Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1412results about "Thermoelectric devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Remote power recharge for electronic equipment
InactiveUS7068991B2Batteries circuit arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
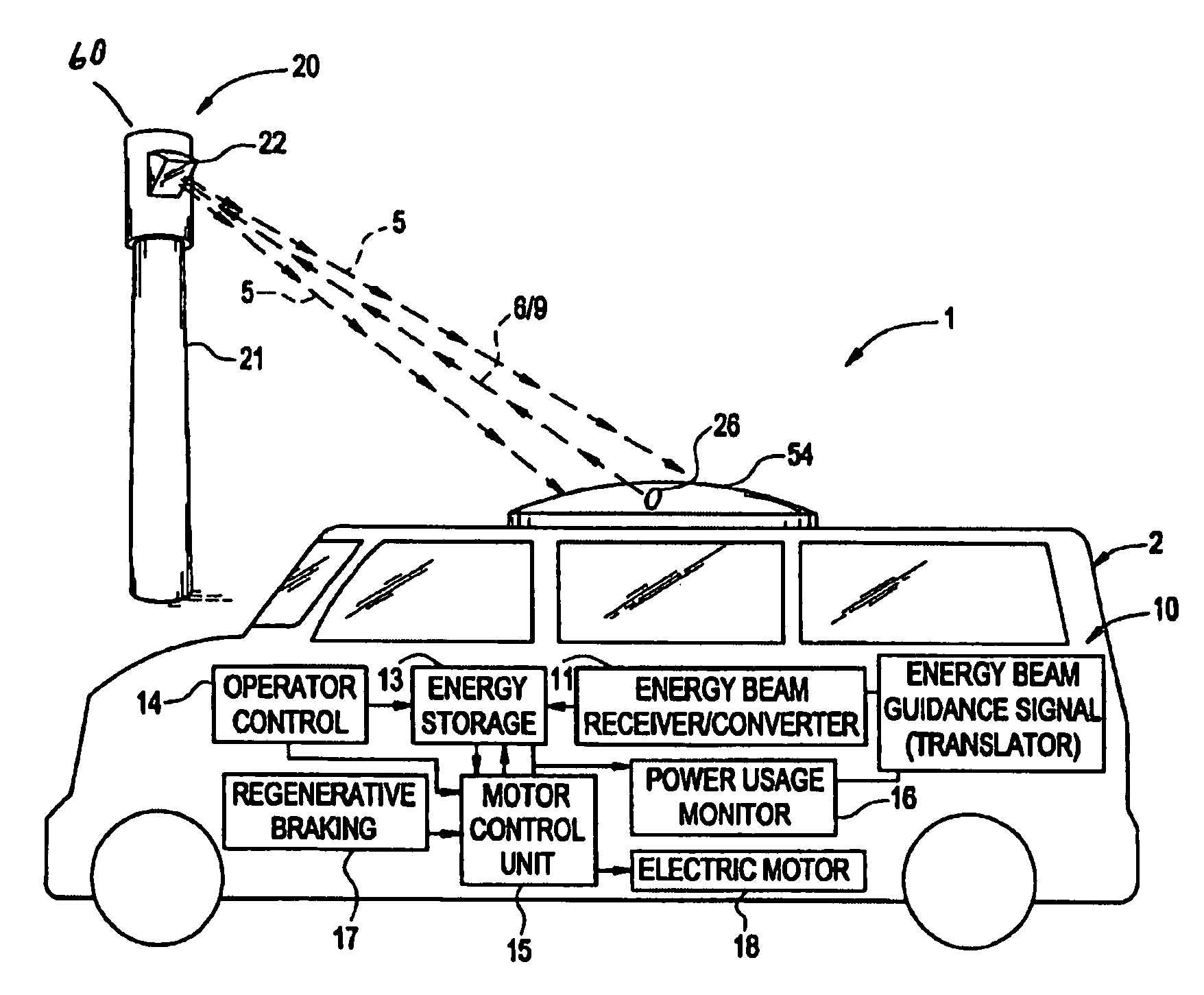
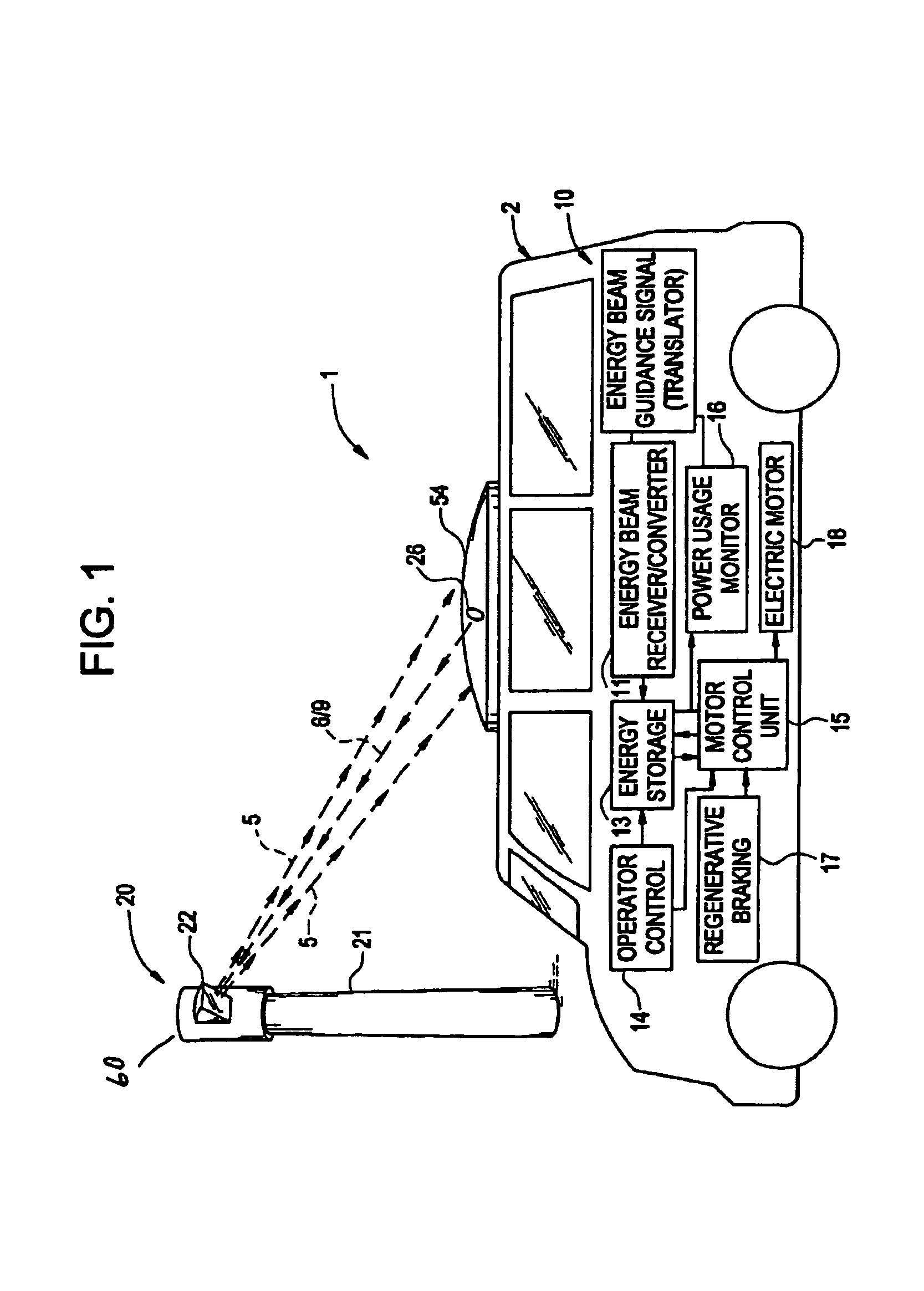
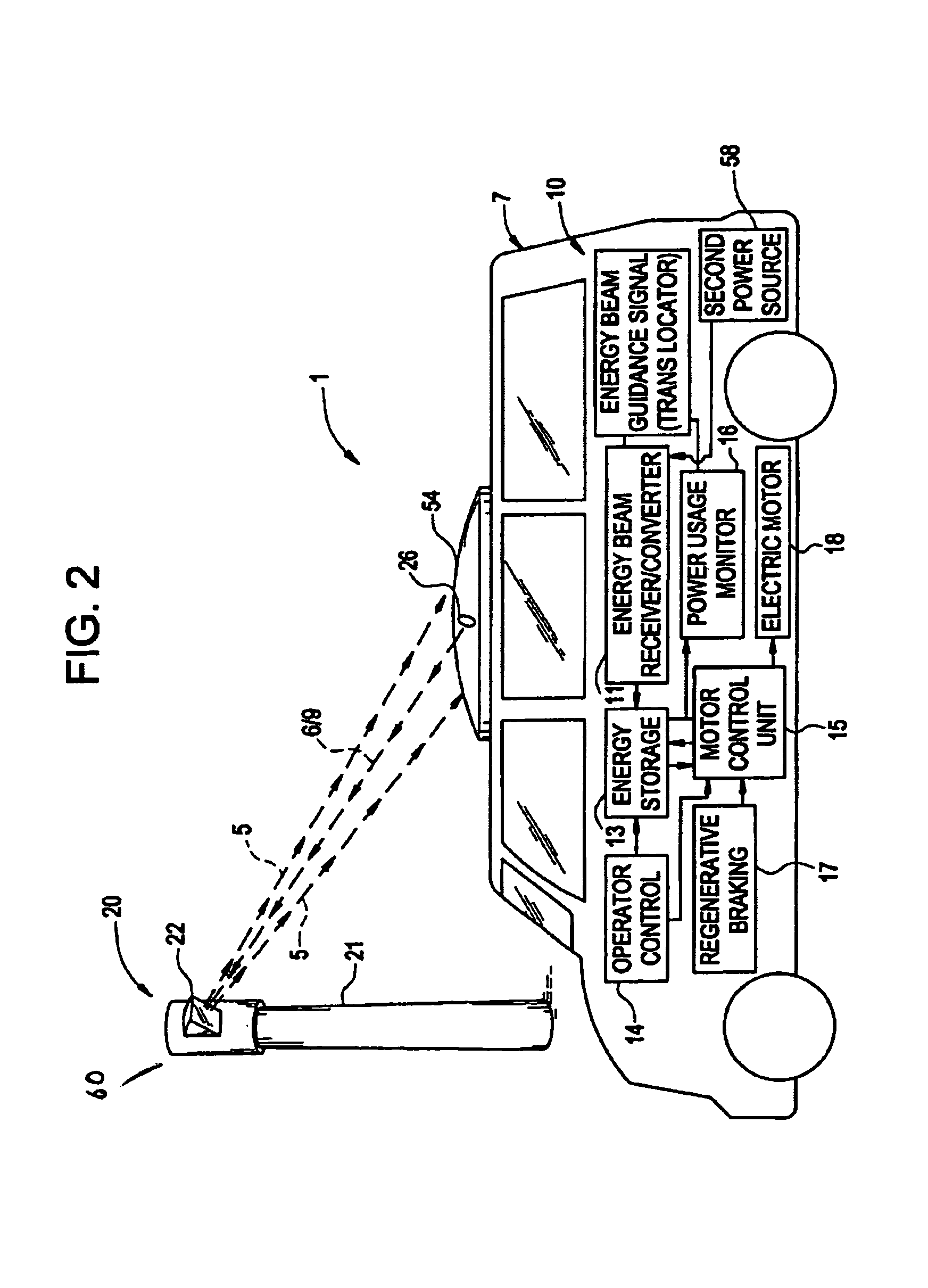
A conductorless charging and power system for electronic appliances and method for communicating power to a power receiver employing wireless energy transmission are disclosed. The remote charging system includes a power transmission unit, which transmits energy as a directional power beam, and a power receiver system that receives the transmitted energy. The power receiver system is preferably incorporated in an appliance and includes an energy receptor capable of receiving the wireless power beam and transferring the energy from the beam to an energy storage device included in the appliance. The power transmission unit receives and tracks a power request signal from the power receiver system to track the power receiver system location during energy transmission. Data streams may be incorporated into the wireless signals of the remote charging system, allowing the remote charging system to function as a communications pathway as well as a power delivery system.
Owner:PARISE RONALD J
Temperature sensor with processable front
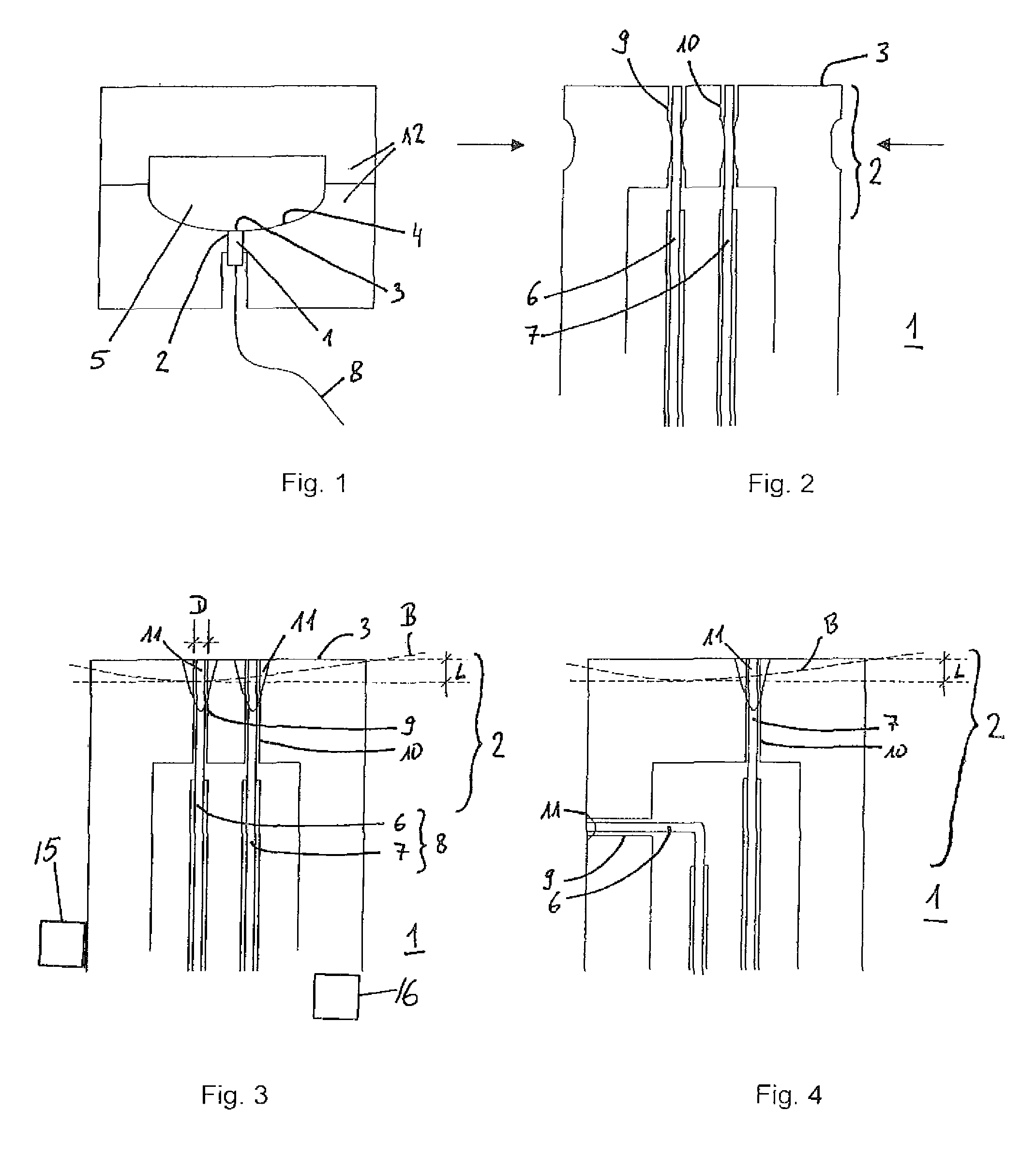
ActiveUS7789559B2Thermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermocouple WireBiomedical engineering
A temperature sensor has a sensor tip and a front for measuring the temperature of the inner walls of tools, particularly inner walls of injection molding tools. The tip of the temperature sensor has two thermocouple wires of a thermocouple. Each thermocouple wire of the thermocouple guided to the front is welded to the sensor tip up to a depth which is larger than the total processing depth behind the front. The sensor tip is processable by removing of material at the front up to that processing depth.
Owner:KISTLER HLDG AG
Indication systems and methods
Methods and apparatus for generating an information signal. Exemplary methods and apparatus may comprise (A) electrically associating at least one LED with a Seebeck power generator; (B) thermally associating the Seebeck power generator with a surface; and (C) heating the surface to cause the Seebeck power generator to generate electricity to energize the at least one LED. In one example, such methods and apparatus may be used to provide an indication of the temperature of a surface.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
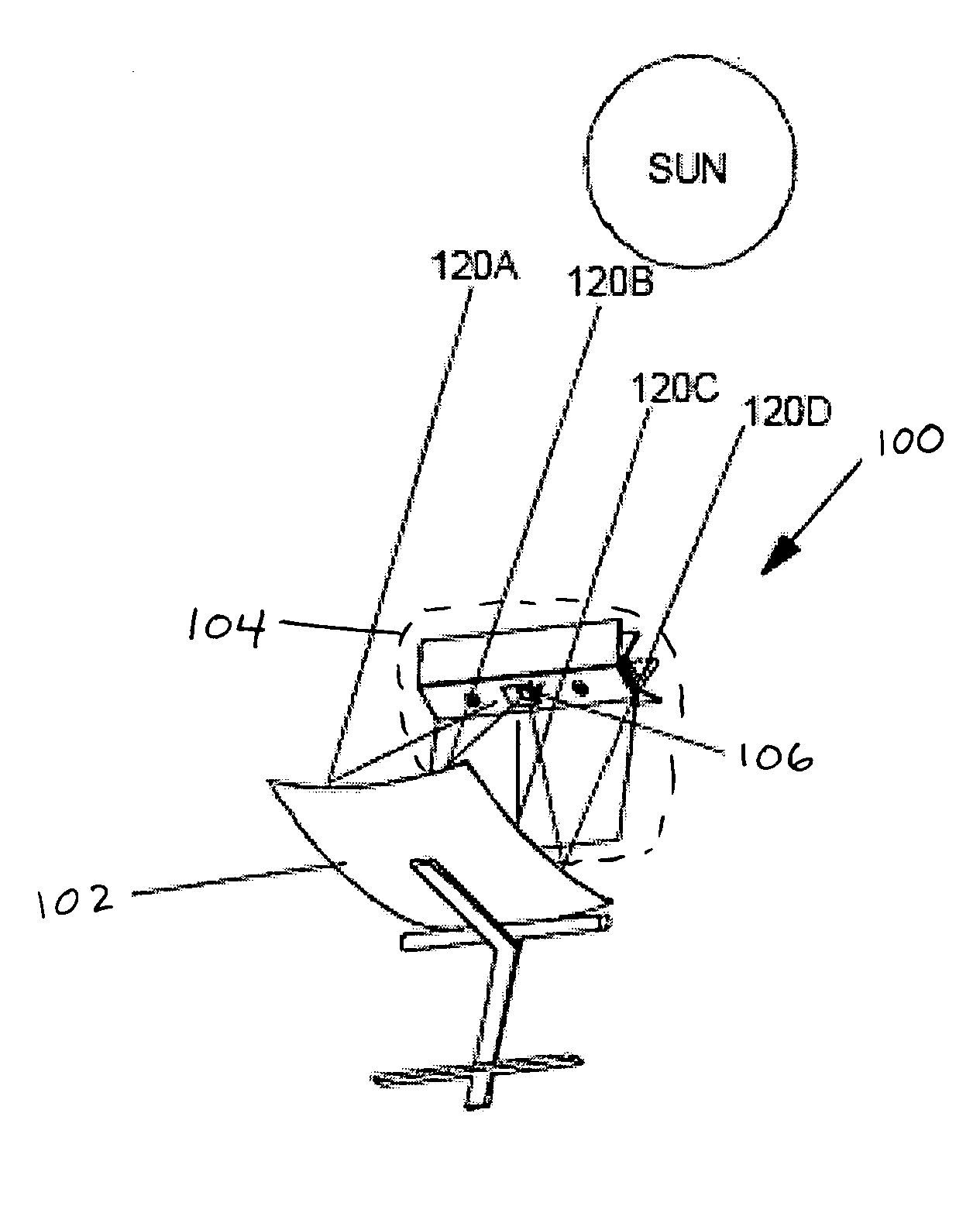
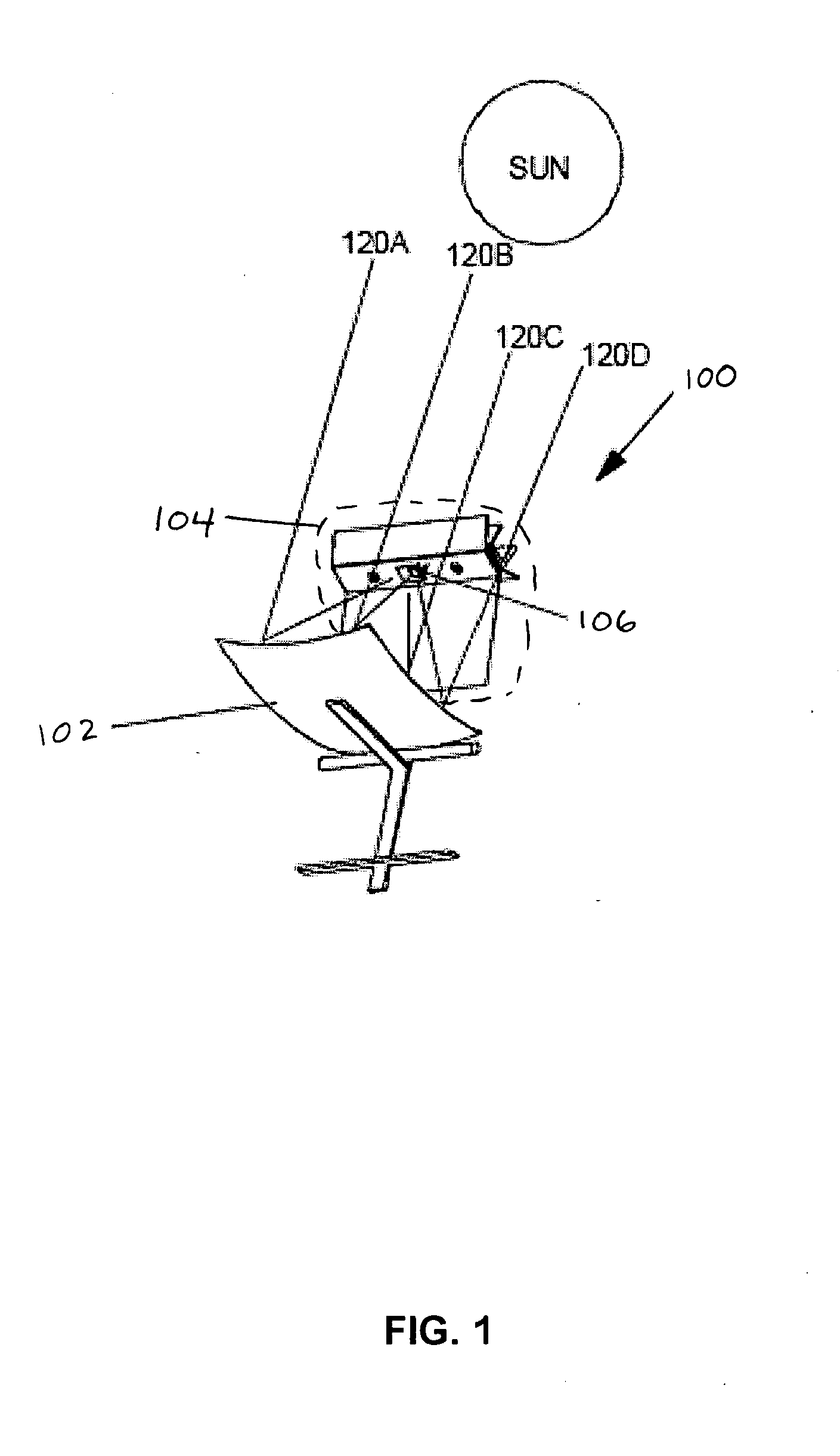
Tracking solar power system
A tracking solar power system is disclosed. The tracking solar power system includes: a solar power substructure and a platform having a first degree of freedom. The solar power substructure is mounted on the platform in a manner such that it has a second degree of freedom relative to the platform. The solar power substructure may include a solar collector and a receiver arranged to receive energy from the solar collector. The receiver may be mounted in a manner that avoids shading of the solar collector during operation. The solar collector may have an area focus at the receiver. The solar power substructure may include a non-concentrating solar power substructure.
Owner:GREENVOLTS INC
Radio frequency IC tag and method for manufacturing the same
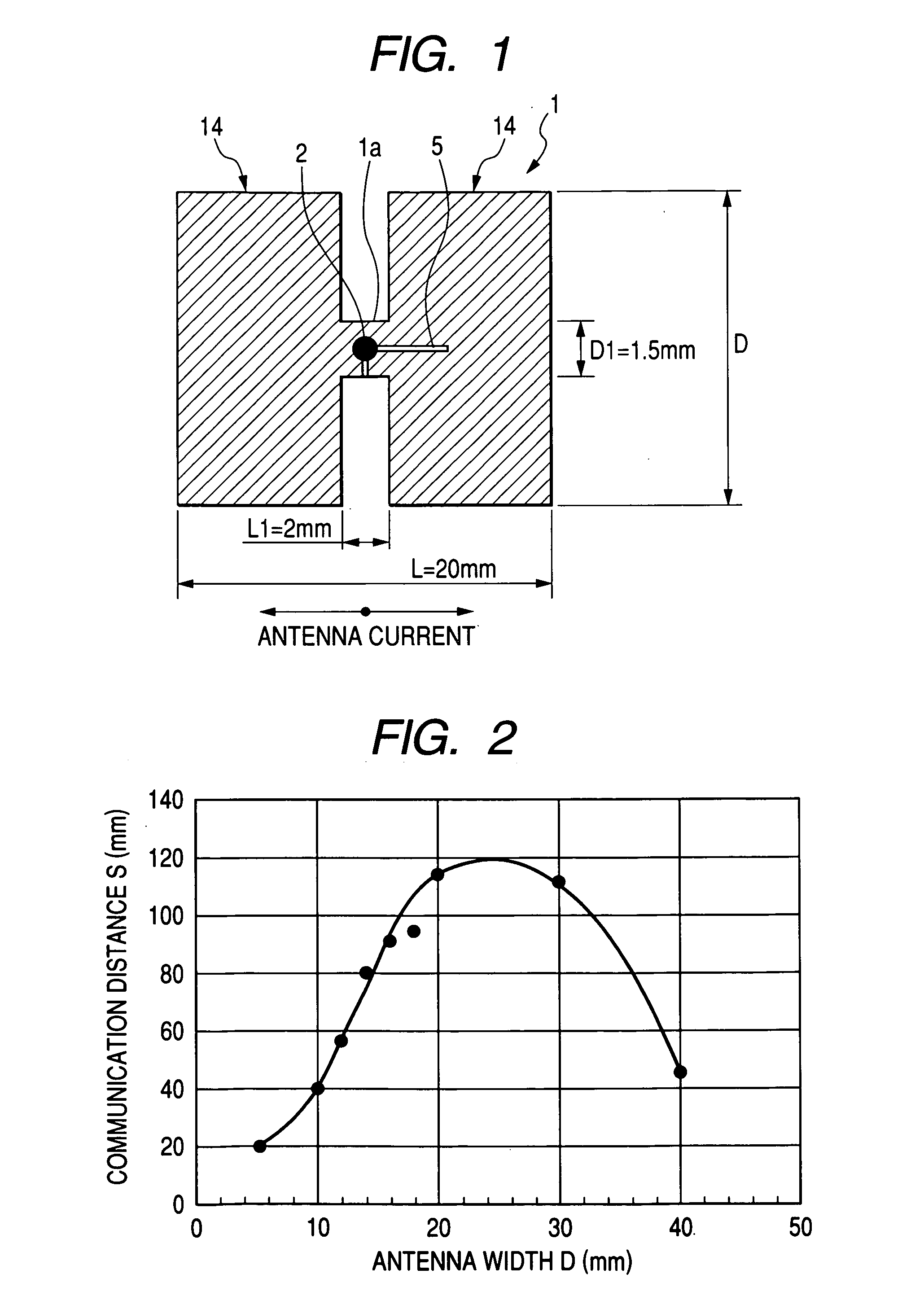
InactiveUS20050275539A1Maximum antenna efficiencyReduces efficiency of antennaAntenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRadio frequencyElectric power
A radio frequency IC tag and a manufacturing method for the same includes an IC chip on which information is stored, and an antenna for transmitting the information that is stored on the IC chip. In the antenna, a power-feeding part on which the IC chip is mounted extends along a direction in which an electric current flows. Radiation parts are formed so that the width of the radiation parts becomes wider than that of the power-feeding part with respect to the longitudinal axis of the power-feeding part. The radiation parts extend from the power-feeding part, at both sides thereof, along the direction in which the electric current flows.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Metal-oxide electron tunneling device for solar energy conversion
InactiveUS6534784B2Improve performancePV power plantsSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionEngineering
The electron tunneling device includes first and second non-insulating layers spaced apart such that a given voltage can be provided therebetween. The device also includes an arrangement disposed between the non-insulating layers and configured to serve as a transport of electrons between the non-insulating layers. This arrangement includes a first layer of an amorphous material such that using only the first layer of amorphous material in the arrangement would result in a given value of a parameter in the transport of electrons, with respect to the given voltage. The arrangement further includes a second layer of material, which is configured to cooperate with the first layer of amorphous material such that the transport of electrons includes, at least in part, transport by tunneling, and such that the parameter, with respect to the given voltage, is increased above the given value of the parameter.
Owner:UNIV TECH
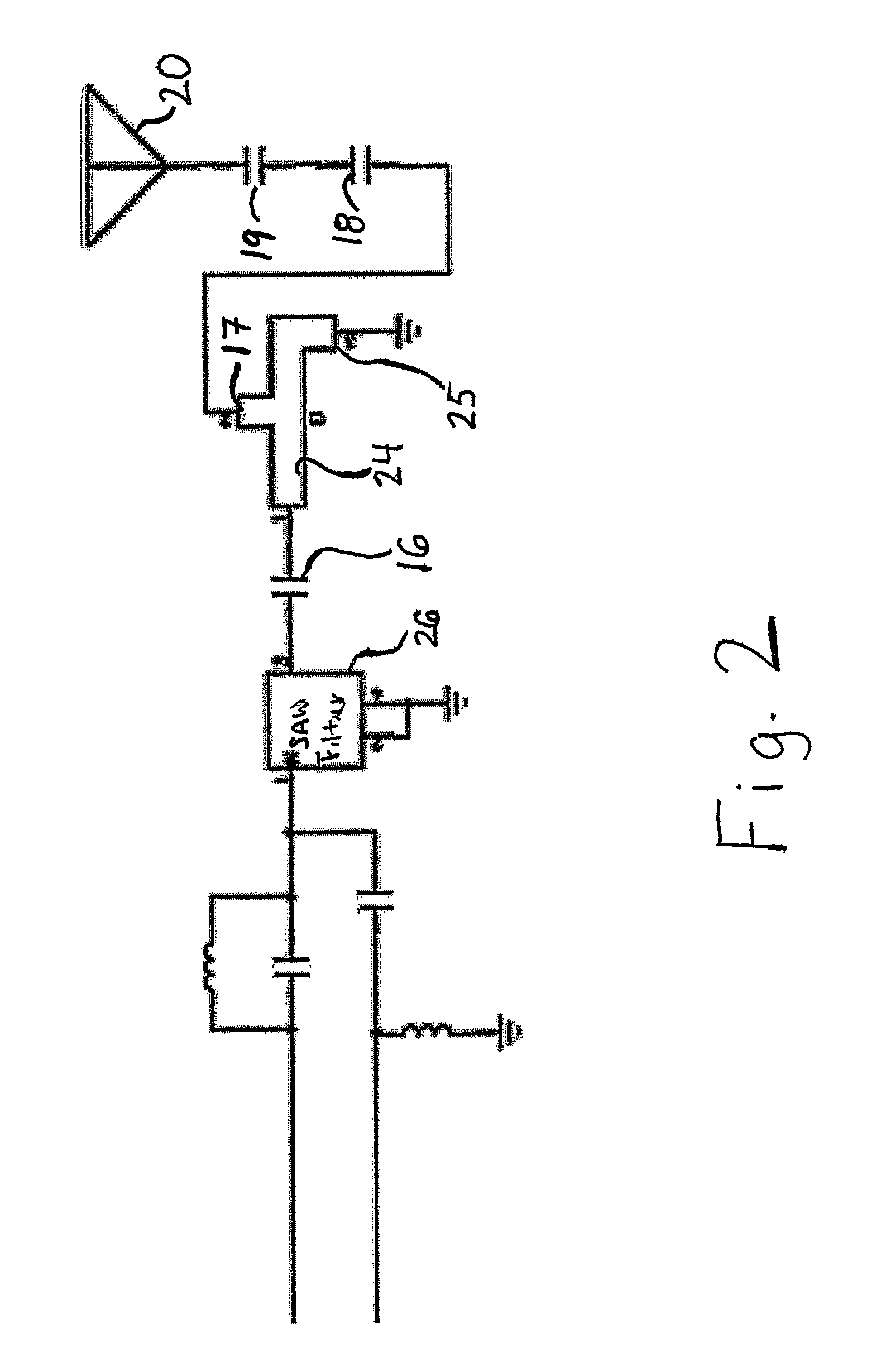
Electromagnetic antenna apparatus
InactiveUS6845253B1Easy to operateEasy to manufactureShort antennas for non-sinusoidal wavesRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
An apparatus for transferring electromagnetic energy intermediate a host device and a medium or free space adjacent to the apparatus in an impulse radio system includes: (a) an energy guiding means for guiding the electromagnetic energy; the energy guiding means is connected with the host device; (b) an electromagnetic energy channeling structure effecting the transferring and including a plurality of gap interfaces; and (c) a transition means for coupling the energy guiding means with at least one gap interface of the plurality of gap interfaces. The transition means conveys the electromagnetic energy intermediate the energy guiding means and the at least one gap interface. The at least one gap interface intersects the transition means in a substantially continuous curve in selected planes intersecting the gap interface and the transition means.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
Antennas
Owner:MBDA UK
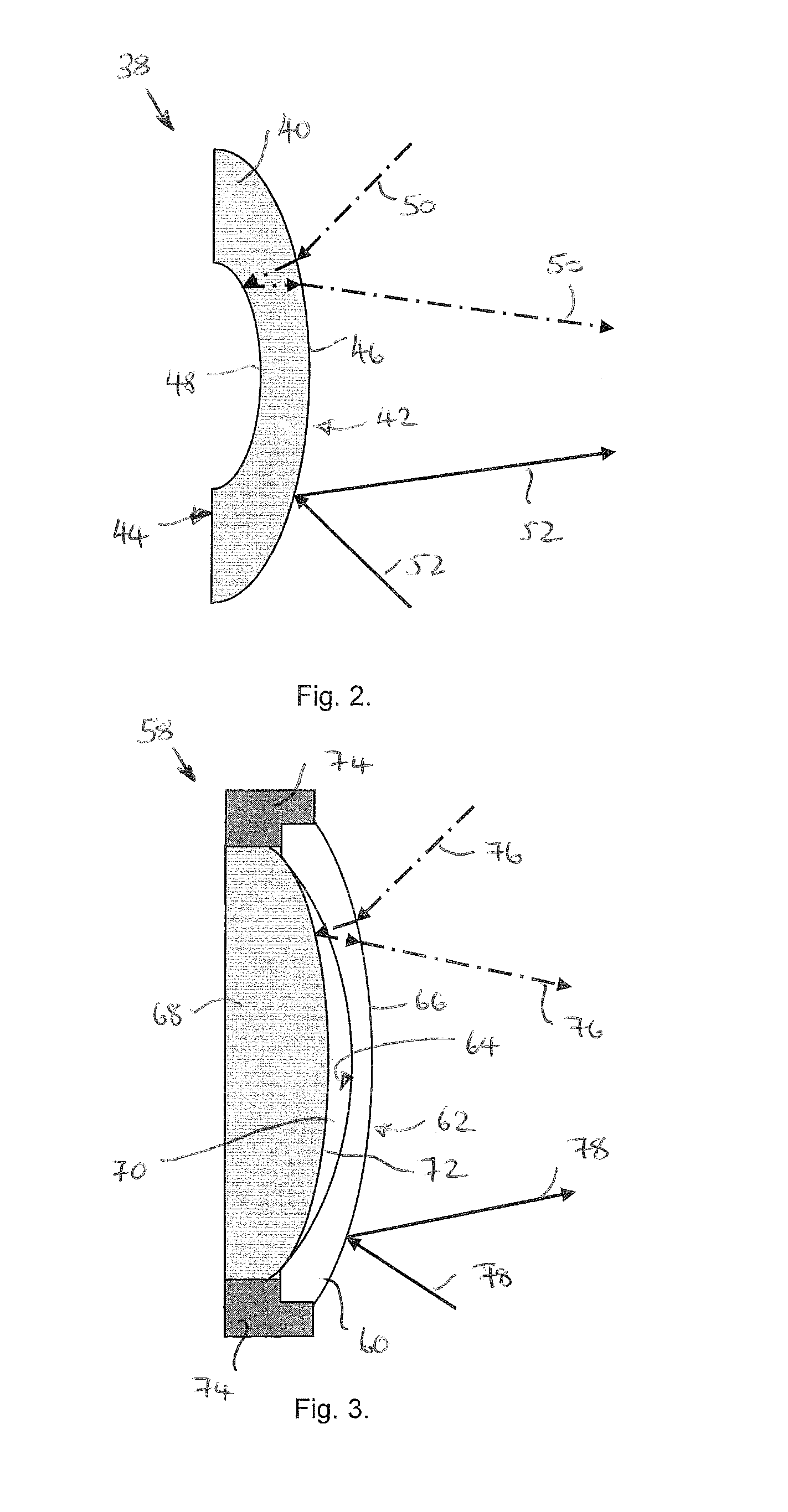
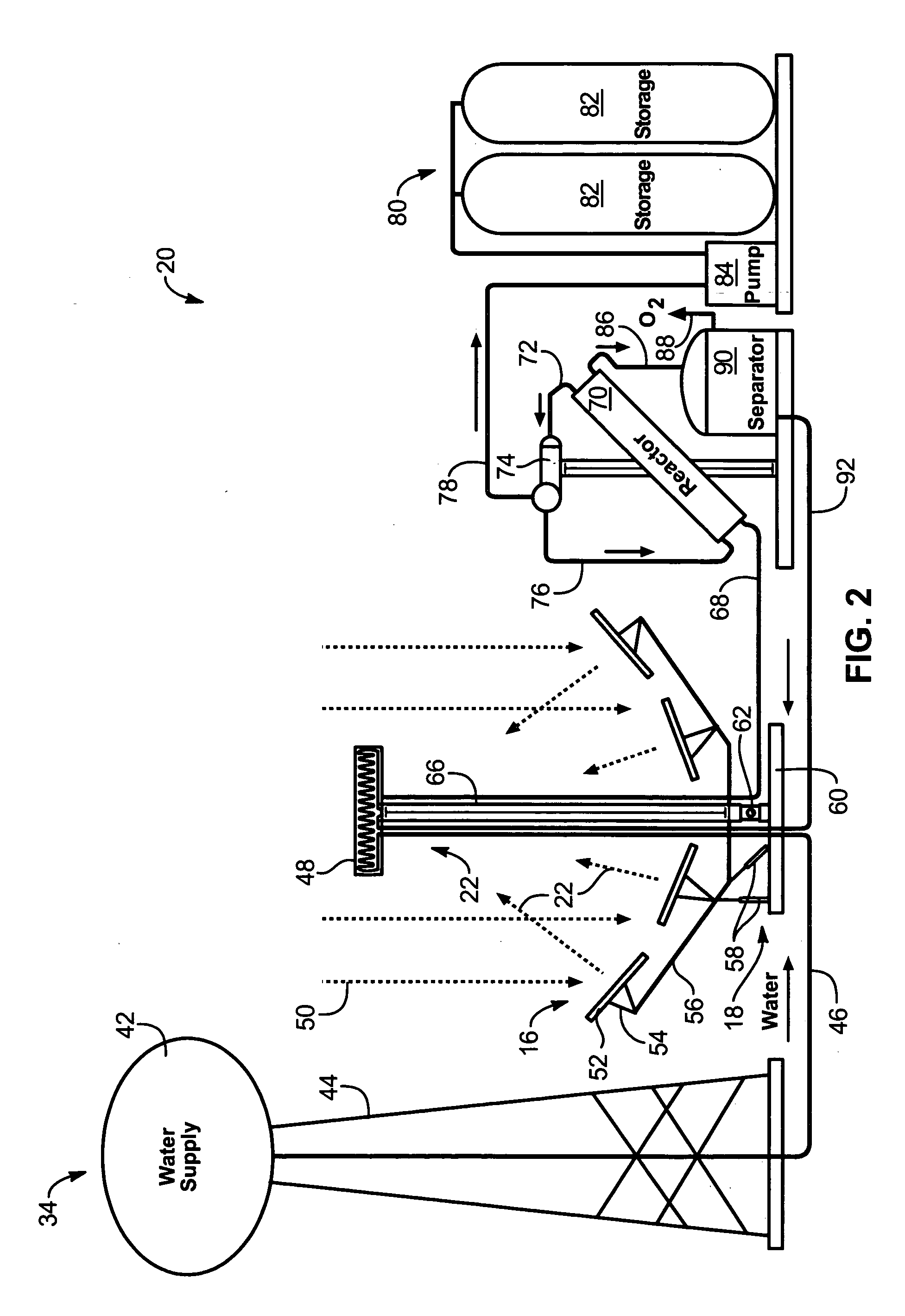
Solar, catalytic, hydrogen generation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060048808A1High thermodynamic availabilityLoss in efficiencySolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersThermal energyPorosity
An apparatus for producing hydrogen may include a collector of radiation to concentrate solar radiation on a converter having an absorptivity to convert the solar radiation to thermal energy to drive a chemical process using a feedstock to dissociate into an output chemical and a byproduct. A separator separates the output and byproduct, after which a reactor reacts the output to form a storage chemical, reactive to produce energy but sufficiently stable for safe handling outside designation as an energetic material. The separator may have a porosity to substantially pass hydrogen and block oxygen and water. A sweep gas may sweep hydrogen away from the separation barrier to change equilibrium. Catalysts may reduce temperature of dissociation and a subsequent reaction to combine it in a more stable, storable form.
Owner:PURESCI
Method, system and apparatus for using electromagnetic radiation for monitoring a tissue of a user
InactiveUS20110160549A1High resolutionPerson identificationRadiating elements structural formsTransducerEngineering
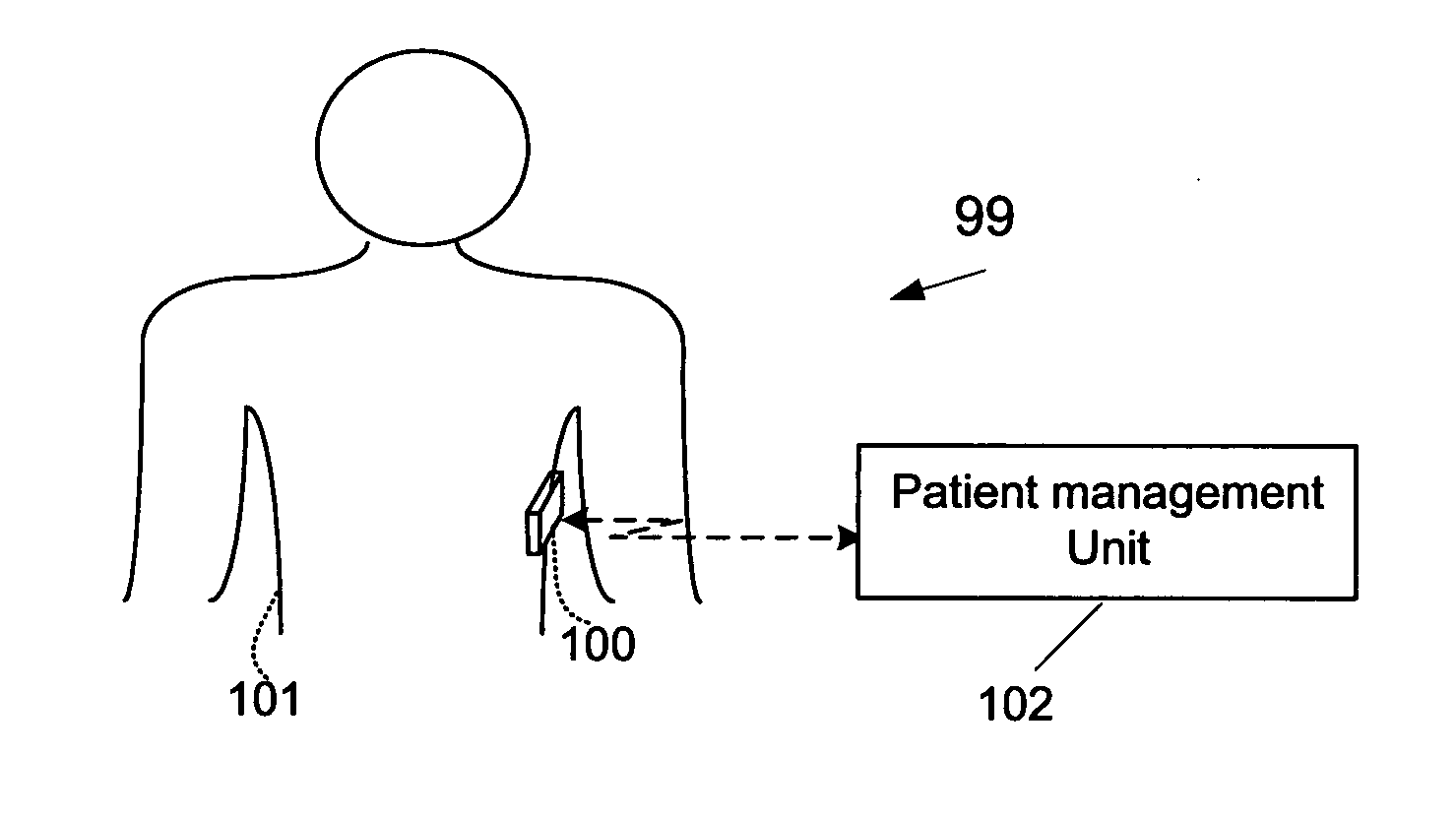
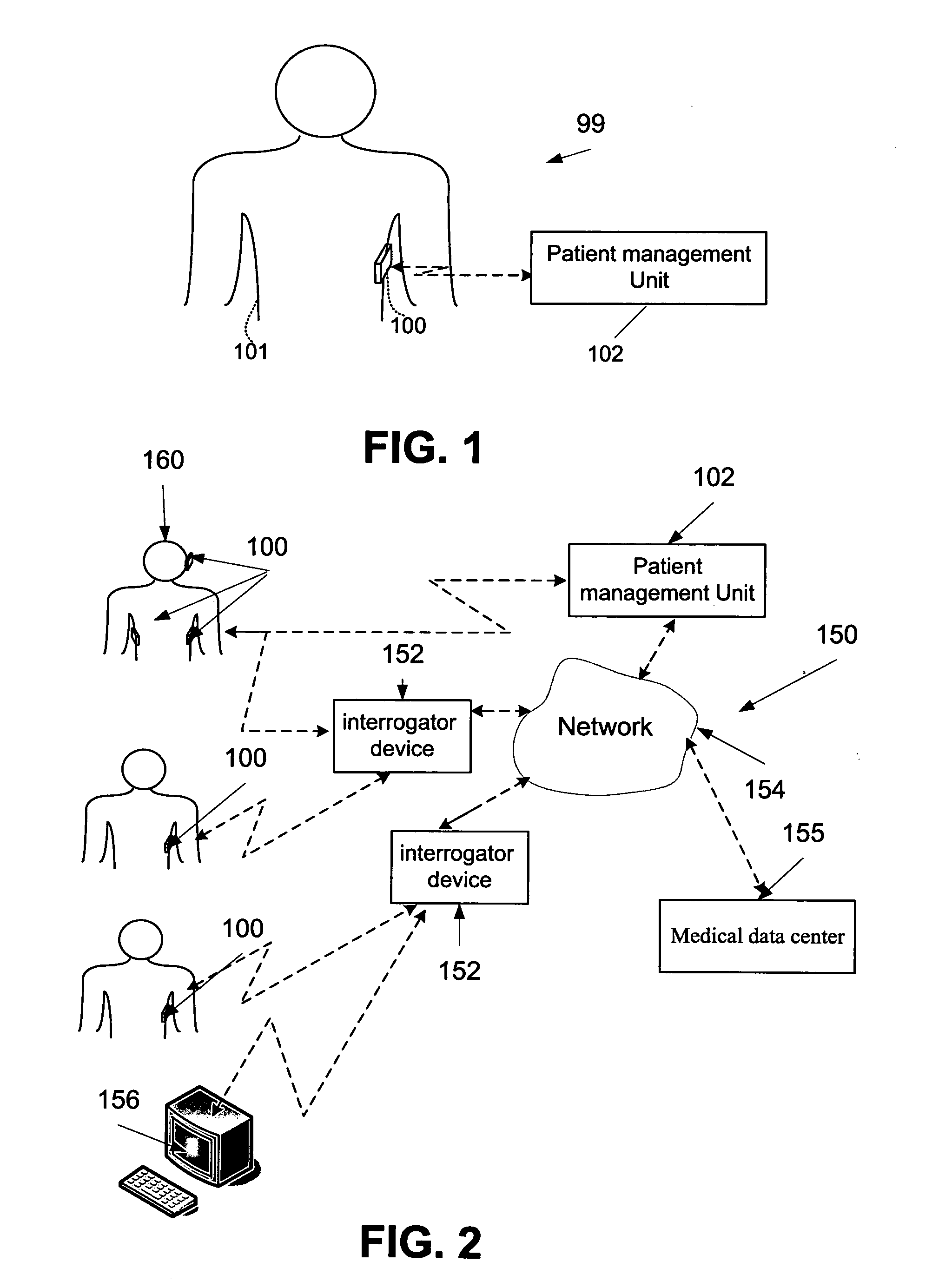
A wearable monitoring apparatus for monitoring at least one biological parameter of an internal tissue of an ambulatory user. Said wearable monitoring apparatus comprises at least one transducer configured for delivering electromagnetic (EM) radiation to said internal tissue and intercepting a reflection of said EM radiation said reform in a plurality of transmission sessions during at least 24 hours, a processing unit configured for analyzing respective said reflection and identifying a change in said at least one biological parameter accordingly, a reporting unit configured for generating a report according to said change, and a housing for containing said at least one transducer, said reporting unit, and said processing unit, said housing being configured for being disposed on said body of said ambulatory user.
Owner:SENSIBLE MEDICAL INNOVATIONS LTD
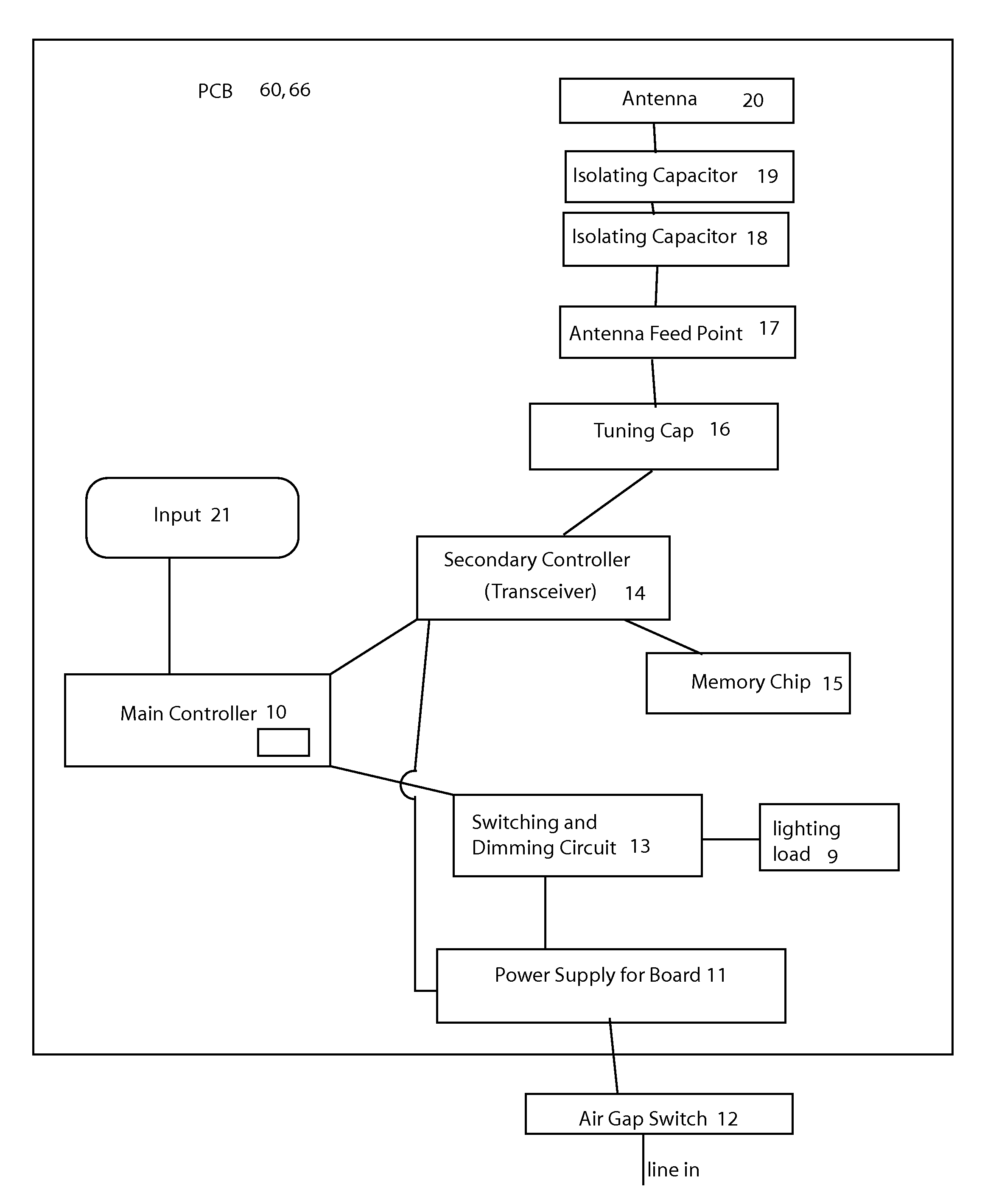
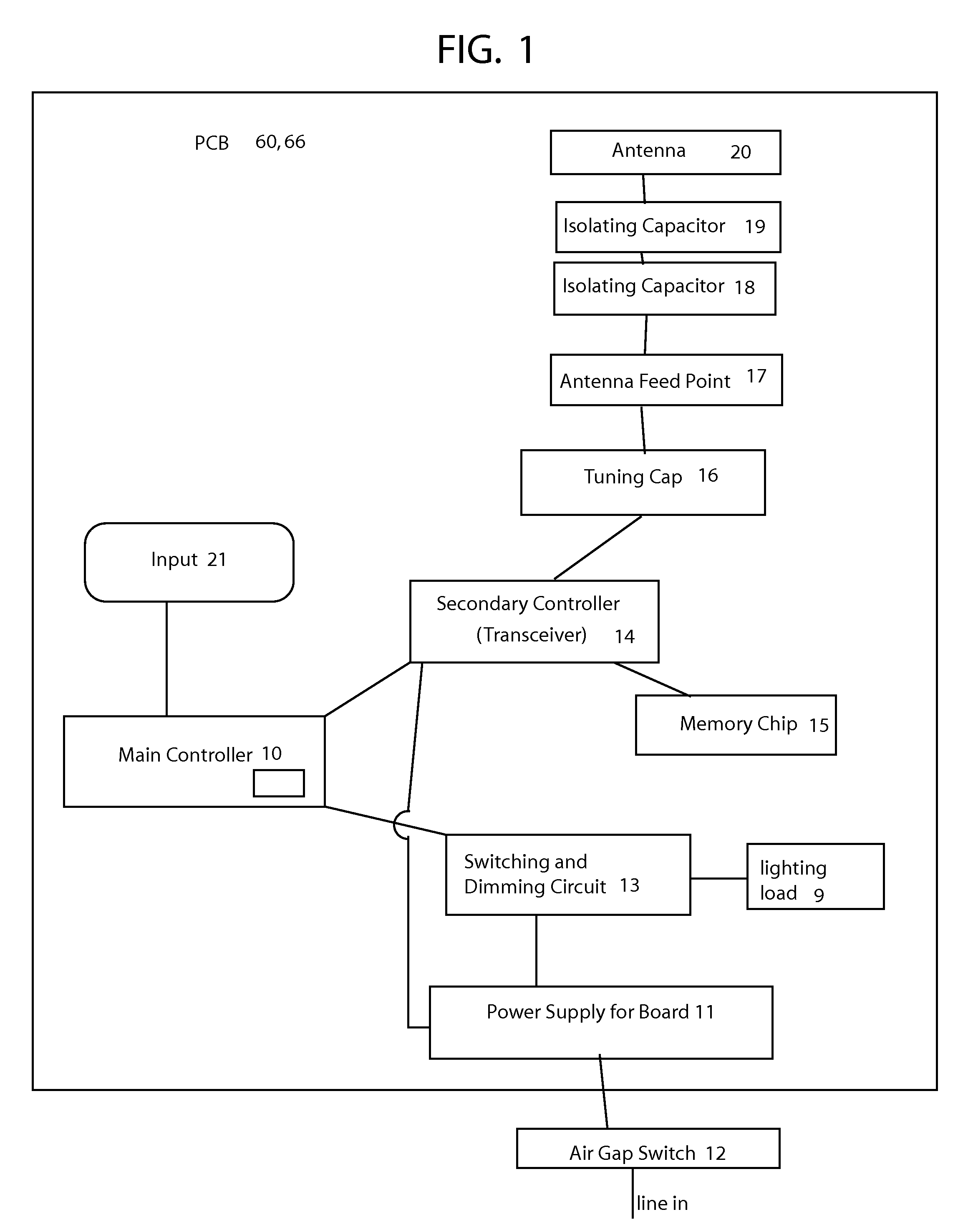
RF antenna integrated into a control device installed into a wall switch box
A remote control electrical device which can communicate with a remote control device. The electrical control device is adapted to fit into a housing which fits into a wall mounting. The remote control electrical device can comprise a control circuit disposed in the housing, a transmitter disposed in the housing, a receiver disposed in the housing wherein said transmitter and said receiver are in communication with the control circuit. There is also a support plate having an inside face facing into the housing and an outside face facing away from the housing body. The support plate is coupled to the housing, wherein there is also an antenna disposed on the outside face of the support plate. This antenna does not receive any power-line AC frequencies or DC, instead it is capacitively coupled to the rest of the electrical components and disposed on the outside face of the support plate.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
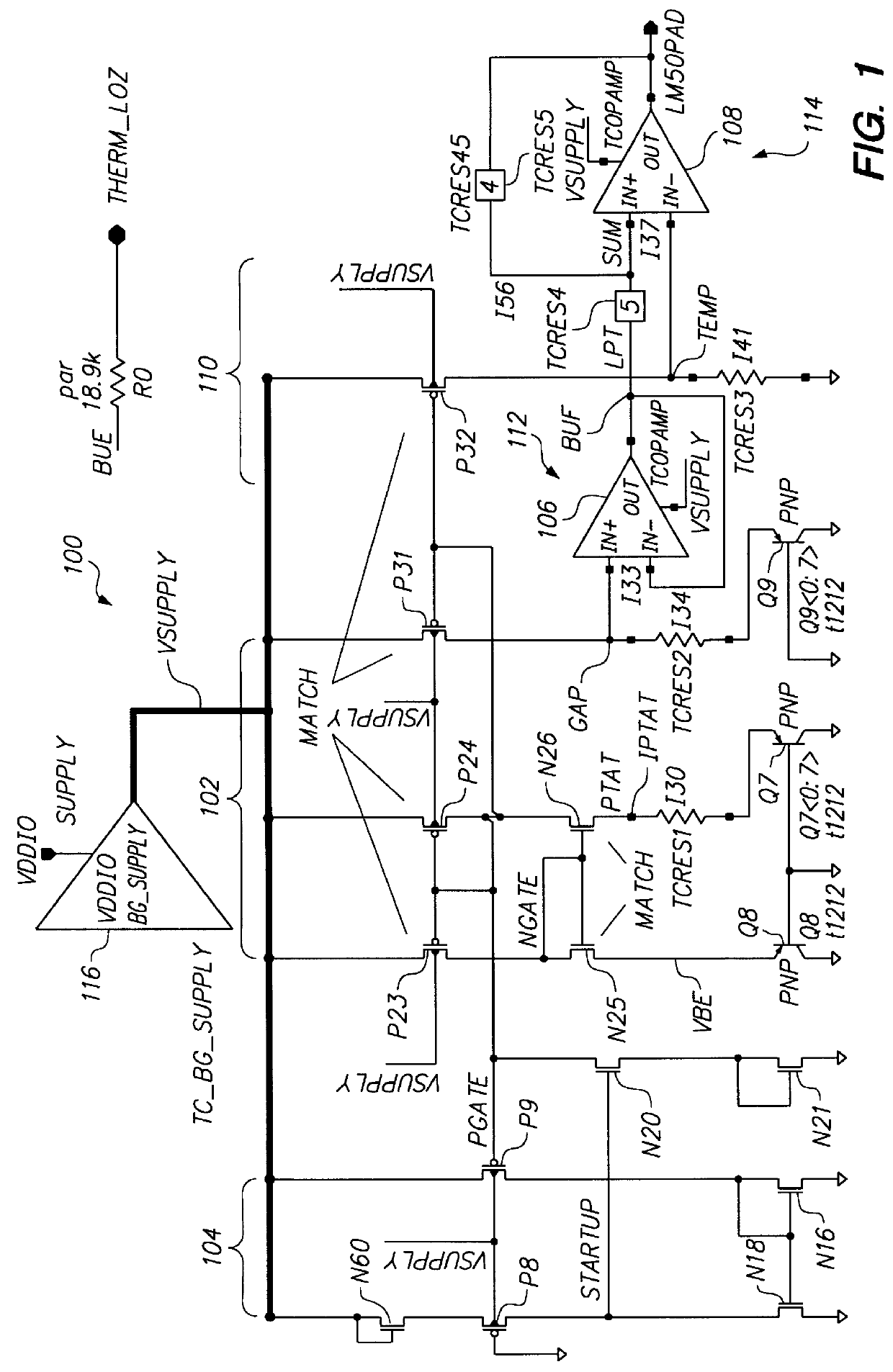
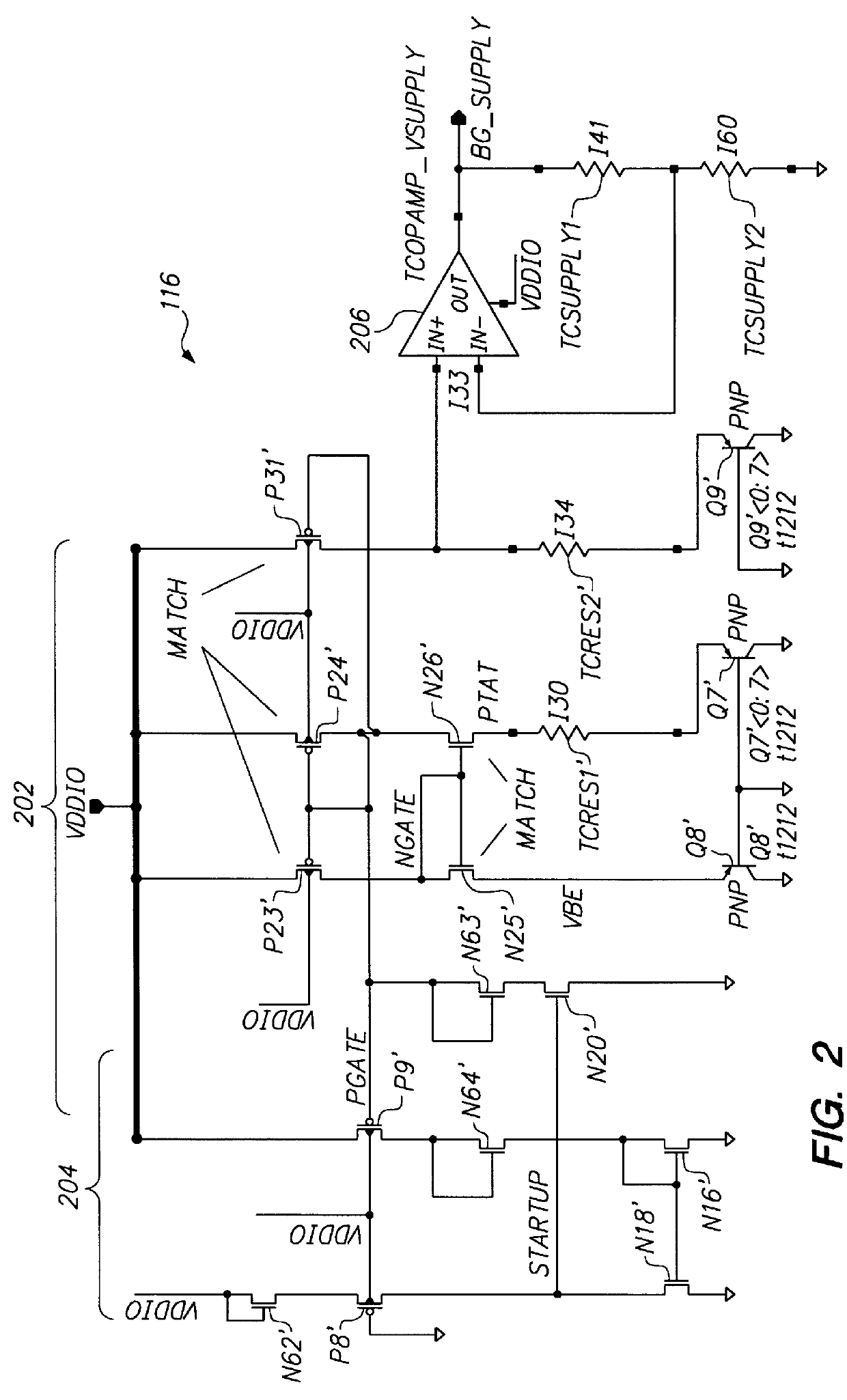
Power supply independent temperature sensor
InactiveUS6157244AMultiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
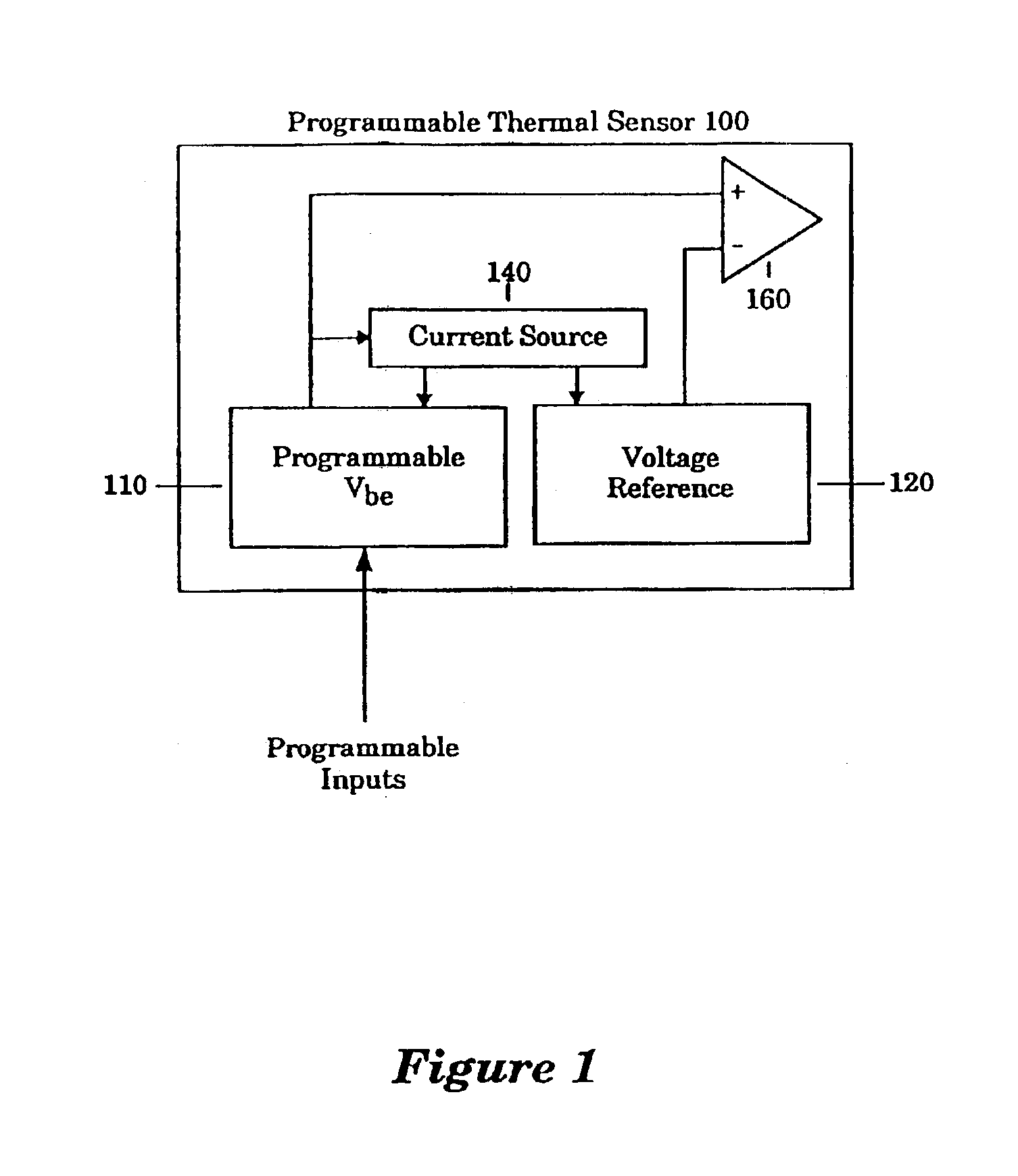
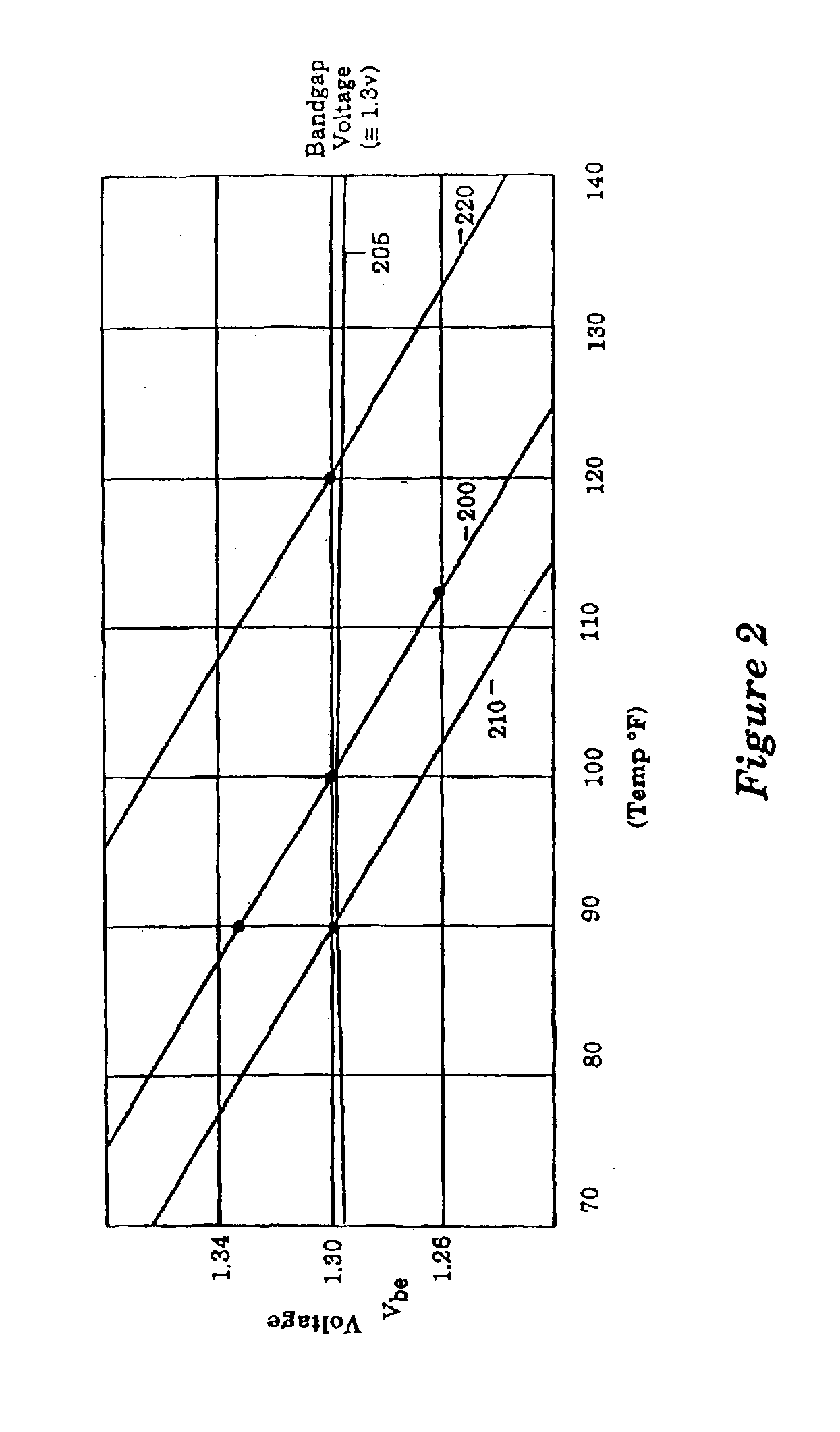
A temperature sensor is fabricated in an integrated circuit in combination with another device such as a microprocessor using a fabrication technology that is suitable for fabricating the device. Operation of the temperature sensor is based on the bandgap physics of semiconductors using a bandgap reference circuit and an amplifier that generate two measurement voltages, a voltage that is temperature-dependent and a voltage that is temperature-independent. The temperature sensor includes a bandgap power supply circuit that supplies a power supply voltage that is very stable to drive the temperature sensor so that the temperature sensor generates an output signal that is essentially independent of the power supply voltage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
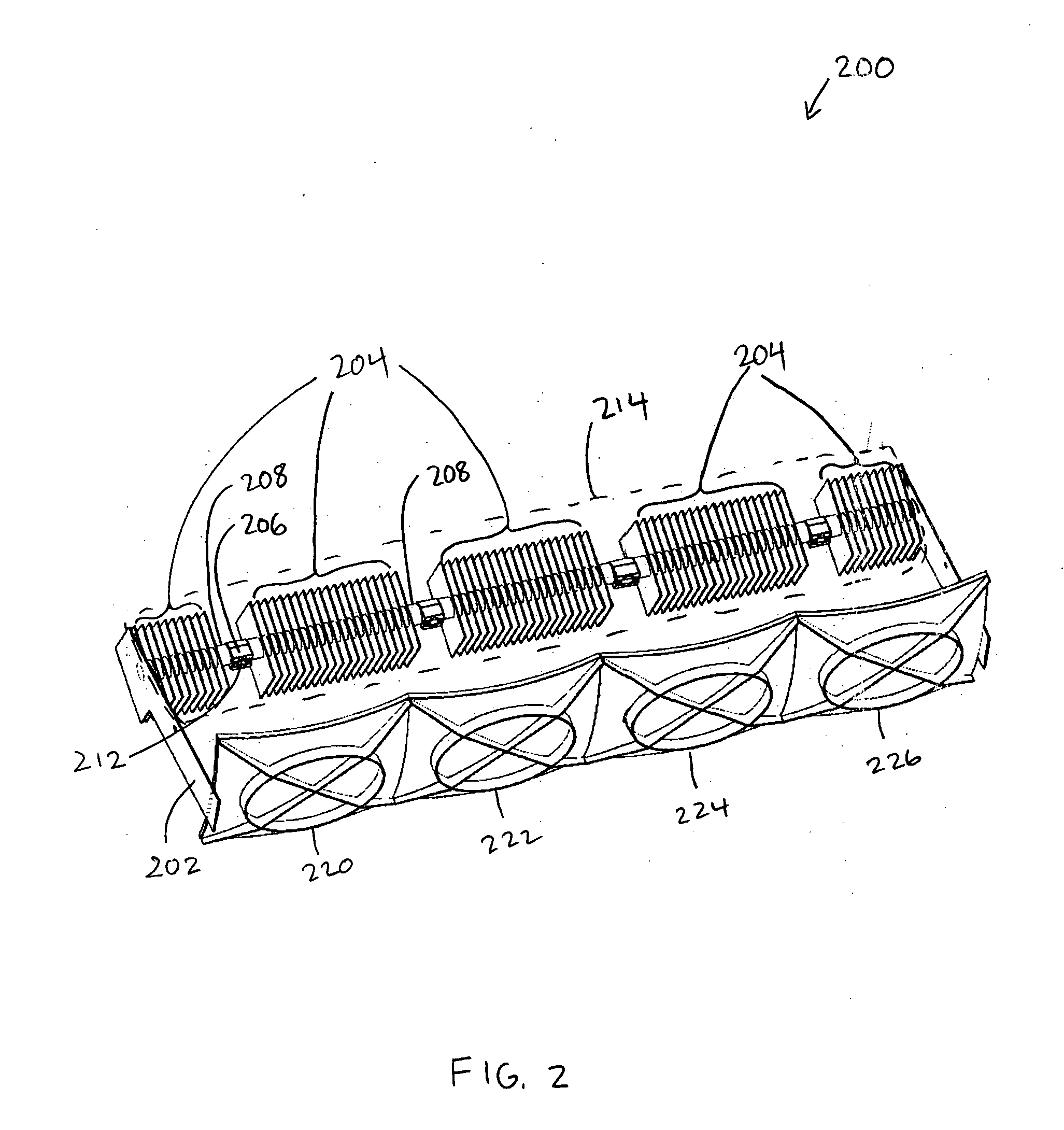
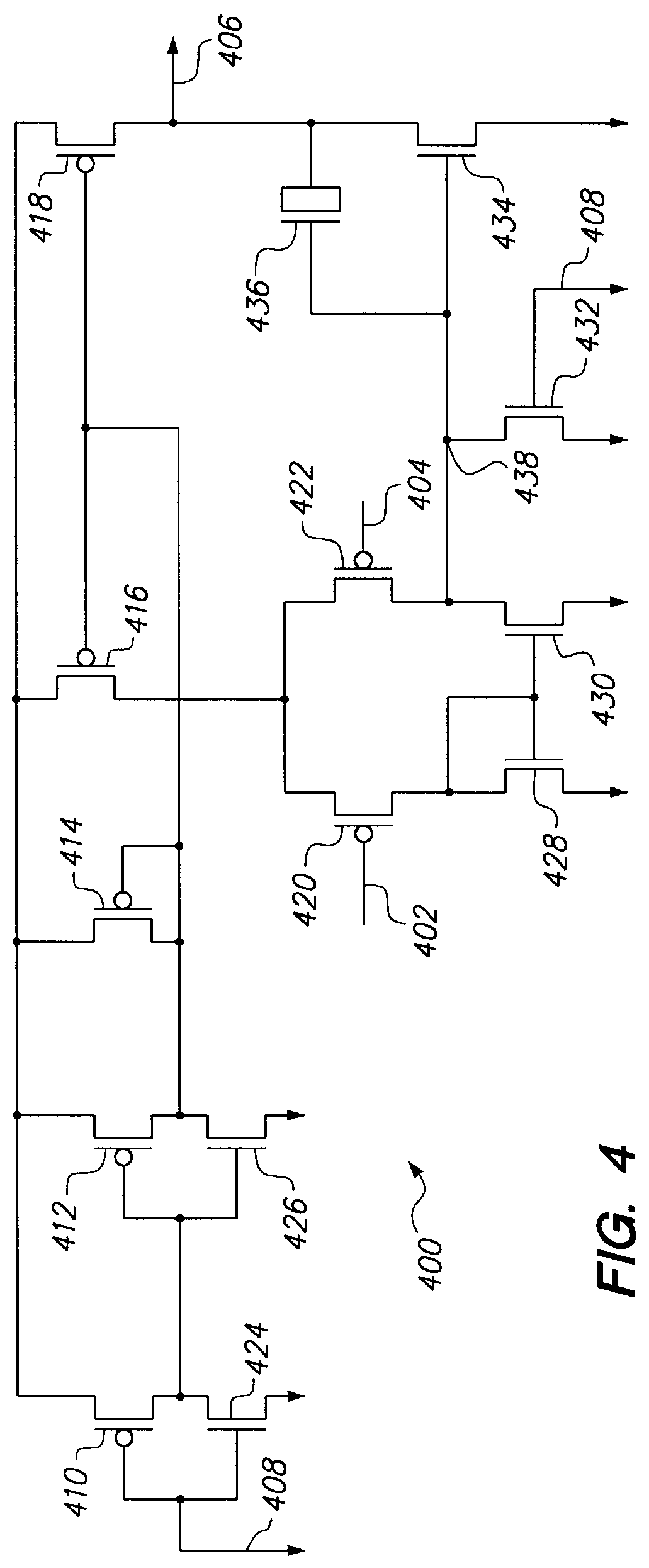
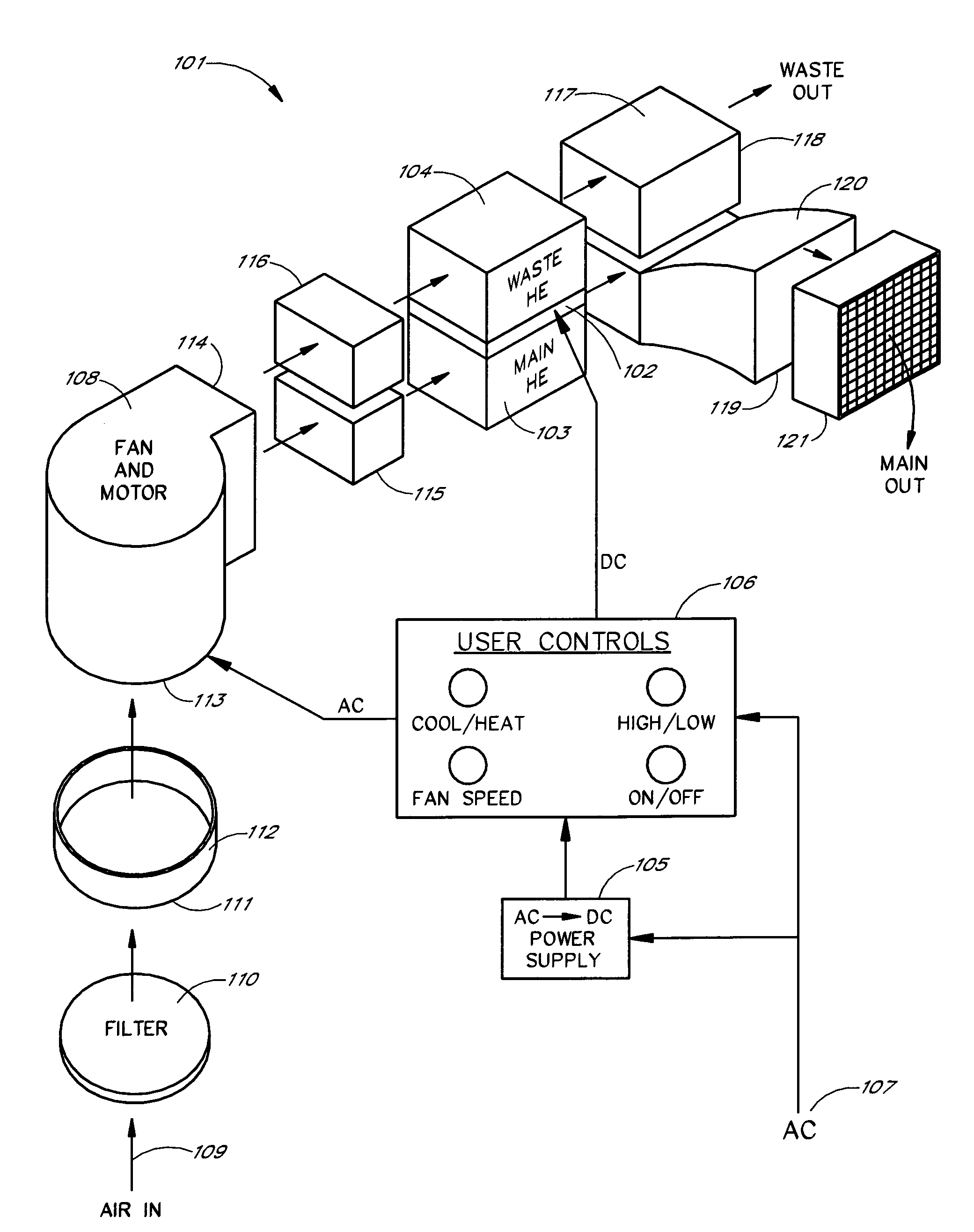
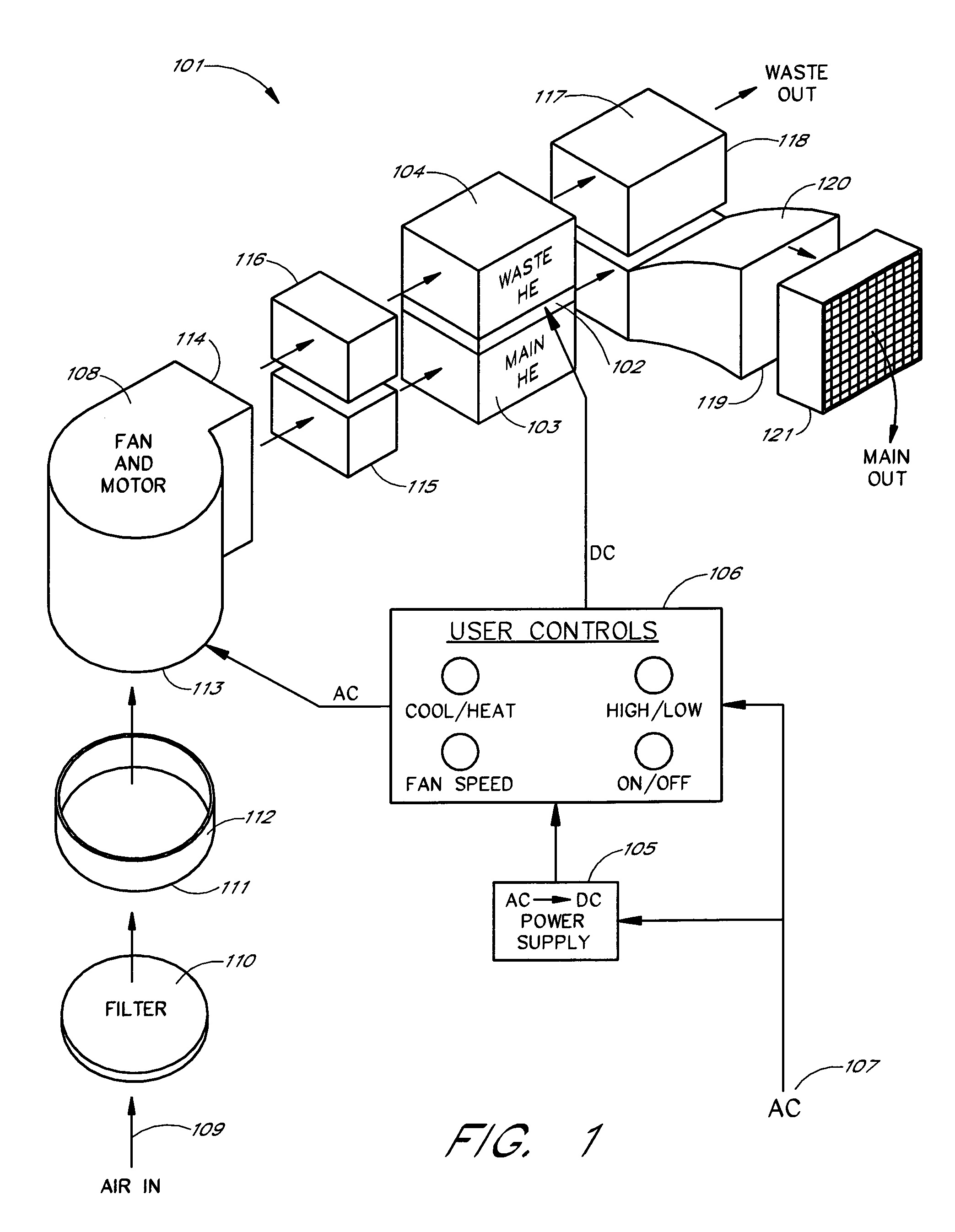
Thermoelectric personal environment appliance
ActiveUS7426835B2Easily discernible effectReduce the required powerDomestic cooling apparatusMachines using electric/magnetic effectsSpace environmentEngineering
A personal environment appliance is disclosed in which a person in a work area can individually control the ambient conditions of that persons localized work space environment. The control permits highly localized adjustment to suit individual preferences, thereby, reducing the impact of individual environmental preferences on the individuals. In addition to environment conditions, a variety of accessories may be provided such as beverage heaters and / or coolers.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
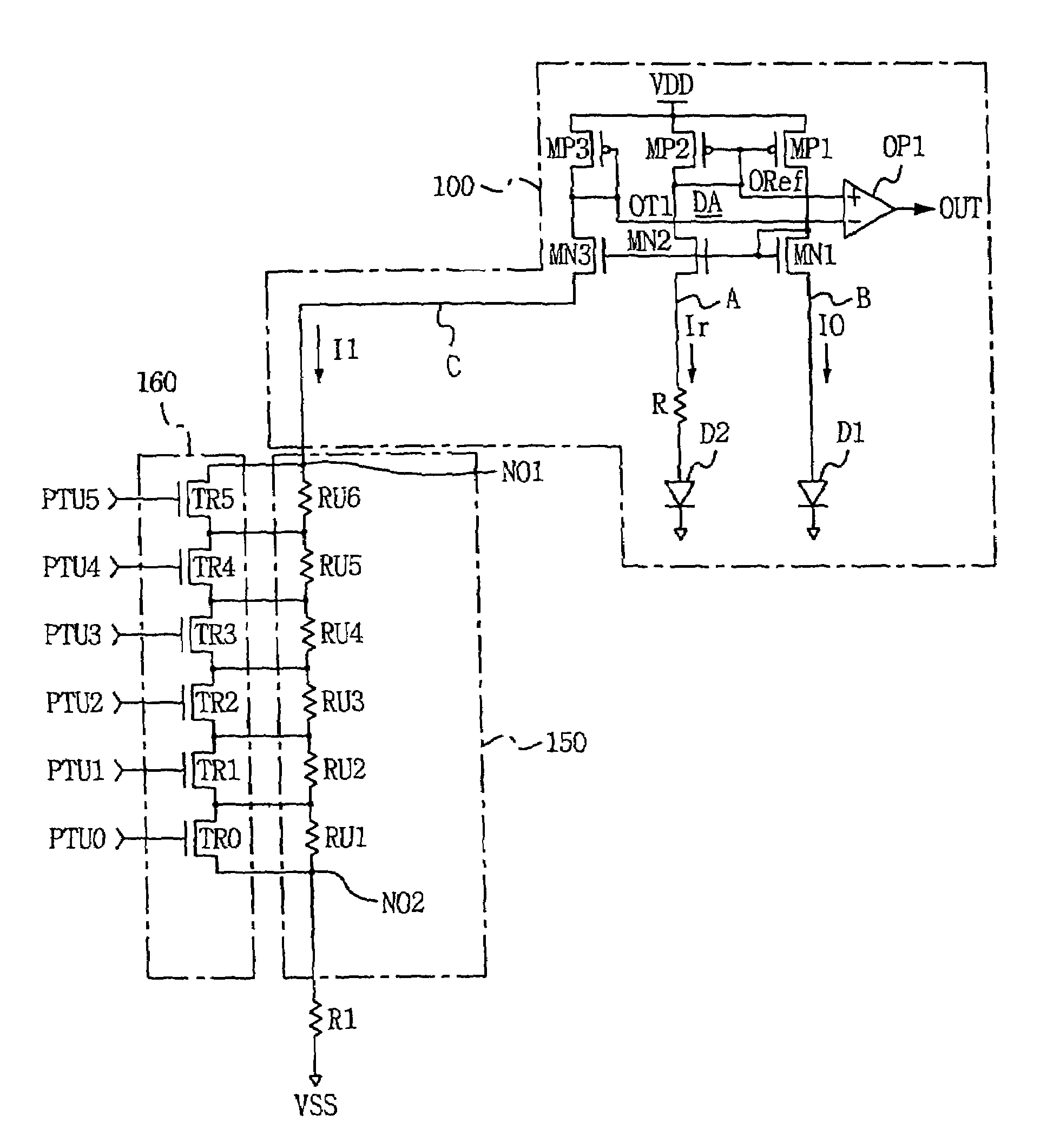
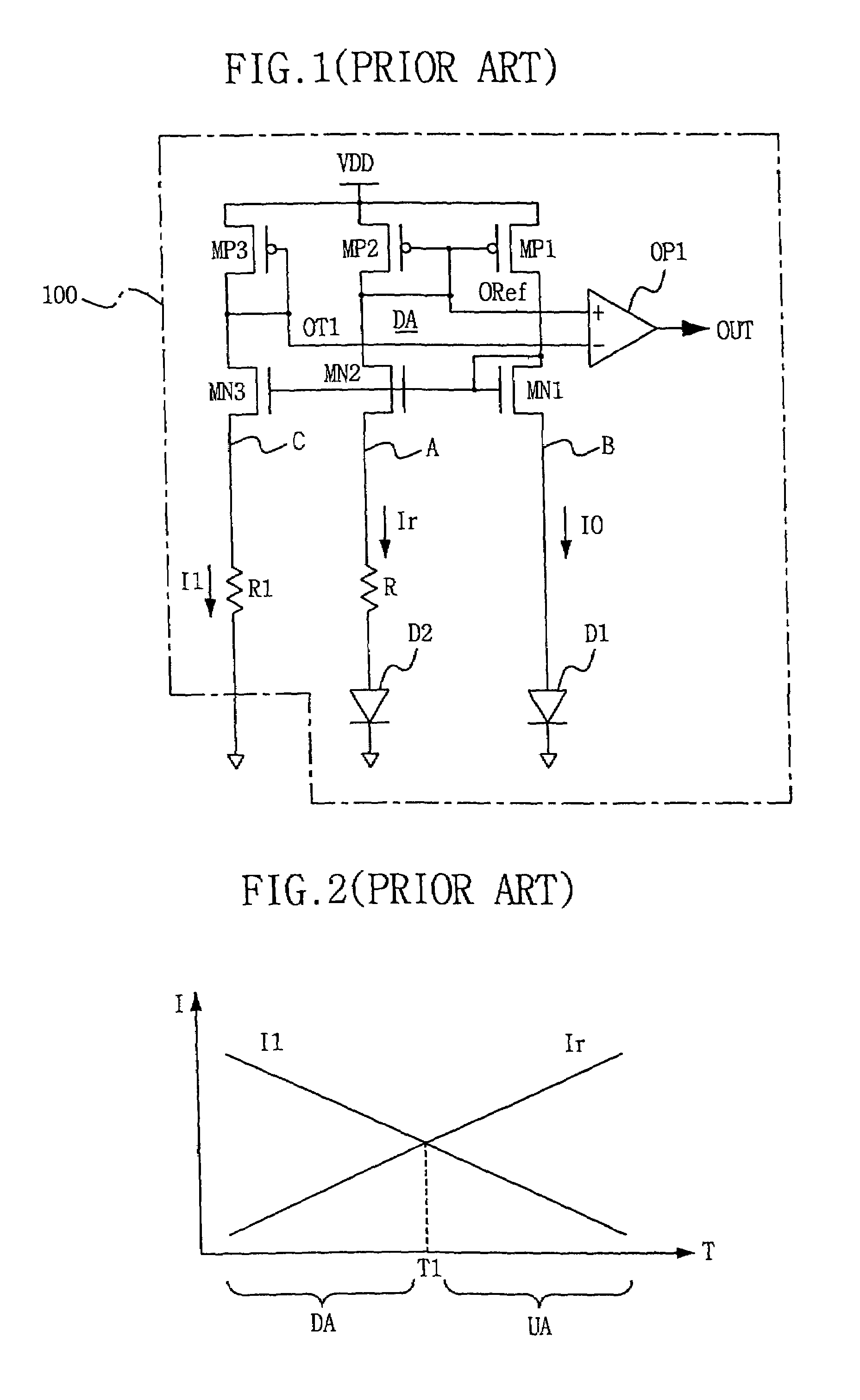
Temperature sensing circuit for use in semiconductor integrated circuit
A temperature sensing circuit has numerous trip points in conformity with a temperature change without adding decrease resistance branches, so as to obtain a fine control based on the temperature change. Accordingly, when employed in a semiconductor memory device, the temperature sensing circuit substantially reduces the consumption of refresh electrical power in a stand-by state without decreasing the reliability of the semiconductor memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit
InactiveUS6876250B2Short refresh cycle timeIncrease temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLow voltageMicroprocessor
A combined low-voltage, low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit is provided for providing a band-gap reference parameter and for sensing the temperature of a chip, such as an eDRAM memory unit or CPU chip, using the band-gap reference parameter. The combined sensor circuit is insensitive to supply voltage and a variation in the chip temperature. The power consumption of both circuits, i.e., the band-gap reference and the temperature sensor circuits, encompassing the combined sensor circuit is less than one μW. The combined sensor circuit can be used to monitor local or global chip temperature. The result can be used to (1) regulate DRAM array refresh cycle time, e.g., the higher the temperature, the shorter the refresh cycle time, (2) to activate an on-chip or off-chip cooling or heating device to regulate the chip temperature, (3) to adjust internally generated voltage level, and (4) to adjust the CPU (or microprocessor) clock rate, i.e., frequency, so that the chip will not overheat. The combined band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit of the present invention can be implemented within battery-operated devices having at least one memory unit. The low-power circuits of the sensor circuit extend battery lifetime and data retention time of the cells of the at least one memory unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Thermal memory cell and memory device including the thermal memory cell
InactiveUS20040188668A1Facilitate writing informationEasy to readSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical impedance
A memory cell includes a storage medium having a programmable thermal impedance, and a heater in thermal communication with the storage medium for programming the thermal impedance. In another aspect, a memory cell includes a storage medium having a programmable electrical impedance, and a heater in thermal communication with the storage medium for programming the electrical impedance. In a third aspect, a memory device includes a plurality of the memory cells in accordance with the first and / or second aspect of the present invention.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
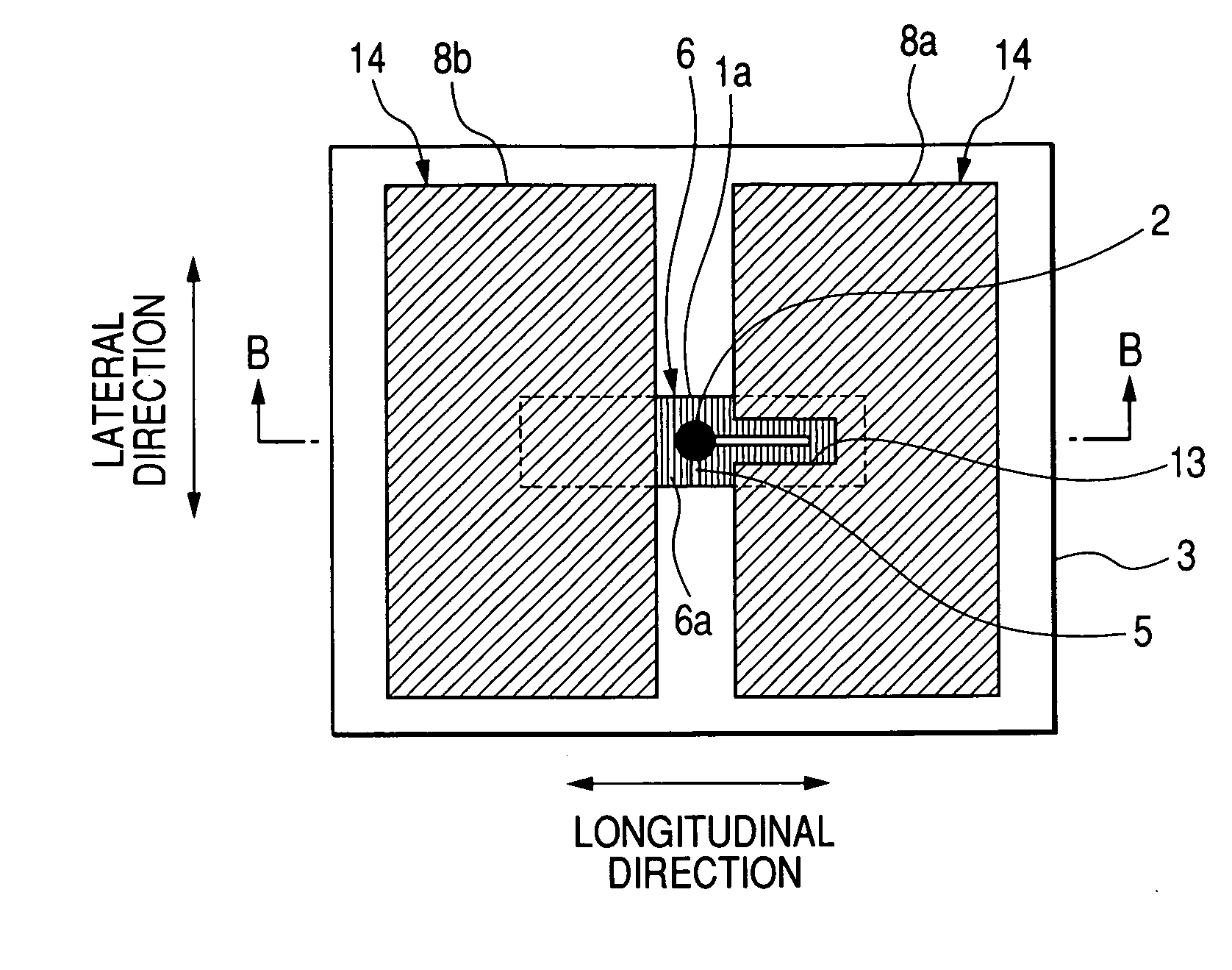
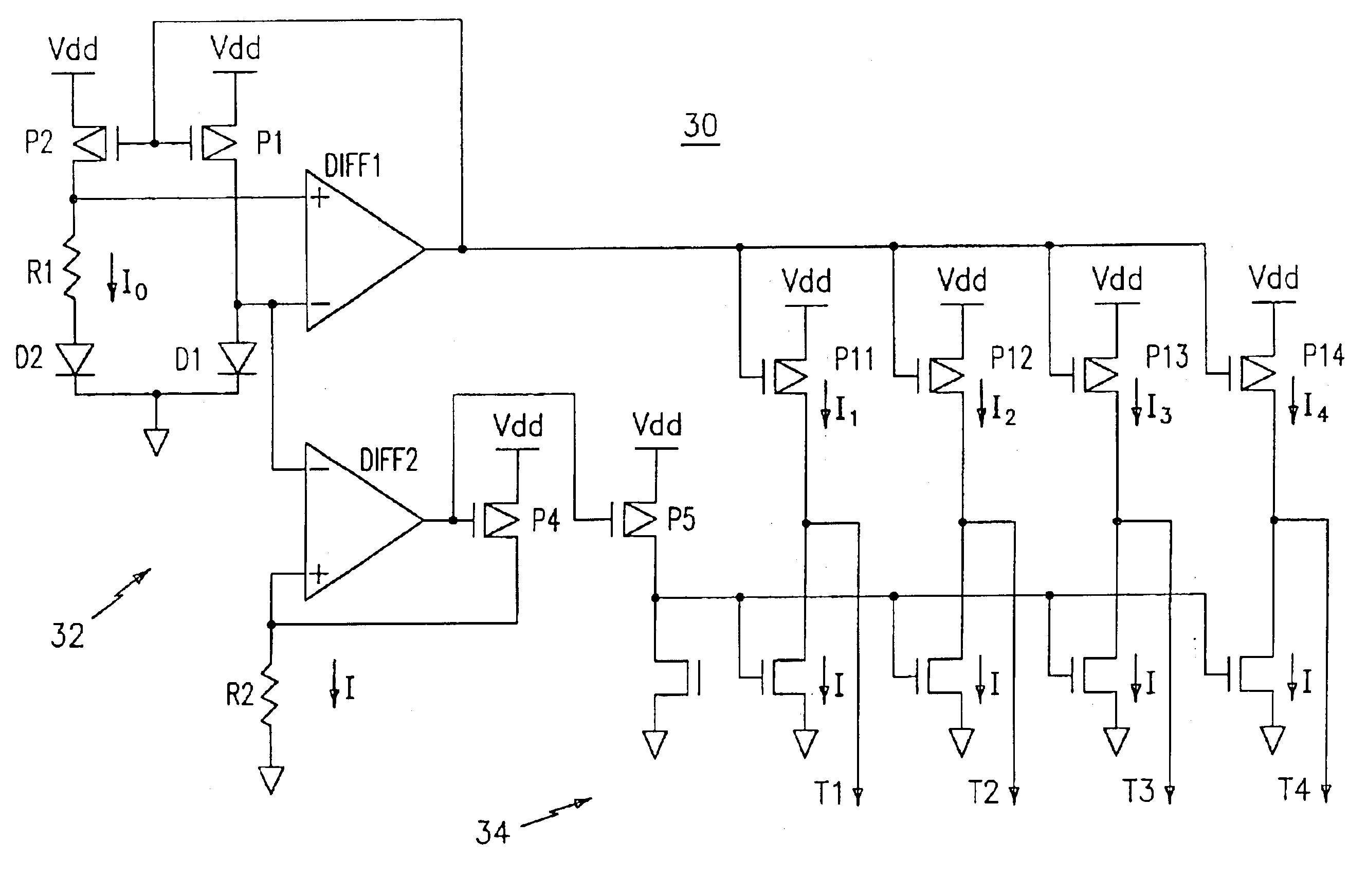
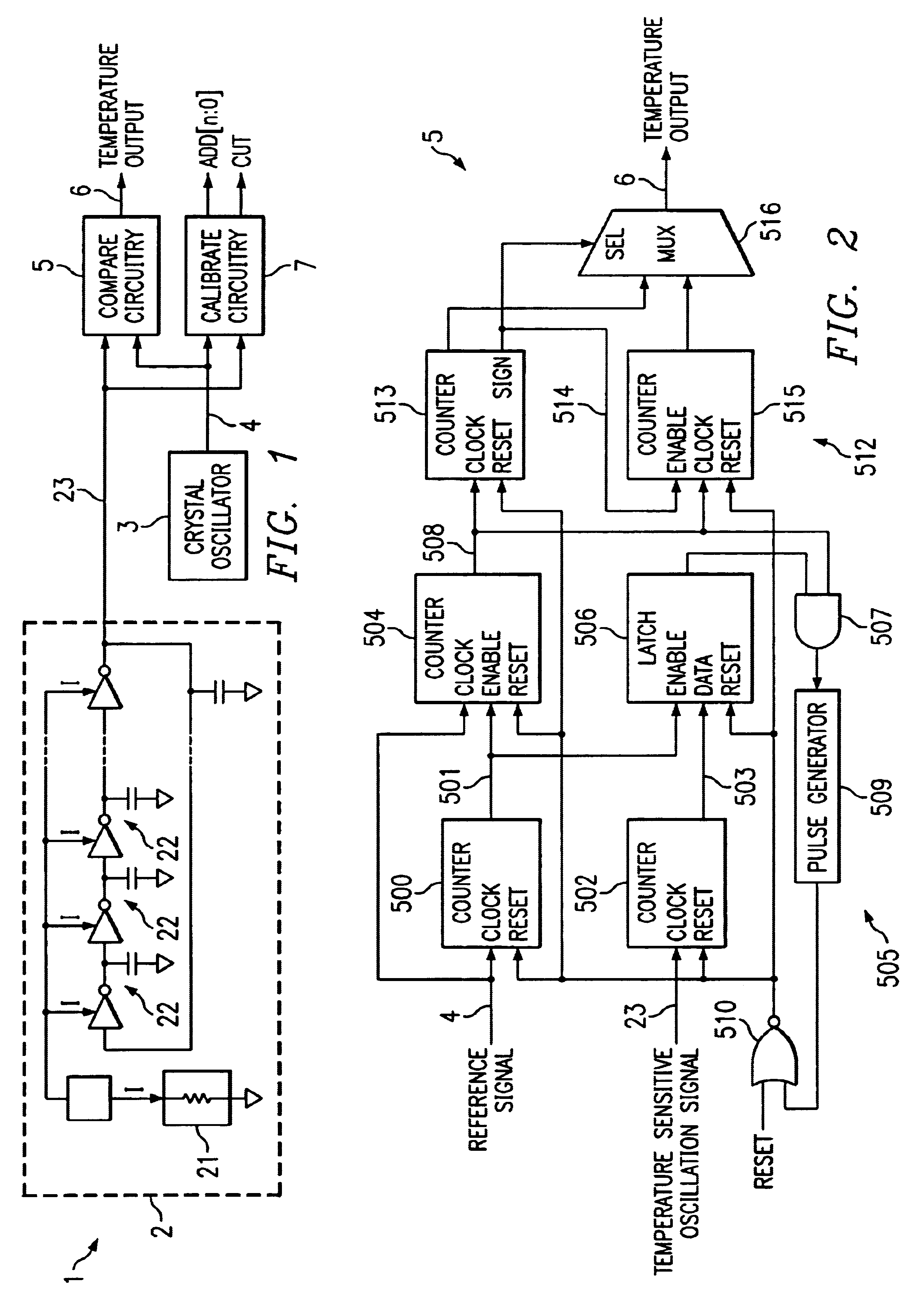
Method and a measuring circuit for determining temperature from a PN junction temperature sensor, and a temperature sensing circuit comprising the measuring circuit and a PN junction
ActiveUS7010440B1Accurate representationEliminate the effects ofThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionSwitched currentExcitation current
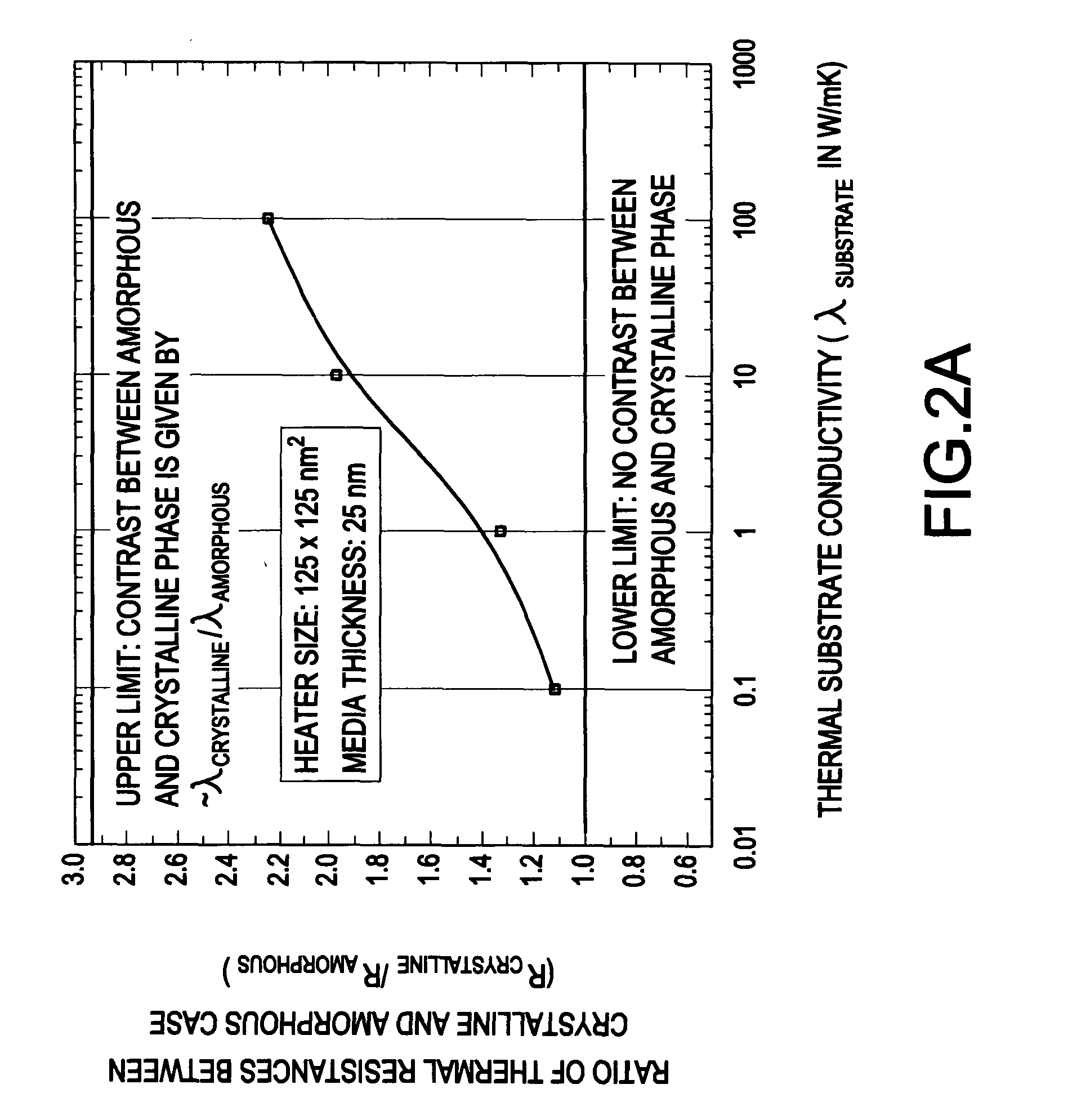
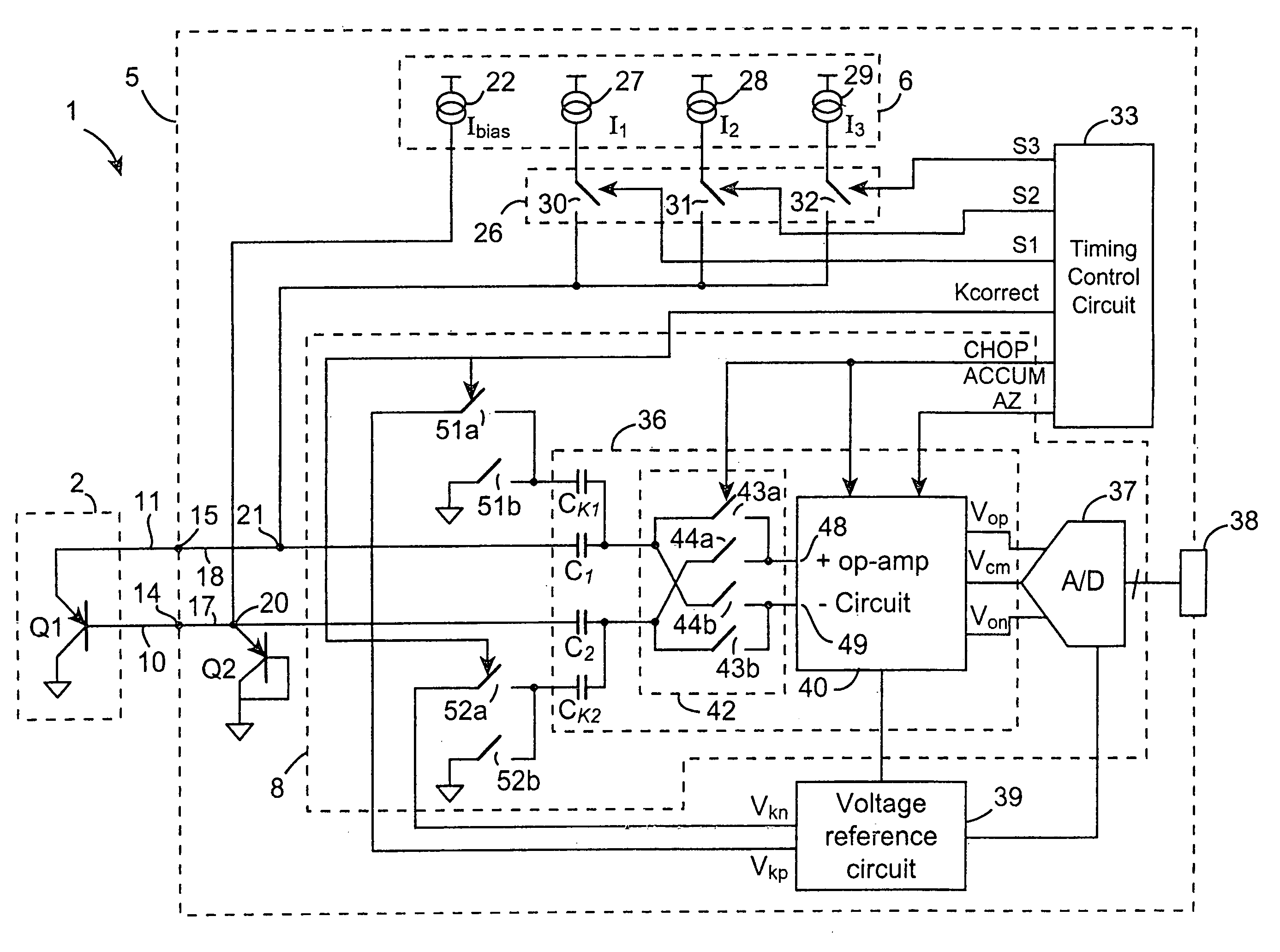
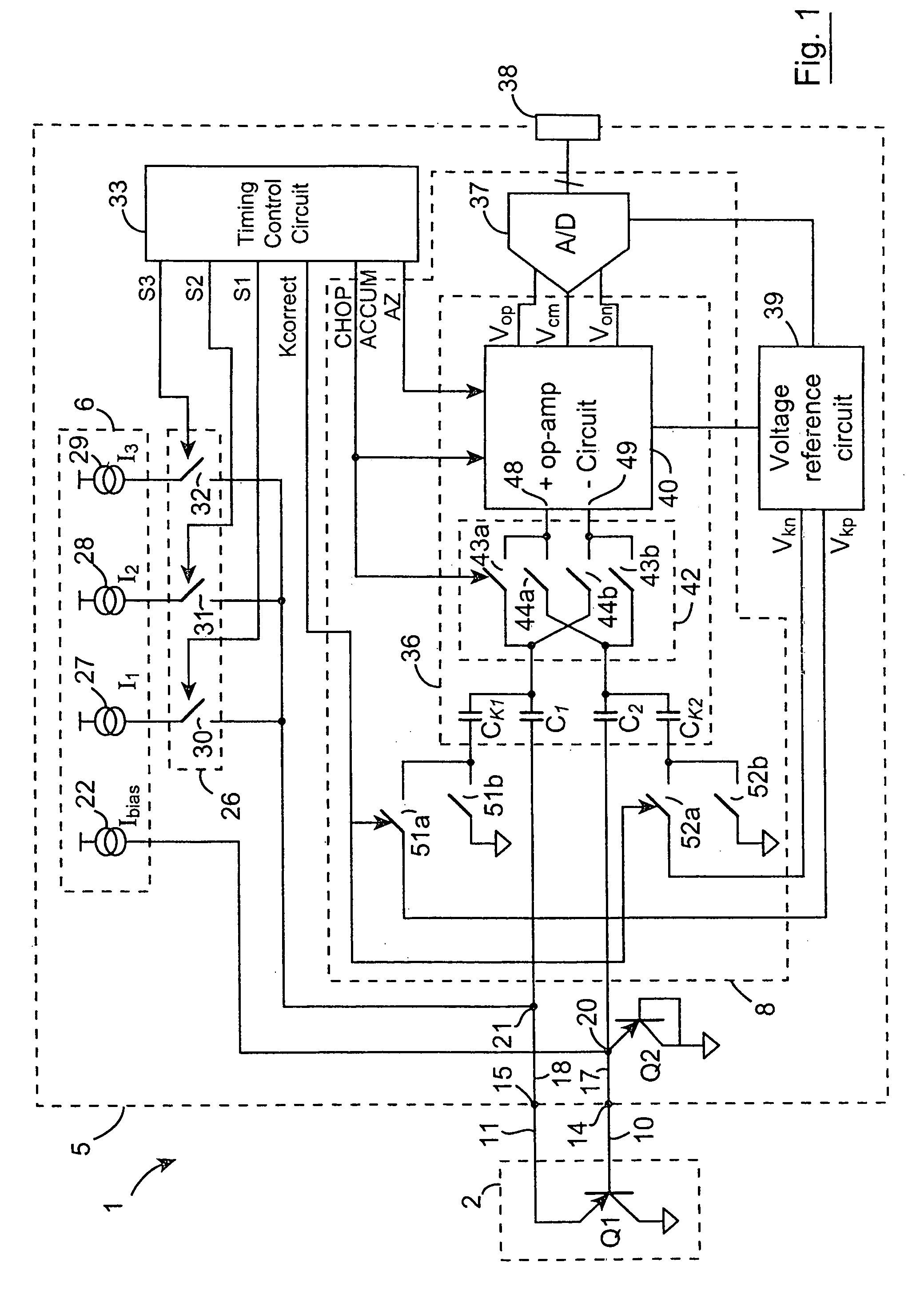
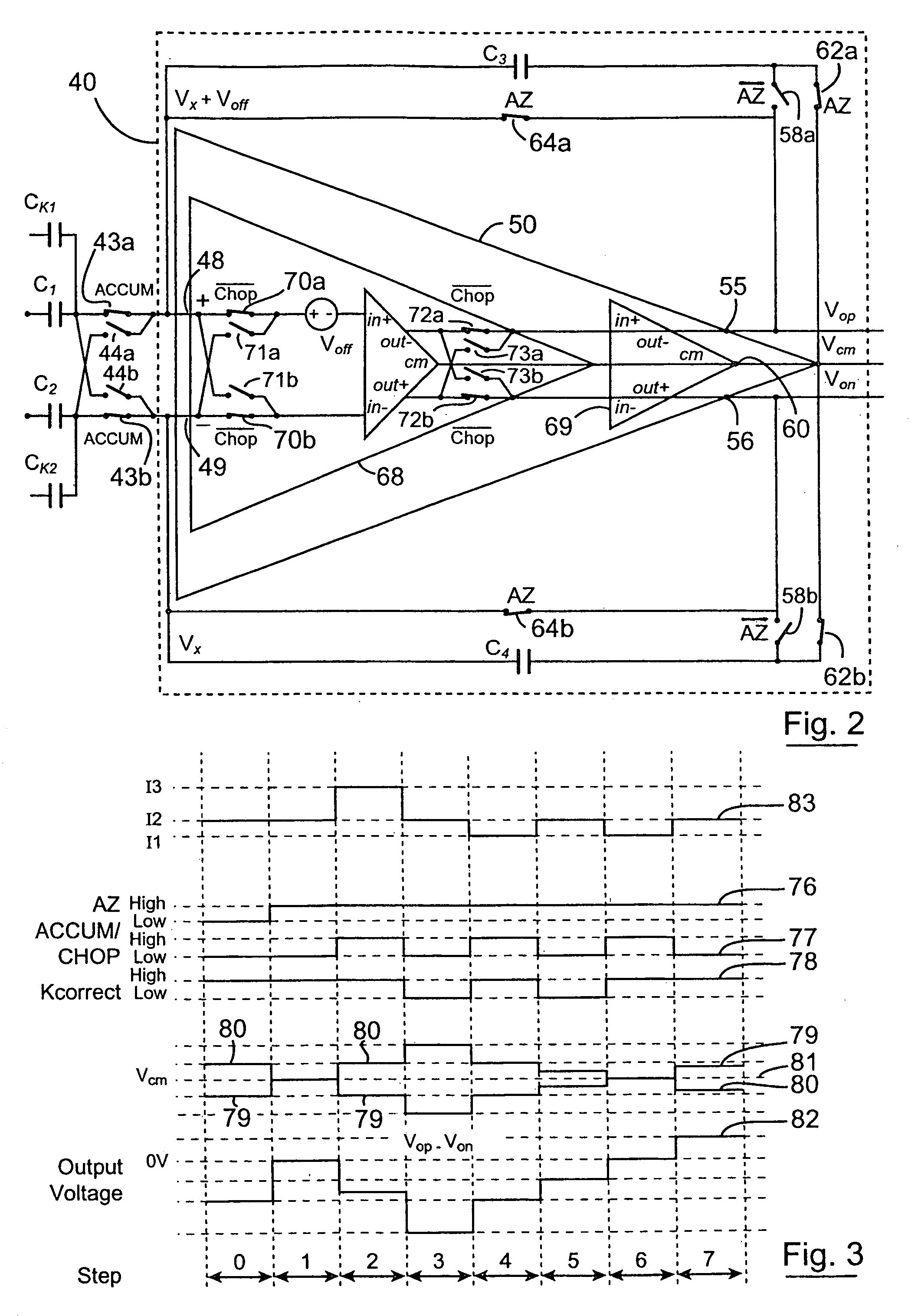
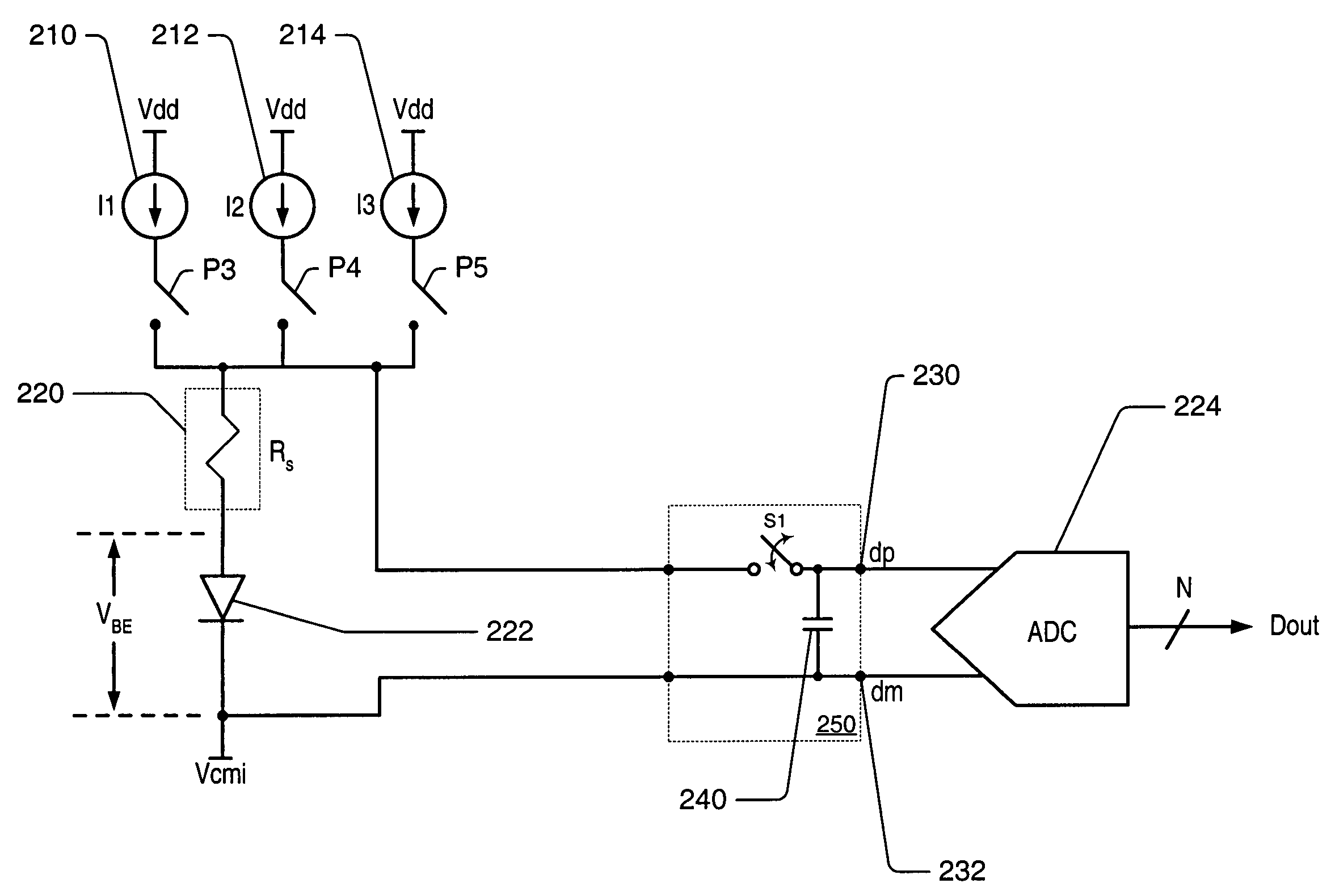
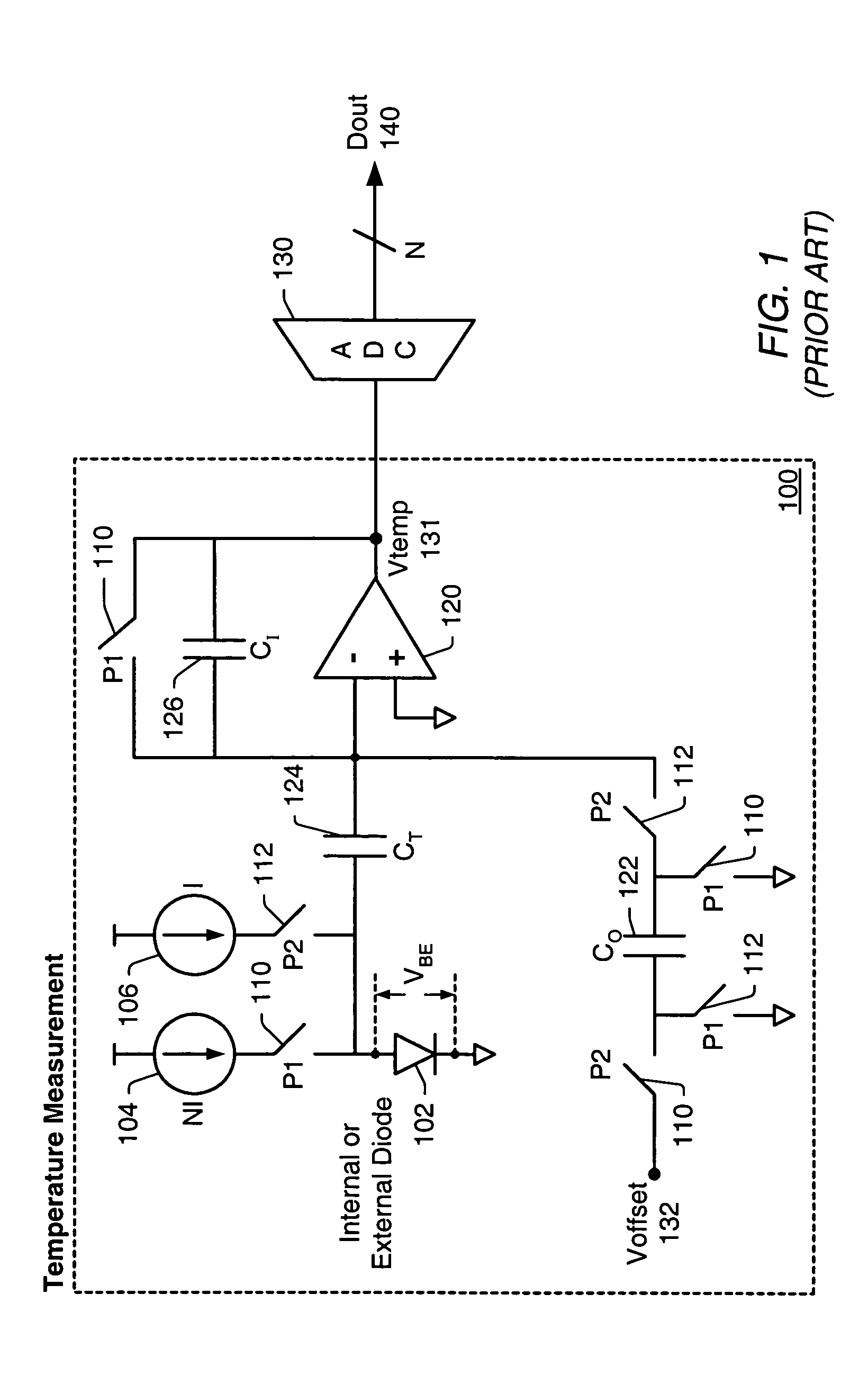
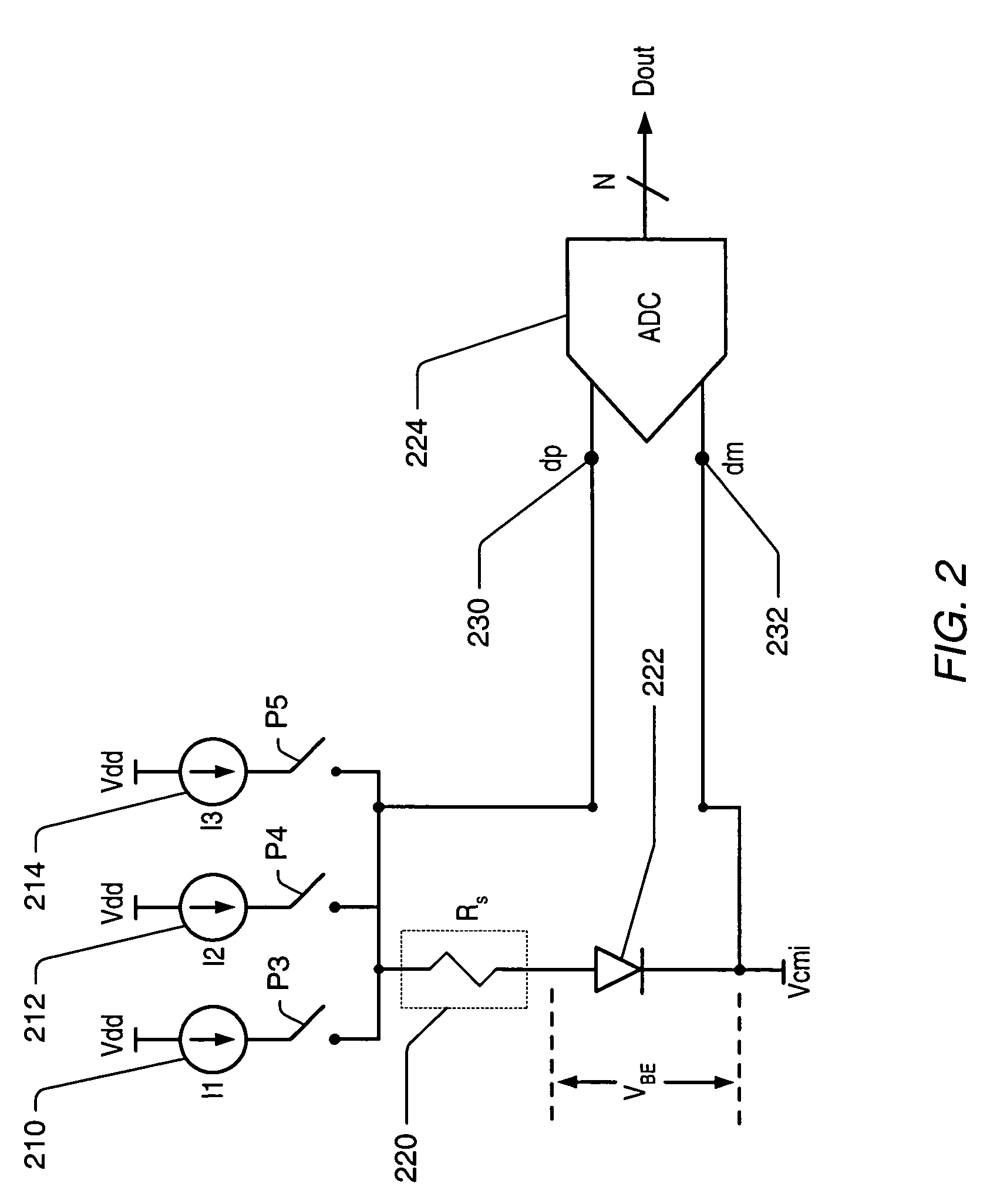
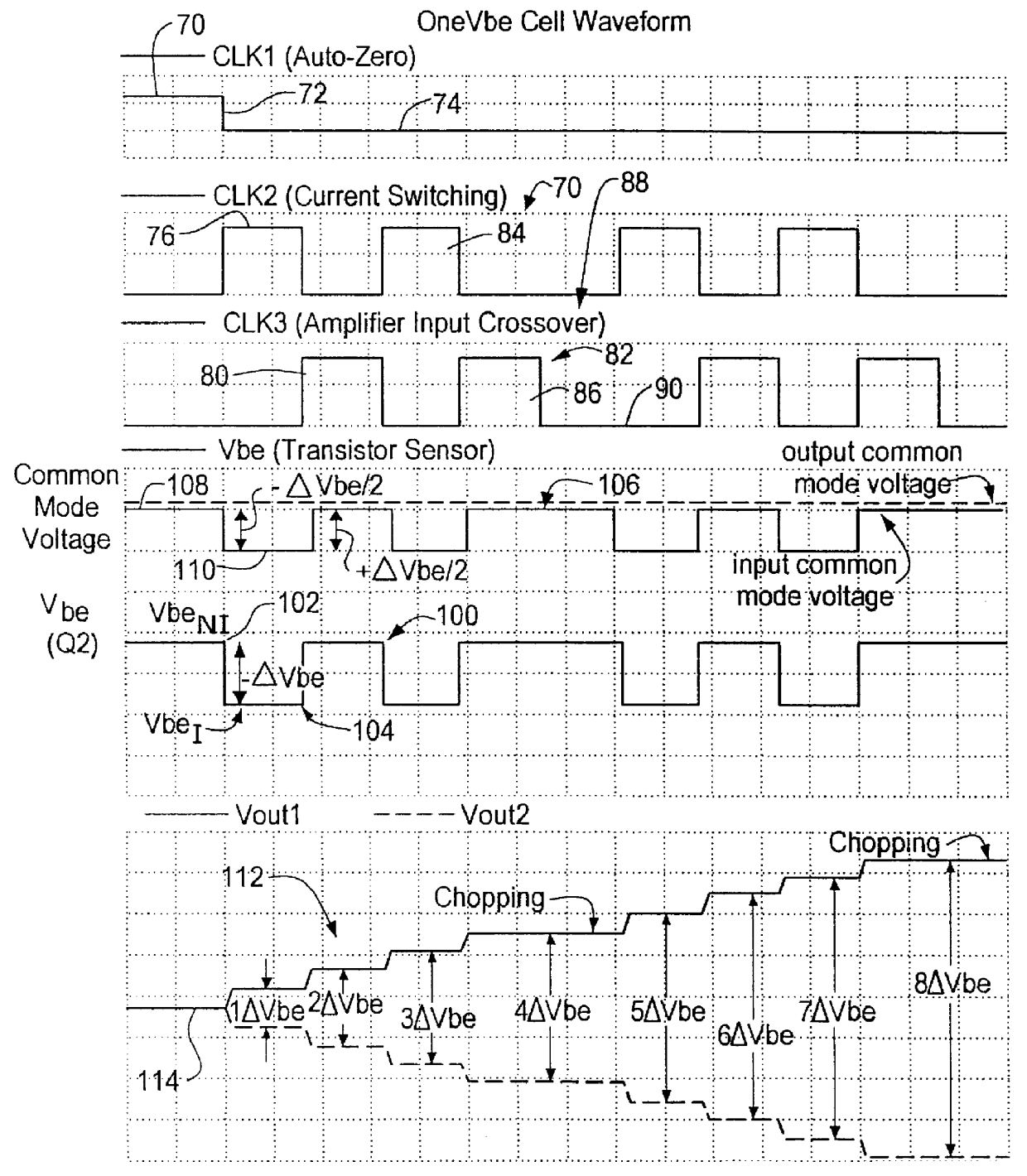
A switched current temperature sensing circuit (1) comprises a measuring transistor (Q1) which is located remotely of a measuring circuit (5) which applies three excitation currents (I1,I2,I3) of different values to the measuring transistor (Q1) in a predetermined current sequence along lines (10,11). Resulting base / emitter voltages from the measuring transistor (Q1) are applied to the measuring circuit (5) along the same two lines (10,11) as the excitation currents are applied to the measuring transistor (Q1). Voltage differences ΔVbe of successive base / emitter voltages resulting from the excitation currents are integrated in an integrating circuit (36) of the measuring circuit (5) to provide an output voltage indicative of the temperature of the measuring transistor (Q1). By virtue of the fact that the measuring transistor (Q1) is excited by excitation currents of three different values, the effect of current path series resistance in the lines (10,11) on the output voltage indicative of temperature is eliminated. The predetermined current sequence in which the excitation currents are applied to the measuring transistor (Q1) is selected to minimize the voltages in the integrating circuit (36) during integration of the voltage differences ΔVbe.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Integrated resistance cancellation in temperature measurement systems
ActiveUS7281846B2Eliminate needThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceIntegrator
A temperature measurement device may be implemented by coupling a PN-junction, which may be comprised in a diode, to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that comprises an integrator. Different currents may be successively applied to the diode, resulting in different VBE values across the diode. The ΔVBE values thus obtained may be successively integrated. Appropriate values for the different currents may be determined based on a set of mathematical equations, each equation relating the VBE value to the temperature of the diode, the current applied to the diode and parasitic series resistance associated with the diode. When the current sources with the appropriate values are sequentially applied to the diode and the resulting diode voltage differences are integrated by the integrator comprised in the ADC, the error in the temperature measurement caused by series resistance is canceled in the ADC, and an accurate temperature reading of the diode is obtained from the output of the ADC.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
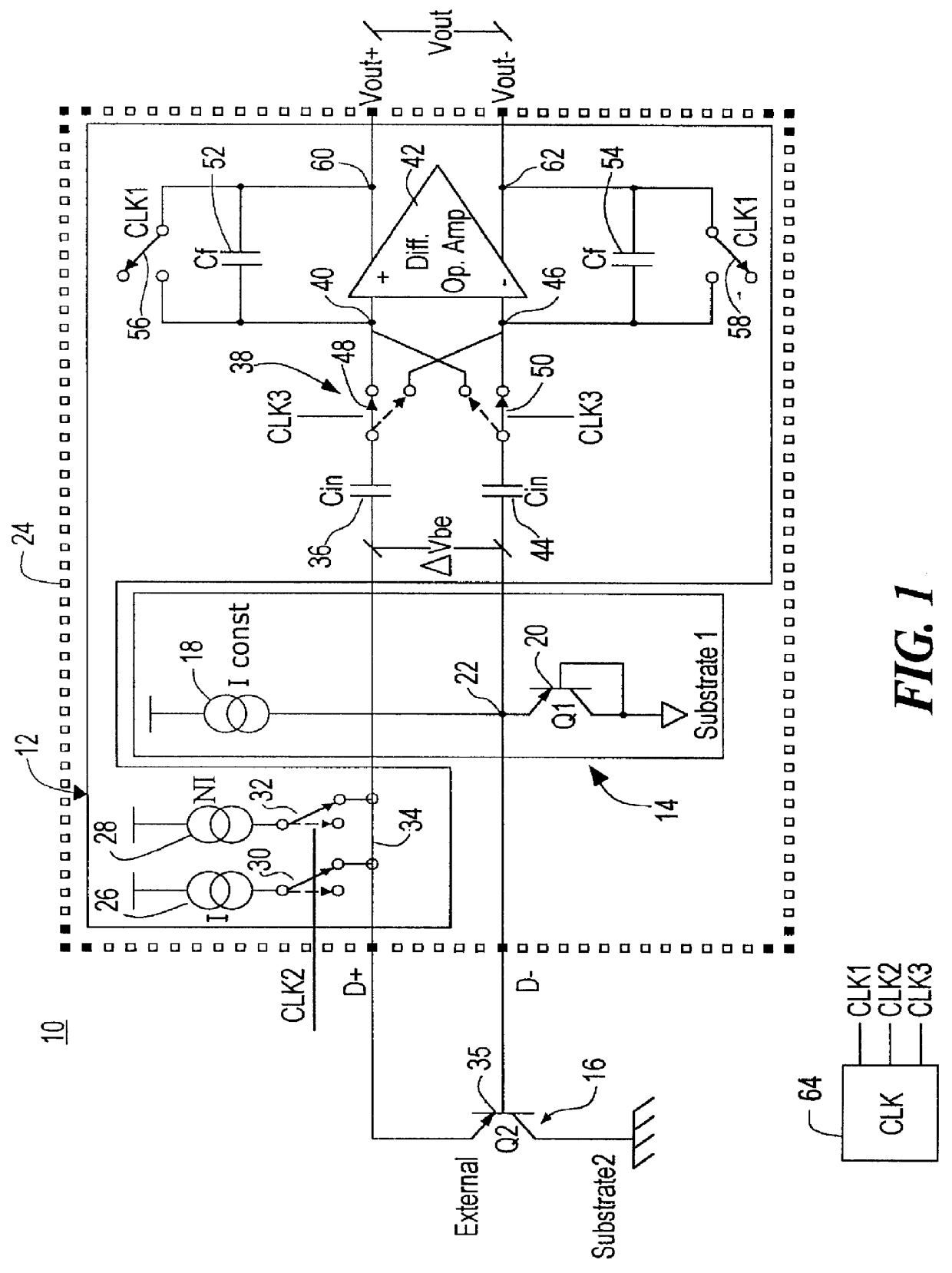
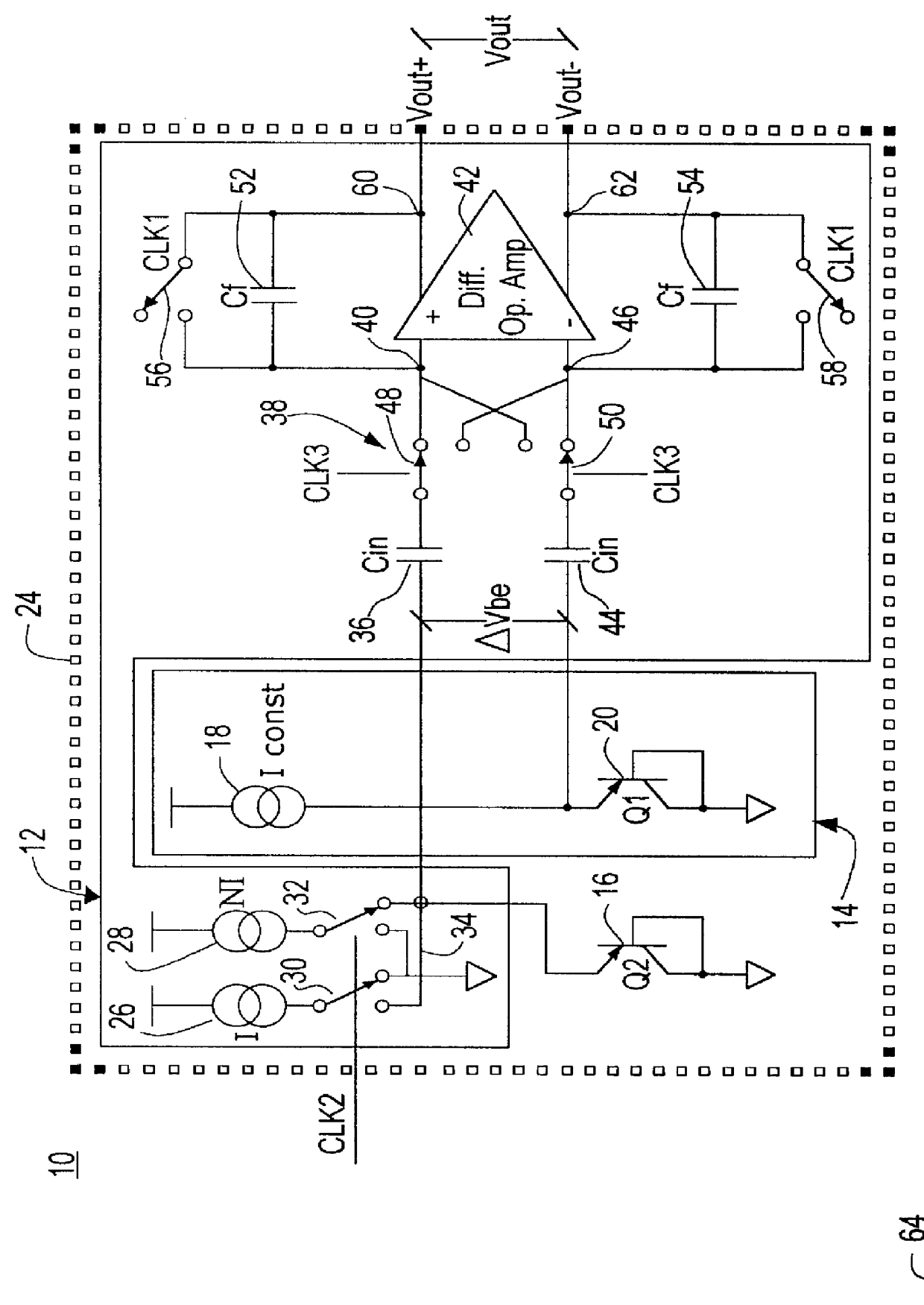
Decoupled switched current temperature circuit with compounded DELTA V be
InactiveUS6097239AThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectronic switchingDelta-vAudio power amplifier
A decoupled switched current temperature circuit with compounded DELTA Vbe includes an amplifier having an inverting input with corresponding non-inverting output and a non-inverting input with a corresponding inverting output; a PN junction connected to the non-inverting input through a first input capacitor and a voltage reference circuit is connected to the inverting input through a second input capacitor; a current supply includes a low current source and a high current source; a switching device applies the high current source to the PN junction and applies the low current source to the PN junction for providing the DELTA Vbe of the PN junction to the first capacitor; a first feedback capacitor is interconnected between the inverting output and the non-inverting input and a second feedback capacitor is interconnected between the non-inverting output and inverting input of the amplifier to define the gain on each of the inputs to produce a differential voltage across the outputs representative of the temperature of the PN junction; first and second reset switching devices discharge the first and second feedback capacitors, respectively, and a multi-phase switched device alternately interchanges the connection of the first and second input capacitors with the amplifier inputs for compounding the single DELTA Vbe .
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
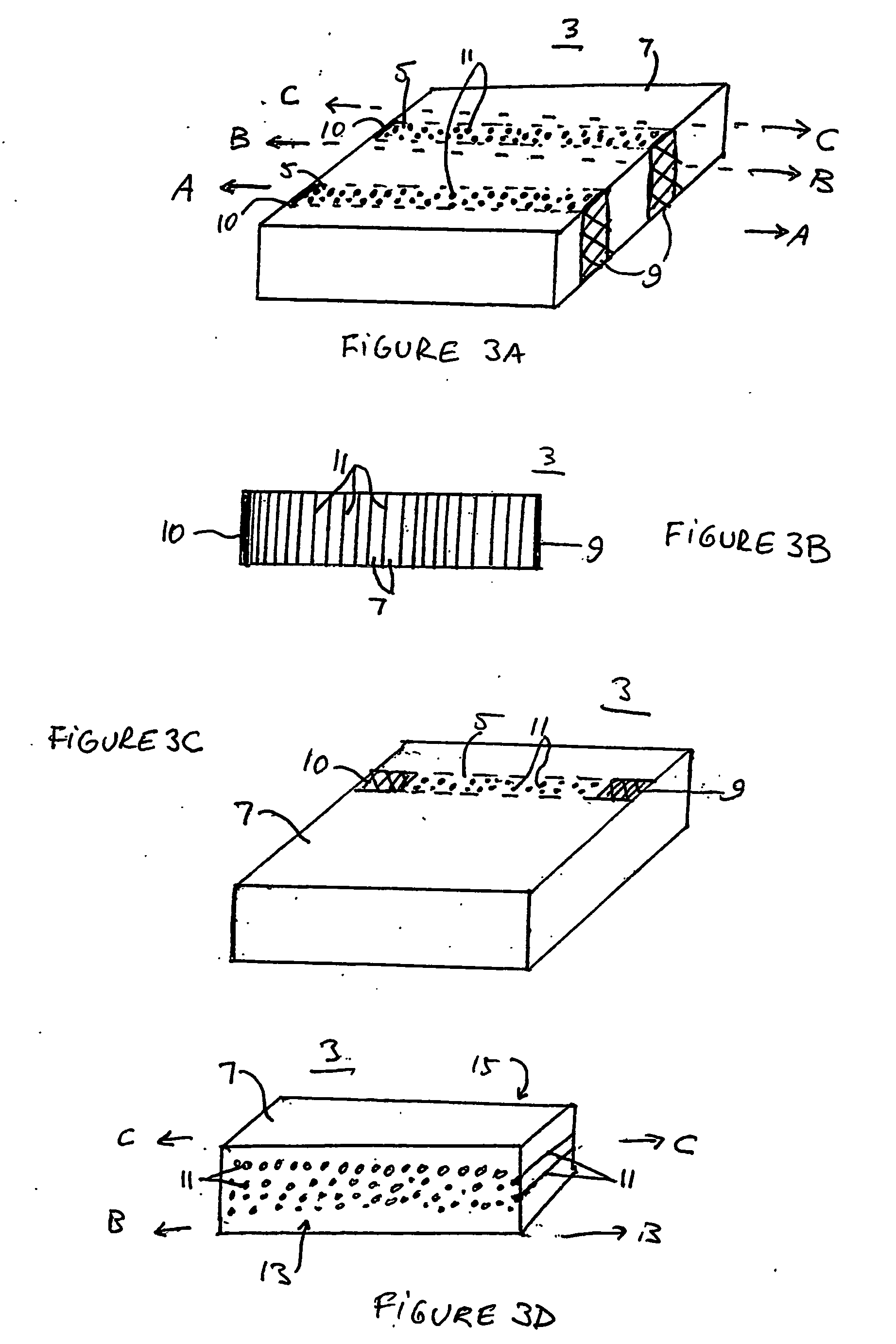
Embedded nanotube array sensor and method of making a nanotube polymer composite
ActiveUS20070138010A1Material nanotechnologyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPolymer compositesMaterials science
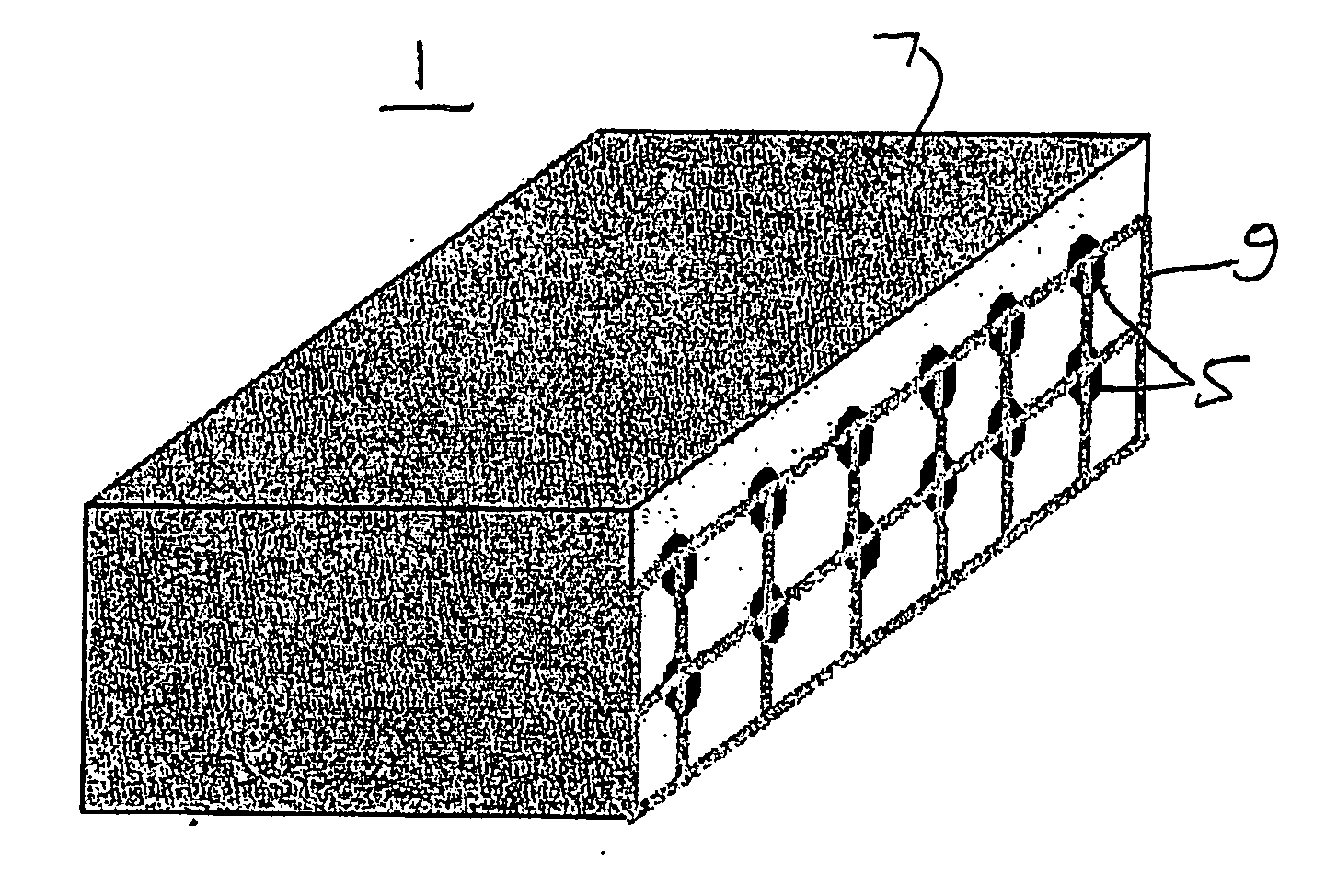
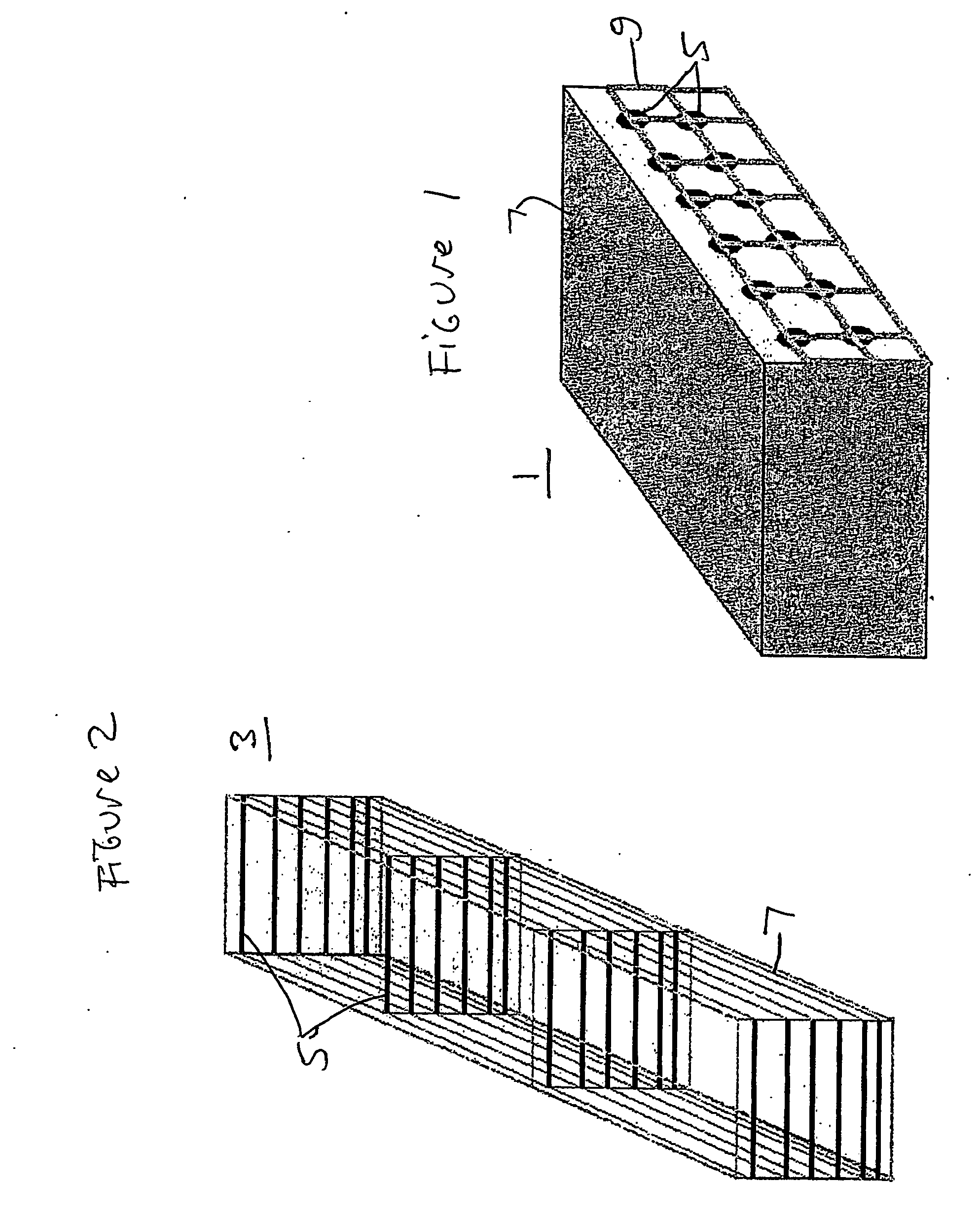
A method of producing polymer / nanotube composites where the density and position of the nanotubes (11) within the composite ca be controlled. Carbon nanotubes (11) are grown from organometallic micropatterns. These periodic nanotube arrays are then incorporated into a polymer matrix (7) by deposing a curable polymer film on the as-grown tubes. This controlled method of producing free-standing nanotube / polymer composite films may be used to form nanosensor (3) which provide information regarding a physical condition of a material (20), such as an airplane chassis or wing, in contact with the nanosensor (3).
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
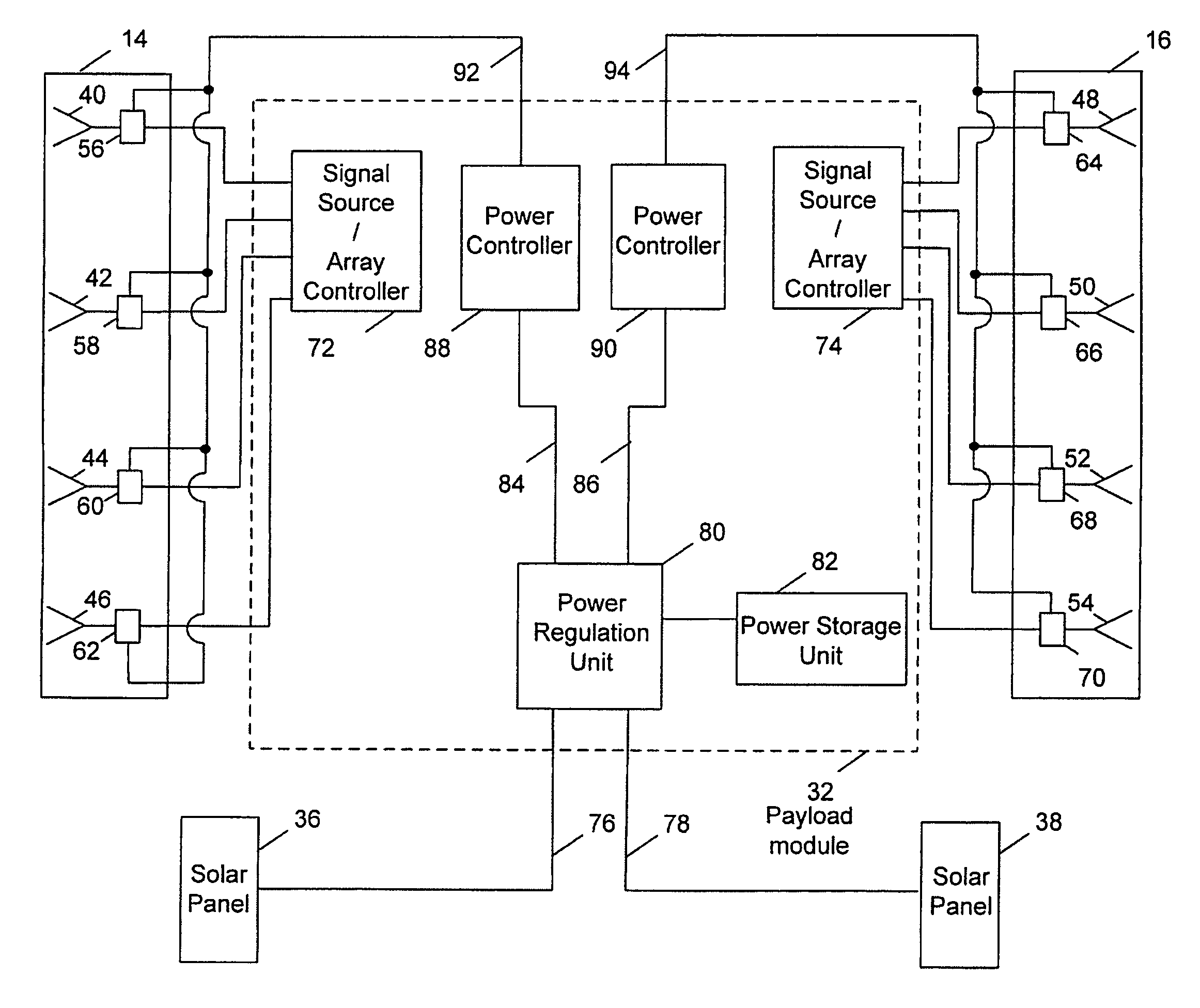
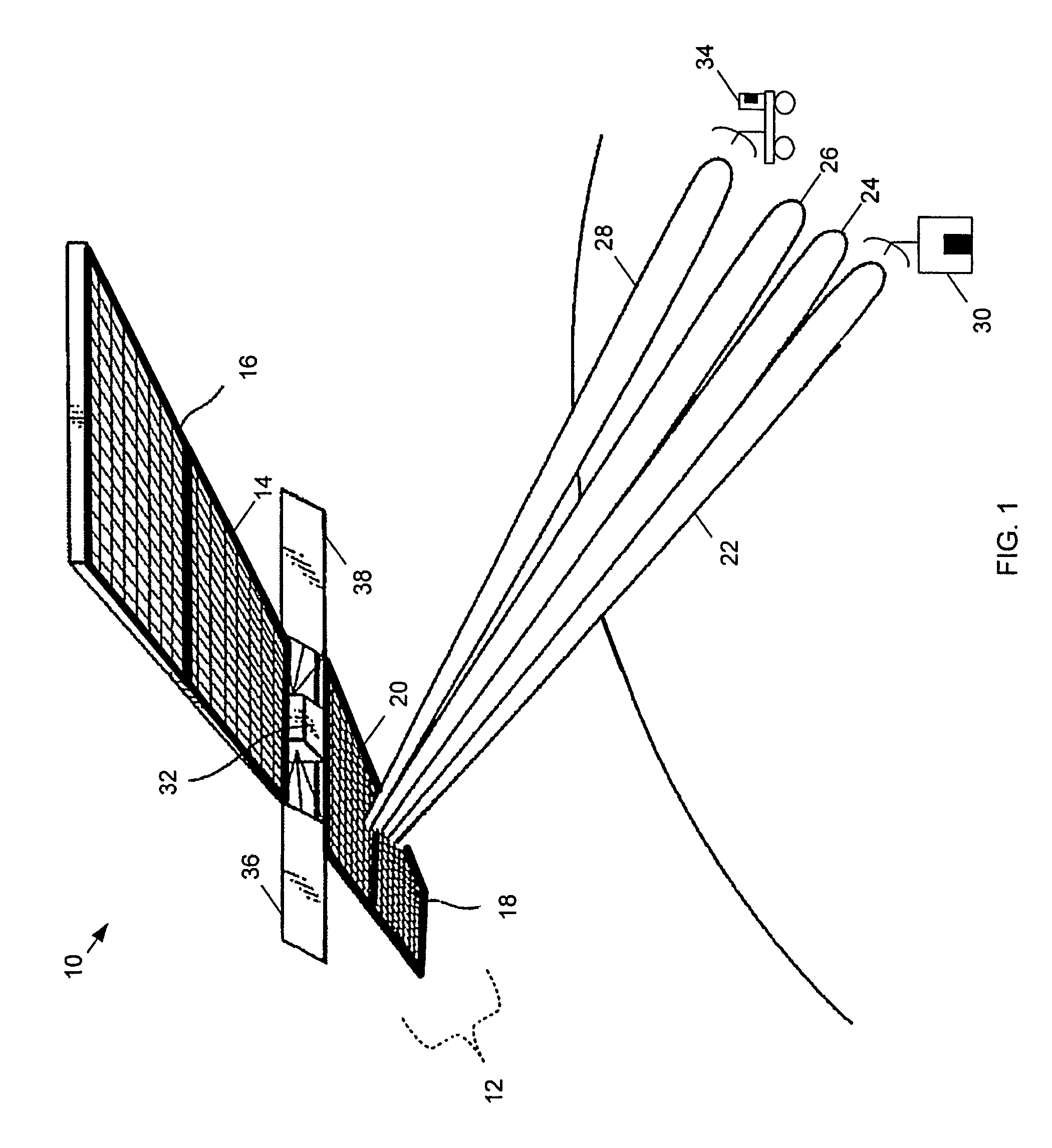
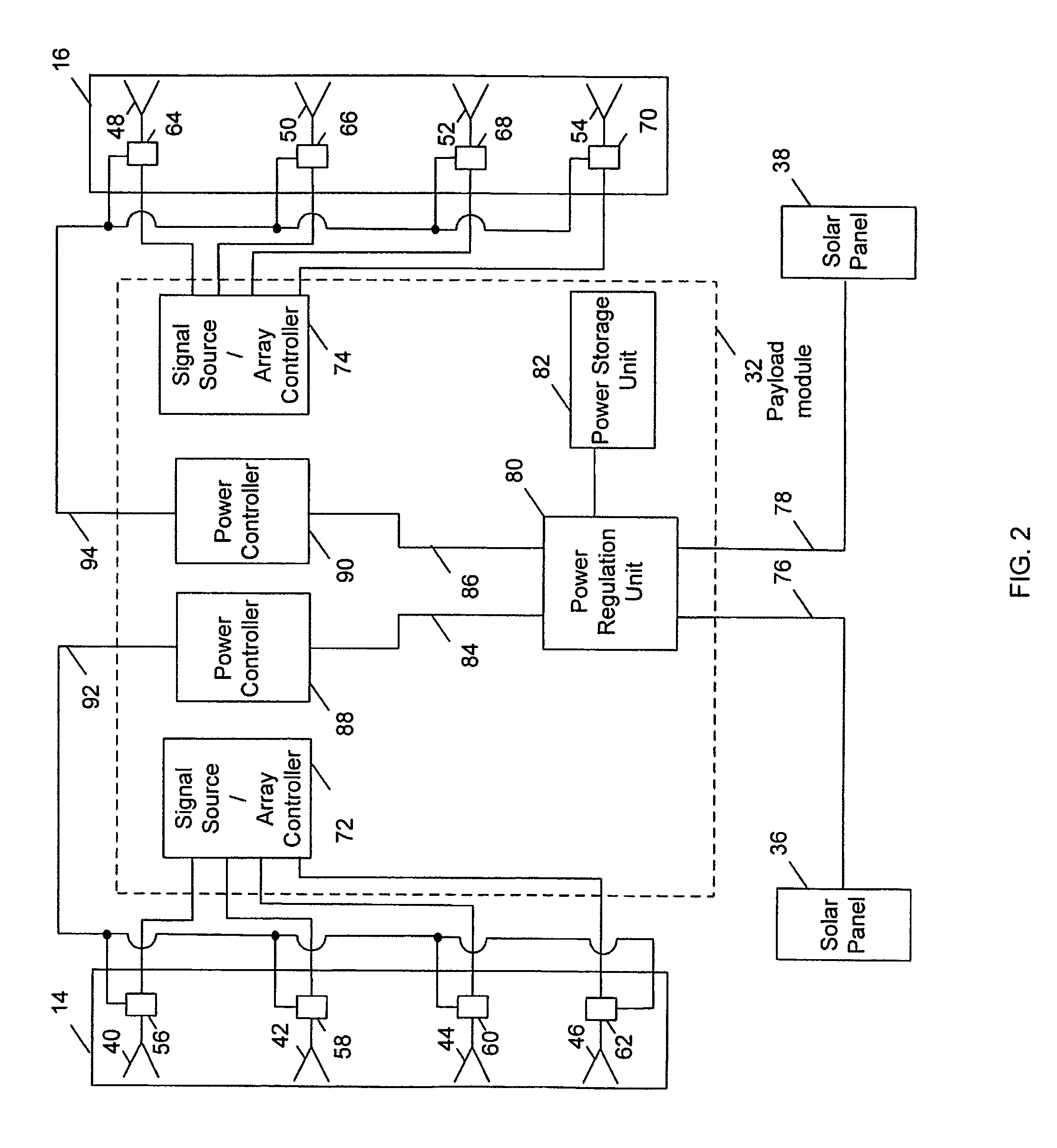
Method and system for flexibly distributing power in a phased array antenna system
ActiveUS7392011B1Improve efficiencyImprove distribution efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementAudio power amplifierElectric power system
A power system flexibly distributes power among phased array antenna apertures of a satellite (or other type of platform). By allocating the power provided by a power source among the apertures, if one aperture is not providing useful coverage (due to orientation, light traffic volume, aperture operating frequency and / or polarization, etc.), power being supplied to that aperture may be reallocated to one or more other apertures that are providing useful coverage. To flexibly allocate power among the apertures, power amplifiers and attenuators associated with each antenna element are adjusted to provide a wide range of RF output powers with high efficiency at all output power levels. By increasing power allocation efficiency, the size of the satellite power source may be reduced while appropriate power is still provided.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
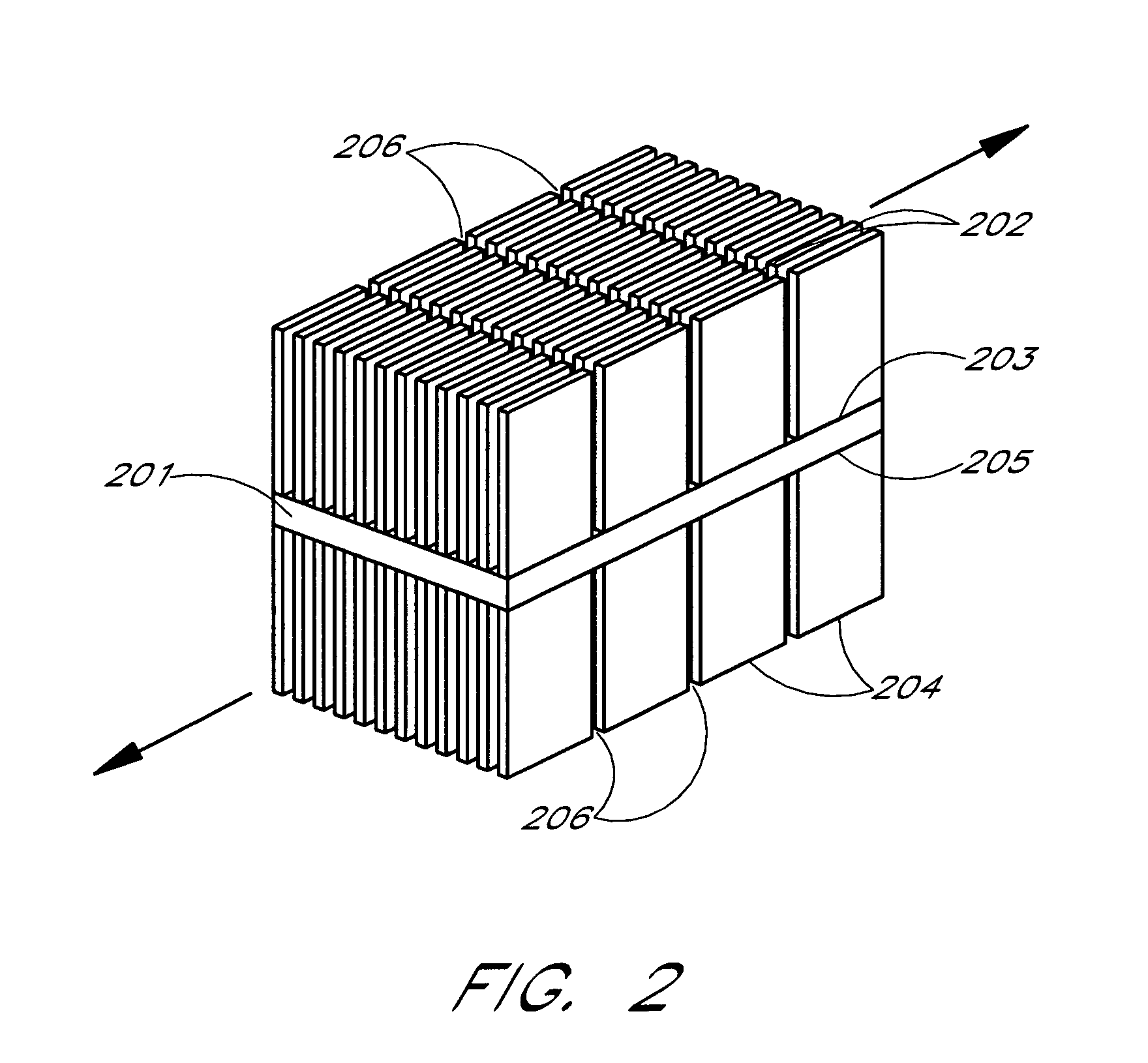
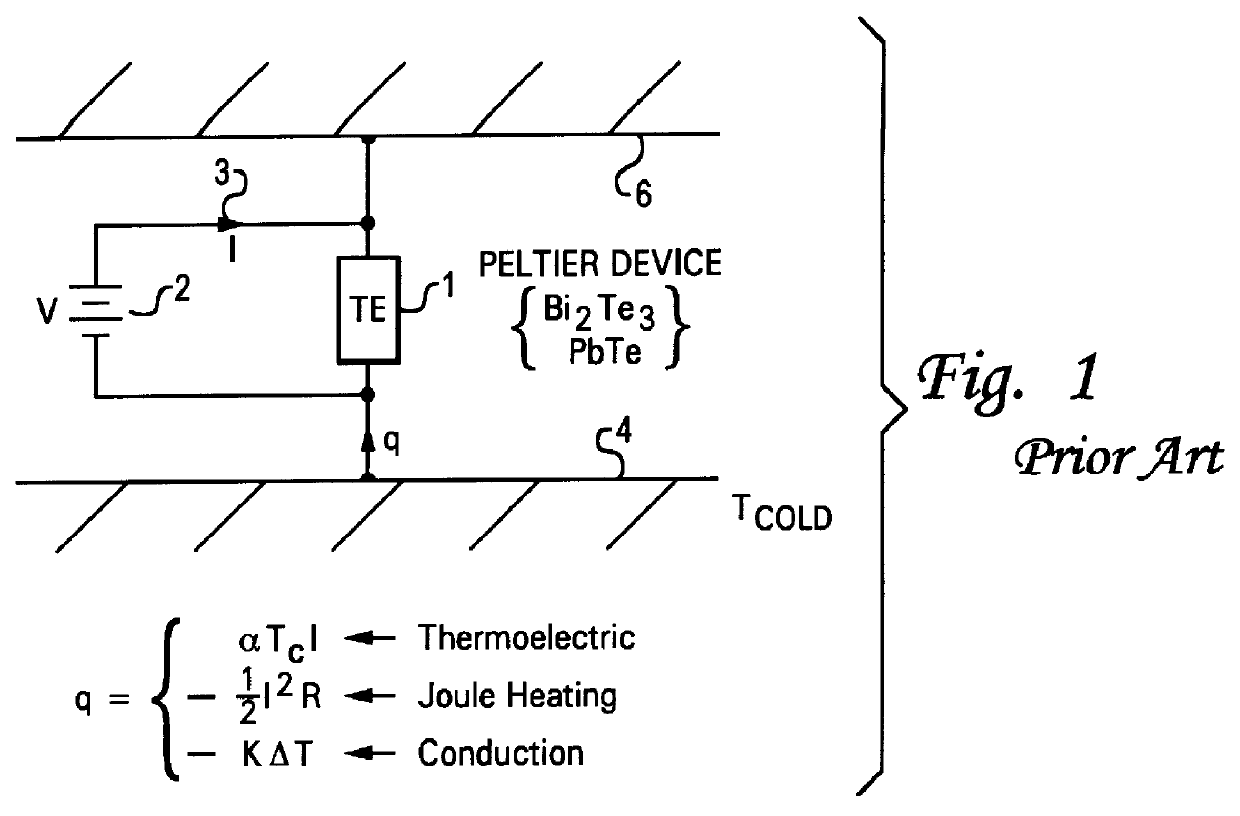
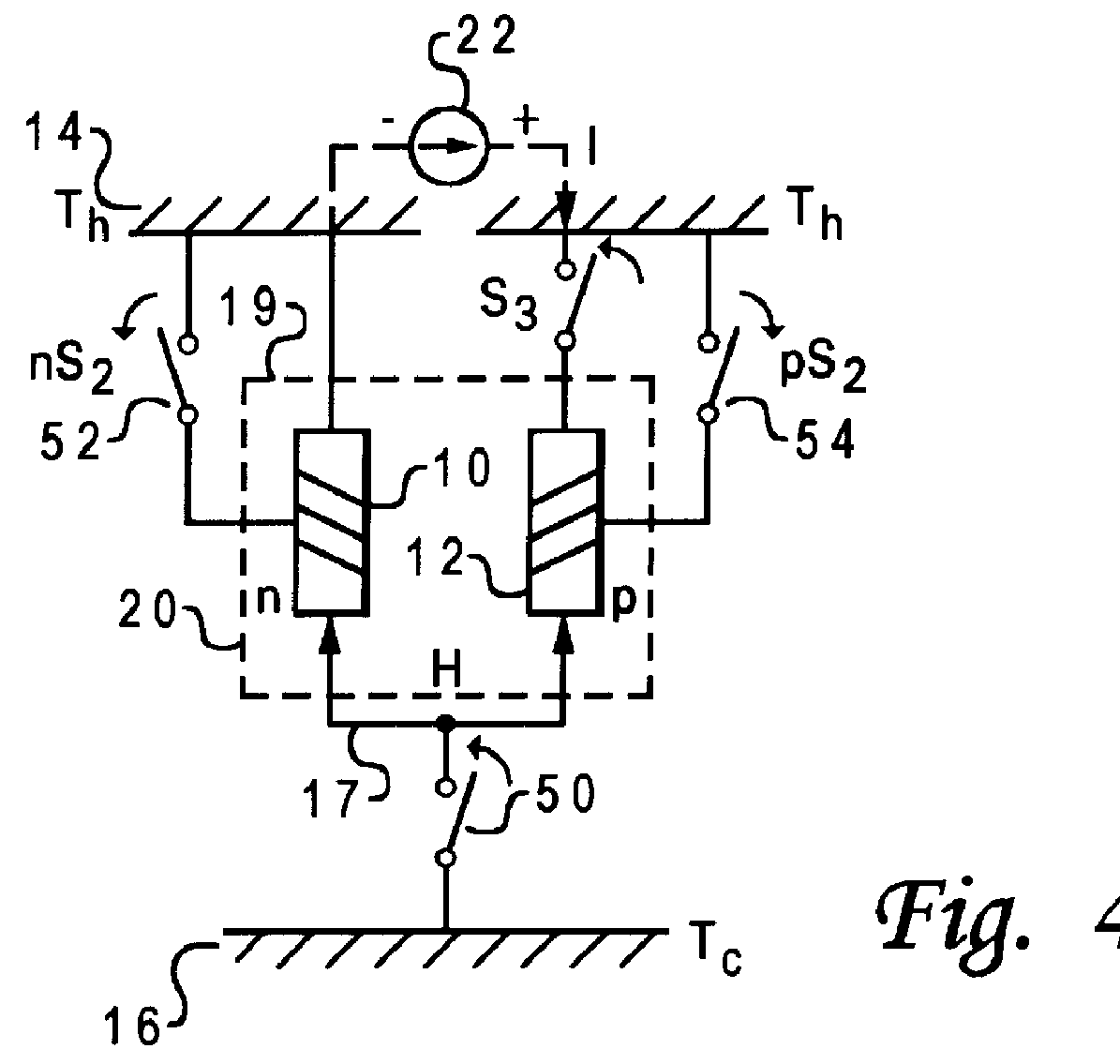
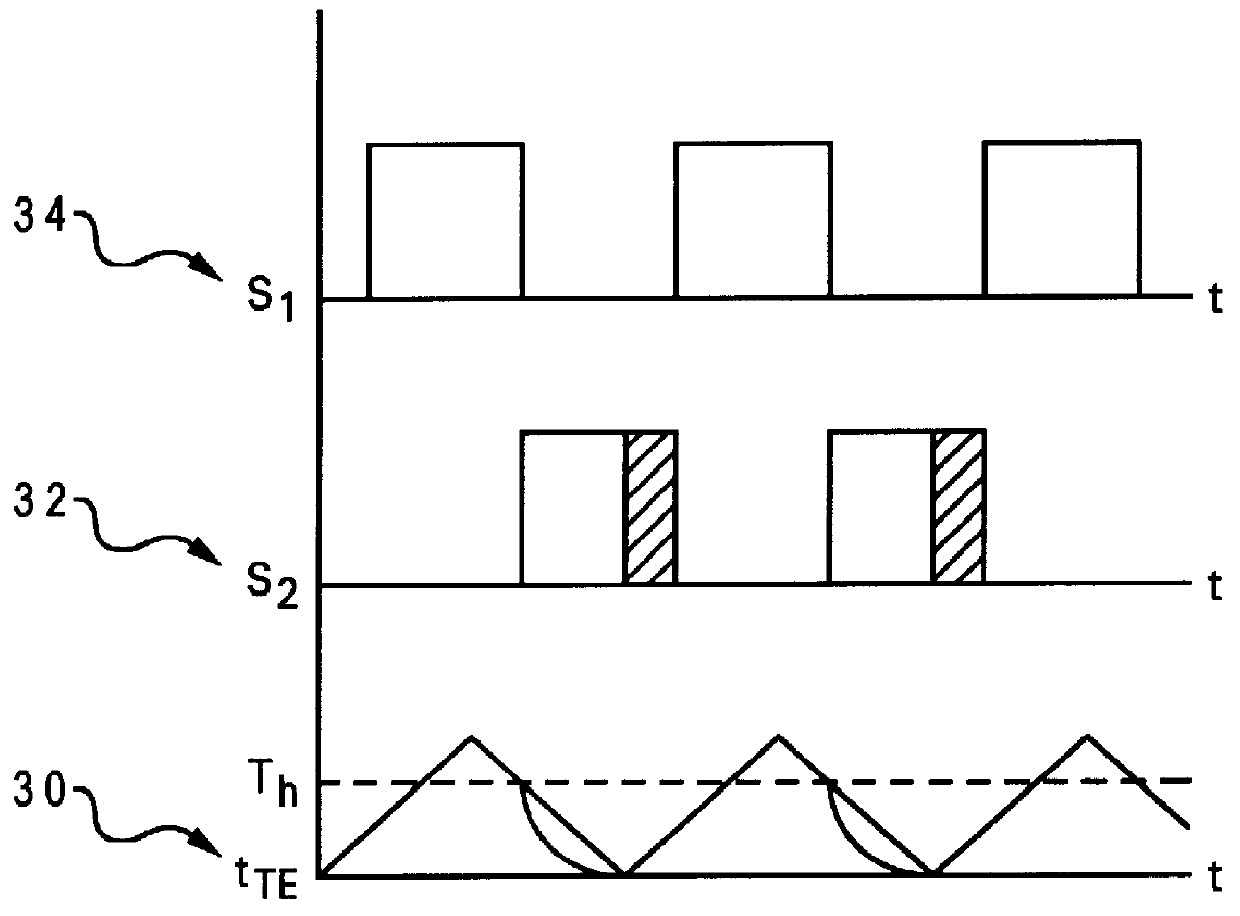
Enhanced duty cycle design for micro thermoelectromechanical coolers
InactiveUS6161388AMachines using electric/magnetic effectsThermoelectric devicesThermoelectric coolingEngineering
A thermoelectric cooling apparatus which includes a Peltier device or a thermoelectric element coupled to a hot source and a cold sink. The hot source dissipates heat produced by the thermoelectric element. The cold sink is coupled to a mass to be cooled. A means for supplying power to the thermoelectric element is provided and a means for selectively thermally coupling the thermoelectric element to the hot source is provided. Selectively thermally switching the thermoelectric element to the hot source allows heat to be dissipated to the hot source when the thermoelectric element possesses excess heat. Dissipating the excess heat when the excess heat is present allows higher efficiencies to be attained in thermoelectric cooling.
Owner:IBM CORP
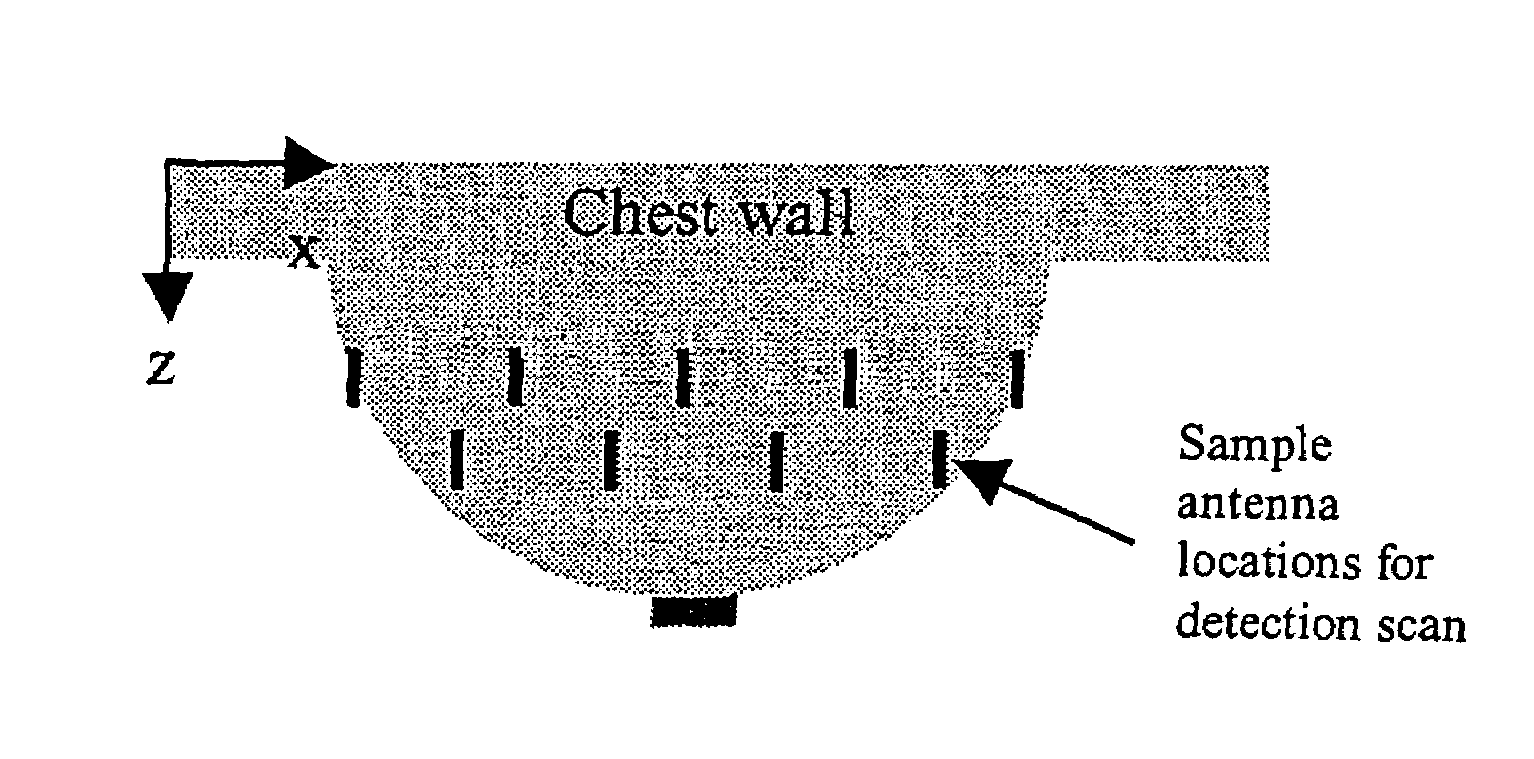
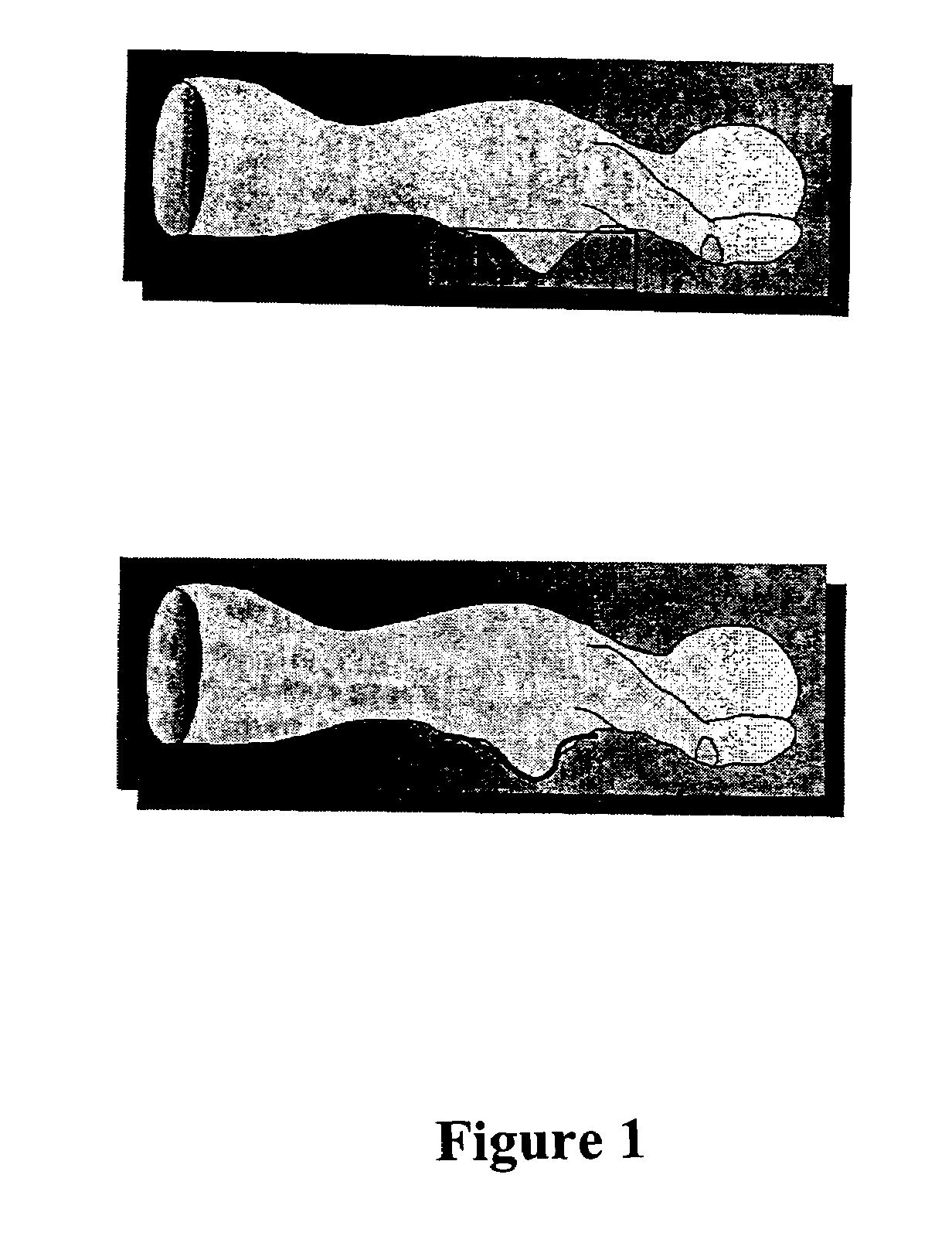
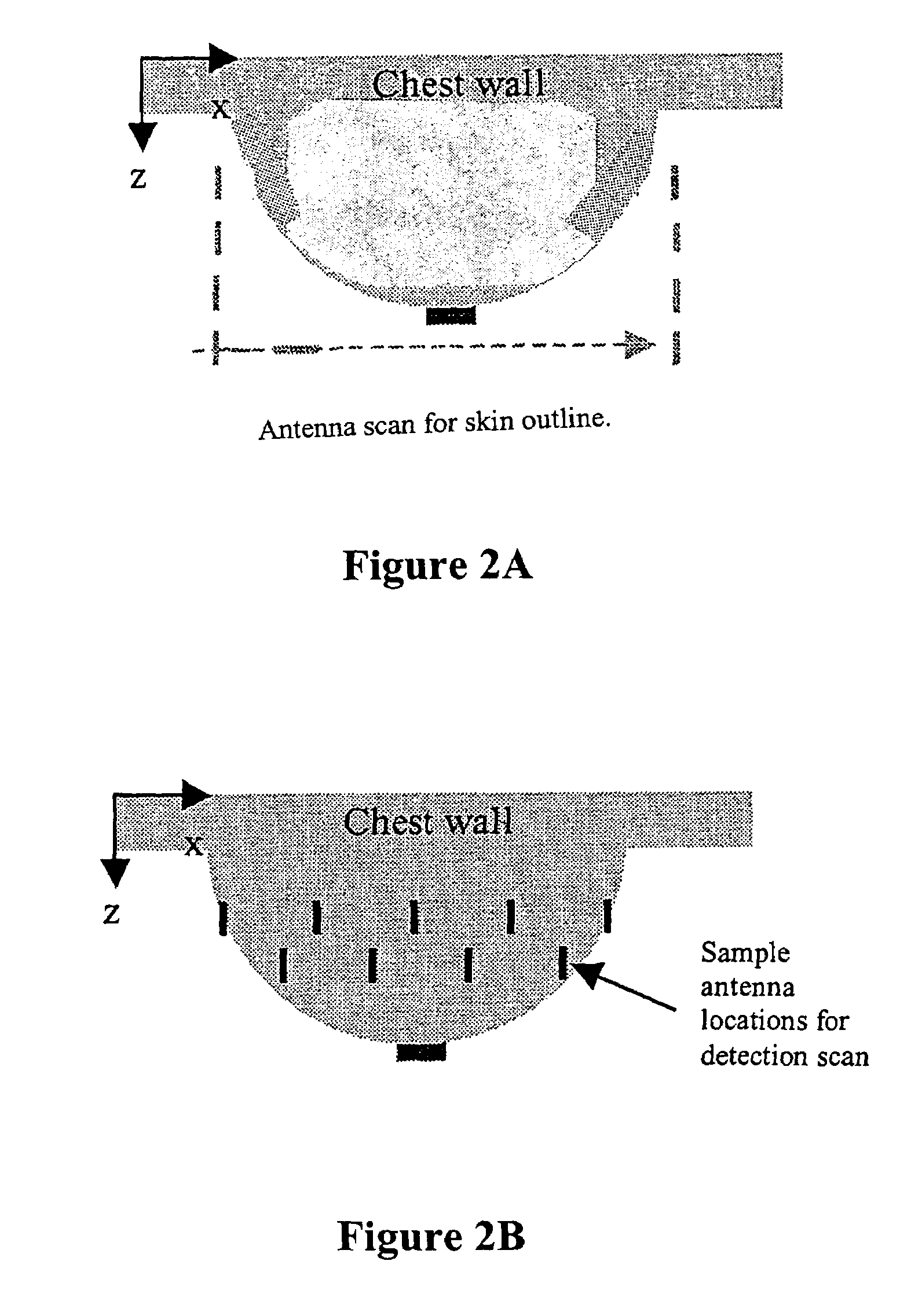
Tissue sensing adaptive radar imaging for breast tumor detection
InactiveUS7454242B2Big imageImage is often very smallElectrotherapyPolarisation/directional diversityMicrowaveRadar imaging
Owner:UTI LLP
Temperature-based cooling device controller apparatus and method
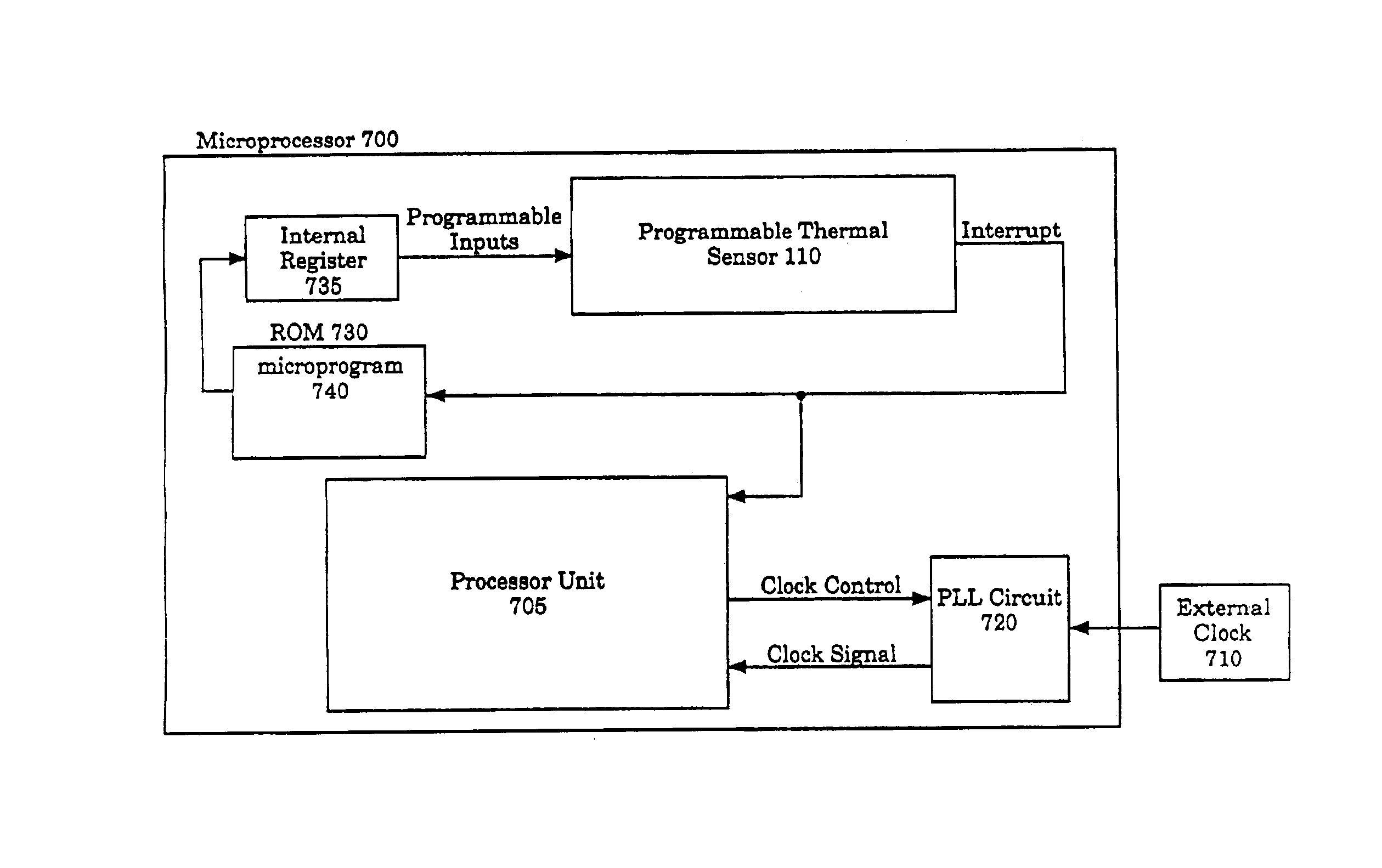
InactiveUS6975047B2Reduce clock frequencySystem clock frequency is increasedEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerThreshold temperature
A temperature-based cooling device controller is implemented in an integrated circuit such as a microprocessor. The temperature-based cooling device controller includes a register to store a threshold temperature value, a thermal sensor, and clock adjustment logic to activate a cooling device in response to the thermal sensor indicating that the threshold temperature value has been exceeded. In a microprocessor implementation, the microprocessor contains a plurality of thermal sensors each placed in one of a plurality of different locations across the integrated circuit and an averaging mechanism to calculate an average temperature from the plurality of thermal sensors. Threshold adjustment logic increases the threshold temperature value to a new threshold temperature value in response to the thermal sensor indicating that the threshold temperature value has been exceeded. Threshold adjustment logic further lowers the new threshold temperature to detect decreases in temperature.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Autonomous, modular power generation, storage and distribution apparatus, system and method thereof
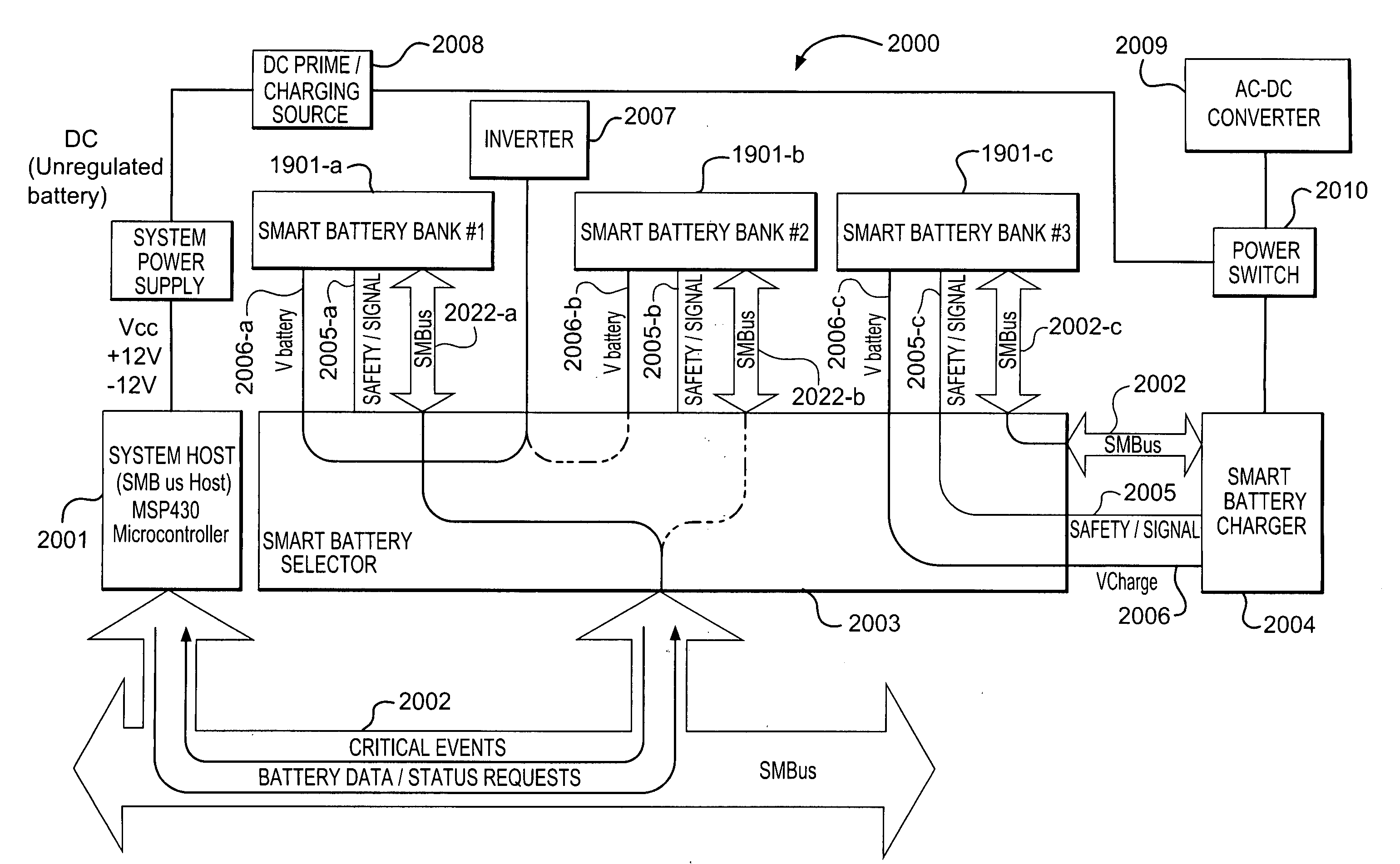
ActiveUS20090133733A1Increase capacityImprove safety and efficiencyPrimary cell to battery groupingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical batteryModularity
An autonomous, modular energy generation, storage and transmission apparatus, system, and method is provided. An apparatus is tube shaped and includes solar and thermionic energy conversion layers, and a battery module. A system of modular apparatuses may be connected together to form an transmission network. Such devices are particularly suited for outdoor application on highway jersey walls, and for indoor application on office cubicle walls. A method of charging battery modules in the apparatus is provided, along with a method of distributing the same in commerce.
Owner:GRIDKICKER LLC
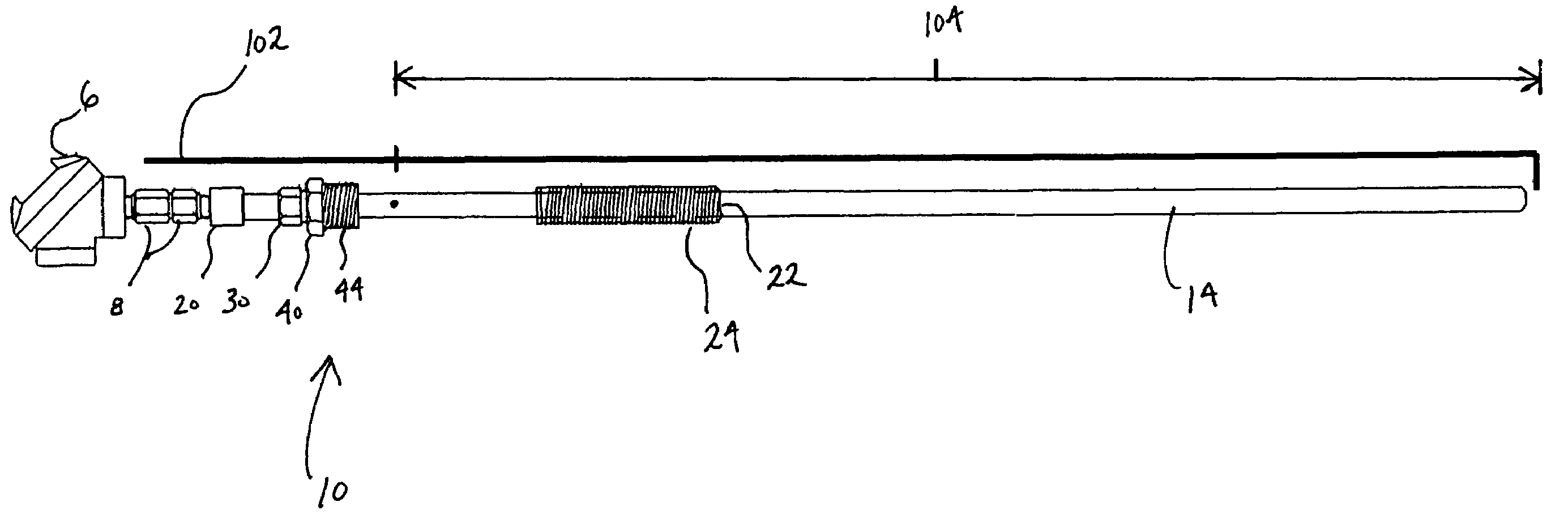
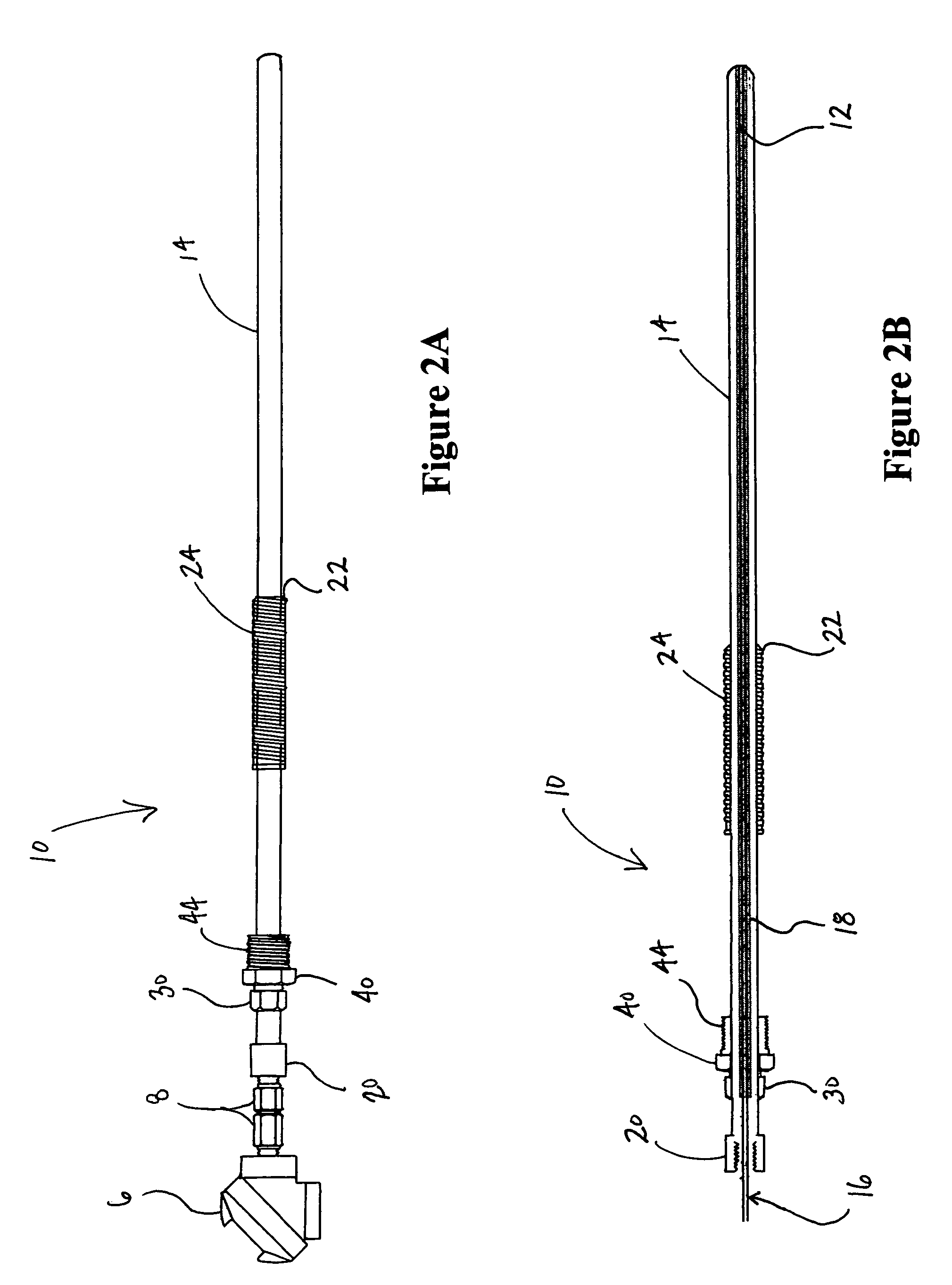
Adjustable length thermowell
ActiveUS7465086B1Easy to adjustThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsEngineeringThermowell
Owner:FOREMAN INSTR & CONTROLS
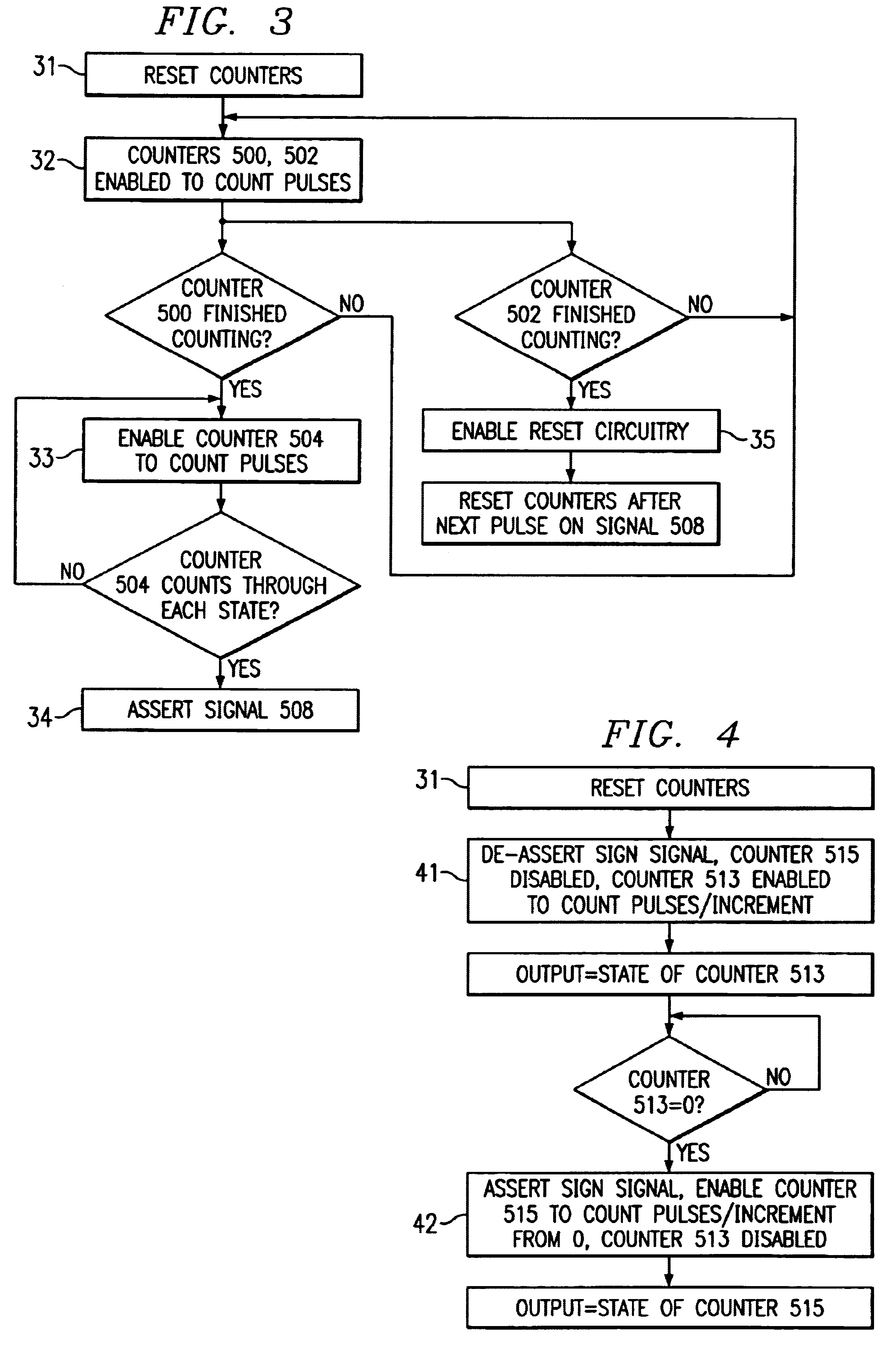
Temperature sensing circuit and method
InactiveUS6695475B2Optical radiation measurementTemperatue controlElectrical and Electronics engineeringTemperature sensing
A method and circuit are disclosed for measuring temperature. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes a first oscillator circuit that generates a first signal having a frequency that is dependent upon a sensed temperature. Difference circuitry determines a difference in frequency between the first signal and the second signal having a frequency that is substantially independent of temperature, and generates a difference signal having a number of pulses thereon based upon the difference. A counter circuit is responsive to the difference circuitry for offsetting a predetermined temperature level based upon the pulses appearing on the difference signal, to obtain an output signal indicative of the sensed temperature.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Optically transitioning thermal detector structures
ActiveUS20110266445A1Good effectHeat dissipationPhotometrySolid-state devicesMaximum temperatureTemperature sensitive
A thermal absorption structure of a radiation thermal detector element may include an optically transitioning material configured such that optical conductivity of the thermal absorption structure is temperature sensitive and such that the detector element absorbs radiation less efficiently as its temperature increases, thus reducing its ultimate maximum temperature.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
Temperature sensing circuit for use in semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050074051A1Reduce consumptionReduce needThermometer detailsTesting/calibration apparatusEngineeringSemiconductor
A temperature sensing circuit has numerous trip points in conformity with a temperature change without adding decrease resistance branches, so as to obtain a fine control based on the temperature change. Accordingly, when employed in a semiconductor memory device, the temperature sensing circuit substantially reduces the consumption of refresh electrical power in a stand-by state without decreasing the reliability of the semiconductor memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device, temperature sensor, and electronic apparatus comprising it
InactiveUS7176701B2Improve accuracyImprove linearityElectronic circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringFeedback circuits
A temperature sensor including two transistors having different emitter current densities and performing temperature detection based on the fact that the difference in voltage between base and emitter changes with temperature. The temperature sensor is provided with a feedback circuit for controlling respective collector voltages and emitter currents such that the collector voltages of both transistors vary according to similar temperature characteristics.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com