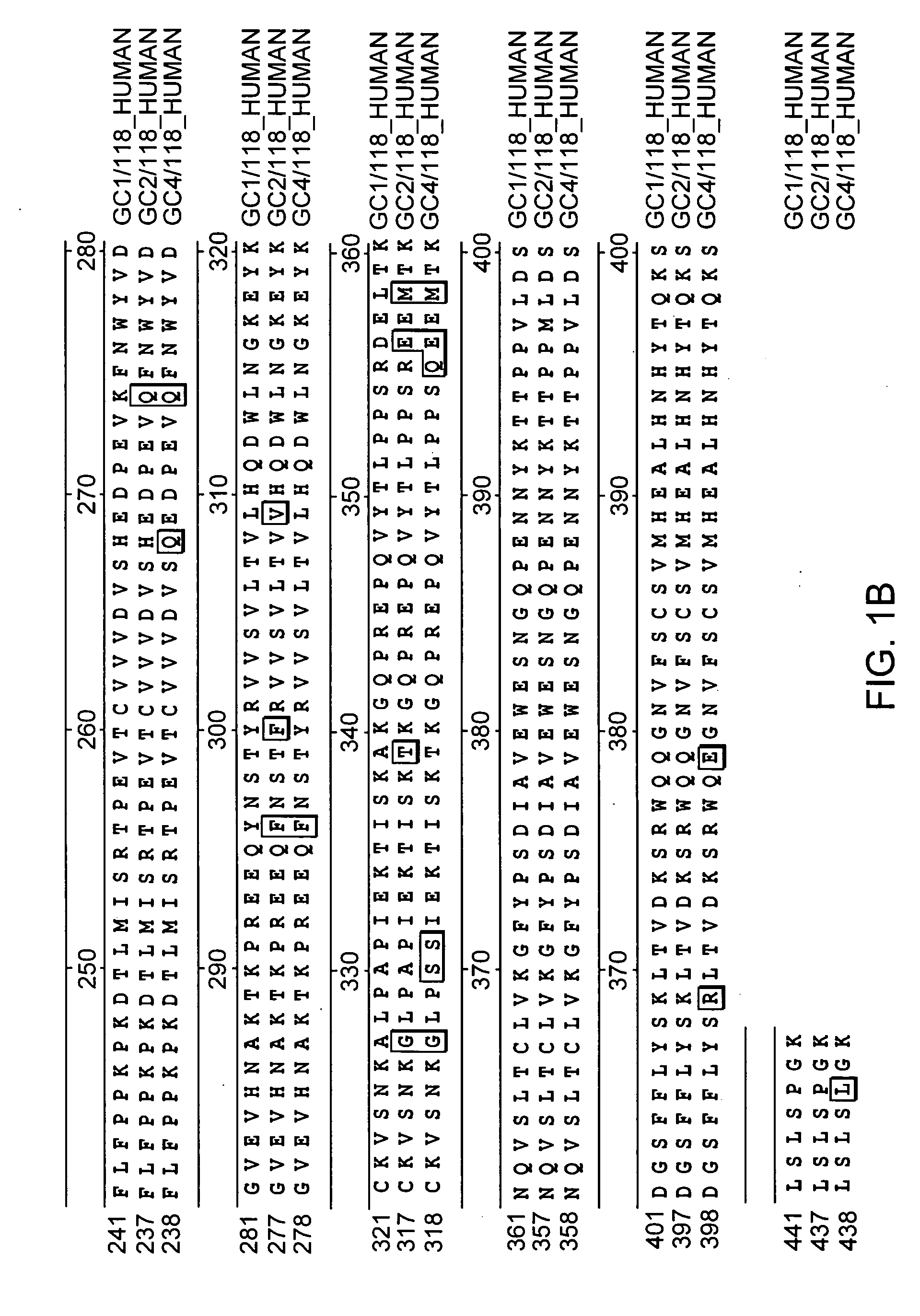
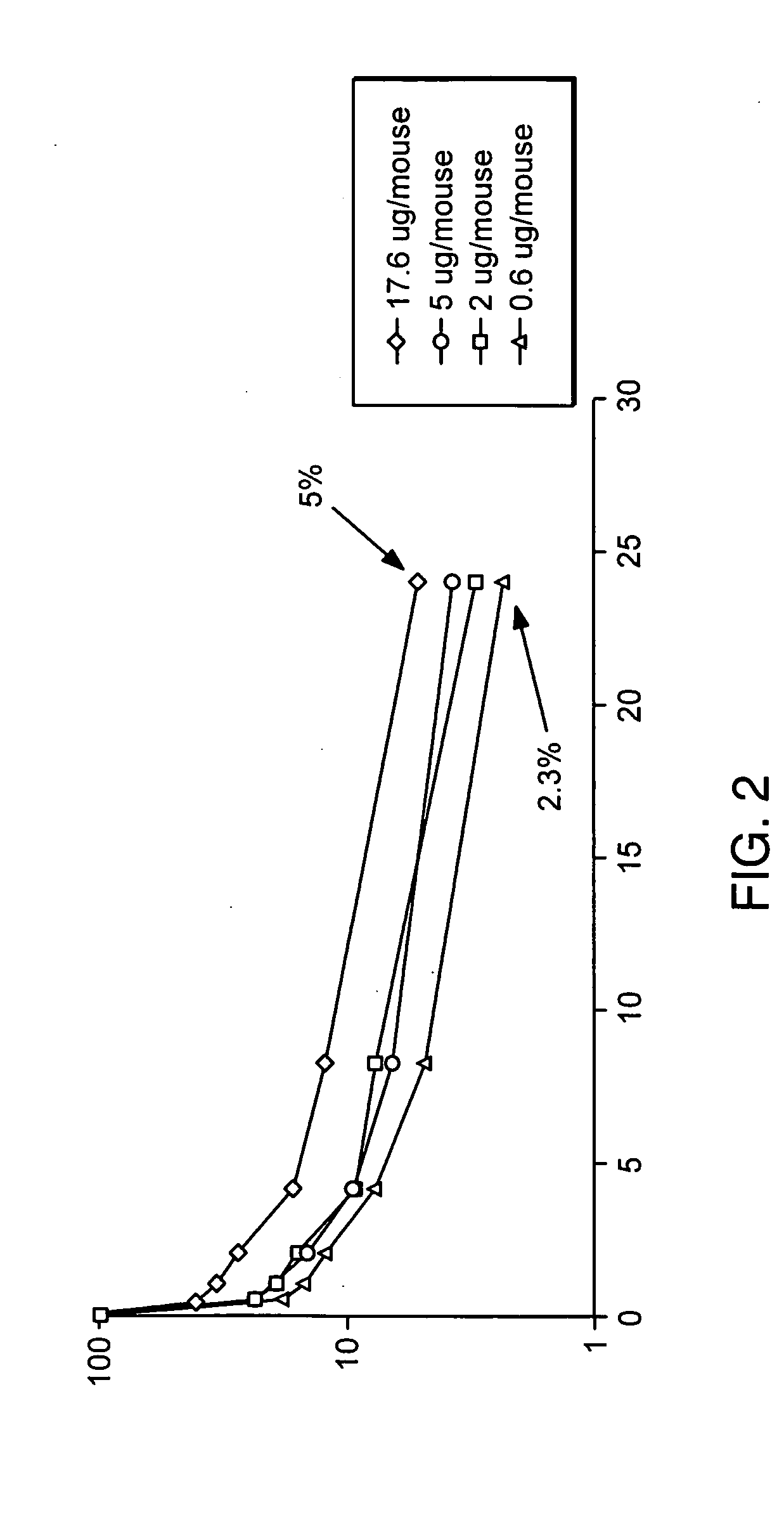
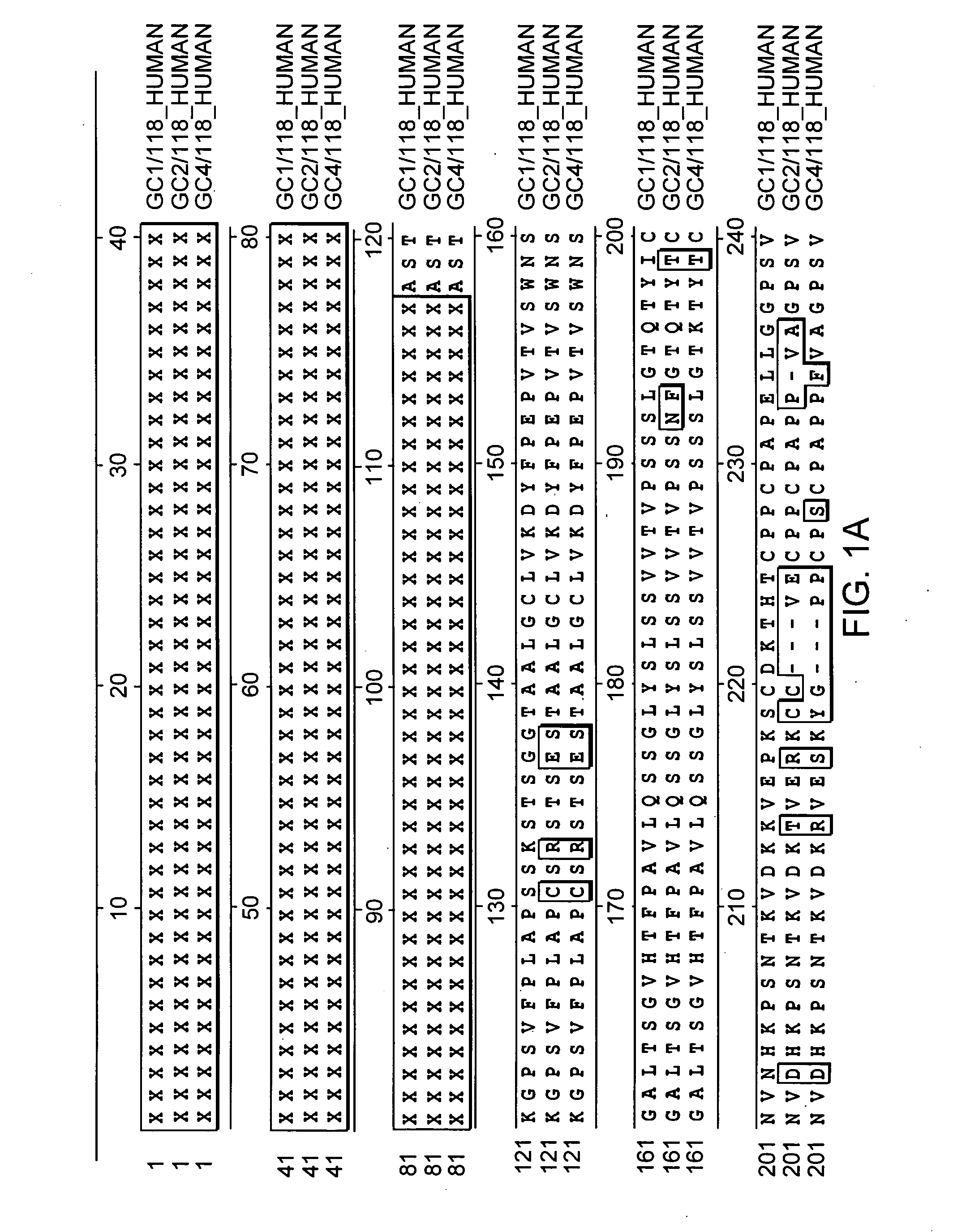
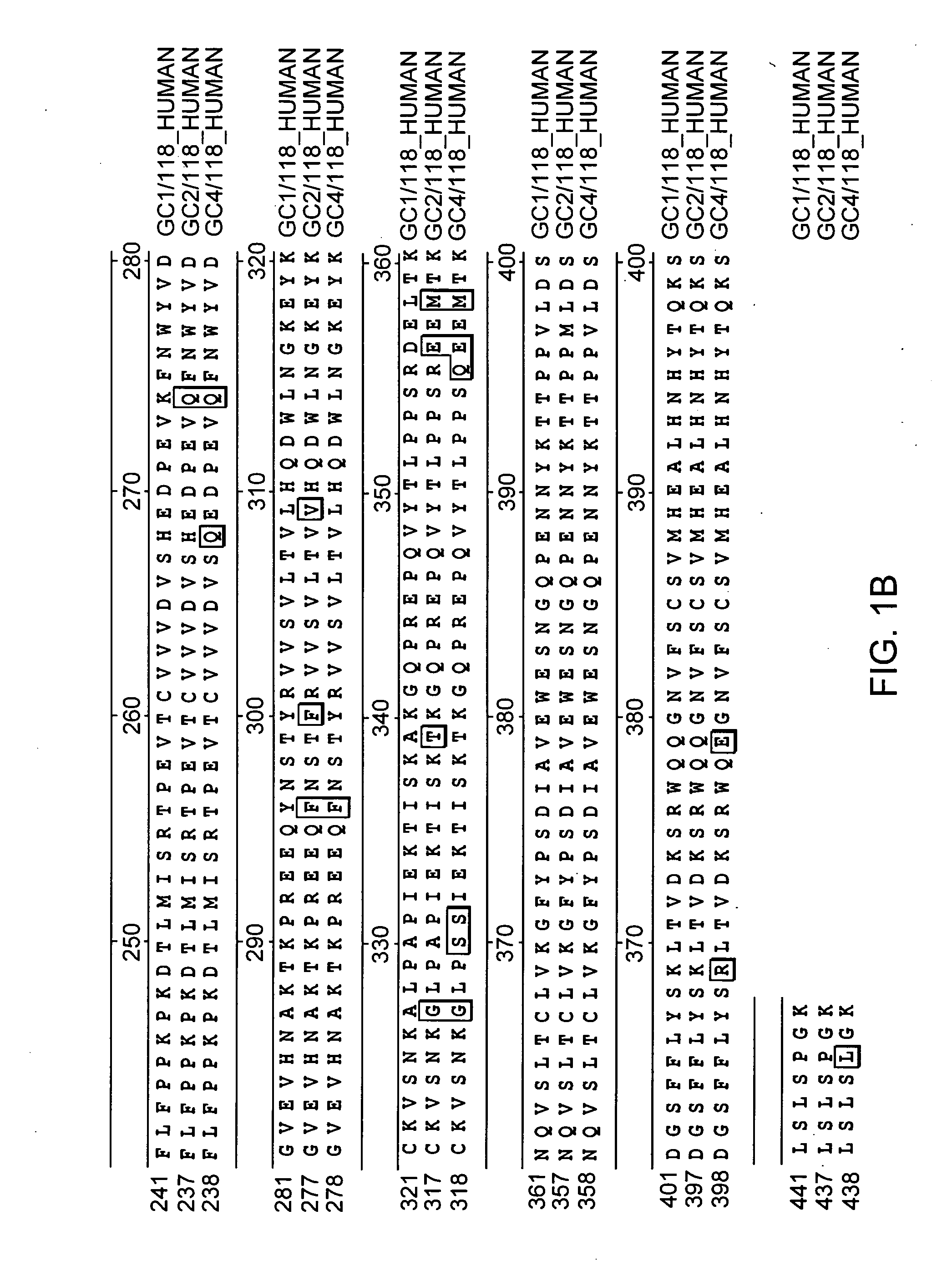
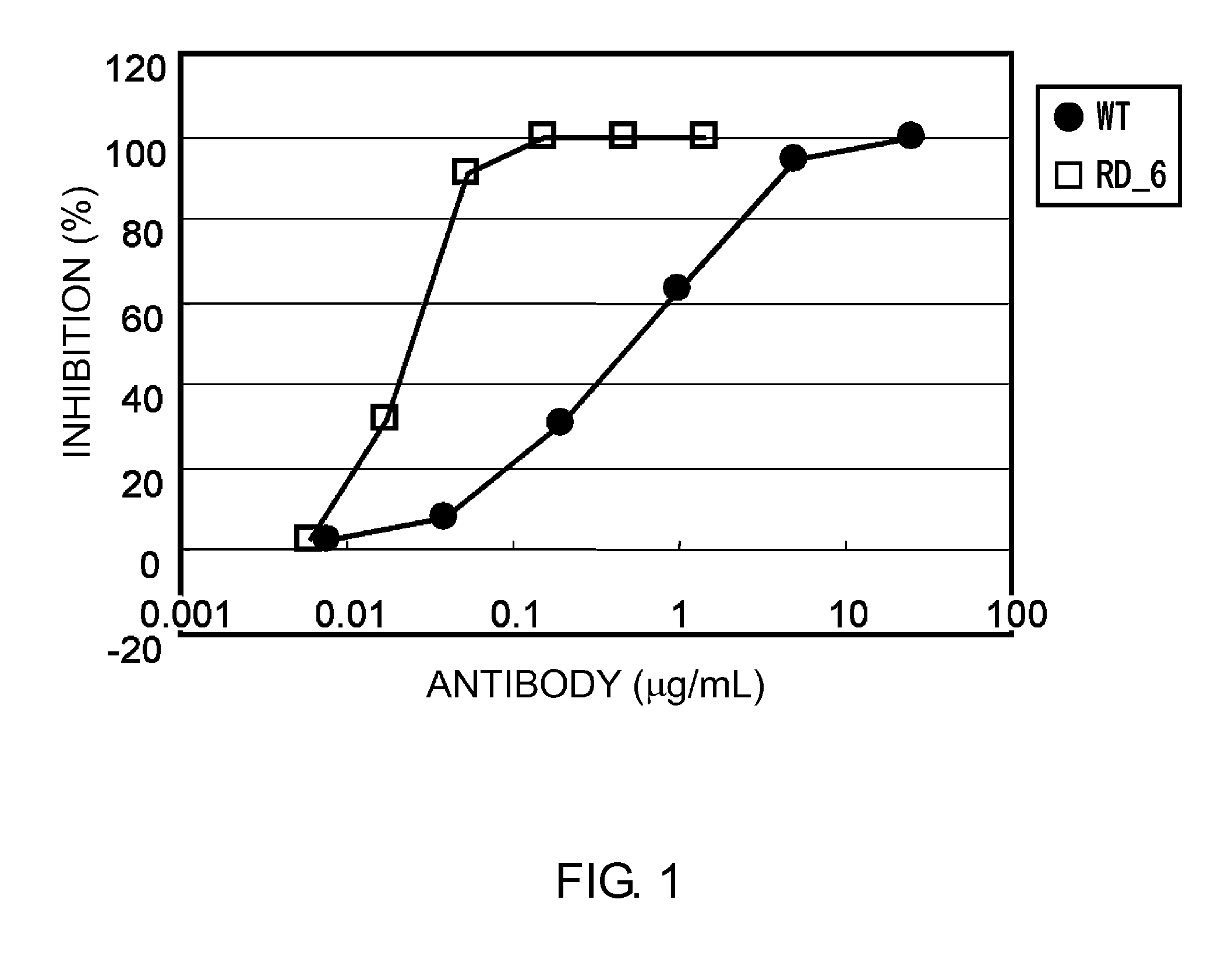
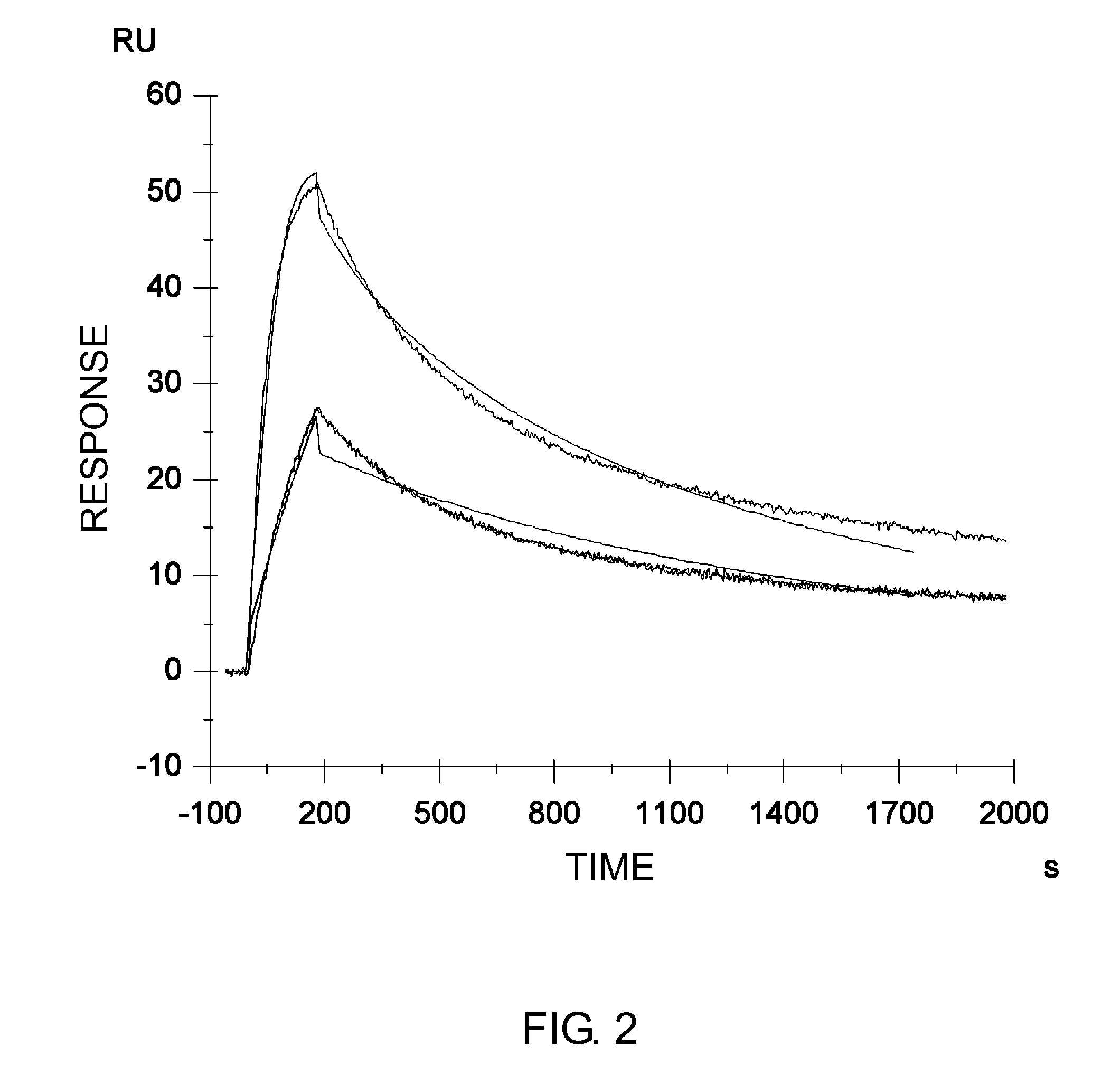
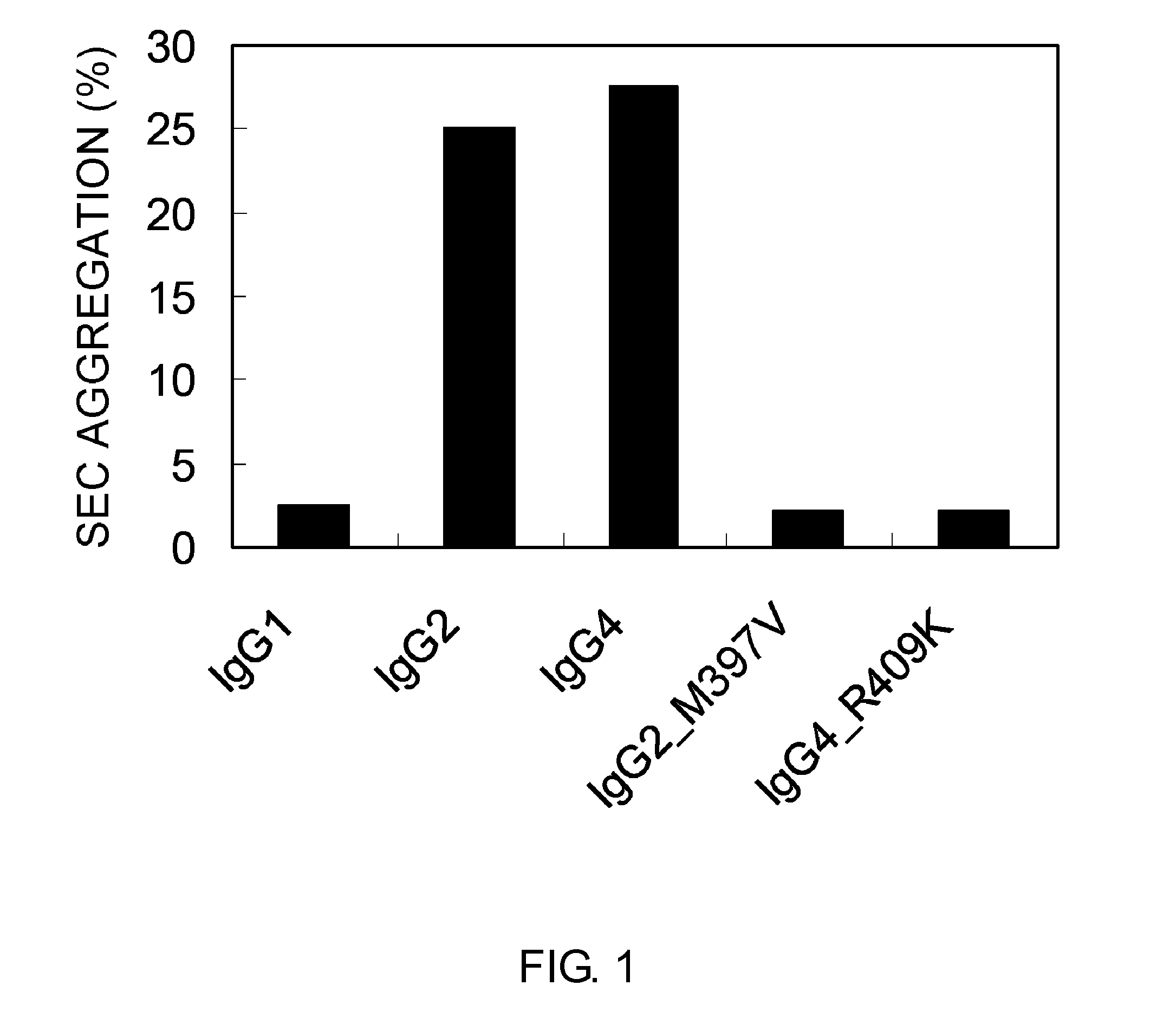
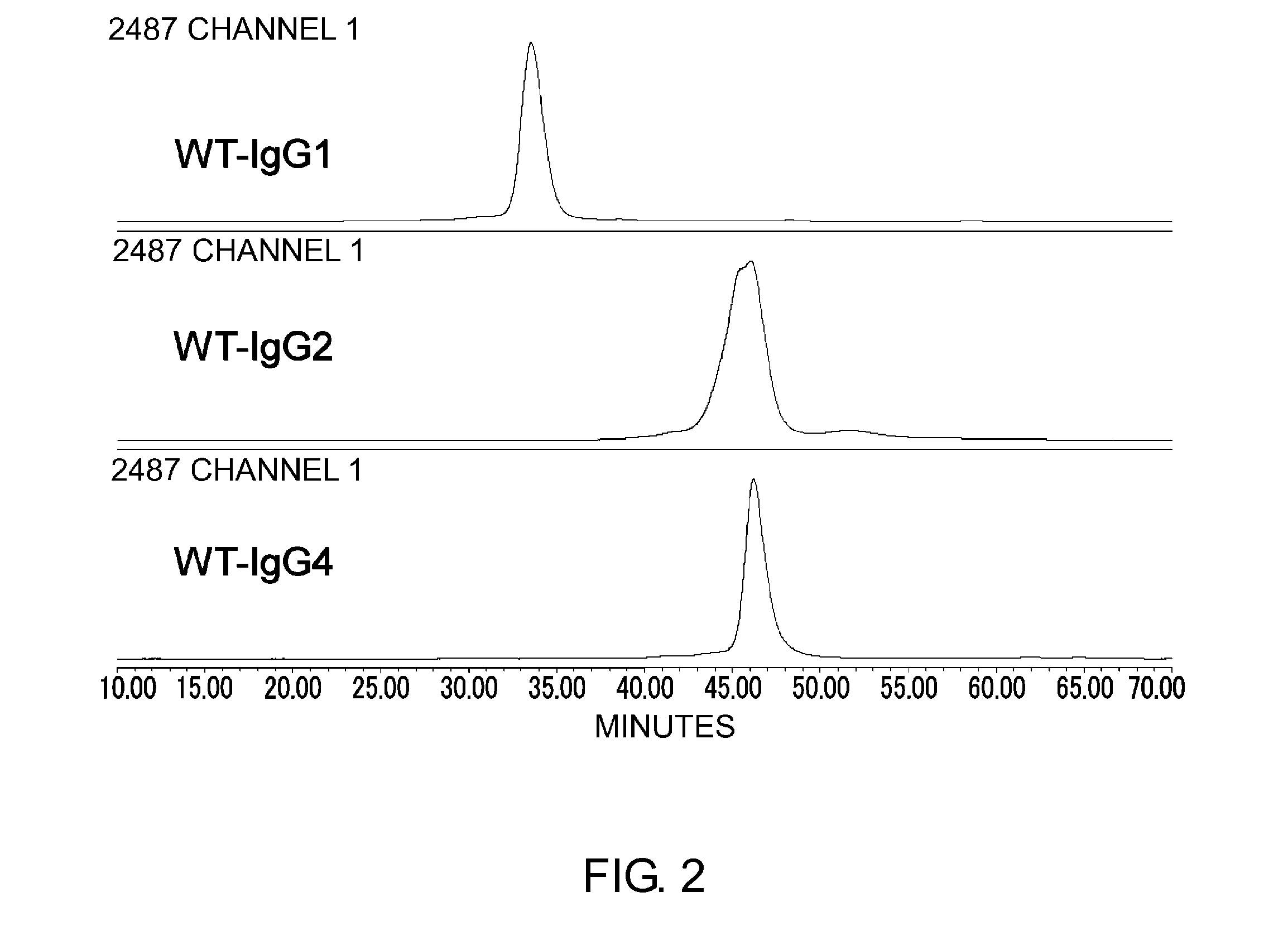
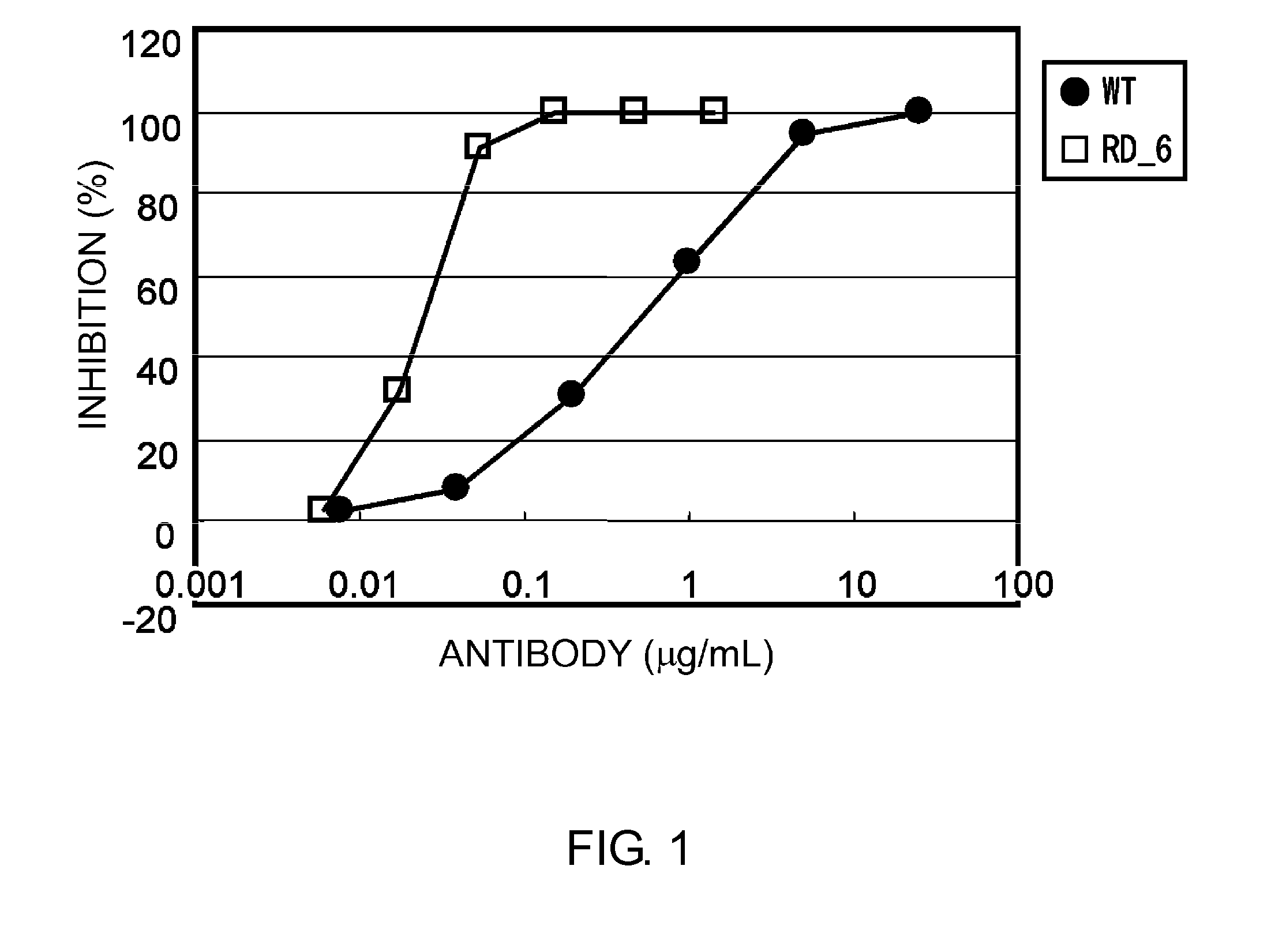
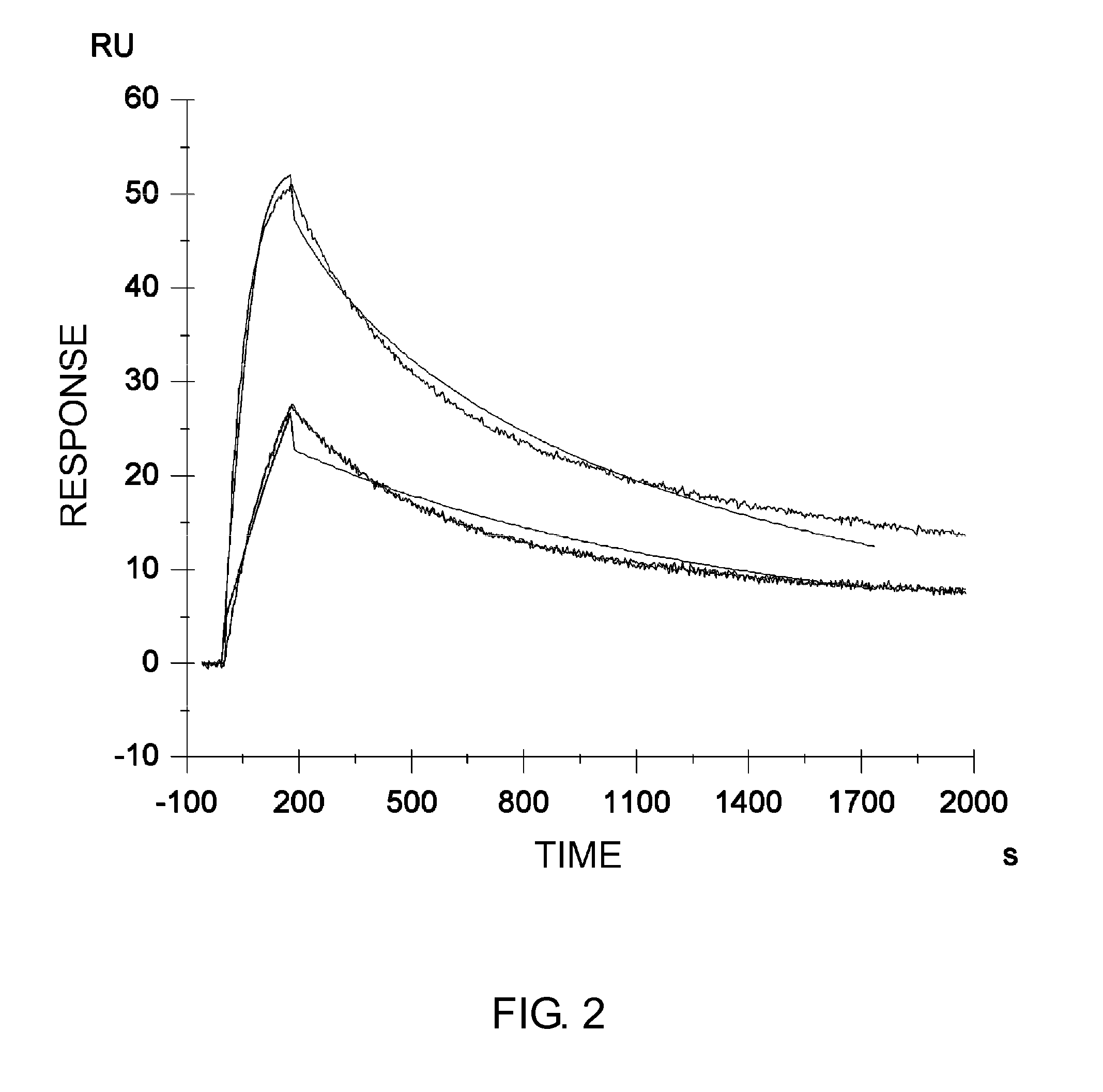
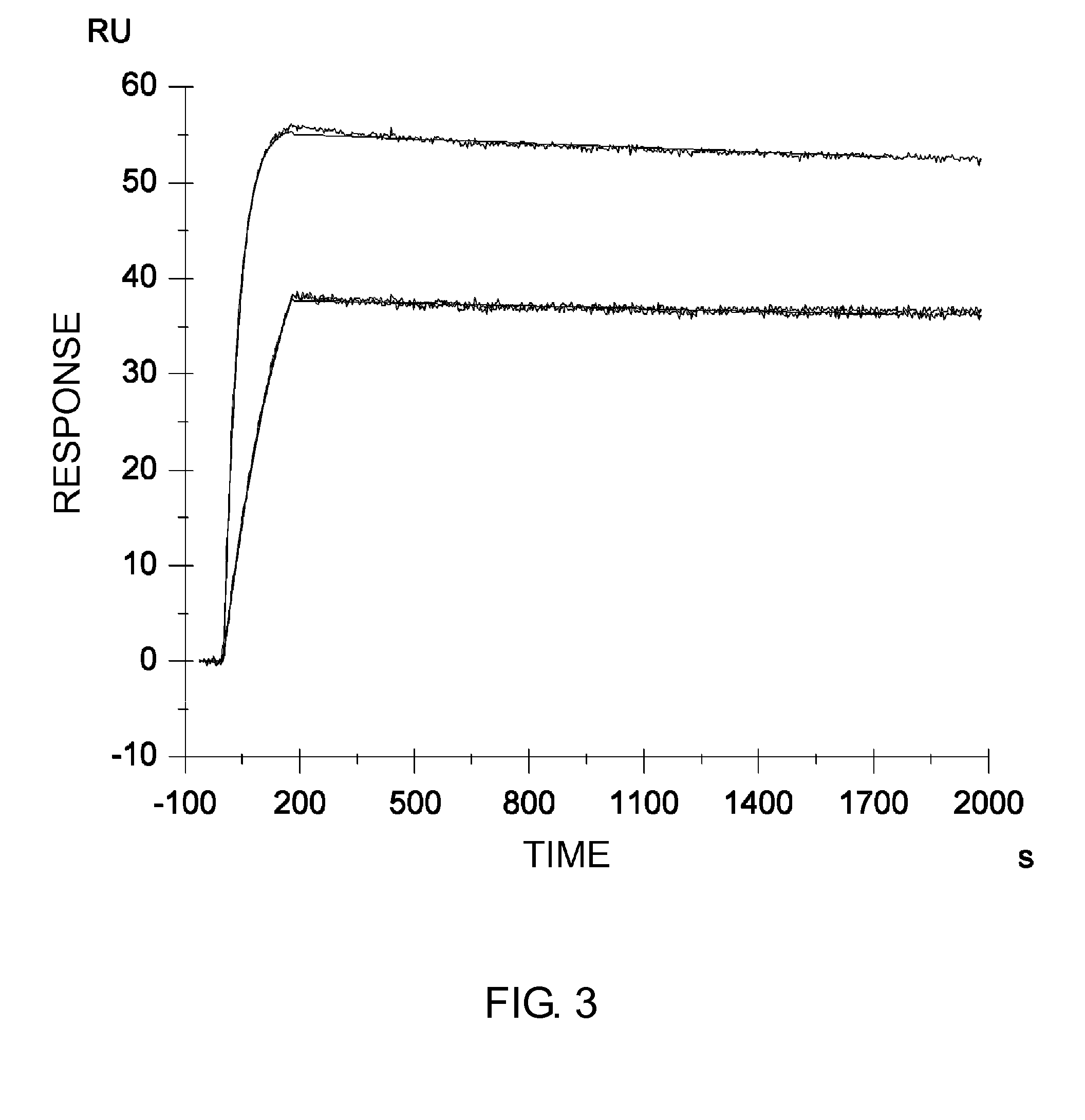
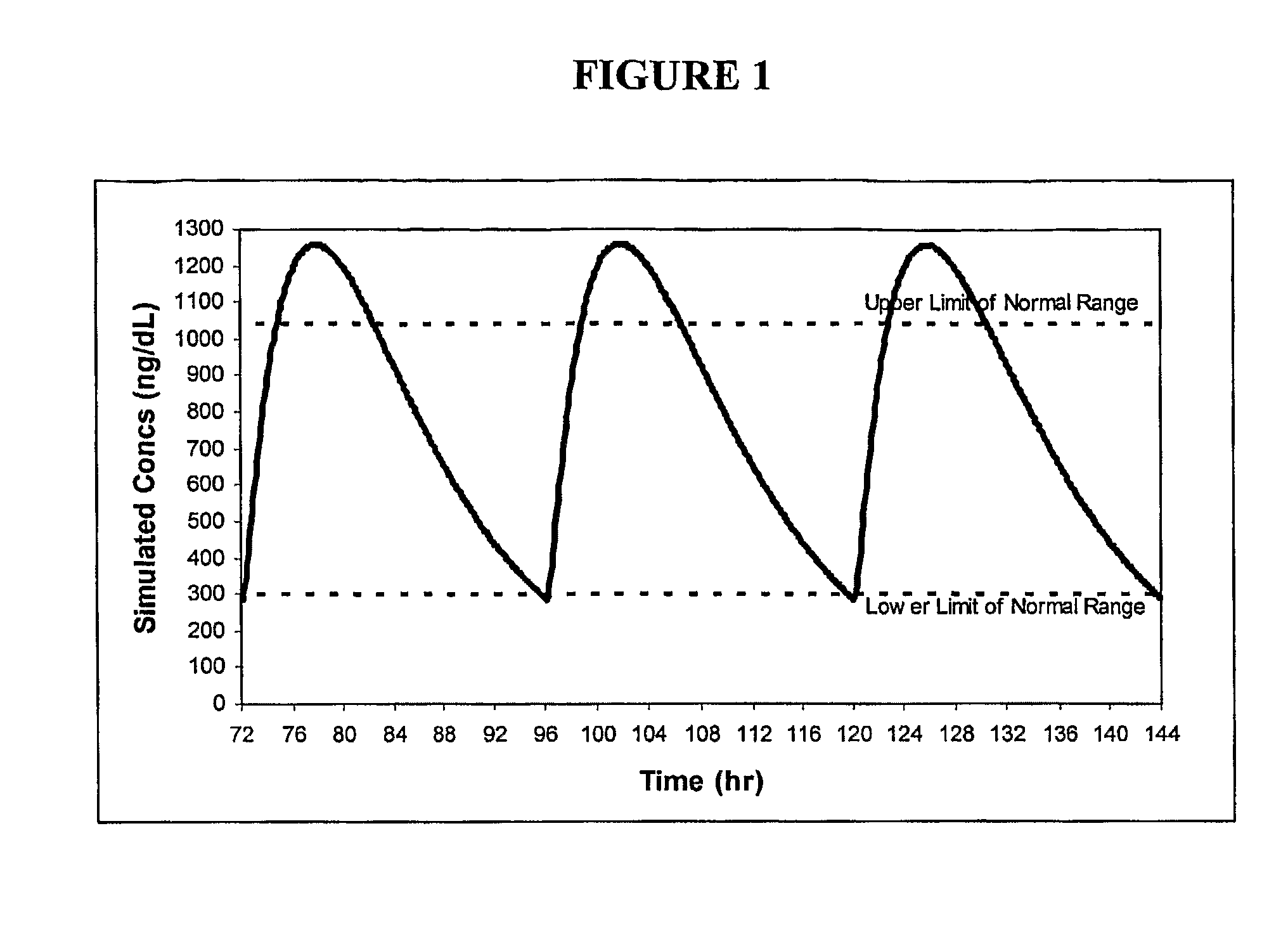
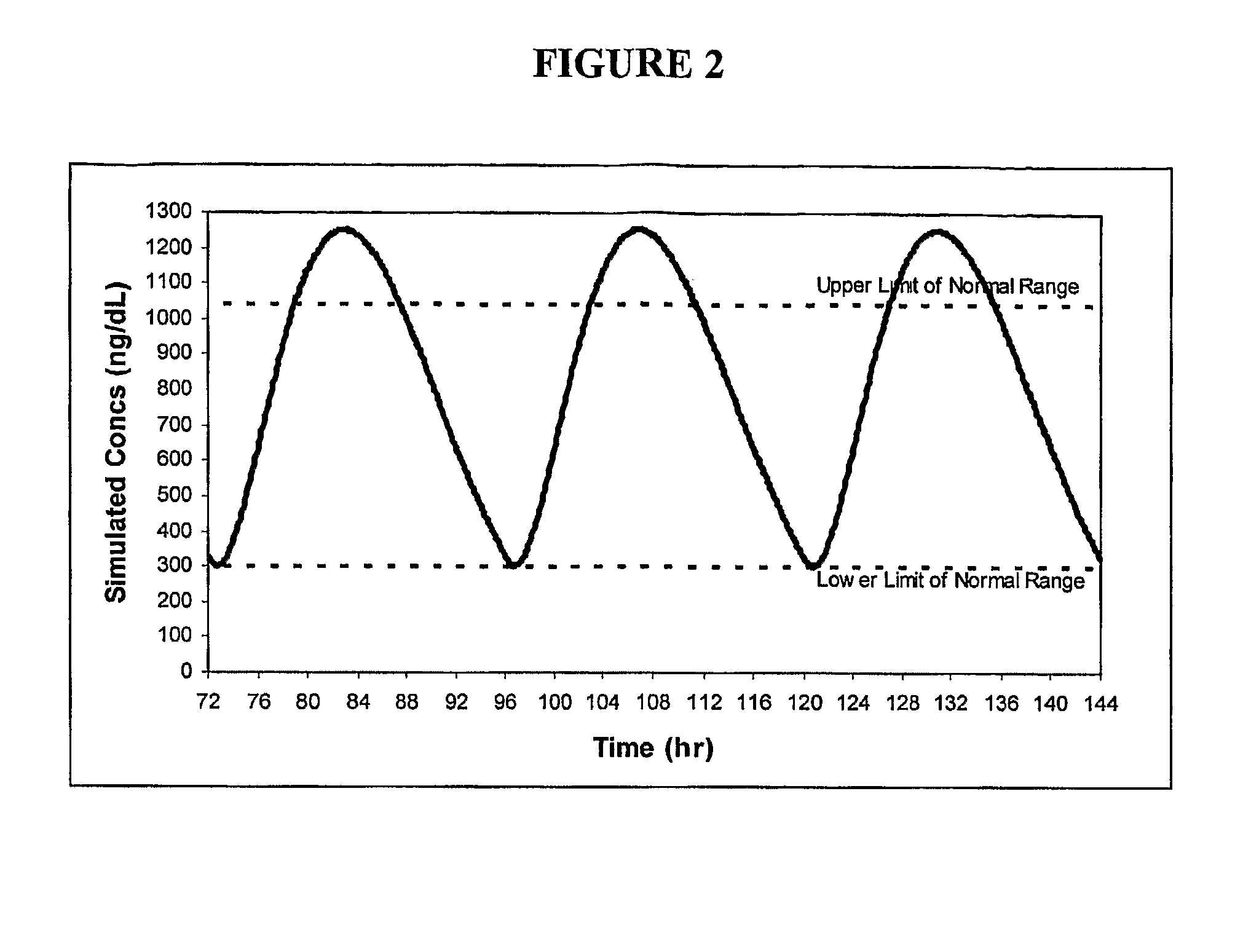
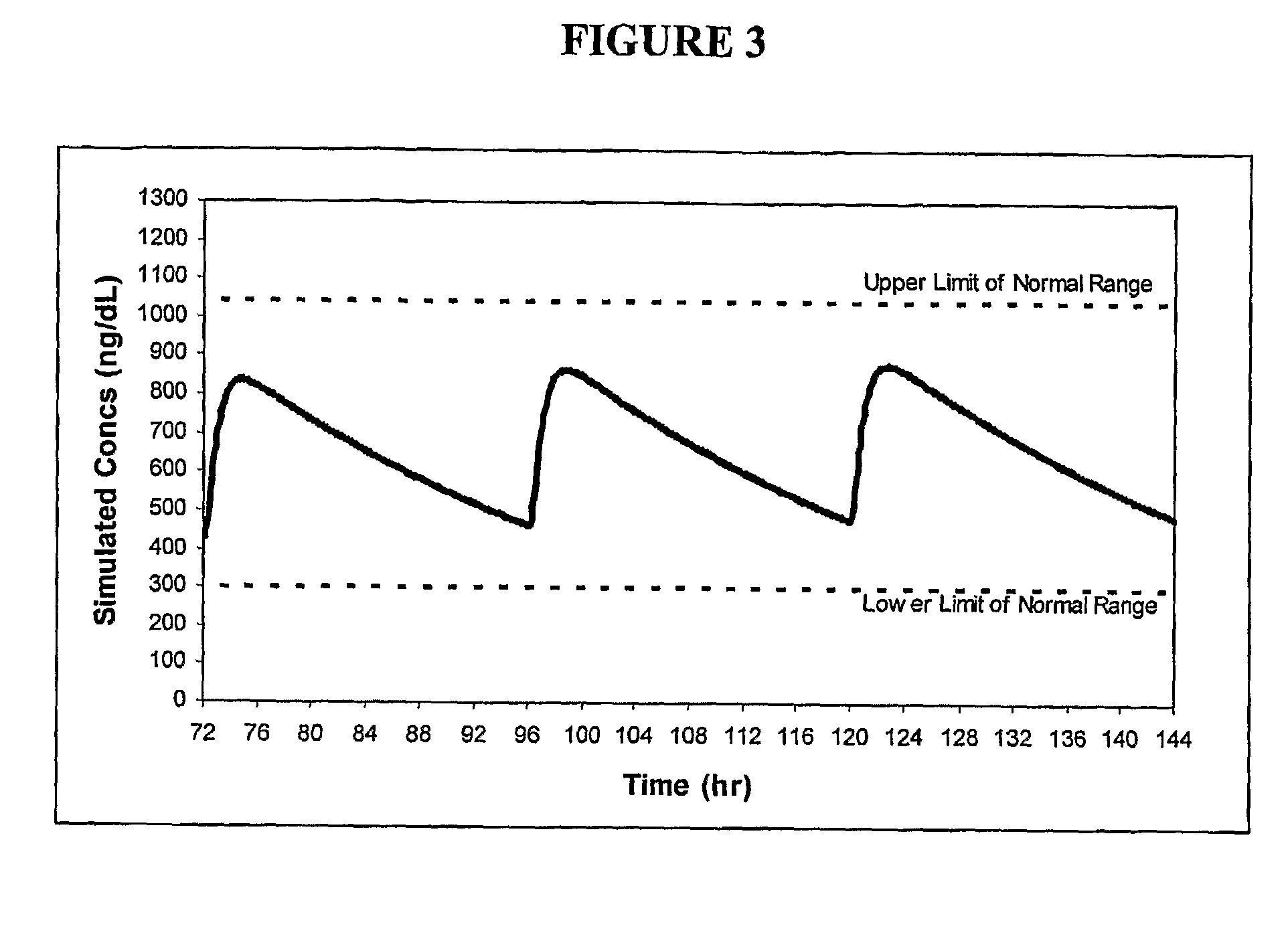
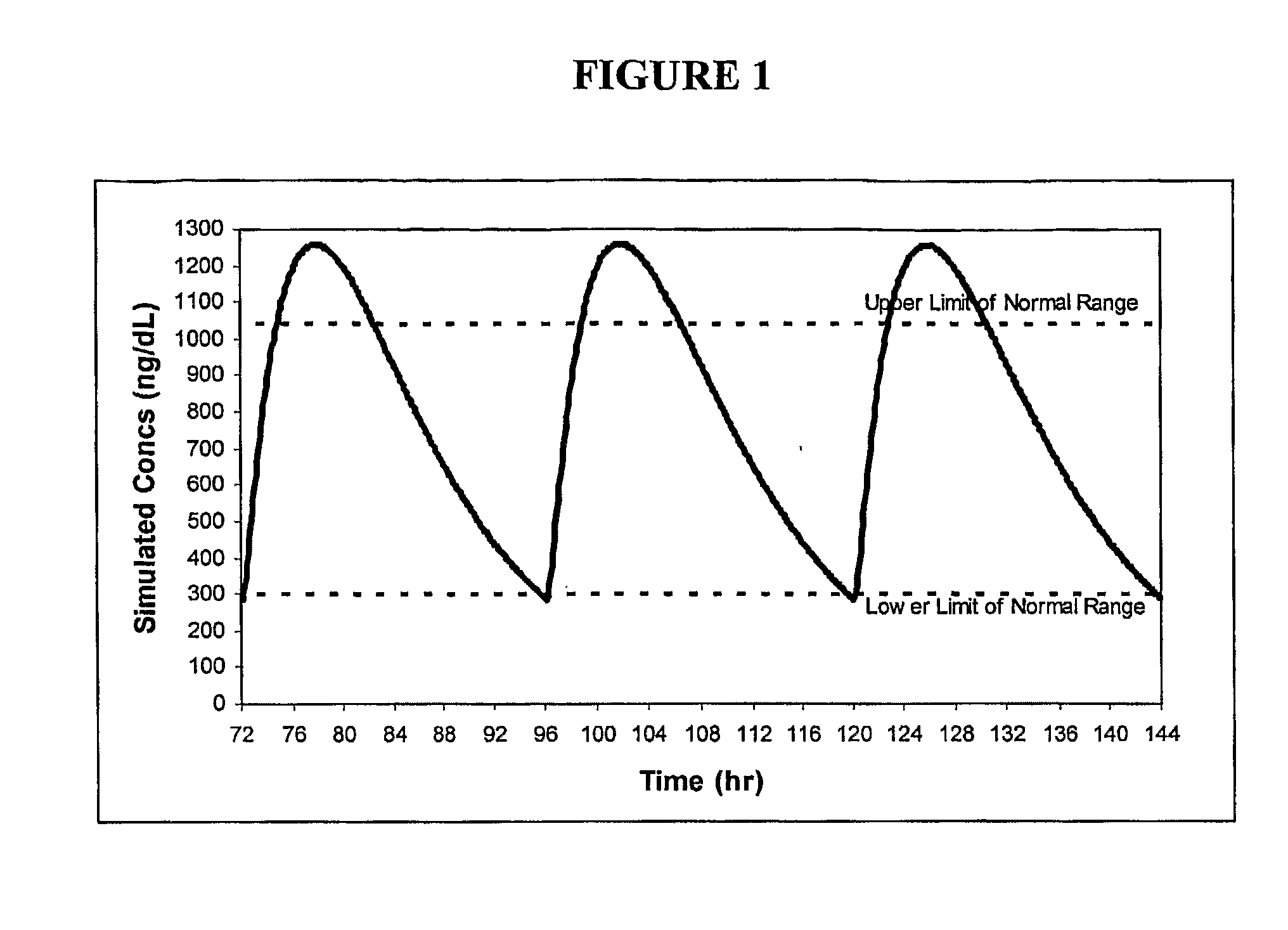
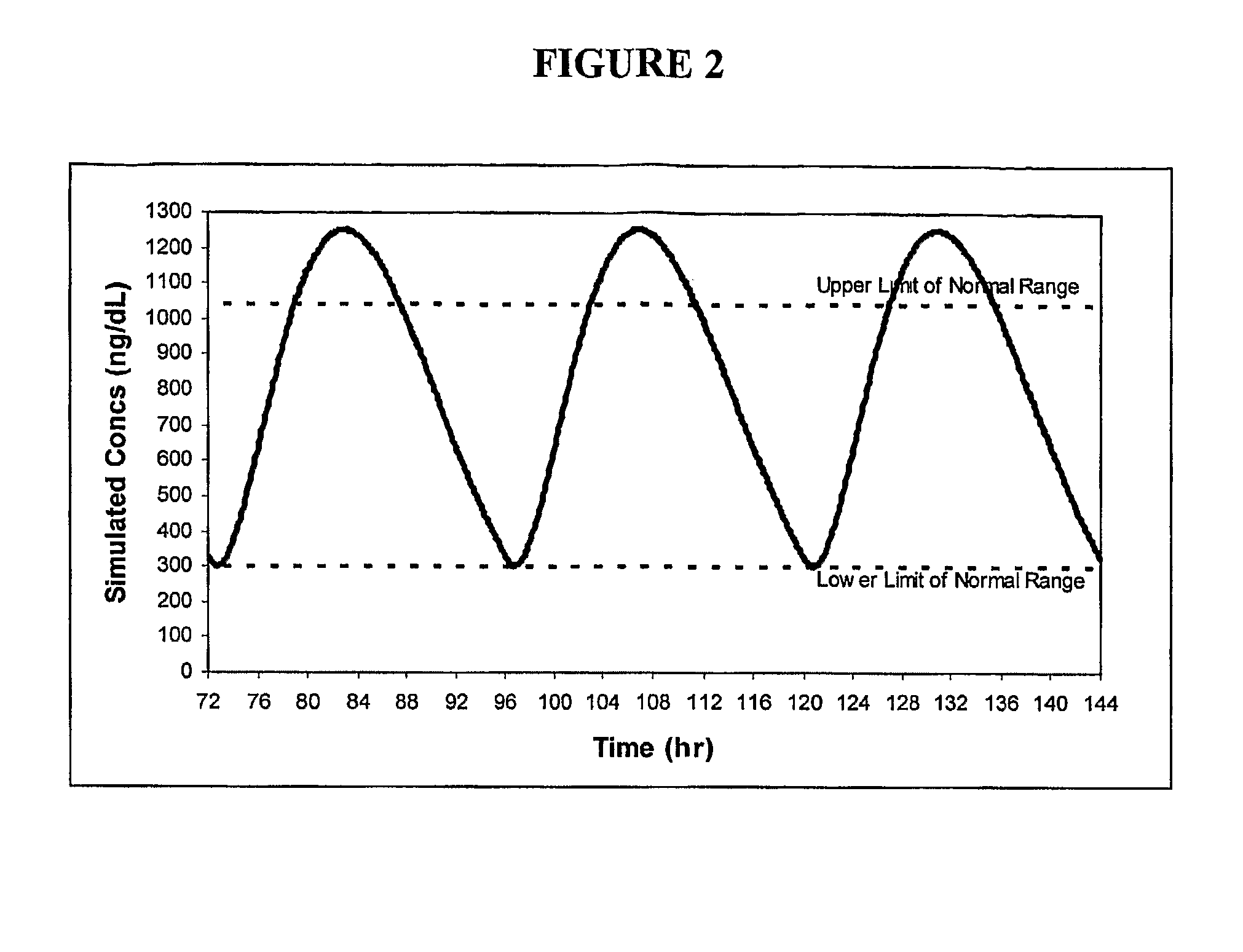
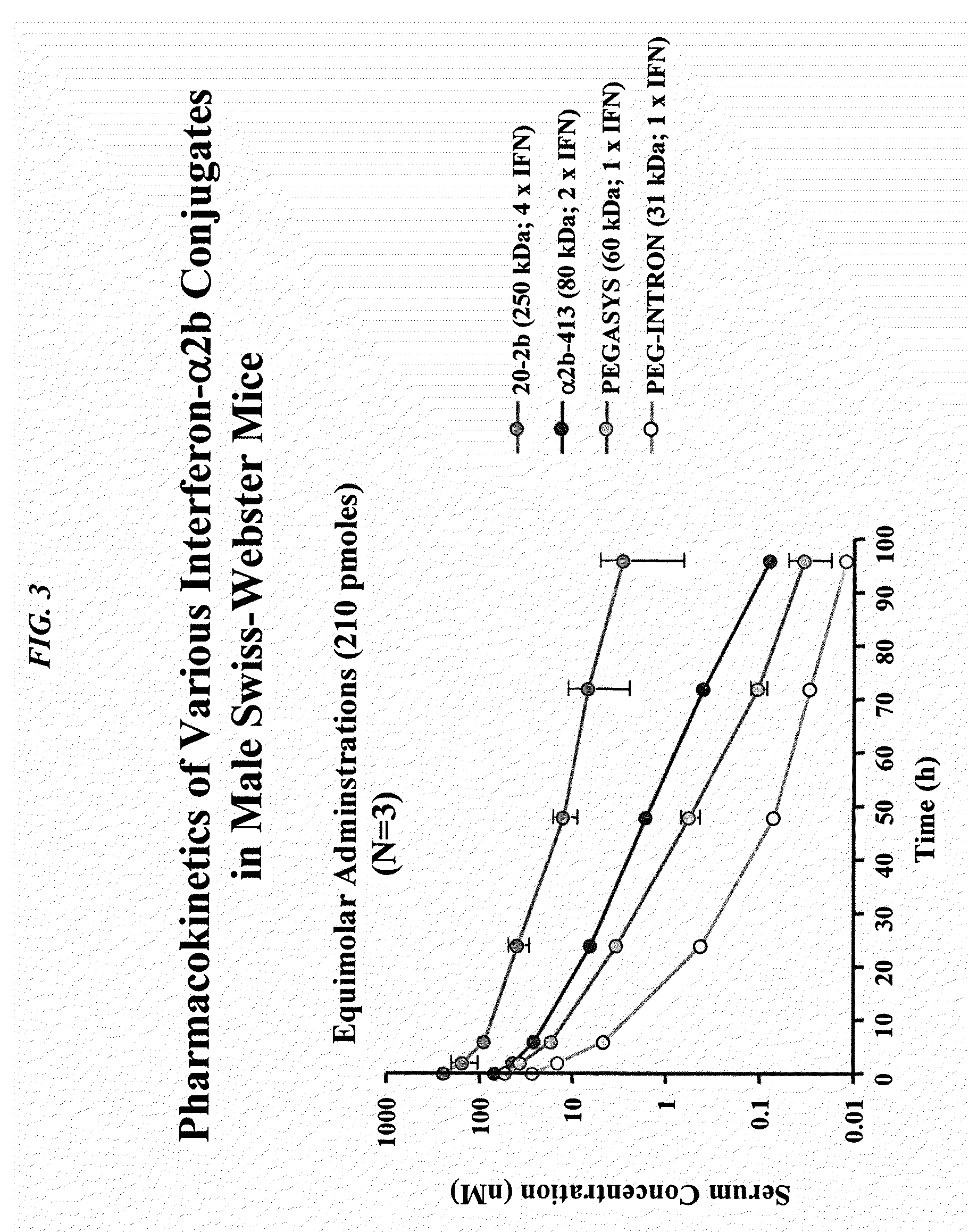
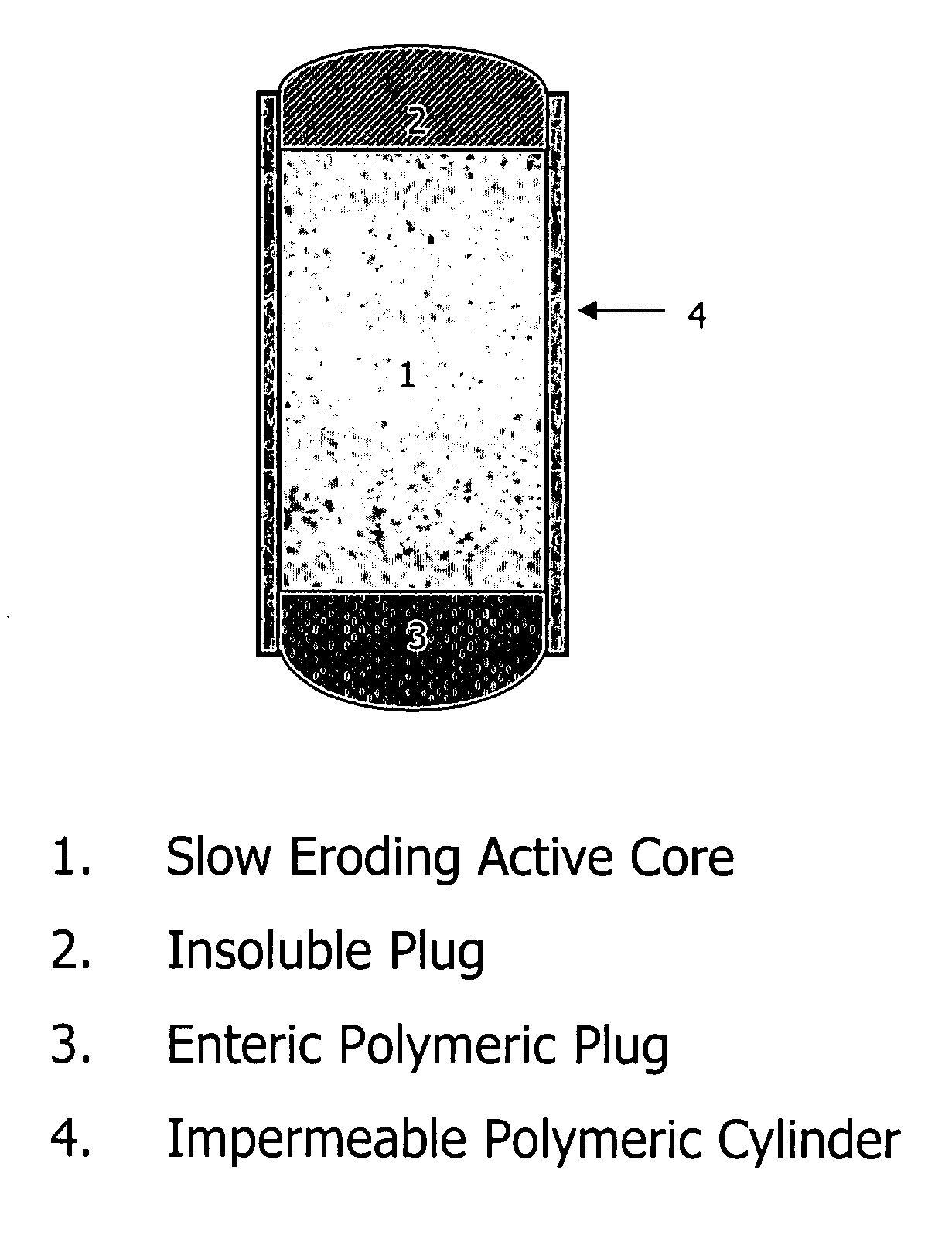
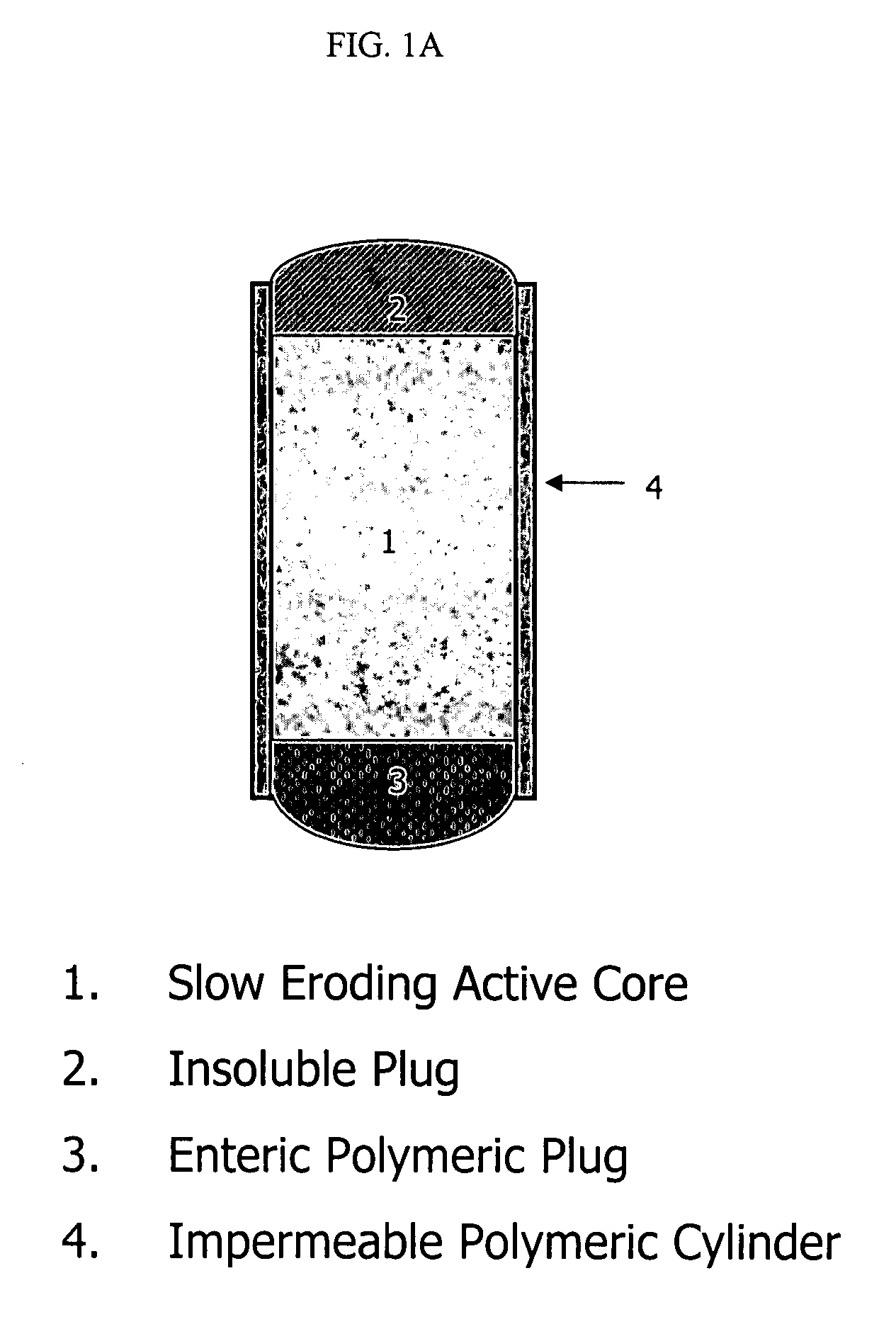
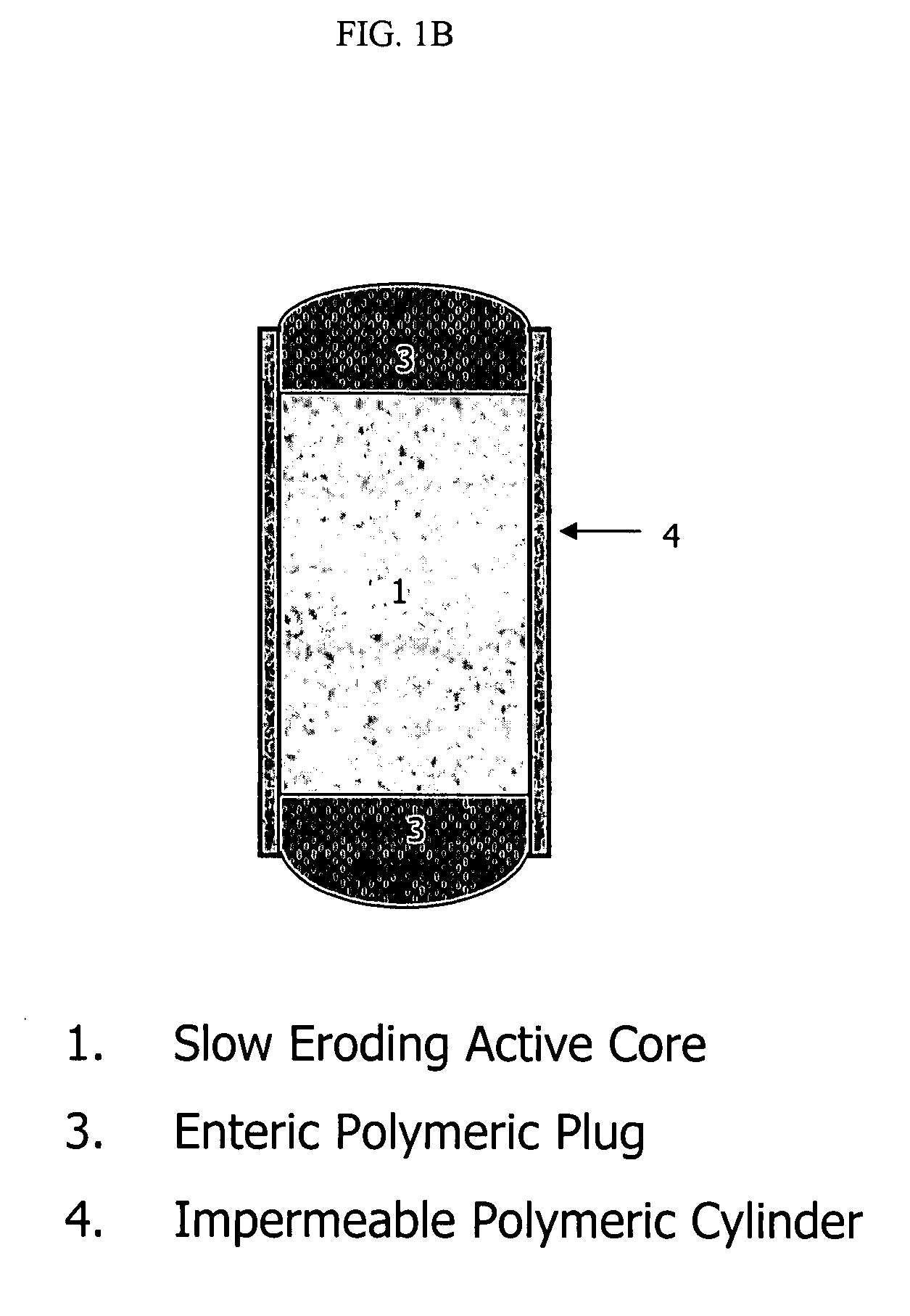
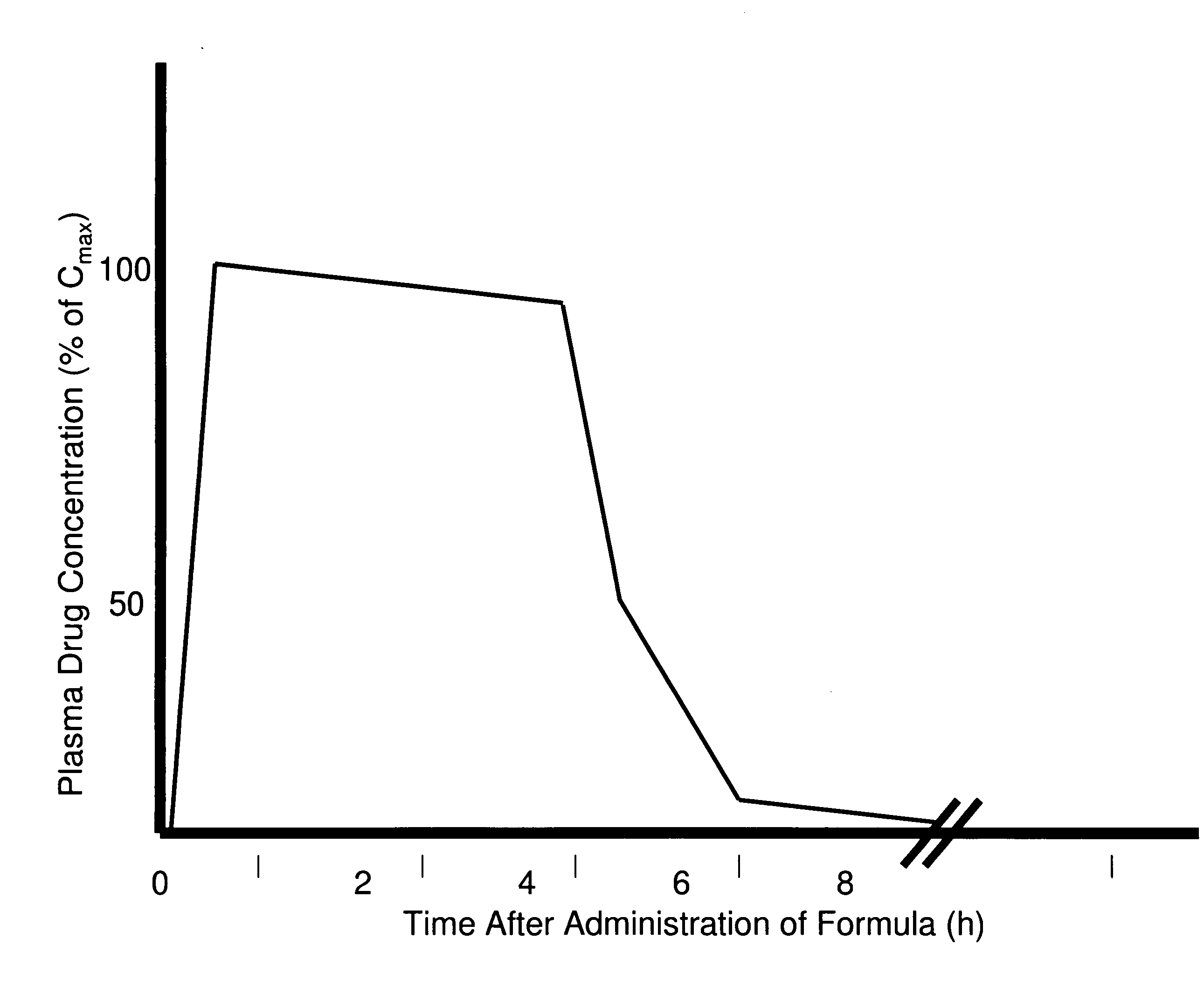
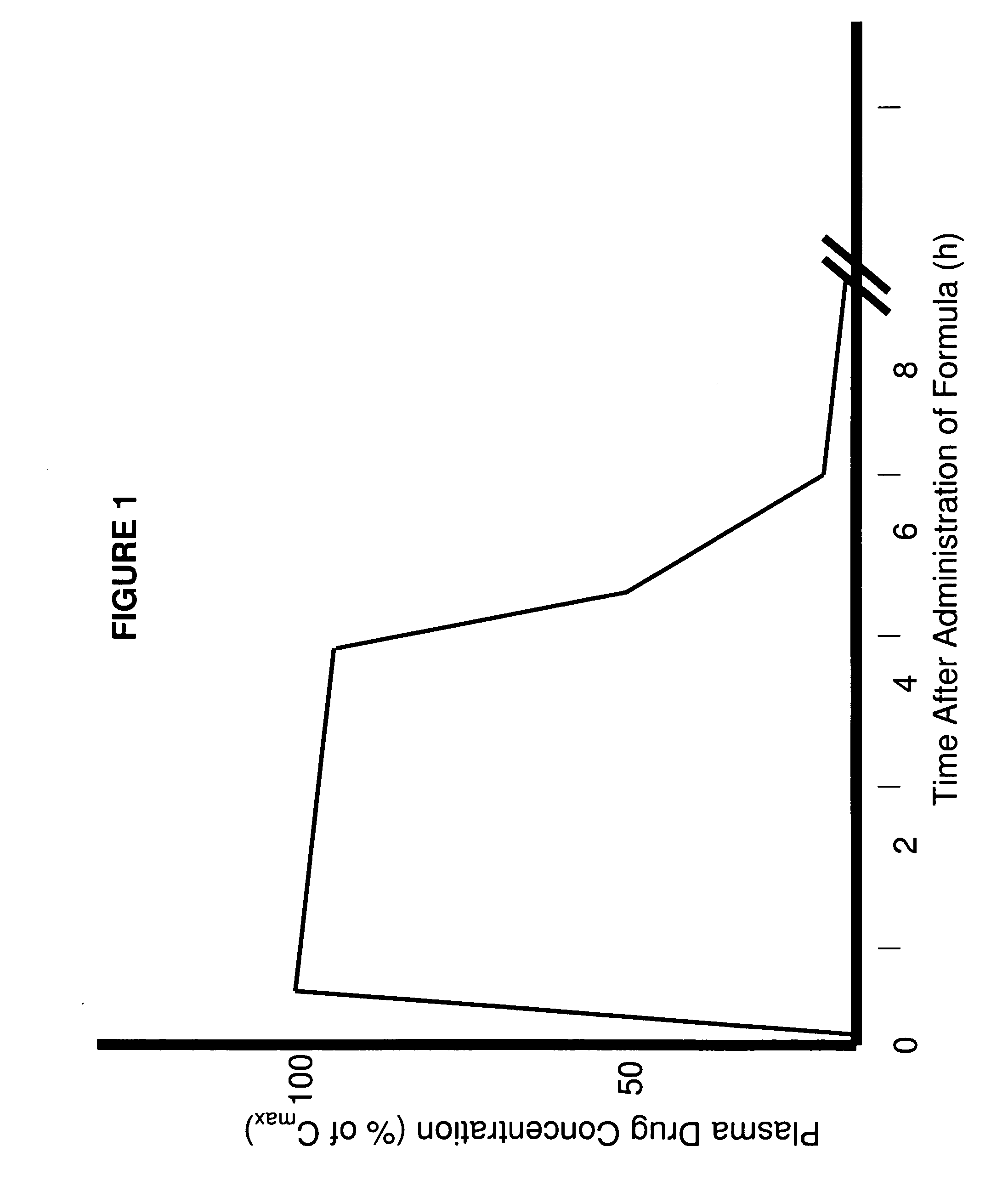
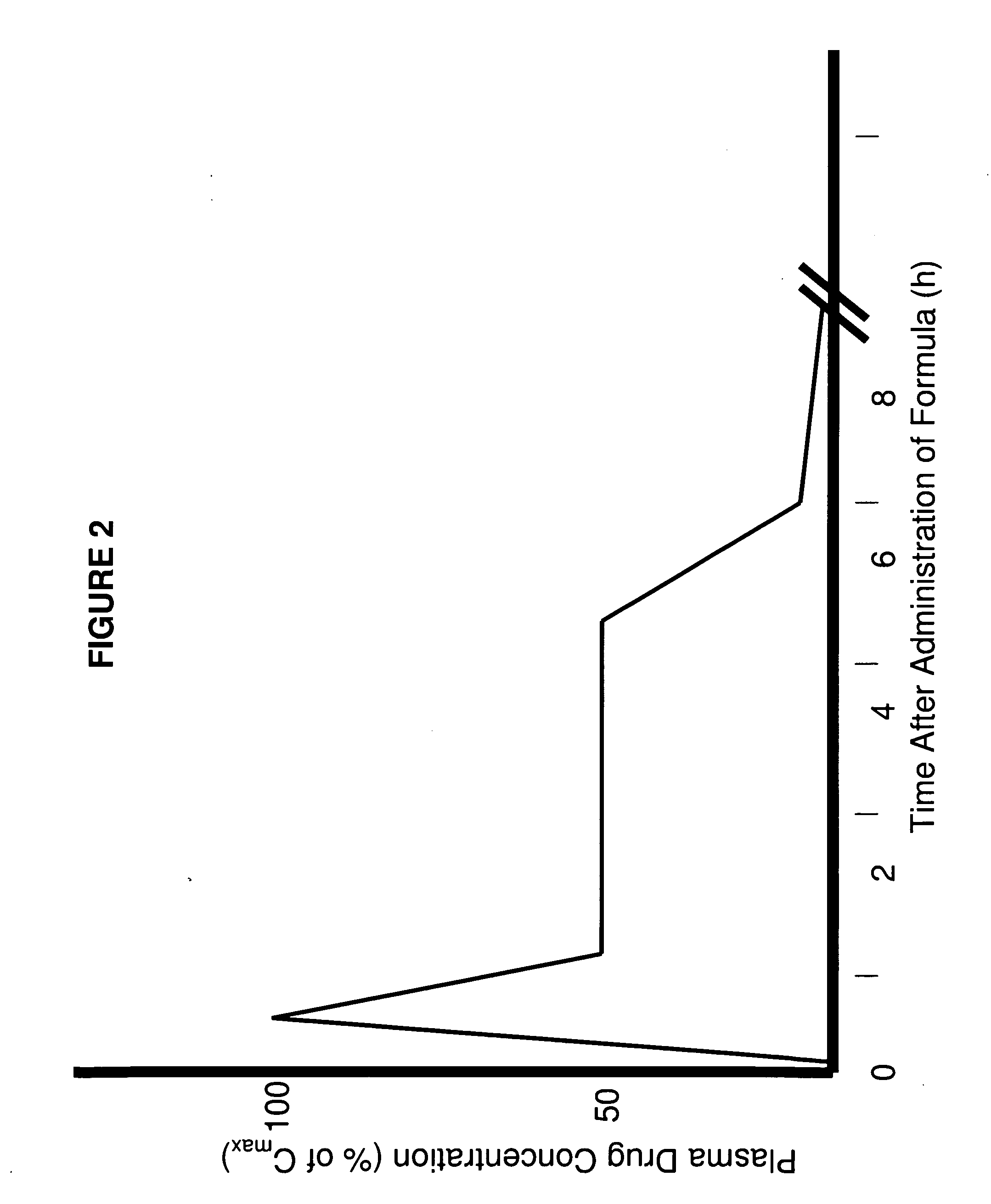
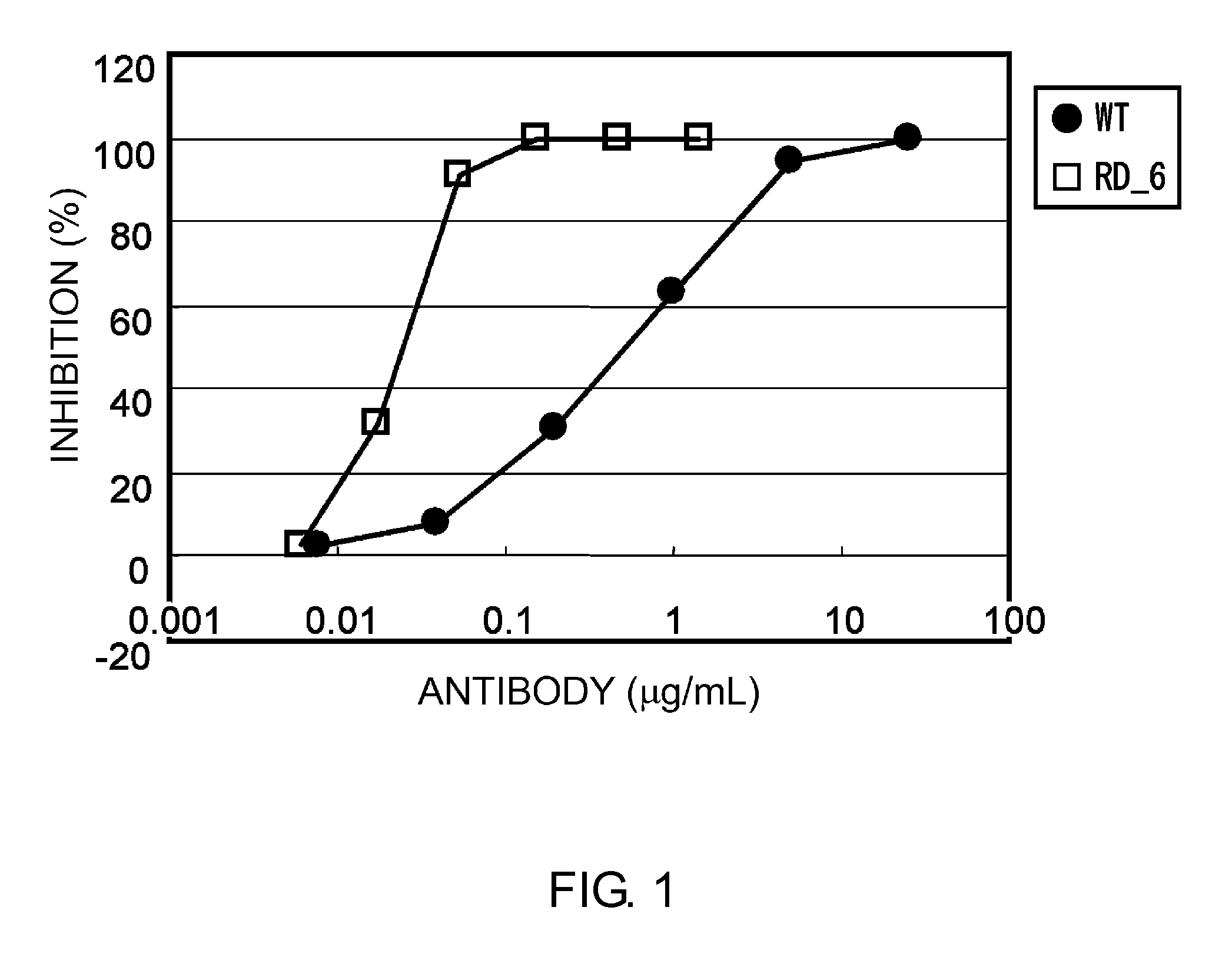
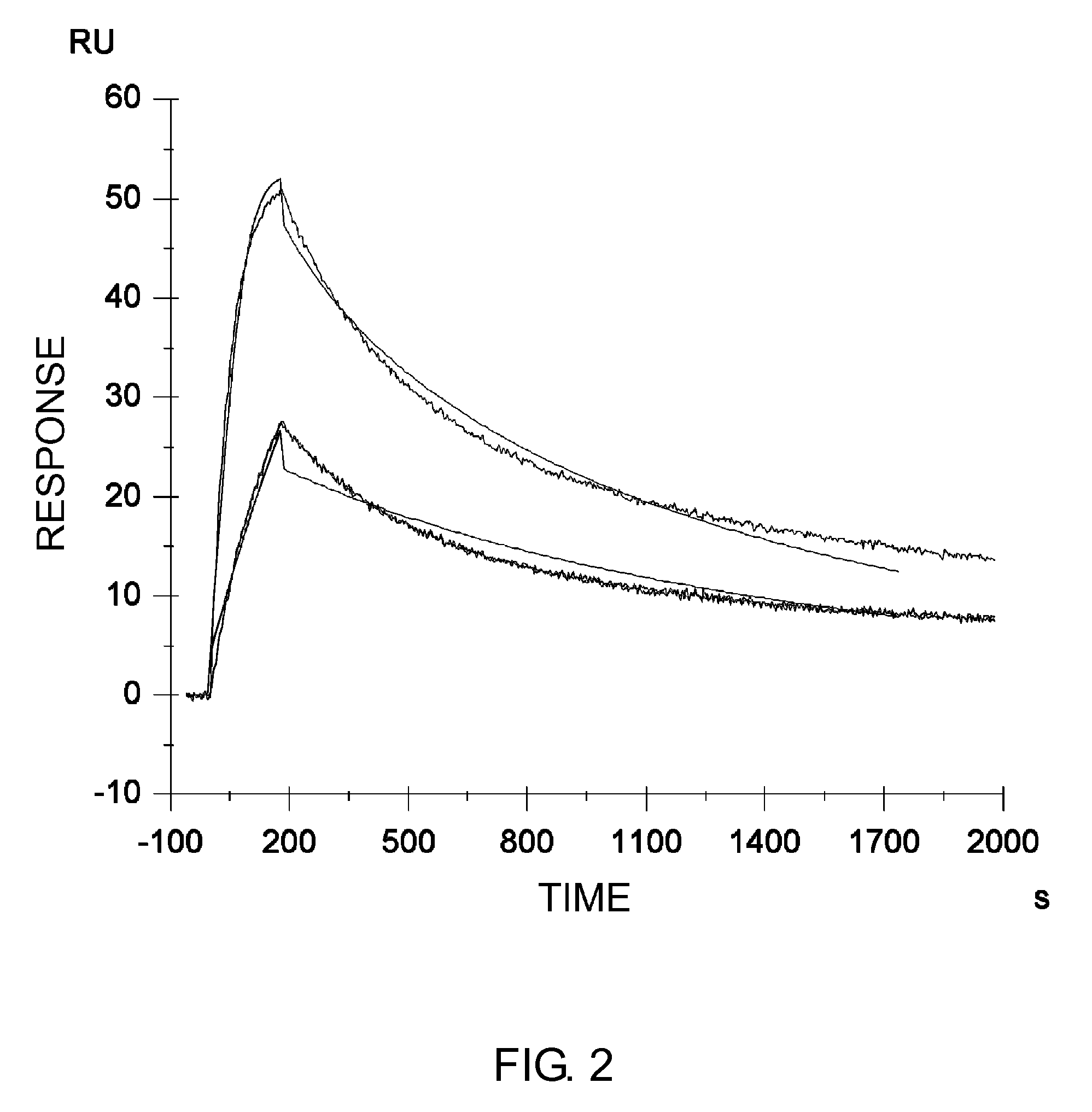
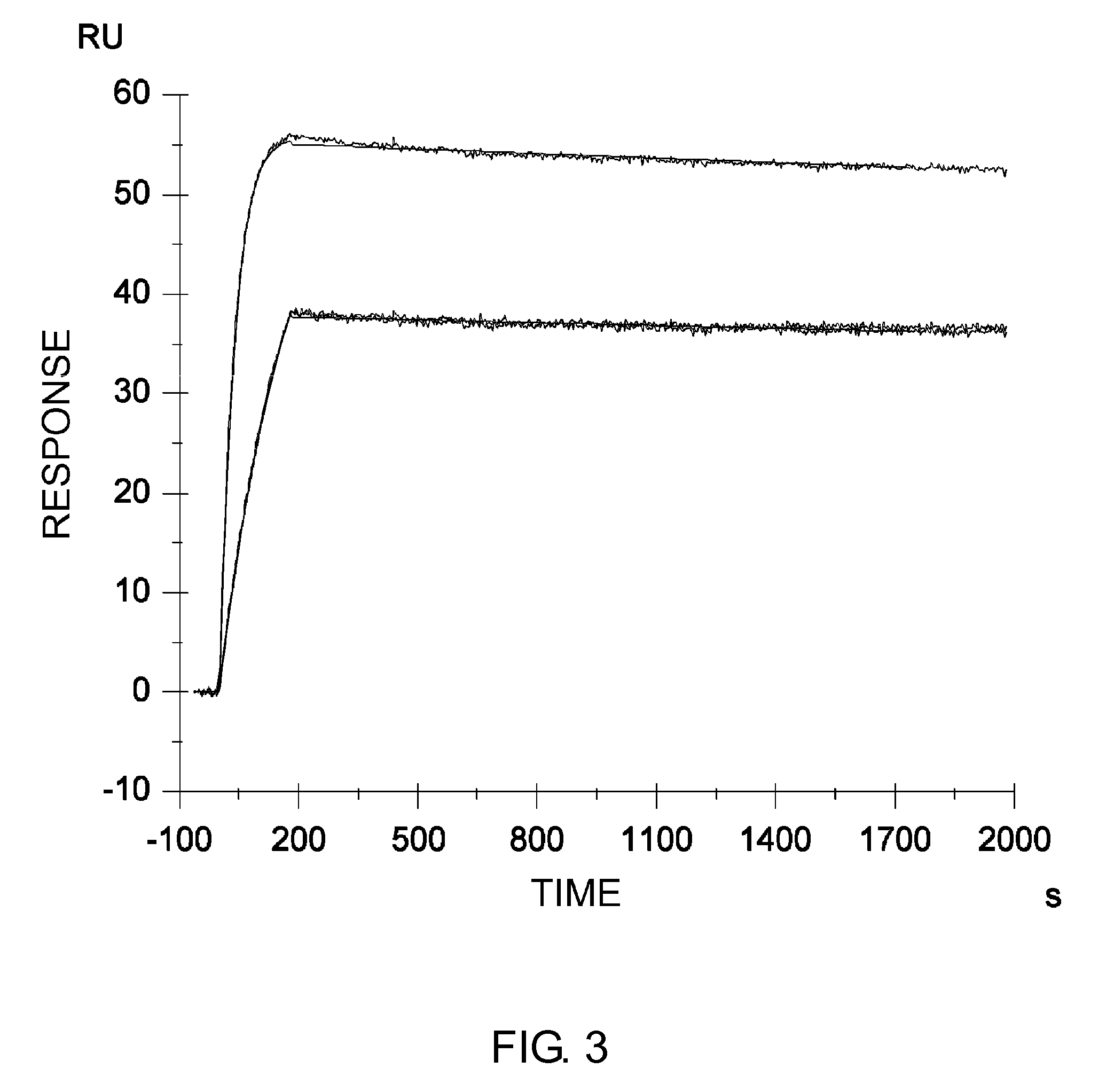
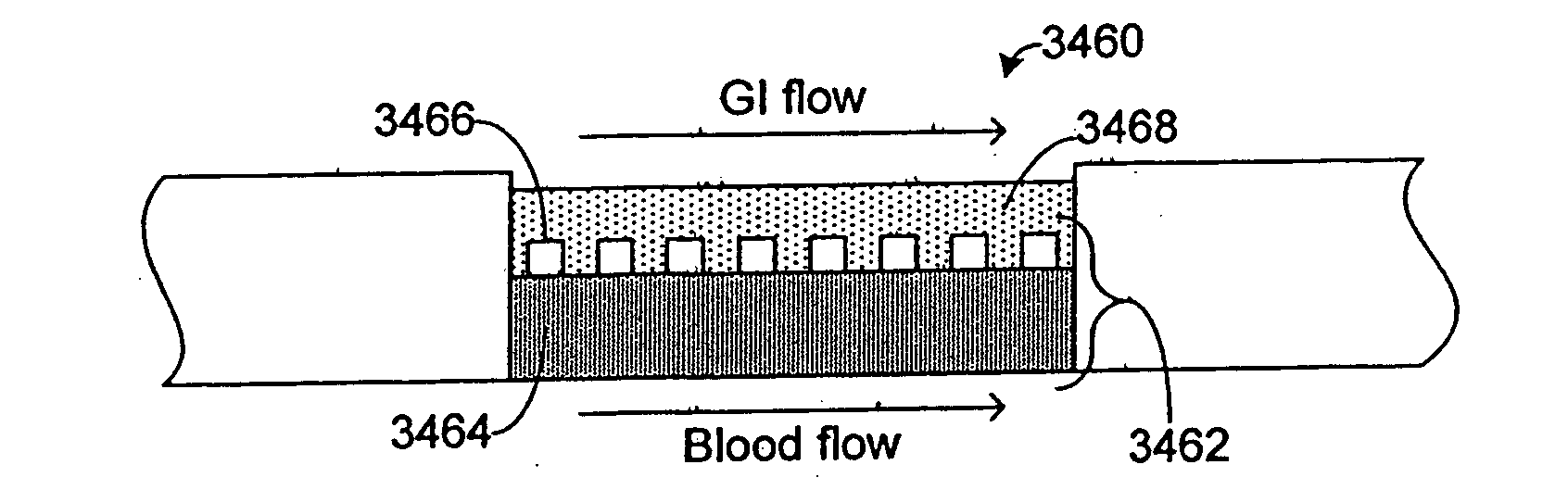
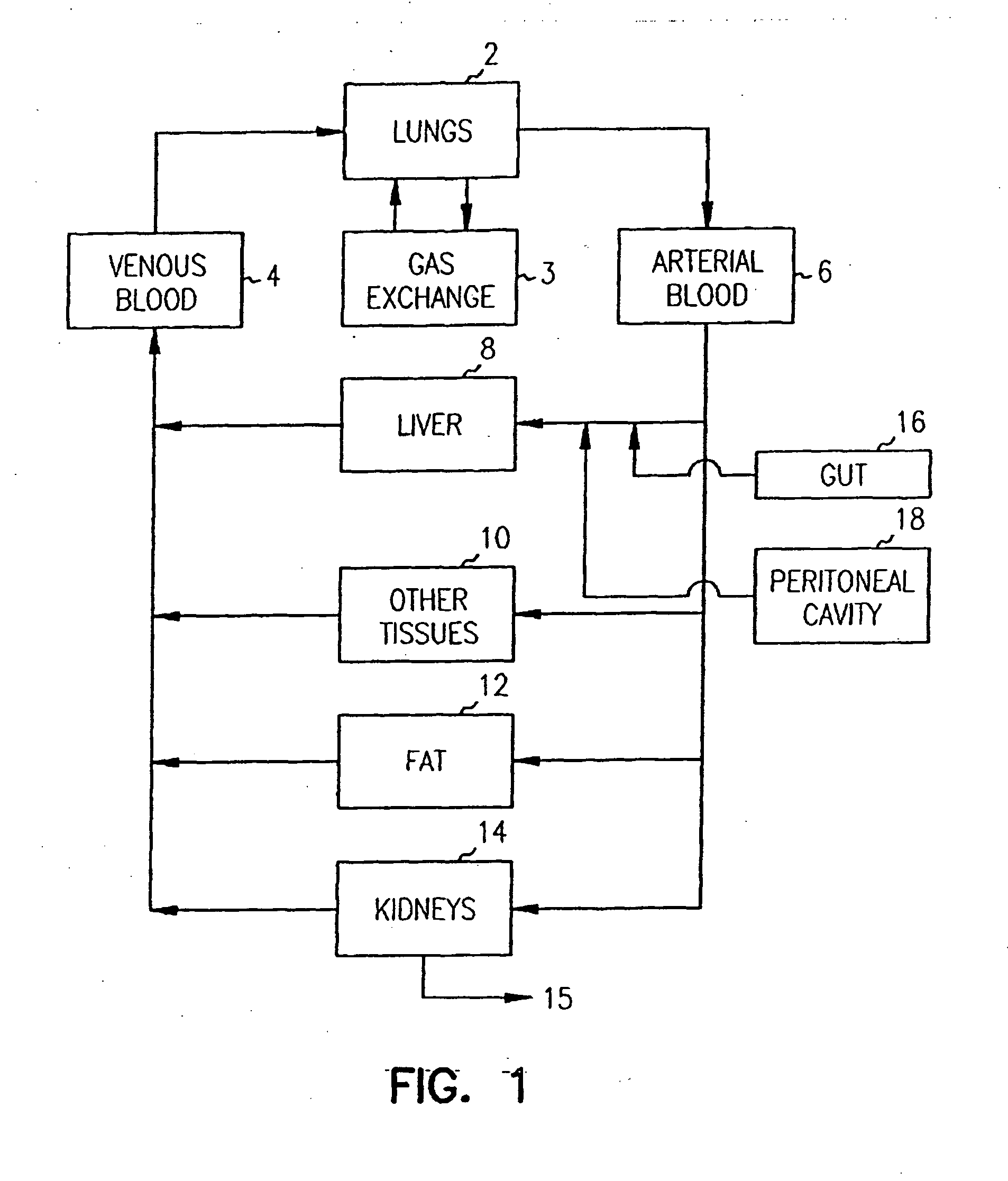
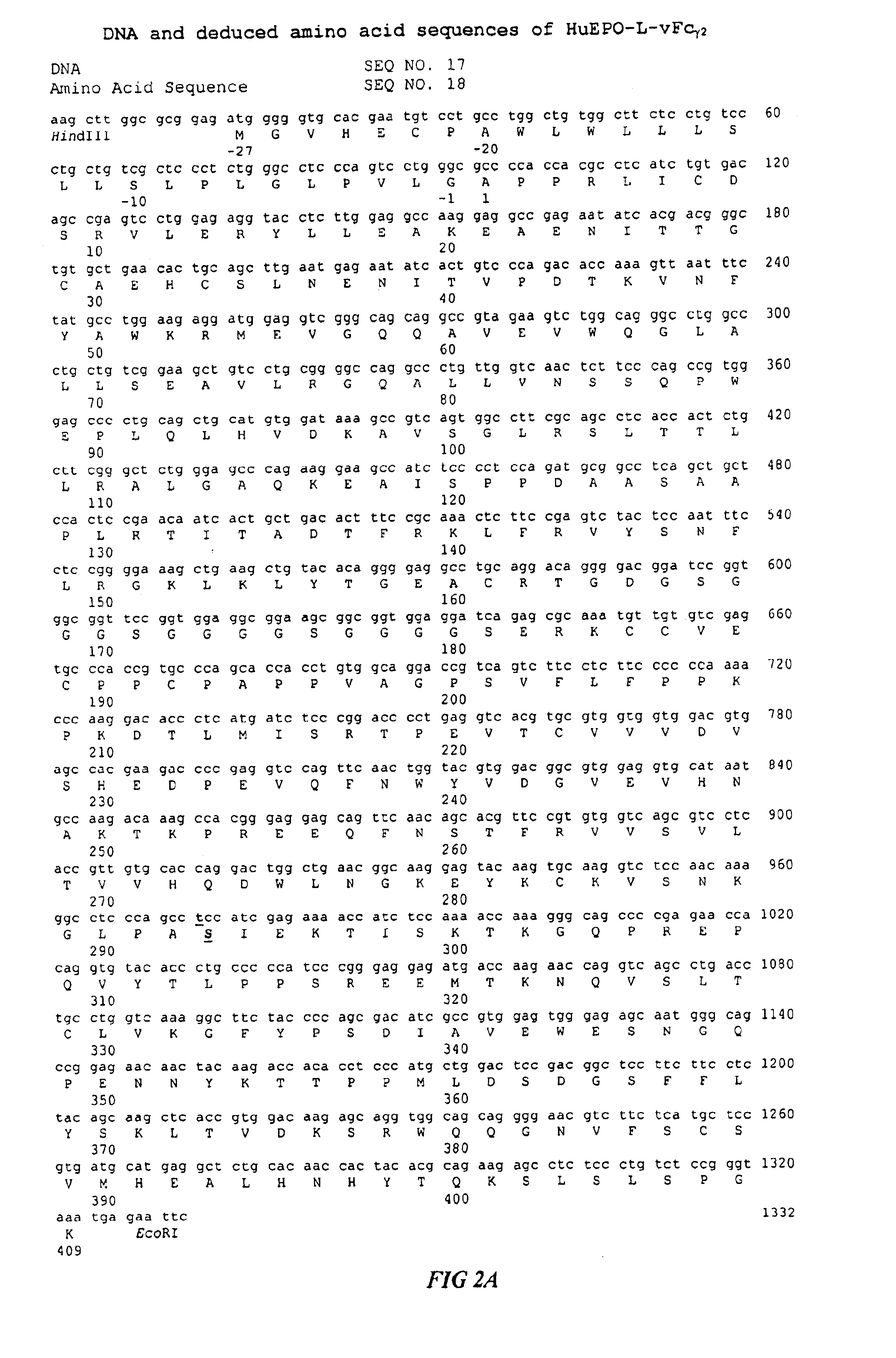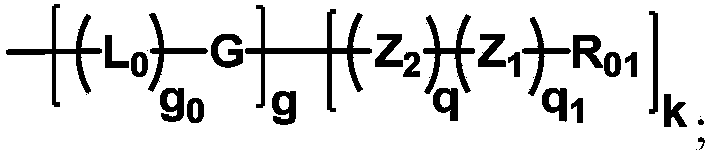Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
518 results about "Pharmacokinetic Concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
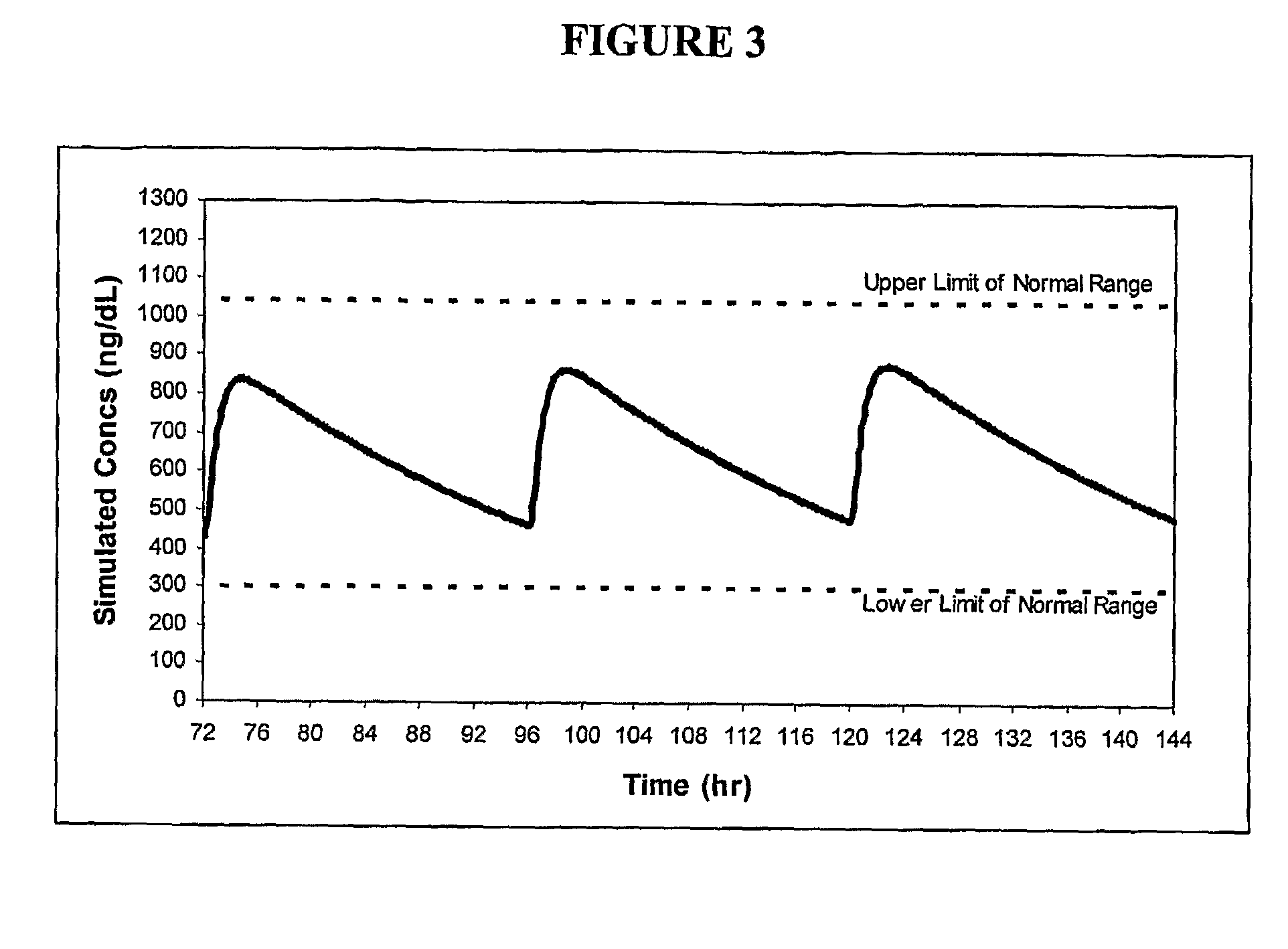
Pharmacokinetics is a branch of pharmacology which studies what the body does to a drug. Pharmacokinetics looks at how a substance enters, moves through and exits the body. It relates how the dose delivered affects the concentration within the body.
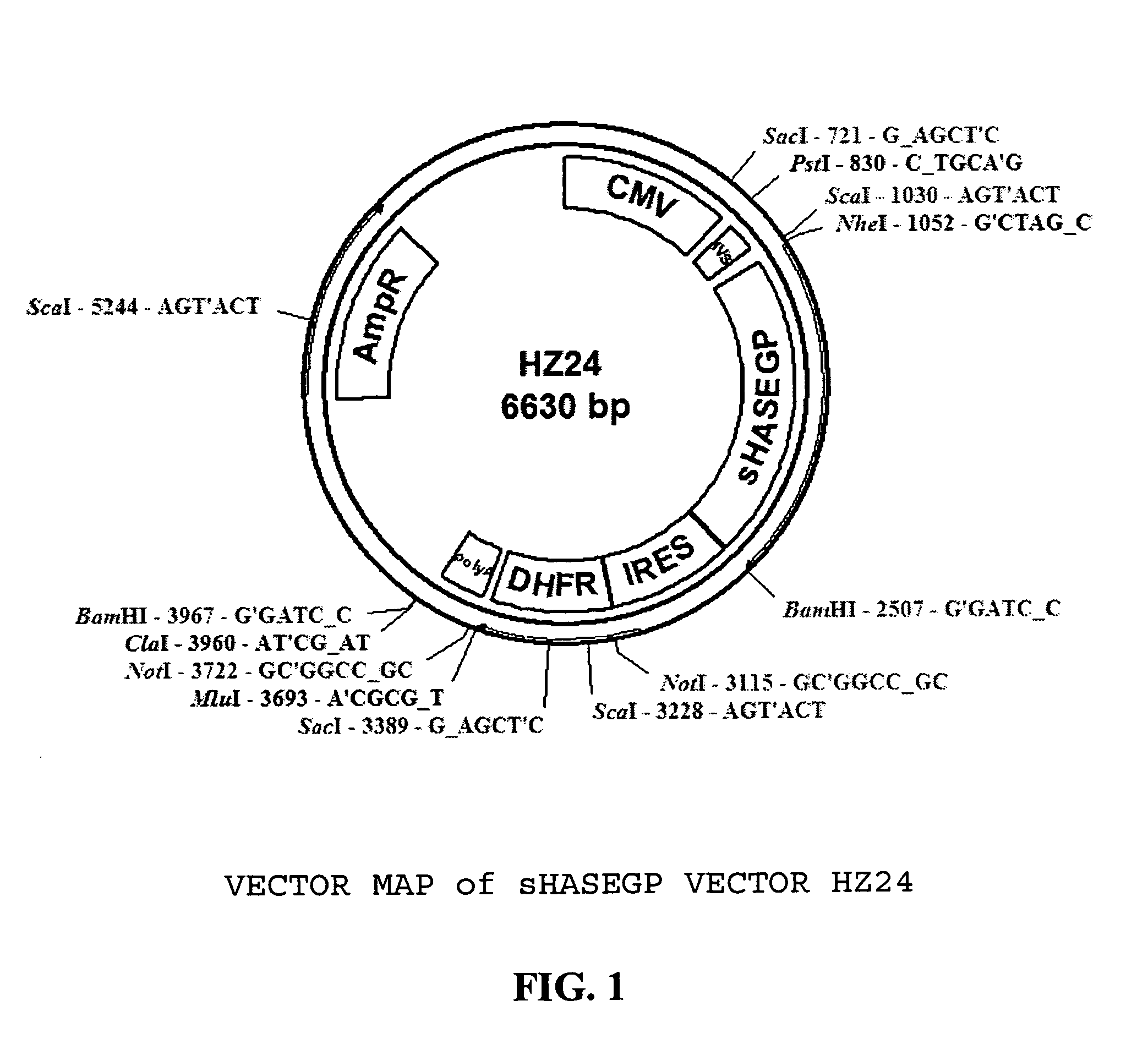
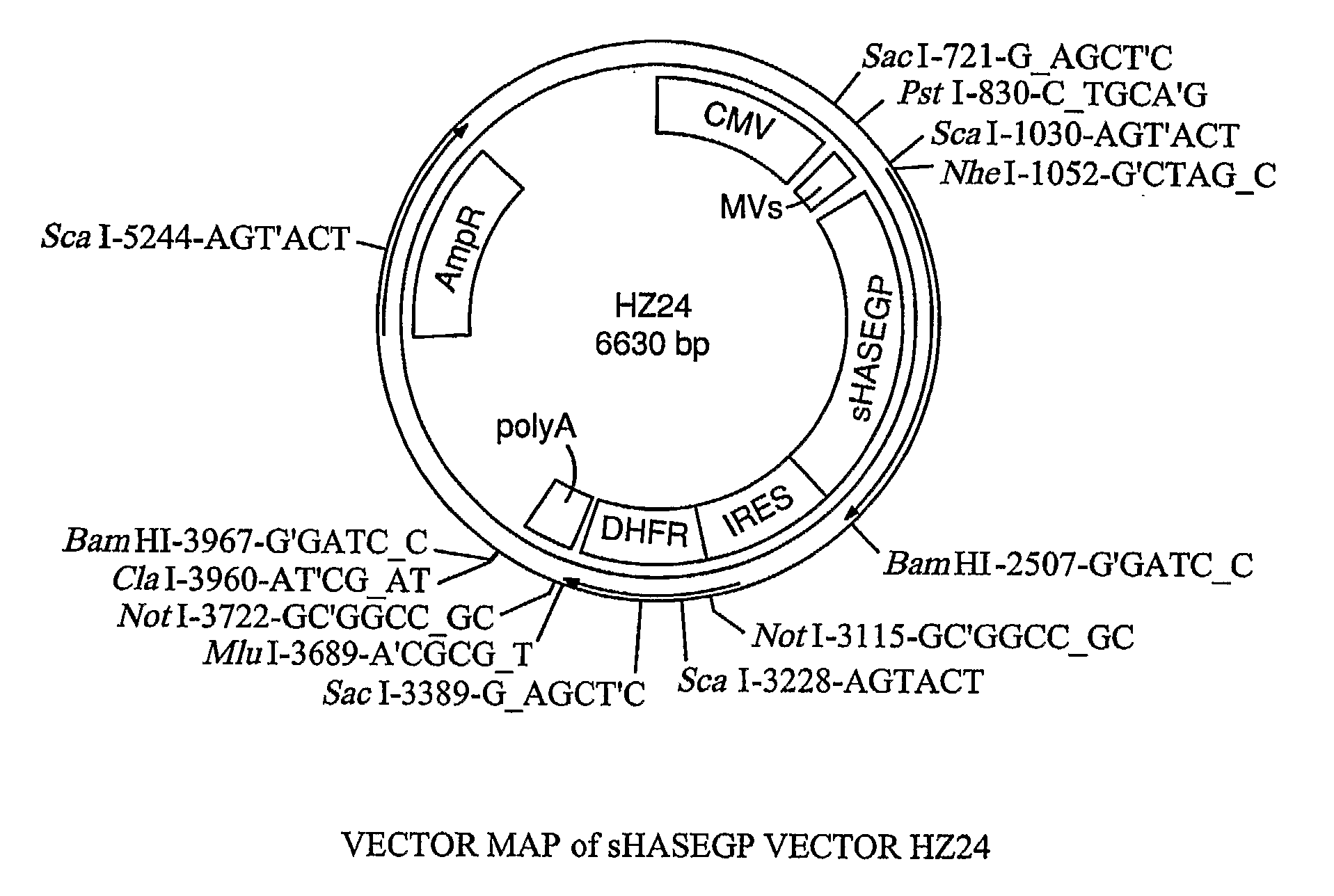
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
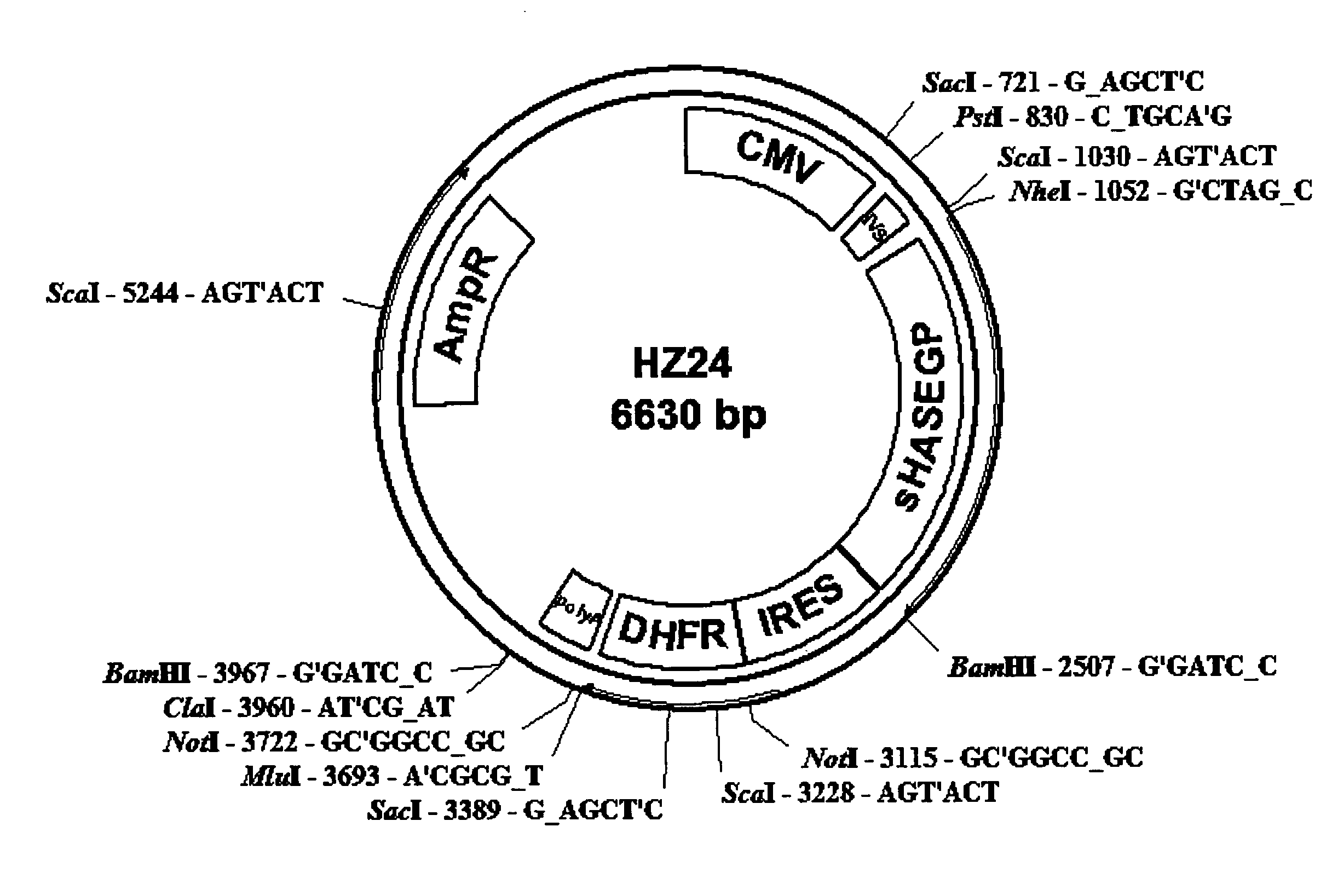
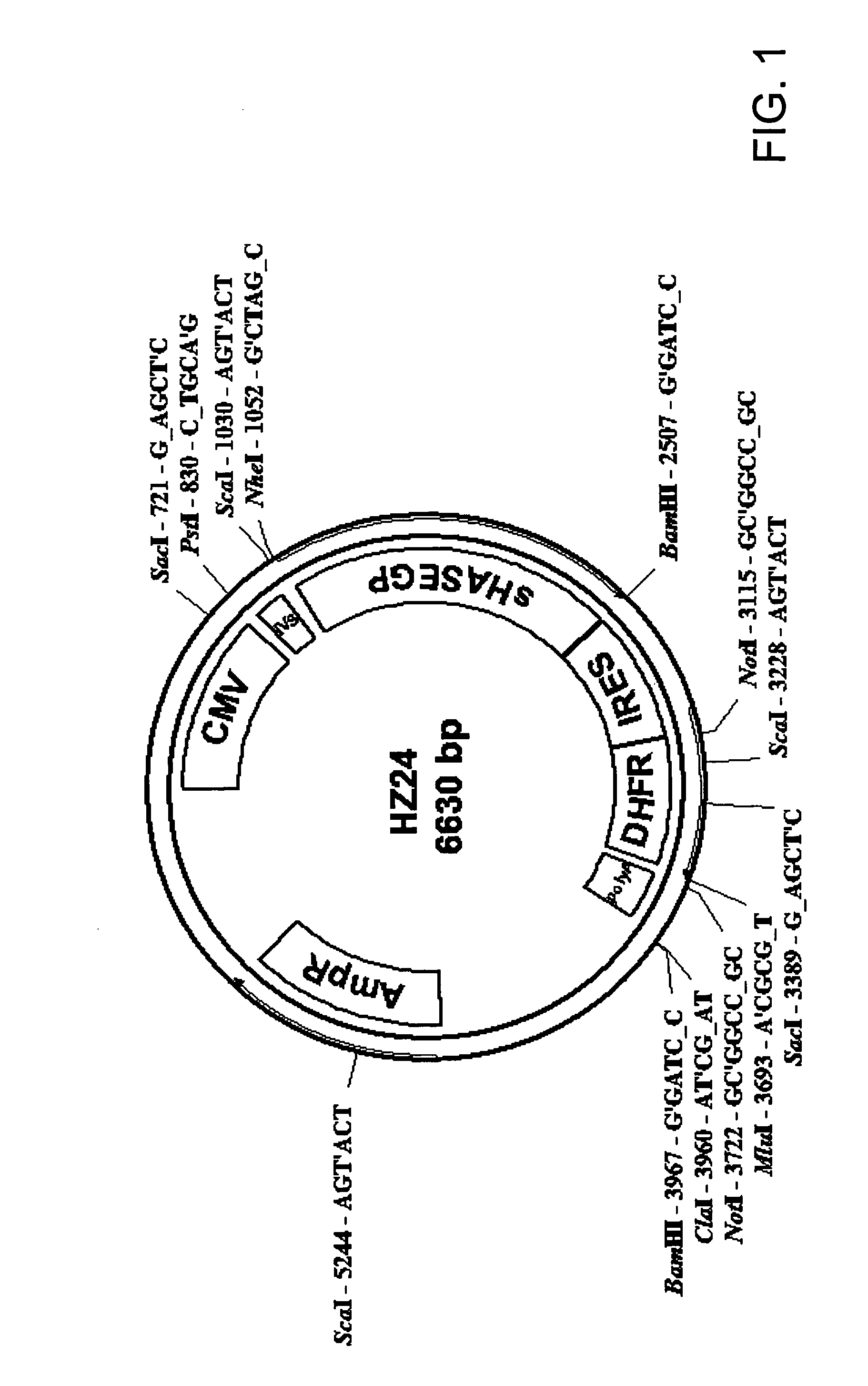
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
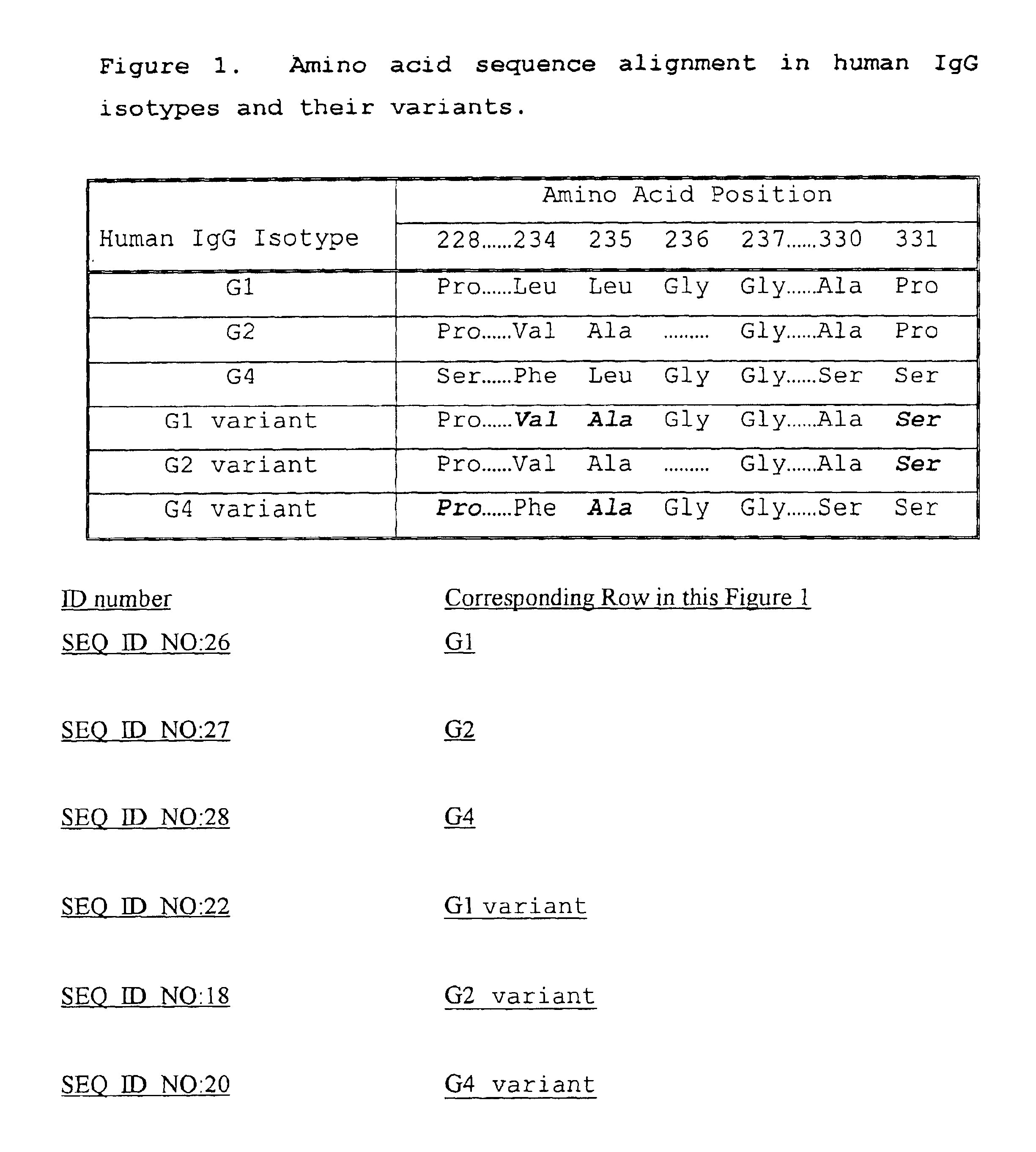
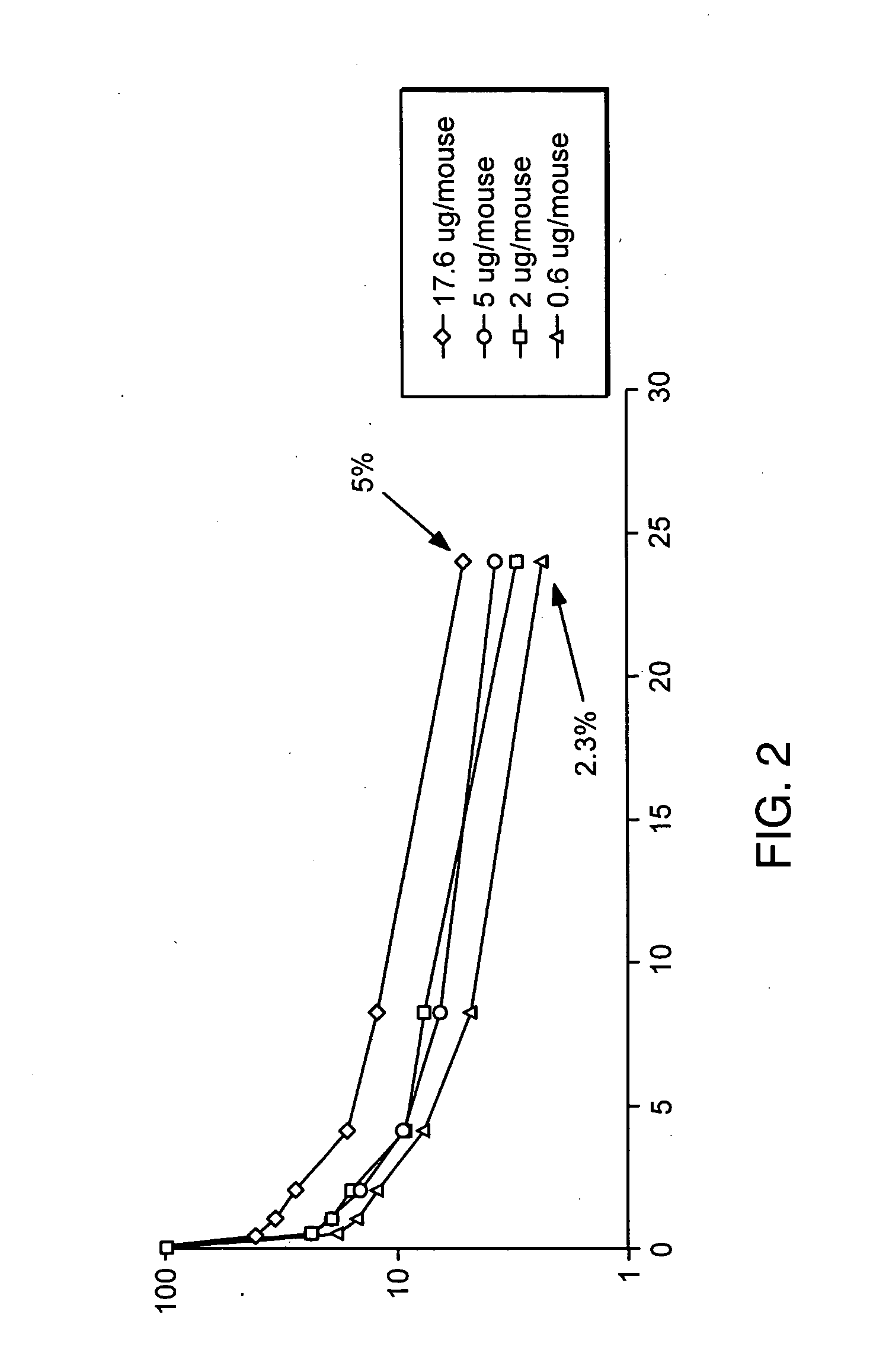
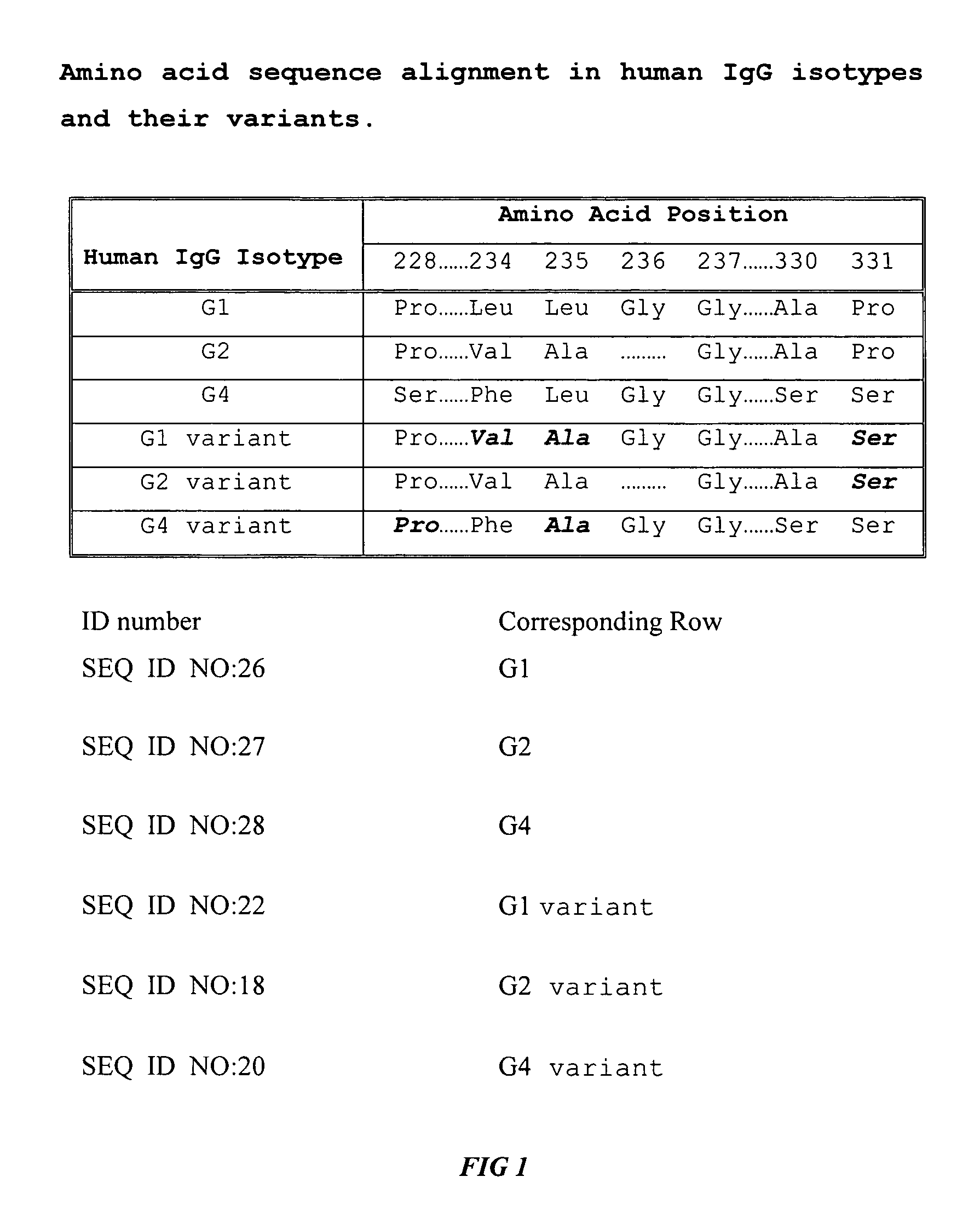
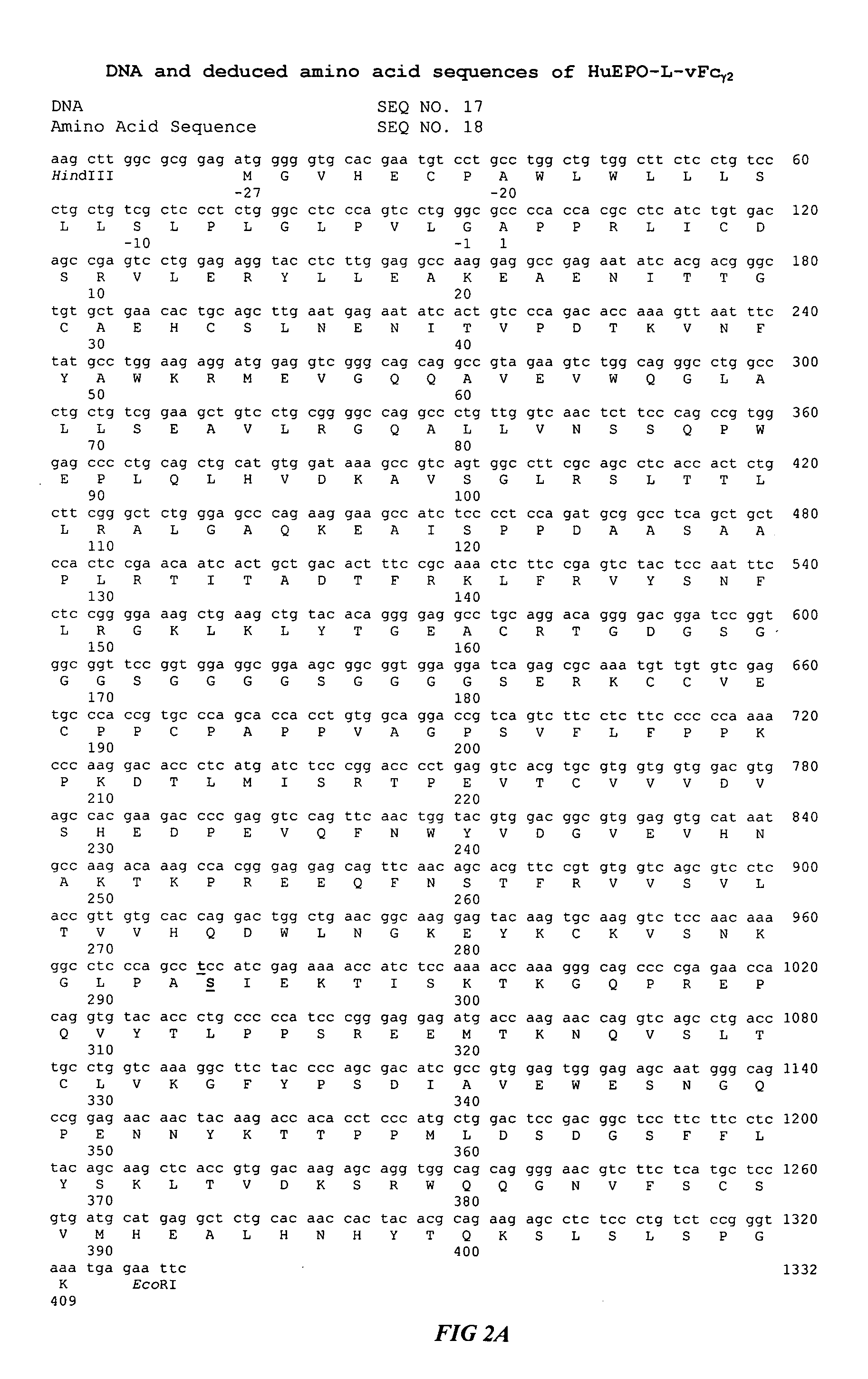
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS6900292B2Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:LONGBIO PHARM (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050202538A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050192211A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
The present invention provides Fc-erythropoietin (“Fc-EPO”) fusion proteins with improved pharmacokinetics. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the production and practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS20050124045A1Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:SUN LEE HWEI K +2
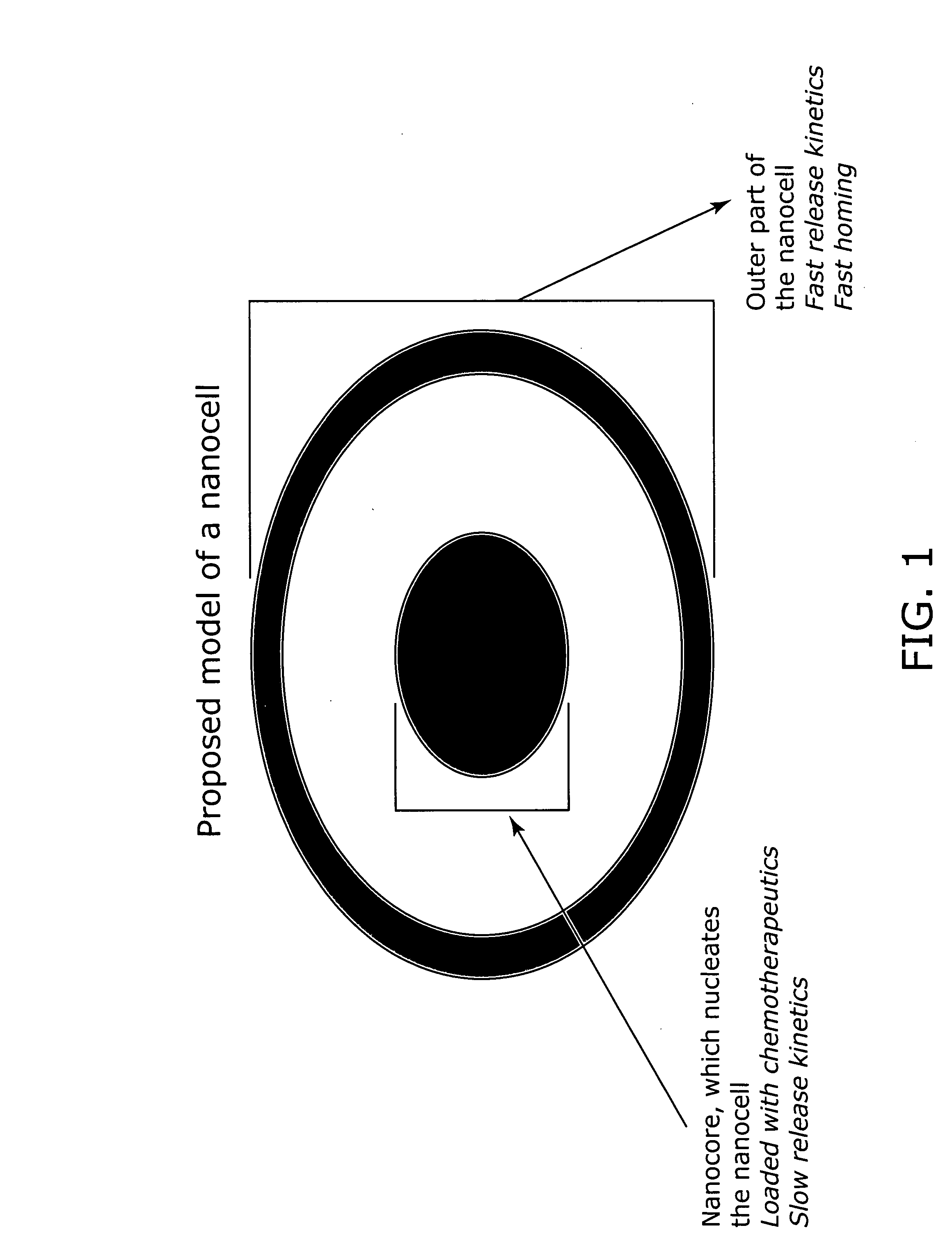
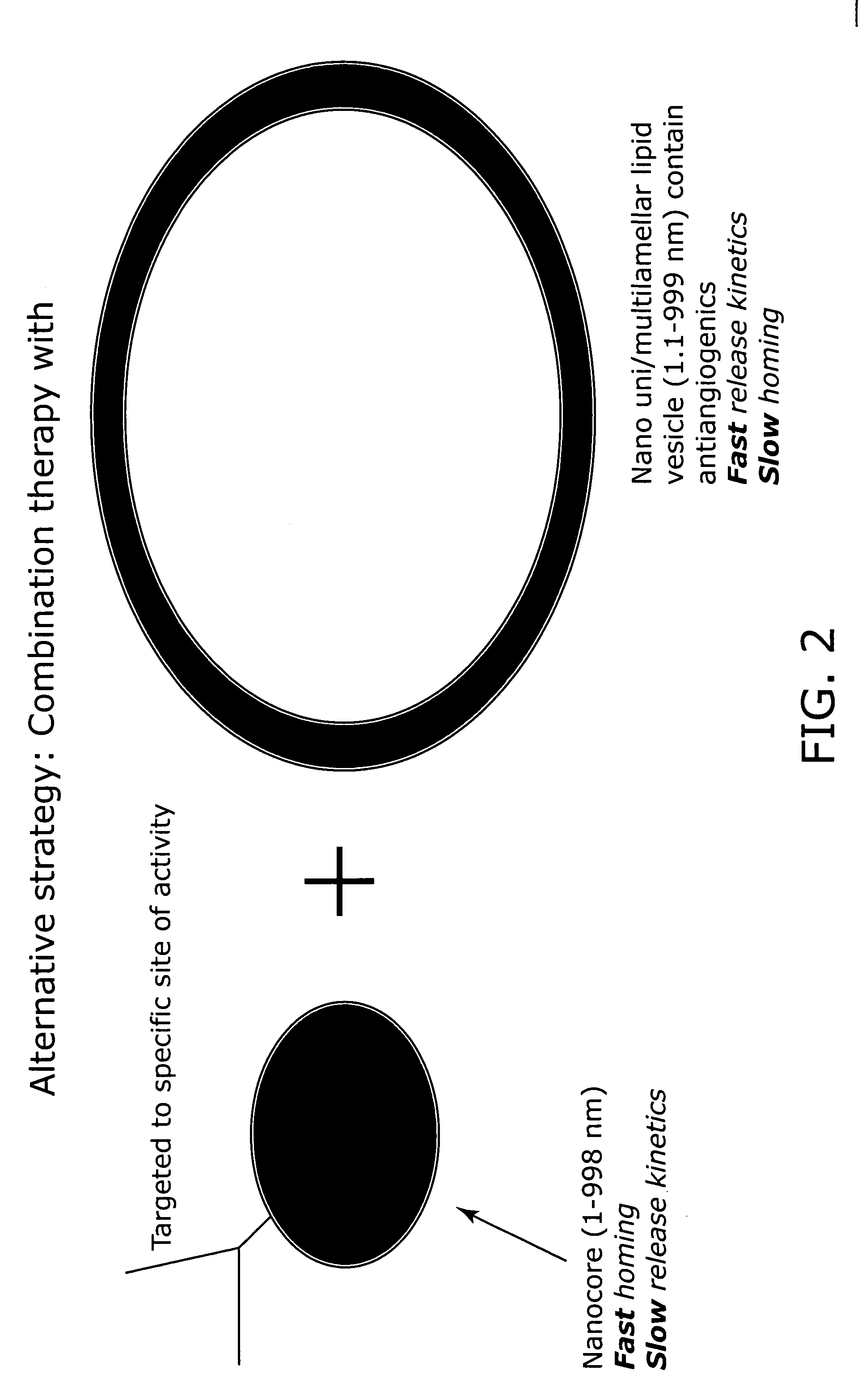
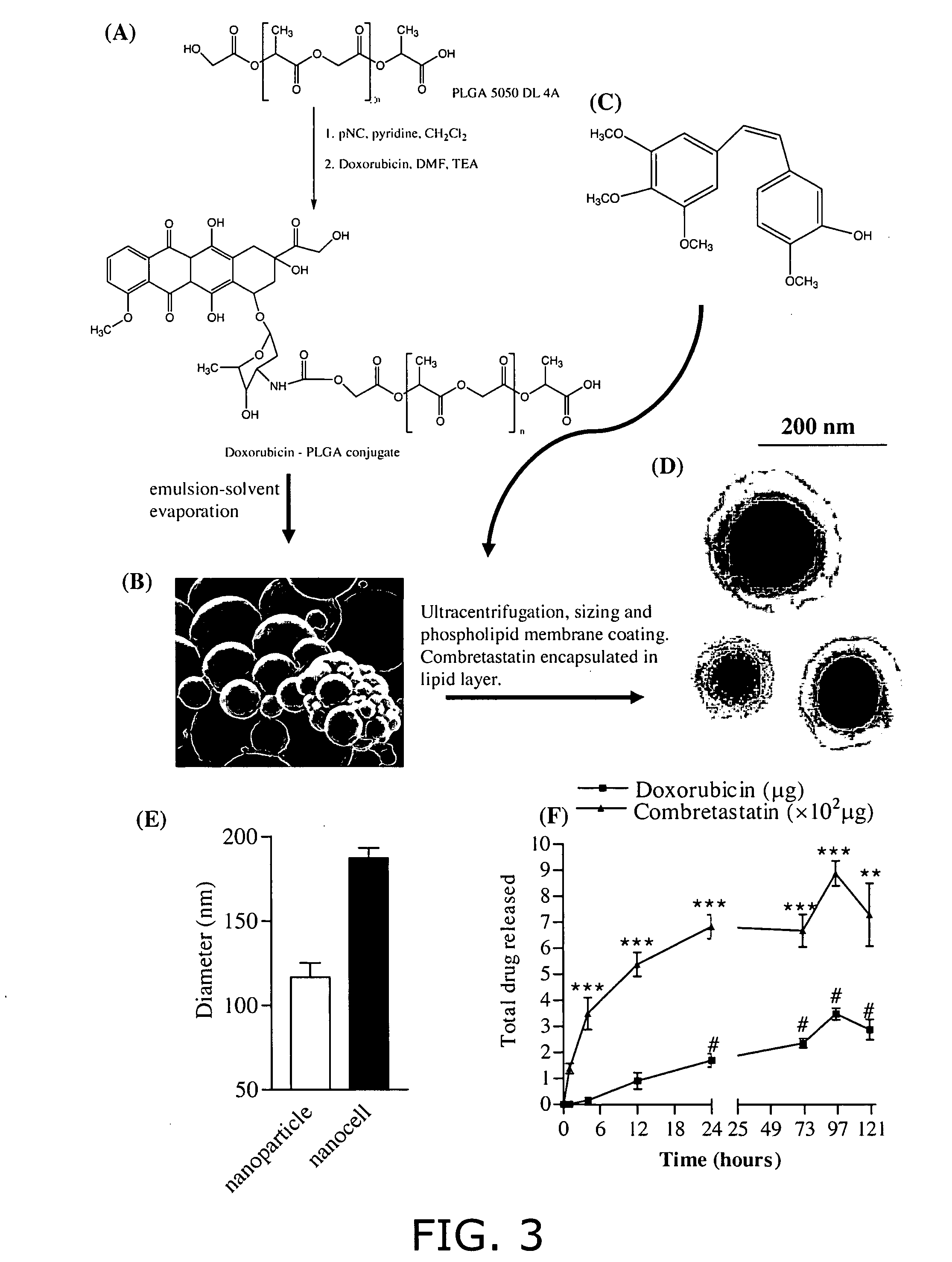
Nanocell drug delivery system
InactiveUS20050266067A1Avoid flowIncreased toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationAntigen
Nanocells allow the sequential delivery of two different therapeutic agents with different modes of action or different pharmacokinetics. A nanocell is formed by encapsulating a nanocore with a first agent inside a lipid vesicle containing a second agent. The agent in the outer lipid compartment is released first and may exert its effect before the agent in the nanocore is released. The nanocell delivery system may be formulated in pharmaceutical composition for delivery to patients suffering from diseases such as cancer, inflammatory diseases such as asthma, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, infectious diseases, and neurological diseases such as epilepsy. In treating cancer, a traditional antineoplastic agent is contained in the outer lipid vesicle of the nanocell, and an antiangiogenic agent is loaded into the nanocore. This arrangement allows the antineoplastic agent to be released first and delivered to the tumor before the tumor's blood supply is cut off by the antianiogenic agent.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Antibodies with modified isoelectric points
ActiveUS20120028304A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHalf-lifeBlood plasma
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for altering the isoelectric point of an antibody, and in some cases, resulting in improved plasma pharmacokinetics, e.g. increased serum half-life in vivo.
Owner:XENCOR
Method of Modifying Isoelectric Point of Antibody Via Amino Acid Substitution in CDR
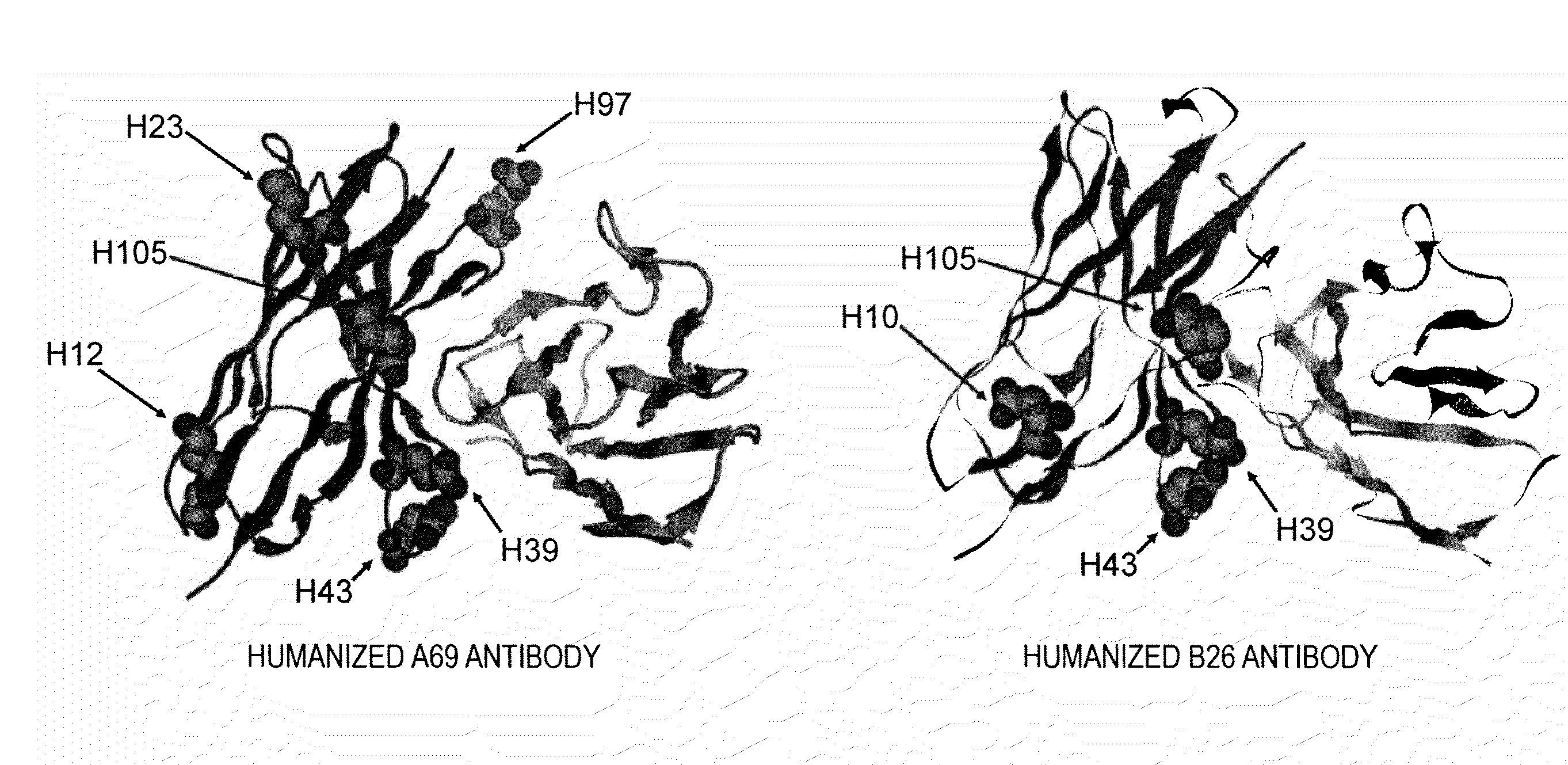
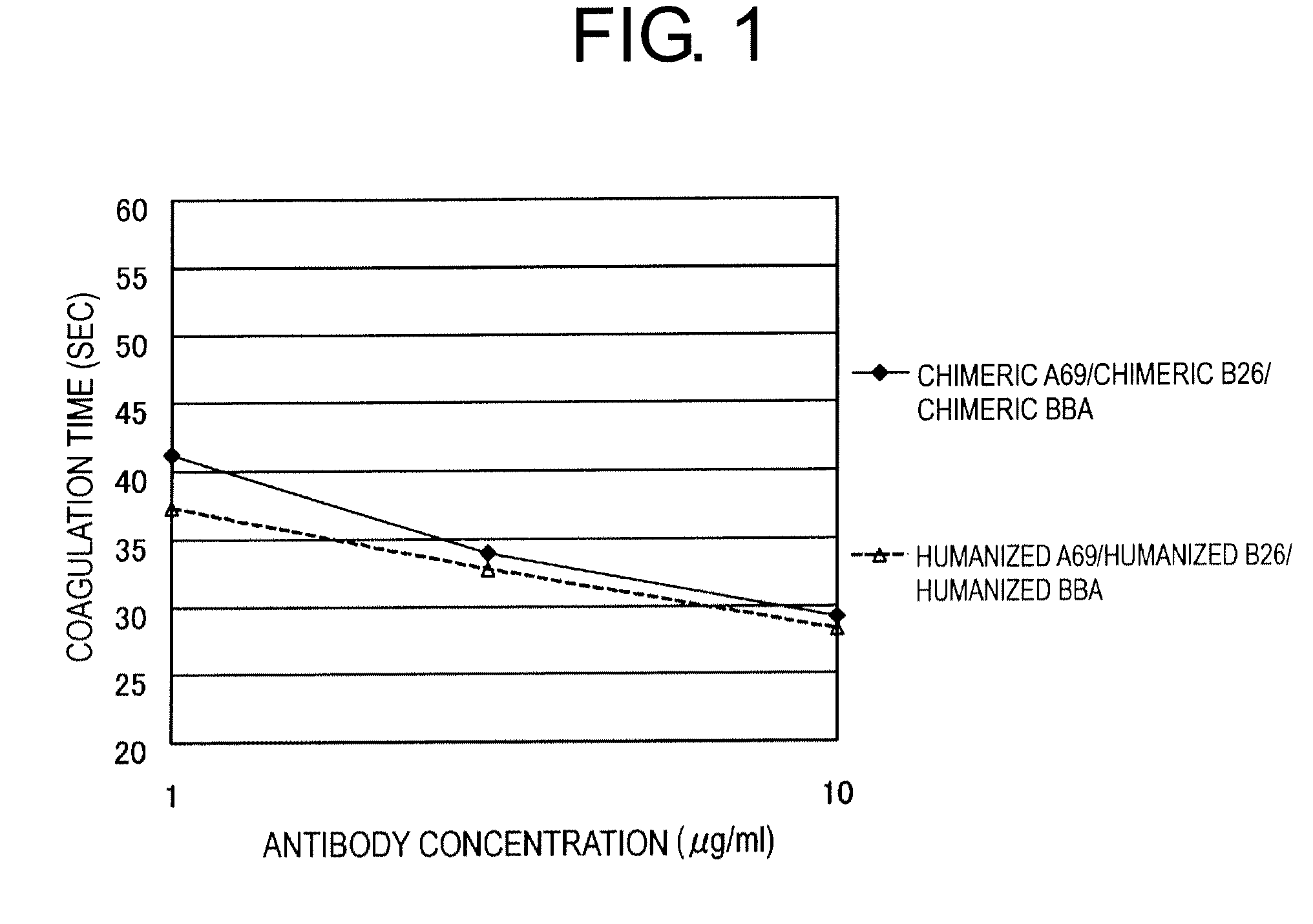
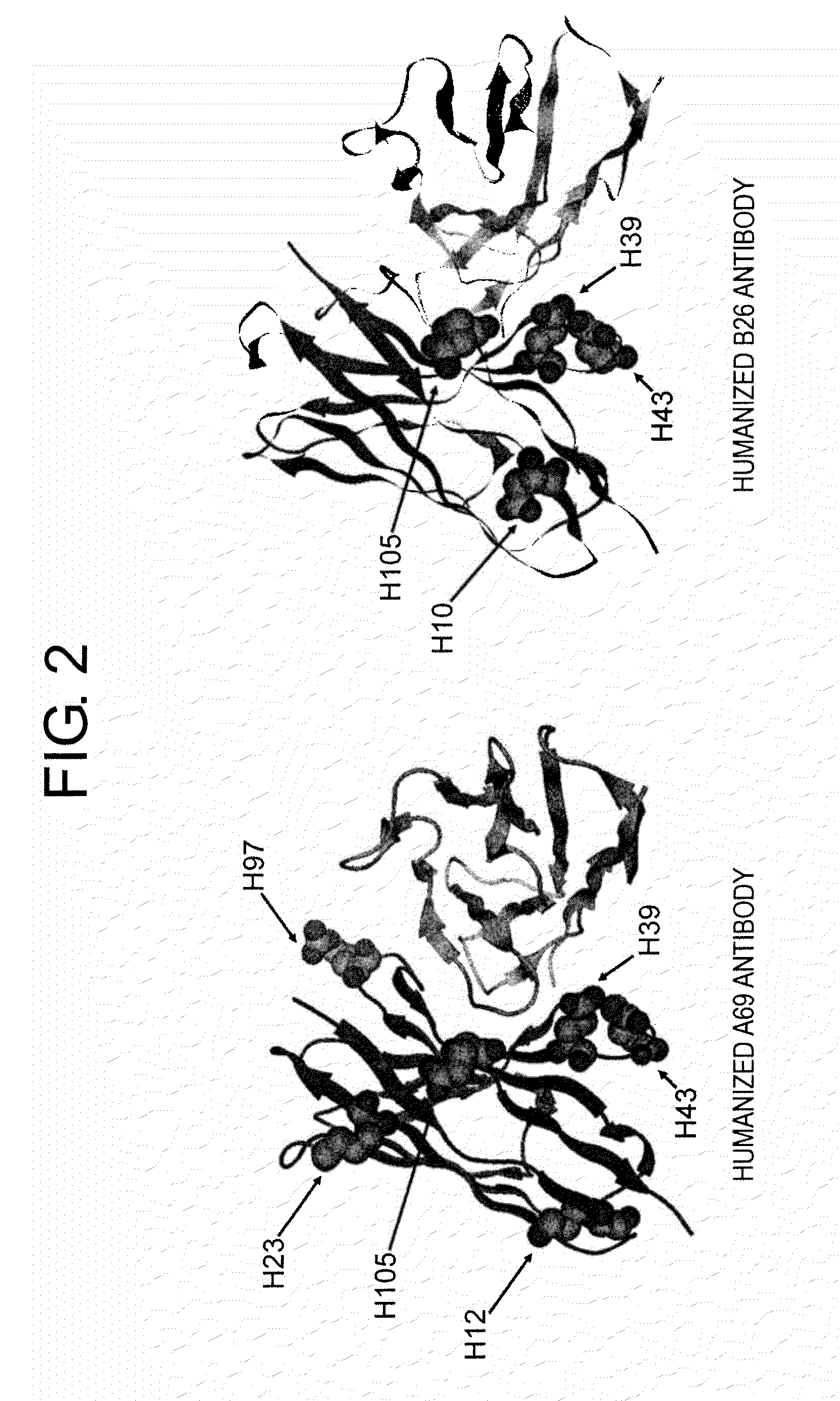
ActiveUS20110076275A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityImprove retentionSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
The present inventors provide methods for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The present invention also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point. The present invention further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Modified Antibody Constant Region
ActiveUS20100298542A1Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesAntipyreticAnalgesicsHigh concentrationHinge region
The present inventors succeeded in improving the antibody constant region to have increased stability under acid conditions, reduced heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, reduced heterogeneity originated from the H chain C terminus, and increased stability at high concentrations as well as in discovering novel constant region sequences having reduced Fcγ receptor-binding, while minimizing the generation of novel T-cell epitope peptides. As a result, the present inventors successfully discovered antibody constant regions with improved physicochemical properties (stability and homogeneity), immunogenicity, safety, and pharmacokinetics.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
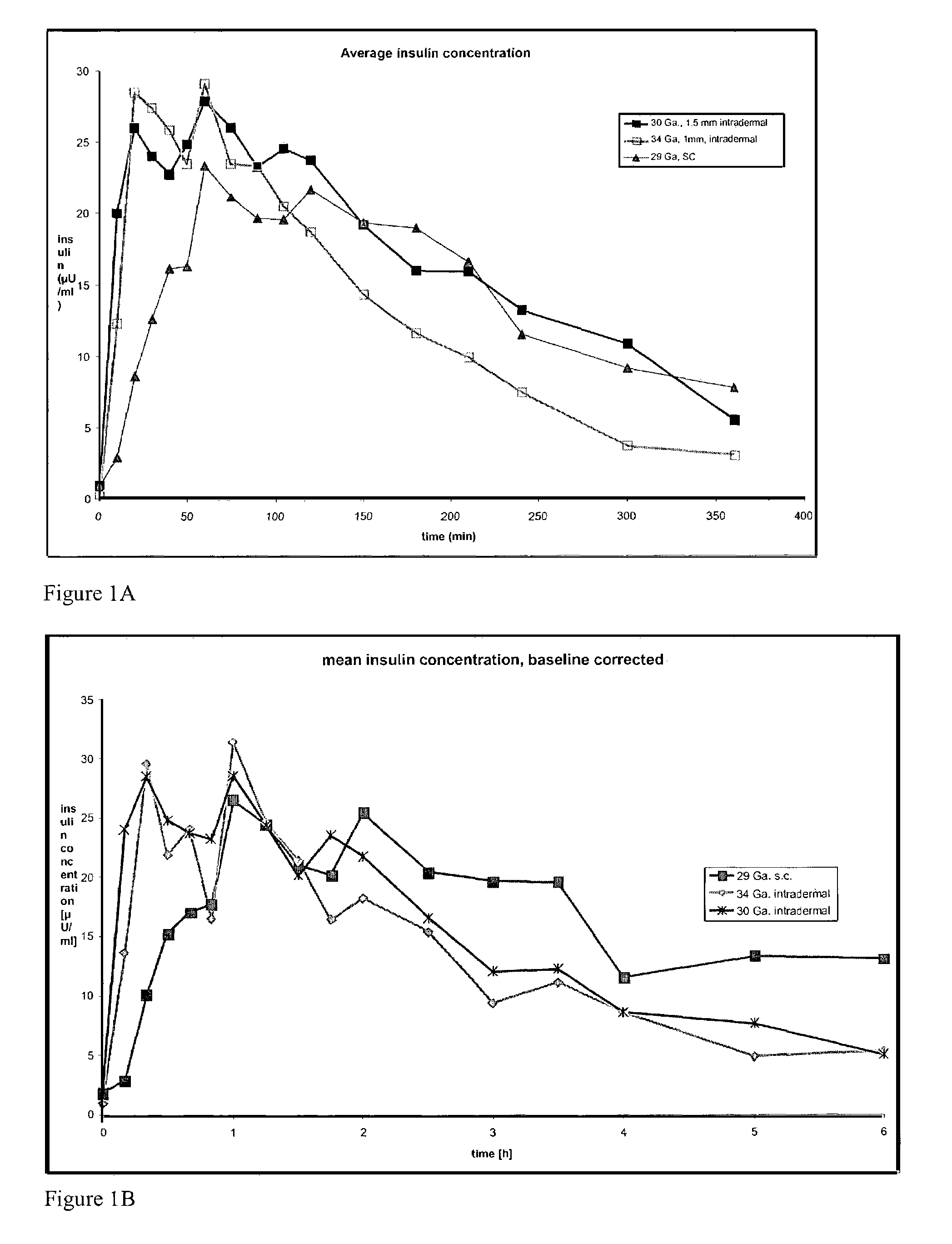
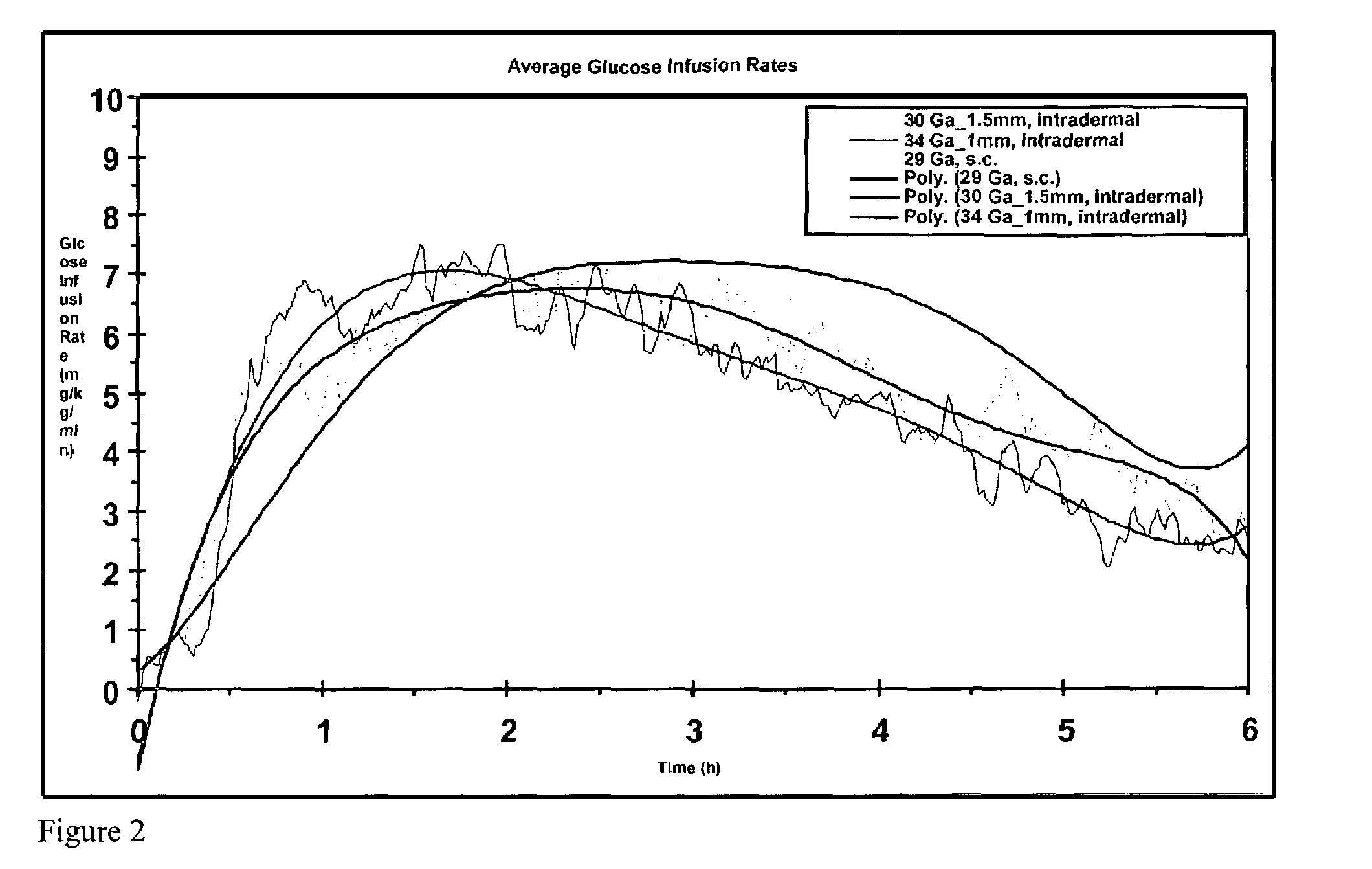
Intra-dermal delivery of biologically active agents
InactiveUS20050163711A1Rapid uptakeFast shippingMetabolism disorderDigestive systemLymphatic vesselDiagnostic agent
The present invention relates to methods and devices for delivering one or more biologically active agents, particularly a diagnostic agent to the intradermal compartment of a subject's skin. The present invention provides an improved method of delivery of biologically active agents in that it provides among other benefits, rapid uptake into the local lymphatics, improved targeting to a particular tissue, improved bioavailability, improved tissue bioavailability, improved tissue specific kinetics, improved deposition of a pre-selected volume of the agent to be administered, and rapid biological and pharmacodynamics and biological and pharmacokinetics. This invention provides methods for rapid transport of agents through lymphatic vasculature accessed by intradermal delivery of the agent. Methods of the invention are particularly useful for delivery of diagnostic agents.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
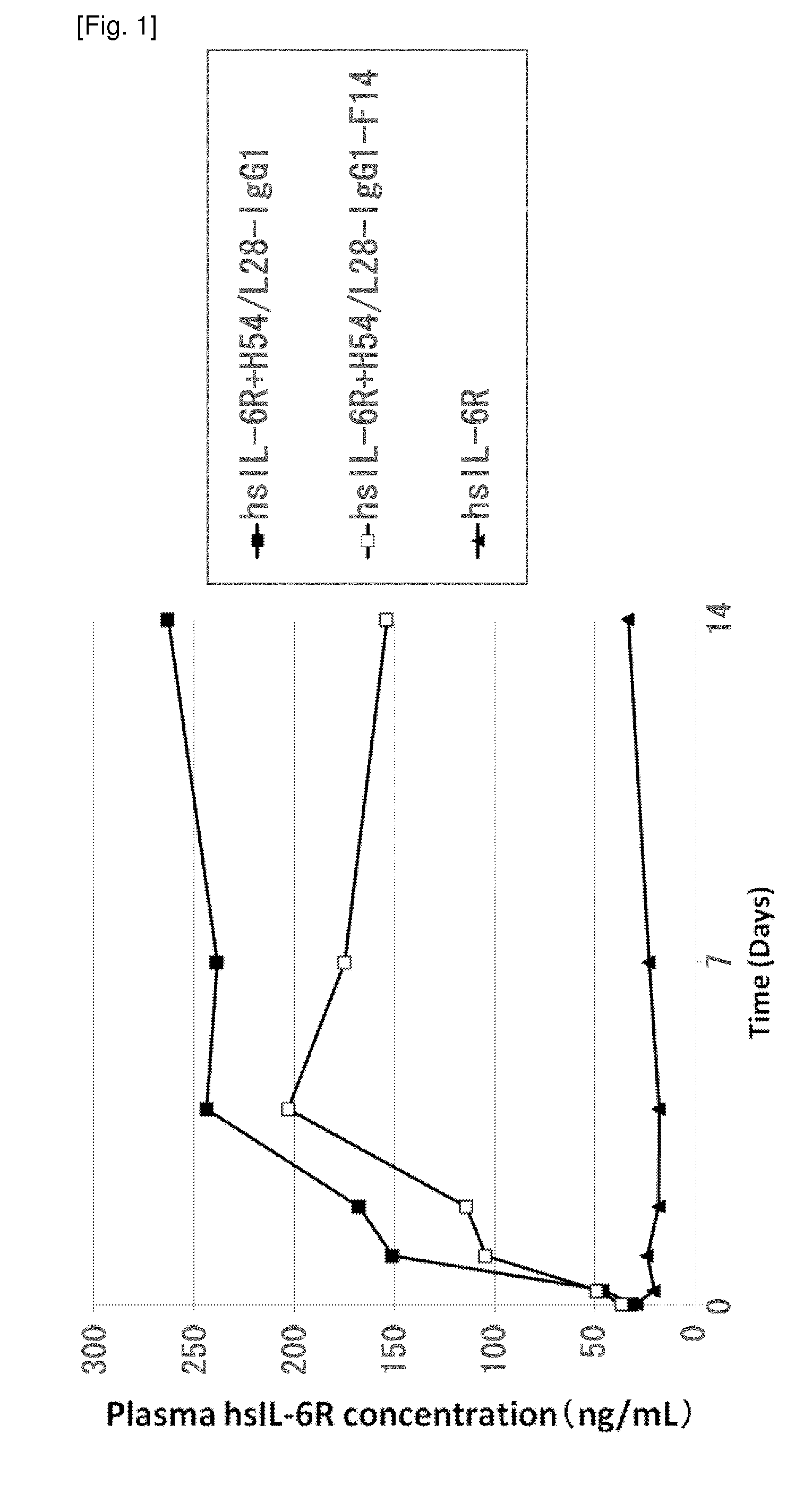
Anti-IL-6 Receptor Antibody
InactiveUS20110245473A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activity and pharmacokineticsGood treatment effectCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh concentrationHinge region
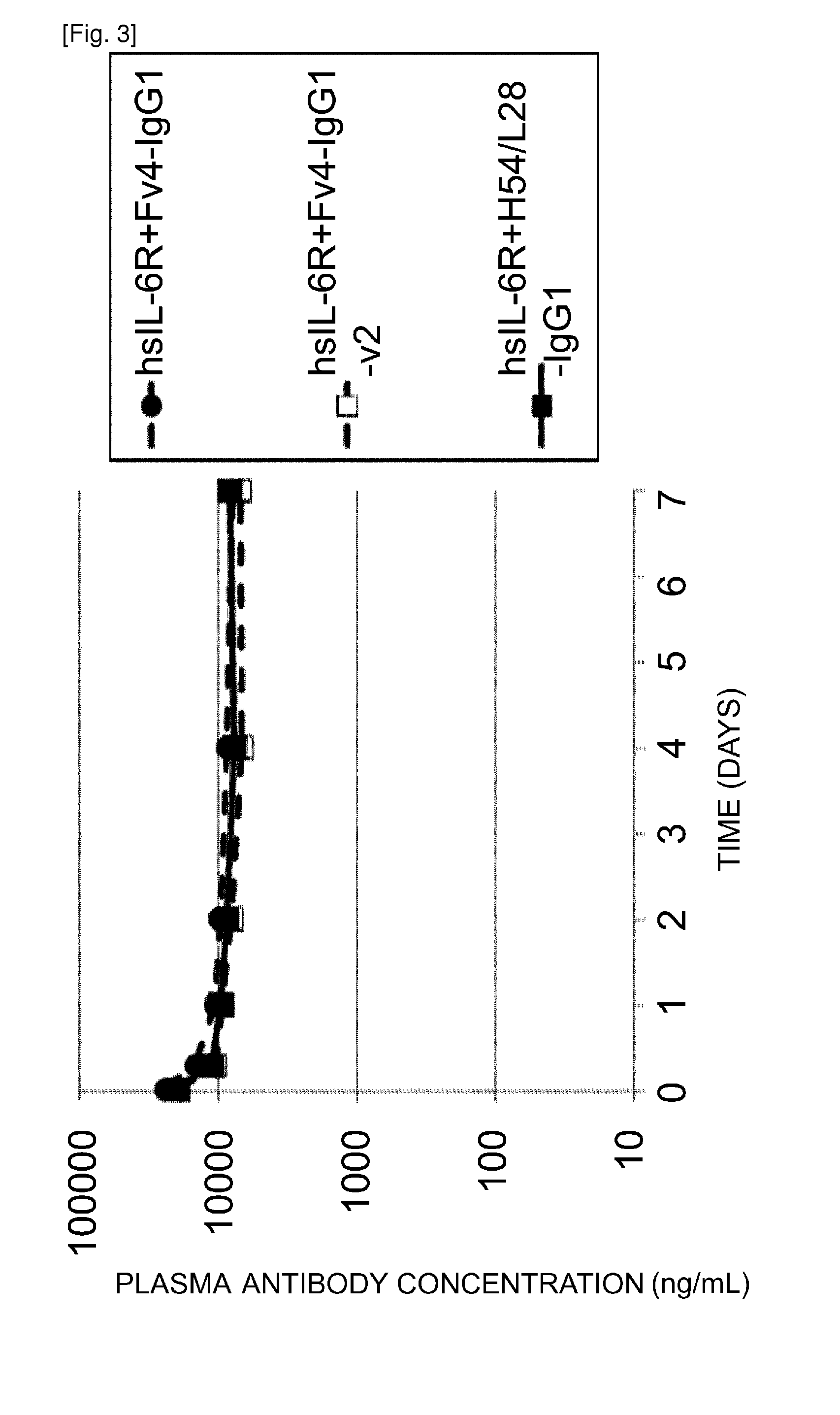
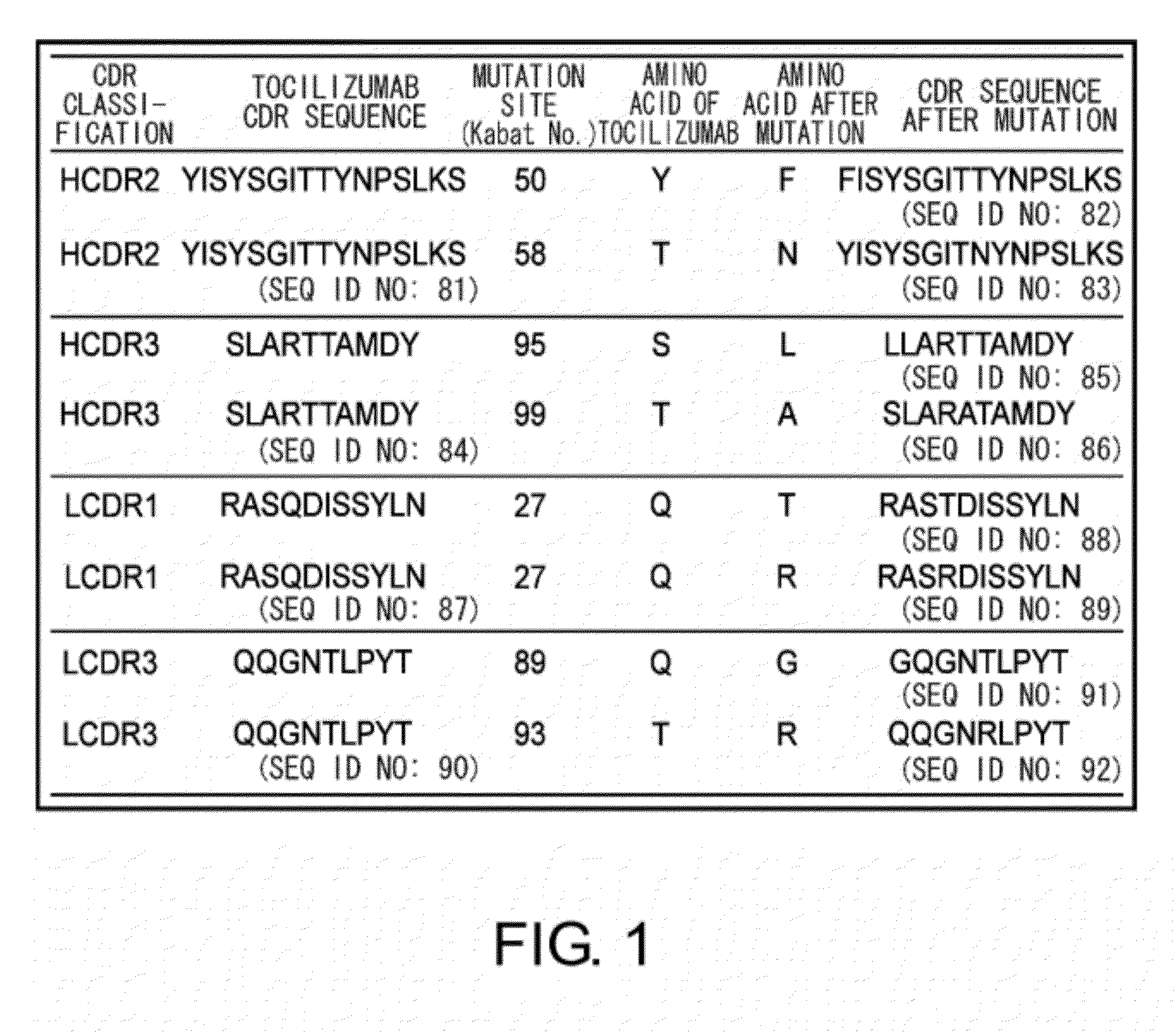
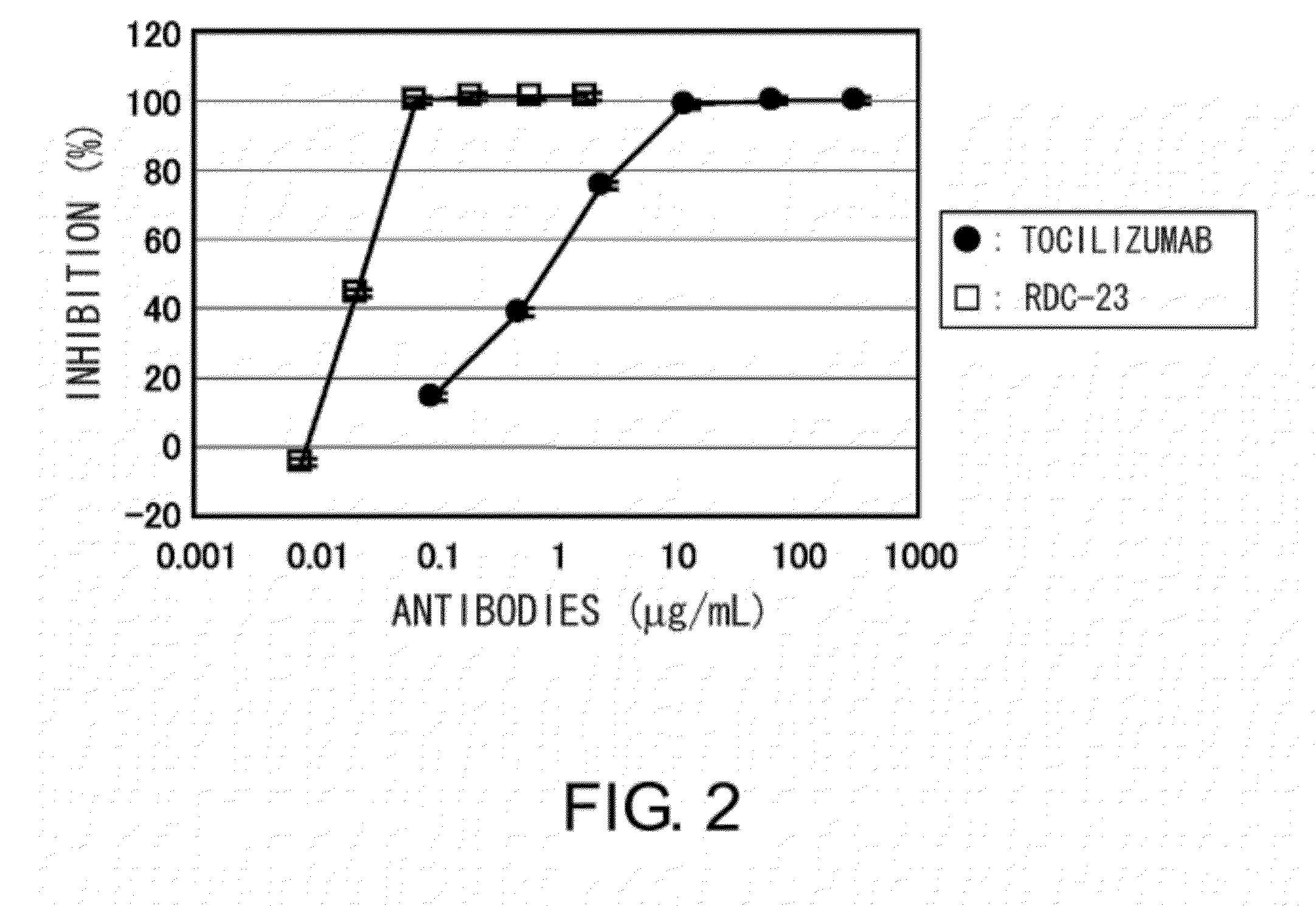
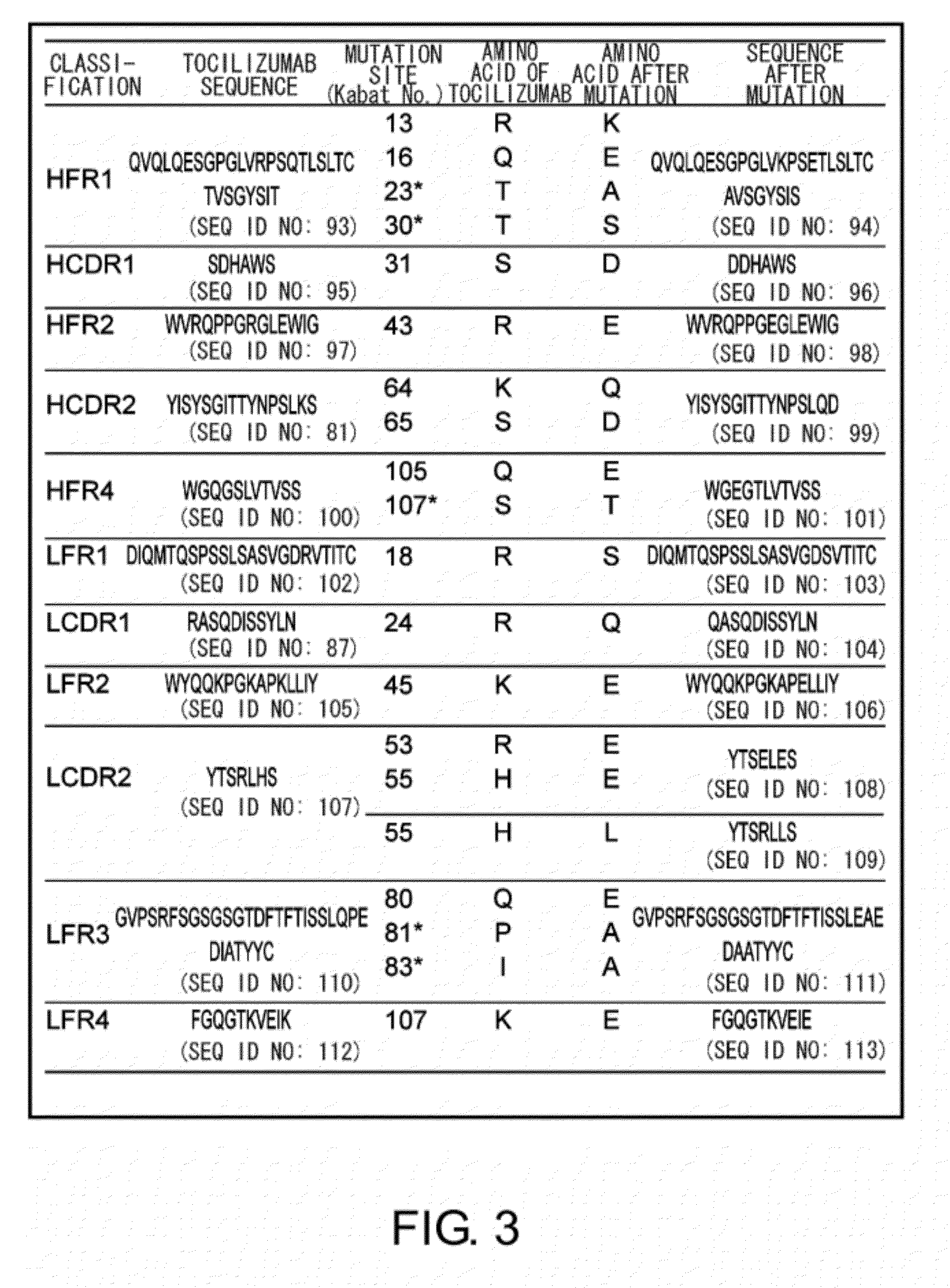
The present inventors succeeded in discovering specific amino acid mutations in the variable region, framework region, and constant region of TOCILIZUMAB, and this enables to reduce immunogenicity risk and the heterogeneity originated from disulfide bonds in the hinge region, as well as to improve antigen binding activity, pharmacokinetics, stability under acidic conditions, and stability in high concentration preparations.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Pharmaceutical delivery systems for hydrophobic drugs and compositions comprising same
ActiveUS8241664B2Preventing and alleviating symptomInhibition releaseBiocideOintment deliveryOral medicationMedicine
A drug delivery system for oral administration of hydrophobic drugs with enhanced and extended absorption and improved pharmacokinetics is provided. In one embodiment, formulations comprising testosterone and testosterone esters, e.g., testosterone palmitate, are disclosed. Methods of treating a hormone deficiency or effecting male contraception with the inventive formulations are also provided.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Pharmaceutical Delivery Systems for Hydrophobic Drugs and Compositions Compositions Comprising Same
ActiveUS20080317844A1Preventing and alleviating symptomInhibition releaseBiocideOintment deliveryOral medicationDelivery system
A drug delivery system for oral administration of hydrophobic drugs with enhanced and extended absorption and improved pharmacokinetics is provided. In one embodiment, formulations comprising testosterone and testosterone esters, e.g., testosterone palmitate, are disclosed. Methods of treating a hormone deficiency or effecting male contraception with the inventive formulations are also provided.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Methods for controlling blood pharmacokinetics of antibodies
The present inventors discovered that the half-life in blood of an IgG antibody which is a polypeptide comprising an FcRn-binding domain can be controlled by controlling the surface charge through modification of residues exposed on the surface among residues in the variable regions of the IgG antibody. Antibodies whose half-life in blood had been controlled by the methods of the present invention were confirmed to actually retain the original activity. The methods of the present invention are widely applicable to polypeptides comprising an FcRn-binding domain, such as IgG antibodies, which are recycled via the FcRn salvage pathway regardless of the type of target antigen.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
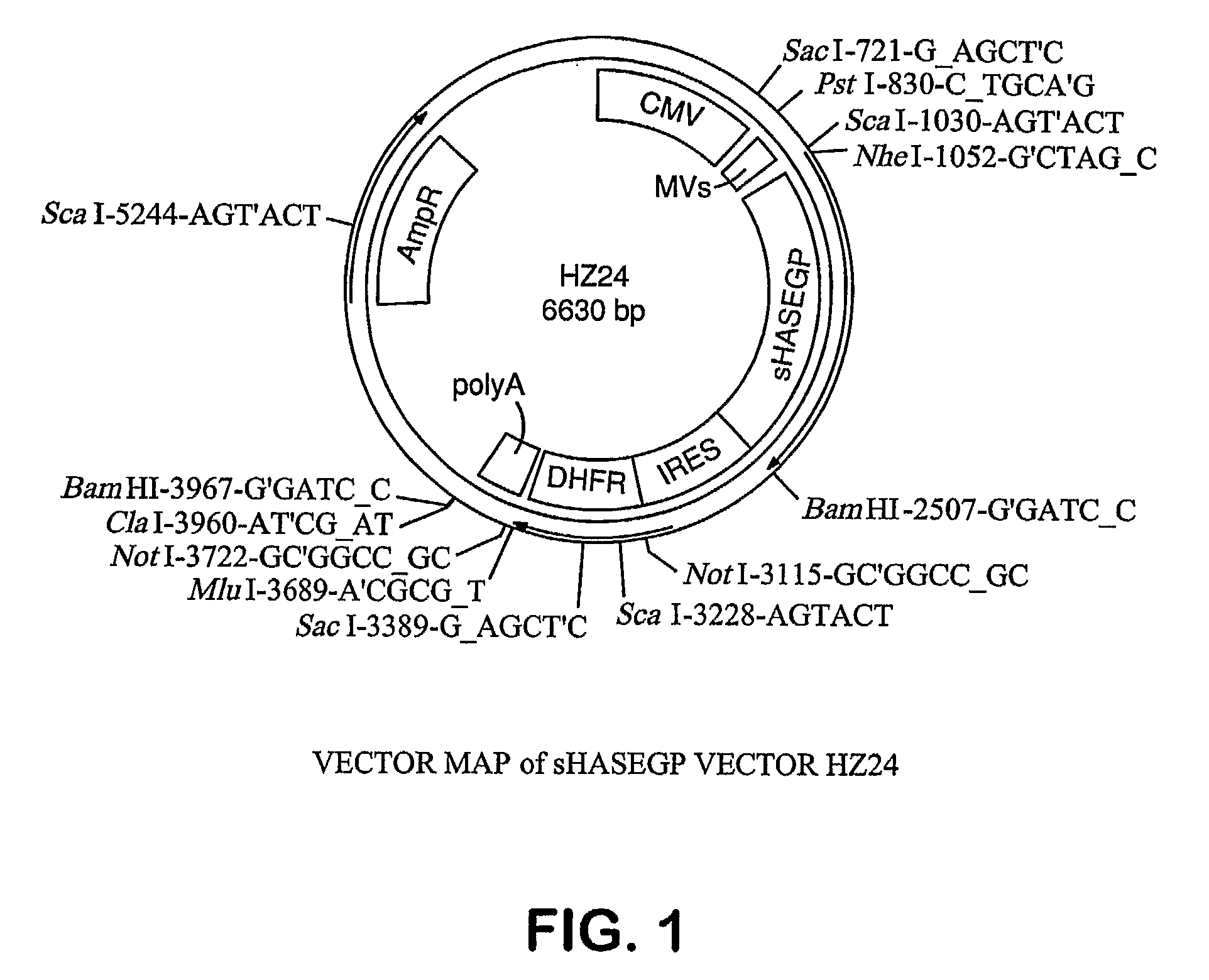
Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases and Methods of Preparing and Using Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases
InactiveUS20090123367A1Facilitated DiffusionEnhance convective transportBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME +6
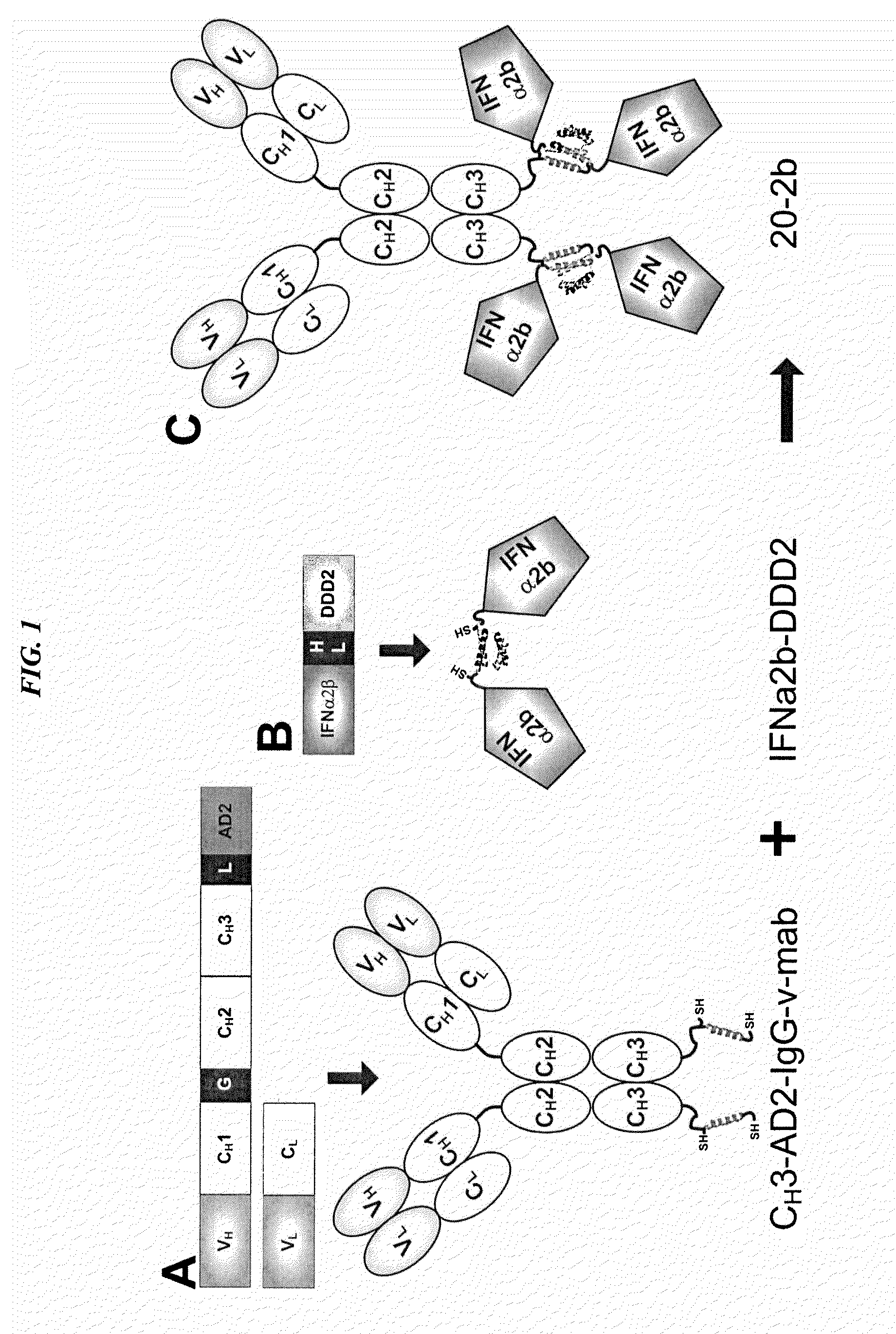
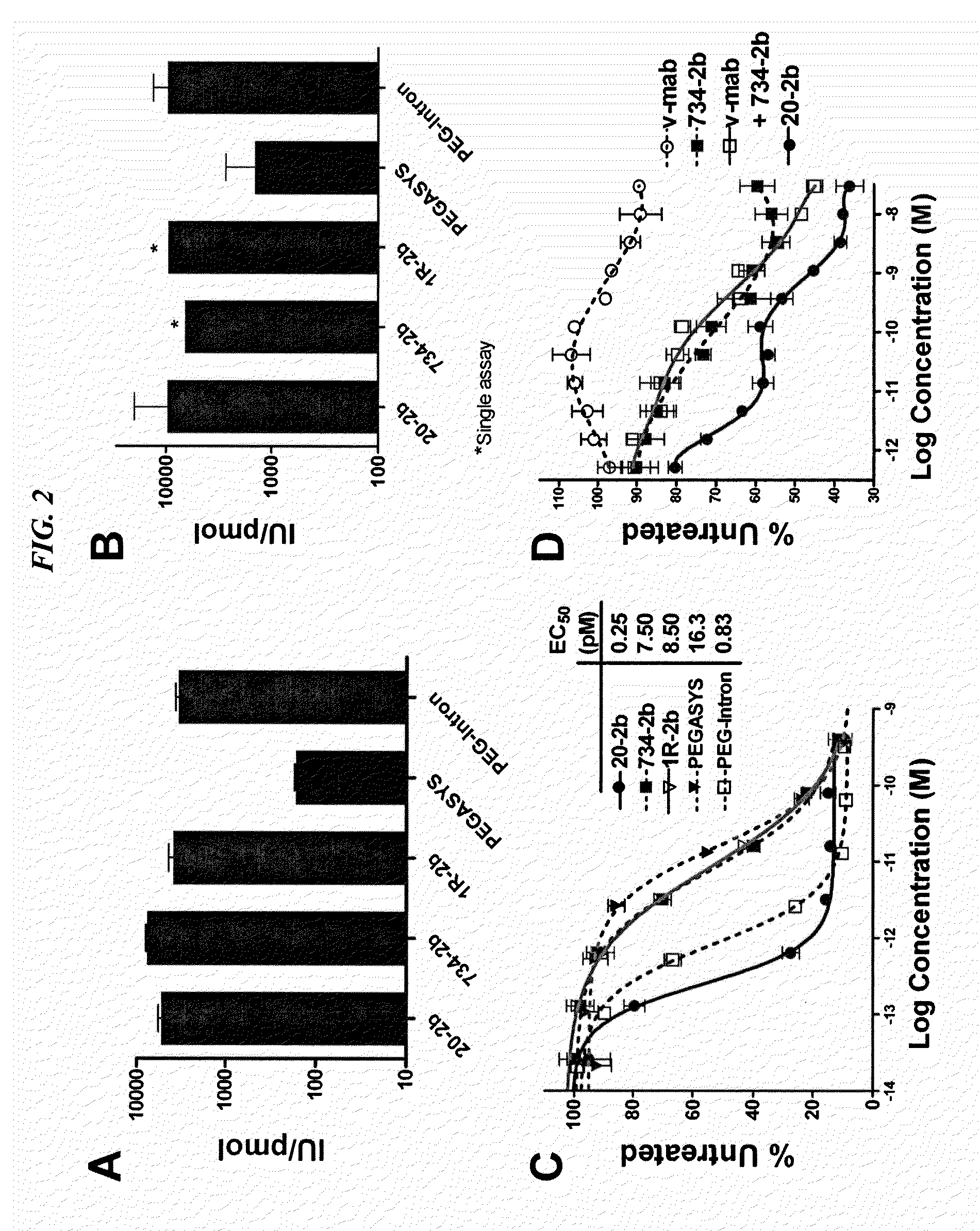
Tetrameric cytokines with improved biological activity
ActiveUS8034352B2Keep for a long timeLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In more preferred embodiment the cytokine is G-CSF, erythropoietin or INF-α2b.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Parenteral formulations of dopamine agonists
InactiveUS20100035886A1Reducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorReducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorsBiocideMetabolism disorderParenteral nutritionParenteral Dosage Form
This invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration comprising dopamine agonists and peripheral acting agents useful for treatment of metabolic disorders or key elements thereof. The parenteral dosage forms exhibit long stable shelf life and distinct pharmacokinetics.
Owner:VEROSCI
Topiramate compositions and methods of enhancing its bioavailability
ActiveUS20080085306A1Reduced adverse eventConvenient treatmentBiocideNervous disorderRegimenImmediate release
Owner:SUPERNUS PHARM INC
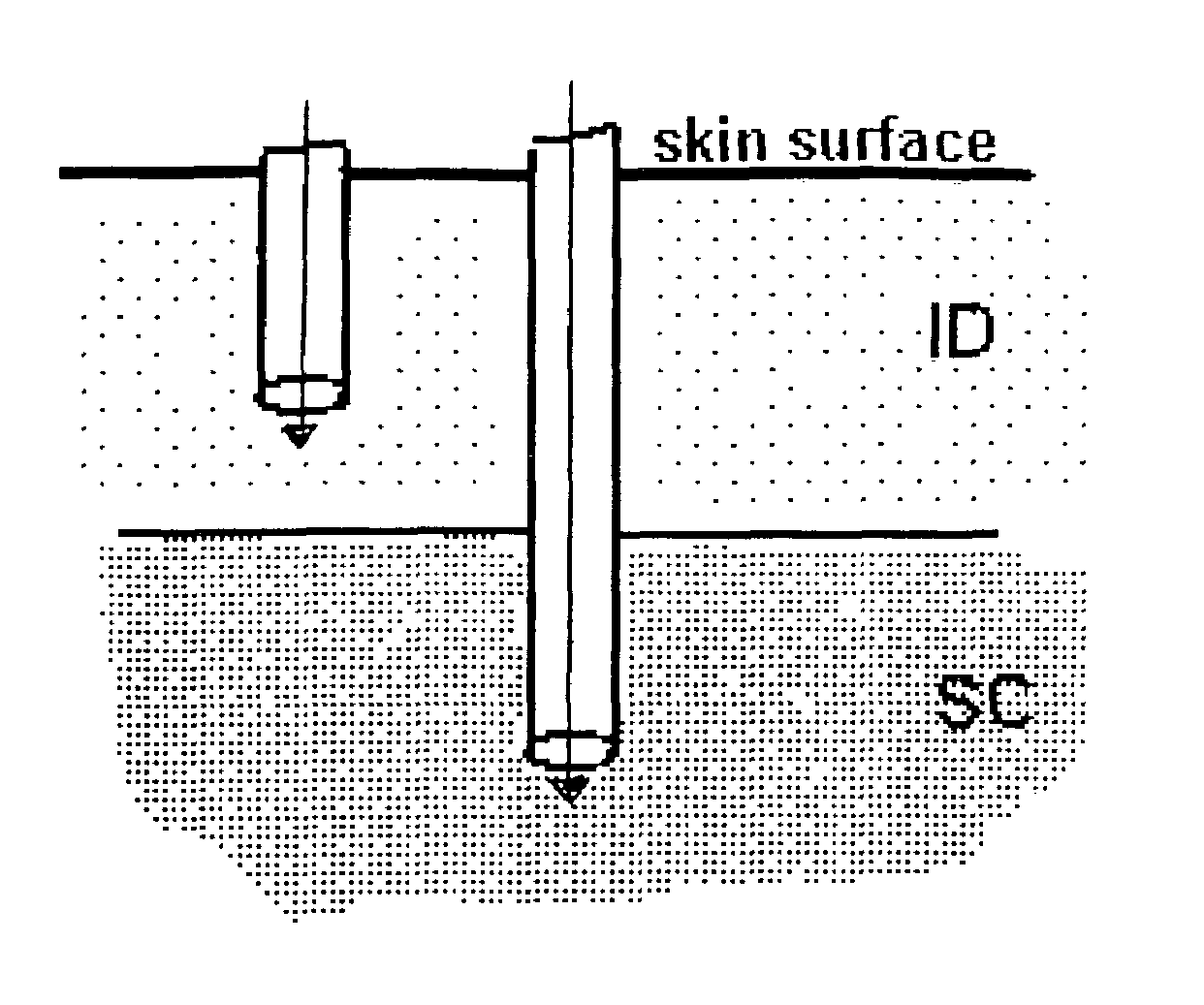
Method and device for controlling drug pharmacokinetics
The invention pertains to methods and devices for controlling the pharmacokinetics of administered substances, particularly therapeutic substances by combining advantages of delivery to two or more compartments within the skin. The invention provides methods and devices for delivering substances to subcutaneous and intradermal compartments of the skin to achieve a hybrid pharmacokinetic profile that has a portion similar to that achieved by intradermal delivery, e.g., rapid and high peak onset levels of the substance, and a portion similar to that achieved by subcutaneous delivery, e.g., longer circulating levels of the substance.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
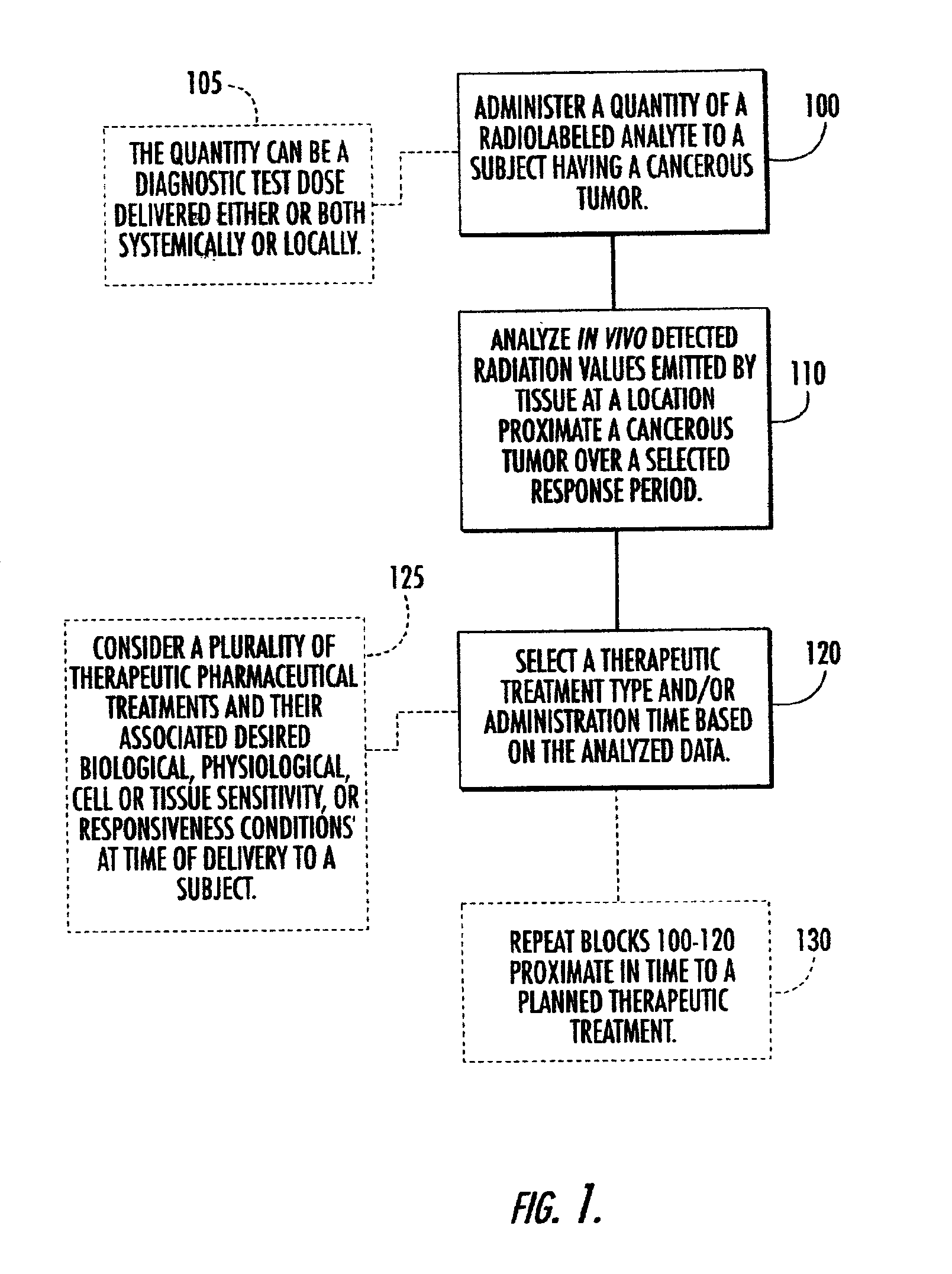
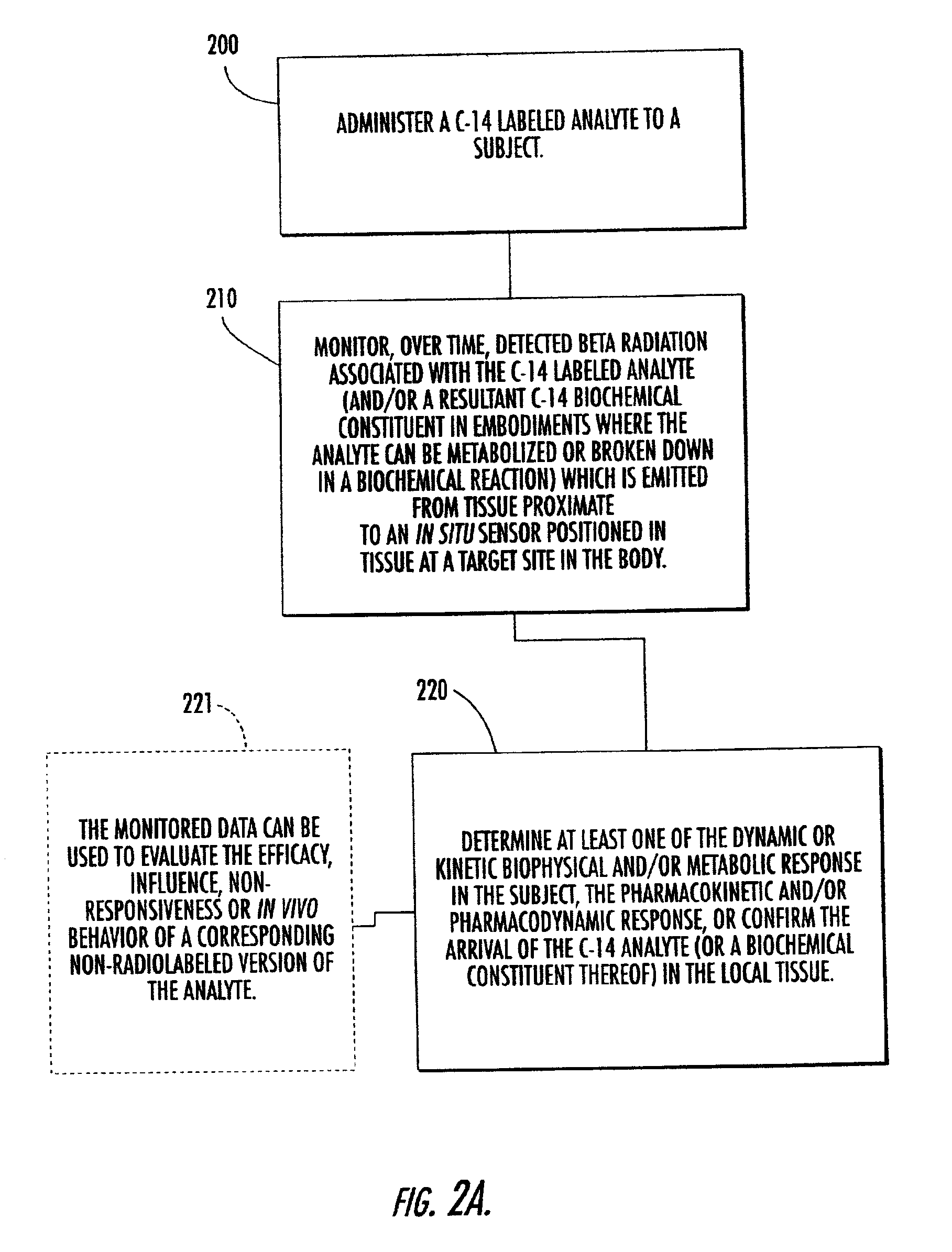
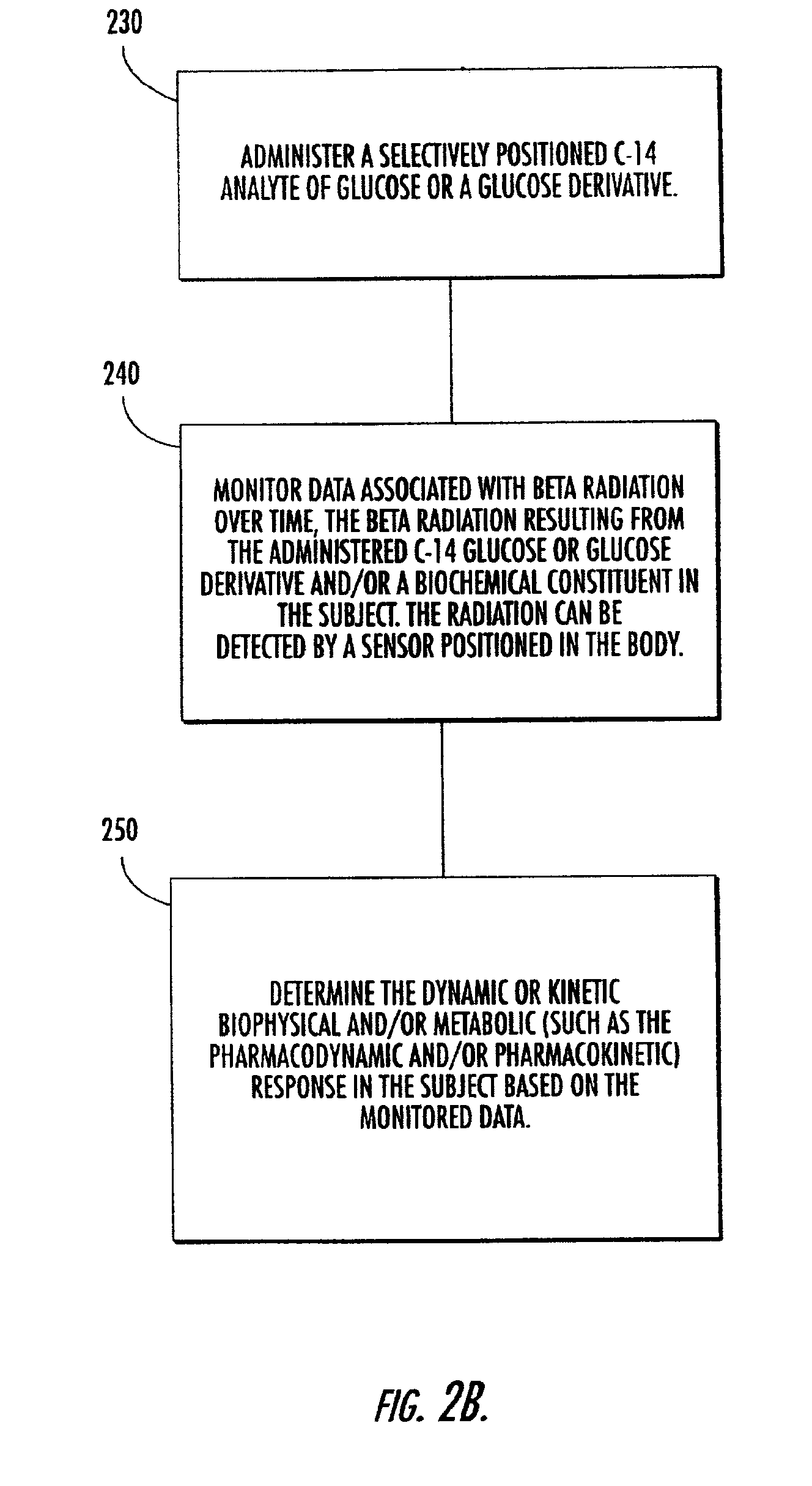
Systems, methods and devices for in vivo monitoring of a localized response via a radiolabeled analyte in a subject
InactiveUS7011814B2Cost-effective minimally invasiveImprove responseCompounds screening/testingRadioactive preparation carriersAbnormal tissue growthAnalyte
Methods, systems, devices and computer program products monitor in vivo detected radiation in a target localized site within a subject, over a selected time period, to do one or more of: (a) quantify a radiation dose received at a local site; (b) assess bioreceptiveness to a particular treatment time or type; (c) evaluate the pharmacokinetics of a radiolabeled analyte corresponding to a non-radiolabeled analyte; (d) monitor or evaluate metabolic activity; or (e) evaluate a tumor prior to or after a therapeutic treatment.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
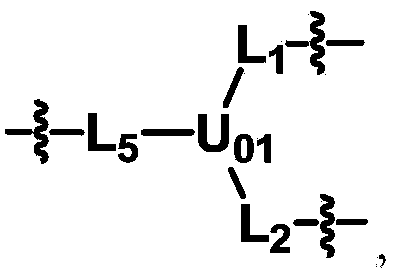
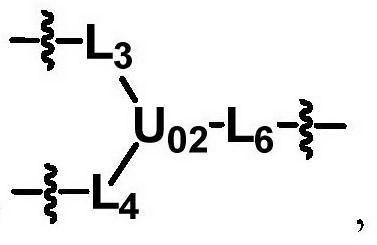
Biologically related substances modified by multifunctional H-type polyethylene glycol derivative
ActiveCN104530413ALow immunogenicityImprove distributionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFluorescencePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses biologically related substances modified by a multifunctional H-type polyethylene glycol derivative. The derivative comprises a linear main axis LPEG and four PEG branched chains, and n1, n2, n3 and n4 are polymerization degrees of the branched chains, respectively; U1 and U2 are trivalent branching groups connecting the main axis LPEG with two PEG branched chains; F1 and F2 contain functional groups or their protected forms R01, and the number of R01 is one or more than one. Any linking group in the molecule or linking groups formed with adjacent heteroatom groups are stable or degradable; any PEG chain segment in the molecule independently shows polydispersity or monodispersity. One H-type molecule can modify multiple types of or multiple biologically related substances; the modified product has a flexible branching structure, a high drug loading capacity, optimized pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution, and can also carry two biologically related substances with different functions, so as to generate fluorescence property or targeting function.
Owner:XIAMEN SINOPEG BIOTECH
Parenteral Formulations of Dopamine Agonists
ActiveUS20090143390A1Reducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorReducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorsBiocideAntipyreticEnteral administrationParenteral Dosage Form
This invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration comprising dopamine agonists and peripheral acting agents_useful for treatment of metabolic disorders or key elements thereof. The parenteral dosage forms exhibit long stable shelf life and distinct pharmacokinetics.
Owner:VEROSCI
Method of modifying isoelectric point of antibody via amino acid substitution in CDR
ActiveUS9096651B2Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityGood treatment effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
Methods are described for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The disclosure also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies with a modified isoelectric point. The disclosure further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Biliary barrier
InactiveUS20070048727A1Increased toxicityIncrease valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDrug compoundMedicine
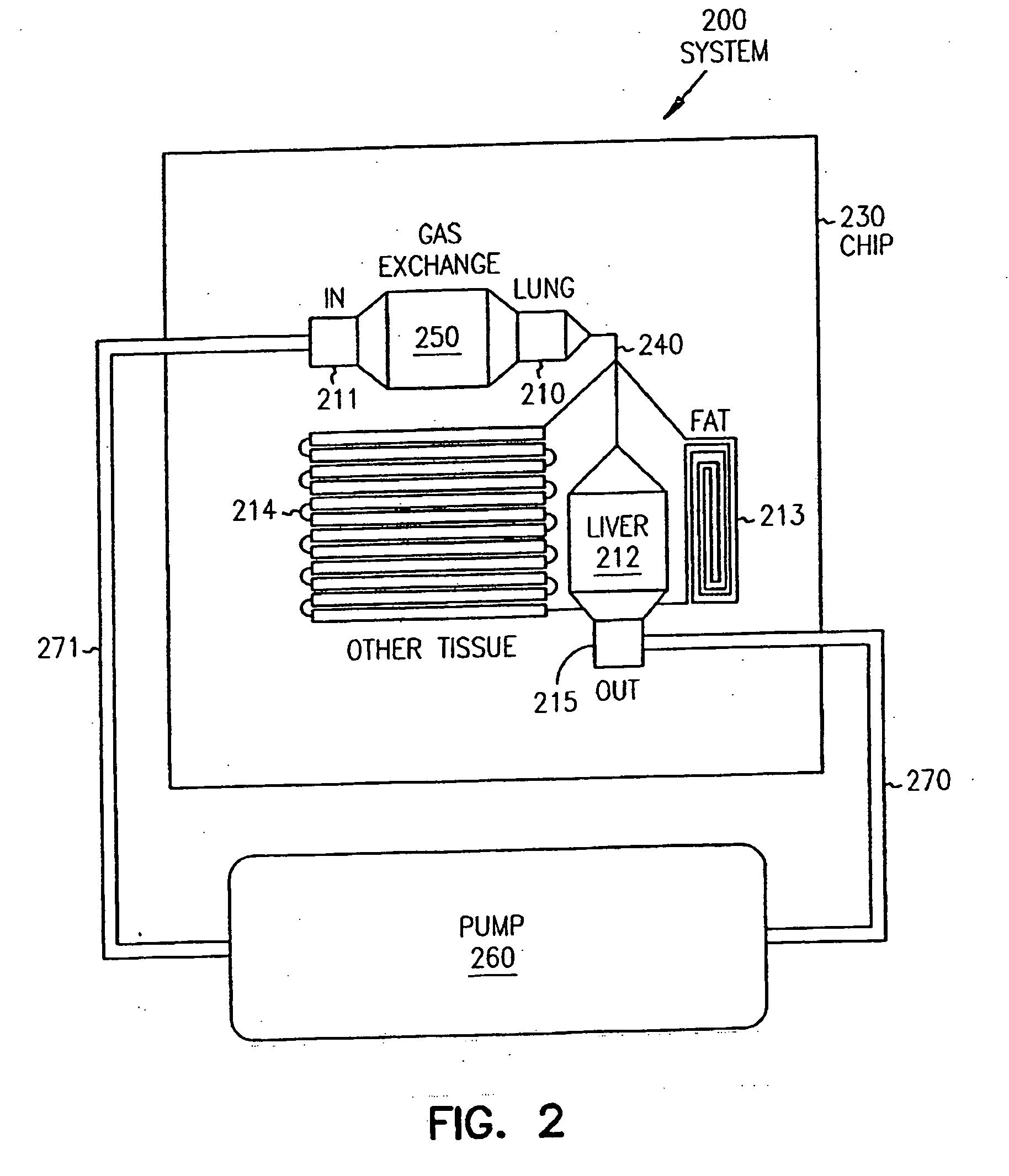
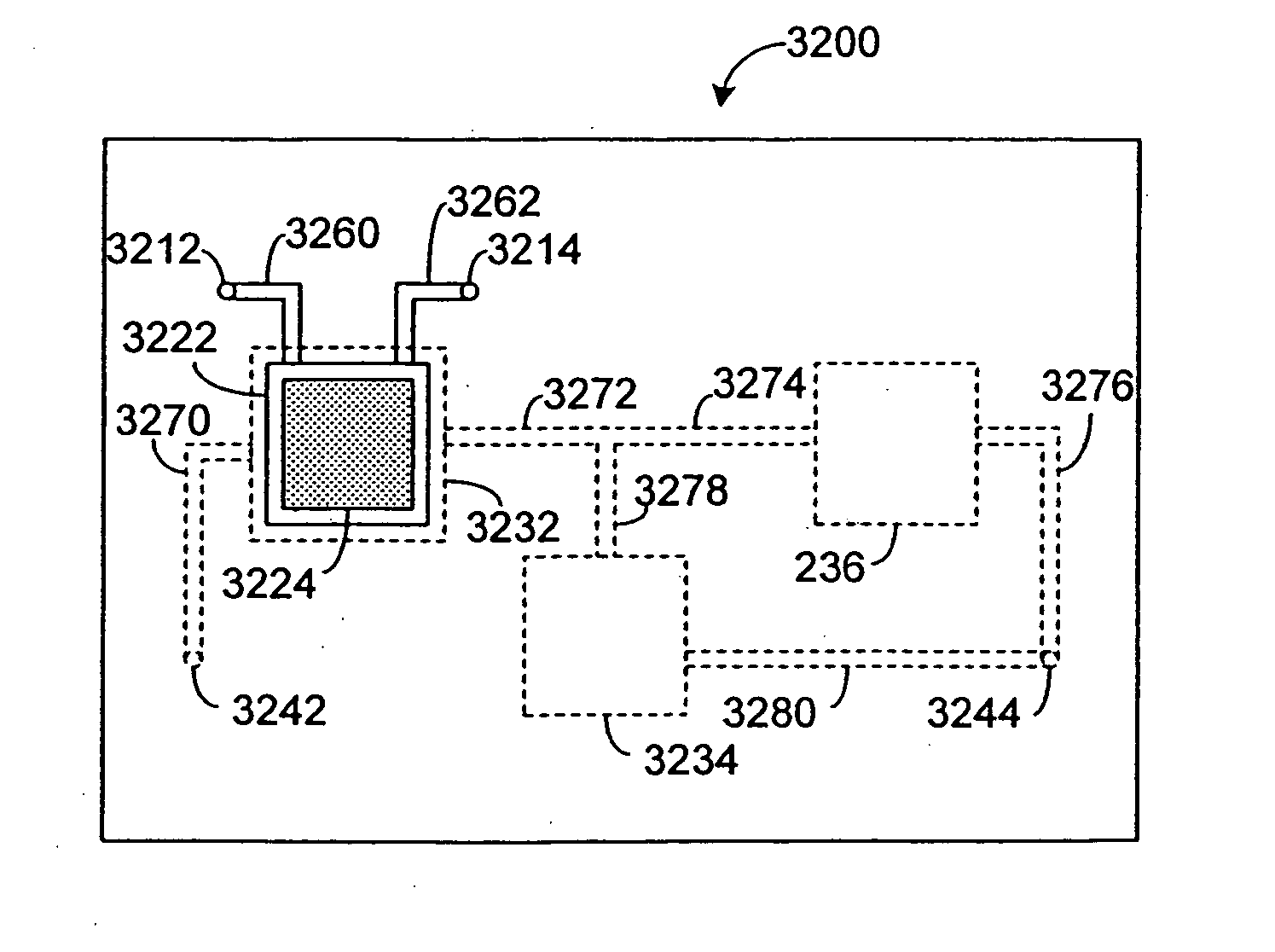
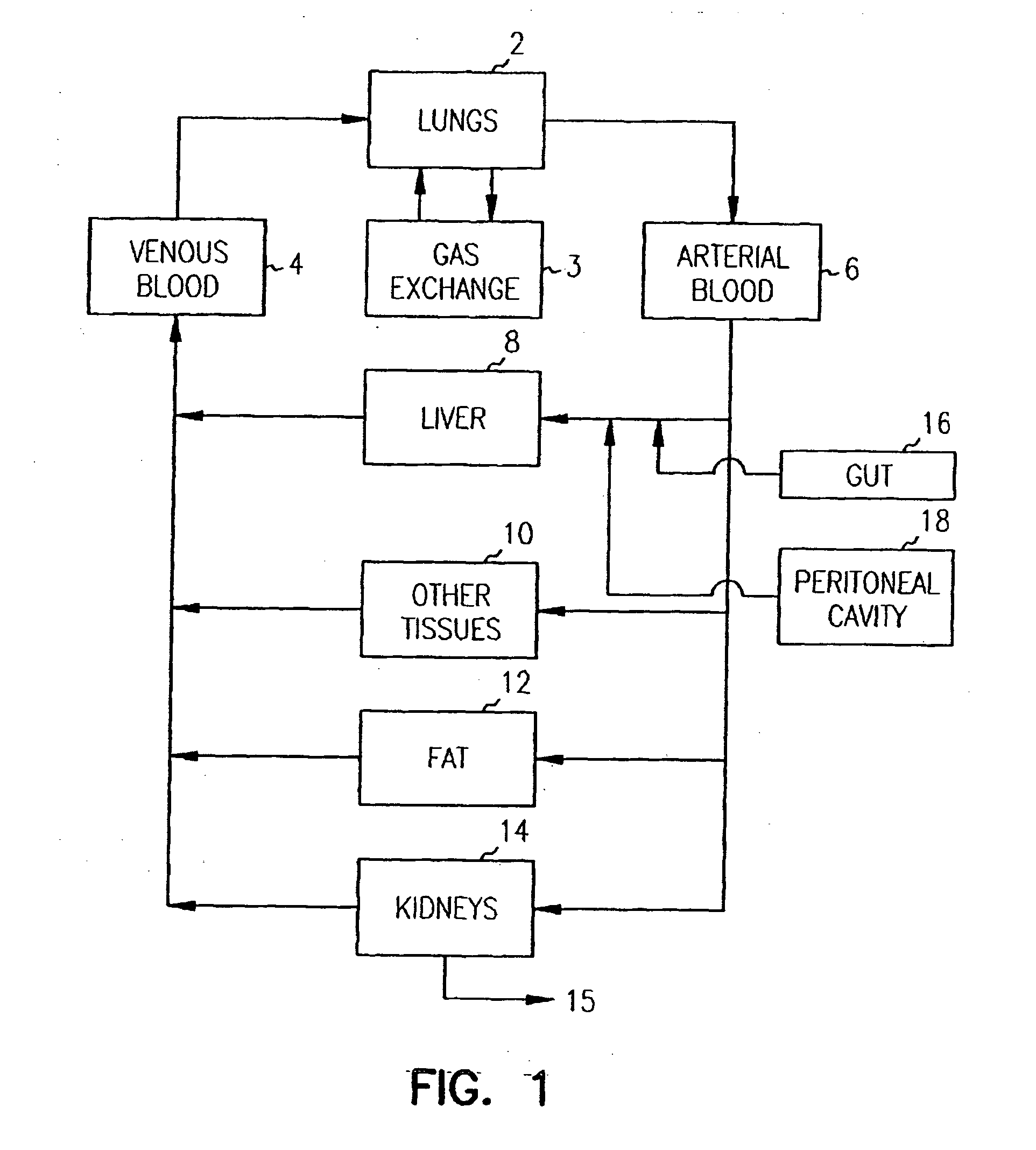
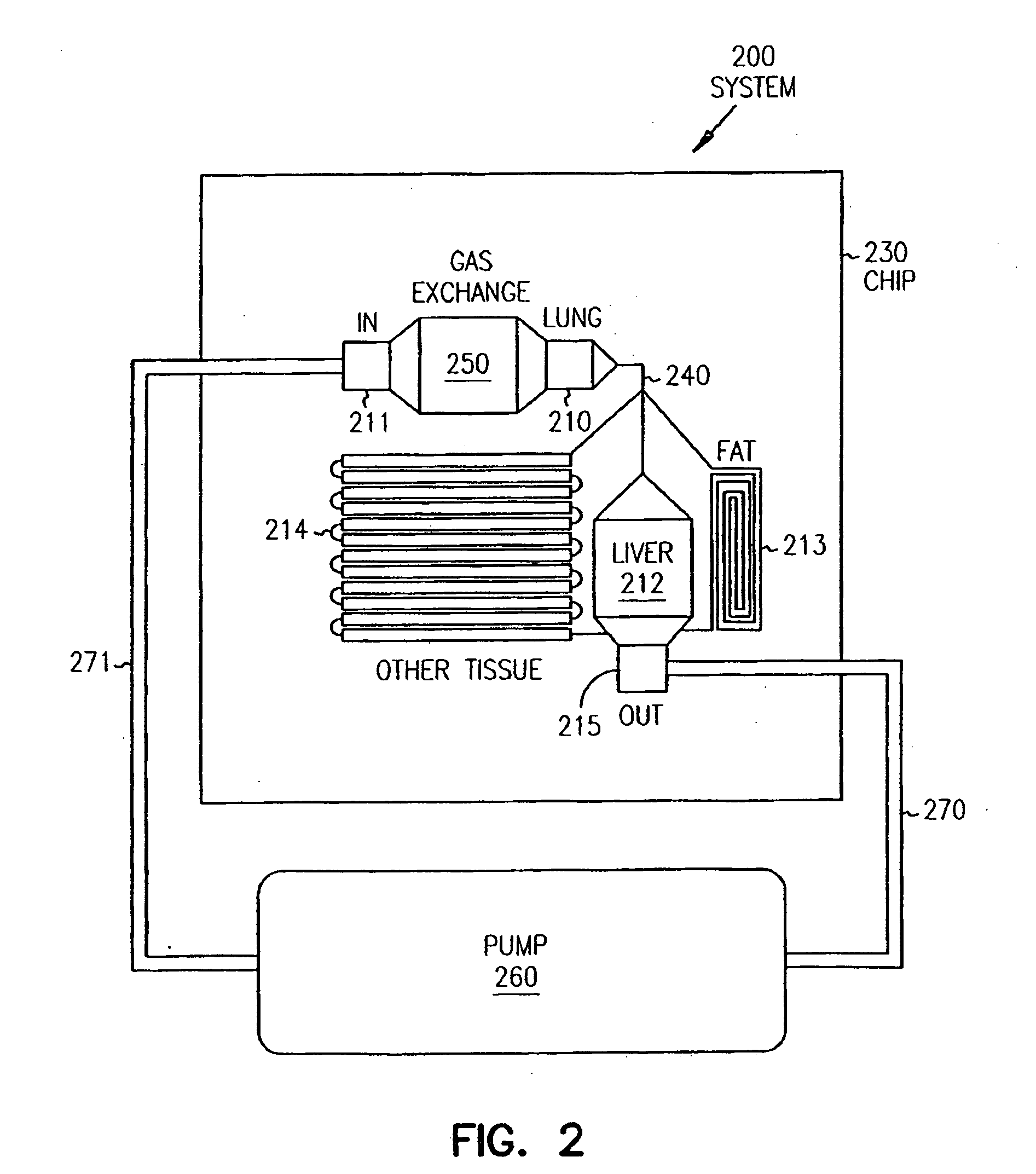
Systems and methods are disclosed for microscale pharmacokinetics. Various organs and their interactions with drug compounds can be simulated in vitro by use of microscale compartments that can be interconnected by microscale channels. Cells or cellular materials associated with the organs can be cultured in such compartments to allow interactions with drug compounds in one or more fluidic flows. Such fluidic systems can include, by way of examples, gastrointestinal flow, blood flow, bile flow, urinary flow, and brain fluid flow. Interactions between fluidic systems can be simulated by a microscale permeable member. In one example, blood-biliary interaction can be simulated by a microscale permeable material having hepatocytes bound to a permeable substrate via a binder.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Pharmacokinetic-based culture system with biological barriers
InactiveUS20070037277A1Increase valueIncreased toxicityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood flowDrug compound
Systems and methods are disclosed for microscale pharmacokinetics. Various organs and their interactions with drug compounds can be simulated in vitro by use of microscale compartments that can be interconnected by microscale channels. Cells or cellular materials associated with the organs can be cultured in such compartments to allow interactions with drug compounds in one or more fluidic flows. Such fluidic systems can include, by way of examples, gastrointestinal flow, blood flow, bile flow, urinary flow, and brain fluid flow. Interactions between fluidic systems can be simulated by a microscale permeable member. In one example, blood-biliary interaction can be simulated by a microscale permeable material having hepatocytes bound to a permeable substrate via a binder.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
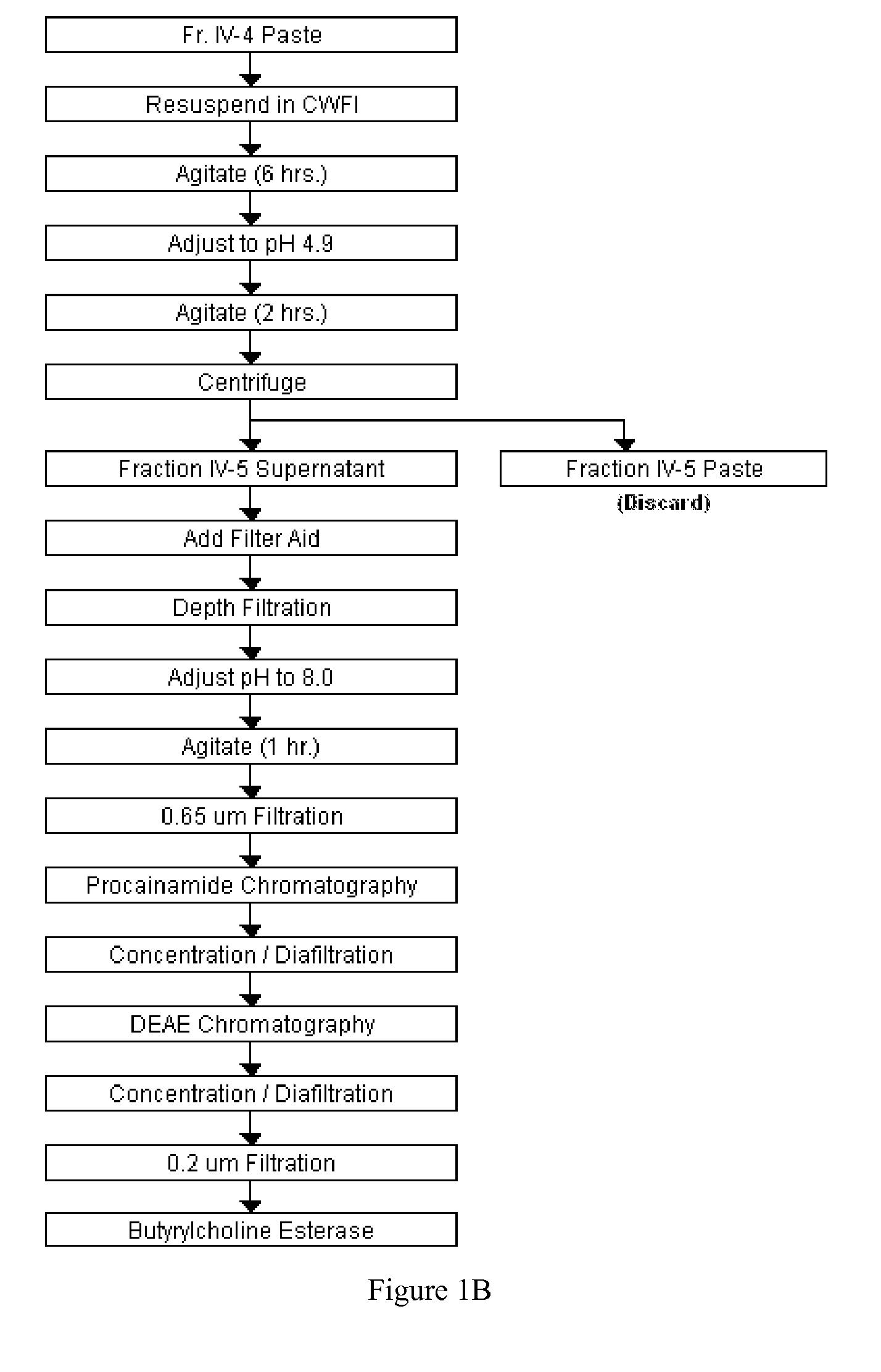
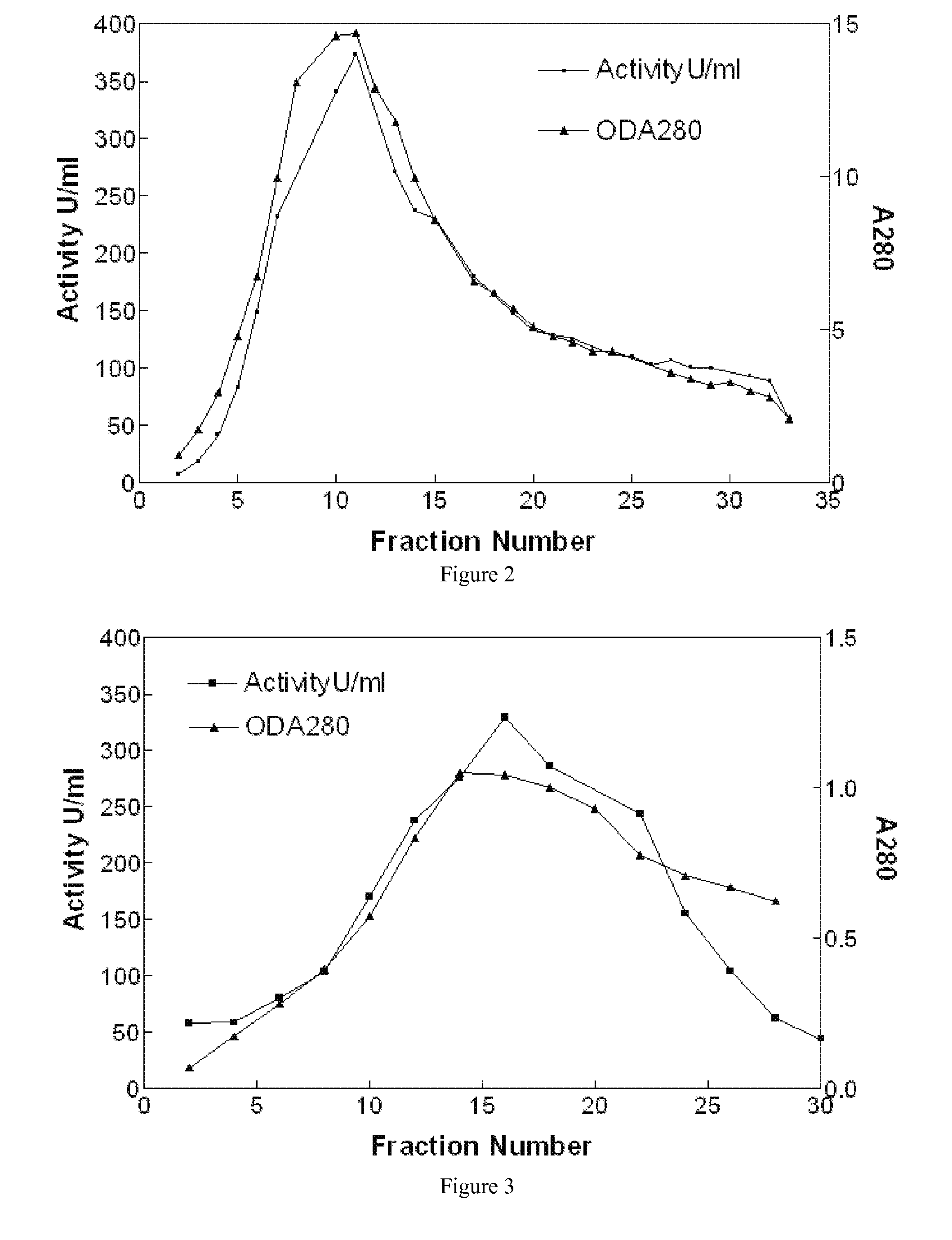
Large-Scale Production of Human Serum Butyrylcholinesterase as a Bioscavenger
InactiveUS20070184045A1Treating and preventing and inhibiting toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesCholinesteraseButyrylcholinesterase
Disclosed herein are methods for the large-scale preparation of human butyrylcholinesterase (HuBChE) preparations from Cohn Fraction IV-4. As disclosed, the methods provide HuBChE preparations that are about 99% or more pure with recovery yields of about 60%. Also disclosed are the pharmacokinetics, safety and toxicity, stability and efficacy of the HuBChE preparations.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090181032A1Extended half-lifeImprove distributionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Antibodies with modified affinity to fcrn that promote antigen clearance
InactiveUS20130131319A1Increase the number ofSuperior in vivo effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen bindingAntigen uptake
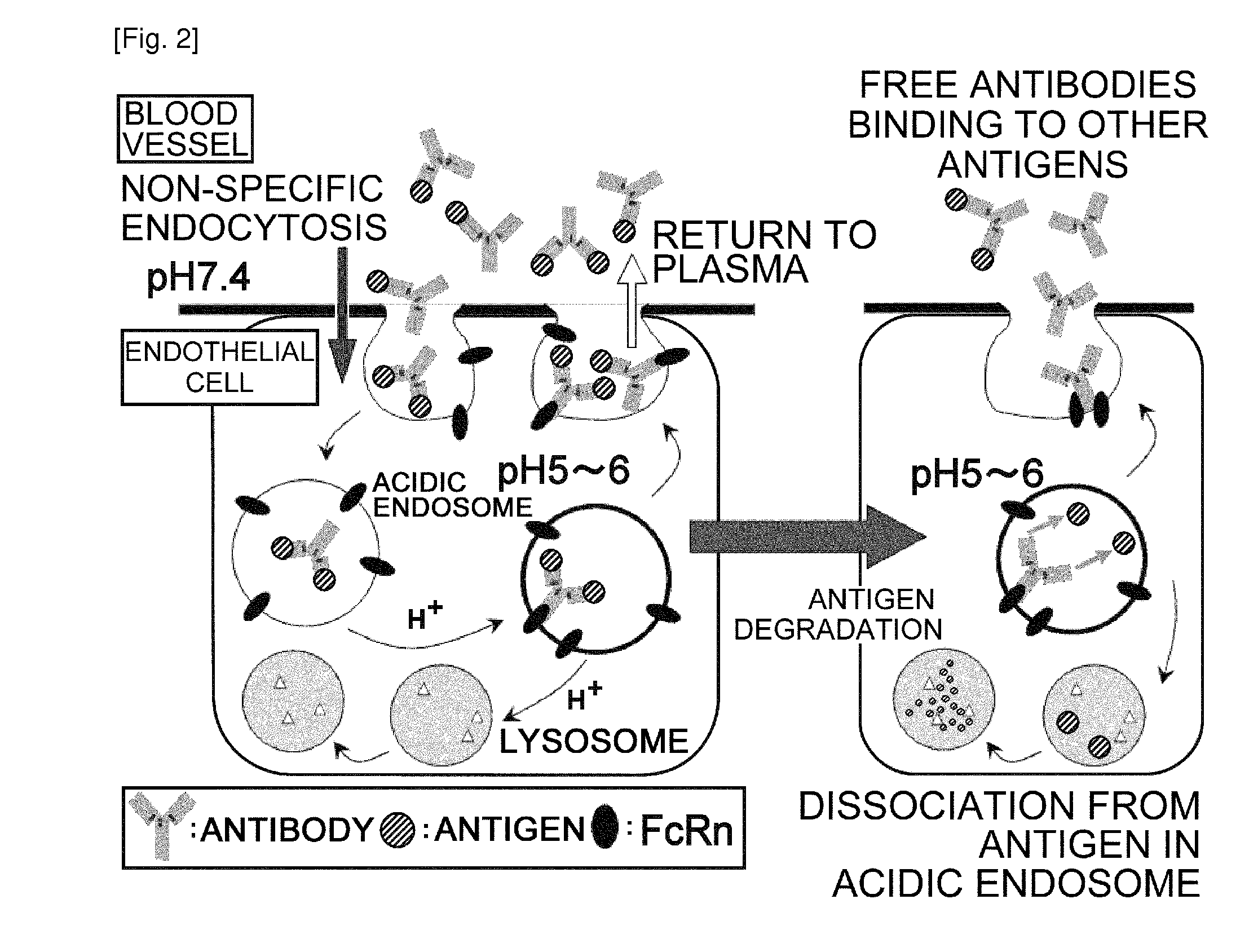
An objective of the present invention is to provide methods for facilitating antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells, methods for facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, methods for increasing the number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind, methods for improving pharmacokinetics of antigen-binding molecules, antigen-binding molecules improved for facilitated antigen uptake into cells, antigen-binding molecules capable of facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, antigen-binding molecules capable of repeatedly binding to antigens, antigen-binding molecules with improved pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such an antigen-binding molecule, and methods for producing those described above. The present inventors discovered that antigen uptake into cells is facilitated by an antibody having human FcRn-binding activity at the plasma pH and a lower antigen-binding activity at the early endosomal pH than at the plasma pH; such antibodies can increase the number of antigens to which a single antibody molecule can bind; the reduction of antigen in plasma can be facilitated by administering such an antibody; and antibody pharmacokinetics can be improved by using such antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090181013A1Reduce deliveryImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Antibody molecules that bind to il-6 receptor
InactiveUS20120253016A1Good curative effectImprove pharmacokineticsFungiSenses disorderTherapeutic effectIL-2 receptor
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising second-generation molecules that are superior than TOCILIZUMAB, by altering the amino acid sequences of the variable and constant regions of TOCILIZUMAB, which is a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor IgG1 antibody, to enhance the antigen-neutralizing ability and increase the pharmacokinetics, so that the therapeutic effect is exerted with a less frequency of administration, and the immunogenicity, safety and physicochemical properties (stability and homogeneity) are improved. The present invention also provides methods for producing these pharmaceutical compositions. The present inventors have successfully generated second-generation molecules that are superior to TOCILIZUMAB by appropriately combining amino acid sequence alterations in the CDR domains, variable regions, and constant regions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com