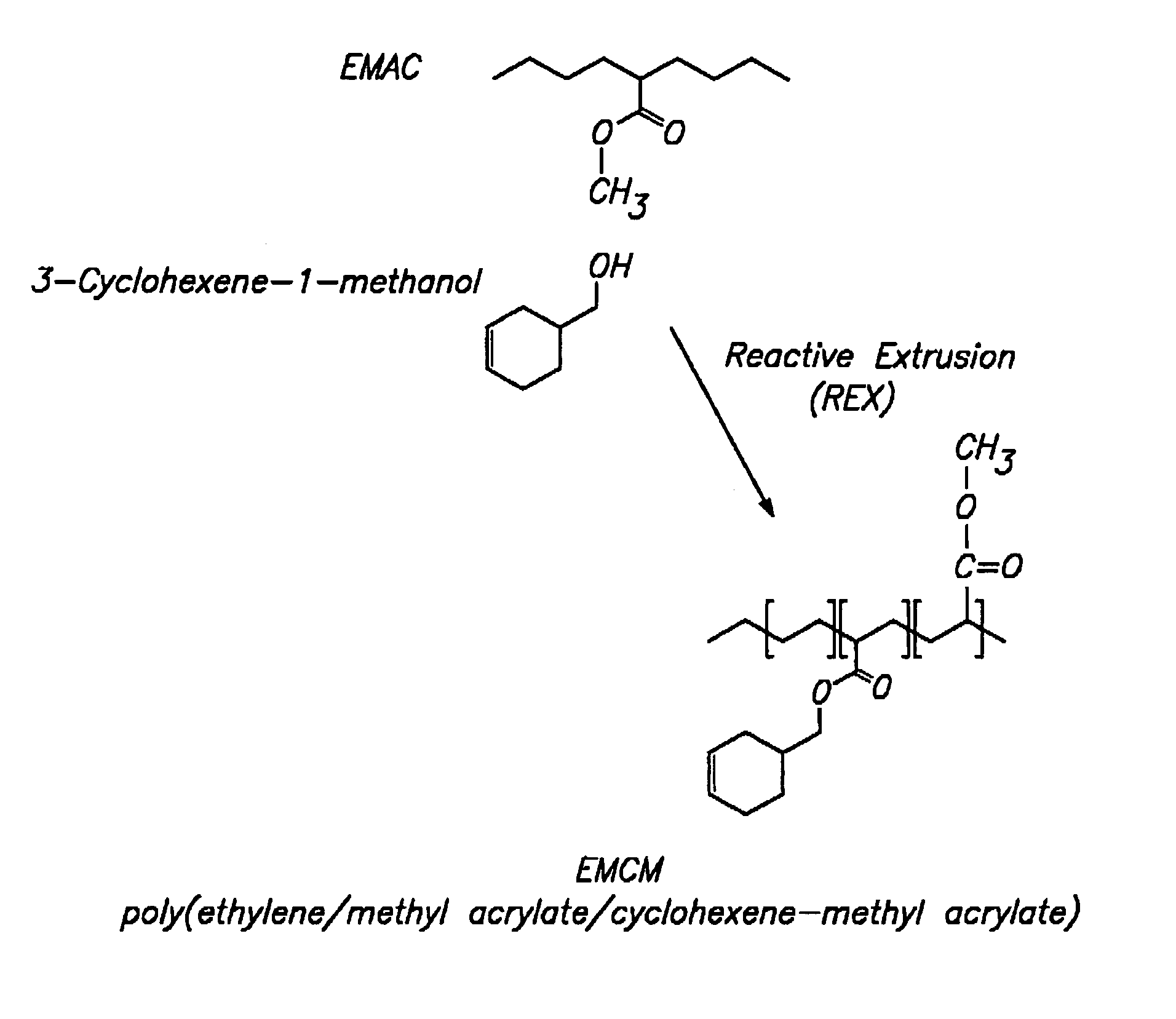
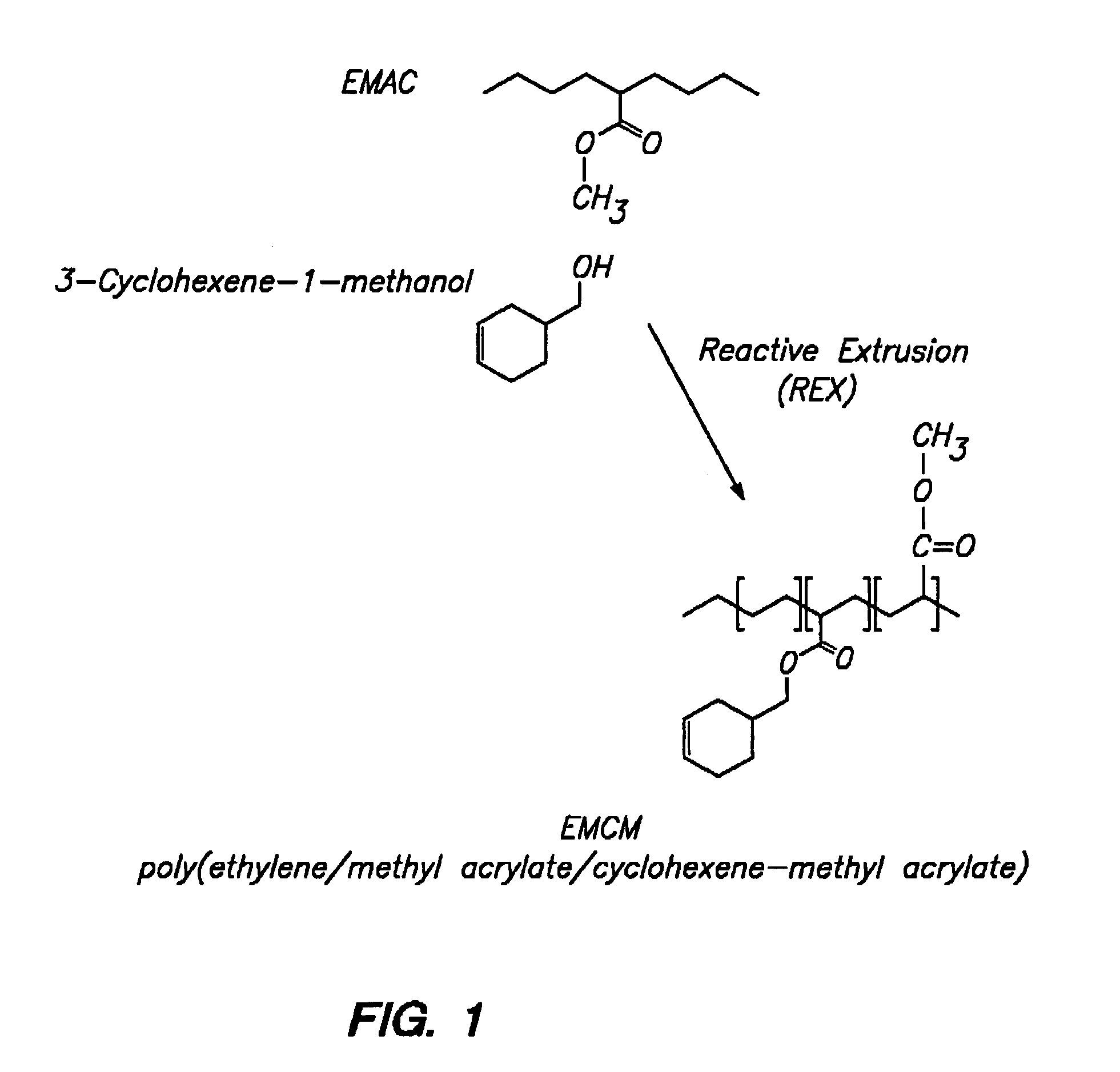
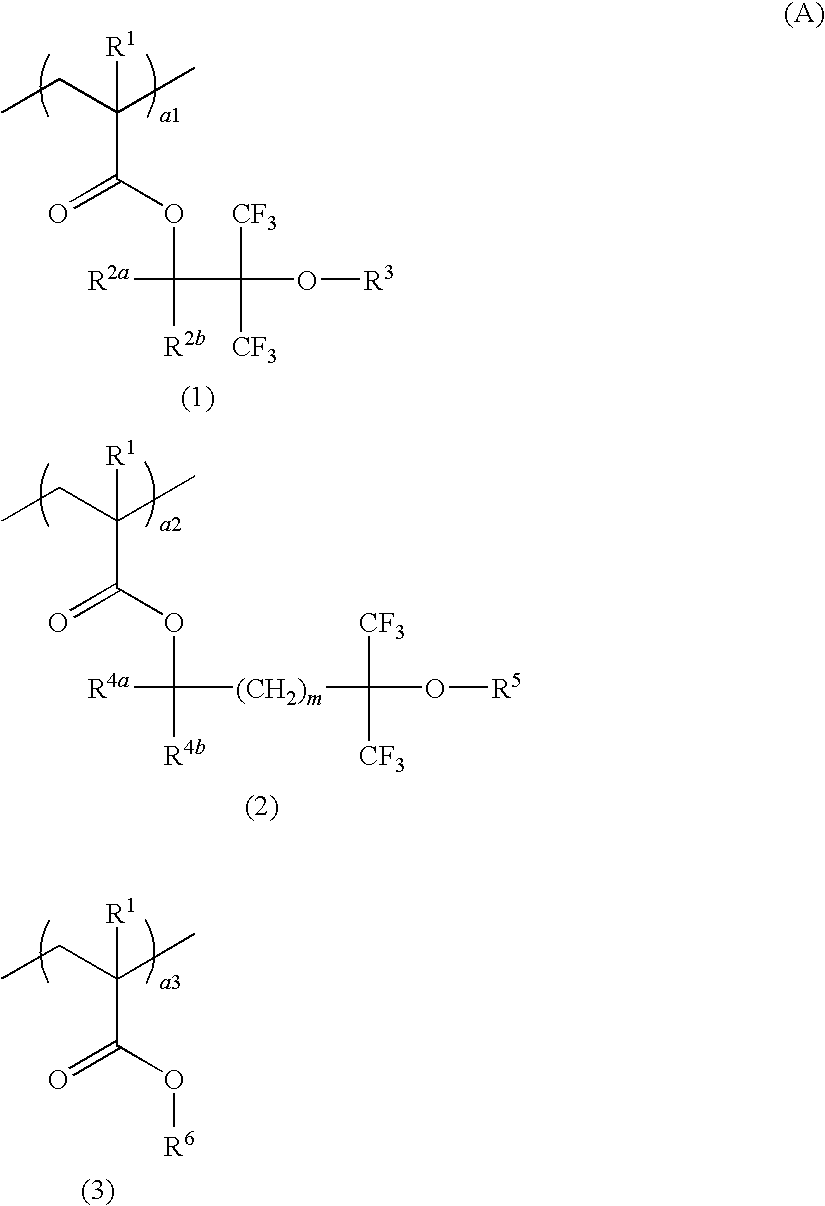
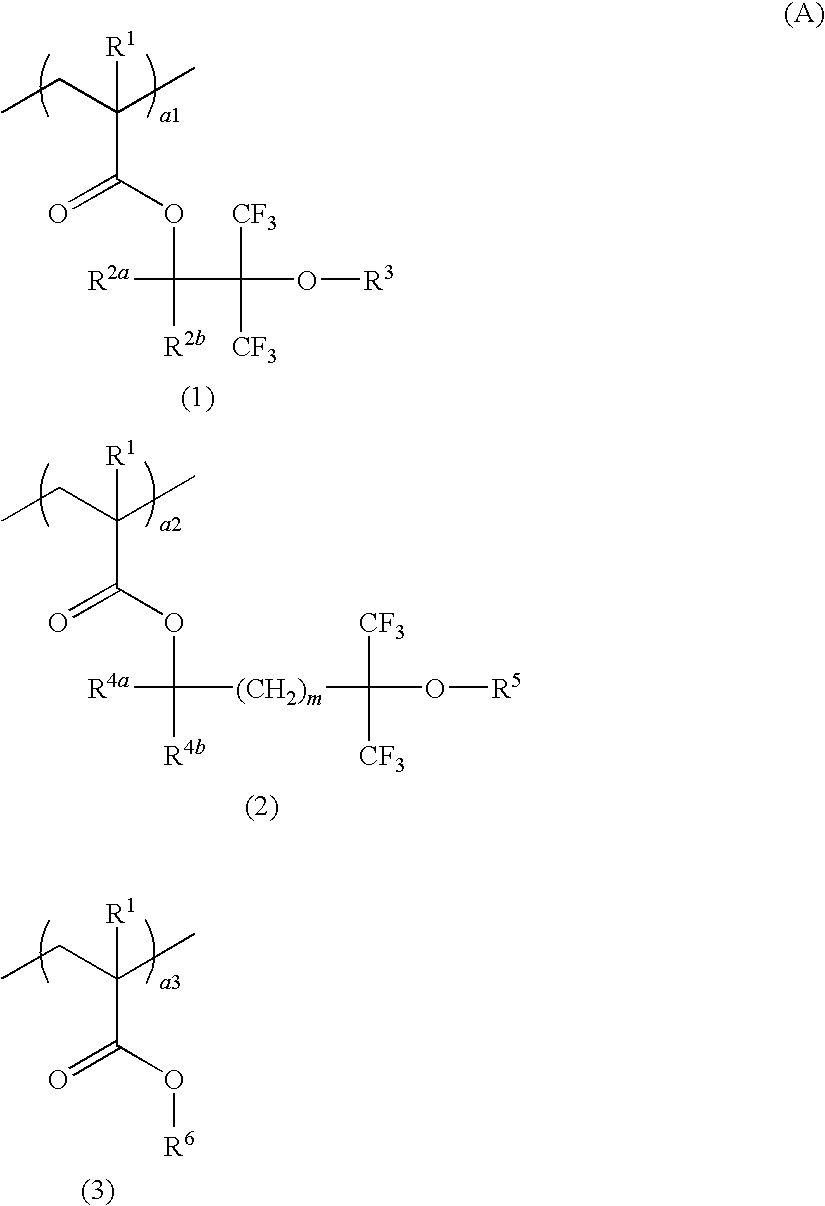
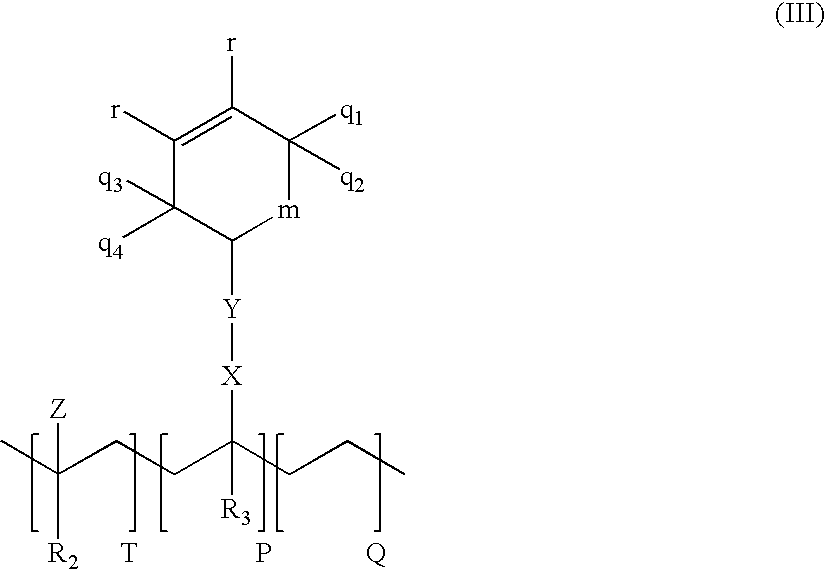
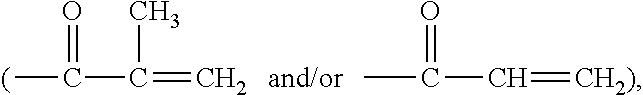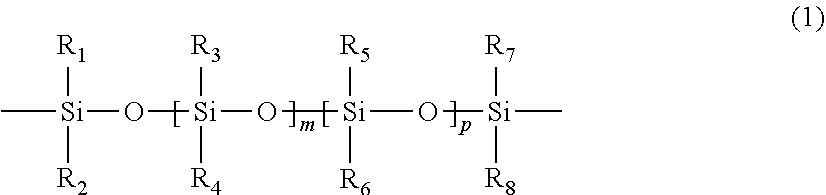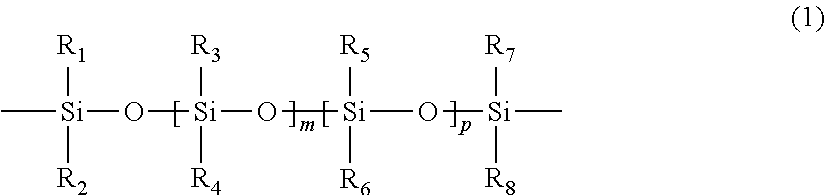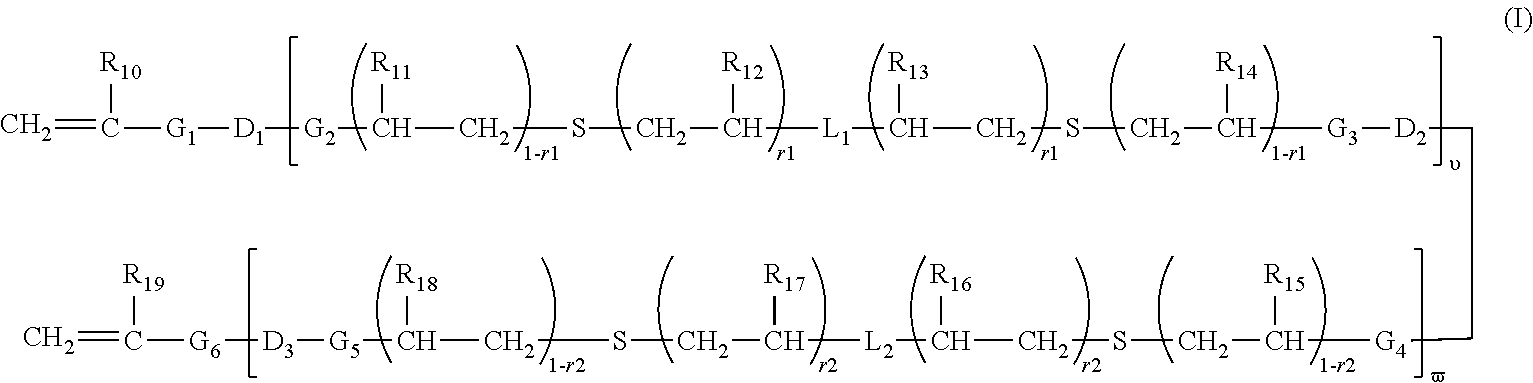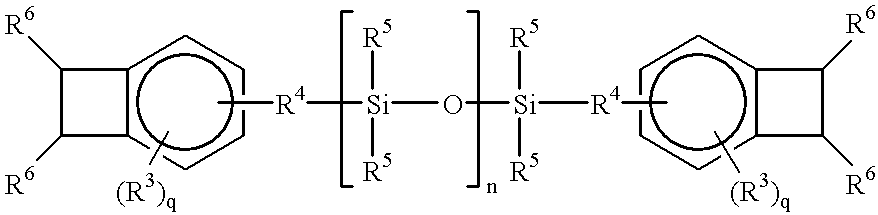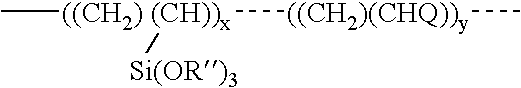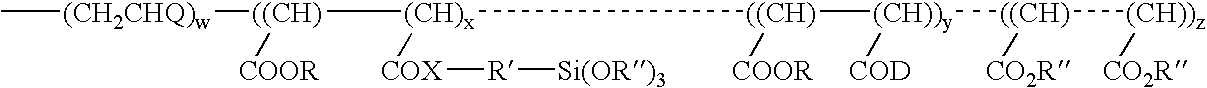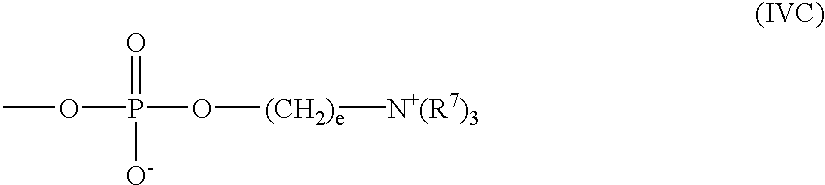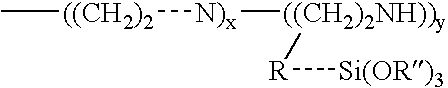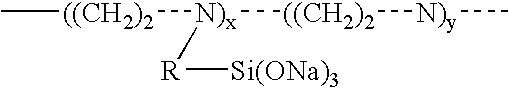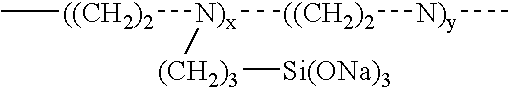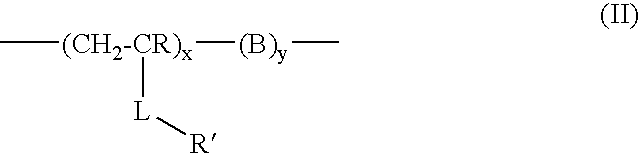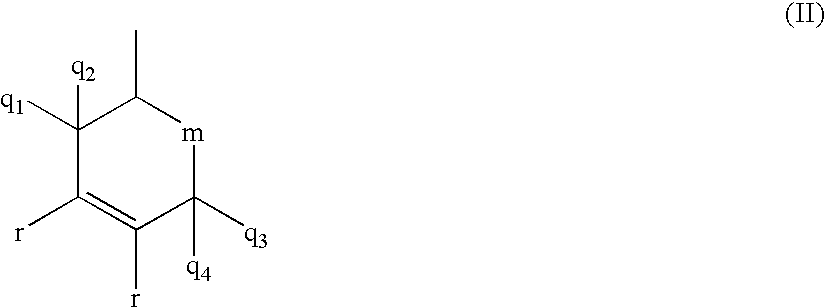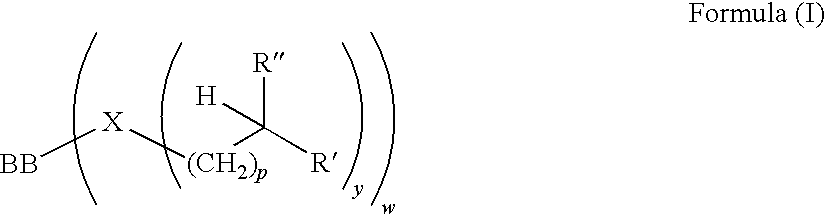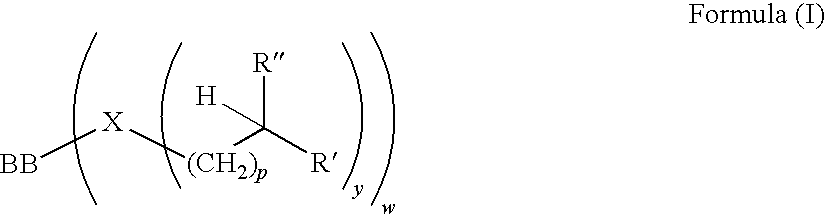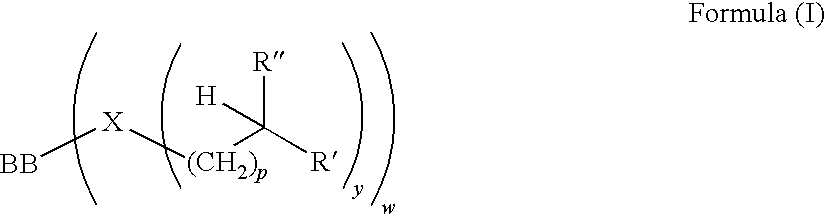Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
840 results about "Pendant group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
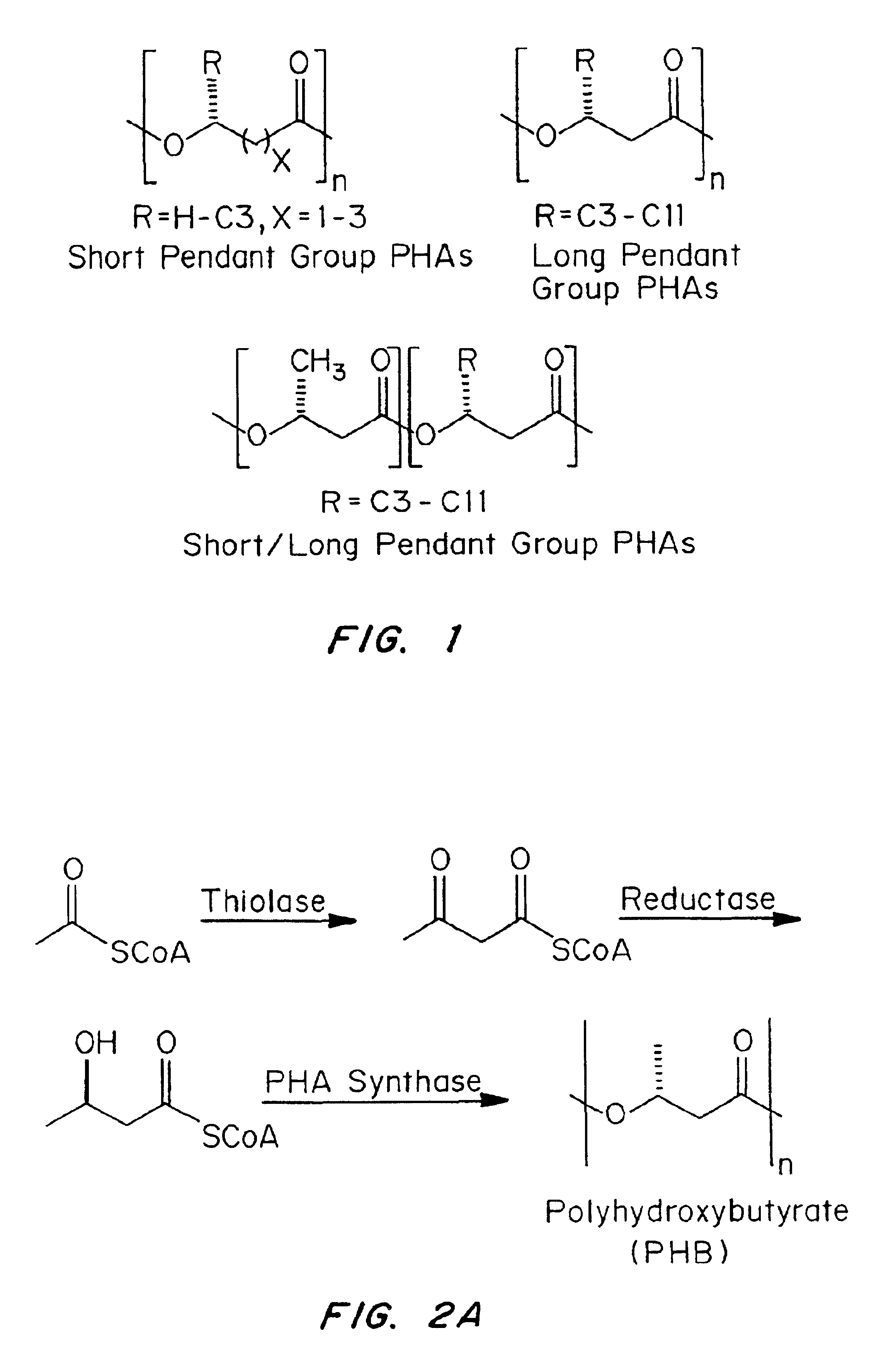
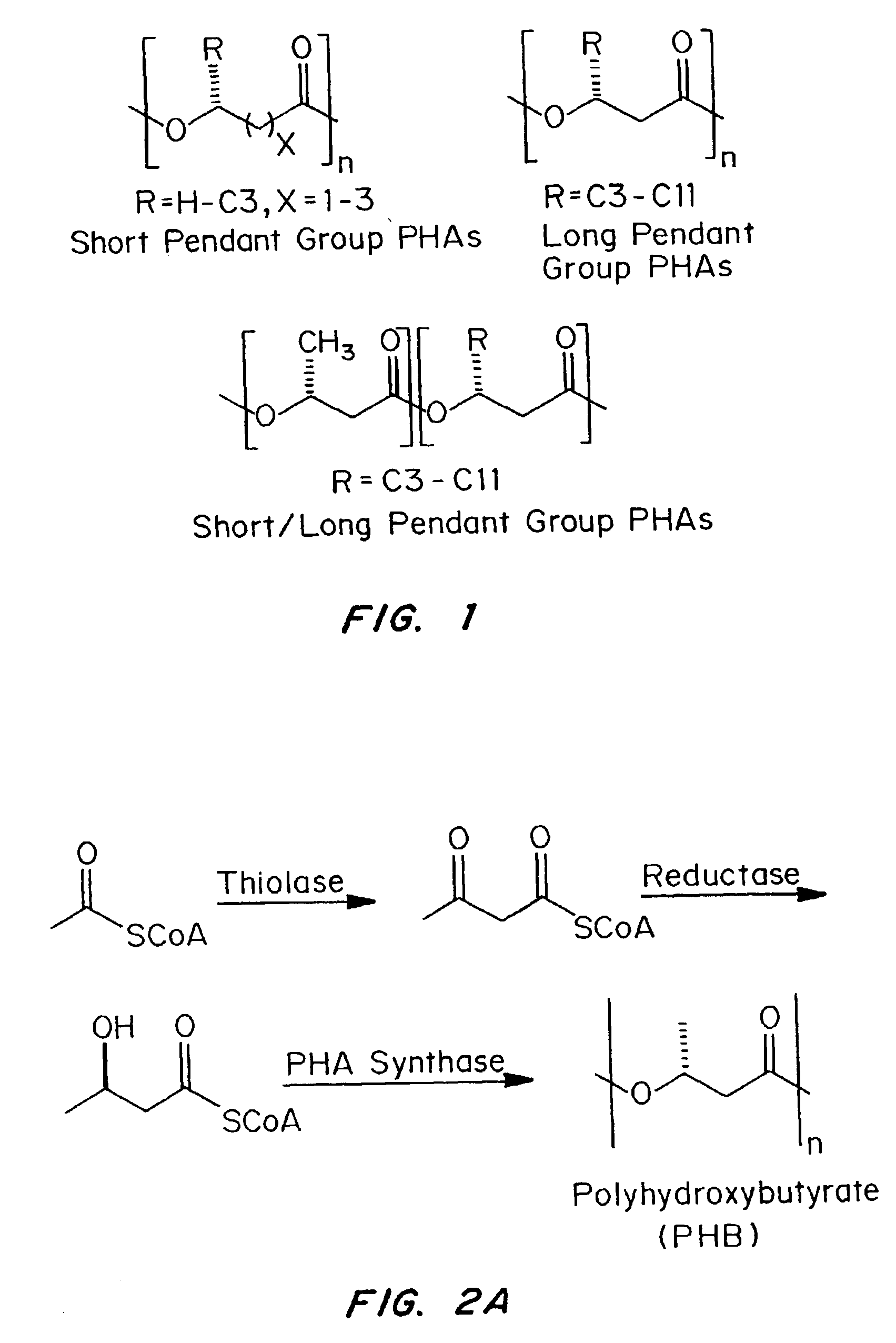
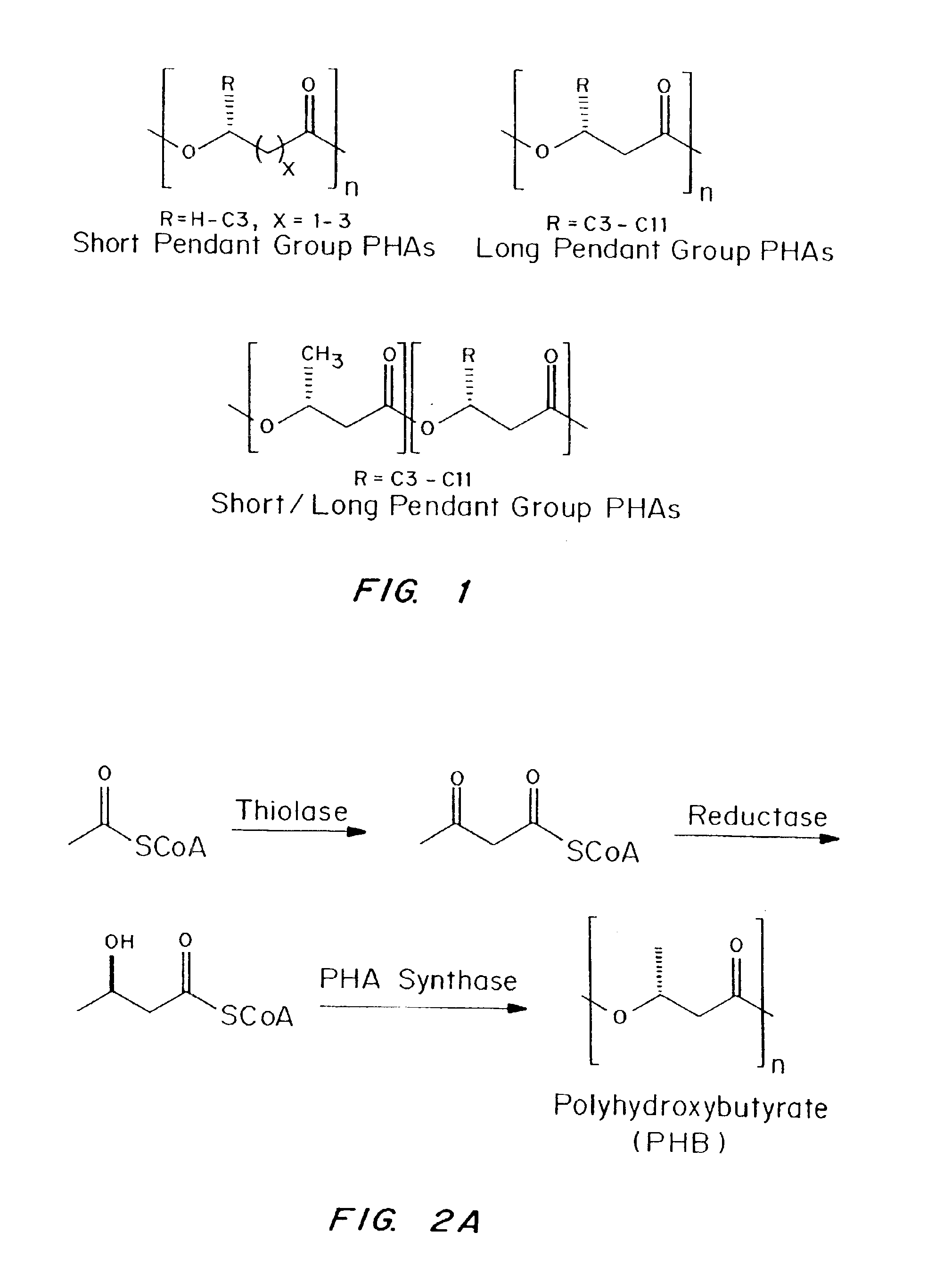
A pendant group (sometimes spelled pendent) or side group is a group of molecules attached to a backbone chain of a long molecule. Usually, this molecule would be a polymer. Pendant groups are different from pendant chains, as they are neither oligomeric nor polymeric.
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Compositions with Improved Adhesion to Low Surface Energy Substrates
InactiveUS20080113094A1Excellent low surface energyImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesOligomerEnd-group
Acrylic-based pressure sensitive adhesives are modified with a telechelic hydrocarbon oligomer. The oligomer comprises a hydrocarbon polymer chain or backbone and a functional end group, e.g., an oligomer prepared from a mono hydroxyl polybutadiene polymer and toluene diisocyanate. The oligomer attaches to the acrylic backbone of the polymer as a pendant group and in a preferred embodiment, the oligomer is mixed with the PSA shortly before the PSA is coated.
Owner:BRADY WORLDWIDE INC
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Imageable element with solvent-resistant polymeric binder
InactiveUS20050003285A1Enhances on-press solvent resistanceProlong lifeRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolventPendant group
The present invention provides an imageable element including a lithographic substrate and an imageable layer disposed on the substrate. The imageable layer includes a radically polymerizable component, an initiator system capable of generating radicals sufficient to initiate a polymerization reaction upon exposure to imaging radiation, and a polymeric binder having a hydrophobic backbone and including both constitutional units having a pendant cyano group attached directly to the hydrophobic backbone, and constitutional units having a pendant group including a hydrophilic poly(alkylene oxide) segment. When the imageable element is imaged and developed, the resulting printing plate may exhibit improved on-press solvent resistance and longer press life.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
Water-developable infrared-sensitive printing plate
ActiveUS20050123853A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersPendant groupAqueous solution
The present invention provides an imageable element including a lithographic substrate and an imageable layer disposed on the substrate. The imageable layer includes a radically polymerizable component, an initiator system capable of generating radicals sufficient to initiate a polymerization reaction upon exposure to imaging radiation, and a polymeric binder having a hydrophobic backbone and including constitutional units having a pendant group including a hydrophilic poly(alkylene oxide) segment. The imageable element can be developed using an aqueous developer solution. Alternatively, the imageable element can be developed on-press by contact with ink and / or fountain solution.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
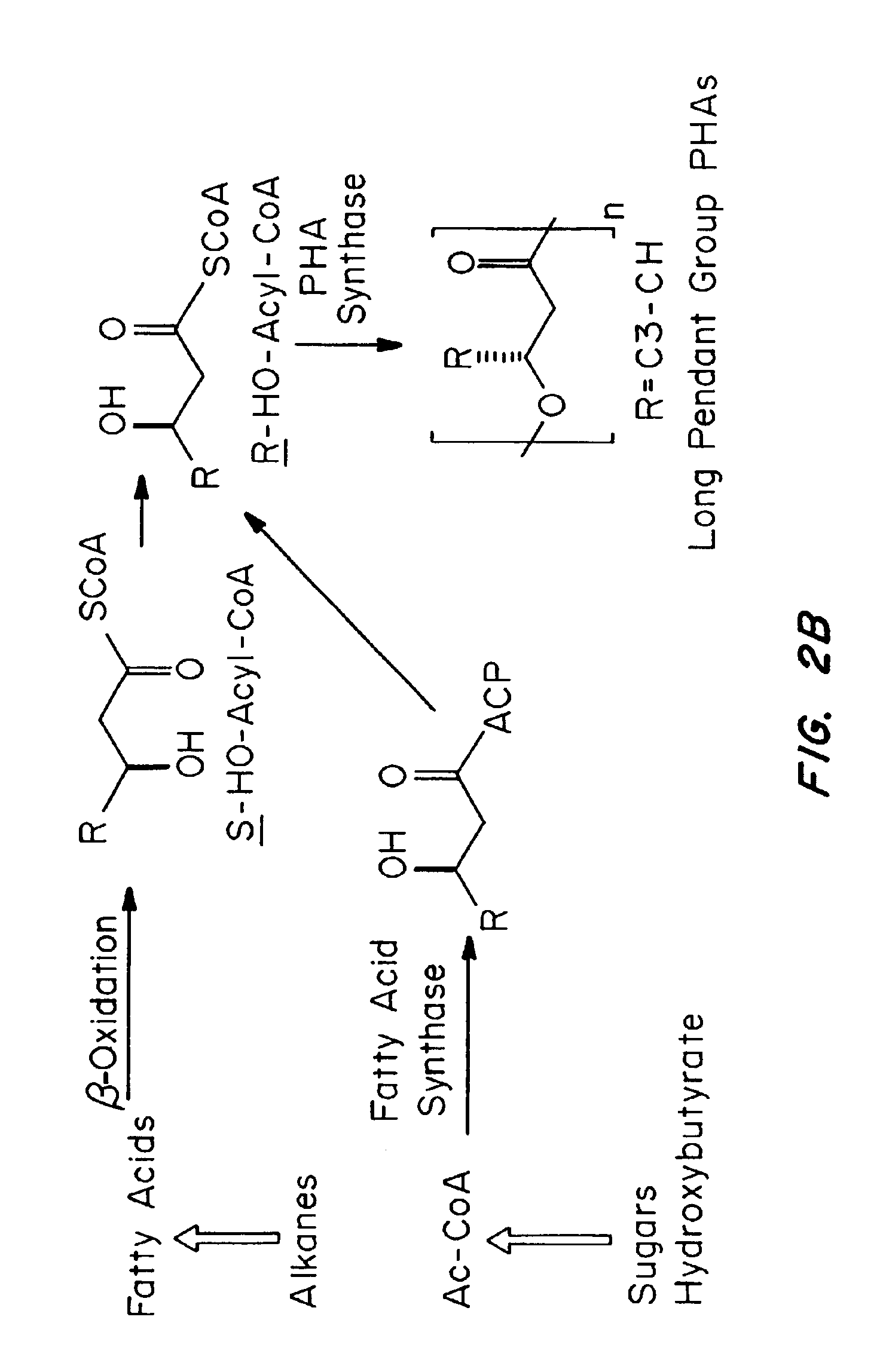
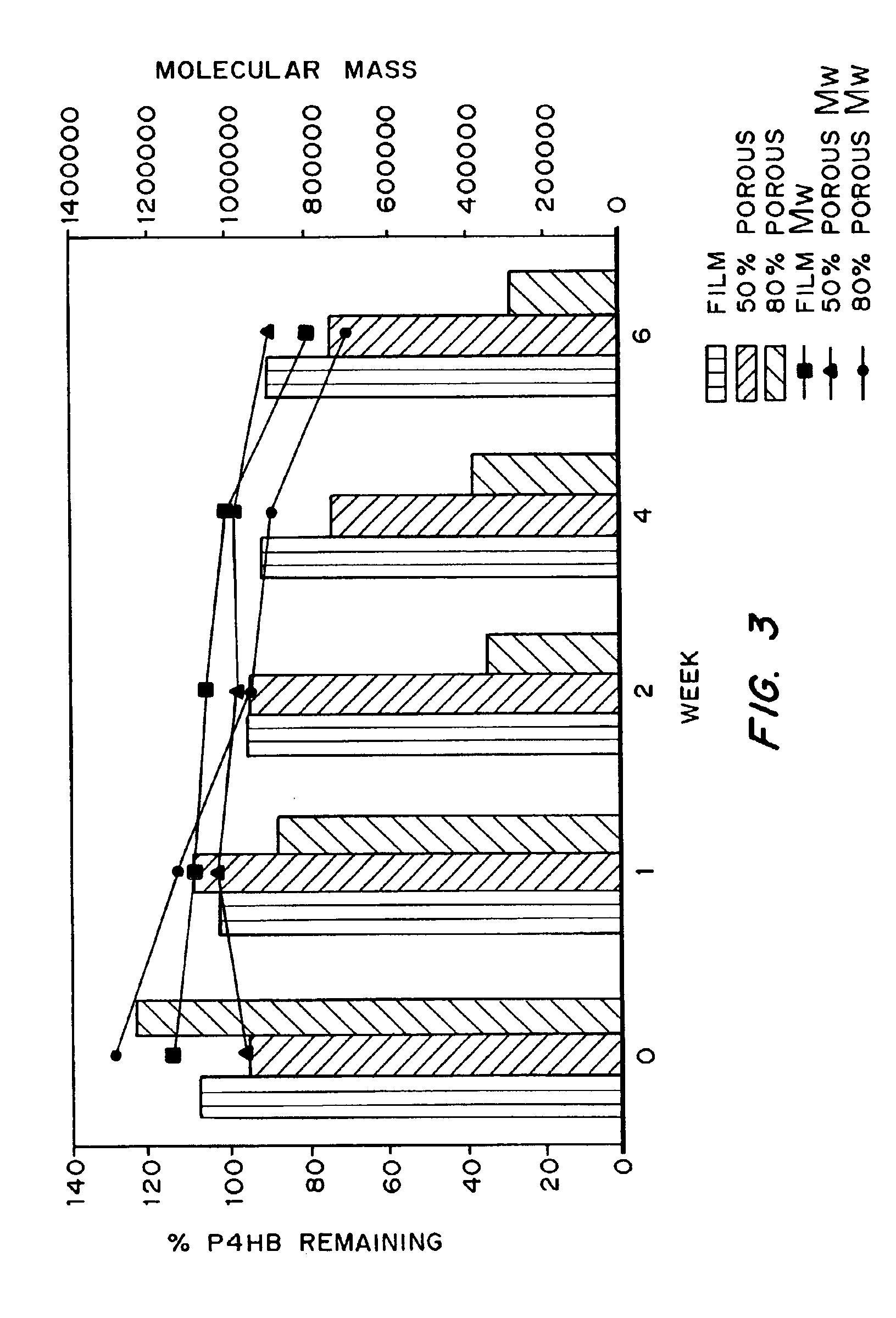
Polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions having controlled degradation rates
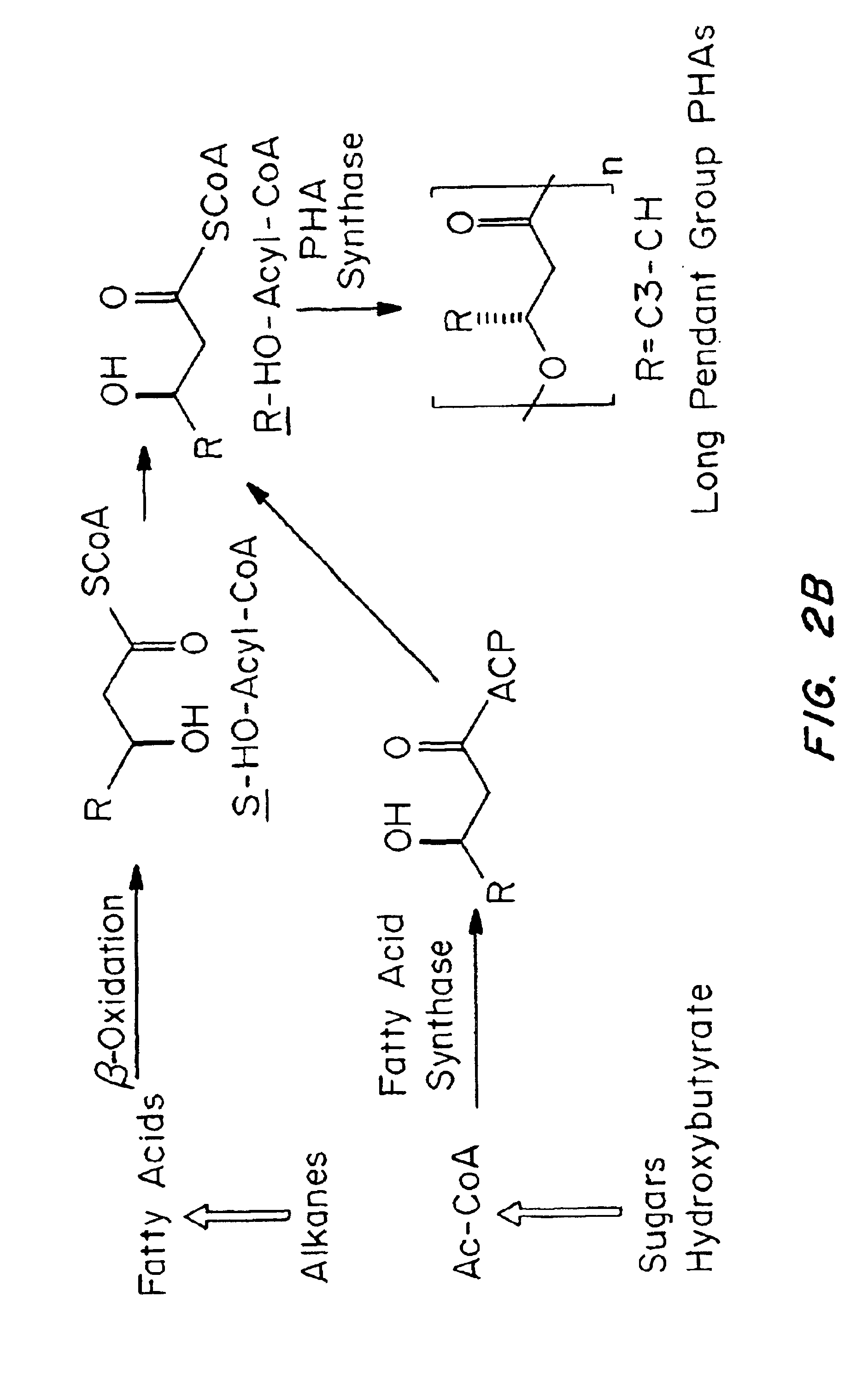
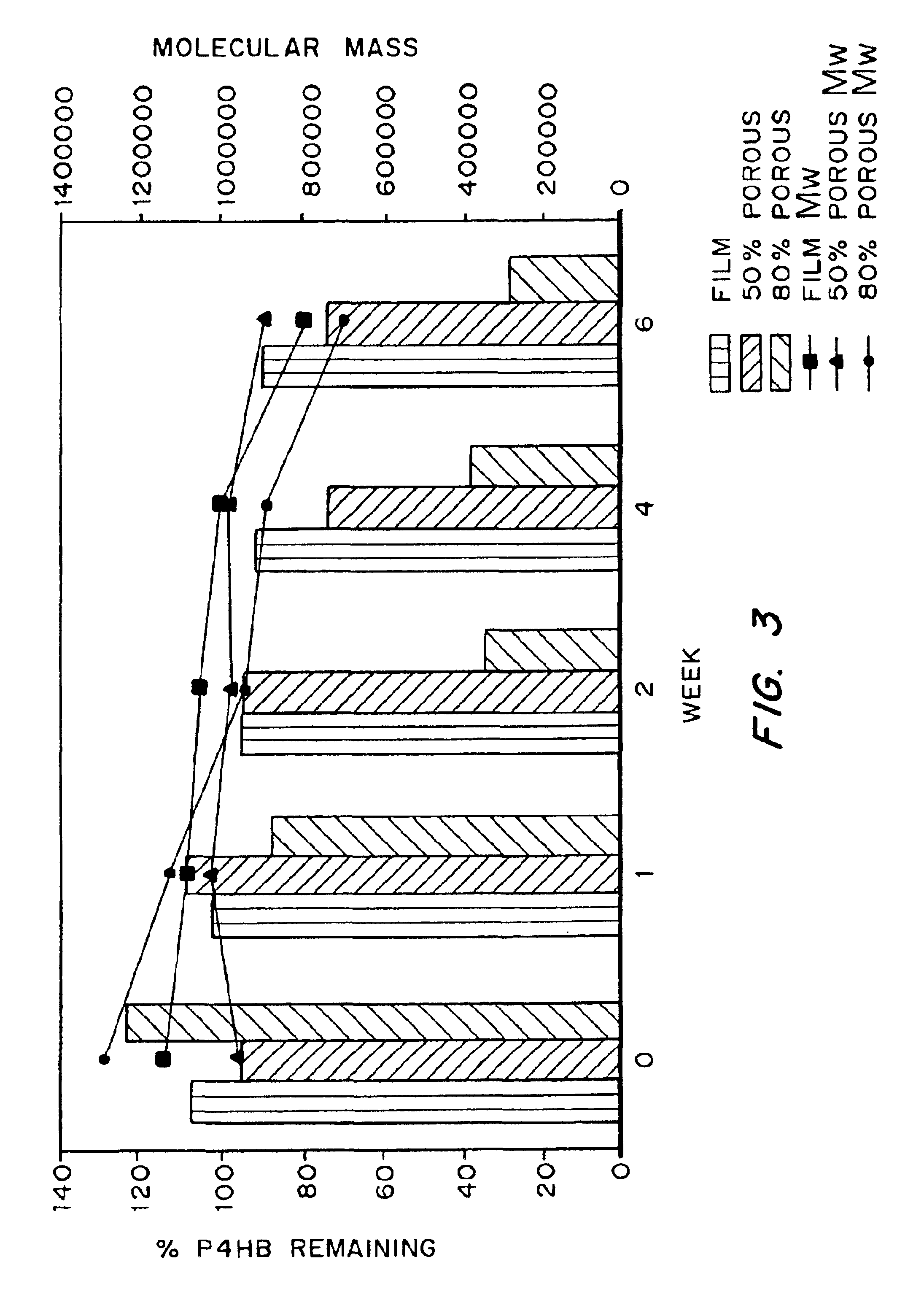
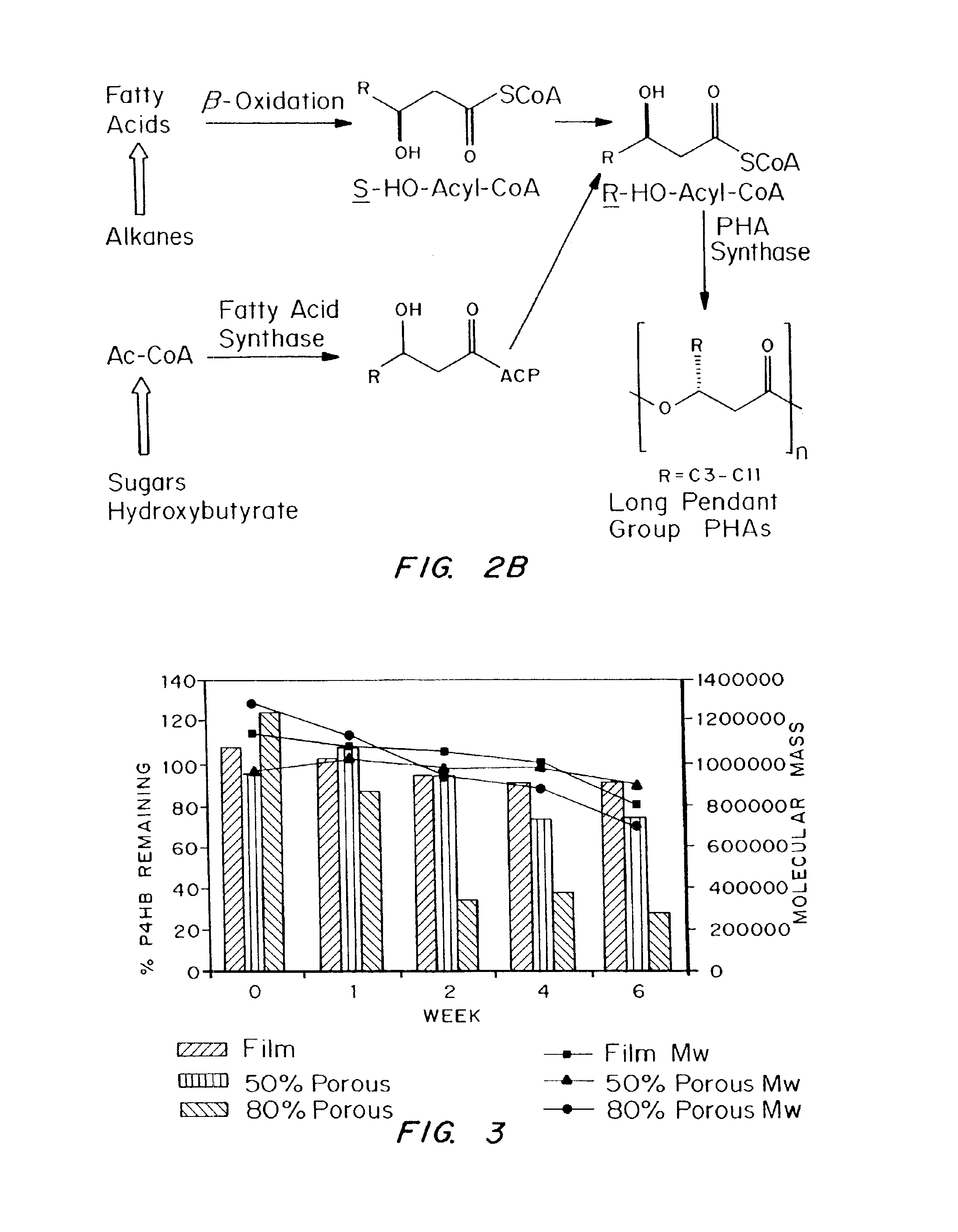
Biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions with controlled degradation rates have been developed. In one embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates contain additives to alter the degradation rates. In another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones to alter their degradation rates. In still another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are chemically modified. Methods for manufacturing the devices which increase porosity or exposed surface area can be used to alter degradability. For example, as demonstrated by the examples, porous polyhydroxyalkanoates can be made using methods that creates pores, voids, or interstitial spacing, such as an emulsion or spray drying technique, or which incorporate leachable or lyophilizable particles within the polymer. Examples describe poly(4HB) compositions including foams, coatings, meshes, and microparticles. As demonstrated by the examples, these polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions have extremely favorable mechanical properties, as well as are biocompatible and degrade within desirable time frames under physioogical conditions. These polyhydroxyalkanoate materials provide a wider range of polyhydroxyalkanoate degradation rates than are currently available. Methods for processing these materials, particularly for therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic applications, or into devices which can be implanted or injected, are also described.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Imageable element with solvent-resistant polymeric binder
InactiveUS7261998B2Enhances on-press solvent resistanceProlong lifeRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceBackbone chain
The present invention provides an imageable element including a lithographic substrate and an imageable layer disposed on the substrate. The imageable layer includes a radically polymerizable component, an initiator system capable of generating radicals sufficient to initiate a polymerization reaction upon exposure to imaging radiation, and a polymeric binder having a hydrophobic backbone and including both constitutional units having a pendant cyano group attached directly to the hydrophobic backbone, and constitutional units having a pendant group including a hydrophilic poly(alkylene oxide) segment. When the imageable element is imaged and developed, the resulting printing plate may exhibit improved on-press solvent resistance and longer press life.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
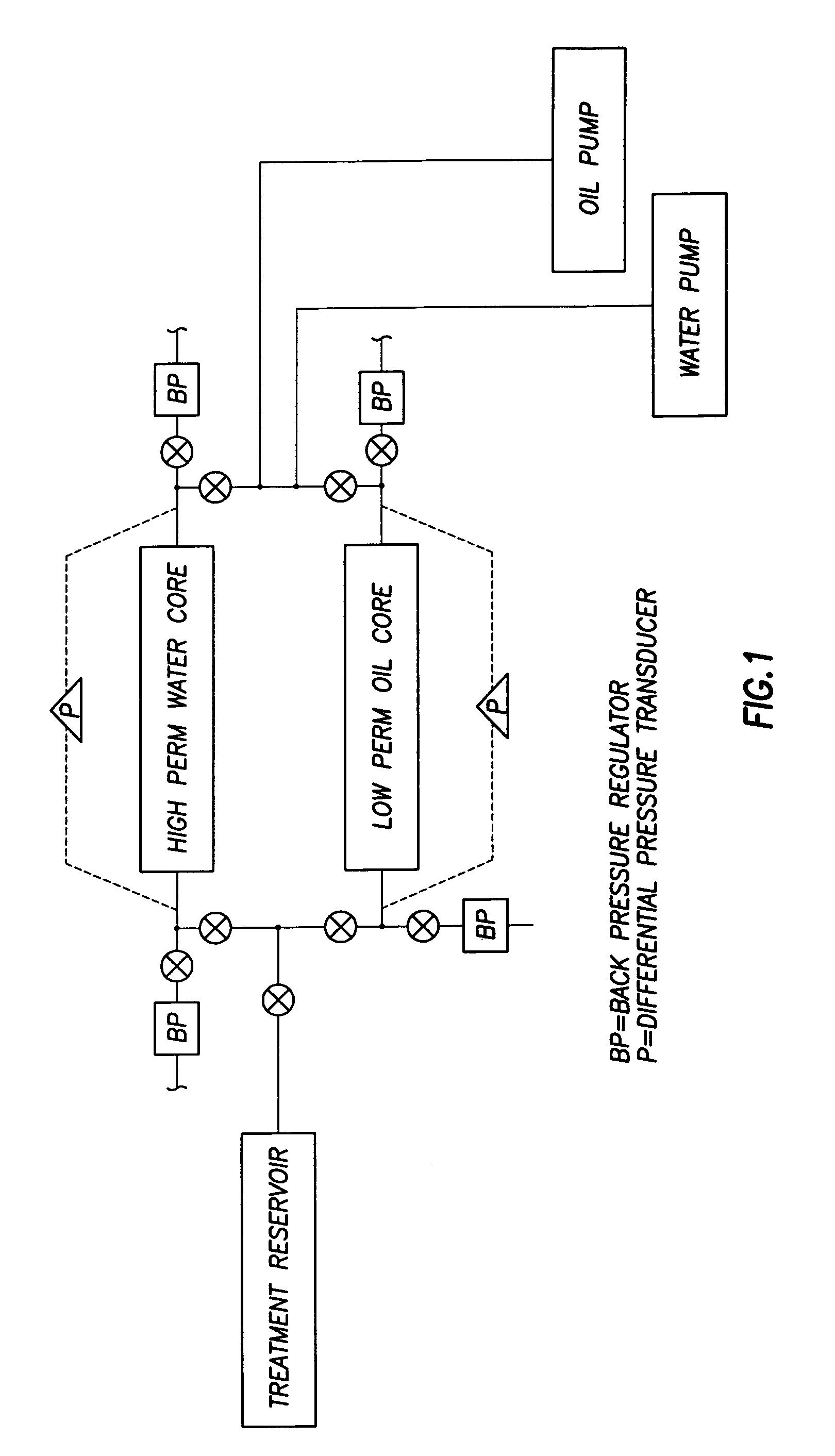
Methods of reducing water permeability for acidizing a subterranean formation
InactiveUS20050000694A1Reducing and precluding production of waterEliminate needFluid removalFlushingHydrophilic polymersHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The present invention provides a method of stimulating a subterranean formation penetrated by a well. The formation has a water-bearing section and a hydrocarbon-bearing section. The method includes the steps of: (a) introducing into the formation an aqueous treatment fluid containing a hydrophobically-modified relative permeability modifier, and (b) introducing an acidizing treatment fluid into the formation. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can be formed and introduced into the formation in several ways. For example, the hydrophobically-modified RPM can be the reaction product of a hydrophilic polymer and a hydrophobic compound that are capable of reacting with each other. The hydrophilic polymer is a polymer containing reactive amino groups in the polymer backbone or as pendant groups, which are capable of reacting with a hydrophobic alkyl halide compound. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can include, for example, a polymer of DMAEMA quaternized with an alkyl halide, wherein the alkyl halide has an alkyl chain length of 6 to 22 carbons.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Polymerizable chain-extended polysiloxanes with pendant hydrophilic groups
The invention provide a class of chain-extended polysiloxane crosslinkers which comprises (1) at least two polysiloxane segments, wherein each pair of adjacent polysiloxane segments is linked by one divalent organic radical which includes at least one pendant hydrophilic group (hydroxyl and / or carboxyl groups) or at least one dangling hydrophilic polymer chain and a di-thioether linkage —S-DR-S— in which DR is a divalent organic radical; and (2) two terminal ethylenically unsaturated groups. The present invention is also related to a polymer comprising crosslinking units derived from chain-extended polysiloxane crosslinker of the invention and to ophthalmic lenses comprising such a polymer.
Owner:ALCON INC
Polymerizable chain-extended polysiloxanes with pendant hydrophilic groups
The invention provide a class of chain-extended polysiloxane crosslinkers which comprises (1) at least two polysiloxane segments, wherein each pair of adjacent polysiloxane segments is linked by one divalent organic radical which includes at least one pendant hydrophilic group (hydroxyl and / or carboxyl groups) or at least one dangling hydrophilic polymer chain and a di-thioether linkage —S-DR—S— in which DR is a divalent organic radical; and (2) two terminal ethylenically unsaturated groups. The present invention is also related to a polymer comprising crosslinking units derived from chain-extended polysiloxane crosslinker of the invention and to ophthalmic lenses comprising such a polymer.
Owner:ALCON INC
Acid functional polymers based on benzocyclobutene
InactiveUS6361926B1Improve adhesionExcellent of constantDiazo compound compositionsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusImage resolutionSolvent
The invention is a curable cyclobutarene based polymer comprising acid functional pendant groups. The cured polymer displays excellent qualities of toughness, adhesion, dielectric constant, and low stress. The preferred system is soluble in an aqueous base and can be used to generate patterned films with excellent resolution without the need to handle organic developer solvents.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
Organic semiconductor device having an active dielectric layer comprising silsesquioxanes
InactiveUS6891237B1Solid-state devicesPretreated surfacesOrganic field-effect transistorLow temperature curing
An organic field effect transistor (FET) is described with an active dielectric layer comprising a low-temperature cured dielectric film of a liquid-deposited silsesquioxane precursor. The dielectric film comprises a silsesquioxane having a dielectric constant of greater than 2. The silsesquioxane dielectric film is advantageously prepared by curing oligomers having alkyl(methyl) and / or alkyl(methyl) pendant groups. The invention also embraces a process for making an organic FET comprising providing a substrate suitable for an organic FET; applying a liquid-phase solution of silsesquioxane precursors over the surface of the substrate; and curing the solution to form a silsesquioxane active dielectric layer. The organic FET thus produced has a high-dielectric, silsesquioxane film with a dielectric constant of greater than about 2, and advantageously, the substrate comprises an indium-tin oxide coated plastic substrate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Methods of reducing water permeability for acidizing a subterranean formation
InactiveUS7182136B2Reducing and precluding production of waterEliminate needFluid removalFlushingHydrophilic polymersChain length
The present invention provides a method of stimulating a subterranean formation penetrated by a well. The formation has a water-bearing section and a hydrocarbon-bearing section. The method includes the steps of: (a) introducing into the formation an aqueous treatment fluid containing a hydrophobically-modified relative permeability modifier, and (b) introducing an acidizing treatment fluid into the formation. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can be formed and introduced into the formation in several ways. For example, the hydrophobically-modified RPM can be the reaction product of a hydrophilic polymer and a hydrophobic compound that are capable of reacting with each other. The hydrophilic polymer is a polymer containing reactive amino groups in the polymer backbone or as pendant groups, which are capable of reacting with a hydrophobic alkyl halide compound. The hydrophobically-modified RPM can include, for example, a polymer of DMAEMA quaternized with an alkyl halide, wherein the alkyl halide has an alkyl chain length of 6 to 22 carbons.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
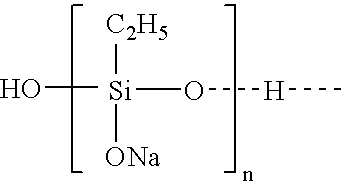
Method of preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in a bayer process
ActiveUS20050010008A2Reduce and eliminate aluminosilicate scalingReduce and even completely prevent formationSilicon organic compoundsAluminium compoundsPlate heat exchangerEnd-group
Abstract of the DisclosureMaterials and a process are provided whereby polymers with the pendant group or end group containing --Si(OR")3 (where R" is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in a Bayer process. When materials of the present invention are added to the Bayer liquor before the heat exchangers, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on heat exchanger walls. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
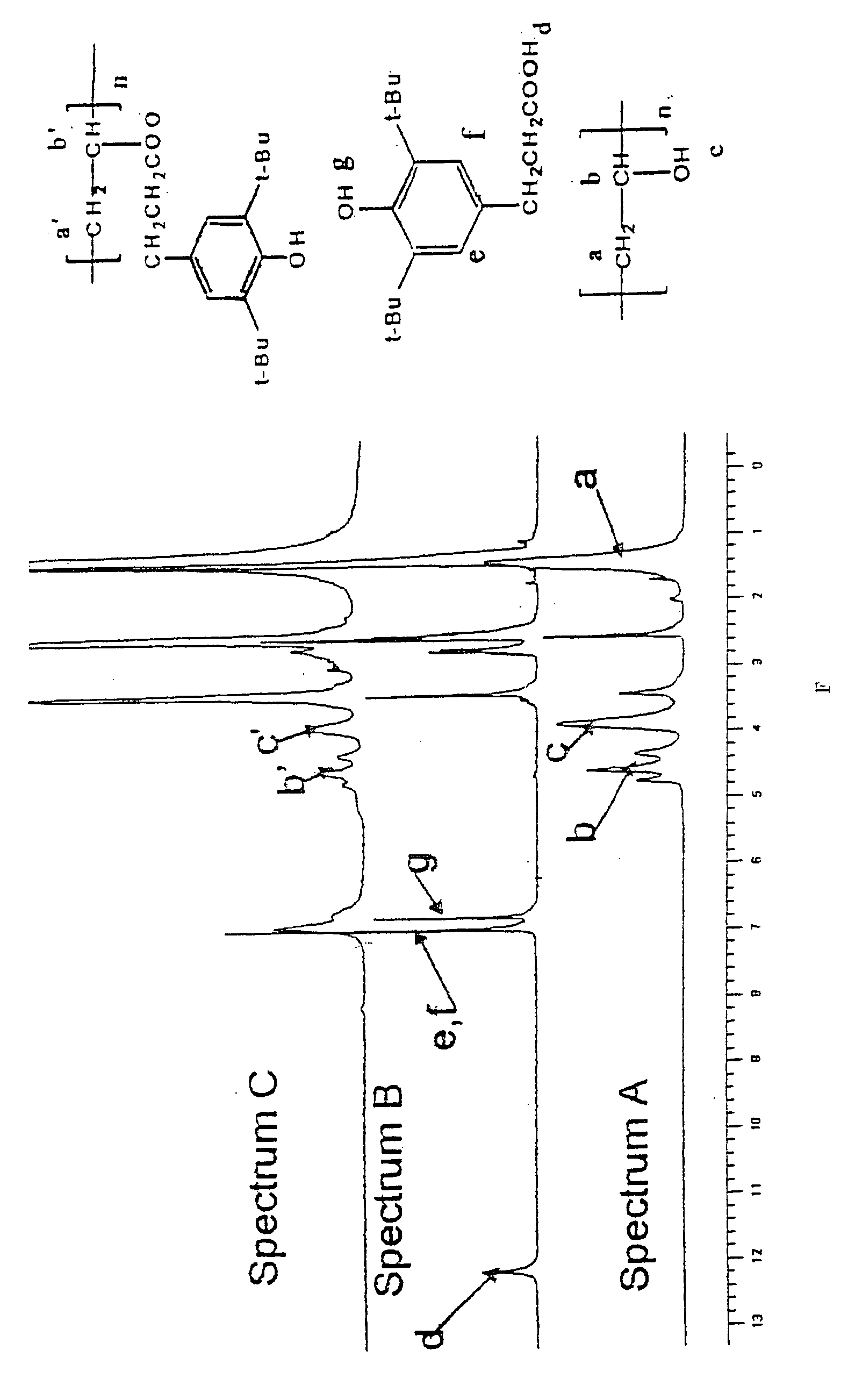
Post-coupling synthetic approach for polymeric antioxidants
A method of preparing an antioxidant polymer includes forming or obtaining a first polymer having reactive pendant groups, where the first polymer does not include cyclic anhydride repeat units, and derivatizing the first polymer with an antioxidant. Another method of preparing an antioxidant polymer includes forming or obtaining a first polymer having reactive pendant groups and derivatizing the first polymer with an antioxidant, where the antioxidant is attached to the first polymer by an acetal, amide, amine, carbamate, carbonate, ester, ether or thioether linkage or by a carbon-carbon bond. The invention is also directed to polymers that are generally prepared by these methods, compositions that include such polymers and methods of using such polymers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS LOWELL
Methods and reagents for preparing biomolecule-containing coatings
InactiveUS20050281857A1Reduced throughput timeLow costPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesPolymer scienceBio molecules
Polymeric coatings that include coupled biomolecules are formed on the surface of articles, such as medical devices. A coated layer that includes a synthetic polymer including a reactive group is formed on a surface and then a biomolecule is attached to the reactive group. The synthetic polymer can be an acrylate polymer or an amine-containing polymer having pendent photoreactive groups.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Polymeric surface coatings
A biocompatibilising process in which a substrate having a surface which bears substrate pendant functional groups is biocompatibilised by coating it with a coating composition containing a polymer formed from a radical polymerisable monomers including a radical polymerisable zwitterionic monomer and a radical polymerisable monomer containing a reactive group to form a polymer having zwitterionic groups and pendant reactive groups and the said pendant reactive groups are reacted to form covalent bonds with said substrate pendant functional group and thereby form a stable coating of polymer on the said surface.
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Buffer compositions
Buffer compositions comprising semiconductive oxide particles and at least one of (a) a fluorinated acid polymer and (b) a semiconductive polymer doped with a fluorinated acid polymer are provided. Semiconductive oxide particles include metal oxides and bimetallic oxides. Acid polymers are derived from monomers or comonomers of polyolefins, polyacrylates, polymethacrylates, polyimides, polyamides, polyaramids, polyacrylamides, polystyrenes. The polymer backbone, side chains, pendant groups or combinations thereof may be fluorinated or highly fluorinated. Semiconductive polymers include polymers or copolymers derived from thiophenes, pyrroles, anilines, and polycyclic heteroaromatics. Methods for preparing buffer compositions are also provided.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Polymer with pendent cyclic olefinic functions for oxygen scavenging packaging
InactiveUS7097890B1Increase initiativeSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolymer scienceOxygen
A family of polymers containing selected cyclic allylic pendent groups for oxygen scavenging packaging which has minimal organoleptic by-products after oxidation.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
Method of preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in kraft pulp mills
InactiveUS20050274926A1Reduce and eliminate aluminosilicate scalingReduce and even prevent formationAluminium compoundsDigestersEnd-groupPulp mill
Materials and a method are provided whereby polymers with least 0.5 mole % of the pendant group or end group containing —Si(OR″)3 (where R″ is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in an industrial process having an alkaline process stream such as a pulping mill process stream. When materials of the present invention are added to the alkaline process stream, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on equipment surfaces such as evaporator walls and heating surfaces. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Imageable members with improved chemical resistance
InactiveUS7247418B2Increased “ chemical resistance ”Improved thermal bakeabilityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsCarbamateChemical compound
Both single-layer and multilayer imageable elements have a substrate and at least one imageable layer. The elements can be used to prepare either negative- or positive-working imaged elements, for example as lithographic printing plates. The imageable elements also include a radiation absorbing compound and a solvent-resistant polymer comprising pendant phosphoric acid groups, pendant adamantyl groups, or both. When this polymer comprises pendant adamantyl groups, they are connected to the polymer backbone through a urea or urethane group. The imageable elements have improved chemical resistance and thermal bakeability from the presence of the unique solvent-resistant polymer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Purification of proteins
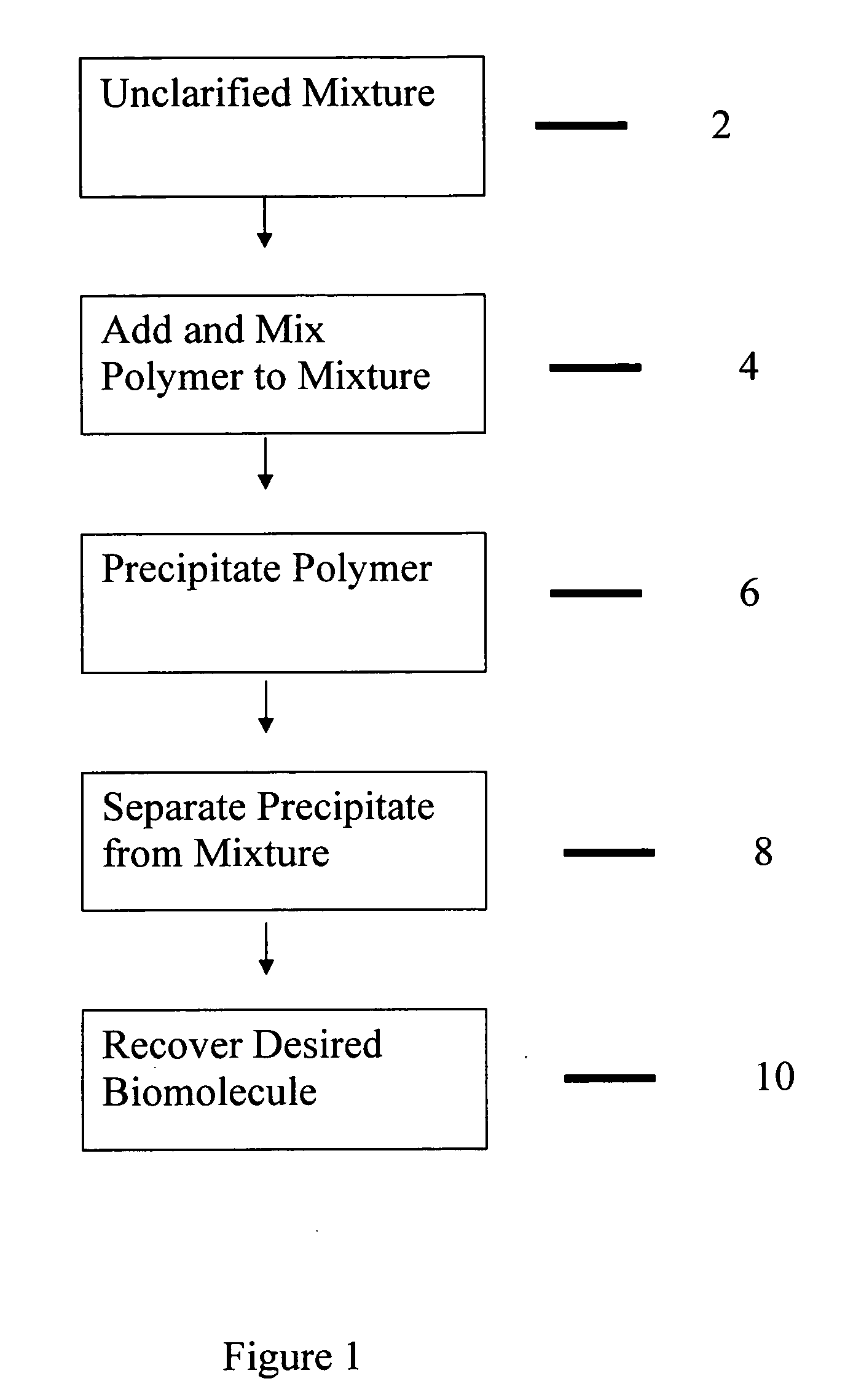
InactiveUS20110020327A1Speed up the processPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsParticulatesSolid particle
The present invention relates to a bimodal polymer such as a soluble polymer capable of irreversibly binding to insoluble particulates and a subset of soluble impurities and also capable of reversibly binding to one or more desired biomolecules in an unclarified biological material containing stream and the methods of using such a material to purify one or more desired biomolecules from such a stream without the need for prior clarification. Such a polymer comprises domains of charged pendant groups such as primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary amines, (first mode) and is rendered insoluble and precipitates out of solution simply upon complexing with oppositely charged solid particulates and a fraction of the soluble impurities in an amount sufficient to form an aggregate that can no longer be held in solution. The polymer further comprises other domains of pendant groups that are charged or uncharged, hydrophilic or hydrophobic or have a ligand that is selective for the biomolecule of interest depending on the process conditions such as pH, ionic strength, salts, and the like (second mode). When present in one mode, such as the uncharged form, said pendant groups are capable of binding to one or more desired biomolecules within the stream (protein, polypeptide, etc) in an unclarified cell broth. The precipitate can then be removed from the stream, such as by being filtered out from the remainder of the stream and the desired biomolecule is recovered such as by selective elution.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Polymer, resist composition, and patterning process
ActiveUS20090208873A1Improved water repellency and water slipFew development defectElectric discharge tubesPhotosensitive materialsPolymer sciencePendant group
A polymer obtained through copolymerization of a monomer having a hexafluoroalcohol pendant whose hydroxyl moiety has been protected and a monomer having an acid labile group is useful as an additive to a photoresist composition for immersion lithography. When processed by immersion lithography, the resist composition exhibits good water repellency and water slip and produces few development defects.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Container having oxygen-scavenging core layer
InactiveUS7056565B1Extend freshnessExtended shelf lifeSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingOrganolepticPolymer
Rigid containers are provided comprising oxygen scavenger compositions that produce only low levels of volatiles or by-products as a consequence of oxygen scavenging. In particular, a family of polymers containing selected cyclic olefinic pendent groups are used in the rigid containers to achieve oxygen scavenging that is associated with minimal or no organoleptic by-products after oxidation.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
Ionomers and ionically conductive compositions
Disclosed are ionomers comprising functionalized polyolefins having fluoroalkyl sulfonate pendant groups and ionically conductive compositions formed therefrom by the addition of solvents.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Substituted heterocyclic compounds
InactiveUS6077954ASimple designOrganic chemistry methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundNitrogen
Novel compounds having the formula: wherein the constituent variables are defined herein. The compounds are constructed to include a central aromatic, aliphatic, or heterocyclic ring system. Attached to the central ring system are two linear groups having nitrogenous moieties that are derivatized with chemical functional groups. The ring system can include further nitrogenous moieties, either as ring atoms or on pendant groups attached to the ring, that may also be derivatized with chemical functional groups. The totality of the chemical functional groups imparts certain conformational and other properties to the these compounds. In accordance with certain embodiments of the invention, libraries of such compounds are prepared utilizing permutations and combinations of the chemical functional groups and the nitrogenous moieties to build complexity into the libraries.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Photosensitive compositions based on polycyclic polymers
InactiveUS7022790B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingArylStructural formula
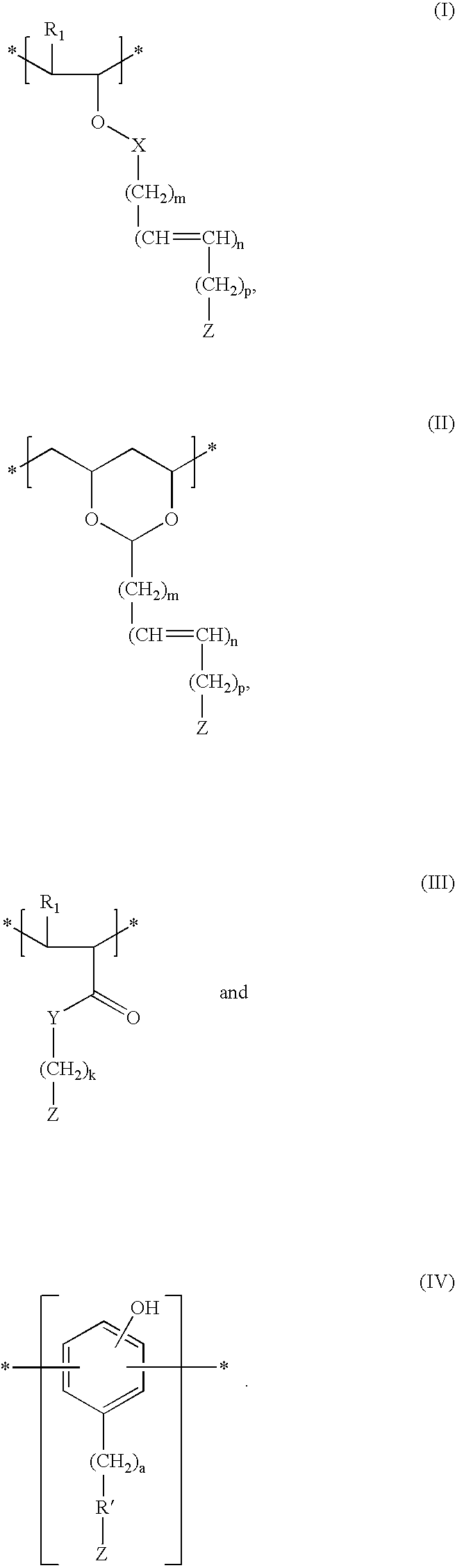
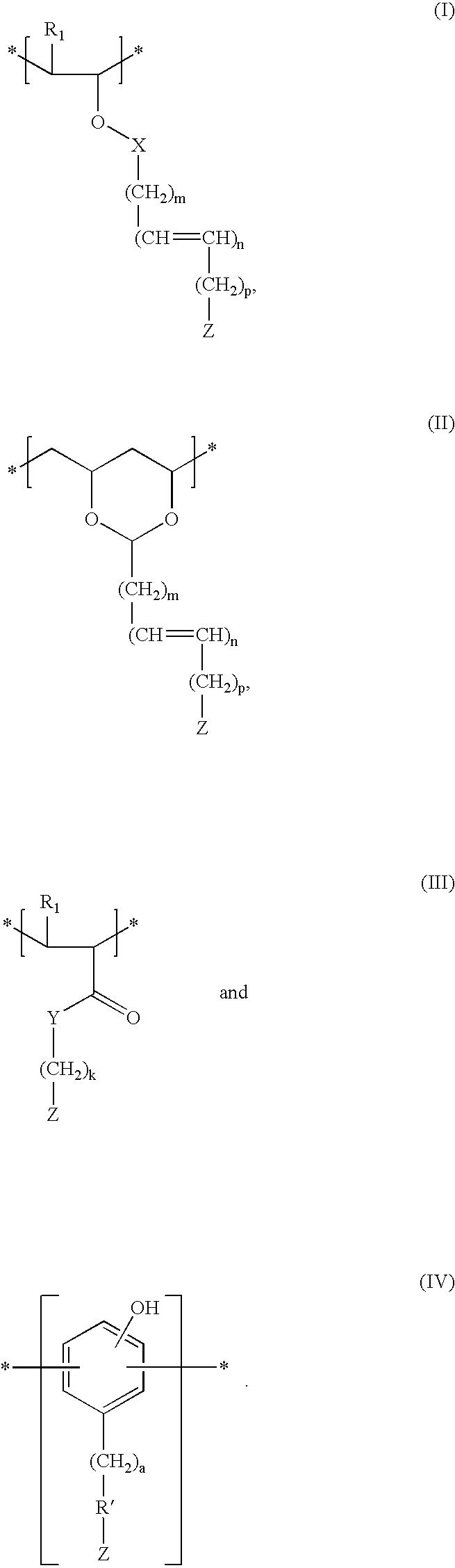
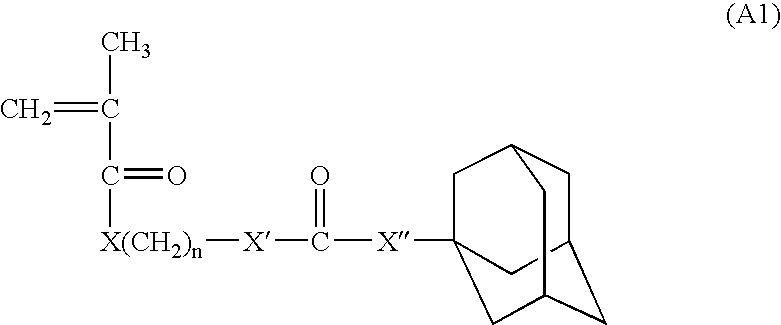
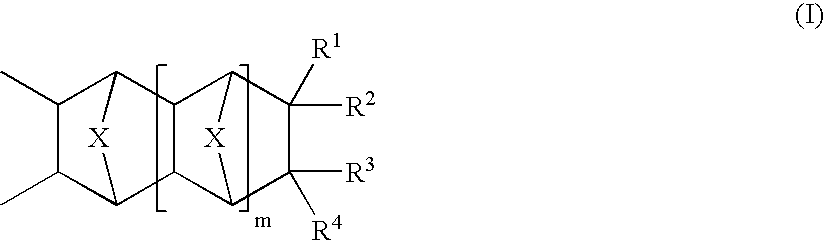
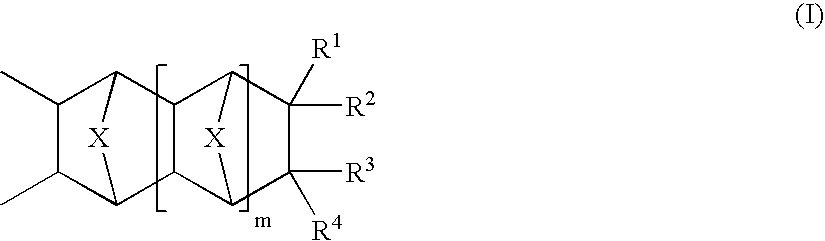
A copolymer composition including a copolymer having repeat units of structural formula I: where X is selected from —CH2—, —CH2—CH2— and O; m is an integer from 0 to 5; and each occurrence of R1–R4 are independently selected from H; C1 to C25 linear, branched, and cyclic alkyl, aryl, aralkyl, alkaryl, alkenyl and alkynyl that can include one or more hetero atoms selected from O, N, and Si; a group that contains an epoxy functionality; —(CH2)nC(O)OR5; —(CH2)nC(O)OR6; —(CH2)nOR6; —(CH2)nOC(O)R6; —(CH2)nC(O)R6; —(CH2)nOC(O)OR6; and any combination of two of R1, R2, R3, and R4 linked together by a linking group. A portion of the repeat units having structural formula I contain at least one epoxy functional pendant group. The copolymer composition can be included with a material that photonically forms a catalyst in a photodefinable dielectric composition, which can be used to form a photodefinable layer on a substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Polymer-coated substrates for immobilization of biomolecules and cells
ActiveUS20030198968A1Rapid and uniform introductionVersatile and cost-effective processBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsSide chainPendant group
Methods for preparing a substrate for the arraying and immobilizing of biomolecules or cells are described. The methods include providing a solid support and depositing by a chemical plasma-mediated polymerization process a polymeric coating on the surface. The polymeric coating comprises at least one pendant functional group capable of attaching a biomolecule or a cell. A material of the polymeric coating is preferably selected in such a way that its surface properties enhance binding between the pendant group and the biomolecule or cell. A substrate for the immobilization of biomolecules and cells is also provided. The substrate comprises a solid support made of a polymeric material. The solid support has at least one first pendant functional group suitable for attaching a first biomolecule or a first cell on its surface. The substrate further comprises a polymeric coating deposited on the surface of the substrate. The polymeric coating increases the attachment of the first biomolecule or the first cell to the first functional group.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Low outgassing photo or electron beam curable rubbery polymer material, preparation thereof and device comprising same
ActiveUS7256221B2Reduce outgassingLow outgassing of the adhesiveRubber derivative coatingsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
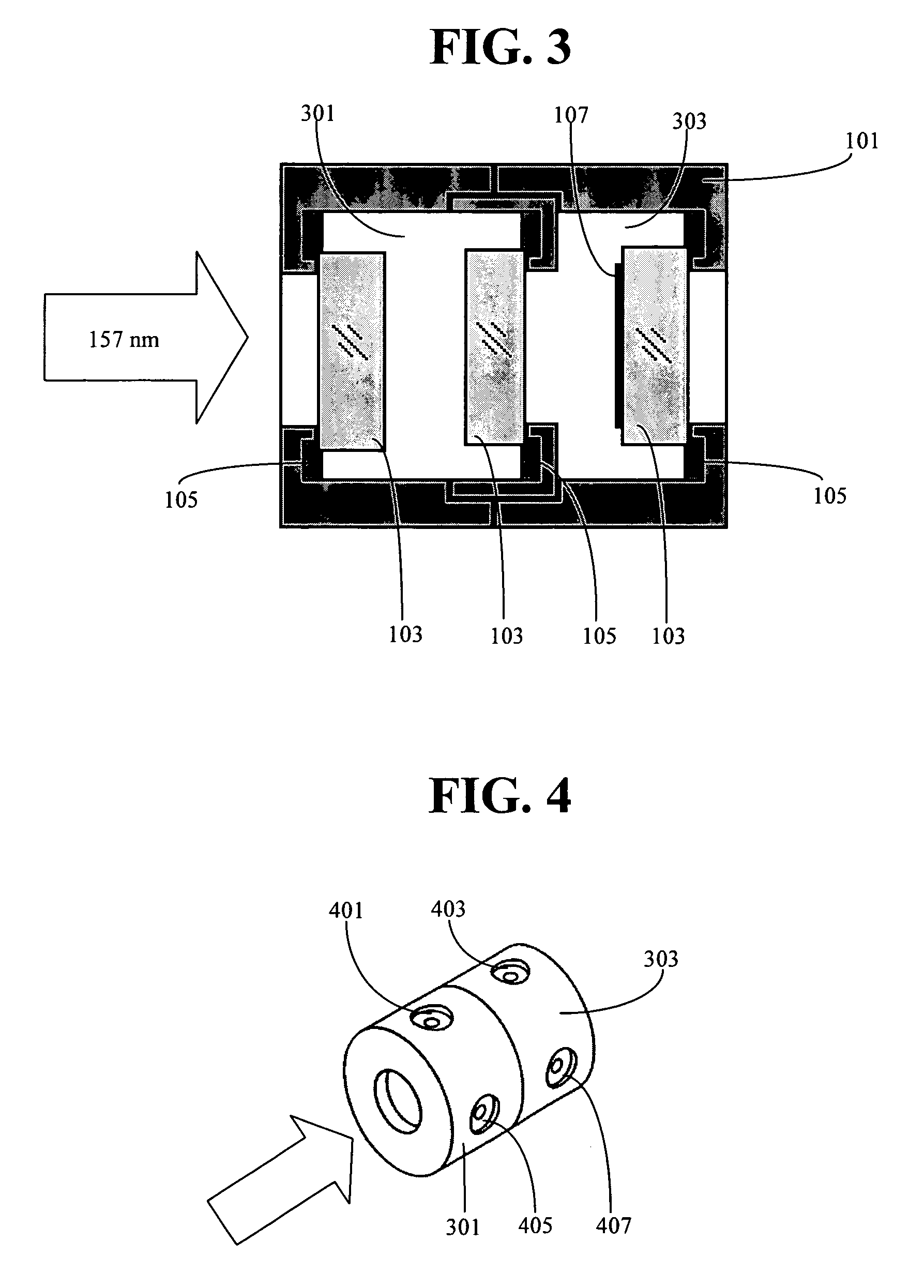
Disclosed are photo or electron beam polymerizable compositions, and preparation thereof and devices containing them. The composition contains completely or substantially completely hydrogenated hydrocarbon-based material completely free or substantially free of carbon-carbon double and triple bonds containing photo or electron beam curable terminal or pendant groups, low-outgassing photoinitiators, an optional viscosity adjustment component and an optional filler. The composition is visible light, UV or electron beam curable. It cures into a low-modulus, low outgassing polymer material. The composition can be used as an adhesive, sealant or lens potting material. It is ideal for use in lithographic tools involving deep or vacuum ultraviolet radiations, in particular, as lens potting materials for 157 nm lithographic tools.
Owner:CORNING INC
Novel Polymers and Methods of Controlling Viscosity
ActiveUS20090221461A1Acceptable/improved shear stabilityShear stableAdditivesFoam dispersion/preventionViscosity indexPendant group
The present invention relates to a novel polymer with pendant groups. The invention further provides for a lubricating composition containing said polymer. The invention further provides a method and use of controlling viscosity index by supplying to an oil of lubricating viscosity the polymer with pendant groups.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com