Expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in yeast employing truncated alpha-factor leader sequences
a technology of alpha-factor leader sequence and heterologous protein, which is applied in the field of recombinant proteins production in yeast, can solve the problems of not having, not generally predictable, heterologous protein in the patent, and achieve the effect of efficient direct expression and secretion of heterologous polypeptides, and improving the efficiency of expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
The following examples are provided for illustrative purposes only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. It is believed that the deposit of the starting biological materials is not necessary for the practice of the present invention since either the same or equivalent materials are publicly available.
example i
The following example provides a comparison of the levels of expression and secretion obtained with modified .alpha.-factor constructs used to express human proinsulin. Three constructs employ full-length .alpha.-factor leaders; one having .alpha.-factor leader with the three native glycosylation sites, one having all three of the glycosylation sites eliminated, and one having all of the sites, except the one at Asn.sub.23, removed. The fourth construct is a truncated .alpha.-factor leader which retains a single glycosylation site at Asn.sub.23.
A. pYGAI1
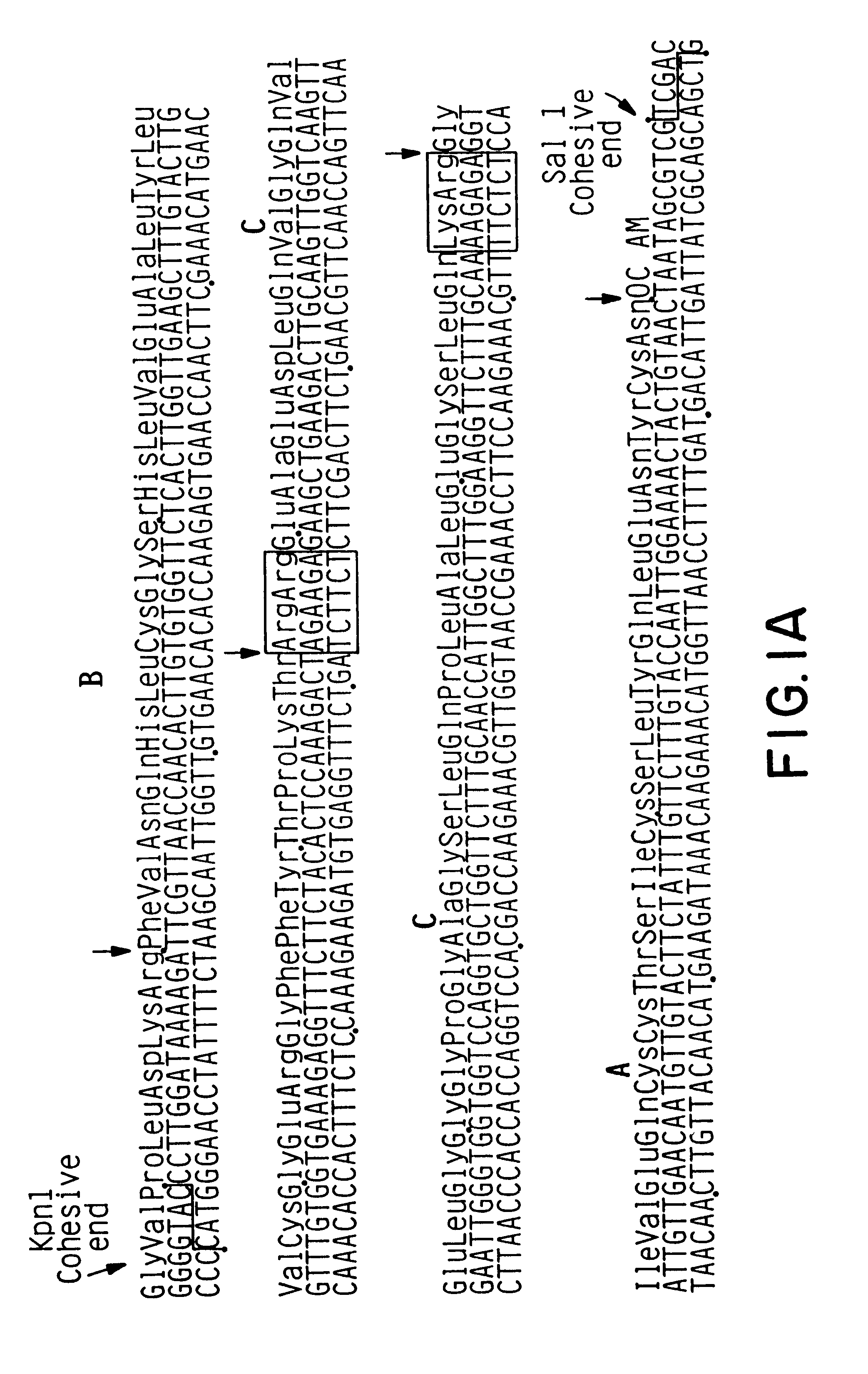
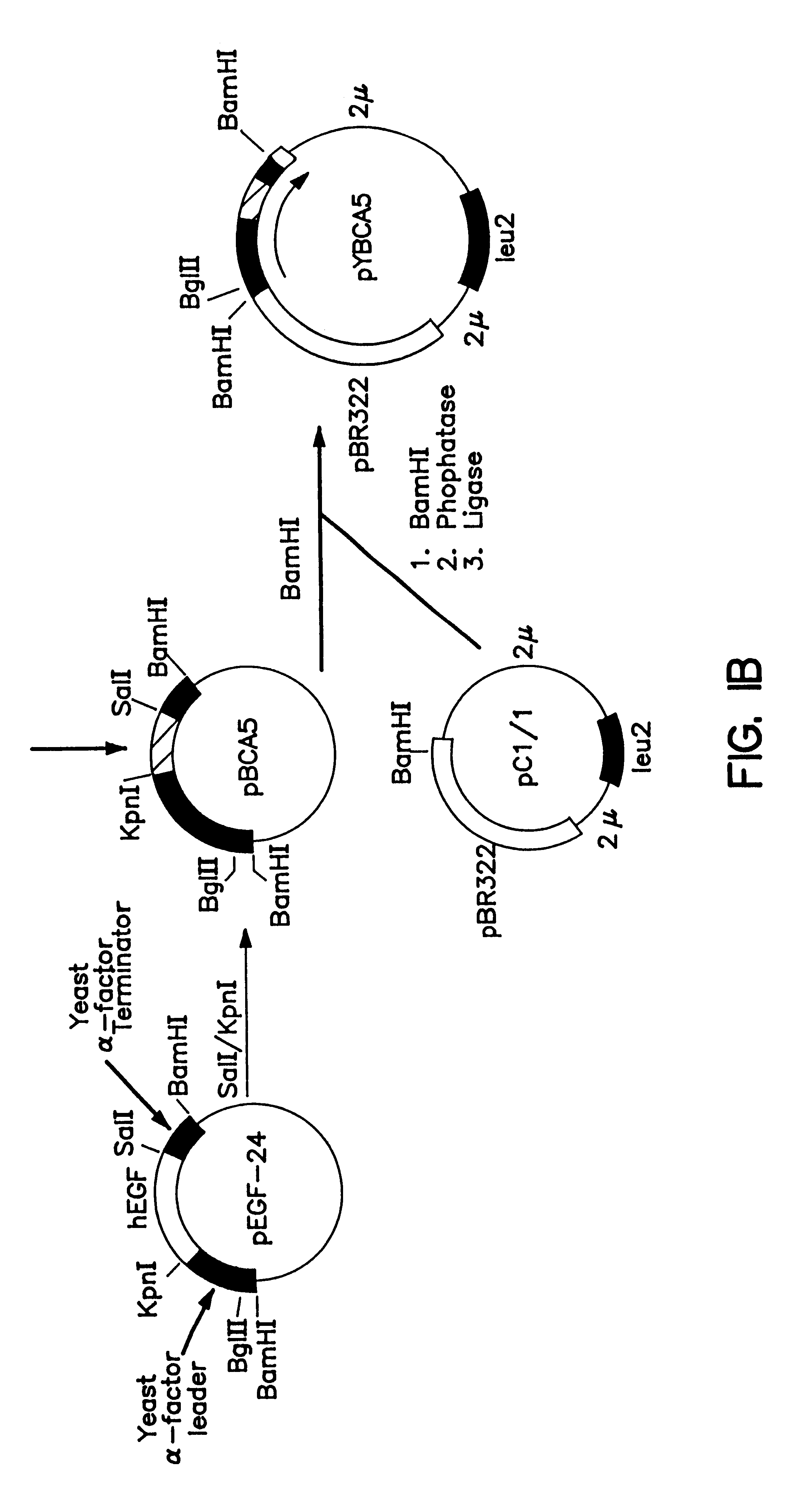
This plasmid encodes an .alpha.-factor leader [Brake et al. (1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:4642-4646; EPO Publication No. 116,201] linked to human proinsulin. The proinsulin is encoded by a synthetic gene made with yeast preferred codons (FIG. 1). The .alpha.-factor leader sequence, the synthetic proinsulin gene and the .alpha.-factor terminator sequence are from pYBCA5, the construction of which is shown in FIG. 1. Transcripti...
example ii
This example compares the expression of a full-length .alpha.-factor leader construct, retaining all glycosylation sites, to an expression construct employing a truncated .alpha.-factor sequence retaining only a single glycosylation site at Asn.sub.23. The non-yeast protein employed in this example is a human proinsulin analog wherein the connecting "C" peptide has been replaced by a yeast KEX2 endopeptidase cleavage site.
A. pYGAIC3
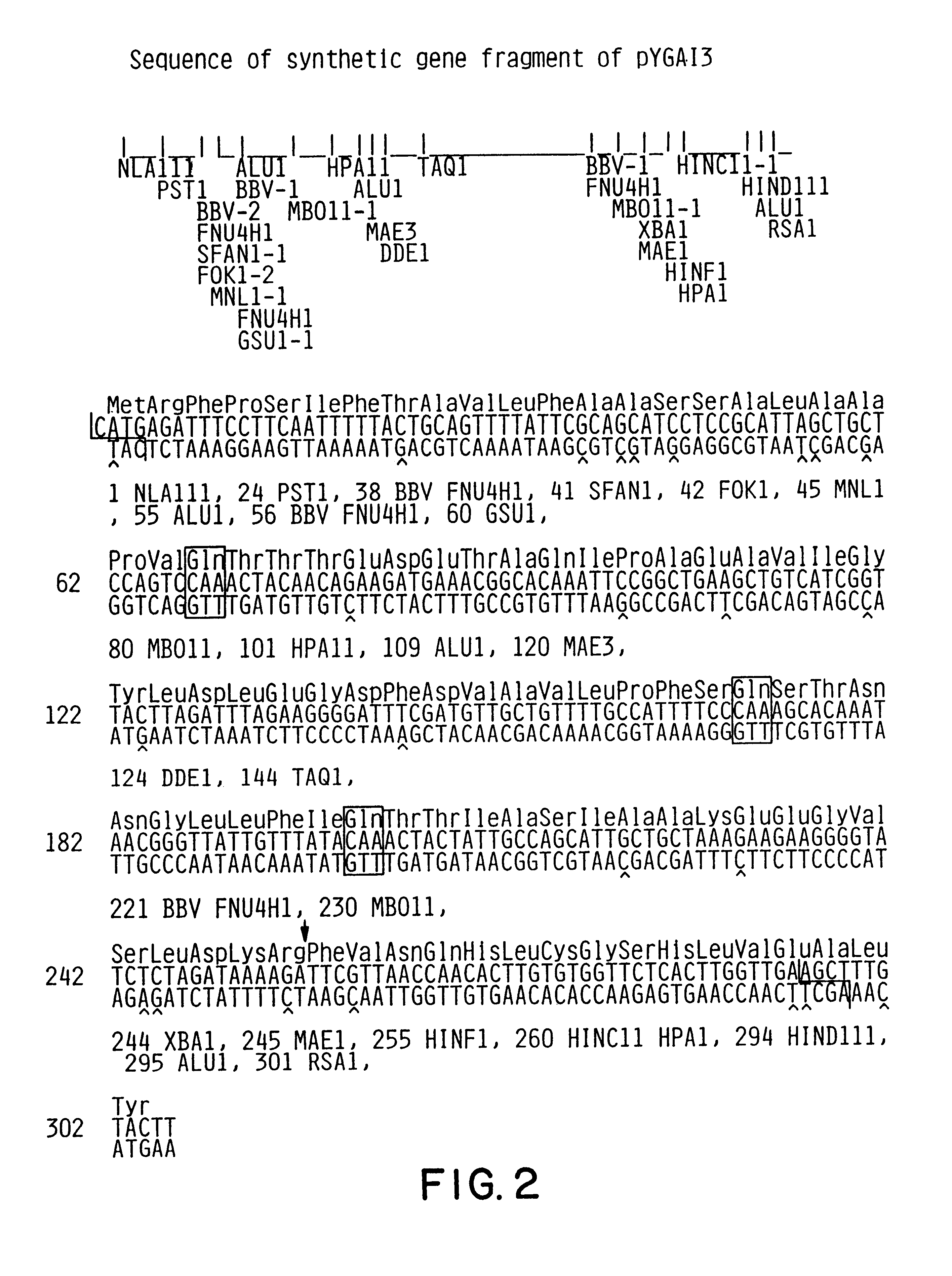
The plasmid pGAIC3 was made by replacing the 231 bp HindIII-SalI fragment of pGAI1 which encodes amino acids 14 through 30 of the B chain, the C-peptide, the A chain and 2 translation stop codons with a 132 bp synthetic HindIII-SalI gene fragment (shown in FIG. 3) which encodes amino acids 14 through 30 of the B chain, a Lys-Arg KEX2 endopeptidase cleavage site, the A chain, and translation stop codons. The plasmid pYGAIC3 was prepared from pGAIC3 as follows.
Plasmid pGAIC3 was digested with BamHI, and the 1107 bp BamHI expression cassette containing the G...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com