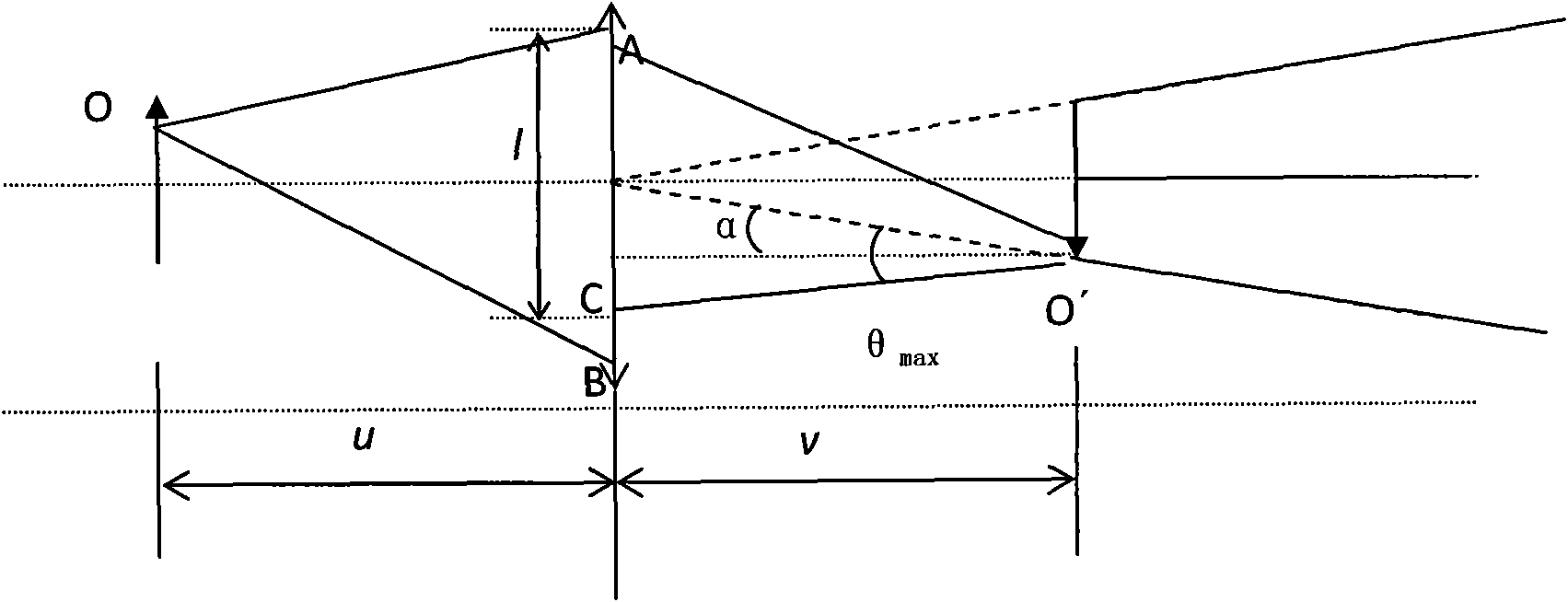
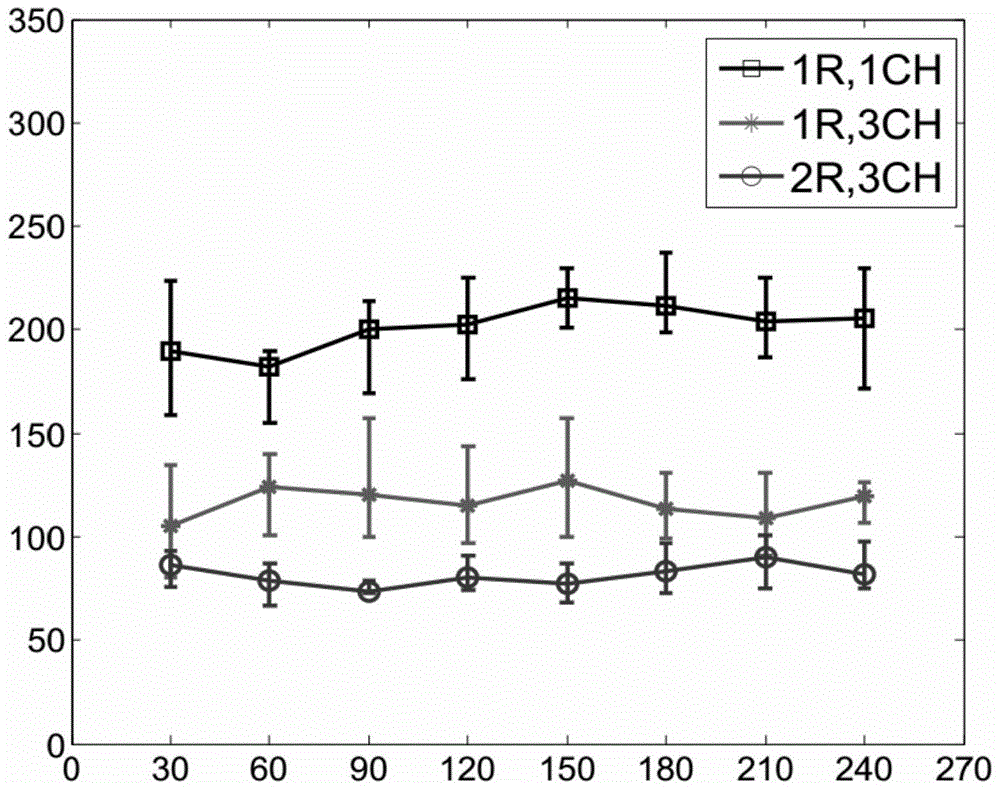
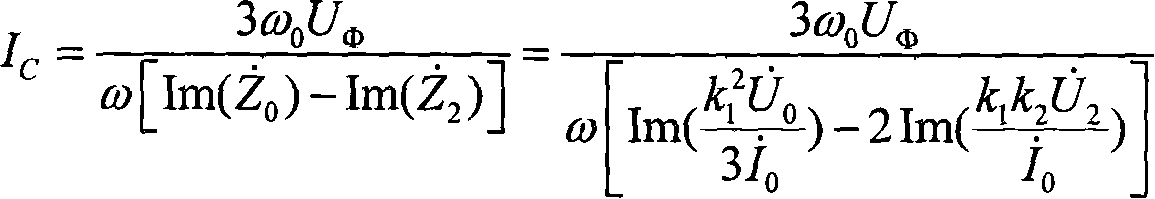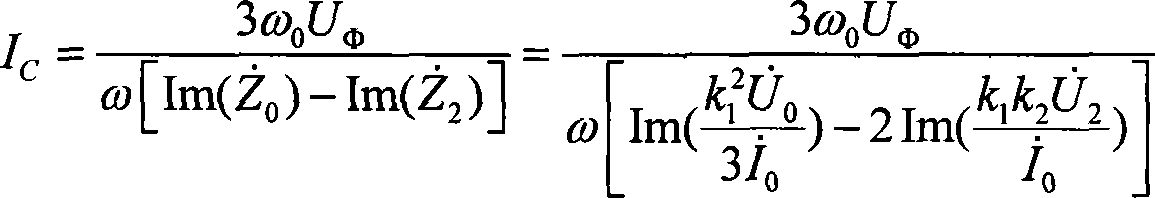Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Free distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
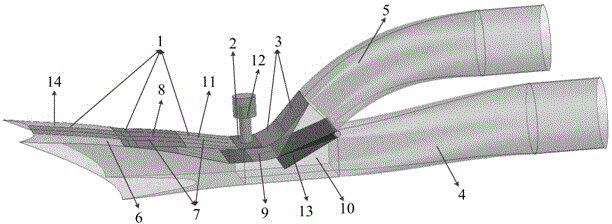
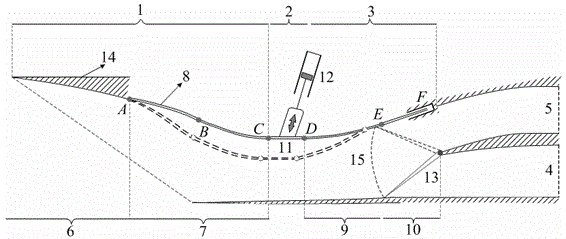
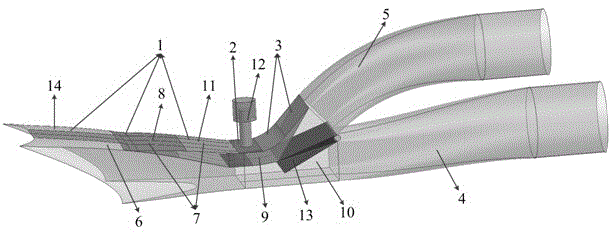
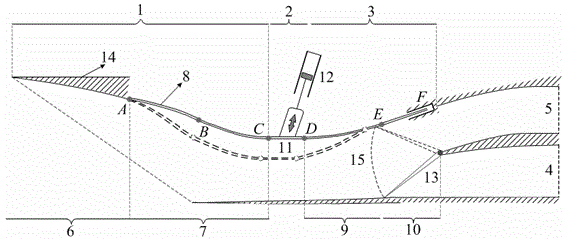
Internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet adopting binary variable-geometry manner
ActiveCN104632411AImprove flow coefficientSmall flow coefficientGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsThroatPunching
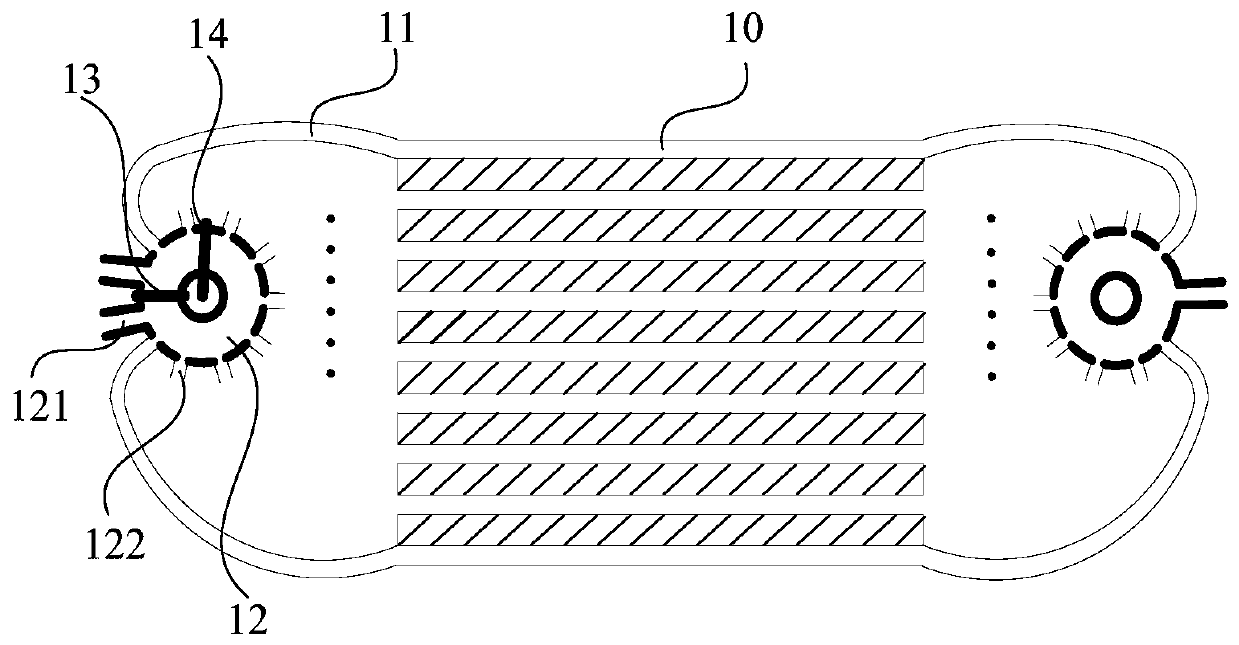
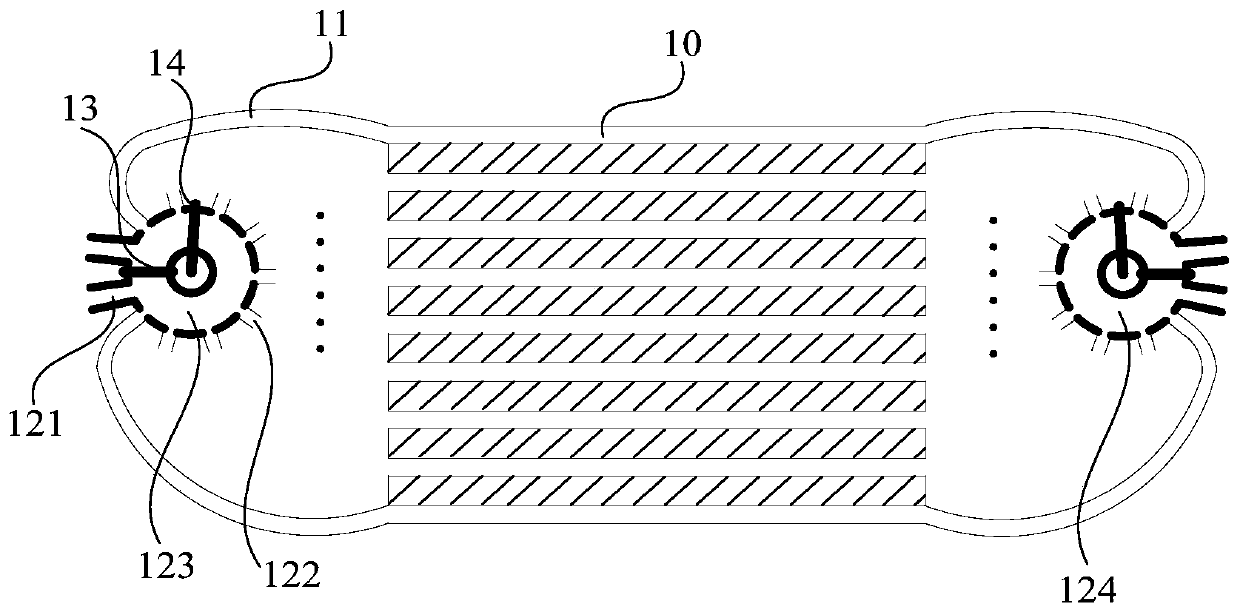
The invention discloses an internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet adopting a binary variable-geometry manner. The internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet structurally comprises a gas inlet internal waverider compression section 1, a throat section 2, an expansion and distribution section 3, a punching channel 4, a turbine channel 5, a fixed-geometry three-dimensional internal waverider compression representing section 6, an adjustable internal waverider compression representing section 7, an adjustable internal waverider compression section representing variable-geometry compression surface 8, an adjustable expansion representing section 9, a sharp point-free distribution representing section 10, a machine body proximity representing movable upper arm 11, a movable upper arm driving representing servo action cylinder 12, a distribution representing plate 13, an internal waverider-derived fixed-geometry representing profile 14 and a distribution representing cross section 15. The internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet has the advantages of small outer resistance, high flow coefficient, good airflow quality and the like; meanwhile, profile deformation and distribution plate deflection caused by compression in a three-dimensional internal waverider manner can be controlled by only two regulating parameters, the deformation is convenient and reliable, and the requirement on an acting servo device is relatively easily met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
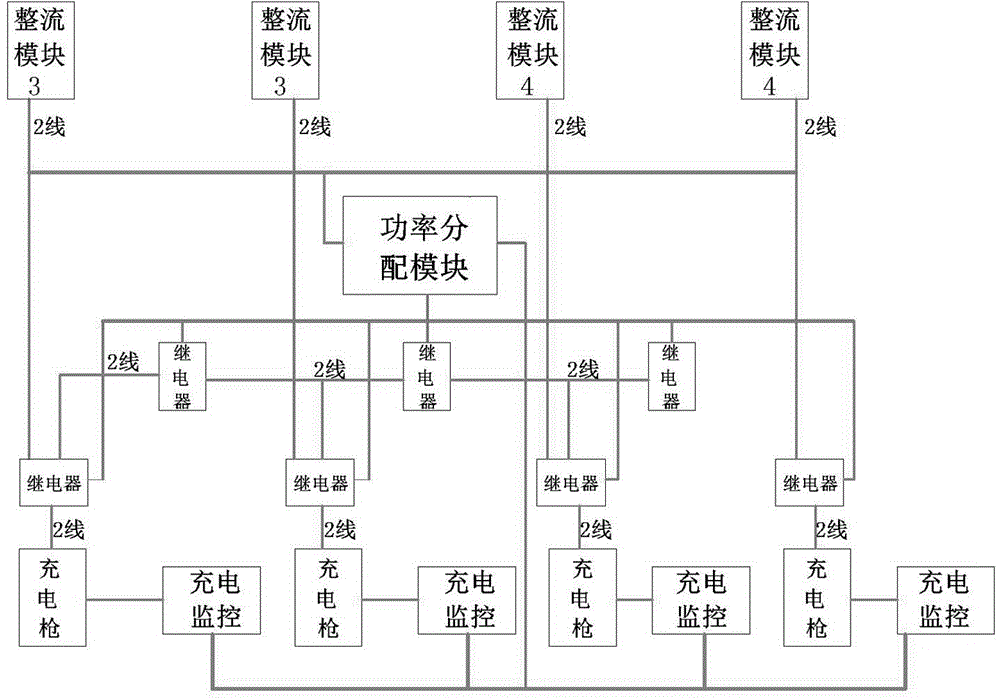
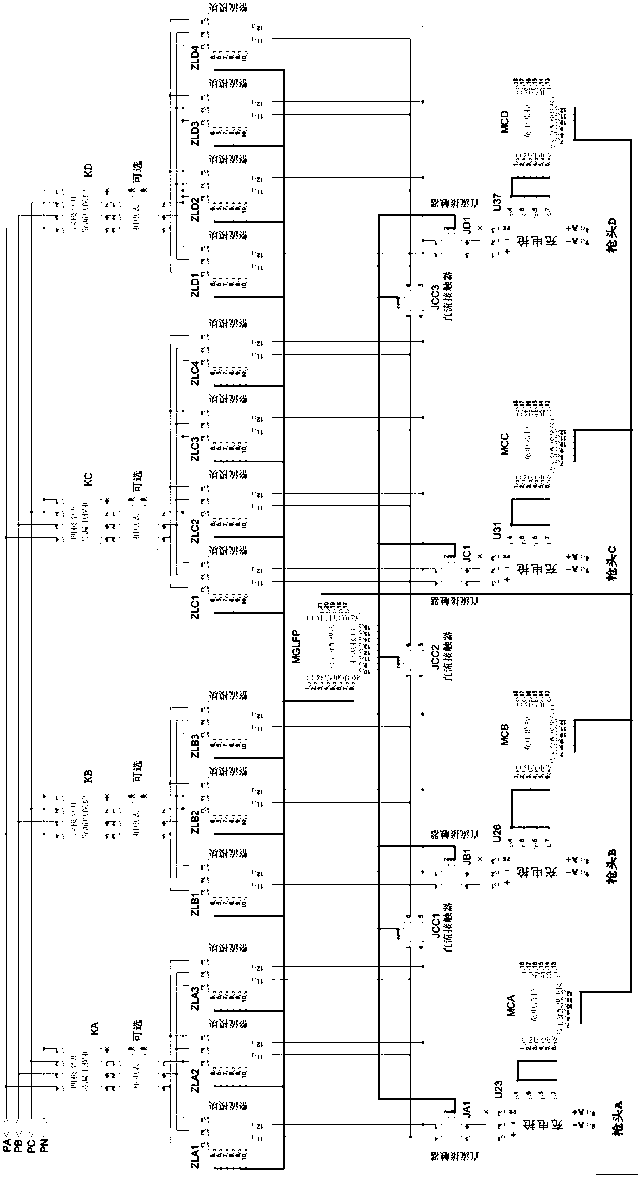
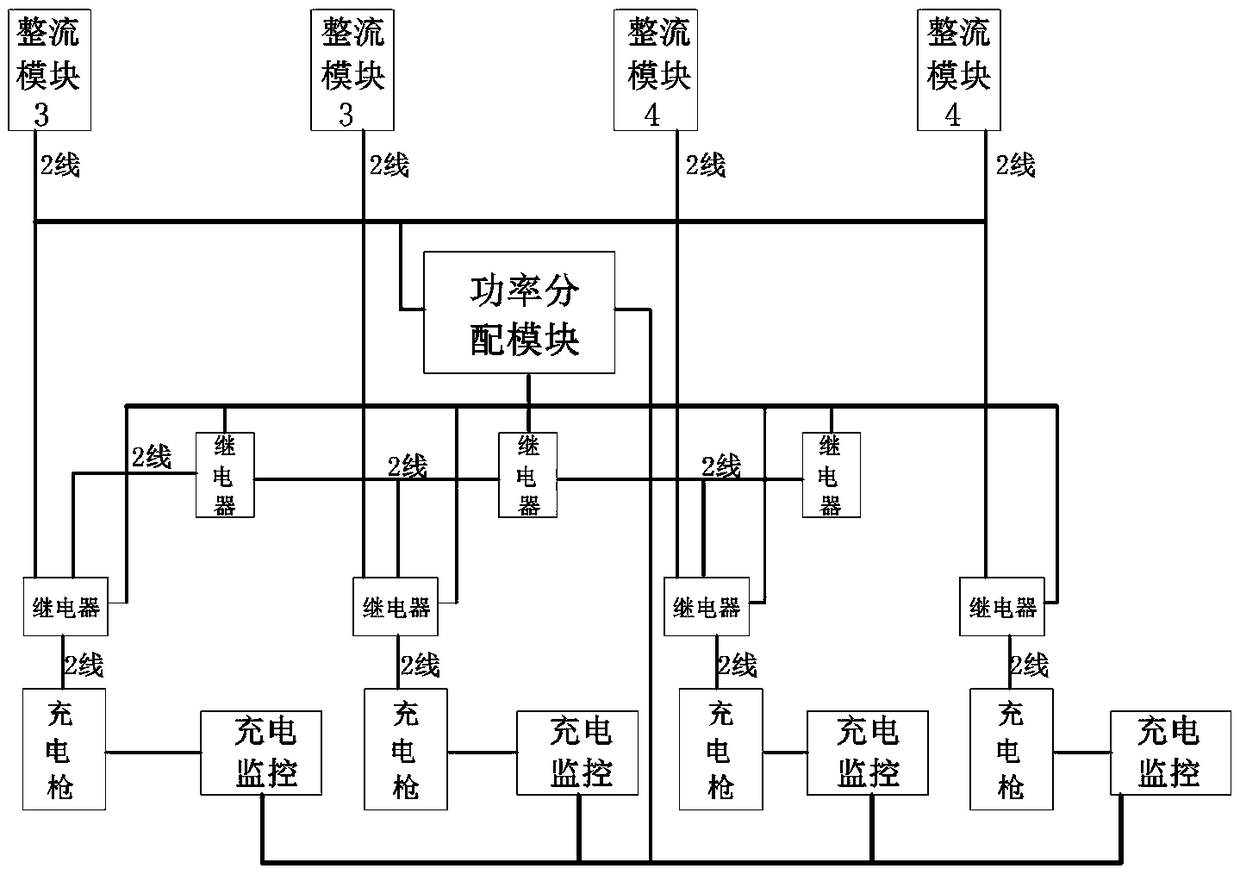
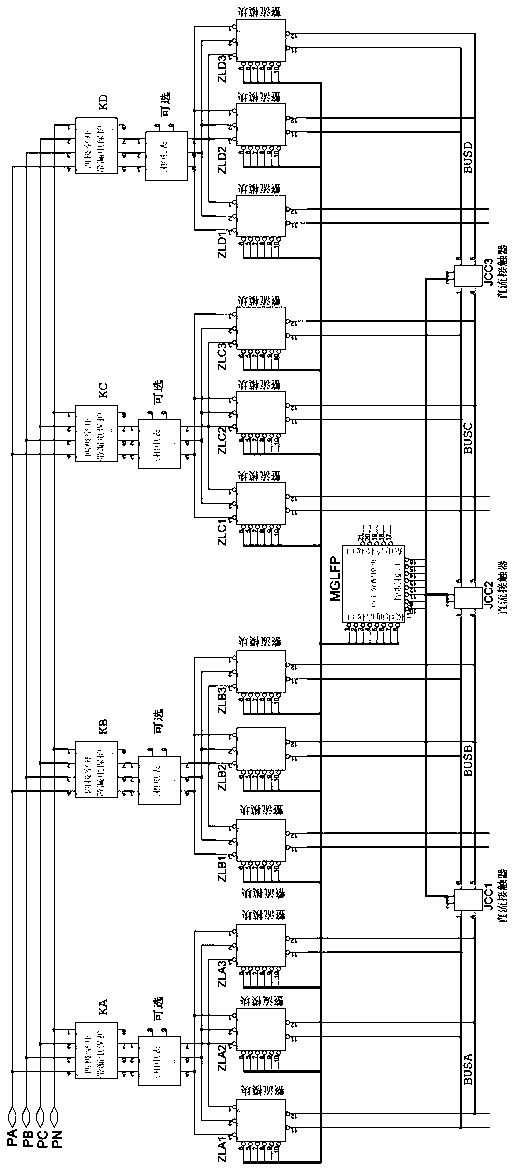
Multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system
ActiveCN105990883AImprove general performanceLow costBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system. The multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system comprises rectification units, charging guns, electric monitoring units and a power distribution module, wherein the number of the charging guns is 2 or more than 2; the number of the rectification units are corresponding to the number of the charging guns; the power distribution module is connected with each rectification unit and each charging gun; each charging gun is connected with the power distribution module through a charging monitoring unit. The multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system is not only provided with a plurality of charging guns, but also is provided with the power distribution module, so that free distribution of the charging power for each charging gun is realized. For the multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system, the plurality of gun heads can charge multi kinds of vehicles at the same time, such as a large vehicle, a mini-bus and a small vehicle. Practice has proved that the multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system has the advantages of being high in practicability, reliability and universality, saving the cost and the space, being high in the utilization rate, and being low in investment.
Owner:肖伟
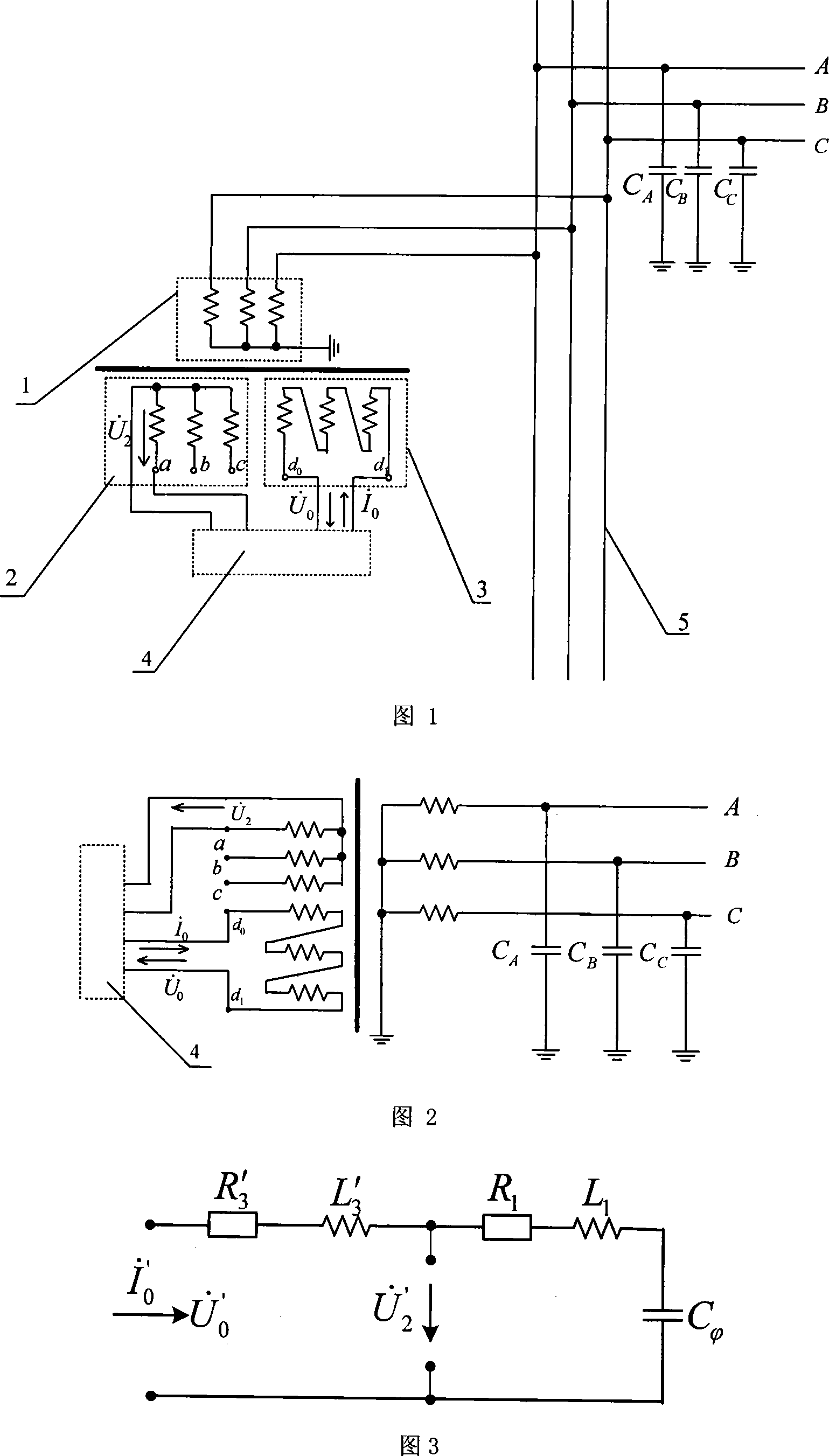
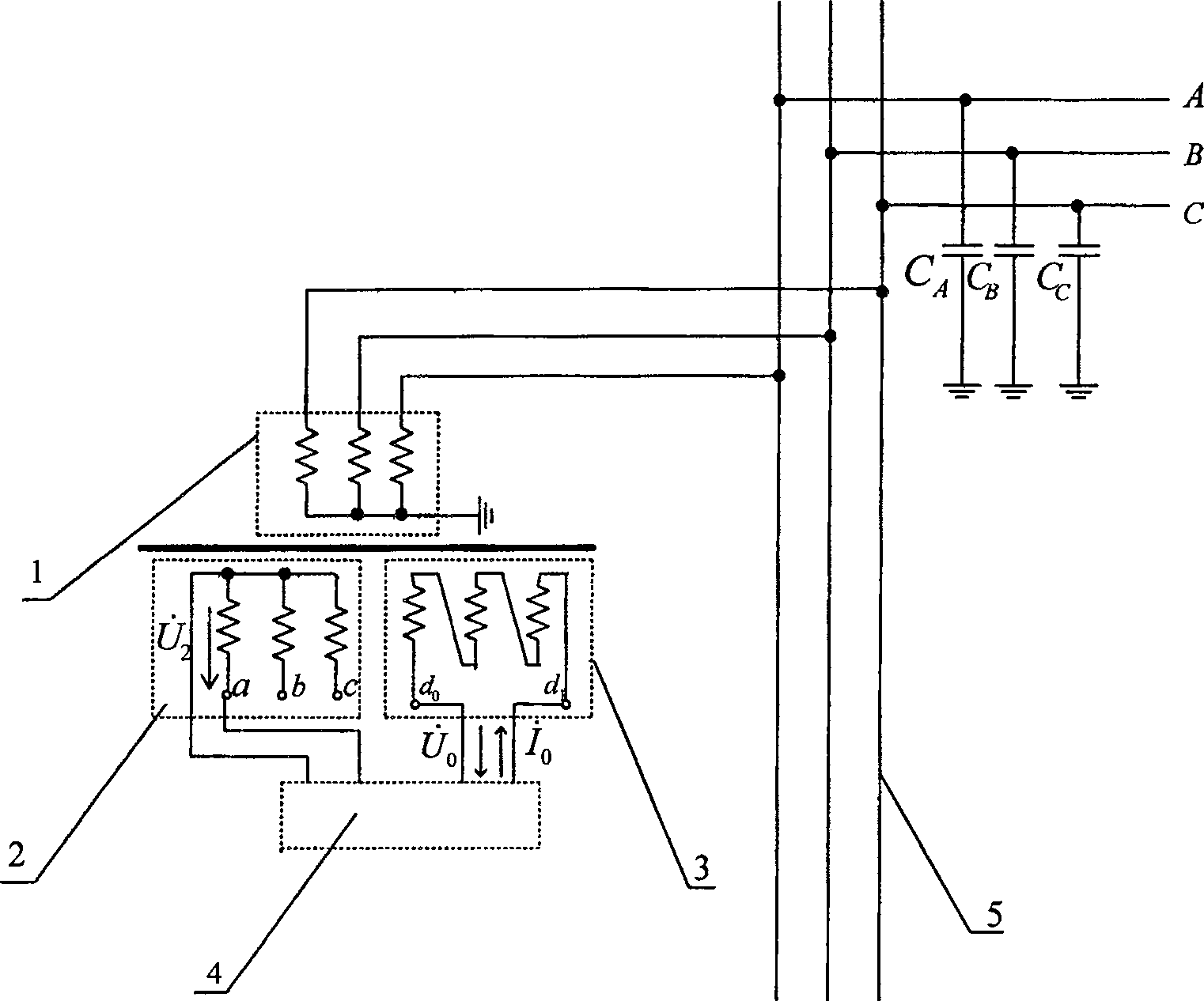
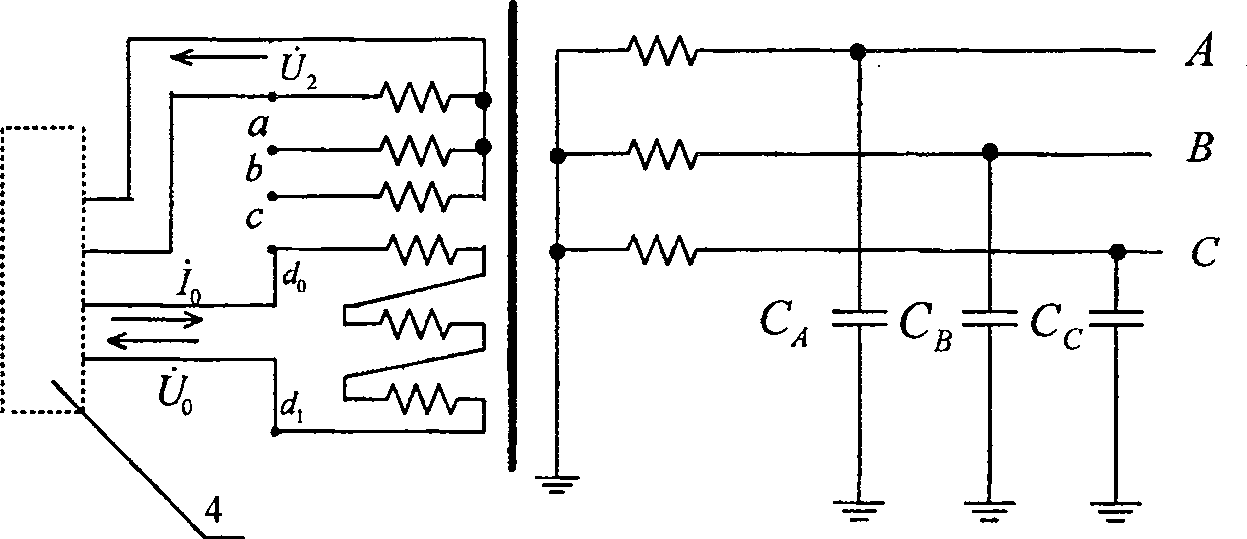
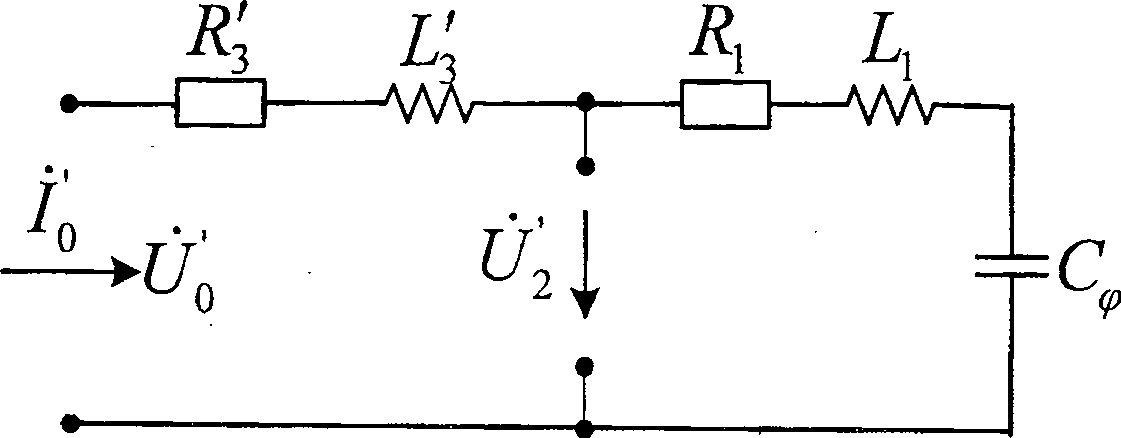
Neutral-point earth-free distributing network direct-to-ground capacitance current measuring method
InactiveCN101021554AAvoid influenceAccurate measurementCurrent/voltage measurementFault locationCapacitanceEngineering
This invention discloses a measurement method of the neutral earth-free distribution network towards the direct earth capacitance. It has such steps as injecting stable current signal from the open-delta of bus-bar potential transformer of the substation, measuring the open-delta voltage and the second star side-voltage. It detects the current of the direct earth capacitance of the distribution network according to the injected current signal and the measured voltage signal. This invention thoroughly avoids the influence of the short circuit of the open-delta of bus-bar potential transformer of the substation and the injected signal frequency toward the measuring result without changing the first connection and influencing the good running of the distribution network. It has such merits as safe, convenient, accurate and it completely settles the technical puzzle of the measuring accuracy of the short circuit of the open-delta of bus-bar potential transformer of the substation towards error current of the distribution network.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
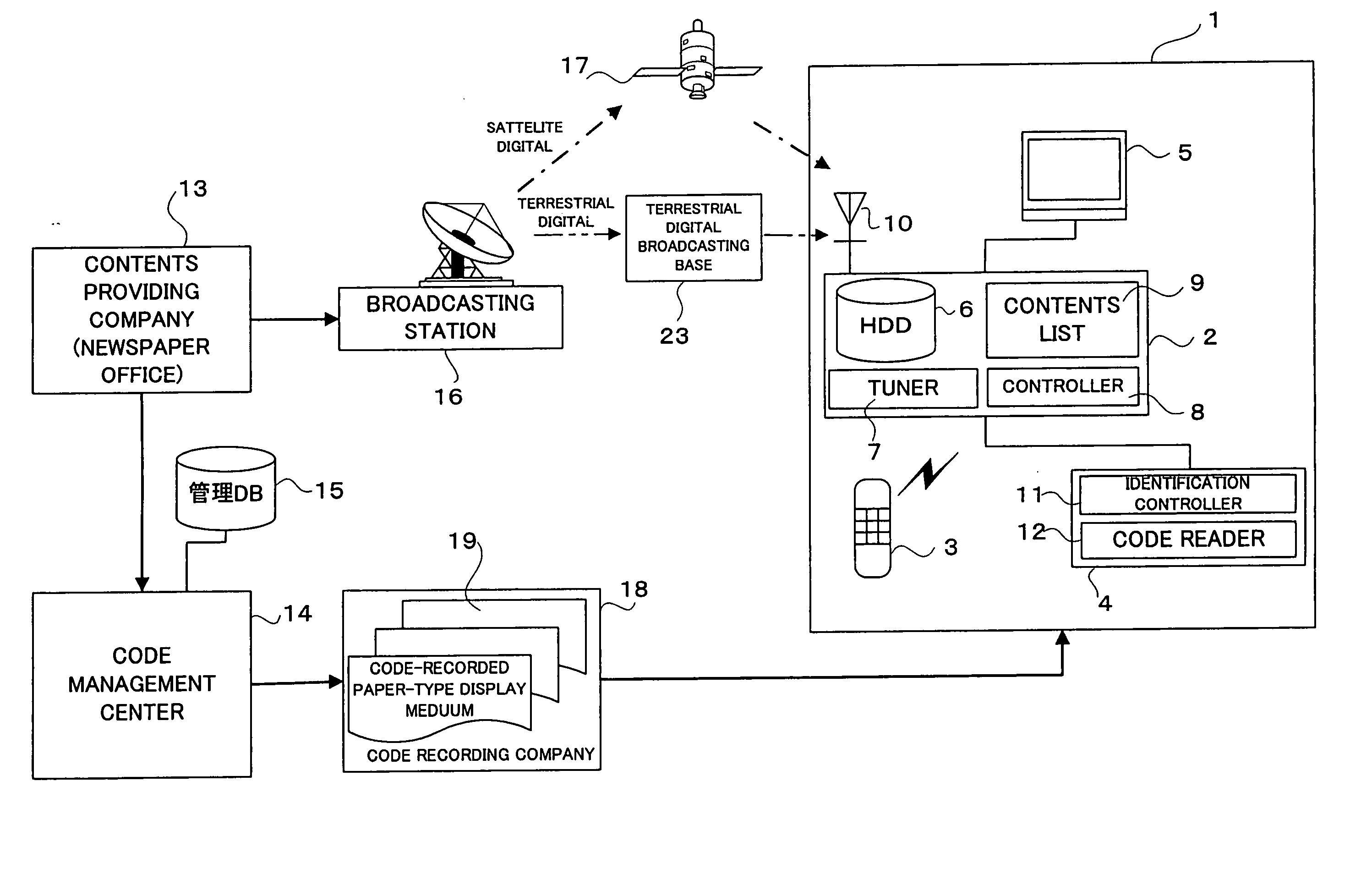
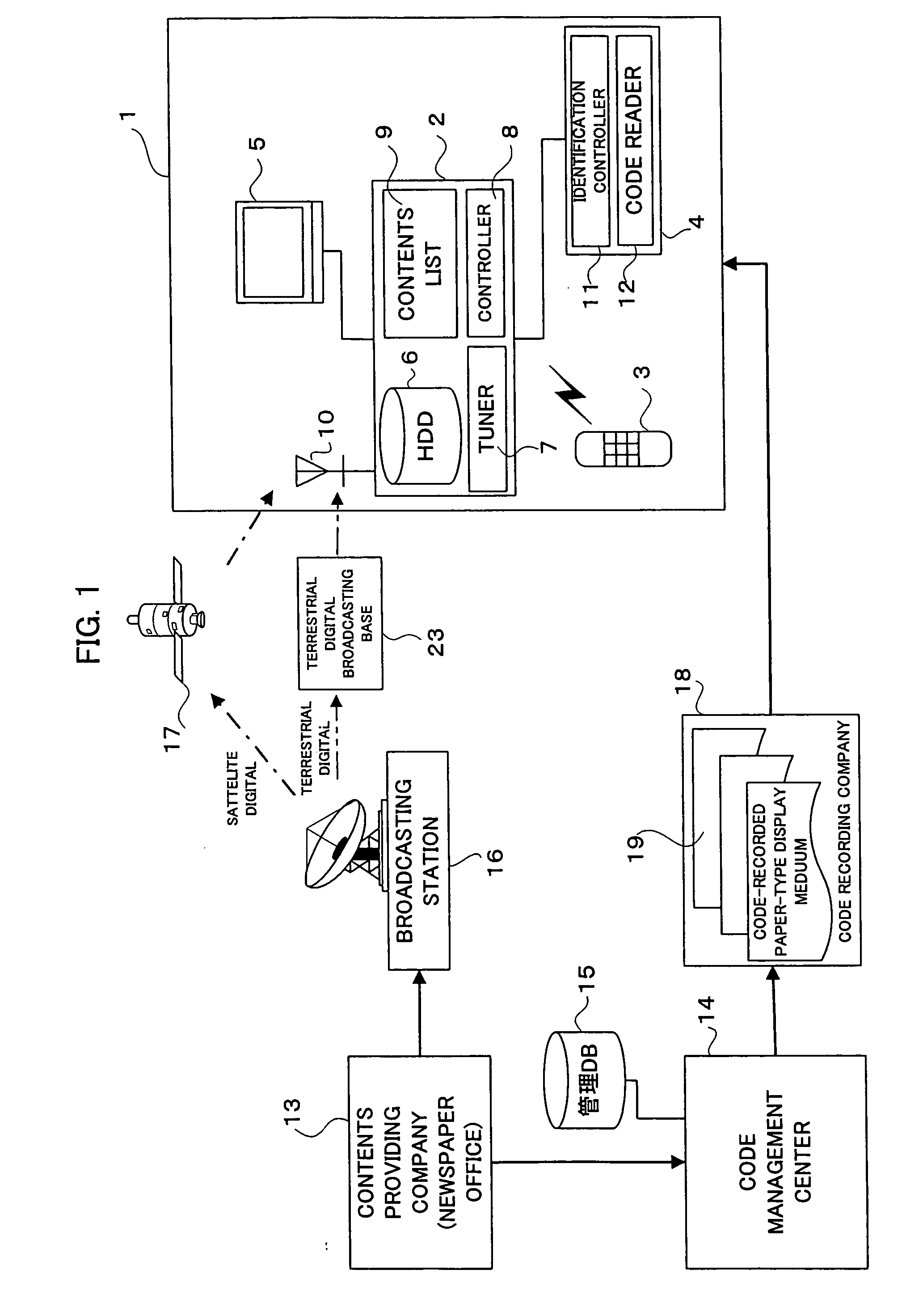
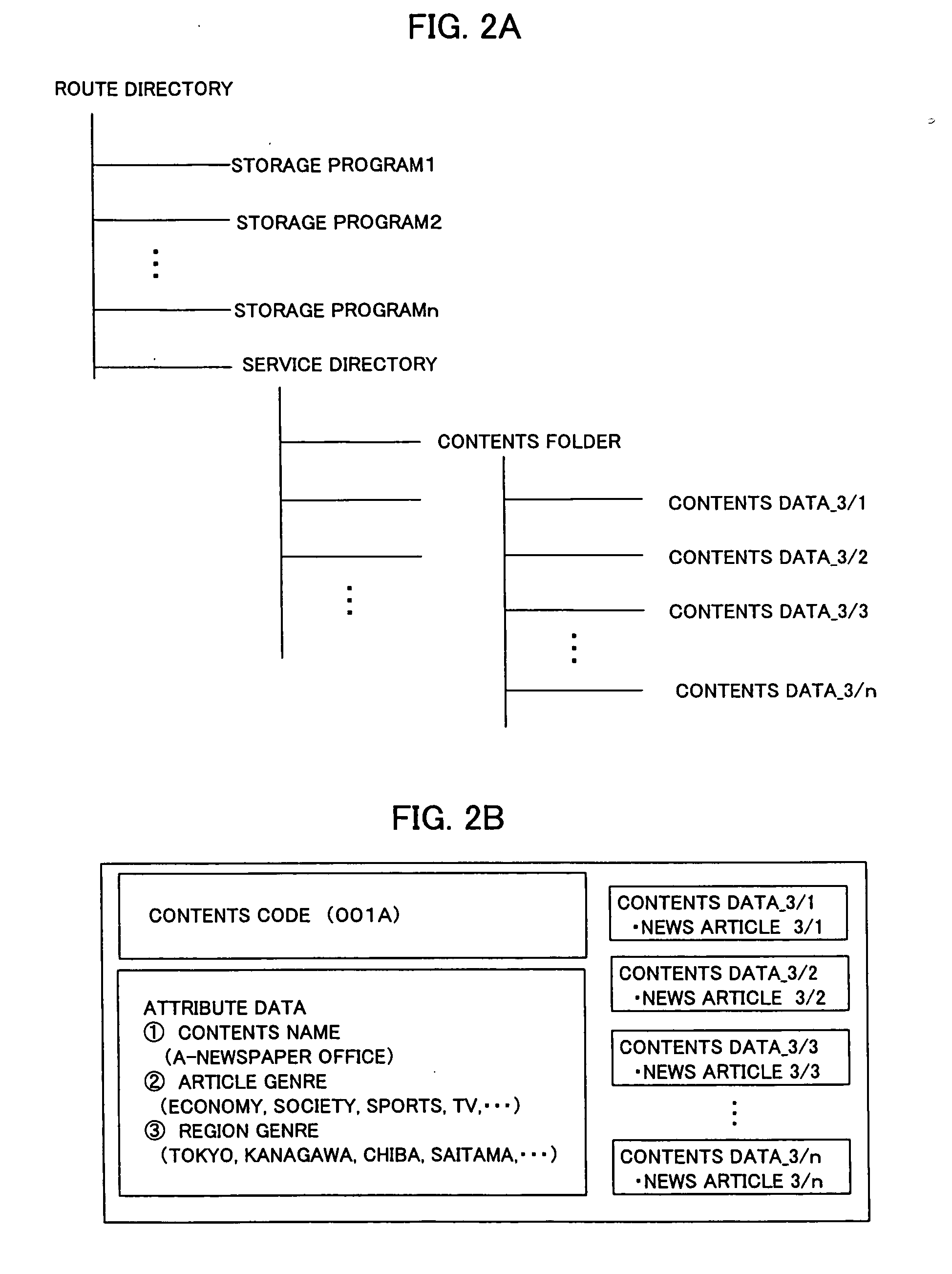
Information providing system and paper-shaped display medium
InactiveUS20050114882A1Simple procedureLow costDigital data information retrievalPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesThe InternetBroadcasting
The information providing system receives contents and a contents code corresponding to the contents by utilizing the broadcasting waves transmitted from a broadcasting station or the Internet, for example, and stores them. The contents may be information of newspaper article or else, and the contents code may be a code uniquely assigned to the contents. On the other hand, a paper-type display medium on which a similar contents code is recorded in advance is provided to a user by selling it or free distribution. When the user sets the paper-type display medium on the broadcasting receiver in a household, the code reading unit reads the contents code recorded on the paper-type display medium. Then, the receiver obtains the contents corresponding to the read contents code and displays it on the paper-type display medium.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Security risk assessment method for intelligent substation automation system
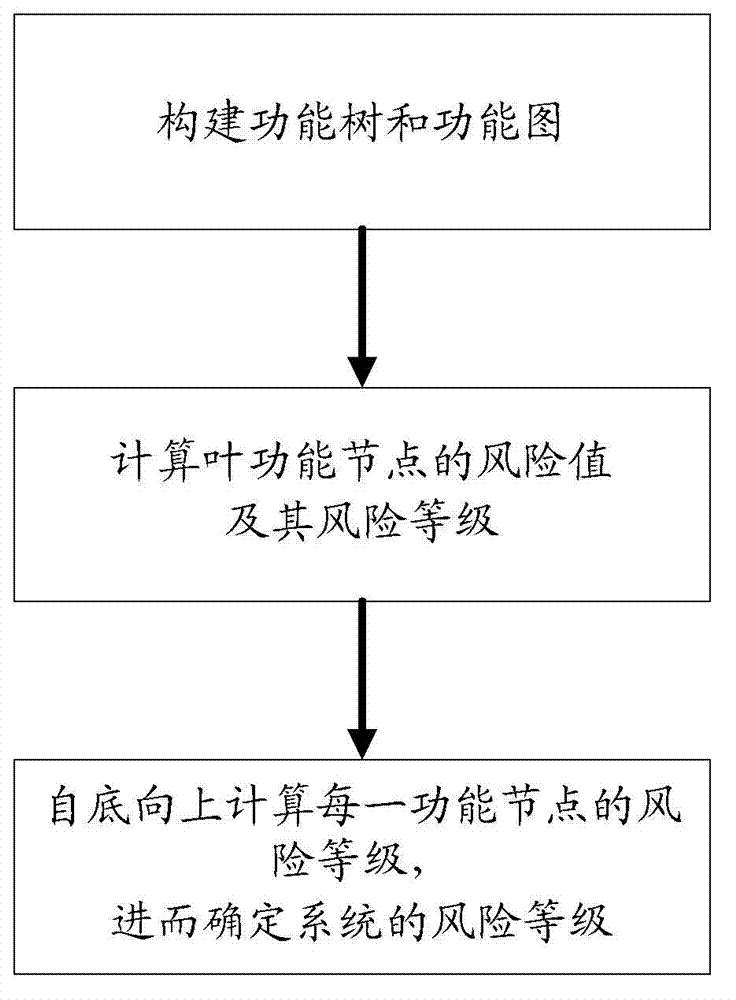
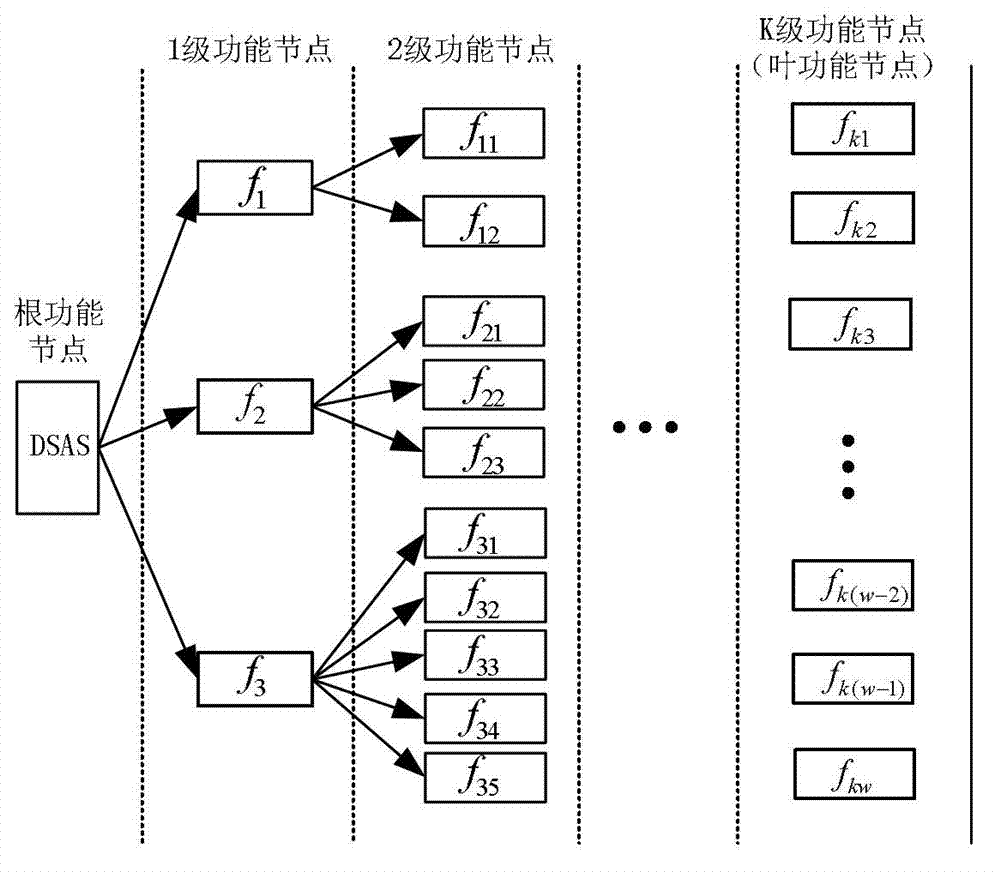
The invention discloses a security risk assessment method for an intelligent substation automation system, which comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a function tree and a functional diagram; (2) calculating the value at risk and the risk grade of a leaf function node; and (3) calculating the risk grade of each function node from bottom to top so as to determine the risk grade of the system. With the method disclosed by the invention, the service function of the intelligent substation automation system is used as the basis, security risk confronted by the intelligent substation automation system can be truly reflected under different operation conditions; influence on the security of the intelligent substation automation system by software and hardware is comprehensively considered; a reference can be provided for the free distribution scheme of the intelligent substation automation system function on different pieces of intelligent electronic equipment by the obtained risk grades of the intelligent substation automation system and the function node; and a favorable technical support is provided for the security risk management for the intelligent substation automation system.
Owner:广东立胜综合能源服务有限公司 +2
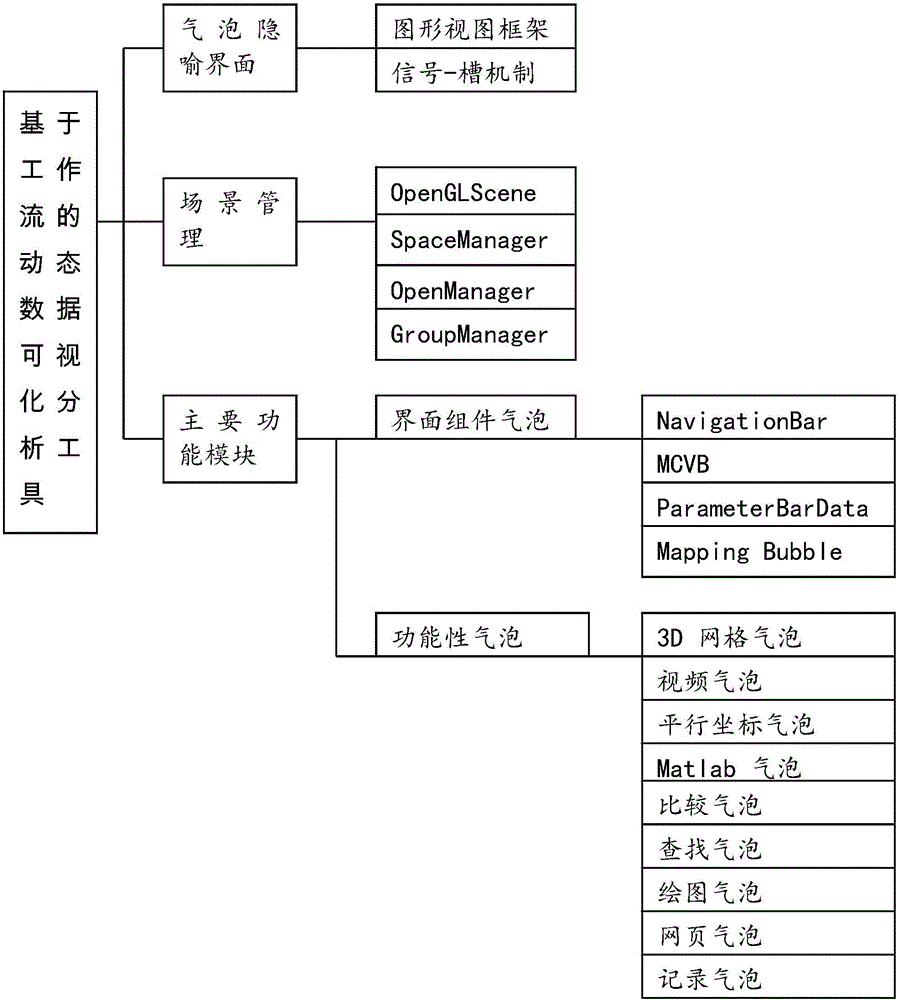
Dynamic data visualized analysis tool based on workflows
The invention discloses a dynamic data visualization analysis tool based on workflow. The invention extends the static multi-view display to the metaphorical interface of the bubble, so that the data analysis task can be supported by free layout. Each bubble is a functional unit, which can be used for programming calculations, and can also be used to create a visualization instance. It supports the operation of multiple bubbles forming a group, and the operation of bubbles in the same group is unified, which enhances the user experience. The invention can effectively connect different stages of the data analysis pipeline, reduce the efficiency loss of creating visualization instances and program transfer, and improve the efficiency of dynamic data visualization. Transforming causality-based data exploration into a pipelined approach can support transfer between procedures, automation of repetitive tasks, data capture records, and reuse of complex data analysis processes at different levels of detail. Provides more convenience for program pipelines in a broader framework.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Aluminum alloy product refinement and applications of aluminum alloy product refinement
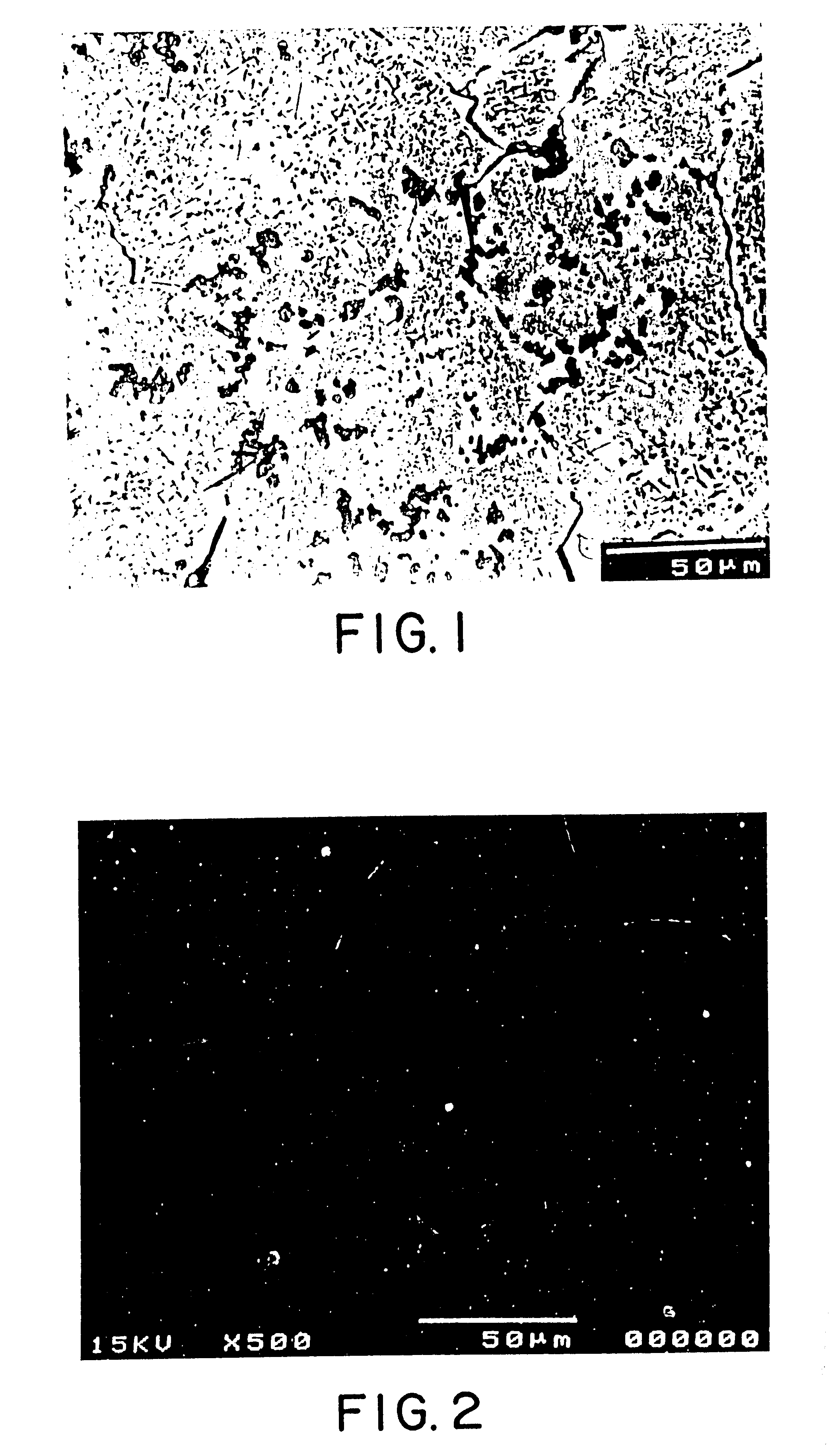
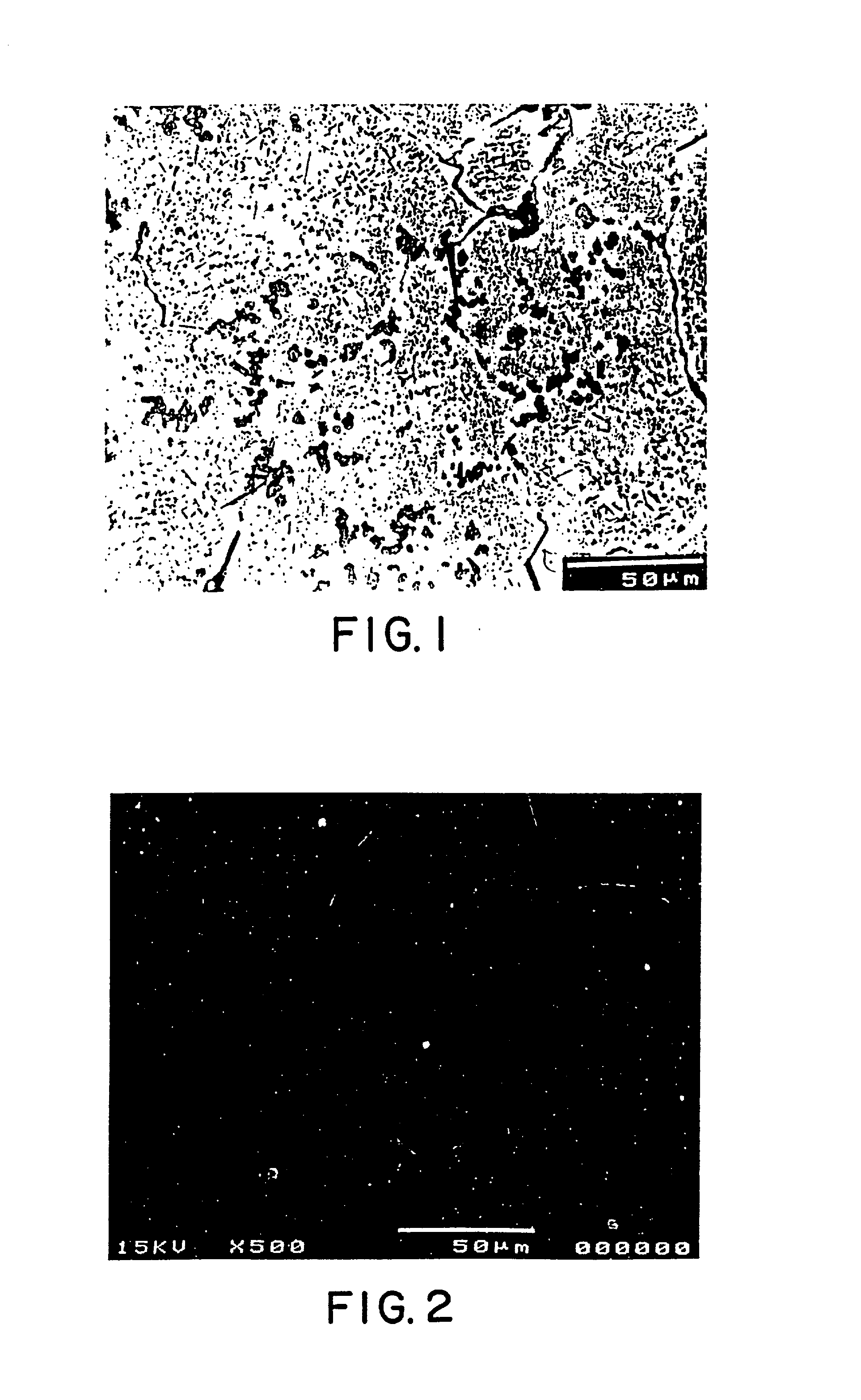
A novel product composed of a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal, including uniformly distributed, finely sized carbide phase particles formed in situ in a molten metal and a novel method for producing such a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal are disclosed. A salt-based liquid state reaction involving a liquid metal / alloy containing a liquid Ti, B, Si, Sc, Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr, Mo, Al (when the molten metal matrix is not aluminum), or V and a halide salt containing carbon particles forms a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the metal matrix. The ceramic dispersoid in metal product of the present invention includes at least about 50 volume percent of a matrix metal of aluminum; and up to about 50 volume percent of a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the aluminum metal matrix, wherein the finely sized ceramic phase particles have an average particle diameter of less than about 2.5 microns, and wherein the uniform distribution consists of a substantially cluster-free distribution of no more than two particles attached to one another at a magnification of 500×.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
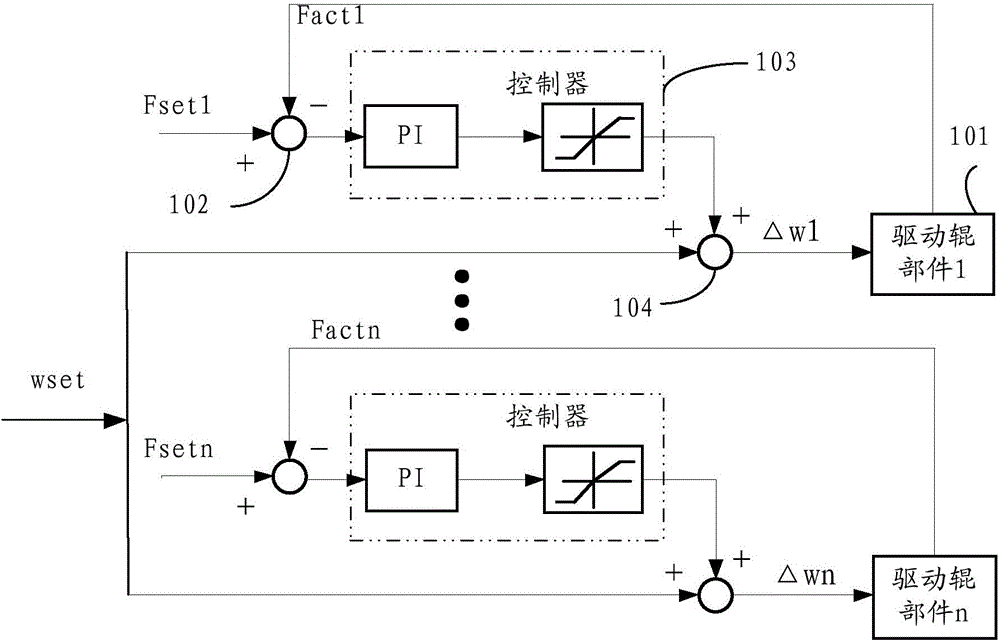
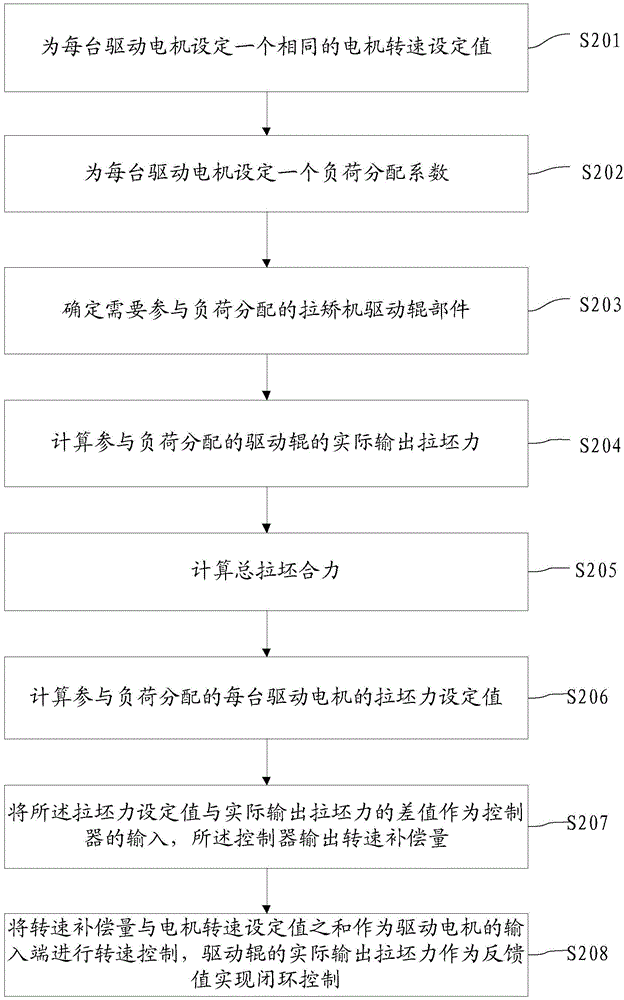
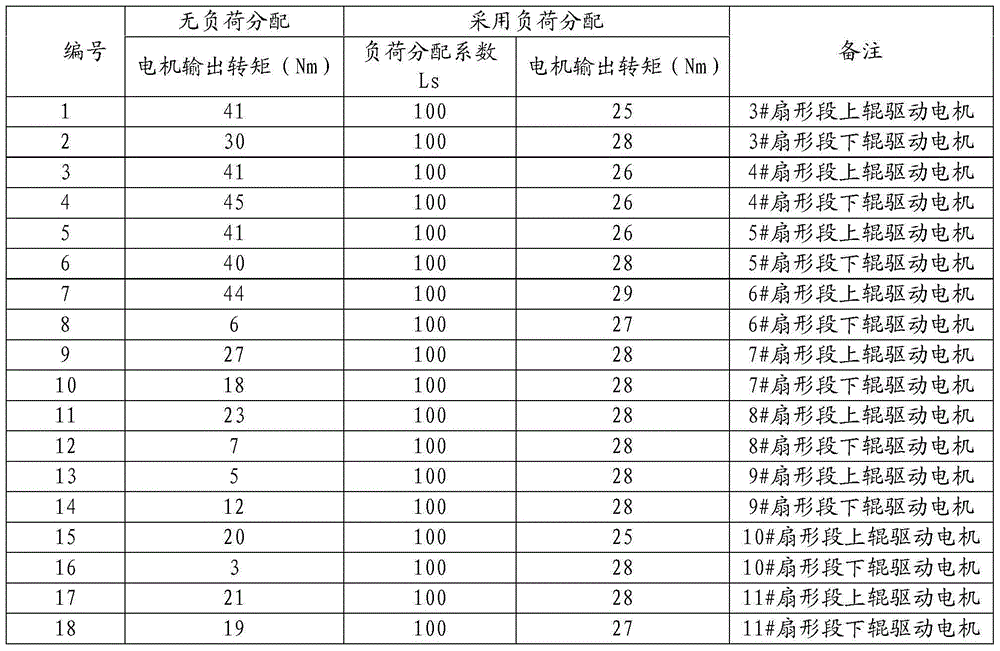
Continuous-casting withdrawal and straightening unit system and load distributing method
ActiveCN104001886AEliminate the no-load phenomenonImprove working conditionAutomatic controlClosed loop
The invention discloses the technical field of continuous-casting equipment, and provides a continuous-casting withdrawal and straightening unit system and a load distributing method. The method comprises the steps that the same motor rotating speed set value is set for all driving motors; a load distributing coefficient is set for each driving motor; withdrawal and straightening unit driving roller components needing to participate in load distribution are determined; actual output throwing force of driving rollers participating in load distribution is calculated; the total throwing resultant force is calculated; the throwing force set value of each driving motor participating in load distribution is calculated; a controller outputs the rotating speed compensation dosage; the sum of the rotating speed compensation dosage and the motor rotating speed set value is used as the input ends of the driving motors for rotating speed control, and the actual output throwing force of the driving rollers is used as feedback values to achieve closed-loop control. The load distributing coefficients are introduced to achieve free distribution of withdrawal and straightening unit total loads in withdrawal and straightening units, automatic control over the throwing force is achieved through closed-loop adjustment, and meanwhile according to the method, the pull speed changes can not be caused, and the production technology is not affected.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Thermally improved semiconductor qfn/son package
ActiveUS20100096734A1Improved QFN/SON thermal performanceImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringThermal contact
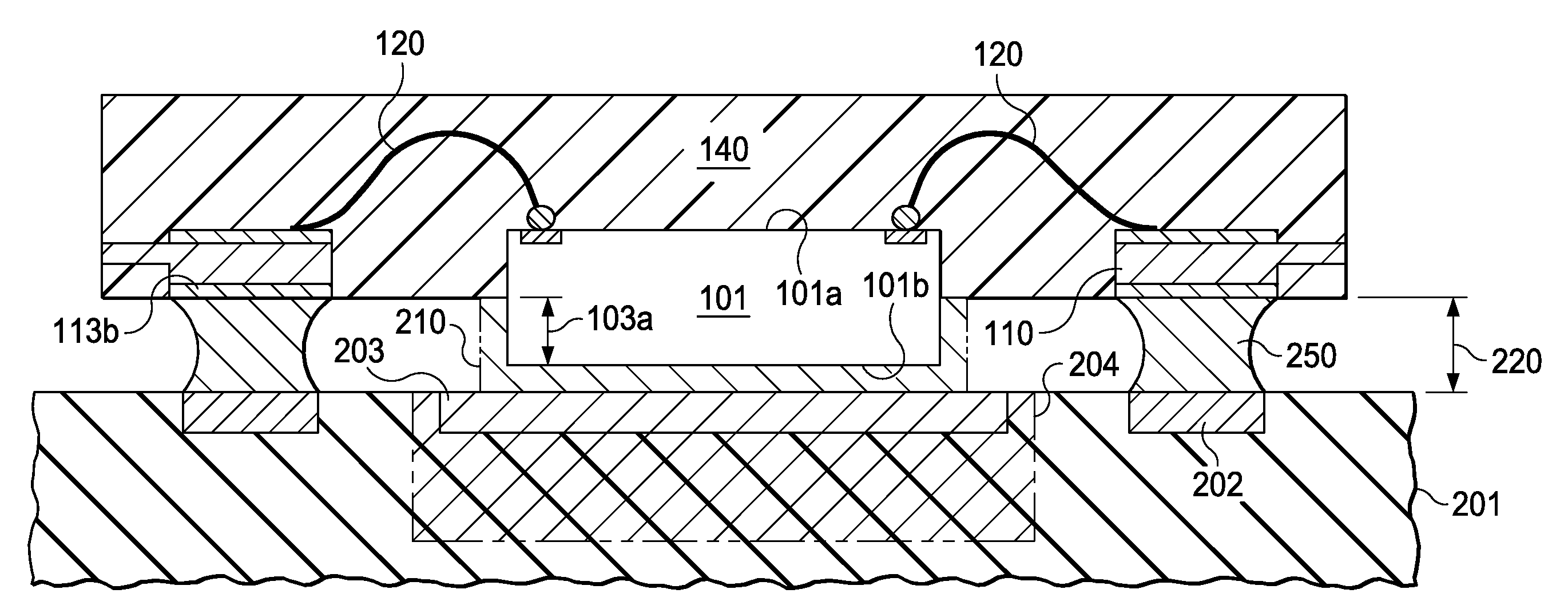
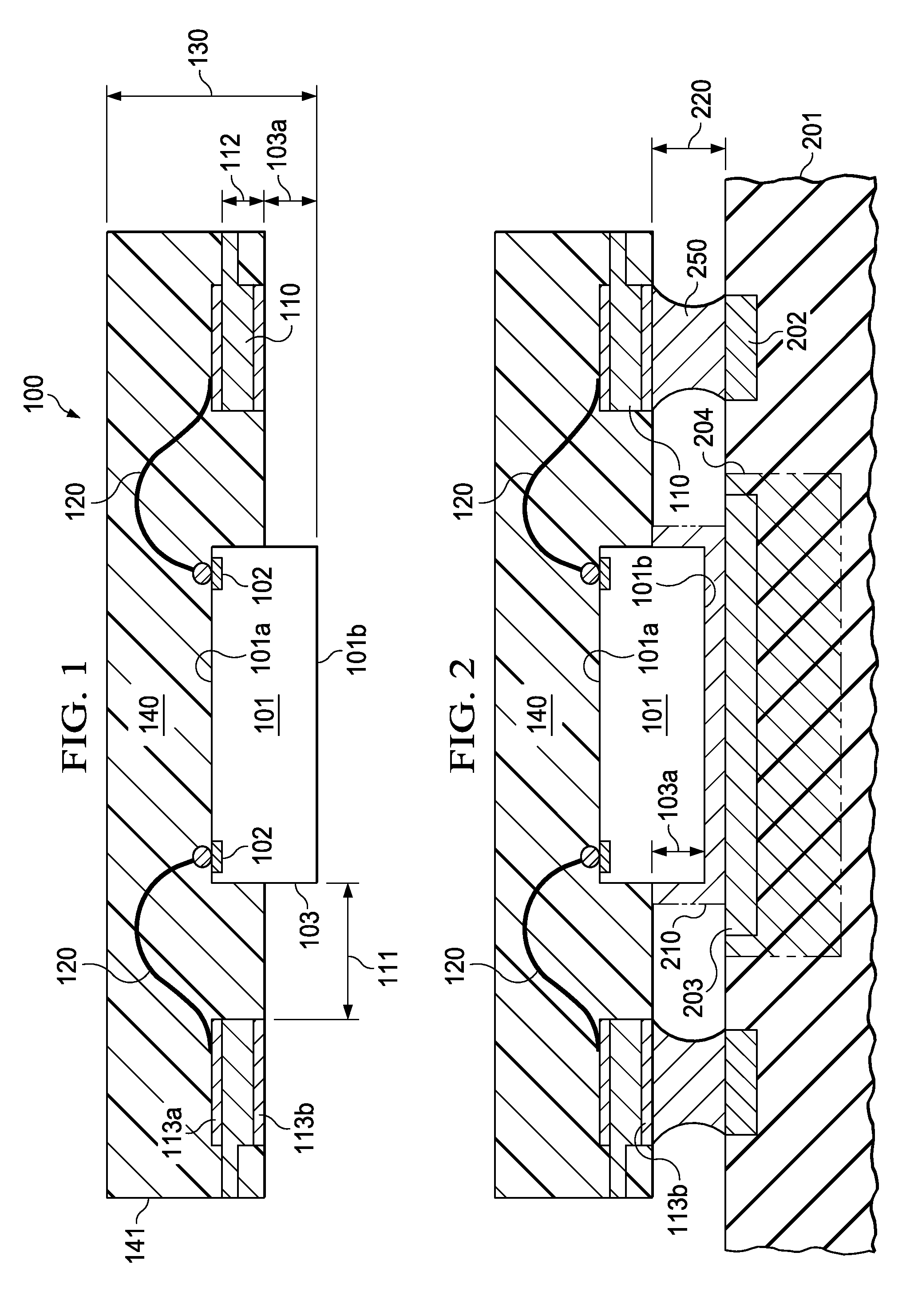
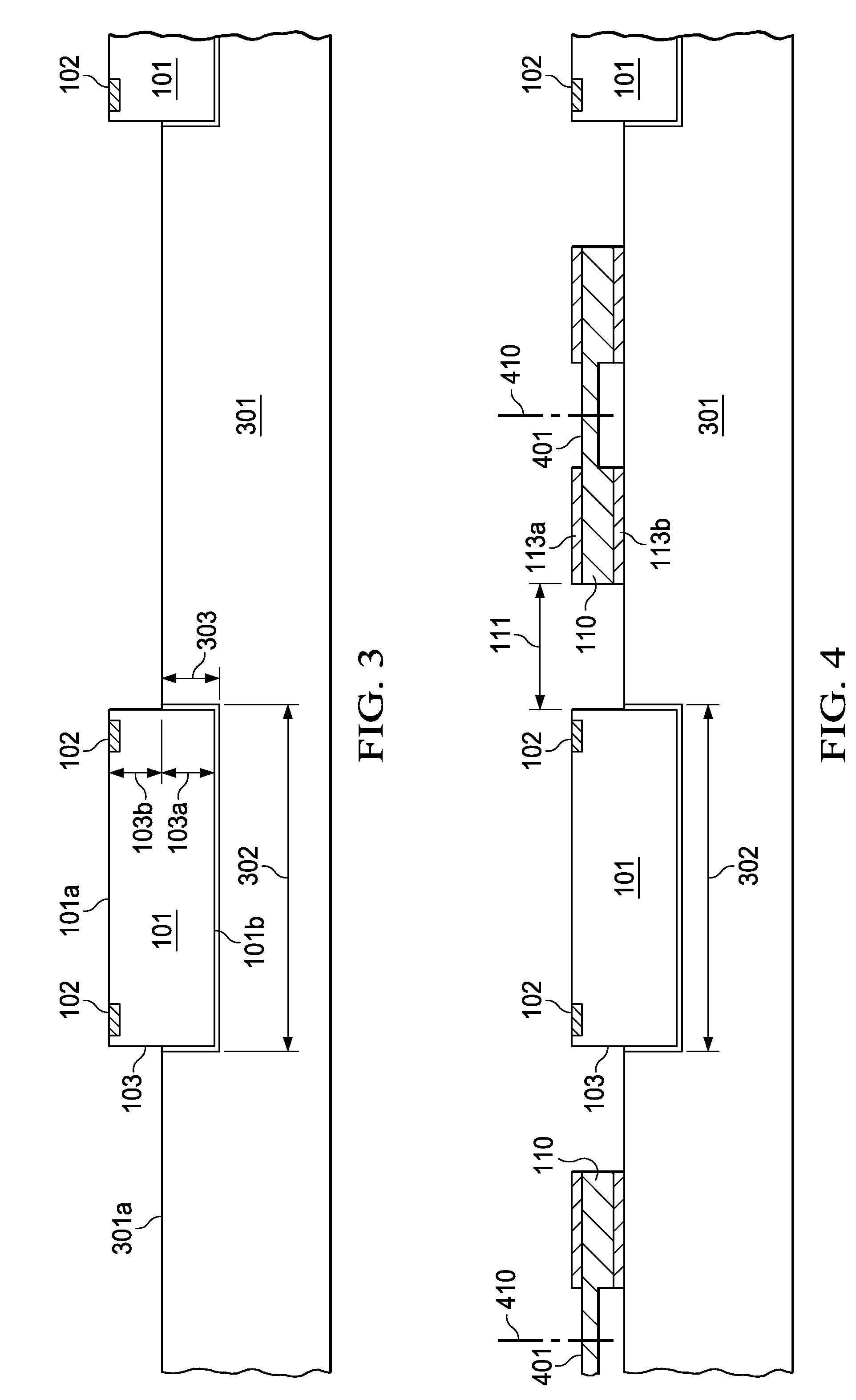
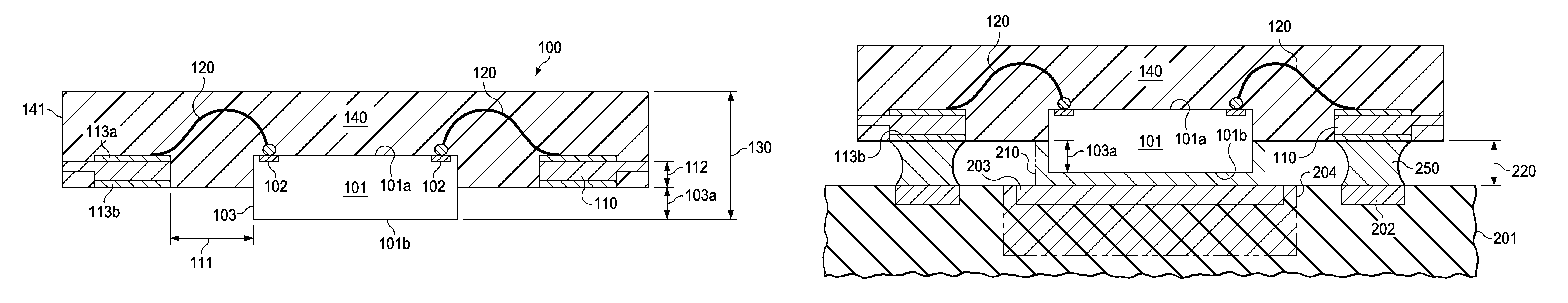
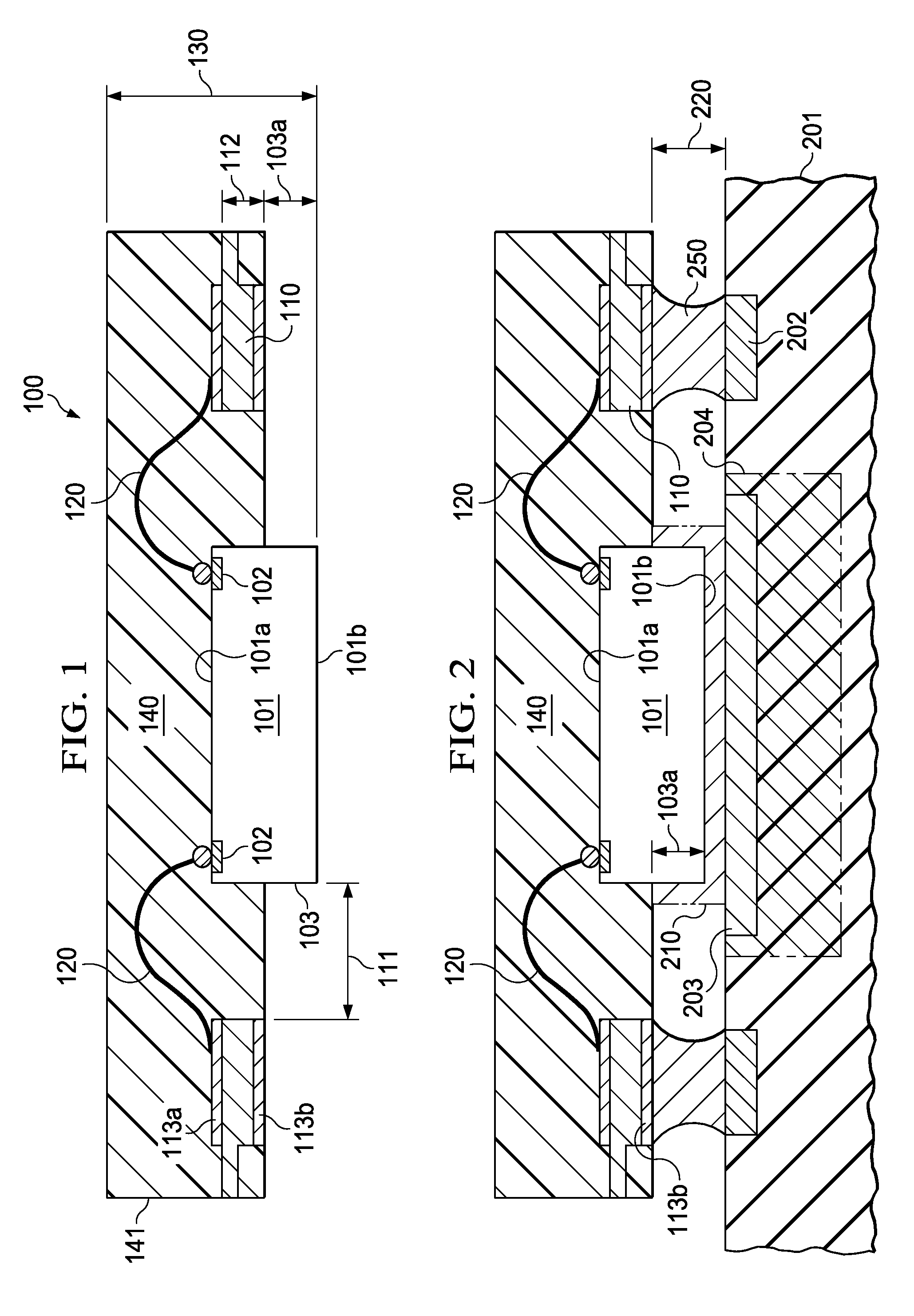
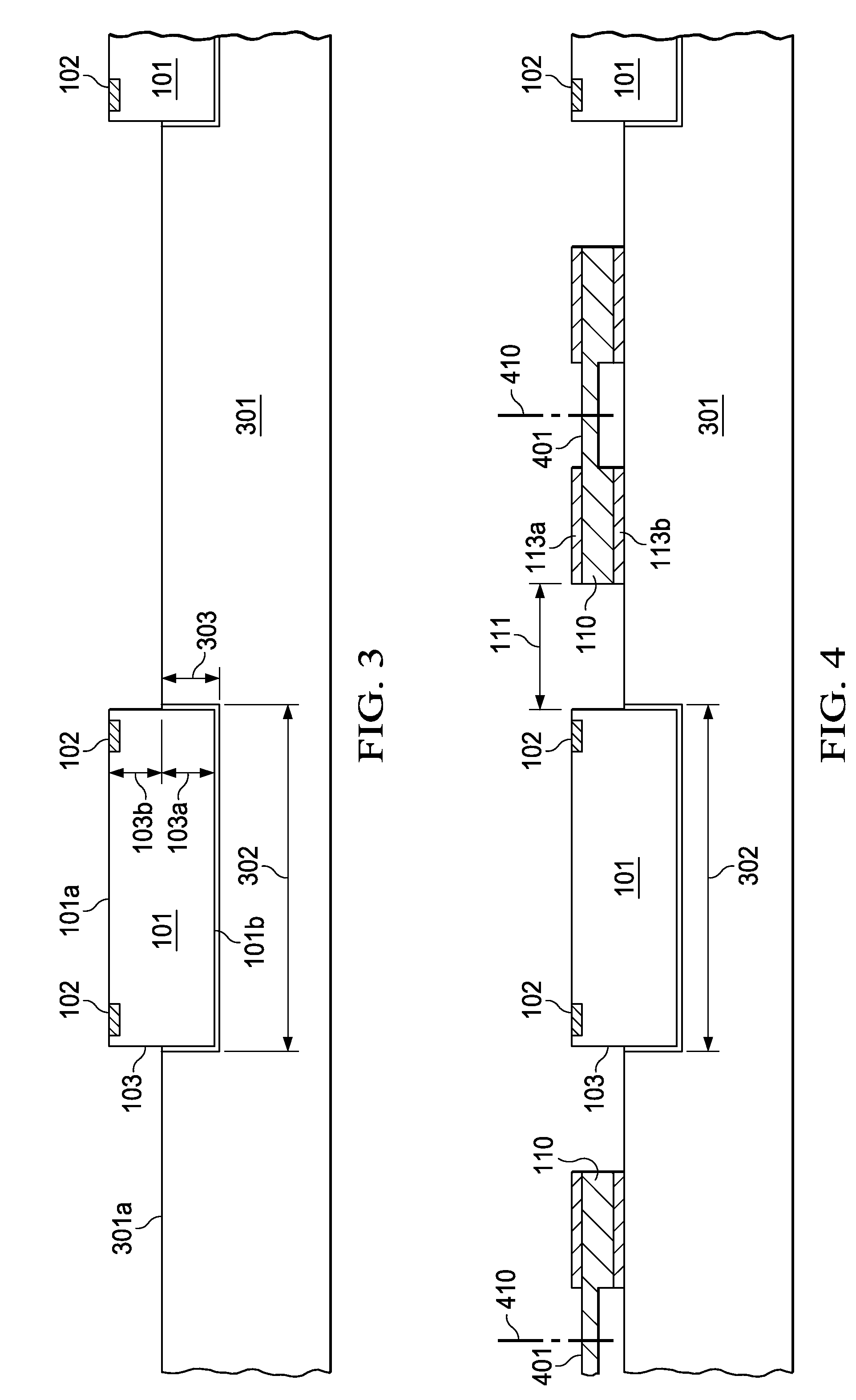
A semiconductor device without cantilevered leads uses conductive wires (120) to connect the chip terminals to the leads (110), and a package compound (140) to encapsulate the chip surface (101a) with the terminals, the wires, and the lead surfaces with the attached wires. The chip surface (101b) opposite the terminals together with portions (103) of the chip sidewalls protrude from the package, allowing an unimpeded thermal contact of the protruding chip surface to a substrate (201) to optimize the thermal flux from the chip to the substrate. Solder bodies (250) attached to the compound-free lead surfaces (113b) can be connected to the substrate so that the solder bodies are as elongated as the protruding chip height, facilitating the void-free distribution of an underfill compound into the space between chip and substrate, and improving the absorption of thermomechanical stresses during device operation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Uniformly dispersed, finely sized ceramic particles in metals and alloys
A novel product composed of a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal, including uniformly distributed, finely sized carbide phase particles formed in situ in a molten metal and a novel method for producing such a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal are disclosed. A salt-based liquid state reaction involving a liquid metal / alloy containing a liquid Ti, B, Si, Sc, Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr, Mo, Al (when the molten metal matrix is not aluminum), or V and a halide salt containing carbon particles forms a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the metal matrix. The ceramic dispersoid in metal product of the present invention includes at least about 50 volume percent of a matrix metal of aluminum; and up to about 50 volume percent of a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the aluminum metal matrix, wherein the finely sized ceramic phase particles have an average particle diameter of less than about 2.5 microns, and wherein the uniform distribution consists of a substantially cluster-free distribution of no more than two particles attached to one another at a magnification of 500x.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Aluminum alloy product refinement and applications of aluminum alloy product refinement
A novel product composed of a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal, including uniformly distributed, finely sized carbide phase particles formed in situ in a molten metal and a novel method for producing such a ceramic phase particle dispersoid in metal are disclosed. A salt-based liquid state reaction involving a liquid metal / alloy containing a liquid Ti, B, Si, Sc, Hf, Nb, Ta, Zr, Mo, Al (when the molten metal matrix is not aluminum), or V and a halide salt containing carbon particles forms a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the metal matrix. The ceramic dispersoid in metal product of the present invention includes at least about 50 volume percent of a matrix metal of aluminum; and up to about 50 volume percent of a uniform distribution of finely sized ceramic phase particles formed and dispersed in-situ in the aluminum metal matrix, wherein the finely sized ceramic phase particles have an average particle diameter of less than about 2.5 microns, and wherein the uniform distribution consists of a substantially cluster-free distribution of no more than two particles attached to one another at a magnification of 500x.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
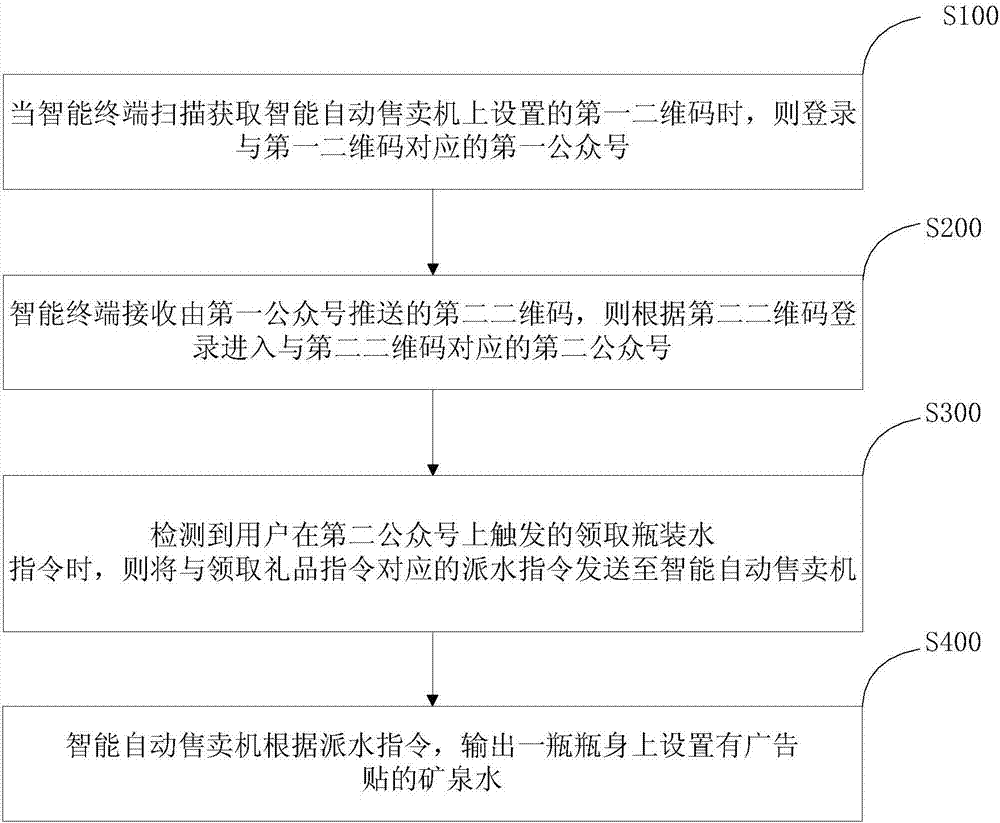
Code-scanning and official account-following water free distribution implementation method and system by means of smart vending machine
InactiveCN107230284ARealize functionAdvertisementsCoin-freed apparatus detailsBottleComputer science
The invention discloses a code-scanning and official account-following water free distribution implementation method and system by means of a smart vending machine. The water free distribution implementation method comprises that when a smart terminal obtains a first two-dimensional code arranged on the smart vending machine through scanning, the smart terminal logs in a first official account corresponding to the first two-dimensional code; the smart terminal receives a second two-dimensional code pushed by the first official account, and logs in a second official account corresponding to the second two-dimensional code in dependence on the second two-dimensional code; when a bottled water getting instruction triggered by the user on the second official account is detected, a water distribution instruction corresponding to the bottled water getting instruction is sent to the smart vending machine; and the smart vending machine outputs a bottle of mineral water with the bottle body having an advertisement sticker in dependence on the water distribution instruction. According to the invention, a code-scanning fans-attracting mode is employed, water is freely distributed to masses of consumers, and therefore the advertising communication and two-dimensional code promotion functions of the smart vending machine are achieved.
Owner:深圳市弘森网络科技有限公司
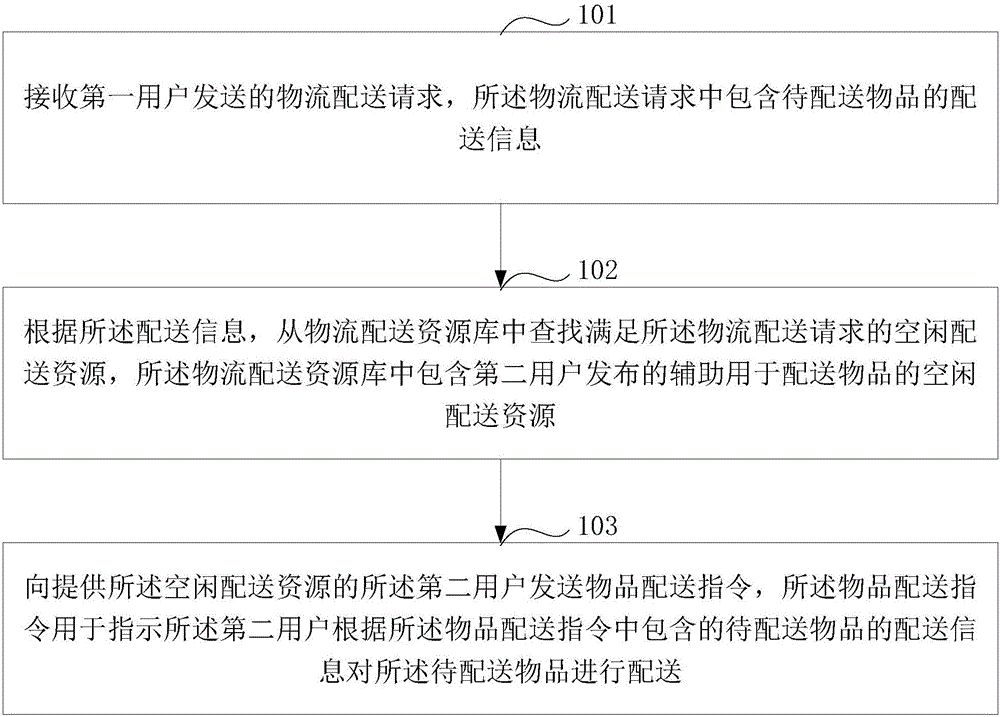
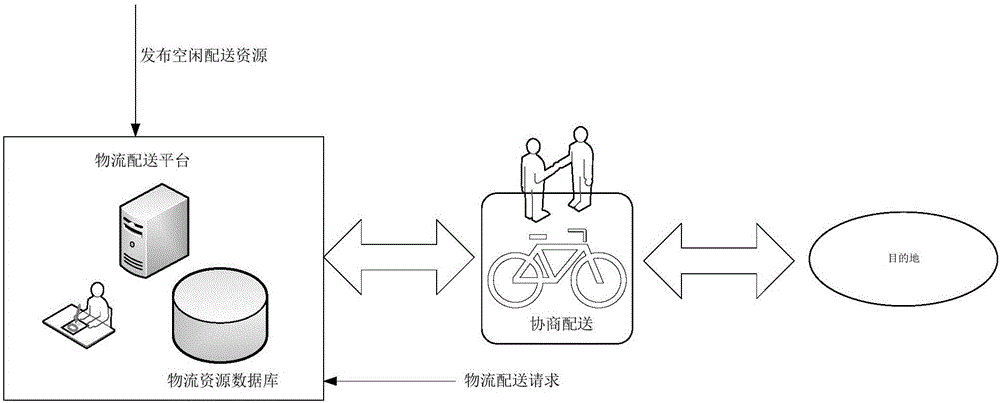
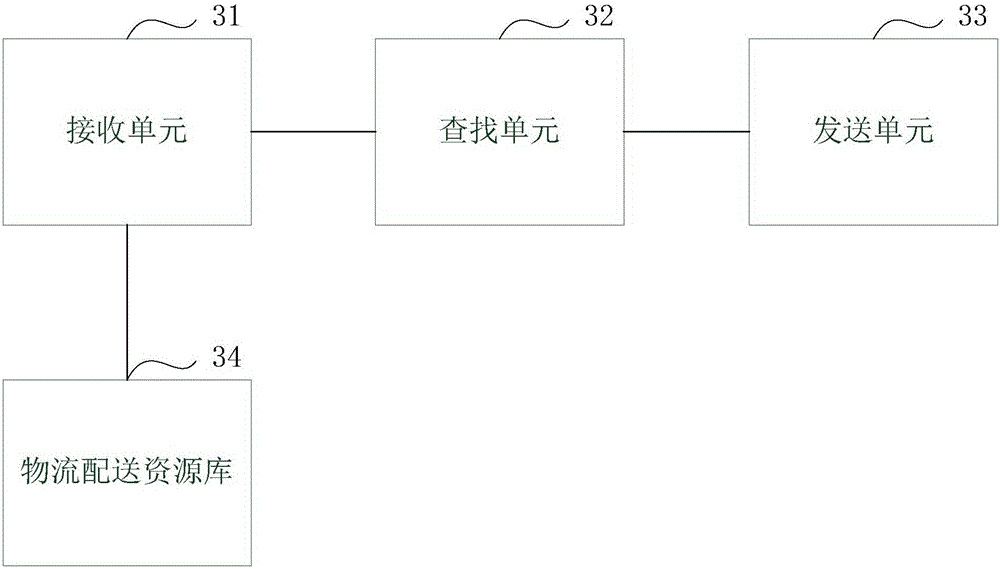
Logistic distribution method and equipment
InactiveCN106156985AImprove distribution efficiencyEfficient use ofLogisticsLogistics managementComputer science
The invention discloses a logistic distribution method and equipment. The logistic distribution method comprises the following steps: receiving a logistic distribution request sent by a first user and containing distribution information of an article to be distributed; according to the distribution information, looking up a free distribution resource meeting the logistic distribution request from a logistic distribution resource library, wherein the logistic distribution resource library contains the free distribution resource issued by a second user and assisting article distribution; sending an article distribution instruction to the second user providing the free distribution resource, wherein the article distribution instruction is used for instructing the second user to distribute the article to be distributed according to the distribution information of the article to be distributed contained in the article distribution instruction. For the logistic distribution request of the first user, the free distribution resource issued by the second user and assisting the article distribution can be selected from the logistic distribution resource library for providing distribution service for the first user, so that the free distribution resource can be effectively utilized, the logistic distribution efficiency is improved, and the distribution pressure of a logistic distribution system is alleviated.
Owner:蒋建宏
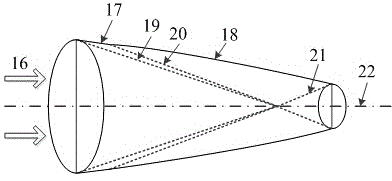
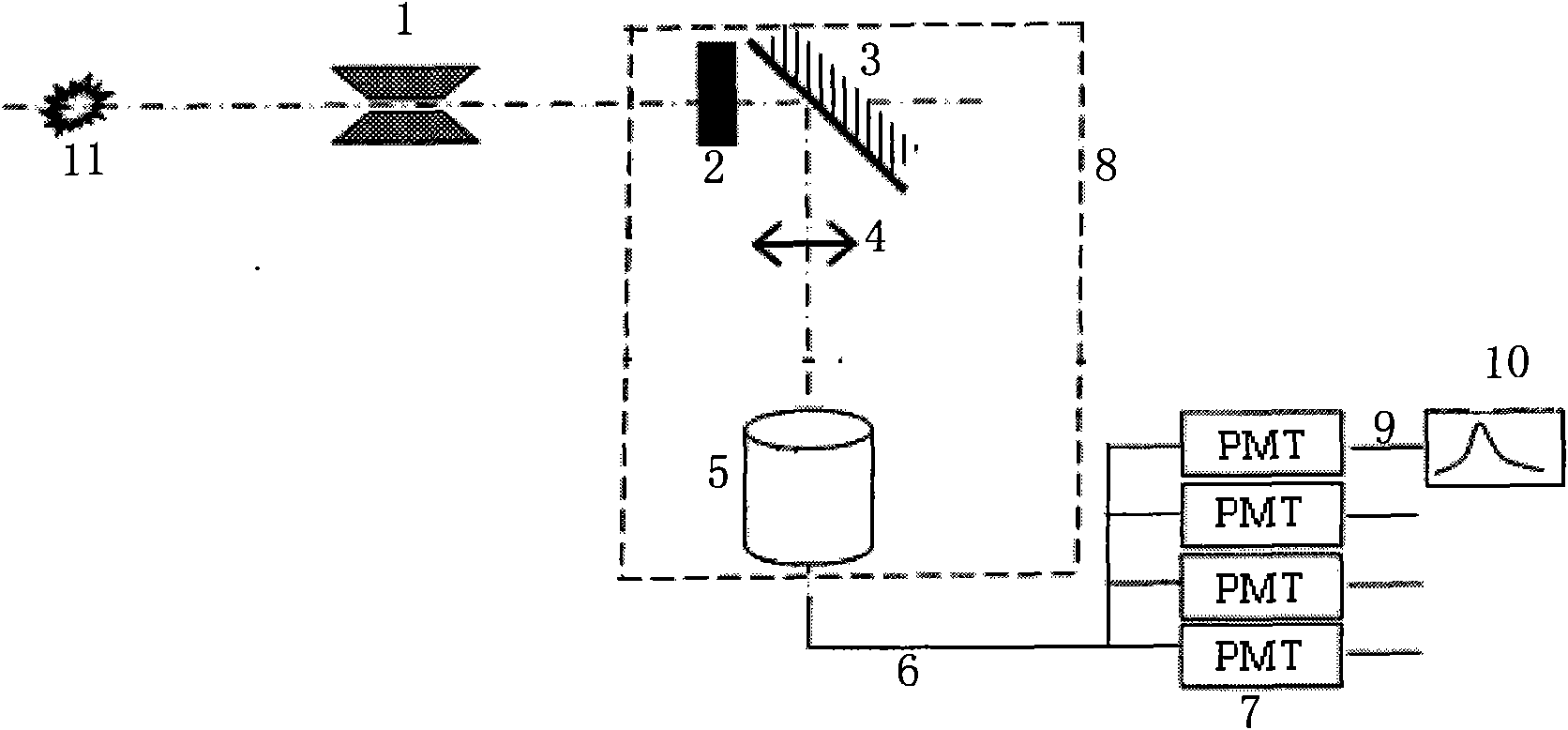
Pulse radiating field time-space resolution measuring system based on optical fiber beam
InactiveCN101876712AGuaranteed bandwidthHigh sensitivityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsRadiation intensity measurementPhotovoltaic detectorsUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a pulse radiating field time-space resolution measuring system based on an optical fiber beam, which comprises a thick pinhole (1), a scintillator (2), an optical system, an optical fiber beam array (5), a transmission optical cable (6) and a photoelectric detector (7). The invention solves the technical problems of low sensitivity and small dynamic range of the traditional time-space resolution measuring way, improves the sensitivity of the system, can realize the output of signals with different strengths and achieve the aims of range division and improvement of dynamic range of the system and has convenient maintenance and processing and free distribution.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Suspension type power distribution cabinet with convenience in height adjustment
InactiveCN107887808AEasy to moveStable supportSubstation/switching arrangement casingsArchitectural engineeringFree distribution
Owner:SICHUAN LIZHI JIUCHUANG INTPROP OPERATION CO LTD
Thermally improved semiconductor QFN/SON package
ActiveUS7863103B2Improve toleranceReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringThermal contact
A semiconductor device without cantilevered leads uses conductive wires (120) to connect the chip terminals to the leads (110), and a package compound (140) to encapsulate the chip surface (101a) with the terminals, the wires, and the lead surfaces with the attached wires. The chip surface (101b) opposite the terminals together with portions (103) of the chip sidewalls protrude from the package, allowing an unimpeded thermal contact of the protruding chip surface to a substrate (201) to optimize the thermal flux from the chip to the substrate. Solder bodies (250) attached to the compound-free lead surfaces (113b) can be connected to the substrate so that the solder bodies are as elongated as the protruding chip height, facilitating the void-free distribution of an underfill compound into the space between chip and substrate, and improving the absorption of thermomechanical stresses during device operation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Expandable shopping bag carrier
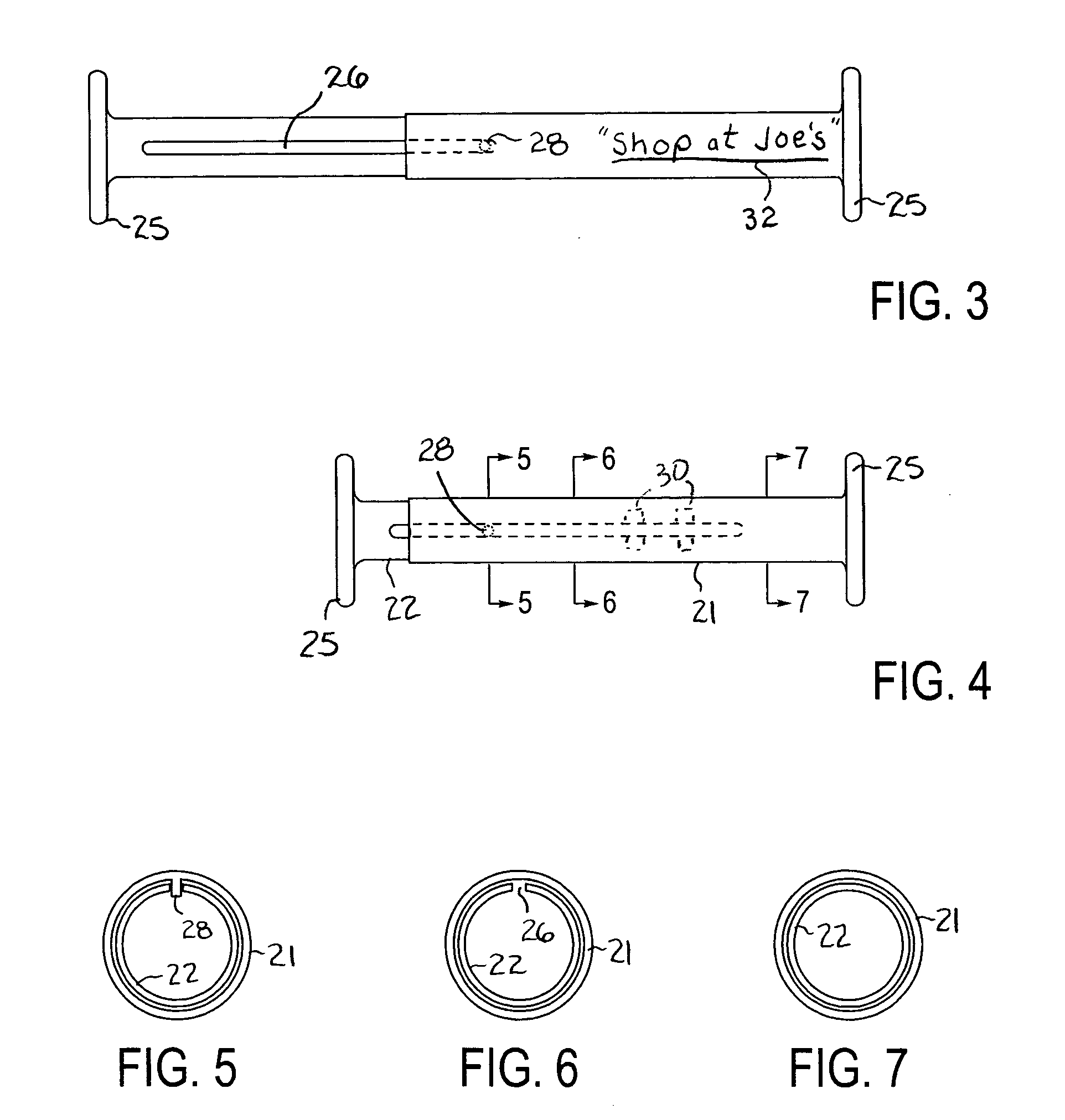
InactiveUS20070170738A1Limit its extensionTravelling carriersHoldersPlastic materialsBiomedical engineering
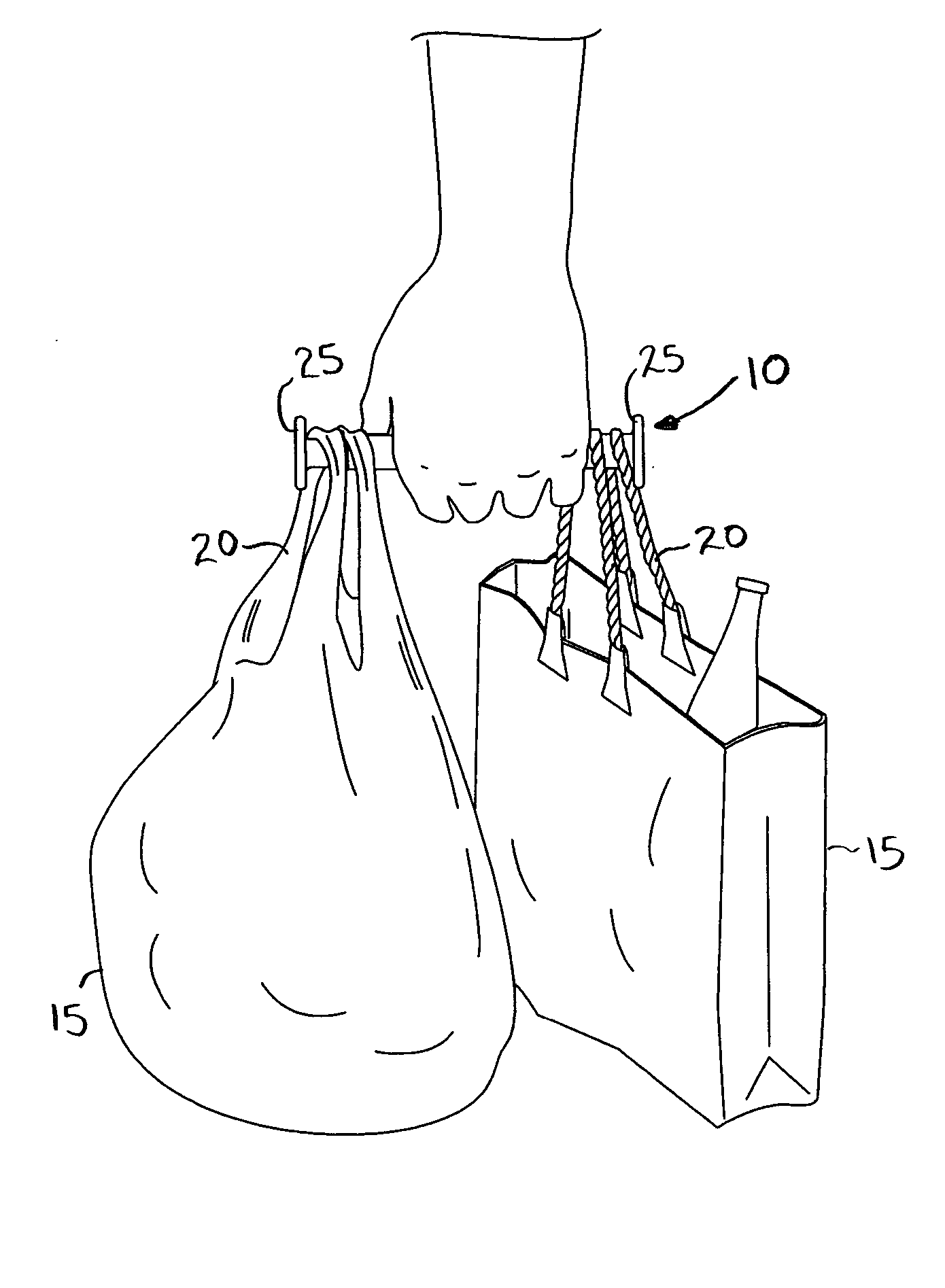
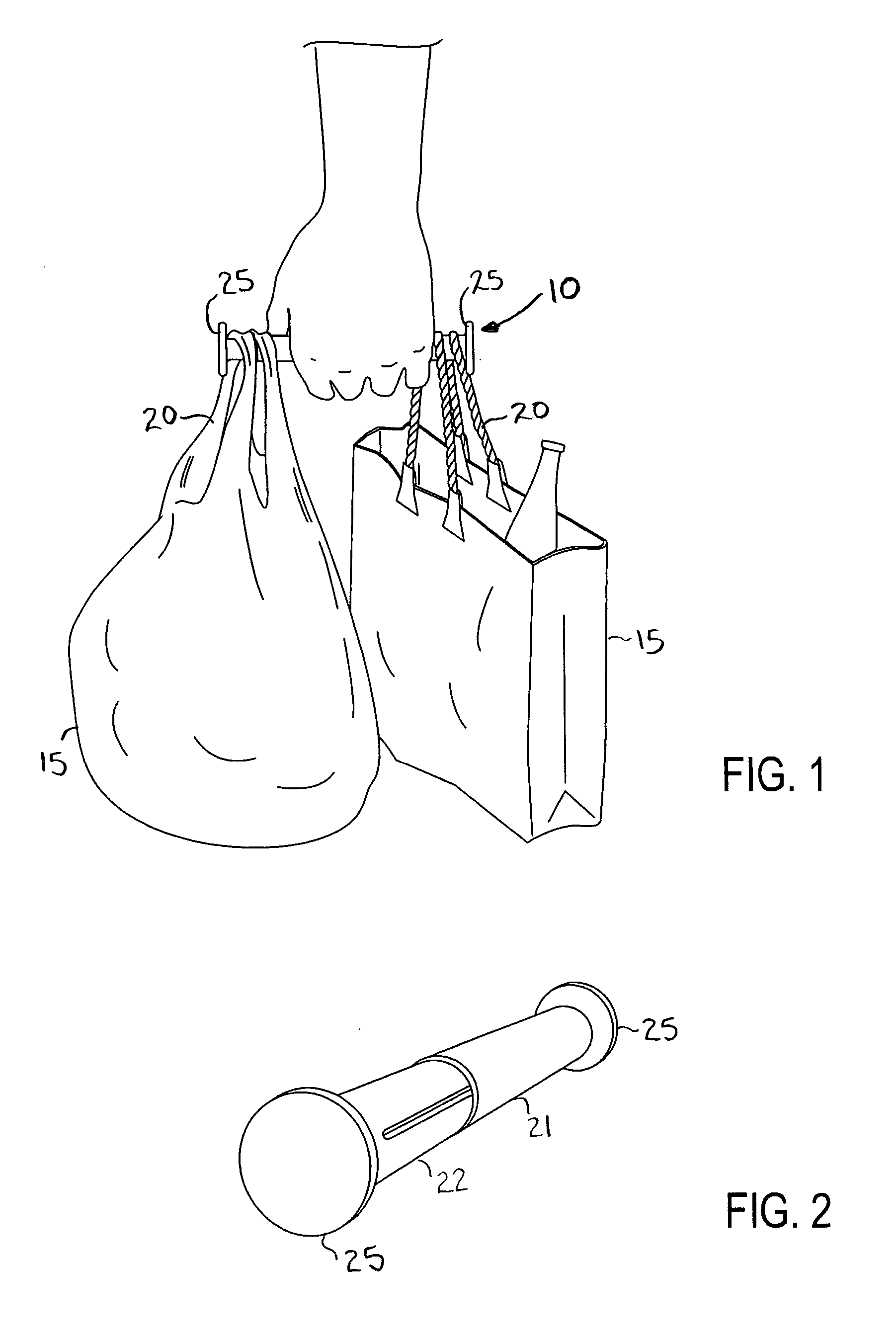
An expandable shopping bag carrier includes two cylindrical tubes telescoping within one another to expand and contract as needed. At respective outer ends of the carrier are radially extending annuli that serve to retain handles of conventional shopping bags thereon whilst a middle portion of the carrier is grasped by a hand, leveraging the weight of the shopping bags and providing a more ergonomically favorable surface to grasp. The carrier can include advertising and be made of an inexpensive plastic material so as to be suitable for free distribution by stores.
Owner:BONGARD PETER
Test rack system for four-wheel-drive bridge assembly
InactiveCN110243613AReduce manufacturing costLower purchase costVehicle testingWork measurementNew energyData acquisition
The invention discloses a test rack system for a four-wheel-drive bridge assembly. The test rack system for the four-wheel-drive bridge assembly is used for testing an electric new energy automobile, the electric new energy automobile is controlled by a central control system to operate and consists of an electric system and a control system, the electric system consists of a power measuring device, a driving system and a power supply system, the driving system is connected with the power measuring device, and the power supply system is connected with the driving system; and the control system consists of a torque sensor, a real-time system, a data collection device and an upper computer. The structure can complete test items which are completed by a traditional two-wheel-drive rack and also has the functions such as free distribution of power between shafts and free distribution and simulation of power between wheels, the system is directly connected with the central control system of the automobile through a computer, data collection and control can be carried out by using functions of the automobile, the production cost of enterprises is saved, and simultaneously, the purchase cost of users is reduced.
Owner:南通常测机电设备有限公司
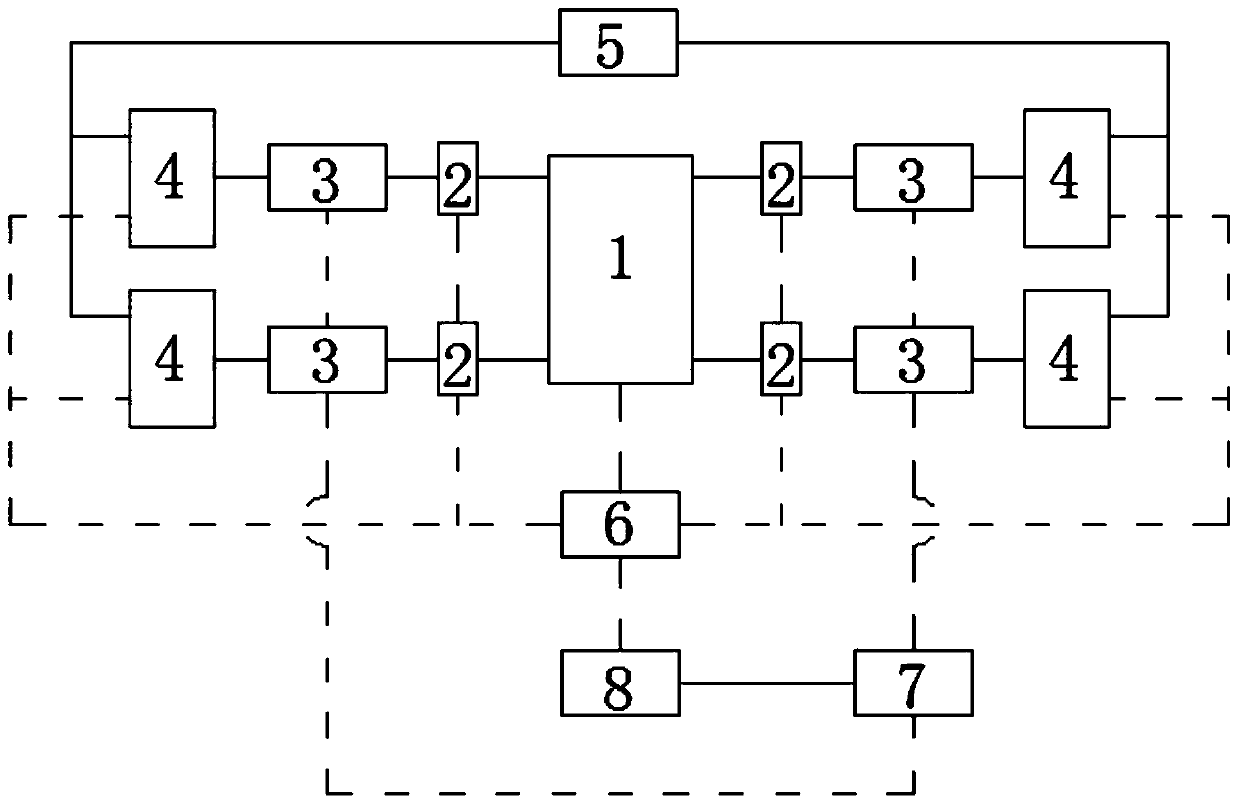
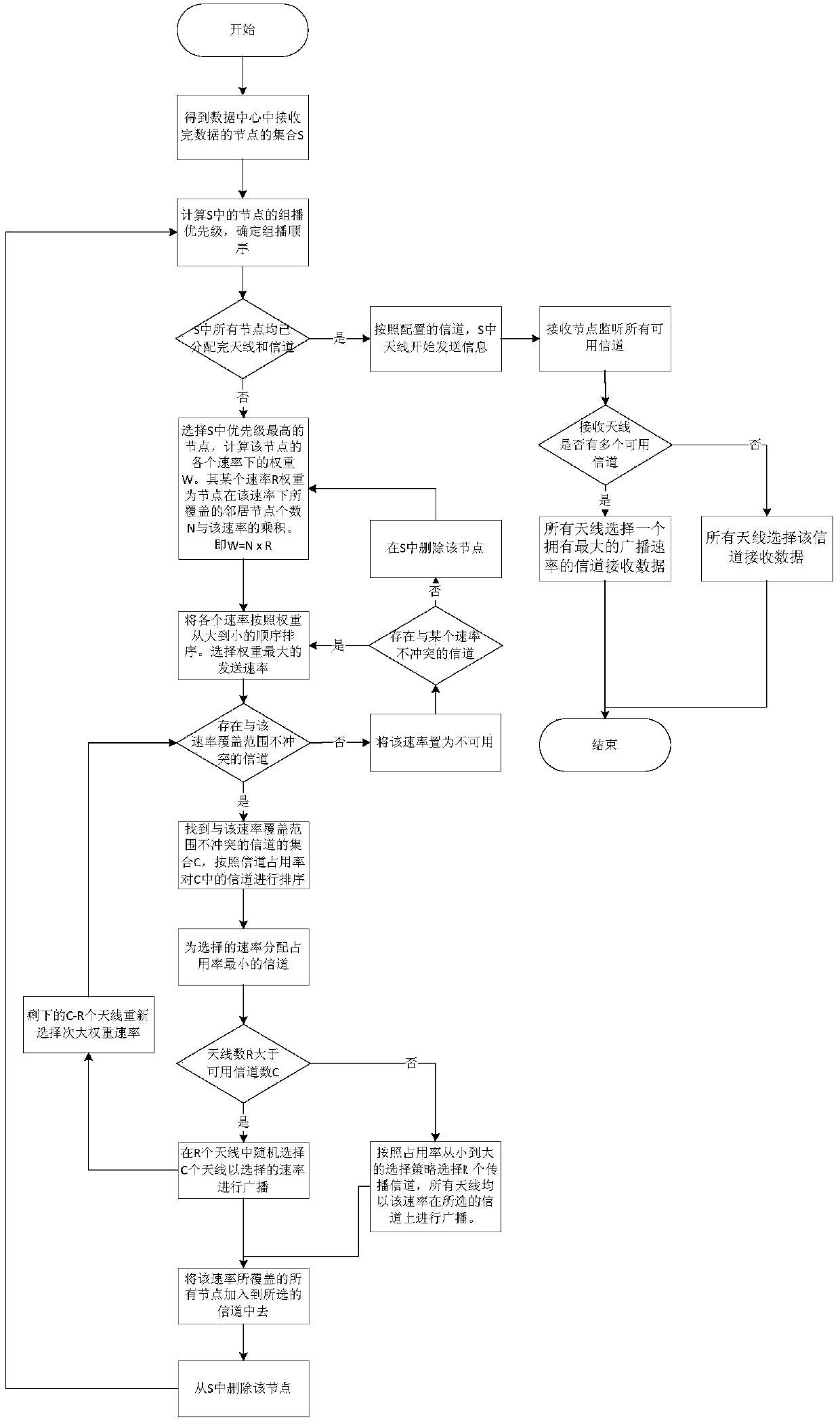
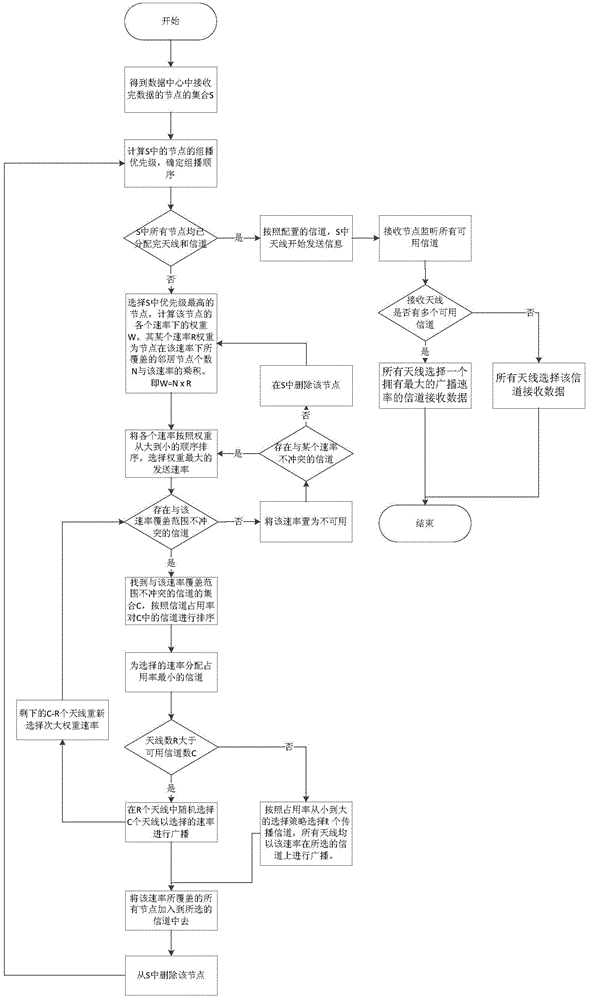
Multi-antenna configuration and channel distribution method applicable to wireless data center network
ActiveCN103997741AImprove throughputReduce transmission delayNetwork planningWireless transmissionData center
Disclosed is a multi-antenna configuration and channel distribution method applicable to a wireless data center network. The method includes the following steps: finding out all nodes which finish receiving of all data and using the nodes as nodes which are to send data in the next step; selecting a node which carries out data multicast most firstly and according to coverage ranges under different rates of the node, finding out an adjacent node set of the node, wherein the adjacent node set is effective in transmission under the rates, and obtaining a weight of each transmission rate through calculation; firstly, selecting a channel for a rate which has the largest weight; ranking channels, which do not conflict with the rate, in an aggregated-data center network; then according to the weights, distributing channels for antennae of all nodes which are to carry out multicast; and all antennae which obtain the channels sending data and reception nodes monitoring all available channels and carrying out reception according to the condition. The multi-antenna configuration and channel distribution method solves a problem of mutual matching of the antennae and the channels of a wireless data center and realizes free distribution of the different channels on the antennae of a fixed number so that the wireless transmission bandwidth in the data center network is improved to the largest degree.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
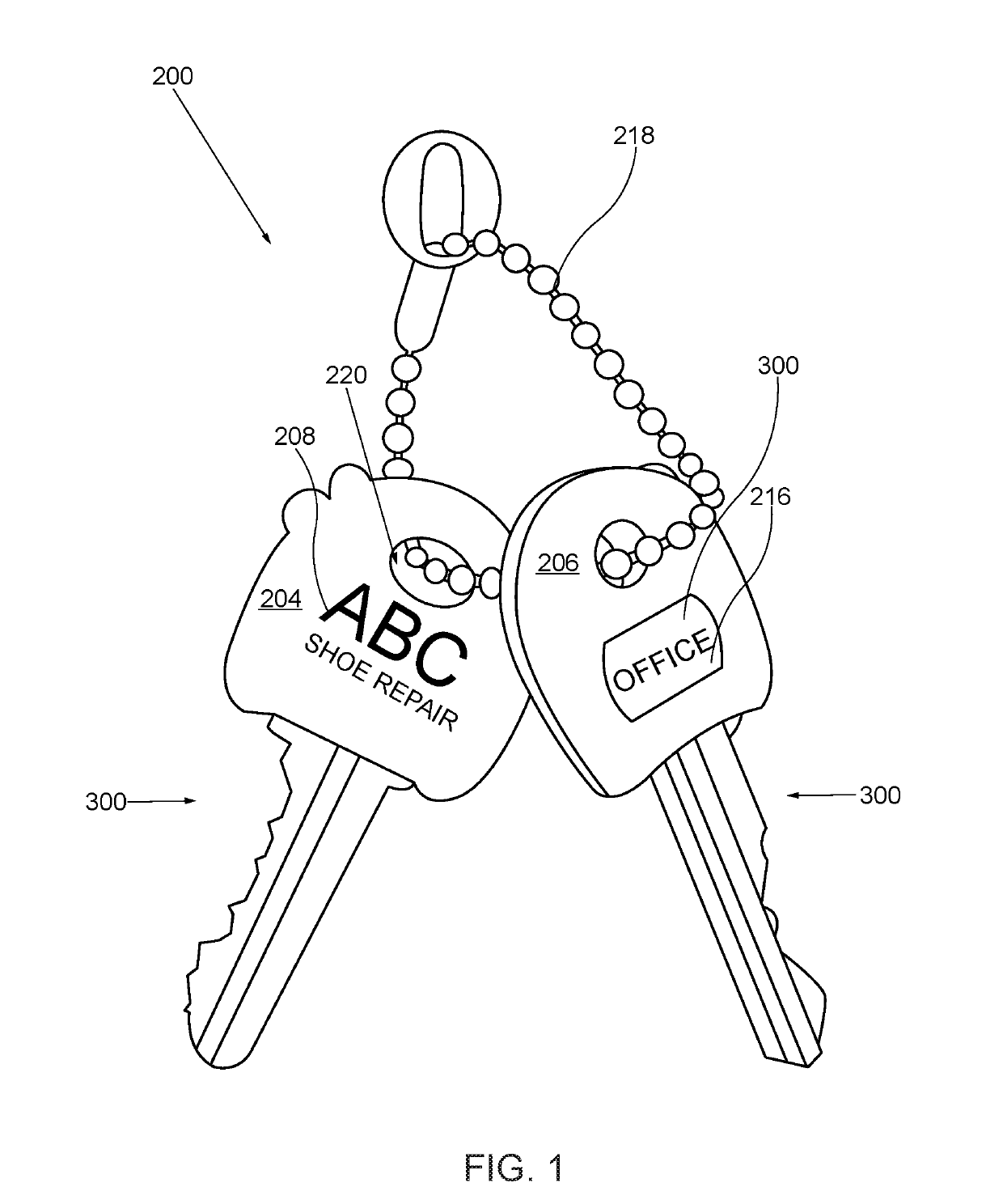
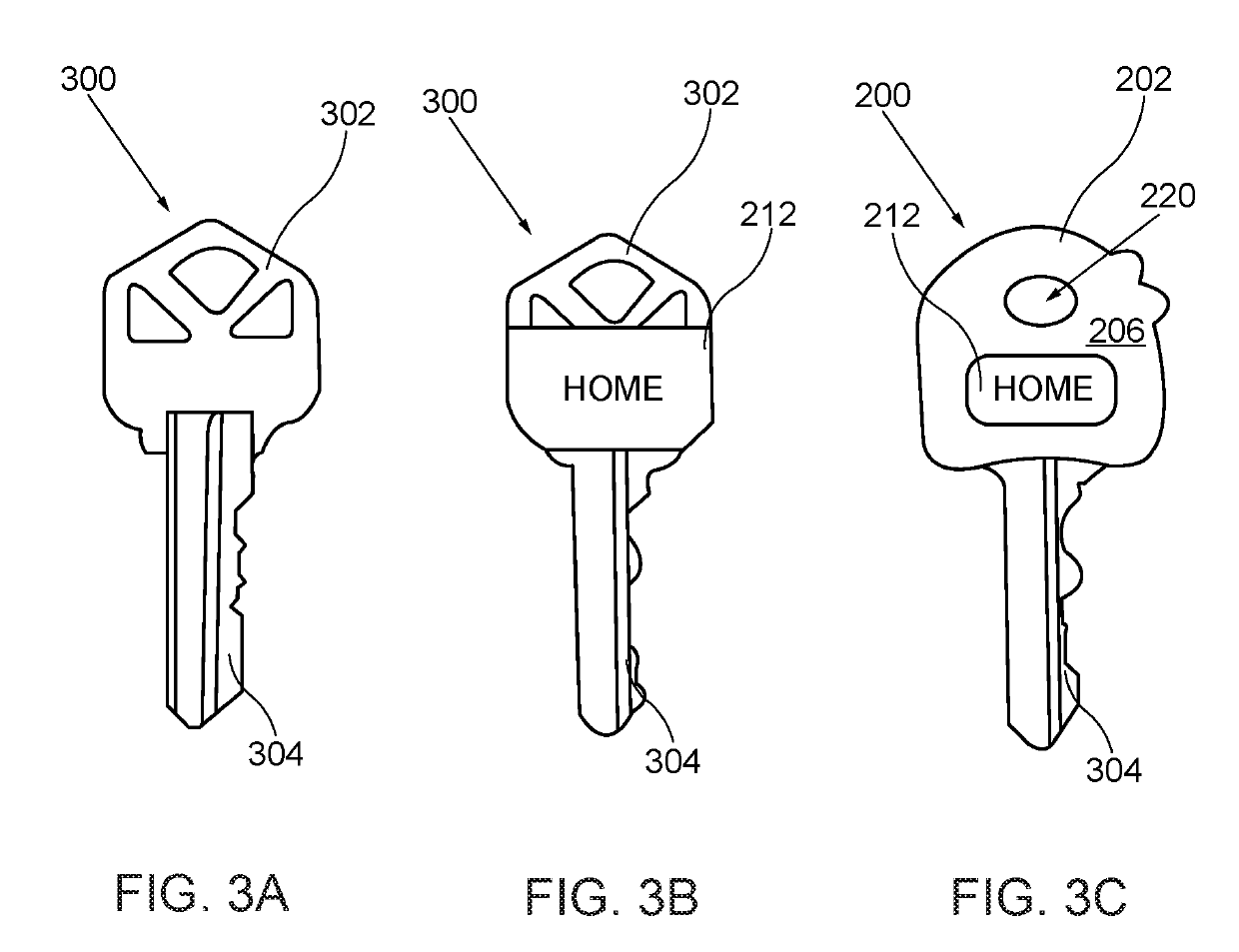
Key Labeling System and Method of Promotional Advertising through Distribution of Labeled Key Head Covers
InactiveUS20190139458A1Increase salesImprove overall revenueStampsData processing applicationsTrademarkEngineering
A key labeling system and method of promotional advertising through distribution of labeled key head covers enables free distribution of a labeled key head cover to potential consumers for personal use, whereby, the potential consumer frequently views advertisements, messages, and logos that display on the key. The method is also marketed to promotional catalogues. The labeled key head cover comprises a circular-shaped sleeve having a first face, a second face, an inner cavity for retaining the key head, a through opening to fit around the key head, and a resilient material fitting around the key head. The first face comprises a printed promotional indicia that can include: an advertisement, a contact identifier, a promotion, a trademark, a product name, a business name, and a logo. A gap forms in the second face of sleeve for receiving and viewing an insert label that can be marked and customized by the consumers.
Owner:LNK INNOVATIONS LLC
Neutral-point earth-free distributing network direct-to-ground capacitance current measuring method
InactiveCN100501419CAccurate measurementMeasurement results are stableCurrent/voltage measurementFault locationCapacitanceEngineering
This invention discloses a measurement method of the neutral earth-free distribution network towards the direct earth capacitance. It has such steps as injecting stable current signal from the open-delta of bus-bar potential transformer of the substation, measuring the open-delta voltage and the second star side-voltage. It detects the current of the direct earth capacitance of the distribution network according to the injected current signal and the measured voltage signal. This invention thoroughly avoids the influence of the short circuit of the open-delta of bus-bar potential transformer of the substation and the injected signal frequency toward the measuring result without changing the first connection and influencing the good running of the distribution network. It has such merits as safe, convenient, accurate and it completely settles the technical puzzle of the measuring accuracy of the short circuit of the open-delta of bus-bar potential transformer of the substation towards error current of the distribution network.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
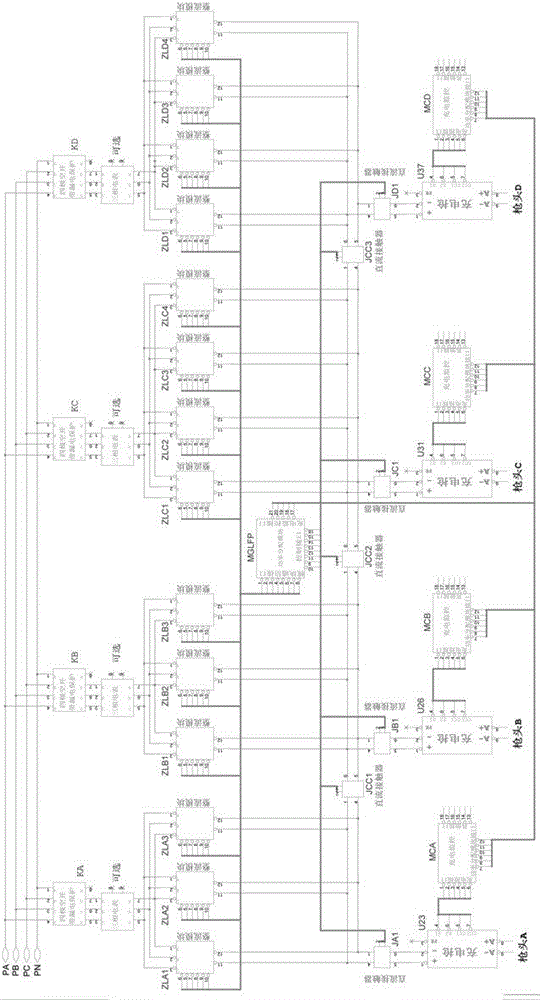
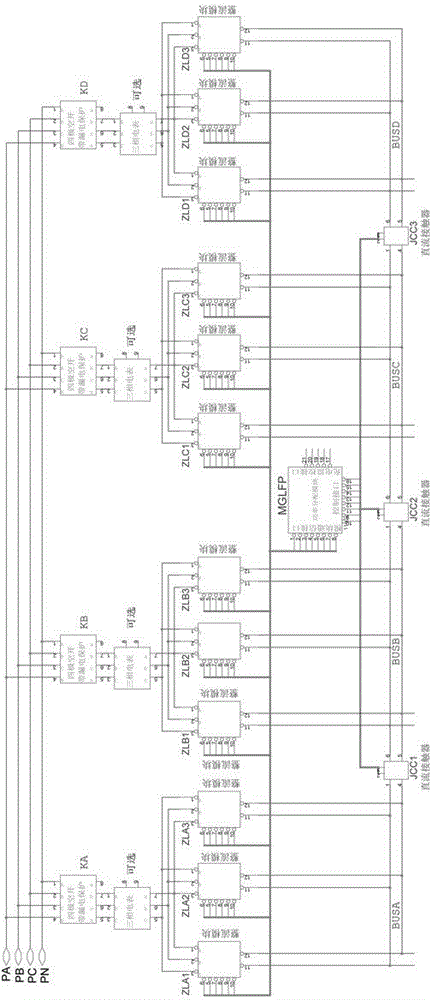
Intelligent power distribution method for multi-port quick charger
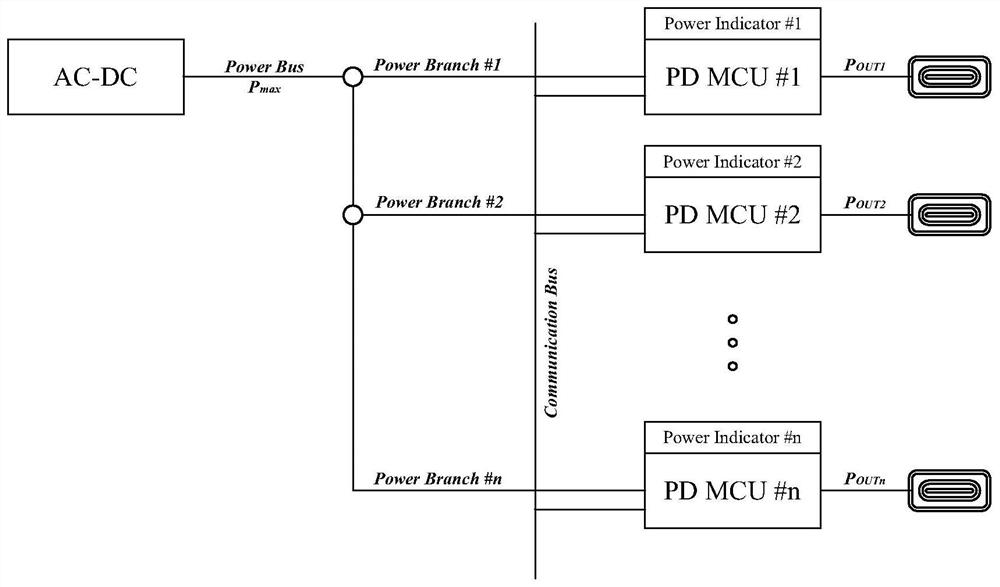
PendingCN114094662AOutput power distribution freelyBatteries data exchangeCircuit monitoring/indicationDistribution methodControl engineering
The invention provides an intelligent power distribution method for a multi-port quick charger. The method comprises the steps that the maximum power Pmax which can be distributed and is output by a preceding stage AC-DC of the multi-port quick charger and the number n of output ports are included, the multi-port quick charger comprises n MCUs with built-in PD controllers, the MCUs communicate with one another through communication buses, the output power of the n output ports is dynamically adjusted according to the following mode that when a new charging device i to be charged is connected to the output port i, the MCU corresponding to the output port i provides the actual output power Pii to the output port i according to the distributable power Pmax-sigma Pout and the charging requirement of the charging device i, and sigma Pout is the distributed output power. According to the invention, free distribution of output power of each port of the multi-port quick charger can be realized based on real-time multi-port charging power requirements according to mainstream quick charging protocol standards.
Owner:闪极科技(深圳)有限公司
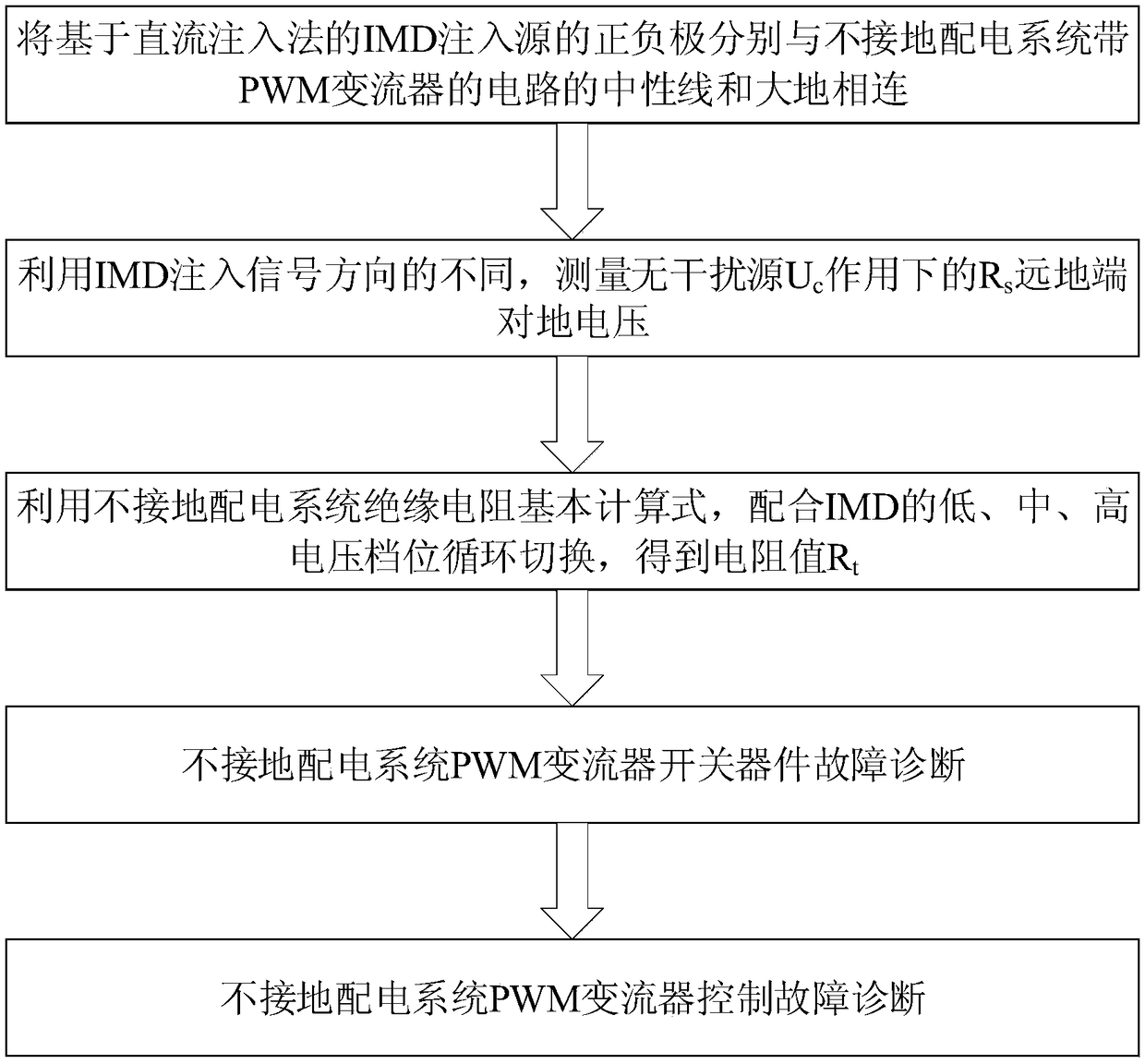
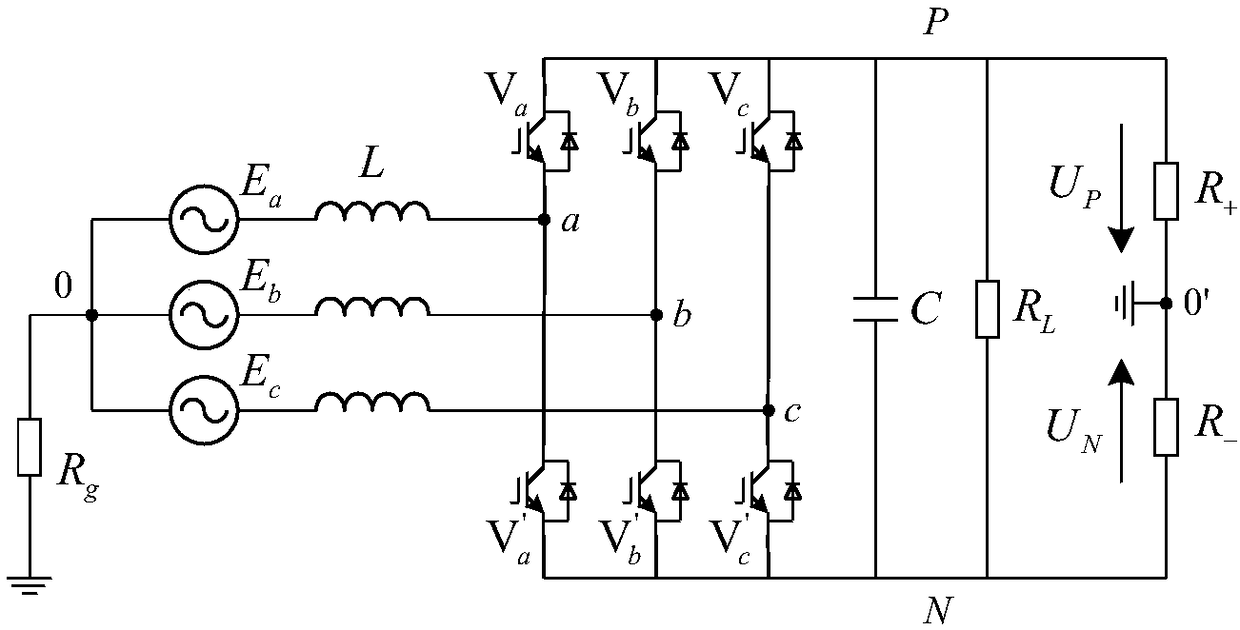
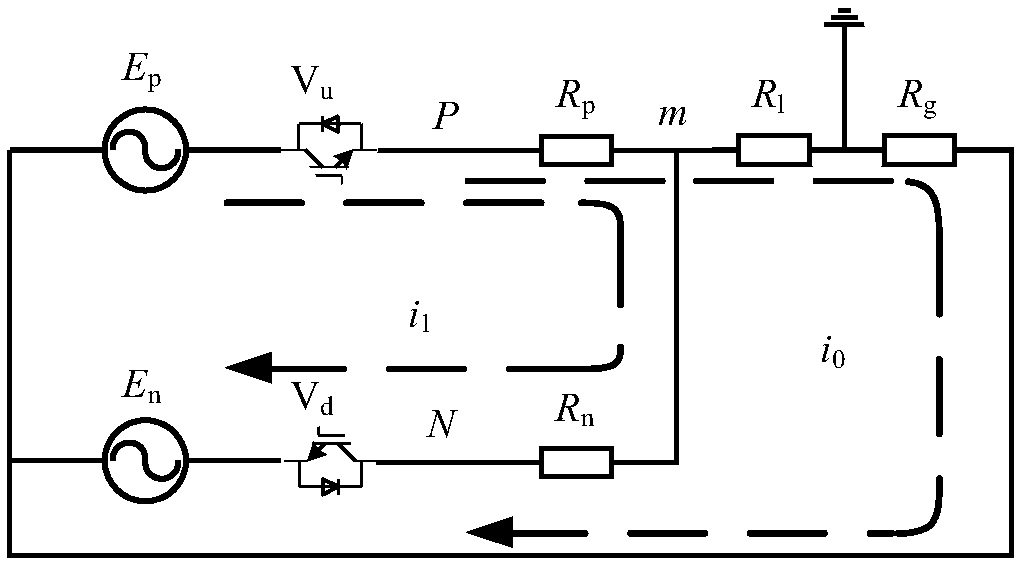
A Fault Diagnosis Method of PWM Converter Based on Insulation Monitoring Device and Chaotic Detection Circuit
ActiveCN106124978BEasy maintenanceEnsure safetyCircuit interrupters testingElectrical resistance and conductanceDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a PWM converter fault diagnosis method based on an insulation monitoring device (IMD) and a chaotic detection circuit. The method comprises: (a), a positive electrode and a negative electrode of an IMD injection source based on a direct-current injection method are connected with a neutral line and a ground of an earth-free distribution system with a PWM converter circuit respectively; (b), because of a difference of IMD injection signal directions, a far-side voltage to earth of a Rs without the effect of an interference source Uc is measured; (c), on the basis of a basic formula of an insulation resistor of the earth-free distribution system, cooperation with cyclic switching of low, medium, and high voltage gears of the IMD is carried out, so that a resistance value Rt; (d), a fault of a switching device of a PWM converter of the earth-free distribution system is diagnosed; and (e), a control fault of the PWM converter of the earth-free distribution system is diagnosed. According to the invention, with utilization of the insulation monitoring function of the IMD and the chaotic detection circuit, features of the fault of the switching device and the control fault of the PWM converter are extracted; and when a fault occurs at the converter or a fault degrades, the diagnosis can be carried out rapidly and system maintenance can be carried out conveniently.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
A multi-antenna configuration and channel allocation method suitable for wireless data center networks
ActiveCN103997741BImprove throughputReduce transmission delayNetwork planningTelecommunicationsWireless transmission
Disclosed is a multi-antenna configuration and channel distribution method applicable to a wireless data center network. The method includes the following steps: finding out all nodes which finish receiving of all data and using the nodes as nodes which are to send data in the next step; selecting a node which carries out data multicast most firstly and according to coverage ranges under different rates of the node, finding out an adjacent node set of the node, wherein the adjacent node set is effective in transmission under the rates, and obtaining a weight of each transmission rate through calculation; firstly, selecting a channel for a rate which has the largest weight; ranking channels, which do not conflict with the rate, in an aggregated-data center network; then according to the weights, distributing channels for antennae of all nodes which are to carry out multicast; and all antennae which obtain the channels sending data and reception nodes monitoring all available channels and carrying out reception according to the condition. The multi-antenna configuration and channel distribution method solves a problem of mutual matching of the antennae and the channels of a wireless data center and realizes free distribution of the different channels on the antennae of a fixed number so that the wireless transmission bandwidth in the data center network is improved to the largest degree.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Heat dissipating device, heat dissipating system and car
ActiveCN109854356AAvoid the problem of uneven heat dissipationEven heat dissipationCoolant flow controlMachines/enginesEngineeringFree distribution
The invention relates to the technical field of heat dissipaters, in particular to a heat dissipating device, a heat dissipating system and a car. The heat dissipating device comprises a plurality ofheat dissipating pipes and at least one multi-way valve. Each multi-way valve comprises at least two first openings and i second openings. The first openings are used for being connected with a cooling pipeline of a heating device. The second openings communicate with the heat dissipating pipes through connecting pipes correspondingly. The interior of each multi-way valve is divided into multiplemutual independent areas. Each area communicates with at least one first opening and n second openings, wherein n is equal to 0, 1 to i, and i is an integer not smaller than 2. When a certain loop requires for the large heat dissipating amount while the other loop requires for the small heat dissipating amount, by means of the multiple mutual independent areas divided in the interior of each multi-way valve, free distribution of the heat dissipating pipes in the loops can be achieved, and then difference of flow of cooling liquid of the cooling loops of the whole heat dissipating device is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY AUTOMOBILE RES INST CO LTD +1
Method for dendroctonus armandi disorientation control by pheromones
InactiveCN110419515AAvoid gatheringSolve the difficult problems of field control during the raising periodBiocidePest attractantsPaleontologyDendroctonus armandi
The invention discloses a method for dendroctonus armandi disorientation control by pheromones. The method includes the steps: dividing an armandi distribution area into an affected area, an unaffected area and an armandi-free distribution area in an emergence period of dendroctonus armandi; preparing host plant volatiles and dendroctonus armandi aggregation pheromones into attractants; suspendinga slow-release bottle with the attractants in the armandi-free distribution area; preparing anti-aggregation substances by taking anti-aggregation pheromones and organic matter liquid without attracting and avoiding functions for the dendroctonus armandi as solvents. By combined use of the aggregation pheromones and the anti-aggregation pheromones, the efficiency of the dendroctonus armandi harming healthy armandi is effectively reduced, and the problem of difficulty in field control of the dendroctonus armandi in the emergence period is solved. By comprehensively using three identified aggregation pheromone substances of the dendroctonus armandi, the efficiency of trapping and attracting the dendroctonus armandi is improved, and the dendroctonus armandi is disorientated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A multi-head high-power DC charging pile system
ActiveCN105990883BImprove general performanceLow costBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system. The multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system comprises rectification units, charging guns, electric monitoring units and a power distribution module, wherein the number of the charging guns is 2 or more than 2; the number of the rectification units are corresponding to the number of the charging guns; the power distribution module is connected with each rectification unit and each charging gun; each charging gun is connected with the power distribution module through a charging monitoring unit. The multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system is not only provided with a plurality of charging guns, but also is provided with the power distribution module, so that free distribution of the charging power for each charging gun is realized. For the multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system, the plurality of gun heads can charge multi kinds of vehicles at the same time, such as a large vehicle, a mini-bus and a small vehicle. Practice has proved that the multi-gun-head large power direct current charging pile system has the advantages of being high in practicability, reliability and universality, saving the cost and the space, being high in the utilization rate, and being low in investment.
Owner:肖伟
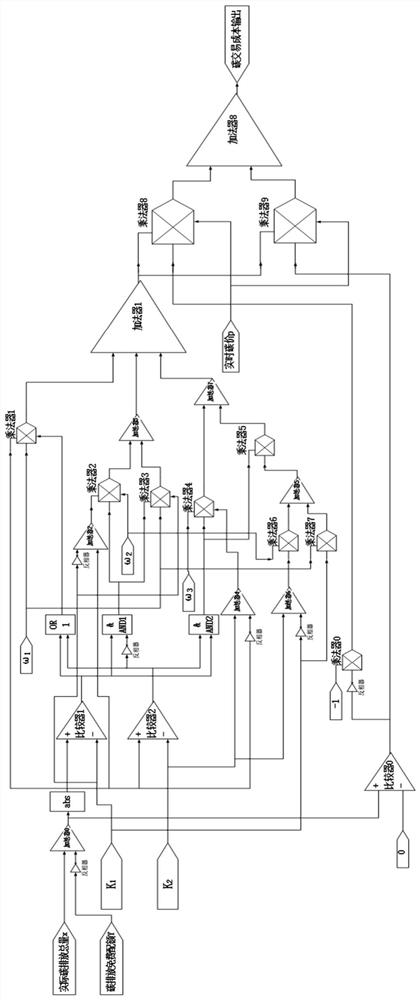
Multi-energy system stepped carbon transaction mechanism design method and system
PendingCN114358890APromote transformation and developmentHigh feasibilityBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMarketingCarbon emission tradingProcess engineering
The invention discloses a multi-energy system stepped carbon transaction mechanism design method and system, and the method comprises the steps: employing the difference value between the actual carbon emission of a multi-energy system and the free quota carbon emission in a certain range, and carrying out the calculation of a new round of free distribution quota before the distribution of a new round of free distribution quota; according to the relative value of the actual carbon emission amount and the free quota carbon emission amount, the stepped trading transaction of the carbon emission permit can be carried out, and the carbon emission condition of the multi-energy system after the end of a distribution period is cleared. And when the relative value of the actual carbon emission and the free quota emission is greater than a certain set value, transaction is carried out at the market carbon price according to a certain weight, and when the relative value is greater than another set value, transaction is carried out at the market carbon price according to a new weight, so that stepped transaction is realized. The method is provided for the multi-energy system to participate in the carbon emission trading market, practicability and guidance are high, and the multi-energy system can be promoted to be transformed and developed towards the low-carbon direction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAYUN ELECTRIC POWER ENG DESIGN CONSULTATION CO LTD
Inner wave-riding turbine-based combined power inlet with binary variable geometry
ActiveCN104632411BImprove flow coefficientSmall flow coefficientGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsThroatPunching
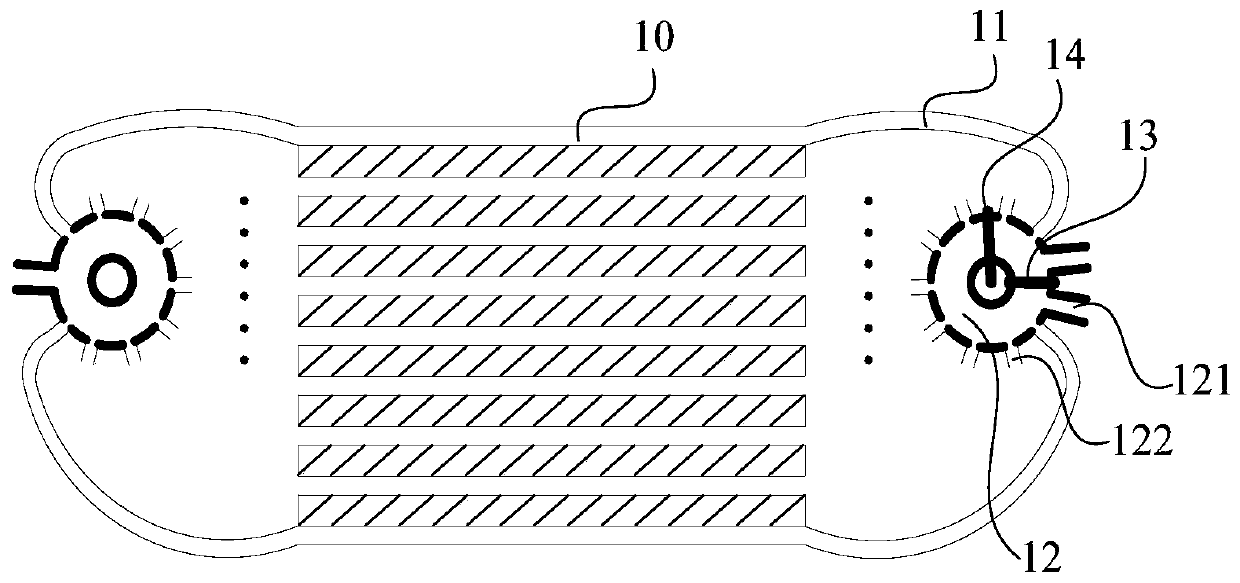
The invention discloses an internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet adopting a binary variable-geometry manner. The internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet structurally comprises a gas inlet internal waverider compression section 1, a throat section 2, an expansion and distribution section 3, a punching channel 4, a turbine channel 5, a fixed-geometry three-dimensional internal waverider compression representing section 6, an adjustable internal waverider compression representing section 7, an adjustable internal waverider compression section representing variable-geometry compression surface 8, an adjustable expansion representing section 9, a sharp point-free distribution representing section 10, a machine body proximity representing movable upper arm 11, a movable upper arm driving representing servo action cylinder 12, a distribution representing plate 13, an internal waverider-derived fixed-geometry representing profile 14 and a distribution representing cross section 15. The internal waverider-derived turbine base combined dynamic gas inlet has the advantages of small outer resistance, high flow coefficient, good airflow quality and the like; meanwhile, profile deformation and distribution plate deflection caused by compression in a three-dimensional internal waverider manner can be controlled by only two regulating parameters, the deformation is convenient and reliable, and the requirement on an acting servo device is relatively easily met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com