Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Ustilago esculenta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ustilago esculenta is a species of fungus in the Ustilaginaceae, a family of smut fungi. It is in the same genus as the fungi that cause corn smut, loose smut of barley, false loose smut, covered smut of barley, loose smut of oats, and other grass diseases. This species is pathogenic as well, attacking Manchurian wild rice (Zizania latifolia), also known as Manchurian ricegrass, Asian wild rice, and wateroat. This grass is its only known host.
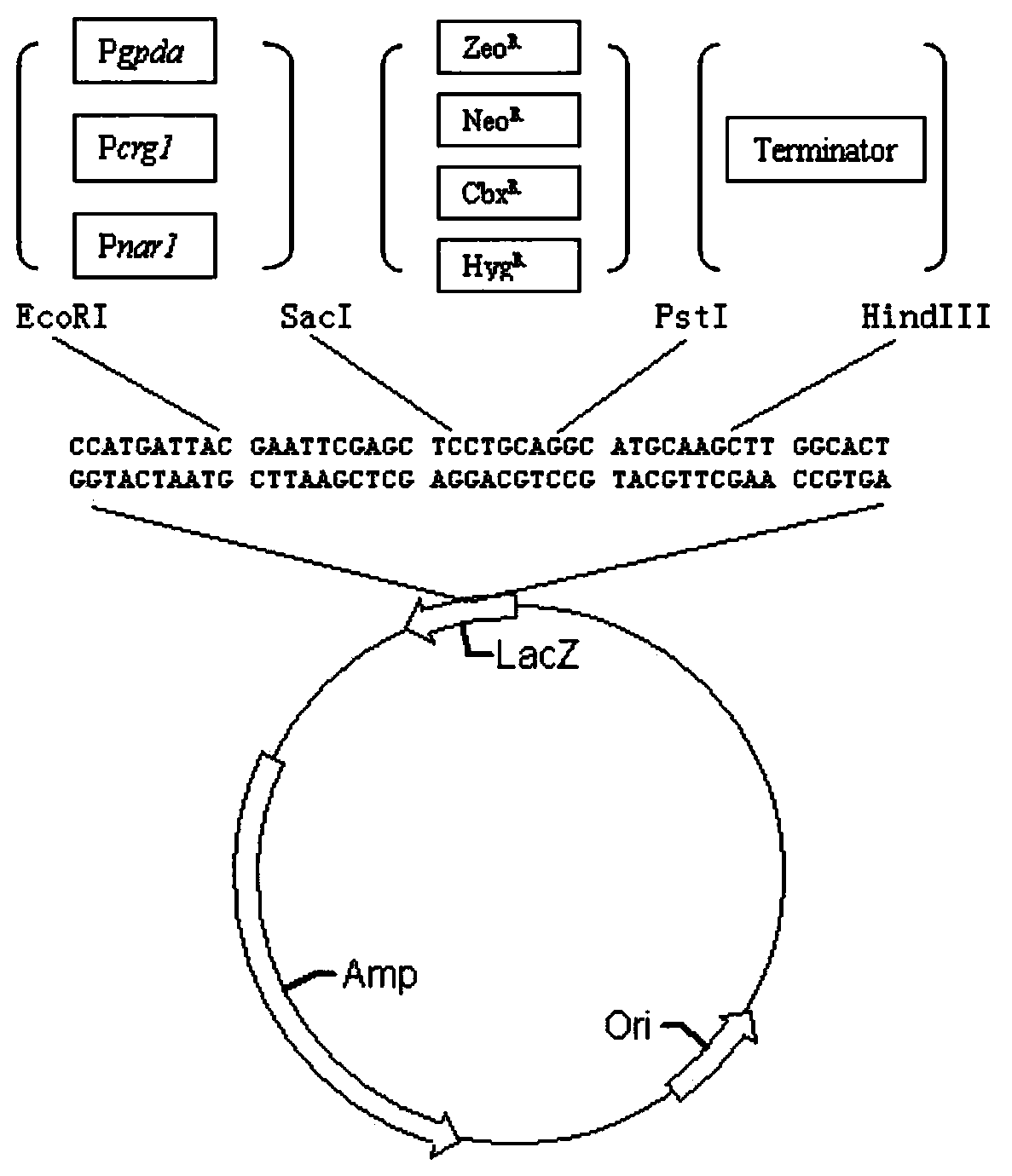
Agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta transformant strain as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of biology breeding and in particular relates to an agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta (Ustilago esculenta) transformant strain as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta transformant strain, an agrobacterium infected receptor of the transformant strain refers to ustilago esculenta (Ustilago esculenta). The method for preparing the agrobacterium-mediated ustilago esculenta transformant strain comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a fungal expression vector; (2) preparing agrobacterium competence; (3) performing electrotransformation on the agrobacterium; and (4) performing agrobacterium-mediated transformation, thereby obtaining the transformant. A complex protoplast is not needed, the receptor source is simple, and spores and hypha of the fungi can be directly used for transformation; and the transformation efficiency is high. In addition, the obtained transformant is large in single-copy ratio, and marker genes are conveniently obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD +1
Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 and use thereof
ActiveCN105838616AImprove environmental adaptabilityControl dating timeFungiMicroorganism based processesUstilago esculentaMicrobiology
The invention discloses an Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 and a use thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 11843. Zizania aquatica artificial breeding needs common invasion of two sexual compatible haploid strains. The strain can be used as a zizania aquatica artificial breeding mother strain, through screening, a sexual compatible haploid strain is obtained and artificial zizania aquatica breeding is realized through artificial inoculation. The haploid strain UEMT2 can be used for gene engineering reconstruction and provides an implementation base material for zizania aquatica improvement such as zizania aquatica environmental adaptability and zizania aquatica growth time control in zizania aquatica breeding.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 and use thereof
ActiveCN105838615AImprove environmental adaptabilityControl dating timeFungiMicroorganism based processesUstilago esculentaMicrobiology
The invention discloses an Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 and a use thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 11844. Zizania aquatica artificial breeding needs common invasion of two sexual compatible haploid strains. The strain can be used as a zizania aquatica artificial breeding mother strain, through screening, a sexual compatible haploid strain is obtained and artificial zizania aquatica breeding is realized through artificial inoculation. The haploid strain UEMT2 can be used for gene engineering reconstruction and provides an implementation base material for zizania aquatica improvement such as zizania aquatica environmental adaptability and zizania aquatica growth time control in zizania aquatica breeding.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Wild rice stem smut fungus strain capable of producing anti-fungus antibiotic and its use
The present invention discloses a kind of Ustilago esculenta strain UEZC1 capable of producing antifungal antibiotic and its use. The Ustilago esculenta strain UEZC1 features that the teleutospore is germinated on potato glucose liquid culture medium to form basidium promycelium with 1-4 basidiospore promycelia, and the basidiospore after falling off further grow to form fusiform short hypha for inserting basidiospore. The present invention can produce antifungal antibiotic, and may be used in developing and producing medical and agricultural antifungal antibiotic.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
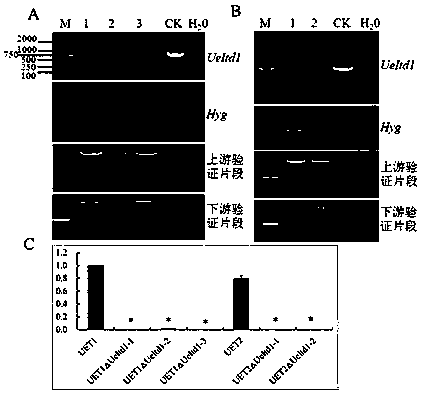
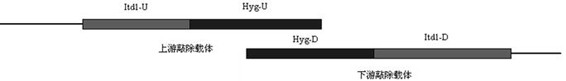
Ustilago esculenta teliospore formation related gene Itd1 and application thereof
The invention discloses an ustilago esculenta teliospore formation related gene Itd1 and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. On one hand, the key gene Itd1promoting formation of field zizania latifolia infected with sporidial strain of ustilago esculenta and ustilago esculenta teliospore is provided, on the other hand, the application of the key gene Itd1 to normal pregnant zizania latifolia is provided, and a new direction is provided for zizania latifolia breeding.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for artificially breeding normal wild rice shoots
The invention discloses a method for artificially breeding normal wild rice shoots, and belongs to the technical field of wild rice shoot cultivation. The method comprises the following steps that Ustilago esculenta haploid strains UET1deltaLtd1 and Ustilago esculenta haploid strain solutions are mixed isovolumetrically for inoculation; 3-5 leaf stage wild rice shoot seedlings are selected as inoculation objects; the mixed bacteria solution is injected to the seedling base through an injector till the bacteria solution overflows from the upper portion of sheaths; the processed inoculation seedlings are trimmed; transition culture is performed, and inoculation is performed after two weeks, and transplanting can be performed for outdoor cultivation; transplanting to outdoor cultivation is performed. The Ustilago esculenta of Ustilago esculenta haploid strains UET1delta ltd1 and Ustilago esculenta haploid strains UET2delta ltd 1 is inoculated to wild rice shoots, and normal wild rice shoots can be successfully produced. The method is easy to implement and effective, and a new direction is provided for wild rice shoot breeding.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for improving yield of fruiting bodies of cordyceps takaomontana
ActiveCN103865802AIncrease productionGood effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyUstilago esculenta
The invention discloses a method for improving yield of fruiting bodies of cordyceps takaomontana. The method comprises the steps of activating an ustilago esculenta GZUIFR-DX091 bacterial strain by applying a PDA culture medium, picking three loops for the activated bacterial strain by applying an inoculating loop to access into the ustilago esculenta culture medium, centrifuging culture liquor for 5 minutes at 5000r / min after culturing for 5 days at 28 DEG C at 160r / min, and getting liquid supernatant to obtain fermentation liquor of the ustilago esculenta GZUIFR-DX091 bacterial strain; infecting silkworms with cordyceps takaomontana, and starting producing fruiting bodies for later use when the infected silkworms are hardened; pre-sterilizing a culture container, and tiling single layer or double layers of sterilized water-absorbing paper at the bottom of the container; slowly adding the prepared fermentation liquor of the ustilago esculenta GZUIFR-DX091 bacterial strain onto the water-absorbing paper at the bottom of the container, placing the infected silkworms into a container which is added with the cane shoot fermentation liquor, and carrying out culture under light for 12 hours at 20-23 DEG C, wherein the culture temperature can be lowered by 5 DEG C for culturing at a dark culture stage. In the culture process, if the added fermentation liquor is dried, the fermentation liquor is needed to be timely complemented; the fruiting bodies of cordyceps takaomontana can be harvested after culturing for 3-4 weeks. The method disclosed by the invention can greatly improve the yield of the fruiting bodies of cordyceps takaomontana.
Owner:度测(上海)科技服务中心
Culture medium capable of maintaining in-vitro growth of hyphae of ustilago esculenta
ActiveCN105543109ACompatibility is reasonableMaintain in vitro growthFungiMicroorganism based processesUstilago esculentaBiotechnology
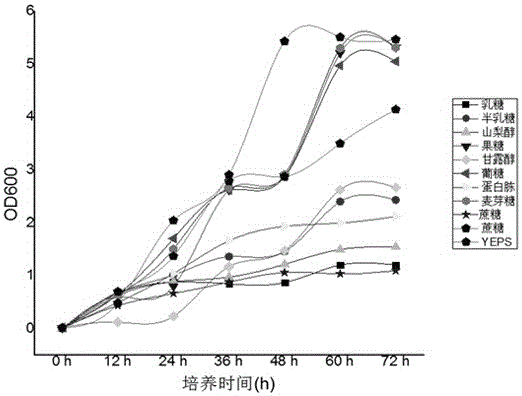
The invention discloses a culture medium capable of maintaining in-vitro growth of hyphae of ustilago esculenta, and belongs to the technical field of culture media. Every liter of the culture medium comprises the following components: 0.85 to 1.15 grams of K2HPO4, 0.45 to 0.55 gram of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.008 to 0.012 gram of FeSO4.7H2O, 0.45 to 0.55 gram of KCl, 2 to 3 grams of yeast powder, 4 to 6 grams of peptones, 3 to 4 grams of sucrose, 4.5 to 5.9 grams of histidine and 10 to 15 grams of agar. The culture medium capable of maintaining maintaining in-vitro growth of the hyphae of the ustilago esculenta is reasonable in compatibility; optimal carbon and nitrogen sources are added into a basic culture medium, so that in-vitro growth of the hyphae of the ustilago esculenta can be maintained by the culture medium.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UEMT3 and use thereof
ActiveCN105838617AImprove environmental adaptabilityControl dating timeFungiMicroorganism based processesUstilago esculentaZizania aquatica
The invention discloses an Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UEMT3 and a use thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UEMT3 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 11842. Zizania aquatica artificial breeding needs common invasion of two sexual compatible haploid strains. The strain can be used as a zizania aquatica artificial breeding mother strain, through screening, a sexual compatible haploid strain is obtained and artificial zizania aquatica breeding is realized through artificial inoculation. The haploid strain UEMT2 can be used for gene engineering reconstruction and provides an implementation base material for zizania aquatica improvement such as zizania aquatica environmental adaptability and zizania aquatica growth time control in zizania aquatica breeding.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Pair of ustilago esculenta for successfully achieving artificial breeding of normal zizania caduciflora and application of pair of ustilago esculenta
The invention discloses a pair of ustilago esculenta for successfully achieving artificial breeding of normal zizania caduciflora and application of the pair of ustilago esculenta, and belongs to thefield of biotechnology. The pair of ustilago esculenta comprises an ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 delta Itd1 and an ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 delta Itd1, wherein the ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 delta Itd1 has the preservation number of CGMCC No. 16723; and the ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 delta Itd1 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 16724. Accordingto the invention, the sexual compatible ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 delta Itd1 and ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 delta Itd1 are obtained by an artificial breeding method; the pairof ustilago esculenta can be inoculated in zizania aquatica to successfully produce normal zizania caduciflora, thereby providing a new idea for the artificial breeding of zizania caduciflora.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UEMT2 and use thereof
ActiveCN105838618AImprove environmental adaptabilityControl dating timeFungiMicroorganism based processesUstilago esculentaMicrobiology
The invention discloses an Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UEMT2 and a use thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UEMT2 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 11841. Zizania aquatica artificial breeding needs common invasion of two sexual compatible haploid strains. The strain can be used as a zizania aquatica artificial breeding mother strain, through screening, a sexual compatible haploid strain is obtained and artificial zizania aquatica breeding is realized through artificial inoculation. The haploid strain UEMT2 can be used for gene engineering reconstruction and provides an implementation base material for zizania aquatica improvement such as zizania aquatica environmental adaptability and zizania aquatica growth time control in zizania aquatica breeding.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Sterilizing composition
InactiveCN107691460ASynergistic effect is obviousReduce pollutionBiocideFungicidesDiseaseSeptoria musiva
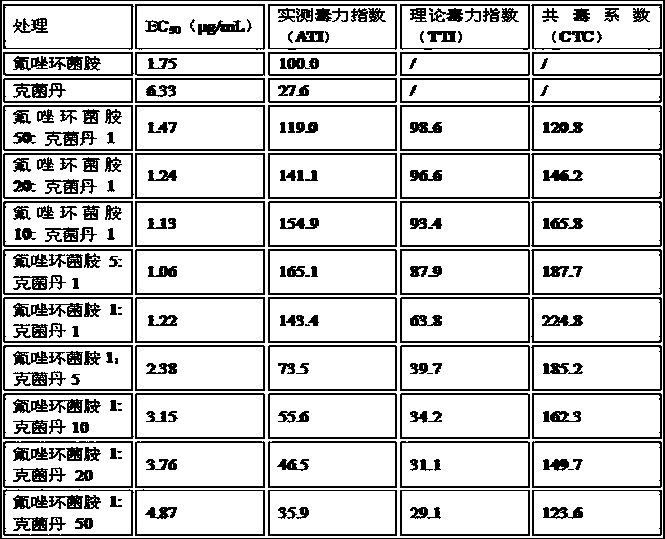
The invention discloses a sterilizing composition. The effective components are Sedaxane and captan, the mass ratio of the both is 50:1-1:50. The composition has obvious synergism and is effective totreat diseases caused by rhizoctonia solani, puccinia horiana, pyrenophora graminea, ustilago esculenta, Tilletia, Erysiphe, pyrenophora teres, Septoria musiva, and Ramularia; the composition has special effect to seed-borne disease. The composition can be applied to treat seeds and spray stems and leaves, the effect duration lasts for 4-6 weeks; the composition can be applied to the disease prevention and treatment of cereal type crops; particularly, it is applied to the seed treatment for preventing wheat ustilago esculenta, wheat tilletia, wheat basal rot, sphacelotheca reiliana, corn stalkrot, corn gall smut and rice bakanae disease.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
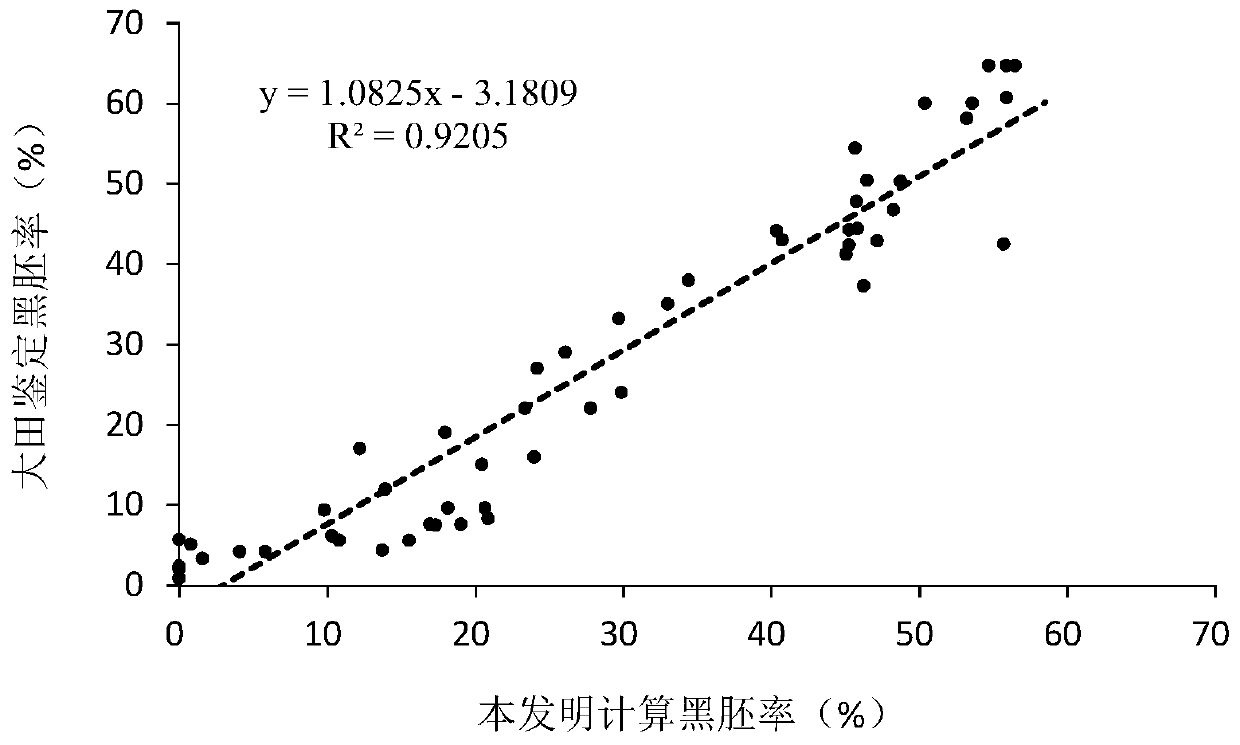
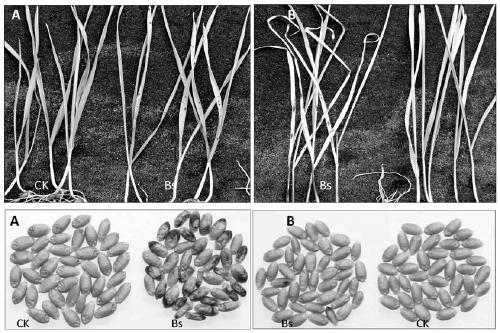
Method for indoor quick recognition of wheat resistance to wheat root rot Umbilical Verticillium chlamydosporium black embryo disease
ActiveCN111549094ASeed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementSporelingUstilago esculenta
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Wild rice stem smut fungus strain capable of producing anti-fungus antibiotic and its use
The present invention discloses a kind of Ustilago esculenta strain UEZC1 capable of producing antifungal antibiotic and its use. The Ustilago esculenta strain UEZC1 features that the teleutospore is germinated on potato glucose liquid culture medium to form basidium promycelium with 1-4 basidiospore promycelia, and the basidiospore after falling off further grow to form fusiform short hypha for inserting basidiospore. The present invention can produce antifungal antibiotic, and may be used in developing and producing medical and agricultural antifungal antibiotic.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
A kind of wild rice smut haploid bacterial strain uetsp and application thereof
The invention relates to a haploid strain of Ustilago smut UeTSP and an application thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. On the one hand, the present invention provides a new Ustilago smut haploid strain UeTSP, and on the other hand provides the use of the Ustilago smut haploid strain UeTSP in pregnant bamboo. Beneficial effects of the present invention: the smut fungus of the present invention ( Ustilago esculenta ) The haploid strain UeTSP can directly infect Zizania japonica plants and make Zizania zizania gestation without producing teliospores, that is, without the unfavorable phenotype of gray horns, which provides a new idea for zizania zizania artificial pregnancy.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A kind of smut haploid strain uet1 and its application
ActiveCN105838616BImprove environmental adaptabilityControl dating timeFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyUstilago esculenta
The invention relates to a haploid strain of Ustilago smut UET1 and its application, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The smut fungus ( Ustilago esculenta ) haploid strain UET1, the preservation number is: CGMCC No.11843. Zizania artificial breeding requires the co-infection of two sexually compatible haploid strains. This strain can be used as the mother strain of Zizania artificial breeding. Artificially pregnant watermelon. At the same time, the haploid strain can be genetically engineered to provide basic materials for the subsequent improvement of Zizania varieties, such as improving the environmental adaptability of Zizania, controlling the time of mating and so on.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A kind of wild rice smut haploid strain uemtsp and its application
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for extracting and purifying wild rice stem total proteins
InactiveCN101250217BHigh protein contentLow nucleic acid contentPeptide preparation methodsTotal proteinGenome
The invention provides an extraction method of zizania latifolia protein in the interaction of zizania latifolia and zizania smut, which simulates the interaction between zizania latifolia and zizania smut, to extract zizania latifolia gene groups and proteins which are not mixed. The invention can prepare the zizania total protein product without the protein of zizania smut, whose protein content is high, impurity content is low and nucleic acid content is low, thereby satisfying the demand of two-dimensional electrophoresis to protein purity.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A kind of separation method of smut and used culture medium
ActiveCN106085880BGood filtering effectReduce pollutionFungiMicroorganism based processesPhosphateMicroscopic observation
The invention relates to an ustilago esculenta separation method and a used culture medium. The separation method comprises the steps that vessel coating and culture are conducted on a sample, the used culture medium does not contain any nitrogen source and is prepared from, by mass, a carbon source 0.4%-1%, calcium carbonate 0.2%-0.6%, magnesium sulfate 0.01-0.05%, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.01-0.03% and agar powder 1.2-2%, wherein a pH value is 6.5-7.0. The culture medium also contains antibiotics capable of inhibiting bacteria rather than fungi. A white single colony is selected for fungus shaking after culture till turbidity can be seen with naked eyes, and if no sundry fungus pollution exists through microscopic observation, the fungus is a target strain obtained through separation. The two large problems of material limitations and pollution of a large number of sundry fungi are solved to the great degree, the ustilago esculenta separation method has no special requirement for separation materials, and the working efficiency of ustilago esculenta separation and purification is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A Pair of Ustilago smut and Its Application Successfully Achieved the Artificial Breeding of Zizania and Normal Zizania
The invention relates to a pair of wild rice smut fungus which successfully realizes the artificial breeding of Zizania and normal Zizania and its application, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The pair of Ustilago smut includes haploid strain UET1△Itd1 and UET2△Itd1. The Ustilago haploid strain UET1△Itd1 has a preservation number of CGMCC No. .16723, the preservation number of the Ustilago smut haploid strain UET2△Itd1 is CGMCC No.16724. The present invention obtains the sexually compatible Ustilago smut haploid strain UET1△Itd1 and Ustilago smut haploid strain UET2△Itd1 through artificial breeding, and uses the pair of Ustilago to inoculate wild bamboo , can successfully conceive normal Zizania, which provides a new idea for artificial inoculation of Zizania.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for breeding zizania latifolia plant seedlings
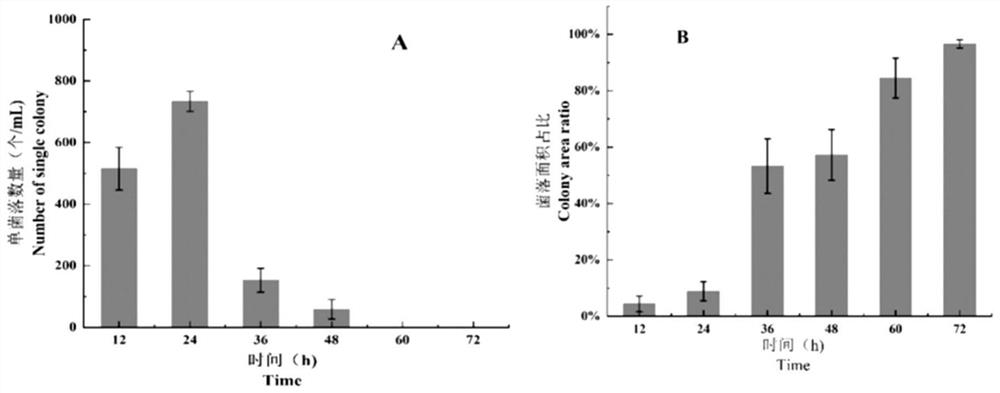
PendingCN114438258AEasy to grow seedlingsReduce economic lossMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyForward primer
The invention discloses a method for breeding zizania latifolia plant seedlings. The method comprises the following steps: extracting DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a to-be-detected sample containing Ustilago esculenta as an amplification template; a fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method is used for detection, and a primer pair used for detection comprises a forward primer with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 and a reverse primer with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2; the nucleotide sequences of the probes used for detecting the MT type Ustilago esculenta and the T type Ustilago esculenta are as shown in SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No.4; predicting the phenotype of the zizania latifolia plant in the mature period according to the ratio of the content of the T-type zizania latifolia to the content of the MT-type zizania latifolia, and breeding zizania latifolia plant seedlings. By analyzing the content of T-type and MT-type zizania esculenta in stem node or stem tip tissues of zizania aquatica plants, whether grey zizania aquatica or male zizania aquatica can be formed in the future can be effectively predicted, so that the zizania aquatica seedling raising process is optimized, and economic losses are reduced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
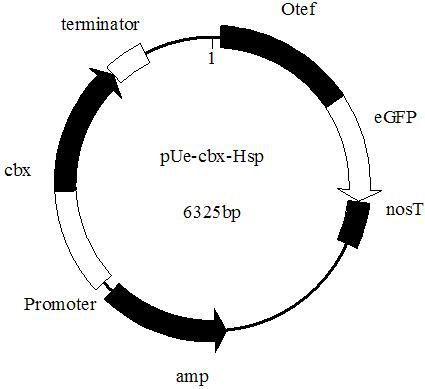
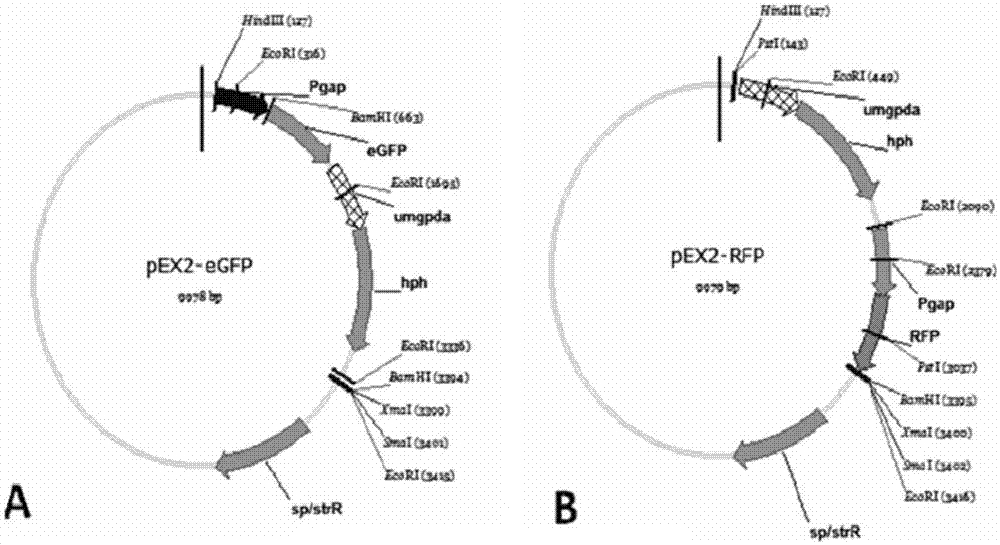
A kind of endogenous strong promoter phsp of smut smut and its expression vector and application
ActiveCN112725341BImprove expression strengthFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementUstilago esculentaNucleotide
The invention discloses an endogenous strong promoter pHSP of smut smut and its expression vector and application, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The present invention includes: a strong endogenous promoter pHSP of Ustilago smut, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; an expression vector containing strong endogenous promoter pHSP of Ustilago smut; Driving the transcription and expression of the eGFP gene, constructing a stable expression system and obtaining the application of engineering smut smut has improved eGFP expression intensity and fluorescence stability. The present invention combines endogenous pHSP promoter and strong terminator nosT of Ustilago smut with eGFP The genes are connected to construct an effective plasmid vector pUe-cbx-Hsp, which improves eGFP The expression intensity of the start eGFP Compared with otef and TFIID2, the gene transcription level was enhanced by more than 9 times and 11 times respectively.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Crispr/cas9 plasmid and its construction method and usage method
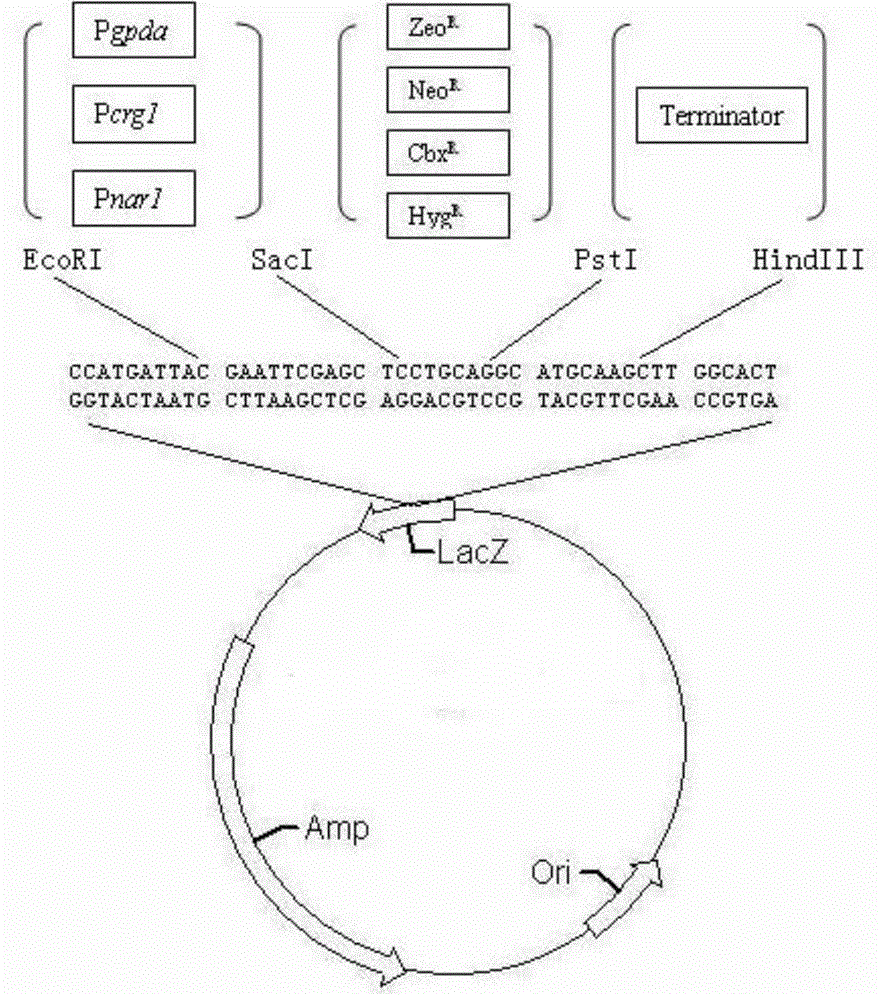
ActiveCN109593772BArtificial breeding is convenient and efficientFungiStable introduction of DNAUstilago esculentaNucleotide
The invention discloses CRISPR / Cas9 plasmid as well as a construction method and a use method of the CRISPR / Cas9 plasmid and belongs to the technical field of biotechnology. A nucleotide sequence of the CRISPR / Cas9 is shown in SEQ ID No.3. The CRISPR / Cas9 plasmid for artificial breeding of zizania latifolia is constructed with a CRISPR / Cas9 technology and converts ustilago esculenta, a gene knockout strain can be obtained, and the CRISPR / Cas9 plasmid can be more conveniently and efficiently applied to artificial breeding of the zizania latifolia.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Agrobacterium-mediated Zizania smut transformant strain and its preparation method and application
The invention relates to the field of biological breeding, in particular to an Agrobacterium-mediated Ustilago esculenta transformant strain and a preparation method and application thereof. Agrobacterium mediates the transformant strain of Ustilago esculenta, and the Agrobacterium infection receptor of the transformant strain is Ustilago esculenta. A method for preparing the above-mentioned Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Zizania smut transformant strain, the steps are as follows: 1) Preparation of fungal expression vector; 2) Preparation of Agrobacterium competent; 3) Electrotransformation of Agrobacterium; 4) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation Guided transformation to obtain the transformant. The present invention does not need to prepare complex protoplasts, the source of the receptor is simple, and the spores and hyphae of the fungus can be directly used for transformation; the transformation efficiency is high; in addition, the single-copy ratio of the obtained transformants is relatively large, which is beneficial to obtain marker genes .
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD +1
A medium for maintaining the growth of wild black powder fungus mycelium in vitro
ActiveCN105543109BCompatibility is reasonableMaintain in vitro growthFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses a culture medium capable of maintaining in-vitro growth of hyphae of ustilago esculenta, and belongs to the technical field of culture media. Every liter of the culture medium comprises the following components: 0.85 to 1.15 grams of K2HPO4, 0.45 to 0.55 gram of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.008 to 0.012 gram of FeSO4.7H2O, 0.45 to 0.55 gram of KCl, 2 to 3 grams of yeast powder, 4 to 6 grams of peptones, 3 to 4 grams of sucrose, 4.5 to 5.9 grams of histidine and 10 to 15 grams of agar. The culture medium capable of maintaining maintaining in-vitro growth of the hyphae of the ustilago esculenta is reasonable in compatibility; optimal carbon and nitrogen sources are added into a basic culture medium, so that in-vitro growth of the hyphae of the ustilago esculenta can be maintained by the culture medium.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for constructing Ustilago esculenta T-DNA mutant library and analyzing insertion sites
PendingCN114736897ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenome resequencingGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a construction and insertion site analysis method of an Ustilago esculenta T-DNA mutant library, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: by taking a constructed Ustilago esculenta self-fusion strain TSP as a starting strain and a plasmid containing a geneticin resistance gene as a carrier, constructing a Ustilago esculenta T-DNA mutant library through ATMT, carrying out genome re-sequencing on the constructed Ustilago esculenta T-DNA, and analyzing a T-DNA insertion site of the Ustilago esculenta T-DNA. The method lays a foundation for subsequent regulation and control mechanism research of Ustilago esculenta two-form conversion.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
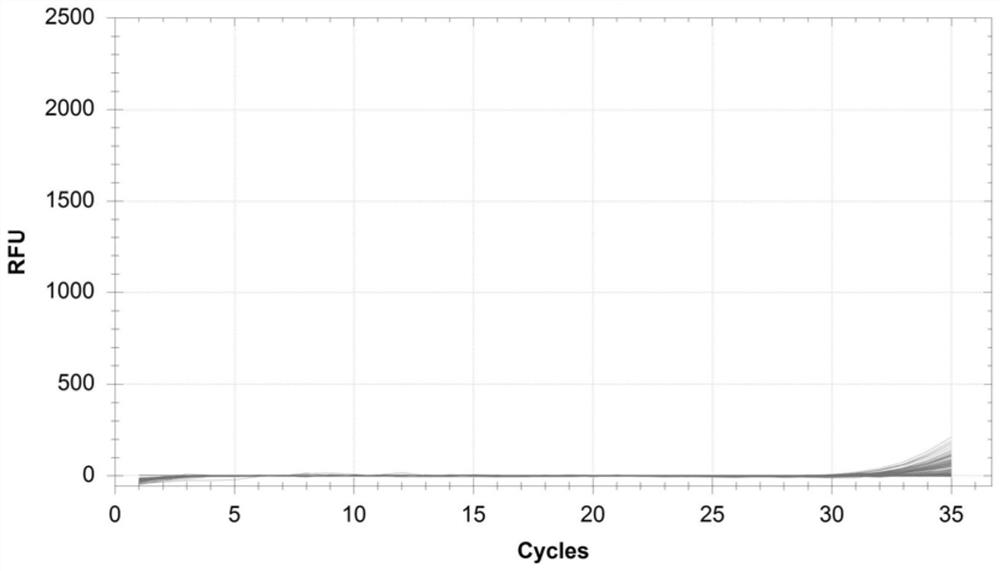
Ustilago esculenta typing identification method and application thereof
PendingCN114703313ALow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyUstilago esculenta
The invention discloses an Ustilago esculenta typing identification method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The invention provides a target for typing identification of Ustilago esculenta. The target is derived from T-type Ustilago esculenta, and the nucleotide sequence of the target is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. According to the Ustilago esculenta typing identification method provided by the invention, T-type Ustilago esculenta in a complex sample can be quantitatively detected, the detection limit is as low as 0.0088 ng / [mu] L (22.36 copies / [mu] L), and meanwhile, the quantitative detection of the T-type Ustilago esculenta in different tissues in different stages of plants is realized.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +1
Agrobacterium tumefacien mediated genetic transformation method for ustilago esculenta
InactiveCN107299108AAdvance breeding workEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSporeUstilago esculenta
The invention discloses an agrobacterium tumefacien mediated genetic transformation method for ustilago esculenta, wherein an ustilago esculenta spore is taken as a transformation acceptor material, the agrobacterium tumefacien containing a binary vector and the ustilago esculenta spore are mixed, co-cultured, and screened by an antibiotic, so as to obtain a resistant transformant. The method is simple in operation, high in transformation efficiency and high in stability, an ustilago esculenta mutant library is created according to the method, the rick screening bacteria source is provided for screening a binary transformation mutant of the ustilago esculenta, meanwhile, a means is provided for cloning a binary transformation gene of the ustilago esculenta and an interaction related gene of the ustilago esculenta and a zizania aquatica plant, and the method is of great significances for clarifying the stem swelling mechanism of the zizania aquatica and promoting the breeding of the zizania aquatica.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院生物技术研究所
A method of artificial inoculation of smut fungus that successfully makes Zizania zizania plants pregnant
ActiveCN105830760BEasy to operatePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsUstilago esculentaInoculation methods
The invention provides an Ustilago esculenta artificial inoculation method capable of realizing successful stem-swelling of a water bamboo plant, belonging to the technical field of artificial inoculation of water bamboo. According to the invention, by inoculating Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET1 and Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UET2 selected from Ustilago esculenta in wild water bamboo, stem-swelling of the wild water bamboo is successfully realized. The method provided by the invention has simple operation, is effective, and provides a new direction for seed breeding of the water bamboo.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
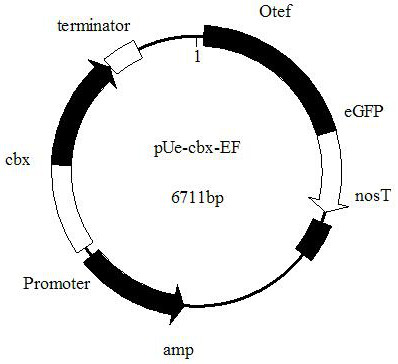
Ustilago esculenta endogenous promoter pEF as well as expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN112680449AImprove expression strengthEnhanced gene transcription levelsFungiMicroorganism based processesNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses an ustilago esculenta endogenous promoter pEF as well as an expression vector and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the ustilago esculenta endogenous promoter pEF is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention discloses the expression vector containing the ustilago esculenta endogenous promoter pEF, an application of the ustilago esculenta endogenous promoter pEF to driving transcription and expression of an eGFP gene, constructing a stable expression system and obtaining engineering ustilago esculenta, and an application of the ustilago esculenta endogenous promoter pEF to improving expression intensity and fluorescence stability of eGFP. The ustilago esculenta endogenous pEF promoter and a strong terminator nosT are connected with the eGFP gene, an effective plasmid vector pUe-cbx-EF is constructed, more choices are provided for construction of an ustilago esculenta genetic transformation vector, and a foundation is laid for functional gene research of the ustilago esculenta.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com