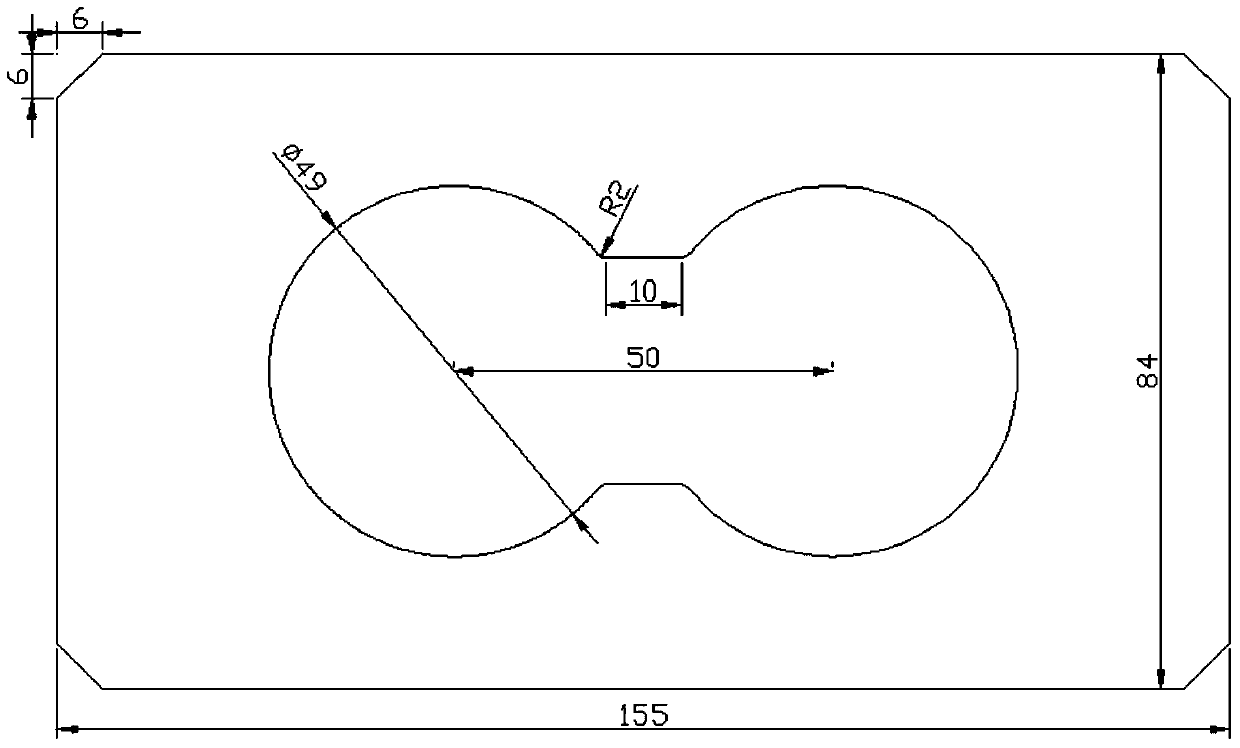
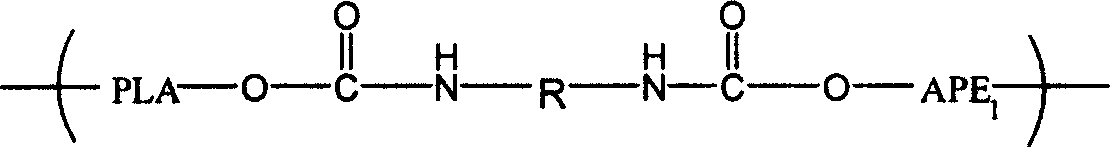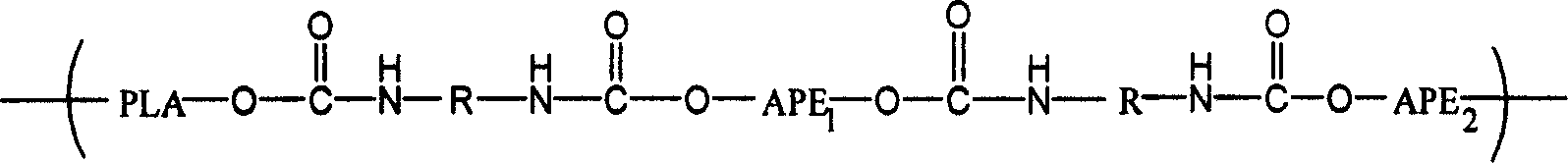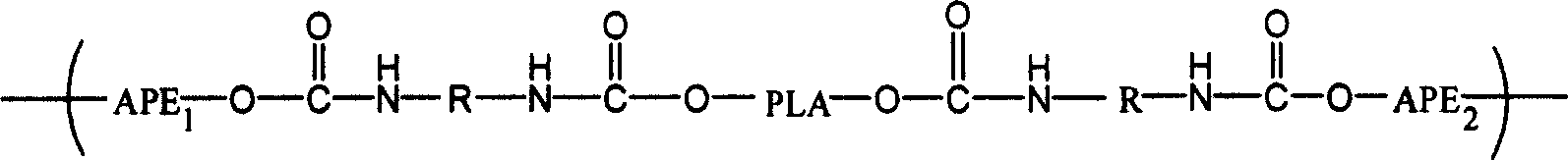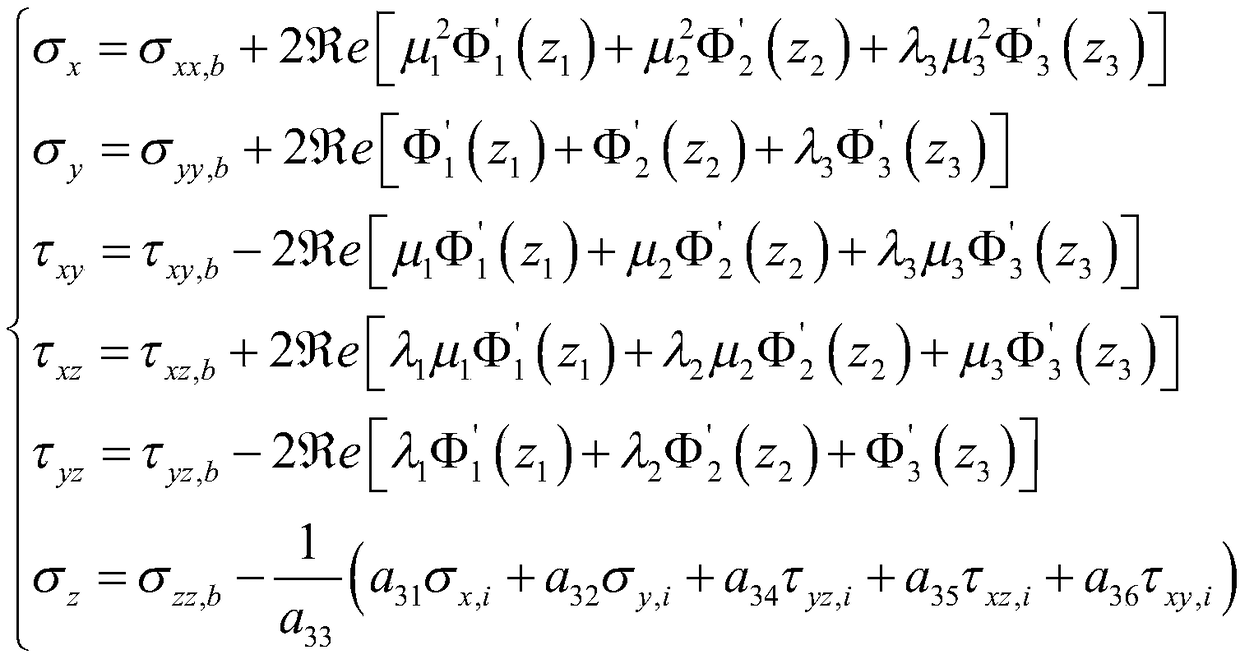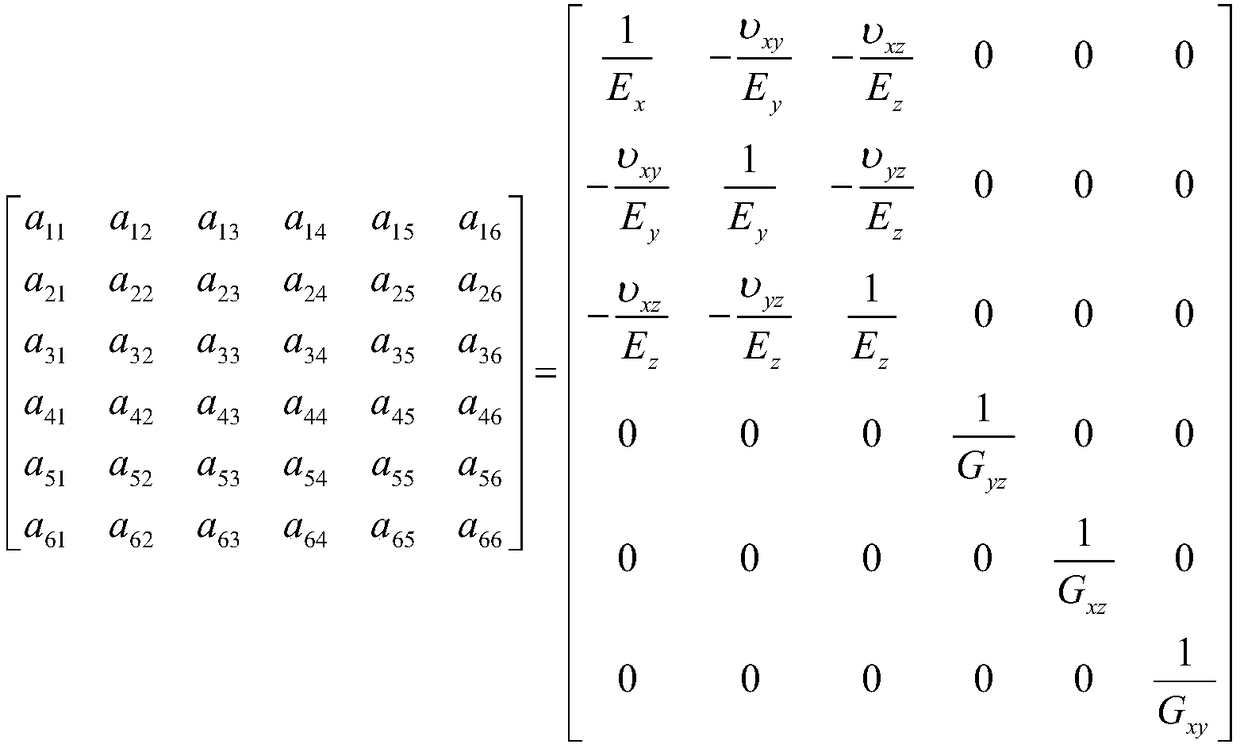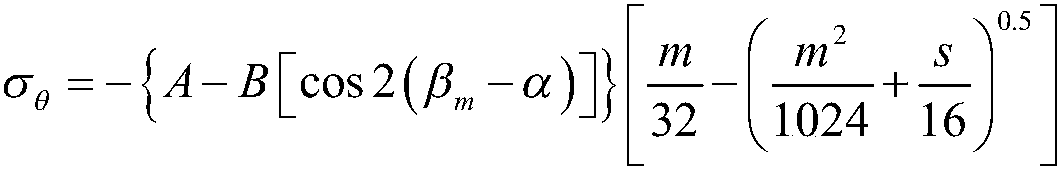Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
306 results about "Tensile fracture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for testing flow conductivity of self-supported crack in riverfrac treatment
The invention relates to a method for testing flow conductivity of self-supported cracks in riverfrac treatment. The method comprises the steps of: manufacturing a core test piece which satisfy closed state of the crack wall surface after pressure relief return of riverfrac treatment, drilling a phi 50*100 mm cylindrical test piece, enabling the cylindrical test piece to be orthogonal with a pre-formed scratch, splitting the pre-formed scratch to manufacture a tensile fracture type crack wall surface, dislocating the crack wall surface, smoothly grinding the end surface of the core test pieceto obtain a non-proppant non-engaged crack wall surface combination; then testing the flow conductivity of the crack, putting the manufactured core test piece into a core clamping system, simulating formation stress and temperature, setting and sending a control instruction, enabling each system to work and feed back signals, and finally, collecting the test results and calculating the flow conductivity of self-supported crack in the riverfrac treatment. The method in the invention can really reflect the tensile fracture and shear slip process of the riverfrac treatment, and reduce the process to a pressure and temperature environment under the ground to test the flow conductivity; and the test method is achievable.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Molded article and method for producing the same
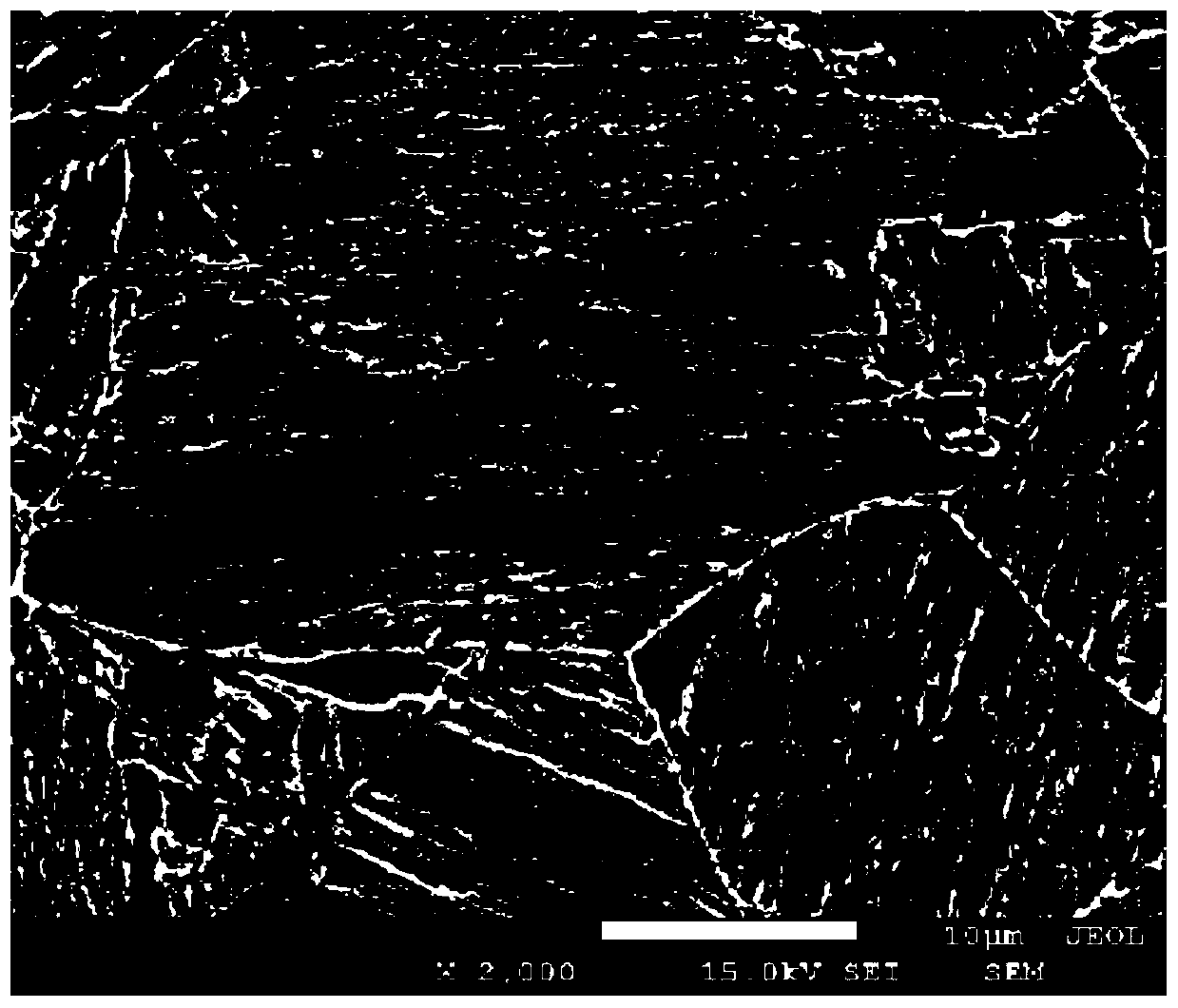
InactiveUS20090208721A1Improve impact resistanceReduce frequencySynthetic resin layered productsMedical devicesFiber-reinforced compositeUltimate tensile strength
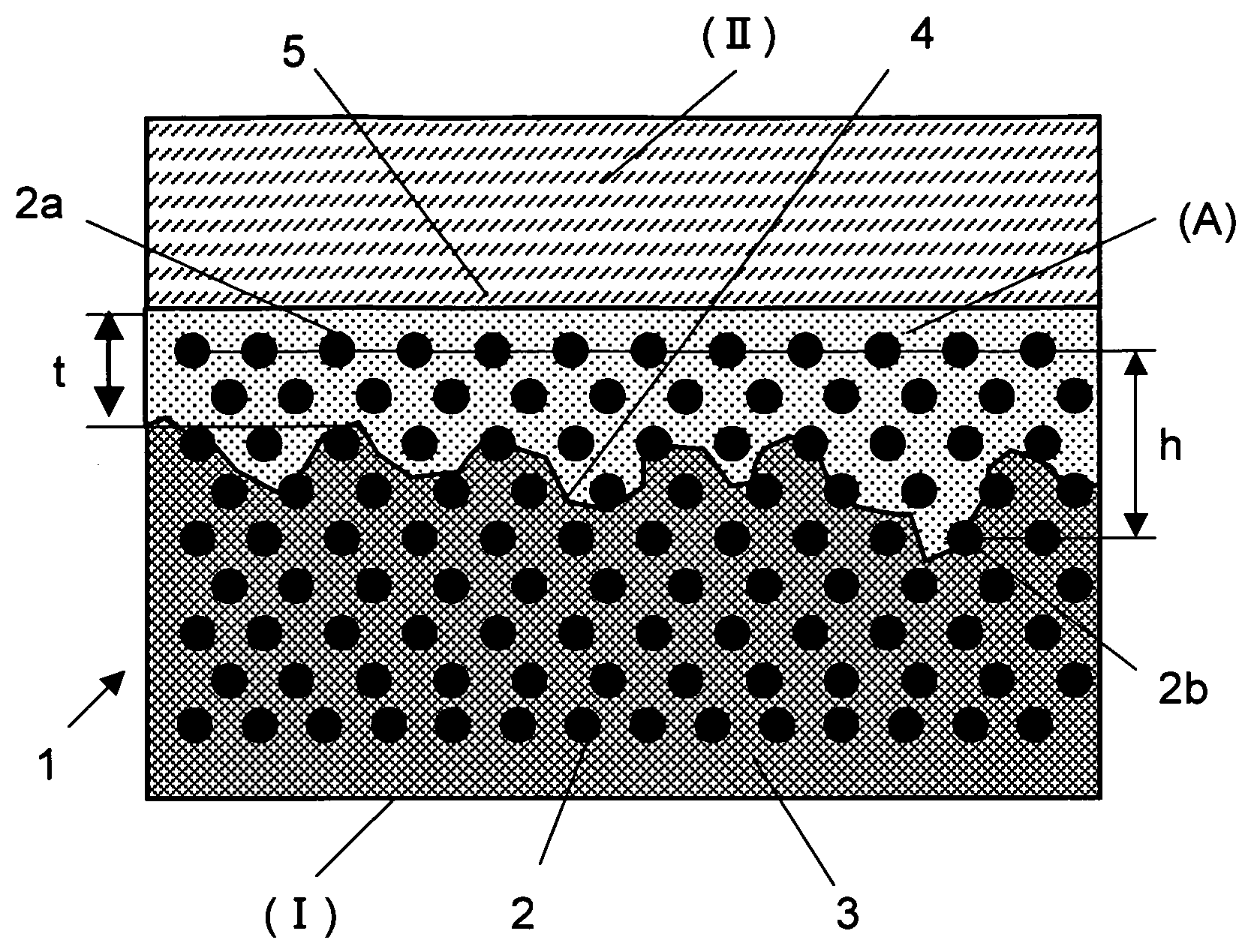
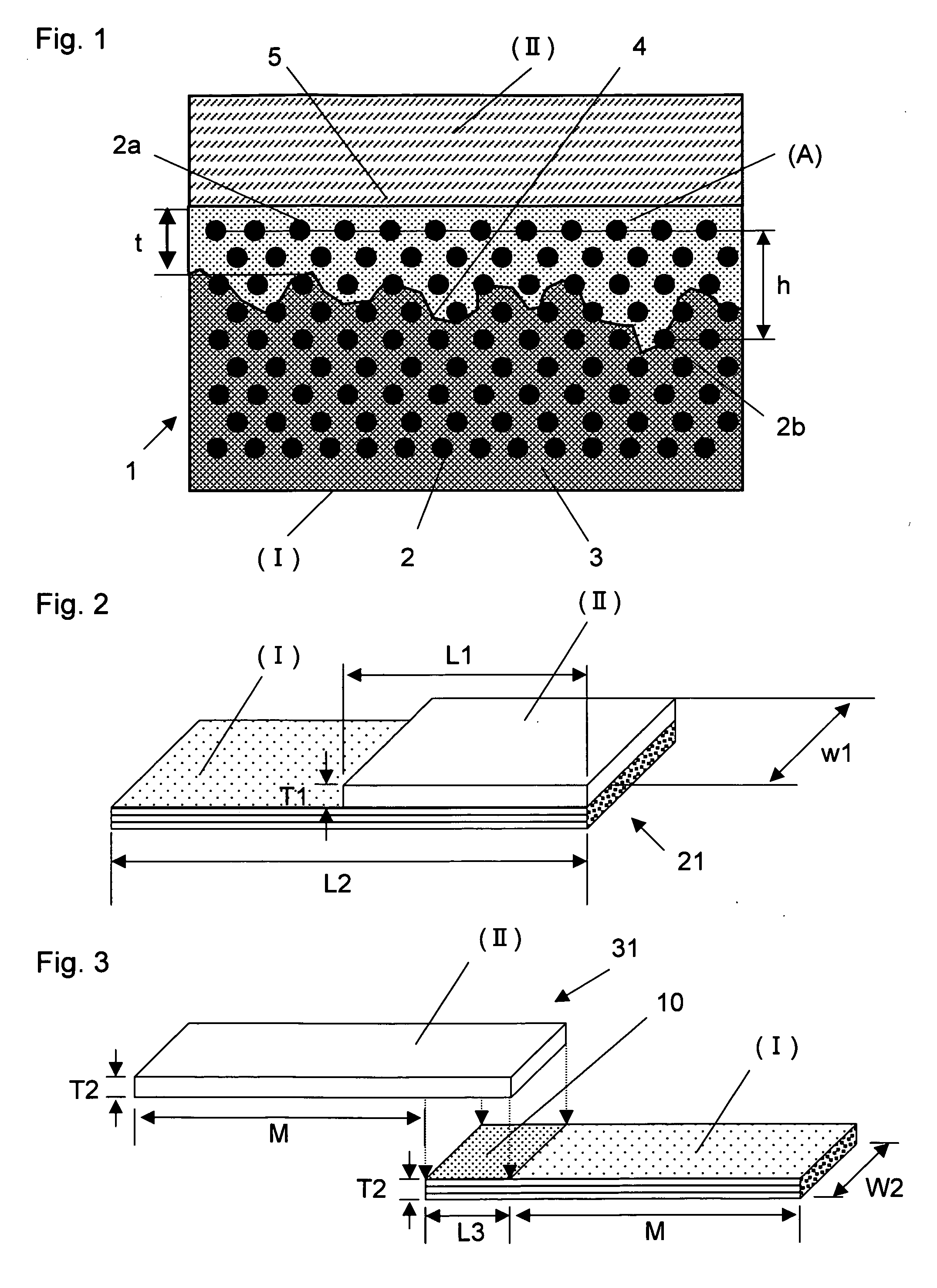
Disclosed is a molded article composed of a fiber-reinforced composite material (I) containing a continuous reinforcing fiber and a thermosetting matrix resin, and a thermoplastic resin member (II) which is joined to and integrated with at least a part of the surface of the fiber-reinforced composite material (I) by using a thermoplastic resin (A). The joined surface between the thermoplastic resin (A) and the fiber-reinforced composite material (I) has projections and recesses in the cross-section in the thickness direction of the molded article, and the maximum impregnation depth h of the thermoplastic resin (A) in the fiber-reinforced composite material (I) is not less than 10 μm. The thermoplastic resin (A) has a tensile strength at break of not less than 25 MPa and a tensile elongation at break of not less than 200%. The impact adhesive strength at the joined portion of the fiber-reinforced composite material (I) and the thermoplastic resin member (II) is not less than 3,000 J / m2.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
System and method for measuring direct tensile strength and deformation of rock
InactiveCN103674707AAccurately measure deformation dataTroubleshooting Stretch FailuresMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementStress concentrationRock sample
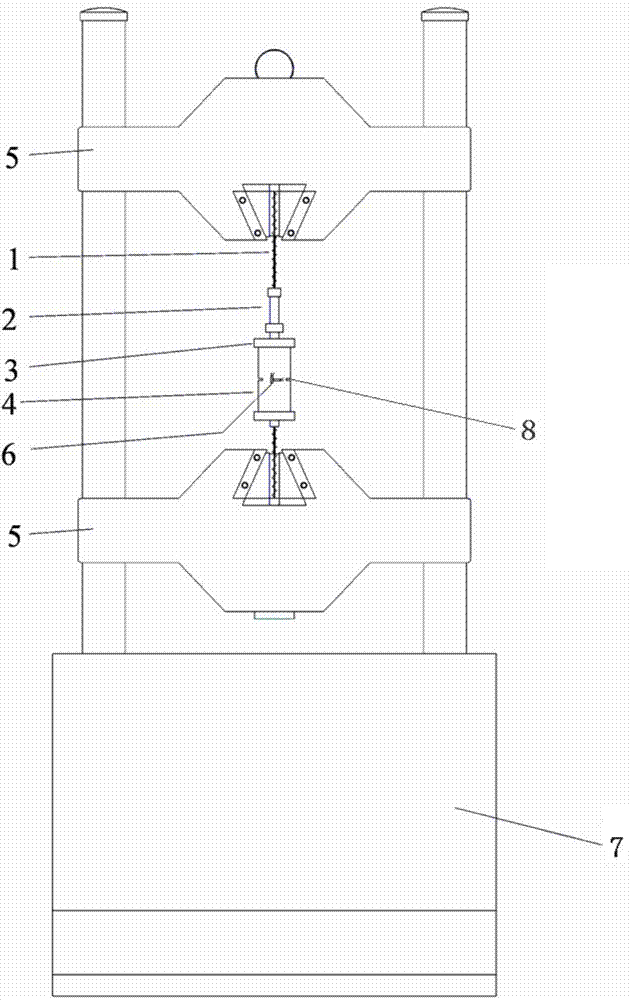
The invention provides a system and a method for measuring direct tensile strength and deformation of rock by using manual kerfs. The system comprises test loading equipment, a rock sample, metal sleeve caps, a flexible connecting mechanism and a tensile load sensor, wherein the rock sample is cylindrical, two kerfs are symmetrically cut in two sides of the middle position of the rock sample, and the kerf directions are the radial direction of the sample; and an upper metal sleeve cap and a lower metal sleeve cap are arranged at two ends of the rock sample respectively, the upper metal sleeve cap is connected with an upper clamp clamping opening of the test loading equipment through the flexible connecting mechanism and the tensile load sensor sequentially, and the lower metal sleeve cap is connected with a lower clamp clamping opening of the test loading equipment 7 through the flexible connecting mechanism. According to the technical scheme, the defects that the rock sample is prone to bend or produce torsion stress in a direct tensile test are overcome, at the same time, the situation that tensile fracture is not produced during fracture due to the end stress concentration effect of the rock sample is avoided, and the rock tensile strength and the axial and radial deformation of the rock in a stretching process can be accurately and effectively measured.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Microrelief structural body, decorative sheet, decorative resin molded body, method for producing microrelief structural body, and method for producing decorative resin molded body
ActiveUS20160052227A1High flexibilityHigh stretchabilitySynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageElastic modulusEngineering
A structural body which comprises a base and a microrelief structure layer having a microrelief structure. The microrelief structure layer is laminated on the base so as to form the surface layer of this structural body, and the microrelief structure layer has at least one physical property selected from the group consisting of (A) and (B) described below. (A) The elastic modulus at 25° C. is 50 MPa or more, and the elastic modulus at 80° C. is 30 MPa or less. (B) The tensile elongation at break at 80° C. is from 20% to 100% (inclusive).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
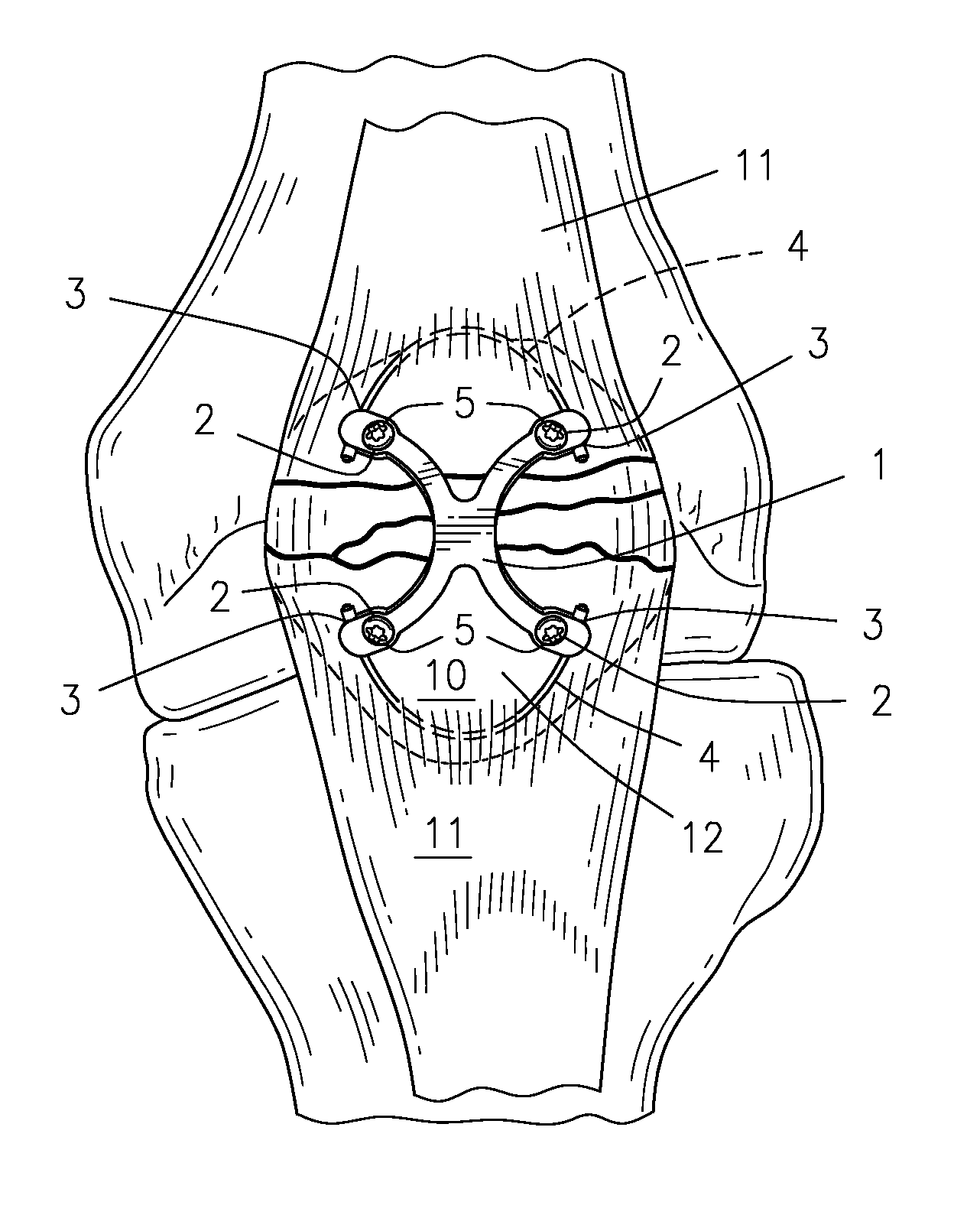
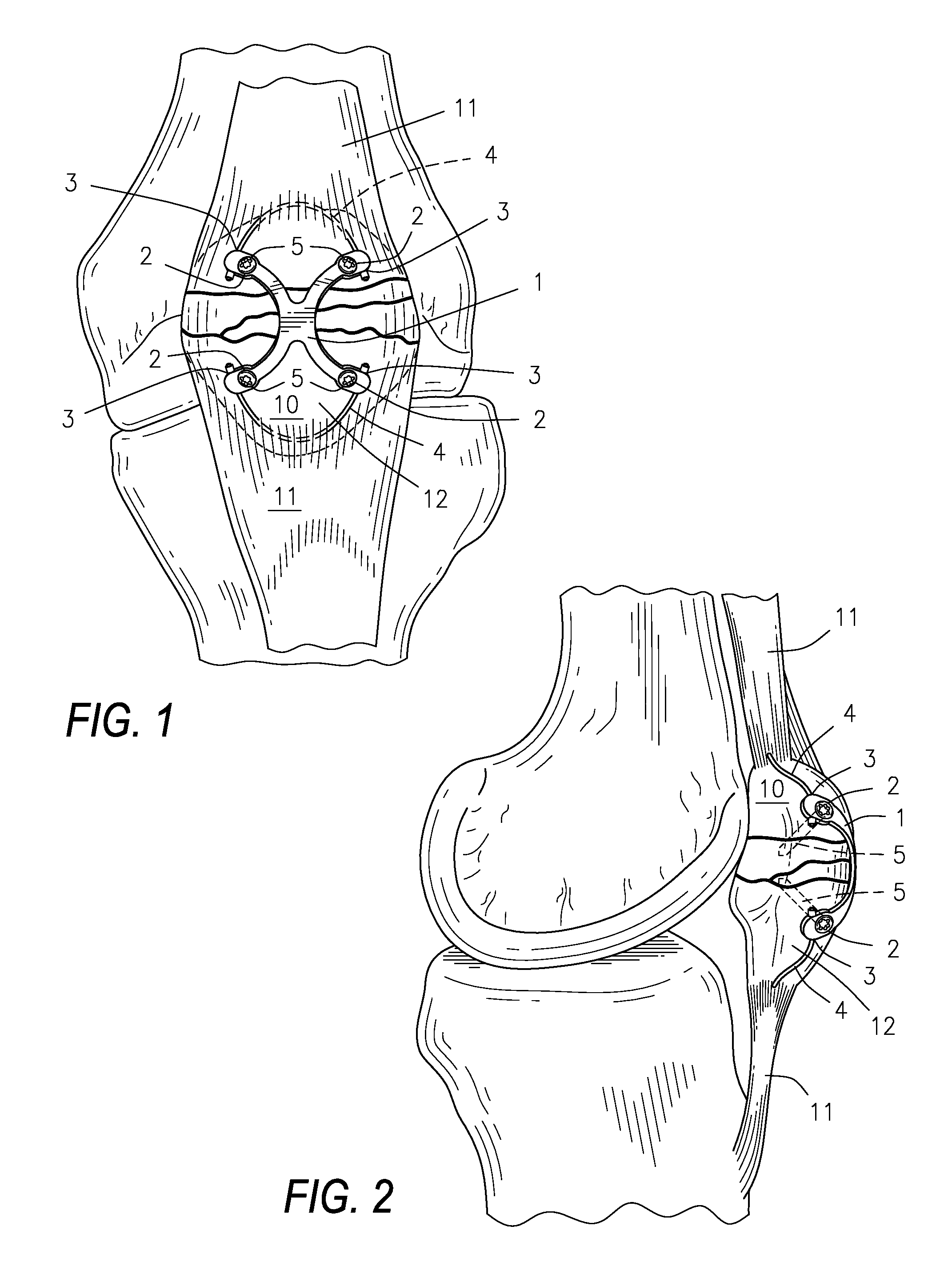
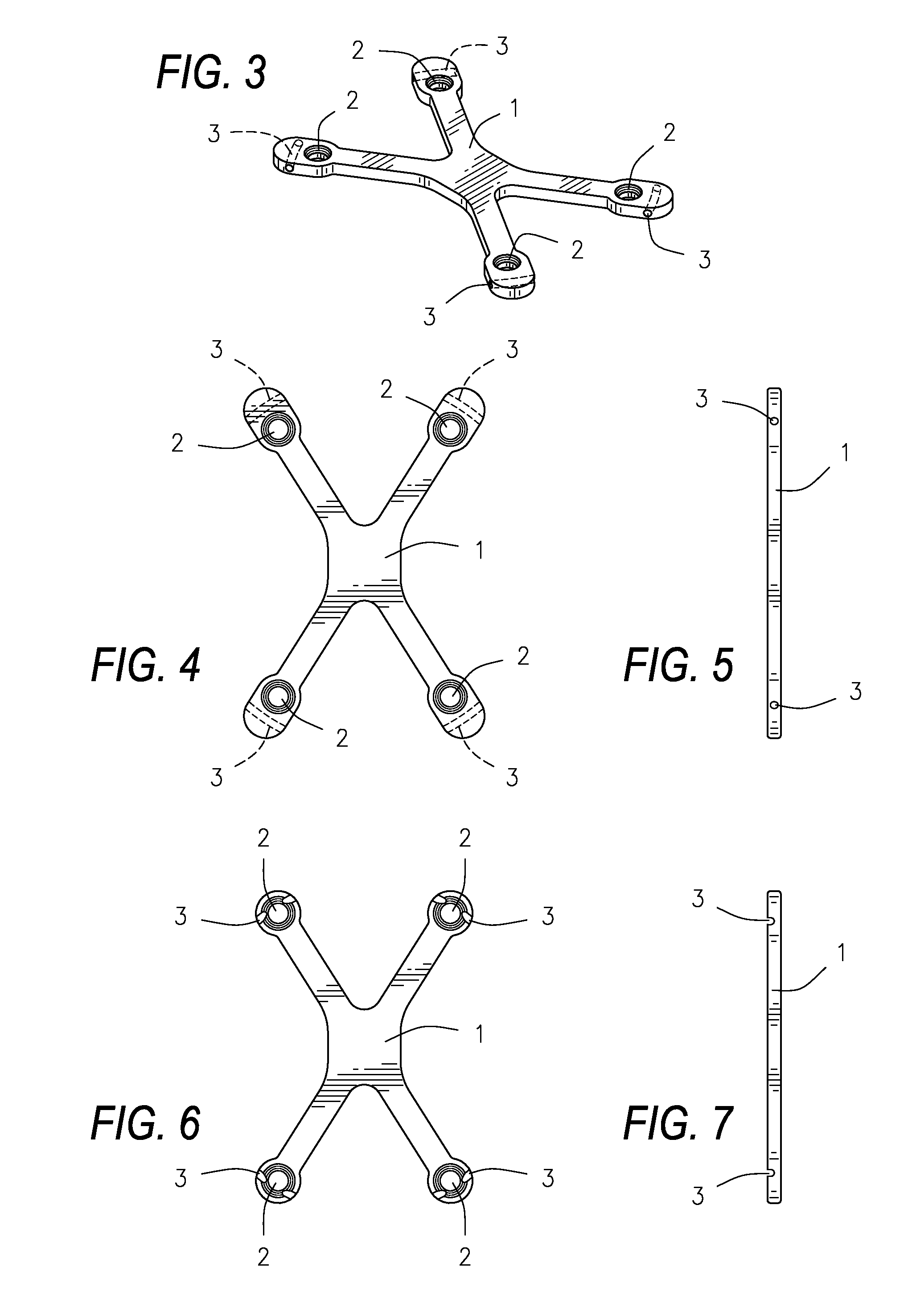
Low profile periarticular tension band plating system with soft tissue neutralization cable tunnel/channel
A bone plating system comprising: a plate, where the plate is low-profile and capable of contouring to a bone; a variable number of screw holes, locking or non-locking; at least one channel or tunnel through the plate; and at least one flexible device passing through the channel or tunnel and passing through soft tissue attached to the bone. The low profile plate, in combination with the flexible device passing through the surrounding soft tissue, functions as a tension band and acts to neutralize the muscle forces tending to pull the bone apart at a fracture. The low profile tension band plating system is targeted for periarticular tensile fractures for repair of patella, olecranon, greater trochanter, greater tuberosity, radial styloid, lateral or medial malleoli, or lateral malleolus.
Owner:NORRIS SURGICAL LLC
Biaxially Oriented Polyarylene Sulfide Film and Laminated Polyarylene Sulfide Sheets Comprising the Same
InactiveUS20070299219A1Excellent formabilityHigh elongationSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticPolymer science
A biaxially oriented polyarylene sulfide film and laminated polyarylene sulfide sheets of the film contain polyarylene sulfide and other thermoplastic resin A different from the polyarylene sulfide, wherein the contents of the polyarylene sulfide and the thermoplastic resin A are 70 to 99 parts by weight and 1 to 30 parts by weight respectively when the total amount of the polyarylene sulfide and the thermoplastic resin A is taken as 100 parts by weight and the resin thermoplastic A forms a dispersed phase with an average particle diameter of 10 to 500 nm and the biaxially oriented polyarylene sulfide film exhibits a tensile elongation at break of 110 to 250% in at least one of the longitudinal direction and width direction and a tensile fracture elongation of 80 to 250% in the other direction.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Low profile periarticular tension band plating system with soft tissue neutralization cable tunnel/channel
A bone plating system comprising: a plate, where the plate is low-profile and capable of contouring to a bone; a variable number of screw holes, locking or non-locking; at least one channel or tunnel through the plate; and at least one flexible device passing through the channel or tunnel and passing through soft tissue attached to the bone. The low profile plate, in combination with the flexible device passing through the surrounding soft tissue, functions as a tension band and acts to neutralize the muscle forces tending to pull the bone apart at a fracture. The low profile tension band plating system is targeted for periarticular tensile fractures for repair of patella, olecranon, greater trochanter, greater tuberosity, radial styloid, lateral or medial malleoli, or lateral malleolus.
Owner:NORRIS SURGICAL LLC
Polyester resin and resin composition for molding, and formed product thereof
In a saturated polyester resin or a composition with the saturated polyester resin as the main component for molding, the melt viscosity at 200° C. is at least 5 dPa.s and not more than 1000 dPa.s, and the product axb is at least 500 where a (N / cm2) is the tensile breaking strength and b (%) is the tensile breaking elongation of a film shape formed product. Preferably, the polyester resin has a glass transition temperature of not more than -10° C., a melting point of at least 70° C. and not more than 200° C., and an ester group concentration of at least 1000 equivalents / 106 g and not more than 8000 equivalents / 106 g. A material superior in water resistance, electrical insulation, durability, working environment and productivity as a molding material for an electric electronic component having a sophisticated configuration is provided.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Polylactic-acid block copolymer and its preparing method
ActiveCN101024696ALow costAvoids a host of problems associated with ring-opening polymerization processesPolyesterPolymer science
The invention discloses a poly-lactic acid block copolymer. The feature is that it is made from the end hydroxyl poly-lactic acid with intrinsic viscosity of 0.05-0.5dL / g and aliphatic polyester glycol with intrinsic viscosity of 0.1-1.0dL / g taking fusion reaction under existing of diisocyanate. The intrinsic viscosity of the copolymer is 0.7-2.5dL / g, and tensile strength is 10-40MPa, elongation at break is 100-800%. The invention also discloses the manufacturing method for the copolymer. It has the advantages of good toughness, strong tensile strength, high tensile fracture elongation, etc.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Alignment loading device used for stretching test of nanoscale, micron-size thin film materials
InactiveCN102221499AEliminate empty travelEliminate idle travel effectsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDirect observationEngineering
The invention relates to an alignment loading device used for stretching test of nanoscale, micron-size thin film materials, which comprises a reverse thread alignment loading framework and a flexible hinge loading sensing parts; the reverse thread alignment loading framework comprises a base plate, two vertical plates, two guide bars, two slide plates, two guide groove blocks, an adjusting leading screw and a handwheel, a left-right turning screw rod thread is arranged on the adjusting leading screw between the two vertical plates, central leading screw apertures on two slide plates are respectively cooperated with the left-right turning screw rod thread on the adjusting leading screw and perform a synchronous relative movement along two guide bars; the flexible hinge loading sensing part has an integral type framework structure, wherein two S-shaped sensing parts used for pasting foil gauges are symmetrically arranged in the central part. The invention has the advantages of compact structure and small size, and is suitable for directly observing and measuring under a microscope; the flexible hinge is connected with the framework structure by integrating with a sensor, which can improve the measure precision, as well as measure and evaluate the interface combination performance of the nanoscale, micron-size thin film substrate structure test piece and tensile fracture performance of the films.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Degradable rubber member for downhole tools, degradable seal member, degradable protecting member, downhole tool, and method for well drilling
ActiveUS20170016298A1Reduce expensesReduce processFluid removalDrilling compositionRubber materialLoss rate
A degradable rubber member for a downhole tool formed from a rubber material containing from 0.1 to 20 parts by mass of a degradation accelerator relative to 100 parts by mass of a degradable rubber (optionally containing other rubber materials and / or reinforcing materials), of which, preferably, the decrease rate of the mass or the 50% strain compressive stress after immersion for 24 hours in 150° C. water is not less than 5%, and / or the mass loss rate after immersion for 72 hours in 150° C. water is from 5 to 100%, and further, as desired, the tensile fracture strain at 66° C. is not less than 50%, the 70% strain compressive stress is not less than 10 MPa, and the compressive fracture strain is not less than 50%; a degradable seal member or a protecting member for downhole tools comprising such a rubber member; and a downhole tool such as a plug for well drilling, and a method for well drilling.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Molding packaging material and battery case
ActiveUS20140134475A1Good chemical resistanceGood formabilityWrappersDomestic containersBreaking strengthMetal foil
Provided is a molding packaging material that can have an increased use life, can suppress a decrease over time in inter-layer lamination strength, and has superior molding properties in extrusion molding, draw forming, and the like. The laminate molding packaging material contains: an outside substrate layer (2) comprising a heat-resistant resin; an inside sealant layer (3) comprising a thermoplastic resin; and a metal foil provided between the two layers as a barrier layer (4). In the heat-resistant resin of the outside substrate layer (2), a biaxially oriented polyethyleneterephthalate film is used that, when the tensile breaking strength in the M direction is MB and the tensile breaking strength in the T direction is TB, the following are satisfied:500 MPa=MB+TB=700 MPa; and formula (I)|MB−TB|=30 MPa. formula (II)
Owner:SHOWA DENKO PACKAGING CO LTD
Large-thickness lamellar tearing-resistant high-strength steel plate with 960 MPa-level yield strength and production method thereof
ActiveCN110318008APromoting degenerationImproved through-thickness performanceFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyMechanical propertyMaterials science
The invention relates to a large-thickness lamellar tearing-resistant modulated high-strength steel plate with 960 MPa-level yield strength and a production method thereof. The chemical components ofthe large-thickness lamellar tearing-resistant modulated high-strength steel plate with 960 MPa-level yield strength comprises, by weight, 0.15-0.20% of carbon, 0.10-0.40% of silicon, 0.90-1.30% of manganese, 0.010-0.040% of niobium, 0.010-0.045% of vanadium, smaller than or equal to 0.010% of titanium, 0.03-0.06% of aluminum, 0.50-1.00% of nickel, smaller than or equal to 0.1% of copper, 0.30-0.80% of chromium, 0.20-0.70% of molybdenum, 0.001-0.005% of boron, 0.001-0.005% of calcium, smaller than or equal to 0.010% of phosphorus, smaller than or equal to 0.002% of sulphur, smaller than or equal to 0.002% of oxygen, smaller than or equal to 0.004% of nitrogen, smaller than or equal to 0.00015% of hydrogen and the balance iron and inevitable impurity elements. The technological steps of thesteel plate comprises smelting, secondary refining, vacuum degassing, calcium treatment, continuous casting, heating, rolling, steel plate slow cooling, quenching and tempering. The large-thickness lamellar tearing-resistant modulated high-strength steel plate with 960 MPa-level yield strength has high comprehensive mechanical property; the yield strength is greater than or equal to 960 MPa; thetensile strength is greater than or equal to 1000 MPa; the Charpy impact power at a low temperature of minus 40 DEG C is greater than or equal to 30J; the Z-direction tensile fracture surface shrinking rate is greater than or equal to 35%; and the lamellar tearing-resistant property is good.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
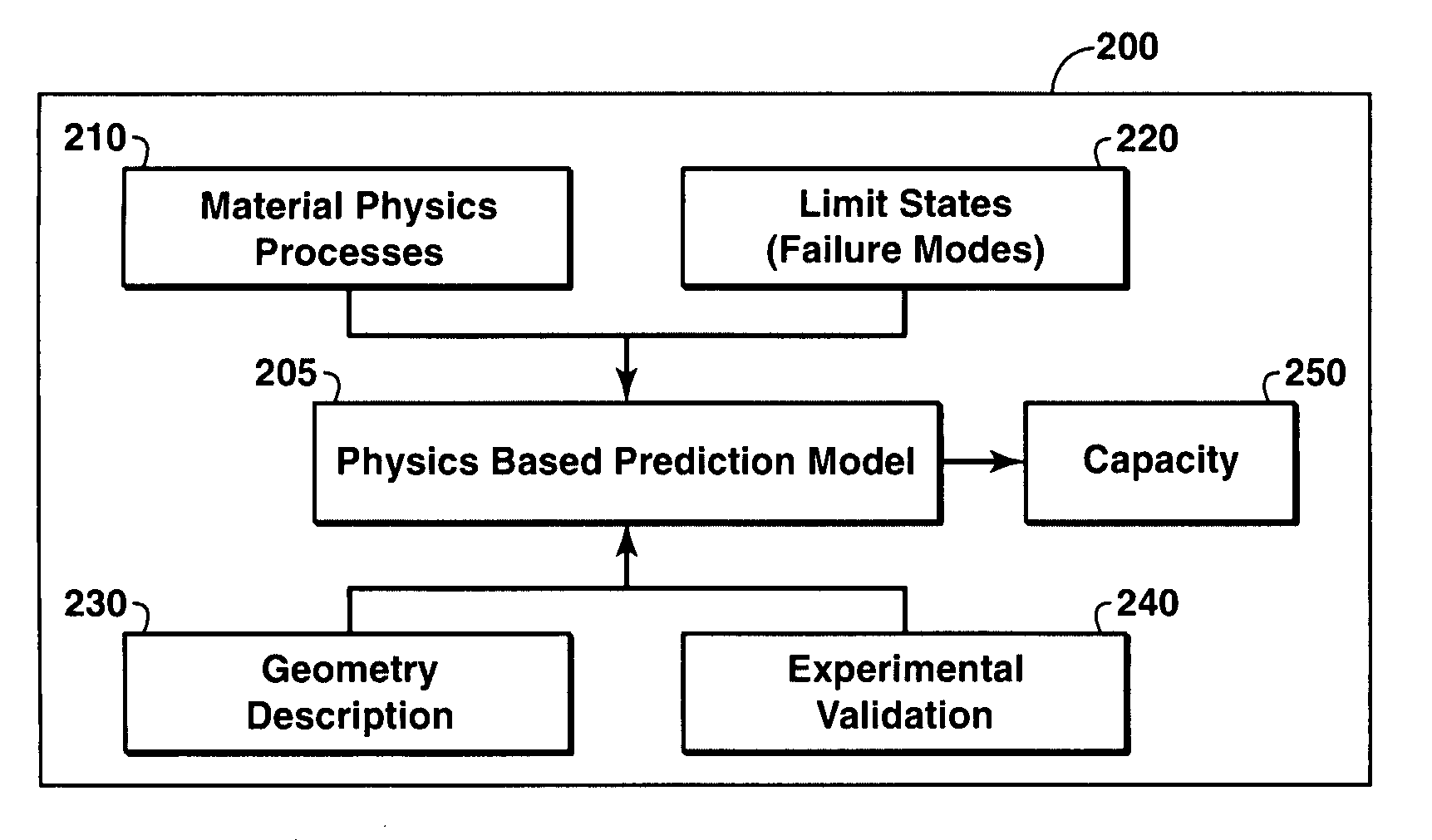
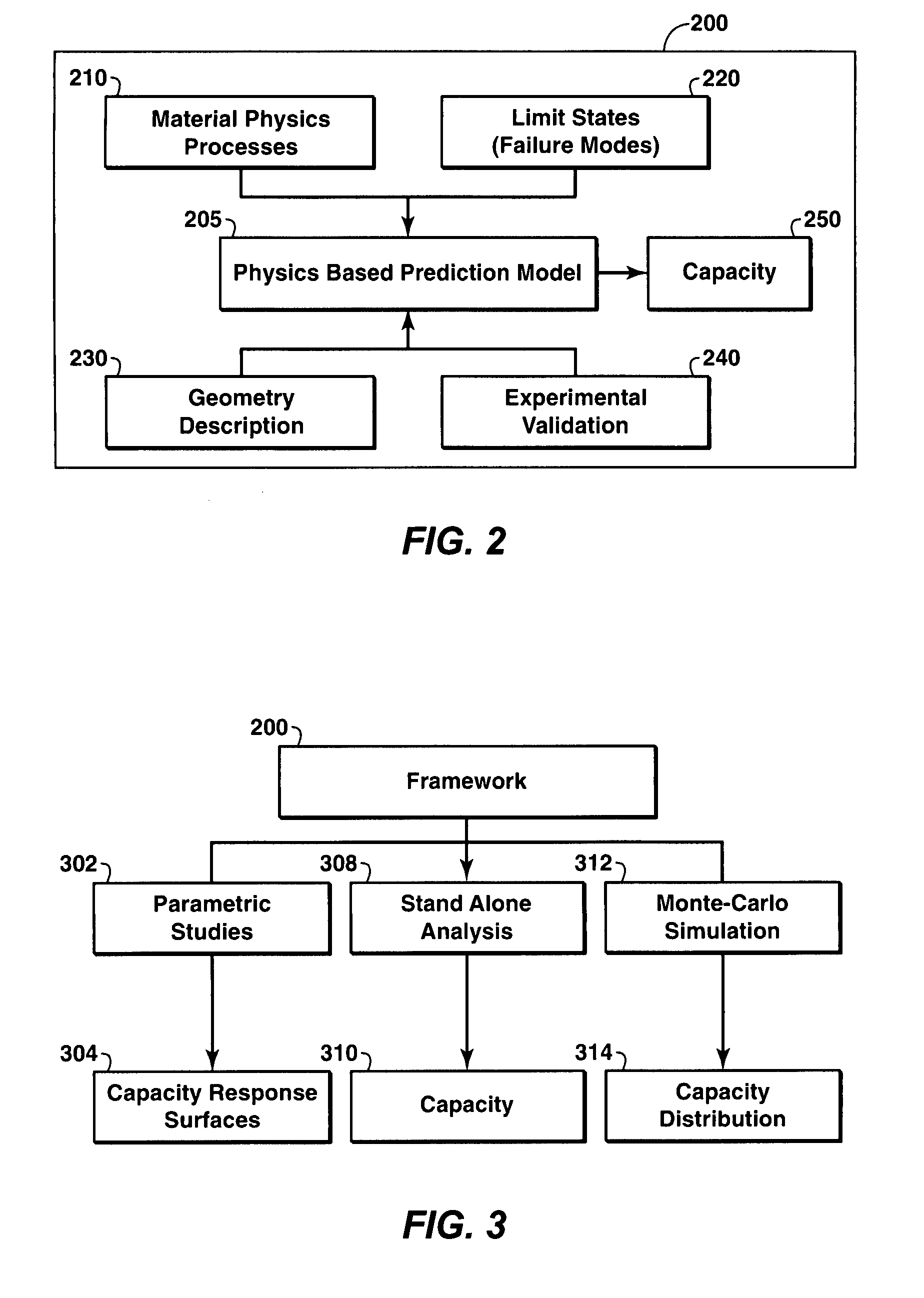
Framework to Determine the Capacity of A Structure
InactiveUS20100042379A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPhysics basedType distribution
A framework for determining or predicting the capacity of a structure. The framework includes predicting the capacity of the structure utilizing a physics-based prediction model. The prediction model may be constructed from a variety of numerical analysis approaches. The prediction model further incorporates at least one material physics process, at least one geometry description, and at least one limit state. The limit states may include collapse, tensile fracture, and buckling. The framework calls for validation of the predicted capacity of the structure via experimental verification or other methods. In some embodiments, the structure is a pipeline for producing hydrocarbons and the modes of operation may include parametric studies, Monte-Carlo type distributions, or stand-alone values.
Owner:MINNAAR KAREL +4
Method for producing polyurethane toughness-reinforcing cast form nylon composite material
InactiveCN101195706AHigh mechanical strengthIncreased tensile elongation at breakNylon materialToughness
The invention relates to a preparation method of polyurethane plasticizing monomer casting nylon compound material. The material is made through pouring the raw material of polyurethane prepolymer, and caprolactam, etc. The main performance of the material is characterized in that the mechanical strength is improved, the tensile fracture elongation rate is increased along with increasing of the use amount of the polyurethane prepolymer, the impact strength is enhanced along with the increasing of the use amount of the polyurethane prepolymer, and the tribology performance and the antistatic performance are improved remarkably.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adhesive tape for protecting surface of semiconductor wafer
ActiveCN102754200AFilm/foil adhesivesAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentWaferingPhysical chemistry
An adhesive tape for protecting the surface of a semiconductor wafer comprises a substrate resin film and an adhesive layer directly on the substrate resin film with an intermediate resin layer, in which base resin components containing an acrylic polymer and / or polyurethane acrylate are cross-linked, interposed therebetween. The repulsion coefficient (?) obtained by dividing repulsion force (a) per unit width, which is found from the load of loop stiffness obtained by measuring the adhesive tape for protecting the surface of the semiconductor wafer under a specific condition, by the square of the thickness (ss) of a substrate is 100 mN / mm3 or more, the repulsion force (a) is 13 mN / mm or less, and the difference between tensile fracture elongations in a longitudinal direction and a lateral direction is 35% or less.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Composite waterproof adhesive layer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102433817AGuaranteed crack resistanceImprove crack resistanceIn situ pavingsChipsealAdhesive
The invention relates to a ''composite waterproof adhesive layer and a preparation method thereof'', and belongs to the technical field of road construction. The composite waterproof adhesive layer comprises the following three structural layers from bottom to top: a glass fiber geogrid layer, a rubber asphalt layer and a single grain diameter gravel layer; the glass fiber geogrid is formed by bidirectional warp knitting, the longitudinal and transverse tensile strength at break in each linear meter is not less than 25kN / m, and the longitudinal and transverse elongation at break is not more than 4 percent; the rubber asphalt is high-viscosity asphalt, and the spray value is 2.0 to 2.6kg / m<2>; and the grain diameter range of the single grain diameter gravel is 13.2 to 19 millimeters, the single grain diameter gravel exceeding the grain diameter range is not more than 10 percent, and the spread area is 60 to 85 percent. The composite waterproof adhesive layer has strong bonding capacity with an upper bearing layer or a lower bearing layer, can integrally improve the adhesion and the waterproof performance among pavement structure layers, and obviously improves the integral cracking resistance of the pavement structure.
Owner:RES INST OF HIGHWAY MINIST OF TRANSPORT +1
Gas metal arc welding process of medium-manganese wear-resistant steel and Q345B low-alloy steel
ActiveCN105345233AReduce construction costsImprove welding efficiencyArc welding apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesWear resistantShielding gas
The invention creatively provides a gas metal arc welding process of medium-manganese wear-resistant steel and Q345B low-alloy steel. The process is characterized in that the welding current, welding voltage, welding speed and interpass temperature are optimized, and proper protecting gas and gas flow rate are selected, and the tensile strength of an obtained welded joint is more than 470MPa; the tensile failure occurs at the Q345B low-alloy steel side; the impact energy Akv of a welding seam is more than 100J; the welded joint is qualified in a bending test in which the bending diameter is 8d and a bending center angle is 180 degrees. Compared with a traditional welding process, the gas metal arc welding process has the advantages that a base material is free of preheating treatment before welding, and the welding seam is free of stress relief annealing treatment after welding, so that the construction cost can be saved, the welding efficiency can be improved, the welding difficulty is reduced, and the industrial popularization can be conveniently carried out for a construction site.
Owner:TIANJIN WILL LONG SCI &TECH CO LTD
Calculation method for crack initiation pressure of shale formation fracturing crack
InactiveCN108825198AAvoids the disadvantage of not being able to take into account the anisotropic nature of shale failureThe calculation result of crack initiation pressure is true and reliableSurveyData processing applicationsRectangular coordinatesFracturing fluid
The invention relates to a calculation method for the crack initiation pressure of a shale formation fracture crack. The calculation method specifically comprises the steps that 1, the magnitude of ground stress, the pore pressure of formation and the elastic modulus and Poisson ratio in different directions of a shale are tested; 2, a certain well depth value is selected for a layer section of atarget well, and a borehole rectangular coordinate system, a ground stress coordinate system and a geodetic coordinate system are converted according to designed wellbore structure data that; 3, stress components of the borehole wall caused by the ground stress and the fracturing fluid pressure in a wellbore are calculated; 4, the effective stress of the stress components on the borehole wall in the borehole rectangular coordinate system is converted into a effective stress form under polar coordinates of the wellbore; 5, a mechanical criterion of a tensile fracture of a rock of the fracturingwall of the shale formation is derived; and 6, the fracturing fluid pressure in the layer section wellbore of the target well is calculated along the circumferential direction of the wellbore when tensile fractures are generated at different positions of the borehole wall, and the minimum value of the fracture is determined as the crack initiation pressure. The calculation method for the crack initiation pressure of the shale formation fracture crack enables the calculation result of the crack initiation pressure more realistic and reliable, and reduces the construction cost.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Method for testing change rule of microstructure in soil stretching process
InactiveCN103743624AAccurately measure tensile strengthAvoid Tensile Stress ConcentrationsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringStressed state
The invention discloses a method for testing a change rule of a microstructure in a soil stretching process. The method comprises the steps of (1) compacting a soil body in a die, manufacturing a soil body sample with two cylindrical holding ends at two ends and a cube stretching section in the middle, disassembling the die and removing the surface of an observation side to expose a fresh side of the sample; (2) fixing two holding ends of the soil body sample in two stretching clamps which are adaptive to the holding ends in size; (3) calibrating a stretching device, then setting a loading rate and beginning to apply continuous stretching load; (4) collecting images of detail structures of the soil body under different stress states; (5) fusing and splicing the collected images; and (6) extracting parameters of the microstructure with processed images to perform quantitative analysis. According to the method, through the observation and the later quantitative analysis of the soil body detail structures in the stretching process, analysis of a tensile fracture mechanism of the soil body and building of a tensile fracture criterion are facilitated.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for manufacturing molded foam
A method for manufacturing molded foam which uses cheap materials, is light in weight and which is excellent in impact resistance. In the method for manufacturing molded foam, propylene homopolymer with a long chain branch, propylene ethylene block copolymer and low density polyethylene are mixed in the base resin at a prescribed mixing ratio. A blowing agent is added to carry outfoaming. A prescribed mixing ratio is determined based on the value arrived at by a multiplying melt tension of each material mixed with the melt flow rate and the Tensile Rupture Elongation.
Owner:KYORAKU CO LTD
Stretchable display back plate and stretchable display device
ActiveCN110444575AImprove reliabilityEasy to stretchDigital data processing detailsSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention provides a stretchable display back plate and a stretchable display device. The stretchable display back plate includes a wiring area and a display area defined along a first direction on a substrate; the display area includes a plurality of display units distributed in an array and a plurality of connection units, and a connection unit is arranged between any two adjacent display units; multiple functional layers are sequentially stacked in the display area; multiple hollow structures penetrate the multiple functional layers and the substrate, and the hollow structures are arranged in the center of four field-shaped display units, and each hollow structure has a first extension part having a first length along the second direction; the first length in the first transition area of the display area close to the wiring area is no greater than the first length in the center area of the display area. Thus, the extension length of the hollow structure in the first transition area in the direction perpendicular to the tensile direction is no greater than the center area, the tensile strength of the first transition area can be increased, thereby reducing the risk of tensile fracture in the first transition area.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
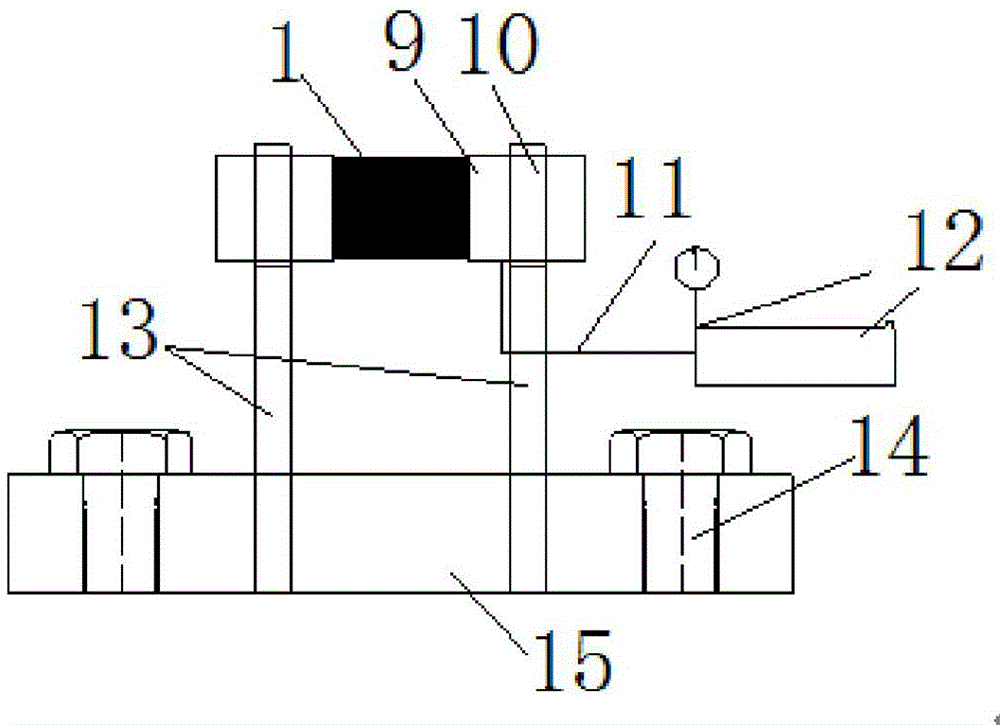
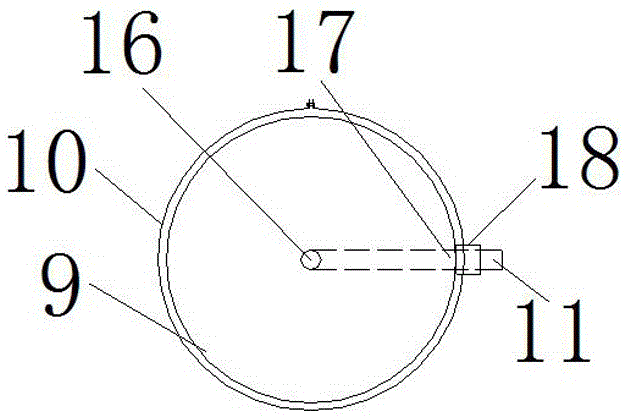
Test device for splitting tensile fracture under impact-static-hydraulic coupling effect of rock and test method
PendingCN106404519AImprove the experimental effectSimple structureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention relates to a test device for splitting tensile fracture under an impact-static-hydraulic coupling effect of rock. The test device comprises a pressing rod device and a hydraulic loading device, wherein the hydraulic loading device comprises a hydraulic loading pressing head, a circular ring clamp, a connecting pipe and a pressurizing pump; the circular ring clamp is connected with a base fixed on the pressing rod device through a brace; the hydraulic loading pressing head is fixed in the circular ring clamp; a water outlet in an end face of the hydraulic loading pressing head is communicated with a water inlet in a side wall; the water inlet in the side wall of the hydraulic loading pressing head is connected with the pressurizing pump through the connecting pipe. In a test process, a tested piece is firstly fixed between an incidence rod and a transmission rod along a radial direction, an axial static loading device is utilized to apply static pressure to the tested piece, then hydraulic pressure is applied to the two axial ends of the tested piece, the pressurizing pump with a pressure gage is used for adjusting the hydraulic pressure to a preset value, and then a high-pressure air bottle is utilized to drive a bullet to strike the incidence rod so as to break the tested piece and lastly the data is collected for treatment analysis. According to the invention, the dynamic mechanic characteristics of the splitting tensile fracture of the rock under the impact-static-hydraulic coupling effect can be effectively researched. The test device provided by the invention has guiding significance for evaluating the damaging mechanism of the water-containing rock under dynamic and static loads.
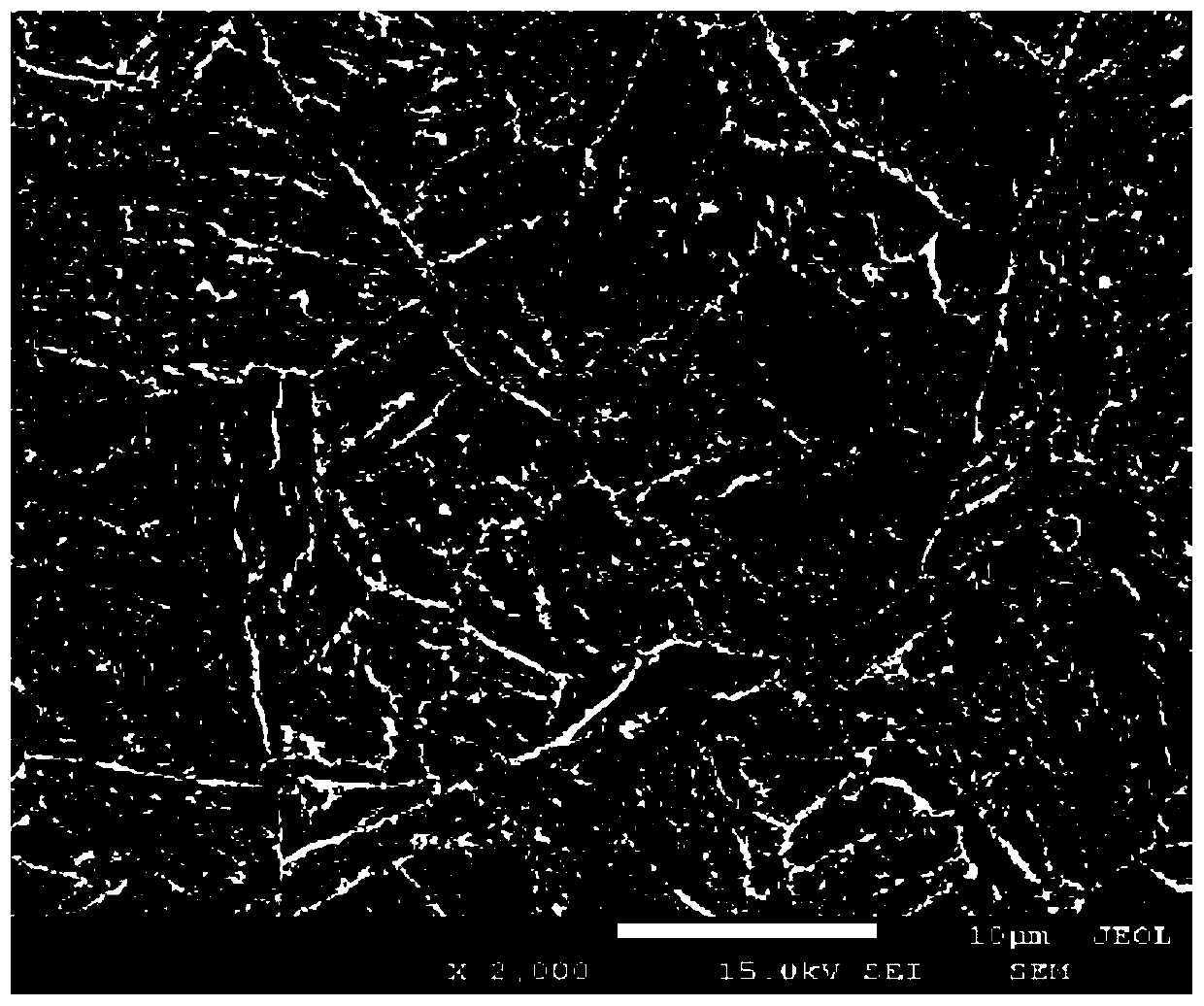
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mutual non-solid-solution system metal infiltration process and device based ion implantation radiation damage
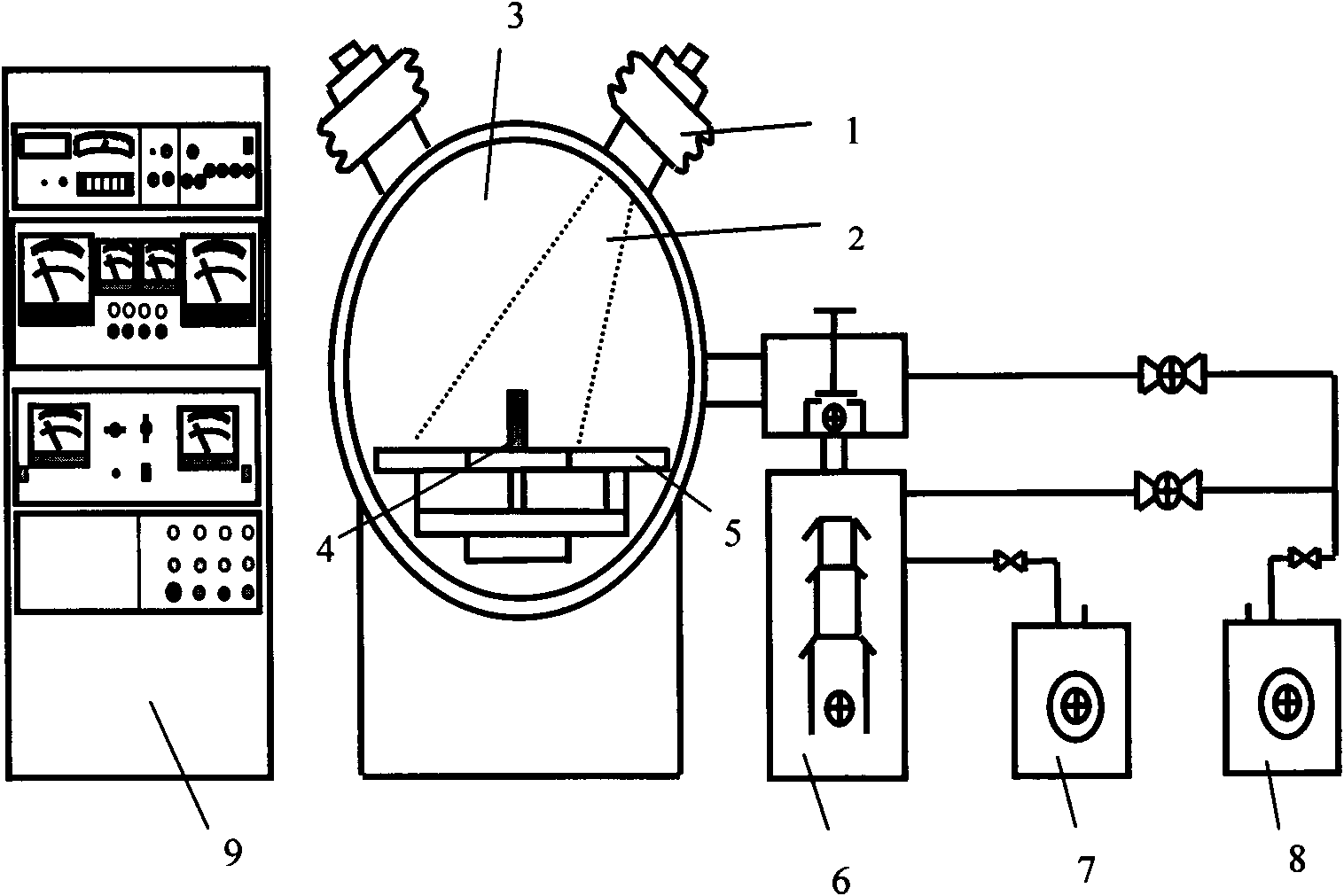
InactiveCN102140618AVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingScanning electron microscopeSolar cell
The invention relates to a mutual non-solid-solution system metal infiltration process and device based ion implantation radiation damage. The process comprises the following steps of polishing and ultrasonic cleaning of pure tungsten metal, vacuum drying, silver metal plasma implantation, tungsten metal surface vacuum evaporation silver coating, vacuum drying, argon protection silver infiltration, hot-pressing infiltration supplementation, section scanning electron microscope (SEM) observation of a tungsten / silver composite metal material, section line scanning component analysis, Auger energy spectrum analysis of components along the material depth, welding strength test when the tungsten / silver composite metal material is used for spot-welding electrodes, and SEM observation of welding head tensile fractures. In the invention, a metal plasma implantation technology is utilized to combine with the vacuum evaporation technology, the high-temperature silver infiltration technology and the hot-pressing infiltration supplementation technology, thus silver metal is successfully infiltrated to the surface of a metal tungsten workpiece to prepare the tungsten / silver composite metal material. Test results show that when a tungsten / silver composite metal material electrode is utilized to carry out resistance spot welding on a silver metal interconnection sheet and an aerospace craft solar cell sheet, the single-spot welding strength is up to 450gf which excesses Chinese military standard and current enterprise standard, and the welding head tensile fractures is determined to be ductile fractures through SEM analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
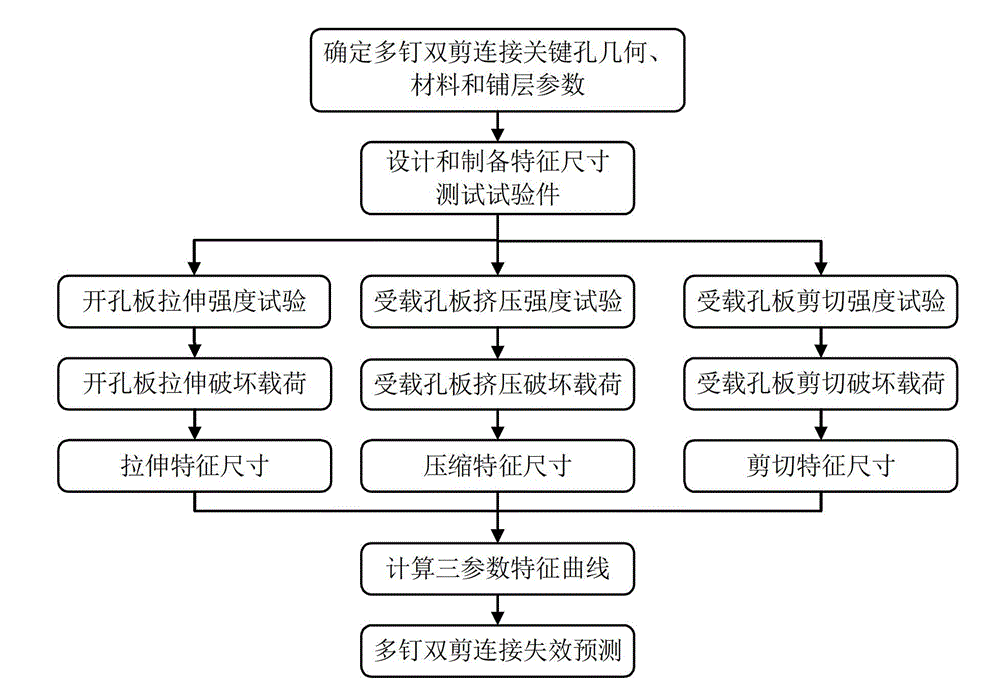
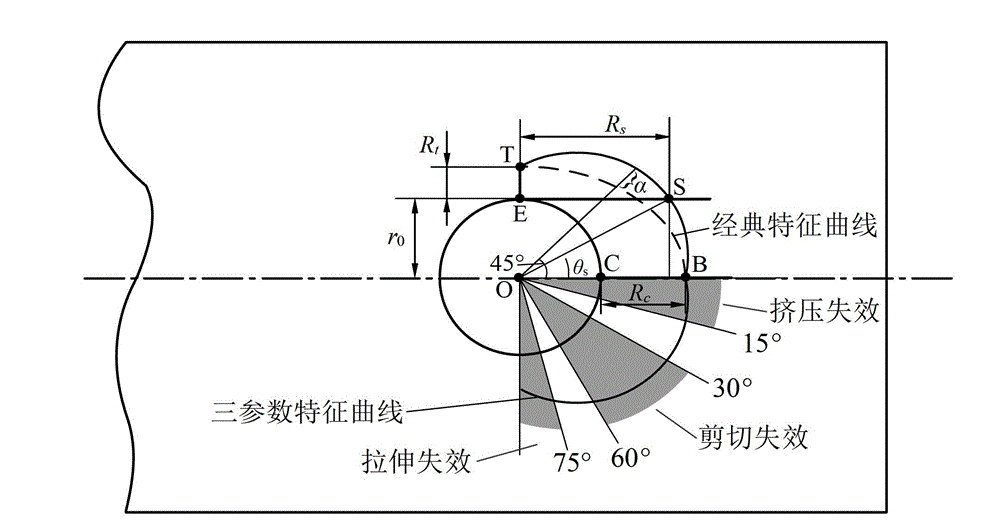
Composite material multi-nail and double-shear connection failure prediction method based on three-parameter characteristic curve
InactiveCN103335886APredict failure modePredicted Failure LoadMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesEngineeringFracture load
The invention provides a composite material multi-nail and double-shear connection failure prediction method based on a three-parameter characteristic curve. The composite material multi-nail and double-shear connection failure prediction method comprises the following steps of: (1) designing and preparing a test piece of a tensile, compression and shear characteristic size test according to parameters of geometry, a material, a laying layer and the like of a multi-nail and double-shear connection key hole of a composite material; (2) carrying out a static-force tensile test to obtain a tensile fracture load of an opening laminated board, an extrusion fracture load of a carrying hole laminated board, and a shearing fracture load of the carrying hole laminated board; (3) calculating tensile, compression and shear characteristic sizes according to the fracture loads; (4) acquiring the three-parameter characteristic curve based on the tensile, compression and shear characteristic sizes, wherein the curve passes through a tensile characteristic point, an extrusion characteristic point and a shearing characteristic point of the key hole; and (5) predicating a failure mode and a fracture load of a multi-nail and double-shear connection structure of the composite material based on the three-parameter characteristic curve. The composite material multi-nail and double-shear connection failure prediction method disclosed by the invention is applicable to multi-nail and double-shear connection failure prediction of the composite material in engineering application, and the failure mode and the fracture load of the connection structure can be accurately predicated by considering the shearing characteristic size.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Gas extraction method for region reinforcement of gob-side entry retaining
ActiveCN105351001AImprove the extraction effectDrainage continues to be stableGas removalSealing/packingStress concentrationEngineering
Provided is a gas extraction method for region reinforcement of gob-side entry retaining. The method comprises following steps: penetrating a large drilled hole of a caving zone towards the direction of a top plate along one side of a filling wall of gob-side entry retaining under construction, stuffing a steel sleeve pipe into the large drilled hole such that a grout outlet of a grouting pipe is located in the middle portion of the large drilled hole, closely adhering an expanded polyurethane located in a hole opening of the large drilled hole to a wall surface of the hole opening of the large drilled hole to seal the hole opening; and continuously moving forward to construct a small drilled hole along the interior of the steel sleeve pipe by grouting into the large drilled hole via the grouting pipe, stopping construction and performing drilling withdrawal when the small drilled hole is drilled at the pre-set depth, and connecting the steel sleeve pipe to an extraction pipeline for gas extraction. The gas extraction method for region reinforcement of gob-side entry retaining has following beneficial effects: a method is simple and has a great pore formation property; the likelihood of cutting and tensile fracture for drilled holes is decreased such that gas extraction operation can be performed continuously and stably; and a reinforcing area in the vicinity of gob-side entry retaining is formed in order to prevent a wall body against deformation due to stress concentration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for evaluating non-metallic inclusions in high-strength steel
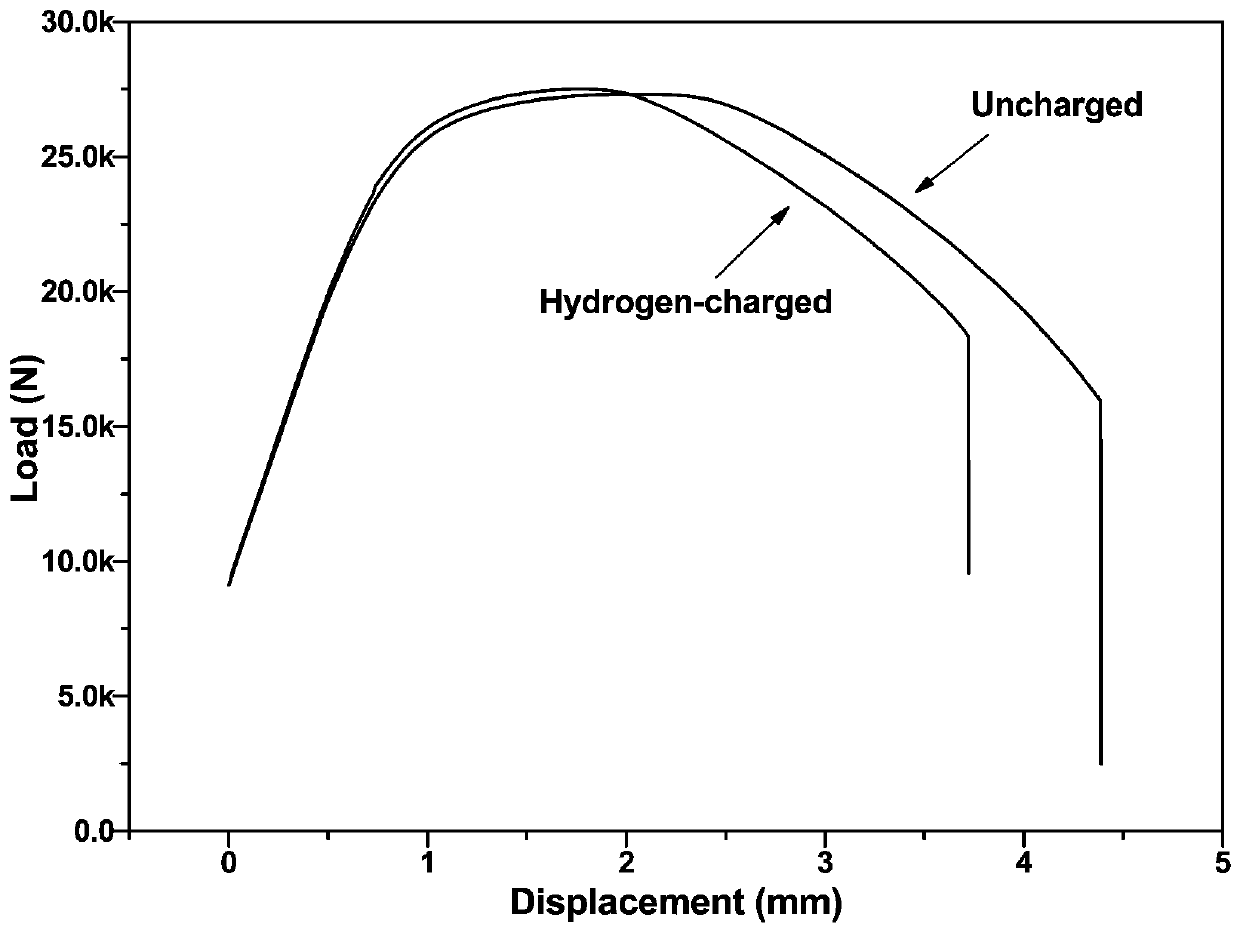
InactiveCN110006751AShorten the timeSave costsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesHydrogenNon-metallic inclusions
The invention provides a method for evaluating non-metallic inclusions in high-strength steel, which belongs to the technical field of steel material quality detection and comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a certain number of tensile samples and carrying out a forced hydrogenation test; performing a conventional tensile test after strong hydrogenation; and carrying out electron microscope analysis and observation on the tensile fracture. A plurality of obvious brittle platforms exist on the hydrogen filling tensile fracture, and non-metallic inclusions exist in the centers of the brittle platforms. The size of the non-metallic inclusions is obtained through fracture observation, and the maximum size of the non-metallic inclusions in a certain volume of steel is estimated bycombining with an extreme value statistical method. The method has the beneficial effects that a novel efficient assessment technology for the non-metallic inclusions in the high-strength steel is provided, the characteristics of convenience, accuracy, economy and the like are achieved, and technical support can be provided for efficient assessment of the metallurgical quality of the steel. Large-size non-metallic inclusions in high-cleanliness steel can be evaluated, and the conditions of components, distribution, content and the like of the inclusions can be accurately obtained.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
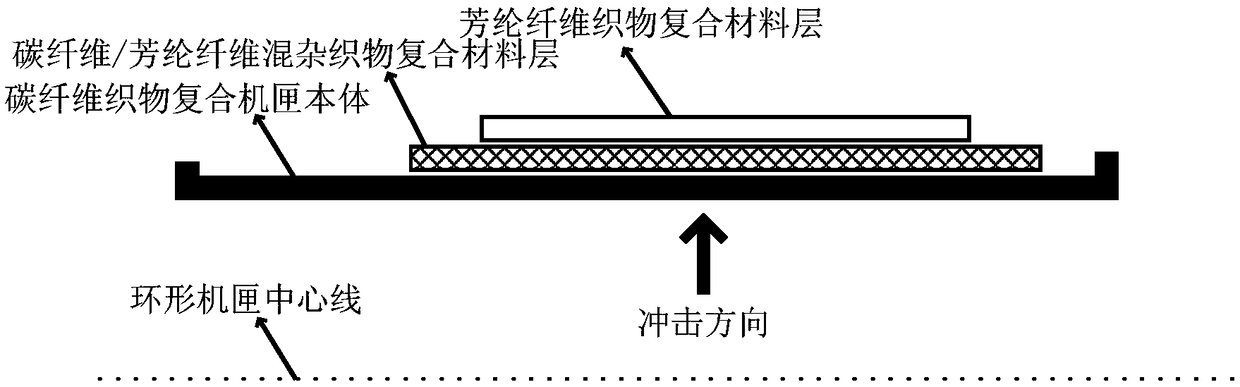
Impact-resistant lightweight density gradient composite material, fan containment casing, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109278372AImprove impact resistanceReduce structural weightSynthetic resin layered productsVehicle componentsResistCarbon fibers
The present invention relate to an impact-resistant lightweight density gradient composite material, a fan containment casing, a preparation method and an application thereof. The impact-resistant lightweight density gradient composite material, the structure form of the composite material fan containment casing, and material delamination are creatively designed, the designs of composite structurelayers of a carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite layer, a carbon fiber / aramid fiber reinforced resin matrix composite layer and an aramid fiber reinforced resin matrix composite layer are adopted, the thickness of each structural layer is optimized, and the carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite layer resists shear failure, the carbon fiber / aramid fiber reinforced resin matrix composite layer resists delamination failure, the aramid fiber reinforced resin matrix composite layer resists tensile fracture failure. The structural design significantly reduces the structural weight and improves the impact resistance of materials.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH +1
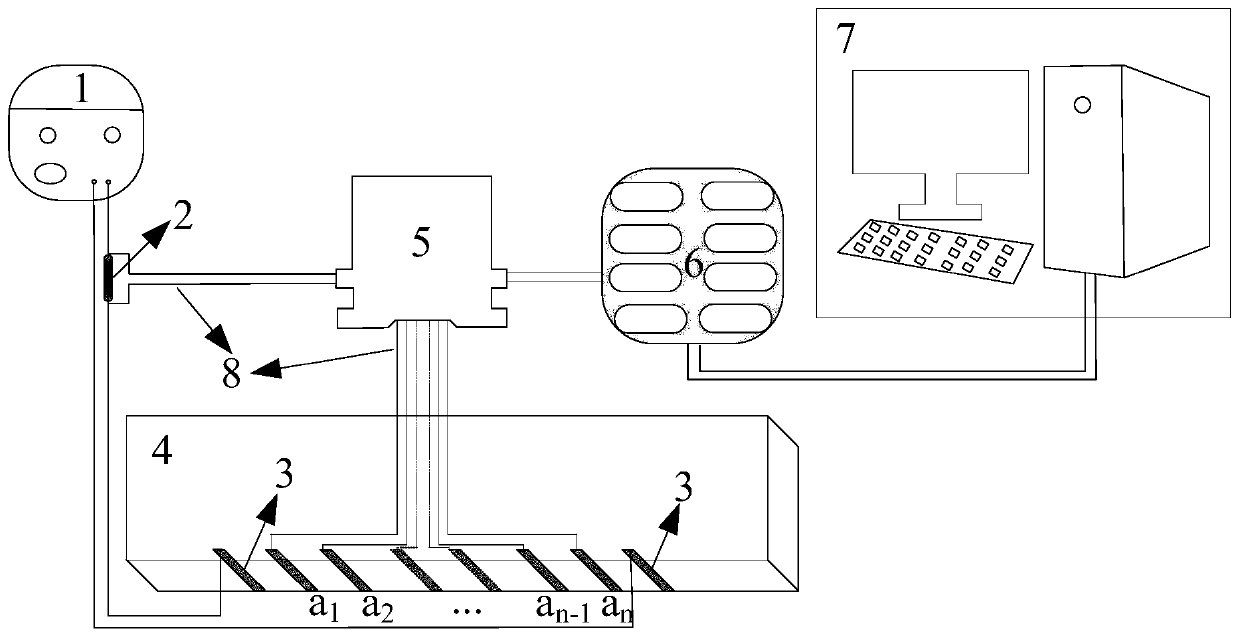
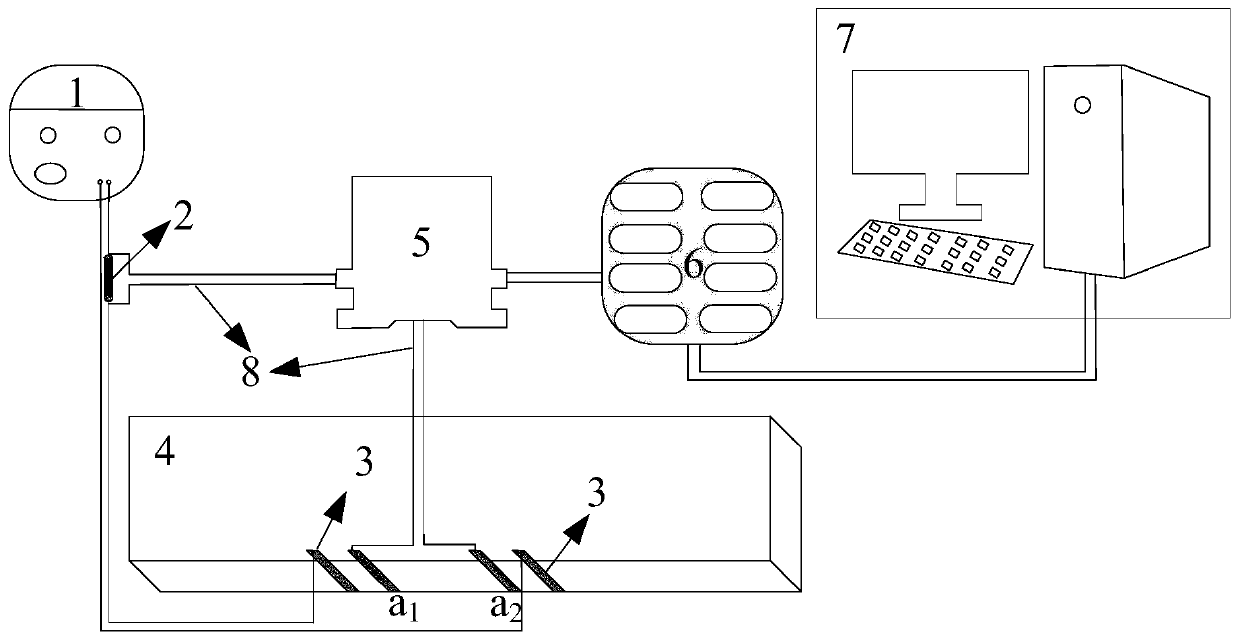
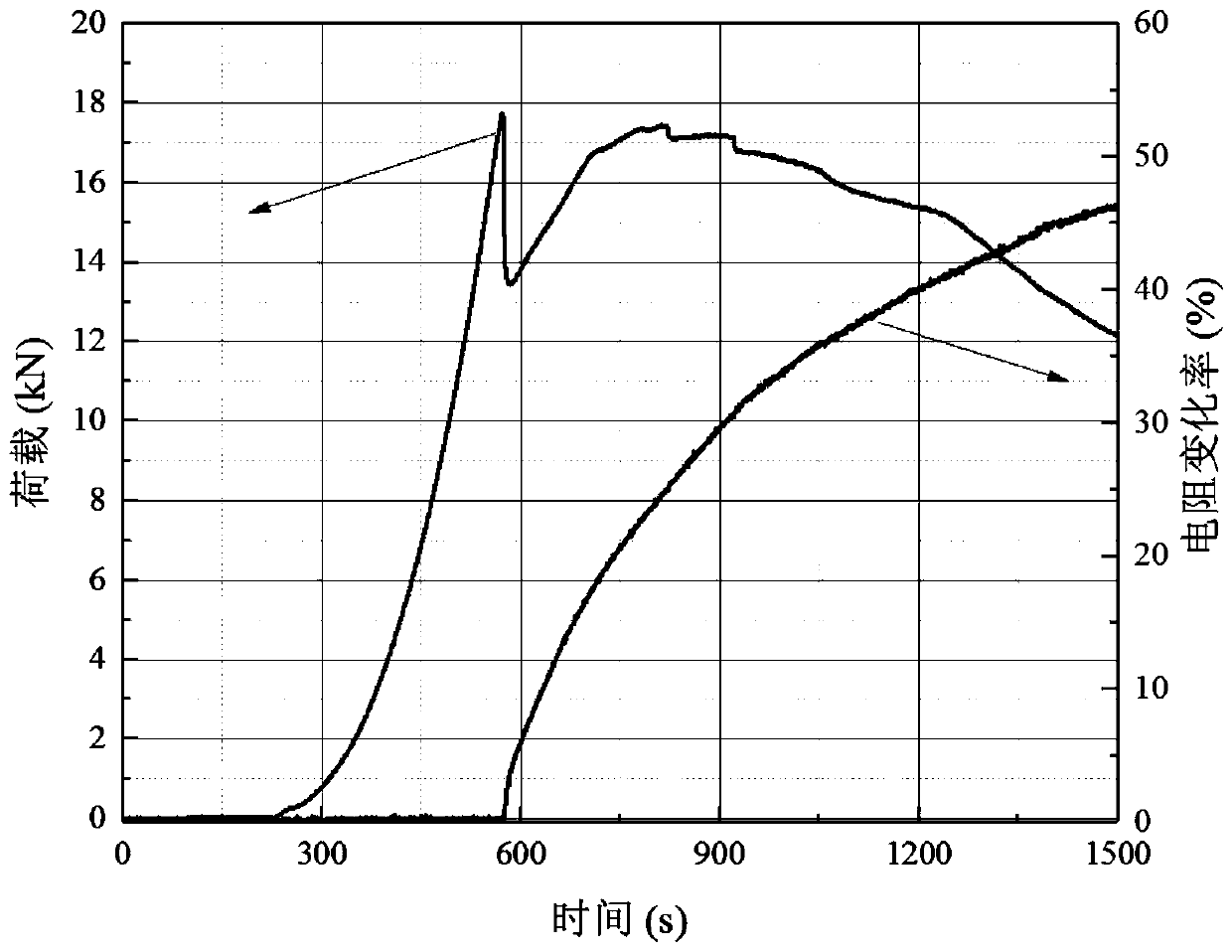
Device and method for width monitoring and regional self-positioning of tensile fracture of concrete
PendingCN110208084AConstruction has no negative impactGood dispersionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesElectrical resistance and conductanceData acquisition
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of civil engineering, provides a device and method for width monitoring and regional self-positioning of a tensile fracture of concrete. The devicecomprises a direct-current voltage-stabilizing power supply, a fixed-value resistor, an external conductive electrode, internal conductive electrodes a1, a2. . . ., an-1, and an, a concrete component,a voltage conversion module, and a computer. The external conductive electrode and the internal conductive electrodes are arranged at a tensile area at the bottom of the concrete component. The external conductive electrode is connected in series with the fixed-value resistor and is connected with positive and negative electrodes in the direct-current power supply; and the two ends of the fixed-value resistor are connected with the voltage conversion module. The internal conductive electrodes ai and a (i+1) are connected to the voltage conversion module. The voltage conversion module is connected to the computer through a data acquisition device. Acording to the invention, the resistance change rate of the concrete target area under the load effect is monitored in real time to realize self-monitoring of the width of the concrete fracture and positioning of a fracture occurrence area. No fracture sensor needs to be arranged at the component additionally and adding of lots of conductivematerials in the concrete base is avoided; and the real-time monitoring of the fracture of the important concrete structural component is guaranteed.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for measuring minimum diameter of diameter shrinkage portion of tensile sample after fracture
ActiveCN103994715AEliminate offset errorsEliminate contact offset errorsElectrical/magnetic diameter measurementsElectrical resistance and conductanceData acquisition
The invention relates to a device and method for measuring the minimum diameter of a diameter shrinkage portion of a tensile sample after fracture. The device comprises a resistance-strain U-shaped sensor with a positioning rod and a measurement clamping tool edge, a U-shaped support, a plurality of standard units of standard cylinders and a data collector provided with measurement software. The sensor is installed on the standard cylinders or the tensile failure sample through cooperation of the positioning rod and the support, a measurement signal containing a standard diameter value or the minimum diameter value of the diameter shrinkage portion of the sample and the contact offset of the measurement clamping tool edge is transmitted to the data collector; a standardization algorithm of the measurement software provides a diameter fitting formula, and contact offset errors caused by different diameters of the standard cylinders are eliminated; a measurement algorithm of the measurement software provides a diameter value of the sample, and the contact offset errors caused by different diameters of the sample are eliminated.
Owner:NINGBO YINZHOU FUCHUN PRECISION CASTING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com