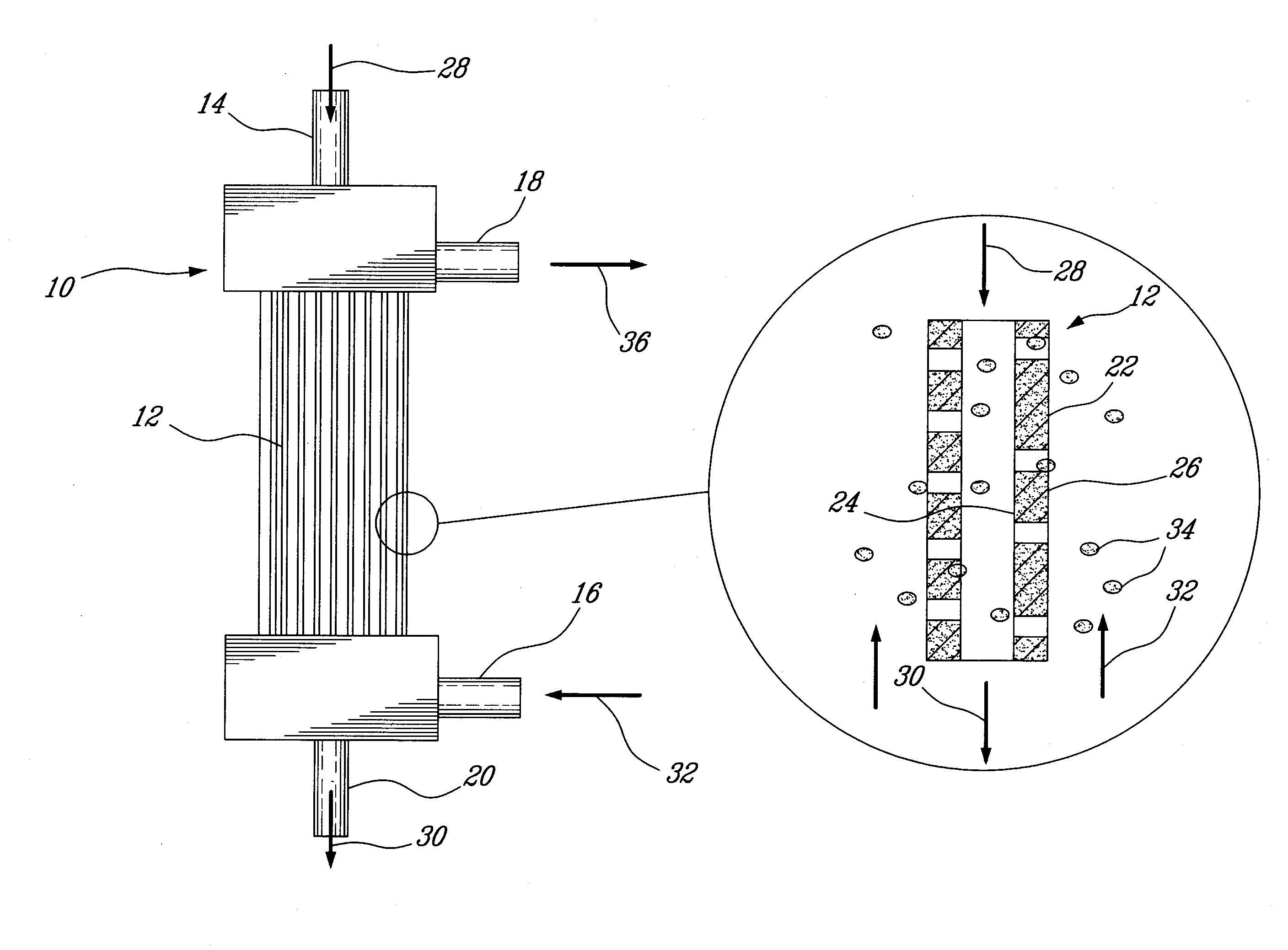
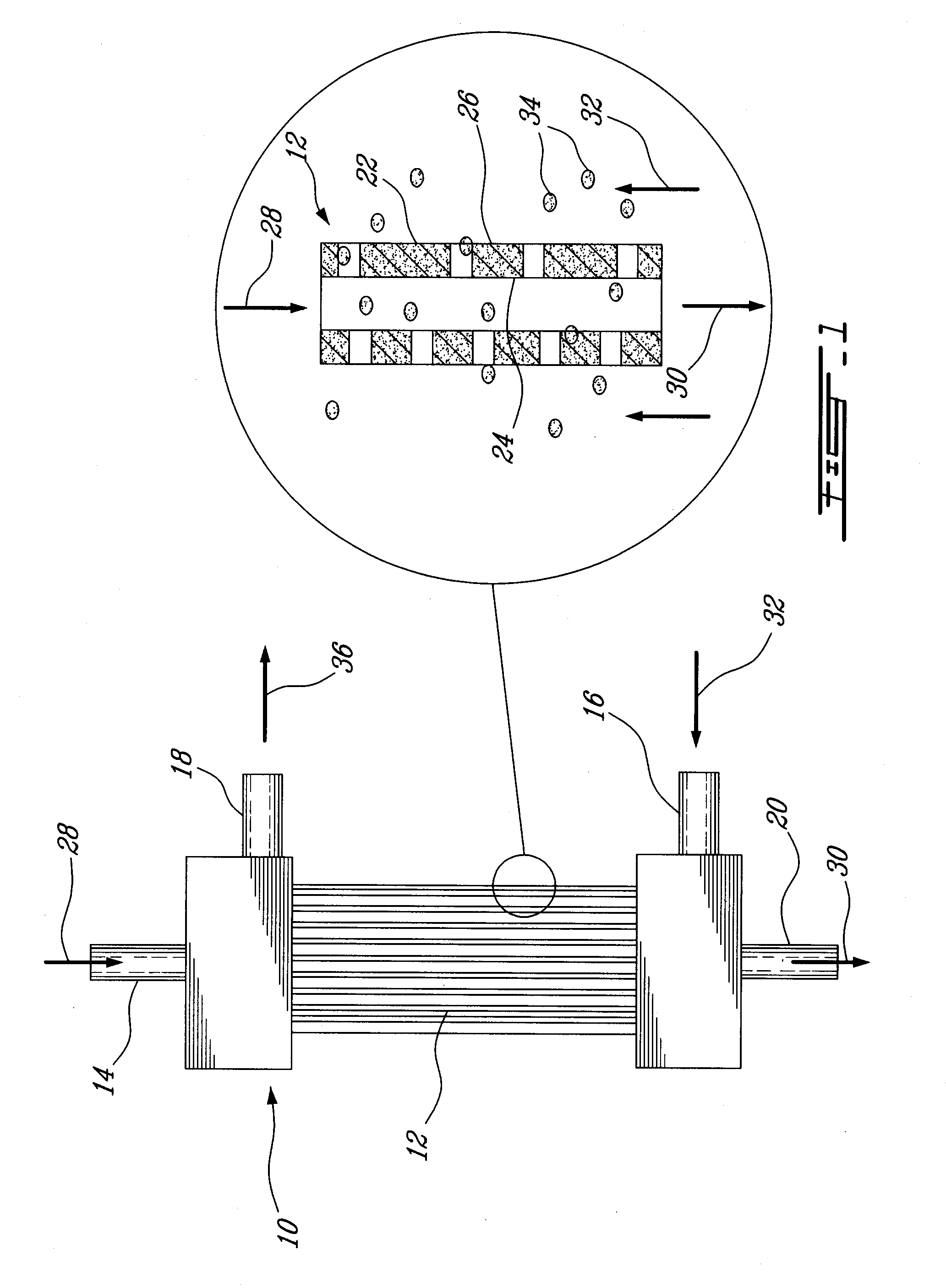
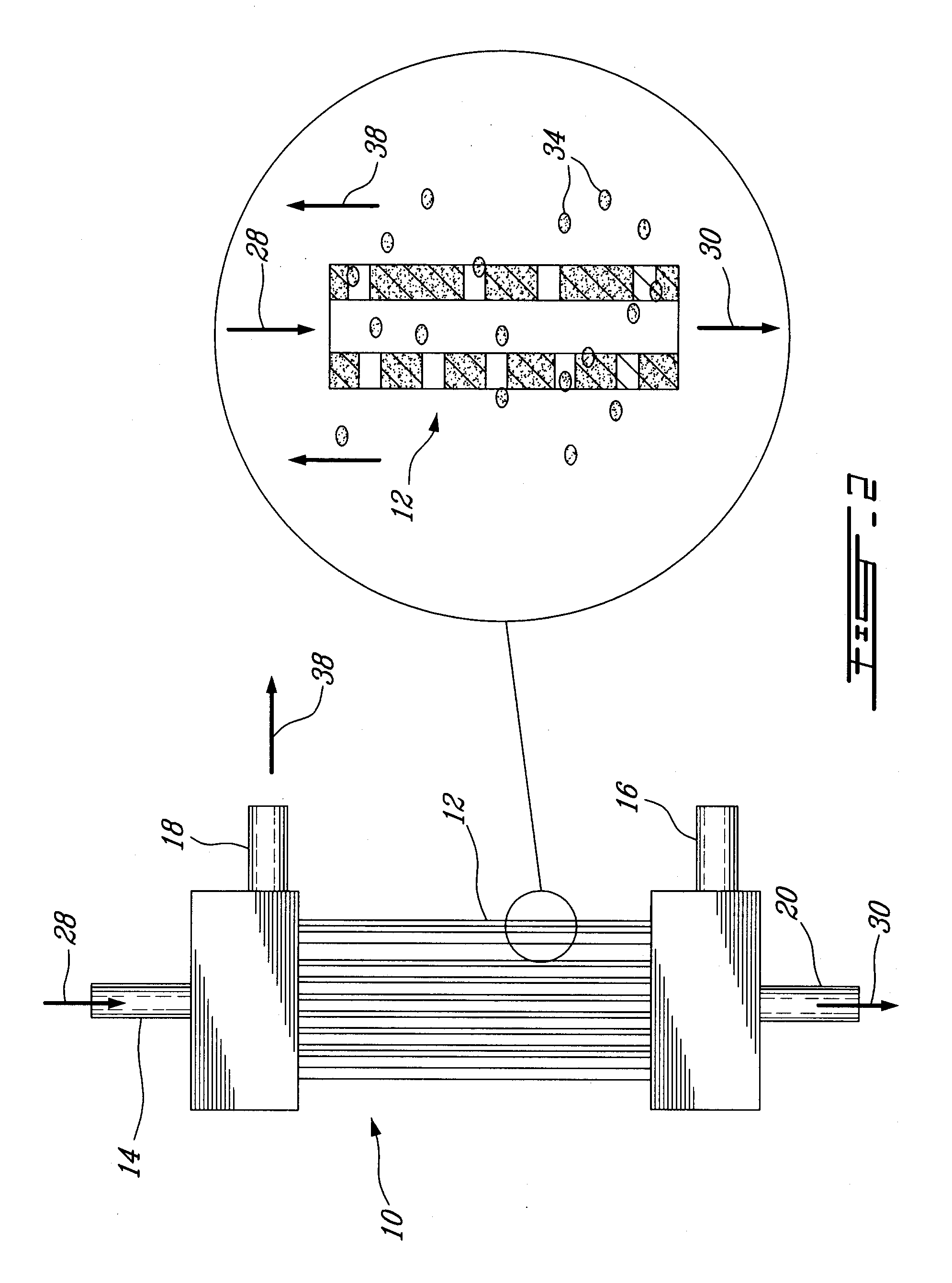
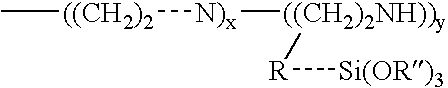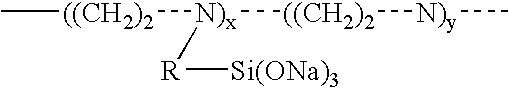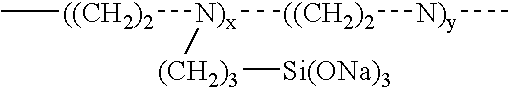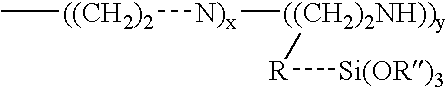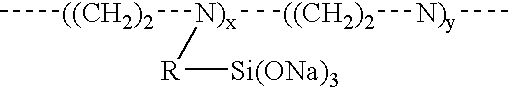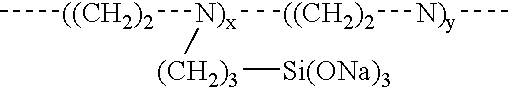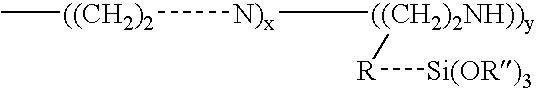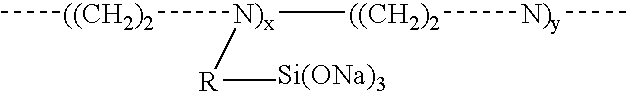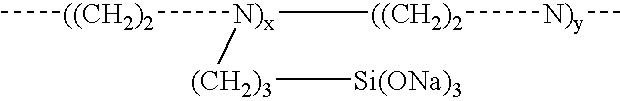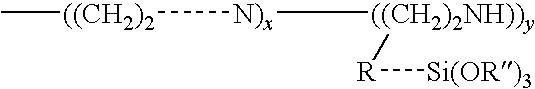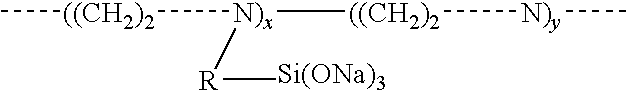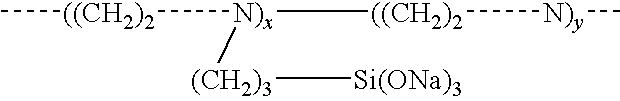Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
171 results about "Pulp mill" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A pulp mill is a manufacturing facility that converts wood chips or other plant fibre source into a thick fibre board which can be shipped to a paper mill for further processing. Pulp can be manufactured using mechanical, semi-chemical or fully chemical methods (kraft and sulfite processes). The finished product may be either bleached or non-bleached, depending on the customer requirements.
Production of levulinic acid and levulinate esters from biomass
InactiveUS20100312006A1Improve production yieldHigh purityPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationPropanoic acidFurfural
A process for producing levulinic acid and its esters from biomass is disclosed comprising: (i) feed preparation module characterized by subjecting biomass to a high-temperature refining treatment; (ii) hydrolysis reaction module that facilitates the hydrolysis of biomass to its respective sugars and their subsequent transformation to levulinic acid, formic acid, furfural, and char as well as facilitates the separation of lignin-based char by-product; (iii) product separation and recovery module utilizing a solvent extraction technique such as using furfural by-product as extracting solvent; and (iv) optionally, conversion of levulinic acid to levulinate ester. When desired, the disclosed process may be integrated into existing pulp mills.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
Method
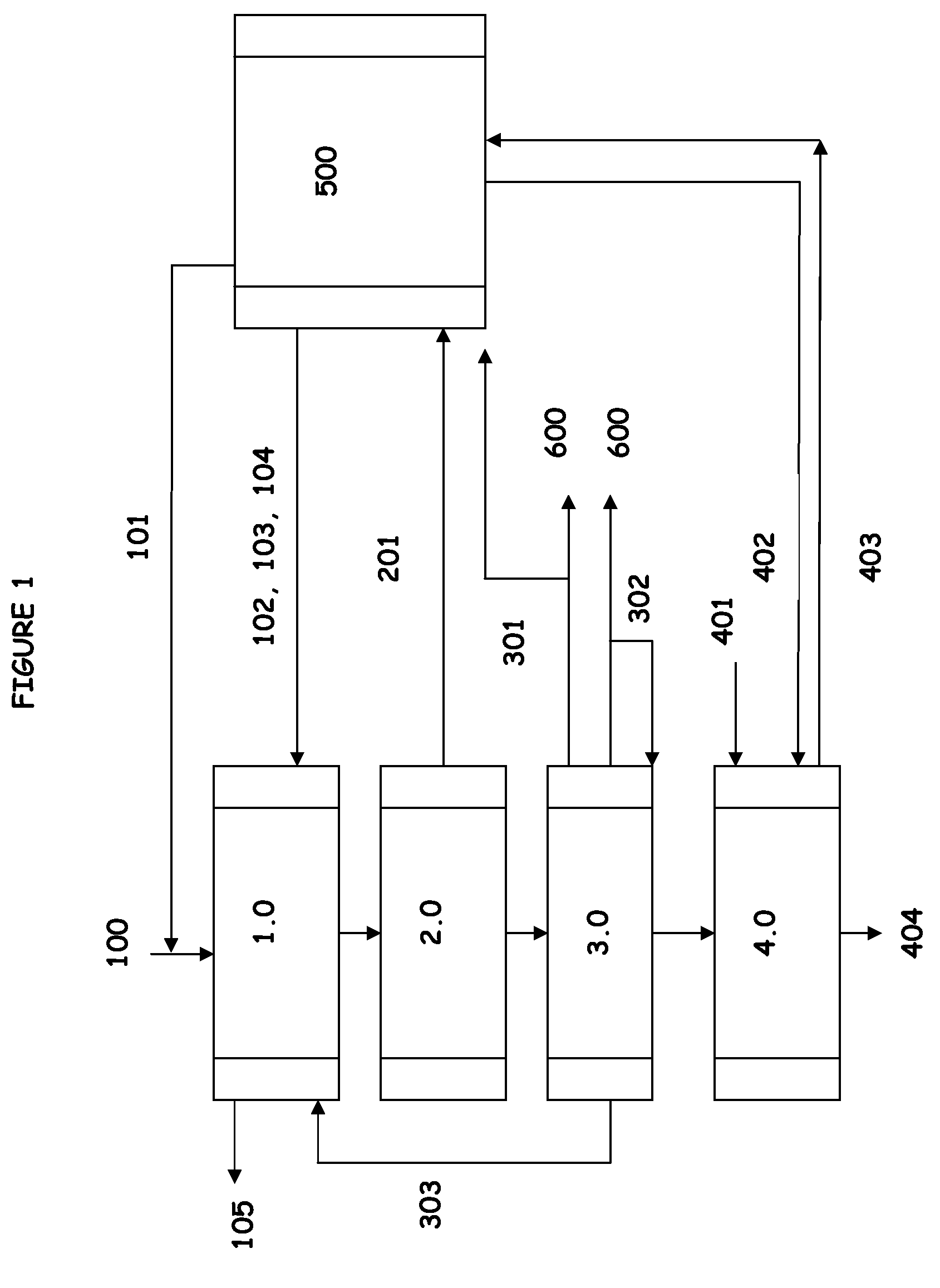
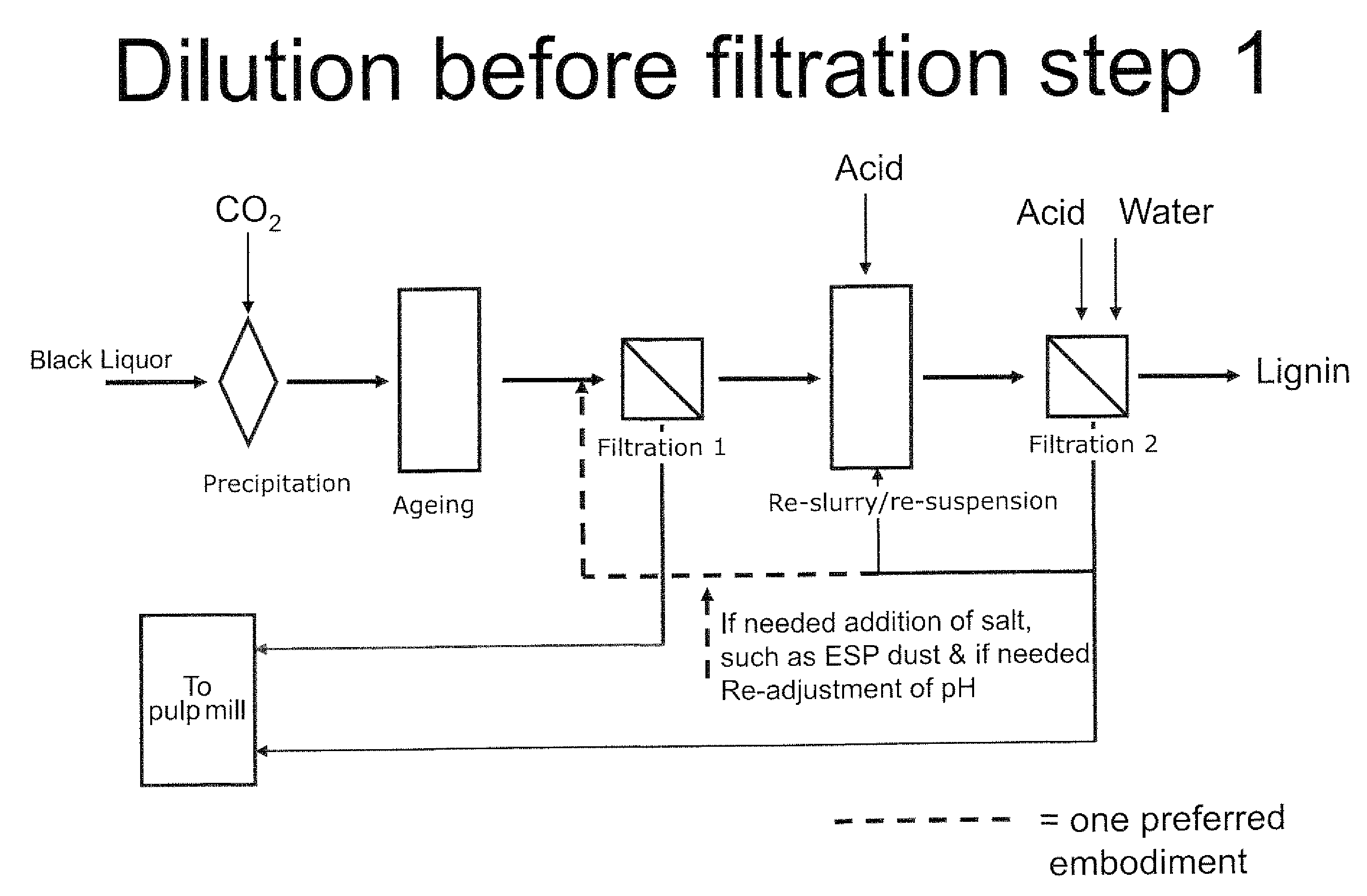
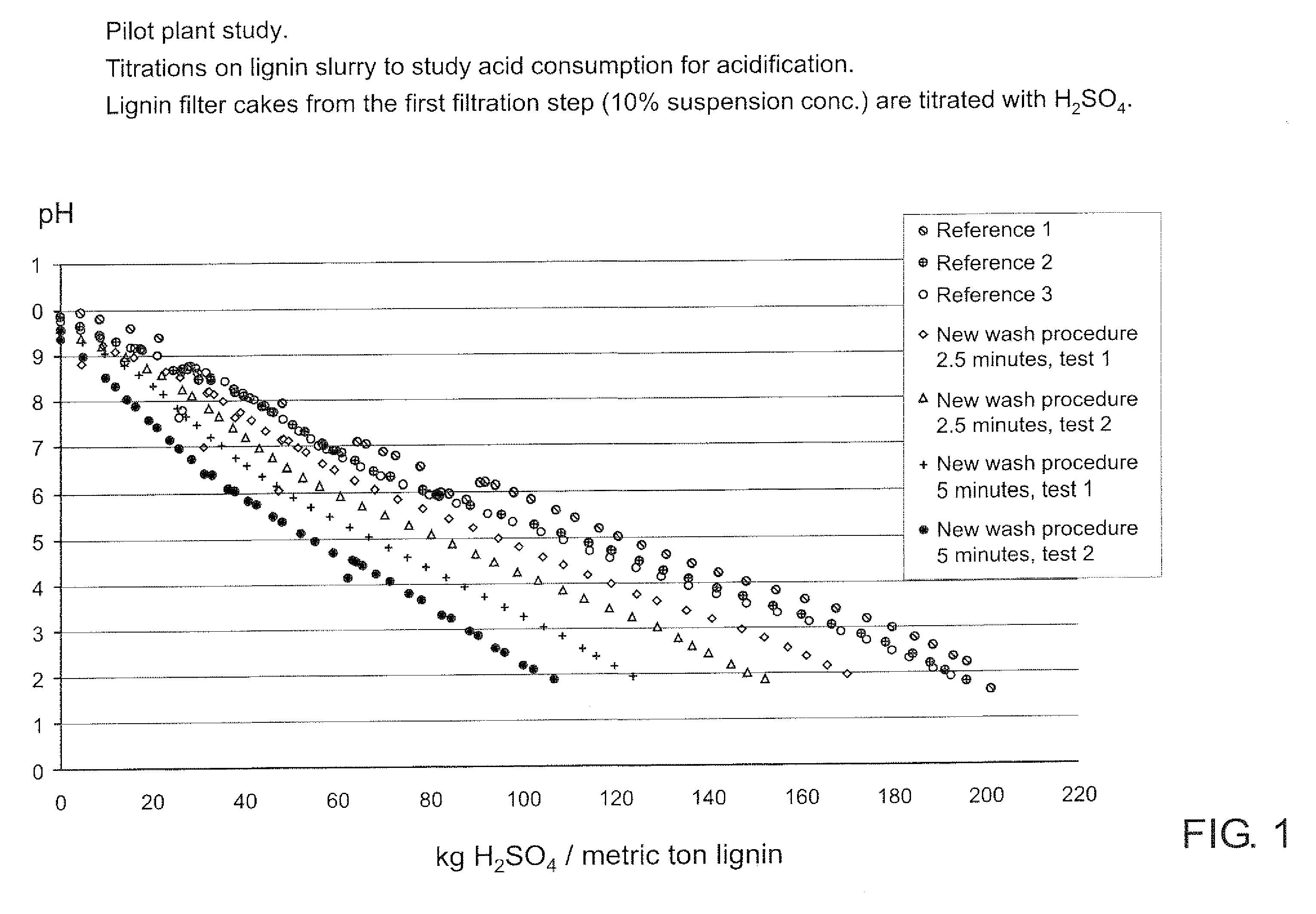
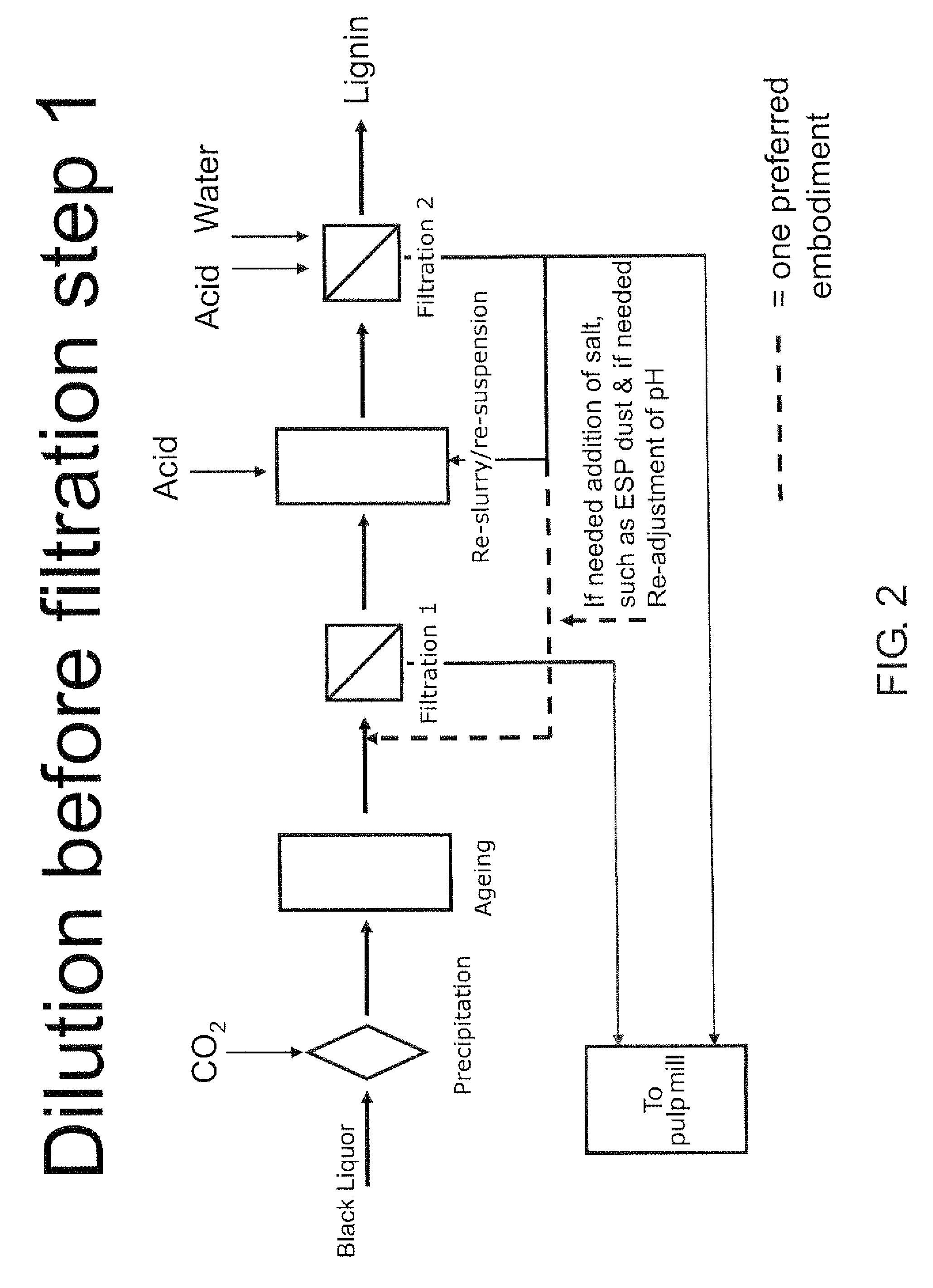
ActiveUS20080214796A1Lower requirementInhibition of dissolutionLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryBlack liquorPulp mill
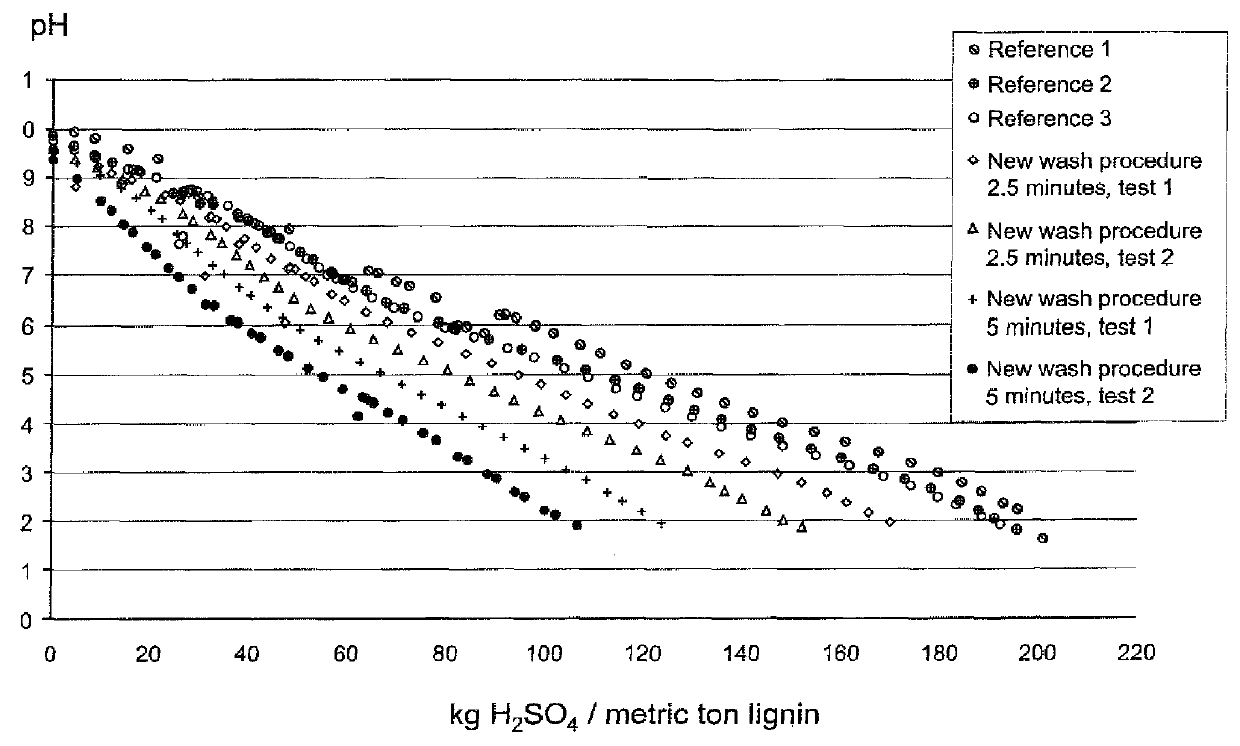
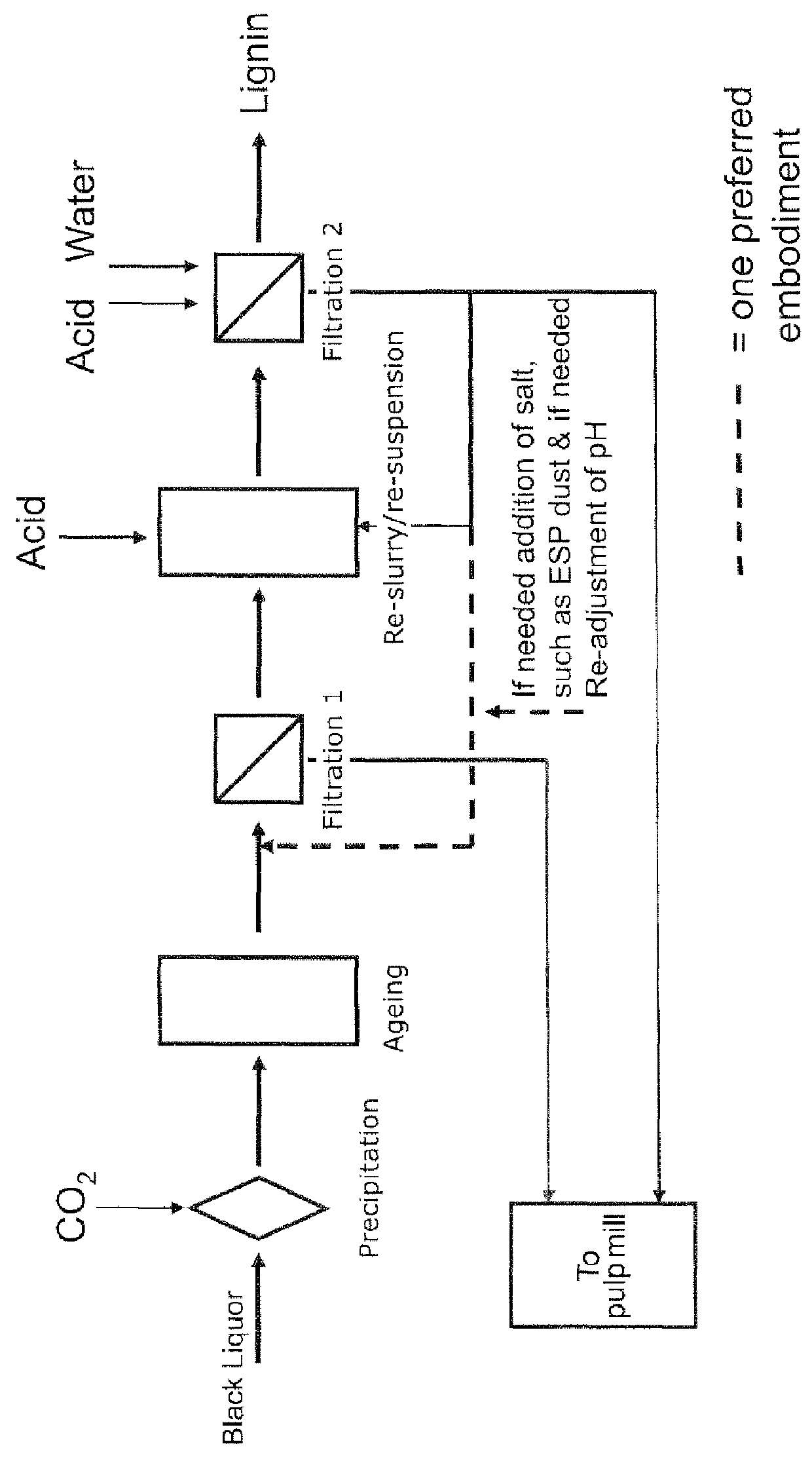
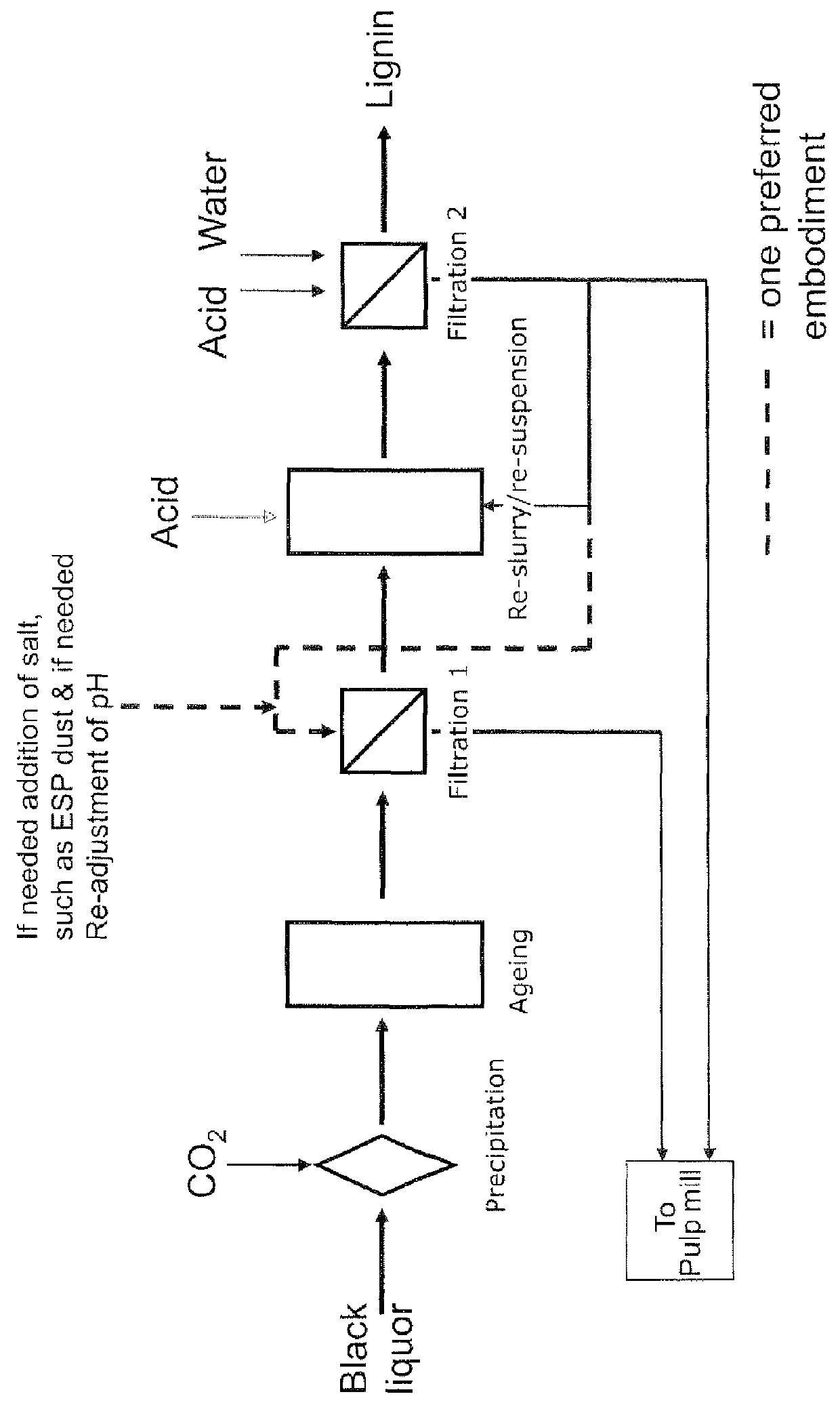
A method for controlling the sodium and sulphur balance of a pulp mill while separating lignin from black liquor, and also a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product obtainable by the method. The present invention also provides use of a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product for the production of fuel (solid, gaseous or liquid) or materials.
Owner:LIGNOBOOST
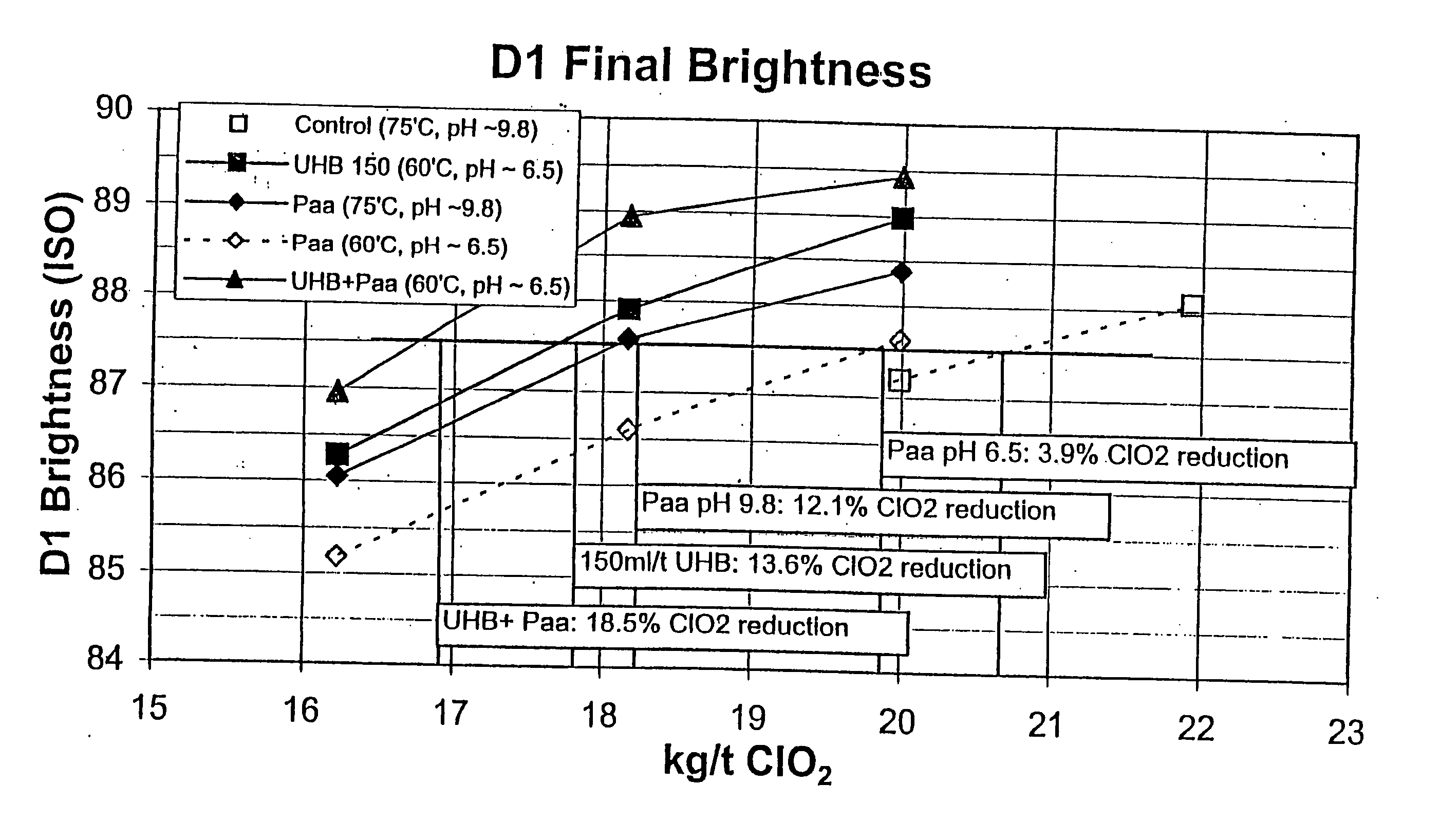
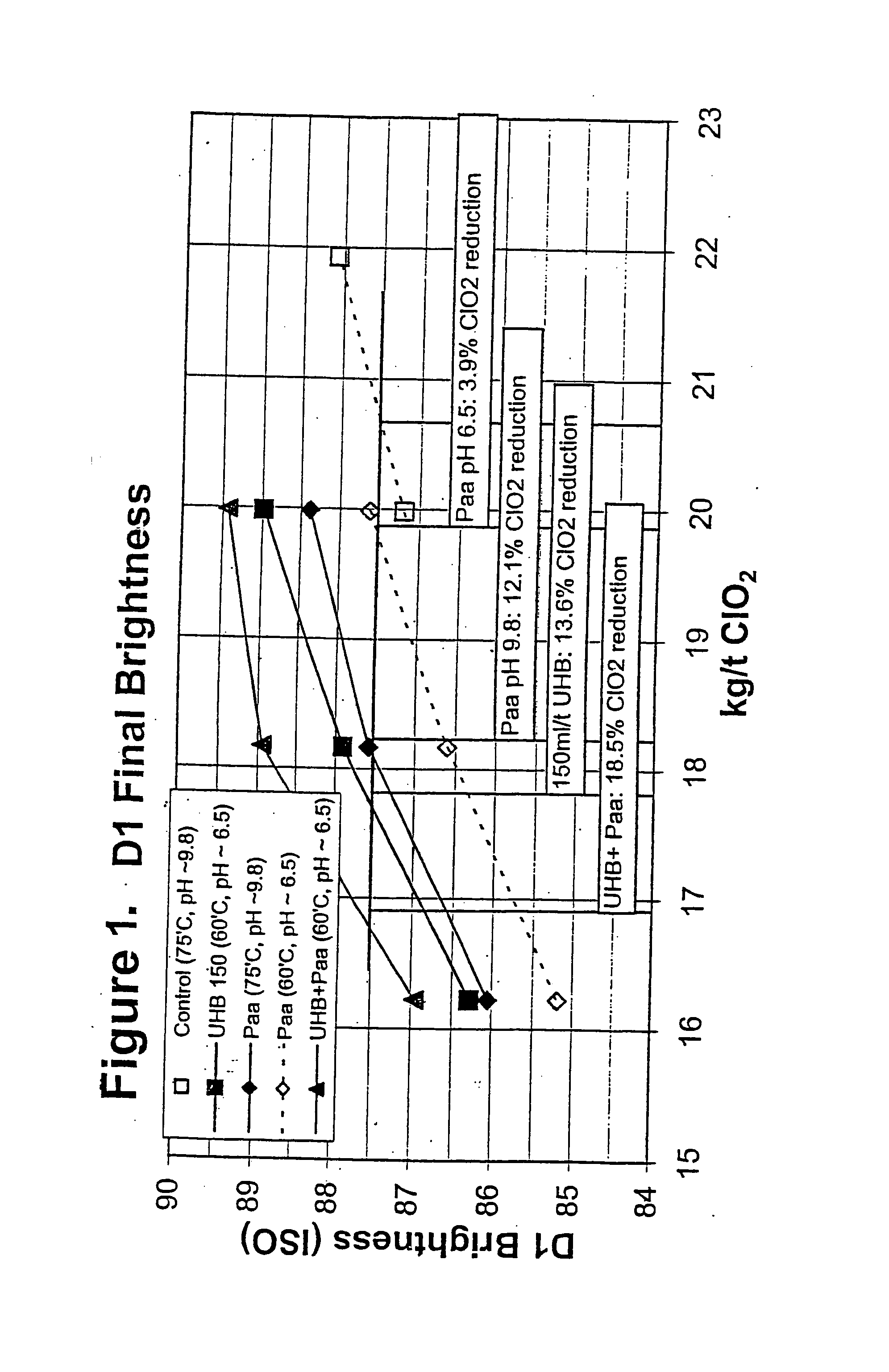
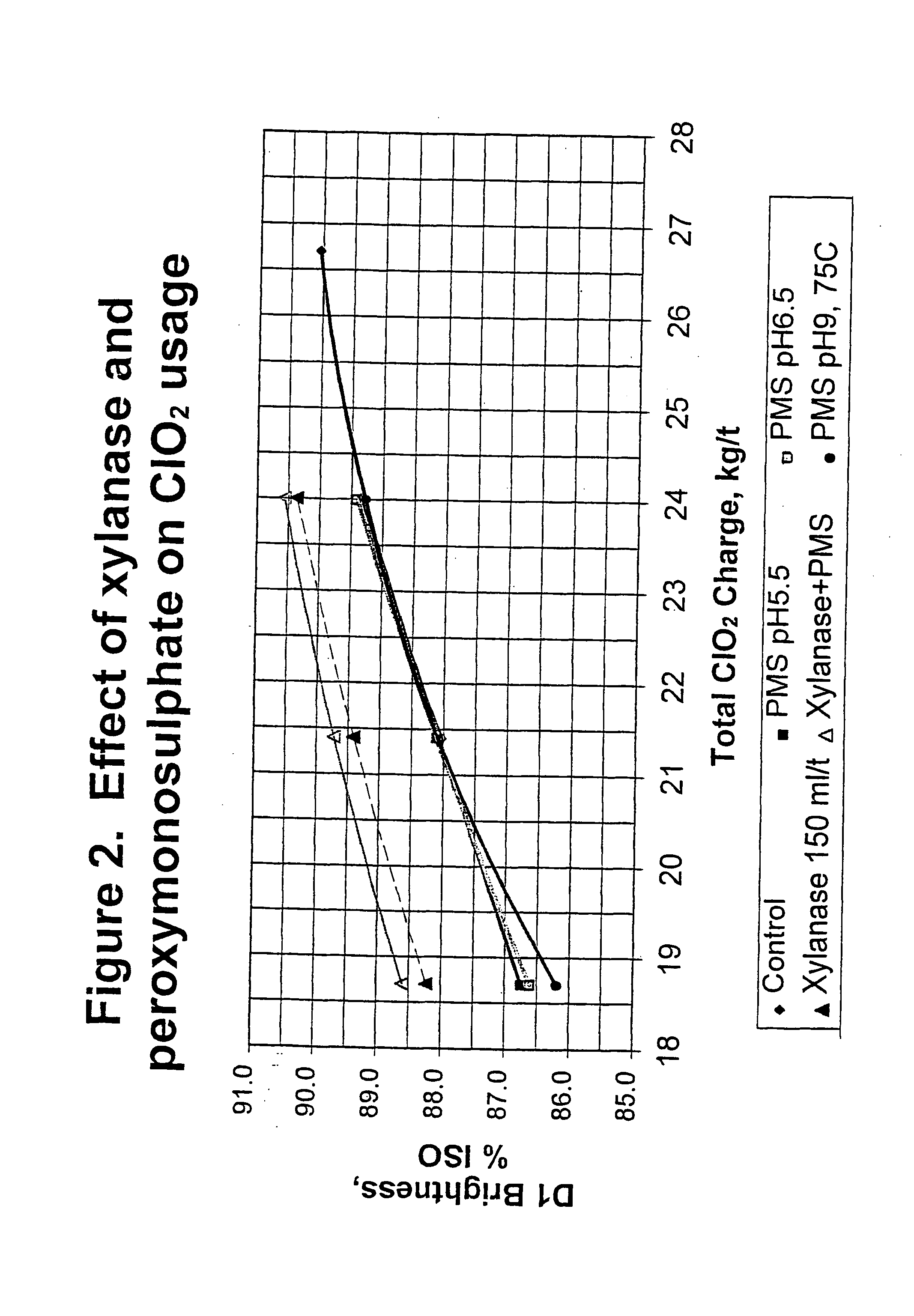
Bleaching stage using xylanase with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a combination thereof
InactiveUS20040112555A1Less-costly bleaching operationReduce usagePulp bleachingPulping with inorganic basesChlorine dioxideXylanase Y
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that combine xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chemical pulping operation, optionally followed by delignifying the pulp with oxygen, then combining xylanase enzymes with hydrogen peroxide, peracids, or a mixture to bleach the pulp. The method allows the mill to use both xylanase and peracids in a single bleaching tower to decrease the usage of chlorine dioxide and other bleaching chemicals. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:IOGEN BIO PRODUCKTS CORP
Method of preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in kraft pulp mills
InactiveUS20050274926A1Reduce and eliminate aluminosilicate scalingReduce and even prevent formationAluminium compoundsDigestersEnd-groupPulp mill
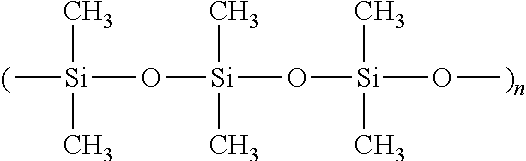
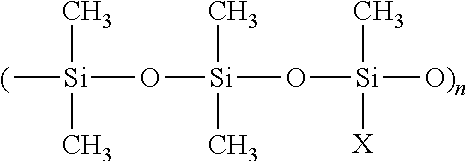
Materials and a method are provided whereby polymers with least 0.5 mole % of the pendant group or end group containing —Si(OR″)3 (where R″ is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in an industrial process having an alkaline process stream such as a pulping mill process stream. When materials of the present invention are added to the alkaline process stream, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on equipment surfaces such as evaporator walls and heating surfaces. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
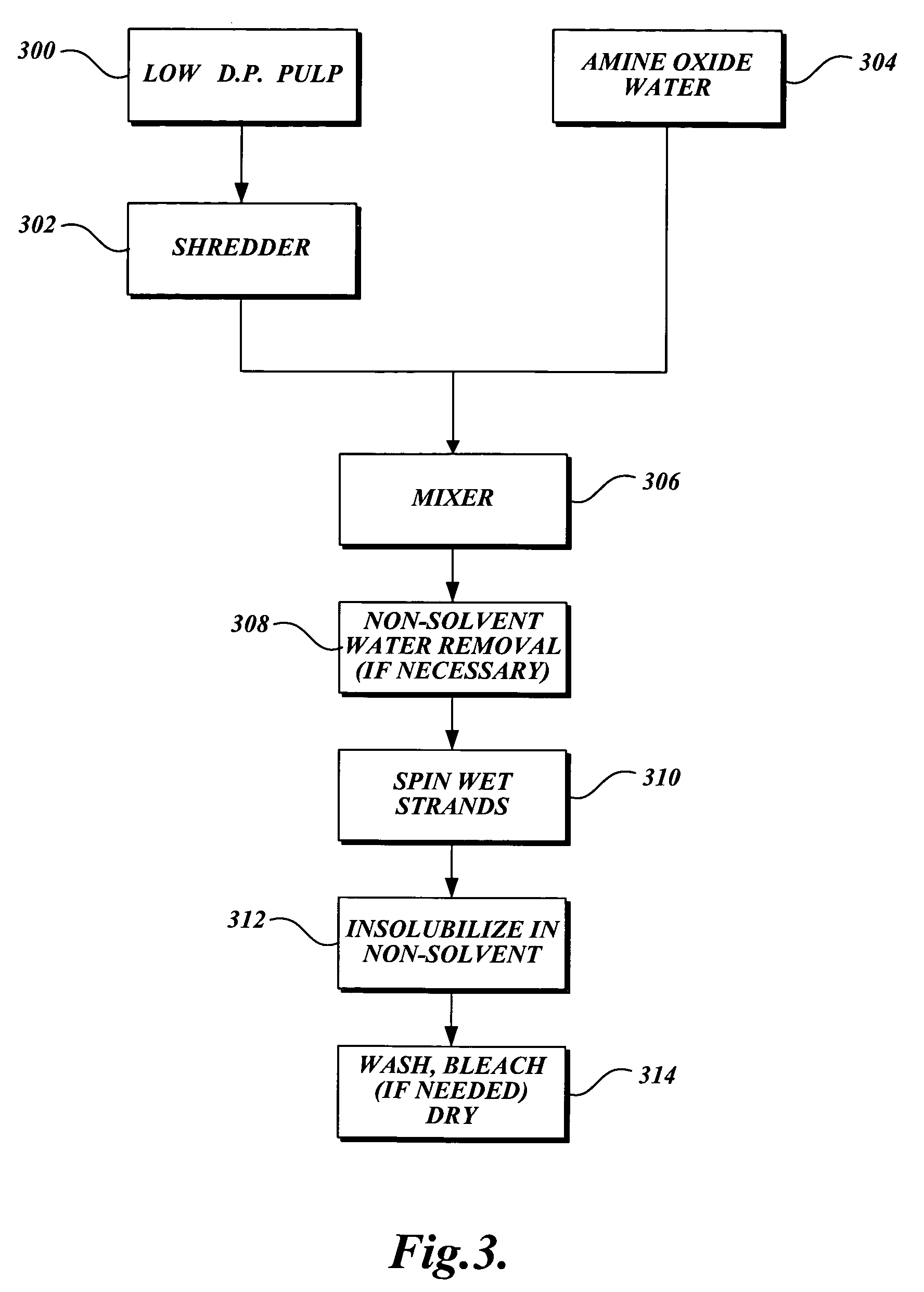
Low pH treatment of pulp in a bleach sequence to produce pulp having low D.P. and low copper number for use in lyocell manufacture
InactiveUS20060070711A1Reduce the degree of polymerizationIncreasing copper numberPulp properties modificationLayered productsBleachPulp mill
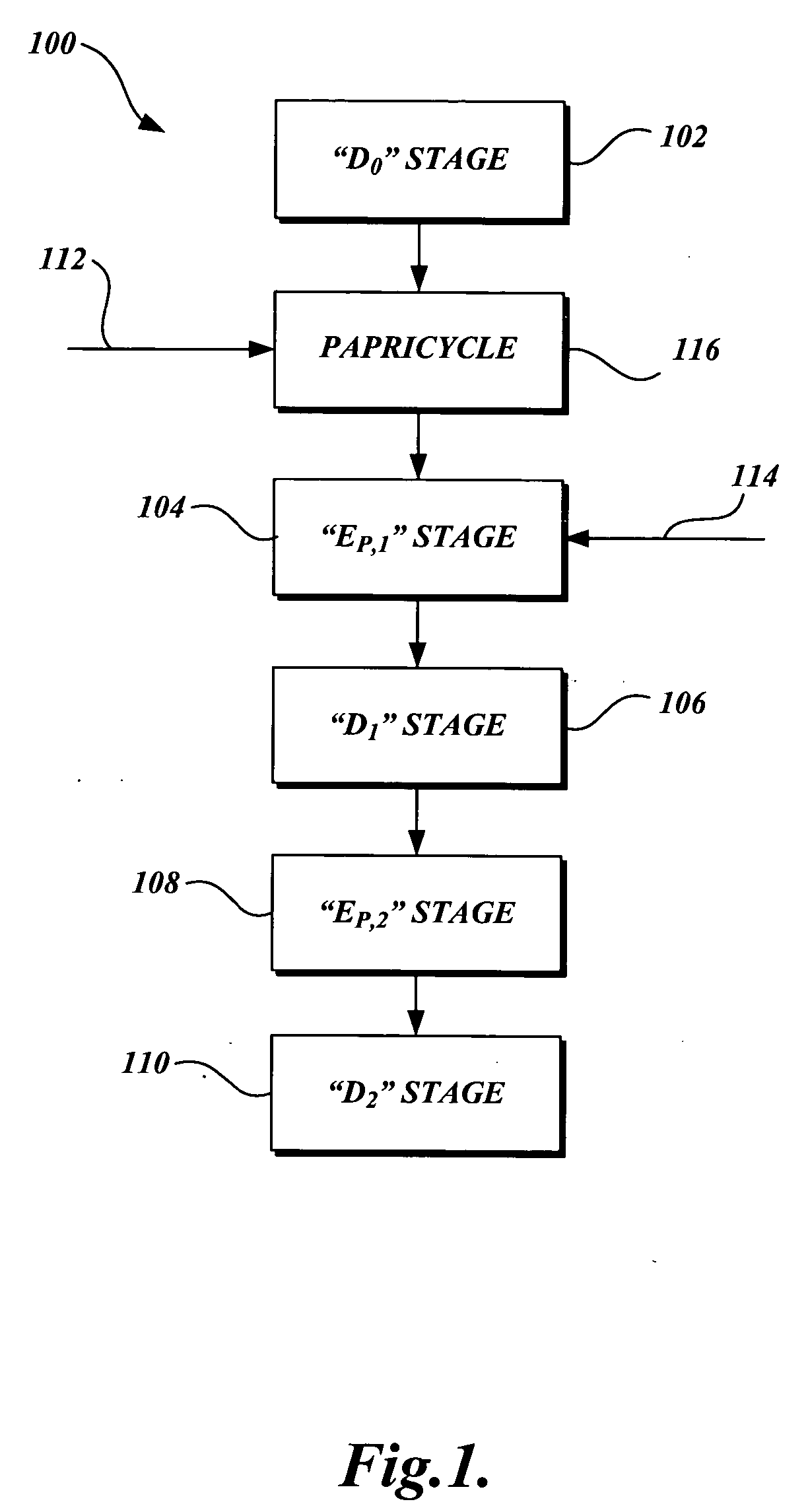
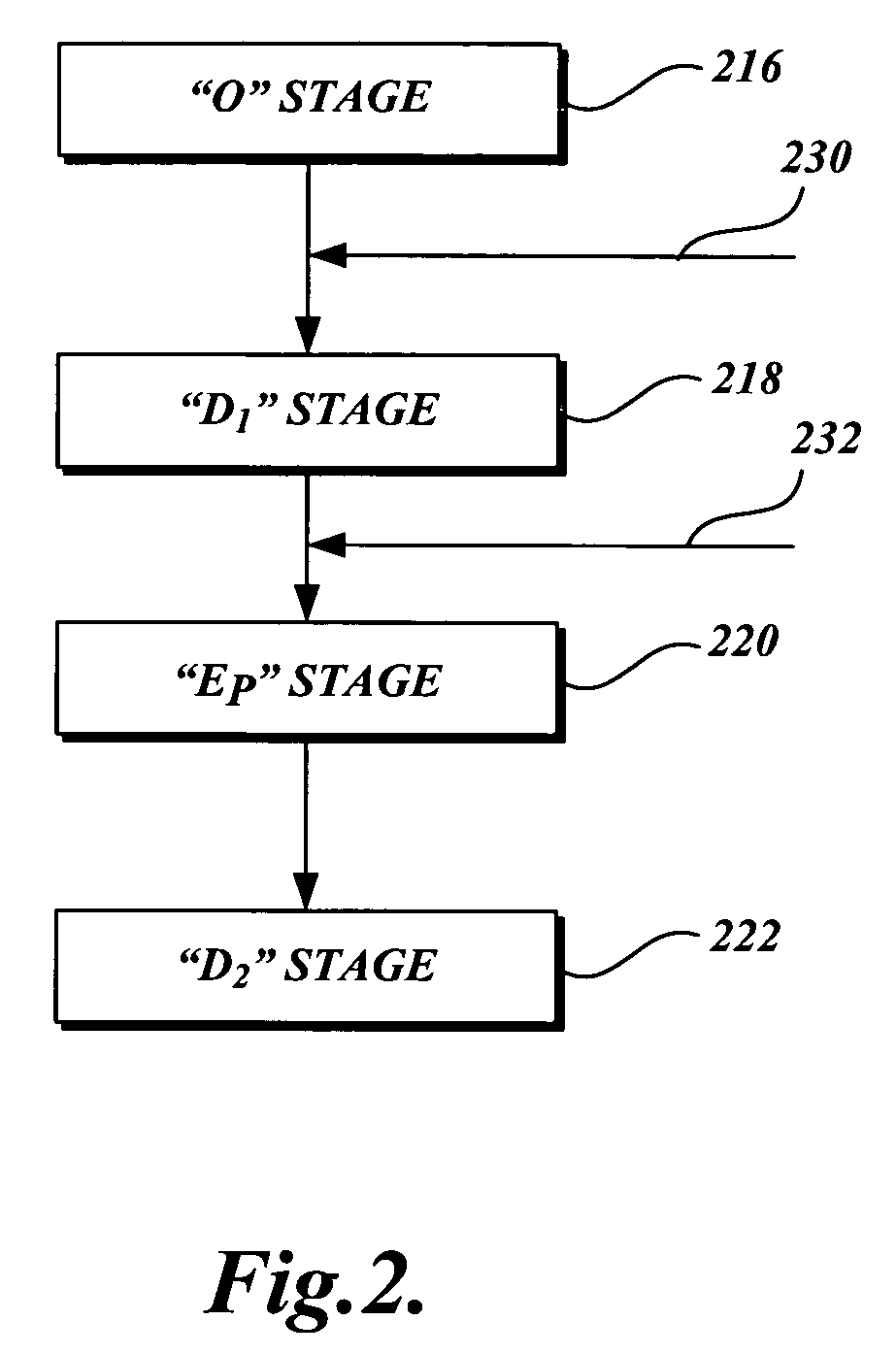
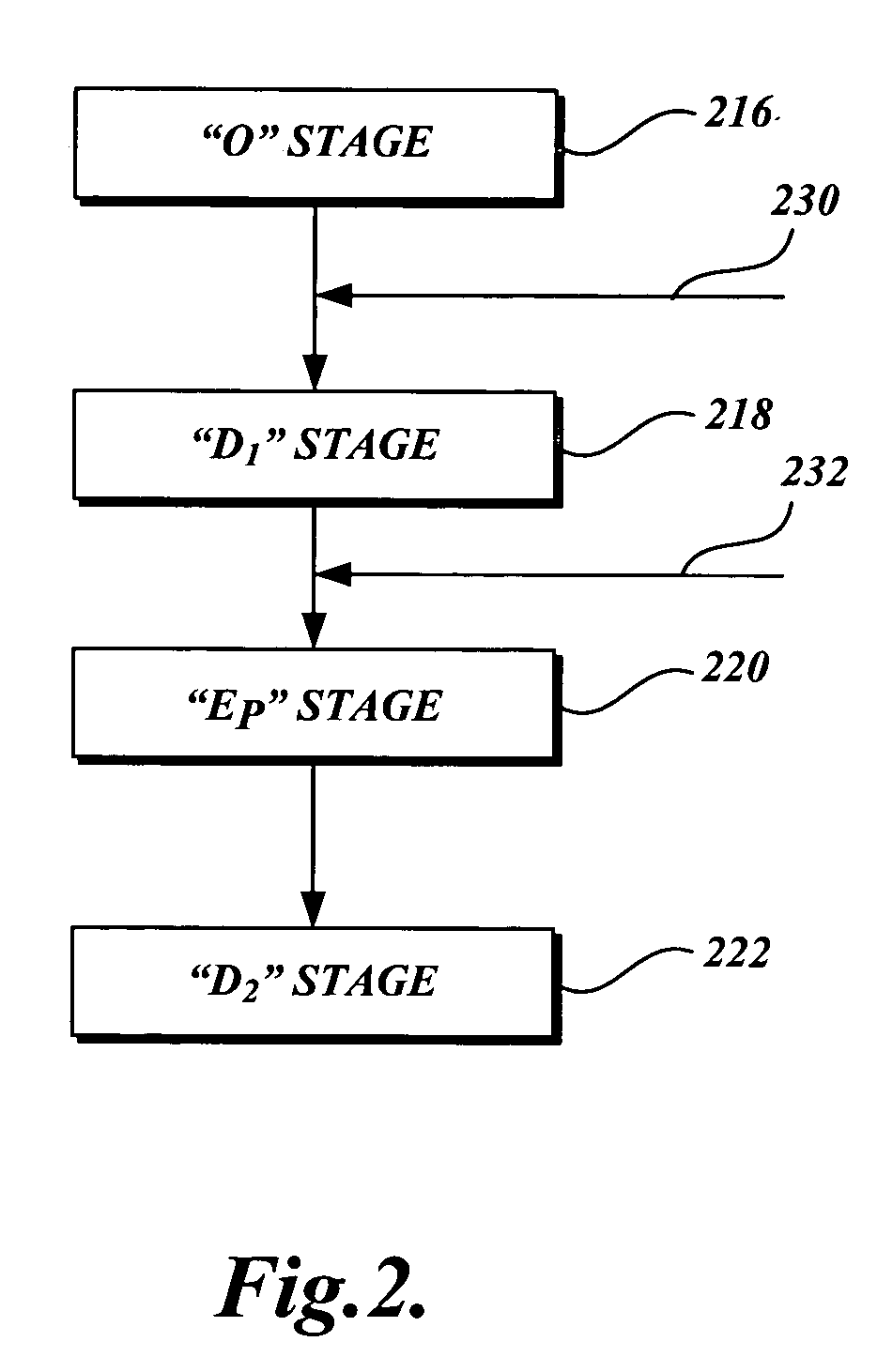
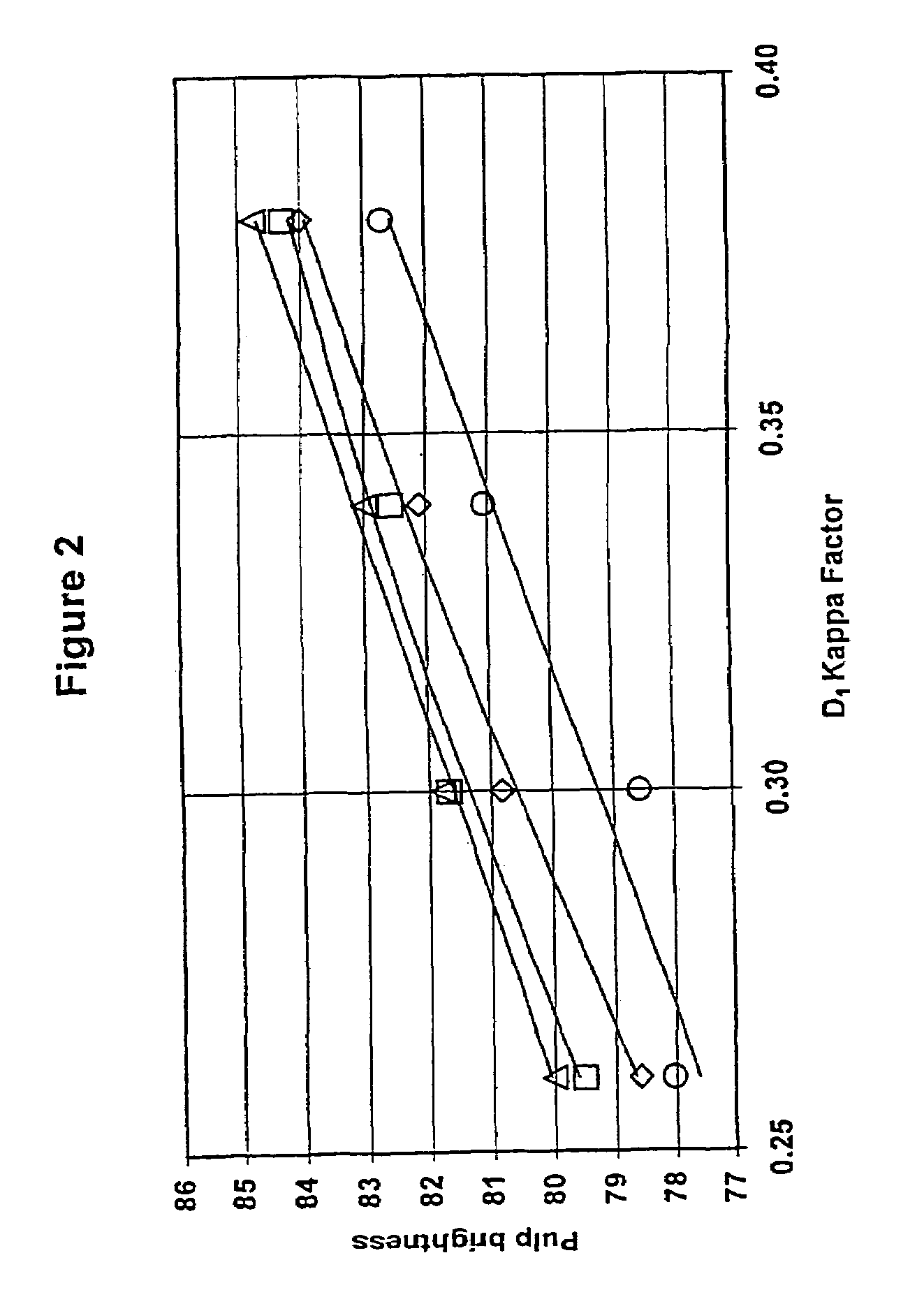
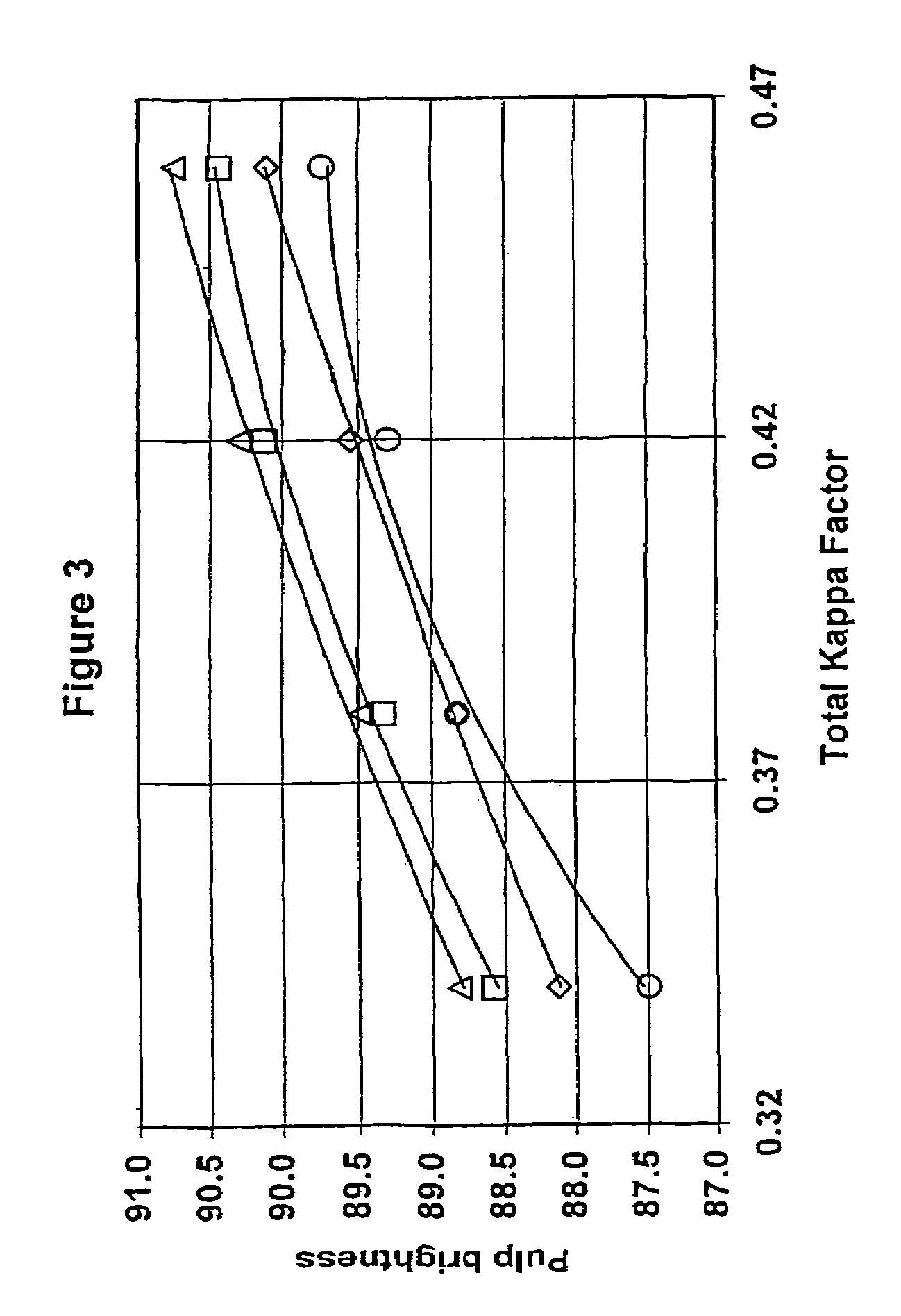
A high pH and a low pH process for reducing the degree of polymerization of a pulp having a hemicellulose content of at least 7%. The high pH is greater than 8, and the low pH process is 2 to 8. The high pH process reduces the degree of polymerization without substantially increasing the copper number. The low pH process requires a subsequent treatment with alkali to reduce the copper number of the pulp to less than 2. The process can be practiced in pulp mills with a bleaching sequence having one or more E or D stages. At the end of the bleach sequence, a pulp having a degree of polymerization of 200 to 1100, a copper number of less than 2, and a hemicellulose content of at least 7% is provided. The pulp can be used to make lyocell fibers.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
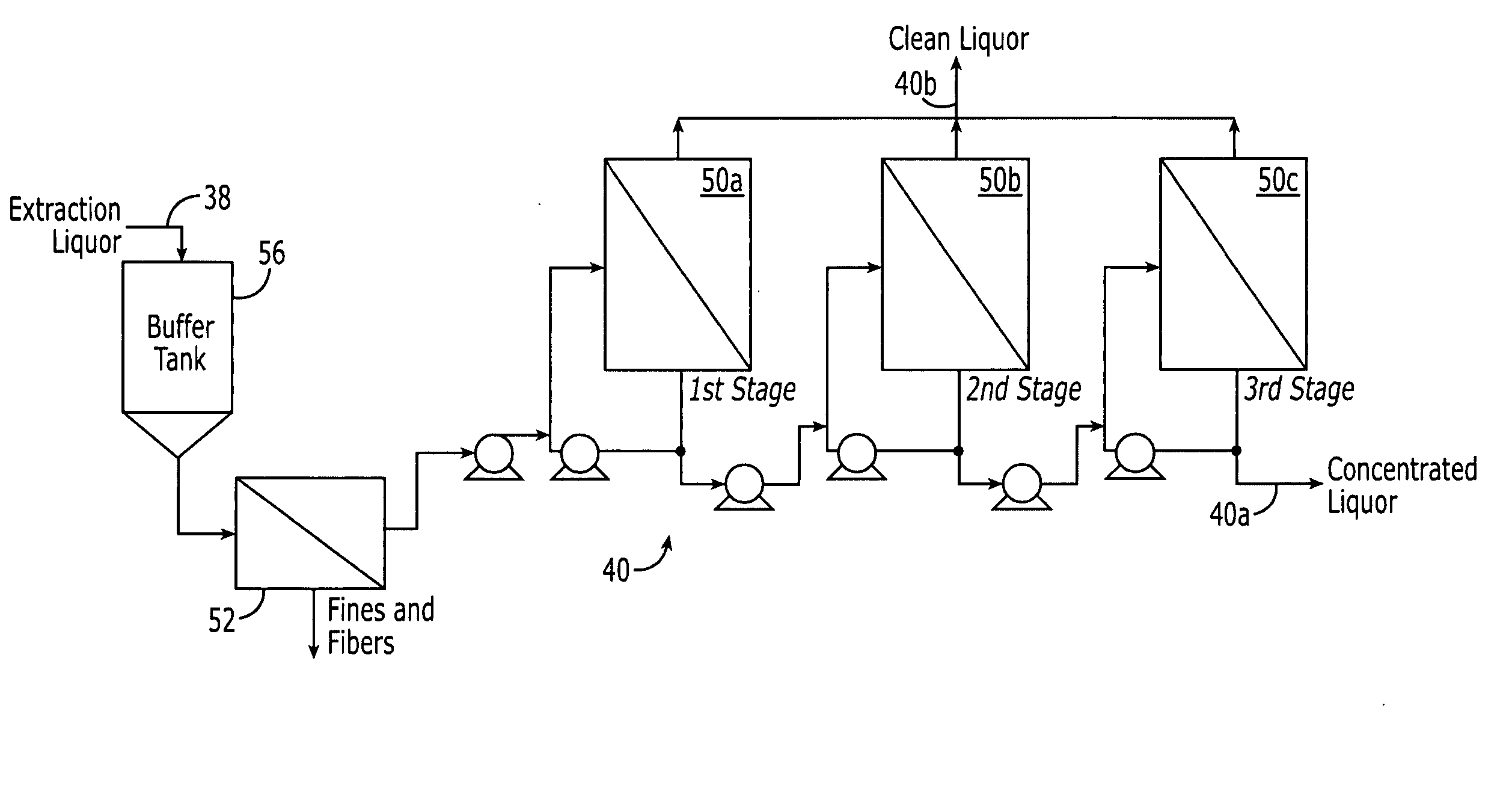
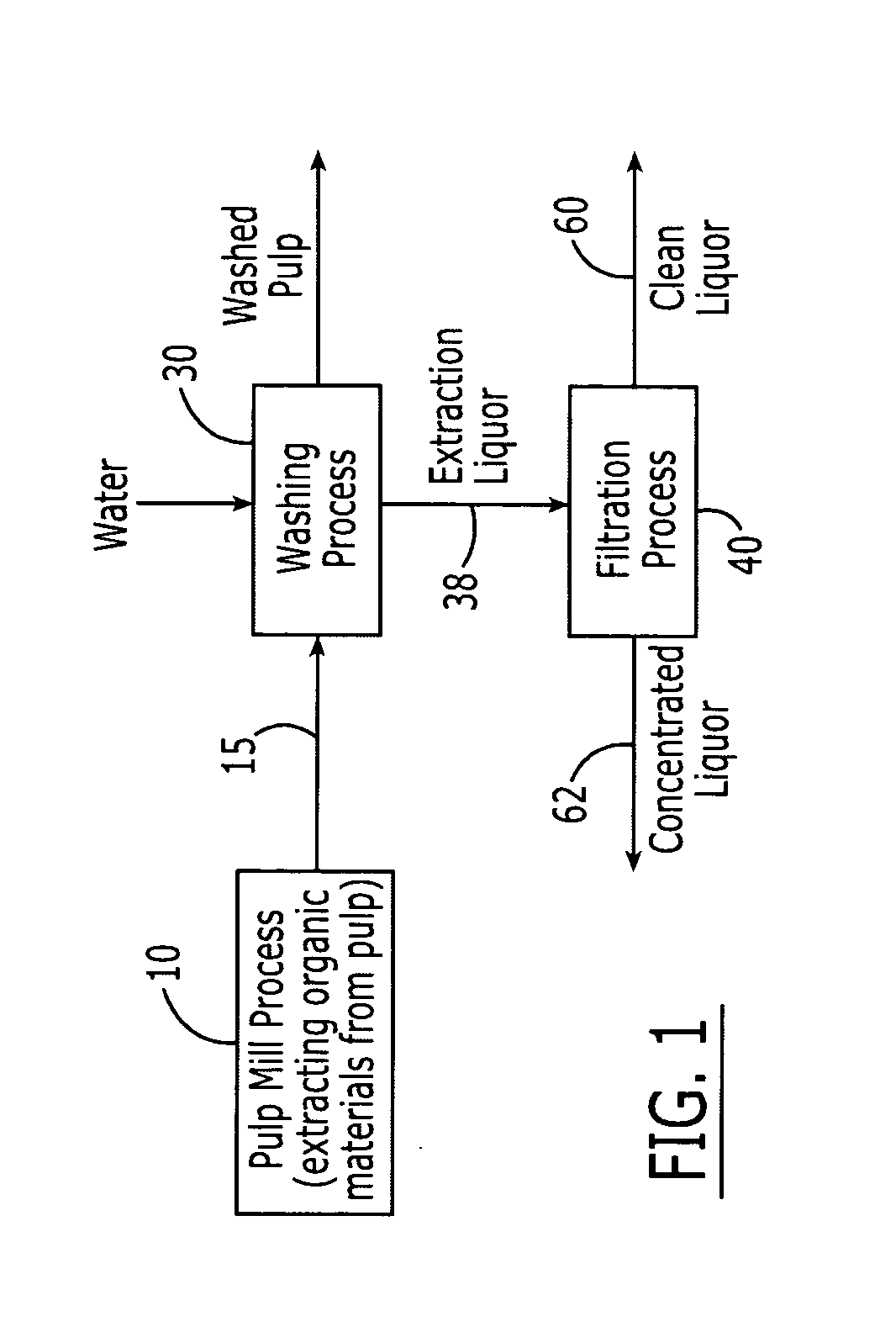
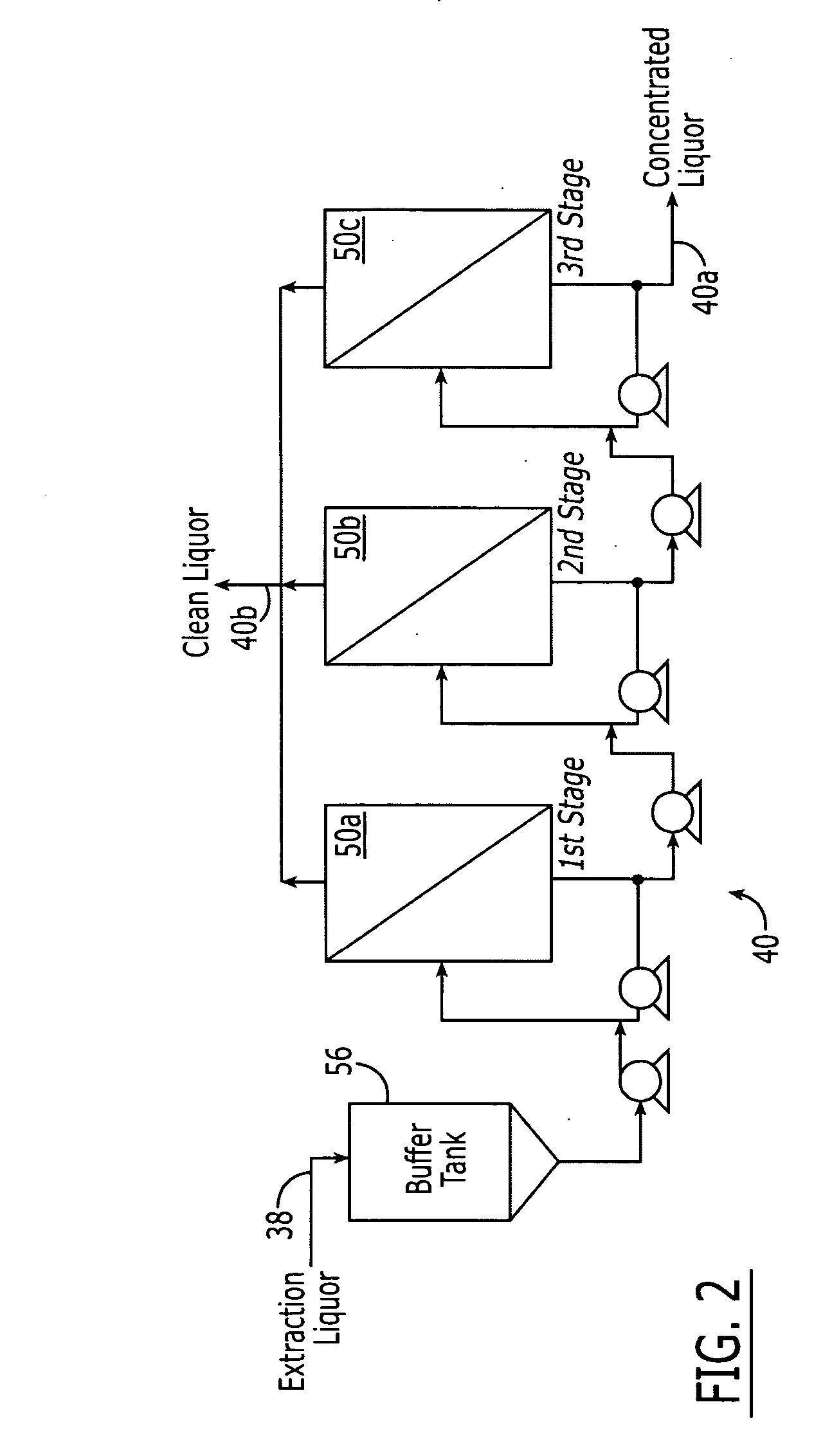
Method of concentrating pulp mill extracts
InactiveUS20060016751A1Reduce loadReduce processMembranesPulp liquors combustionWaste streamPulp mill
A process for separating organic components from a pulp mill waste stream comprising the steps of washing a cellulose pulp to obtain an aqueous extraction liquor containing organic components, and separating at least a portion of said organic components from the extraction liquor by passing the extraction liquor through at least one nanofiltration membrane. The process may be used in conjunction with a variety of pulp mill processes, including kraft cooking processes, hot caustic extraction processes, sulfite cooking processes, and bleaching processes.
Owner:RAYONIER PRODUCTS AND FINANCIAL SERVICES COMPANY
Amino-functionalized pulp fibers
InactiveUS6936136B2Quality improvementImprove abilitiesPulp properties modificationSpecial paperFiberPulp mill
The disclosed invention is directed to pulp fibers suitable for forming a wet-laid paper product which include amino-functionality which is non-extractable in an aqueous phase. The pulp fibers may be prepared by applying an amino-functional additive to a fibrous web prior to the finishing operation at a pulp mill. The fibrous web may then be repulped at a papermaking machine to form a paper web which includes the amino-functionalized fibers of the present invention. A paper web formed of the amino-functionalized fibers may display unique and / or improved reactivity toward certain papermaking additives. For instance, the paper webs of the disclosed invention may show dry tensile strength increases of greater than 40% when treated with a permanent wet strength agent such as a polyamine epichlorohydrin wet strength agent, whereas a paper web which does not include the amino-functionalized fibers of the present invention may show less than a 20% increase in strength properties when treated with the same strength agents.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Xylanase treatment of chemical pulp
InactiveUS20050150619A1Reduce usageHigh strengthPulp bleachingPulping with organic solventsChlorine dioxidePulp mill
The present invention discloses methods of bleaching chemical pulp that use xylanase enzymes after chemical bleaching. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a chlorine dioxide stage to produce a partially bleached pulp, treating the partially bleached pulp with a xylanase enzyme, optionally in the presence of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, in a mild extraction stage, then bleaching the pulp with a second chlorine dioxide stage. The method allows the mill to decrease the usage of sodium hydroxide or other alkali, while decreasing the use of chlorine dioxide, and possibly improving the yield and strength of the pulp, while maintaining a similar level of bleached brightness of the pulp. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method and compositions for preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in alkaline industrial processes
Materials and a method are provided whereby polymers with least 0.5 mole % of the pendant group or end group containing —Si(OR″)3 (where R″ is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in an industrial process having an alkaline process stream such as a pulping mill process stream. When materials of the present invention are added to the alkaline process stream, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on equipment surfaces such as evaporator walls and heating surfaces. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
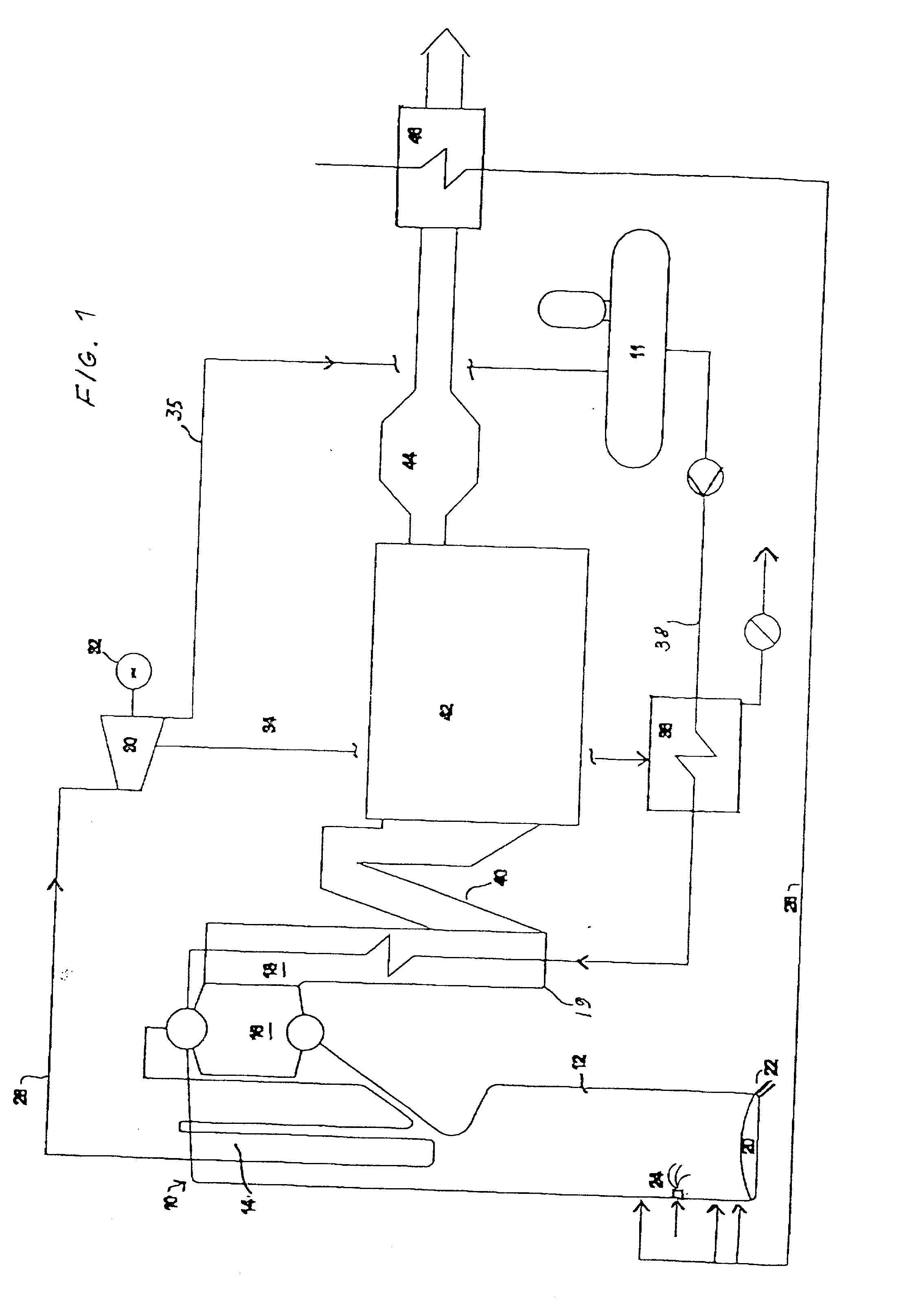
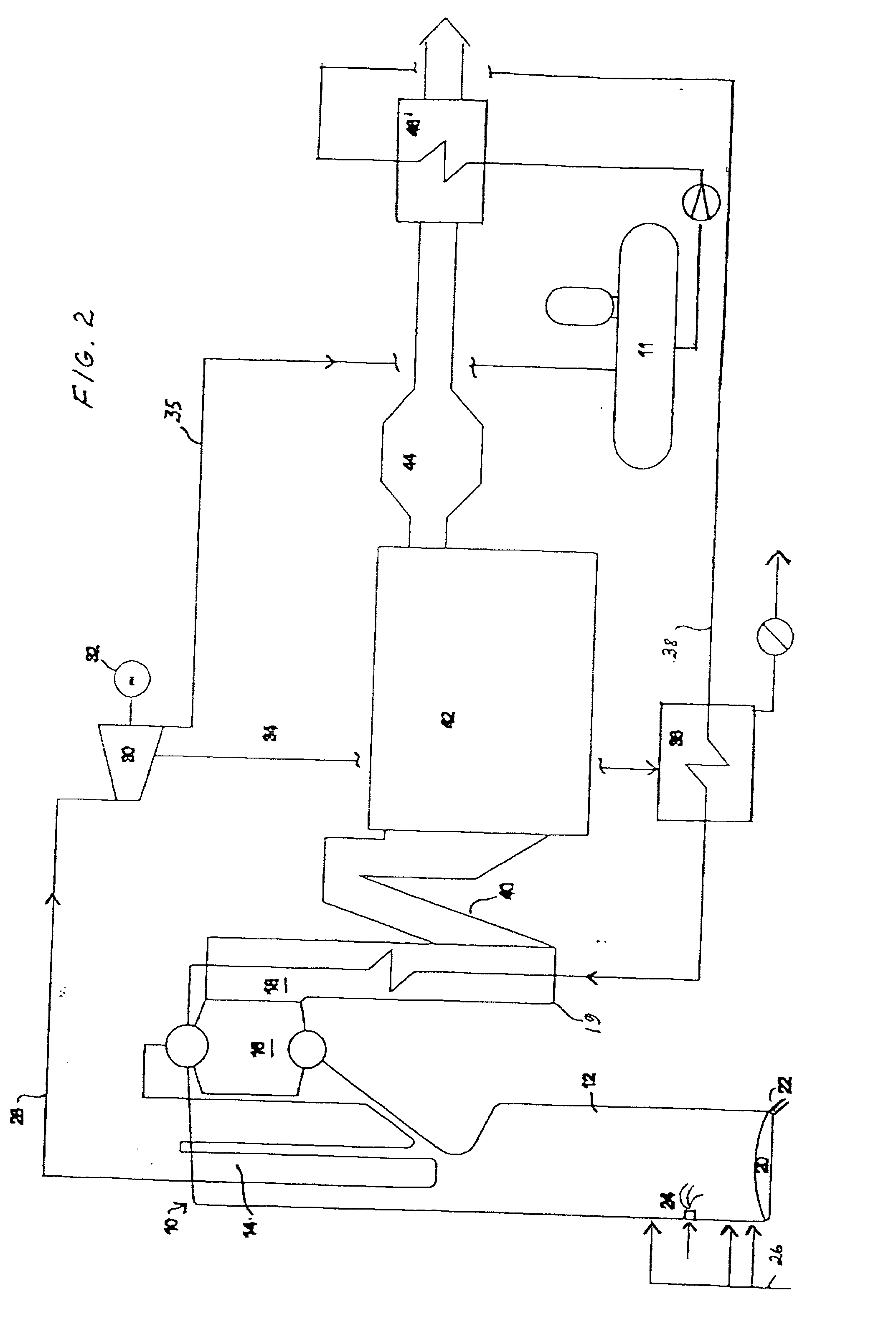
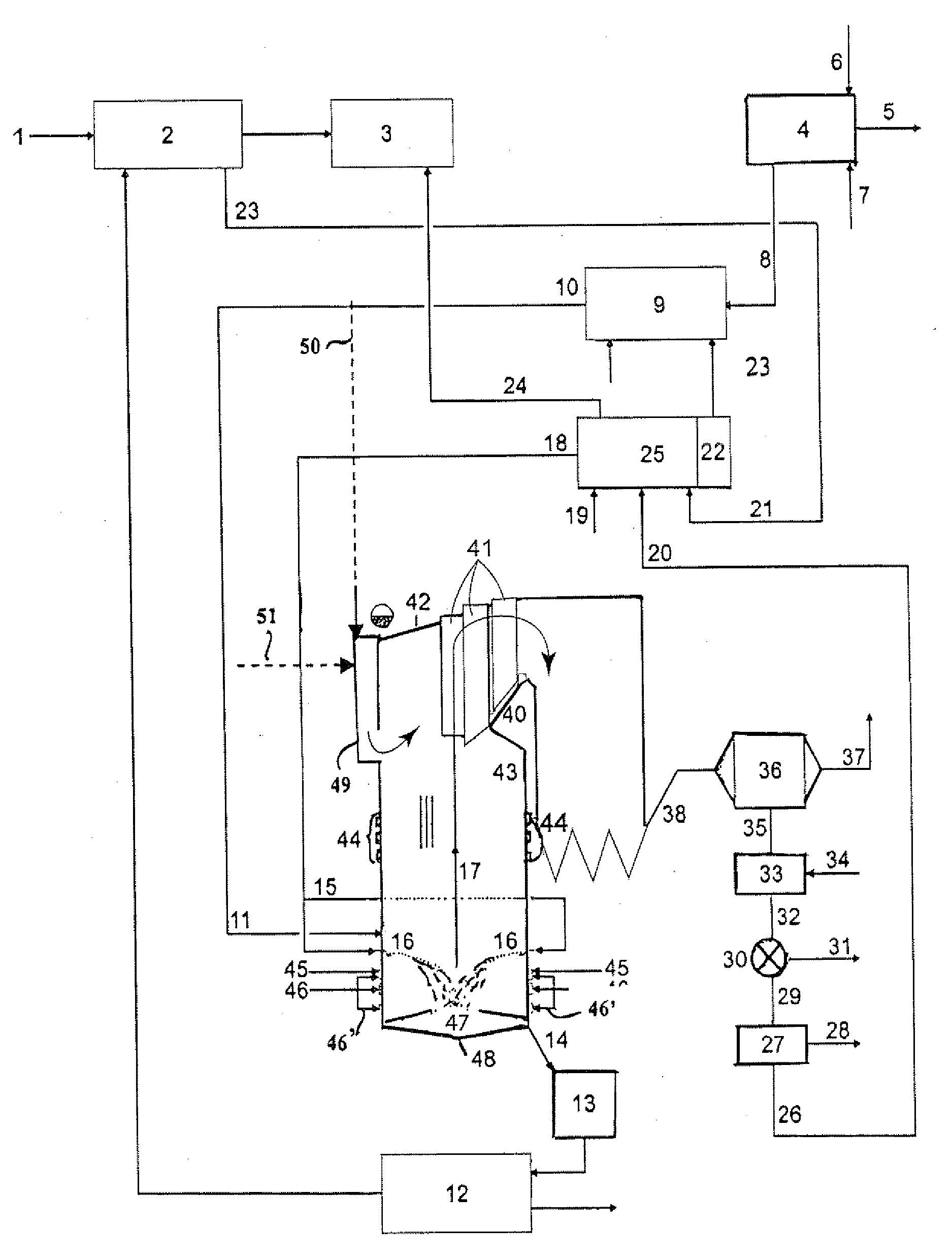
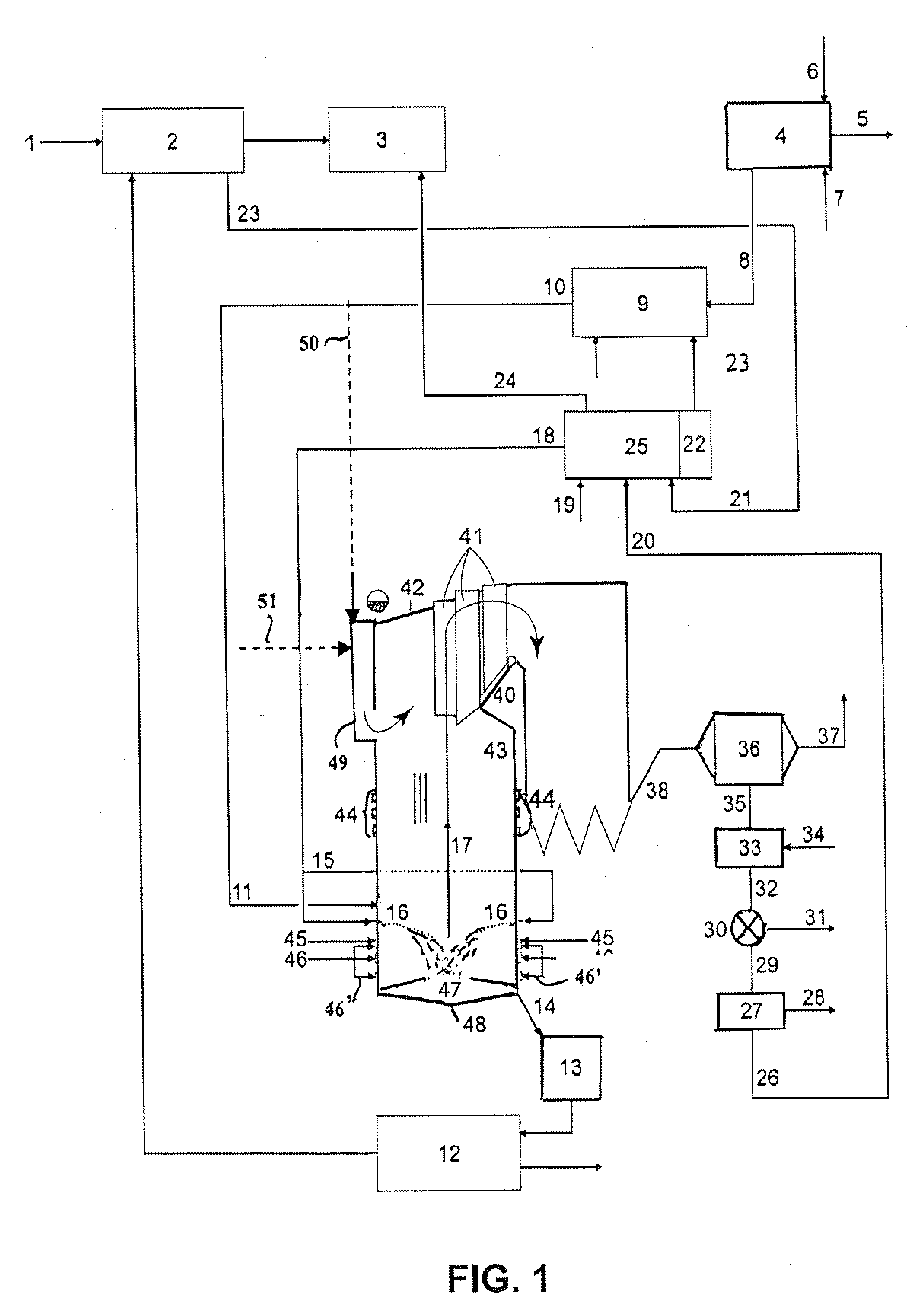
Process for production of synthesis gas in combination with the maintenance of the energy balance for a pulp mill
InactiveUS7294225B2Simpler andImprove energy savingPulp liquors combustionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesEnergy balancingCombustion
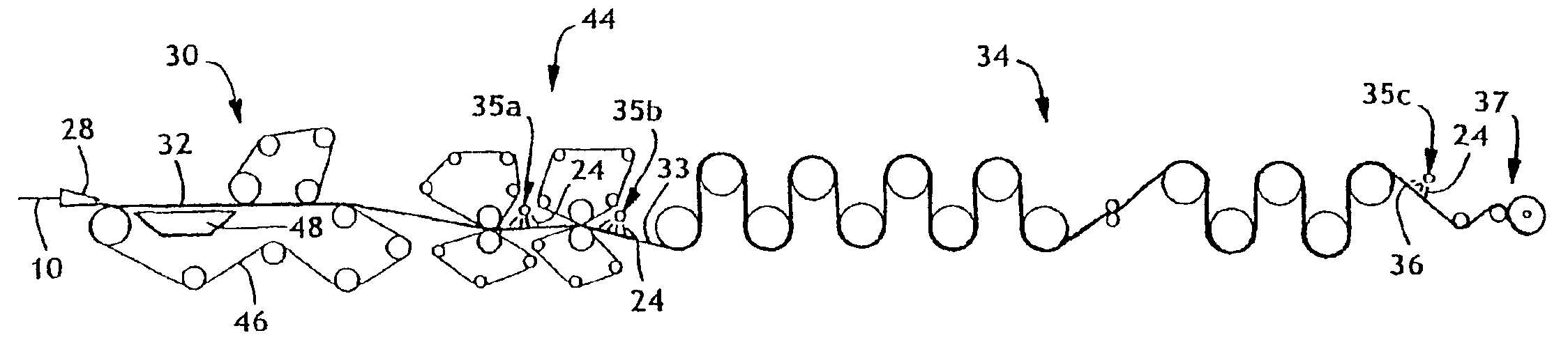
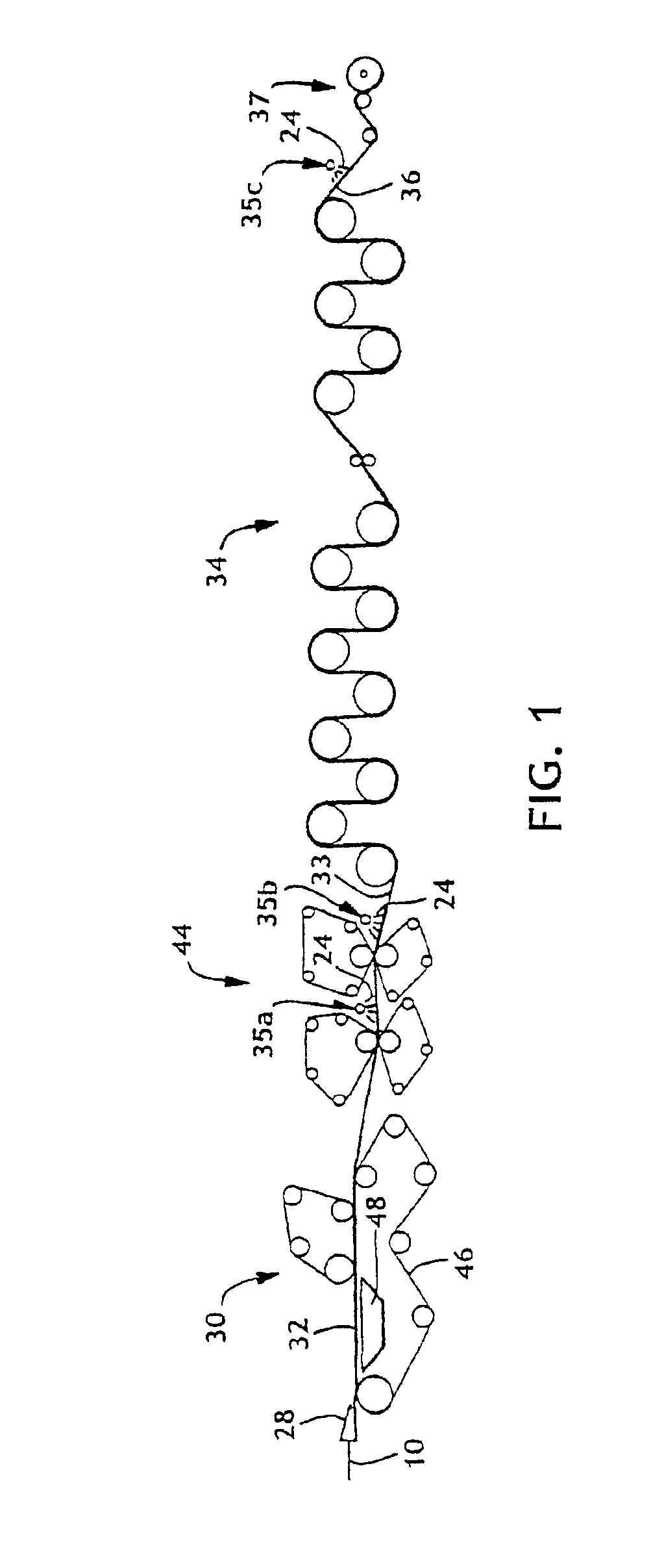
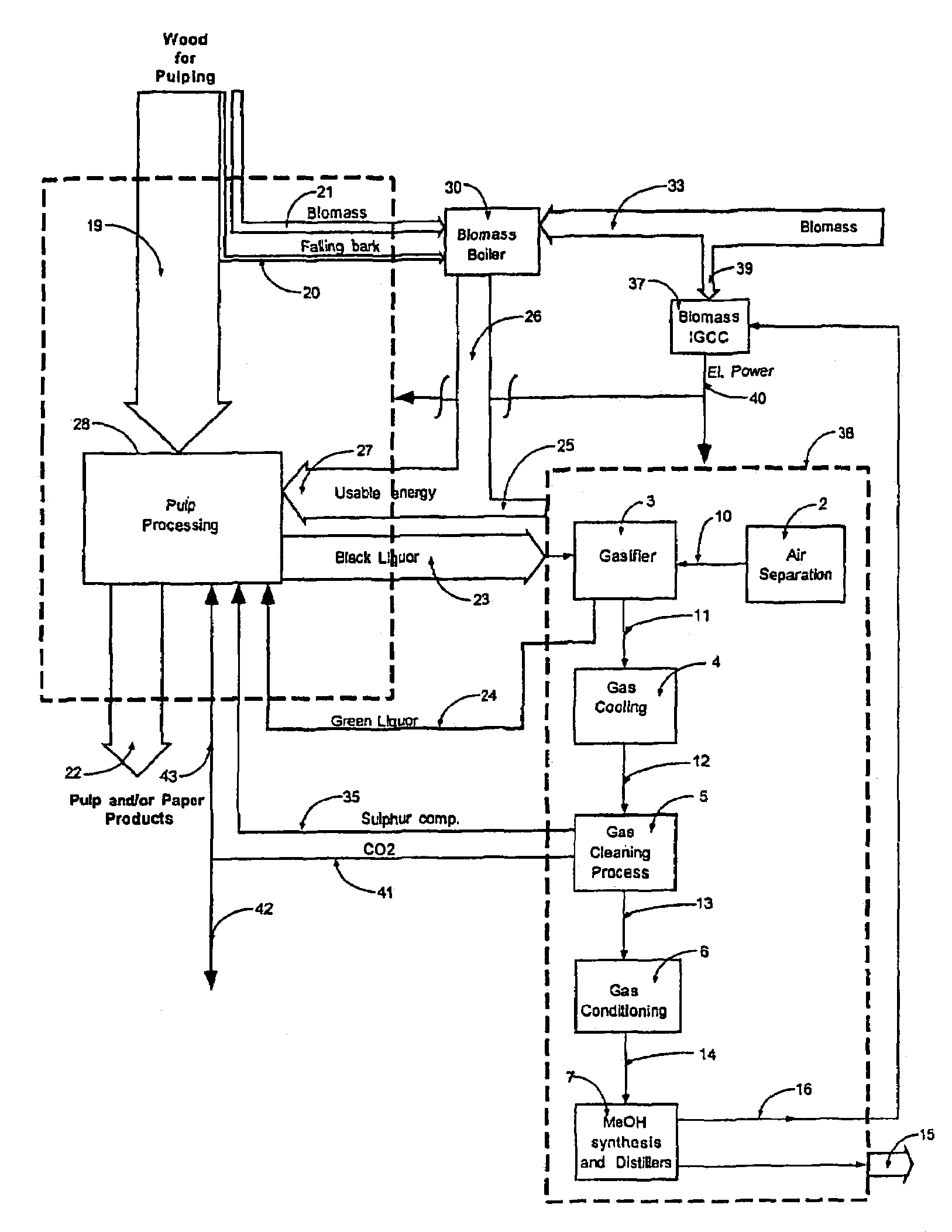
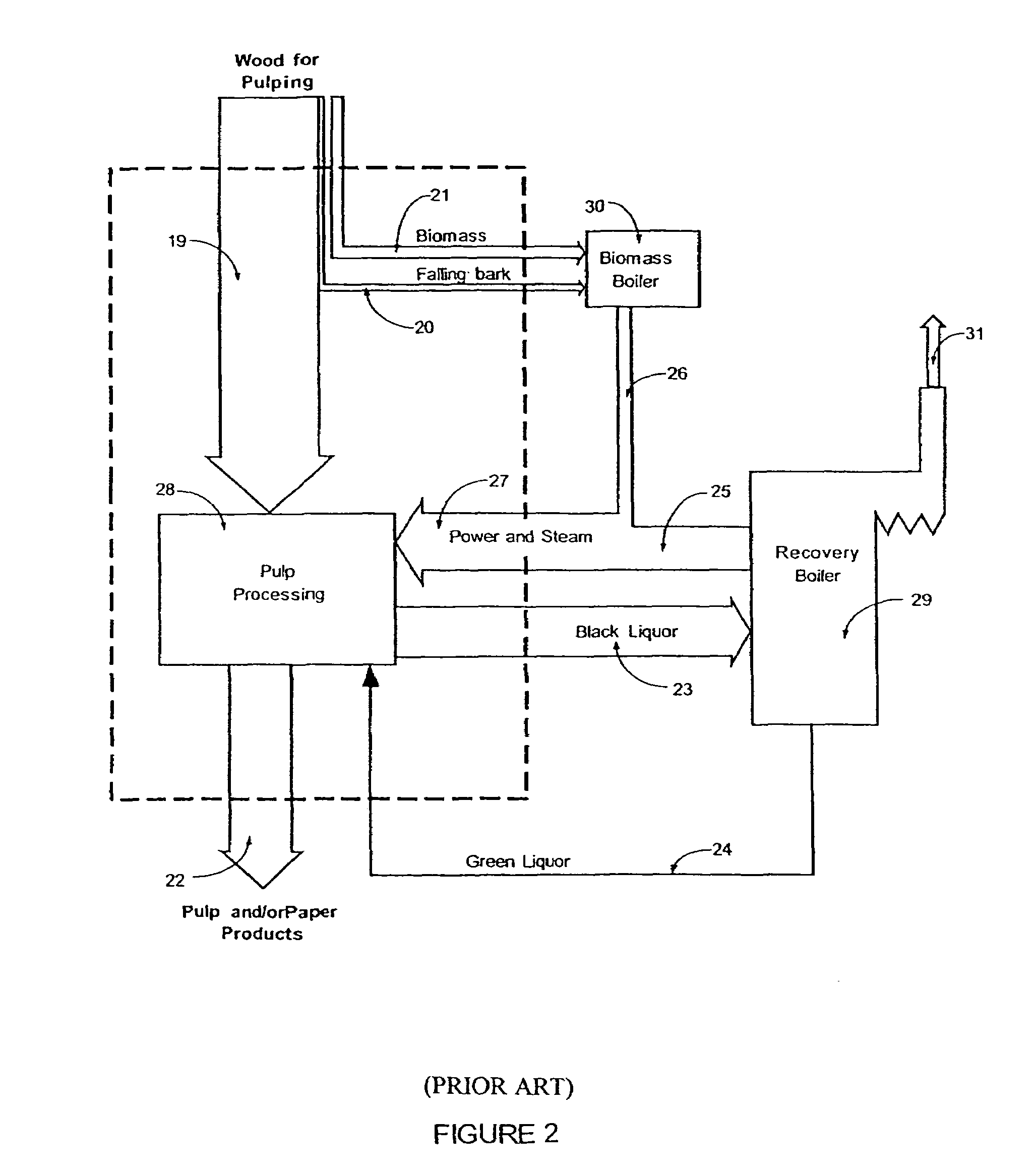
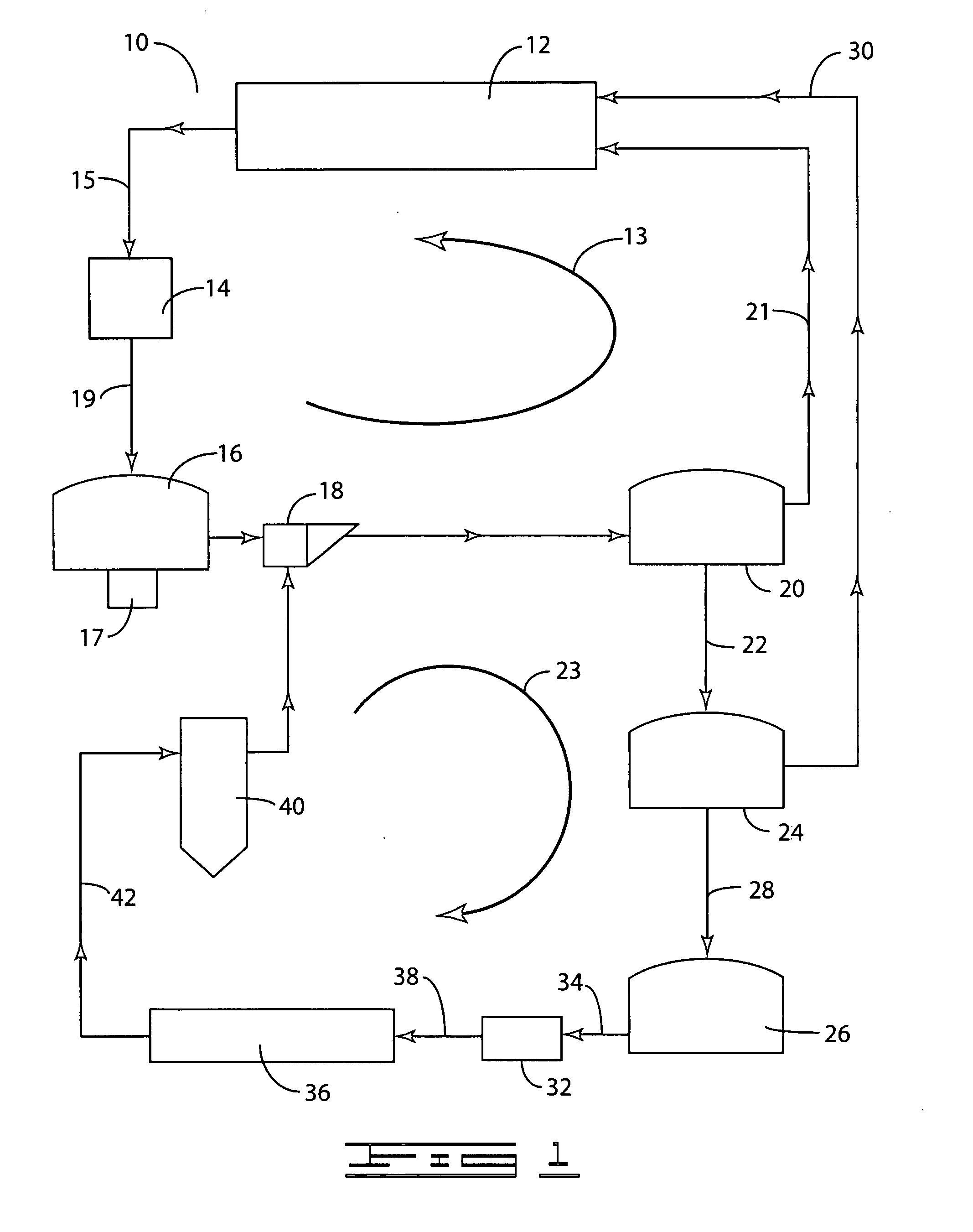
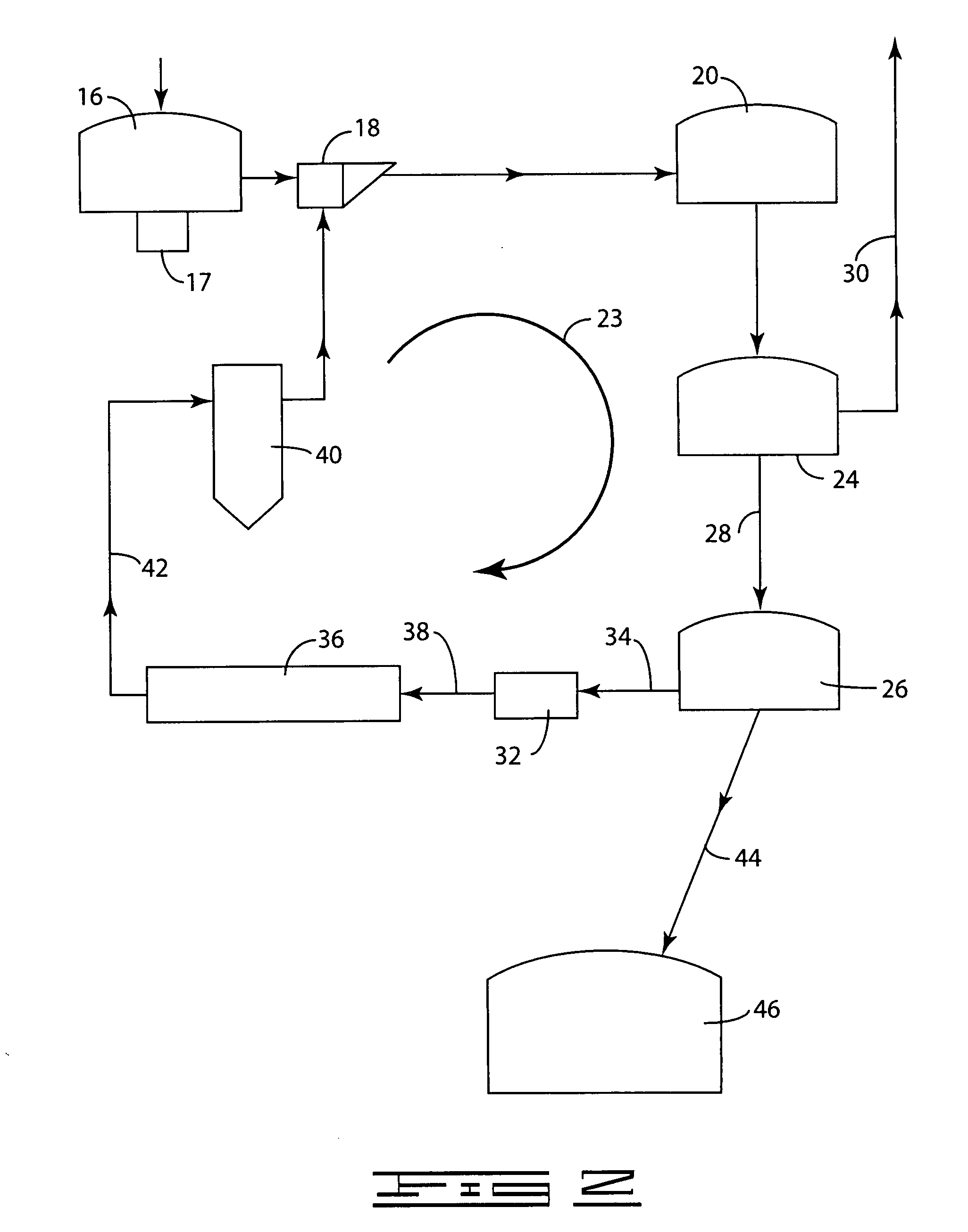
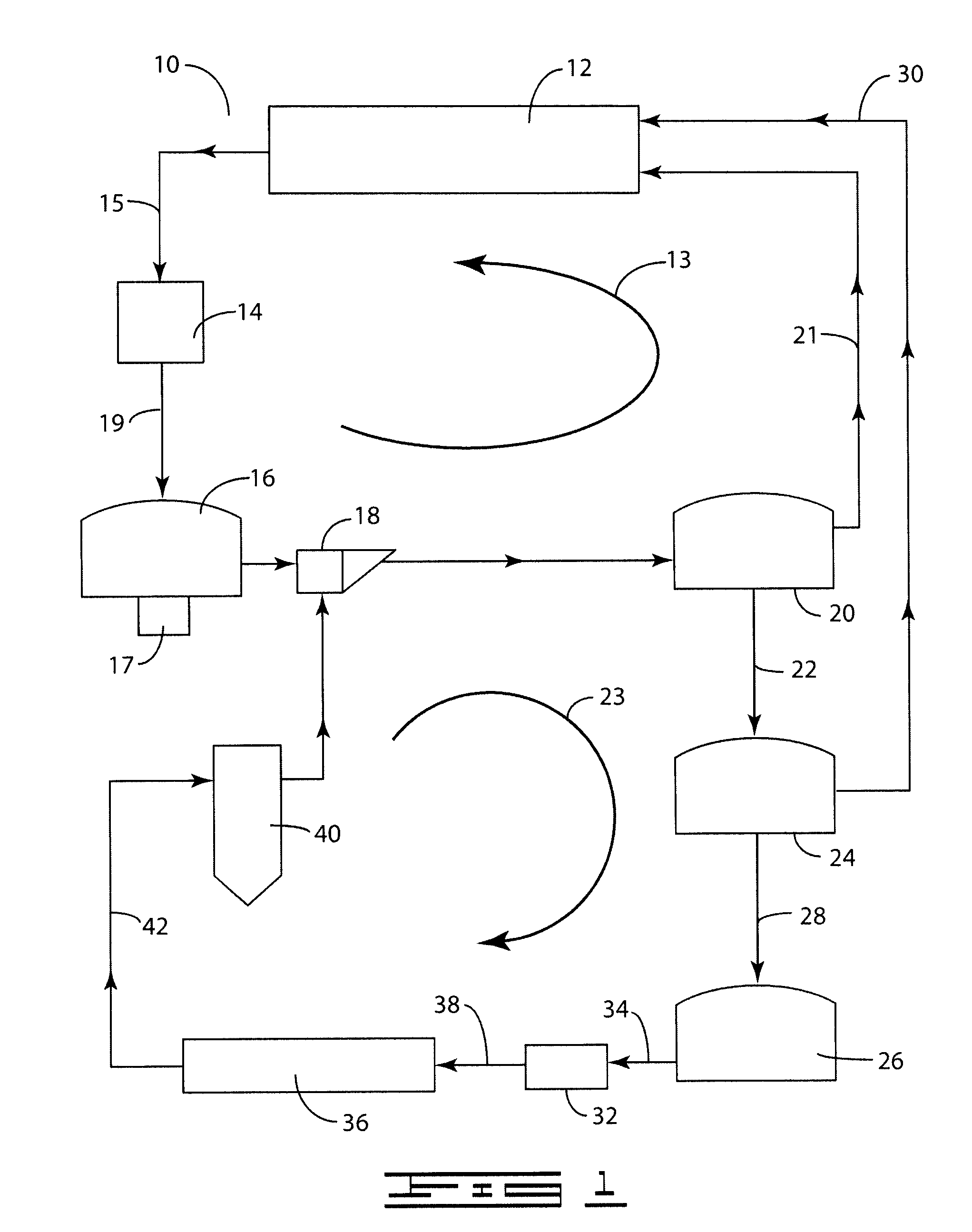
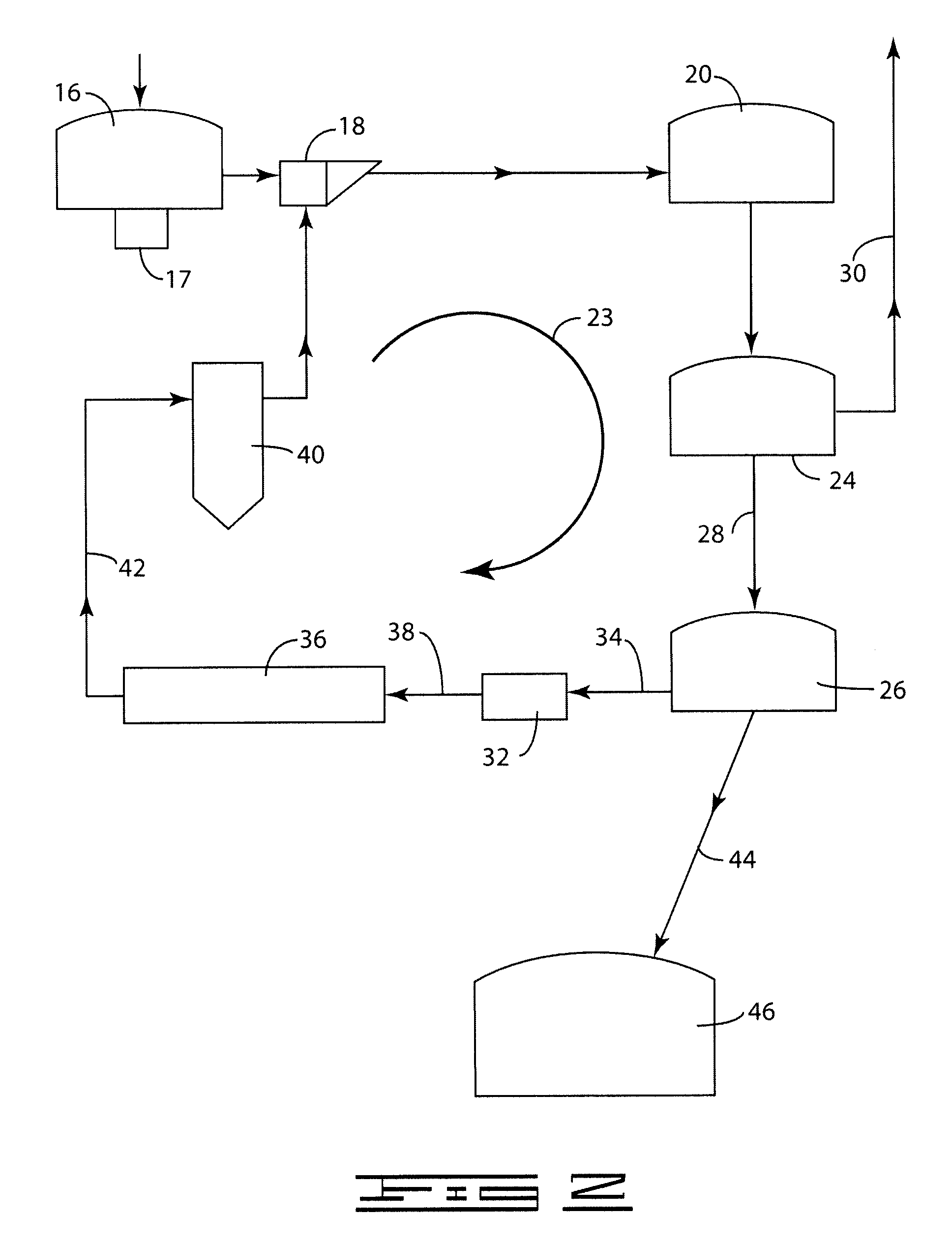
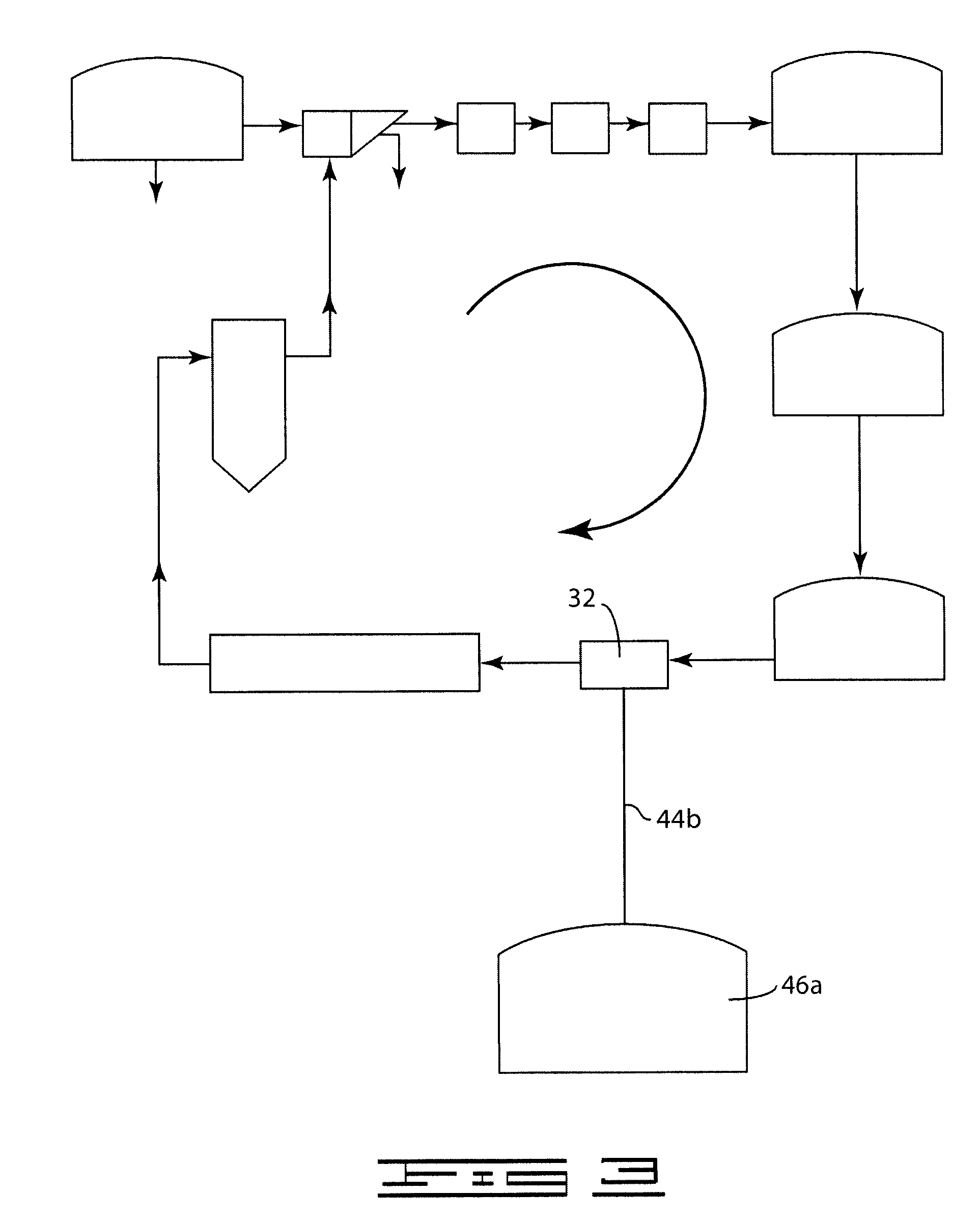
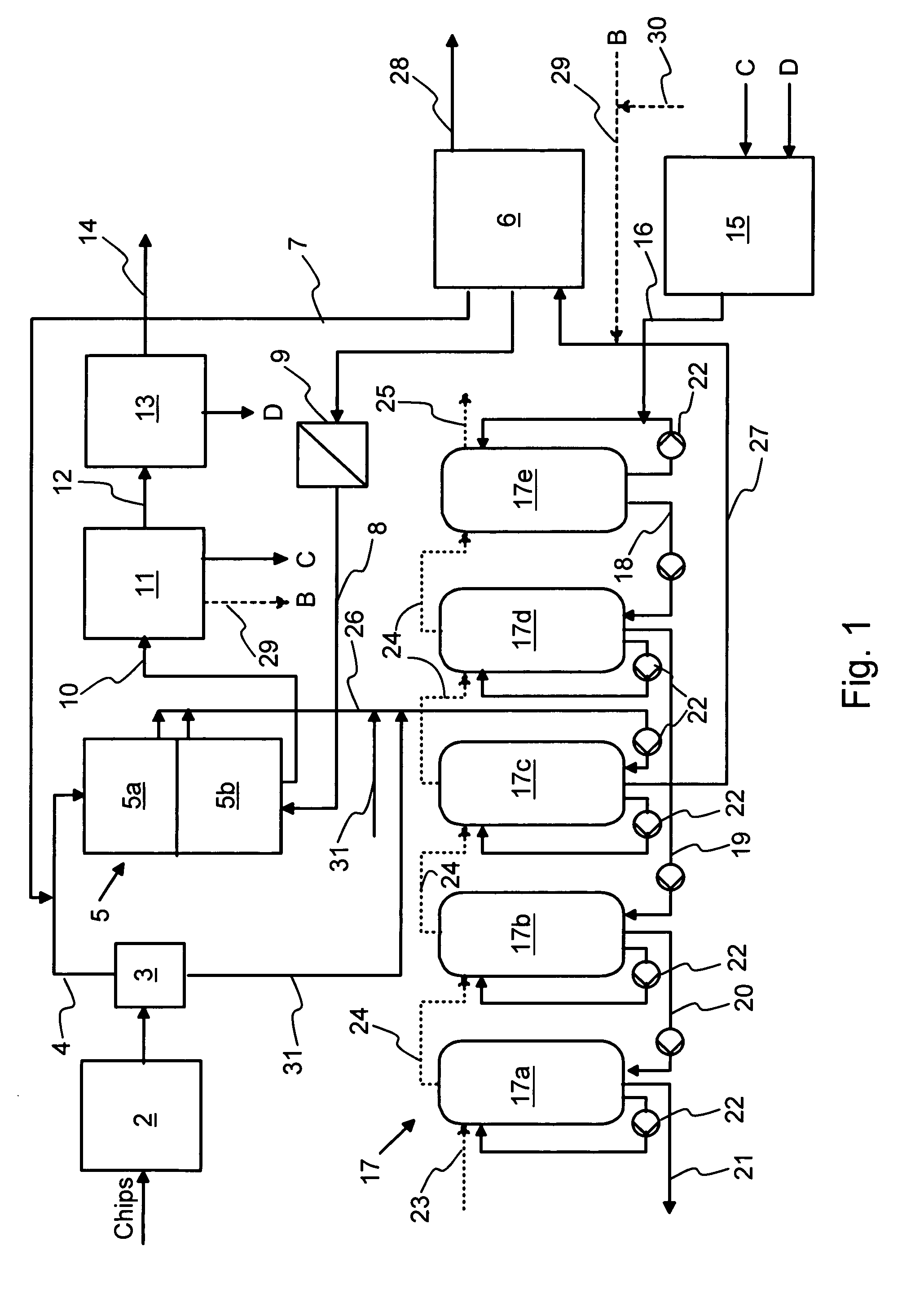
A process (44) for the production of pulp and paper (28), recycling of cooking chemicals (3, 29), combustion of biomass (30, 37) and generation of heat and electric energy (27, 40) comprising a pulp and paper mill (28), in that the part of the process which is recycling cooking chemicals is adjusted from combustion (29) to gasification (3) to generate synthesis gas (14); and that biomass is added (33, 39) in an amount sufficient for compensating of the decrease in heat and electricity generation as a consequence of the generation of synthesis gas (14).
Owner:CHEMREC AB
Defoamer emulsion compositions for pulp mill applications
InactiveUS20060128816A1Reduce usageLow costNatural cellulose pulp/paperDefoamers additionPulp millHydrophobic silica
An oil-in-water emulsion useful as a defoamer for pulp and paper mill applications is described. The defoamer has an oil blend (of a triglyceride oil or a mixture of triglyceride oils and silicone), a stabilizing agent (to make the oil blend stable in the emulsion), hydrophobic silica particles, surfactants, dispersants, and other components. The emulsion is usable directly at low concentrations to control foam.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Removal of inorganic elements from wood chips
InactiveUS20050034823A1Less energy consumptionIncrease moisture contentWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsProduction linePregnant leach solution
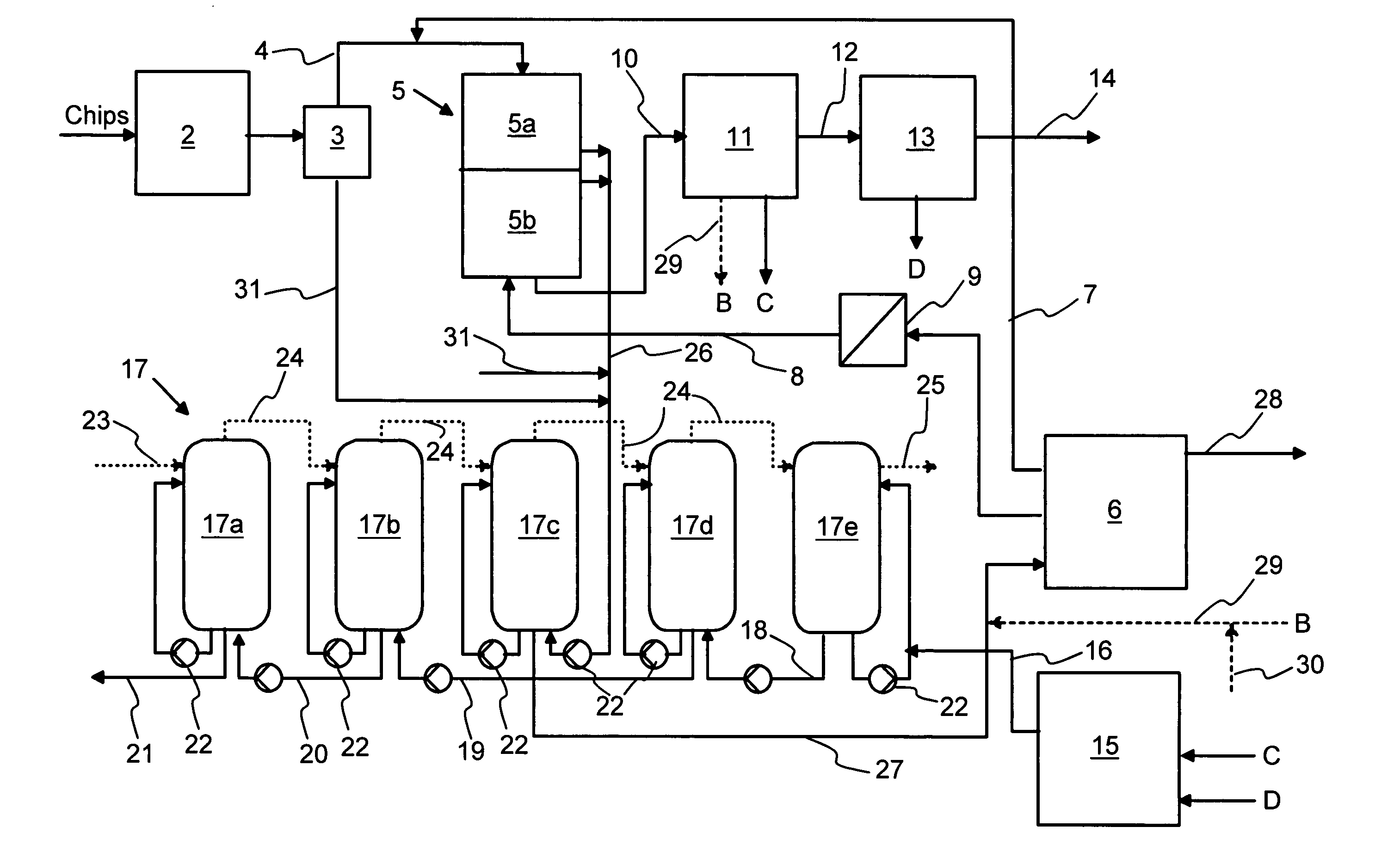
In a process of treating wood chips for reduction of the concentration of undesirable inorganic elements prior to cooking in a production line for chemical pulp, the wood chips, having entrapped air, are treated with an aqueous leaching liquor at elevated temperature and pressure, followed by draining at atmospheric pressure or below atmospheric pressure, the pressures being controlled to yield a moisture content in the wood chips as low as possible for adequate leaching result and behavior of the chips in a subsequent digester. The aqueous leaching liquor is e.g. pulp mill process water with a low content of undesirable inorganic components, such as bleach plant spent liquor or condensate. The aqueous leaching liquor drained from the treated wood chips may be purified and recycled back to the process.
Owner:STFI
Particulate matter and methods of obtaining same from a kraft waste reclamation
InactiveUS20080219912A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesGas treatmentParticulatesChemical composition
A method for obtaining particulate calcium carbonate having an average particle size less than about 12 microns is provided. The method includes the steps of (1) withdrawing from a pulp mill a mixture containing calcium carbonate; (2) treating the mixture to remove contaminants contained in the mixture to produce a treated mixture containing calcium carbonate and further having a chemical composition and / or purity which substantially inhibits the fusing together of calcium carbonate particulates; (3) recovering from the treated mixture particulate calcium carbonate having an average particle size less than about 12 microns. The calcium carbonate produced has a high surface area to volume ratio and is therefore highly reactive and suitable for numerous applications such as in the treatment of soil, filler paper production, paint production, and contaminant containment in coal stack emission assemblies.
Owner:S&S LIME
Production chain of instant dry rice noodles and technique for producing the same
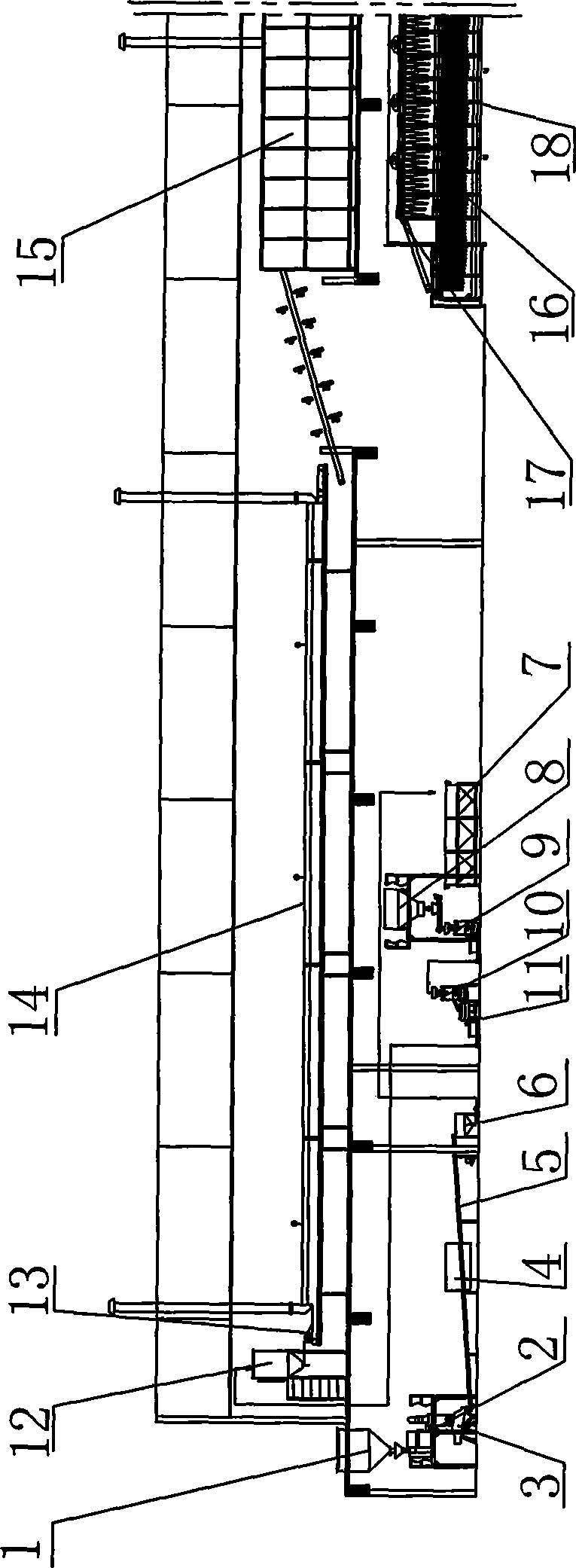
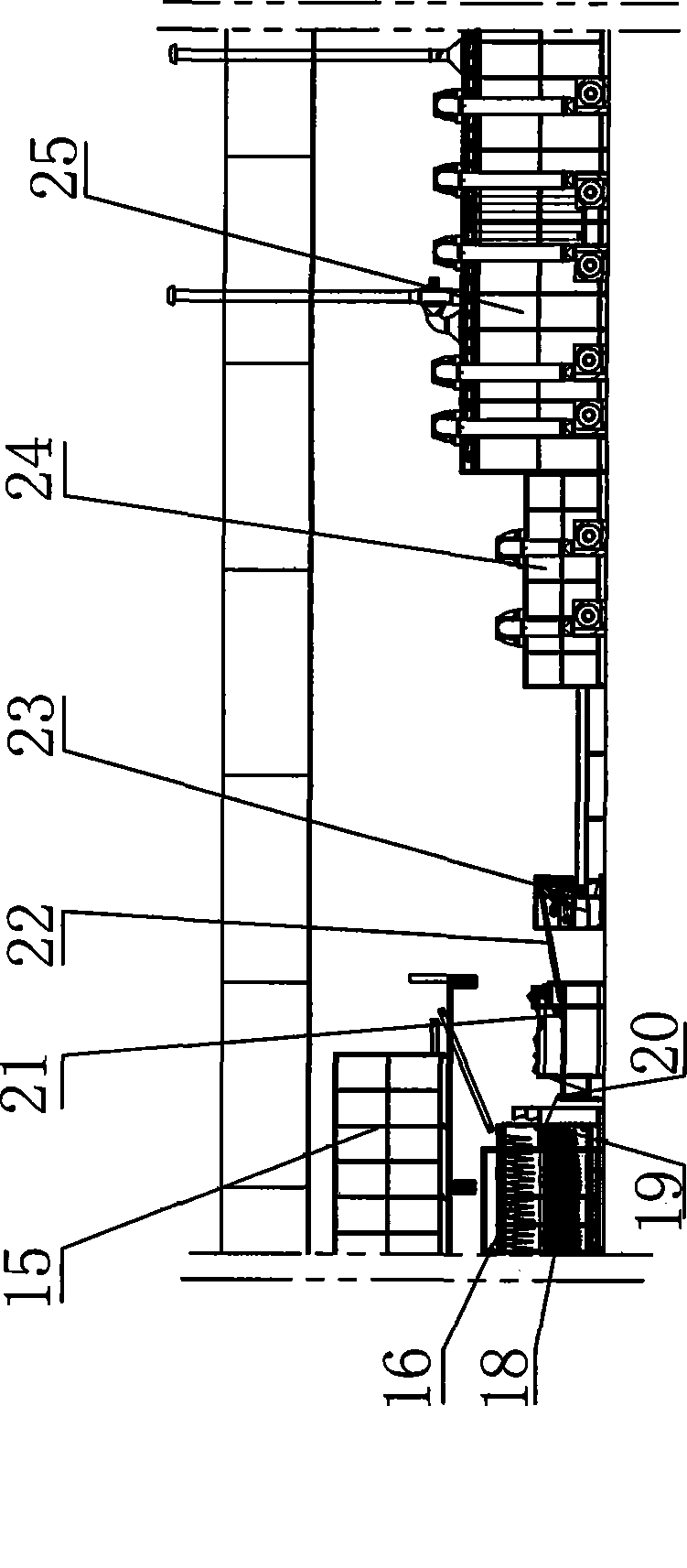
The invention discloses an instant dried rice noodle production line and production technology, The production line comprises: rich falling bucket, air-jetting rice polisher, specific gravity sand removing machine, rice color sorting machine, rice conveyor, rice pumping machine, jet rich washing machine, water riche separating tank, first stage pulp mill, second stage pulp mill, pulp screen, pulp storing machine, stirring type automatic pulp falling machine, noodle steaming machine, sheet jelly pre-drying machine, sheet jelly freezing machine, first sheet jelly recovering machine, second sheet jelly recovering machine, drum type transition conveyor, noodle cutting machine, rice noodle conveyor, quantitative cutting machine, automatic shaping machine, drying machine, air-cooling machine and packaging and conveyor disposed according to the material conveying flow. The production line and production technology of the present invention can realized the full-automatic production from raw material to finished product of instant dried rice noodle, achieve instant dried rice noodle with good quality, and high production efficiency.
Owner:BUHLER WUXI COMML
Process for treating pulp mill condenstates using a hollow fiber contactor
A method and apparatus for the treatment of pulp mill condensates is described. A hollow fiber contactor, incorporating a hydrophobic membrane, was used to remove several undesirable compounds from pulp mill condensates. For example, TRS compounds and SO2 were efficiently stripped from kraft and sulphite mill evaporator condensates, respectively. Methanol was also removed from kraft mill condensates but at a lower efficiency than TRS. Furthermore, other undesirable compounds found in condensates of pulp mills that contribute to the BOD and COD loading to effluent treatment systems were also removed. These contactors are cost effective since air, vacuum or a suitable solvent or scrubbing solution can be used as the stripping medium to drive off through the membrane several undesirable compounds from the feed solution. The undesirable compounds removed can thus be burned in the recovery boiler, lime kiln or a dedicated boiler.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Magnesia-hercynite brick used by high temperature zone of cement kiln and use method thereof
InactiveCN101613214AExtended service lifeOptimizationRotary drum furnacesAdditive ingredientPulp mill
The invention belongs to the field of refractory materials and relates to a magnesia-hercynite brick used by the high temperature zone of a cement kiln and a use method thereof. The brick is characterized in that high-quality magnesia and electric melting synthesis hercynite are taken as main raw materials which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 40-50 percent of 3-1mm coarse magnesia, 10-15 percent of 1-0.088mm medium magnesia, 30-35 percent of fine magnesia less than 0.088mm, and 6.5-11.5 percent of 3-0mm electric melting synthesis hercynite. The raw materials after mixing are added with pulp mill waste for mixing, pressing, drying and sintering at the temperature more than 1,600 DEG C, thus obtaining the magnesia-hercynite brick. The mass percentage of the ingredients of the produced magnesia-hercynite brick is as follows: 2.5-5.5 percent of Fe2O3, 4.0-6.0 percent of Al2O3 and 93.0-89.0 percent of MgO plus other microcomponents. According to different operating situations of different cement kilns and by combining the characteristic of chrome-free brick, the invention replaces magnesite-chrome brick region by region, makes full use of the advantages and bypasses the disadvantages, improves the cost performance of the refractory brick used by the high temperature zone to the greatest extent and realizes chrome-free refractory brick used by the cement kiln.
Owner:BEIJING TONGDA REFRACTORY TECH CO LTD +1
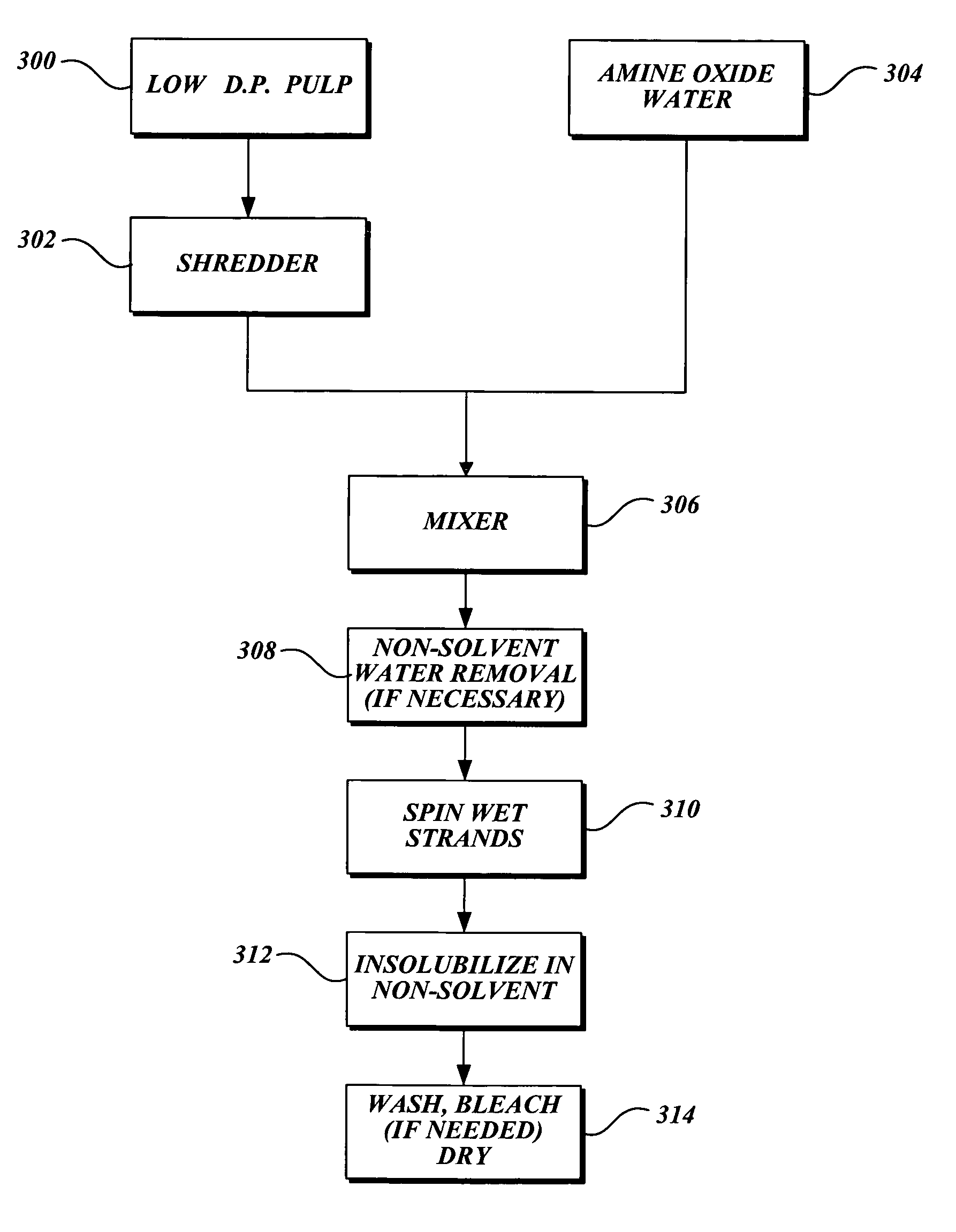
Shaped cellulose manufacturing process combined with a pulp mill recovery system
ActiveUS20120000621A1Low capital intensityImprove the environmentNon-fibrous pulp additionPulp liquors combustionFiberUnit operation
Provided is a process for manufacturing shaped cellulose materials from lignocellulose where a dissolving grade pulp is manufactured and dissolved in an aqueous alkaline or acidic solvent system forming a solution suitable for shaping new cellulose structures including fibers, films and cellulose derivatives. At least a part of the spent cellulose dissolving or cellulose shaping chemicals are recovered in one or more unit operations in a pulp mill chemical recovery cycle.
Owner:TREETOTEXTILE AB
Silane substituted polyethylene oxide reagents and method of using for preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in industrial processes
ActiveUS20080111103A1Reducing aluminosilicate scale buildupEconomical and effectiveSilicon organic compoundsWater treatment parameter controlWaste processingPolyethylene oxide
Materials and a method are provided whereby polymers with least 0.5 mole % of the pendant group or end group containing —Si(OR″)3 (where R″ is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in an industrial process having an alkaline process stream such as a pulping mill process stream or a high level nuclear waste processing plant. When materials of the present invention are added to the alkaline process stream, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on equipment surfaces such as evaporator walls and heating surfaces. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
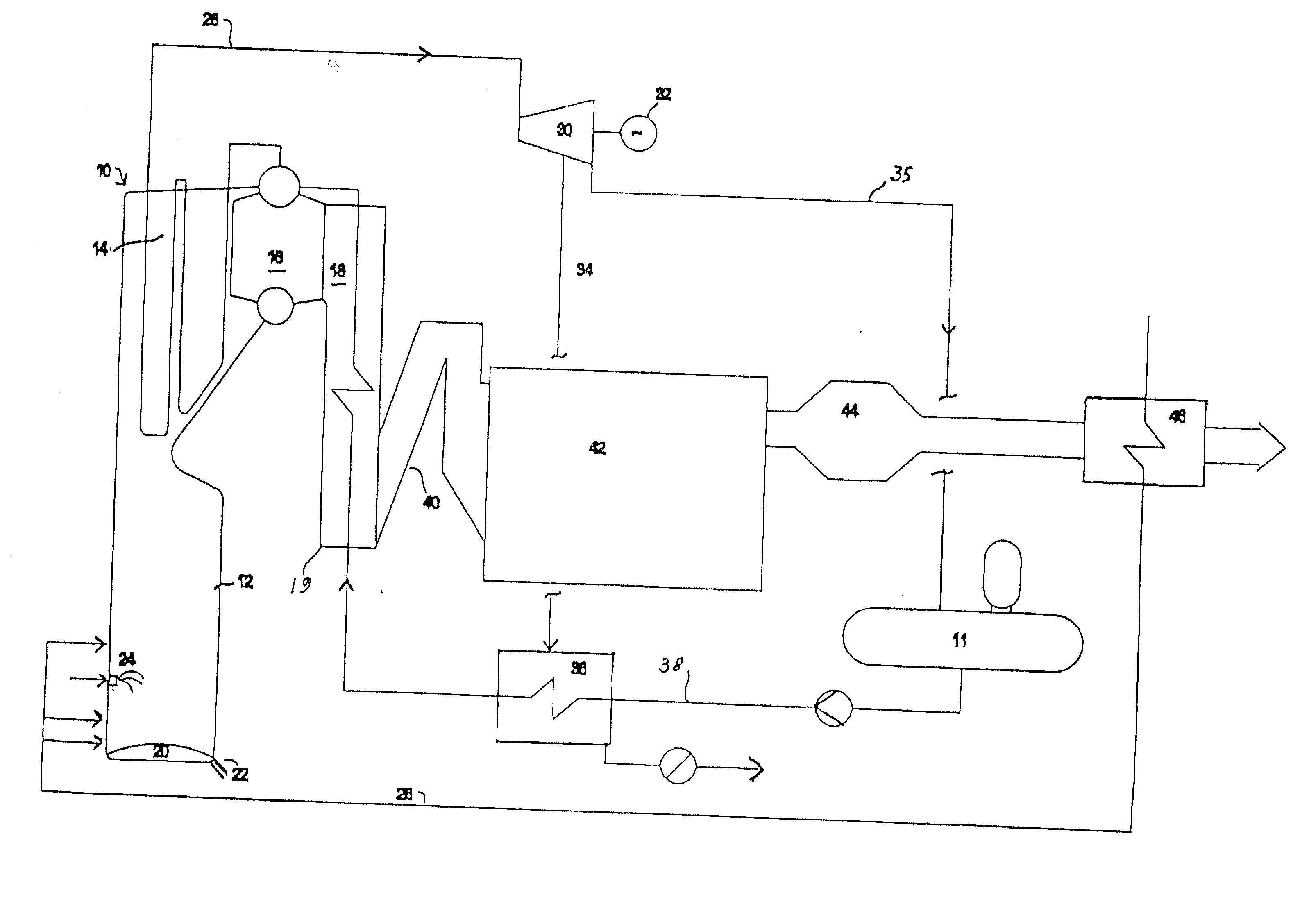
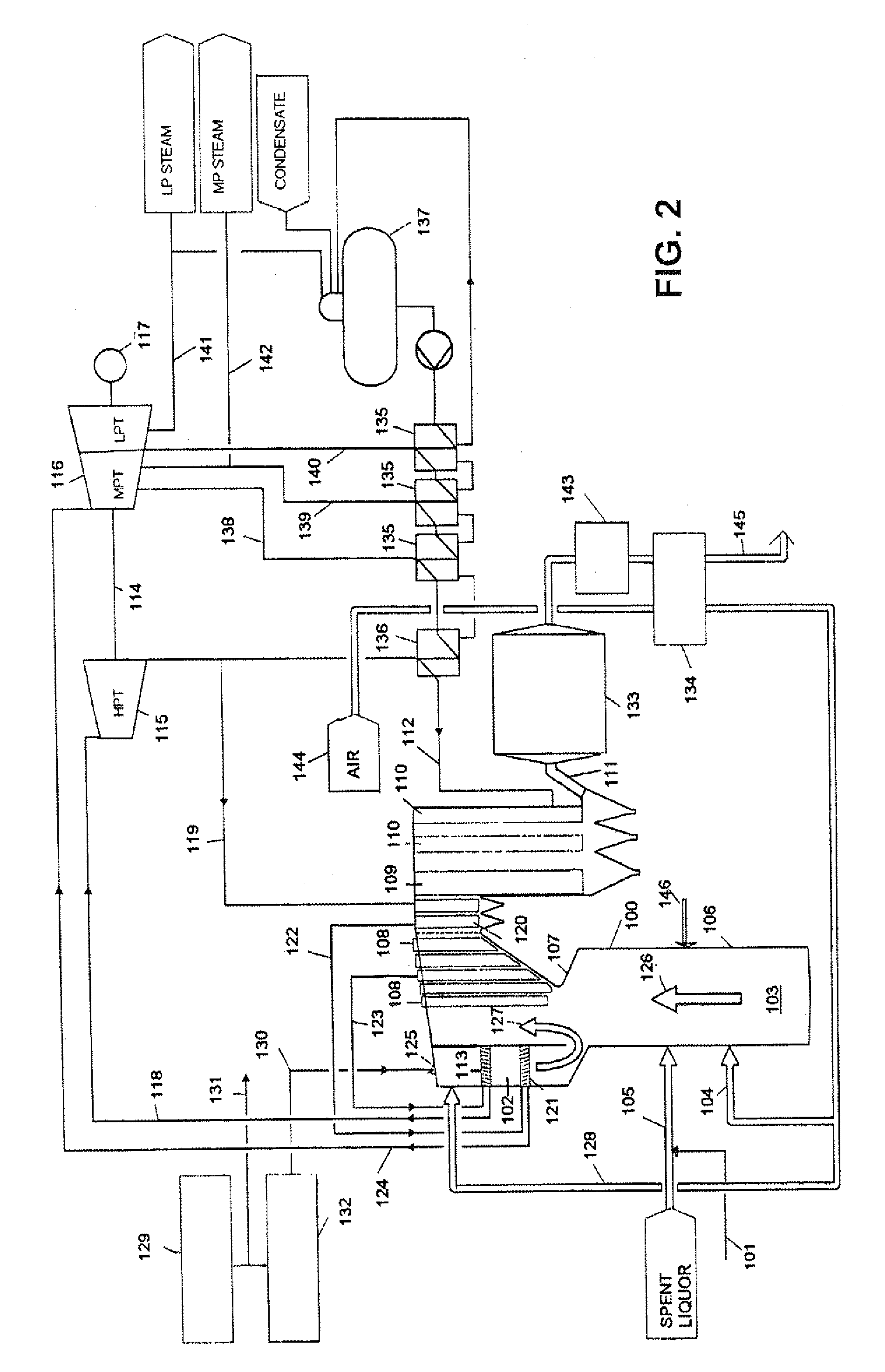
Method and arrangement for producing electrical energy at a pulp mill
InactiveUS20020194849A1Improve power production efficiencyElectrical efficiencyPulp liquors combustionSteam generation using steam absorptionSuperheaterEconomizer
The invention relates to a method and an arrangement in the production of electric energy in a boiler plant of a pulp mill. Black liquor having a dry solids content of more than 80% and combustion air are fed into a furnace of a recovery boiler for combusting black liquor and recovering chemicals contained therein. The flue gases generated in the combustion are led into an economizer of the recovery boiler, in which economizer the feed water for the boiler is heated, and after the economizer to gas cleaning. The feed water is led from the economizer onto the steam-generating bank at a temperature below the saturation temperature and further into a superheater to produce steam having a pressure of more than 80 bar. The steam is led from the recovery boiler to a steam turbine to produce electricity. The temperature of the feed water being led into the economizer is regulated by means of bleed steam of the turbine so that the flue gases exit the economizer at a temperature of more than 250° C. and that after the economizer the flue gases are cleaned in at least a hot electrostatic precipitator and the cleaned flue gases are cooled by the combustion air or the feed water.
Owner:ANDRIZ OY
High PH treatment of pulp in a bleach sequence to produce pulp having low D.P. and low copper number for use in lyocell manufacture
InactiveUS20060065377A1Reduce the degree of polymerizationIncreasing copper numberNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPulp millBleach
A high pH and a low pH process for reducing the degree of polymerization of a pulp having a hemicellulose content of at least 7%. The high pH is greater than 8, and the low pH process is 2 to 8. The high pH process reduces the degree of polymerization without substantially increasing the copper number. The low pH process requires a subsequent treatment with alkali to reduce the copper number of the pulp to less than 2. The process can be practiced in pulp mills with a bleaching sequence having one or more E or D stages. At the end of the bleach sequence, a pulp having a degree of polymerization of 200 to 1100, a copper number of less than 2, and a hemicellulose content of at least 7% is provided. The pulp can be used to make lyocell fibers.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER CO
Process and system for calcination of high solids kraft paper pulp mill lime mud
InactiveUS20090114352A1High melting pointMitigate calciner scaling and fouling and unwanted gaseous emissionsCarbon compoundsDryer sectionSludgeSolid particle
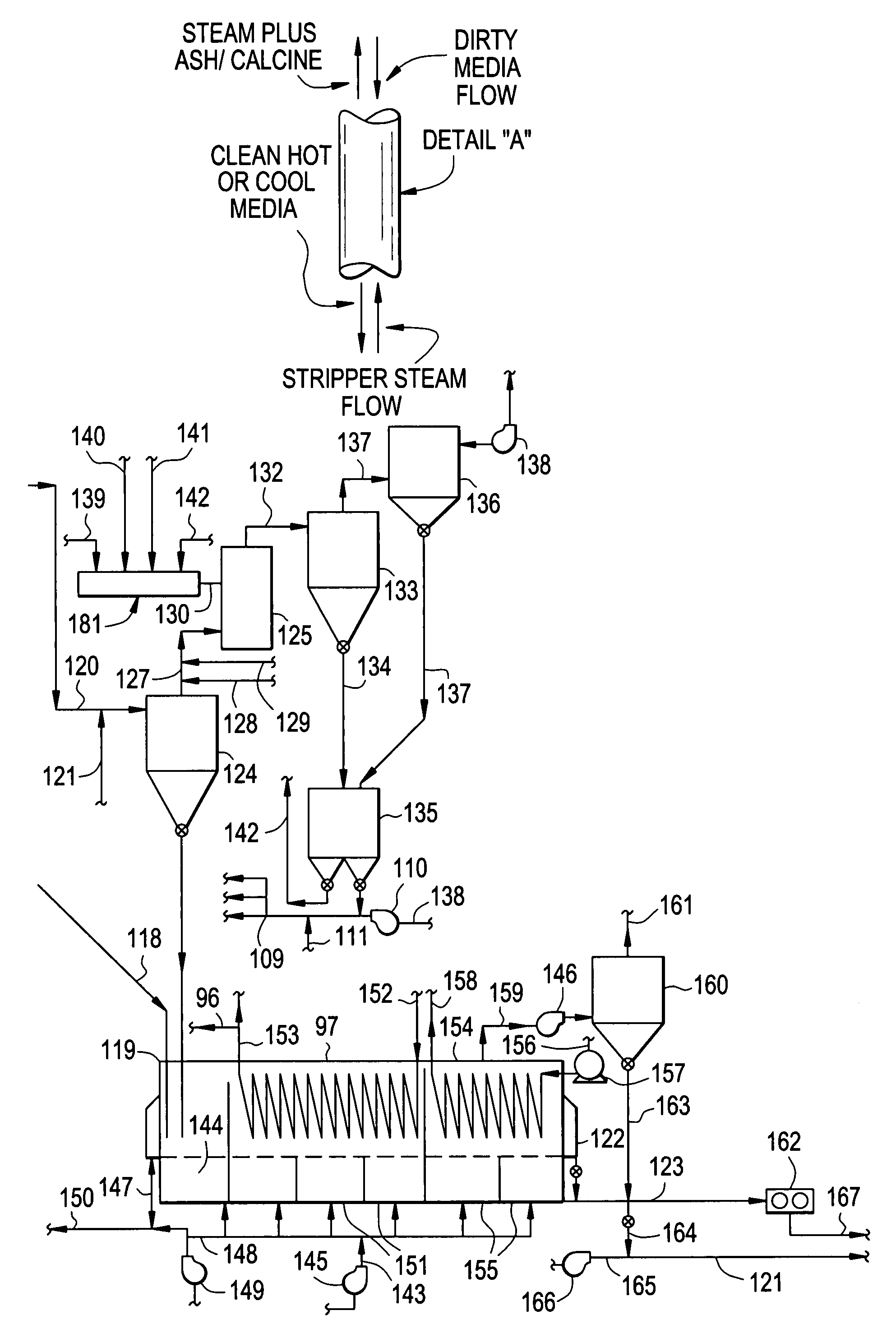
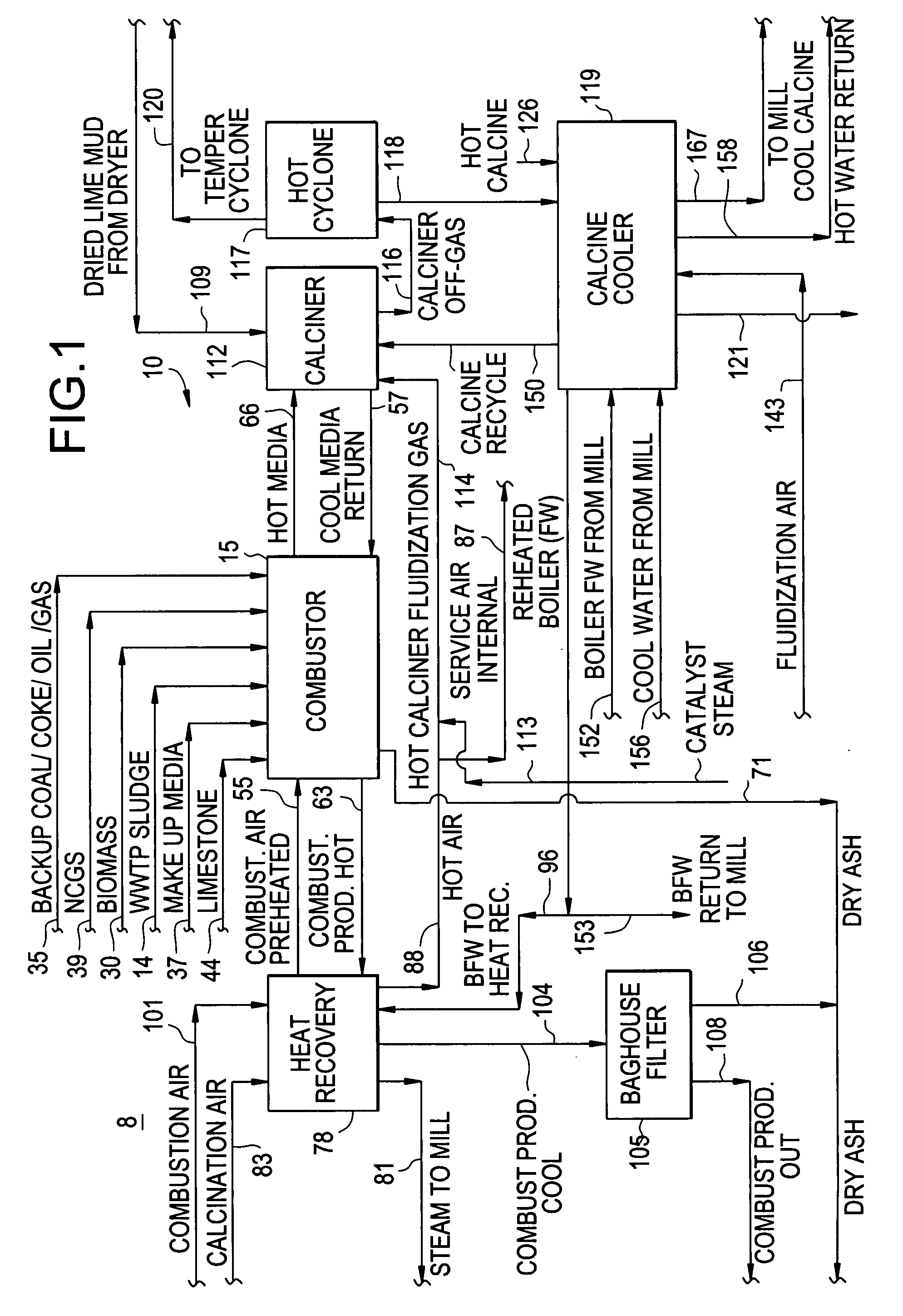
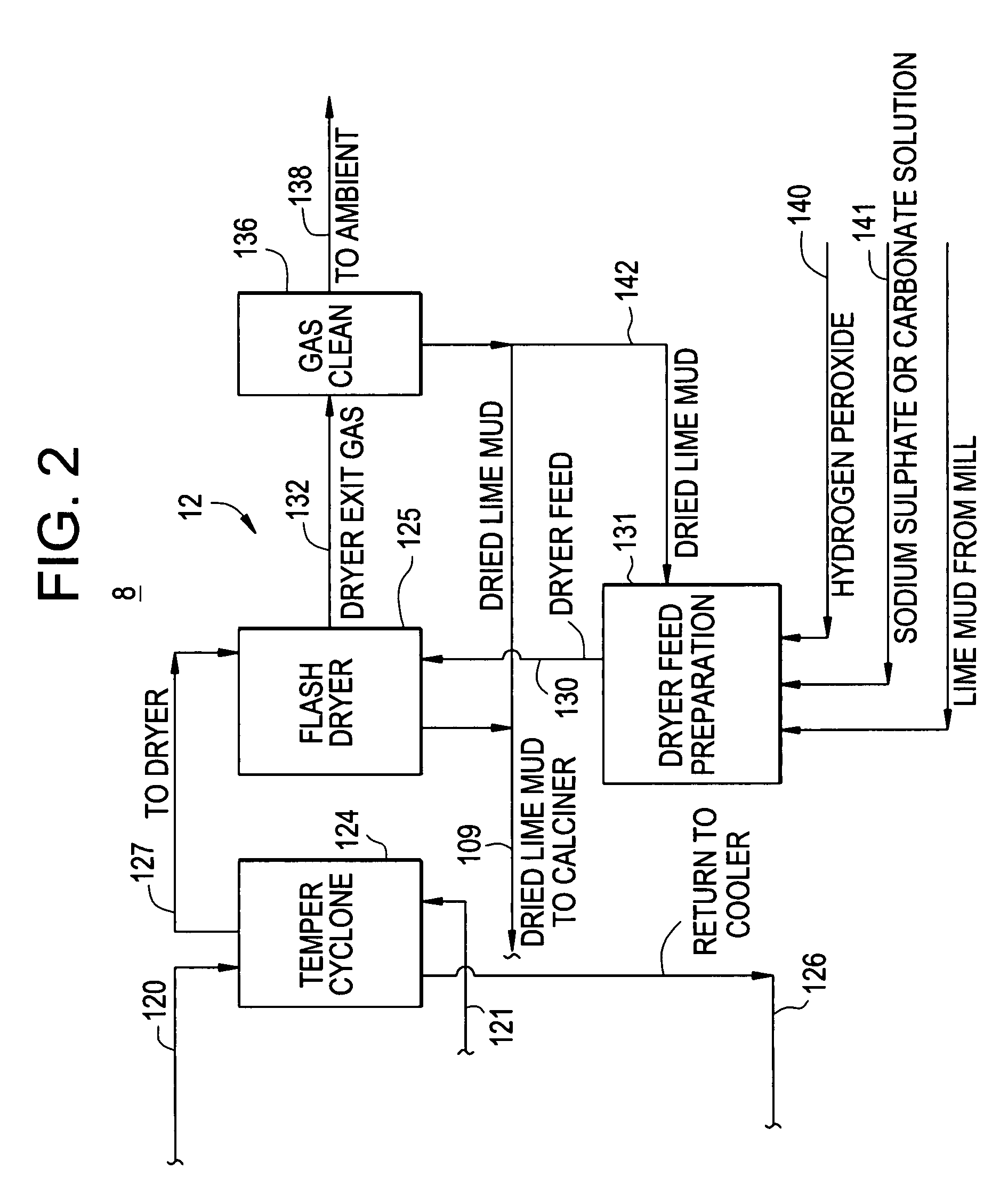
The invention features methods and systems for calcining wet calcium carbonate lime mud produced in a re-causticizing manufacturing operation, for instance, Kraft pulp mill lime mud (“lime mud”) and converting it to re-burned lime by (a) feeding wet lime mud obtained from a re-causticizing manufacturing process into a flash dryer and then feeding the dried lime mud into a bubbling fluid bed calciner thermally linked by moving media heat transfer (MMHT) utilizing solid particulate media to a circulating fluid bed combustor wherein the MMHT provides heat input for calcination and drying; (b) recycling the media being from said calciner to said combustor wherein said combustor receives mill WWTP sludge, or precipitated lignins, or biomass, or NCGs as fuels to re-heat the solid particulate media; and (c) recovering calcined “soft-burned” lime mud from the fluid bed calciner. Steam and heated boiler feed-water are also generated and exported to the mill's steam distribution and generation system as well as hot process water for use in the mill's boiler house and manufacturing operation. The system for calcining calcium carbonate lime mud produced from a re-causticizing manufacturing operation and converting it to re-burned lime comprises a calciner and a combustor linked by a moving media heat transfer MMHT system or apparatus. The MMHT system or apparatus thermally links separate fluid bed combustion (exothermic) and calcination (endothermic) stages. The system further comprises a flash dryer or spray dryer that utilizes exhausted heat from the calcination stage.
Owner:ROSSI ROBERT A
Recovery process and system for a pulp mill
InactiveUS20080289782A1Efficient productionImprove reusePulp liquors combustionFlue gasChemical recovery
A method for burning chlorine-containing liquors in a chemical recovery boiler at a pulp mill, wherein the recovery boiler includes spent liquor sprayers for feeding spent liquor and a number of combustion air levels including: increasing a combustion temperature in the recovery boiler in a burning zone where a chlorine-containing liquor or a chlorine-containing effluent is burned; while burning the liquor or effluent, volatilizing the chlorine in the liquor or effluent to produce chloride-containing salts in flue gases in the boiler, and removing the chloride-containing salts from the flue gases.
Owner:ANDRIZ OY
Defoamer emulsion compositions for pulp mill applications
InactiveUS7893115B2Improve emulsion stabilityReduce usageNatural cellulose pulp/paperDefoamers additionPulp millHydrophobic silica
An oil-in-water emulsion useful as a defoamer for pulp and paper mill applications is described. The defoamer has an oil blend (of a triglyceride oil or a mixture of triglyceride oils and silicone), a stabilizing agent (to make the oil blend stable in the emulsion), hydrophobic silica particles, surfactants, dispersants, and other components. The emulsion is usable directly at low concentrations to control foam.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Method for the production of high yield chemical pulp from softwood
InactiveUS20050155730A1Increase pulp yieldHigh yieldPulp liquors combustionPulp by-products recoveryChemical managementWhite liquor
The present invention relates to a novel method for the production of a high yield chemical pulp from softwood in a pulp mill by the application of a delignification catalyst in a wood impregnation step and by using alkaline pulping liquors comprising boron compounds at a white liquor sulfidity level below about 25%. The method is practiced concurrently with a controlled sulfur chemicals management in the pulp mill thereby providing a pulping process which have low emission of odorous pollutants, low rate of corrosion in mill equipment and which has a rate of delignification and selectivity sufficient to produce softwood pulp in higher yield and at a quality at least on a par with a kraft pulping alternative.
Owner:STIGSSON LARS LENNART
Silane substituted polyethylene oxide reagents and method of using for preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in industrial processes
ActiveUS7674385B2Reduce and even completely prevent formationReduce and eliminate scalingSilicon organic compoundsWater treatment parameter controlWaste processingPolyethylene oxide
Materials and a method are provided whereby polymers with least 0.5 mole % of the pendant group or end group containing —Si(OR″)3 (where R″ is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in an industrial process having an alkaline process stream such as a pulping mill process stream or a high level nuclear waste processing plant. When materials of the present invention are added to the alkaline process stream, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on equipment surfaces such as evaporator walls and heating surfaces. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Flue gas treatment using kraft mill waste products
The present invention relates in general to a process for removing mercury from a mercury-containing flue gas using dregs from a Kraft pulp mill green liquor clarifier. The dregs are washed with water to produce a particulate carbon slurry which is activated with hydrobromic acid and injected into a mercury-containing flue gas to oxidize and adsorb the mercury at temperatures less than about 900° F. A slurry of sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate, optionally also obtained from Kraft mill waste, is injected into the hot flue gas to absorb and remove CO2, SO2, and SO3.
Owner:S&S LIME
Separating lignin from black liquor by precipitation, suspension and separation
ActiveUS8172981B2Lower requirementInhibition of dissolutionLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryBlack liquorPulp mill
A method for controlling the sodium and sulphur balance of a pulp mill while separating lignin from black liquor, and also a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product obtainable by the method. The present invention also provides use of a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product for the production of fuel (solid, gaseous or liquid) or materials.
Owner:LIGNOBOOST
Particulate matter and methods of obtaining same from a kraft waste reclamation
The present invention relates in general to a method for obtaining particulate calcium carbonate and activated carbon particles and methods for using same, and more particularly, to a method for obtaining activated carbon particles having an average particle size less than about 12 microns from a pulp mill.
Owner:S&S LIME
Method and a device for preparing cellulose pulp
InactiveUS20060070710A1Reduce the cooking temperatureImprove economyPulp liquors combustionPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsBlack liquorPulp mill
A method and an apparatus for preparing cellulose pulp, in which a lignin-containing raw material is impregnated with impregnation liquor and the impregnated raw material is cooked. The black liquor obtained by cooking is concentrated in an evaporation plant integrated in a chemical recovery plant. In the impregnation, the lignin-containing raw material is impregnated with a circulating alkaline impregnating liquor, which impregnating liquor is concentrated by evaporating water from it in at least one evaporator unit of the evaporation plant arranged in the chemical recovery plant of a pulp mill.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
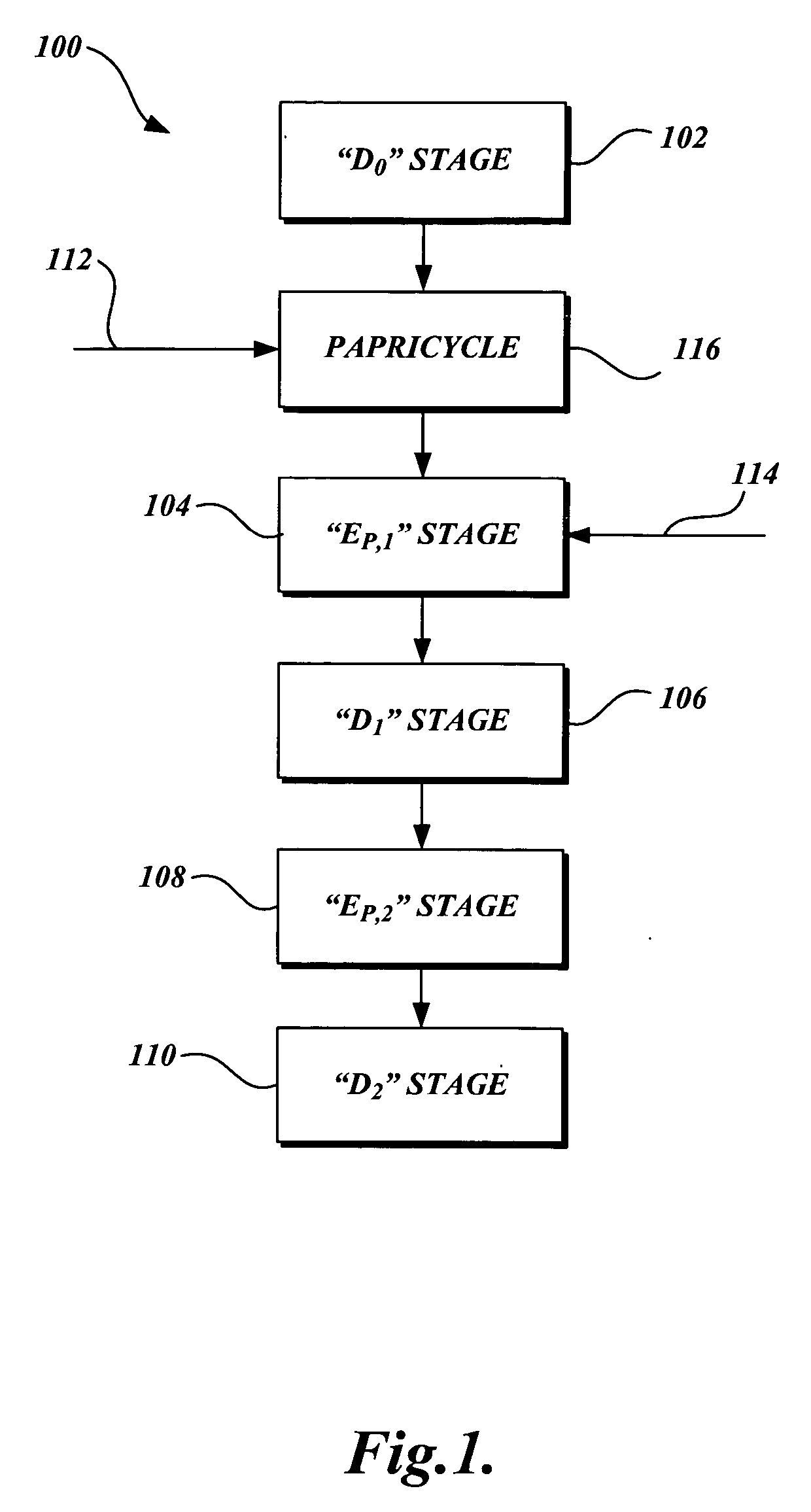
Method of xylanase treatment in a chlorine dioxide bleaching sequence
InactiveUS7320741B2Enhances pulp bleachingEasily integrated into pulp bleaching processPulp bleachingBleaching apparatusChlorine dioxidePulp mill
A method of bleaching chemical pulp with xylanase after chemical bleaching is provided. The method comprises the steps of exposing chemical pulp to a chlorine dioxide bleaching stage to produce a partially bleached pulp, treating the partially bleached pulp with a xylanase in an enzyme treatment stage at a pH of about 3 to about 8, then carrying out an alkaline extraction of the pulp. The pulp bleaching method of the present invention may be performed in a pulp mill as part of a complex pulp bleaching process.
Owner:IOGEN BIO PRODUCKTS CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com