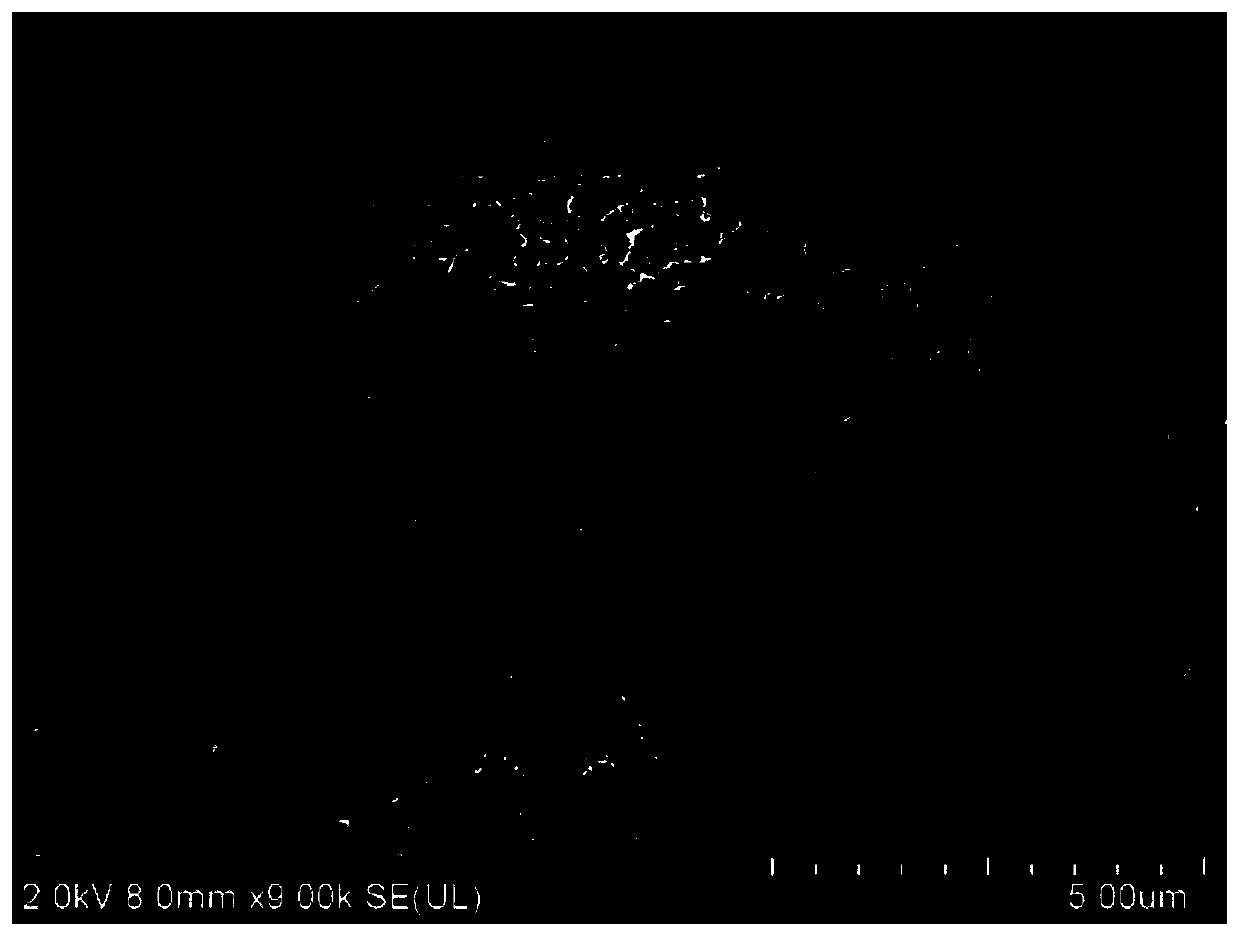
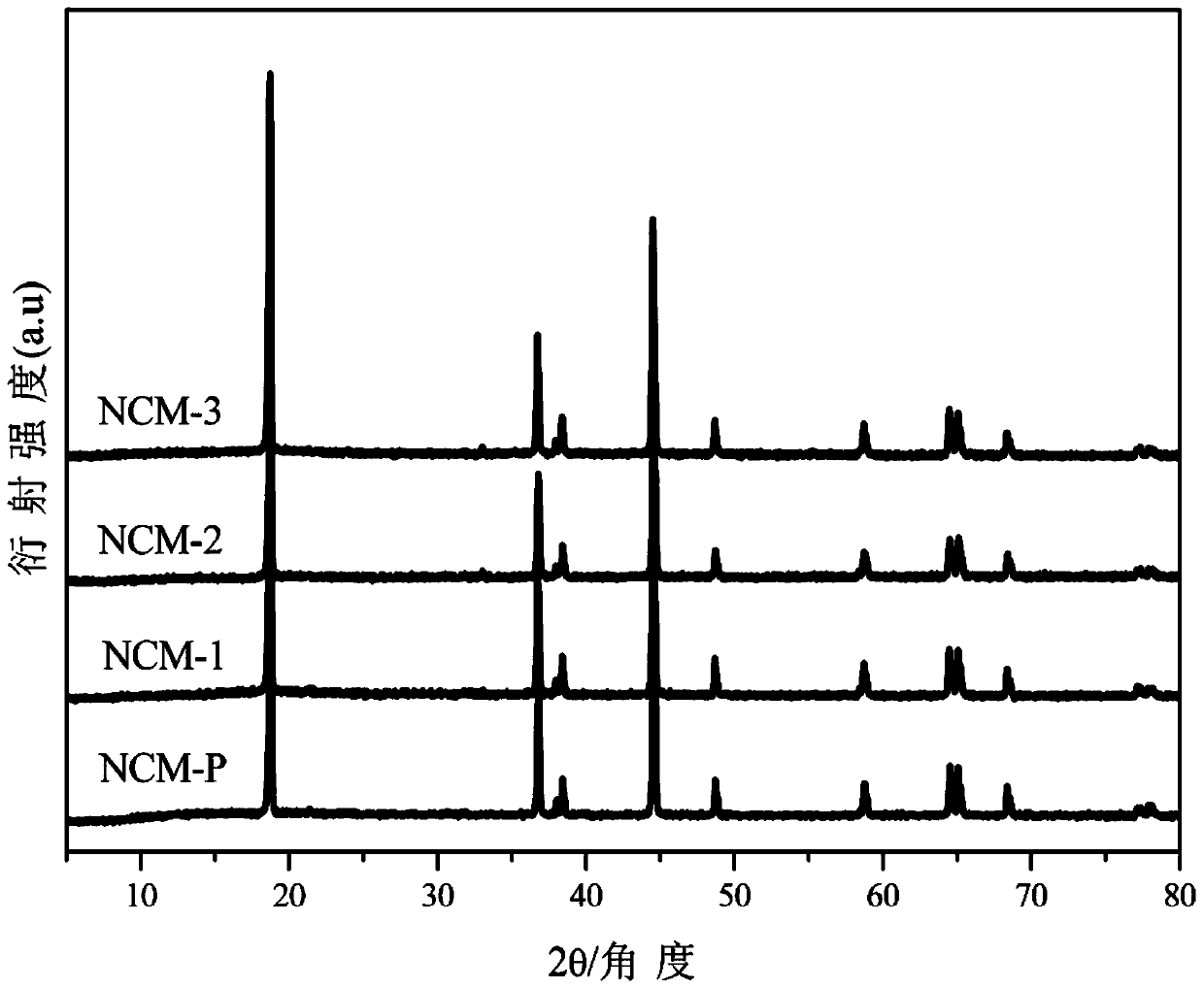
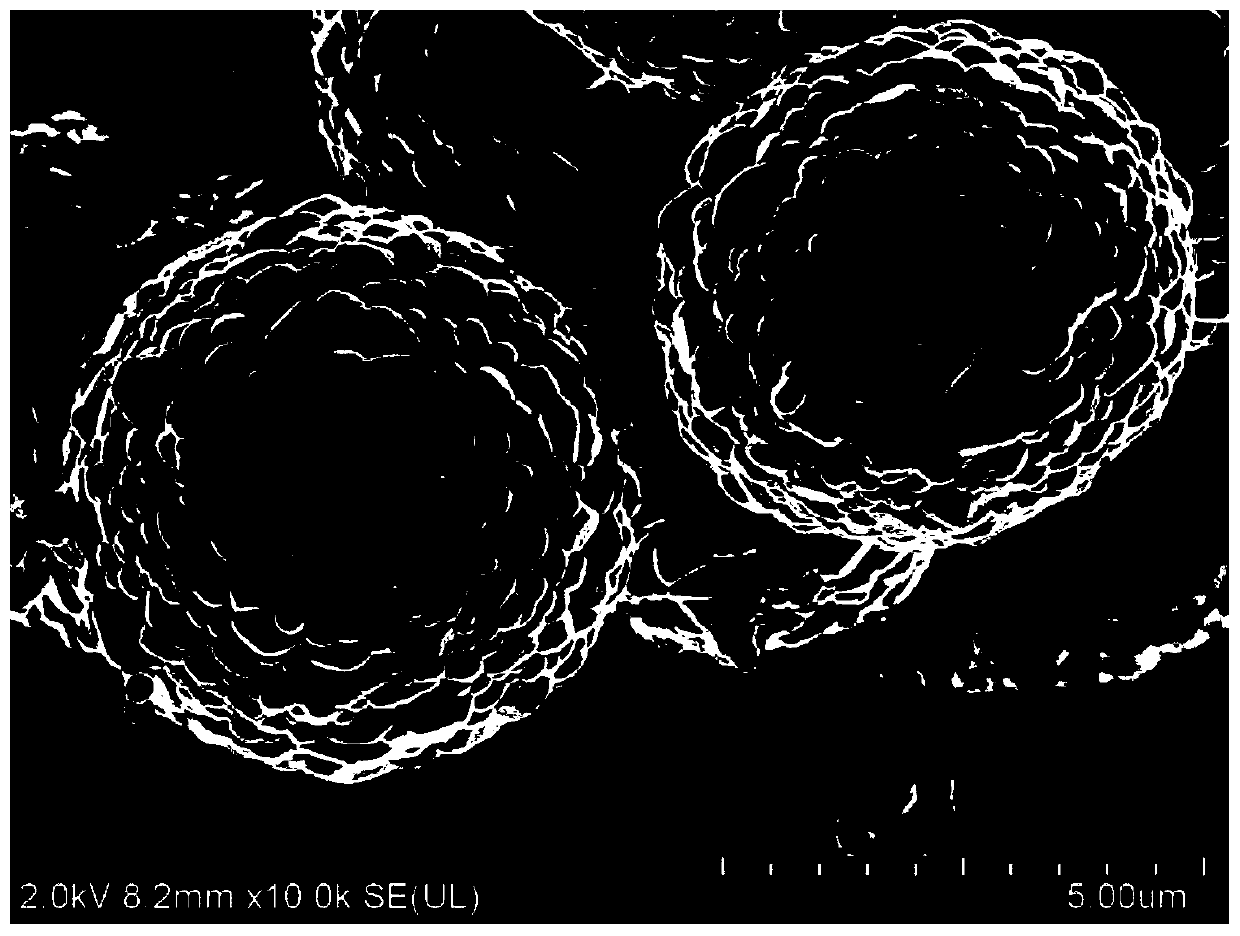
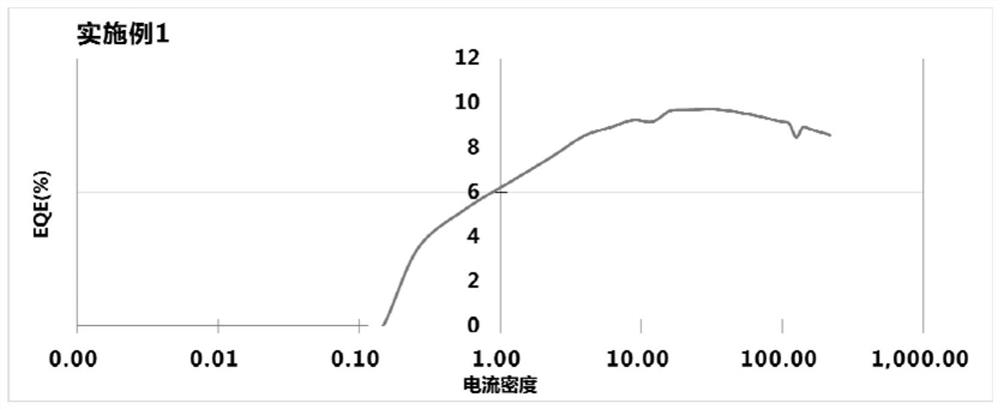
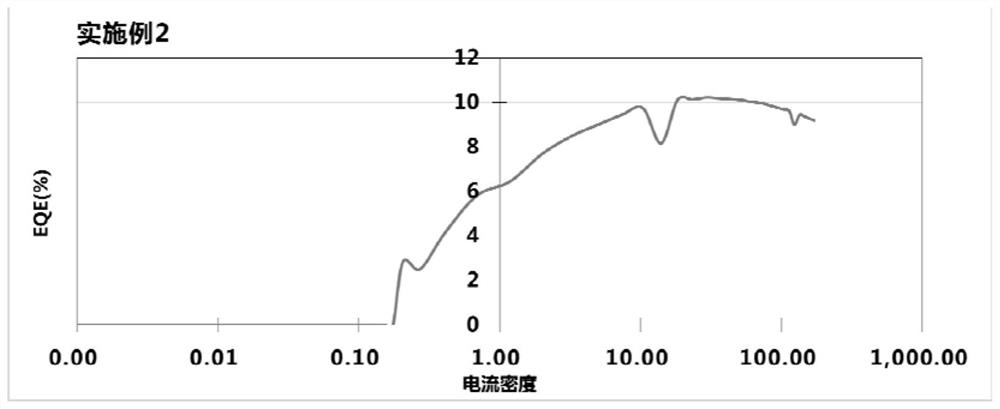
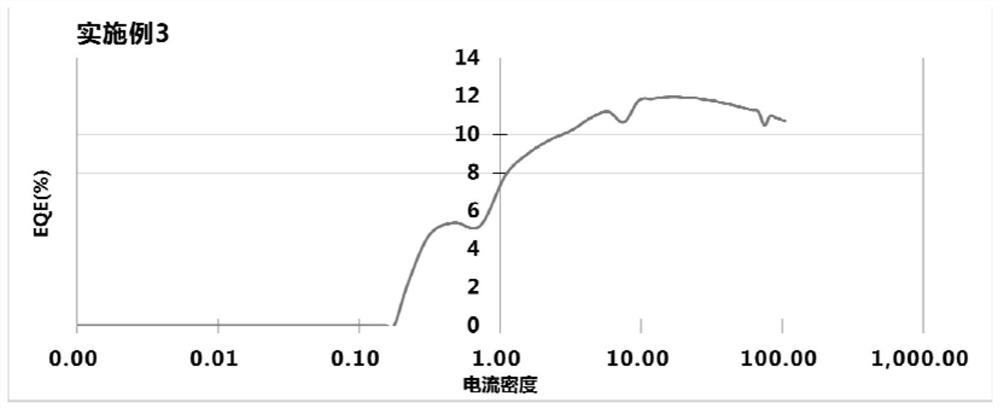
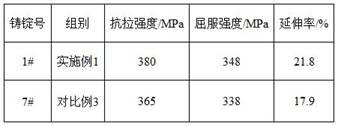
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Cd element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
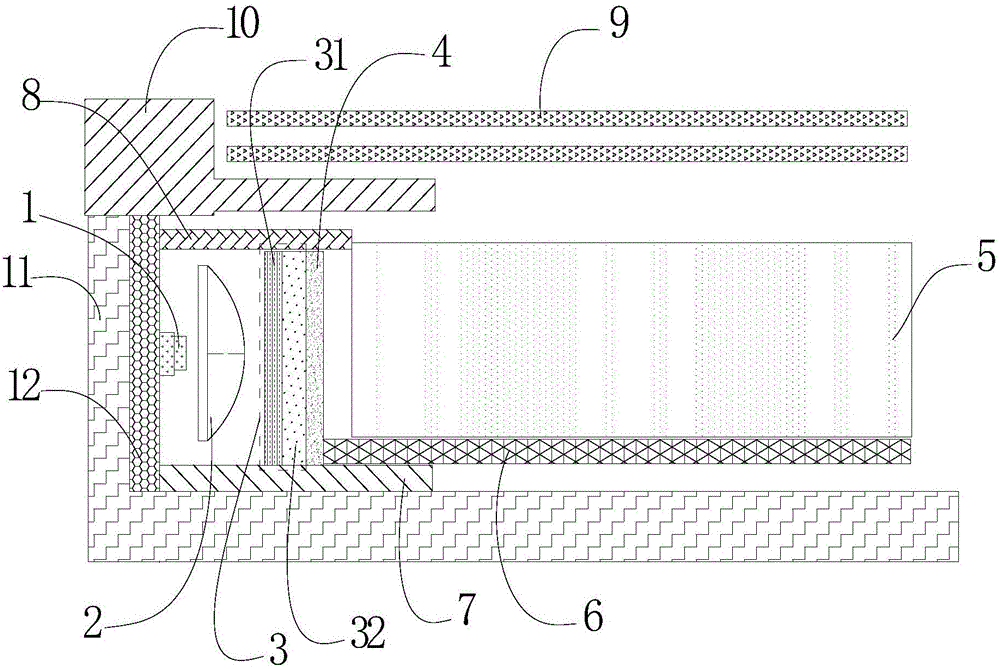
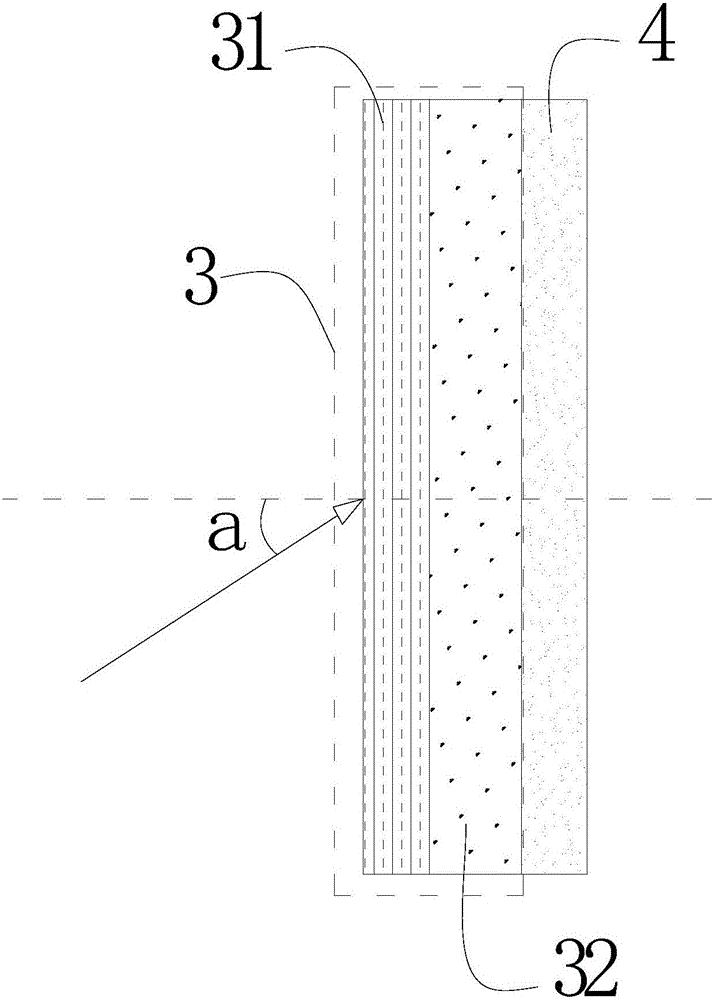
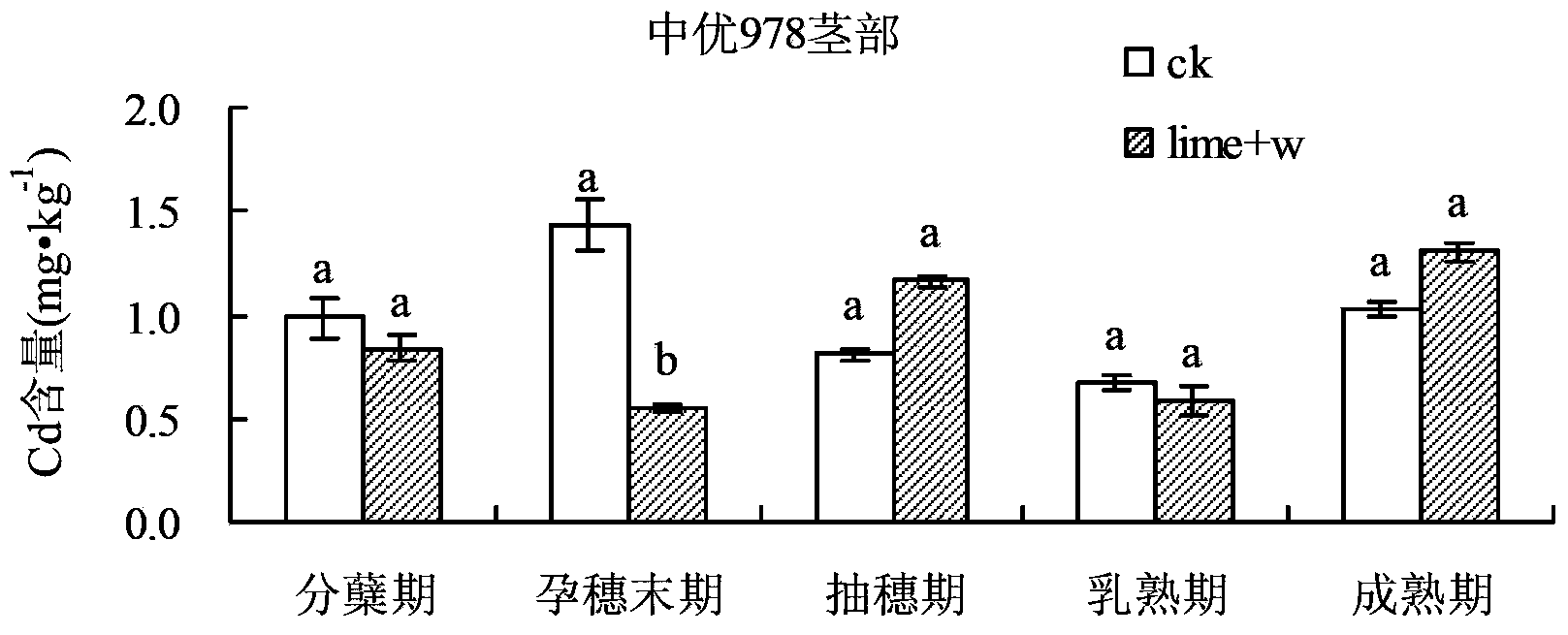
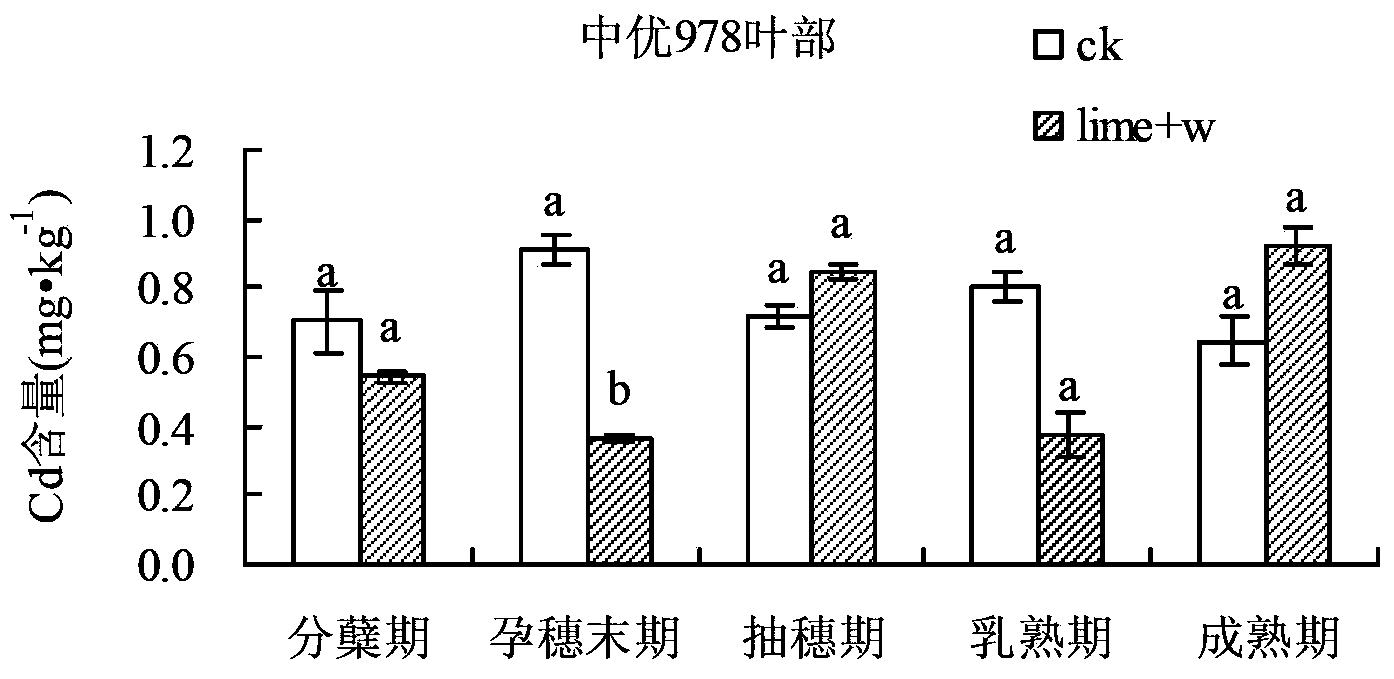
Method for comprehensively controlling cadmium pollution of rice by utilizing modifier and agricultural technology
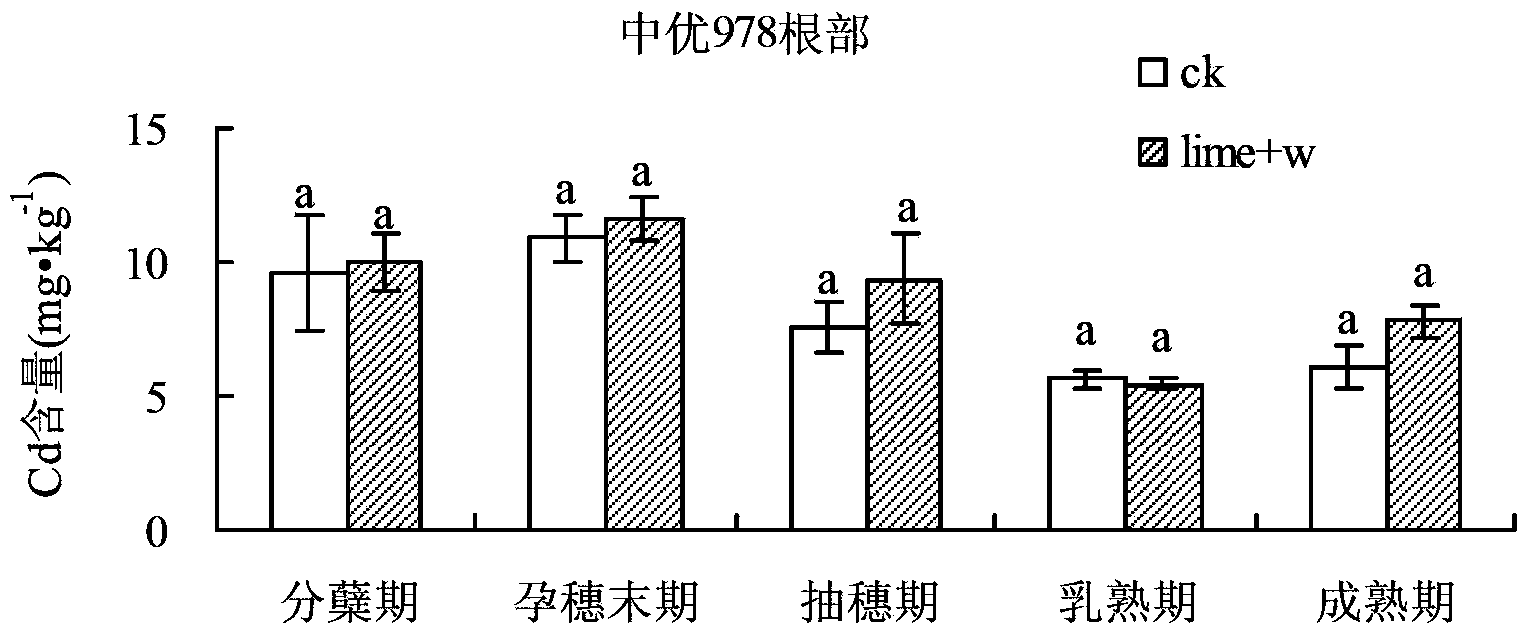
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively controlling cadmium pollution of rice by utilizing a modifier and an agricultural technology. The method comprises the steps of irrigating a rice field at the final booting phase of the rice, keeping a water layer of 2-3 cm on a field surface, broadcasting 60 Kg quicklime per mu into water uniformly, and keeping a waterflooding state of the field till the field is dried or drained by nature transpiration and evaporation 5 days before harvesting. With the adoption of the method, Cd elements in soil are gathered at inedible parts of the rice, such as a root, a stem and a leaf, so that the Cd accumulation amount at a grain part is reduced significantly; the Cd elements are effectively prevented and controlled from migrating to the rice; and the Cd content in the rice is reduced.
Backlight module and liquid crystal displayer
InactiveCN106125403AEnhanced color saturationStrong penetrating powerNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayGamut
The invention provides a backlight module and a liquid crystal displayer. The backlight module comprises an LED light source, a collimating lens, a plurality of layers of optical film light filters, a diffusion layer, a light guide plate, reflector plate, an adhesive frame and a back plate, wherein the collimating lens is used for adjusting light emitted by the LED light source to be light within the preset angle range and enabling the light to be emitted out from the surface; the optical film light filters are used for enabling light with the preset wavelength range to pass and filtering out light which is not within the preset wavelength range. The liquid crystal displayer can reach the color gamut equal to that of an existing Cd element quantum dot liquid crystal displayer, and achieve the purpose of being green and free of Cd elements.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
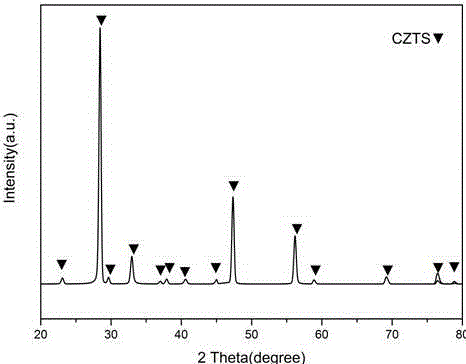
Method for preparing CZTS thin film solar cell based on full vacuum method
InactiveCN105304763ACreate pollutionAvoid pollutionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWater bathsRadio frequency magnetron sputtering
The invention discloses a method for preparing a CZTS thin film solar cell based on a full vacuum method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) after magnetron sputtering, vulcanizing to prepare a CZTS thin film absorbing layer; 2) preparing 50-100nm CdS thin film buffer layer on the absorbing layer through radio frequency magnetron sputtering and then preparing 50-100nm intrinsic ZnO and 400nm Al:ZnO through radio frequency magnetron sputtering; and 3) finally preparing 2mu m Ni / Al electrode through evaporating. The traditional water bath method for preparation of the CdS film has the main defect that since waste water containing Cd (a toxic element) is generated in the preparation process of the CdS thin film, cost is largely increased in the process of waste water treatment, and ammonium hydroxide used in the process of sedimentation has volatility and toxicity and is harmful to human health, and in addition the volatility of ammonium hydroxide can change the pH value of a solution and further influences the property of the buffer layer. The sputtering method does not cause the pollution of waste water containing the Cd element, which occurs after the implementation of the water bath method; therefore, the sputtering method is friendly to the environment and is suitable for online preparation of thin film cells; in addition, the whole preparation process is carried out in vacuum and therefore the possibility of external impurity contamination to the thin film is very small.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for comprehensively controlling cadmium pollution of rice by utilizing modifier and agricultural technology
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively controlling cadmium pollution of rice by utilizing a modifier and an agricultural technology. The method comprises the steps of irrigating a rice field at the final booting phase of the rice, keeping a water layer of 2-3 cm on a field surface, broadcasting 60 Kg quicklime per mu into water uniformly, and keeping a waterflooding state of the field till the field is dried or drained by nature transpiration and evaporation 5 days before harvesting. With the adoption of the method, Cd elements in soil are gathered at inedible parts of the rice, such as a root, a stem and a leaf, so that the Cd accumulation amount at a grain part is reduced significantly; the Cd elements are effectively prevented and controlled from migrating to the rice; and the Cd content in the rice is reduced.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Eu<3+> doped tellurate high density scintillating glass and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an Eu<3+> doped tellurate high density scintillating glass and a preparation method thereof. The high density scintillating glass comprises the following components: TeO2, ZnO,Lu2O3 and Eu2O3. The oxides are high density compounds, and the glass prepared by high temperature melting method has a density of greater than 6 g / cm<3>. Compared with high density glass containingPb, Cd and other heavy metal elements, the glass prepared by the method provided by the invention does not contain high-pollution heavy metals Pb and Cd elements, and is more environmentally friendly.High density Lu2O3 is taken as the glass raw material, the glass density is improved and the radiation resistance of the glass is enhanced. The high density scintillating glass prepared by the methodprovided by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation method, low production cost, high glass density, and strong scintillation light output.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Bearing and preparation technology thereof
ActiveCN107965522ASimple internal structureImprove mechanical propertiesBearing componentsHigh resistanceMetallic materials
The invention discloses a bearing and a preparation technology thereof, and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. The bearing comprises 0.05%-0.07% of Cd, 0.5%-1.5% of Mn, 0.4%-0.8% of C,0.08%-0.12% of Tl, 0.01%-0.05% of Cu, 0.03%-0.07% of Co and the balance Fe and impurities. The Cd element in raw materials can react with Cu in the materials to form hard copper alloy phases dispersed in steel, so that the tensile strength and abrasion resistance of alloy steel are improved obviously. Tl is very important for the alloy steel, not only the alloy strength can be improved, but alsothe alloy hardness and the corrosion resistance of the alloy can be improved, and the Tl is essential for the effect of prolonging the service life of a product. Meanwhile, with the method that the bearing body is combined with polymer layers outside the bearing body, the product has extremely high resistance in complex and variable environment.
Owner:宁波恒力汽配轴承有限公司
Method for rapidly decomposing high silicon dioxide Cd polluted rice soil
InactiveCN106950097AIncrease contentDigestiblePreparing sample for investigationHydrofluoric acidDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for rapidly decomposing high silicon dioxide Cd polluted rice soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) naturally airing a soil sample to a constant weight; (2) sieving a ground soil sample, and sampling the sieved soil sample; (3) adding a to-be-tested soil sample; (4) adding deionized water to wet the soil sample; (5) adding concentrated nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid and perchloric acid for decomposition, and mixing with deionized water, wherein 18%-22% hydrofluoric acid is 40%-45% of volume of a system; and (6) decomposing according to a decomposing procedure. By utilizing the method, the high silicon dioxide Cd polluted rice soil can be rapidly decomposed. Compared with a national standard, the decomposing time is saved by 1.5 hours, and meanwhile, the overnight soaking is omitted. According to the method, technical reference is provided for determining the content of a Cd element in the rapidly decomposed high silicon dioxide Cd polluted rice soil.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT +1
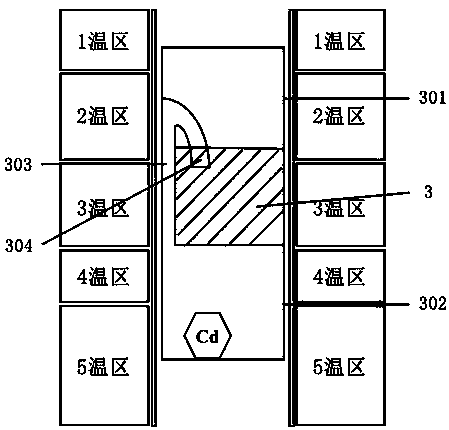
CdGeAs2 single-crystal growing method capable of compensating for cadmium element
InactiveCN108930059AIncrease usable volumeEvenly distributedPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsVertical gradientSingle crystal growth
The invention discloses a CdGeAs2 single-crystal growing method capable of compensating for a cadmium element. The method adopts a vertical gradient freeze (VGF) growth device to control the growth process of a CdGeAs2 single crystal compensated by the Cd element, the VGF growth device comprises a single-crystal growth crucible composed of a quartz raw material crucible and a flat-bottom quartz crucible and a five-temperature zone growth furnace, the quartz raw material crucible part is set as a crystal growth area, the flat-bottom quartz crucible is set as an element compensation area, the element compensation area is located at the lower part of the single-crystal growth crucible, and the two areas communicate with each other through an element compensation tube located on the side wallof the growth crucible; and CdGeAs2 and Cd raw materials are put in the two-layer crucible, growth temperature of the CdGeAs2 single crystal is controlled in different temperature zones and steps, andthe Cd element is compensated in the single-crystal growth process, so that the Cd element located at the head and tail ends of the crystal is uniformly distributed, the problem of non-uniform single-crystal performance caused by inconsistence of the Cd element is solved, an effective use volume of the single crystal is increased, and growth costs of the CdGeAs2 single crystal are reduced.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST
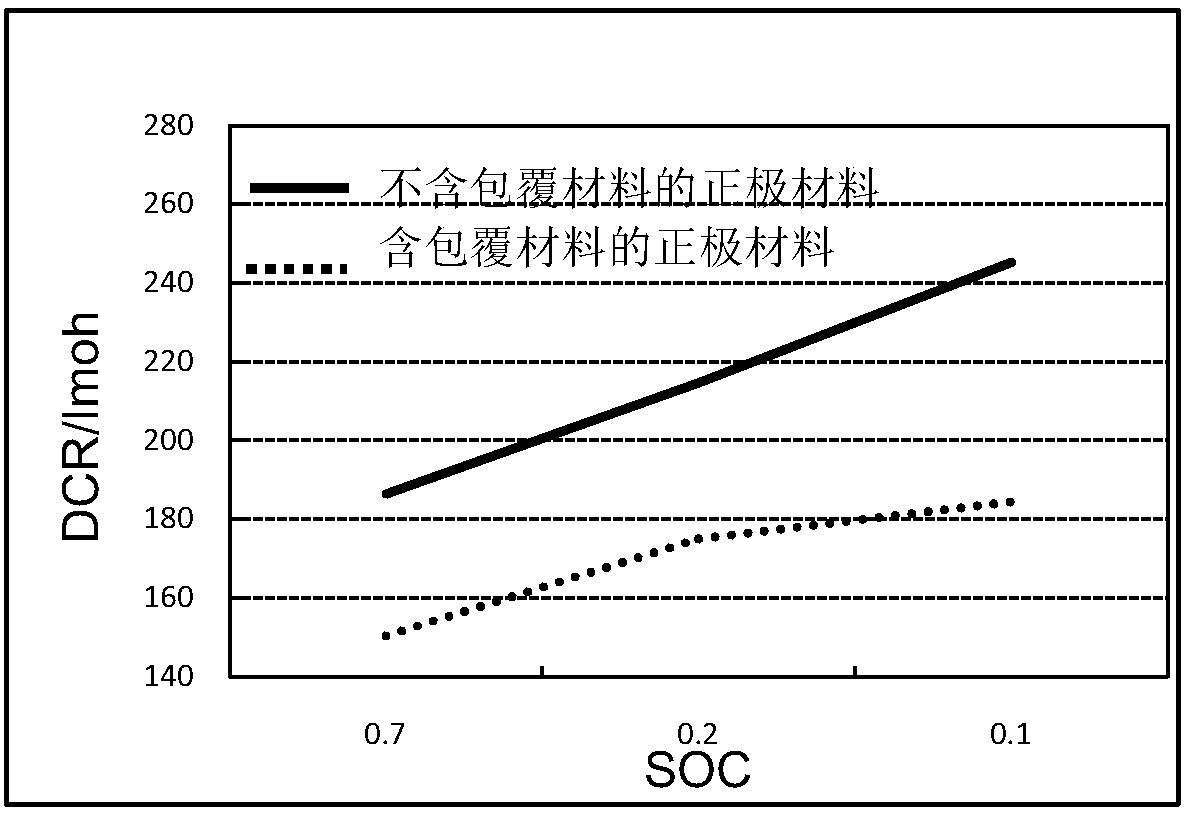
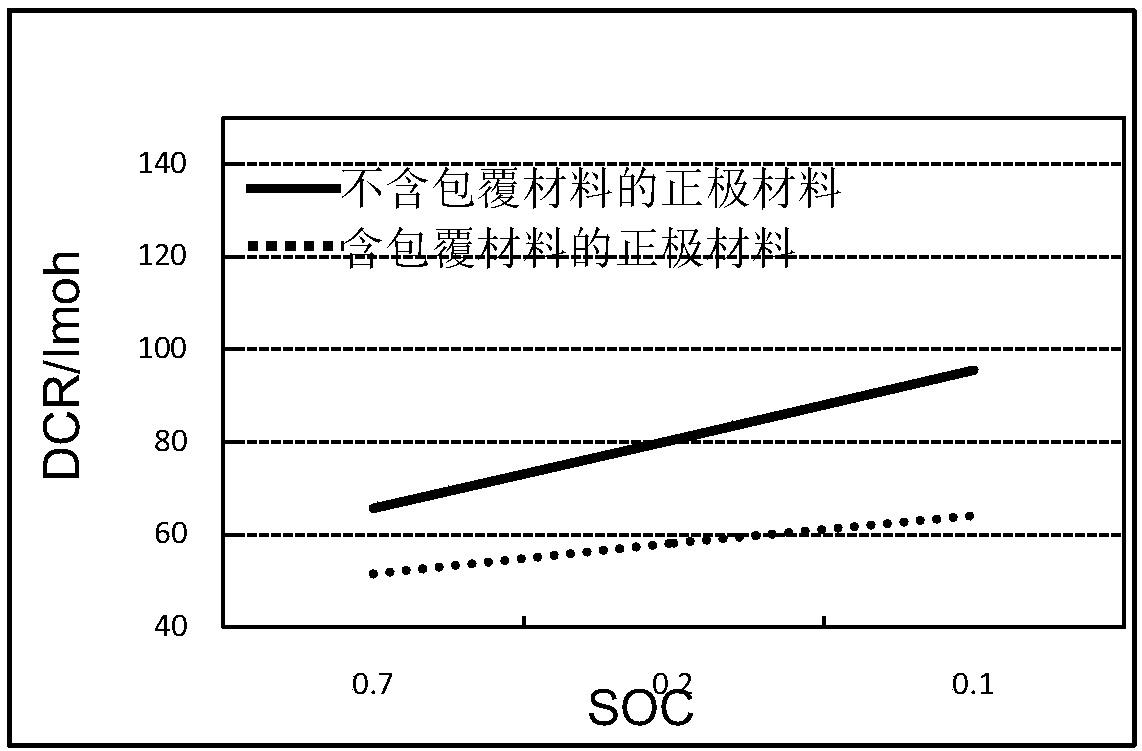
Positive electrode material, preparation method thereof, battery positive electrode, and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN110098383AReduce DCRImproved magnification performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithium-ion batteryBattery cell
The application provides a positive electrode material, a preparation method thereof, a battery positive electrode, and a lithium ion battery. The positive electrode material includes an active material; a coating material coating the active material and comprising at least one of LitAP2O7, wherein 1 <= t <= 2, and A is selected at least one of the group including Gd, V, Co, Fe, Mn, Ba, Sr, Zn, Ti, Mg, Ni, La, Ce, and Cd elements. The inventor discovers that the positive electrode material has a low DCR and the structure of LitAP2O7 contributes to the de-intercalation of Li+, so that the positive electrode material has a good ion guiding ability, good stability, good cycle performance, good first discharge capacity and good use performance.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
Battery cathode material precursor, battery cathode material as well as preparation method and application of battery cathode material precursor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a battery cathode material precursor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving Ni-based nitrate, Co-based nitrate, Mn-based nitrate and Cd-based nitrate in absolute ethyl alcohol, so that mixed solution is obtained; performing solvothermal reaction on the mixed solution, so that Ni, Co, Mn and Cd elements are co-precipitated;and performing post treatment on the obtained precipitates, so that a Ni-Co-Mn-Cd-based battery cathode material precursor is obtained. The preparation method disclosed by the invention utilizes the characteristic that four elements, namely Ni, Co, Mn and Cd, are similar in Ksp, a solvothermal method is utilized for co-precipitating the four elements in a solvothermal synthesis process, so that the Ni-Co-Mn-Cd-based battery cathode material precursor is obtained, and then a Cd doped ternary battery cathode material is synthesized by virtue of a high temperature solid phase roasting method. Cdis taken as an inactive element with good conductivity, and a structure of the material can be stabilized and electronic conductivity of the material can be improved after the Cd is doped.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
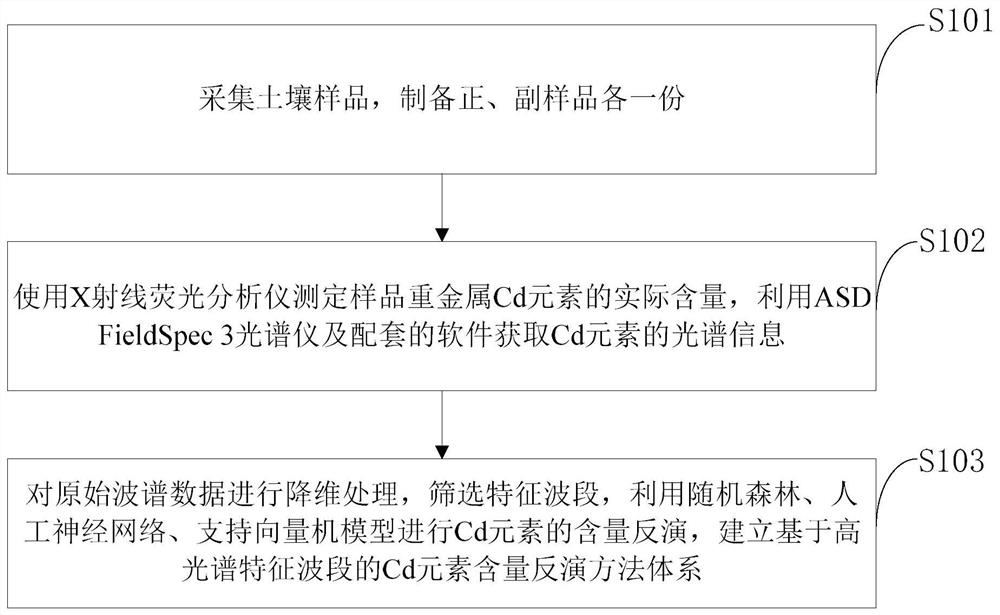
Soil heavy metal Cd content inversion method and system, medium and computer equipment
PendingCN114660105AReduce human errorHigh precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEnsemble learningSoftware systemSoil heavy metals
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil heavy metal pollution detection, and discloses an inversion method and system for the content of heavy metal Cd in soil, a medium and computer equipment. An X-ray fluorescence analyzer is used for detecting, and an ASD FieldSpec 3 spectrograph, matched test equipment and a software system are used for obtaining the actual content value and element spectrum information of the heavy metal Cd in the soil respectively; dimensionality reduction processing and characteristic spectrum screening are carried out on the original spectrum, and random forest, artificial neural network and support vector machine model learning and content inversion are carried out by utilizing the characteristic spectrum of the element. The soil heavy metal Cd content inversion system comprises a soil spectrum information module; a heavy metal content prediction module; and a model prediction evaluation module. The method is high in inversion precision and simple and convenient to operate, and a new technical means is provided for rapid nondestructive detection and regional evaluation of the heavy metal Cd element in the soil.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +2
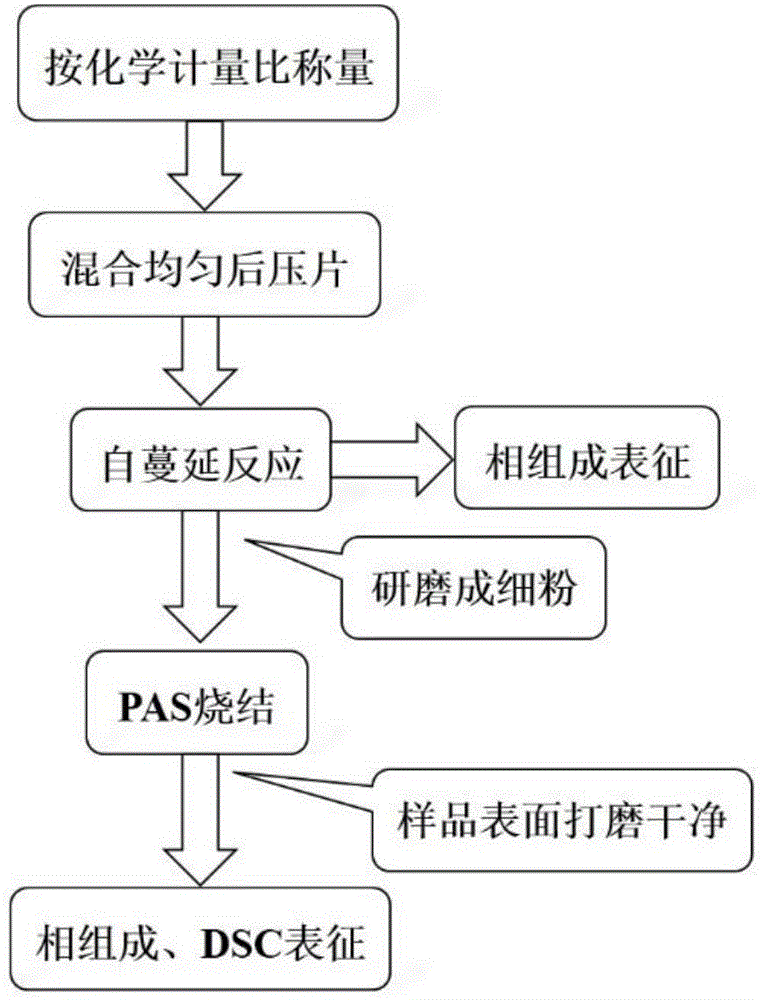
Method for increasing phase inversion temperature of Cu2Se base thermoelectric material
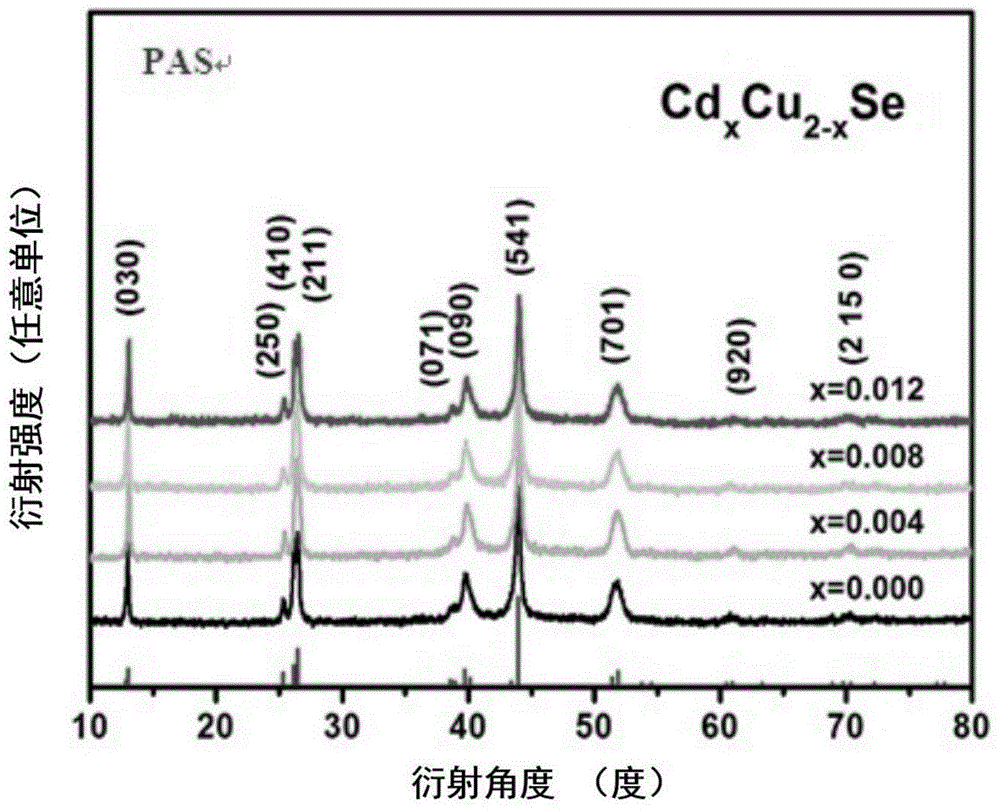
ActiveCN106145063AInhibit migrationRaise the phase transition temperatureBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsThermoelectric materialsFree cooling
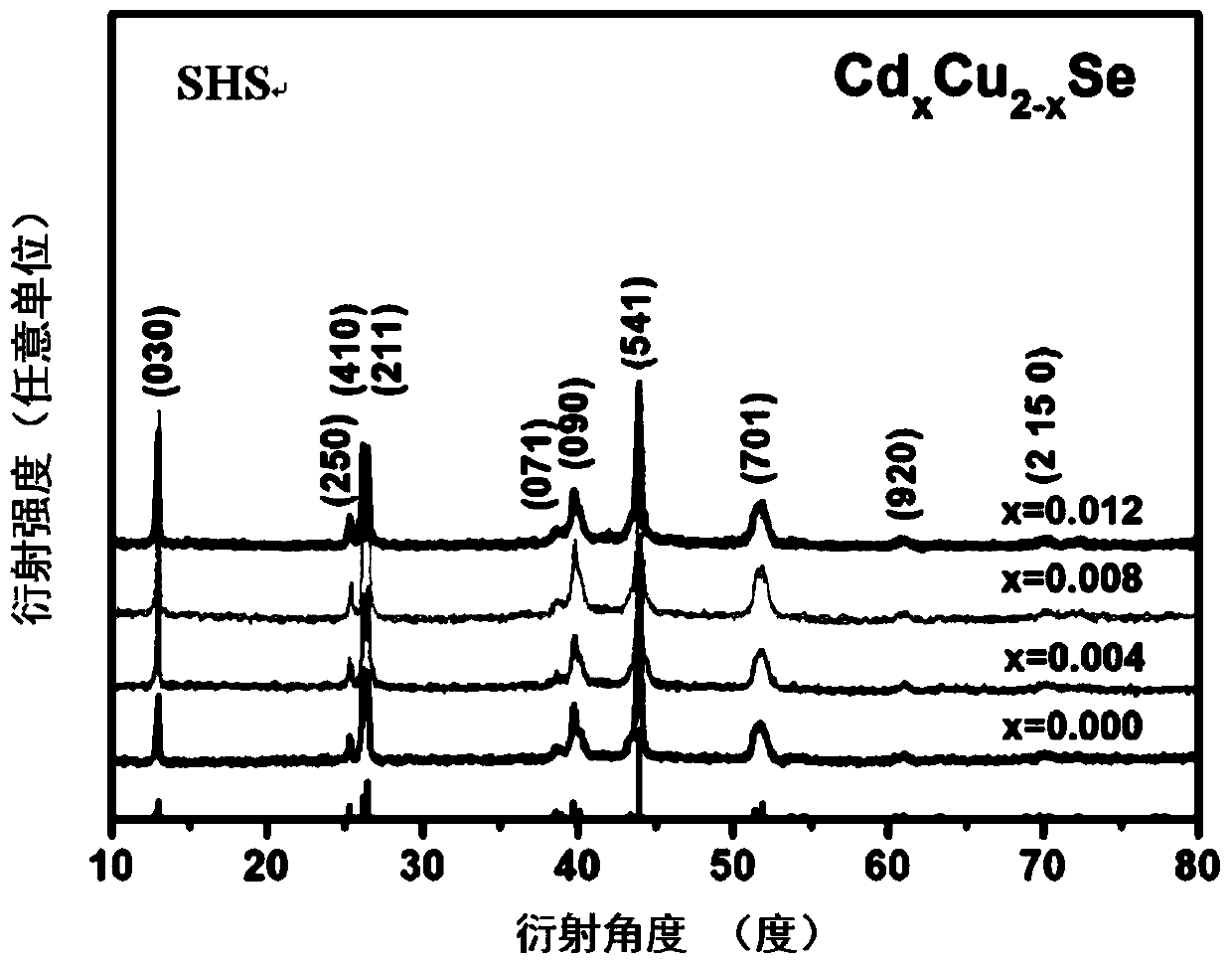
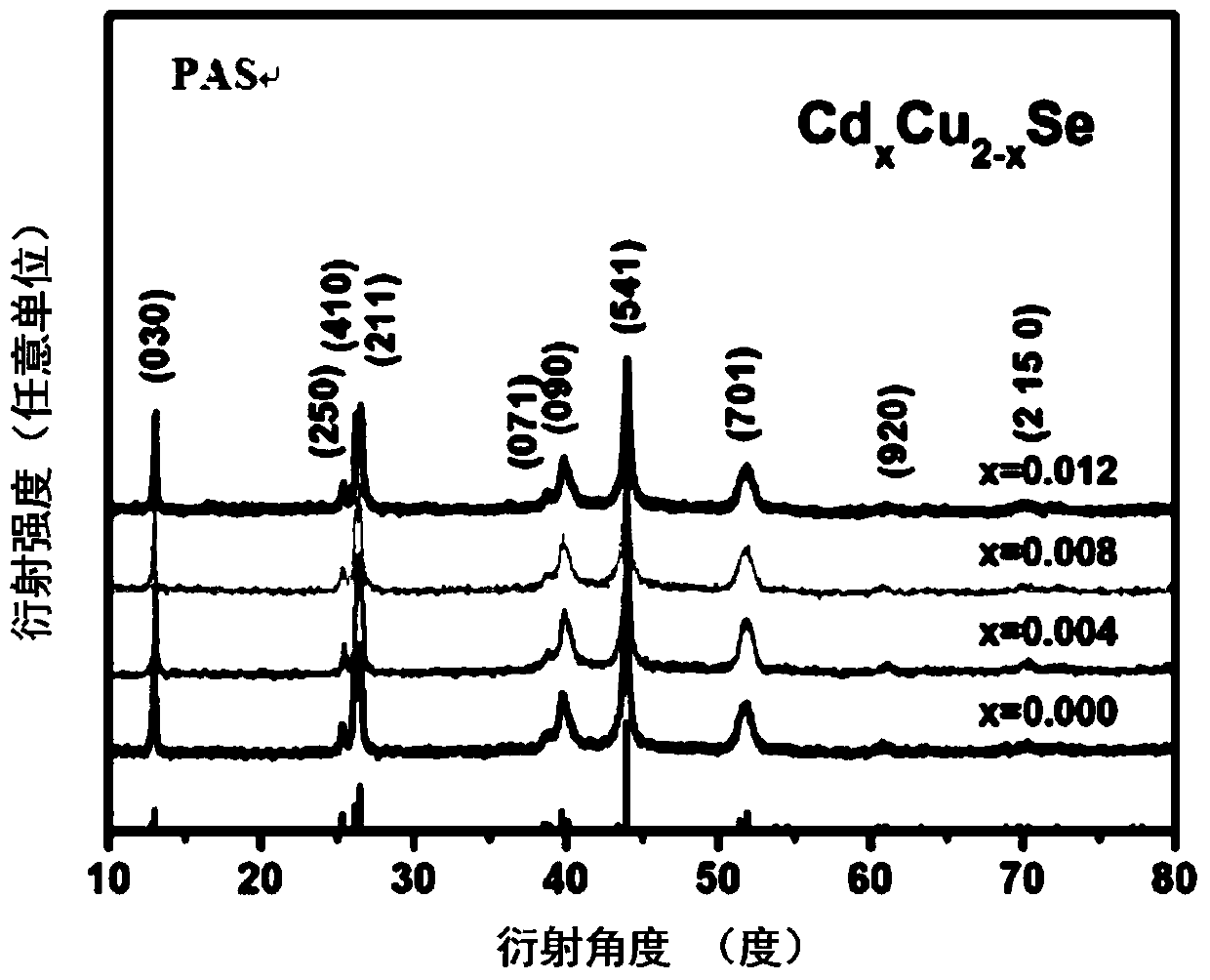
The invention discloses a method for increasing the phase inversion temperature of a Cu2Se base thermoelectric material. A Cd element is mixed into a Cu position of Cu2Se, and the method specifically comprises the following steps that 1, raw materials are weighed on the basis of a stoichiometric ratio of CdxCu2-xSe(0.004<=x<=0.012), and tableted after being mixed to be uniform; 2, column bodies obtained after tableting are subjected to vacuum sealing, then, self-propagating reaction is caused, and after the reaction is completed, natural cooling is performed; 3, reaction products obtained in the step 2 are ground to be fine powder, then, plasma activated sintering is performed, and a dense CdxCu2-xSe block is obtained. The method is simple, high in repeatability, capable of effectively increasing the phase inversion temperature of the Cu2Se base thermoelectric material, and suitable for being applied and popularized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
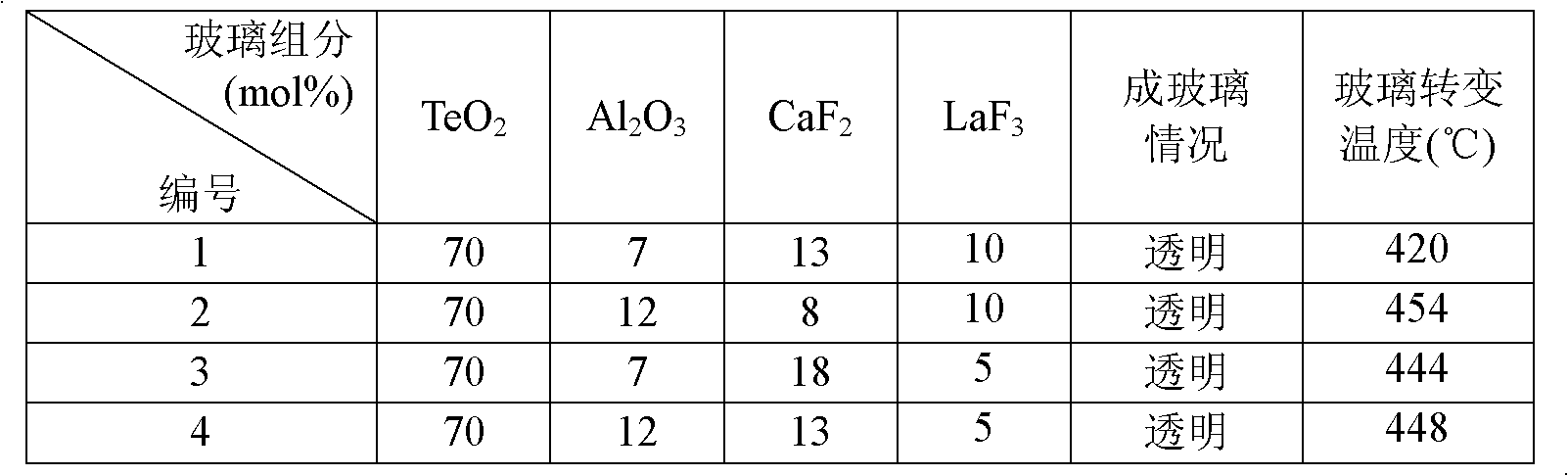
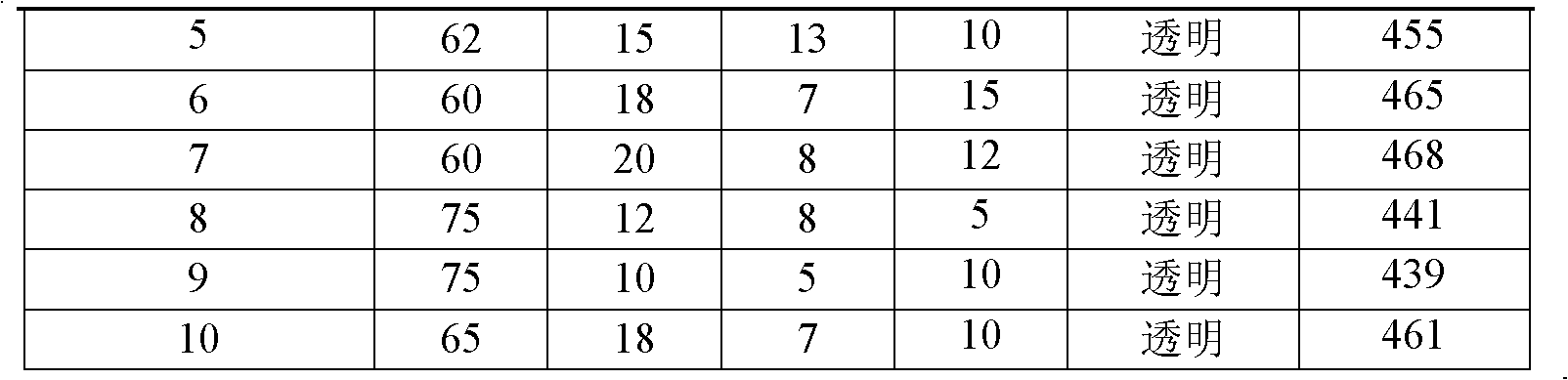
Transparent oxyfluoride tellurite glass
The invention relates to a transparent oxyfluoride tellurite glass, which comprises the following components by mole ratio: 55-75mol% of TeO2, 5-25mol% of Al2O3, 0-18mol% of CaF2, 0-15mol% of LaF3. The oxyfluoride tellurite glass uses a traditional glass melting process for melting and molding. The oxyfluoride tellurite glass possesses excellent thermal stability, and is an ideal rare earth doped up-conversion luminescence matrix material which is capable of enhancing the permeability of the matrix, improving the treatment load of a land infiltration system and improving the denitrification efficiency, the oxyfluoride tellurite glass does not contain toxic heavy metals Pb and Cd elements which are harmful to human body and environment.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
a kind of eu 3+ Doped tellurite high-density scintillation glass and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an Eu<3+> doped tellurate high density scintillating glass and a preparation method thereof. The high density scintillating glass comprises the following components: TeO2, ZnO,Lu2O3 and Eu2O3. The oxides are high density compounds, and the glass prepared by high temperature melting method has a density of greater than 6 g / cm<3>. Compared with high density glass containingPb, Cd and other heavy metal elements, the glass prepared by the method provided by the invention does not contain high-pollution heavy metals Pb and Cd elements, and is more environmentally friendly.High density Lu2O3 is taken as the glass raw material, the glass density is improved and the radiation resistance of the glass is enhanced. The high density scintillating glass prepared by the methodprovided by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation method, low production cost, high glass density, and strong scintillation light output.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
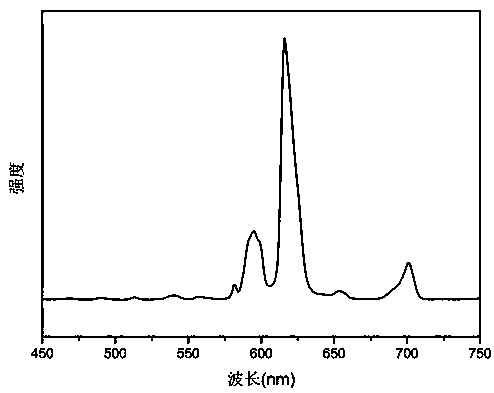
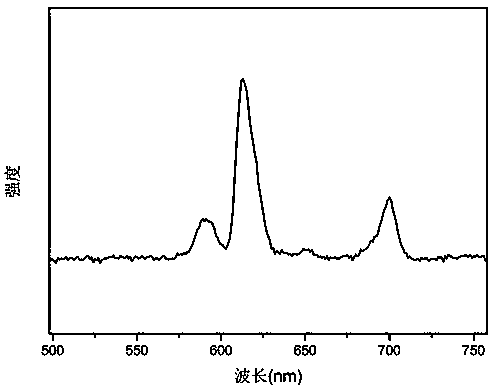
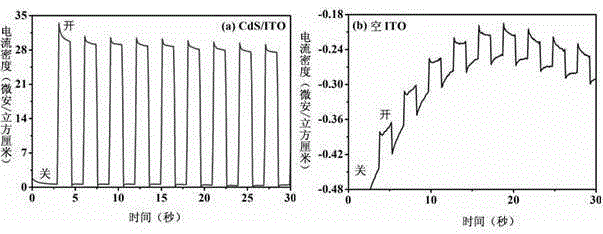
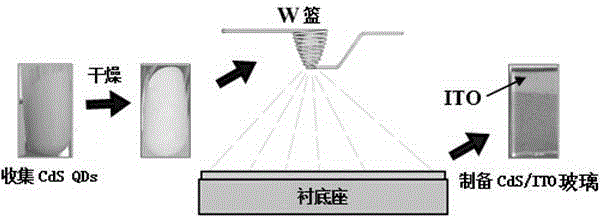
Thermal evaporation method for preparation of near-stoichiometric CdS film with quantum dot as precursor
InactiveCN105177499AAvoid complex controlsSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingVacuum pumpingPower flow
The invention discloses a thermal evaporation method for preparation of a near-stoichiometric CdS film with a quantum dot as the precursor. The method includes: putting a cleaned substrate on a sample rack (Emitech, K950X) of a thermal evaporimeter vacuum chamber, putting 0.1-0.3g of the precursor with an appropriate size into a W basket and closing the chamber, under room temperature, conducting vacuum pumping on the chamber to 1.0*10<3>-1.0*10<5>mbar, adjusting the current passing through the W basket to control the evaporation rate, firstly slowly increasing the current from 0A to 6-10A to wait until the W basket turns red, then further increasing the current to 13-20A and keeping the state for 5-10s, and finally, reducing the current to 0A to complete the whole evaporation process. The method provided by the invention adopts a single-source thermal evaporation technique, avoids the problem of complex control of each evaporation source in multi-source thermal evaporation technique, and adopts CdS QDS rich in Cd element as the precursor. The preparation method is room temperature co-precipitation method, is easy to operate and has high yield.
Owner:XUCHANG UNIV
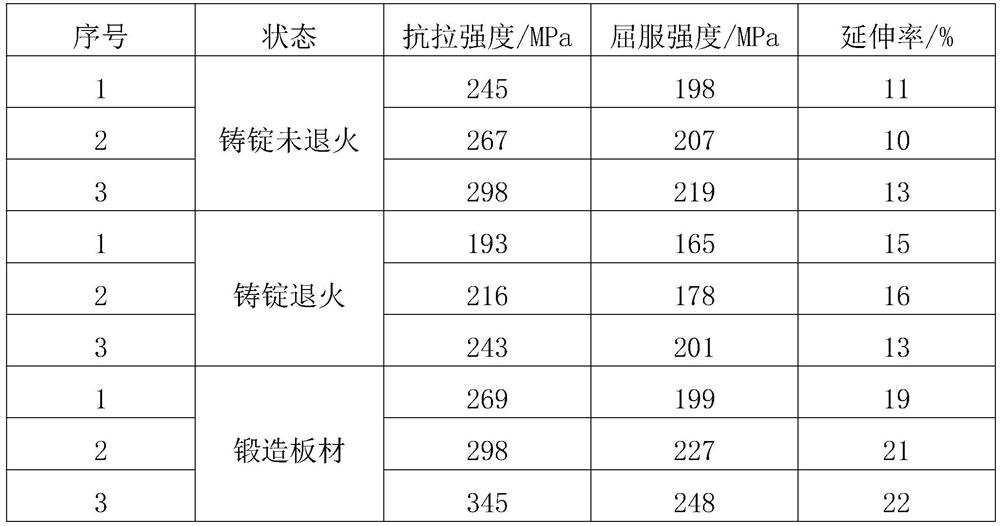
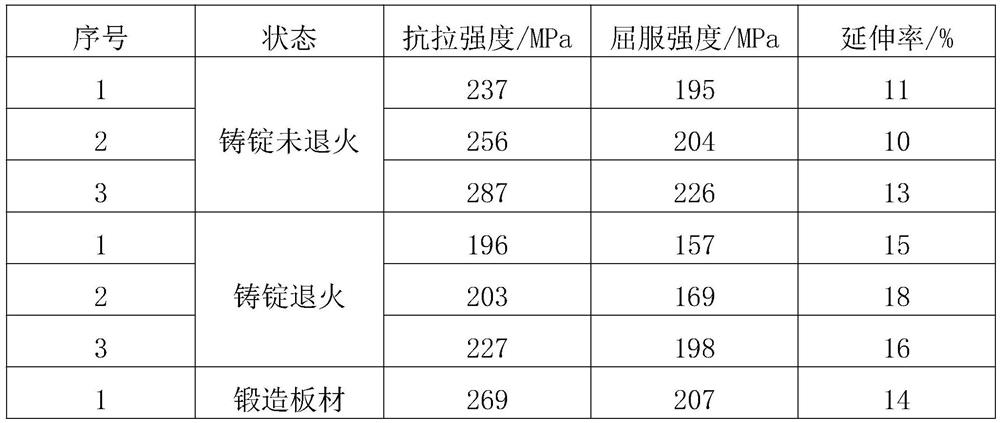
Alloying and heat treatment method for improving plasticity of cast aluminum-copper alloy at room temperature
ActiveCN112662926BImprove room temperature plasticityEasy to reinforceMachining processUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an alloying and heat treatment method for improving room-temperature plasticity of cast aluminum-copper alloys. Ag and Cd elements are added at the same time to form Ag-Cd particles after aging, which can be cut by dislocations during the deformation process and improve dislocations. The free path of motion improves the plasticity of the alloy at room temperature. The addition of Cd element can not only refine the θ′ phase in the alloy grain, but also make the θ′ phase that was bypassed by dislocations can be cut through, greatly improving the free path of dislocation movement, and also significantly promoting the high-Cu aluminum alloy. The non-network discontinuous distribution of the grain boundary equilibrium phase θ reduces the brittleness of the alloy, which can improve the room temperature plasticity of the alloy. The Ag-Cd particles and the dispersed and precipitated θ′ phase can make up for the strength loss caused by the reduction of the Ω phase, improve the strength and toughness of the alloy, and greatly improve the processability of alloy casting and the service safety of castings. The introduction of natural aging after solid solution can promote the formation of GP regions, increase the number density of θ′ phases that are coherent with the matrix and can be cut by dislocations, and the free path of dislocation movement, thereby improving the plasticity of the alloy at room temperature.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Application of celosia cristata in remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil
The invention relates to application of celosia cristata belonging to the Amaranthaceae in remediation of Cd contaminated soil. Annual ornamental flower plant celosia cristata which is large in biomass, easy to breed and short in life cycle is planted on the Cd contaminated soil, and a large amount of Cd in the contaminated soil is absorbed and transferred through the celosia cristata. After the plants grow mature, the plants are harvested, the heavy metal Cd element in the soil is removed, the harvested plants are transported to the flower market to be sold, a new crop of celosia cristata are planted, and the operation is repeated, so that remediation of the cadmium-contaminated soil is achieved. By adopting the phytoremediation method for the Cd contaminated soil, the environment can be beautified, Cd cannot enter the food chain after the contaminated soil is planted, and the application has the advantages of economic value, no influence on physical and chemical properties of the soil and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Transparent oxyfluoride tellurite glass
InactiveCN102515528BLow maximum phonon energyLower melting temperatureUpconversion luminescenceRare earth
The invention relates to a transparent oxyfluoride tellurite glass, which comprises the following components by mole ratio: 55-75mol% of TeO2, 5-25mol% of Al2O3, 0-18mol% of CaF2, 0-15mol% of LaF3. The oxyfluoride tellurite glass uses a traditional glass melting process for melting and molding. The oxyfluoride tellurite glass possesses excellent thermal stability, and is an ideal rare earth doped up-conversion luminescence matrix material which is capable of enhancing the permeability of the matrix, improving the treatment load of a land infiltration system and improving the denitrification efficiency, the oxyfluoride tellurite glass does not contain toxic heavy metals Pb and Cd elements which are harmful to human body and environment.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
Heatproof and anticorrosion rare earth magnesium alloy with high obdurability and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a heatproof and anticorrosion rare earth magnesium alloy with high obdurability and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of light metal material. The rare earth magnesium alloy comprises the following components in proportion by weight: 3-5% of aluminum (Al), 0.1-0.4% of manganese (Mn), 0.8-2.5% of yttrium (Y), 0.3-1.0% of stibium (Sb), 0.3-1% of cadmium (Cd) and balance of magnesium (Mg). The invention has the advantages of solving the problem of reduction of mechanical properties caused by the splitting effect of a bulky Al2Y relative matrix in the alloy structure, improving the obdurability of the alloy and the mechanical properties of the alloy under room temperature and high temperature by making the most of the solution strengthening effect and refined crystalline strengthening effect of the Sb, Y and other elements and the dispersion strengthening effect of the high melting point YSb particle phase mass points, further improving the mechanical properties of the alloy by the grain refinement effect and the solution strengthening effect of the Cd element, and improving the anticorrosion performance of the alloy by improving theelectrode potential of the alloy matrix by the Cd element, so that the obdurability, heatproof performance and anticorrosion performance of the alloy are higher than that of the existing AE series magnesium alloy. The technological requirements for the preparation method provided by the invention are not harsh, and the preparation method can meet the industrialized enlarged production requirements and ensure thorough embodiment of the two technical effects.
Owner:JIANGSU FAVOUR AUTOMOTIVE NEW STUFF SCI TECH
A kind of bearing and its preparation process
ActiveCN107965522BSimple internal structureImprove mechanical propertiesBearing componentsHigh resistanceMetallic materials
The invention discloses a bearing and a preparation technology thereof, and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. The bearing comprises 0.05%-0.07% of Cd, 0.5%-1.5% of Mn, 0.4%-0.8% of C,0.08%-0.12% of Tl, 0.01%-0.05% of Cu, 0.03%-0.07% of Co and the balance Fe and impurities. The Cd element in raw materials can react with Cu in the materials to form hard copper alloy phases dispersed in steel, so that the tensile strength and abrasion resistance of alloy steel are improved obviously. Tl is very important for the alloy steel, not only the alloy strength can be improved, but alsothe alloy hardness and the corrosion resistance of the alloy can be improved, and the Tl is essential for the effect of prolonging the service life of a product. Meanwhile, with the method that the bearing body is combined with polymer layers outside the bearing body, the product has extremely high resistance in complex and variable environment.
Owner:宁波恒力汽配轴承有限公司
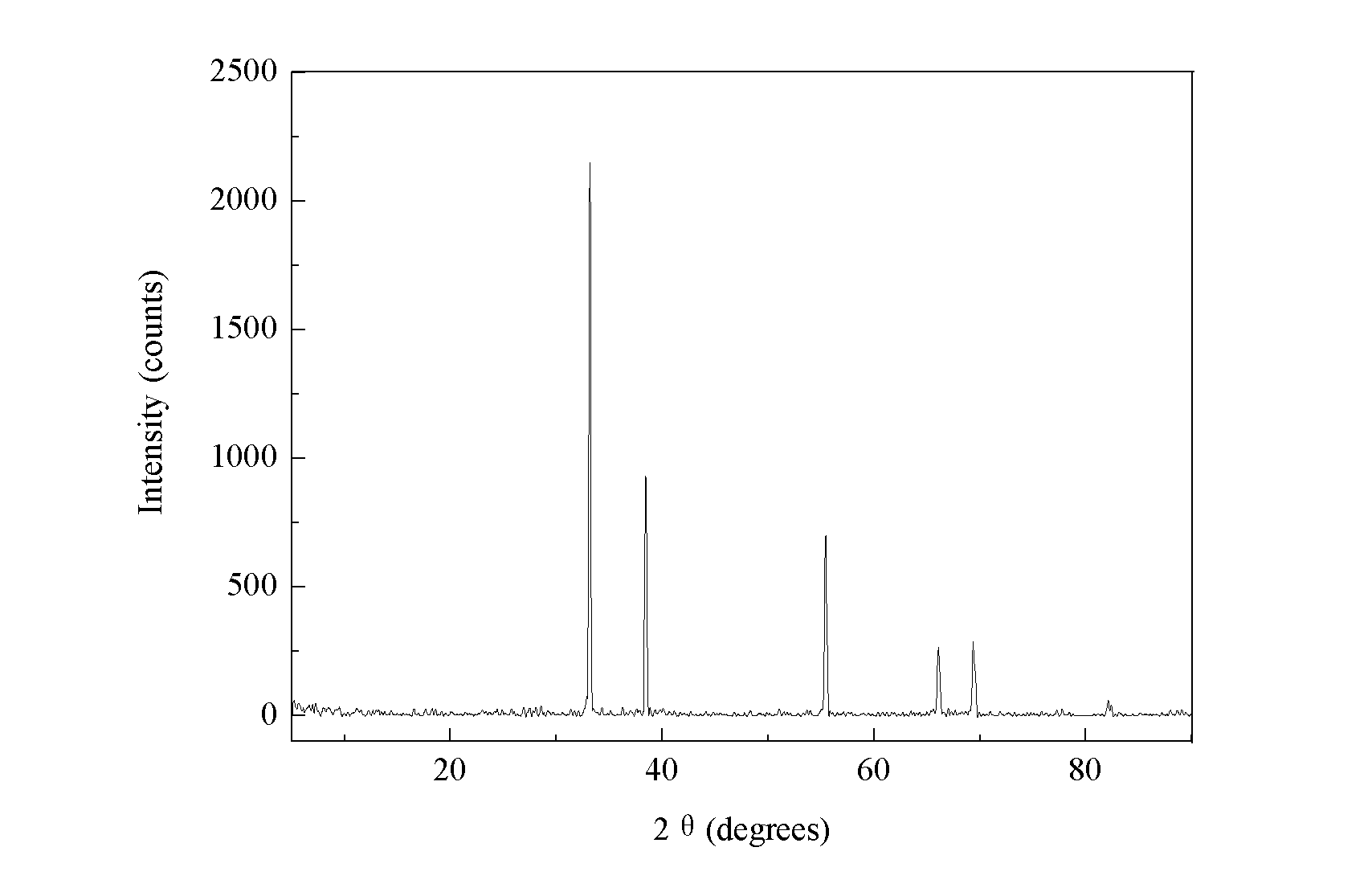
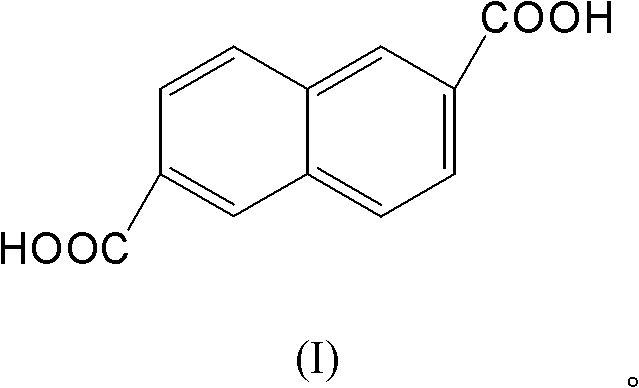
Coprecipitation Cd/Al (Cadmium / Aluminum) catalyst and application of catalyst for catalyzing and synthesizing 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid
InactiveCN102091610ALarge specific surface areaImprove catalytic performancePreparation from carboxylic acid saltsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCoprecipitationCadmium nitrate
The invention discloses a coprecipitation Cd / Al (Cadmium / Aluminum) catalyst which is prepared by the following steps of: under 80 DEG C, dripping mixed solution which is mixed by cadmium nitrate water solution and aluminum nitrate water solution in sodium carbonate water solution, dripping until the pH value is 3.5-4.5; then dripping the sodium carbonate water solution until the pH is 8.5-9.5, standing under 70-80 DEG C, filtering, washing, drying, heating up to 400-650 at the speed of 2 DEG C / min to calcine, and cooling to obtain the coprecipitation Cd / Al catalyst. The invention further discloses the application of the catalyst for catalyzing and synthesizing 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid. The Cd / Al catalyst disclosed by the invention is large in specific surface area, excellent in catalyzing effect and simple in preparation, wherein Al element and Cd element are both doped so as to improve the catalytic activity of the catalyst. The method for synthesizing the 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid by the coprecipitation Cd / Al catalyst can obtain the product by one step; and the product is high in purity, high in productive rate and simple in process route.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Quantum dots and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108998000AWith mass productionSimple processLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesPhotoluminescenceQuantum dot
The invention relates to quantum dots and a preparation method thereof. Quantum dots comprise Zn element, Cd element and Se element, wherein the molar ratio of Zn element, Cd element and Se element is(1.8-2.8):(0.2):(2-3). The quantum dots have good light absorption properties, and can absorb more light emitted by blue LEDs when applied to photoluminescence, so that the usage quantity of the quantum dots in the application process is reduced, and the production cost and the use cost are reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU XINGSHUO NANOTECH CO LTD
Method for synthesizing cadmium selenide/zinc selenide/zinc blende double-shell structural quantum nodes
The invention discloses a synthetic method of cadmium selenide / zinc selenide / zinc sulfide (CdSe / ZnSe / ZnS) double shell quantum dot. The fluorescence of cadmium selenide / zinc selenide / zinc sulfide quantum dot has comparatively strong luminous intensity and stability, thereby preventing cd element from divulging and leading the materials to be more environmental-friendly and safer. The double shell quantum dot is synthesized in the two systems and the specific steps are that: cadmium selenide crystalline core is formed after fast injection of reaction solution in organic solvent and cadmium selenide crystalline core grows to obtain cadmium selenide quantum dot; after two steps of choosing solution and adding solution, shells of zinc selenide and zinc sulfide grow epitaxially outside the cadmium selenide appearance and the double shell quantum dot is obtained. For adopting chemical solvents that are comparatively very safe and easy to be obtained, the invention has the advantages of safety, easy operation, comparatively low cost and being beneficial for controlling cost and scale production. The obtained materials can be applied to fields such as light-emitting devices, biomolecule fluorescence marker, etc.
Owner:TAIZHOU ZECEN BIOTECH CO LTD
High-performance easy-to-forge magnesium alloy material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113564440ARaise the recrystallization temperatureHigh temperature strengthMetal-working apparatusMechanical propertyMaterials science
The invention relates to a high-performance easy-to-forge magnesium alloy material and a preparation method. The magnesium alloy material comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 7.0%-10.0% of Y element, 0.5%-1.5% of Cd element, 3.0%-4.0% of Ce / La, and the balance of magnesium element. The magnesium alloy material is high in mechanical property and easy to forge, and the tensile strength can reach 500 MPa or above.
Owner:西安四方超轻材料有限公司
Quantum dot and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112824481AEasy injectionLower injection barrierMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsElectron holeChemical physics
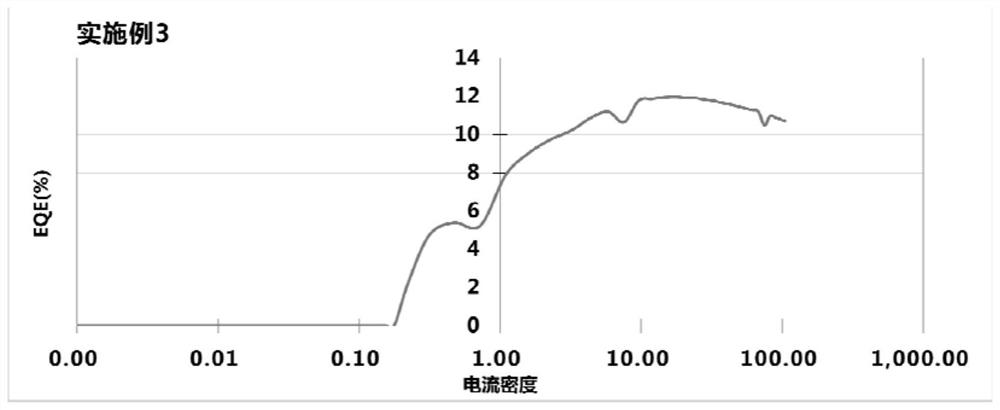
The invention relates to a quantum dot and a preparation method and application thereof. The quantum dot comprises an inner core and a shell layer wrapping the inner core, the inner core is made of CdZnSe, the shell layer is made of CdZnS, and the molar ratio of Cd element to S element in the shell layer is 0.15: 1-0.4: 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing an inner core, mixing the inner core with a first zinc precursor, aliphatic amine and a solvent to form a first precursor solution, respectively or jointly adding a first cadmium precursor and a first sulfur precursor into the first precursor solution at a constant speed to form a second precursor solution, wherein the molar ratio of the element Cd to the element S in the second precursor solution is 0.15: 1-0.4: 1; and reacting the second precursor solution at a first temperature to coat the surface of the inner core to form a shell layer so as to obtain the quantum dot. The energy level structure of the quantum dot is better matched with a hole and an electron transport layer, the carrier injection barrier is low, after the quantum dot is applied to a photoelectric device, under the working current of 5-20 mA / cm < 2 >, the EQE reaches the maximum value, the service life of the photoelectric device is longer, and the commercialization requirement is better met.
Owner:NANJING TECH CORP LTD
Complete gradient alloy quantum dot and preparation method thereof
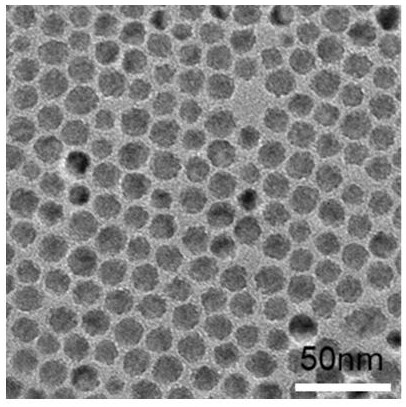
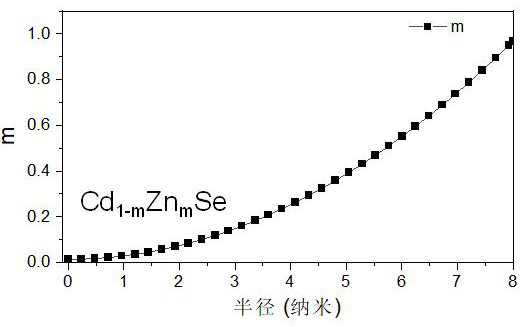
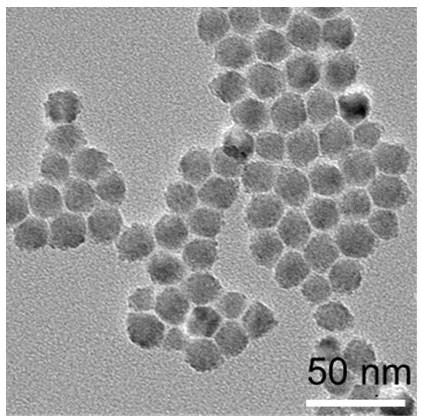
PendingCN114507525ARelief of lattice stressReduce lattice defectsMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsQuantum dotAlloy
The invention provides a complete gradient alloy quantum dot. The structure of the complete gradient alloy quantum dot comprises a core quantum dot, the core quantum dots are Cd1-mZnmSe quantum dots, and m is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1; the Cd element content and the Zn element content of the Cd1-mZnmSe quantum dot are in gradient distribution from the center of a nuclear body to the surface of the nuclear body; the structure further comprises a shell layer; the shell layer is a ZnSeyS1-y shell, and y is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1; the Se element content and the S element content are in gradient distribution from the inner layer of the ZnSeyS1-y shell to the outer layer of the ZnSeyS1-y shell. The invention discloses a method for preparing complete gradient alloy quantum dots. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a core material dispersion liquid; 2, preparing a shell layer material dispersion liquid; and 3, dropwise adding the shell layer material dispersion liquid into the core body material dispersion liquid, and growing a shell layer material on the surface of the core body quantum dot in situ to obtain the complete gradient alloy quantum dot.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Quantum dot and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112824481BEasy injectionLower injection barrierMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a quantum dot and a preparation method and application thereof; the quantum dot comprises an inner core and a shell layer covering the inner core, the material of the inner core is CdZnSe, and the material of the shell layer is CdZnS, wherein the Cd element in the shell layer and the The molar ratio of the S element is 0.15:1 to 0.4:1. The preparation method includes: preparing an inner core, mixing the inner core with a first zinc precursor, aliphatic amine, and a solvent to form a first precursor solution, and then adding the first cadmium precursor and the first sulfur precursor to the first precursor separately or together at a uniform speed. The precursor solution is used to form a second precursor solution, and the molar ratio of Cd element and S element in the second precursor solution is 0.15:1 to 0.4:1; the second precursor solution is reacted at the first temperature to The surface of the inner core is coated to form a shell, resulting in quantum dots. The energy level structure of the quantum dots better matches the hole and electron transport layers, and the carrier injection barrier is lower. 2 At the same working current, the EQE reaches the maximum value, and the optoelectronic device has a longer life and is more suitable for commercialization.
Owner:NANJING TECH CORP LTD
A kind of high-strength and corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy and its preparation method and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal material preparation, and discloses a high-strength and corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy and its preparation method and application, including Mg 0.6-1.0%, Si 0.8-1.2%, Cu 0.1-0.3%, and Mn by weight percentage 0.4‑1.0%, Cr 0.15‑0.35%, Cd 0.05‑0.1%, and Fe≤0.5%. The present invention adds Cd, adopts three-stage homogenization heat treatment, and the Cd element is preferentially homogenized and diffused, and then the Mn and Cr elements take the Cd atomic cluster as the nucleation site, and precipitate to form a highly dispersed AlMnCr phase containing Cd elements, which can be used as a deformation regenerated phase. The nucleation particles of the crystallization realize the grain refinement of the second phase particle-induced recrystallization; the present invention optimizes the design of the aluminum alloy alloy composition based on the principle of alloying, that is, the mass ratio of Mg to Si is (0.65‑0.9):1 The mass ratio of Cu and Si is (0.15‑0.25): 1, and the Mg of highly dispersed distribution is obtained 2 Si strengthening phase and higher strength without forming a Cu-containing phase with poor corrosion resistance; through the present invention, an aluminum alloy with medium and high strength, high plasticity and high corrosion resistance can be obtained, which is suitable as an aluminum alloy for automotive structural parts or applied in its profile.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINGFA ALUMINUM JIANGXI +1
A method for increasing the phase transition temperature of cu2se-based thermoelectric materials
ActiveCN106145063BInhibit migrationRaise the phase transition temperatureBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsThermoelectric materialsFree cooling
The invention discloses a method for increasing the phase inversion temperature of a Cu2Se base thermoelectric material. A Cd element is mixed into a Cu position of Cu2Se, and the method specifically comprises the following steps that 1, raw materials are weighed on the basis of a stoichiometric ratio of CdxCu2-xSe(0.004<=x<=0.012), and tableted after being mixed to be uniform; 2, column bodies obtained after tableting are subjected to vacuum sealing, then, self-propagating reaction is caused, and after the reaction is completed, natural cooling is performed; 3, reaction products obtained in the step 2 are ground to be fine powder, then, plasma activated sintering is performed, and a dense CdxCu2-xSe block is obtained. The method is simple, high in repeatability, capable of effectively increasing the phase inversion temperature of the Cu2Se base thermoelectric material, and suitable for being applied and popularized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
High-performance dual-phase magnesium-lithium alloy material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113430435AImprove mechanical propertiesLow tensile strengthMetal-working apparatusMetallurgyAl element
The invention relates to a high-performance double-phase magnesium-lithium alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The magnesium-lithium alloy material comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 6.0%-12% of a lithium element, 2%-6% of an Al element, 2%-6% of a Zn element, 0.5%-2% of a Cd element, 0.3%-1.5% of a Zr element and the balance of a magnesium element. According to the invention, the single-phase magnesium-lithium alloy material is relatively high in mechanical property, and the lowest tensile strength is 260MPa.
Owner:西安四方超轻材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com