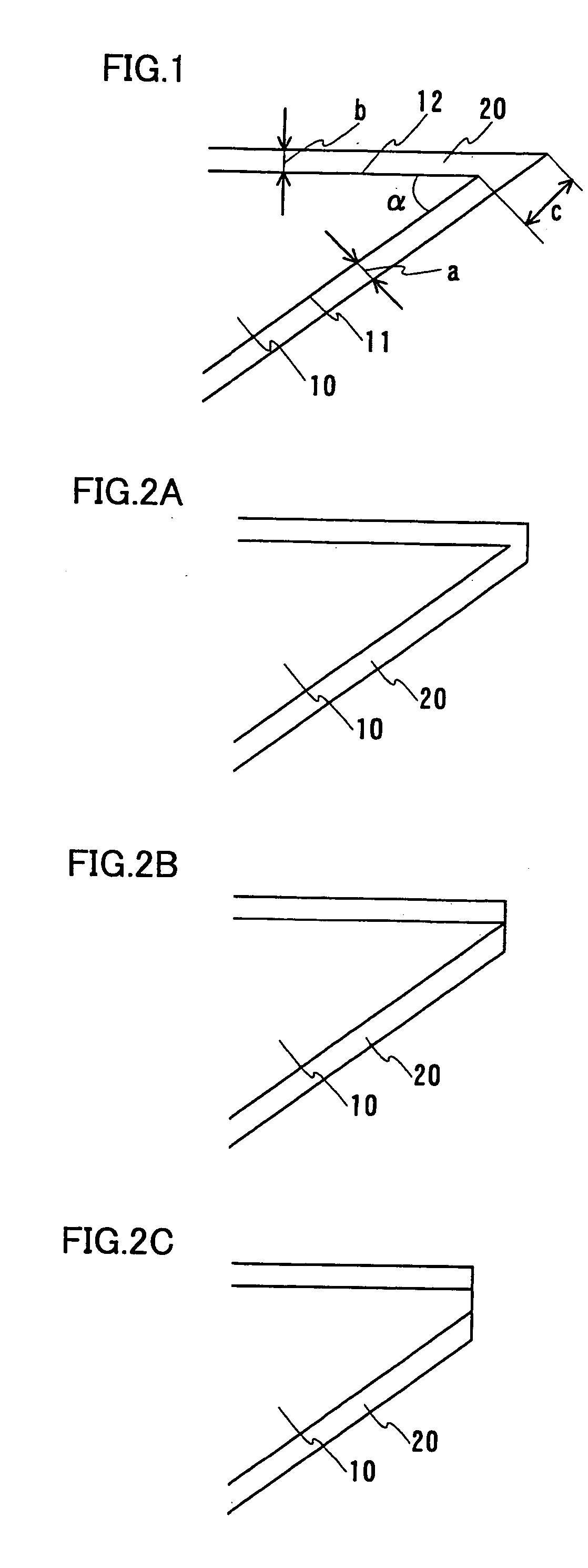
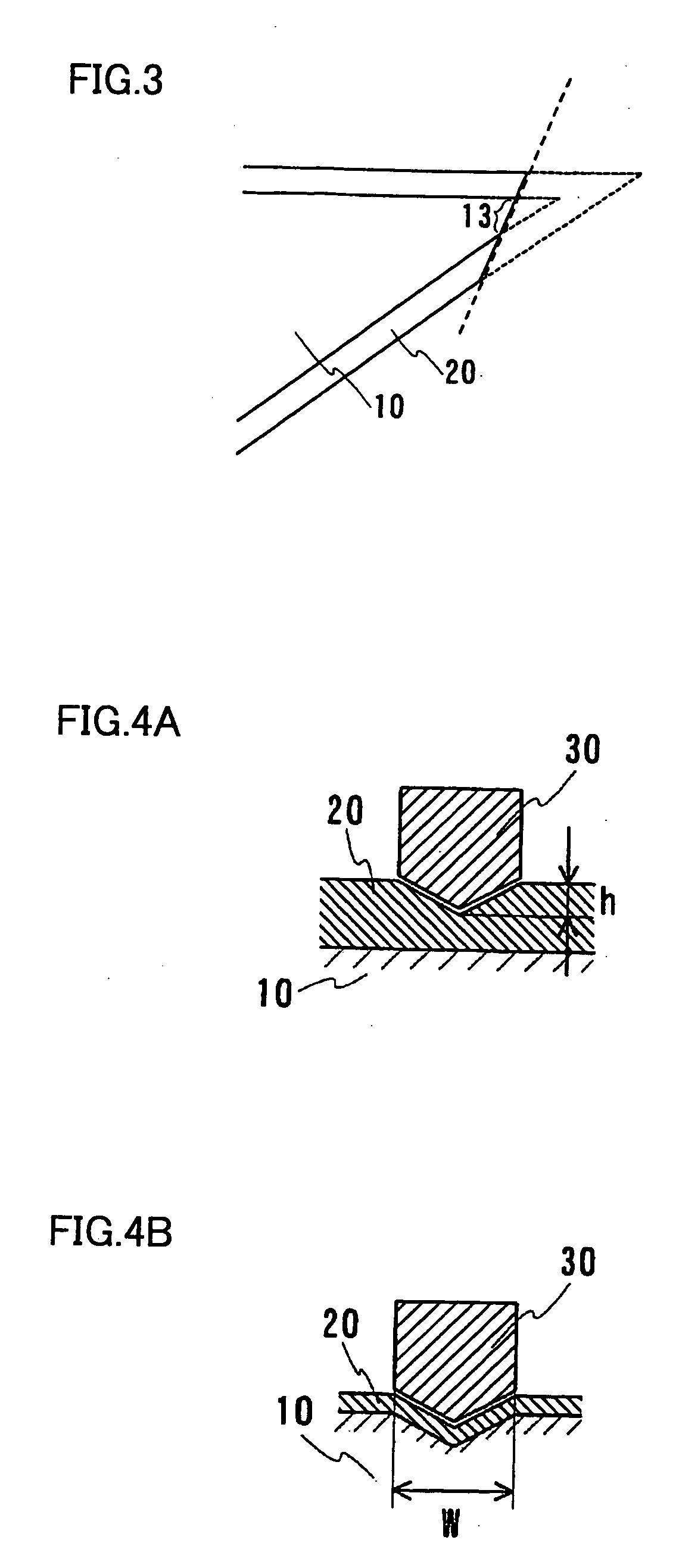
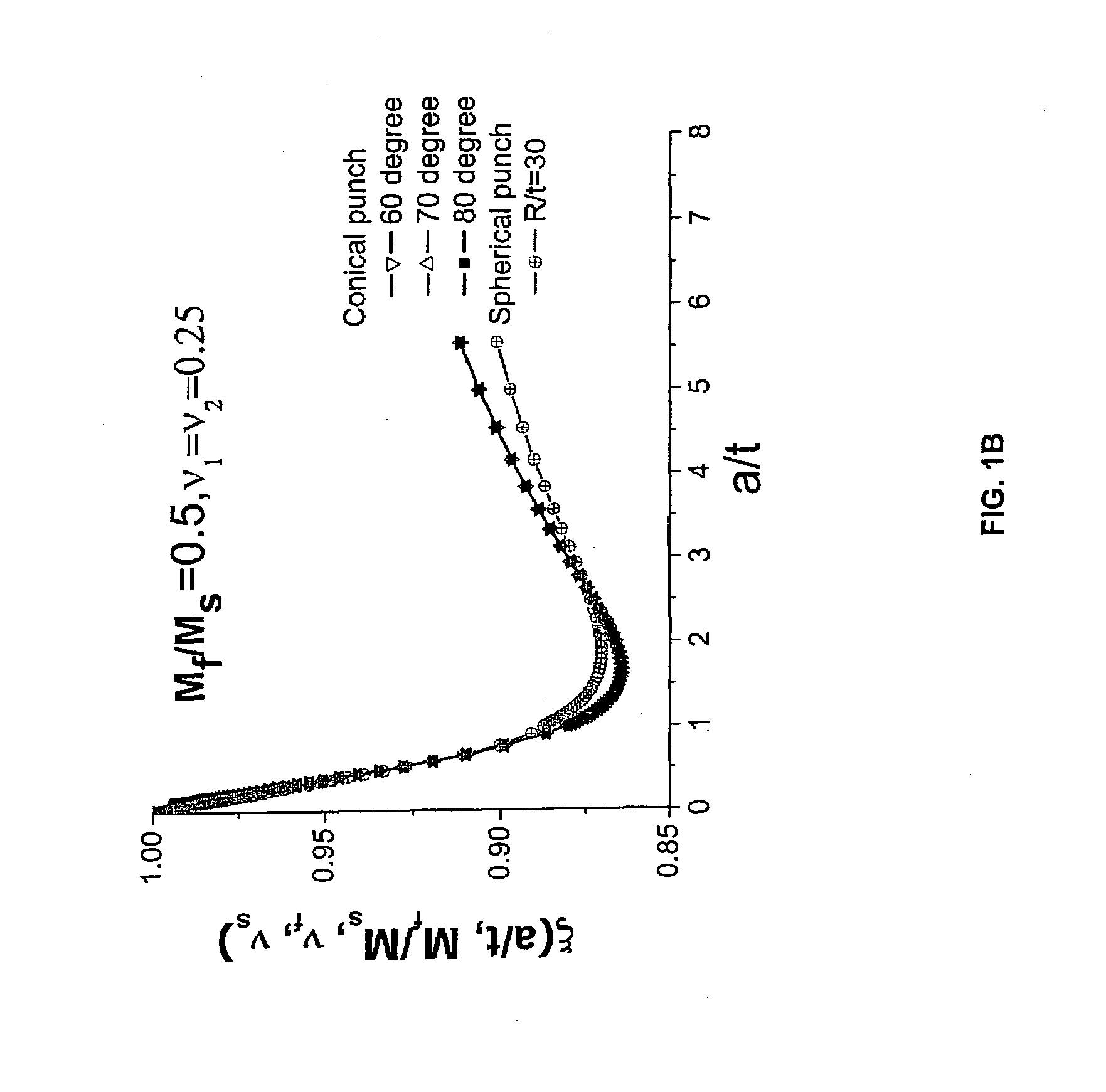
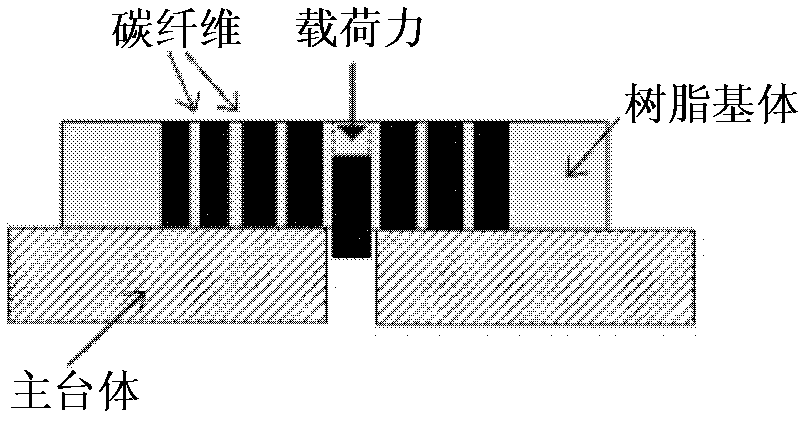
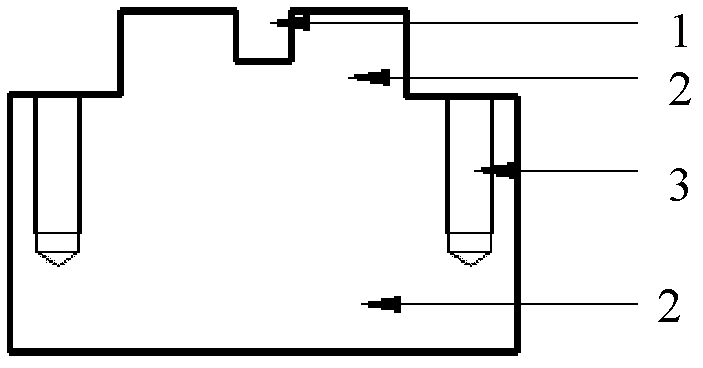
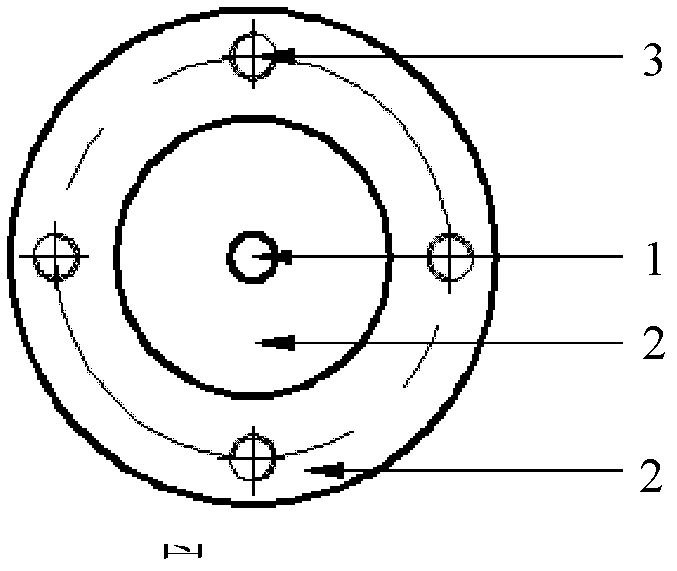
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
198 results about "Nanoindentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
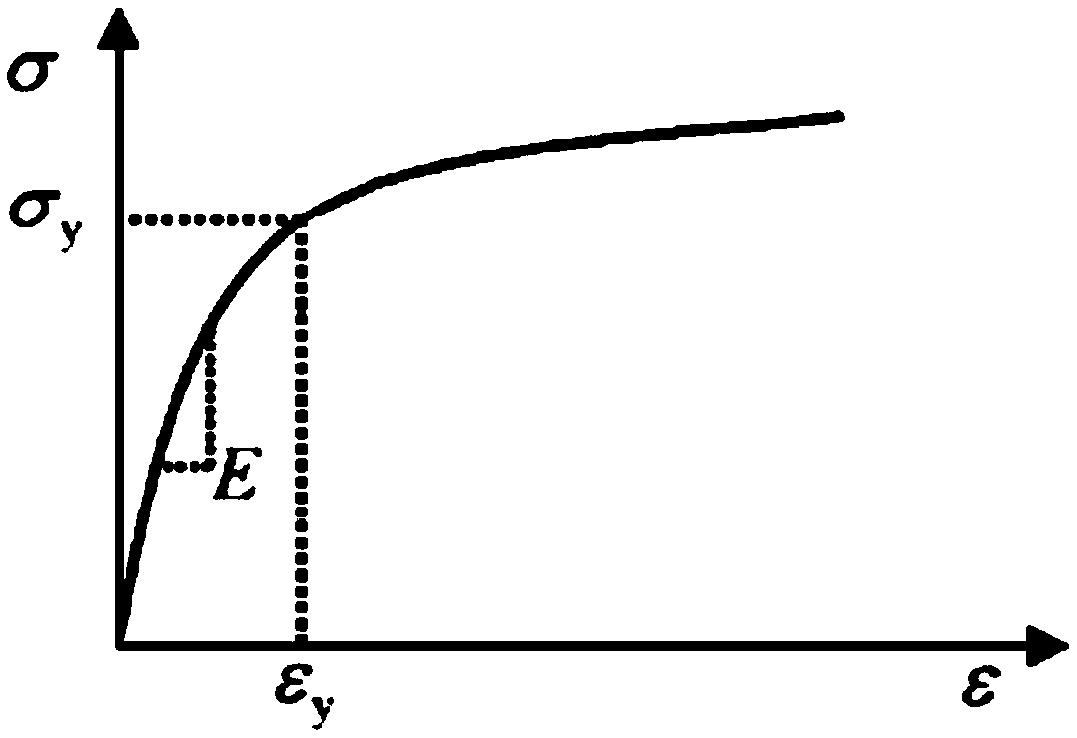
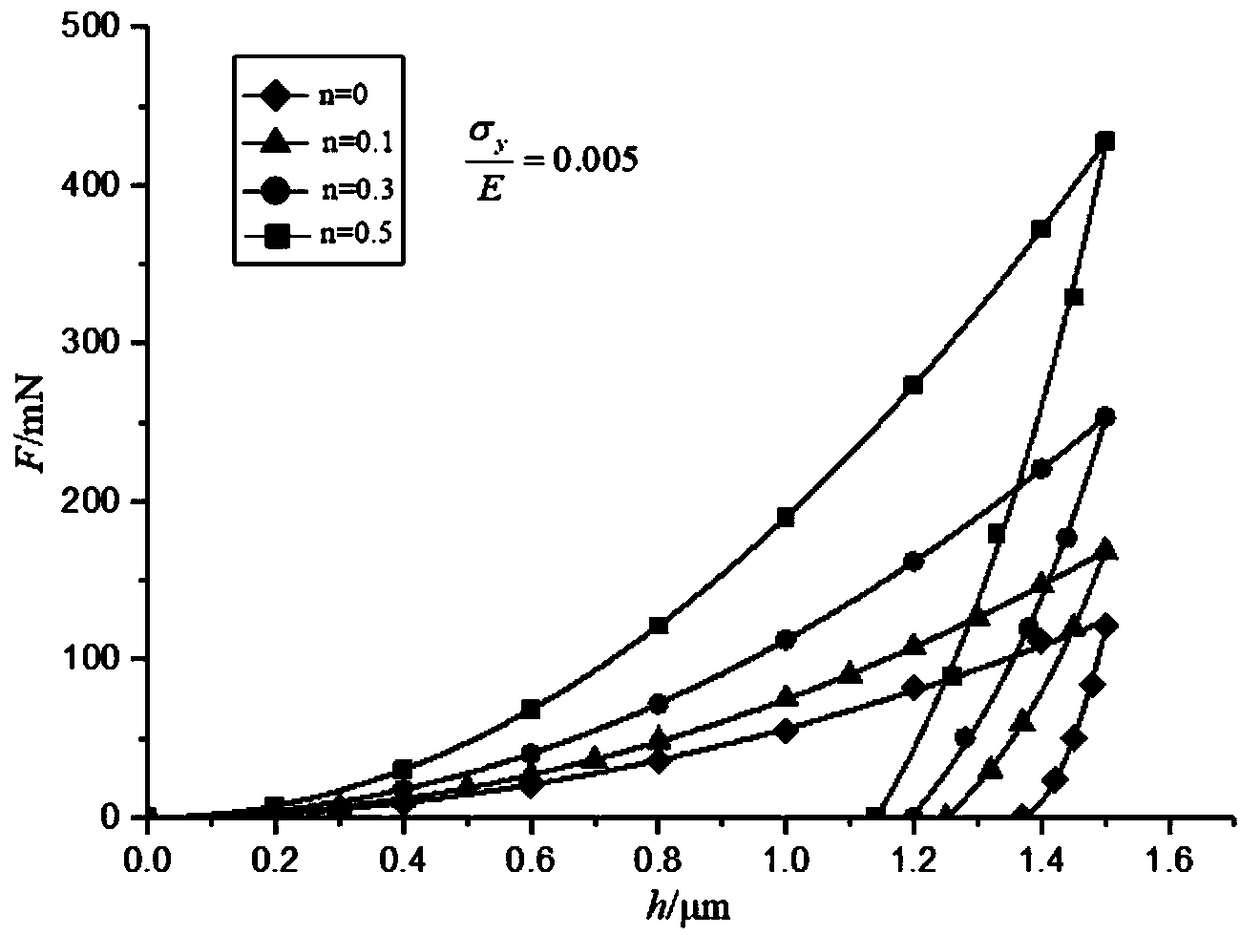
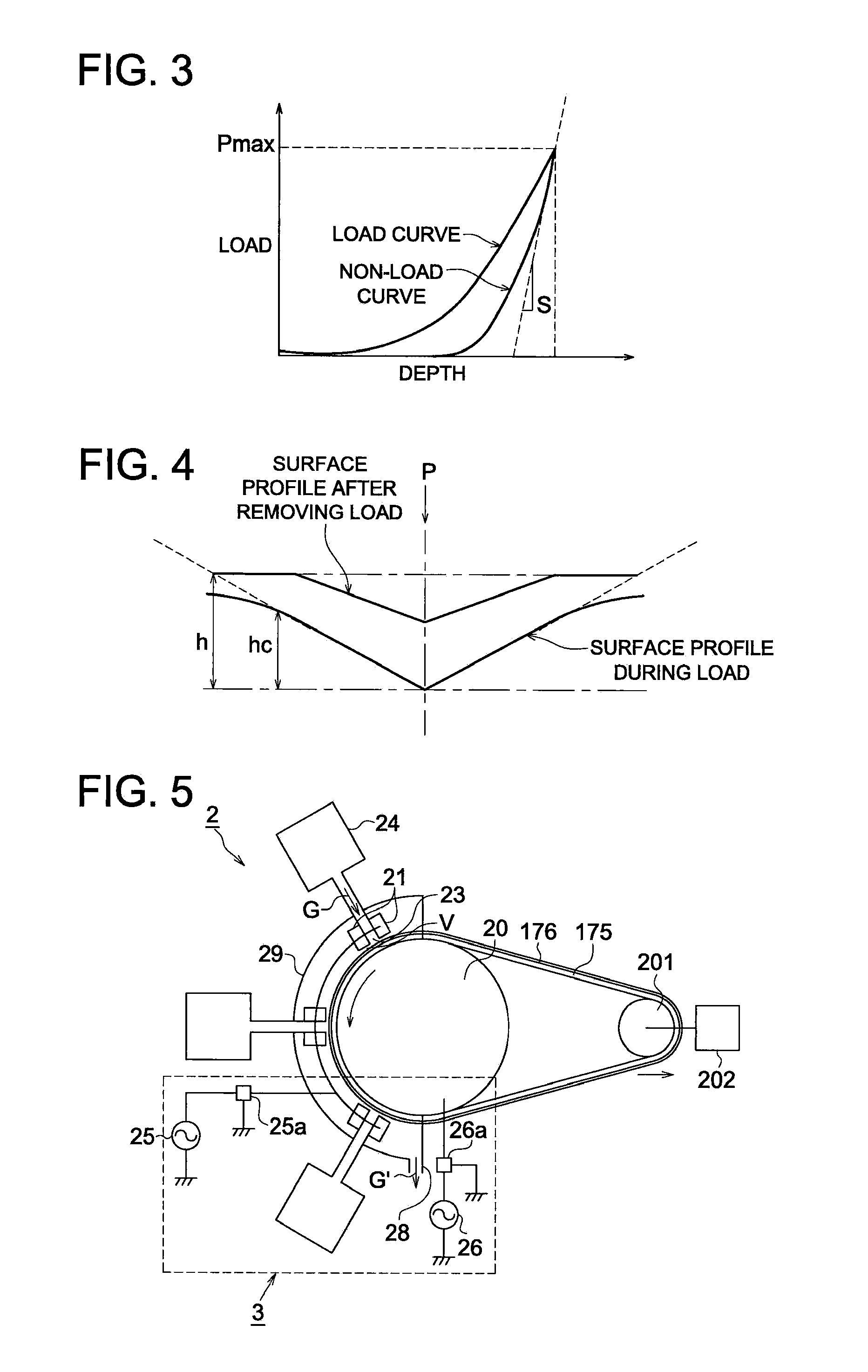
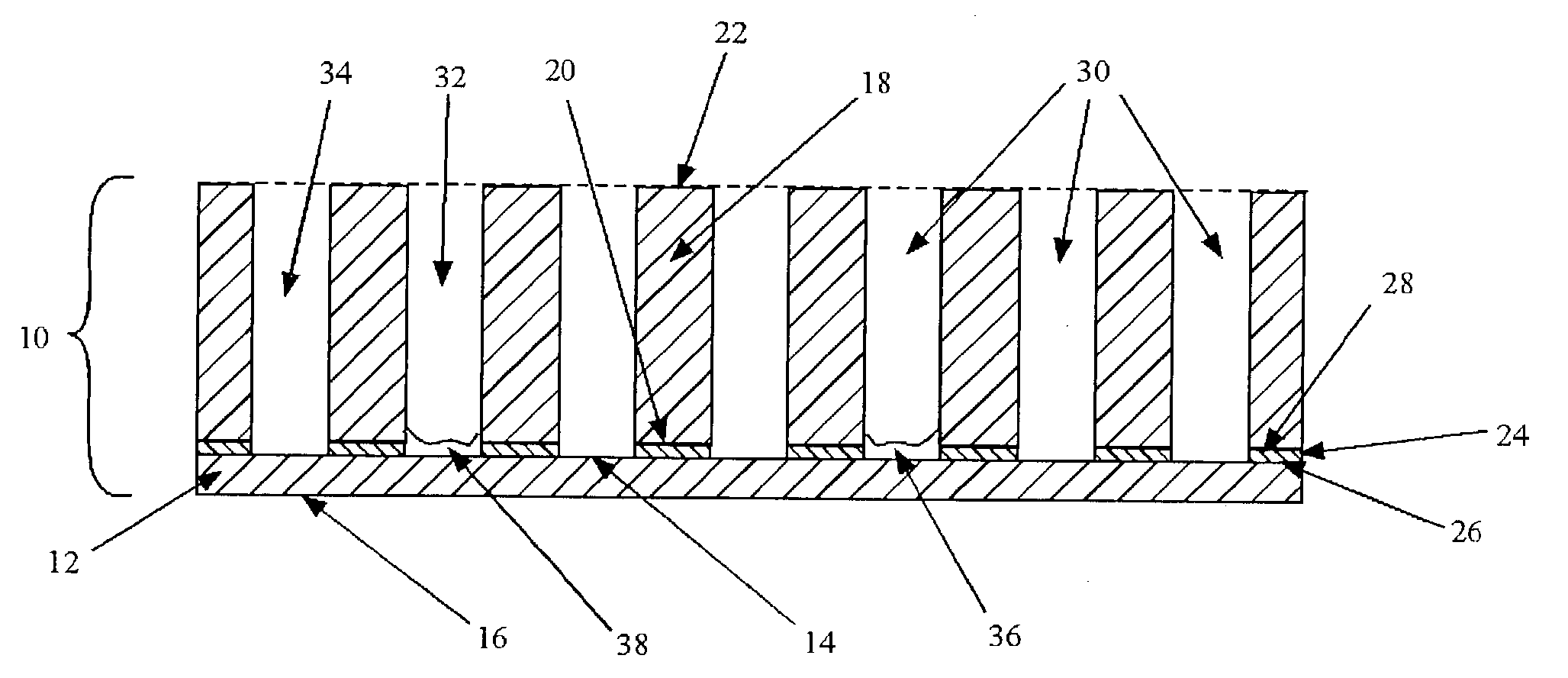
Nanoindentation, also called intrumented indentation testing , is a variety of indentation hardness tests applied to small volumes. Indentation is perhaps the most commonly applied means of testing the mechanical properties of materials. The nanoindentation technique was developed in the mid-1970s to measure the hardness of small volumes of material.
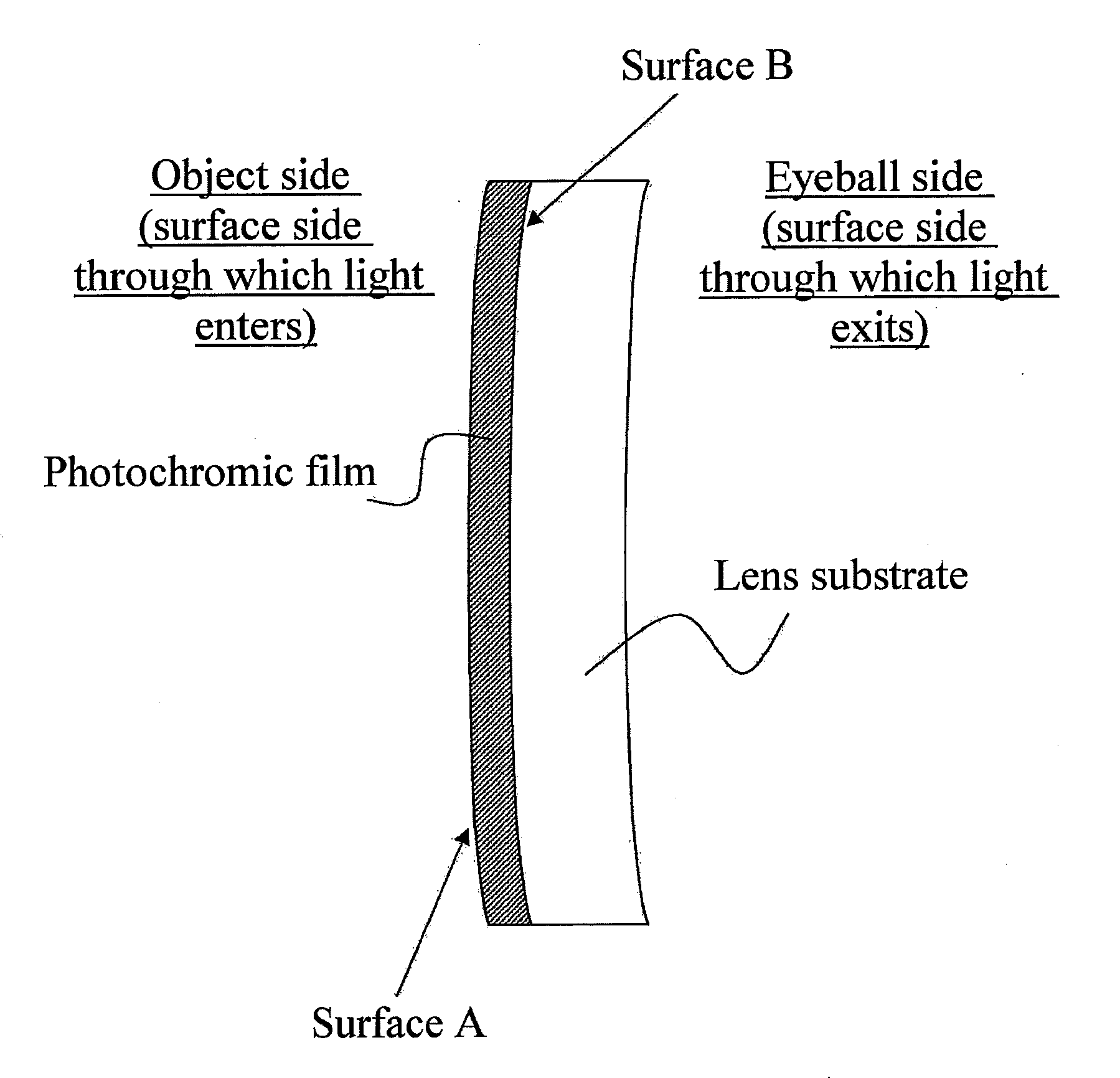
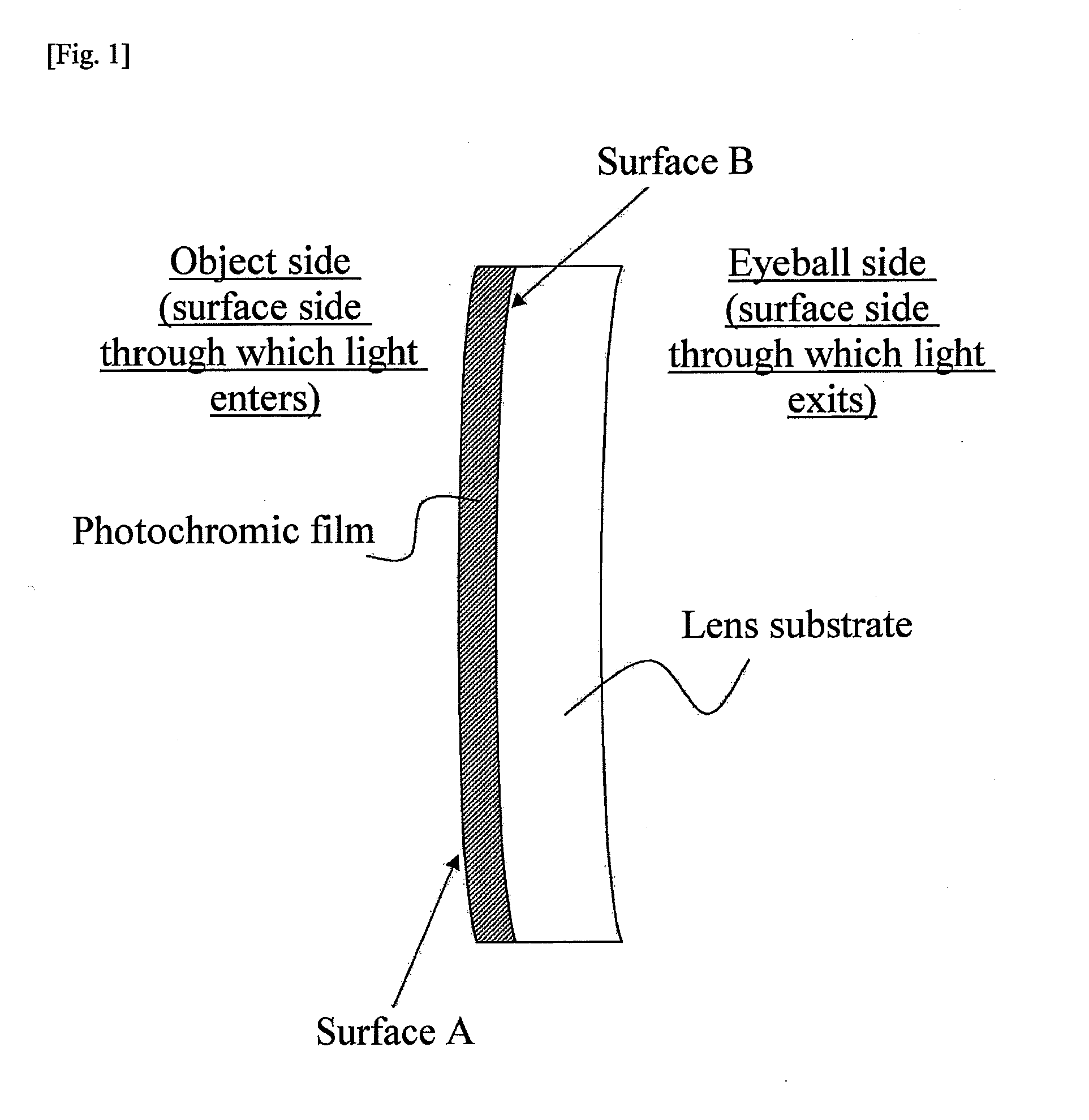
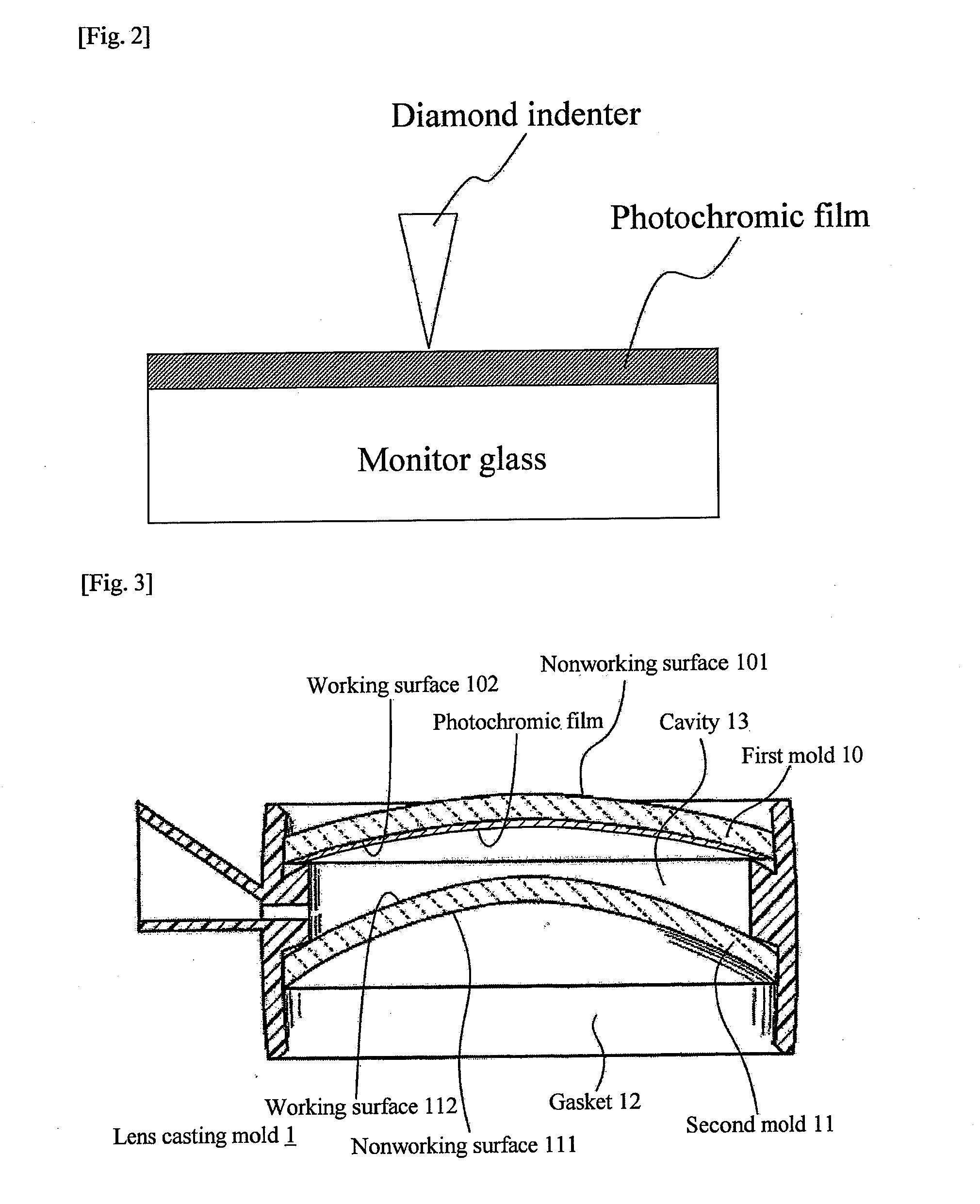
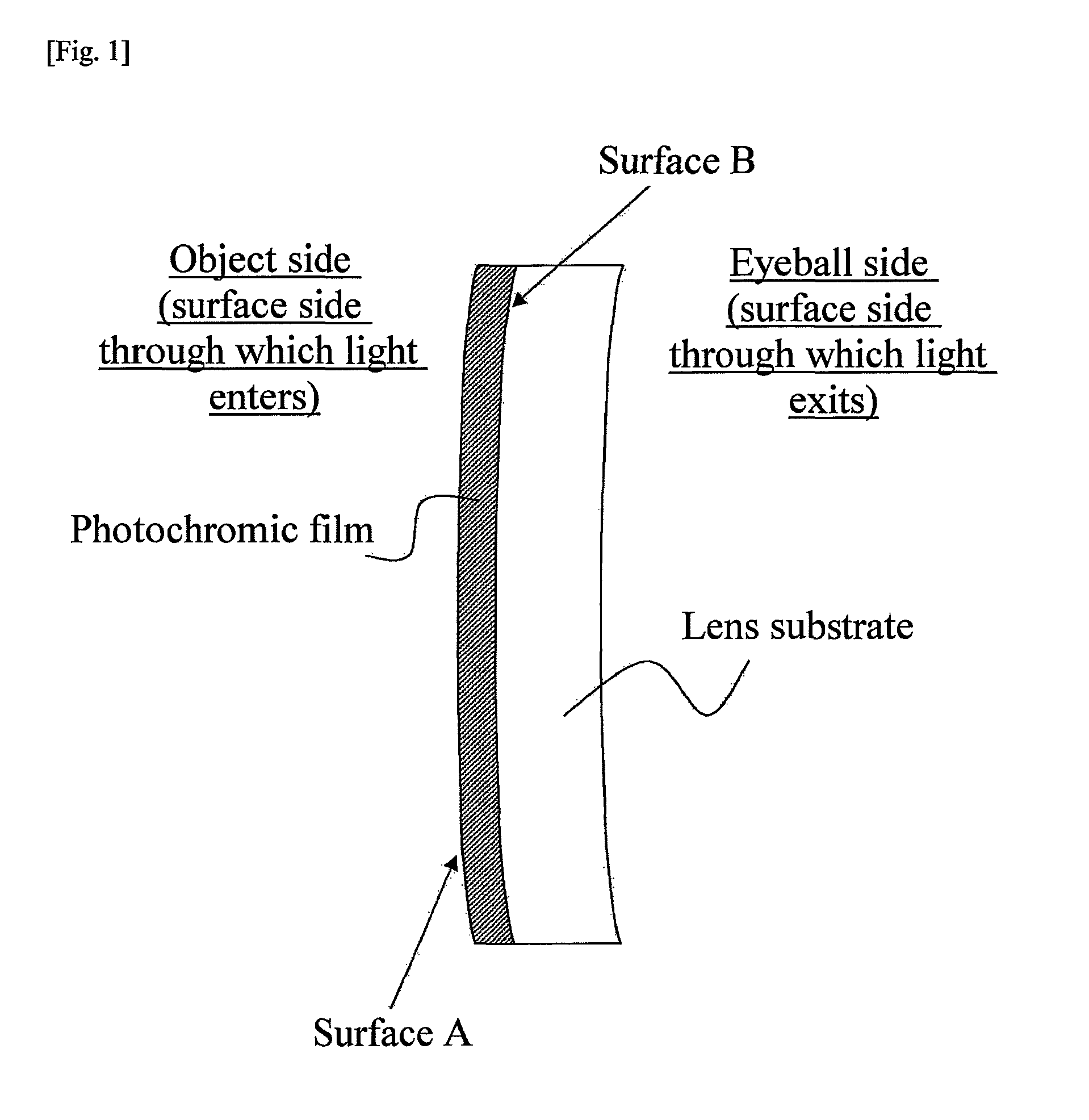
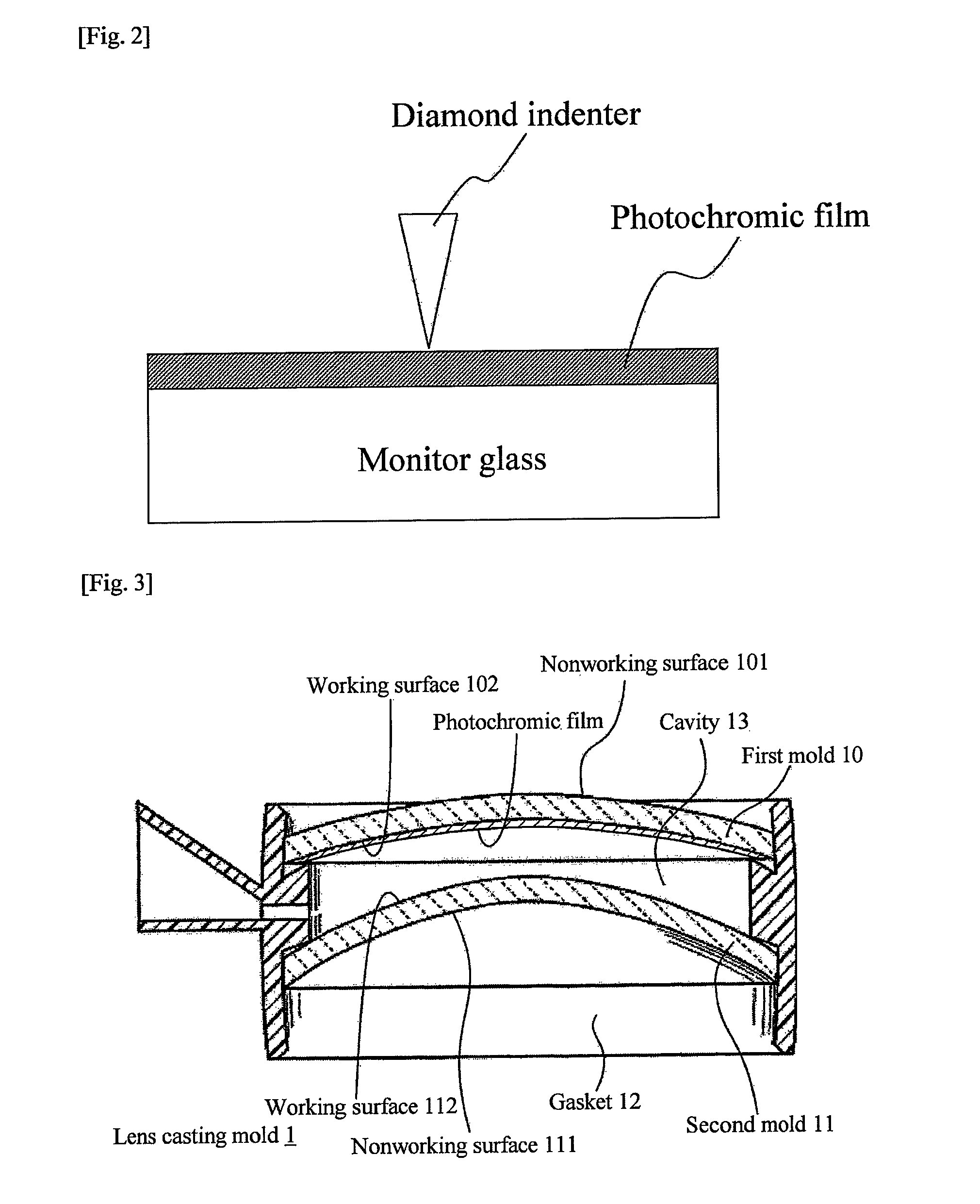
Photochromic film, photochromic lens comprising the same, and method of manufacturing photochromic lens
ActiveUS20090316246A1Good photoresponse performanceImprove featuresDecorative surface effectsOptical articlesPhotochromic lensHardness
The present invention relates to a photochromic film comprising a photochromic dye and a resin component. The photochromic film has a nanoindentation hardness of equal to or greater than 800 nm on at least one of surfaces, surface A, thereof. The present invention further relates to a method of manufacturing a photochromic lens. The method of manufacturing a photochromic lens of the present invention comprises forming a photochromic film having a nanoindentation hardness ranging from 500 to 5000 nm on an outermost surface thereof as well as having a smaller nanoindentation hardness on a surface facing a first mold than that on the outermost surface by coating a photochromic liquid comprising a photochromic dye and a curable component on one surface of the first mold for formation of one of surfaces of a lens and subjecting the photochromic liquid to curing treatment, and a photochromic lens comprising a photochromic film on a lens substrate is obtained by means of the above first mold.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Photochromic film, photochromic lens comprising the same, and method of manufacturing photochromic lens
ActiveUS7999989B2Good photoresponse performanceImprove featuresOptical articlesCoatingsPhotochromic lensHardness
The present invention relates to a photochromic film comprising a photochromic dye and a resin component. The photochromic film has a nanoindentation hardness of equal to or greater than 800 nm on at least one of surfaces, surface A, thereof. The present invention further relates to a method of manufacturing a photochromic lens. The method of manufacturing a photochromic lens of the present invention comprises forming a photochromic film having a nanoindentation hardness ranging from 500 to 5000 nm on an outermost surface thereof as well as having a smaller nanoindentation hardness on a surface facing a first mold than that on the outermost surface by coating a photochromic liquid comprising a photochromic dye and a curable component on one surface of the first mold for formation of one of surfaces of a lens and subjecting the photochromic liquid to curing treatment, and a photochromic lens comprising a photochromic film on a lens substrate is obtained by means of the above first mold.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveUS7410707B2Effectively inhibit the baseImprove fracture resistancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesHardnessNitrogen oxide
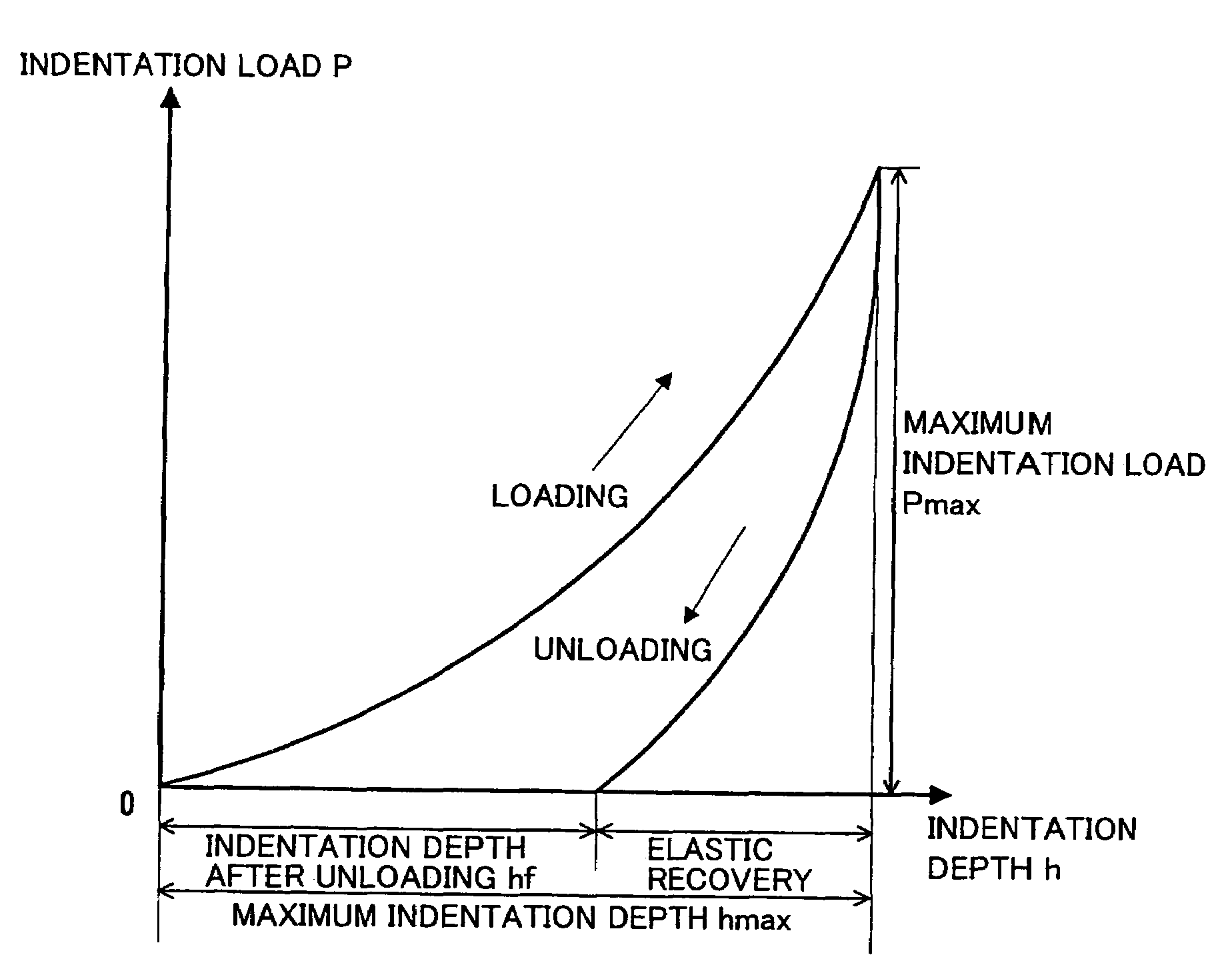
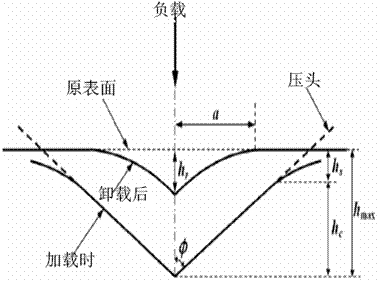
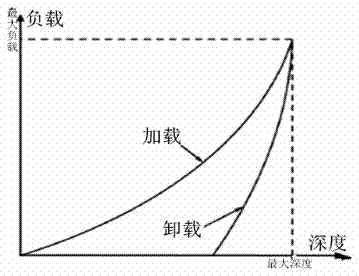
The present invention provides a surface-coated cutting tool comprising a coating film on a base, while the coating film comprises a hard layer constituted of a compound selected from a nitride, a carbonitride, an oxynitride and a carboxynitride of at least one primary element selected from a group consisting of the metals belonging to the groups 4a, 5a and 6a of the periodic table as well as B, Al and Si, and the hard layer satisfies the following: (a) (hmax−hf) / hmax is at least 0.2 and not more than 0.7, assuming that hmax represents the maximum indentation depth and hf represents the indentation depth (dent depth) after unloading in a hardness test according to nanoindentation, (b) the thickness of the hard layer is at least 0.5 μm and not more than 15 μm, and (c) the hardness according to nanoindentation is at least 20 GPa and not more than 80 GPa.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
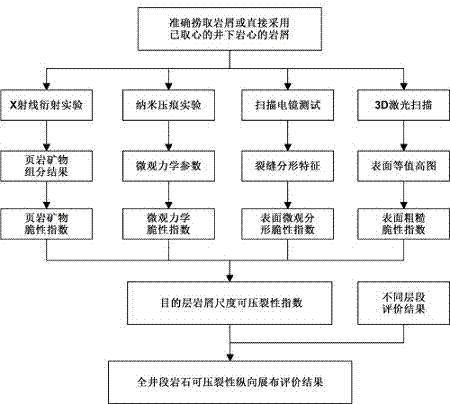
Method for evaluating fracturing property of shale based on rock debris microscopic characteristics
The invention discloses a method for evaluating fracturing property of shale based on rock debris microscopic characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking the rock debris at specific depth in reservoir of an oil gas well; (2) acquiring the relative amount of total-rock minerals through X-ray diffraction test for the rock debris, and calculating a brittleness index I1 of the minerals; (3) testing the nanoindentation microcosmic mechanical parameters of the rock debris and calculating a microcosmic mechanical brittleness index I2 thereof; (4) calculating the surface crack fractal parameter of the rock debris through scanning electron microscope, thereby acquiring a fractal brittleness index I3; (5) performing 3D laser scanning on the rock debris and calculating the surface rough brittleness index I4; (6) weighting the above four brittleness indexes according to the practical condition of the oil field, thereby acquiring a comprehensive fracturing index I; (7) repeating the steps (1)-(6), calculating the fracturing indexes of the rock debris at different depths and drawing a whole-well comprehensive fracturing index longitudinal layout. According to the method provided by the invention, the comprehensive fracturing index of the shale rock debris can be acquired and the necessary basis is supplied for fracture selecting layer with core-taking difficulty or without core shale reservoir.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveUS20060154108A1Improve wear resistanceChipping resistancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesHardnessNanoindentation
The present invention provides a surface-coated cutting tool comprising a coating film on a base, while the coating film comprises a hard layer constituted of a compound selected from a nitride, a carbonitride, an oxynitride and a carboxynitride of at least one primary element selected from a group consisting of the metals belonging to the groups 4a, 5a and 6a of the periodic table as well as B, Al and Si, and the hard layer satisfies the following: (a) (hmax−hf) / hmax is at least 0.2 and not more than 0.7, assuming that hmax represents the maximum indentation depth and hf represents the indentation depth (dent depth) after unloading in a hardness test according to nanoindentation, (b) the thickness of the hard layer is at least 0.5 μm and not more than 15 μm, and (c) the hardness according to nanoindentation is at least 20 GPa and not more than 80 GPa.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
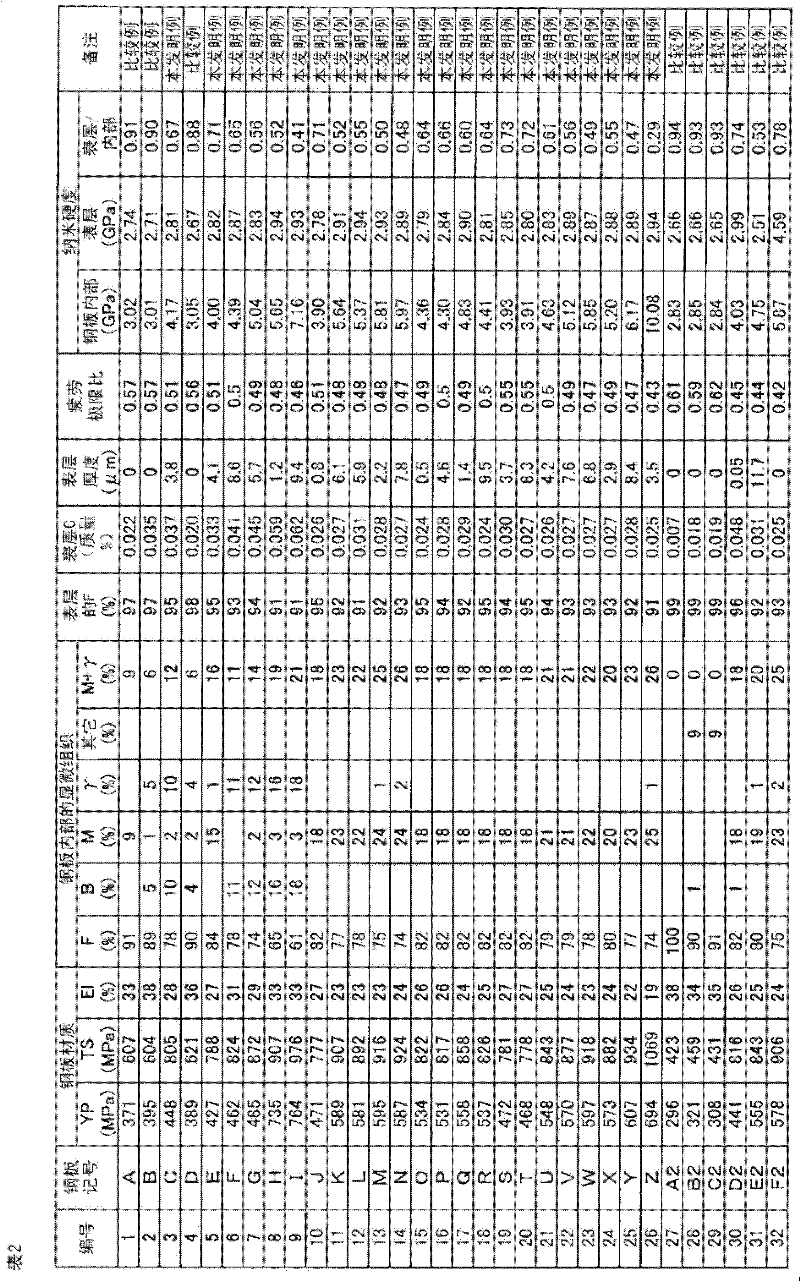
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and process for producing same
ActiveCN102482753AImprove fatigue durabilityExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSoft layerHigh intensity
Disclosed is a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet which comprises a steel sheet part and a deposit formed on the surface of the steel sheet part and has a tensile strength of 770 MPa or higher, wherein the deposit is a zinc layer formed by hot-dip plating or an alloyed zinc layer formed by hot-dip plating, the steel sheet part comprises a soft layer, which is in direct contact with the deposit, and an inner layer, which is the part other than the soft layer, and the thickness (D) of the soft layer is 0.001 to 5% of the thickness (t) of the steel sheet part. In a cross-section along the thickness direction of the steel sheet part, when the hardness of the soft layer measured by a nanoindentation method is expressed by H1 and the representative hardness of the steel sheet part measured by the nanoindentation method is expressed by Ha, then H1 is 5-75% of Ha.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
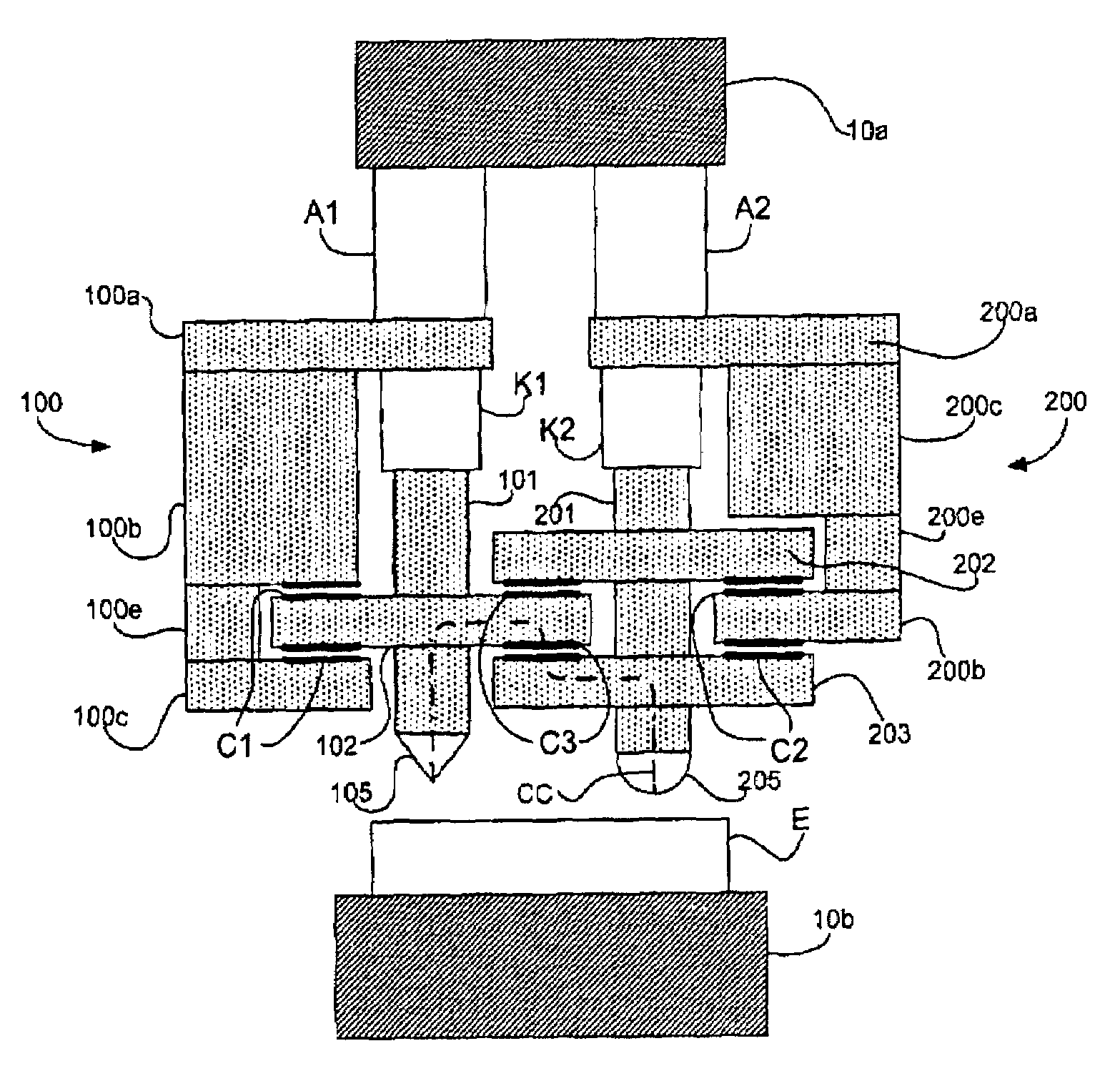
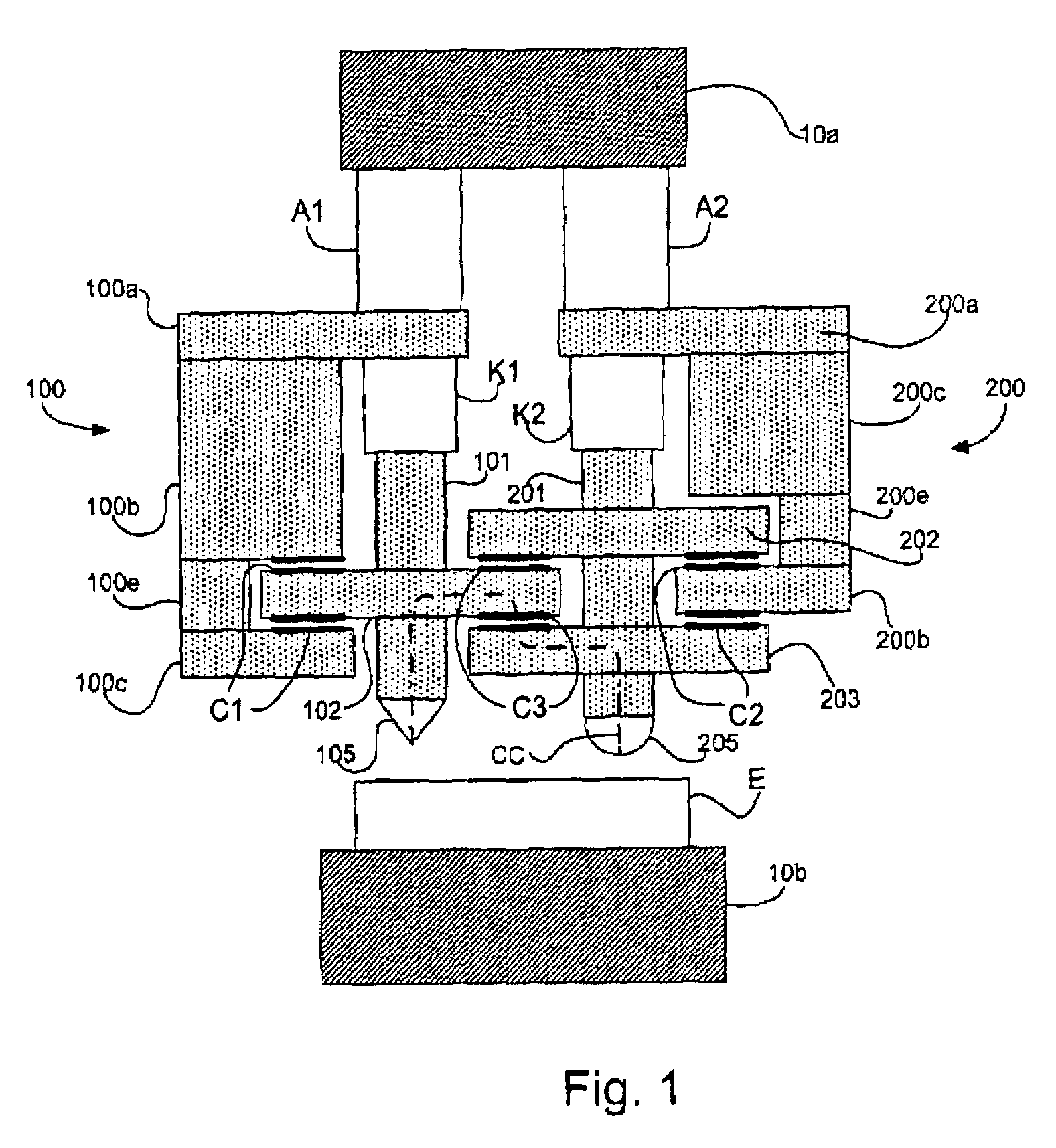
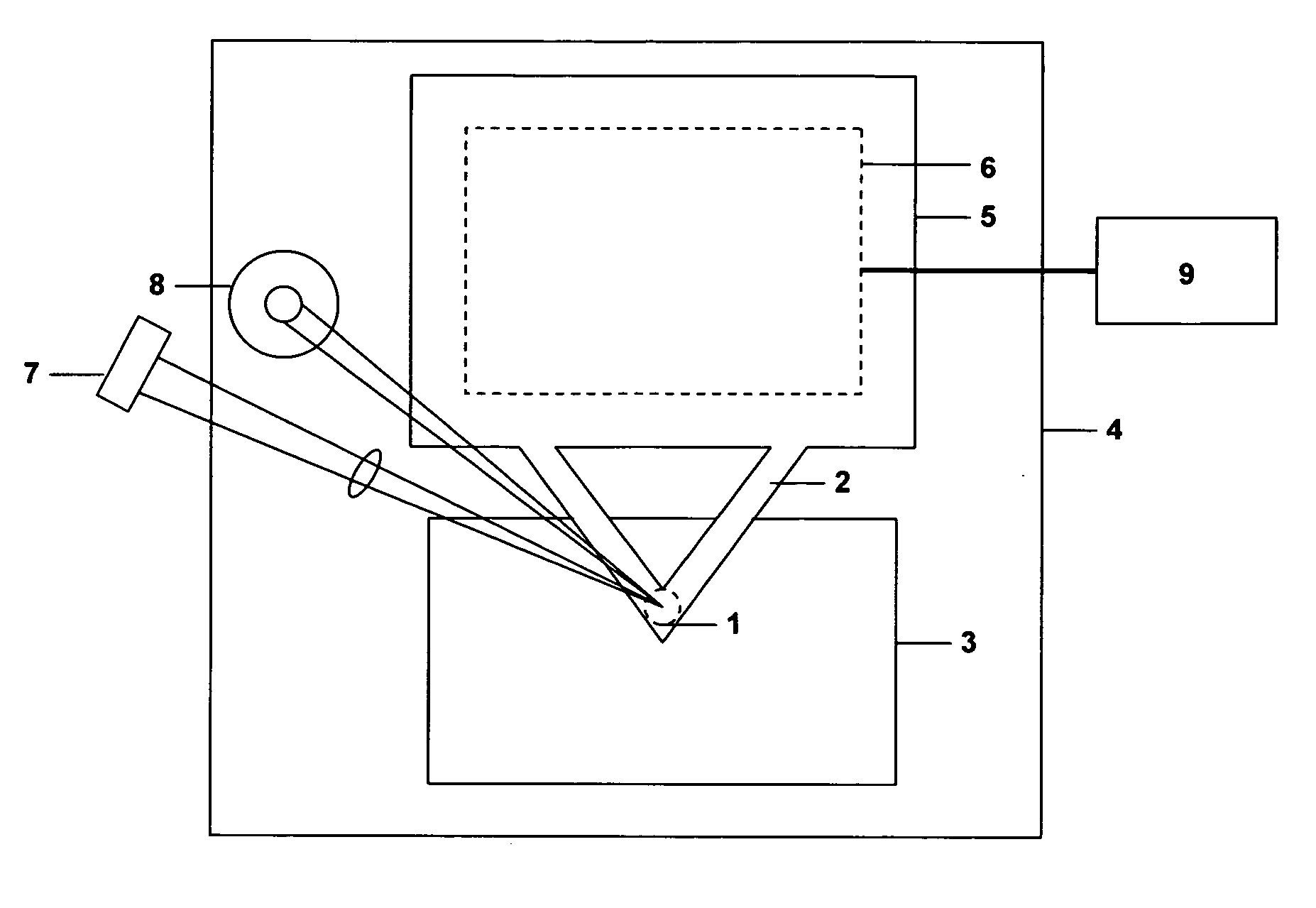
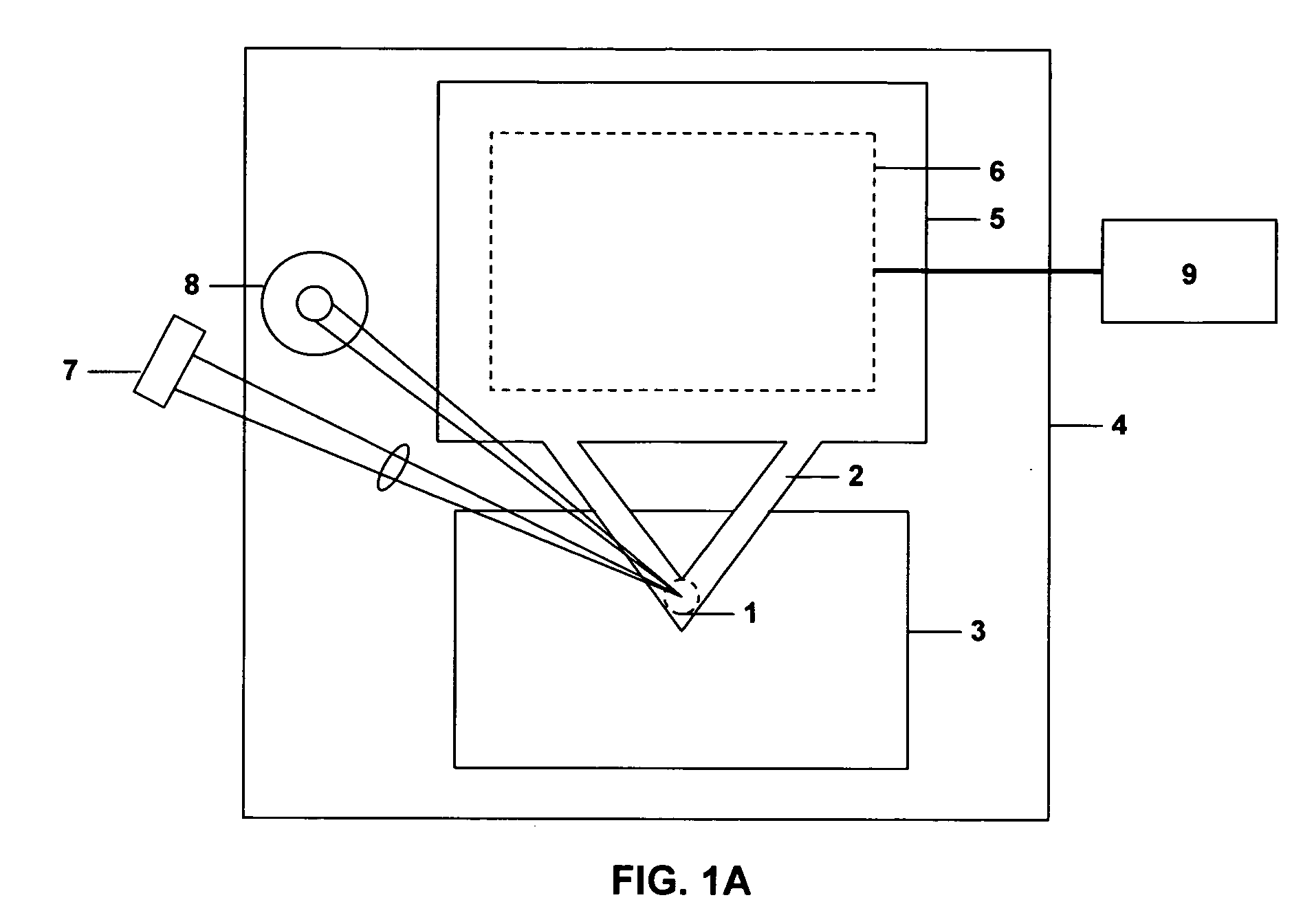
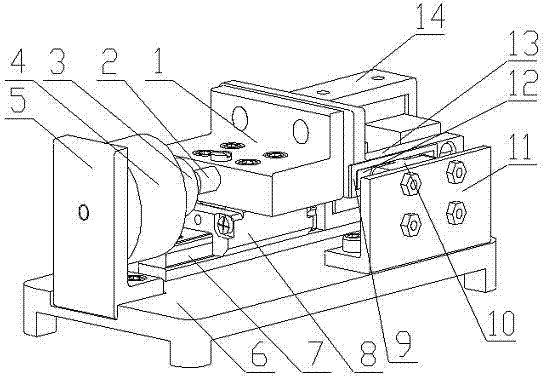
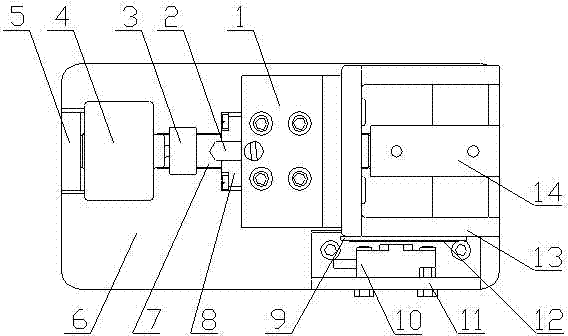
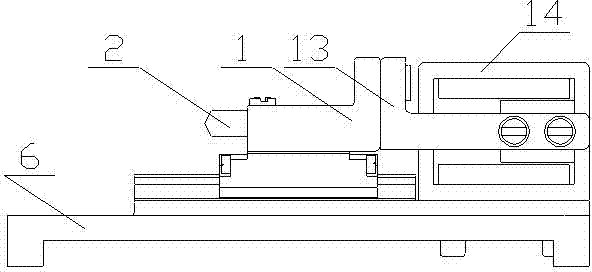
Nanoindentation/cutting test device
InactiveCN102252925ACompact structureReduce volumeUsing optical meansInvestigating material hardnessMaximum dimensionImage resolution
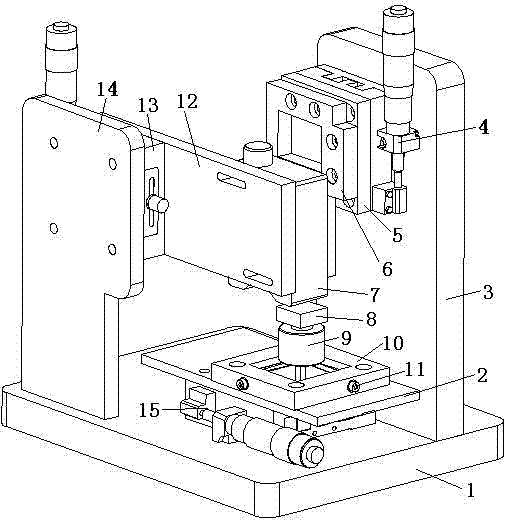
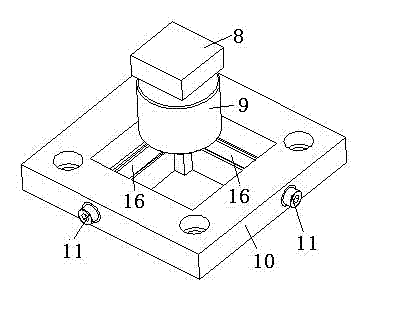
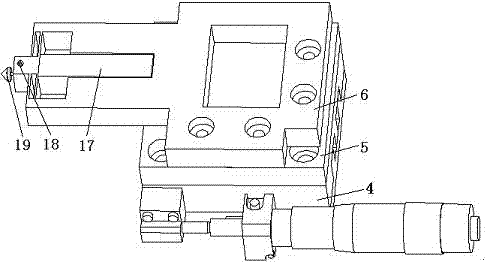
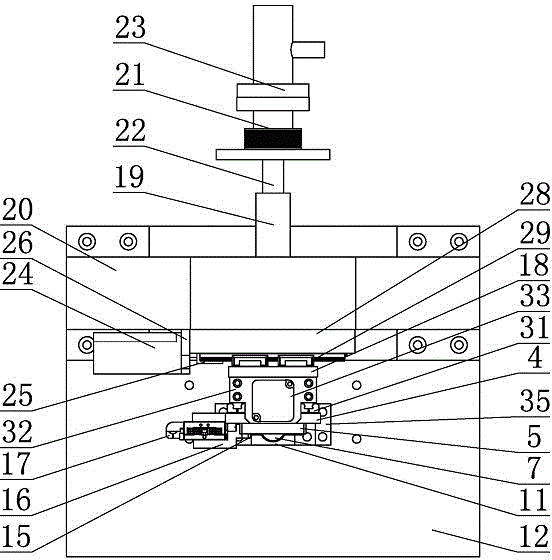
The invention relates to a nanoindentation / cutting test device and belongs to the field of electromechanical integration precise scientific instruments. The nanoindentation / cutting test device comprises an X / Y precise positioning platform, a Z-axis macro-motion adjusting mechanism, a precise indentation driving unit, a load signal detection unit and a displacement signal detection unit, wherein the X / Y precise positioning platform is connected with a coarse adjustment mechanism III15 through a connection plate I2, the adjustment mechanism III15 is fixed on a base 1, and a loading platform 8 is connected with the X / Y precise positioning platform through a force sensor 8; and the precise indentation driving unit is fixed on a side plate I3 through the Z-axis macro-motion adjusting mechanism, and the side plate I3 is fixed on the base 1; and the displacement signal detection unit is fixed on the base 1 through a side plate II14. The nanoindentation / cutting test device has the technical effects of compact structure and small volume. The nanoindentation / cutting test device can be used for realizing the mechanical property test of the three-dimensional test piece of which the characteristic dimension is above the millimeter level (the maximum dimension is up to 20mm*20mm*10mm); and the displacement loading resolution reaches the nanometer level and the loading force resolution reaches the micro-Newton level.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
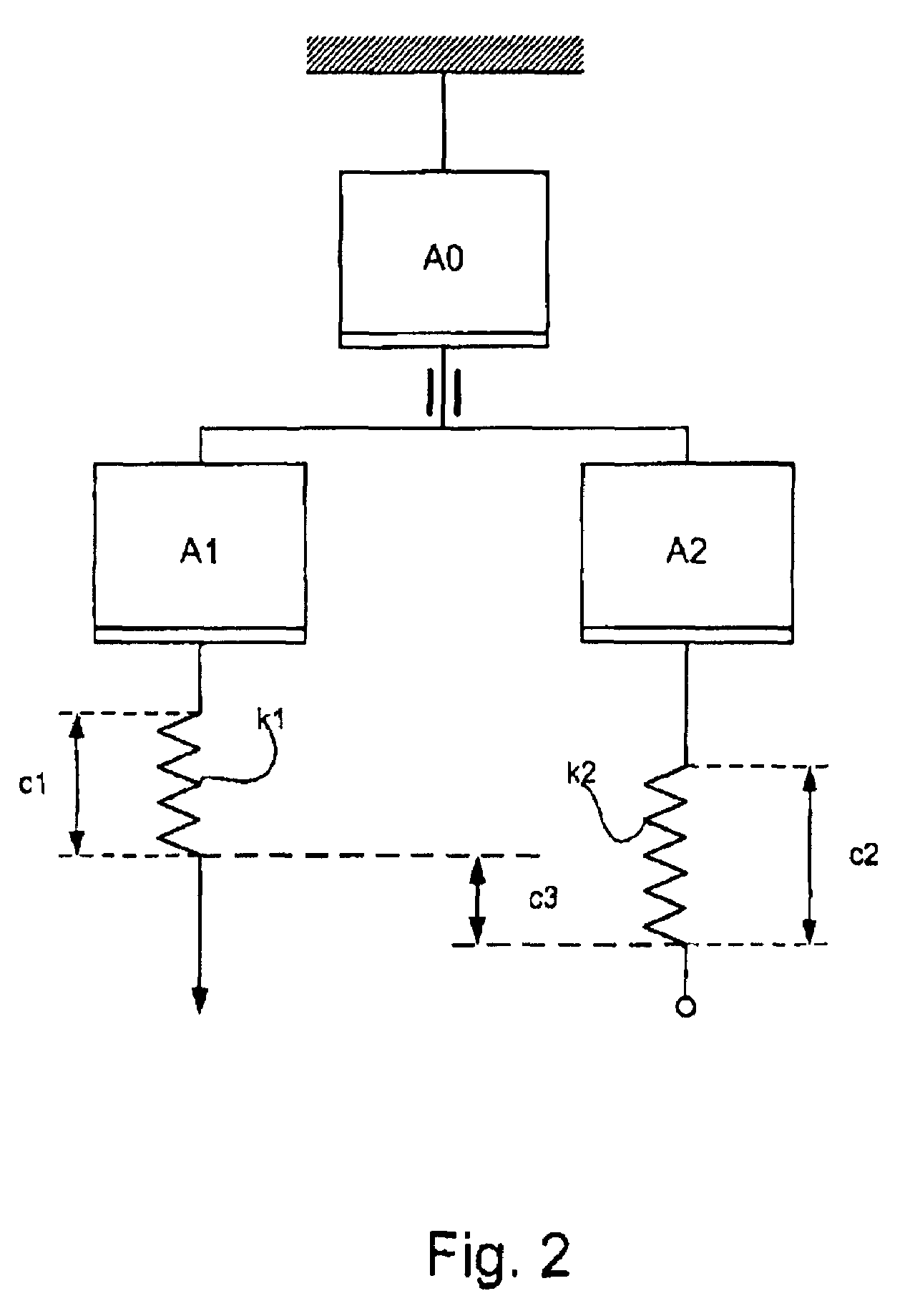
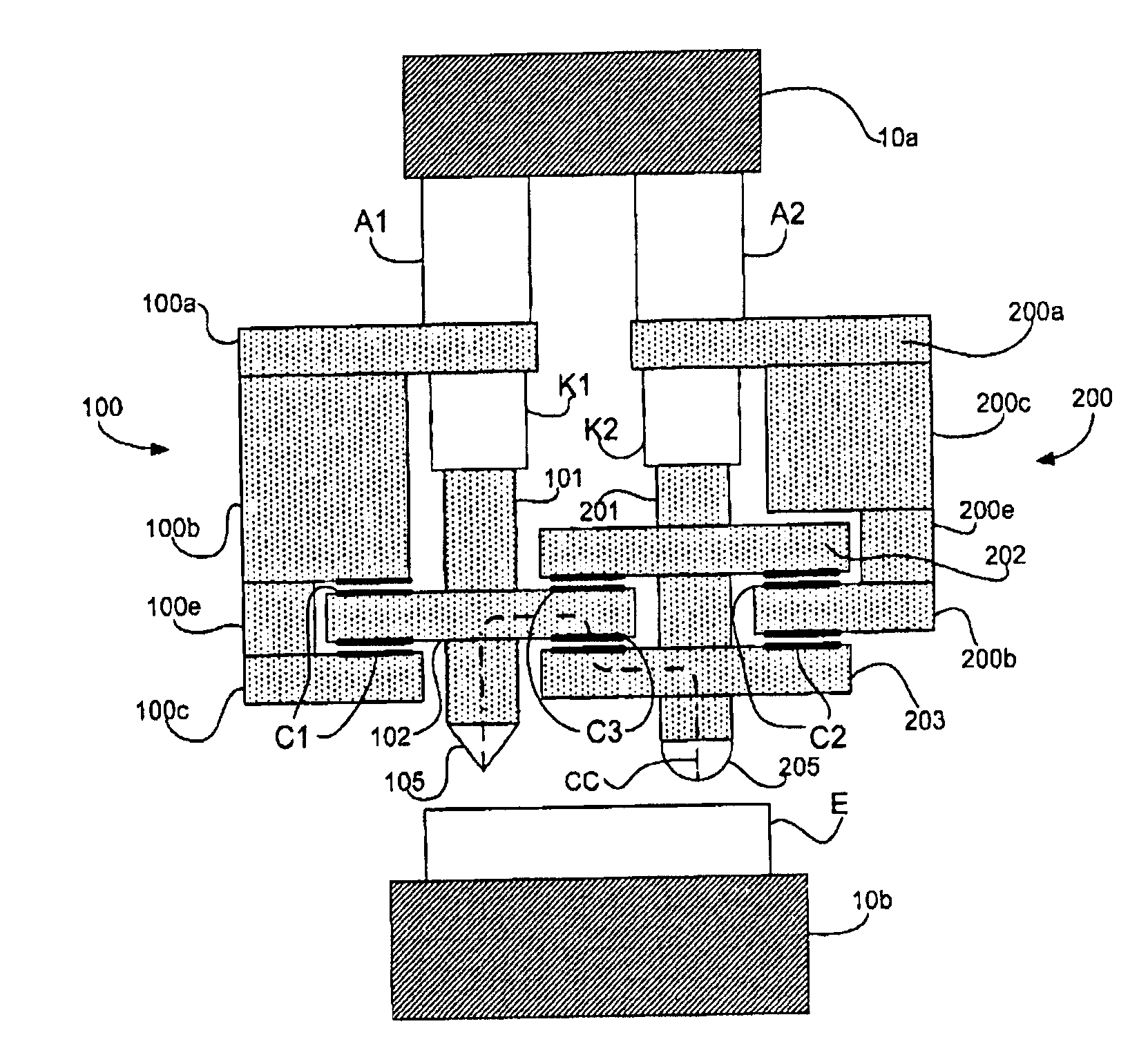
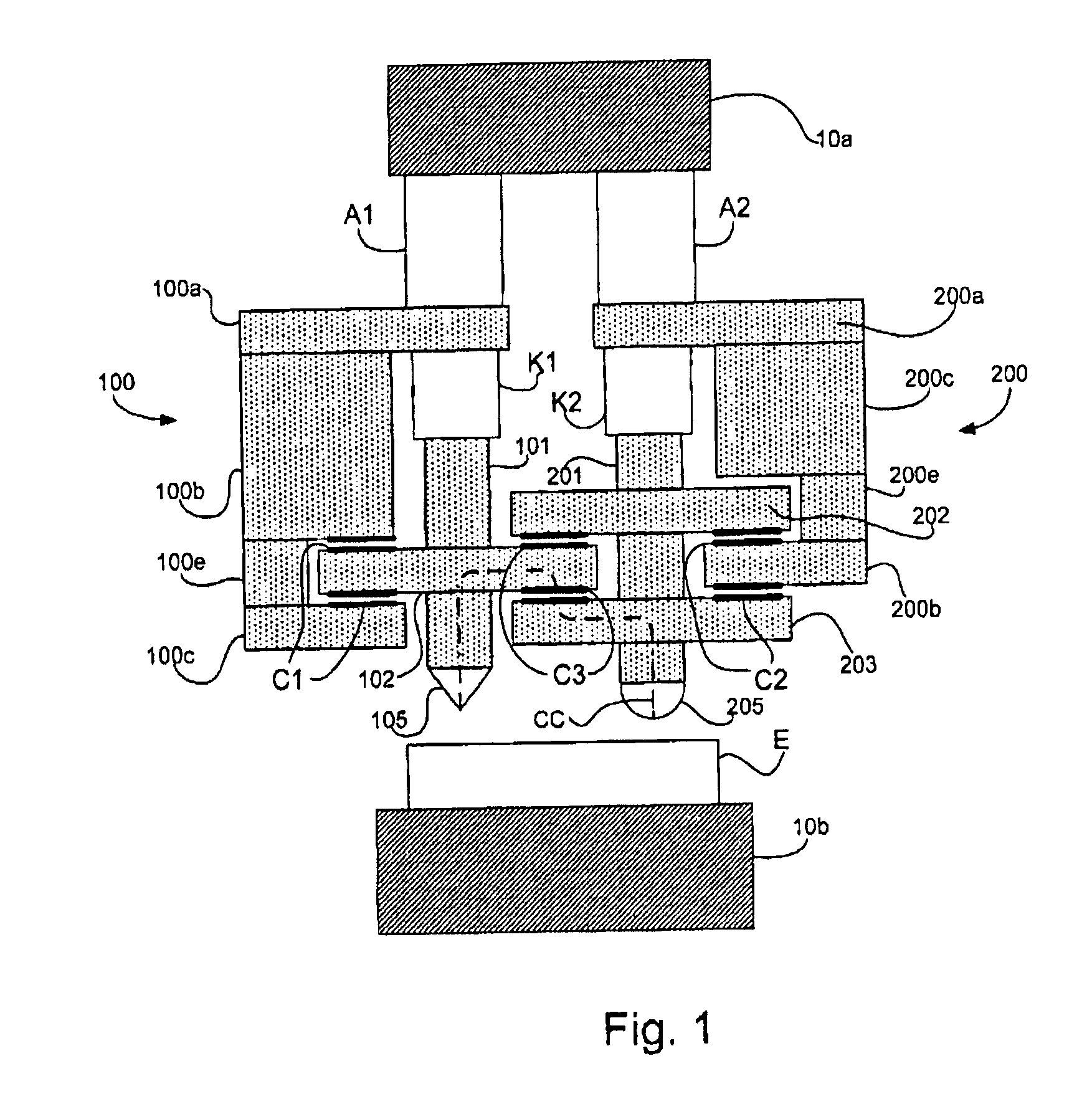
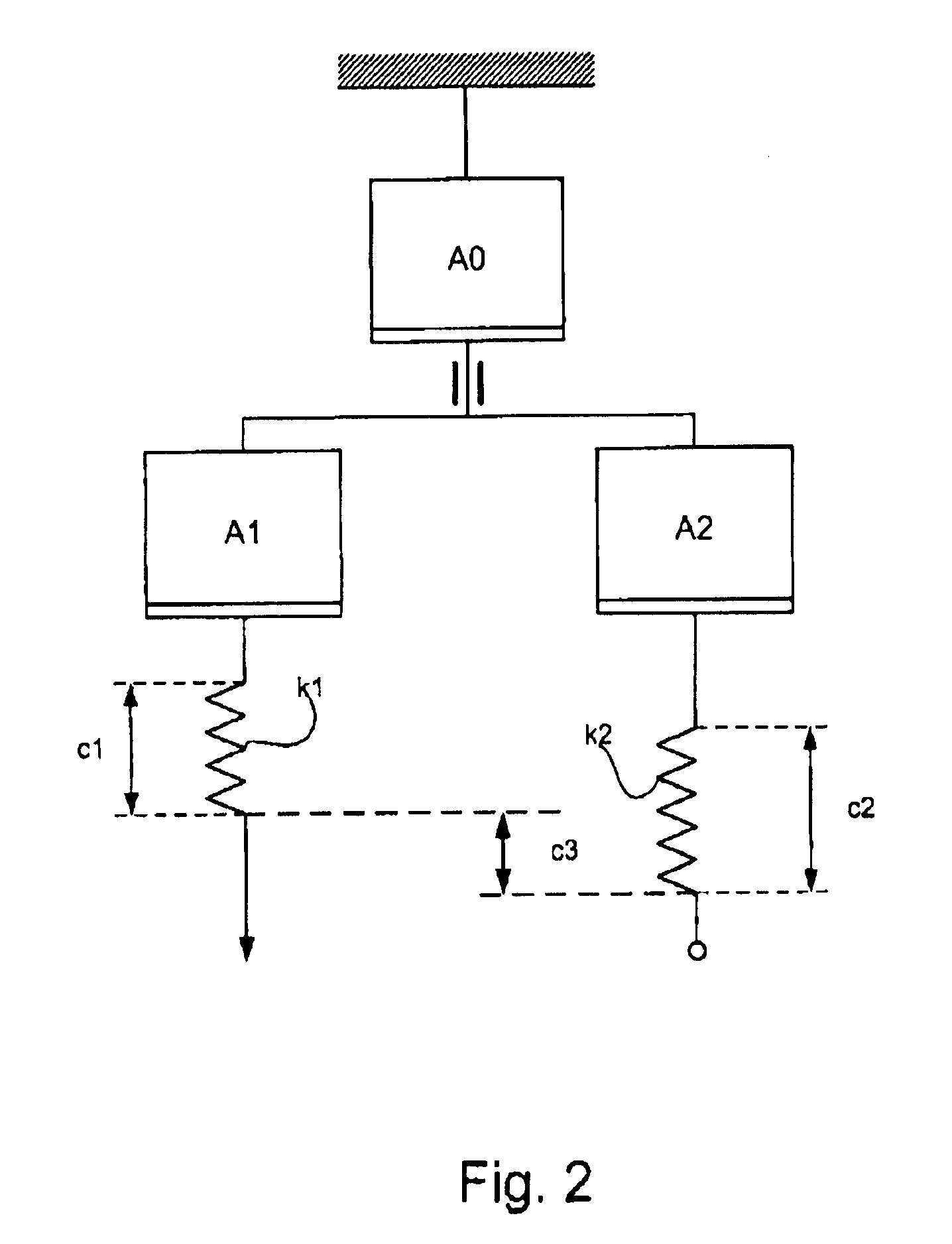
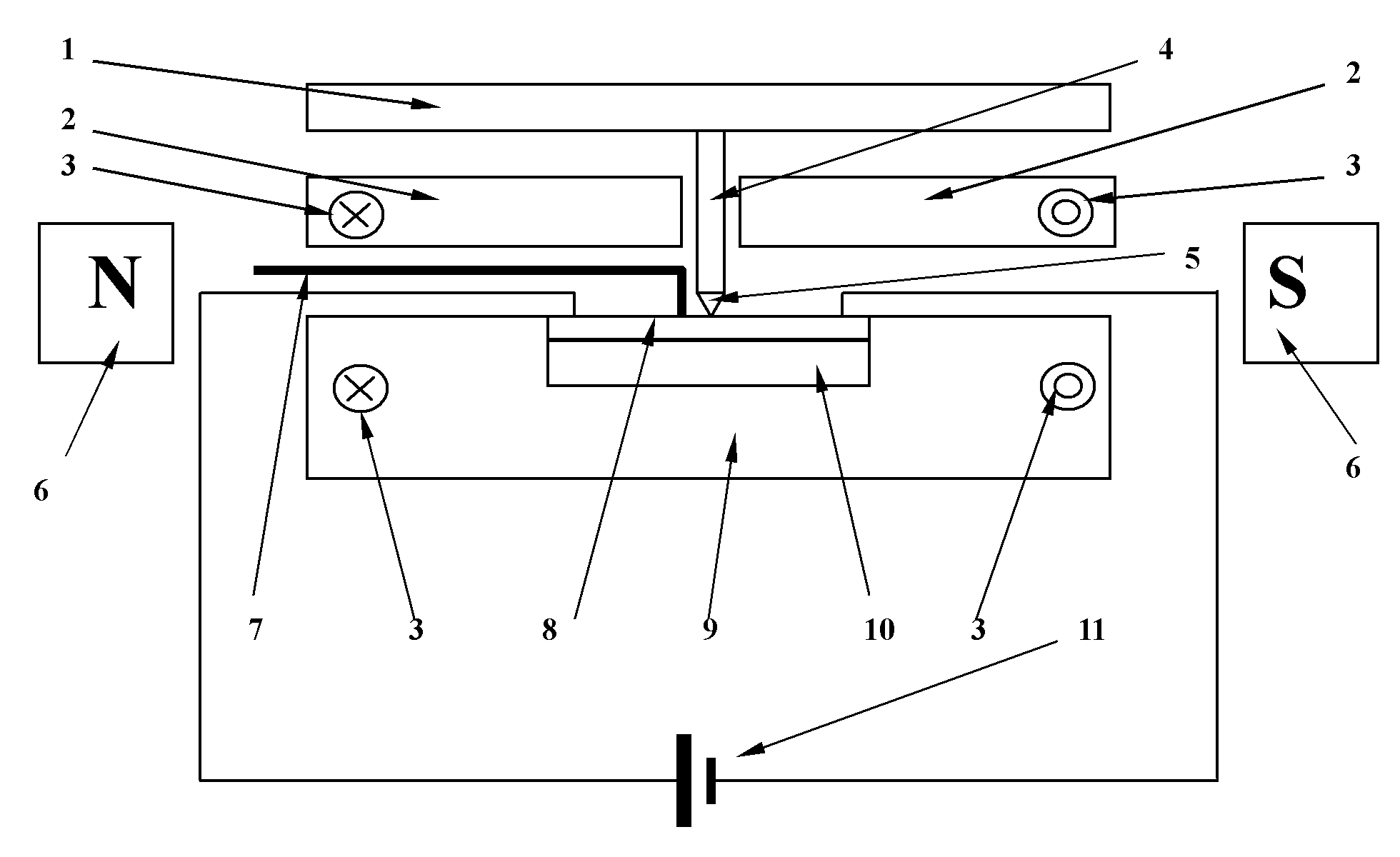
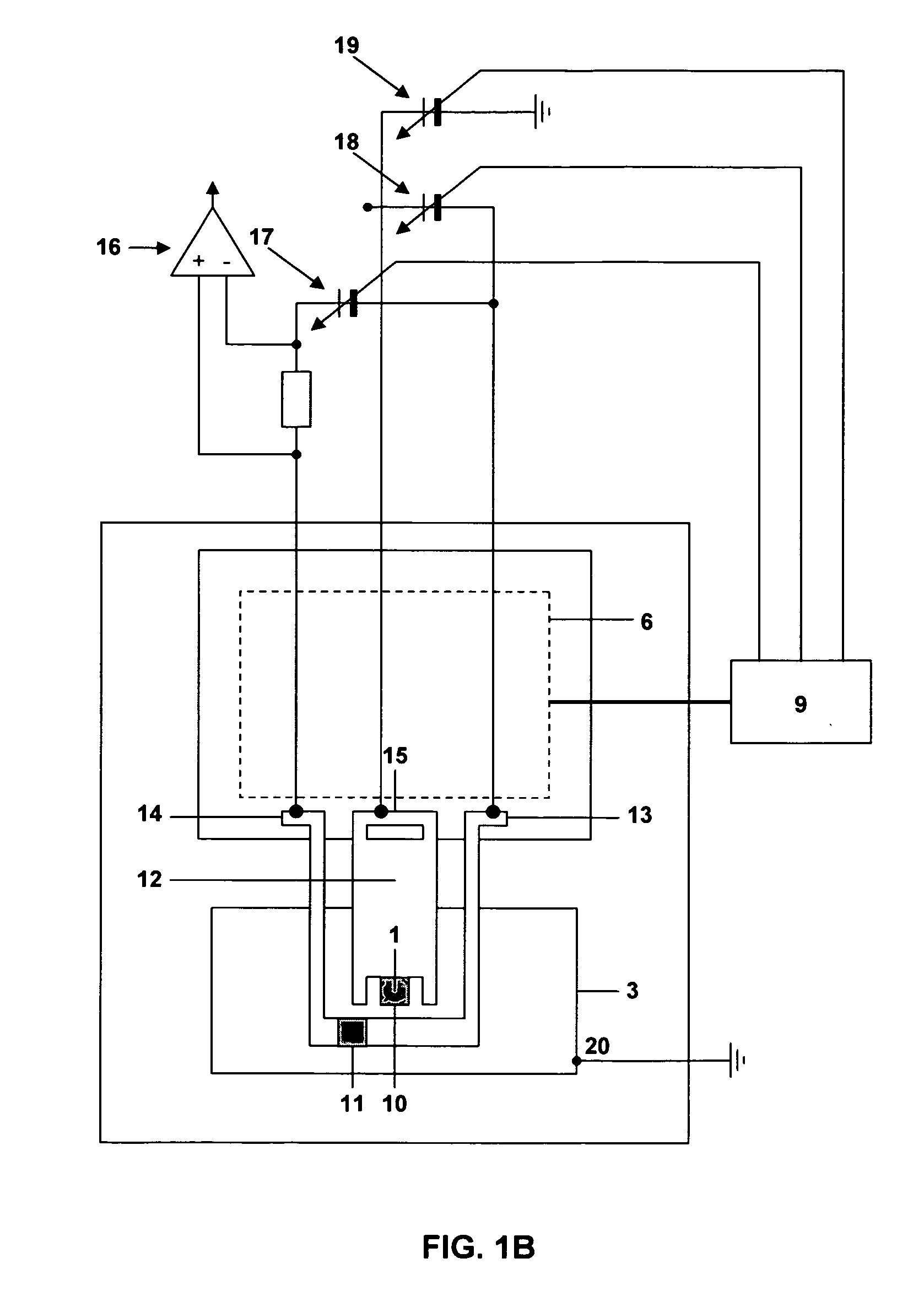
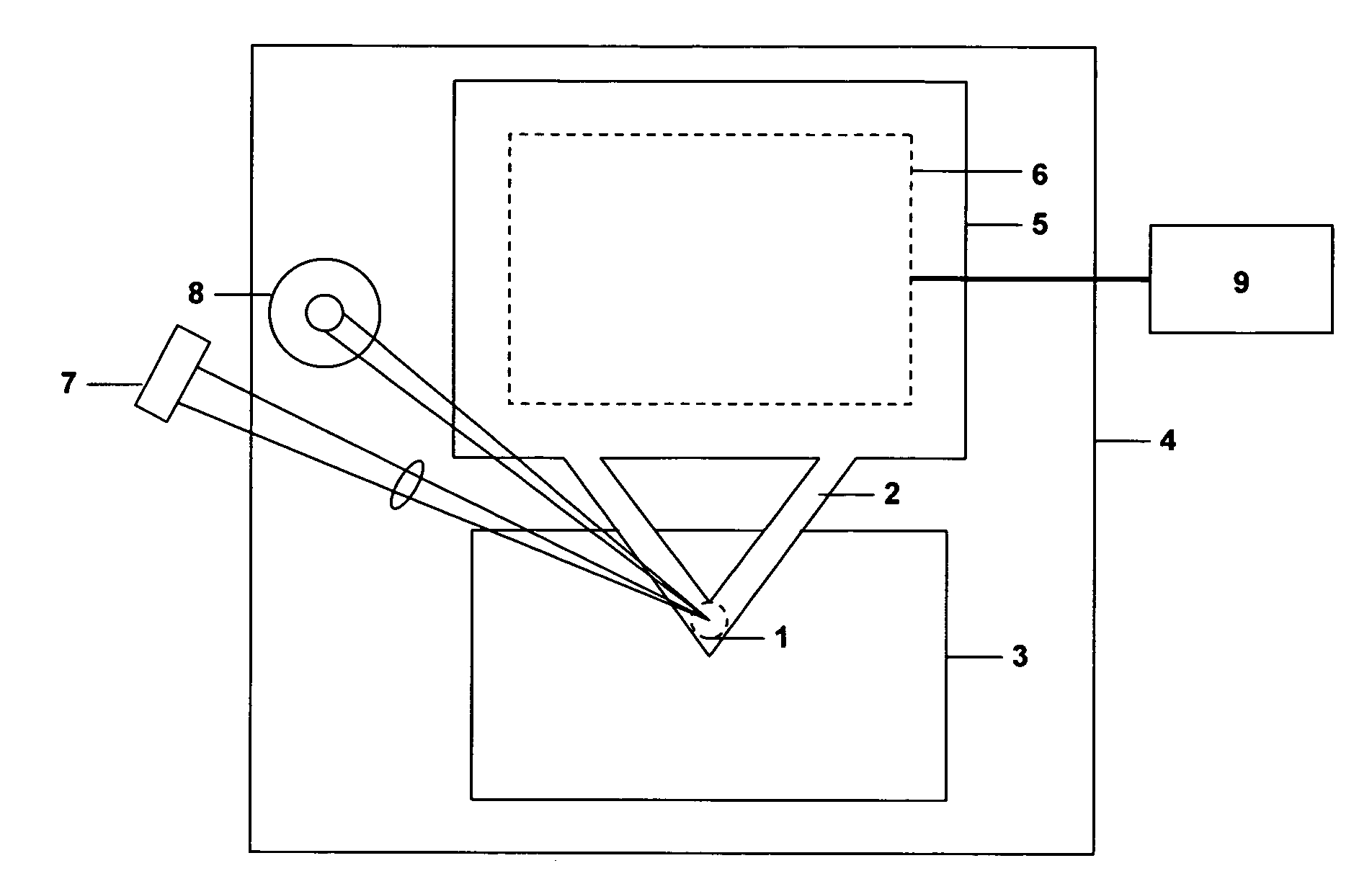
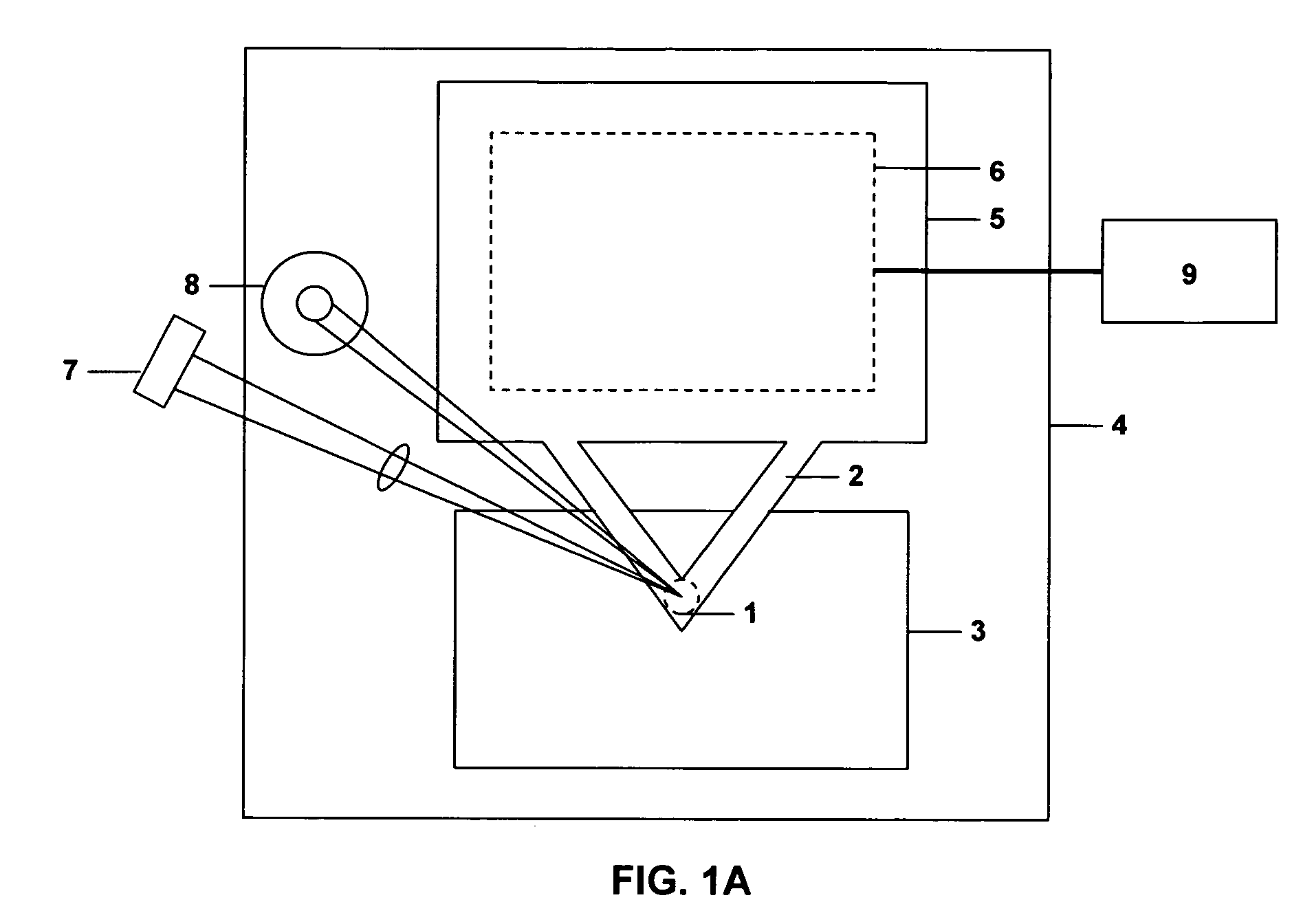
Measuring head for nanoindentation instrument and measuring method using same
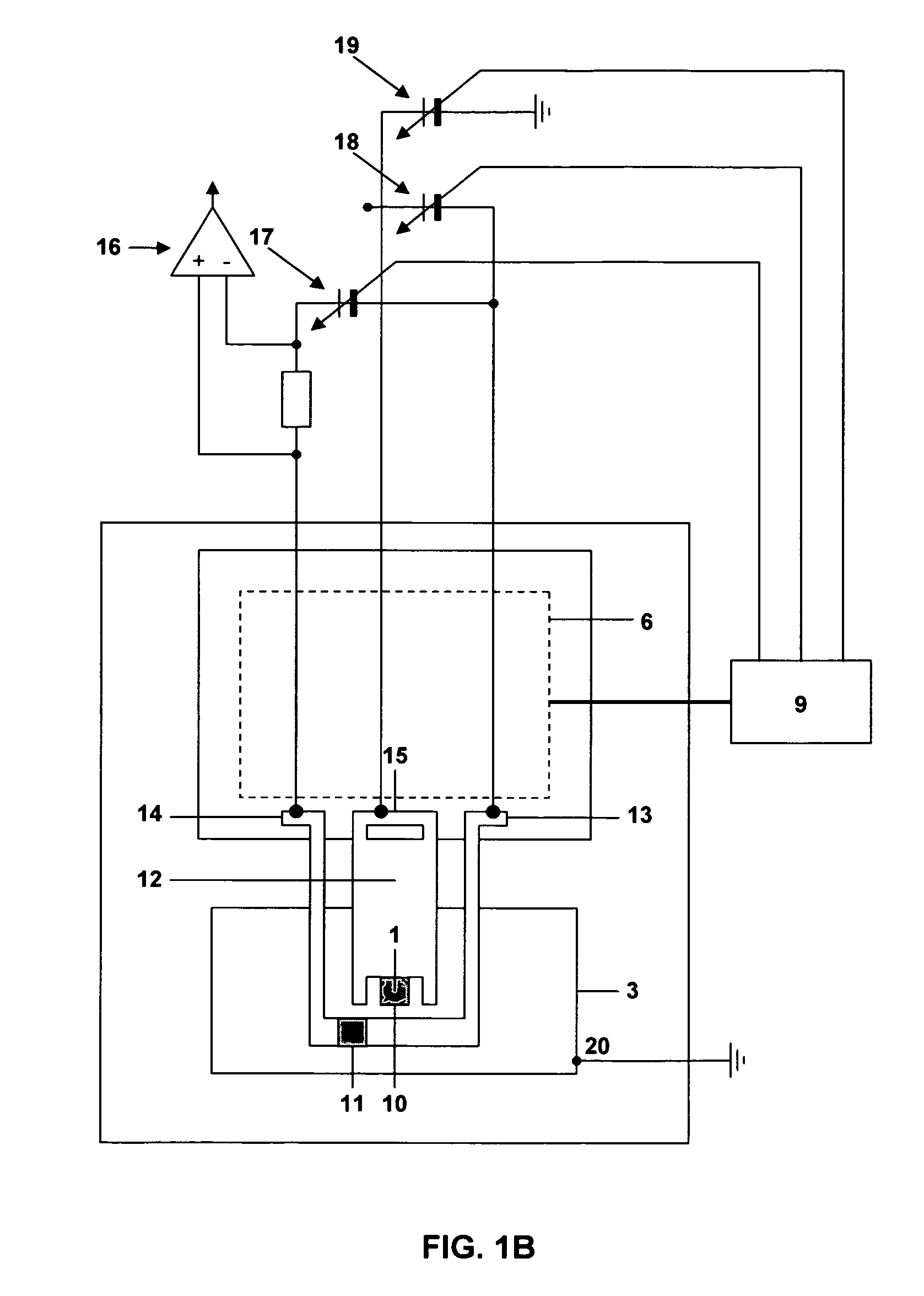
A measuring head for a nano-indentation instrument capable of positioning a sample relatively to the measuring head, which includes a measuring axis, a reference axis and a component for detecting a depth of penetration of an indentor into the sample. The measuring and reference axes are attached to a frame for connection to the instrument. The measuring axis incorporates an actuator and includes the indentor, the reference axis incorporates an actuator and includes a reference tip, and the measuring and reference axes each have a component for detecting a force applied by its actuator. Penetration depth is detected by measuring a displacement of the indentor relatively to the reference tip.
Owner:ANTON PAAR TRITEC SA
Ultra-hard low friction coating based on AlMgB14 for reduced wear of MEMS and other tribological components and system
InactiveUS20050100748A1Superior protective coatHigh hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesMicroelectromechanical systemsAlloy
Performance and reliability of microelectromechanical system (MEMS) components enhanced dramatically through the incorporation of protective thin film coatings. Current-generation MEMS devices prepared by the LIGA technique employ transition metals such as Ni, Cu, Fe, or alloys thereof, and hence lack stability in oxidizing, corrosive, and / or high temperature environments. Fabrication of a superhard, self-lubricating coating based on a ternary boride compound AlMgB14 is described in this letter as a potential breakthrough in protective coating technology for LIGA microdevices. Nanoindentation tests show that hardness of AlMgB14 films prepared by pulsed laser deposition ranges from 45 GPa to 51 GPa, when deposited at room temperature and 573 K, respectively. Extremely low friction coefficients of 0.04-0.05, which are thought to result from a self-lubricating effect, have also been confirmed by nanoscratch tests on the AlMgB14 films. Transmission electron microscopy studies show that the as-deposited films are amorphous, regardless of substrate temperature; however, analysis of FTIR spectra suggests that the higher substrate temperature facilitates formation of the B12 icosahedral framework, therefore leading to the higher hardness.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Diamondlike carbon hard multilayer film formed body and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20070054125A1Improve adhesionImprove wear resistanceLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon filmDiamond-like carbon
A diamondlike carbon hard multilayer formed film body comprises a substrate, a diamondlike carbon film mainly composed of diamondlike carbon, and an intermediate layer between the substrate and the diamondlike carbon film. The diamondlike carbon film is composed of, in order from the substrate side, a first diamondlike carbon film and a second diamondlike carbon film. The surface hardness of the first diamondlike carbon film is within the range from not less than 10 GPa to not more than 40 GPa based on nanoindentation test, and the surface hardness of the second diamondlike carbon film is within the range from more than 40 GPa to not more than 90 GPa based on nanoindentation test. According to such a structure, even if a DLC multilayer containing high-hardness DLC film on the outermost surface side is formed in a thickness of not less than about 3 μm on a substrate of a wide range extending from a material with high hardness such as cemented carbide to an iron-based material with low hardness, excellent adhesion to both the substrate and the DLC film can be ensured in addition to excellent wear resistance.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
AFM (Atomic Force Microscope)-based device for performing nanoindentation measurement on surface of microparticle
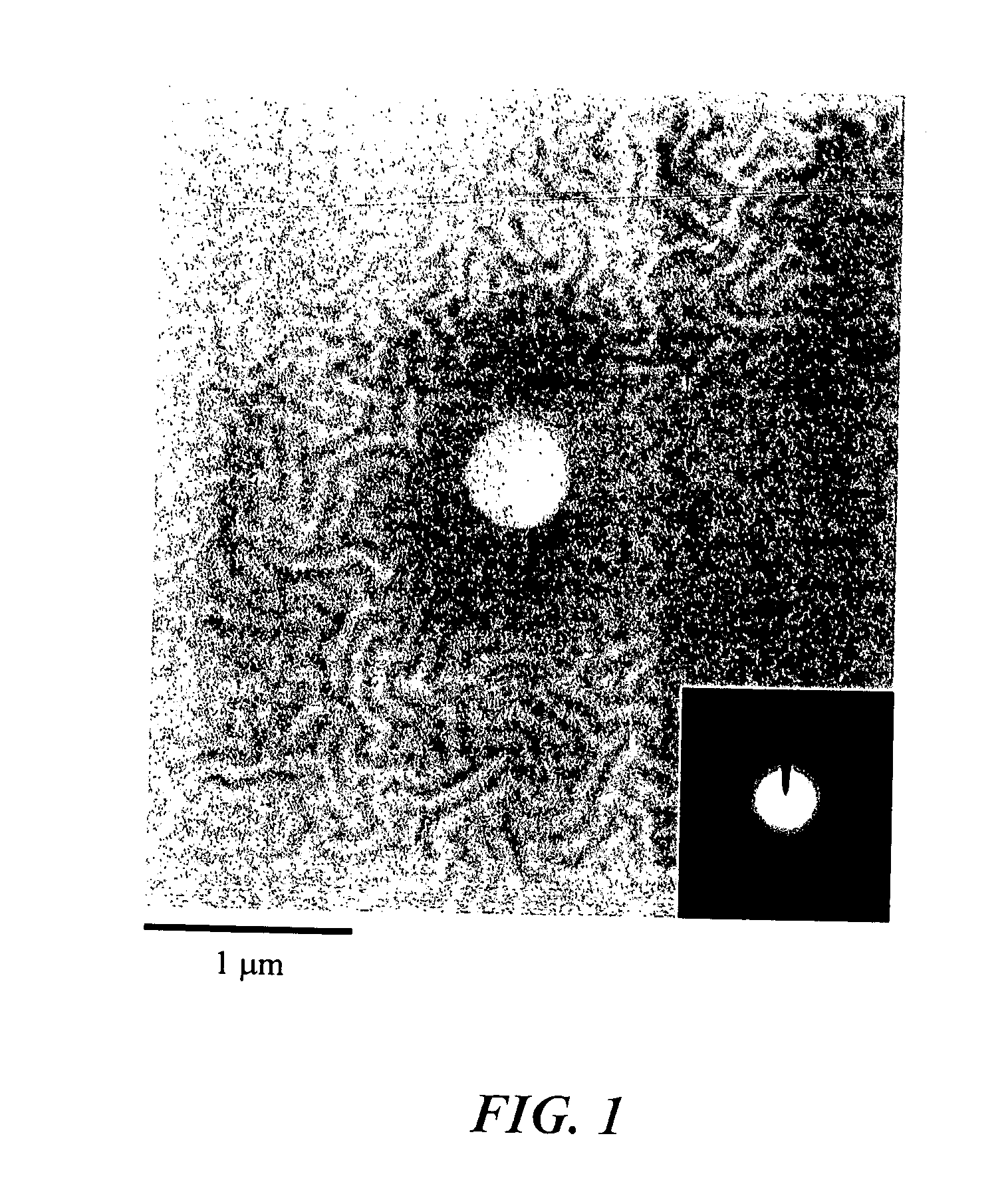
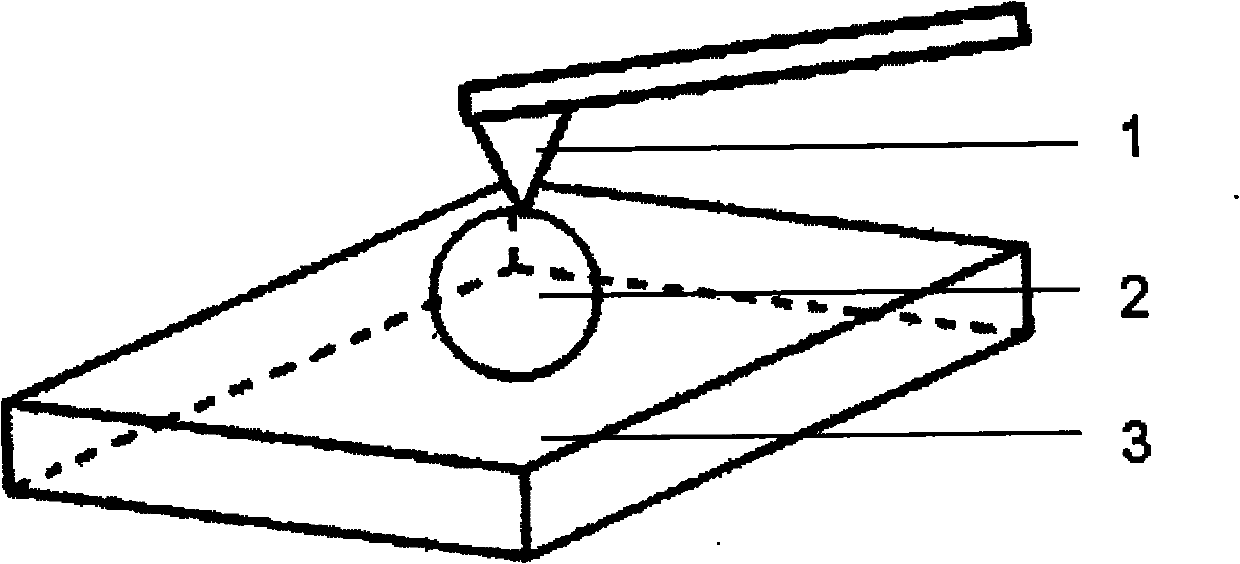
The invention provides an AFM (Atomic Force Microscope)-based device and method for performing nanoindentation measurement on the surface of a microparticle. The device is composed of an AFM system, a sheet-shaped plane for holding a sample to be measured is arranged on a sample platform at the top of a scanatron, a double faced adhesive tape for sticking and fixing the sample to be measured is arranged on the sheet-shaped plane, and a nanoindentation needle tip for scanning and nanoindentation operation is fixed in a needle tip holder and arranged above the sample to be measured. When the device is in use, the sample to be measured is adhered to the sheet-shaped plane with the double faced adhesive tape; the sheet-shaped plane is placed on the sample platform at the top of the scanatron; and then the nanoindentation needle tip fixed in the needle tip holder performs scanning and nanoindentation operation above the sample to be measured, wherein the nanoindentation needle tip is a diamond needle tip and has an elasticity coefficient remained between 100N / m and 300N / m and an resonance frequency of 35-65khz. According to the invention, nanoindentation measurement is successfully carried on the surface of a detected powdery microparticle sample with the particle size of 20-80 micrometers.
Owner:CHINA NAT ACAD NANOTECH & ENG
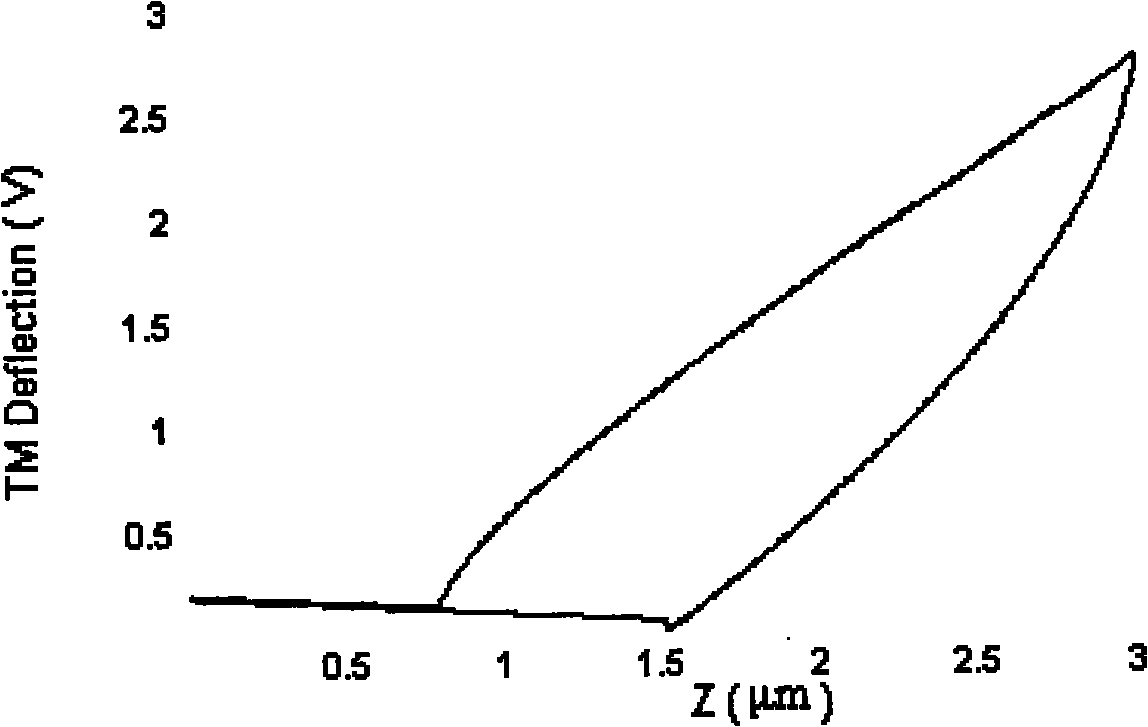
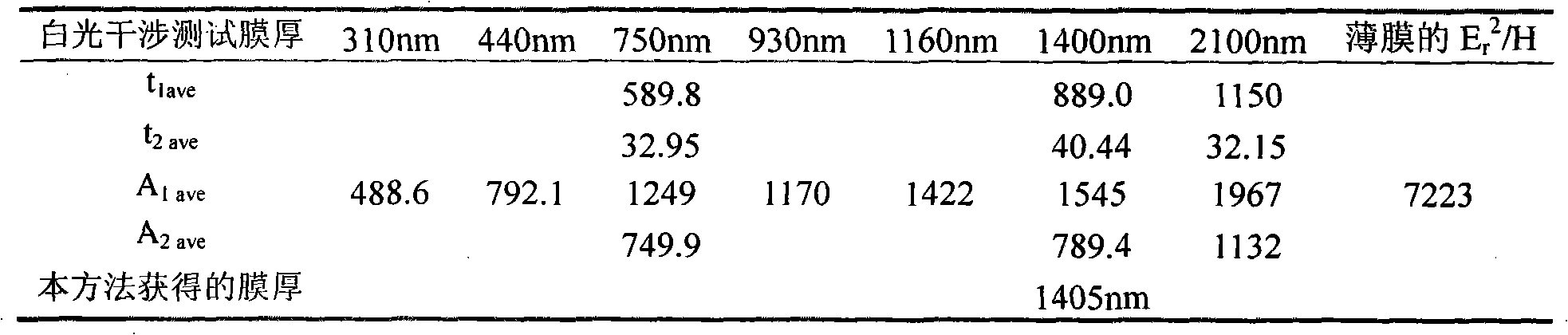
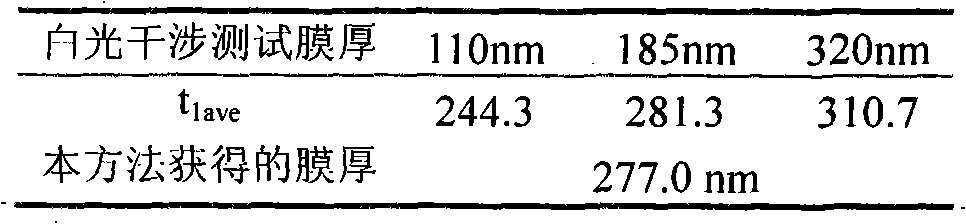
Method for testing physical performances of film and film-substrate interface based on nanometer indentation continuous stiffness curve
InactiveCN101806690AMechanical thickness measurementsInvestigating material hardnessInterface layerEngineering
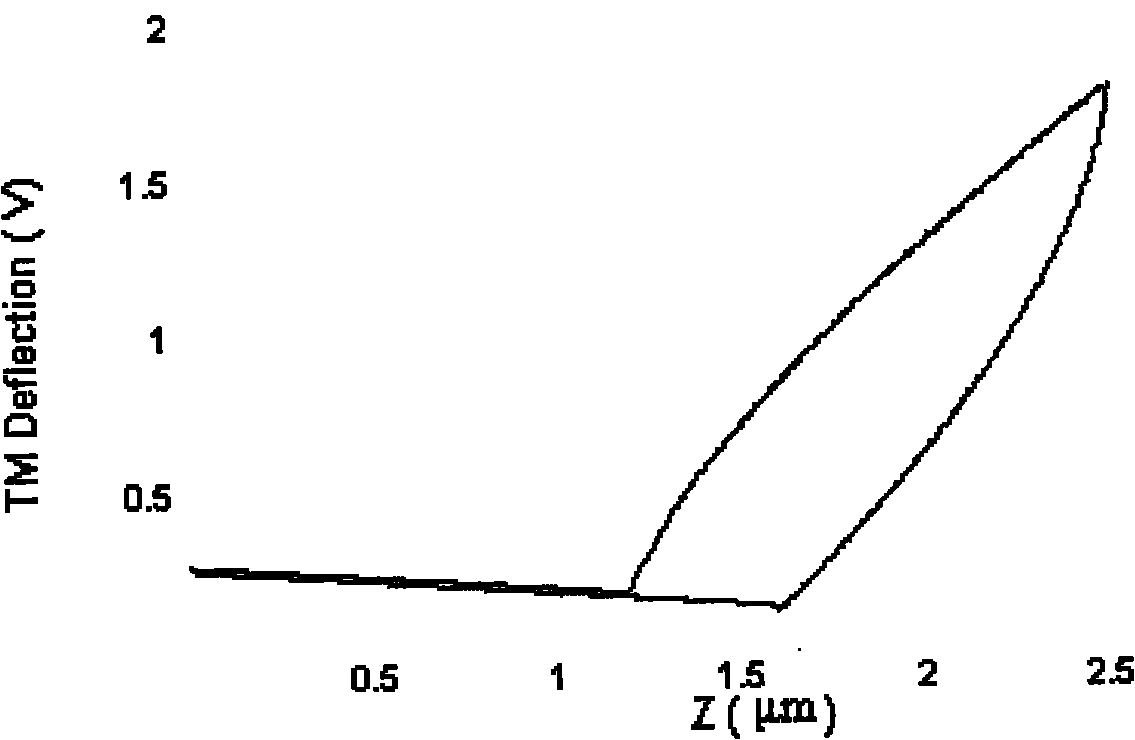
The invention relates to a a method for testing physical performances of a solid film and a film-substrate interface and belongs to the technical fields of analytic instruments and material performance testing. The method is based on a nanometer indentation continuous stiffness curve and takes the ratio of elastic modulus square of a film-substrate system to the hardness as the ordinate and the indentation depth as the abscissa, a curve is fitted in a iteration screening least square method, and fitted parameters are analyzed and demarcated, thus measuring the physical performances of the film which includes the thickness and the ratio of the elastic modulus square to the hardness and representing parameters related to the thickness of an interface layer and parameters related to the ratio of the elastic modulus square of the interface layer to the hardness and the like. In the method, all tests of the physical performances of the film and the film-substrate interface are based on the nanometer indentation technology, the method can be carried out under the condition of not exposing the substrate surface, the existing equipment does not need to be altered, only the analytic method needs to be change, the application range is wide, and any film material with the film thickness less than the maximum indentation depth of a nanometer indenter can use the method.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Measuring Head for Nanoindentation Instrument and Measuring Method Using Same
ActiveUS20090260427A1NanotechnologyInvestigating material hardnessDepth of penetrationNanoindentation
A measuring head for a nano-indentation instrument capable of positioning a sample relatively to the measuring head, which includes a measuring axis, a reference axis and a component for detecting a depth of penetration of an indentor into the sample. The measuring and reference axes are attached to a frame for connection to the instrument. The measuring axis incorporates an actuator and includes the indentor, the reference axis incorporates an actuator and includes a reference tip, and the measuring and reference axes each have a component for detecting a force applied by its actuator. Penetration depth is detected by measuring a displacement of the indentor relatively to the reference tip.
Owner:ANTON PAAR TRITEC SA
Method to measure the elastic modulus and hardness of thin film on substrate by nanoindentation
A method of measuring the elastic modulus and hardness of a thin film on substrate using nanoindentation technique is provided. The method includes calculating a series of experimental corrected stiffness and contact radius pairs associated with one or more presumed parameters and information obtained from a loading curve associated with the thin film and substrate. Also, the method includes calculating a series of theoretical corrected stiffness and contact radius pairs associated with the same one or more presumed parameters and information obtained from the loading curve associated with the thin film and substrate. Furthermore, the method includes using results obtained from the experimental and theoretical corrected stiffness and contact radius pairs to compute the elastic modulus and hardness of the film material.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nanoindentation test desk and experimental method for interfacial shear force of carbon fiber composite
InactiveCN102607947ABuckling controlMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesExperimental methodsSingle fiber
A nanoindentation test desk and an experimental method for interfacial shear force of a carbon fiber composite belong to the technical field of experimental devices and methods. The nanoindentation test desk comprises a desk body and a pressing plate component, wherein a main desk body and a pressing plate are fixed in a normal direction to form a normal loading device. A convex part is arranged in the middle of the main desk body, and a circular hole is arranged at the center of the convex part. A convex part is arranged in the middle of the pressing plate, a circular hole is arranged at the center of the convex part, and the circular hole in the pressing plate is larger than that in the main desk body in diameter and is a through hole. A rubber layer gasket is placed at the bottom of the pressing plate and is a circle of which the center is provided with a circular hole, and the circular hole is aligned to the circular hole in the pressing plate. The test desk and the method realize testing for in situ interfacial mechanical property of an actual composite material without special manufacturing of an experimental sample, and accomplish monitoring for a whole single fiber pressing-out process; a fiber debonding process can be obtained through analysis of loading and unloading curves obtained in an experiment; and the test desk and the method achieve the control of bending of fibrous composite sheets in a press-in process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for representing nano film micro-area deformation area by virtue of combination of photetching technique and transmitted electron microtechnique
ActiveCN103047947AStructural solutionSolve the mechanical propertiesUsing wave/particle radiation meansElectron microscopeNanoindentation
The invention provides a method for representing a nano film micro-area deformation area by virtue of combination of a photetching technique and a transmitted electron microtechnique and belongs to the field of film nanoindentation representation. The invention discloses a method for representing a 10-100 nano film microarea deformation area by virtue of combination of a photetching technique and a transmitted electron microtechnique. According to the method, an indentated film is directly transferred into a transmission electron microscope so as to be observed by virtue of a film transfer technology; the microdefect formation, interaction and evolutionary process during a nano film elastoplasticity transition process in a nanoindentation acting process is directly disclosed from the aspect of atom scale; the direct relation between microstructure and macromechanic performance is disclosed; and the method belongs to a film nanoindentation representation method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device for testing metallic film failure behaviors under the coupling of force, heat, power and magnetism multi-field
InactiveCN102081140AReduce failure rateHigh creep stabilityStrength propertiesIndividual semiconductor device testingMulti fieldMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a device for testing metallic film failure behaviors under the coupling of force, heat, power and magnetism multi-field, which is characterized in that a warm table of embedded resistance wires is arranged above a heat insulation table; the warm table is connected with a power supply; the two ends of the heat insulation table are filled with convection circulating cooling water; a tested metallic film is arranged on the warm table; a thermocouple is arranged on a sample surface; a nanoindentation gearing is connected with a transmission rod; the two sides of the transmission rod between the nanoindentation gearing and the tested metallic film are respectively provided with a thermal baffle; the two sides of each thermal baffle are provided with circulating cooling water; and magnetic poles are arranged at the two sides of the heat insulation table. The device provided by the invention is used to improve prediction and evaluation level for failure behaviors of an electric thin-film material of an integrated circuit, is simple in operation, can really test and reflect failure performances of micro-components under the condition of actual services.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for measuring and representing microcosmic interface phases of asphalt concrete
InactiveCN105259034AHelpful for analysisDeepen understandingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessEpoxySurface phase
The invention discloses a method for measuring and representing microcosmic interface phases of asphalt concrete. According to the method, a small asphalt concrete piece is wrapped with epoxy resin AB glue and cured into a flat cylindrical test piece in a mold to prevent the small asphalt concrete piece from being stripped and deformed in the follow-up polishing process and improve the polishing flatness; the test piece is polished with metallographic abrasive paper, and then a final test piece meeting the requirements is obtained after ultrasonic cleaning is performed on the test piece when polishing is completed; the test piece enters a measuring step, all surface phases of the test piece are observed through amplification with a nanoindentation instrument, a measuring region containing all the phases is selected, equally-spaced dotting measuring is performed, and a load-displacement curve and a microscope image are recorded; after the test is finished, the Young modulus and hardness of all the points are computerized according to the load-displacement curve, and then the modulus and hardness indexes of all the phases are obtained by combining the phases where the measured points are located; finally, the size and the mechanical characteristics of a microcosmic interface transition area between asphalt and aggregates in the test piece can be analyzed and estimated according to the changing condition of the distance among the measured points and the mechanical indexes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for testing continuous thermoregulation high-vacuum low-temperature micro nanoindentation
ActiveCN104697872ARealize contact temperature changeSimple structureInvestigating material hardnessComputer moduleScientific instrument
The invention relates to a method and a device for testing continuous thermoregulation high-vacuum low-temperature micro nanoindentation, belonging to the field of precise scientific instruments. An X-direction precision regulating module is used for regulating the position of a press-in point; a Z-direction precise press-in driving module is used for pressing in precisely, and a displacement signal and force signal precision detection module is used for detecting a displacement signal and a force signal precisely; a variable temperature object support and a cryostat are connected so as to achieve contact thermoregulation of a sample. The device is integrated with a customerized vacuum box so as to achieve micro nanoindentation testing of a sample when the temperature is continuously changed at 77K-500K under the vacuum environment; the problems of precise temperature variation, heat insulation, precise detection and the like in low-temperature micro nanoindentation testing are solved; the blank of the indentation testing technique of a traditional micro nanoindentation in a low-temperature environment when the environment temperature is changed is filled up. According to the device, the structure is simple, the process is convenient, the size is small, the response is rapid, the positioning is accurate, the temperature can be changed and controlled precisely, the displacement load signal can be detected precisely, and the micro precision press-in function can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Nanoindentation surface analysis tool and method
InactiveUS20070193347A1Faster throughputReduce decreaseMeasurement/indication equipmentsNanotechnologyVitrificationHardness
The present invention provides a novel method for determining the mechanical properties of the surfaces of materials including thin films. Generally, the method is comprised of laterally scanning the surface of the film with an array of cantilever tips varying temperature, load and time to obtain a measurement of mechanical properties, such as hardness and glass transition temperature. The method can be used to obtain mechanical properties of films that would otherwise be unobtainable using standard methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
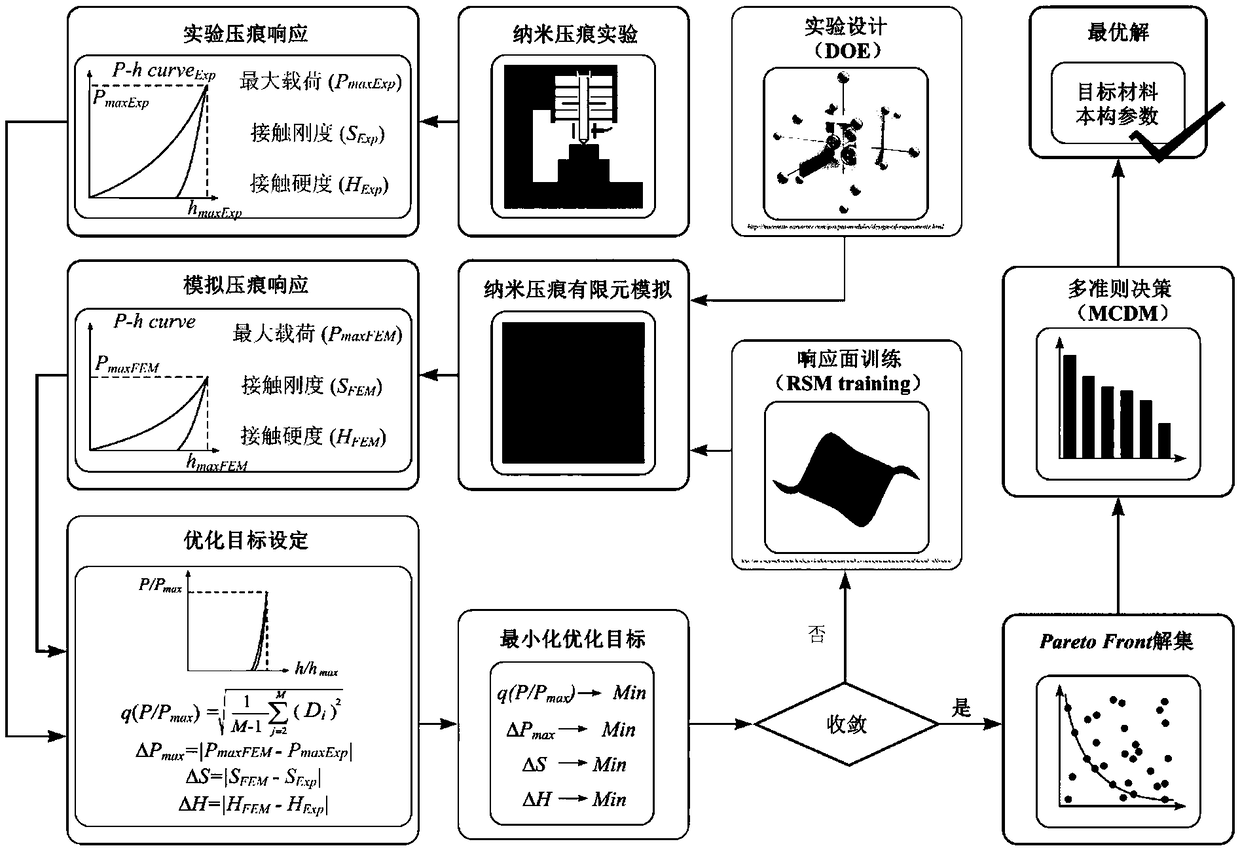
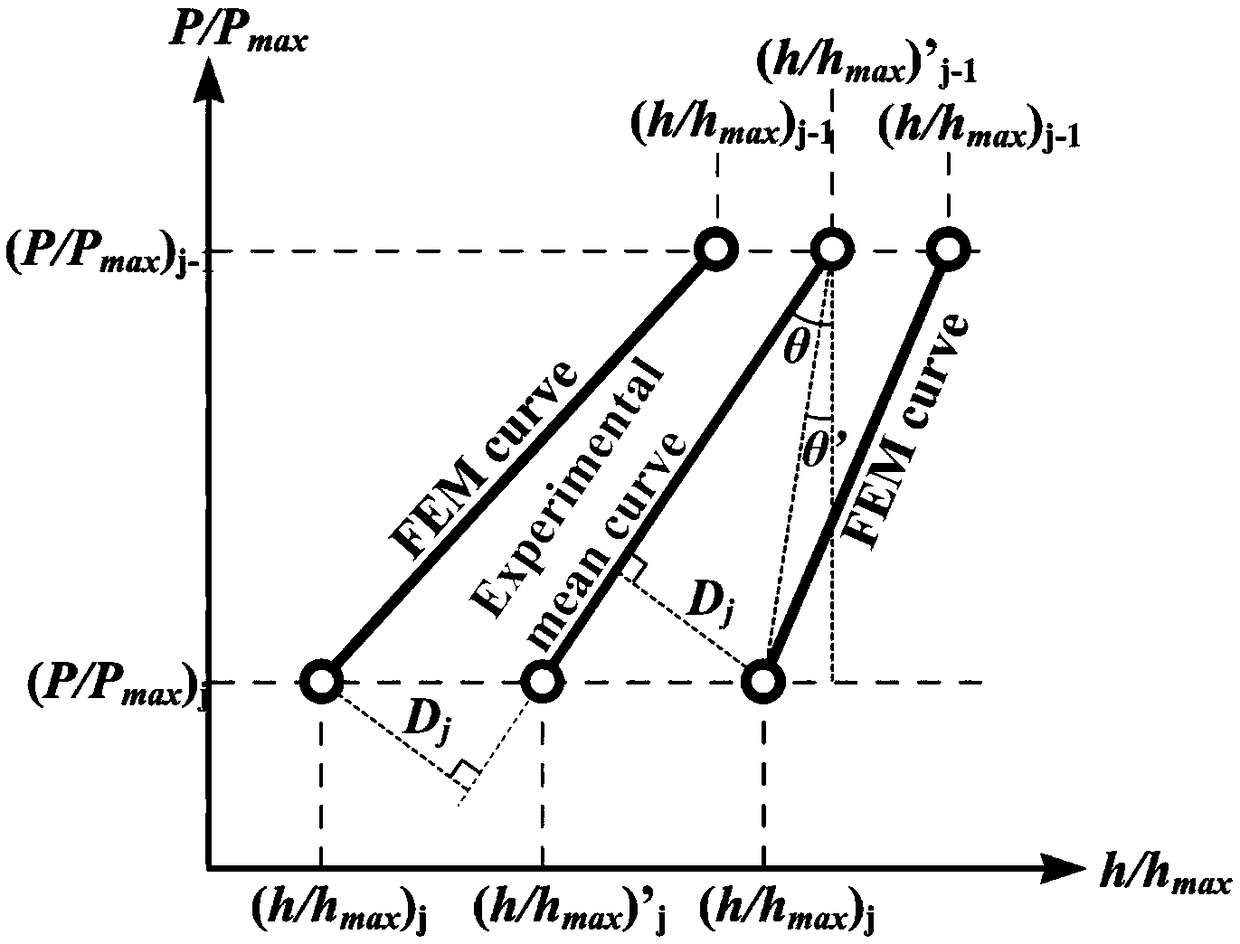
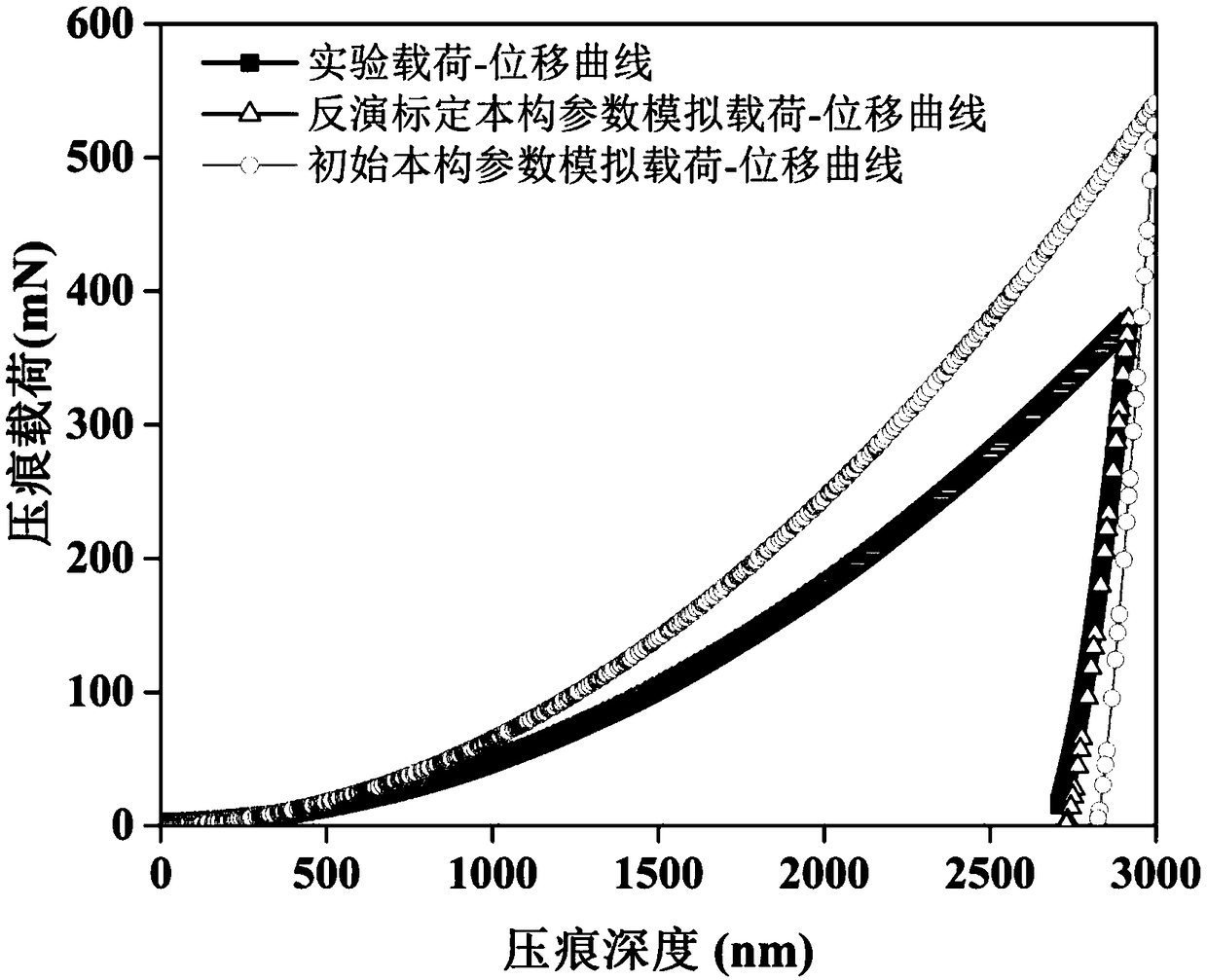
Method for inversion calibration of microscopic constitutive parameters of metal material on the basis of nanoindentation and finite element simulation
ActiveCN108645704AAchieving precise quantitative descriptionAvoid the problem of too large set of non-inferior solutionsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMetallic materialsDisplacement control
The invention discloses a method for inversion calibration of microscopic constitutive parameters of a metal material on the basis of nanoindentation and finite element simulation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out a nanoindentation test on the surface of the metal material through displacement control so as to obtain an experimental indentation response; S2, establishinga nanoindentation and finiteelement model under an ABAQUS or standard module, and carrying out finiteelement simulation to the process of the nanoindentation test on the metal material mentioned in the step S1 so as to obtain a simulated indentation response; and S3, constructing a multi-objective optimization platform, setting optimization objectives and constraint conditions, acquiring a non-inferior optimal solution set Pareto Front through a multi-objective optimization method based on FMOGA-II algorithm, and determining a unique optimal solution. The method provided by the invention has low cost, is rapid and accurate to calculate, is simple and practicable, is extensively applicable to inversion calibration of microscopic constitutive parameters of multi-metal materials, and has highpractical value in computational mechanics, experimental mechanics and engineering practical application.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nanoindentation surface analysis tool and method
InactiveUS7451636B2Faster throughputMeasurement/indication equipmentsNanotechnologyVitrificationHardness
The present invention provides a novel method for determining the mechanical properties of the surfaces of materials including thin films. Generally, the method is comprised of laterally scanning the surface of the film with an array of cantilever tips varying temperature, load and time to obtain a measurement of mechanical properties, such as hardness and glass transition temperature. The method can be used to obtain mechanical properties of films that would otherwise be unobtainable using standard methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
Laminated film and laminated film-coated member
A laminated film is provided which exhibits excellent durability even when formed over a surface of a member (in particular, sliding member) to be used under a high pressure of contacted surface of 2.0 GPa or more. The laminated film includes an intermediate layer which contains one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of a carbide, a boride, and a boron carbide compound of a metal element, and which has a hardness measured by a nanoindentation method (hereinafter referred to as a “nanoindentation hardness”) of not less than 20 GPa nor more than 35 GPa and a thickness of not less than 5 μm nor more than 10 μm, and a diamond-like carbon film which is formed over the intermediate layer, and which has a nanoindentation hardness of not less than 25 GPa nor more than 35 GPa and a thickness of not less than 0.3 μm nor more than 1.0 μm.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
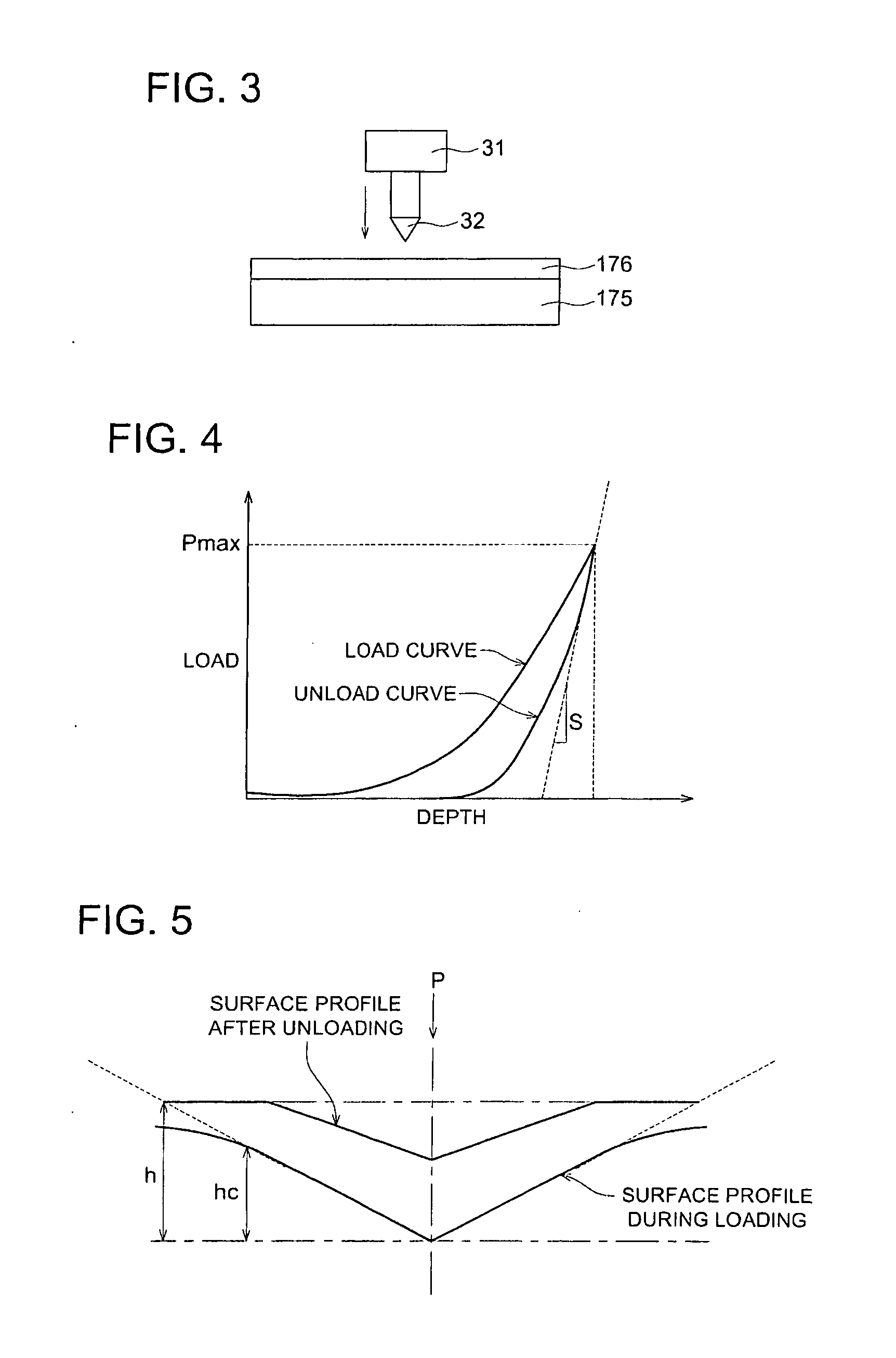
Intermediate transfer member, method of manufacturing intermediate transfer member, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20090041514A1Good release effectImprove transmission efficiencyLayered productsElectrographic process apparatusSurface layerHardness
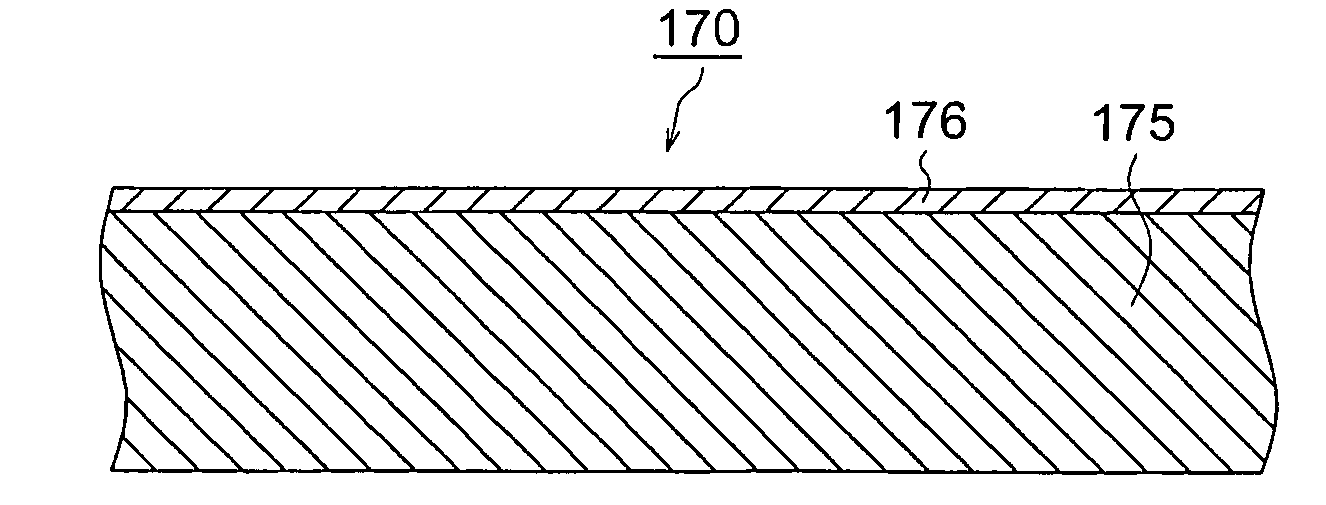
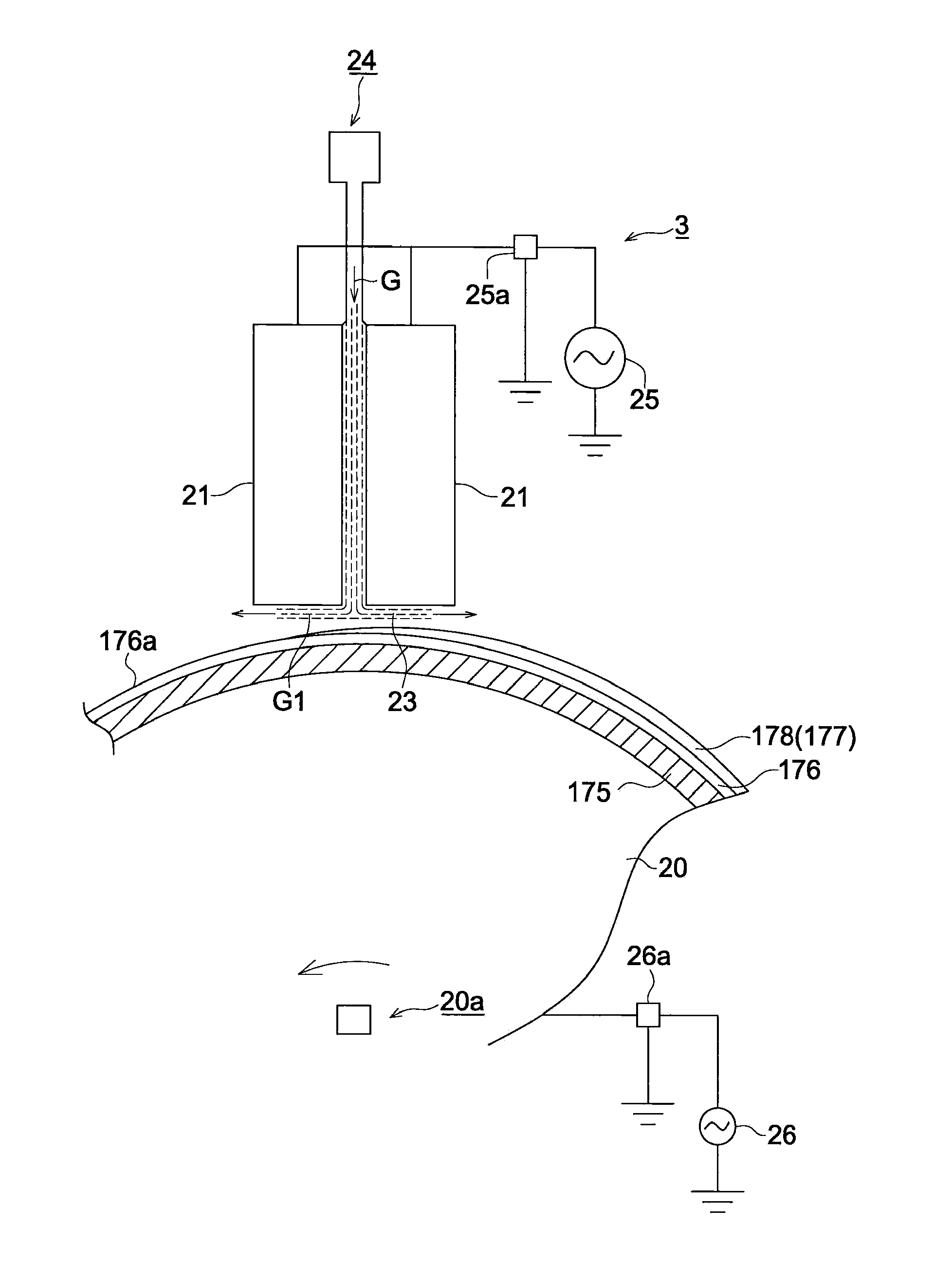
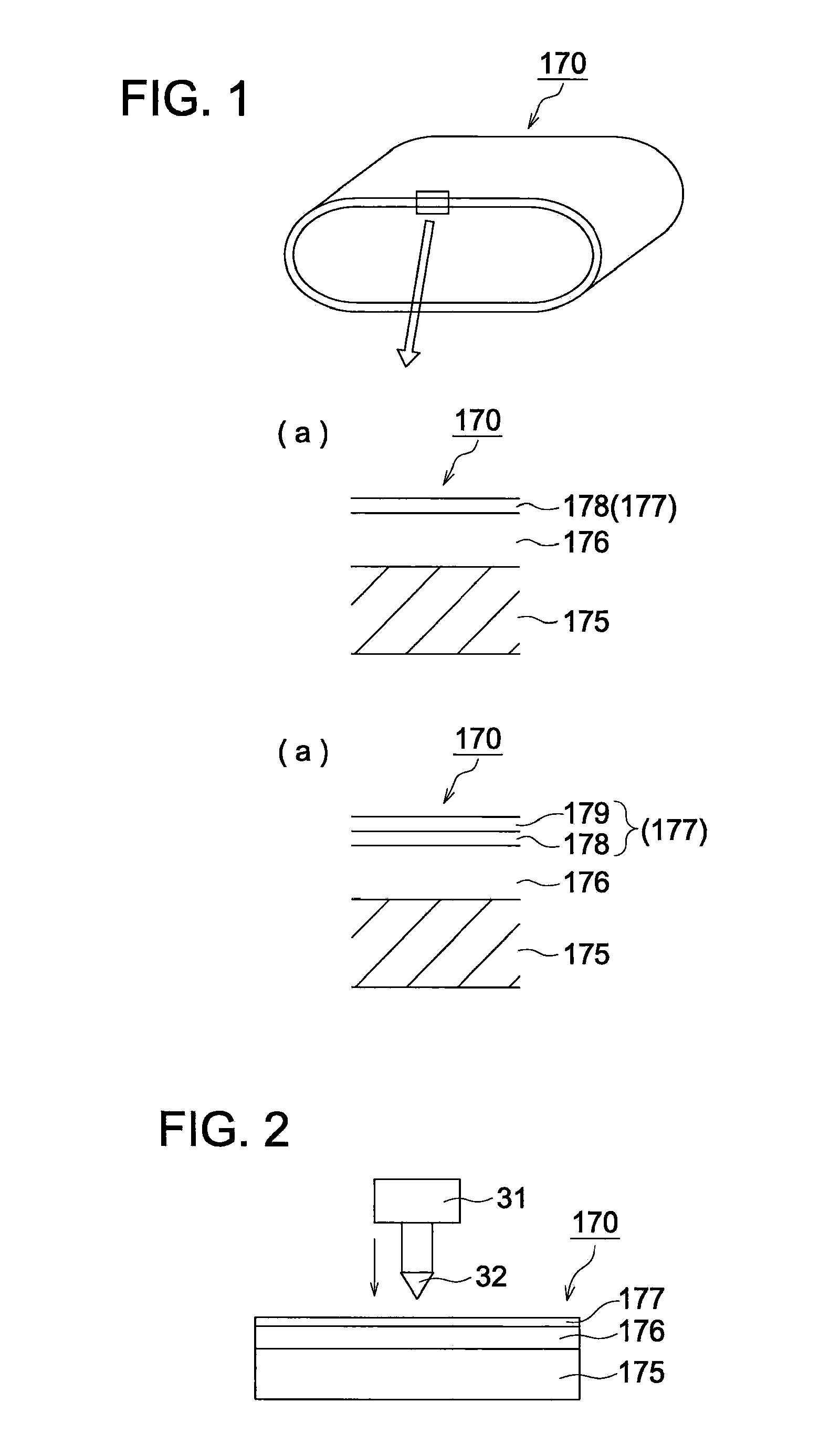
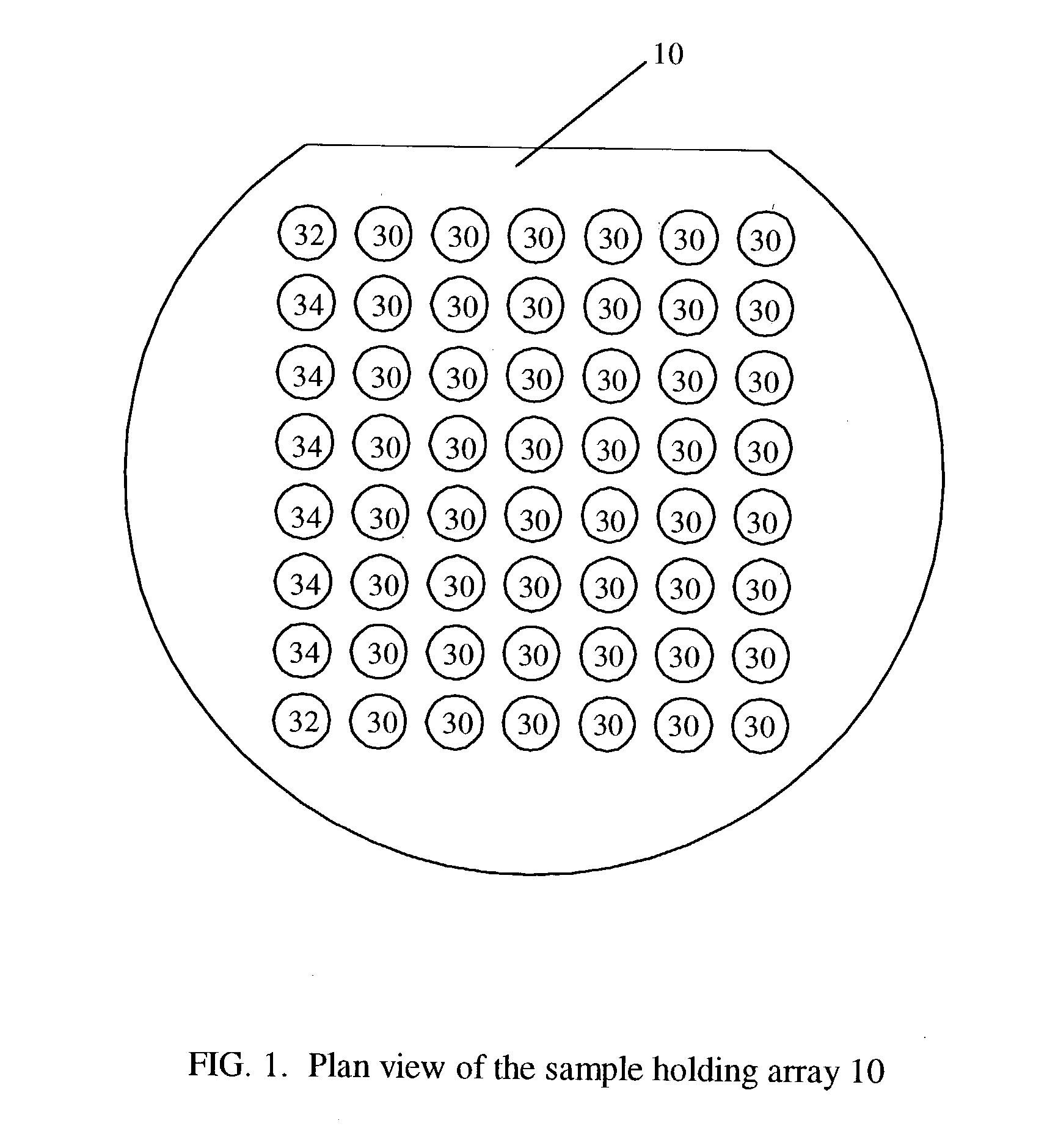
An objective is to provide an intermediate transfer member exhibiting higher transferability together with higher cleaning ability and durability, a manufacturing apparatus of an intermediate transfer member in which no large-scale equipment such as a vacuum evaporator or the like is installed, and an image forming apparatus fitted with the intermediate transfer member. Also disclosed is intermediate transfer member 170 possessing substrate 175 and surface layer 176 composed of at least one layer provided on the surface of substrate 175, wherein foregoing substrate 175 has a universal hardness of 50-190 N / mm2, and foregoing surface layer 176 has a surface hardness of 3-11 GPa measured in accordance with a nanoindentation method.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Temperature-variable indexable micro-nano indention testing device
PendingCN107703012AAccurate measurementExpand the scope of testingInvestigating material hardnessMicro nanoContinuous measurement
The invention relates to a temperature-variable indexable micro-nano indention testing device and belongs to the field of precise instruments. The device comprises a workbench indexing base, a high-and-low-temperature working cavity and an indenter driving / feeding mechanism, the high-and-low-temperature working cavity is mounted on an L-shaped mounting plate of the workbench indexing base, and theindenter driving / feeding mechanism is mounted on an equipment base of the workbench indexing base. The workbench indexing base is mainly used for indexing a workbench and supporting the whole device,the high-and-low-temperature working cavity can provide an environment atmosphere with temperature continuously changing for the process of test piece measuring and can isolate outside interference,and the indenter driving / feeding mechanism is mainly used for feeding an indenter in the vertical direction and acquiring measurement data through a pressure sensor and a displacement sensor. the device has the advantages that the device is accurate in measurement result, wide in measurement range and compact in structure, and the technical field of mechanical performance testing of materials anddevelopment of equipment for mechanical performance testing of the materials are promoted greatly.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
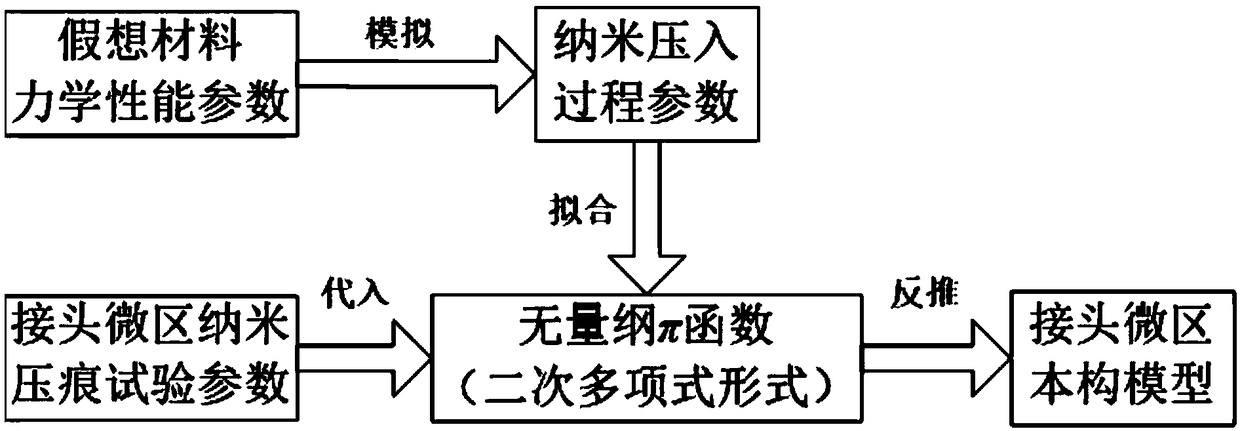
Constitutive model of welded joints based on nanoindentation test
ActiveCN109299568AImprove expression accuracyReduce testing costsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringNanoindentation
The invention provides a method for backward deducing a constitutive model of a welding joint based on a nanoindentation test, comprising the following steps: step 1, constructing a constitutive modelof the welding joint; 2, carry out dimensional analysis to obtain a dimensionless function between stress and strain; 3, selecting that material satisfying the constitutive relation of the step 1, and carry out finite element simulation on the process of pressing the indenter into the material; 4, determining the selected material and the corresponding stress and strain, substituting the selectedmaterial into a dimensionless function, and determining the function value corresponding to each material; 5, fitting the obtained mechanical property parameter and the function value to obtain the expression of the dimensionless function; 6, perform nano indentation test on that weld joint to obtain the mechanical property parameters of the weld joint; Step 7: The constitutive model of the welded joint is deduced backwards by using the mechanical property parameters. The invention provides a reverse inference method for welding joint constitutive model based on nano-indentation test, which has the advantages of wide applicability, low cost and high accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Toner
ActiveUS20190041763A1Improve mechanical stabilityHeavy loadDevelopersDynamic viscoelasticityHorizontal axis
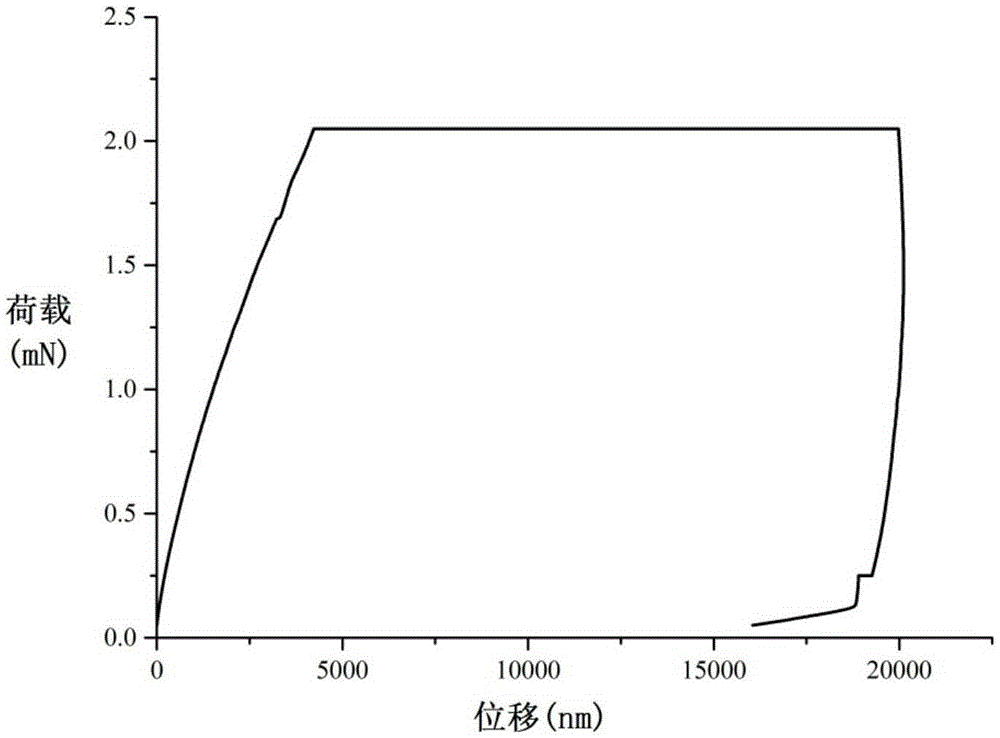
A toner comprising a toner particle that contains a binder resin and a colorant, wherein (1) an average circularity of the toner is at least 0.960, (2) an onset temperature Tε (° C.) of a storage elastic modulus E′ of the toner, as determined by a powder dynamic viscoelastic measurement, is from 50° C. to 70° C., and (3) in a differential curve obtained by differentiation, by load, of a load-displacement curve provided by measurement of the strength of the toner by a nanoindentation procedure, with the horizontal axis being load (mN) and the vertical axis being displacement (μm), the load X that provides the maximum value in the differential curve in the load region from 0.20 mN to 2.30 mN is from 1.00 mN to 1.50 mN.
Owner:CANON KK
Intermediate transfer member
ActiveUS20100158583A1Good effectGood transferabilityElectrographic process apparatusSurface layerImage formation
An intermediate transfer member is provided which enables to maintain superior secondary transferability and enhanced cleaning capability and is also capable of continuing to obtain toner images of superior text reproduction and high quality without causing lack of text images even when making prints of a large number of sheets (e.g., 160,000 sheets). The intermediate transfer member for use in an image forming apparatus having a device capable of transferring a toner image carried on the surface of an electrophotographic photoreceptor primarily to an intermediate transfer member, and secondarily transferring the toner image from the intermediate transfer member to a transfer material, wherein the intermediate transfer member is provided with an elastic layer on the circumference of a resin substrate and further thereon a surface layer, the surface layer exhibits a layer thickness of 10 to 500 nm, the Young's modulus of the surface of the intermediate transfer member which is determined by a nanoindentation method is 0.1 to 5.0 GPa and is 0.0 to 2.0 GPa greater than the Young's modulus of the elastic layer which is determined by a nanoindentation method.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Transmission infrared spectroscopy array and method
InactiveUS20040002162A1Effective approachQuality improvementAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsNanoindentationNanometre
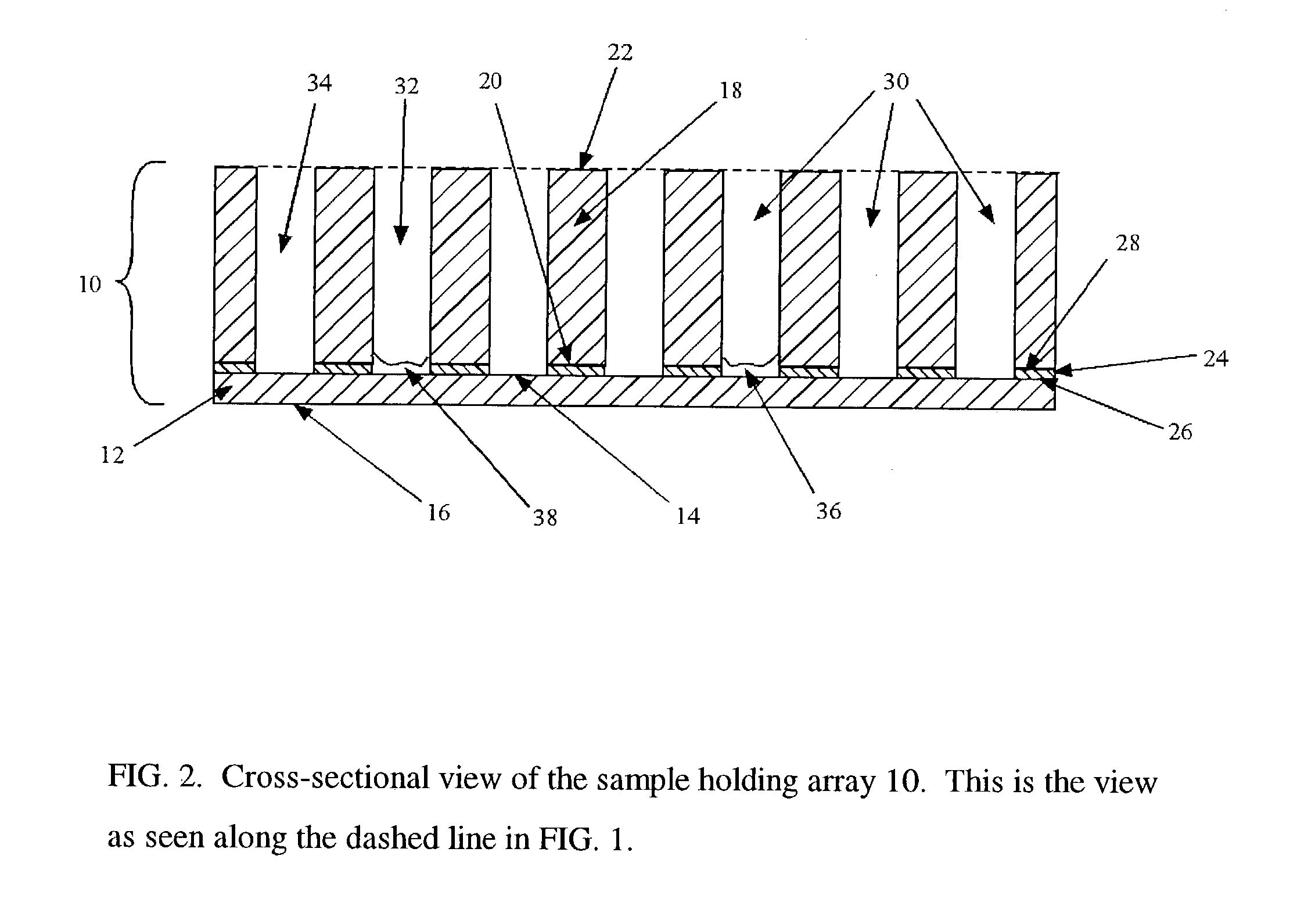
A sample holding array is provided which is particularly advantageous for various IR and near IR transmission spectroscopy analysis that yields high quality spectra with minimal artifacts. The sample holding array may also be used desirably with slight modifications for Raman analysis, x-ray fluorescence and nanoindentation.
Owner:LEUGERS MARY ANNE +3
Precision nano-indentation test device
ActiveCN102288501AHigh displacement resolutionHas a linear force-travel characteristicInvestigating material hardnessScientific instrumentElectric machinery
The invention relates to a precise nanoindentation test device and belongs to the field of precise scientific instruments. The precise nanoindentation test device mainly comprises a precise press-in driving unit, a load signal and displacement signal detection unit and an objective table, wherein the precise press-in driving unit consists of a voice coil motor, a connecting piece, a guide rail and a sliding block; the voice coil motor and the guide rail are arranged on a pedestal; a precise mechanical sensor for detecting pressure of a diamond pressing head pressed into a material is arrangedon the pedestal through a side plate I; a precise displacement sensor for detecting diamond pressing head press-in depth is arranged on the pedestal through a side plate II; the objective table is arranged on the precise mechanical sensor; the diamond pressing head is arranged on the connecting plate; and the connecting plate is assembled on the sliding block through bolts. The precise nanoindentation test device has the advantages of simple structure, convenience for processing, small volume, high positioning precision, quick response and capacity of observing the deformation process and theinjury mechanism of the material in the press-in process in situ under an electron microscope so as to intuitively know the micronano mechanical property of the material.
Owner:长春因赛图精密仪器设备有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com