acid salt system, which comprises the following steps of: grinding the complex low-grade zinc oxide ore, and performing cooperated leaching in the weakly alkaline amino acid salt system under the certain condition to ensure that zinc, lead, cadmium, copper, nickel and the like are dissolved in leachate and calcium, magnesium, iron, silicon and the like are undissolved and stay in leaching residues; adding CaO or Ca(OH)2 into the leachate to ensure that the zinc is precipitated in the form of zinc oxide and recovered, and valuable metals such as the lead, the cadmium, the copper, the nickel and the like are co-precipitated with the zinc and enriched in crude zinc oxide; and regulating the pH of solution in which the zinc is precipitated to be a certain value by using CO2, regenerating a leaching agent, returning the regenerated leaching agent for recycling, and calcining CaCO3 generated in the process of regenerating the leaching agent for recycling. The method for treating the low-grade zinc oxide ore by using the weakly alkaline amino acid salt system can be used for effectively treating various complex low-grade zinc oxide ores with high calcium, magnesium, iron and silicon content, and the operation system is mild and has small toxic and side effects on human bodies and an environment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com