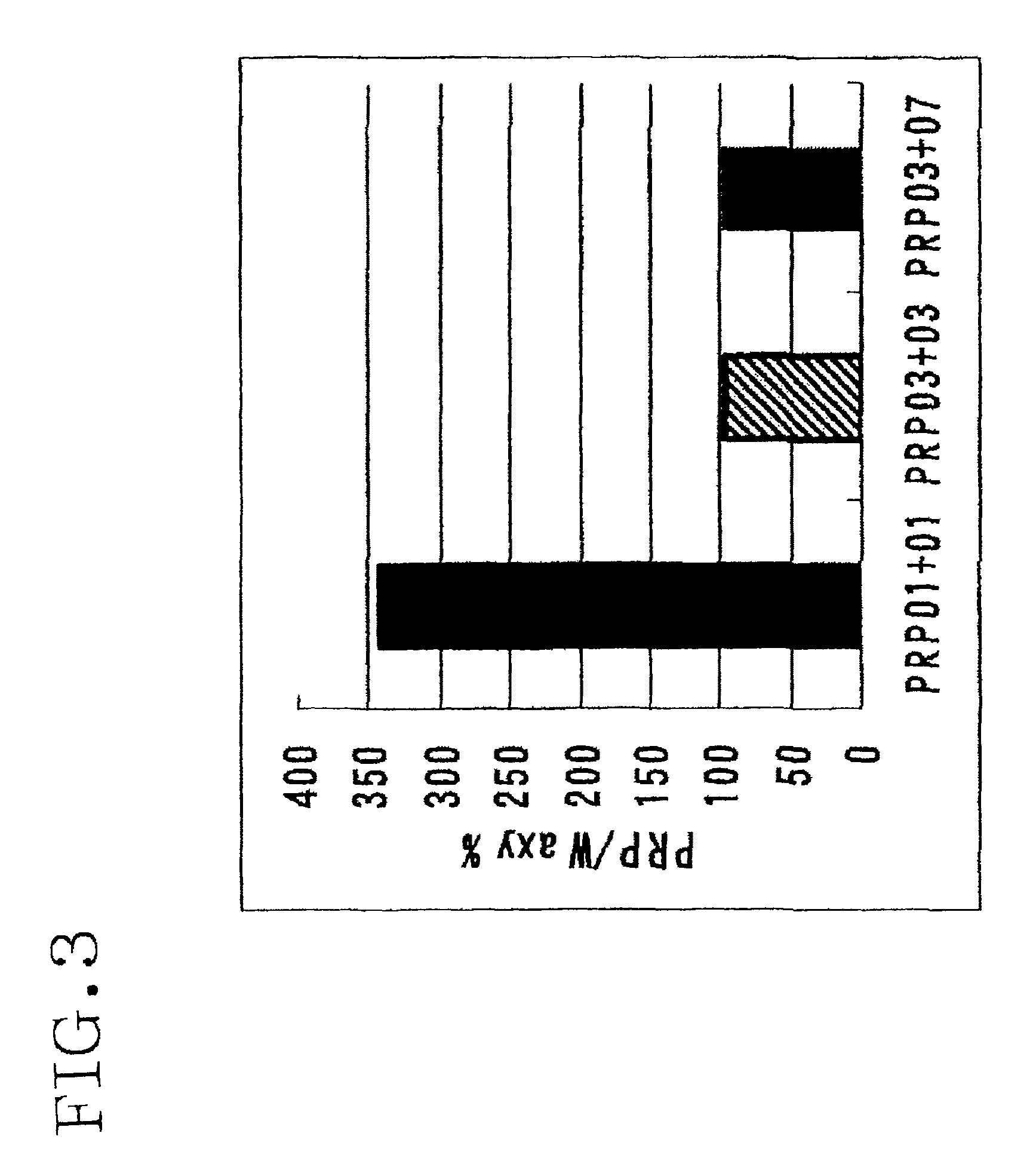
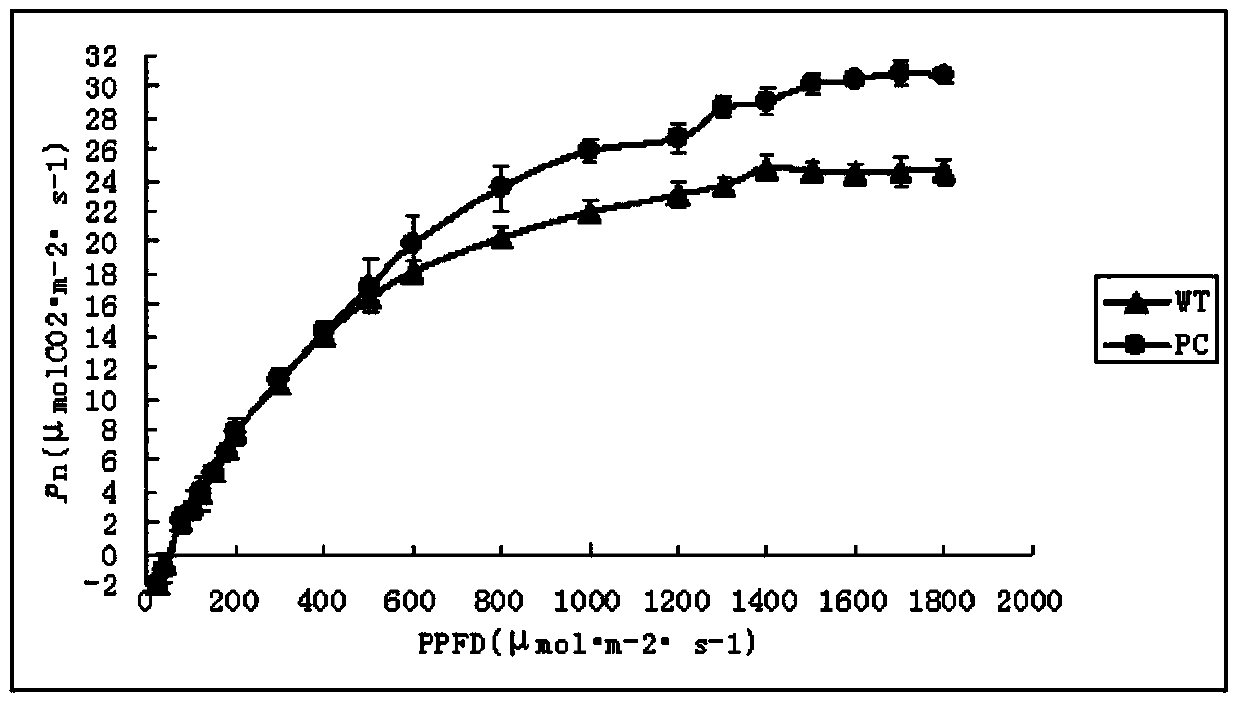
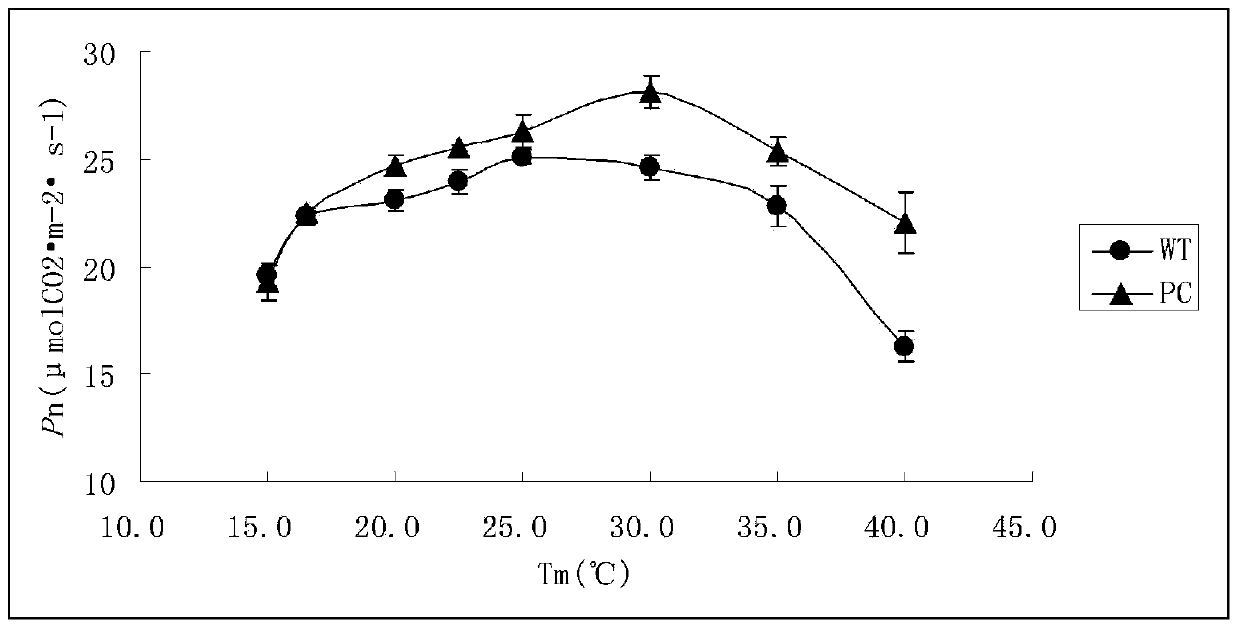
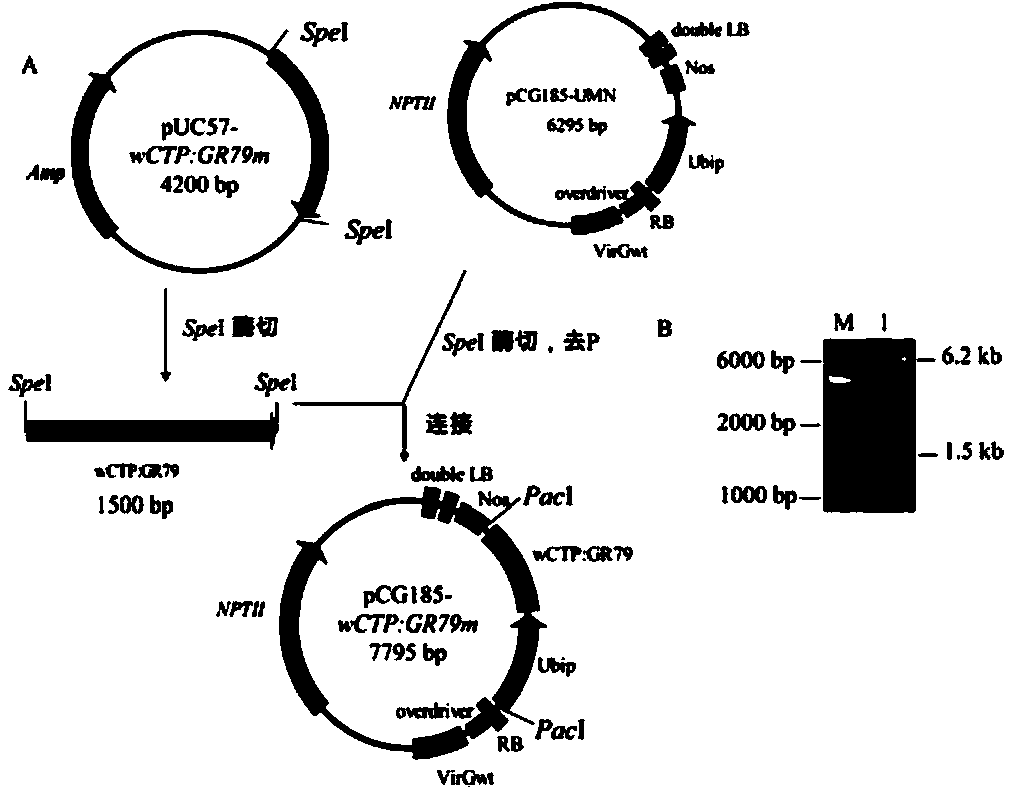
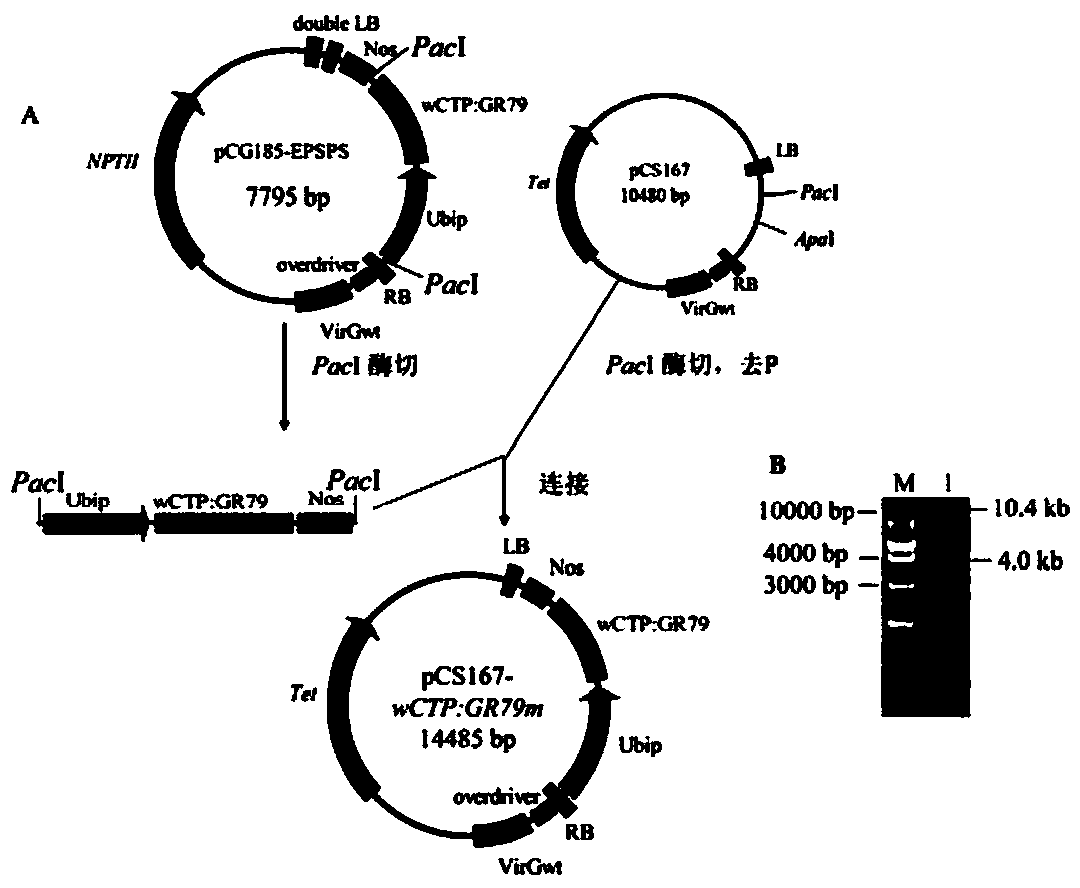
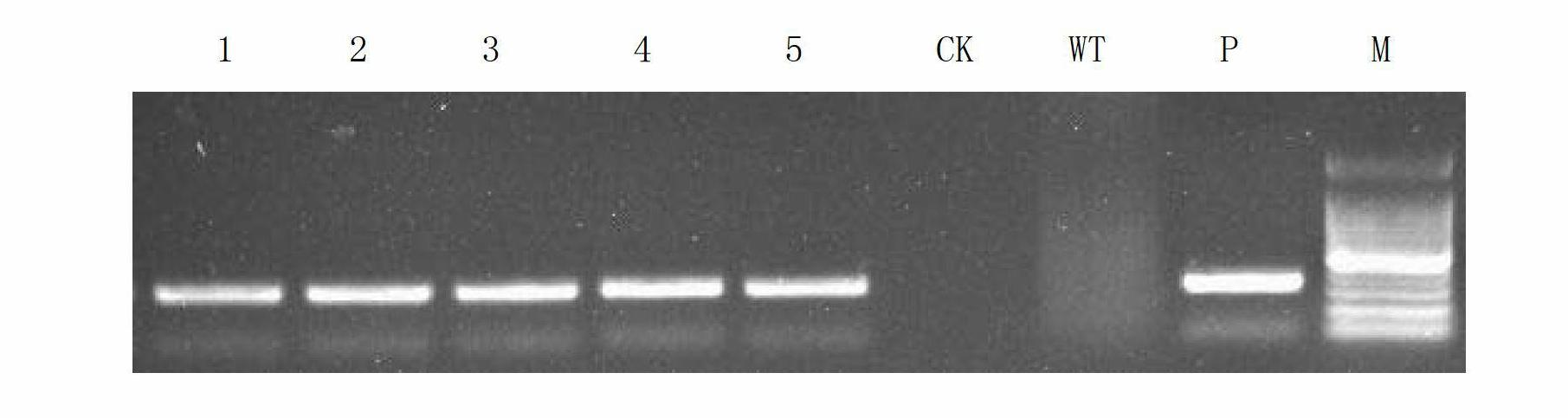
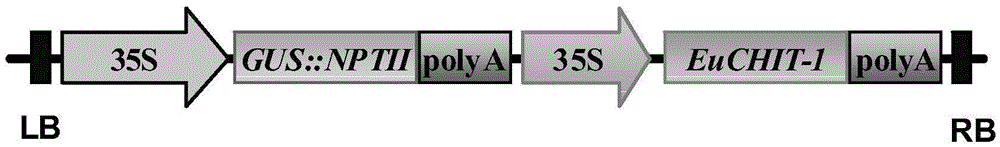
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "Genetically modified wheat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically modified wheat is wheat that has been genetically engineered by the direct manipulation of its genome using biotechnology. As of 2017, no GM wheat is grown commercially, although many field tests have been conducted.
Wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR/Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/-CRISPR-associated protein 9) vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105316327AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionTriticeaeGenetically modified wheat
The invention provides a wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / -CRISPR-associated protein 9) vector and application thereof and belongs to the field of crop molecular biology. The wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector and the application thereof have the advantages that gRNA of a third exon of specificity-targeted TaAGO4a is provided firstly, a DNA sequence of the gRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the gRNA contains an enzyme cutting site XmnI; subsequently, the CRISPR / Cas9 vector containing the gRNA is provided, and through co-transformation of Cas9 and the specific gRNA into a wheat protoplast as well as enzyme cutting and sequencing technologies, the condition that the gRNA can guide the Cas9 to cut three copies positioned on a chromosome 3A, a chromosome 3B and a chromosome 3D of the TaAGO4a respectively can be detected successfully so as to cause frameshift mutation of the gene and result in afunction or excalation of the gene; the wheat TaAGO4a gene CRISPR / Cas9 vector can be used for preparing TaAGO4a gene-deleted transgenic wheat.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wheat cultivar 00WB80404
InactiveUS7563967B2Tissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic MaterialsTriticeae
A wheat cultivar, designated 00WB80404, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of wheat cultivar 00WB80404, to the plants of wheat 00WB80404, and to methods for producing a wheat plant produced by crossing wheat cultivar 00WB80404 with itself or another wheat variety. The invention also relates to methods for producing a wheat plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic wheat plants and plant parts produced by those methods. The invention also relates to wheat varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from wheat cultivar 00WB80404, to methods for producing other wheat varieties, lines or plant parts derived from wheat cultivar 00WB80404, and to the wheat plants, varieties, and their parts derived from the use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid wheat seeds and plants produced by crossing wheat cultivar 00WB80404 with another wheat cultivar.
Owner:RESOURCE SEEDS
Improved method for detecting and identifying transgenic wheat with high sensitivity and high efficiency
InactiveCN103160612AOvercome the problem of unsatisfactory detection effectImprovement of Chromosome Production TechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell divisionFluorescence
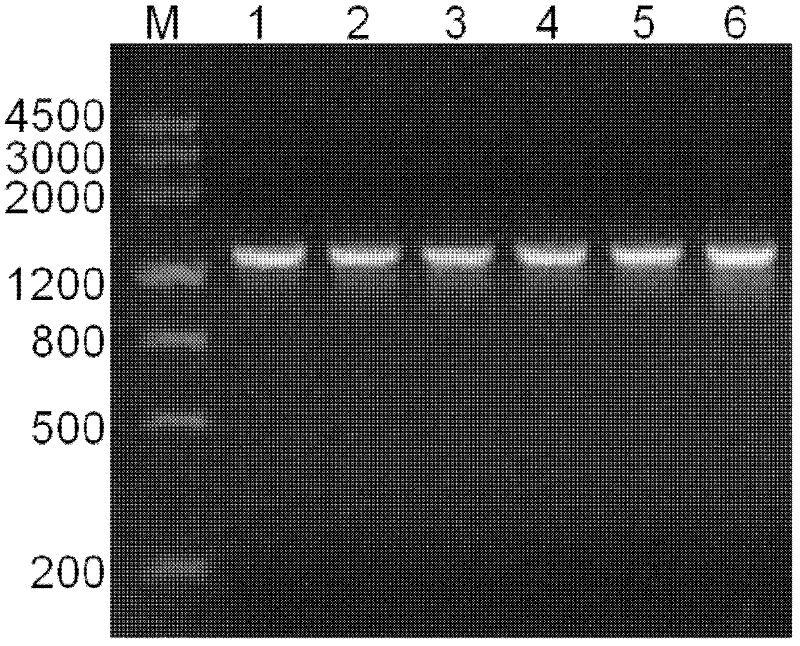
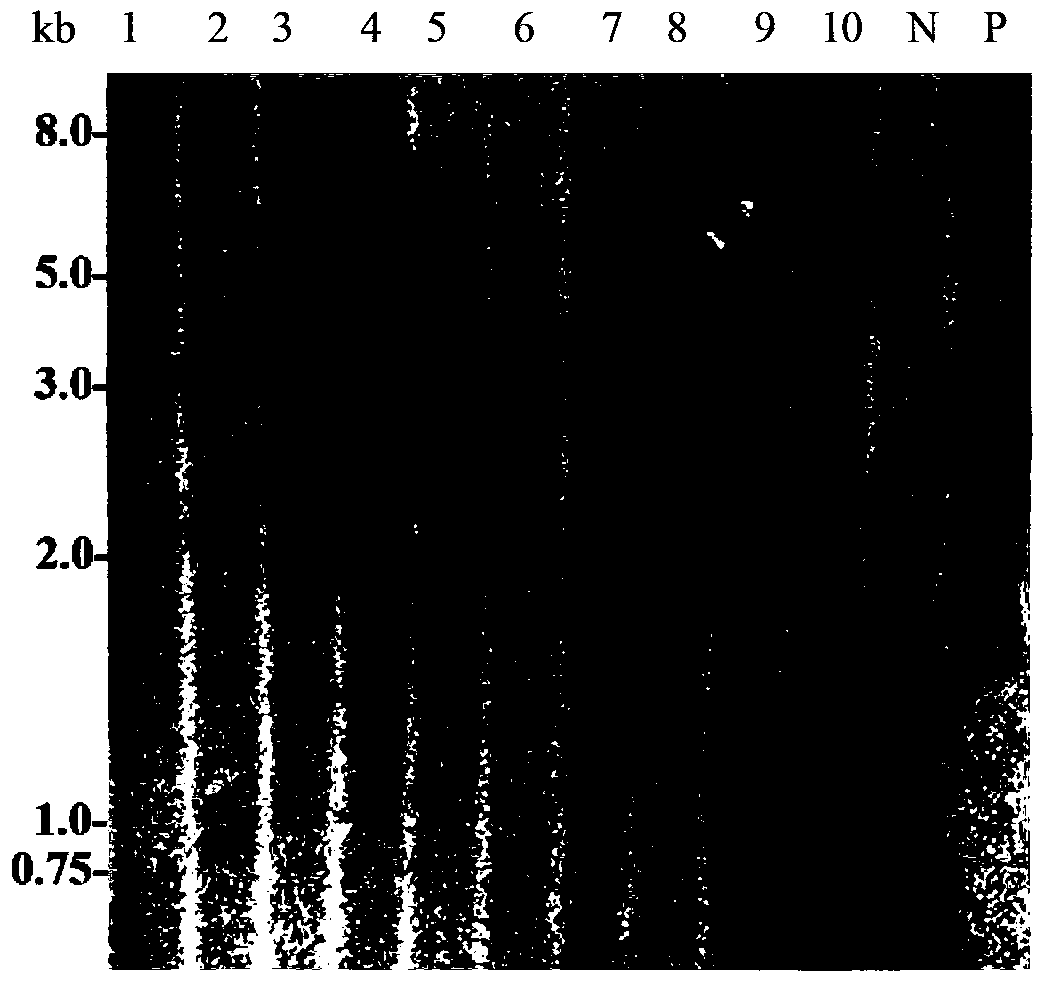
The invention discloses an improved method for detecting and identifying transgenic wheat with high sensitivity and high efficiency. The improved method comprises the steps of: (1) carrying out pretreatment and enzymolysis on tissue with vigorous cell division in a meristematic zone at a root tip of wheat through N2O gas to obtain a metaphase mitotic phase specimen with clear image and good dispersion of chromosomes; (2) marking a fluorescent probe of a target fragment to be detected (for example, a transgenic fragment carried by a transgenic carrier) by utilizing a nick translation method; (3) carrying out fluorescent in-situ hybridization on the metaphase mitotic phase chromosomes of the transgenic wheat obtained in the step (1) by utilizing the fluorescent probe of the target fragment of the transgenic carrier constructed in the step (2); and (4) analyzing fluorescent in-situ hybridization results obtained in the step (3), and comparing the fluorescent in-situ hybridization results with a contrast material to determine the distribution of fluorescent signals in the transgenic wheat to be detected. The improved method provided by the inventions can be applied to chromosomal localization of exogenous transgenic wheat with the sensitivity reaching 2-3kb, and also can be applied in the identification of transgenic signals of other crops.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wheat plants with immunity to wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV)
The present invention provides a transgenic wheat cell or wheat plant, the wheat cell or wheat plant comprising a chimeric DNA molecule which encodes a dsRNA molecule which is capable of inhibiting wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) replication, wherein the wheat cell or plant is immune to WSMV. The present invention also provides a chimeric DNA, the chimeric DNA comprising (i) a wheat expressible promoter; (ii) a region which encodes a dsRNA which is capable of inhibiting WSMV replication; and (iii) a transcription termination and polyadenylation signal. Finally, the present invention provides a process for producing the aforementioned transgenic wheat cell or plant, comprising (i) introducing a chimeric DNA molecule comprising (a) a wheat expressible promoter; (b) a region which encodes a dsRNA which is capable of inhibiting WSMV replication; and (c) a transcription termination and polyadenylation signal into a parental wheat cell; and optionally (ii) regenerating a wheat plant from the wheat cell comprising the chimeric DNA molecule; and (iii) identifying and / or selecting a plant which is immune to WSMV.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Method for breeding aphid-resistant transgenic wheat and special vector
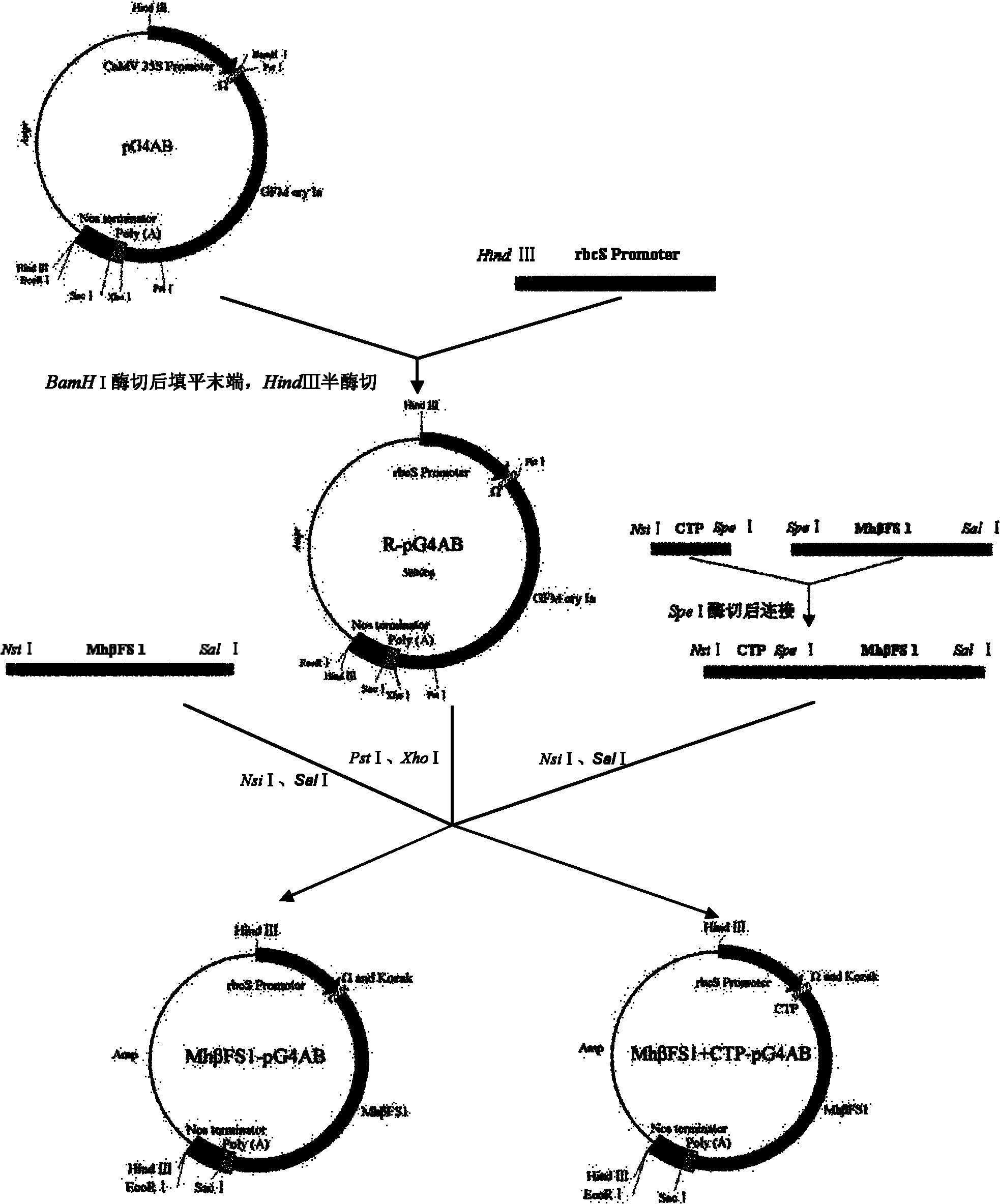
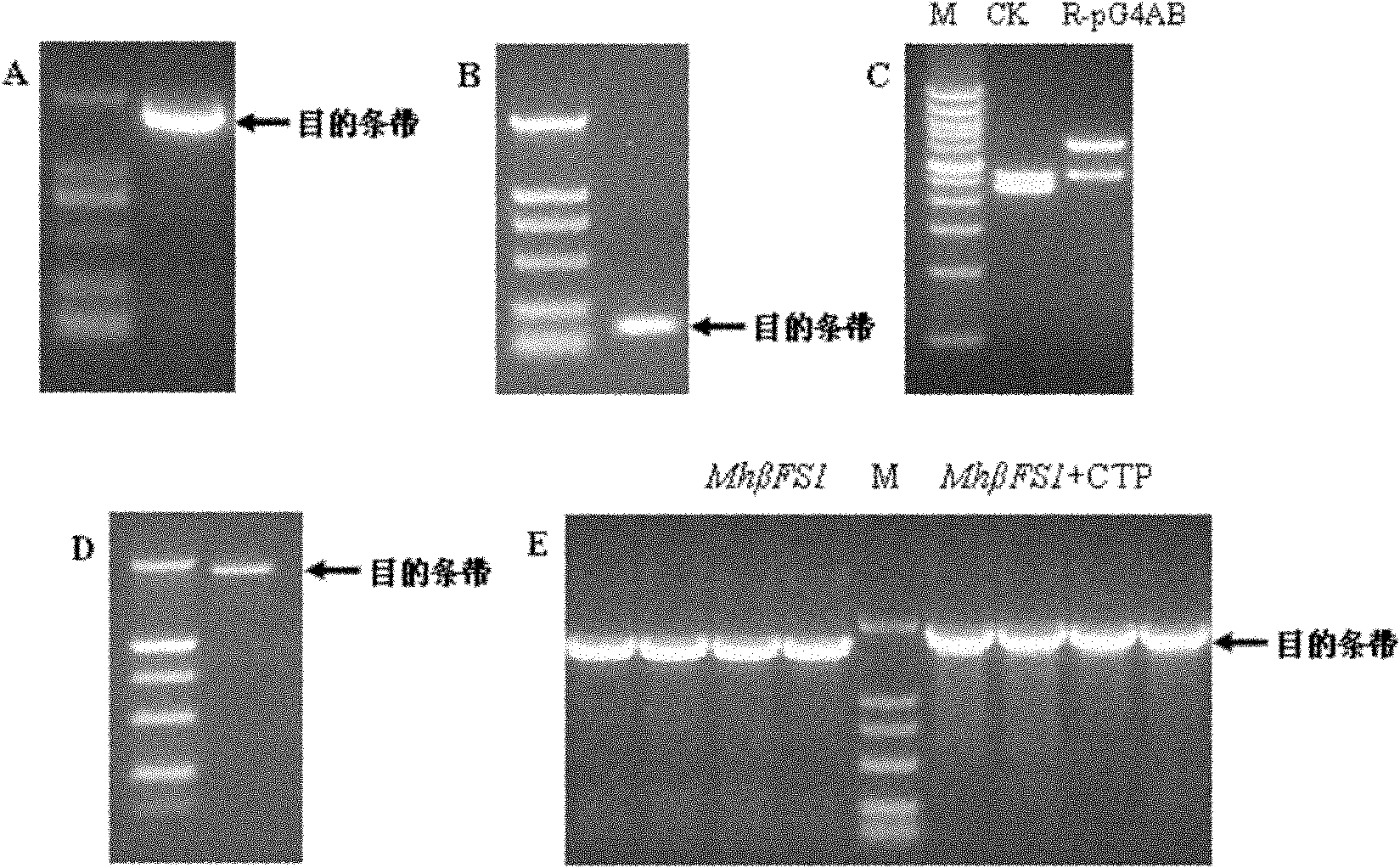
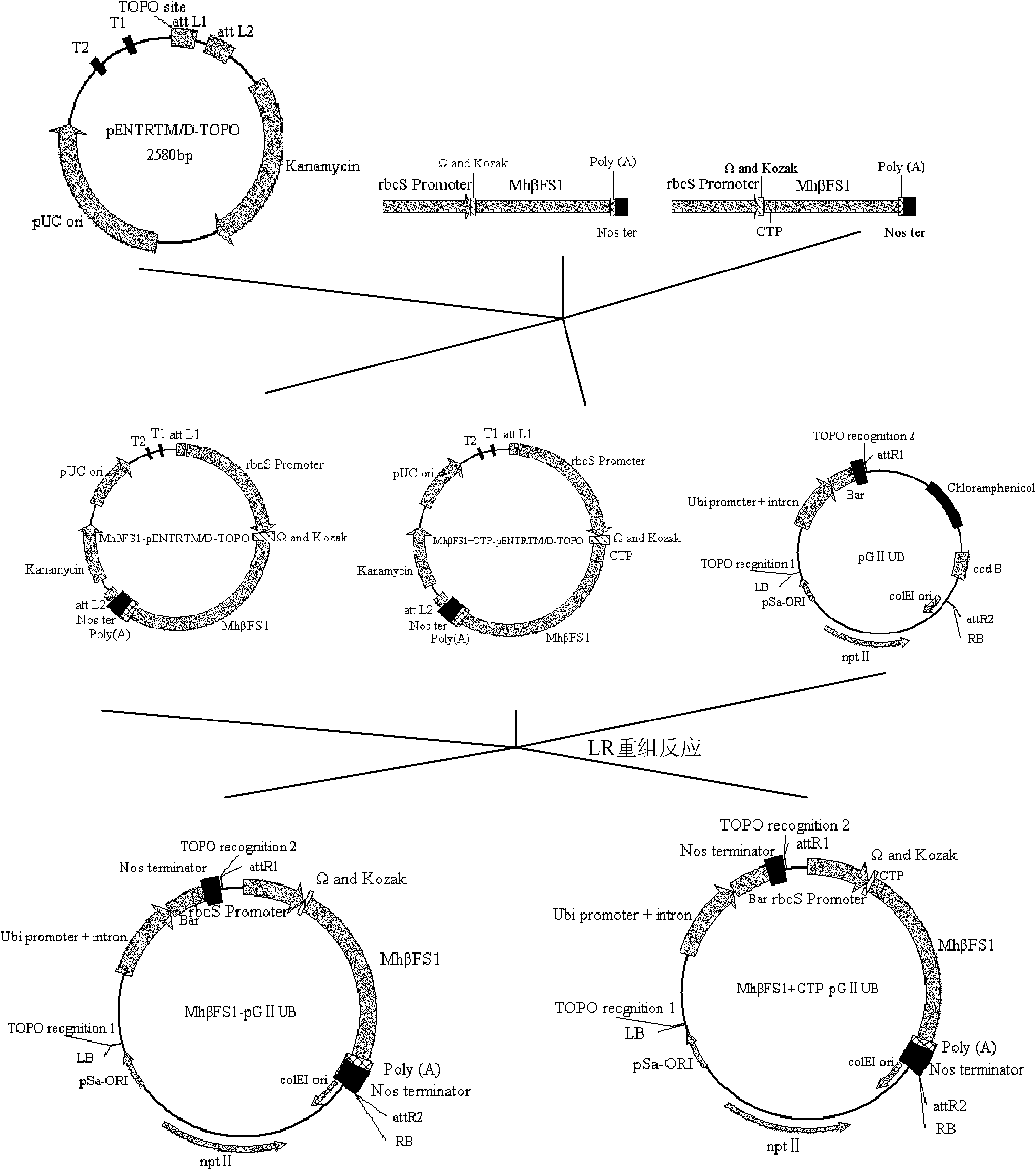
The invention discloses a method for breeding aphid-resistant transgenic wheat and a special expression vector. A recombinant vector provided by the invention is obtained by inserting gene expression cassettes shown as nucleotides at sites 1 to 3,828 from the tail end 5' in SEQ ID NO (Sequence Identity Number): 1 into multiple cloning sites of a vector pG4AB. Experiments prove that the aphid resistance of the transgenic wheat into which the vector is transferred is obviously higher than that of wild wheat, so that the vector has great significance in the field of genetic breeding of plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel method of low-gluten wheat germplasm creation
InactiveCN102732557AReduced gluten strengthVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationGenetic MaterialsTriticeae
The invention discloses a method for breeding low-gluten wheat. The low-gluten wheat breeding method provided by the invention comprises a step that: a Glu-1Ex gene is transferred into a target wheat, such that a transgenic wheat with a gluten strength lower than that of the target wheat is obtained. The method also comprises the steps that: the transgenic wheat is hybridized with a wheat with a gluten strength requiring lowering, such that a hybridized wheat with a gluten strength lower than that of the wheat with the gluten strength requiring lowering is obtained; the hybridized wheat is subjected to backcrossing with the wheat with the gluten strength requiring lowering, such that a backcrossing progeny is obtained; and the backcrossing progeny is subjected to selfing. As a result of experiments, with the transferring of the Glu-1Ex gene, a stably inherited HMW-GS expression co-suppression wheat material can be obtained. When the material is adopted as a breeding genetic material, and is used in backcrossing of other wheat materials with good comprehensive characteristic performances, wheat novel germplasm with reduced gluten strength can be obtained. Therefore, the creation of high-quality low-gluten wheat suitable for cookie and pastry processing can be promoted.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
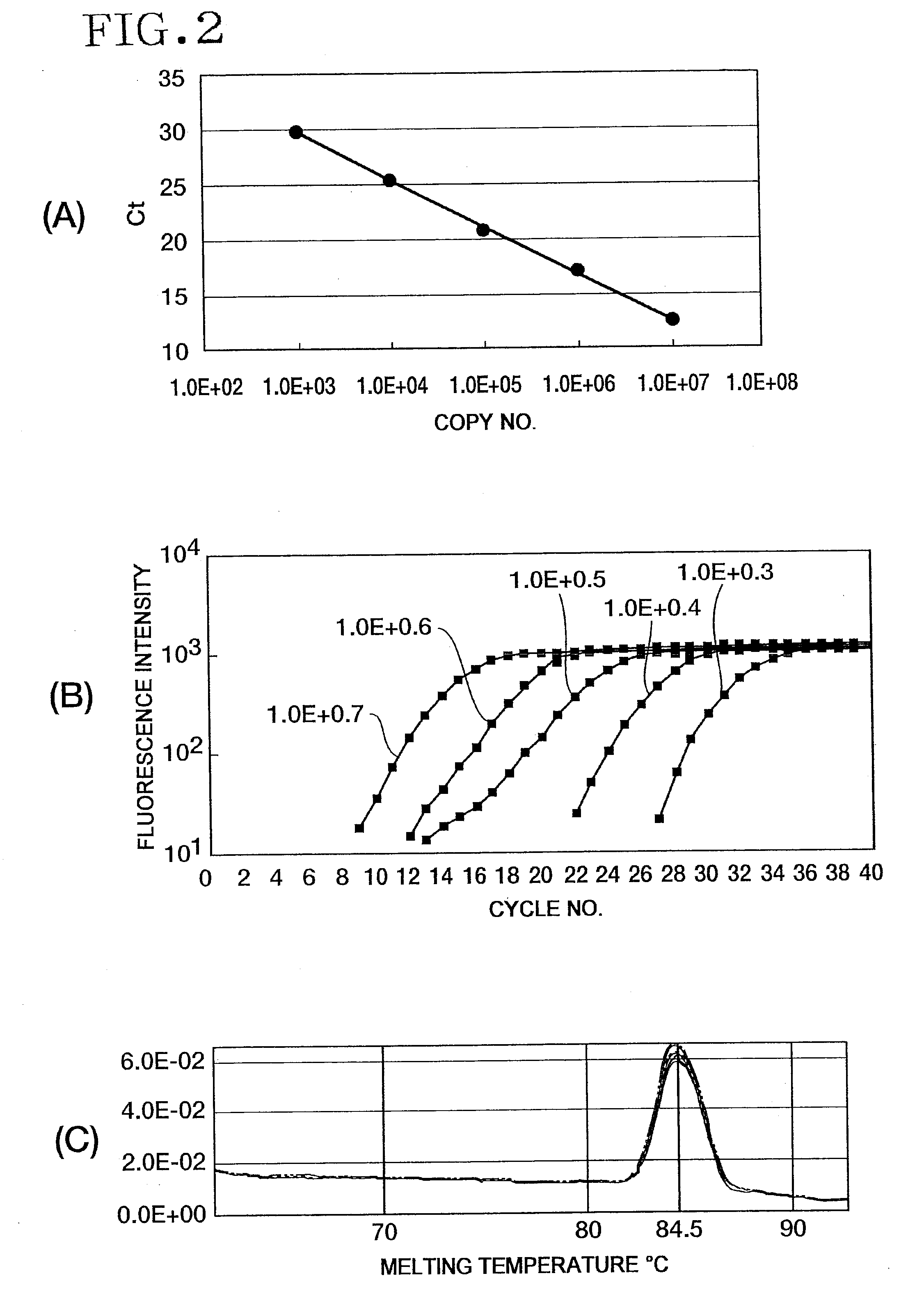
Method for detecting number of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wheat rhizosphere soil based on real-time fluorescence quantification PCR
InactiveCN106011256AStable and repeatable resultsStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiFluorescence
The invention provides a method for detecting the number of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wheat rhizosphere soil based on real-time fluorescence quantification PCR. The method includes the steps that firstly, sample total DNA of wheat rhizosphere soil is extracted and serves as a template of PCR amplification; then, amplification is conducted with SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No. 2 as primers, and specific fragments of 129 bp are obtained; after bond and conversion are conducted, qPCR amplification is conducted. By means of the method, arbuscular mycorrhiza is authenticated, absolute quantification can be conducted on the arbuscular mycorrhiza accurately, the copy number of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in all periods of duration of transgenic wheat is obtained, and in the growth and development stages of wheat, the arbuscular mycorrhiza copy number tends to be gradually increased as a whole. The rapid, convenient and precise authentication method is built, a theoretical and test basis is provided for subsequent tests, great significance is provided for further evaluation of safety of transgenic crops, and compared with an existing method, the method is high in sensitivity, high in specificity, good in repeatability, convenient to operate and visual in result.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Pollen-specific promoter and expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN102533761AReduce adverse effectsAvoid Biosafety ConcernsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAgricultural sciencePollen specific
The invention discloses a pollen-specific promoter and an expression vector thereof. Experiments show that the promoter can drive efficient and specific expression of a target gene in the pollen of transgenic rice. The promoter of the invention can be used for functional analysis and identification of genes related to growth and development of plant pollen, as well as creation of plant male sterile lines, prevention of plant transgenic drift, and the like. Especially, the promoter has an important application value in creation of male sterile lines of rice and other gramineous crops and utilization of heterozygous advantages.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for detecting wheat yellow mosaic virus-resisting transgenic wheat metabolites
ActiveCN103808818AIncrease signal strengthData results are reliableComponent separationMetaboliteGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
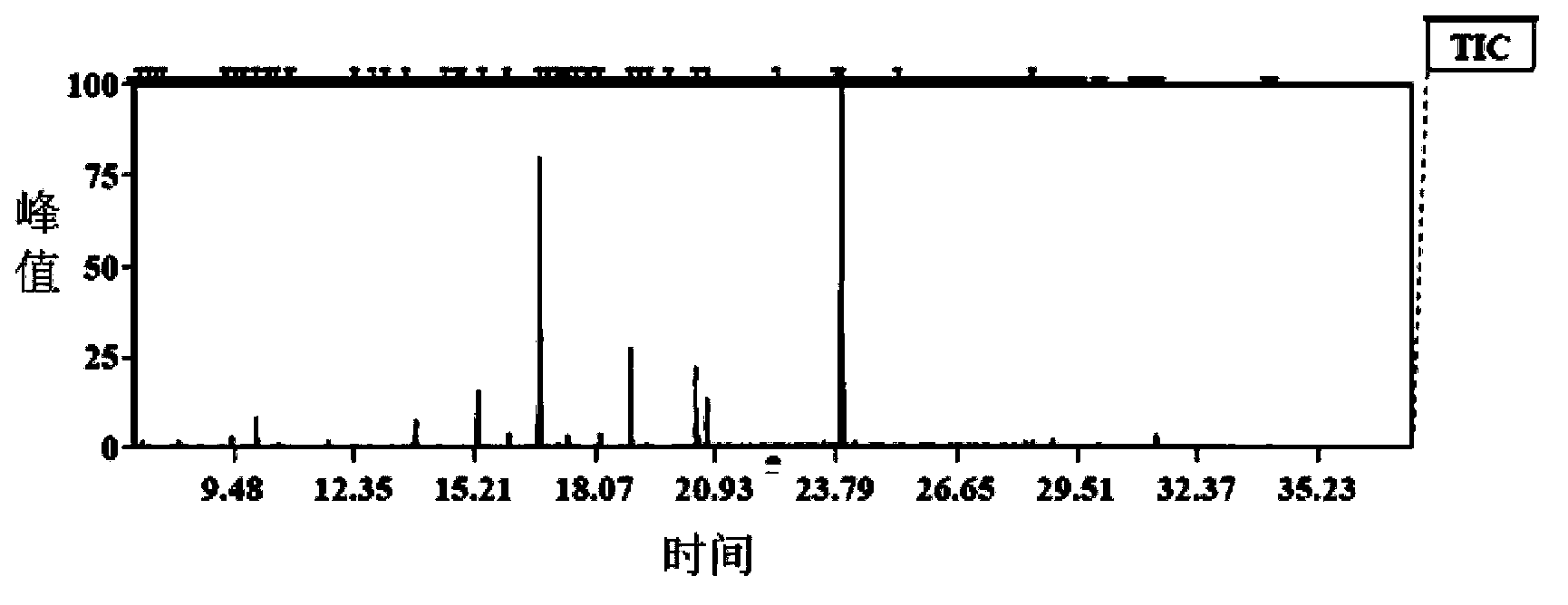
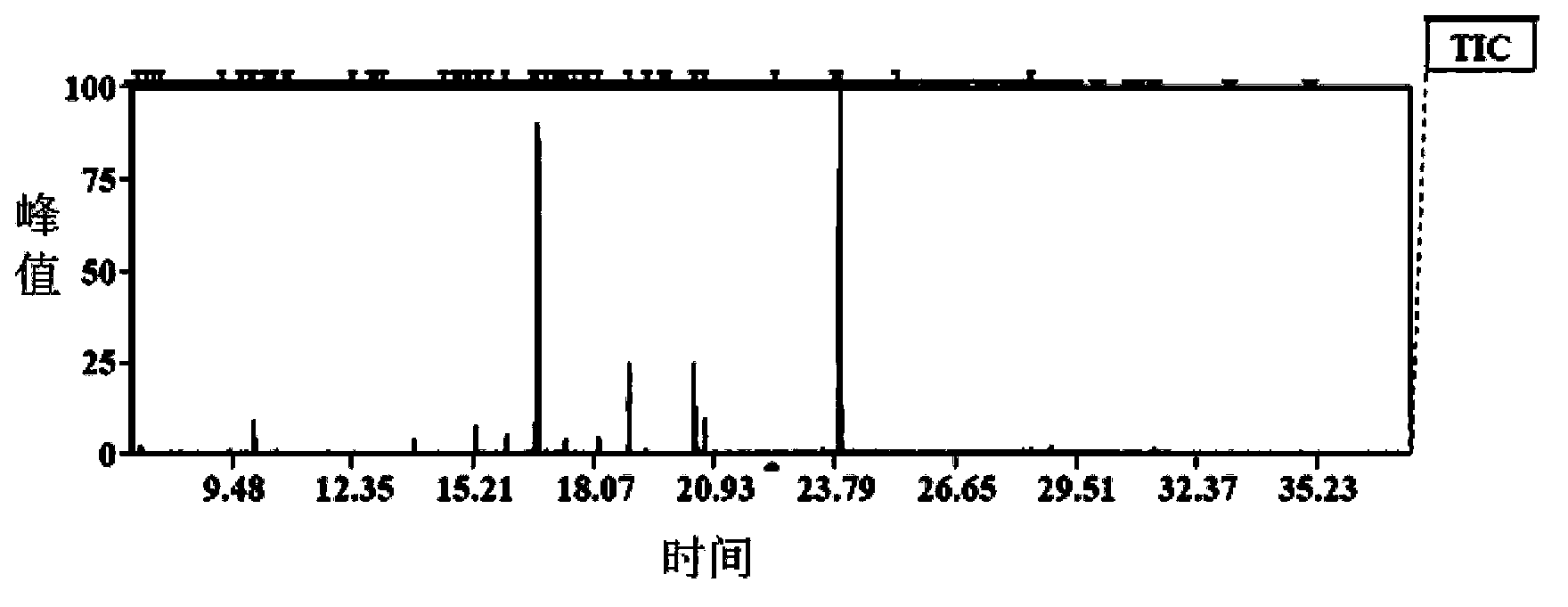
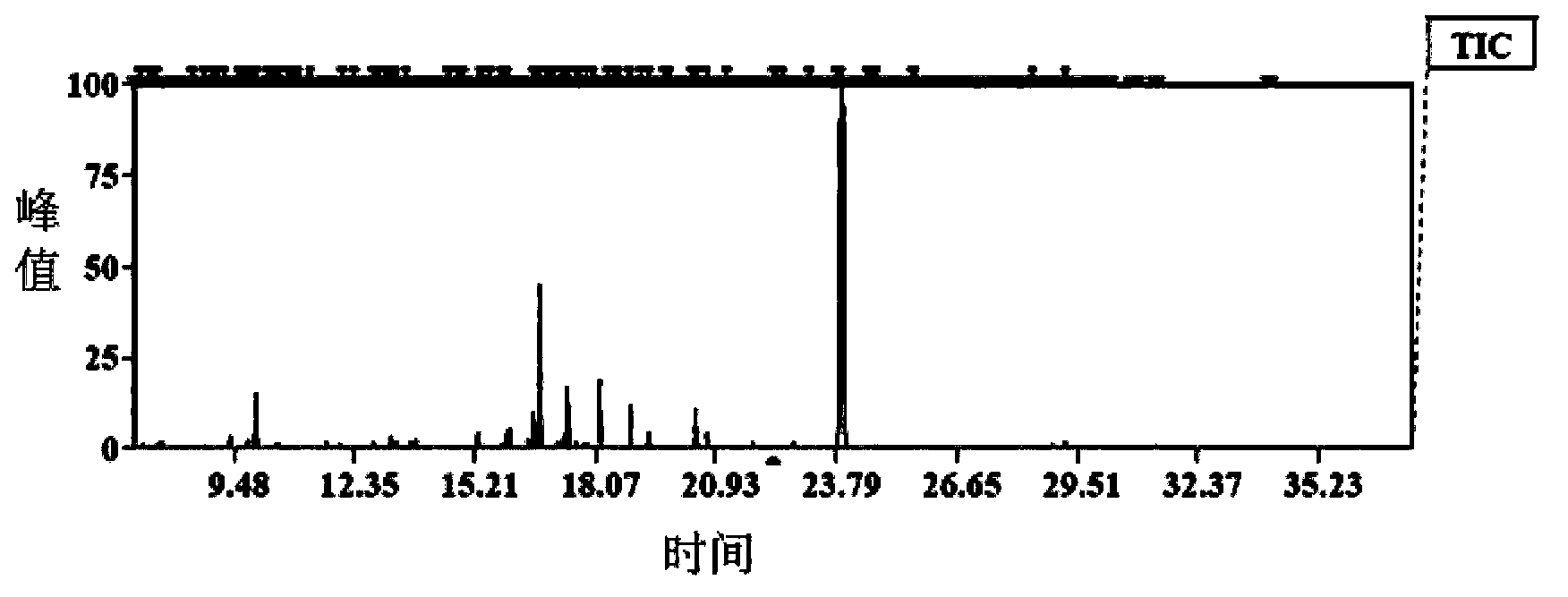
The invention provides a method for detecting wheat yellow mosaic virus-resisting transgenic wheat metabolites on the basis of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technology (GC-MS). The wheat yellow mosaic virus-resisting transgenic wheat metabolites are optimized on the basis of the GC-MS detection method, the type and proportion of an extracted solution, extracting time, volume of the extracted solution, deriving process temperature and time are respectively optimized, the relative peak area is at an optimal detection state under the extracting condition of the extracted solution that the ratio of water to acetonitrile to isopropanol is 2:3:3 when 1mL of extracted solution is added for extracting for 20min, and more metabolites components can be detected. Under the deriving condition that the temperature is 30DEG C and the extracting time is 90min, the relative peak area is large, and the signal intensity is obvious. By adopting the detection method, reliable and effective data can be provided for the study of the metabonomics of the wheat yellow mosaic virus-resisting transgene wheat, and a foundation can be laid for the safety evaluation of the transgenic crop.
Owner:中检科(北京)测试技术有限公司
Method for establishing number of Fusarium sp. copies in rhizosphere soil in growth period of transgenic rice by fluorescence real-time quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
InactiveCN102517385AImprove linearityHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceGenetically modified wheat
The invention relates to a method for establishing number of Fusarium sp. copies in rhizosphere soil in growth period of transgenic rice by fluorescence real-time quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction), which comprises the following steps: establishing five soil sampling points on a diagonal line and marking and locating, and collecting rhizosphere soil samples at the above soil sampling points before seeding and at the growing period; extracting total DNA from the soil samples collected at the soil sampling points, dissolving the total DNA of the samples in double distilled water, and carrying out PCR amplification of the sample DNA at each period with a Fusarium-specific universal primer pair SEQ ID No.2 and SEQ ID No.3 to obtain a specific fragment of size 418bp (base pairs); directly measuring the number of copies of the corresponding Fusarium sp. with a fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument according to the variation of fluorescence signals and a standard curve; and summarizing the number of Fusarium sp. copies in the soil samples at different periods to obtain the number of Fusarium sp. copies in rhizosphere soil in the growth period of transgenic rice.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting quantity of pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizospheric soil during growth period of transgenic wheat by virtue of fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
ActiveCN103397099AConsistent repetitive responseEasy to distinguishMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePseudomonas fluorescensPseudomonas
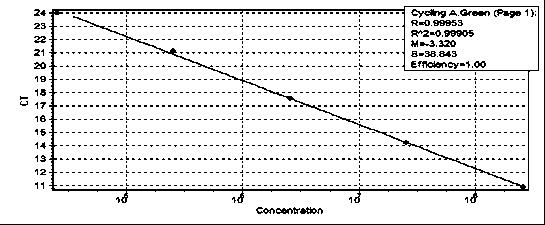
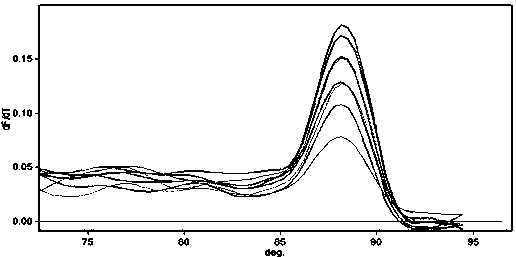
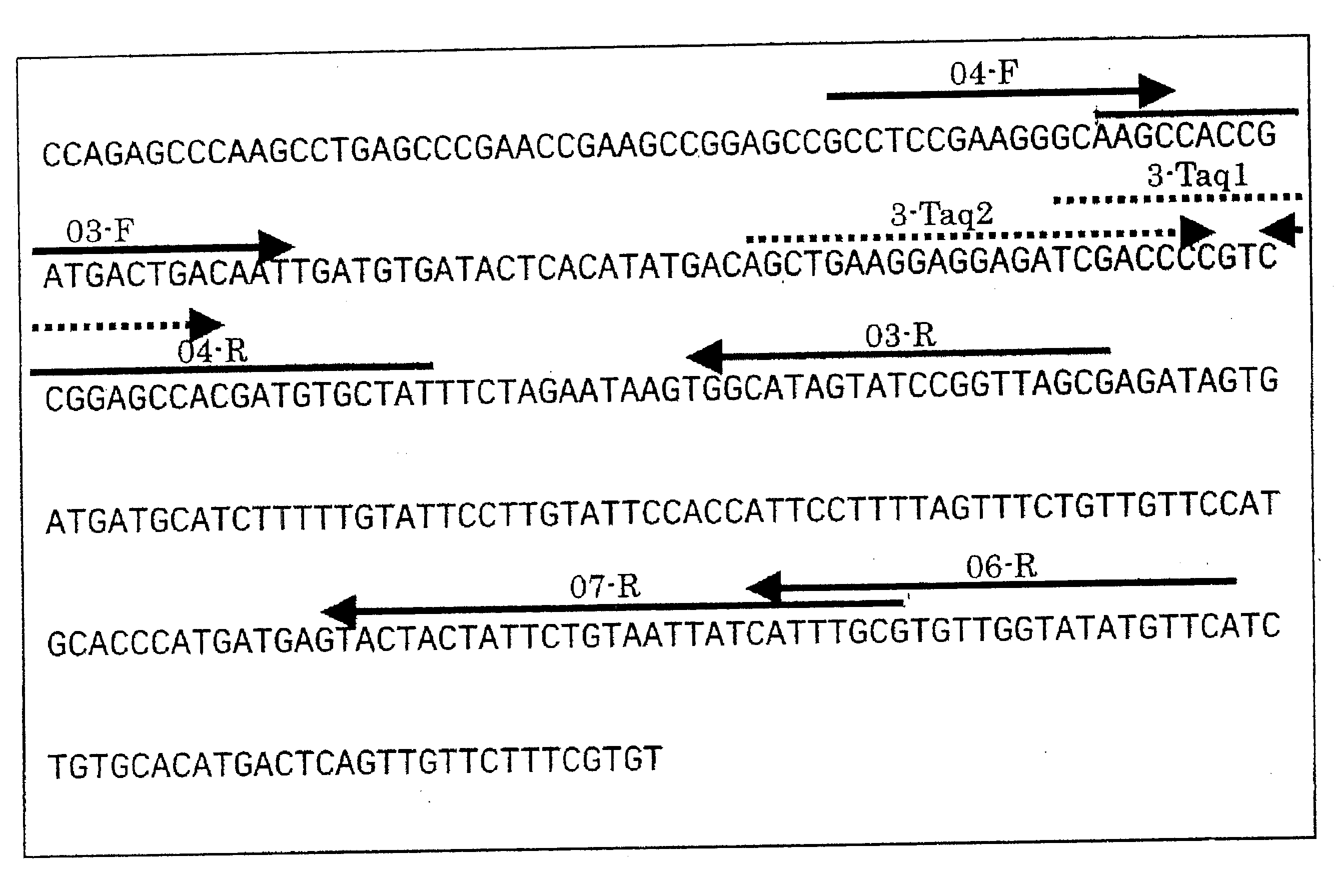
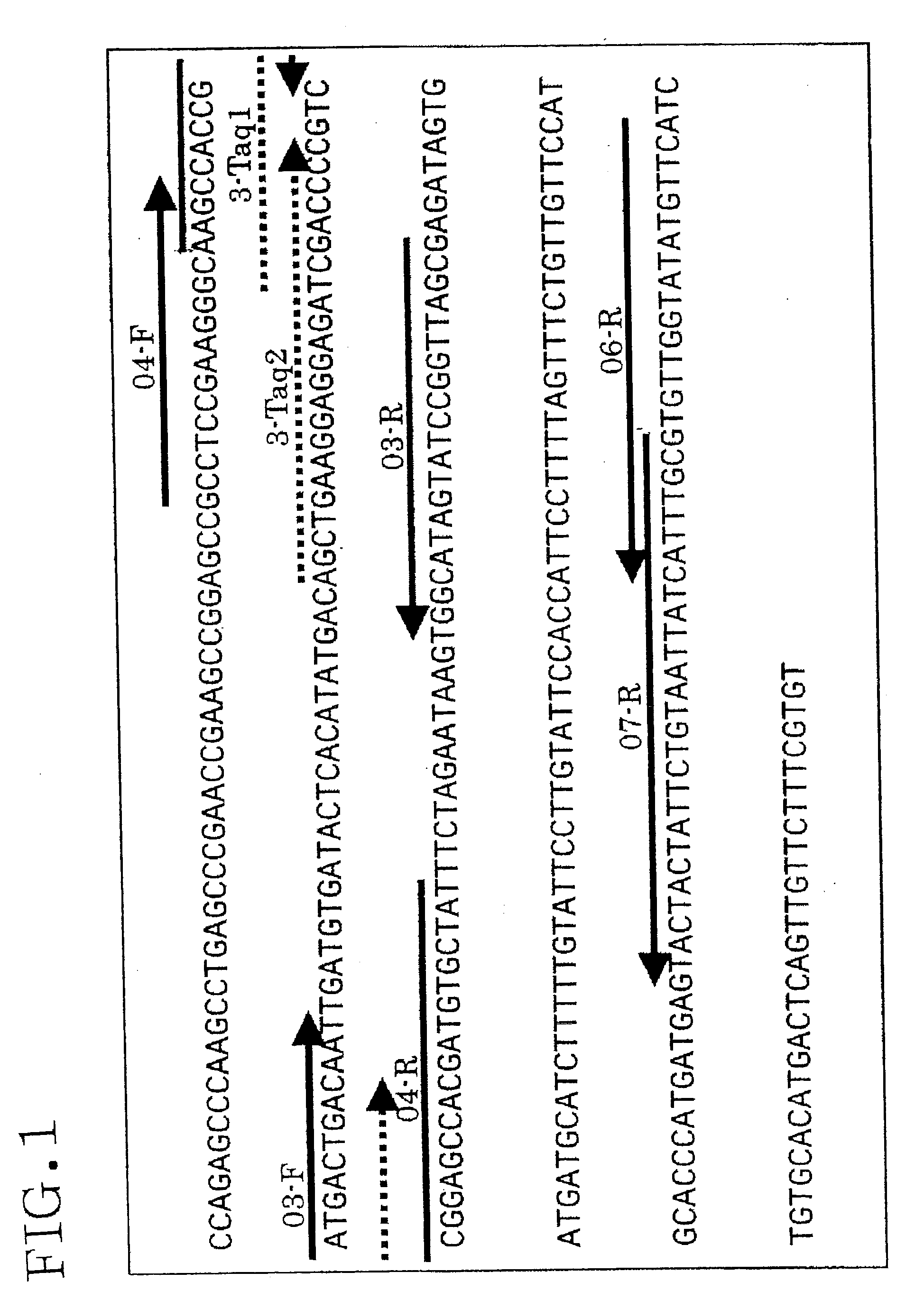
The influence of transgenic crops on rhizospheric microorganisms in soil is an important aspect in environmental biosafety research. The invention establishes a detection system of Real-Time QPCR (Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction)) by carrying out absolute quantification on the quantity of pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizospheric soil during the growth period of transgenic disease-resistant wheat. By virtue of application of the reaction system, the absolute quantification is carried out on the copy number of the pseudomonas fluorescens in the rhizospheric soil during the whole growth period of the transgenic wheat. A result shows that the designed primer has better specificity; the intervals of cycle thresholds (Ct values) of plasmids with various gradient standards in an amplification curve of Real-Time QPCR are uniform, the peak value of a melting curve is more obvious, and for the standard curve, the correlation coefficient R2 is equal to 0.99905, the slope is minus 3.203, and the amplification efficiency E is equal to 100%. In the seeding stage, seedling establishment stage, watery stage and mature stage of the transgenic wheat, the quantity of the pseudomonas fluorescens in the rhizospheric soil takes on a trend of gradually rising.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of detecting or quantitating endogenous wheat DNA and method of determining contamination rate of genetically modified wheat in test sample
ActiveUS20100062432A1Good precisionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTriticeaeTest sample
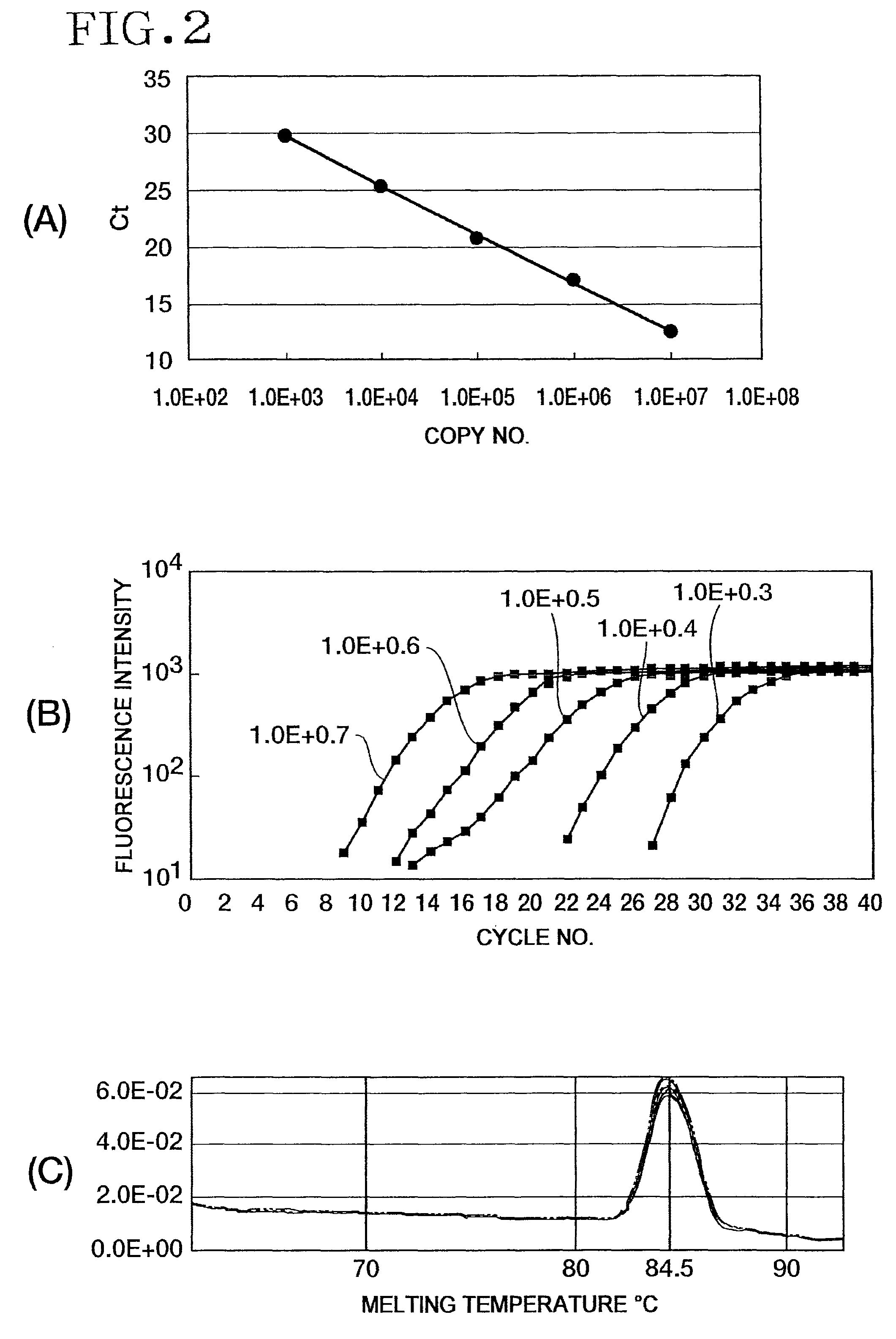
An object of the present invention is to discover an endogenous wheat sequence satisfying the conditions of: a) it is universally present in varieties of wheat, b) the amount present (detected amount) is not affected depending on the wheat variety, c) even if other grains are present, only wheat can be detected without cross-reactivity, and d) it is amplified quantitatively by the PCR reaction. A further object of the present invention is to provide a method of accurately detecting and quantitating endogenous wheat DNA in a test sample by the polymerase chain reaction. The present invention provides a method of detecting or quantitating endogenous wheat DNA in a test sample by the polymerase chain reaction, the method comprising: a step of using a nucleic acid in the test sample or a nucleic acid extracted from the test sample as a template to amplify the nucleic acid of a region consisting of the base sequence identified as SEQ ID NO: 2 or a partial sequence thereof with a primer pair capable of amplifying that region; and a step of detecting or quantitating the amplified nucleic acid.
Owner:NISSHIN SEIFUN GRP INC
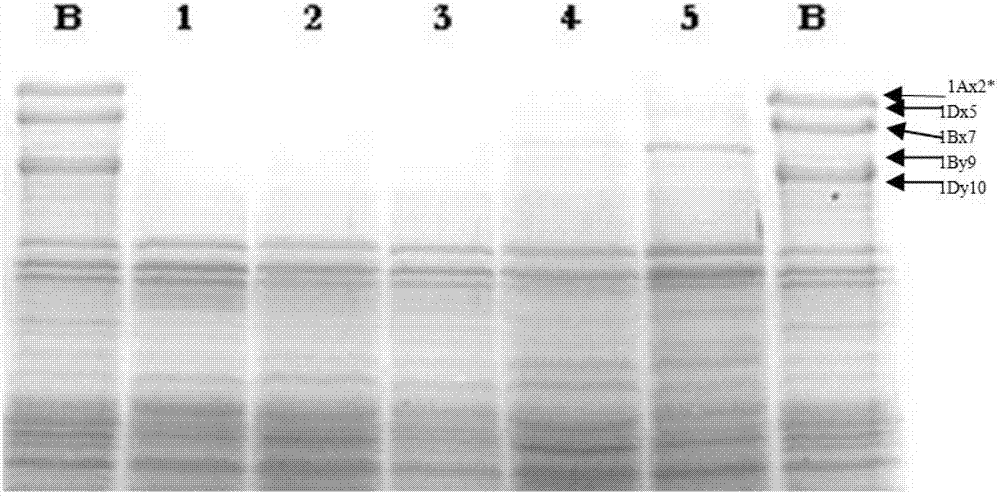
Low molecular weight wheat glutelin subunit, coding gene and use thereof
The invention discloses an einkorn wheat low molecular weight glutenin subunit, its encoding gene and use, wherein the einkorn wheat low molecular weight glutenin subunit is the protein of amino acid residue No.2 sequence in the sequence table, or SEQ ID No.2 derived protein by the substitution, deletion or addition of one or several amino acid residual radicals to the SEQ ID No.2 amino acid residual radical sequence, and having the same activity with the SEQ ID No.2 amino acid residual radical sequence. The encoding gene of the einkorn wheat low molecular weight glutenin subunit is one of the following nucleic acid sequences, (1) DNA sequence of SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table, (2) the polynucleotide of SEQ ID No.2 in the sequence table, (3) DNA sequence having over 90% homology with DNA sequences defined by SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table and encoding the same functional protein. The gene can be used in the cultivation of transgenic wheats.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
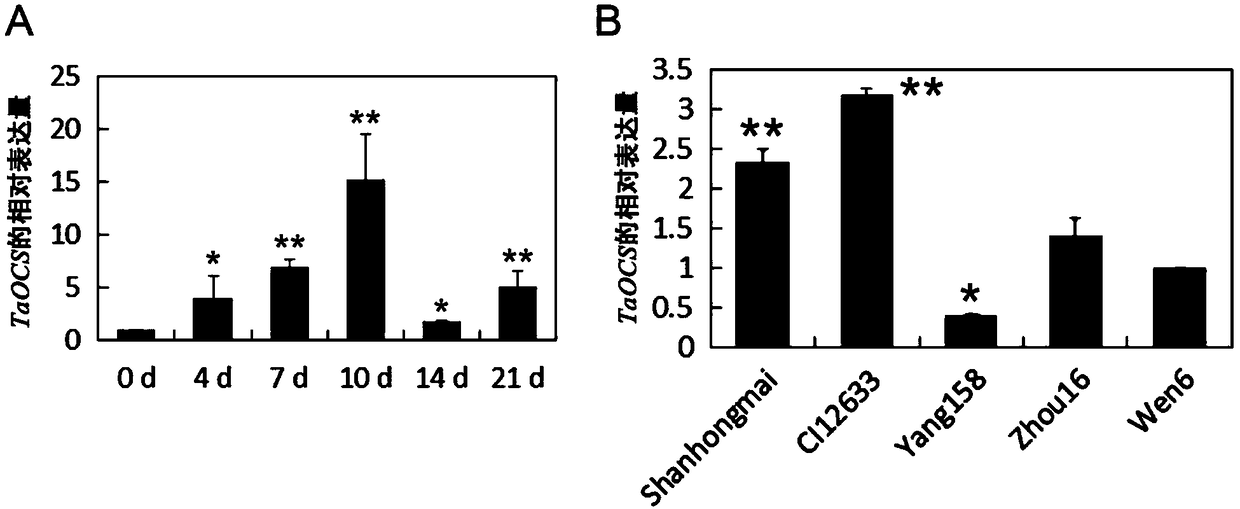
Breeding method for genetically modified wheat capable of resisting both sheath blight and root rot and related biological material thereof
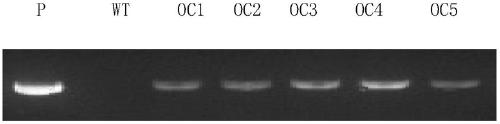
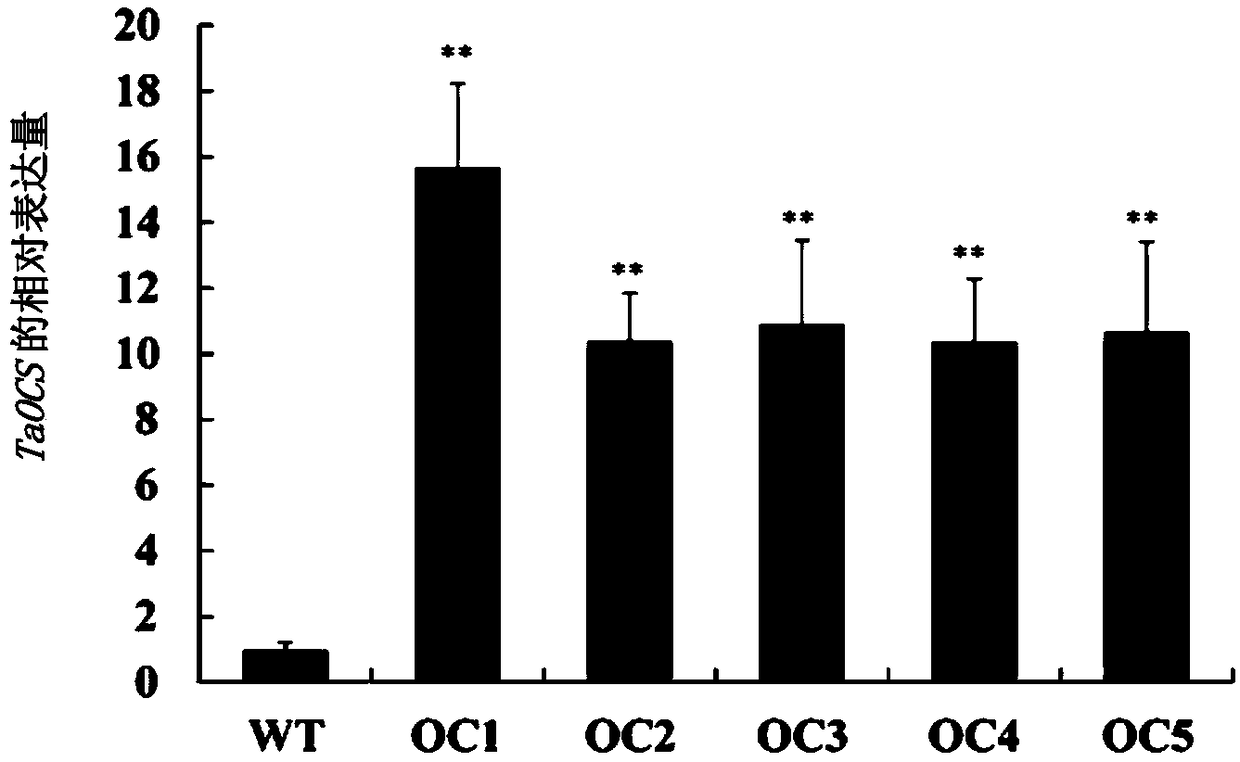
The invention discloses a breeding method for a genetically modified wheat capable of resisting both sheath blight and root rot and a related biological material thereof. The method for breeding the disease-resistant genetically modified wheat comprises the following step: the coding gene of a protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 2 is introduced into a receptor wheat, so that the genetically modified wheat, the disease resistance of which is higher than the disease resistance of the receptor wheat, is obtained; and the disease resistance is resistance to sheath blight and / orresistance to root rot. A transgenic experiment in which TaOCS is introduced into wheat proves that compared with the resistance of the receptor wheat, the resistance of the genetically modified wheat overexpressed by TaOCS to sheath blight and root rot is remarkably enhanced, indicating that TaOCS is a protein related to the sheath blight and root rot of plants, and TaOCS and the coding gene thereof can be used for enhancing the resistance of plants to the sheath blight and / or root rot.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of detecting or quantitating endogenous wheat DNA and method of determining contamination rate of genetically modified wheat in test sample
ActiveUS8173400B2Good precisionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideTransgene
An object of the present invention is to discover an endogenous wheat sequence satisfying the conditions of: a) it is universally present in varieties of wheat, b) the amount present (detected amount) is not affected by the wheat variety, c) even if other grains are present, only wheat can be detected without cross-reactivity, and d) it is amplified quantitatively by the PCR reaction. A further object of the present invention is to provide a method of accurately detecting and quantitating endogenous wheat DNA in a test sample by the polymerase chain reaction. The present invention provides a method of detecting or quantitating endogenous wheat DNA in a test sample by the polymerase chain reaction, the method comprising: a step of using a nucleic acid molecule in the test sample or a nucleic acid molecule extracted from the test sample as a template to amplify the nucleic acid molecule of a region consisting of the nucleotide sequence identified as SEQ ID NO: 2 or a partial sequence thereof with a primer pair capable of amplifying that region; and a step of detecting or quantitating the amplified nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:NISSHIN SEIFUN GRP INC
High-molecular wheat glutelin subunit gene, nucleic acid sequence of promoter thereof, and application thereof
InactiveCN1970765AReduce the numberImprove processing qualityPlant peptidesFermentationDielectricWheat glutelin
The invention discloses a coded gene sequence and amino acid sequence with high-expressive activity macromolecular glutelin subunit with sequence as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 in the biological gene engineering technical domain, which is characterized by the following: providing astopic endosperm promoter with high-expressive activity macromolecular glutelin subunit with sequence as SEQ ID No.3; constructing gene-transmitting carrier; utilizing gene shooting method, agricillin dielectric method and pollen tube channel method to transmit gene to common wheat; culturing superior wheat.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
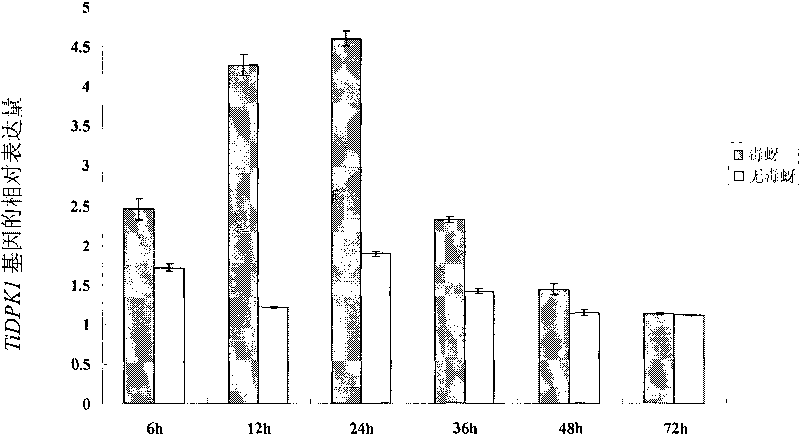
Plant yellow dwarf resistance-associated protein TiDPK1, coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101704883AIncrease resistanceIncrease concentrationFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceGenetically modified wheat
The invention discloses a plant yellow dwarf resistance-associated protein TiDPK1, a coding gene and application thereof. The protein is a protein 1) or 2) as follows: 1) the protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown by a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and 2) the protein which is derived from 1) by performing substitution and / or deletion and / or addition on the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2 in the sequence table and is related to stress resistance of plants. The coding gene TiDPK1 of the protein, transgenic lines and a method also belong to the protection of the invention. Experiment proves that the gene is specifically expressed in yellow dwarf resistant wheat (such as YW642) and is regulated up by the induction of BYDV; TiDPK1 is a membrane protein; BYDV concentration is raised and susceptibility index rises in silent original yellow dwarf resistant wheat YW642 of the TiDPK1; over-expressed transgenic wheat improves resistance to yellow dwarf; and the TiDPK1 gene is shown to be an important gene resistant to yellow dwarf.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of wheat test-tube plantlet blade repeated regeneration
InactiveCN101699992ASolve the problem of repeated regenerationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGenetically modified wheatTransgenic technology
The invention relates to a method of causing wheat test-tube plantlet blades to repeatedly regenerate by the tissue culture of the wheat test-tube plantlet blades. The method belongs to the technical field of the plant tissue culture and comprises steps of: (1) induction of embryonic callie; (2) subculture of callie; (3) acquisition of test-tube plantlets; (4) test-tube plantlet blade inducing the callie; (5) the induction of the secondary regenerate seedlings; (6) inducing rootage; and (7) the transplantation of the secondary regenerate seedlings. The method of wheat test-tube plantlet spire repeated regeneration provided by the invention successfully solves the problem of the difficult repeated regeneration of the wheat test-tube plantlet, is a wheat test-tube plantlet repeated regeneration system firstly established by the wheat test-tube plantlet spire at home and abroad, and makes it possible for obtaining homogenization chloroplast transgenosis wheat by applying the chloroplast transgenosis technique. The experimental statistics prove that by using the method, the frequency of the test-tube plantlet blade induction callie and the frequency of the second regenerative plantlet respectively reach 93% and more than 66%.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for obtaining transgene wheat by using gene gun, and special culture medium
ActiveCN103898155AImprove gene transformation efficiencyImprove stabilityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyTransformation efficiency
The present invention discloses a method for obtaining transgene wheat by using a gene gun, and a special culture medium. According to the present invention, wheat immature embryo is adopted as explant, a hypertonic culture medium provided by the present invention is directly used to carry out a hypertonic treatment without pre-culture, gene gun bombardment is performed, and the special culture medium provided by the present invention is adopted to carry out a hypertonic treatment, callus induction, differentiation and rooting culture after bombardment, wherein a screening agent is used during the differentiation and rooting stages and is not used during the callus induction state so as to significantly improve the wheat gene transformation efficiency, wherein the wheat gene transformation efficiency can be up to 36%; the method has advantages of short transformation period (the time from immature embryo taking to obtaining of the regenerated plant having root, stem and leaf is only 8-10 weeks), high transformation stability and high repeatability; and the effective approach is provided for wheat genetic improvement industrialization, and the broad application prospects are provided.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Methods and compositions for producing and selecting transgenic wheat plants
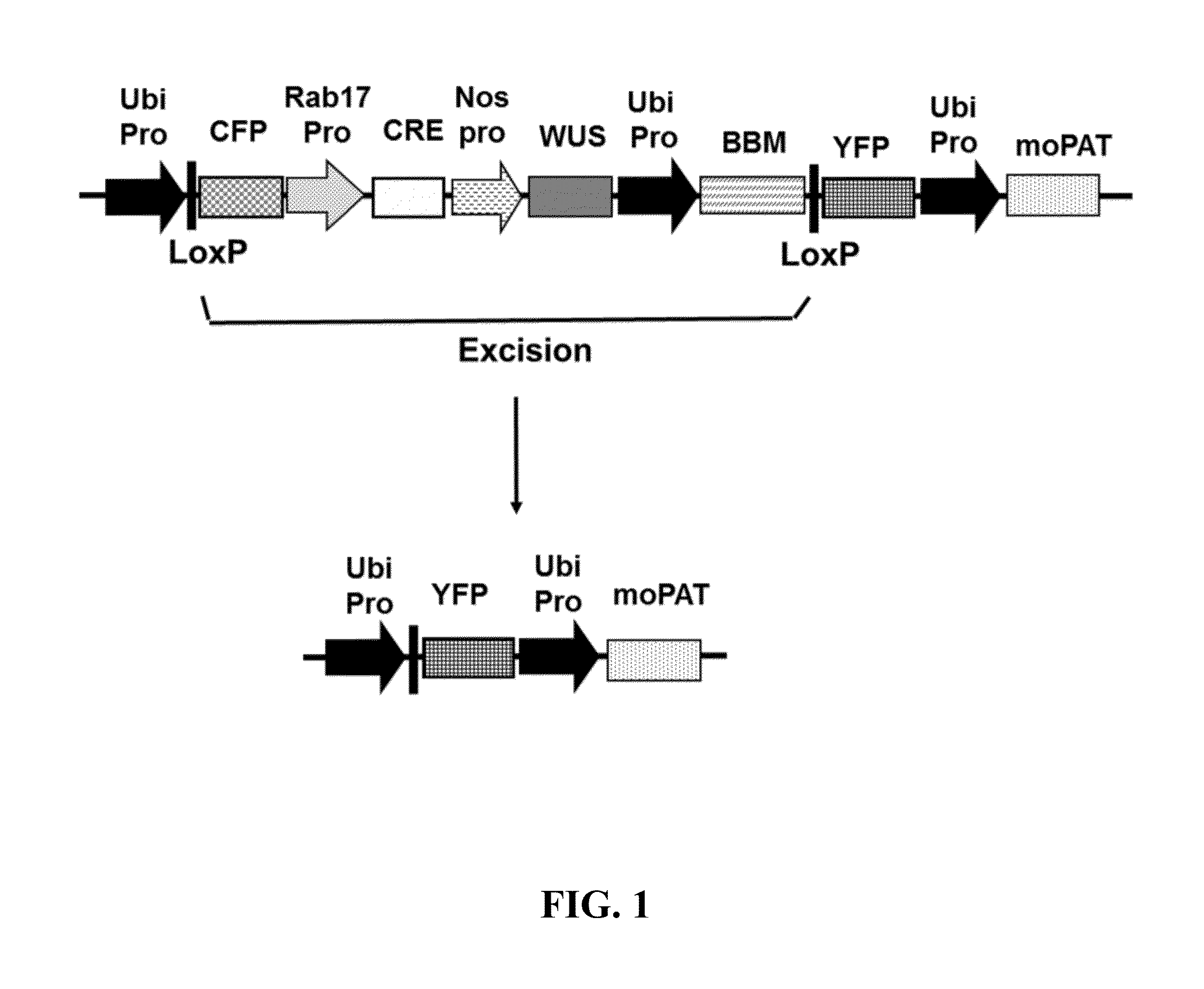
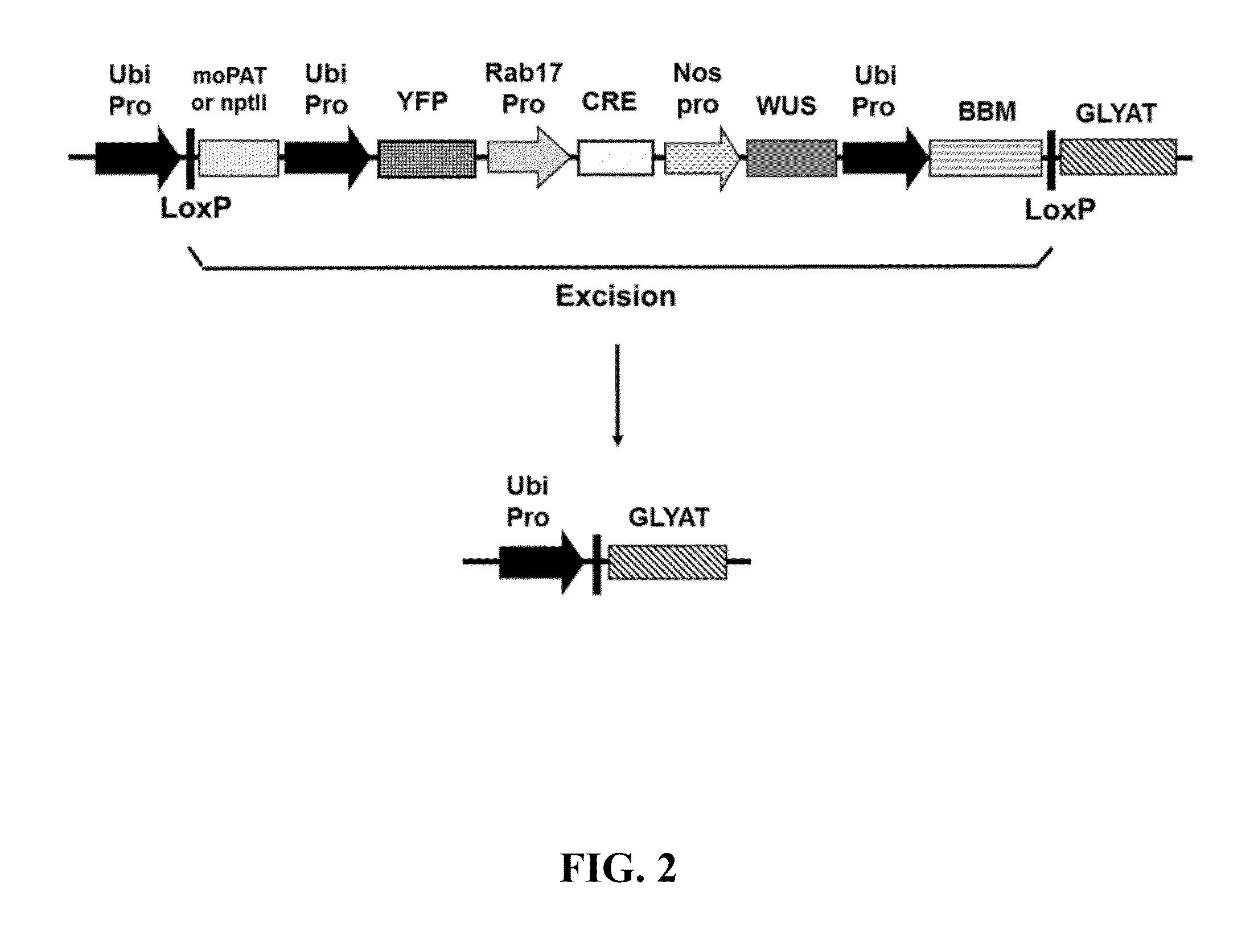
InactiveUS20140173781A1High conversion frequencyRegulate expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSite-specific recombinationGenetically modified wheat
Compositions and methods are provided for the production and selection of transgenic plants and plant parts, for increasing the transformation frequency of a plant or plant part, and for regulating the expression of a transgene, such as a herbicide tolerance polynucleotide. The methods and compositions allow for the delay in the expression of herbicide tolerance polynucleotides until a point in development during which herbicide selection is more efficient. Compositions comprise polynucleotide constructs comprising an excision cassette that separates a transgene, such as a herbicide tolerance polynucleotide, from its promoter and host cells comprising the same. The excision cassette comprises a polynucleotide encoding a site-specific recombinase operably linked to an inducible promoter and expression of the recombinase leads to excision of the excision cassette and expression of the transgene.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
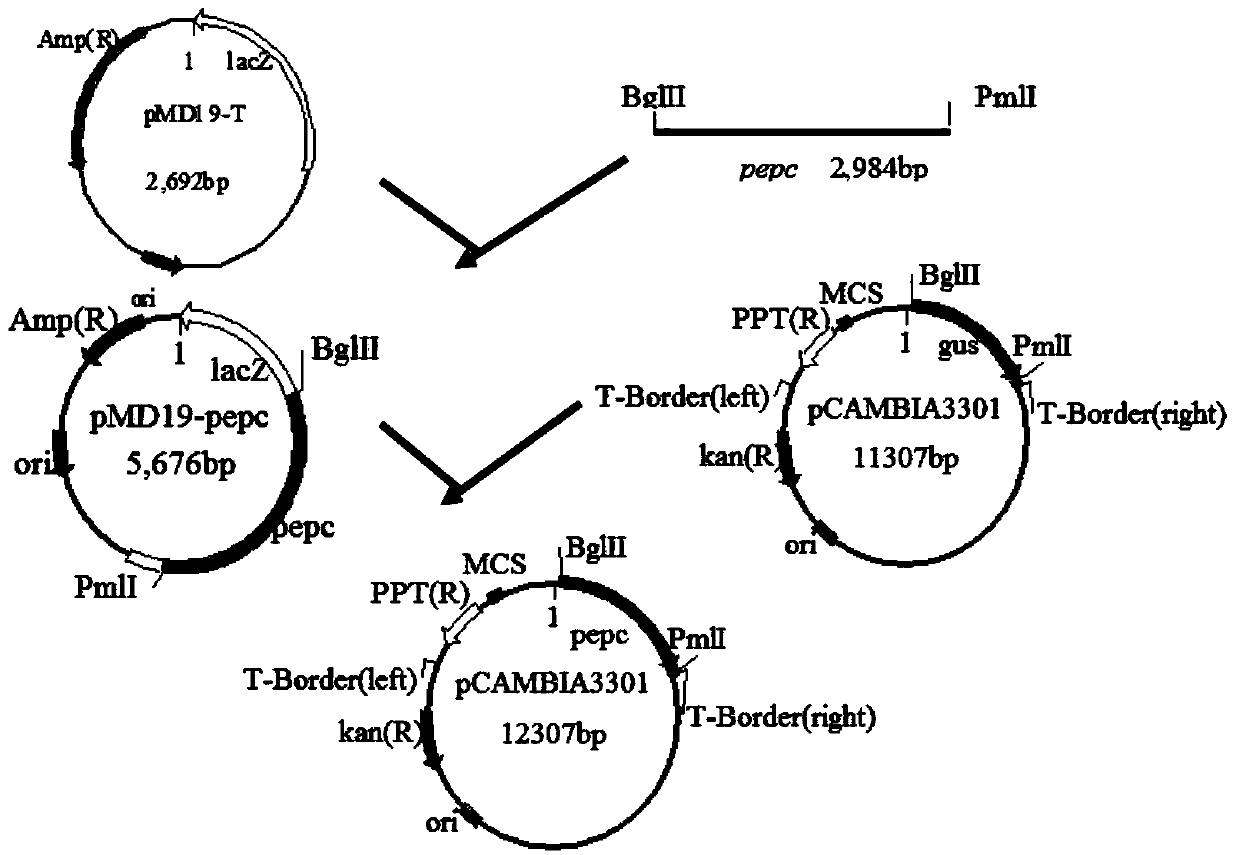
C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene of corn and application thereof in wheat
InactiveCN103805618AImprove photosynthetic efficiencyIncreased breeding yield levelsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPyruvate carboxylasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a C4 type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene of corn and an application thereof in wheat. The novel PEPC gene provided by the invention can be stably expressed and inherited in wheat, and the photosynthetic efficiency is remarkably improved compared with that of an acceptor material, thereby providing an important gene source and parent material support for improving the photosynthetic efficiency of C3 crop by means of a C4 type high photosynthetic efficiency gene and breeding high photosynthetic efficiency transgenetic wheat variety with the level of output greatly improved.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI XIAOMAI INST
Glyphosate-resistant gene, special expression vector and application of glyphosate-resistant gene to preparation of glyphosate-resistant transgenic wheat
The invention discloses a glyphosate-resistant gene, a special expression vector and an application of the glyphosate-resistant gene to preparation of glyphosate-resistant transgenic wheat. The invention provides a protein which is (a) or (b): (a) a protein consists of an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 3 in a sequence table; and (b) a protein which is derived from the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 3 in the sequence table through the substitution and / or deficiency and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues and derived from a sequence 2 related to glyphosate resistance. Experiments prove that artificial design is carried out on wheat by utilizing the condon preference of the wheat and the chloroplast targeting sequence from wheat RubisCO small subunit is added at N segment to obtain a modified gene through an artificial synthesis method; the modified gene is applied as a selection marker gene in wheat transformation so as to obtain the glyphosate-resistant transgenic wheat; and researches prove that the resistance of the transgenic wheat is higher than the transgenic resistance of the wheat before optimization.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for cultivation of transgenic wheat resisting take-all and sharp eyespot and related biological materials thereof
InactiveCN103397048AImprovement of take-all disease resistanceIncrease resistanceFungiBacteriaDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for cultivation of transgenic wheat resisting take-all and sharp eyespot and related biological materials thereof. The method for cultivation of transgenic wheat of disease resistance includes: importing an related gene which has a code sequence composed of 7th-405th nucleotides in the sequence 1 of a sequence table into recipient wheat so as to obtain the transgenic wheat of disease resistance with disease resistance higher than that of the recipient wheat. The transgenic wheat of disease resistance is the wheat of a1 or a2: a1. transgenic wheat resisting take-all and sharp eyespot, with the disease resistance being resistance to take-all and sharp eyespot; and a2. anti-take-all transgenic wheat, with the disease resistance being resistance to take-all. Experiments prove that, compared with Yangmai 18, the anti-take-all effect of the transgenic wheat with the imported anti-take-all related gene is improved by 60%-80%, and the anti-sharp eyespot effect is improved by 20%-33%.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wheat cultivar LA01425
ActiveUS8178765B2Other foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureTriticeaeGenetic Materials
A wheat cultivar, designated LA01425, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of wheat cultivar LA01425, to the plants of wheat LA01425, and to methods for producing a wheat plant produced by crossing wheat cultivar LA01425 with itself or another wheat variety. The invention also relates to methods for producing a wheat plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic wheat plants and plant parts produced by those methods. The invention also relates to wheat varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from wheat cultivar LA01425, to methods for producing other wheat varieties, lines or plant parts derived from wheat cultivar LA01425, and to the wheat plants, varieties, and their parts derived from the use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid wheat seeds and plants produced by crossing wheat cultivar LA01425 with another wheat cultivar.
Owner:NASA +1
Application of GmPGIP3 protein and coding gene thereof to cultivation of plant for resisting root rot and full rot
The invention discloses application of GmPGIP3 protein and coding gene thereof to cultivation of a plant for resisting root rot and full rot. According to the method provided by the invention, a transgenic plant with the disease resistance higher than that of a target plant is obtained by transferring the coding gene of the GmPGIP3 protein into a target plant; the GmPGIP3 protein is shown as the following (a) or (b): (a) the protein consists of the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 1 in the sequence table; and (b) the protein related to the plant disease resistance is obtained by replacing and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 1 and is derived from the sequence 1. The inventor establishes a monocotyledon high expression vector of the coding gene of the GmPGIP3 protein and transfers into wheat to obtain transgenic wheat capable of resisting root rot and full rot. The invention has important value on the breeding of the disease-resistant plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wheat cultivar DA904-32W
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Wheat Cultivar 00WB80404
InactiveUS20080244788A1Tissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesTriticeaeGenetic Materials
A wheat cultivar, designated 00WB80404, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of wheat cultivar 00WB80404, to the plants of wheat 00WB80404, and to methods for producing a wheat plant produced by crossing wheat cultivar 00WB80404 with itself or another wheat variety. The invention also relates to methods for producing a wheat plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic wheat plants and plant parts produced by those methods. The invention also relates to wheat varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from wheat cultivar 00WB80404, to methods for producing other wheat varieties, lines or plant parts derived from wheat cultivar 00WB80404, and to the wheat plants, varieties, and their parts derived from the use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid wheat seeds and plants produced by crossing wheat cultivar 00WB80404 with another wheat cultivar.
Owner:RESOURCE SEEDS
Rapid and efficient genetic transformation method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated wheat stem tips
InactiveCN105602984ALess affected by wheat genotypeReduce the degree of impactVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsTriticeaeTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a rapid and efficient genetic transformation method for agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated wheat stem tips. The method mainly comprises the steps of carrying out water seed soaking, accelerating germination and cold treatment on mature wheat seeds, transversely cutting coleoptiles of the wheat seeds until exposing stem tips, taking the cut wheat seeds as a transformation acceptor material, carrying out genetic transformation by virtue of vacuum treatment mediation on agrobacterium tumefaciens, placing the transformed material in a suitable growth environment, and carrying out transgenic identification after the plants grow, so as to obtain transgenic wheat plants. By virtue of the rapid and efficient genetic transformation method, the culture of callus tissues of the wheat is omitted, so that the influences caused by various factors to the genetic transformation of the wheat are reduced, and the problems of vitrification, browning, cell mutation and the like in the tissue culture process are avoided; the genetic transformation conditions of the wheat are optimized, so that the economic cost of the genetic transformation of the wheat is lowered, the restriction of the genotype of the wheat to the transformation efficiency is effectively overcome, and a large amount of transgenic wheat plants can be rapidly obtained; and the rapid and efficient genetic transformation method has significant values to the culture of high-quality new-variety wheat and the research of the genetic transformation of the wheat.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Identity preservation system for transgenic wheat and triticale
InactiveUS20080134360A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationIntellectual propertyTriticeae
The growing controversy over GM / novel-trait crops and food products that possess novel industrial or nutritional traits, has resulted in an increased need for technologies that allow the rapid and reliable identification of GM / novel-trait crops so that they can be identified, and segregated if necessary, at the various stages of production and processing. A visual seed identity system is described that permits the identification and tracing of each individual seed through the upstream value chain, from field increase to the processing plant. These traits are genetically controlled, transmitted to progeny by either pollen or ovule and expressed in developing seed, showing a xenia effect. That novelty of this proposed IP system will facilitate early mitigation measures if out-crossing or admixtures occur and exceed a threshold limit set by regulatory agencies.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-medicated genetic transformation method of wheat
InactiveCN102533845AWide adaptabilityEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsTriticeaeEmbryo
The invention discloses an agrobacterium tumefaciens-medicated genetic transformation method of wheat. The agrobacterium tumefaciens-medicated genetic transformation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, inoculating recombinant Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing a target DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) into wheat immature embryos; and then co-culturing the inoculated wheat immature embryos for enabling the T-DNA of the recombinant Agrobacterium tumefaciens to be integrated with a chromosome of the wheat; and secondly, directly inoculating the wheat immature embryos co-cultured in the first step in a long-seedling culture medium for culturing to obtain transgenic wheat seedlings with roots, stems and leaves. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the applicability is wide, so that the method is suitable for transforming various wheat species; the method is simple in operation, and thus a transgenic plant can be obtained without inducing a tissue culture and regenerating the plant; and the transformation period is short, i.e. the process from the infection to the obtaining of the transgenic wheat seedlings with the roots, the stems and the leaves only requires 11-14 days. The method has very important significance for genetic improvement on the wheat species and the obtaining of new species of the transgenic wheat.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com