Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
411results about "Nuclear targets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
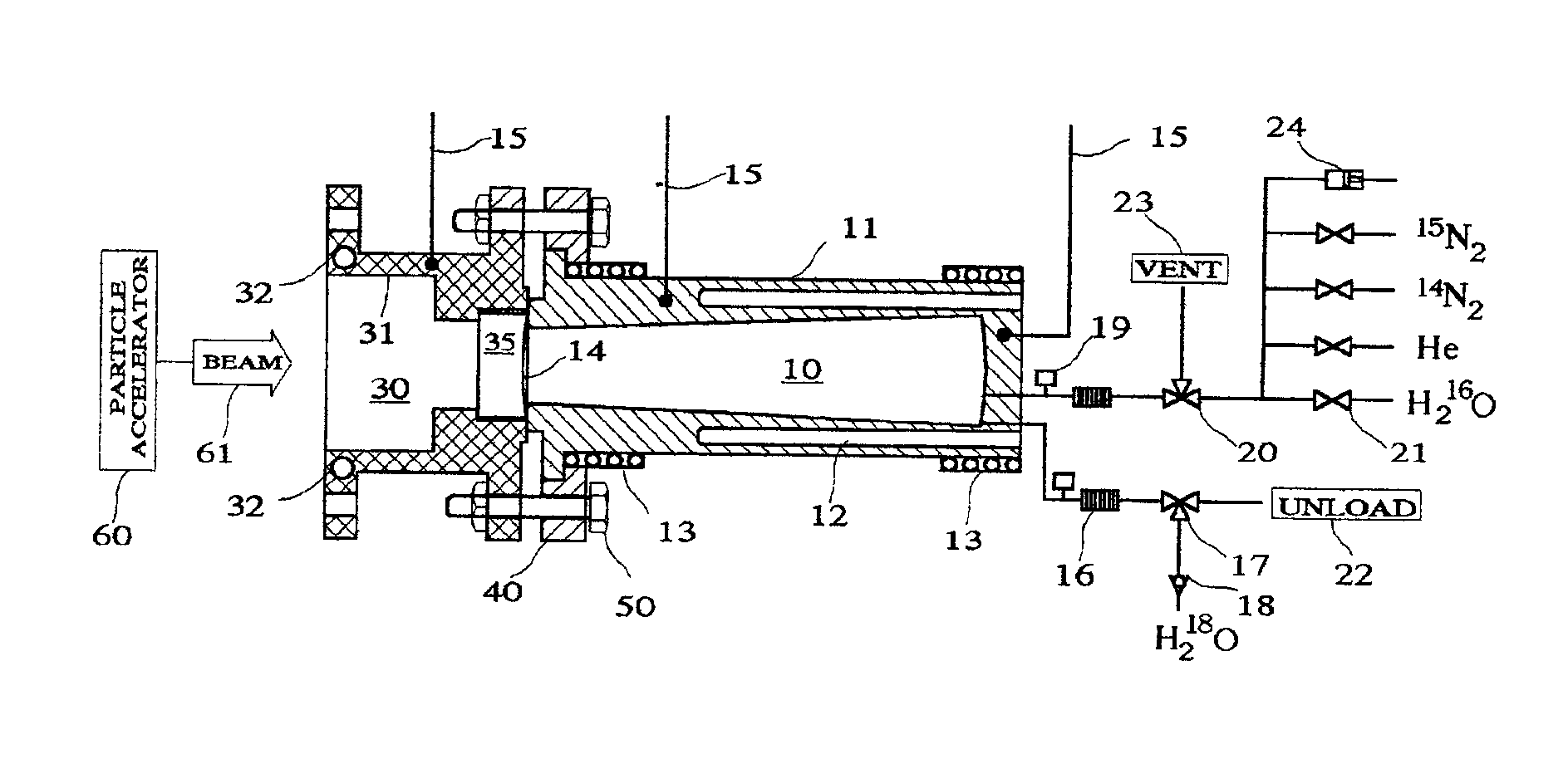
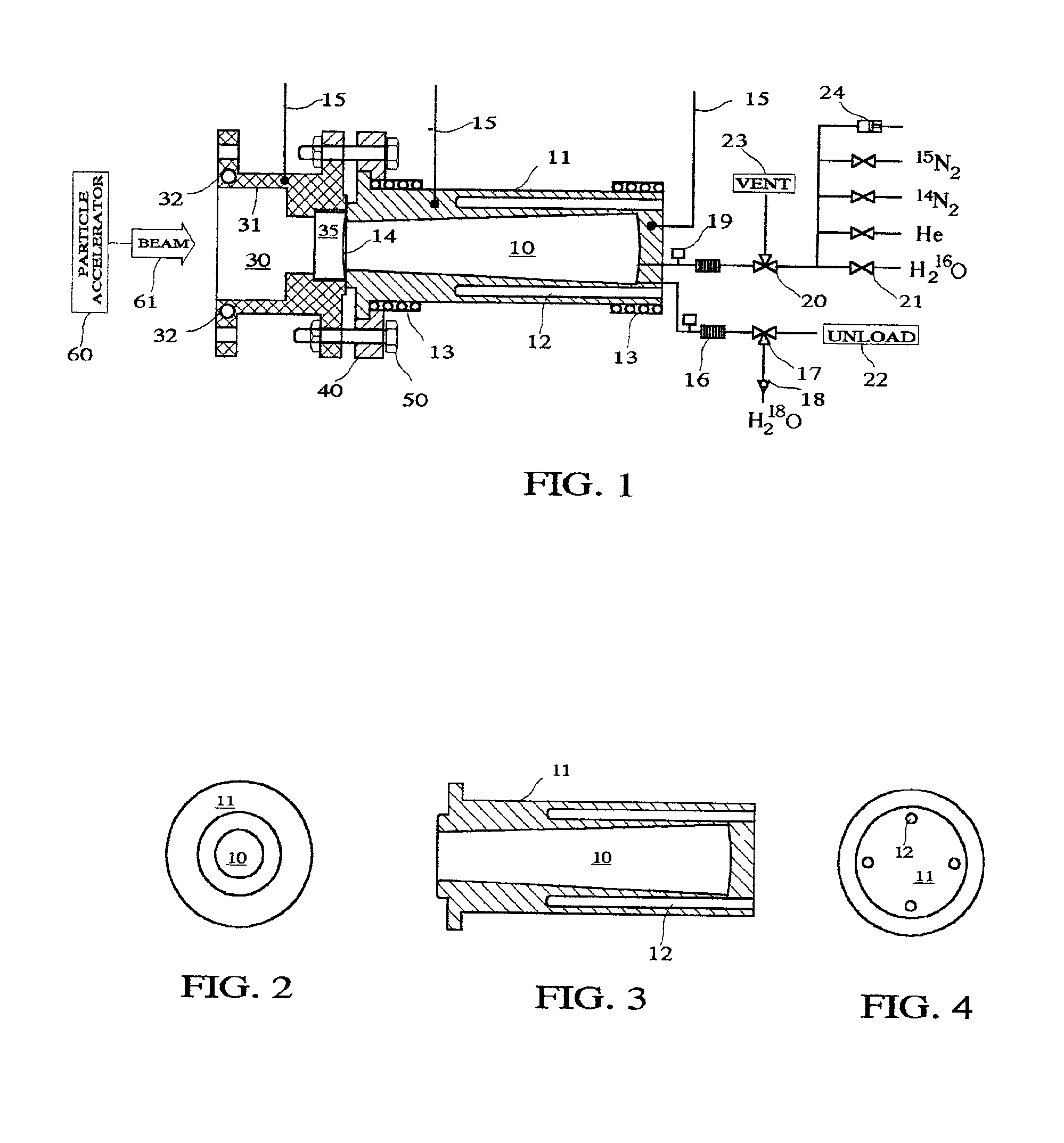
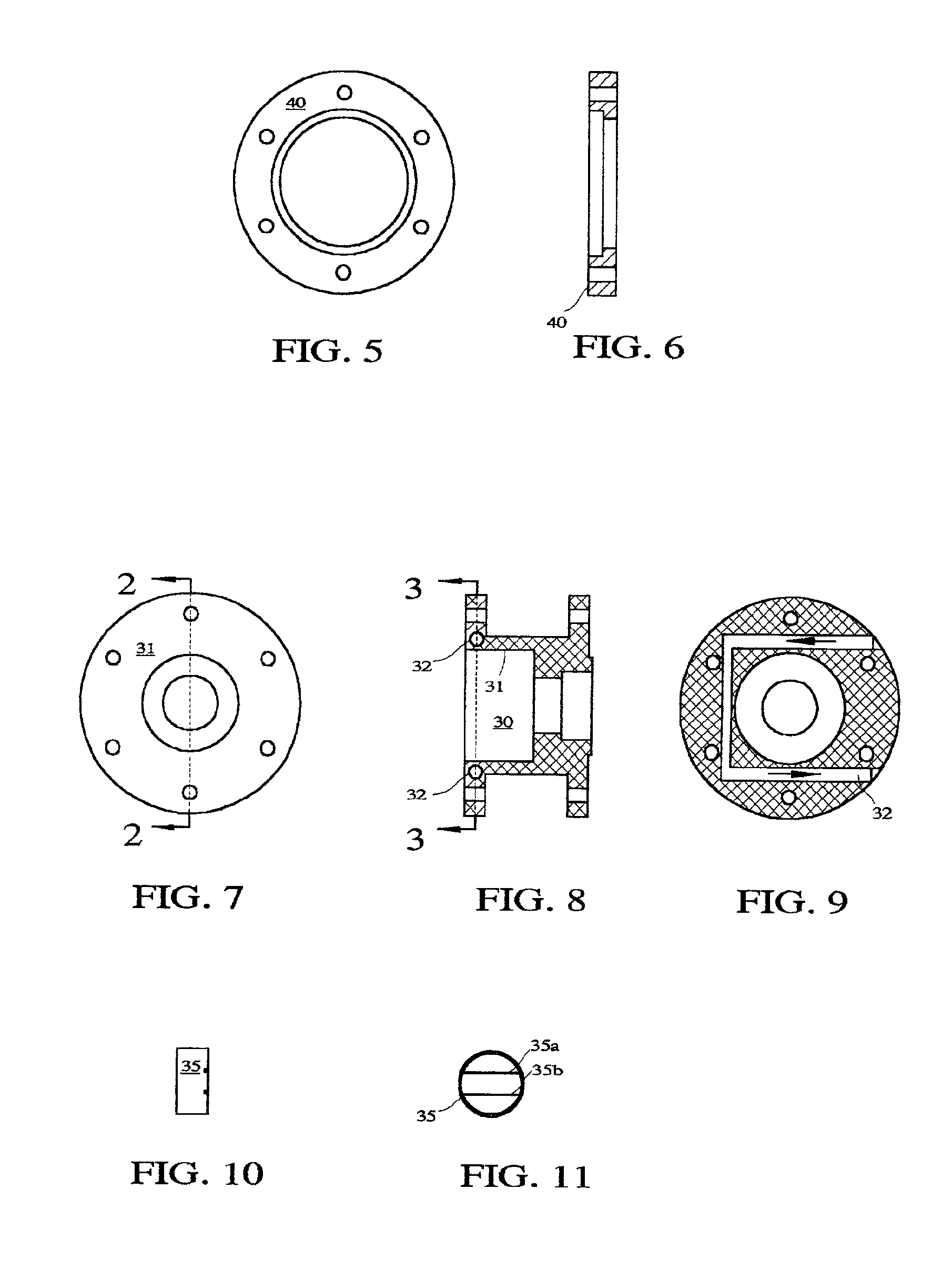
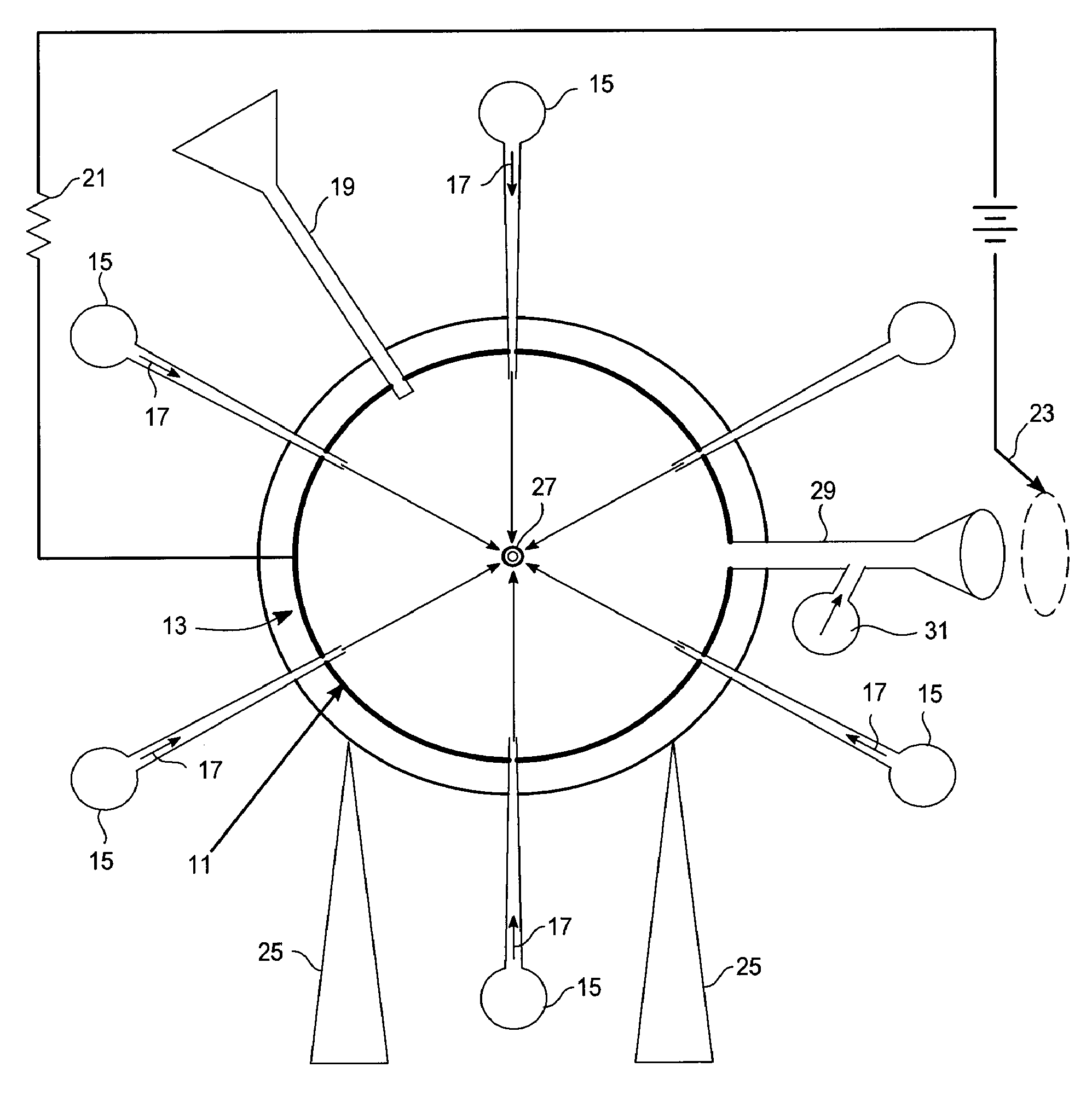
Method And System For Production Of Radioisotopes, And Radioisotopes Produced Thereby
InactiveUS20070297554A1Avoid communicationAvoid contaminationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsHeat fluxParticle beam
A system and method for the production of radioisotopes by the transmutation of target isotopic material bombarded by a continuous wave particle beam. An ion source generates a continuous wave ion beam, irradiating an isotope target, which is cooled by transferring heat away from the target at heat fluxes of at least about 1 kW / cm2.
Owner:SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION
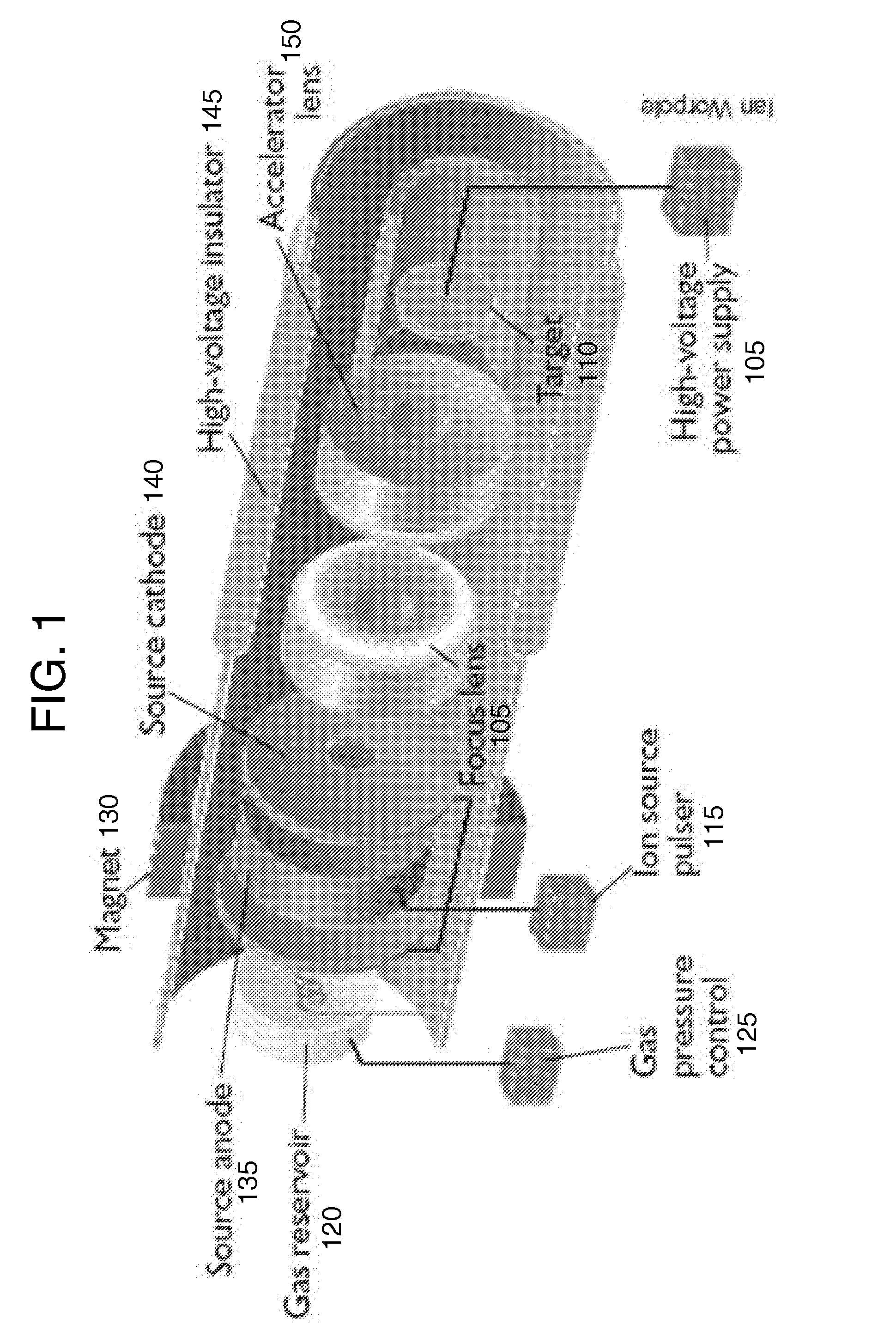
Laser driven ion accelerator
InactiveUS20050167610A1Thermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersIon accelerationIon accelerators
A system and method of accelerating ions in an accelerator to optimize the energy produced by a light source. Several parameters may be controlled in constructing a target used in the accelerator system to adjust performance of the accelerator system. These parameters include the material, thickness, geometry and surface of the target.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Method and apparatus for the production of radioisotopes
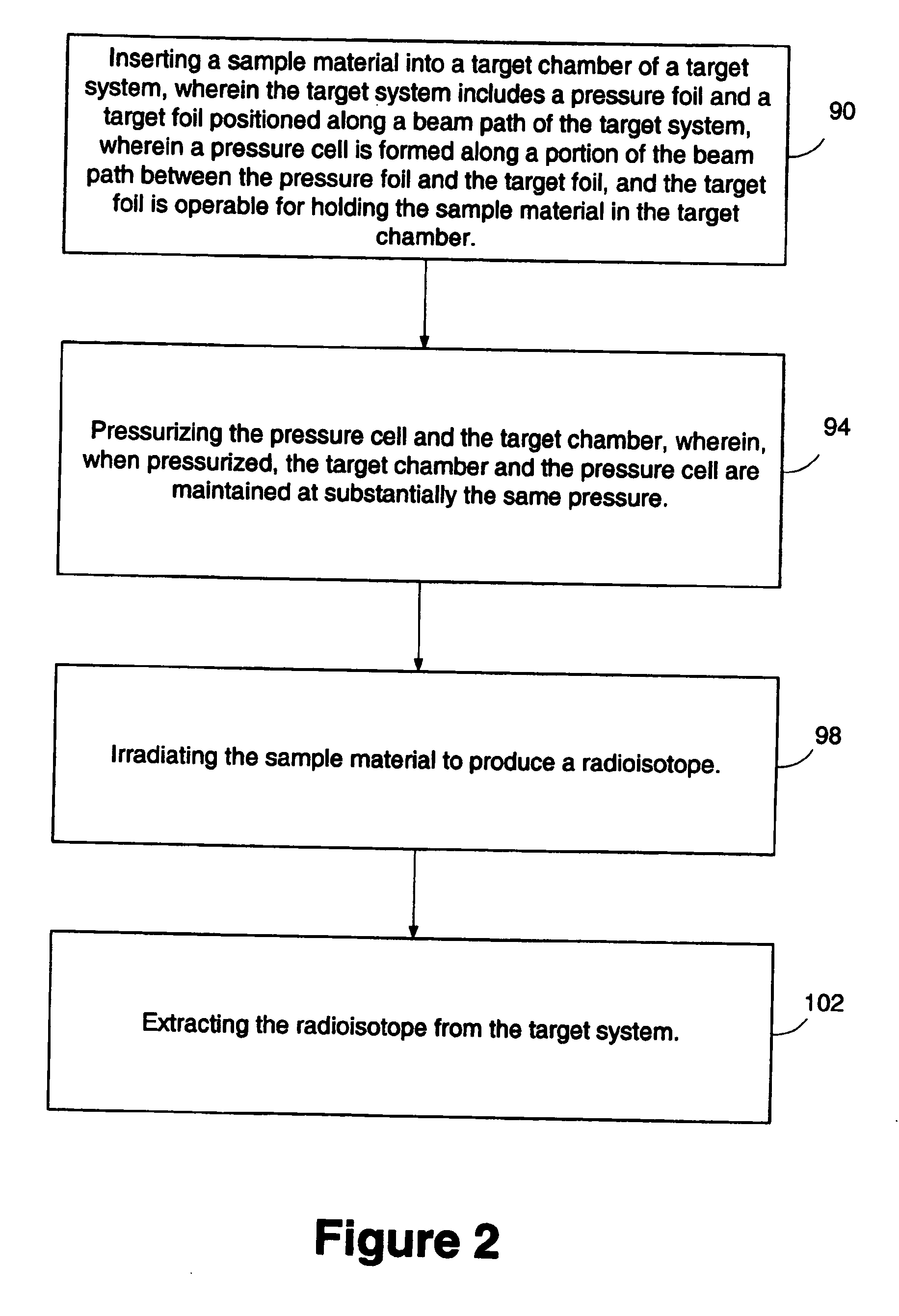
InactiveUS20060062342A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsParticle beamPressure cell
A target system includes a beam path for receiving a particle beam and a target chamber for housing a sample material. A target foil is operable for holding the sample material in the target chamber. A pressure cell is formed along a portion of the beam path between the target foil and a pressure foil. When irradiating the sample material with the particle beam, the pressure inside the target chamber and the pressure cell is increased and maintained at substantially the same pressure. A method includes inserting a sample material into a target chamber of a target system. The target system includes a pressure cell formed along a portion of a beam path between a pressure foil and a target foil, adjacent the target chamber. The pressure cell and the target chamber are pressurized and maintained at substantially the same pressure. The sample material is irradiated to produce a radioisotope.
Owner:HOUSTON CYCLOTRON PARTNERS
Long life high efficiency neutron generator
ActiveUS20110044418A1Small sizeLow efficiencyNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsEngineeringEnergy spectrum
The design of a compact, high-efficiency, high-flux capable compact-accelerator fusion neutron generator (FNG) is discussed. FNG's can be used in a variety of industrial analysis applications to replace the use of radioisotopes which pose higher risks to both the end user and national security. High efficiency, long lifetime, and high power-handling capability are achieved though innovative target materials and ion source technology. The device can be scaled up for neutron radiography applications, or down for borehole analysis or other compact applications. Advanced technologies such as custom neutron output energy spectrum, pulsing, and associated particle imaging can be incorporated.
Owner:STARFIRE IND LLC
Device for fitting of a target in isotope production
InactiveUS6433495B1Minimize radiationFit fastThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInterior spaceIsotope
A device is disclosed for simple and quick disconnection of a target assembly at a cyclotron accelerator producing an ion beam irradiating the target assembly for PET radioisotope production. The device consists of a target body presenting a target space for introduction of target media to be irradiated by the ion beam from the cyclotron accelerator. The target body is separated into three portions by means of two separation window foils. The first separation window separates the internal space of a first body portion from a further internal space portion of a second target body portion and the second separation window separates a further internal space of the second target body portion from an internal space of a third target body portion being in communication with the vacuum space of the cyclotron. This third body portion forms a bayonet fitting to a corresponding bayonet fitting fixed to the cyclotron vacuum casing at a position where the ion beam is extracted, whereby the corresponding bayonet fitting also constitutes an insulating member. The device can by a small twisting be quickly released from the vacuum casing of the cyclotron after the vacuum has been removed for necessary maintenance and service.
Owner:GEMS PET SYST
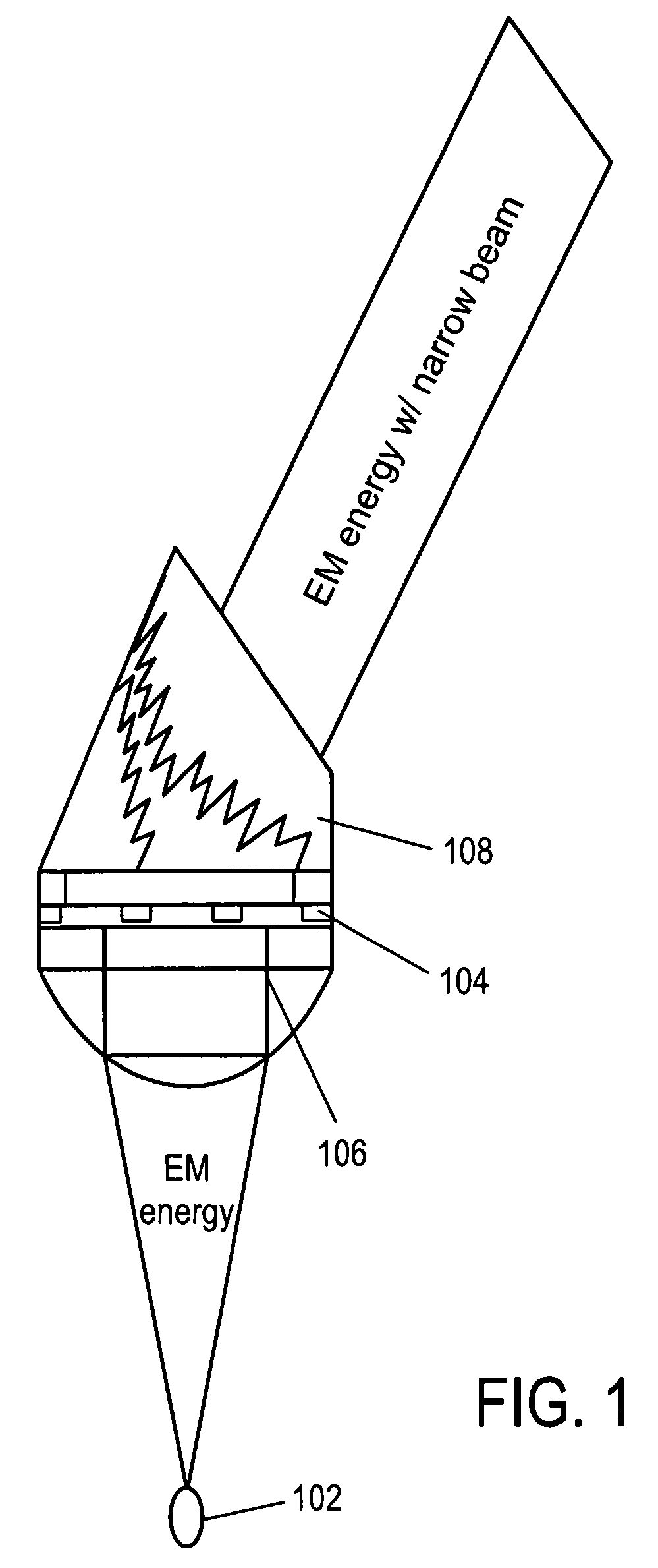
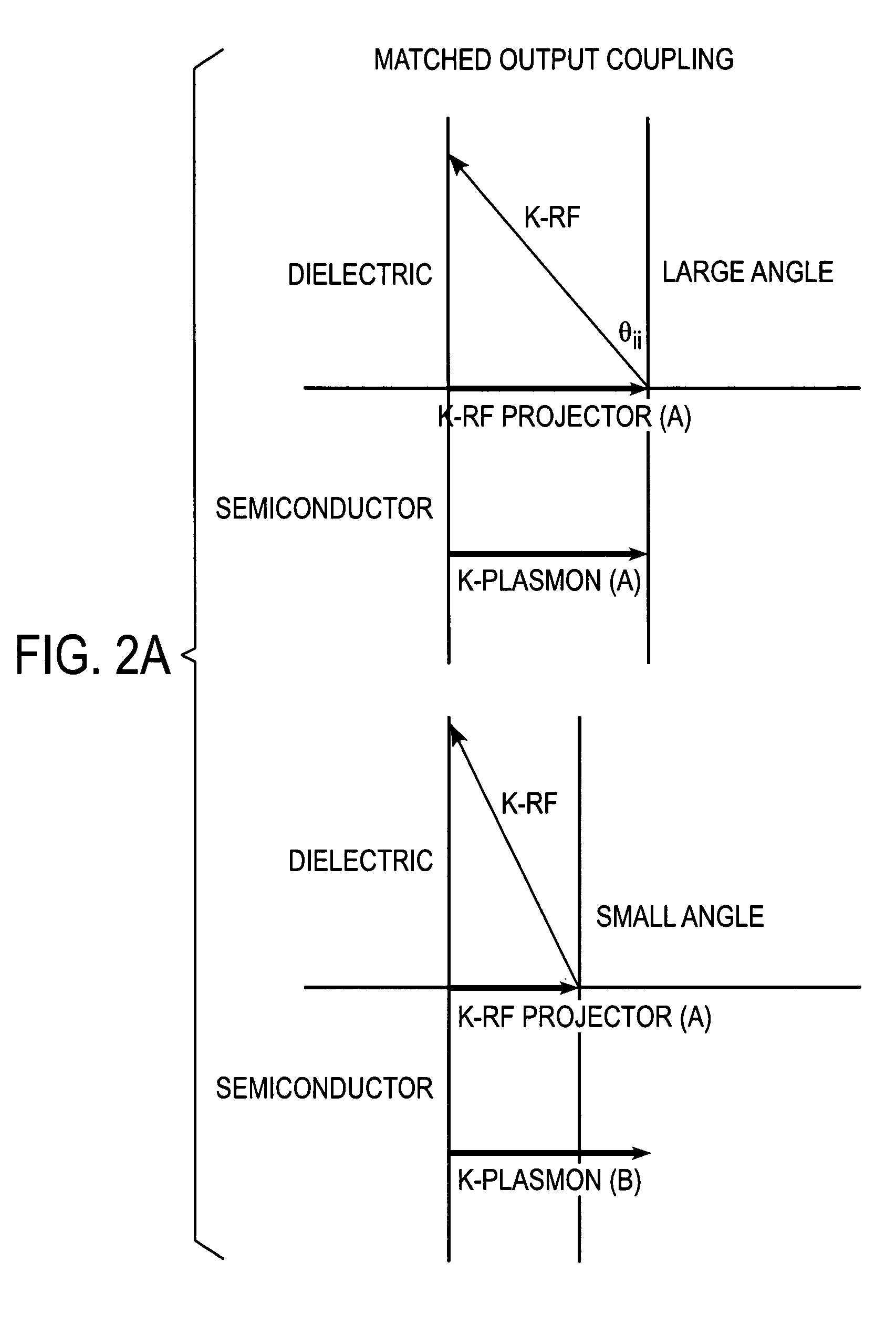
System, method and apparatus for RF directed energy
InactiveUS7820990B2Electric discharge tubesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLength waveField of view
Systems and methods are disclosed for emitting electromagnetic (EM) energy. A source emits EM energy that is incident on a first material. The first material transmits EM energy to a second material. The second material can have a first surface adjacent to the first material and a thickness and shape selected to stimulate surface plasmon polaritons on the first surface of the second material to resonate the EM energy transmitted from the first material such that the resonated EM energy has an EM wavelength in a narrow field of view with substantially no sidelobes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
High power high yield target for production of all radioisotopes for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20050061994A1Avoid low densitySuppress instabilityConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringCoolant flowInstability
A high power high yield target for the positron emission tomography applications is introduced. For production of Curie level of Fluorine-18 isotope from a beam of proton it uses about one tenth of Oxygen-18 water compared to a conventional water target. The target is also configured to be used for production of all other radioisotopes that are used for positron emission tomography. When the target functions as a water target the material sample being oxygen-18 water or oxygen-16 water is heated to steam prior to irradiation using heating elements that are housed in the target body. The material sample is kept in steam phase during the irradiation and cooled to liquid phase after irradiation. To keep the material sample in steam phase a microprocessor monitoring the target temperature manipulates the flow of coolant in the cooling section that is attached to the target and the status of the heaters and air blowers mounted adjacent to the target. When the target functions as a gas target the generated heat from the beam is removed from the target by air blowers and the cooling section. The rupture point of the target window is increased by a factor of two or higher by one thin wire or two parallel thin wires welded at the end of a small hollow tube which is held against the target window. One or two coils are used to produce a magnetic filed along the beam path for preventing the density depression along the beam path and suppression of other instabilities that can develop in a high power target.
Owner:AMINI BEHROUZ
Compact neutron source and moderator
InactiveUS20100061500A1Nuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsSecondary electronsIon source
A novel method and compact neutron source for generating thermal neutrons is described that uses an ion source to emit ions toward a target where neutrons are generated. Surrounding the target is a secondary electron shield, and surrounding the target is a first stage moderator to reduce the energy of generated fast neutrons. Enclosing the first stage moderator is a second stage moderator with a thermal neutron port.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Proton accelerator complex for radio-isotopes and therapy
InactiveUS7554275B2Reduce maintenanceLarge energyMagnetic resonance acceleratorsTransit-time tubesRadio isotopesEngineering
A complex of proton accelerators, includes the following functionally interconnected components: a proton source, a cyclotron, at least one target, located either internally or externally to the cyclotron, a medium energy beam transport magnetic channel, a radiofrequency linear accelerator, a high energy beam transport channel towards an area dedicated to the irradiation of tumors with proton beams, as well as a modular system for supplying radio frequency power capable of feeding, independently two or more accelerating modules of the linac. An integrated computerized system controls the complex of accelerators so to carry out, either in alternation or simultaneously, both the production of radioisotopes—for medical, industrial and therapeutical purposes—and the therapeutical irradiation of, even deep seated tumors. The complex of accelerators produces proton beams which, applying the recently developed ‘spot scanning’ technique, are more suited for the tumor irradiation than the ones produced by cyclotrons and synchrotrons.
Owner:FOND PER ADROTERAPIA ONCOLOGICA TERA
Isotope production system with separated shielding
ActiveUS20100329406A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationParticle beamLight beam
An isotope production system that includes a cyclotron having a magnet yoke that surrounds an acceleration chamber. The cyclotron is configured to direct a particle beam from the acceleration chamber through the magnet yoke. The isotope production system also includes a target system that is located proximate to the magnet yoke. The target system is configured to hold a target material and includes a radiation shield that extends between the magnet yoke and the target location. The radiation shield is sized and shaped to attenuate gamma rays emitted from the target material toward the magnet yoke. The isotope production system also includes a beam passage that extends from the acceleration chamber to the target location. The beam passage is at least partially formed by the magnet yoke and the radiation shield of the target system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
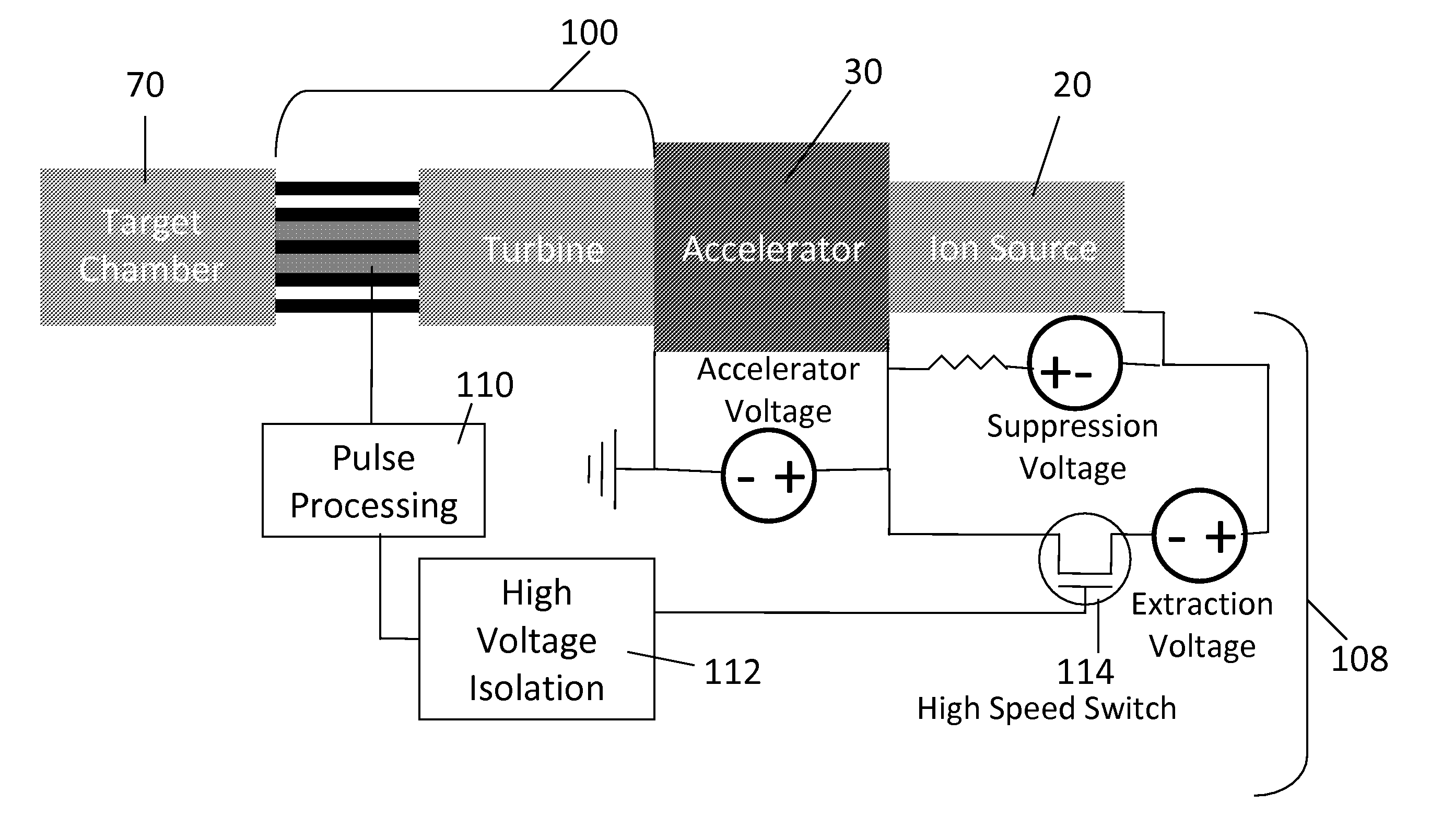
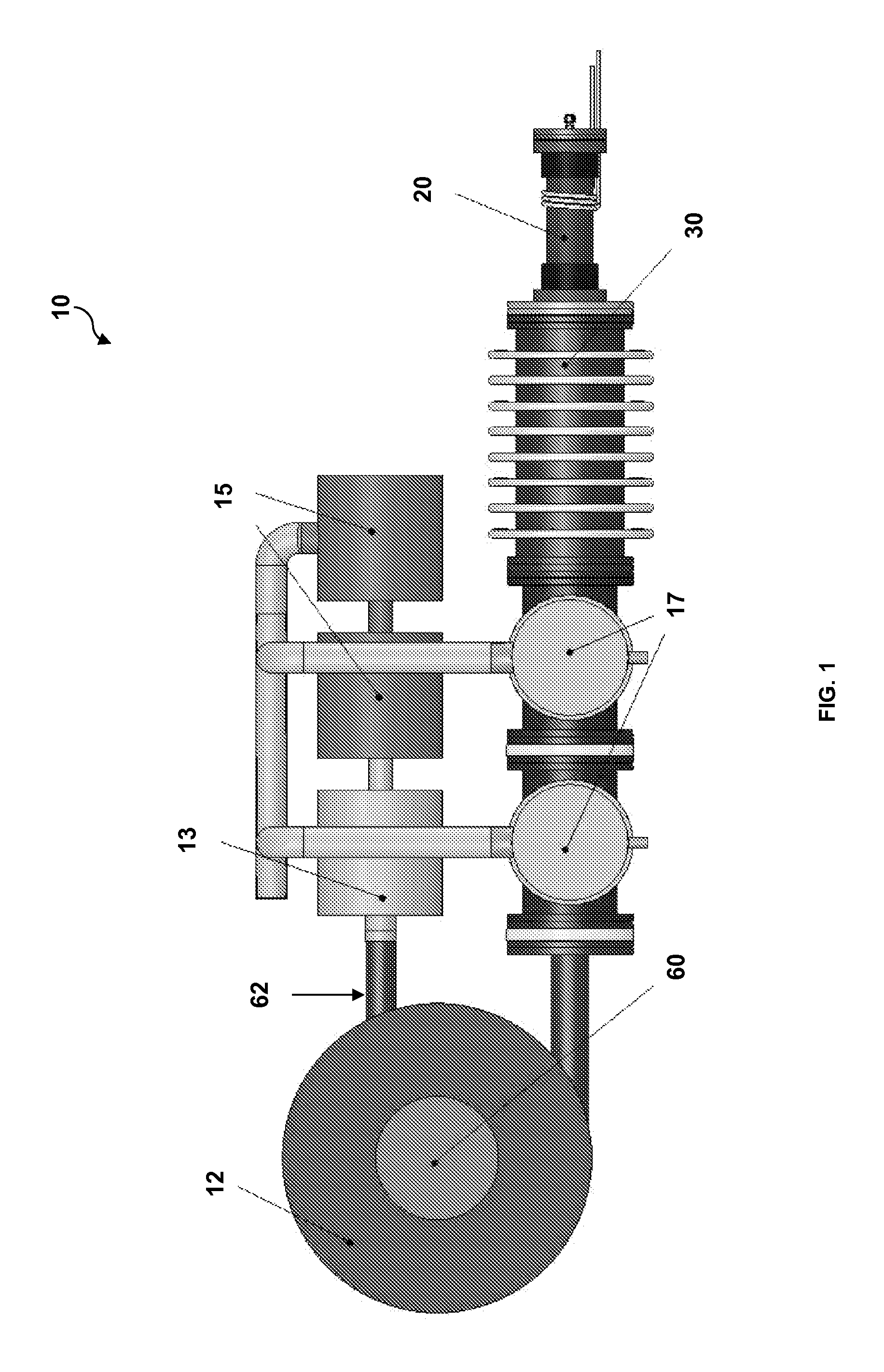
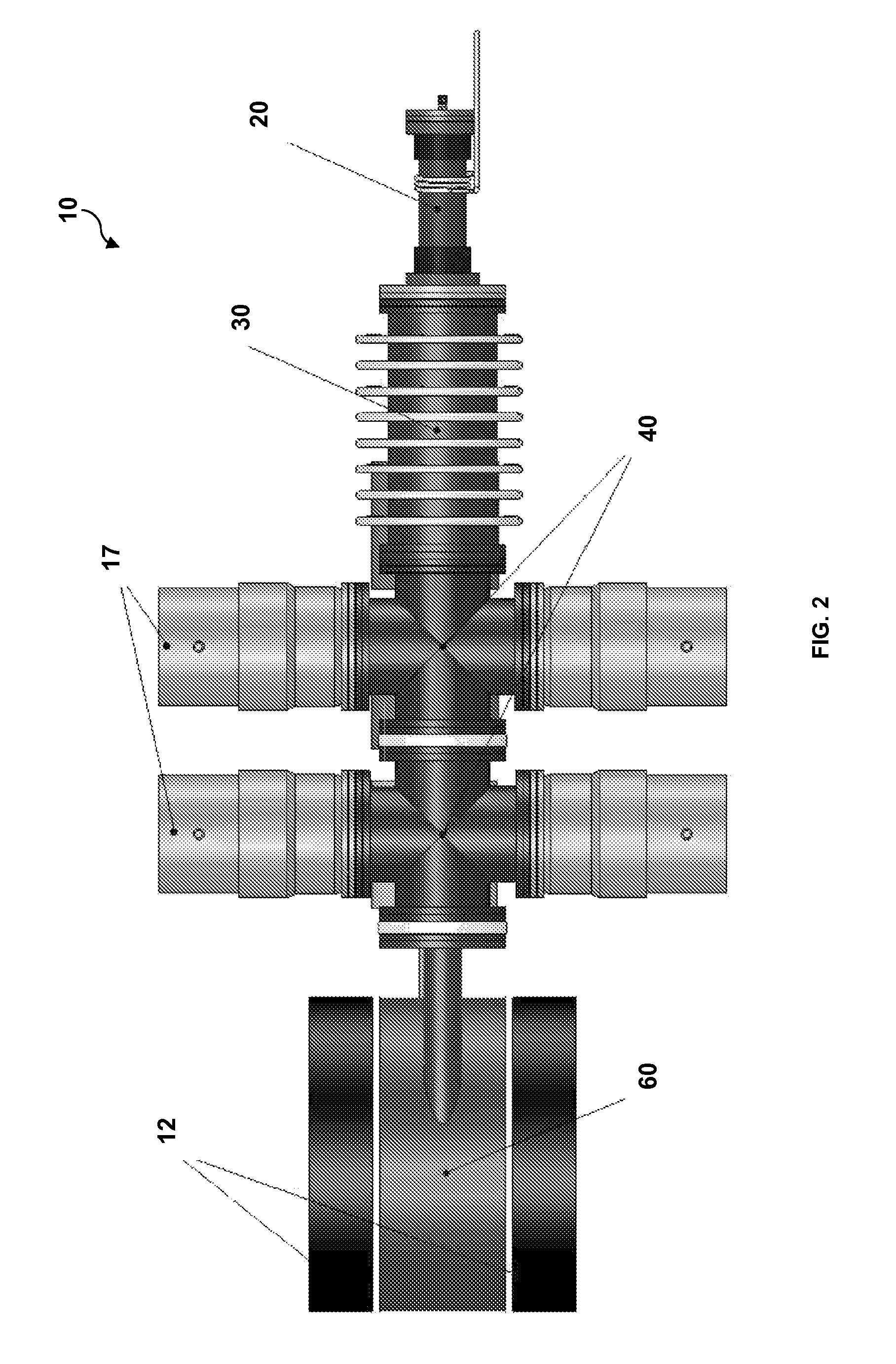
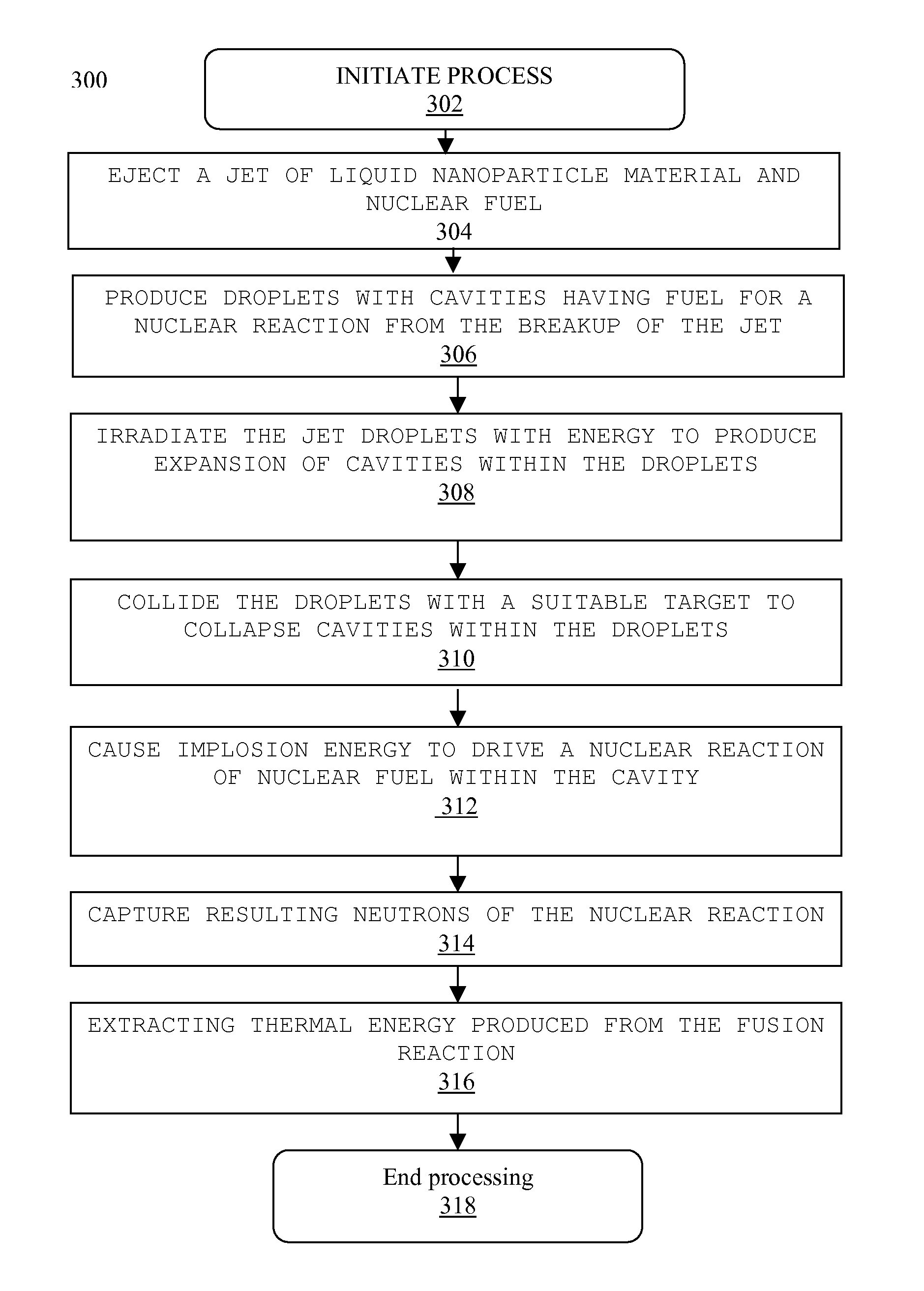
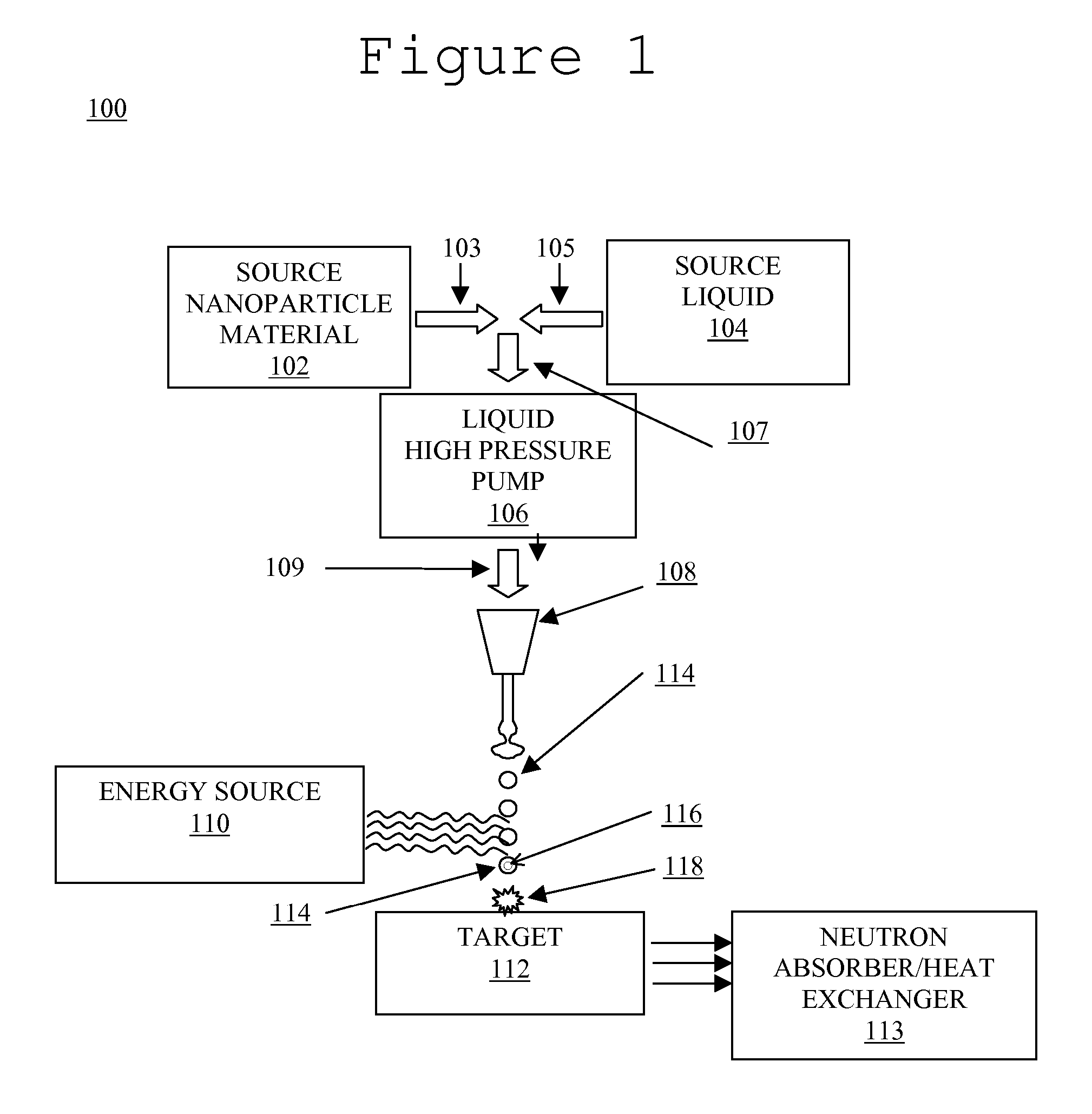
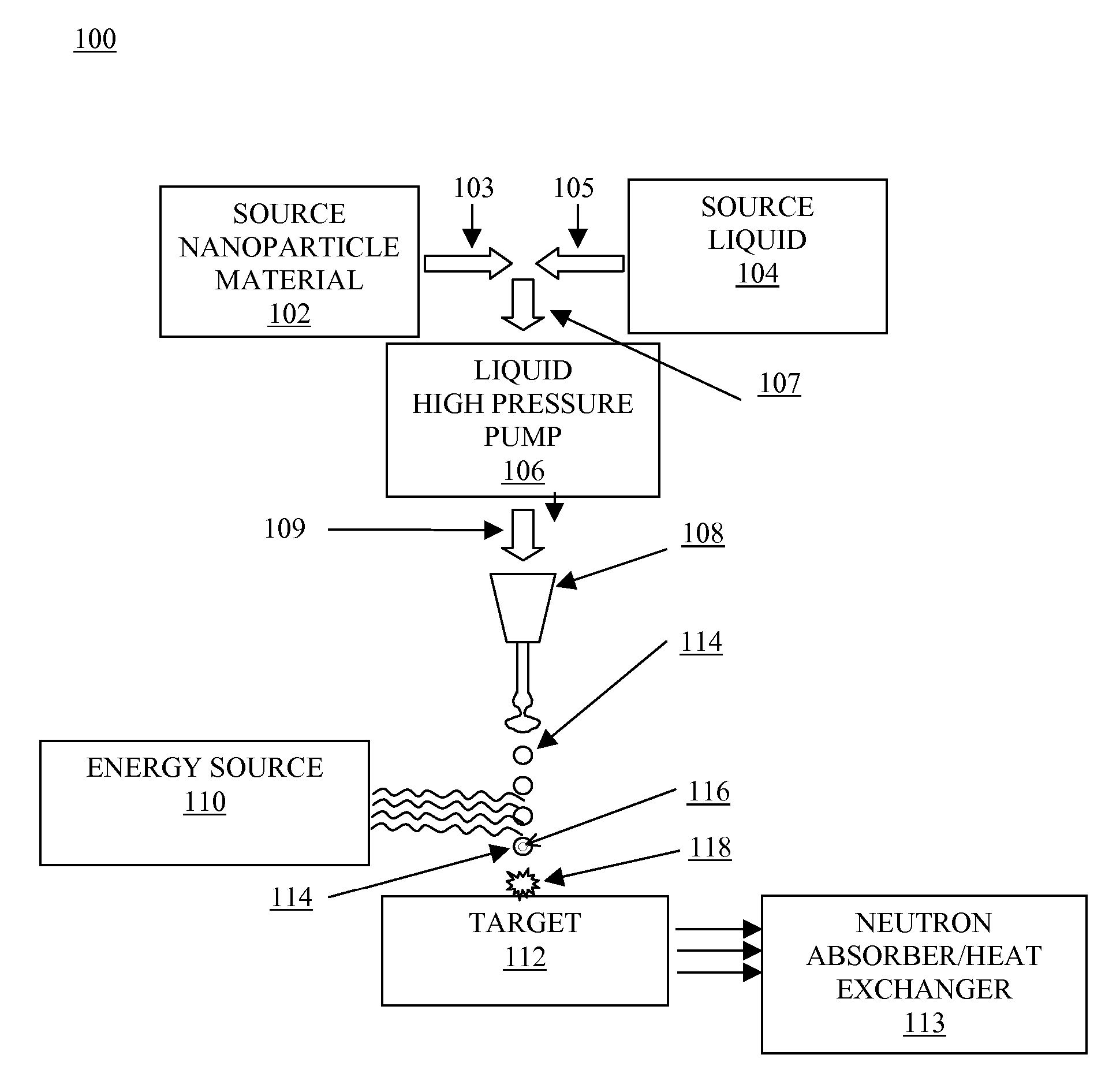
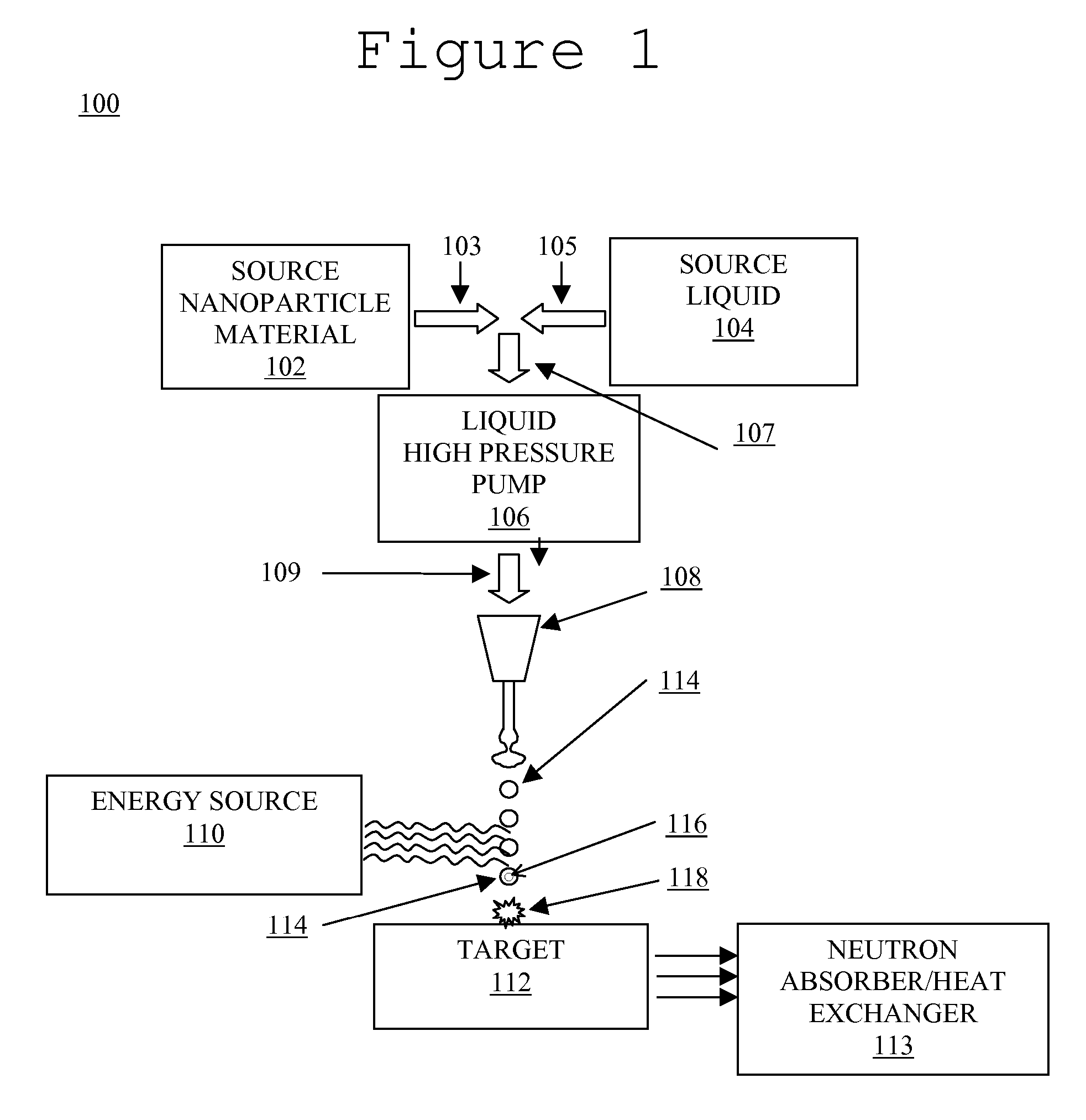
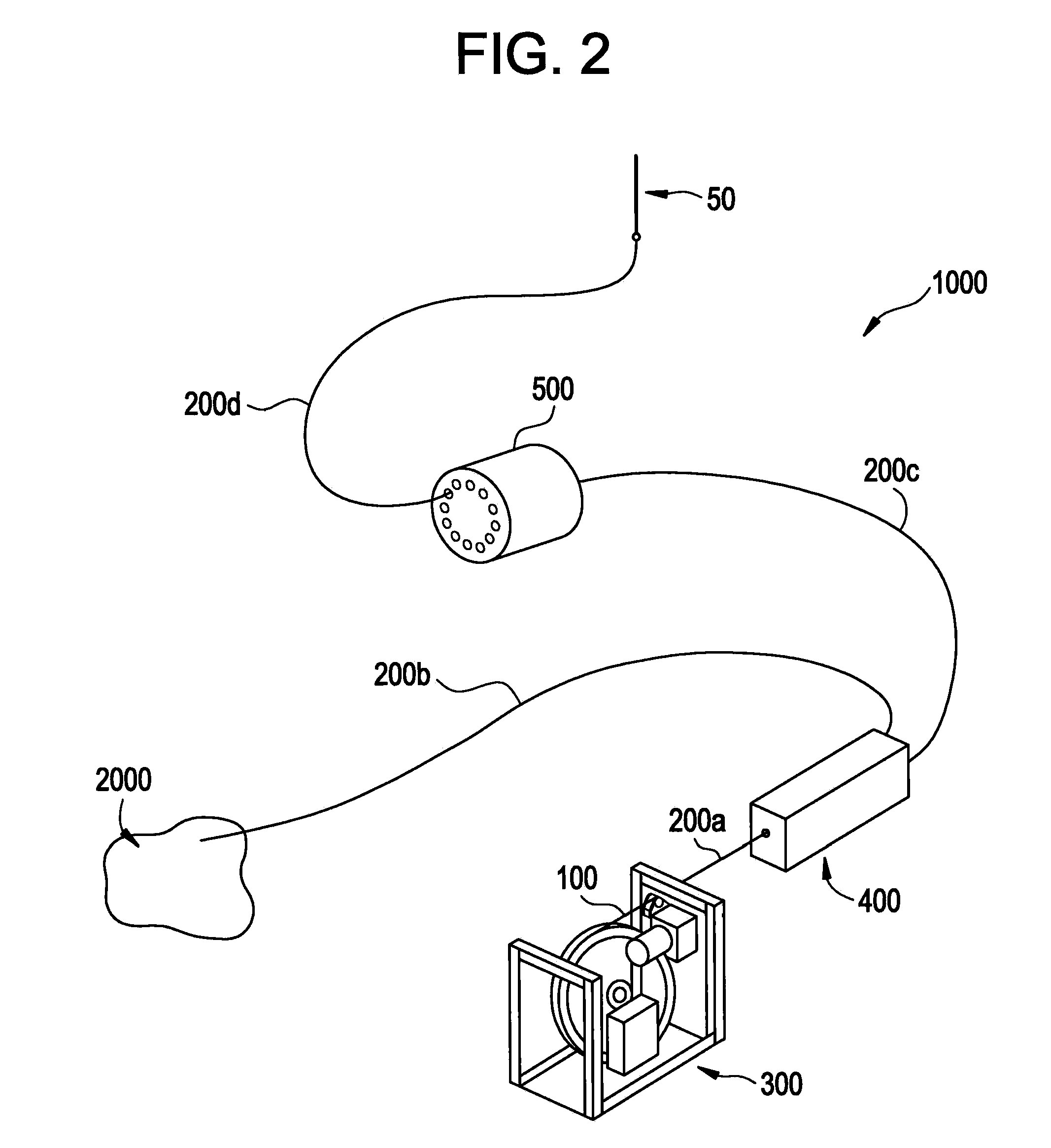
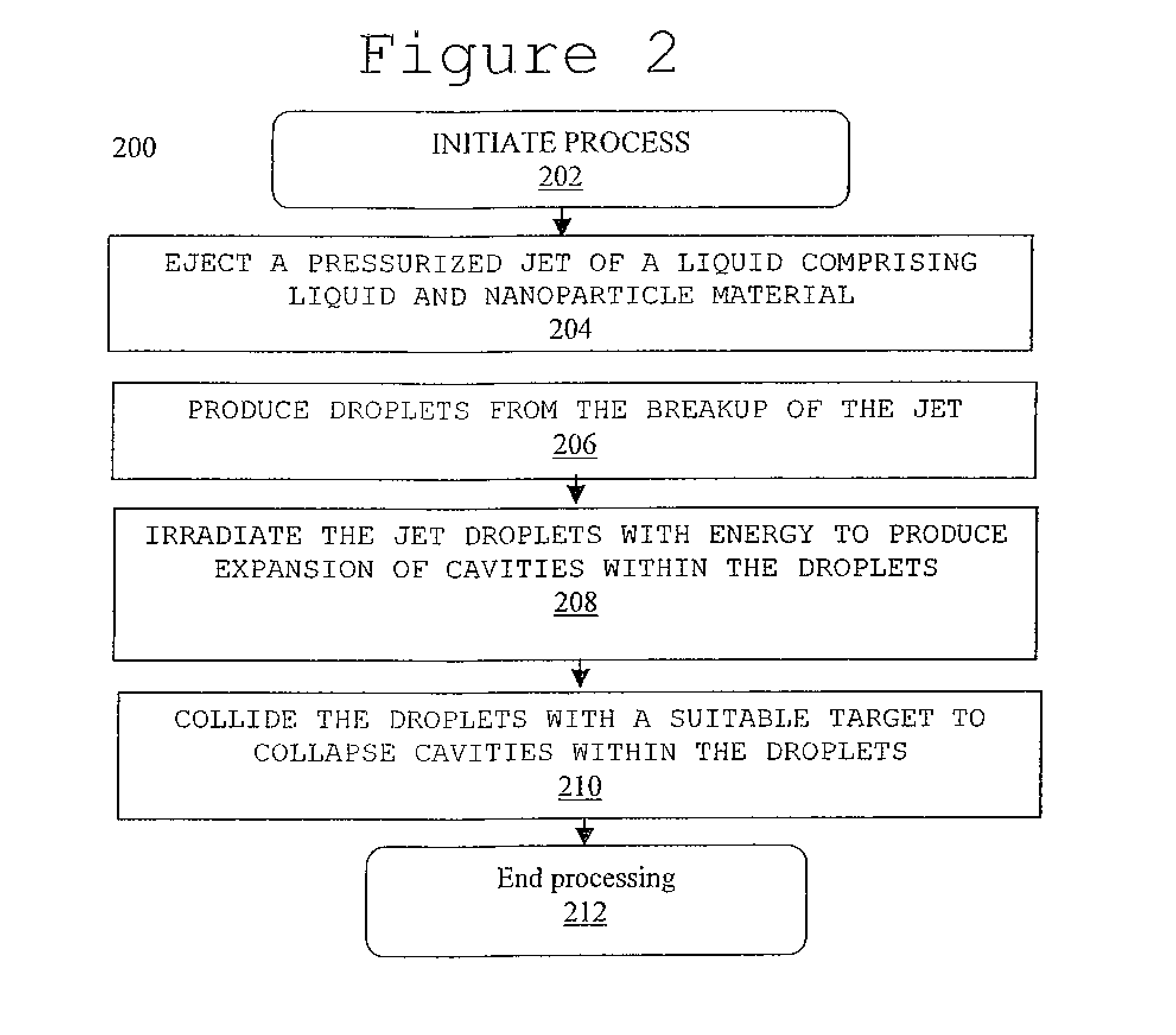
System and method for creating liquid droplet impact forced collapse of laser nanoparticle nucleated cavities for controlled nuclear reactions
InactiveUS7445319B2Promote crashHigh energyMaterial nanotechnologyNuclear energy generationNanoparticleBreakup
Owner:SYNERGY INNOVATIONS INC
Isotope production system and cyclotron
ActiveUS20100282978A1Material analysis by optical meansMagnetic resonance acceleratorsIsotopeCyclotron
A cyclotron that includes a magnet yoke having a yoke body that surrounds an acceleration chamber. The cyclotron also includes a magnet assembly to produce magnetic fields to direct charged particles along a desired path. The magnet assembly is located in the acceleration chamber. The magnetic fields propagate through the acceleration chamber and within the magnet yoke, wherein a portion of the magnetic fields escapes outside of the magnet yoke as stray fields. The cyclotron also includes a vacuum pump that is coupled to the yoke body. The vacuum pump is configured to introduce a vacuum into the acceleration chamber. The magnet yoke is dimensioned such that the vacuum pump does not experience magnetic fields in excess of 75 Gauss.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Laser driven ion accelerator
InactiveUS6906338B2Thermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersIon accelerationIon accelerators
A system and method of accelerating ions in an accelerator to optimize the energy produced by a light source. Several parameters may be controlled in constructing a target used in the accelerator system to adjust performance of the accelerator system. These parameters include the material, thickness, geometry and surface of the target.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Tantalum water target body for production of radioisotopes
InactiveUS20050084055A1Target life is shortenedHigh currentConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsEngineeringCooling capacity
An apparatus for containing and cooling enriched water for the production of activated fluorine (18F). A target assembly is fabricated with internal cooling channels having minimal conduction paths and high Reynolds number flows. In one embodiment, the target assembly is fabricated of tantalum, which has superior oxidation resistance over silver. The superior oxidation resistance and increased cooling capacity allows for high beam currents.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Irradiation target retention assemblies for isotope delivery systems
InactiveUS20110051874A1Quickly and simply harvestedIsotope delivery systemsConversion in nuclear reactorNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
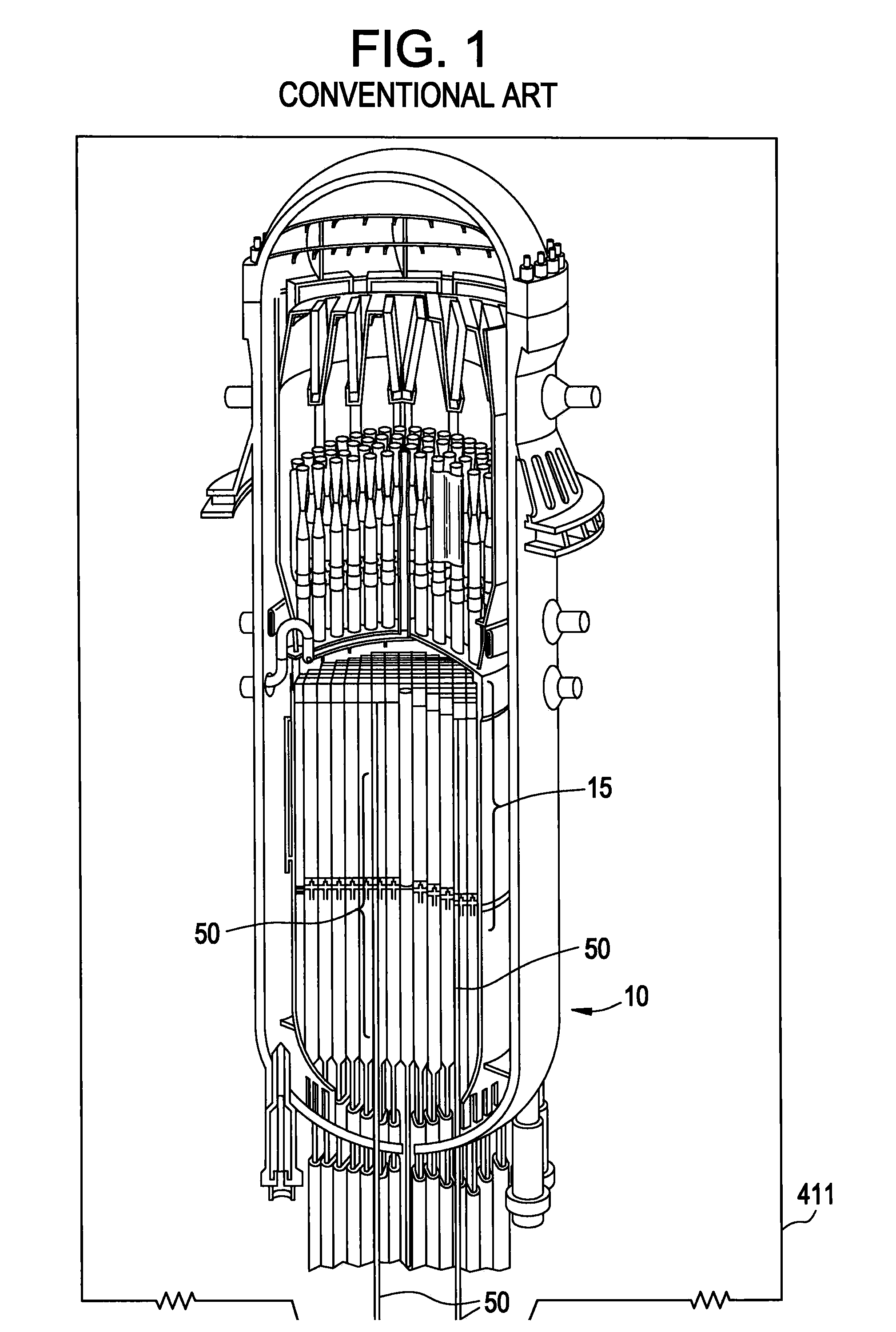
Example embodiments are directed to methods of producing desired isotopes in commercial nuclear reactors and associated apparatuses using instrumentation tubes conventionally found in nuclear reactor vessels to expose irradiation targets to neutron flux found in the operating nuclear reactor. Example embodiments include assemblies for retention and producing radioisotopes in nuclear reactors and instrumentation tubes thereof. Example embodiments include one or more retention assemblies that contain one or more irradiation targets and are useable with example delivery systems that permit delivery of irradiation targets. Example embodiments may be sized, shaped, fabricated, and otherwise configured to successfully move through example delivery systems and conventional instrumentation tubes while containing irradiation targets and desired isotopes produced therefrom.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
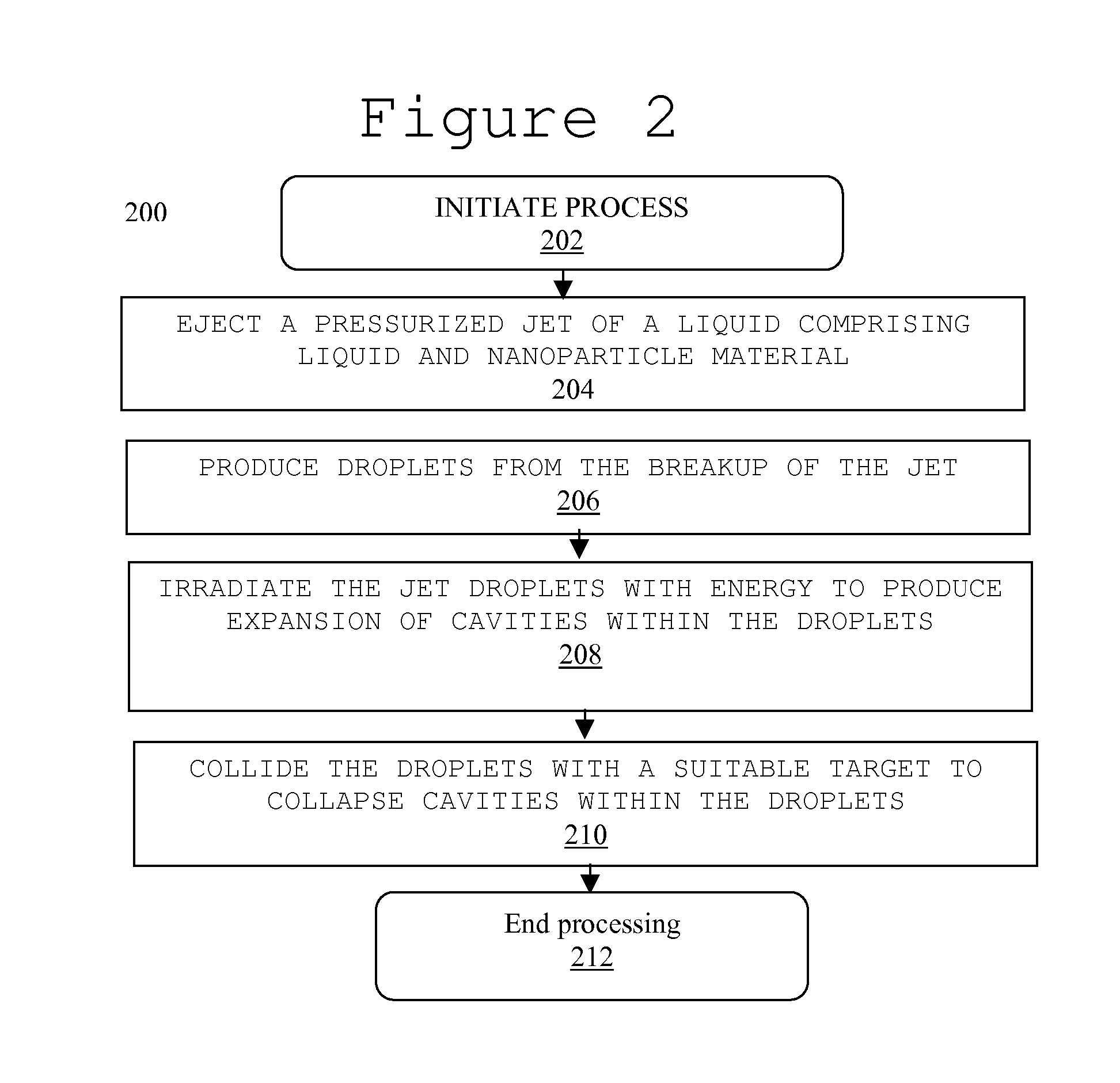
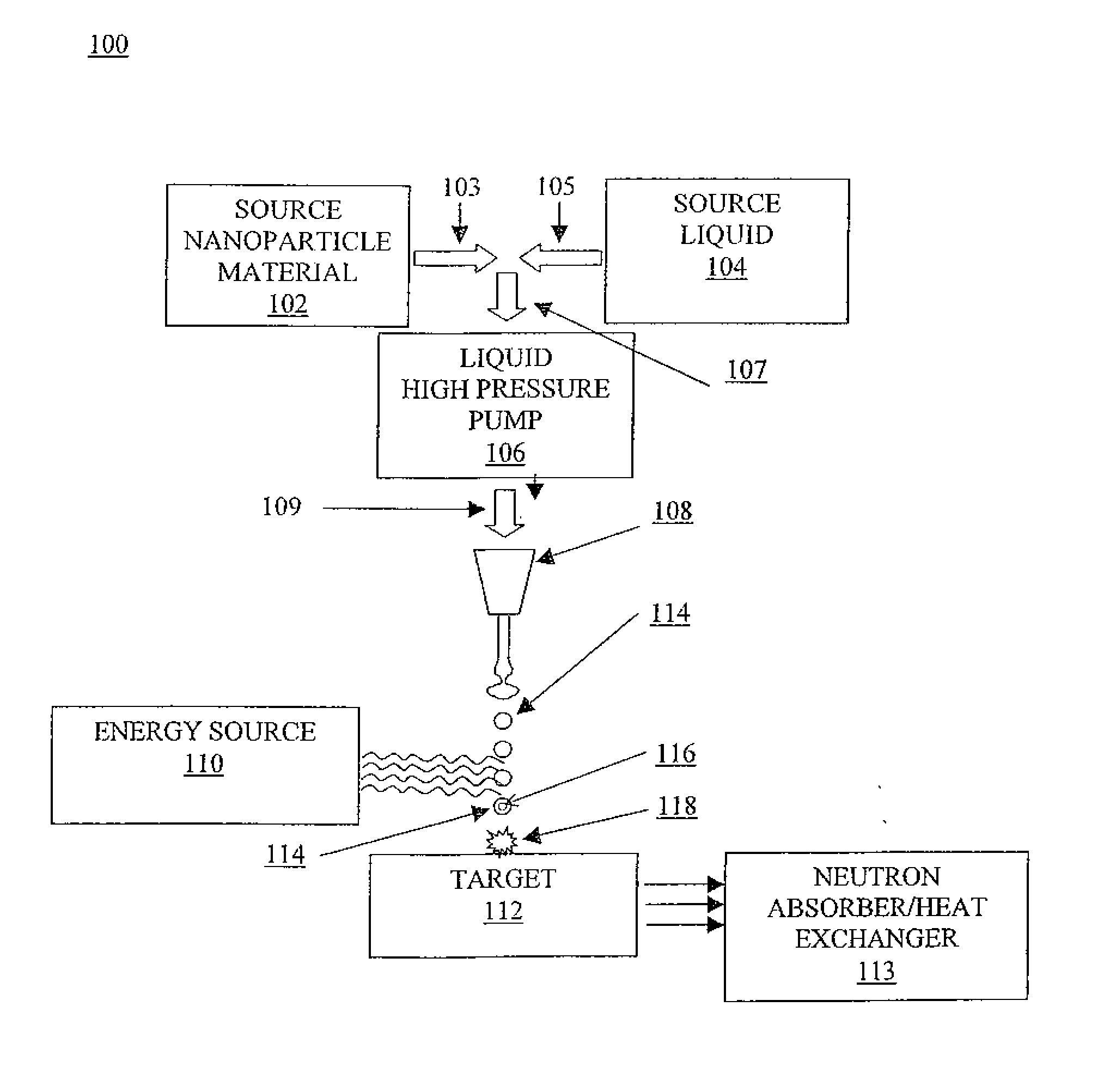
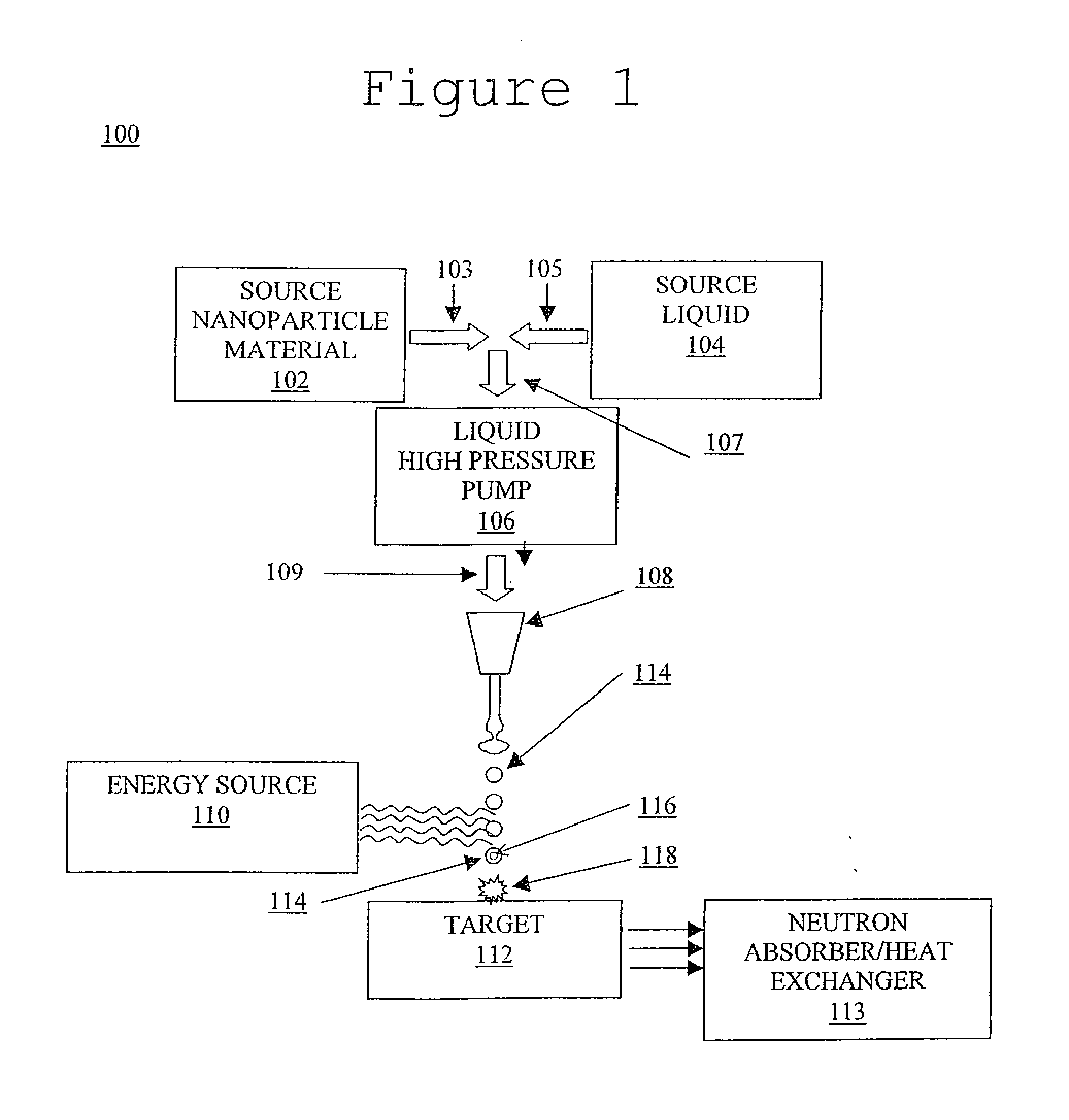
System and method for creating liquid droplet impact forced collapse of laser nanoparticle nucleated cavities
InactiveUS20110228890A1Promote crashEnhance implosion energyNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsNanoparticleBreakup
A device, method and system for causing a controlled collapse of cavities formed within liquid droplets wherein a pressurized jet comprising a liquid and nanoparticle material produces droplets from the breakup of the jet stream. The liquid droplets may be irradiated with energy to produce and expand cavities formed within the droplets by irradiation of the nanoparticles contained within the droplets or alternatively, a volatile fluid with or without a metal nanoparticle may form the cavity. The droplets are collided with a target to collapse the cavities within the droplets. The irradiating (if provided) and colliding are timed to enhance implosion energy resulting from the cavities' collapse. The implosion energy and the fuel in the cavity may be used to activate and sustain a fusion reaction or from any other purposes.
Owner:SYNERGY INNOVATIONS INC
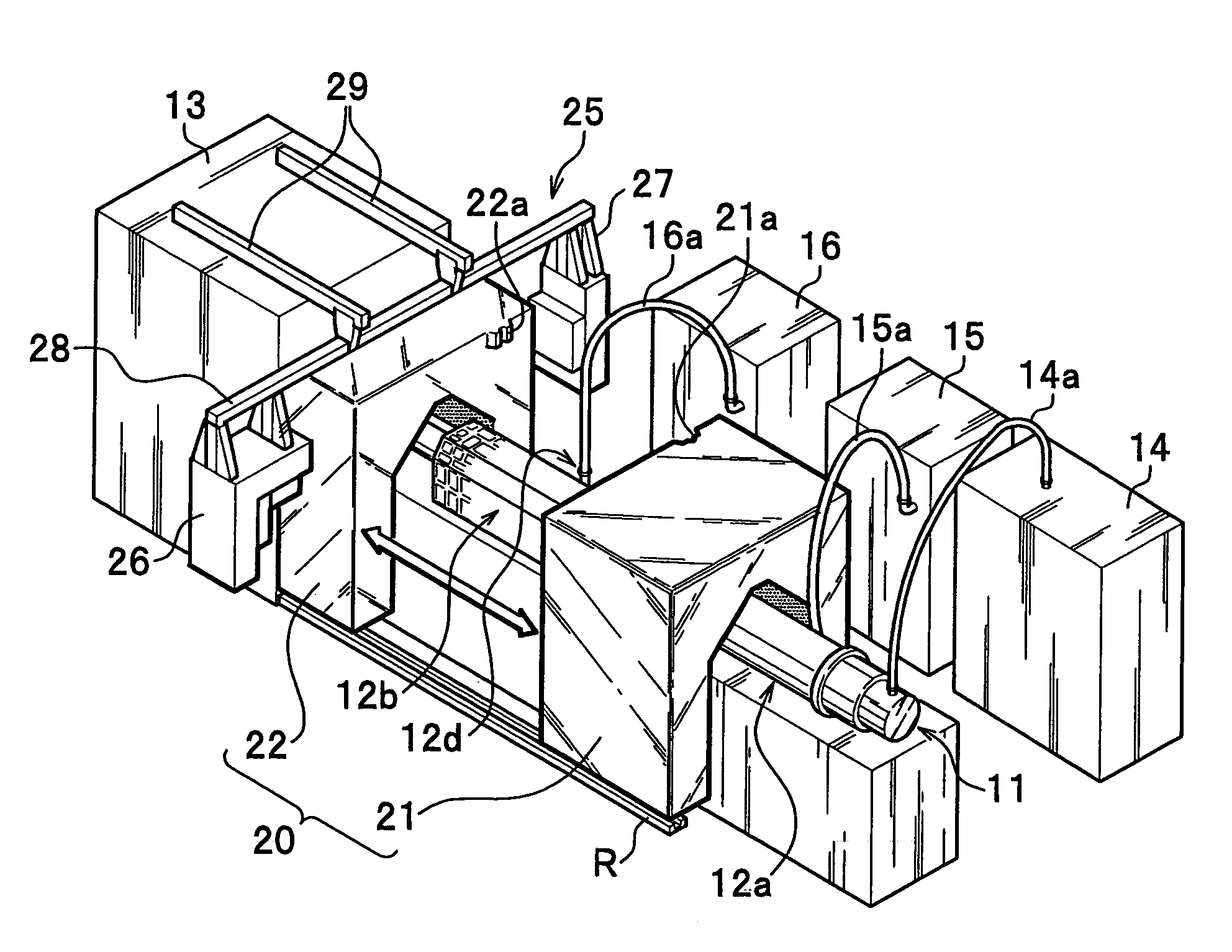
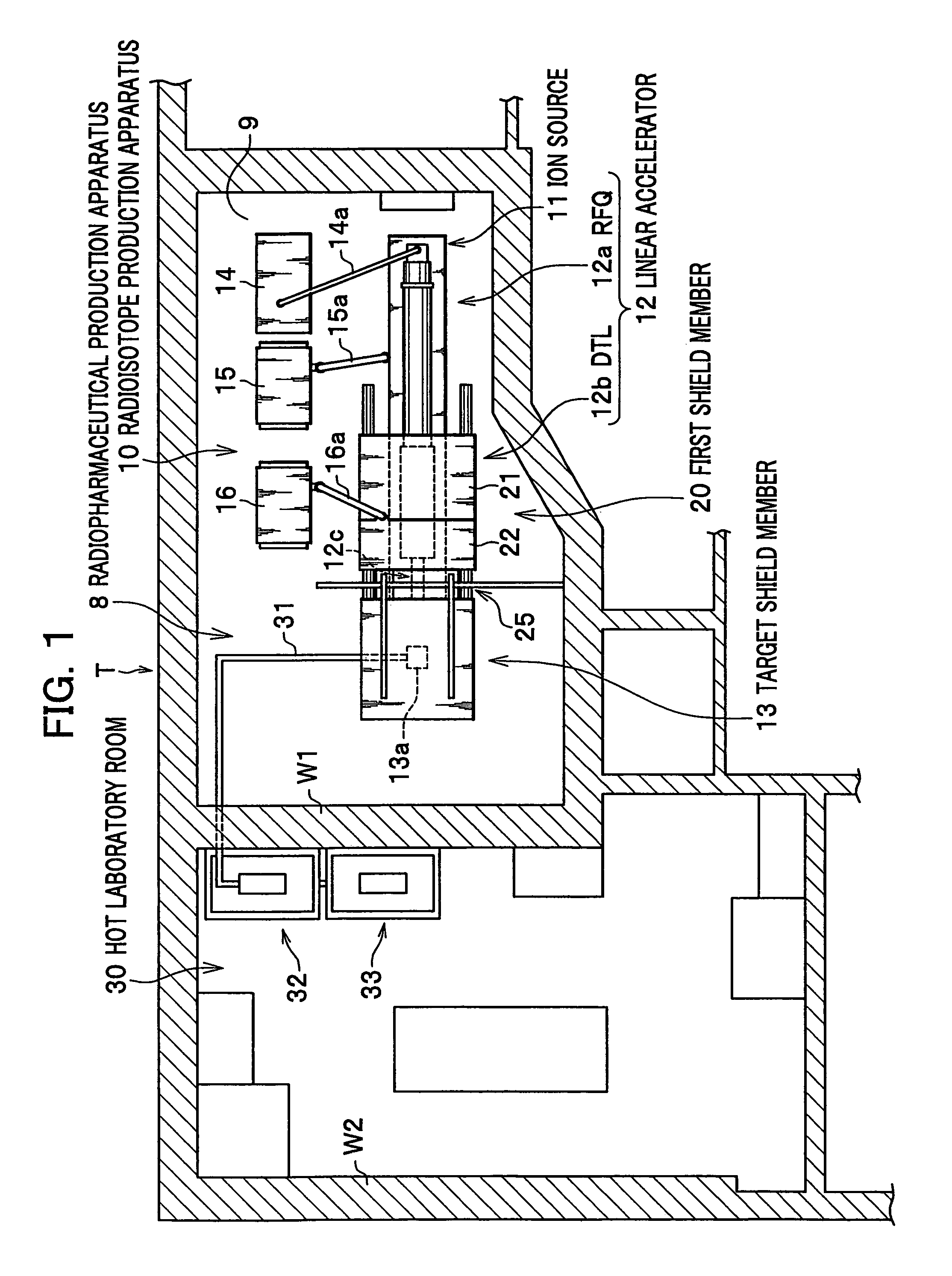
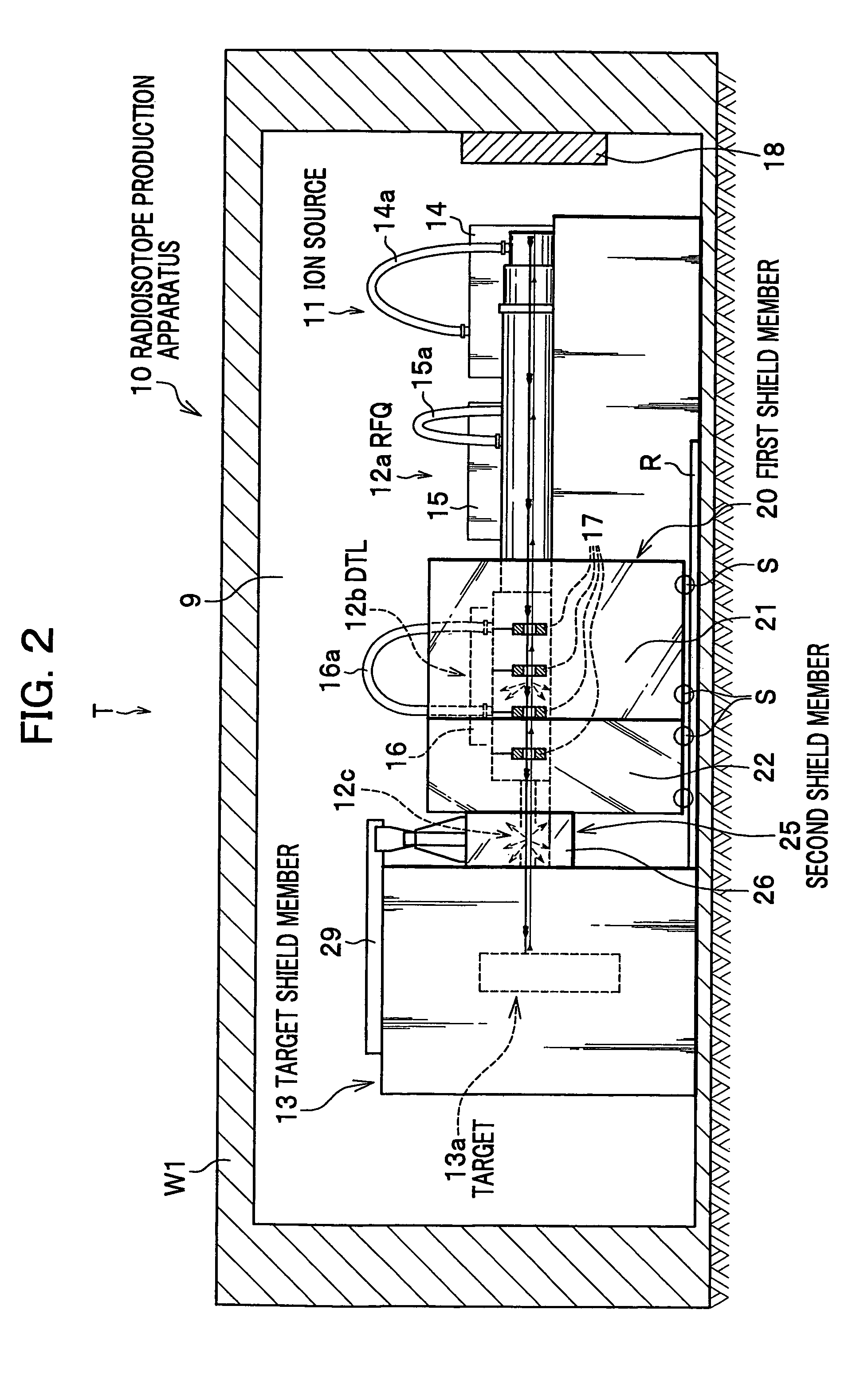
Radioisotope production apparatus and radiopharmaceutical production apparatus
InactiveUS7394081B2Reduce construction costsImprove abilitiesLaser detailsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsEngineeringRadio frequency
A radioisotope production apparatus includes: a linear accelerator for accelerating an ion beam and irradiating a target with the ion beam, radio frequency power supplies for supplying radio frequency waves through coaxial tubes and the linear accelerator, a target shield member containing the target, a first radiation shield member covering the linear accelerator, and a movable second radiation shield member covering the side of target shield member of the linear accelerator between the first radiation shield member and the target shield member. The first radiation shield member is movably divided in opposite directions, respectively, of the axial direction of the linear accelerator from the base point of the connection point of the coaxial tube connected to the linear accelerator.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
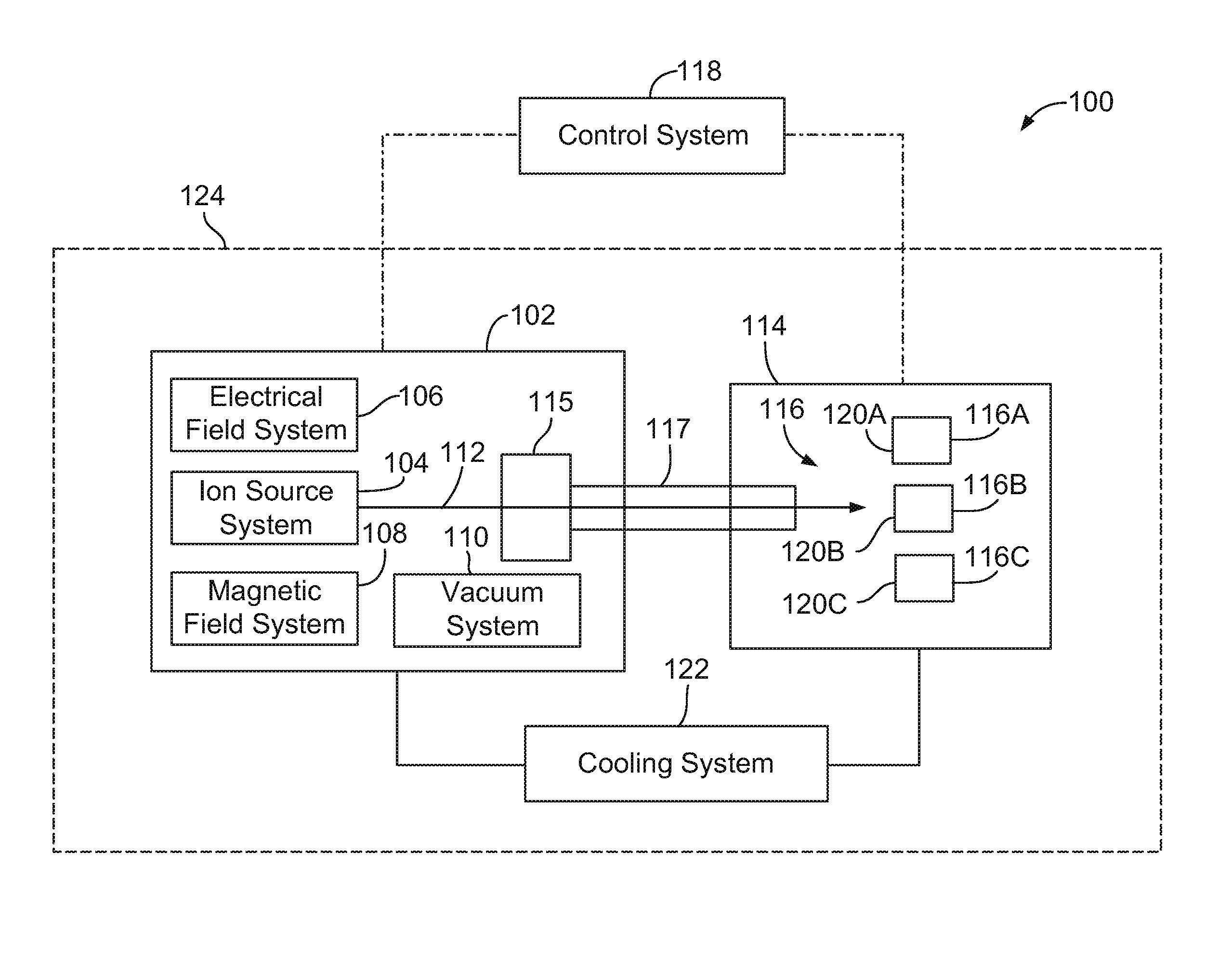
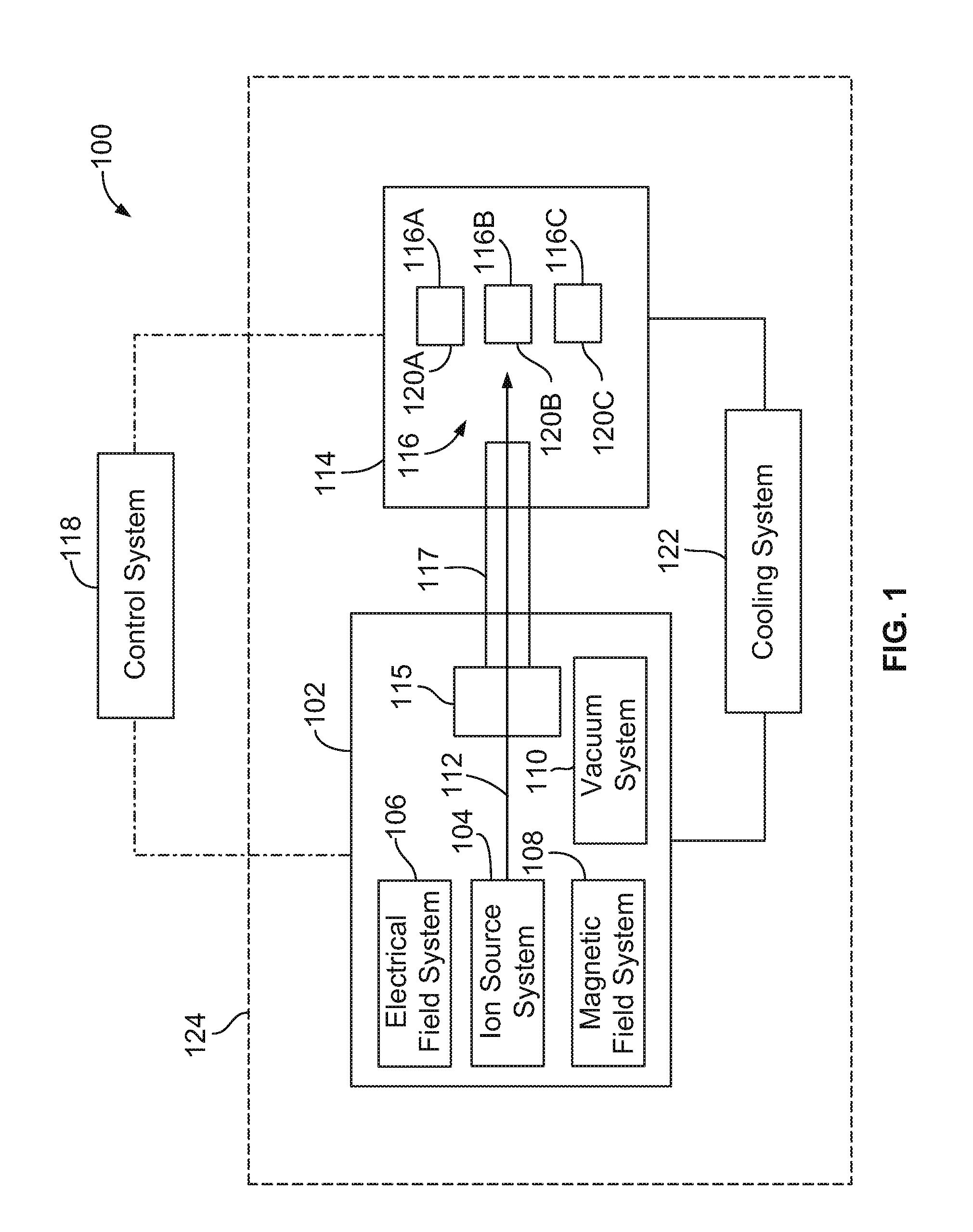
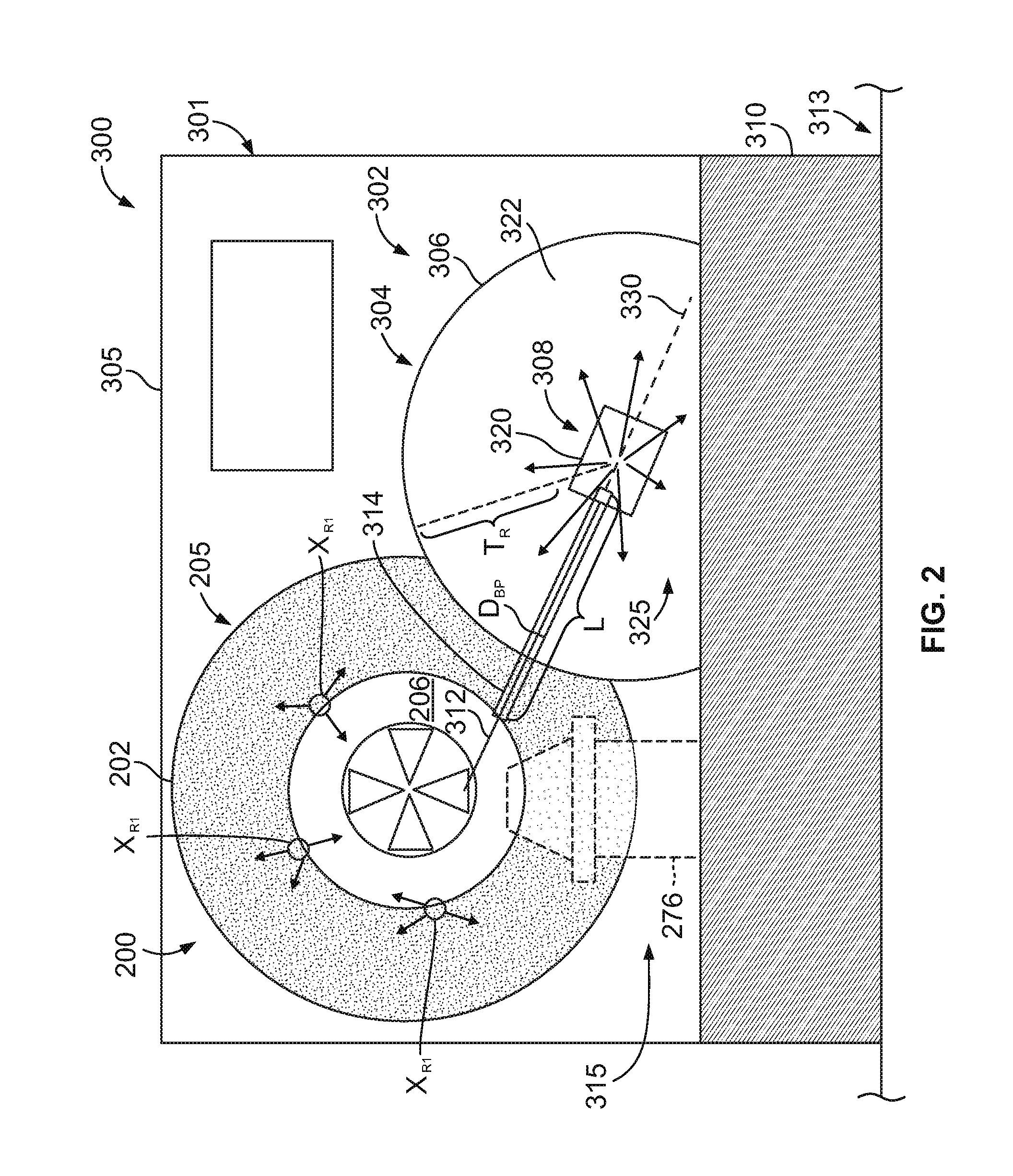
High energy proton or neutron source
ActiveUS20100284502A1Overcome disadvantagesPrevent escapeConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsHigh fluxIsotope
The invention provides a compact high energy proton source useful for medical isotope production and for other applications including transmutation of nuclear waste. The invention further provides a device that can be used to generate high fluxes of isotropic neutrons by changing fuel types. The invention further provides an apparatus for the generation of isotopes including but not limited to 18F, 11C, 15O, 63Zn, 124I, 133Xe, 111In, 125I, 131I, 99Mo, and 13N.
Owner:SHINE TECH LLC
High power high yield target for production of all radioisotopes for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS6917044B2Avoid low densityConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringInstabilityAir blower
A high power high yield target for the positron emission tomography applications is introduced. For production of Curie level of Fluorine-18 isotope from a beam of proton it uses about one tenth of Oxygen-18 water compared to a conventional water target. The target is also configured to be used for production of all other radioisotopes that are used for positron emission tomography. When the target functions as a water target the material sample being oxygen-18 or oxygen-16 water is heated to steam prior to irradiation using heating elements that are housed in the target body. The material sample is kept in steam phase during the irradiation and cooled to liquid phase after irradiation. To keep the material sample in steam phase a microprocessor monitoring the target temperature manipulates the flow of coolant in the cooling section that is attached to the target and the status of the heaters and air blowers mounted adjacent to the target. When the target functions as a gas target the generated heat from the beam is removed from the target by air blowers and the cooling section. The rupture point of the target window is increased by a factor of two or higher by one thin wire or two parallel thin wires welded at the end of a small hollow tube which is held against the target window. One or two coils are used to produce a magnetic filed along the beam path for preventing the density depression along the beam path and suppression of other instabilities that can develop in a high power target.
Owner:AMINI BEHROUZ
Thermonuclear plasma reactor for rocket thrust and electrical generation
InactiveUS20090000268A1Easy to triggerDownsize working reactionCosmonautic vehiclesNuclear energy generationHigh energyNuclear engineering
A reactor system produces plasma rocket thrust using alpha-initiated atomic fuel pellets without the need for a critical mass of fissionable material. The fuel pellets include an outer layer reactive material to alpha particles to generate neutrons (e.g., porous lead or beryllium), an under-layer of fissionable material (e.g., thorium or enriched uranium), and an optional inner core of fusion material (e.g., heavy water ice, boron hydride). The pellets are injected one at a time into a charged reaction chamber containing a set of alpha beam channels, possibly doubling as ion accelerators, all directed toward a common point. Alpha particles converging on each successive pellet initiate an atomic reaction in the fissionable under-layer, via a neutron cascade from the pellet outer layer, producing plasma that is confined within the chamber. This may be enhanced by atomic fusion of the optional inner core. The resulting high-energy plasma creates electrostatic pressure on the chamber and is allowed to exit the chamber through a port. An ion accelerator at the exhaust port of the chamber accelerates outgoing plasma ions, possibly with added reaction mass, to generate the rocket thrust. An electric circuit that includes the charged chamber may collect the electrons in the plasma to help power the ion accelerator(s).
Owner:YURASH GREG J
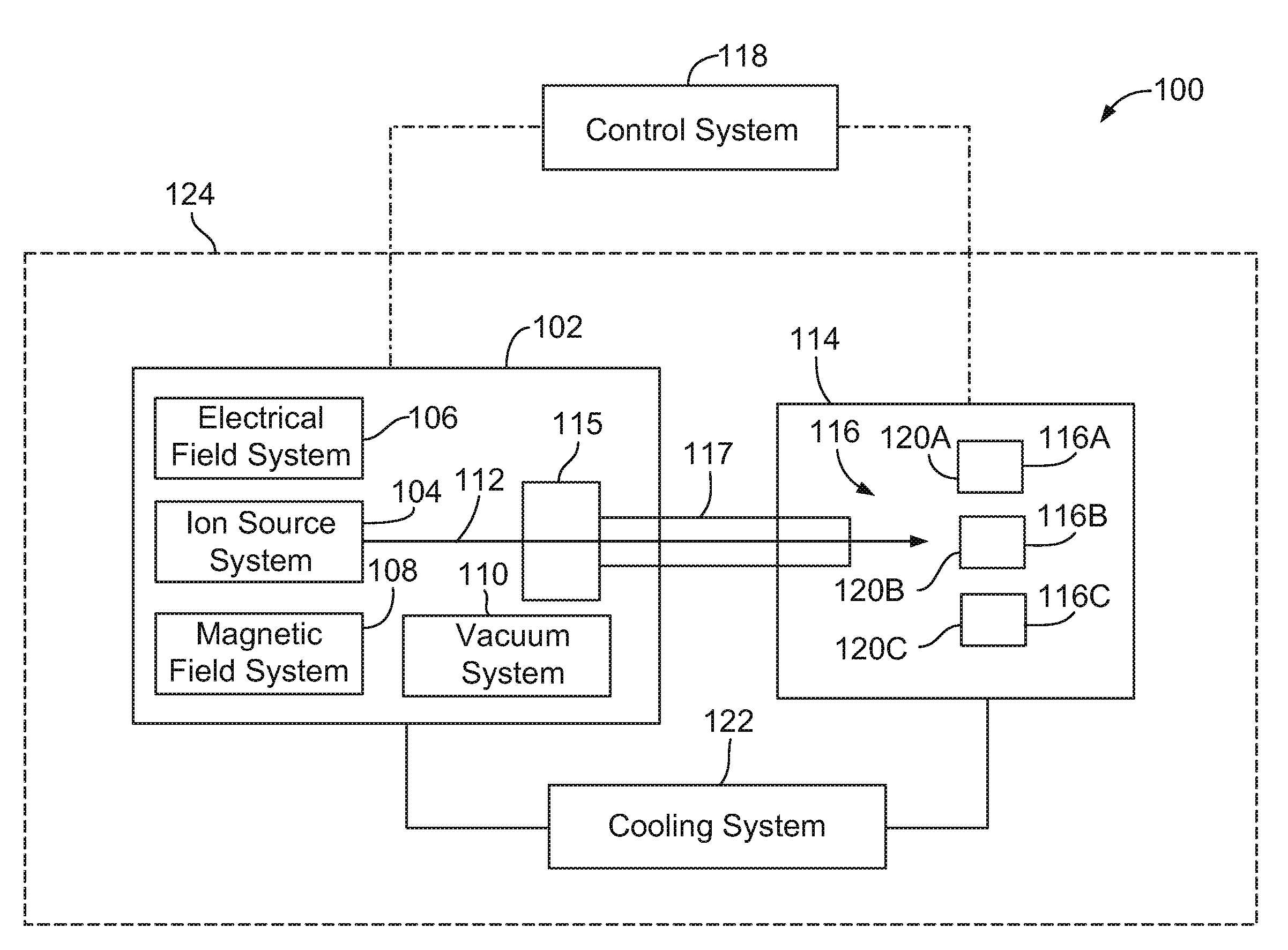
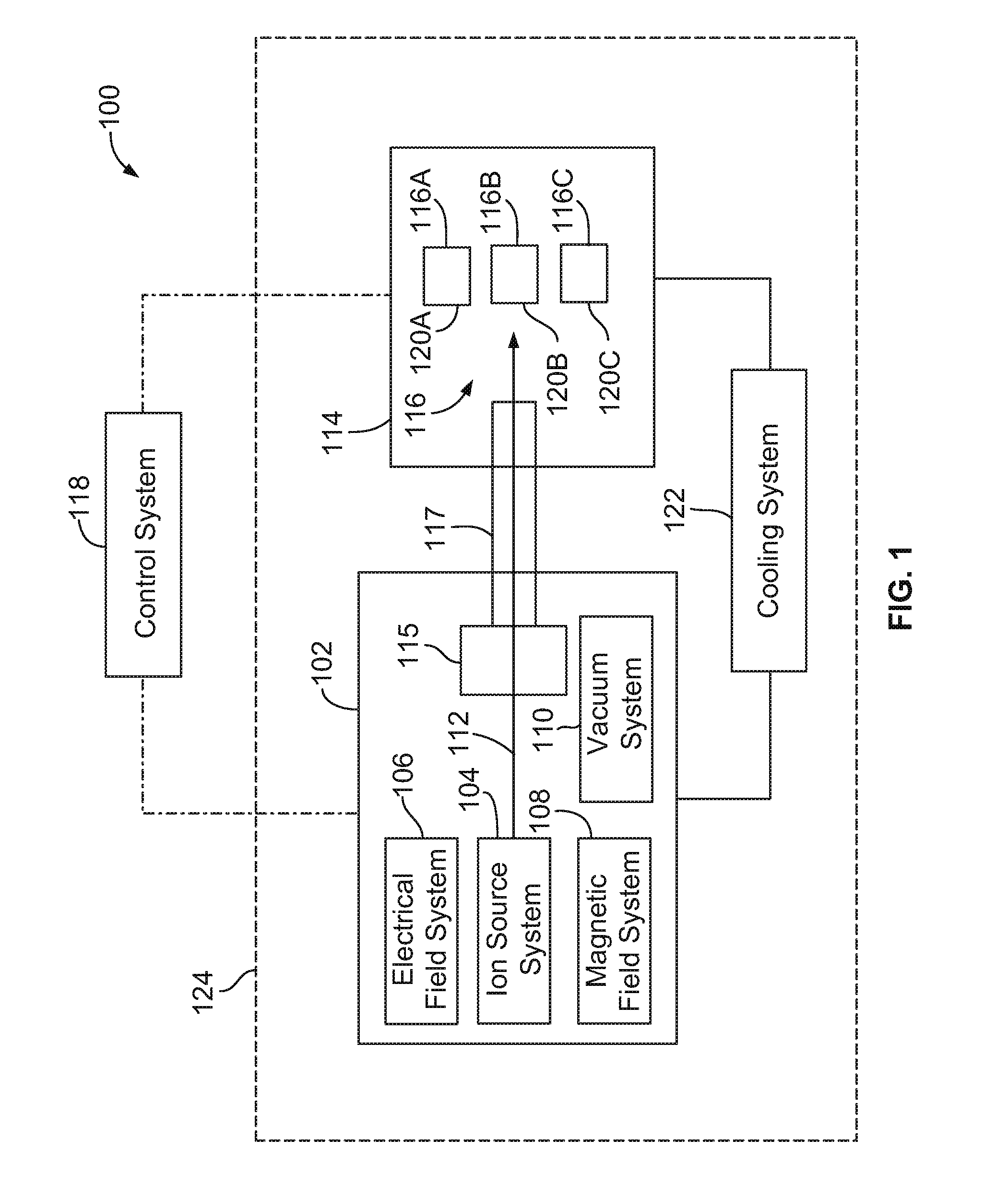
Neutron beam irradiation system
InactiveCN103052425AImprove work efficiencyRadiation/particle handlingMedical devicesNeutron irradiationCharged particle beam
A neutron beam irradiation system that irradiates an irradiation object with a neutron beam includes: a neutron beam generating section that generates a neutron beam by being irradiated with a charged particle beam; a housing section that includes at least a moderator and that houses the neutron beam generating section; a neutron beam converging section that converges the neutron beam with which the irradiation object is irradiated; a mounting stage on which the irradiation object is mounted; and a relative movement means that relatively moves the mounting stage closer to and away from the neutron beam generating section, the housing section, and the neutron beam converging section.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Electromagnetic wave generator
InactiveUS20060249685A1High strengthIncrease speedThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsX-rayHigh intensity
A compact and low-cost electromagnetic wave generator in which X-rays having high intensity can be generated and the energy of generated X-rays can rapidly be switched. In an electromagnetic wave generator including a circular accelerator, a deflection electromagnet incorporated in the circular accelerator focuses injected and accelerated electrons, The circular accelerator produces stable electron closed orbits in a region with a predetermined width in the radial direction of the accelerator that are stable during injection and acceleration of electron. A target is arranged across the stable electron closed orbits and a collision region, where a circulating electron beam collides with the target and a non-collision region where a circulating electron beam does not collide with the target produced. Through control of respective patterns of changes with time in the deflection magnetic field, a given electron closed orbit is shifted between the collision and the non-collision regions, thereby generating X-rays.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Compound isotope target assembly for production of medical and commercial isotopes by means of spectrum shaping alloys
InactiveUS20090274258A1Increase local populationLow neutronConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNeutron captureResonance
Owner:HOLDEN CHARLES S +1
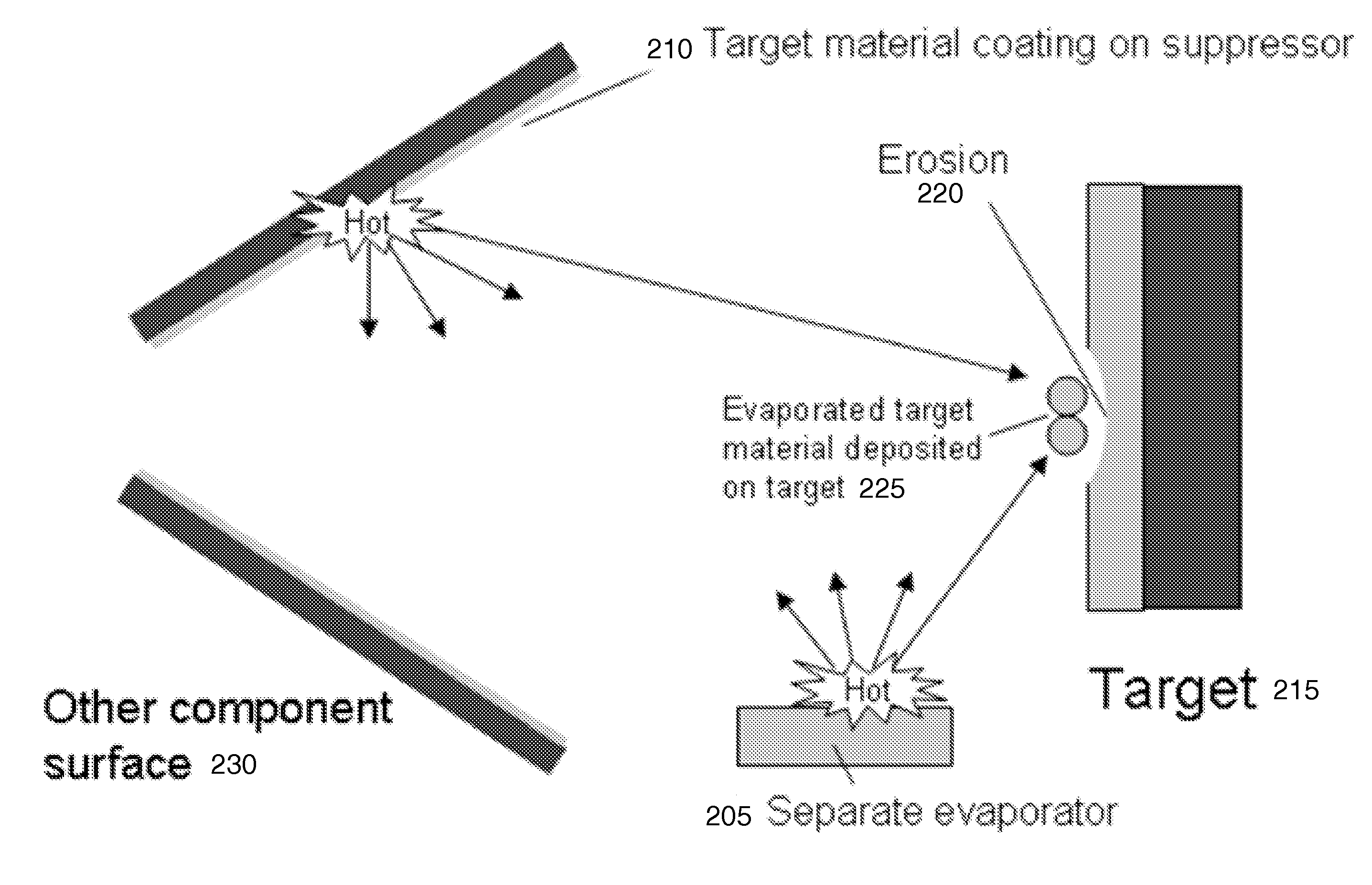
Method and system for in situ depositon and regeneration of high efficiency target materials for long life nuclear reaction devices
ActiveUS20110091000A1Maintain purityMinimize the numberNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsNeutron energy spectrumNuclear reaction
Aspects of the invention relate to several methods to deposit and regenerate target materials in neutron generators and similar nuclear reaction devices. In situ deposition and regeneration of a target material reduces tube degradation of the nuclear reaction device and covers impurities on the surface of the target material at the target location. Further aspects of the invention include a method of designing a target to generate neutrons at a high efficiency rate and at a selected neutron energy from a neutron energy spectrum.
Owner:STARFIRE IND LLC
Higher pressure, modular target system for radioisotope production
InactiveUS20090090875A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsX-ray tube electrodesComputer moduleEngineering
A beam window according to example embodiments may include a foil having an interior region and an exterior region. The interior region of the foil may be dome-shaped, and a central portion of the dome-shaped interior region may be thinner than the exterior region of the foil. The beam window may be welded to a flange to form a window module. One or more window modules may be utilized in a target assembly. The target assembly may further include a cooling unit and / or collimator to form a target system according to example embodiments.
Owner:ADVANCED APPLIED PHYSICS SOLUTIONS
X-ray micro-target source
InactiveUS7050540B2Increase the amount of target material availableImprove efficiencyX-ray tube laminated targetsImaging devicesSoft x rayX-ray
X-ray generation apparatus including an elongated target body and a mount from which the body projects to a tip remote from the mount. The target body includes a substance that, on being irradiated by a beam of electrons of suitable energy directed onto the target body from laterally of the elongate target body, generates a source of x-ray radiation from a volume of interaction of the electron beam with the target body. The mount provides a heat sink for the target body.
Owner:XRT
X-ray Apparatus
X-ray apparatus comprises a linear accelerator adapted to produce a beam of electrons at one of at least two selectable energies and being controlled to change the selected energy on a periodic basis, and a target to which the beam is directed thereby to produce a beam of x-radiation, the target being non-homogenous and being driven to move periodically in synchrony with the change of the selected energy. In this way, the target can move so that a different part is exposed to the electron beam when different pulses arrive. This enables the appropriate target material to be employed depending on the selected energy. The easiest form of periodic movement for the target is likely to be a rotational movement. The target can be immersed in a coolant fluid such as water. The linear accelerator can be of the type disclosed in WO2006 / 097697A1. The target preferably contains at least one exposed area of tungsten and / or at least one exposed area of carbon. These can be present as inhomogeneities in the material of which the target is composed, such as Carbon inserts in a Tungsten substrate (or vice versa), alternating segments of Carbon and Tungsten, Carbon and Tungsten inserts in a substrate of a third material, or arrangements involving other materials in addition to or instead of Carbon and / or Tungsten. Alternatively, the target can be of a homogenous material but have inhomogeneities in its thickness to cater for the different electron energies. The same concept can be applied to the filter. A detector can be provided, operating in synchrony with the energy variation. Such an x-ray apparatus can form a part of a radiotherapy apparatus, in which case the first selected energy can be a diagnostic energy and a second selected energy a therapeutic energy.
Owner:ELEKTA AB +1
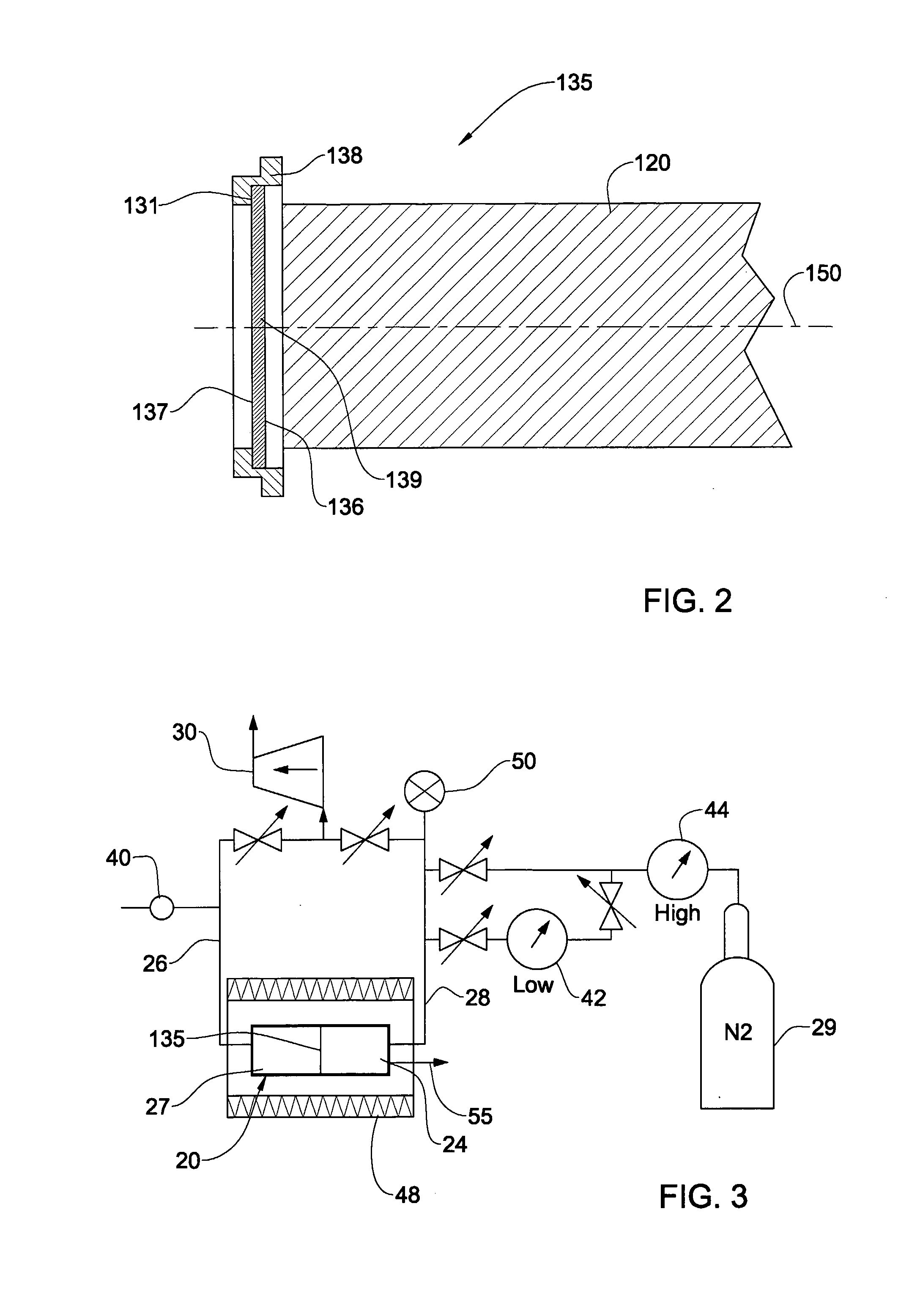
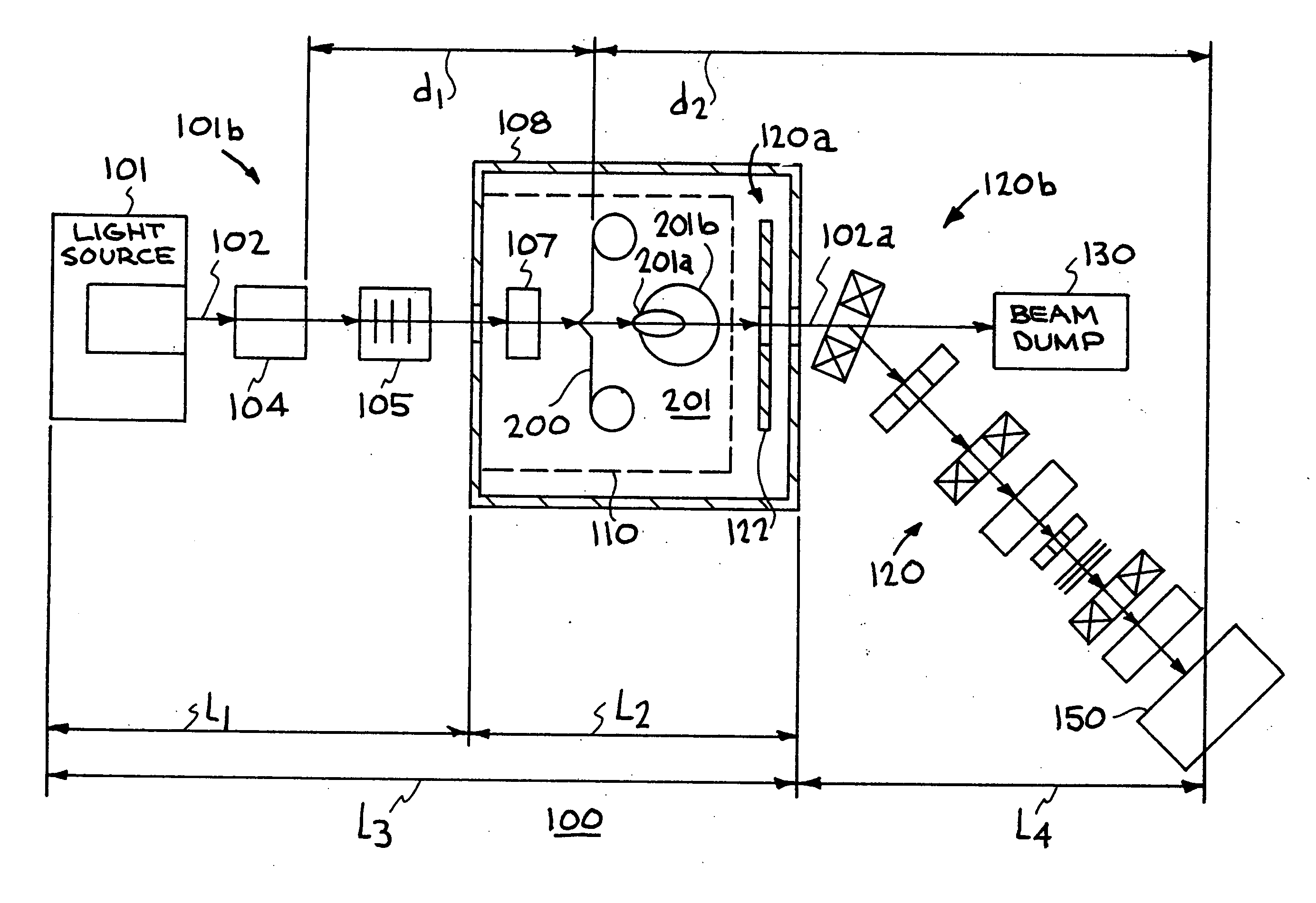
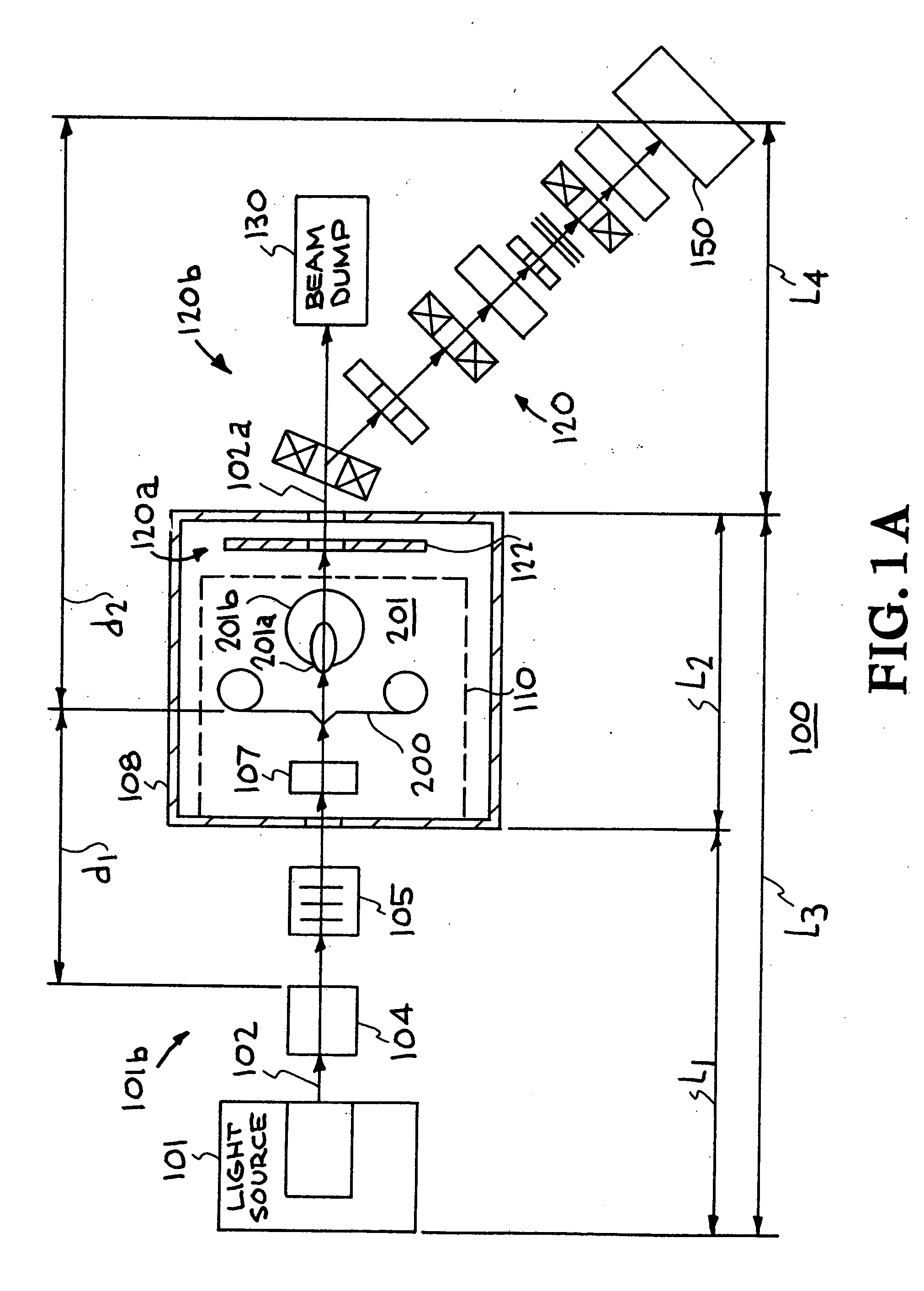
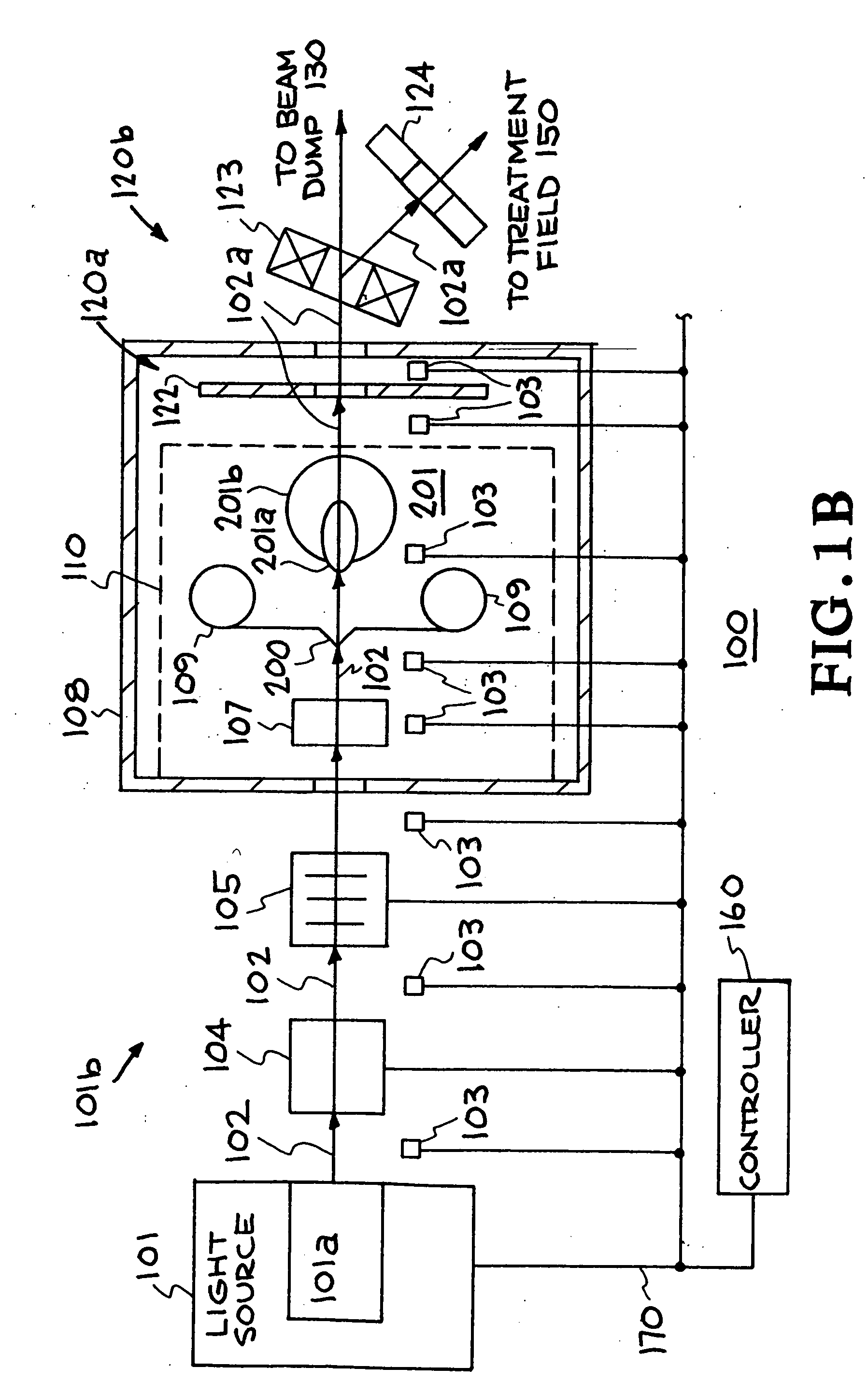
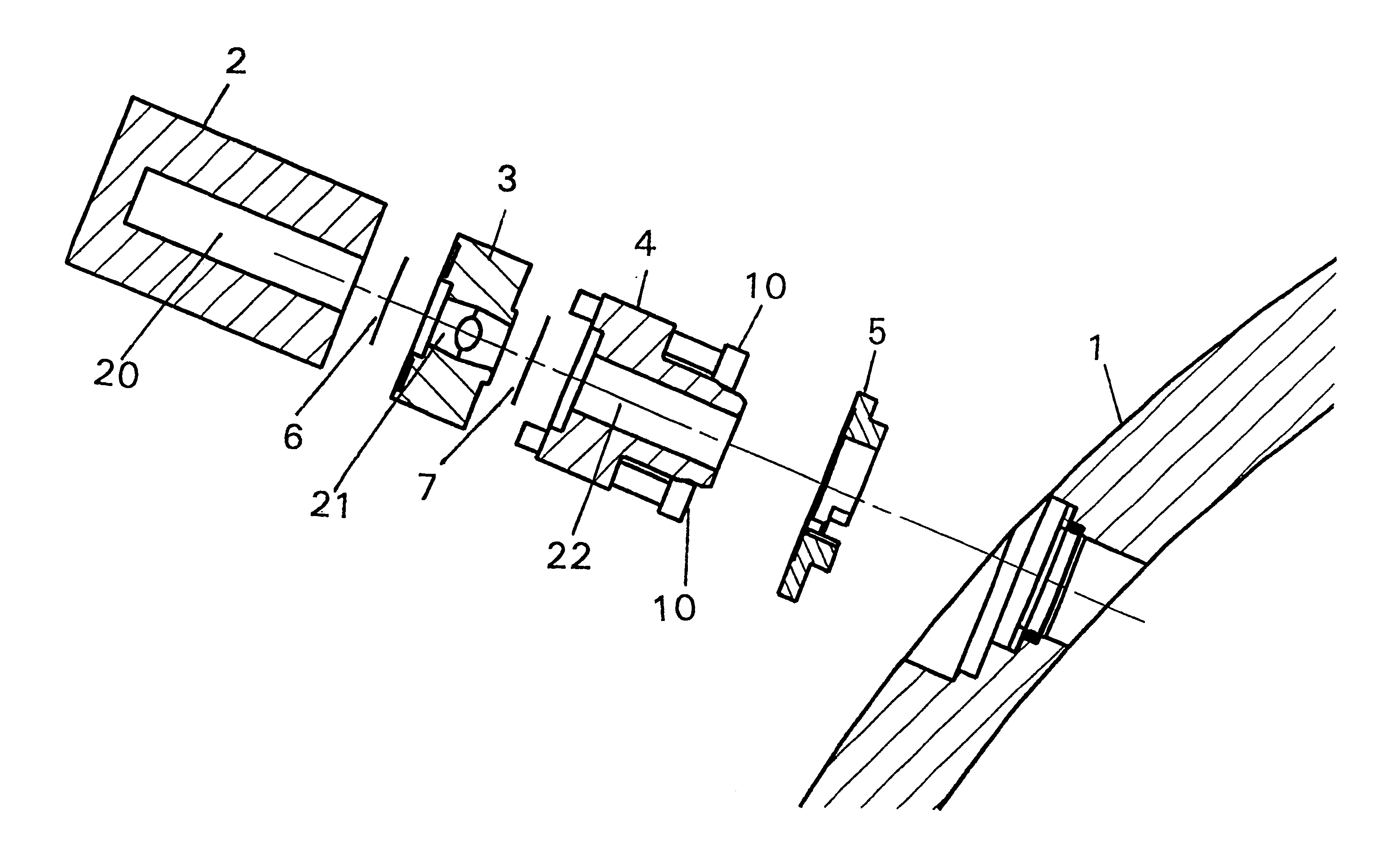
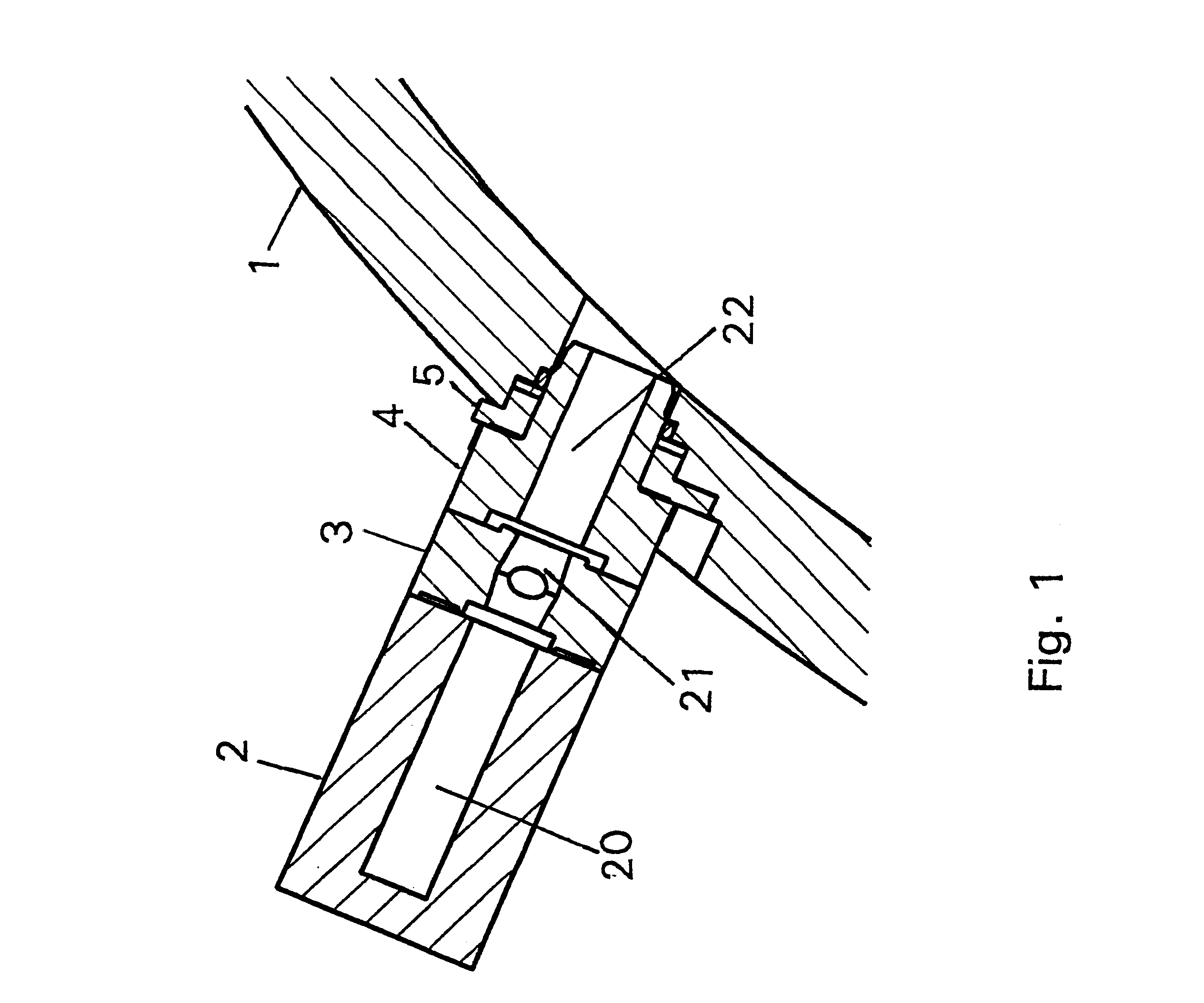
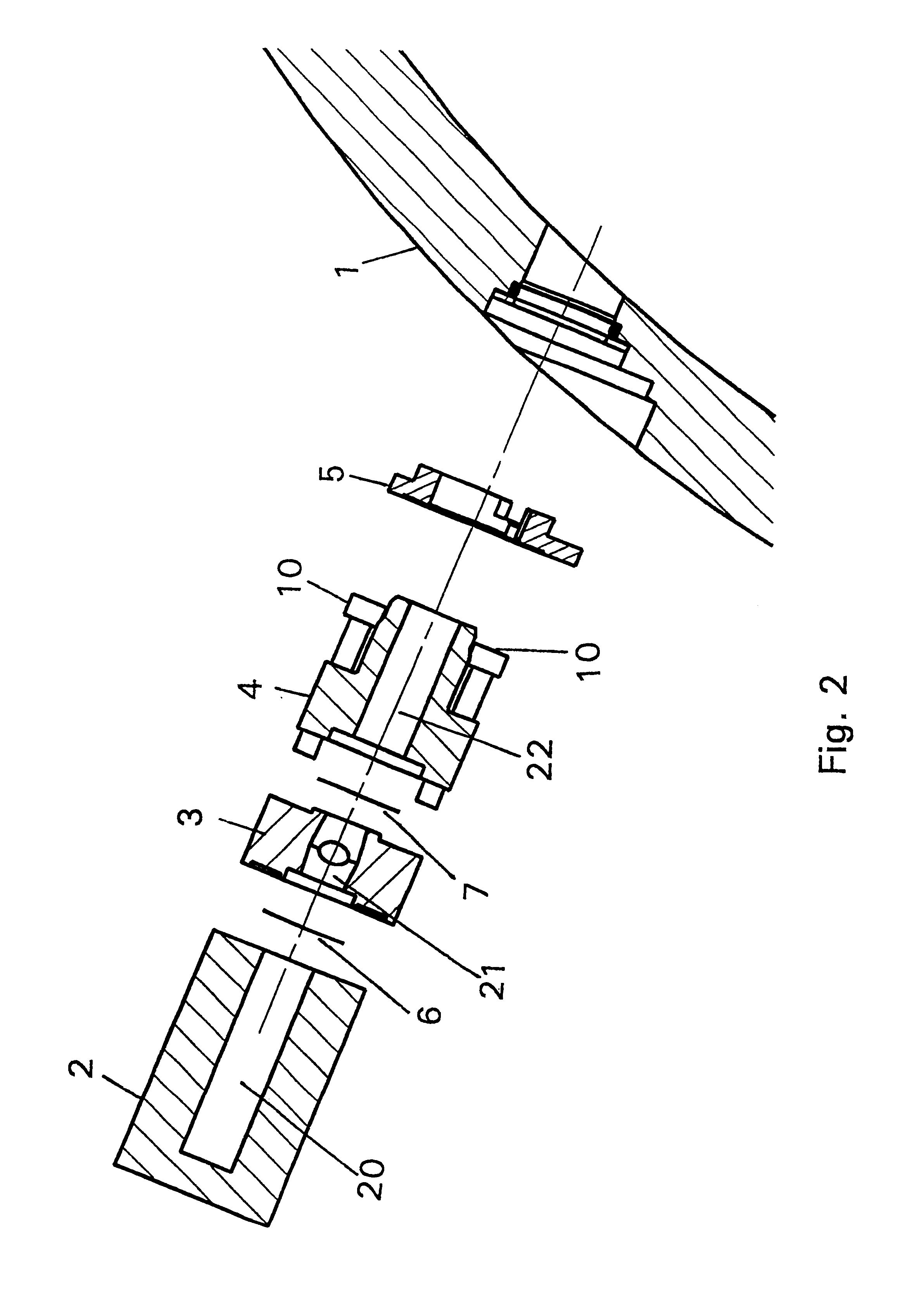
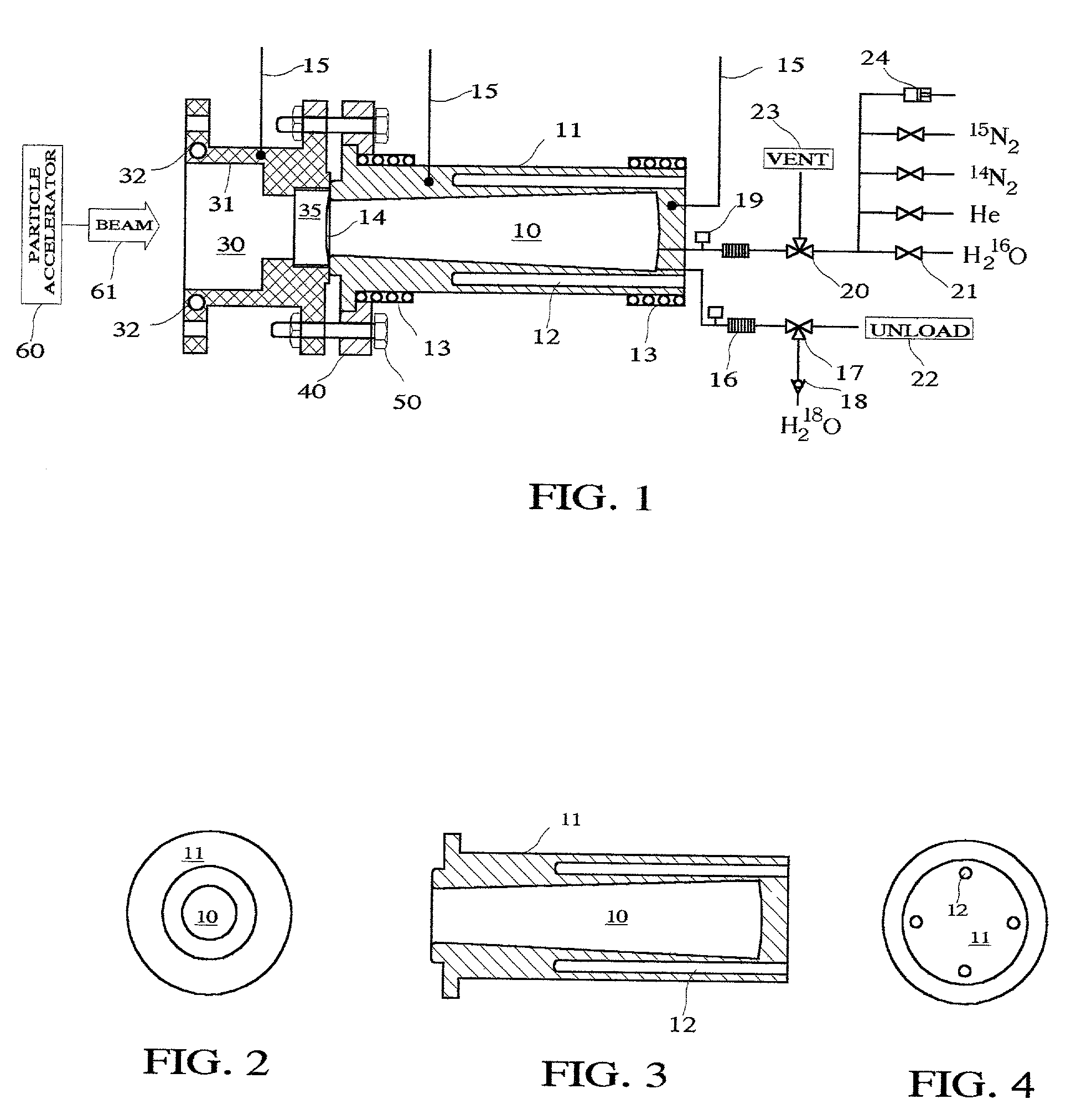
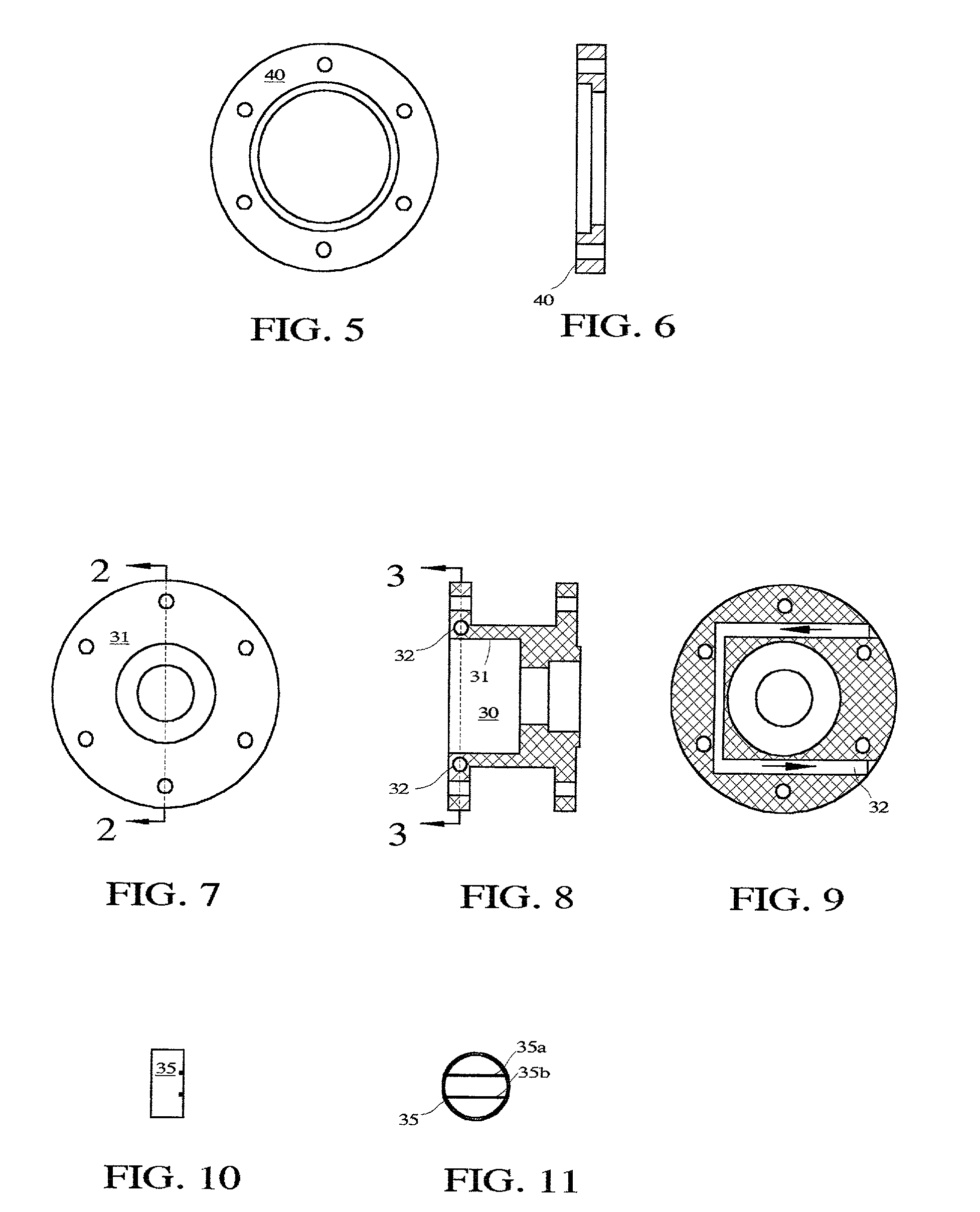
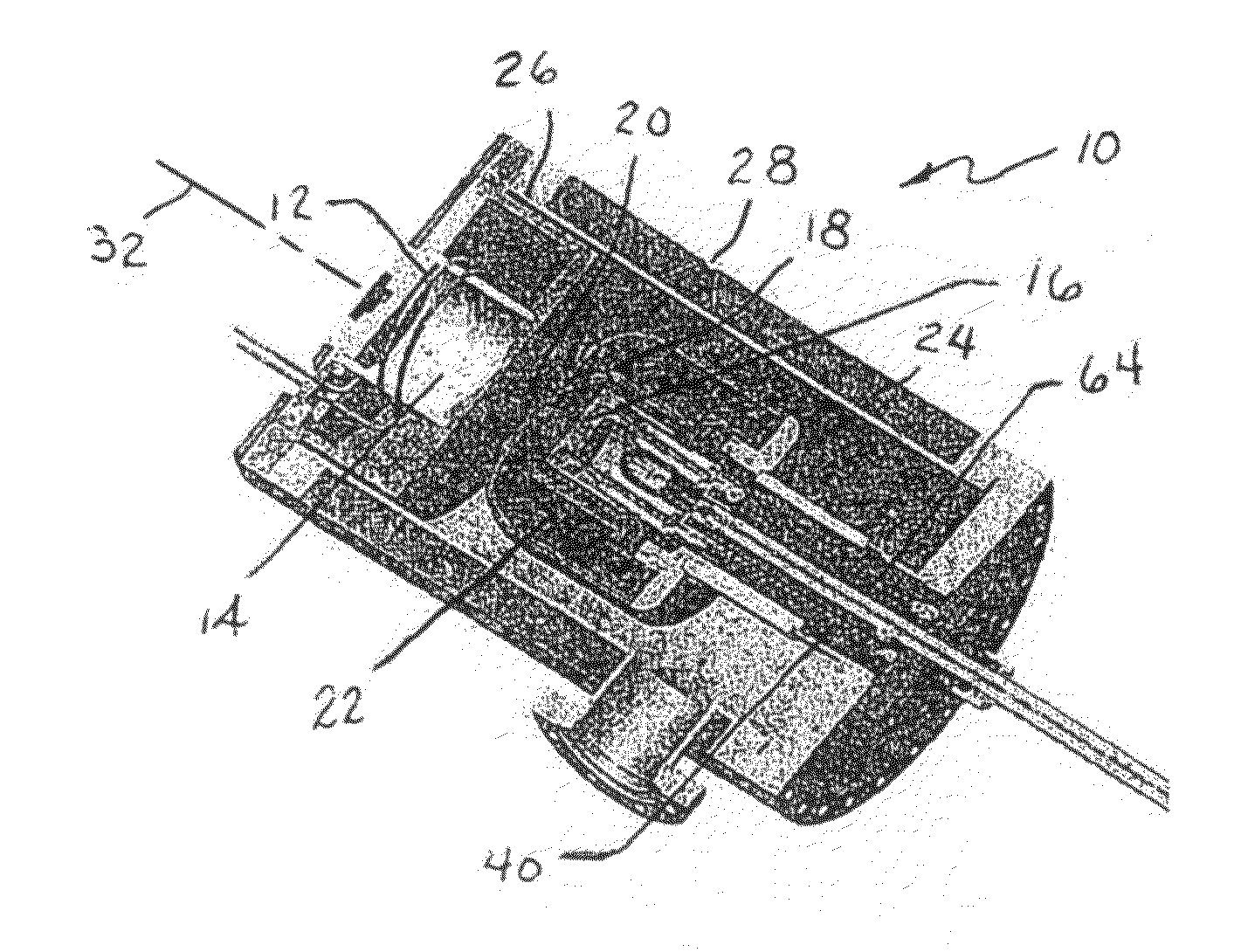
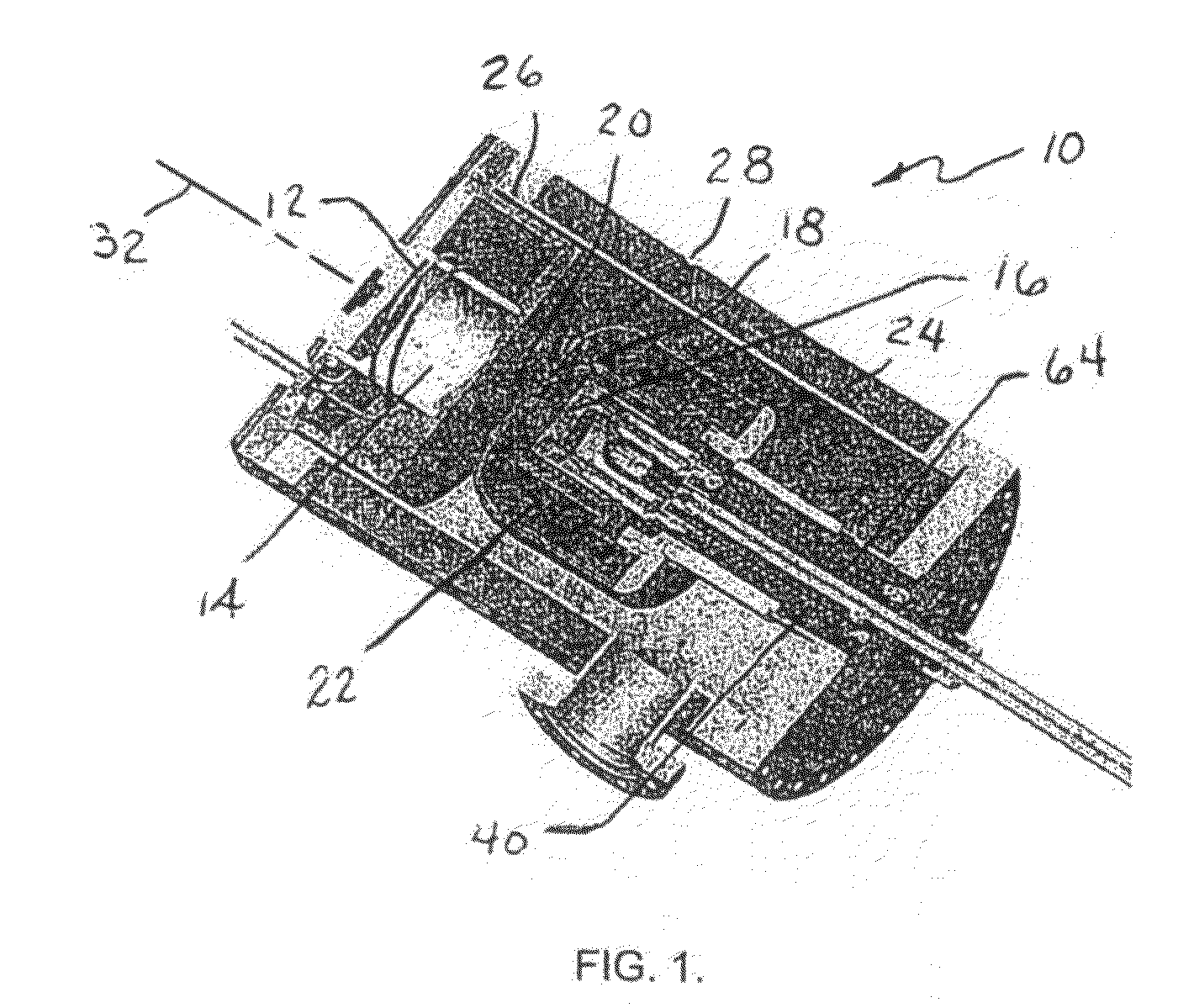
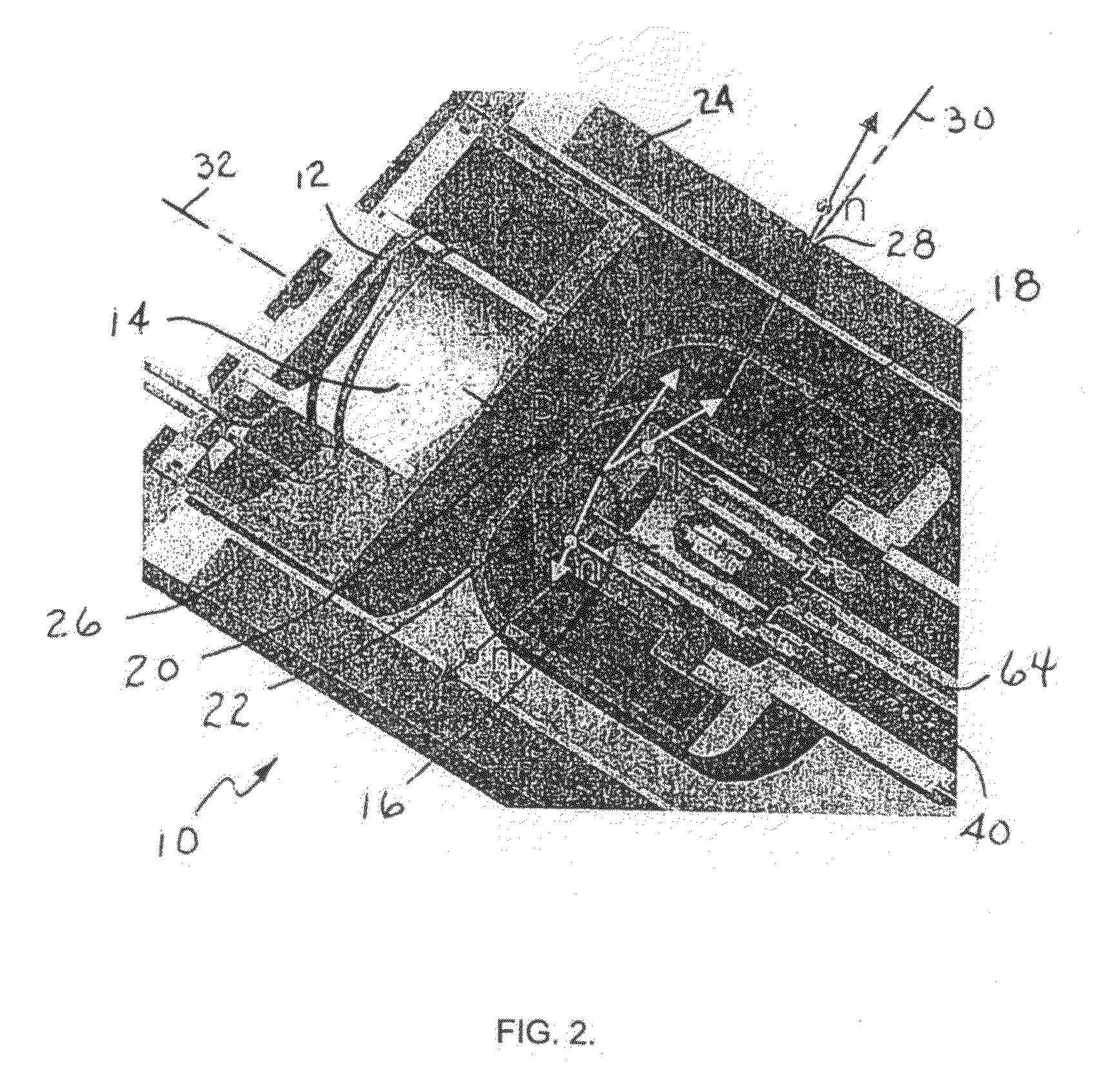
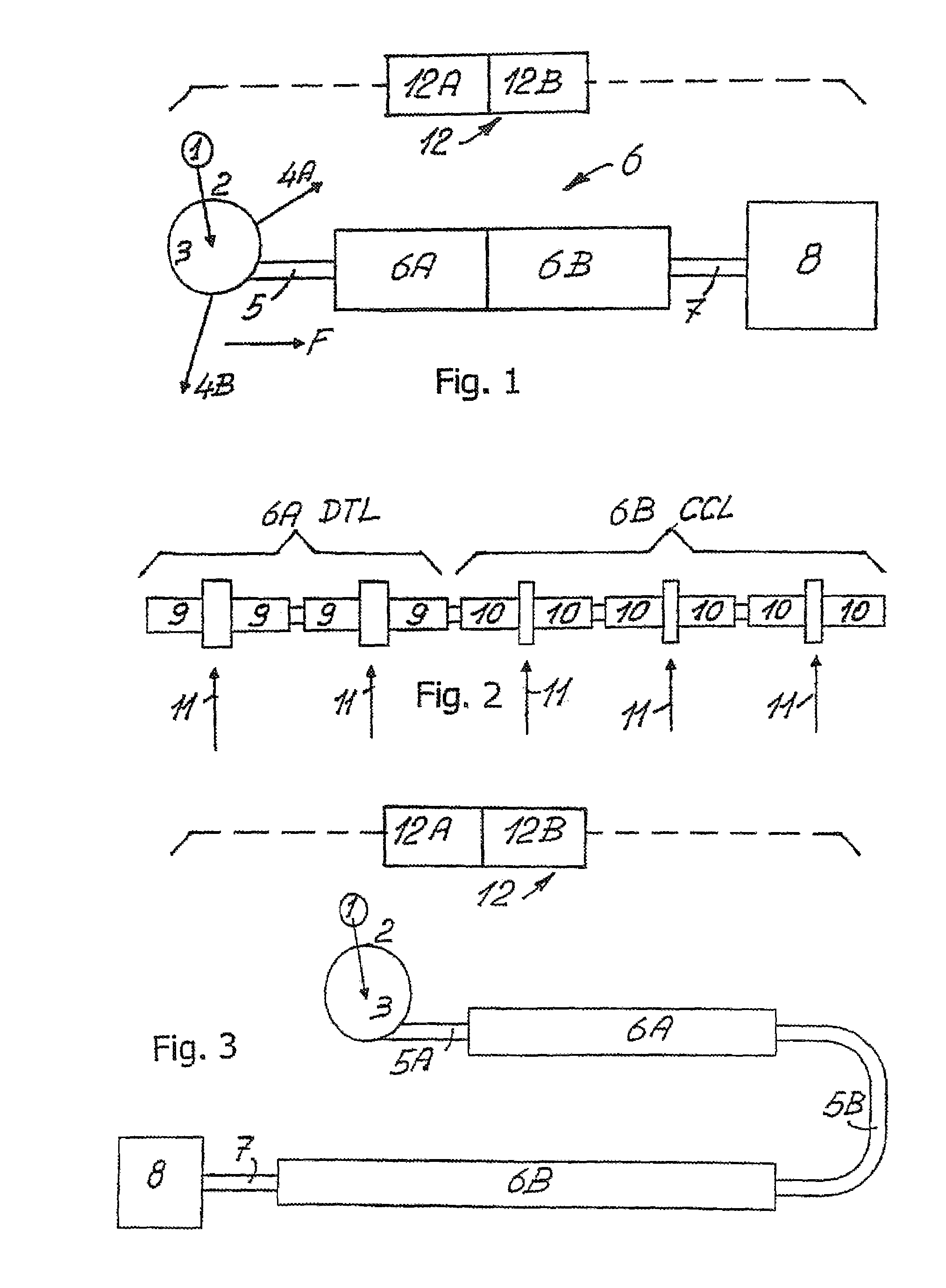
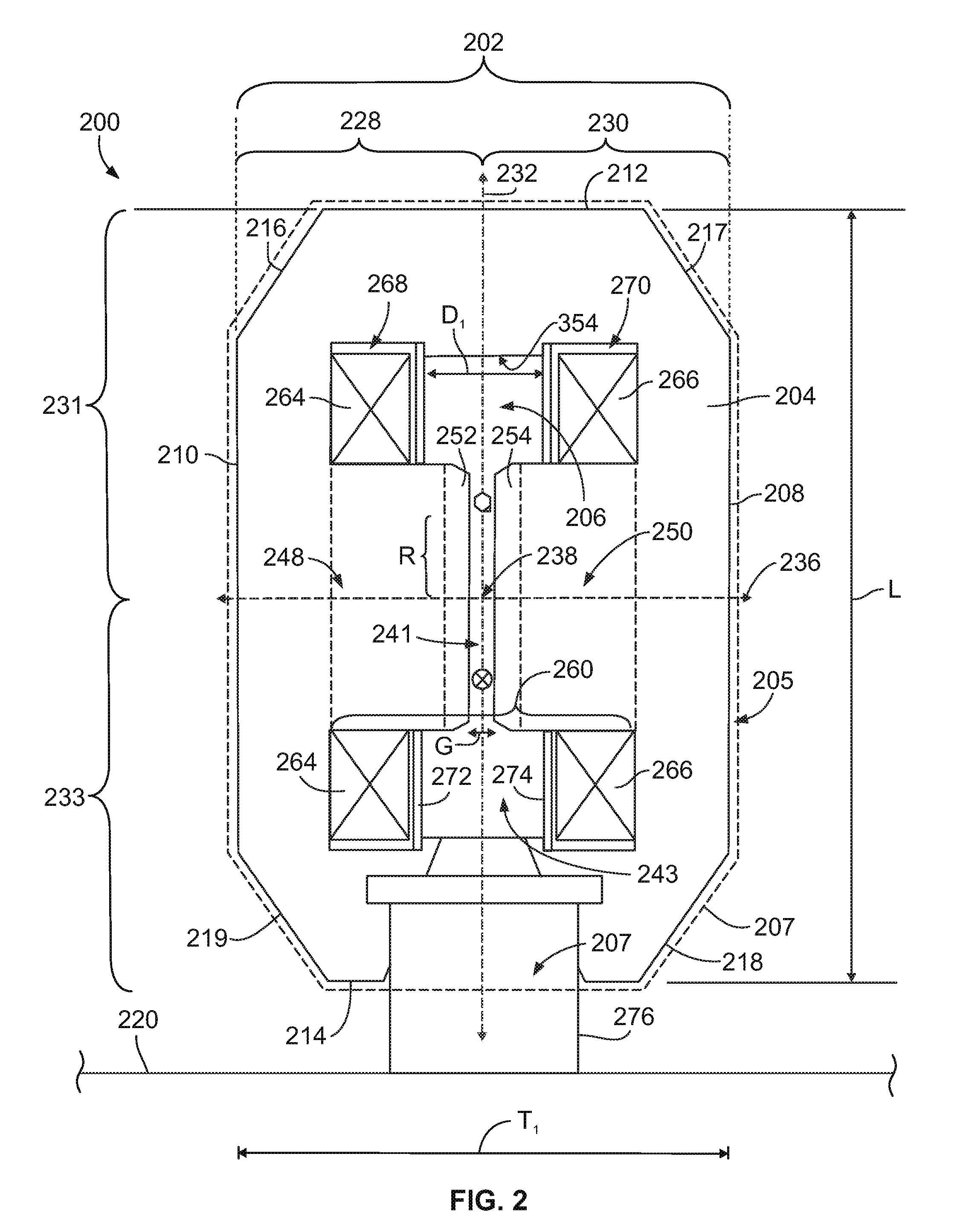
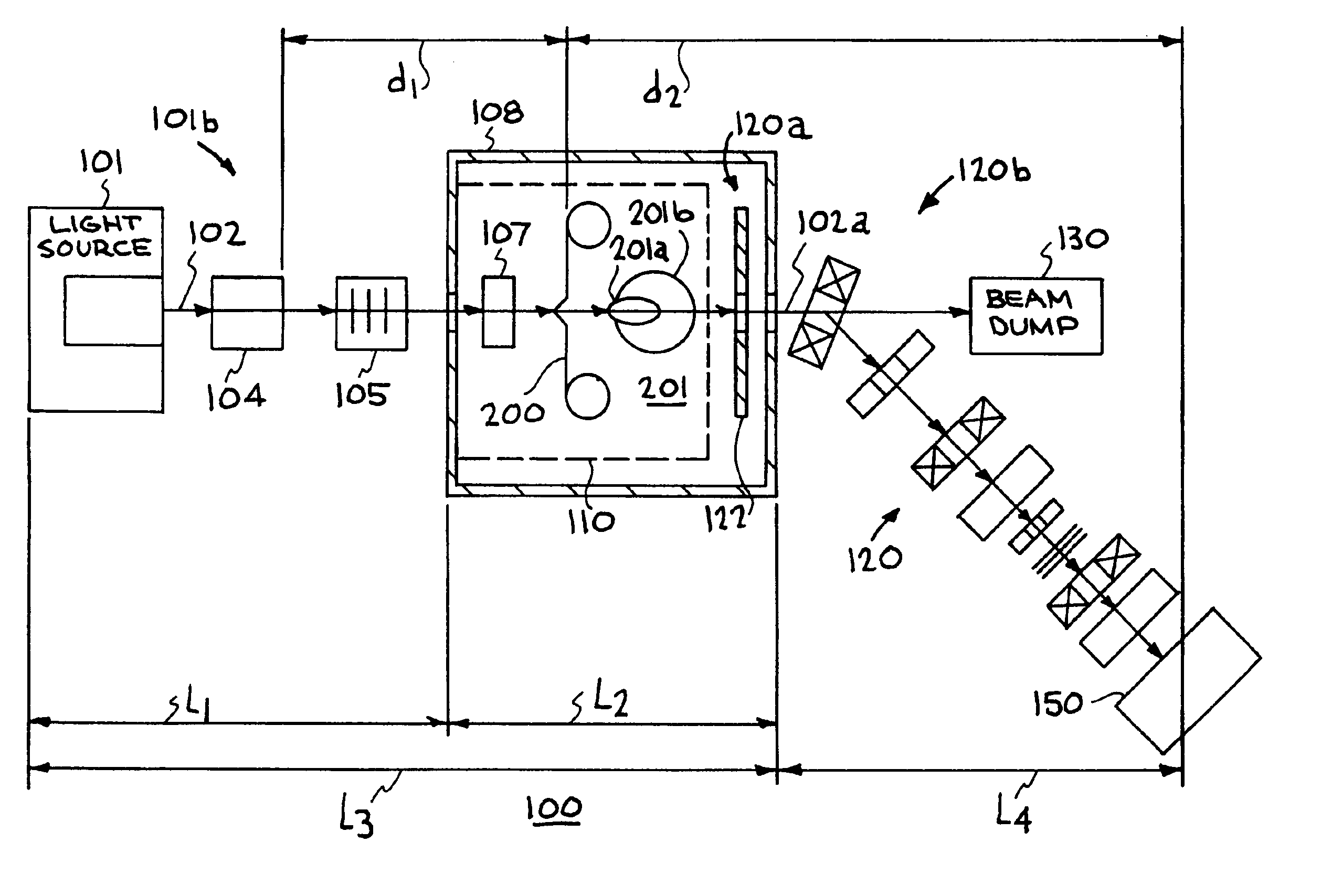
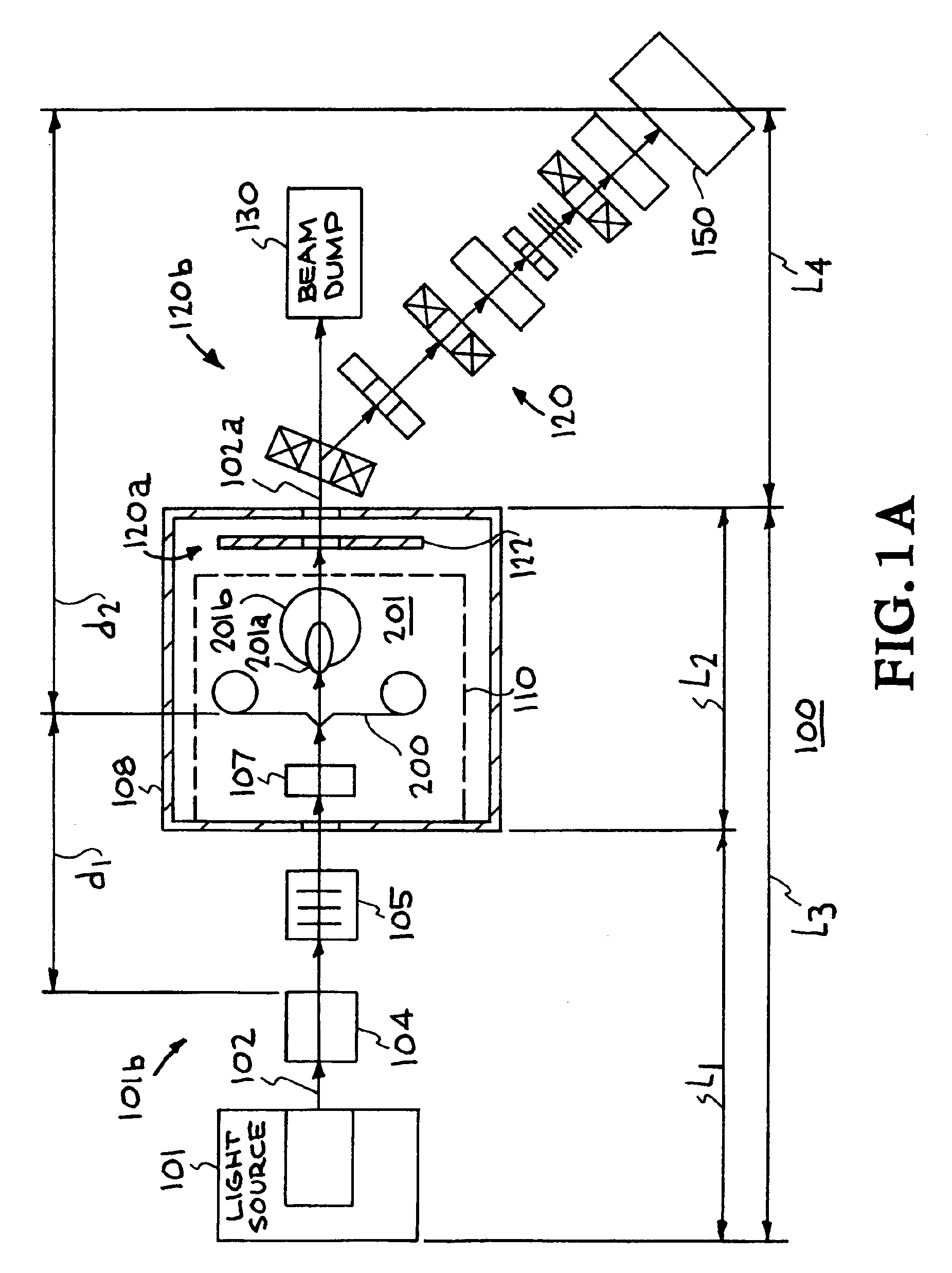
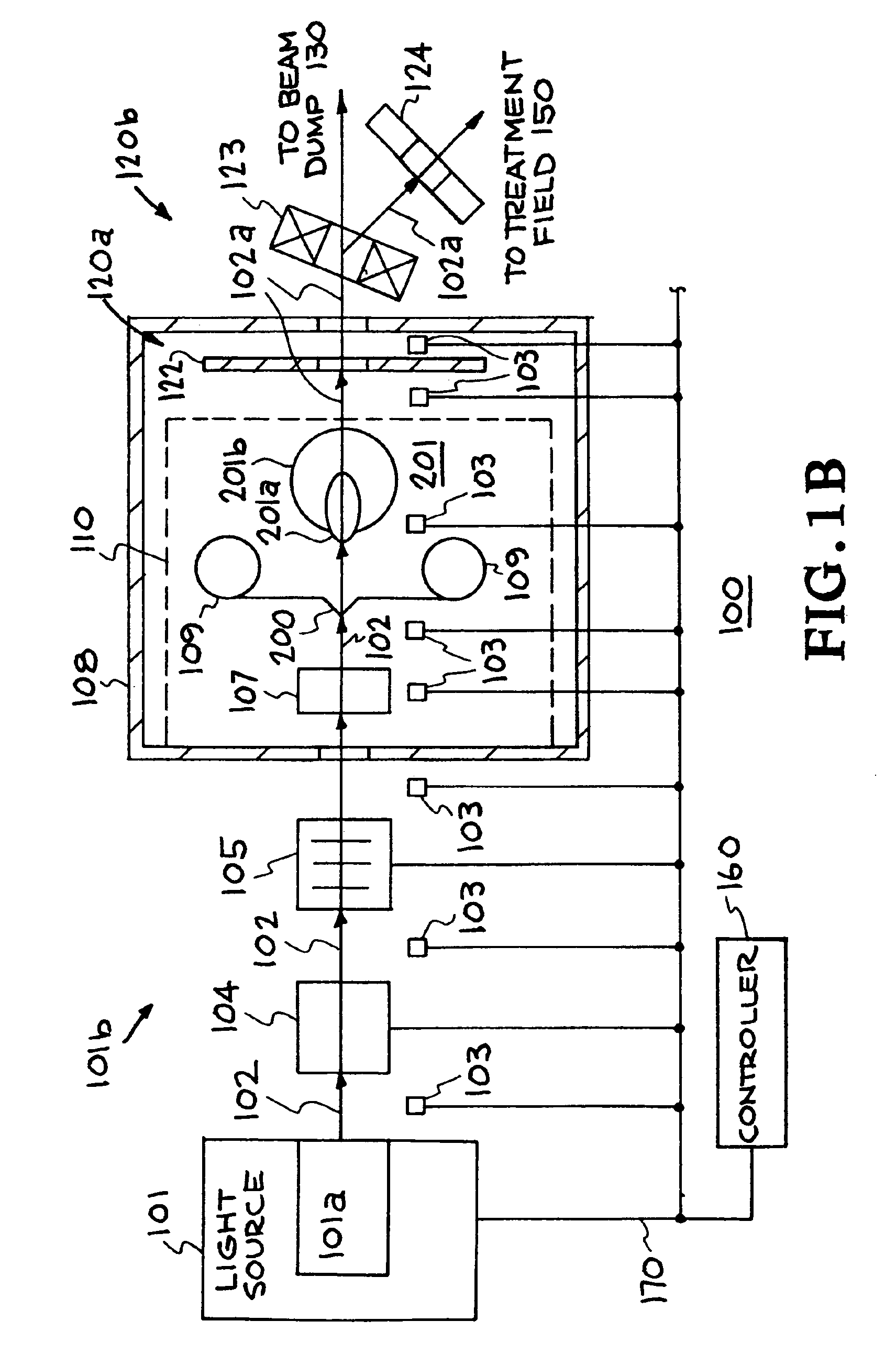
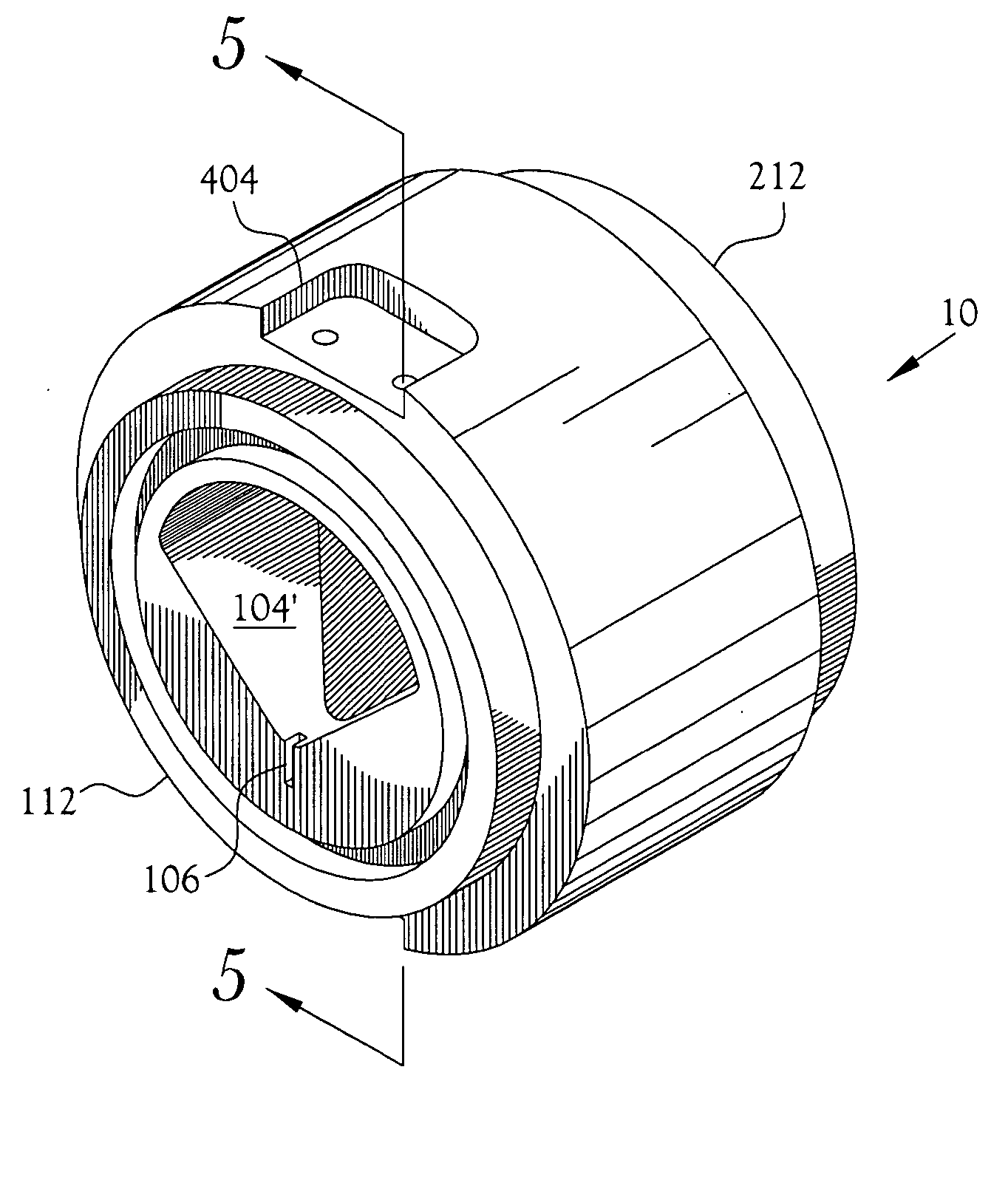
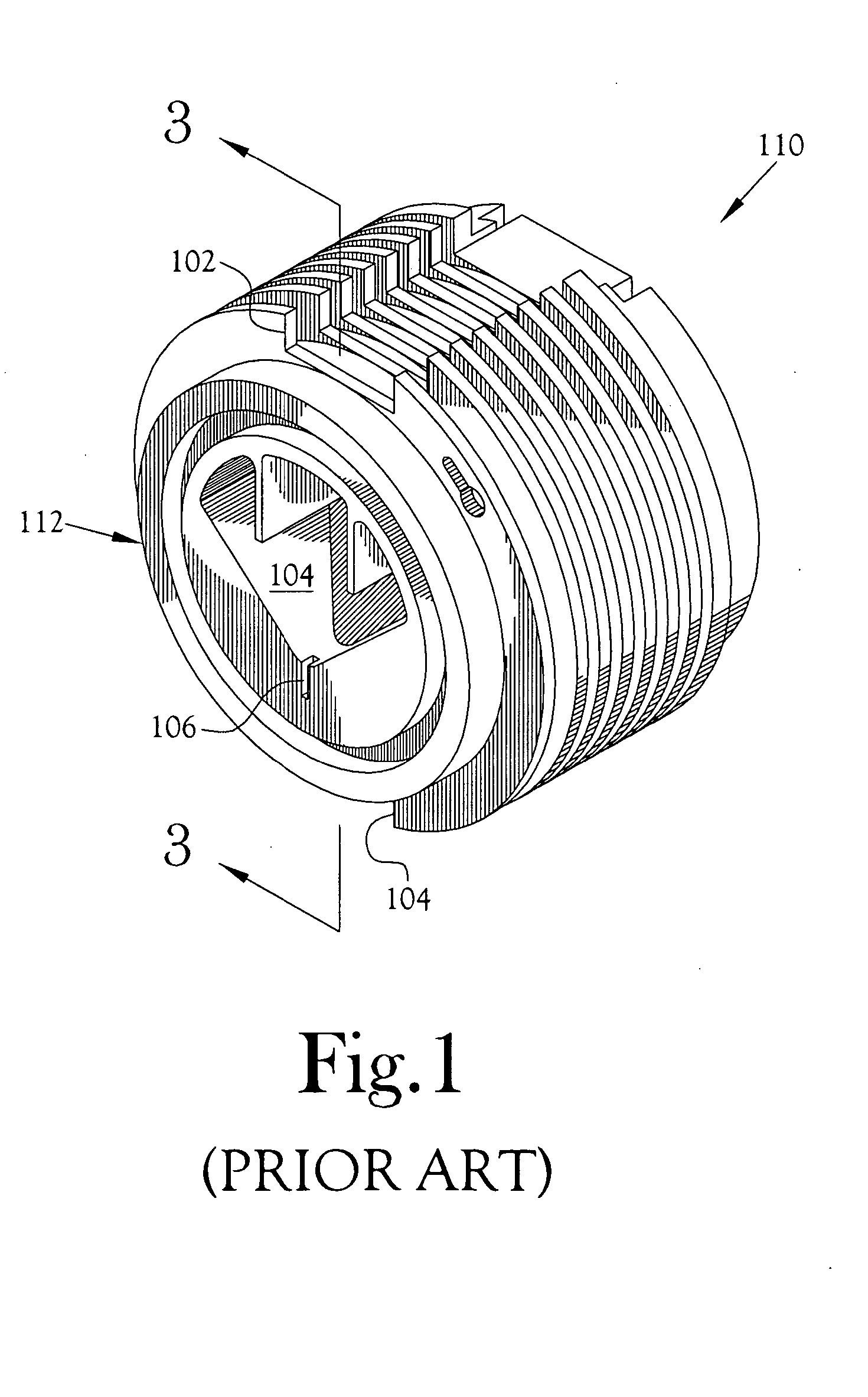
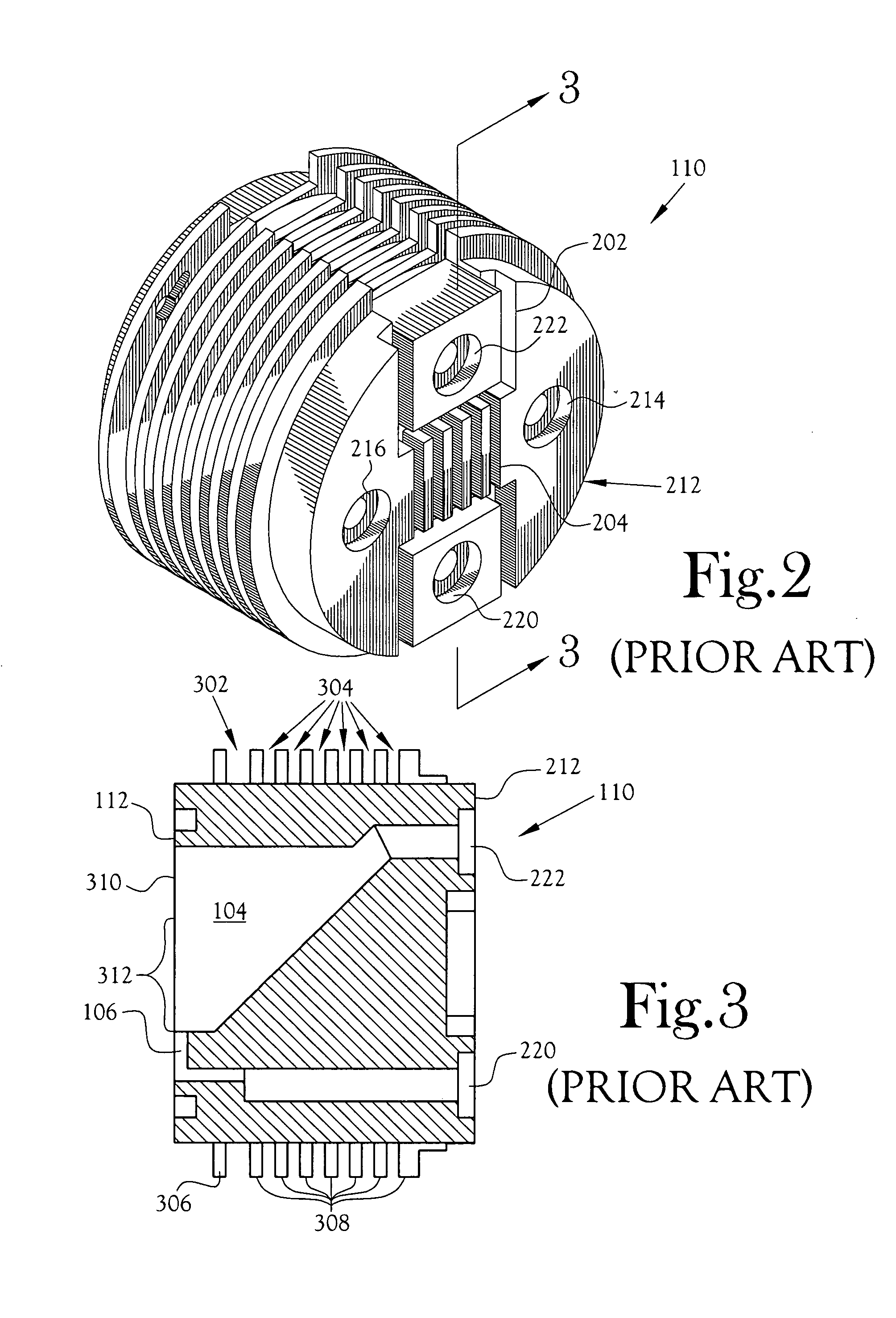
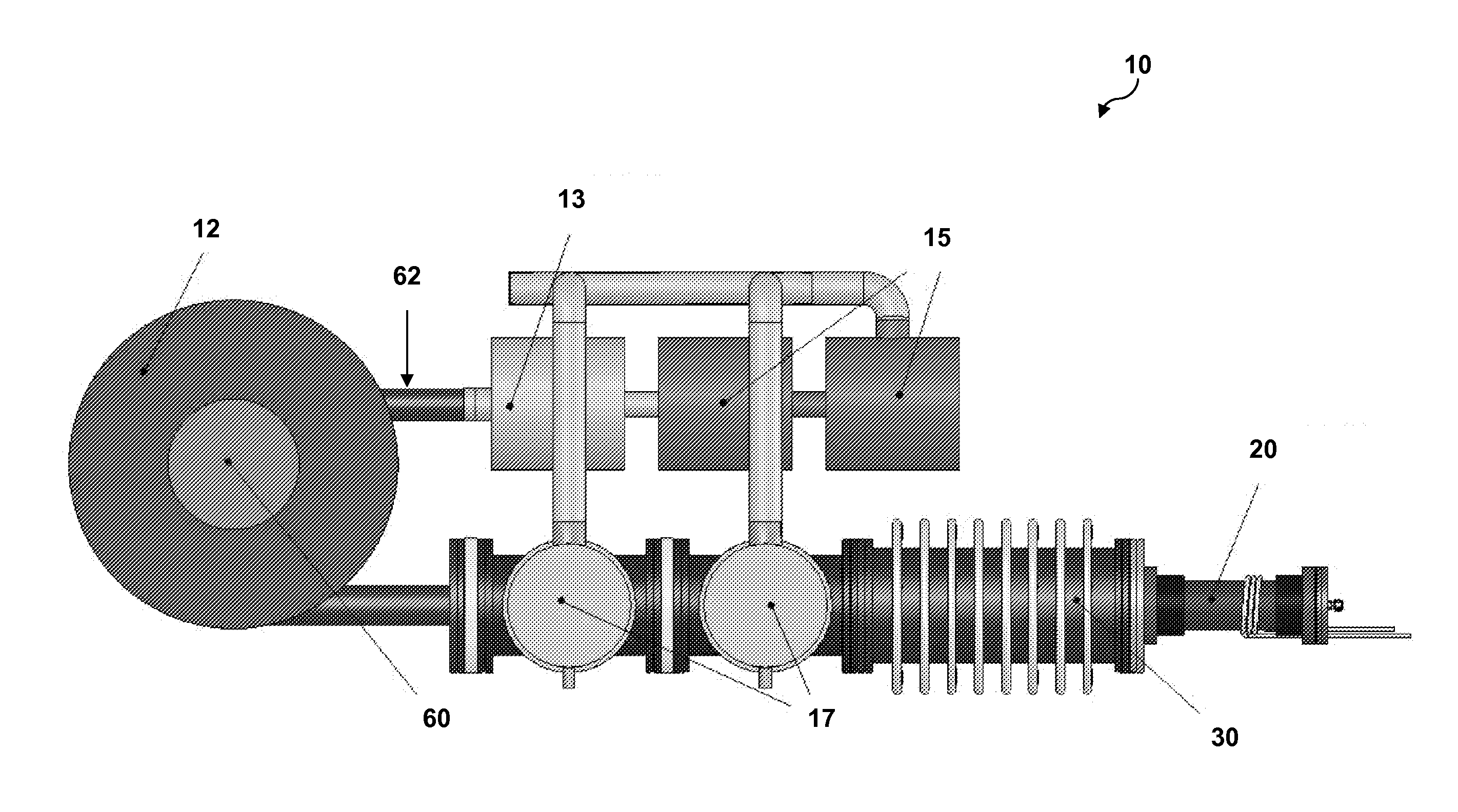
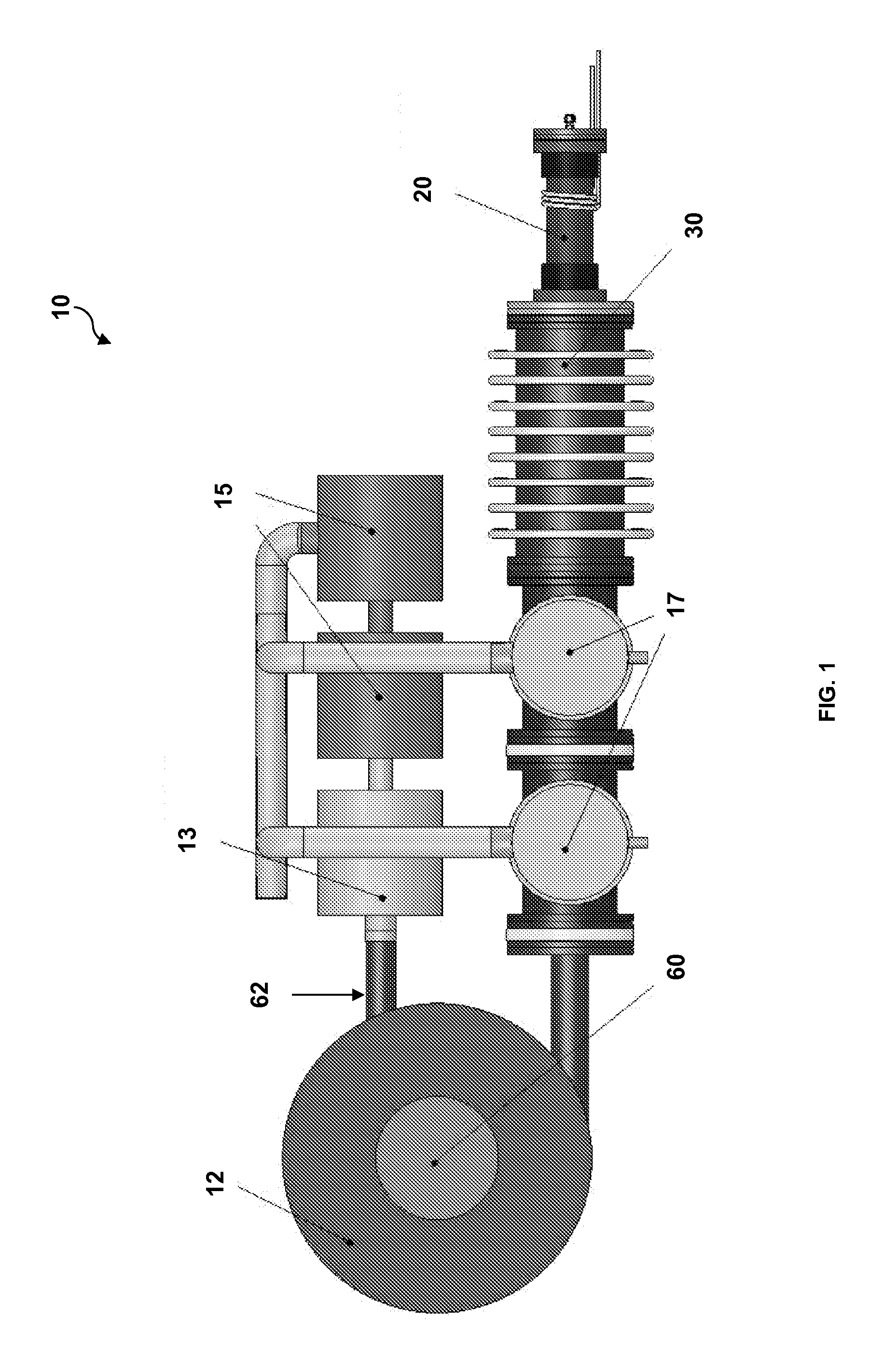
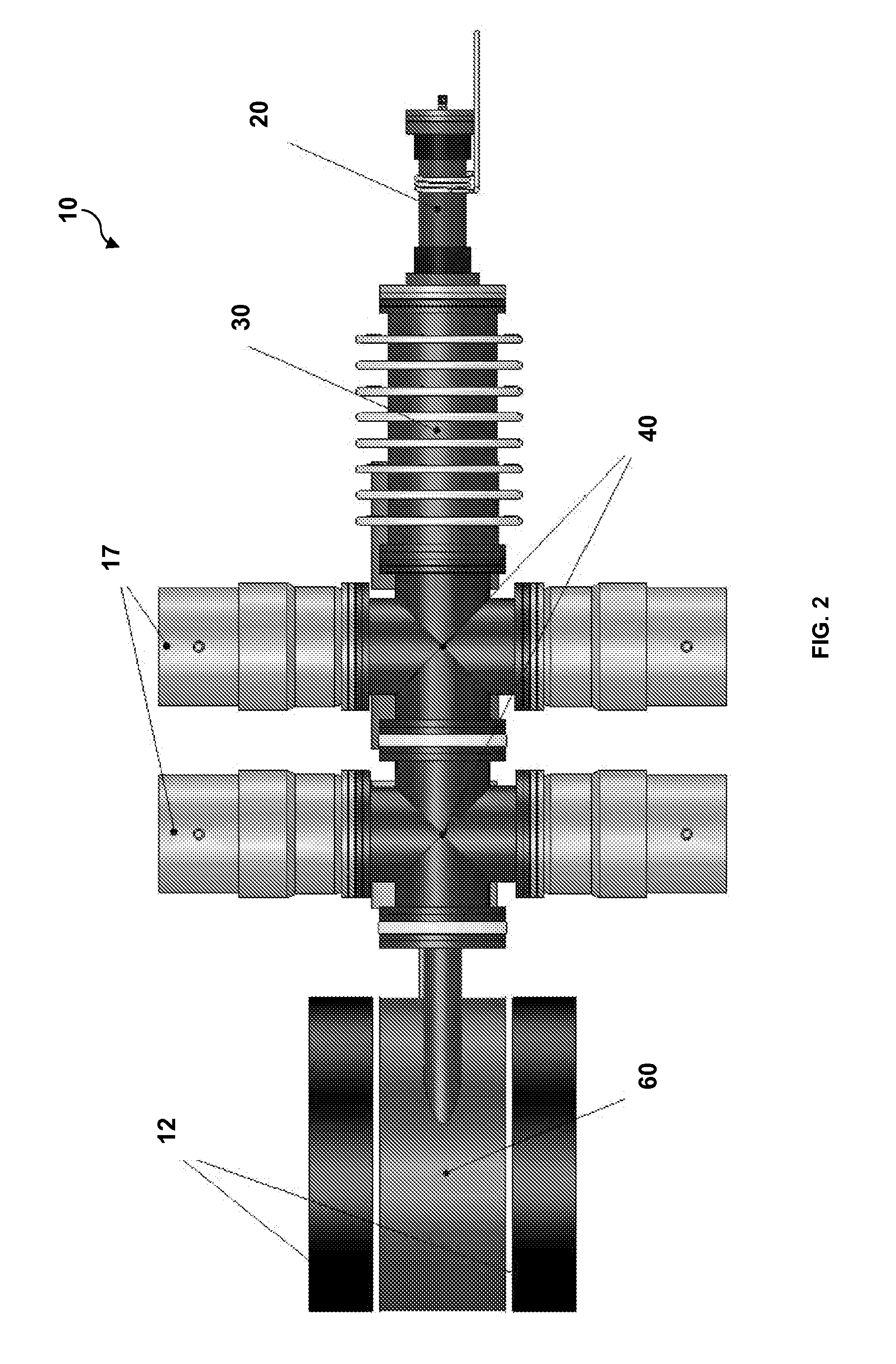
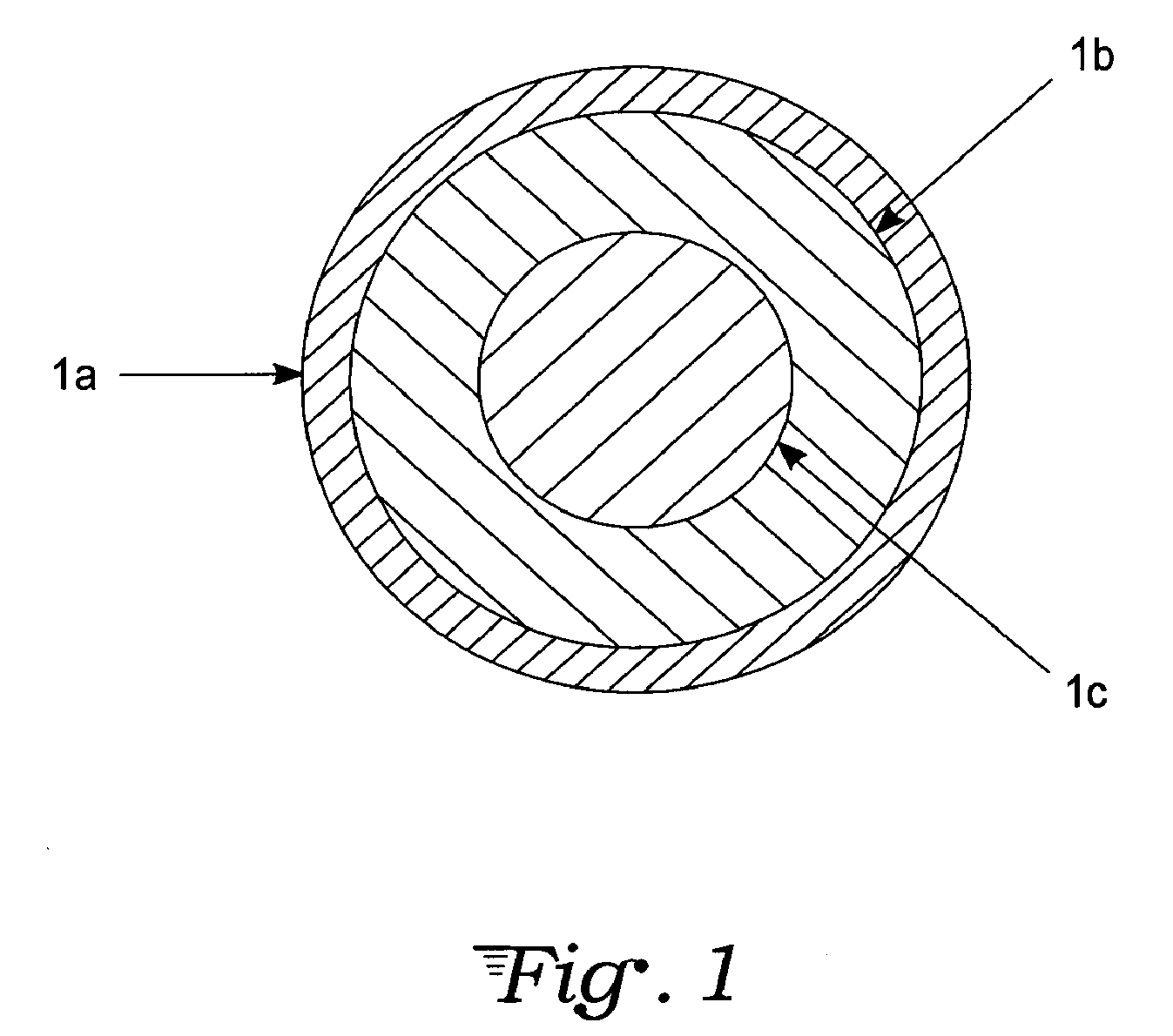
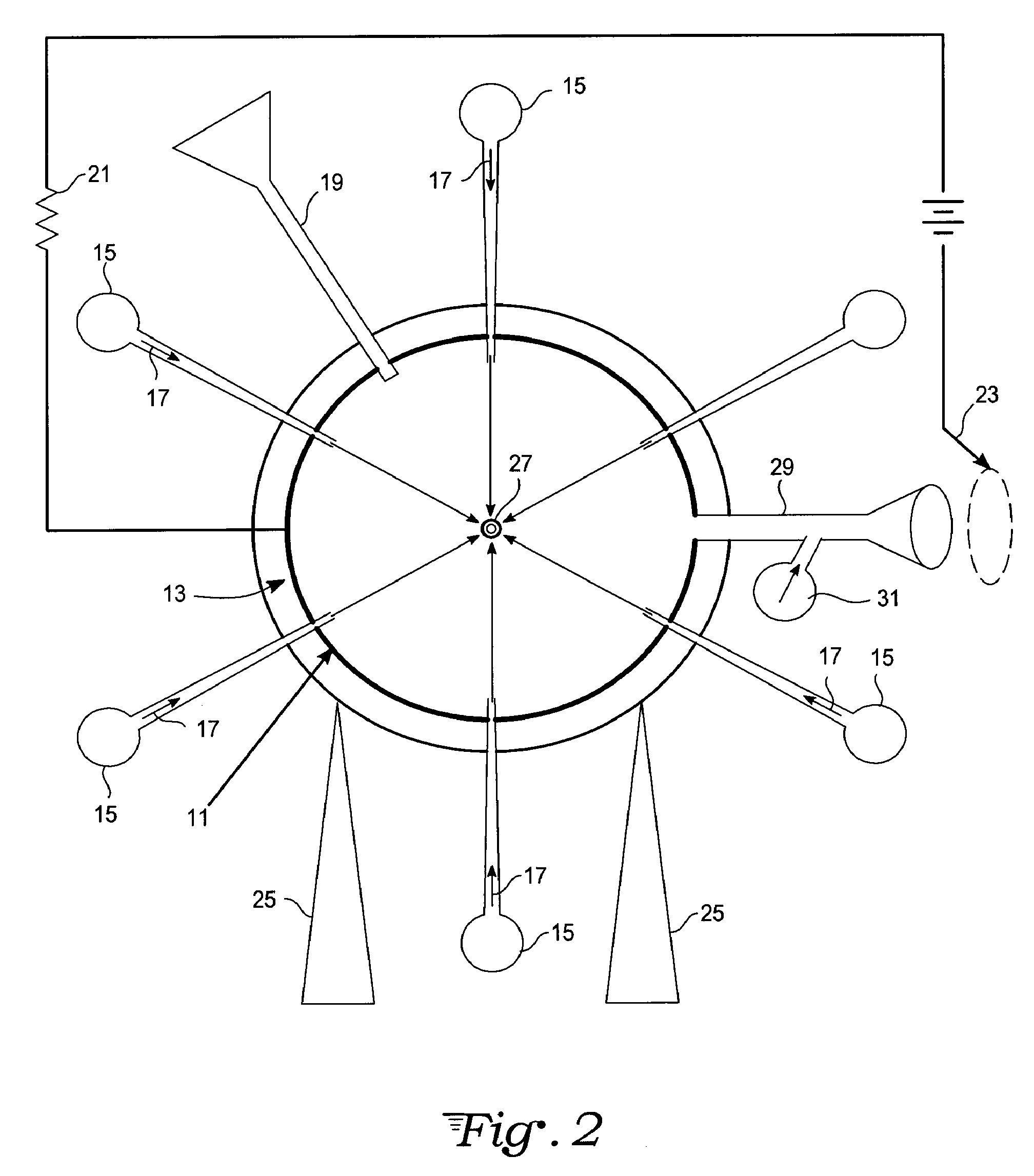
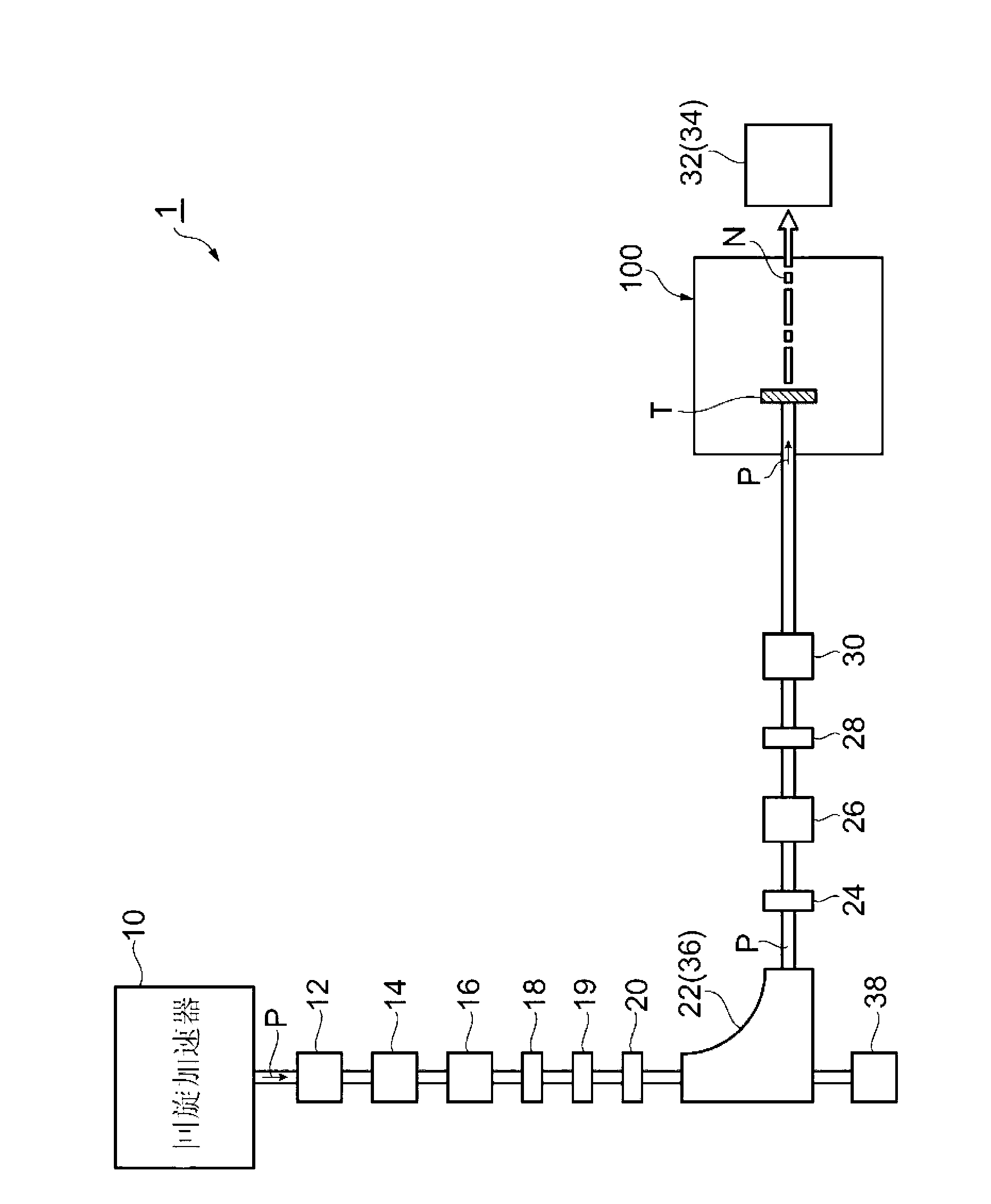
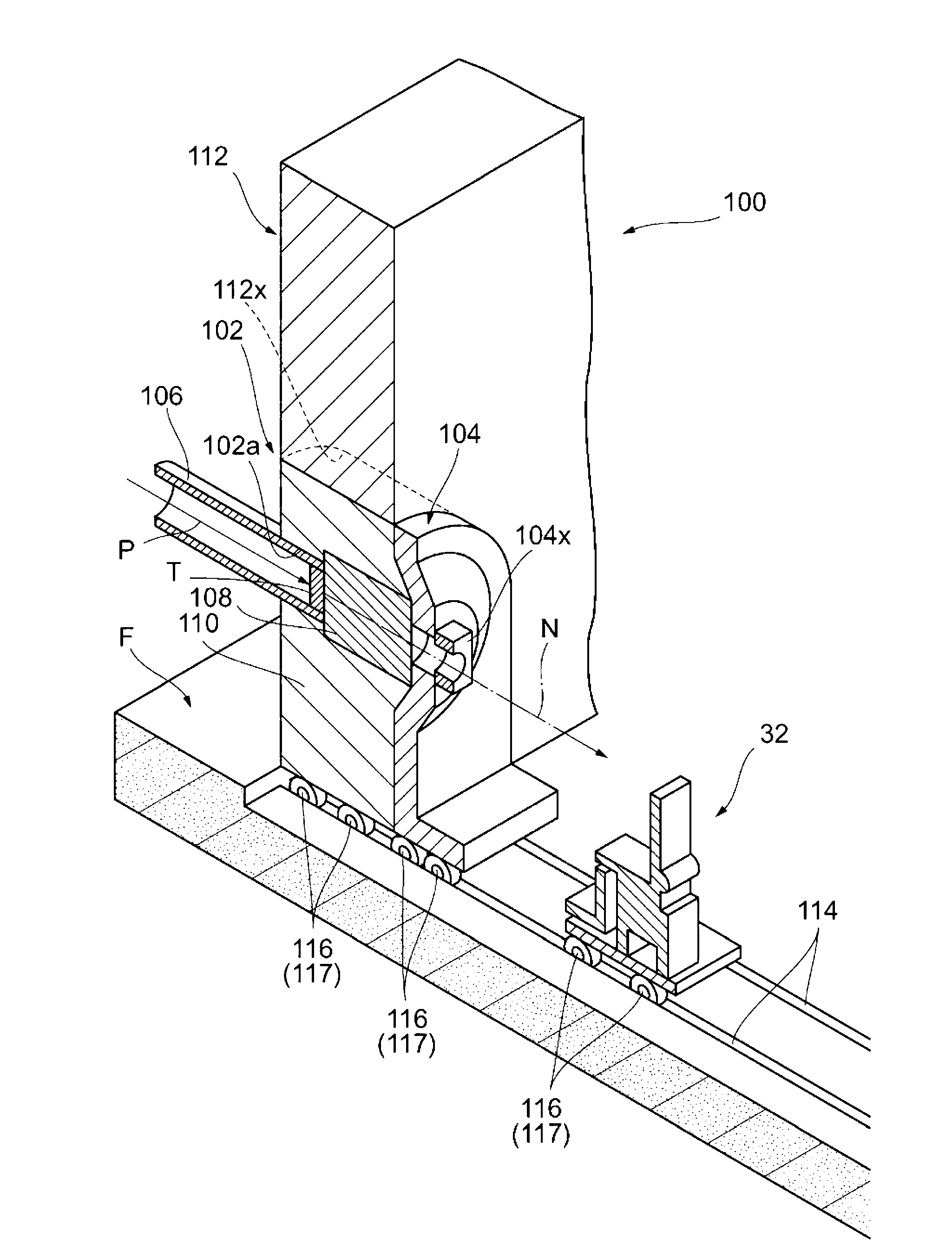
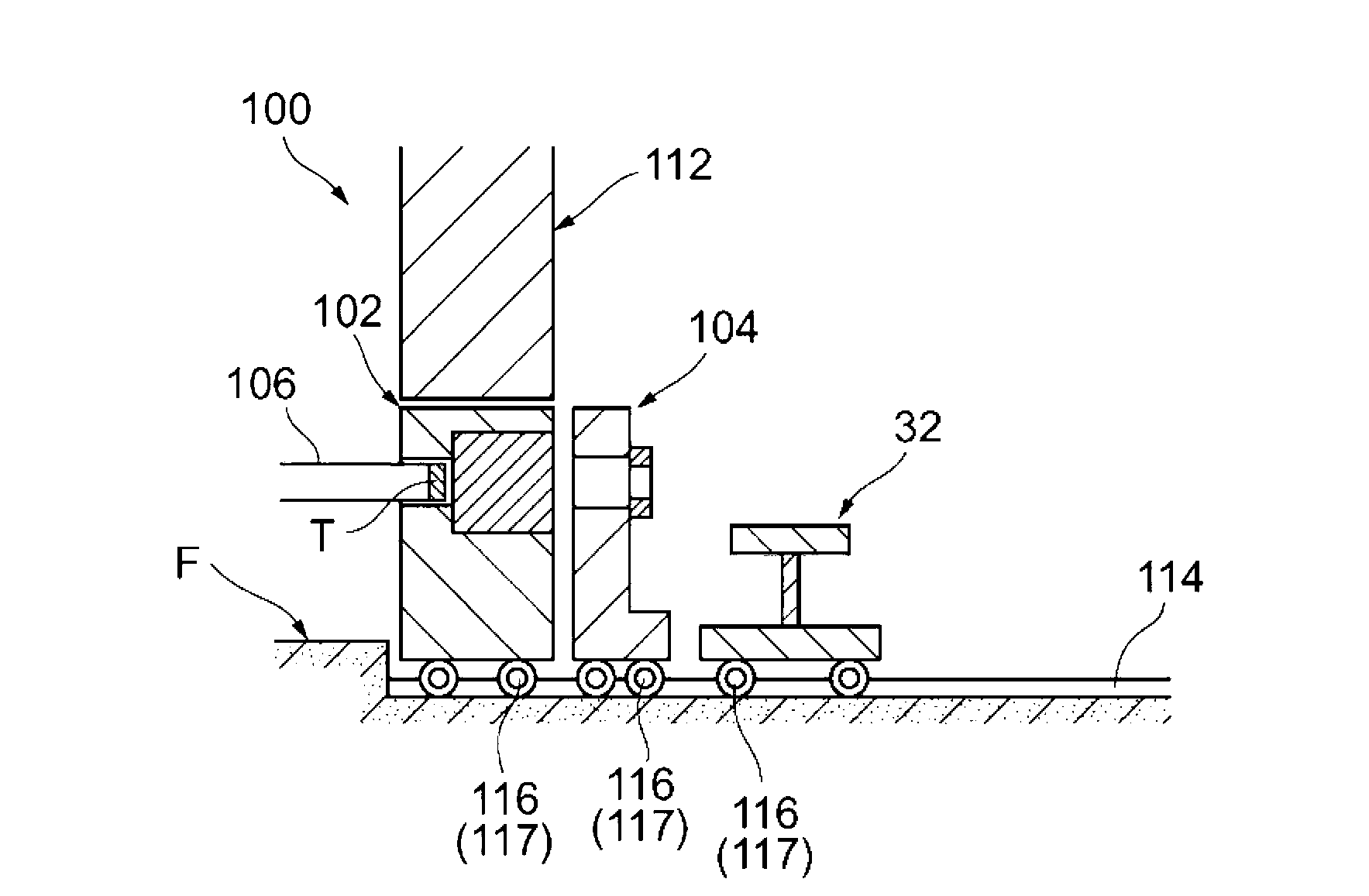
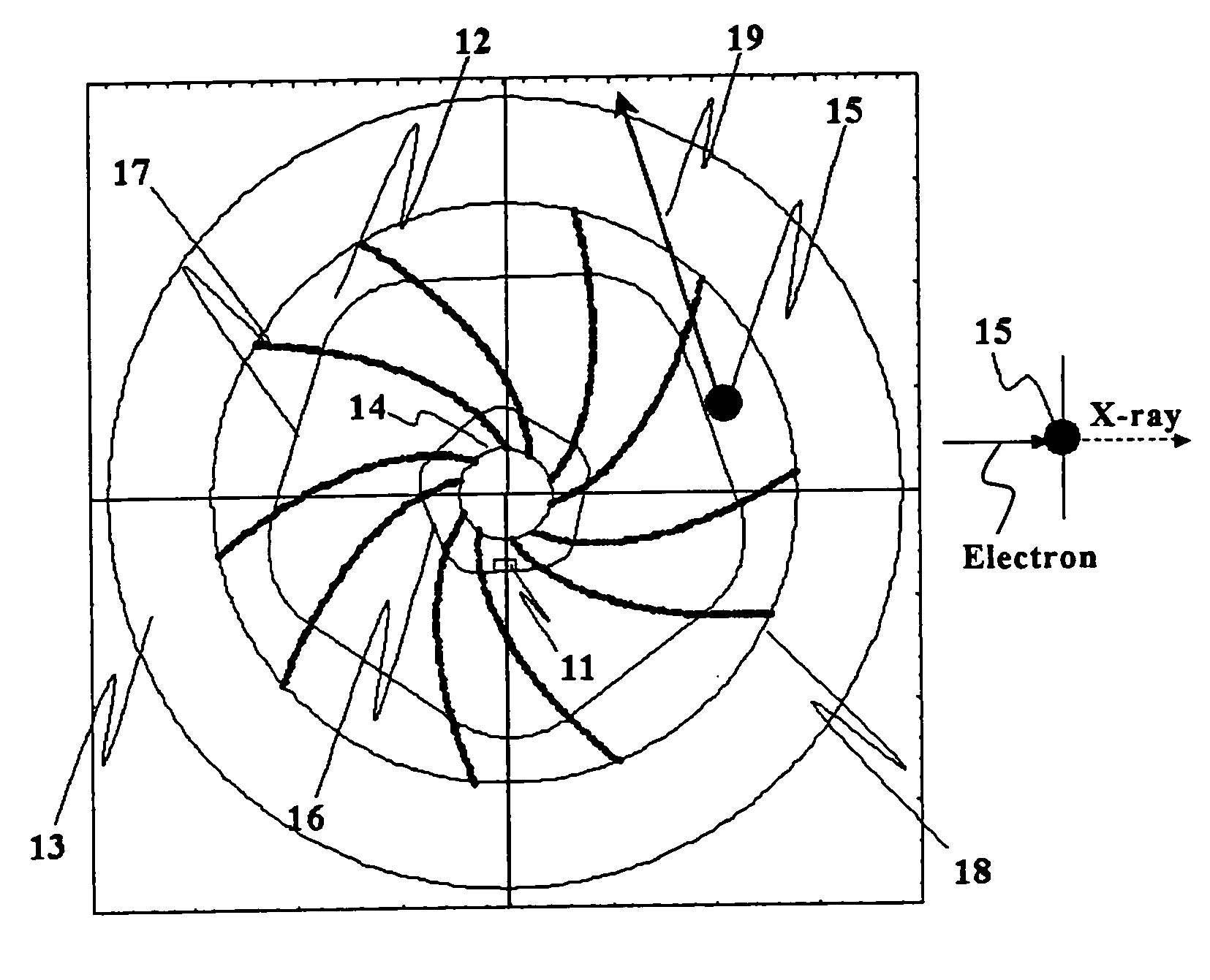
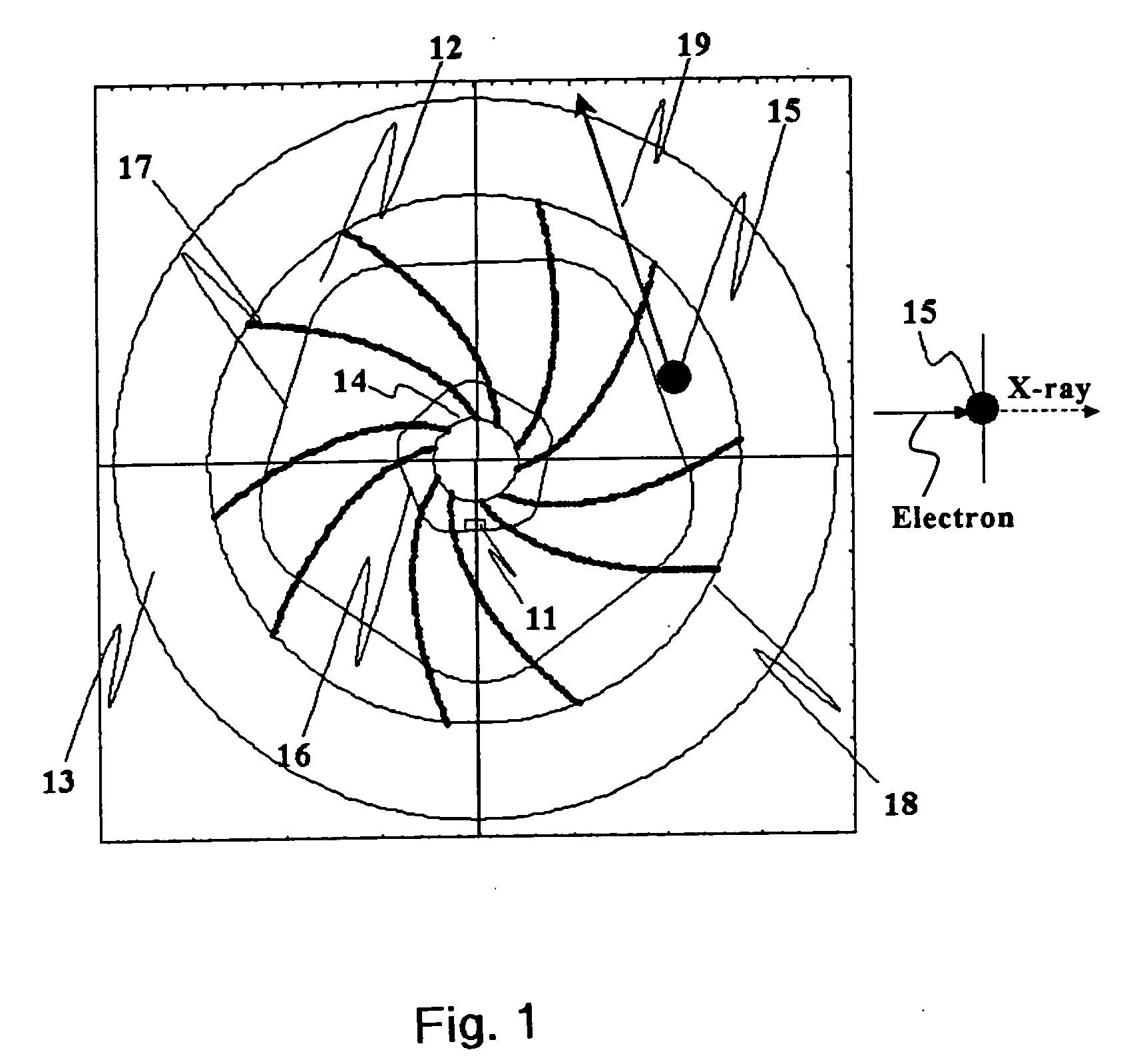
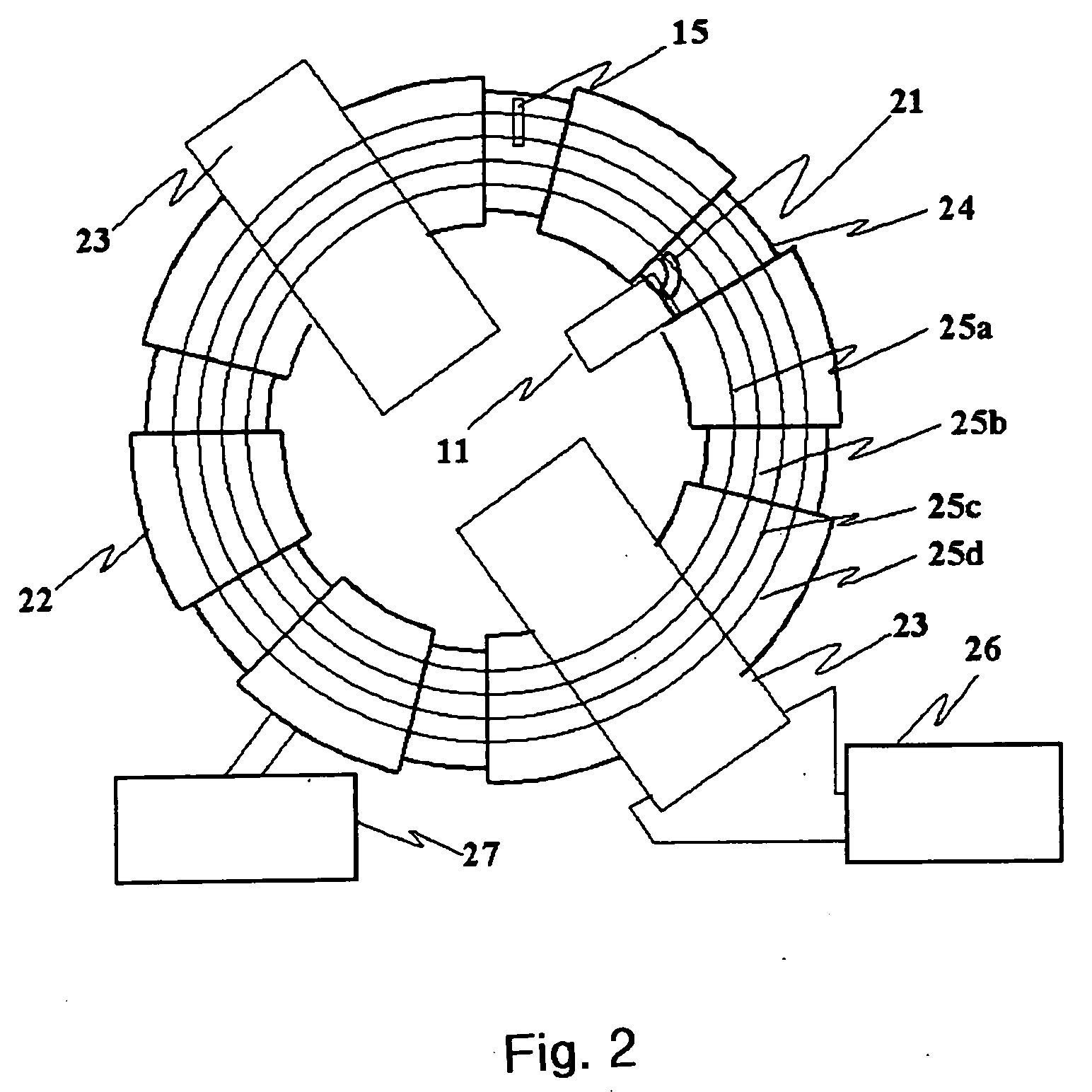
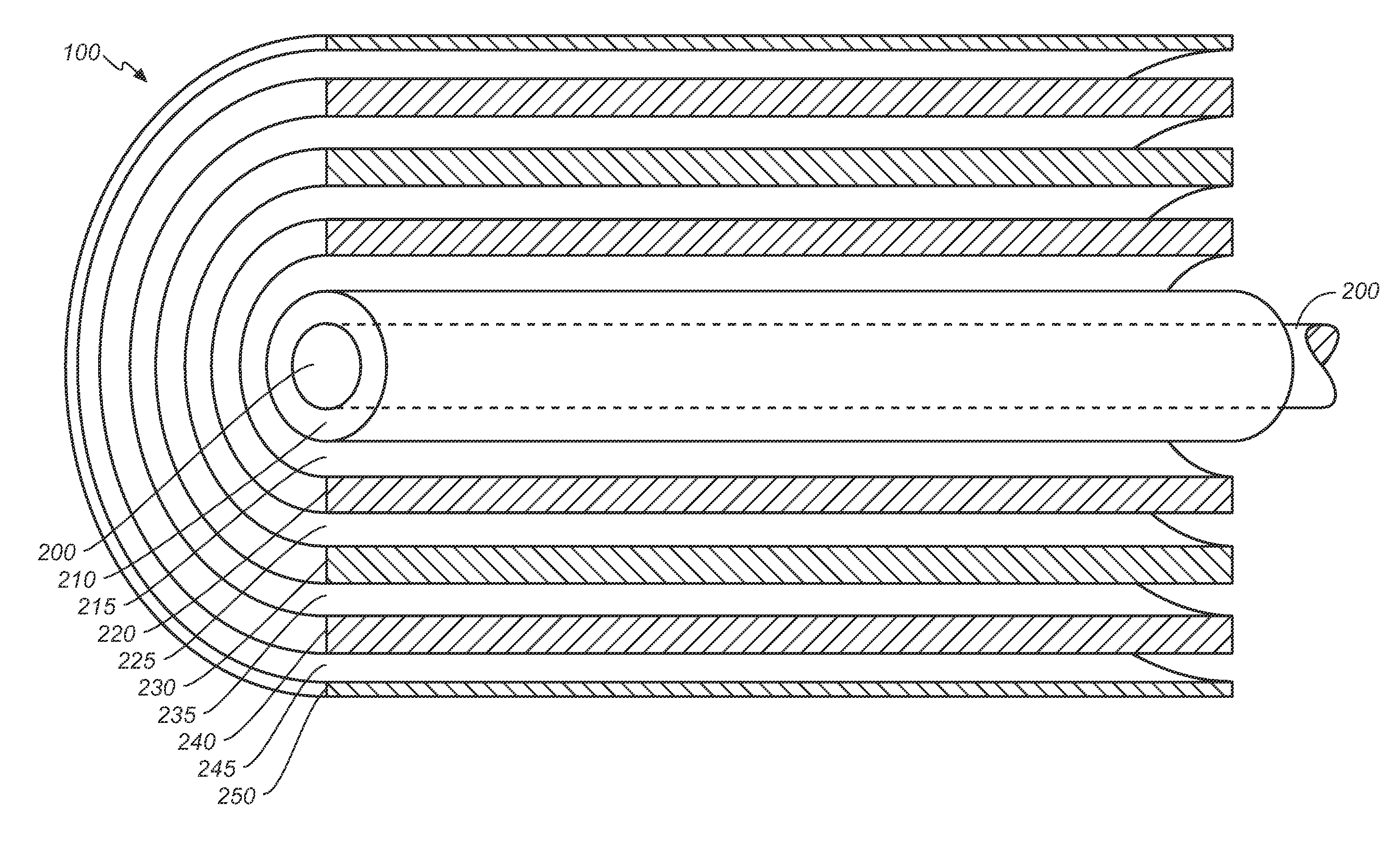
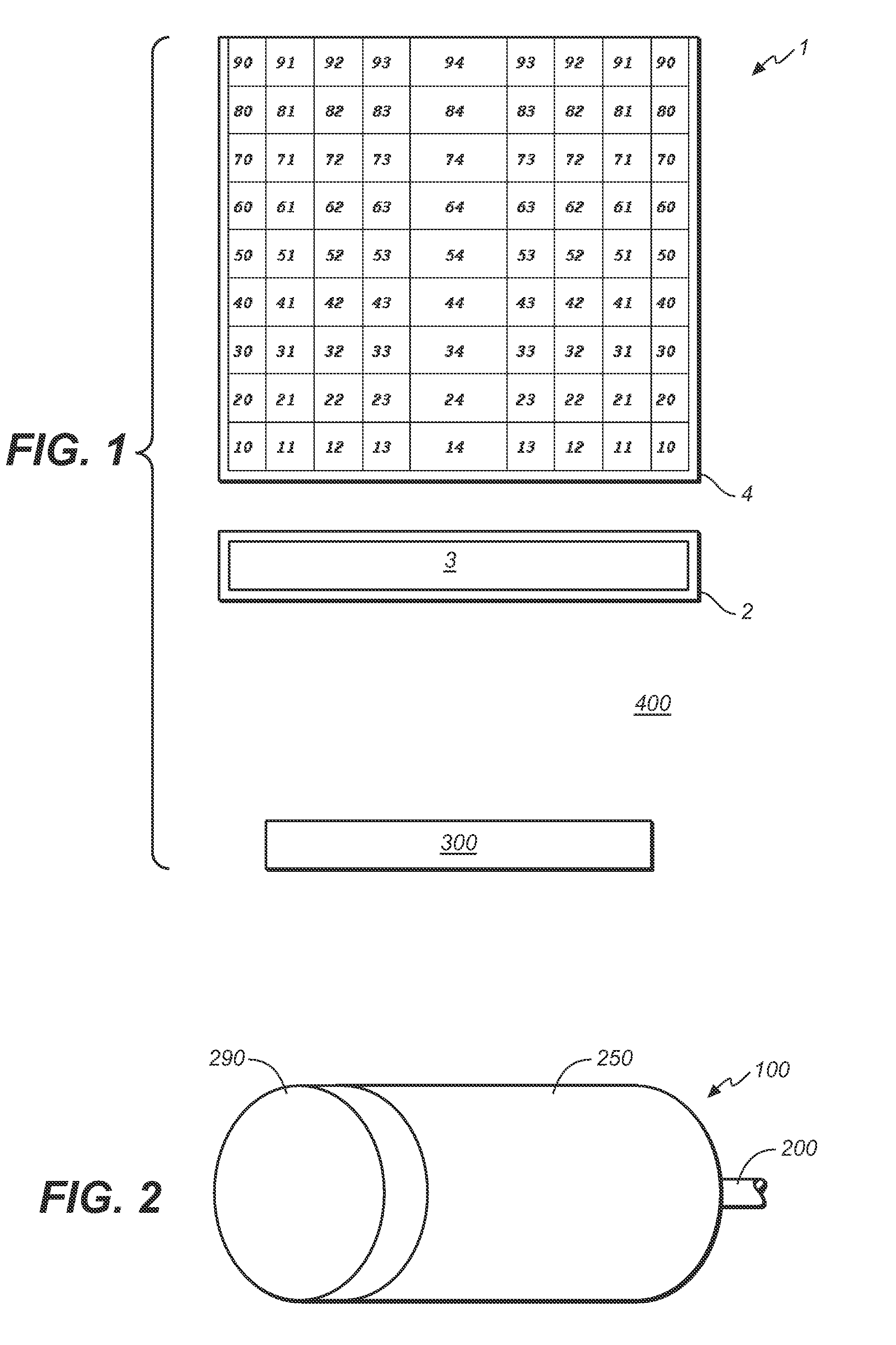
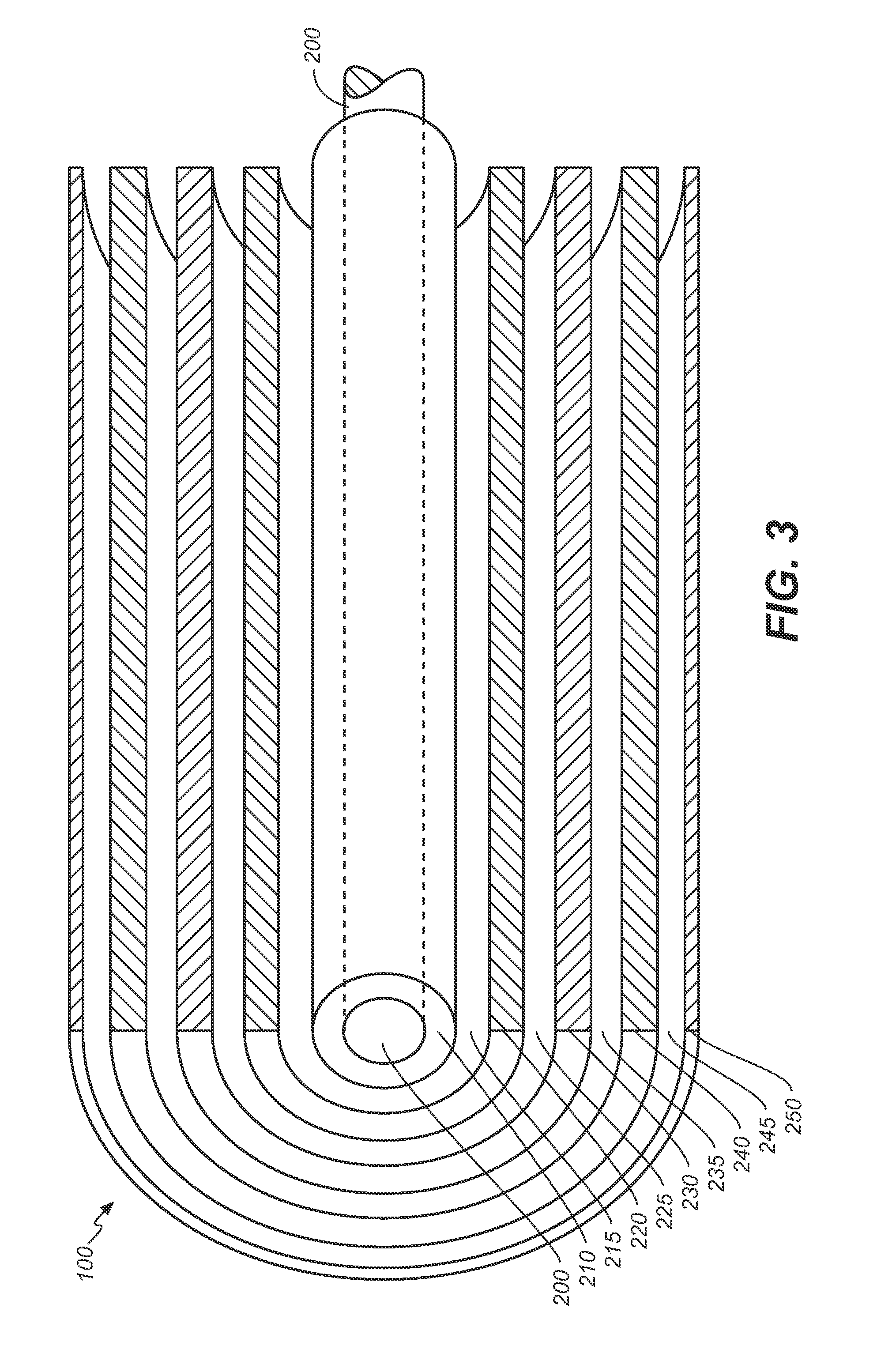
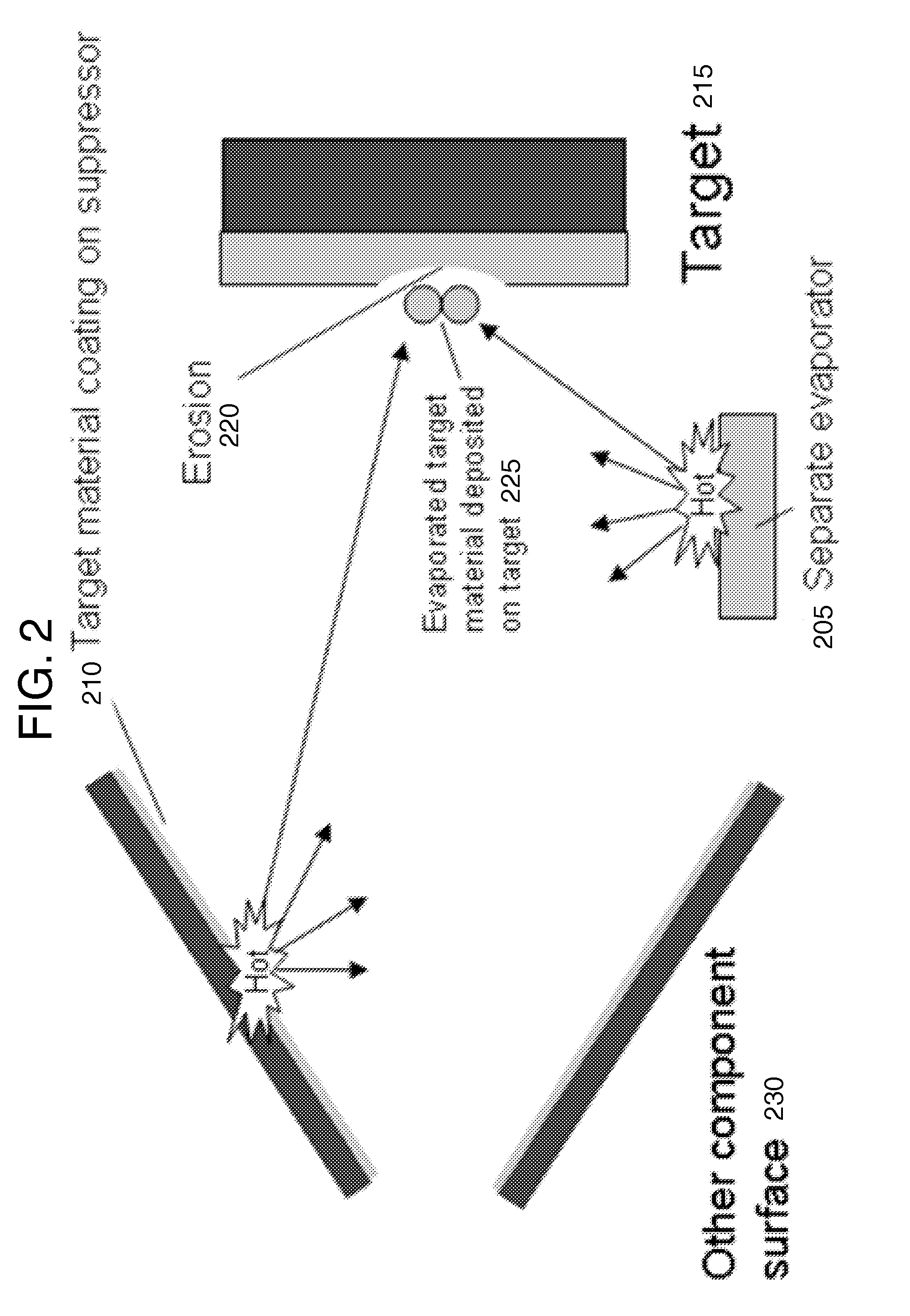
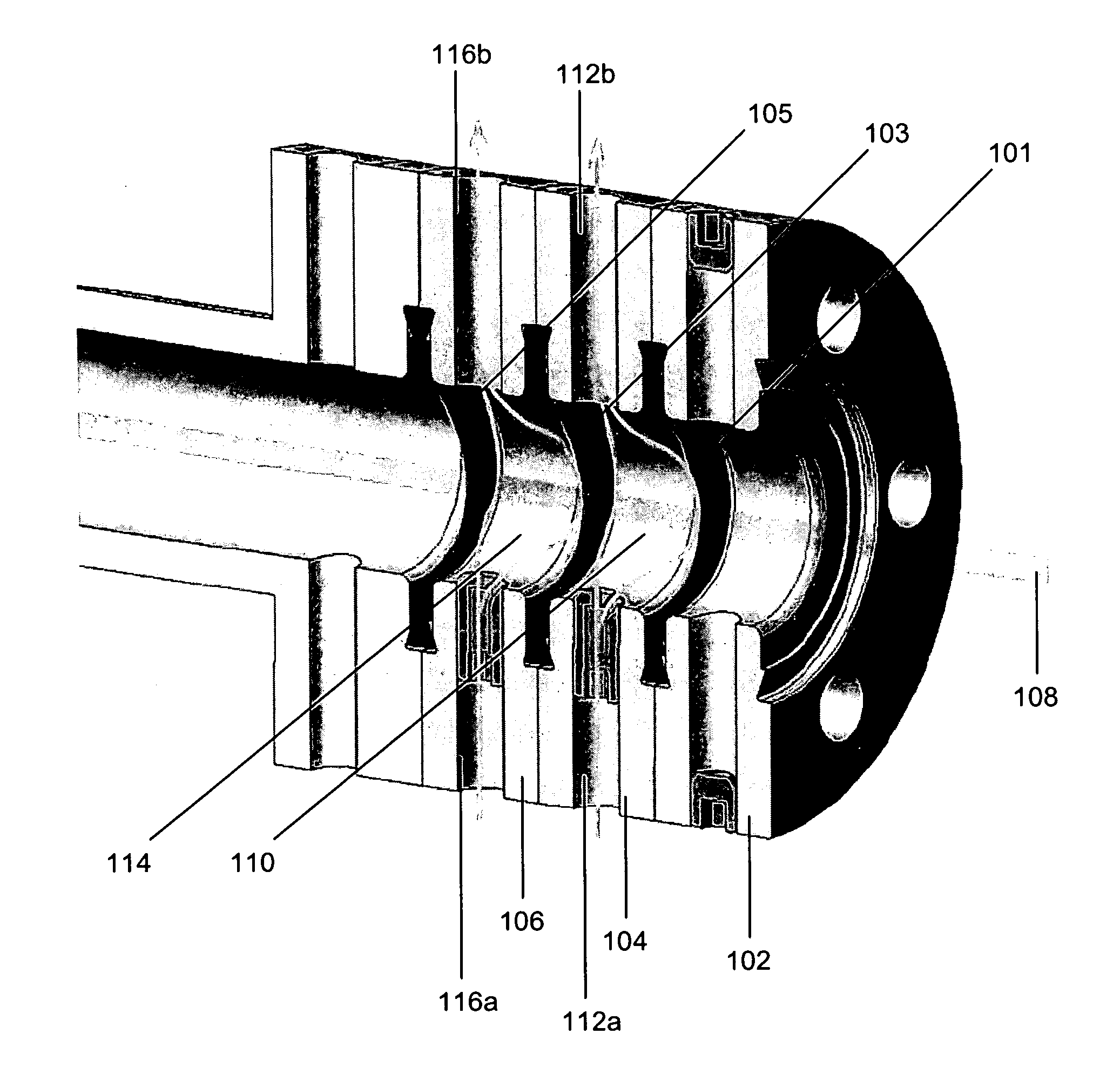
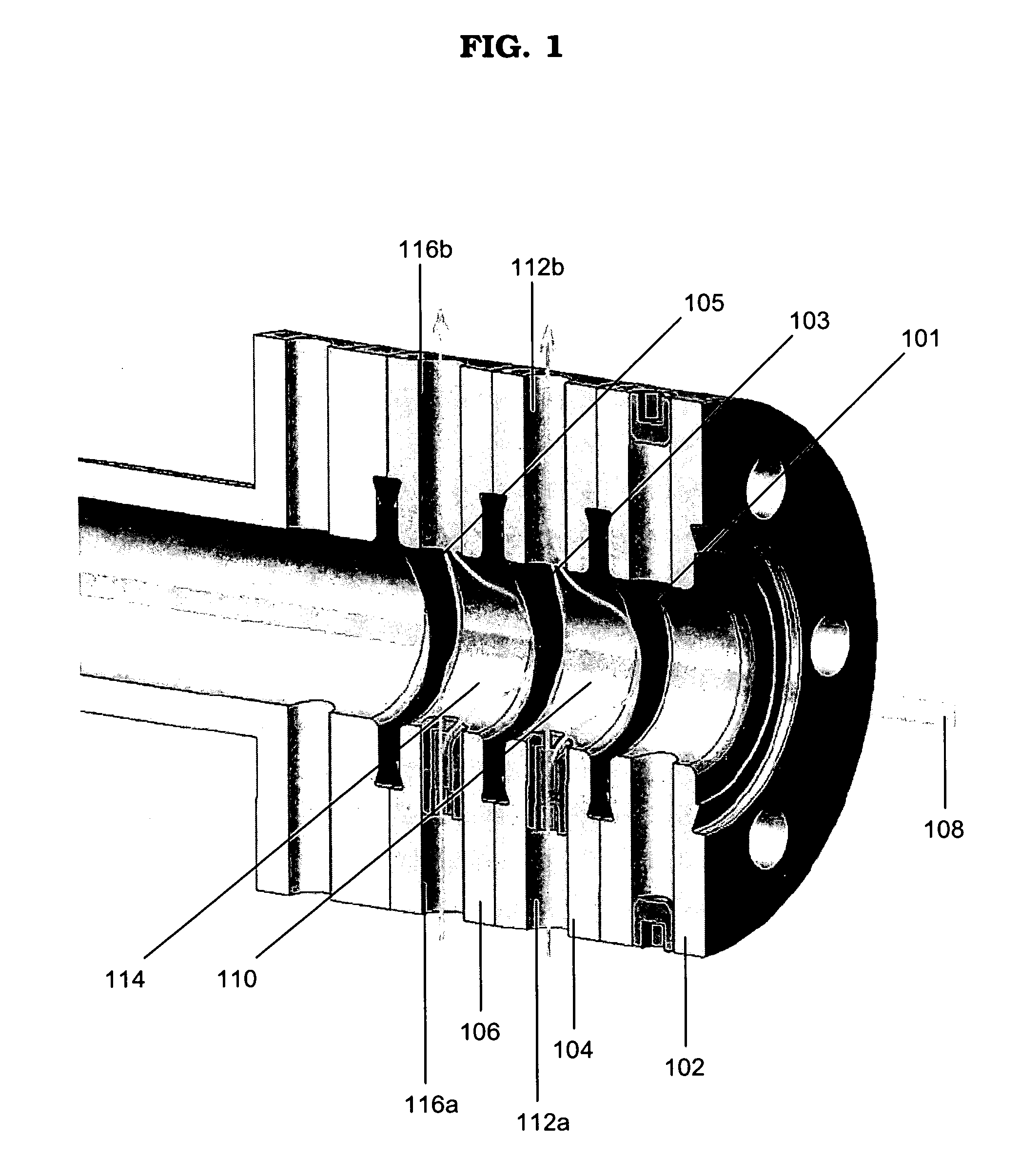
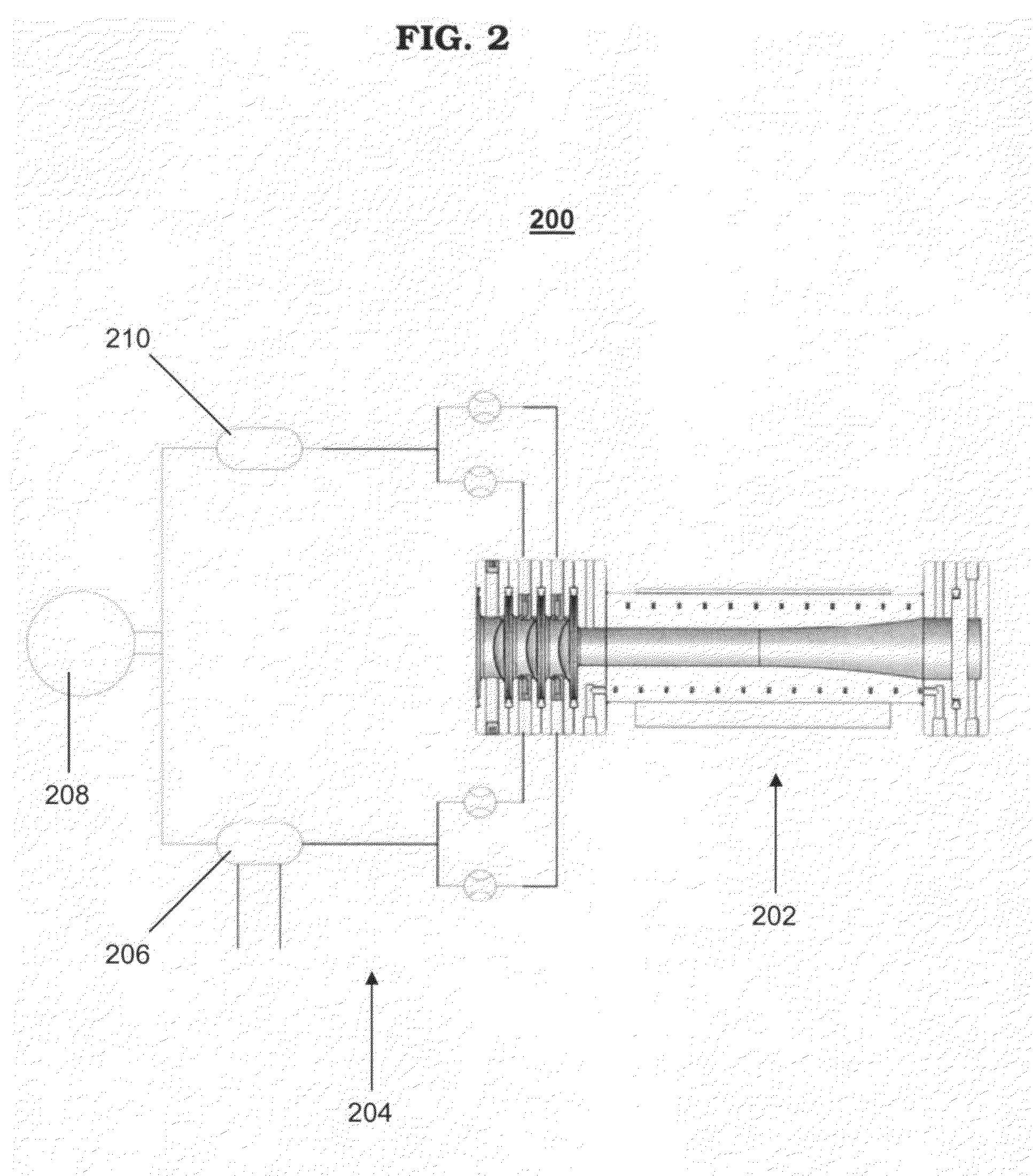
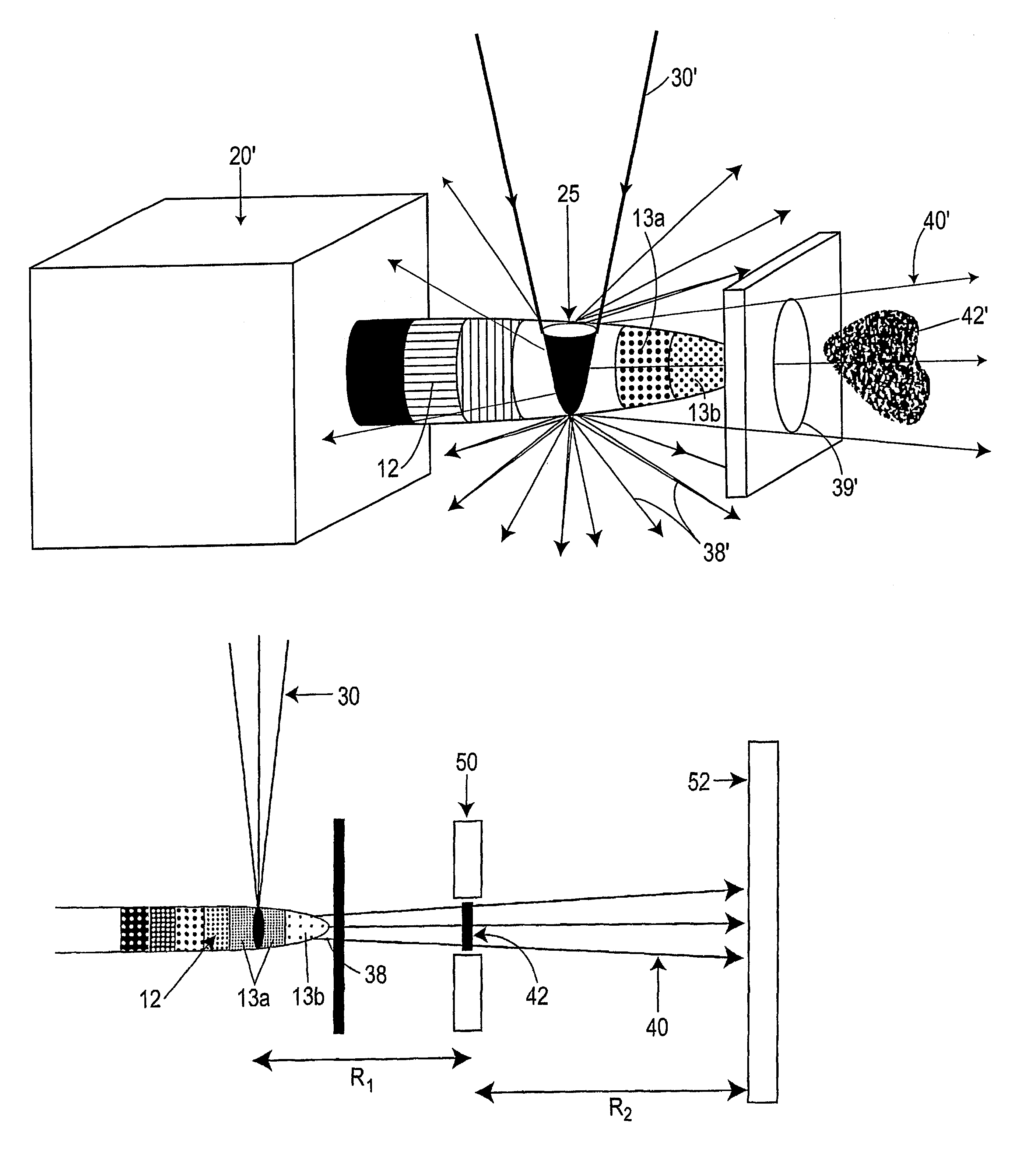
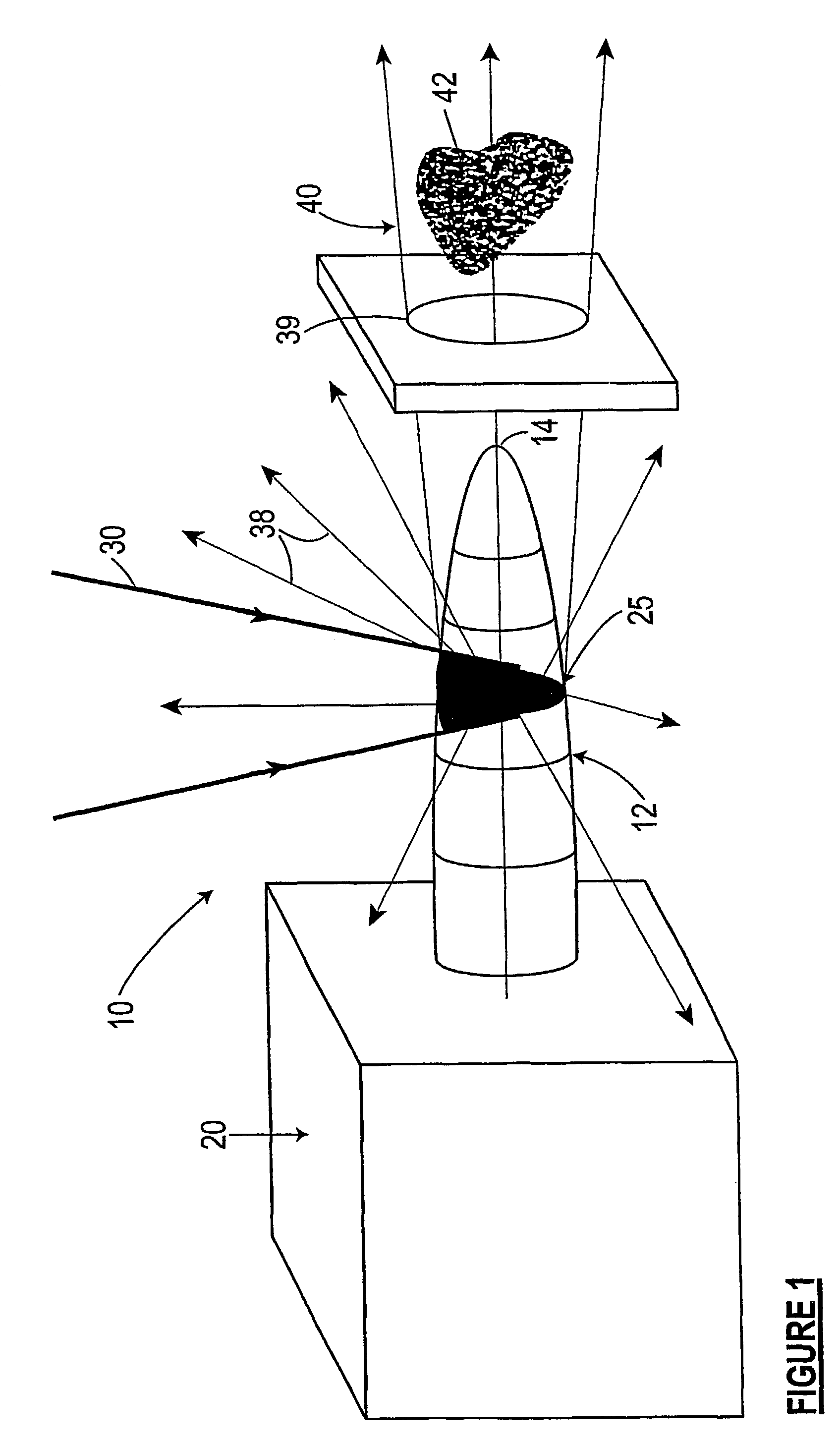
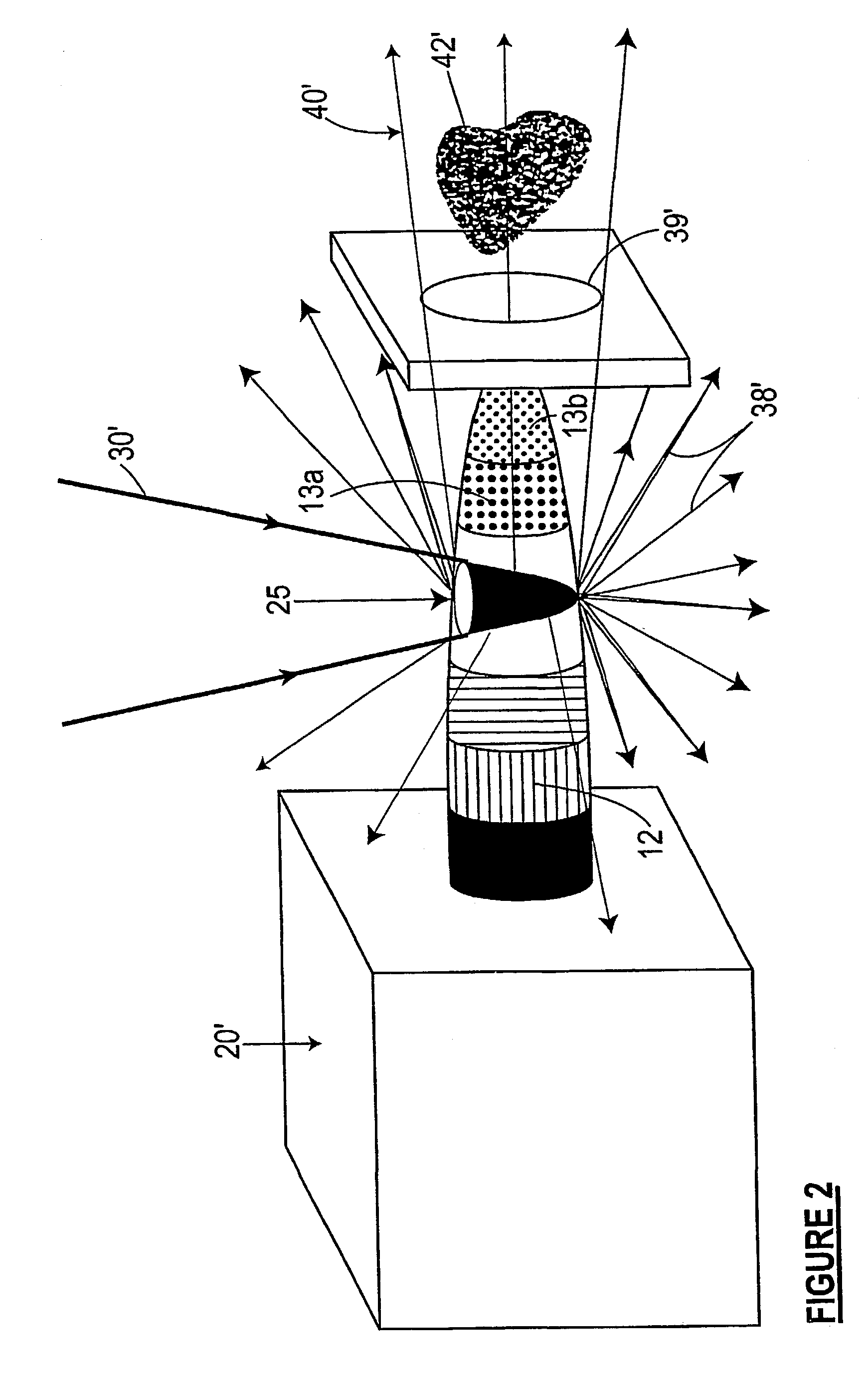
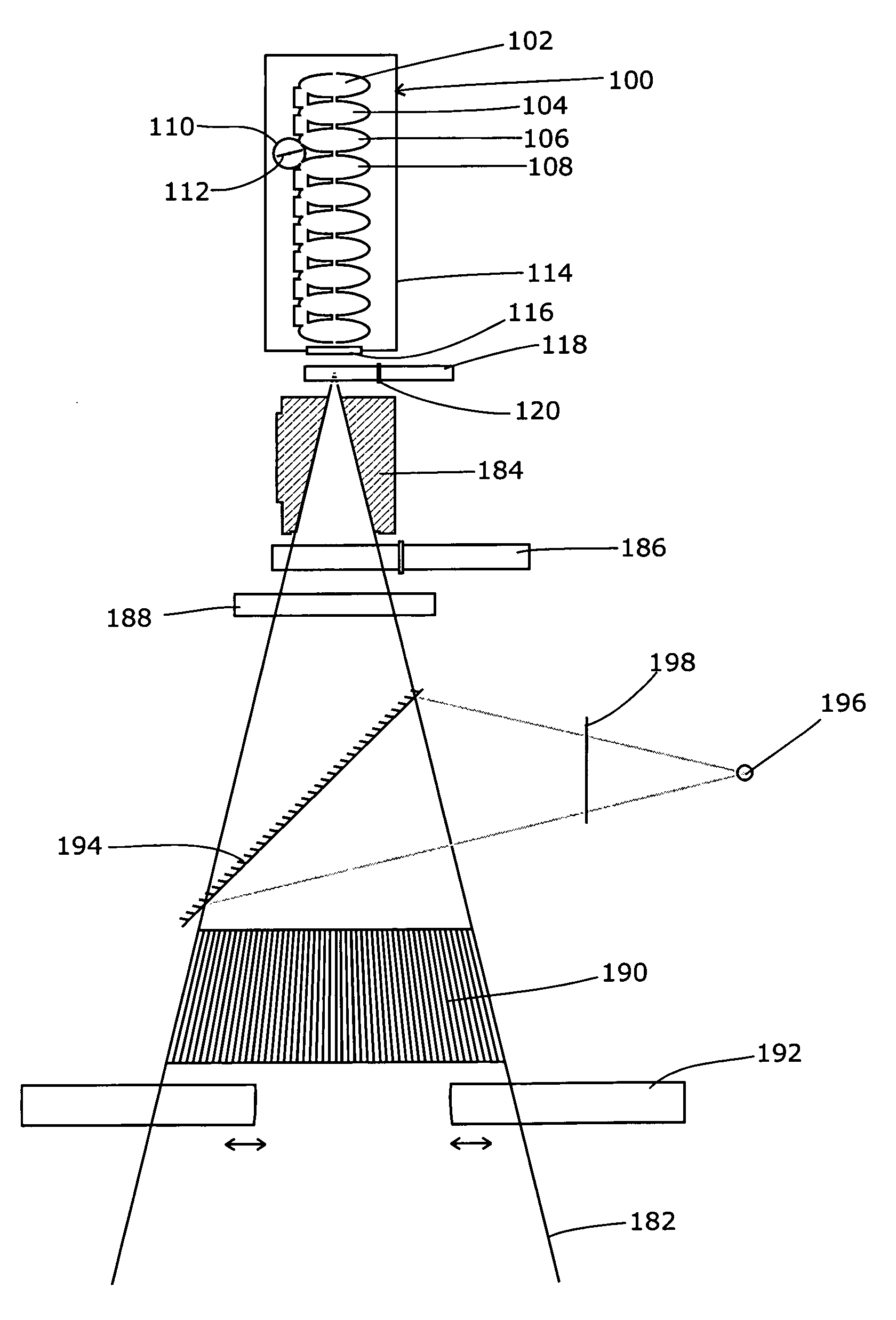
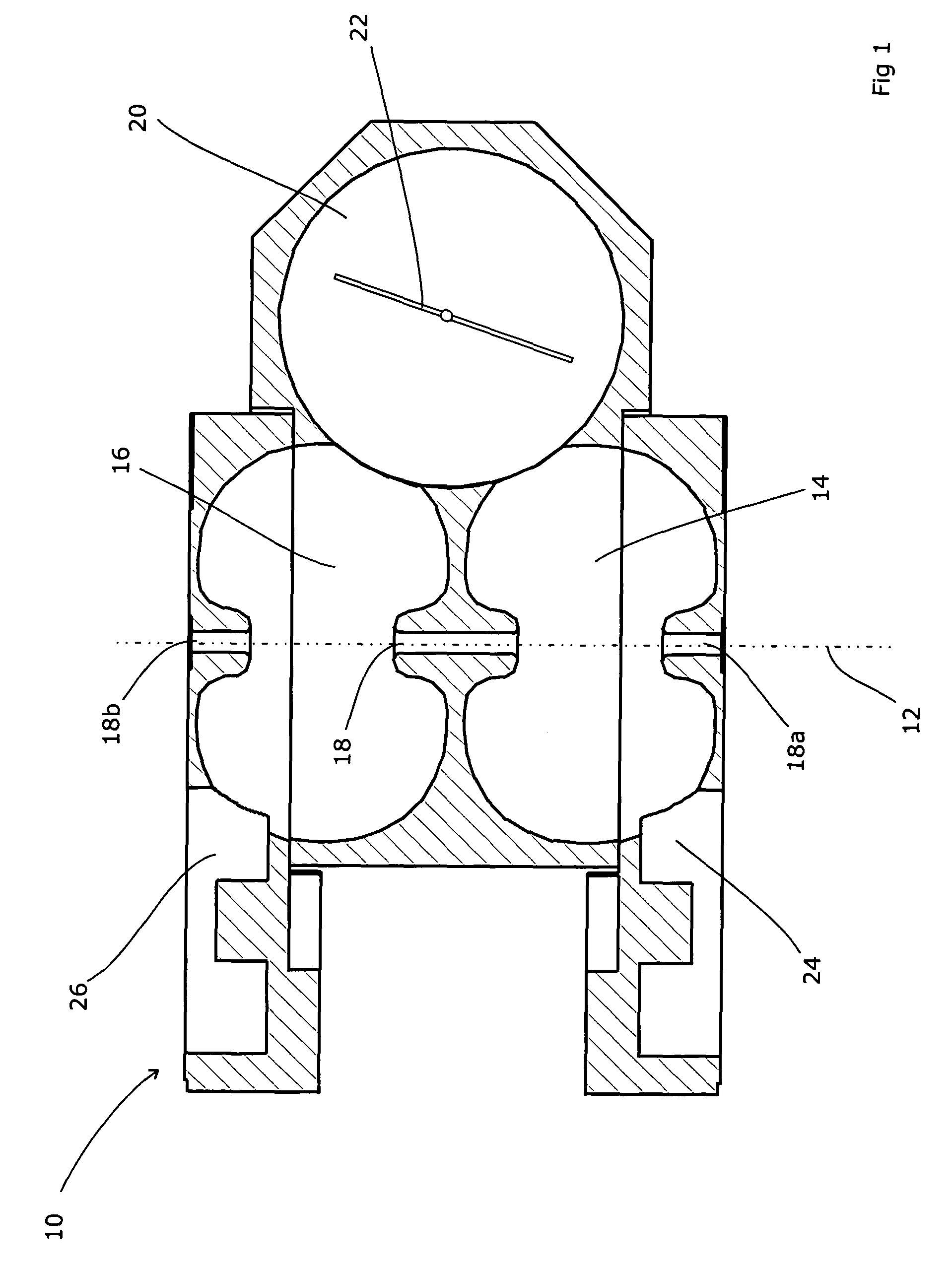
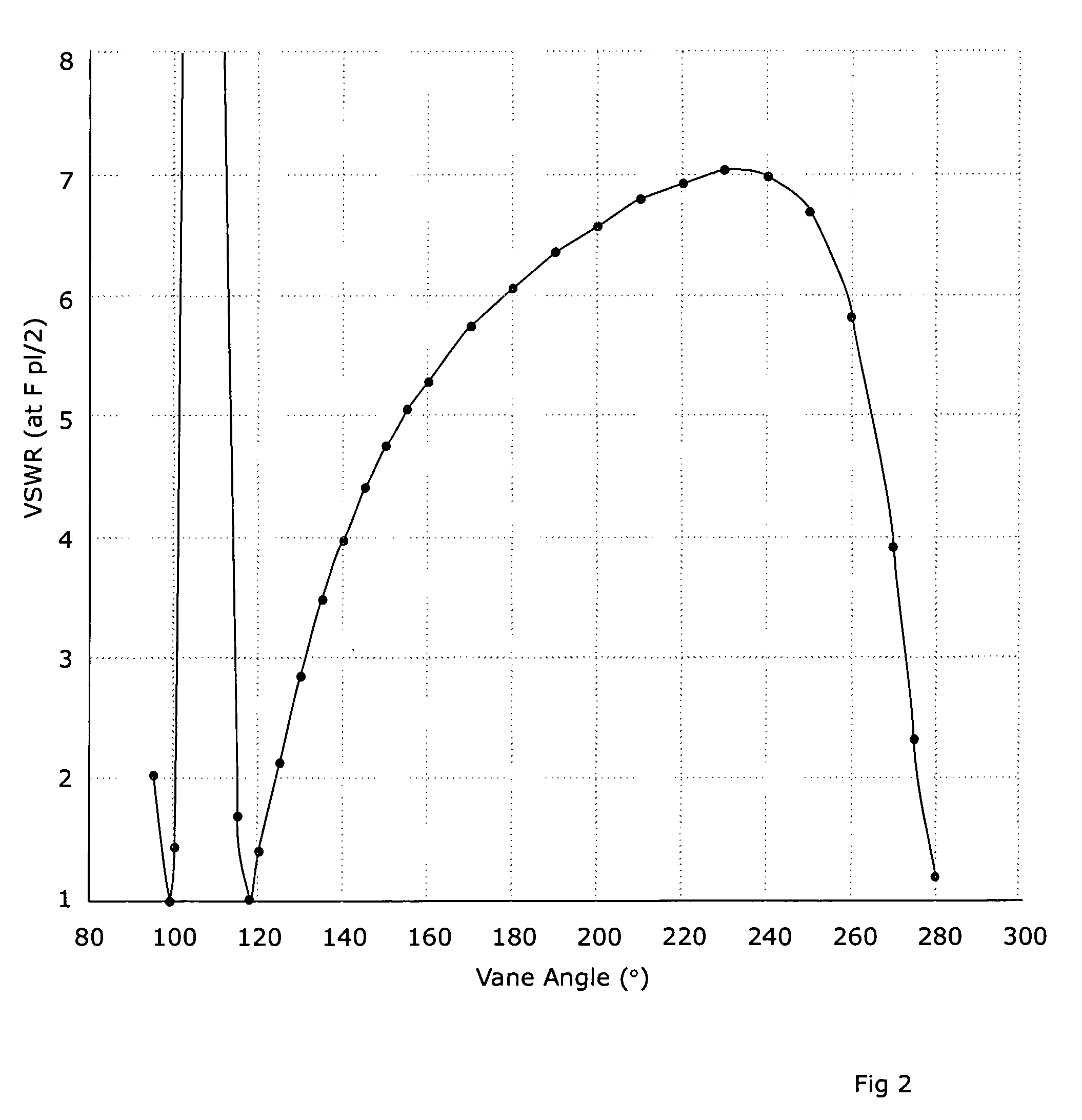
Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator
InactiveUS20090052628A1High strengthConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsX-ray tube electrodesParticle acceleratorNiobium
The invention is directed to a novel foil for use as an entrance window foil during the production of [18F] by irradiation of [18O] using a particle accelerator. The foil is a high strength cobalt based alloy foil, thin film coated with an inert and refractory metal such as niobium.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
High energy proton or neutron source
ActiveUS8837662B2Overcome disadvantagesPrevent escapeConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsDirect voltage acceleratorsHigh fluxEngineering
Owner:SHINE TECH LLC
System and method for creating liquid droplet impact forced collapse of laser nanoparticle nucleated cavities for controlled nuclear reactions
InactiveUS20080037694A1Promote crashEnhance implosion energyMaterial nanotechnologyNuclear energy generationNanoparticleEngineering
A device, method and system for causing a controlled collapse of cavities formed within liquid droplets wherein a pressurized jet comprising a liquid and nanoparticle material and possibly fuel produces droplets from the breakup of the jet stream. The liquid droplets are irradiated with energy to produce and expand cavities formed within the droplets by irradiation of the nanoparticles contained within the droplets. The droplets are collided with a target to collapse the cavities within the droplets. The irradiating and colliding are timed to enhance implosion energy resulting from the cavities' collapse. The implosion energy and the fuel in the cavity may be used to activate and sustain a fusion reaction.
Owner:SYNERGY INNOVATIONS INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/608e22dd-af99-4217-bcfe-89a8d80b969b/US20090052628A1-20090226-D00000.png)
![Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/608e22dd-af99-4217-bcfe-89a8d80b969b/US20090052628A1-20090226-D00001.png)
![Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator Target foil for use in the production of [18f] using a particle accelerator](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/608e22dd-af99-4217-bcfe-89a8d80b969b/US20090052628A1-20090226-D00002.png)