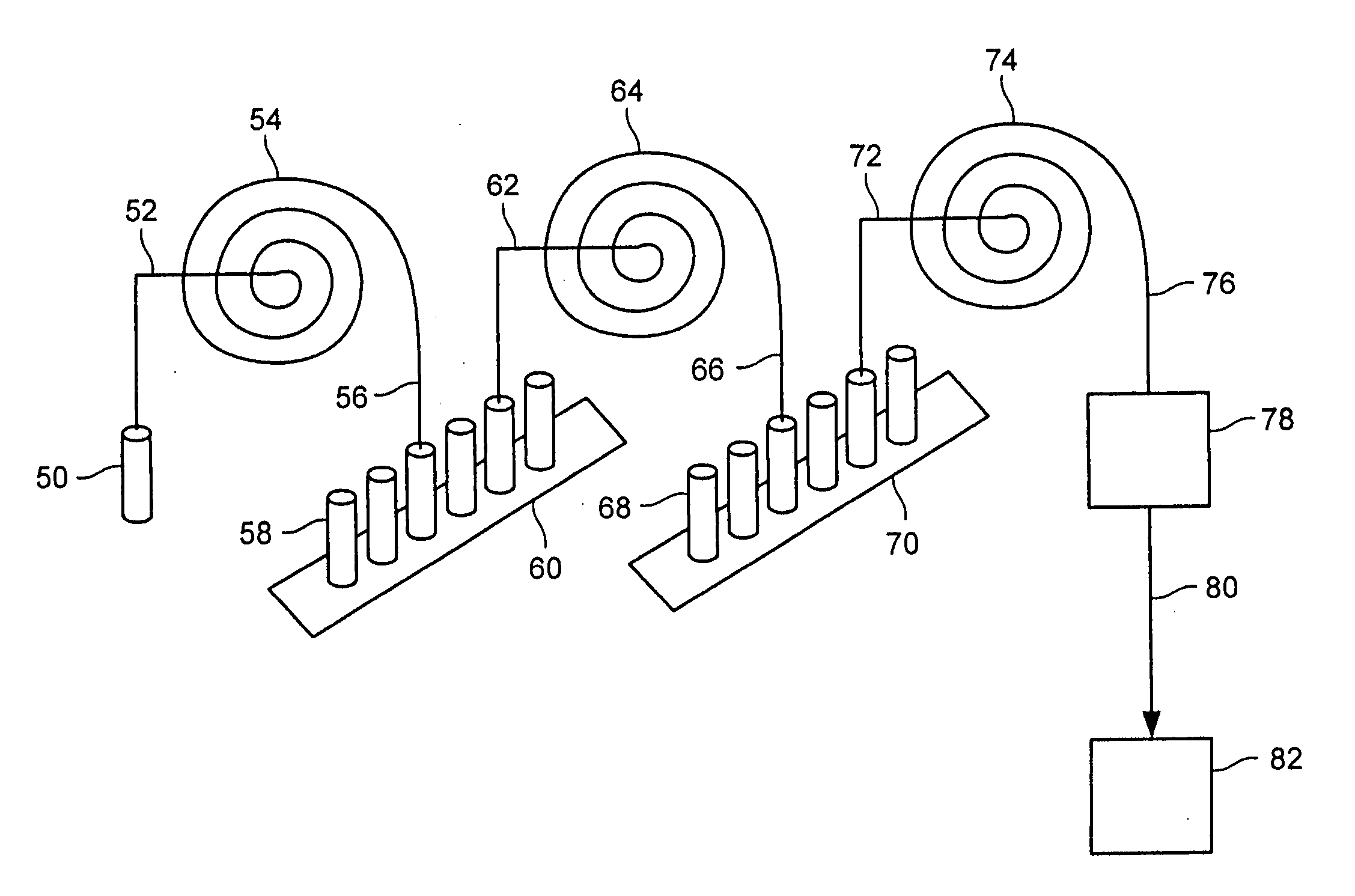
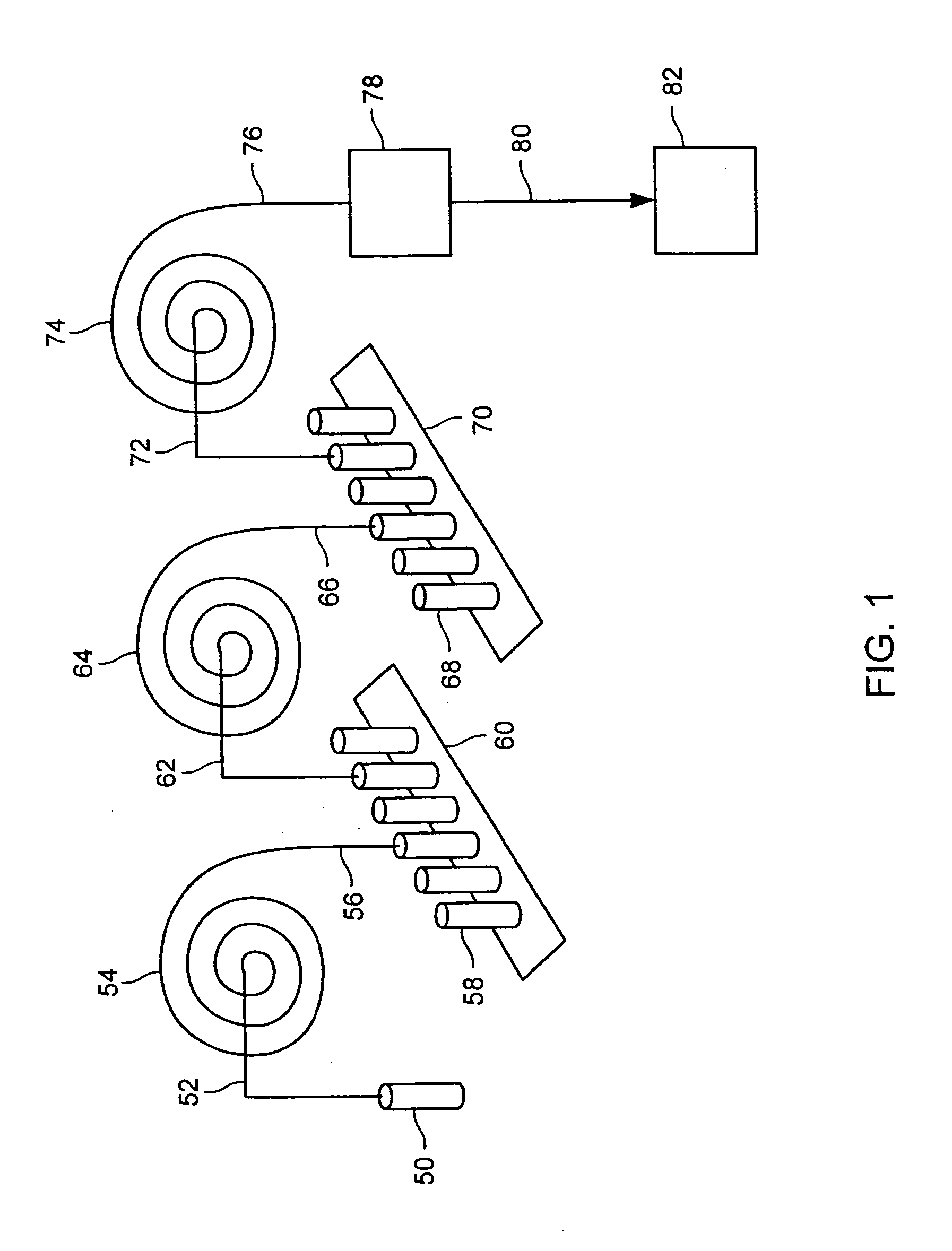
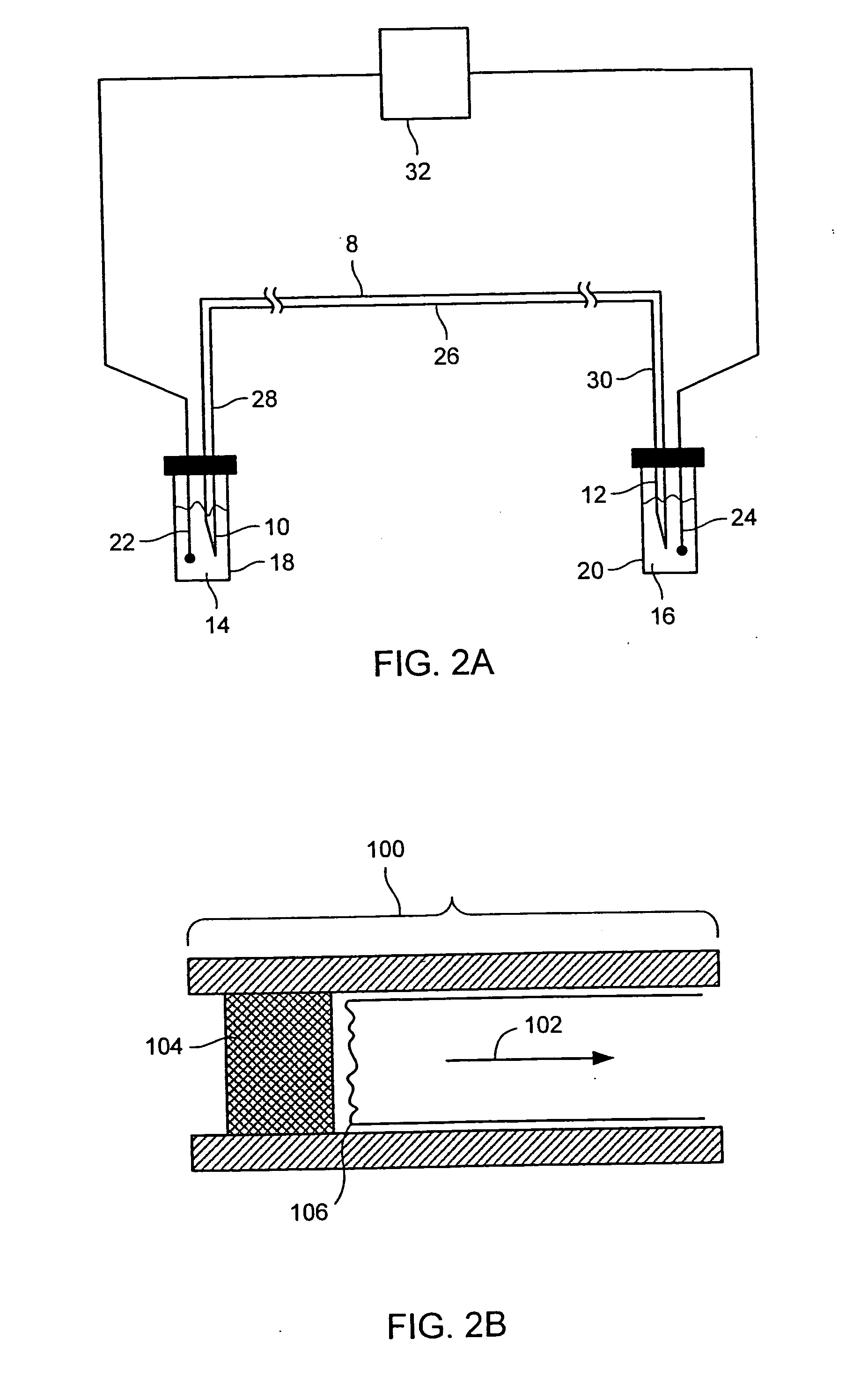
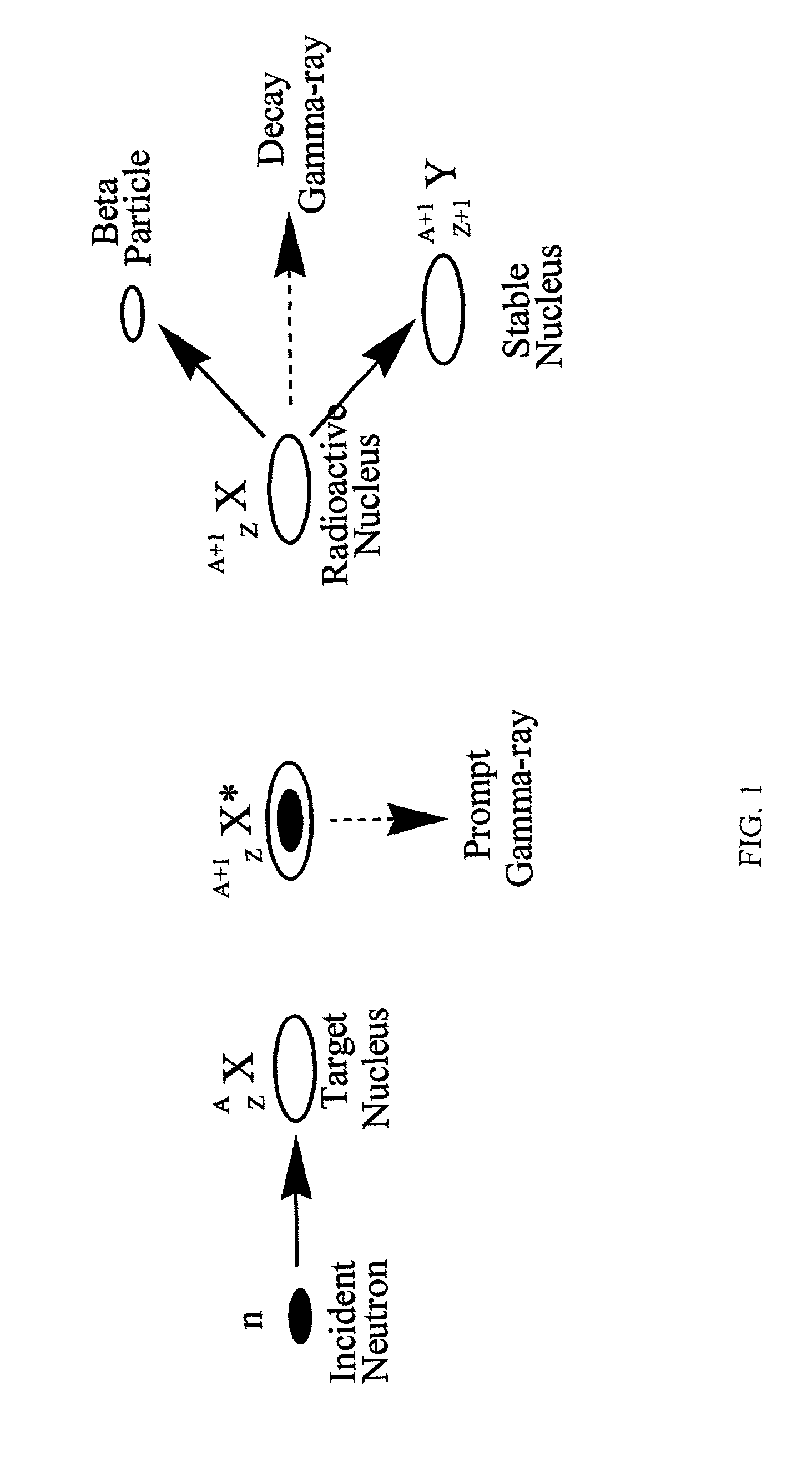
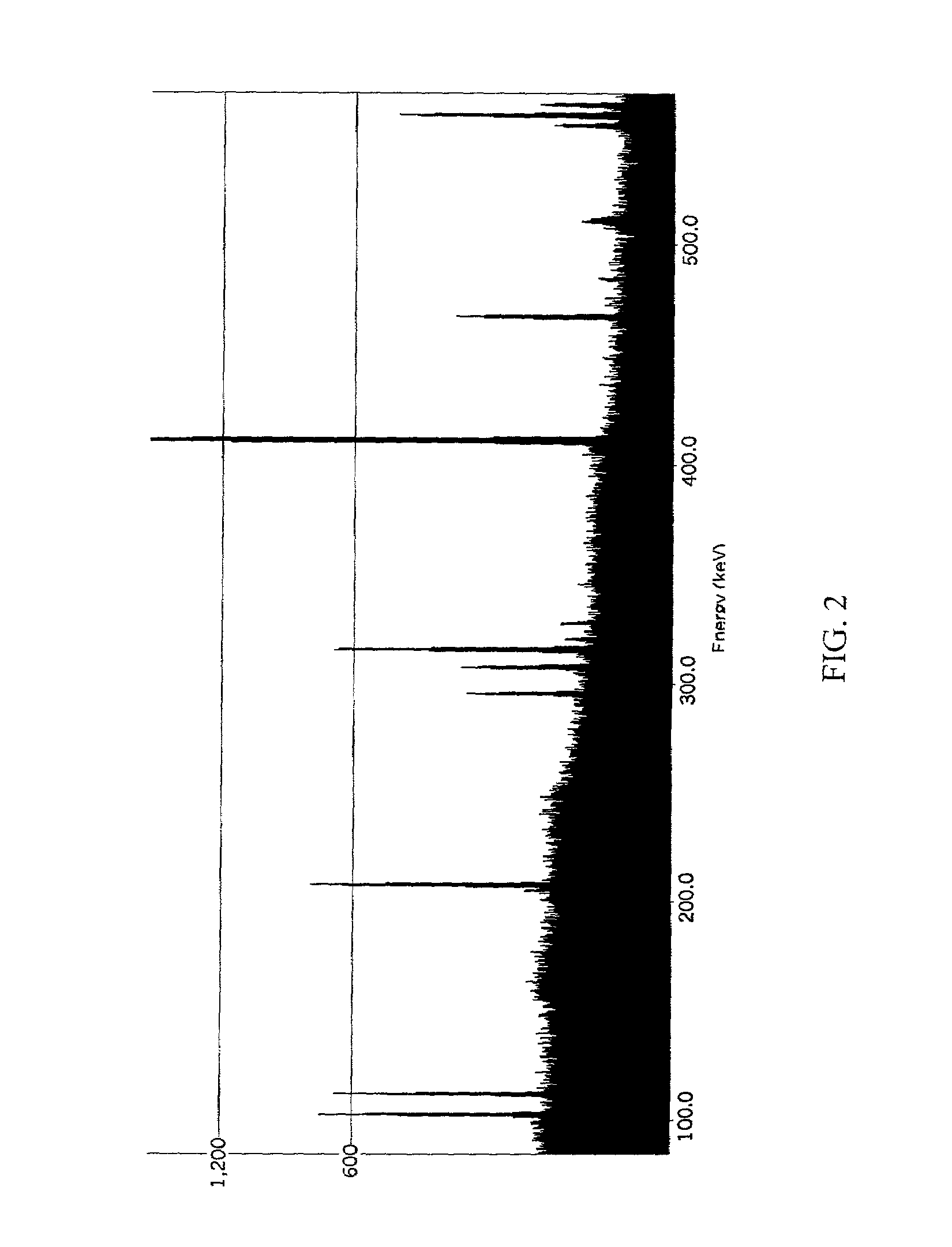
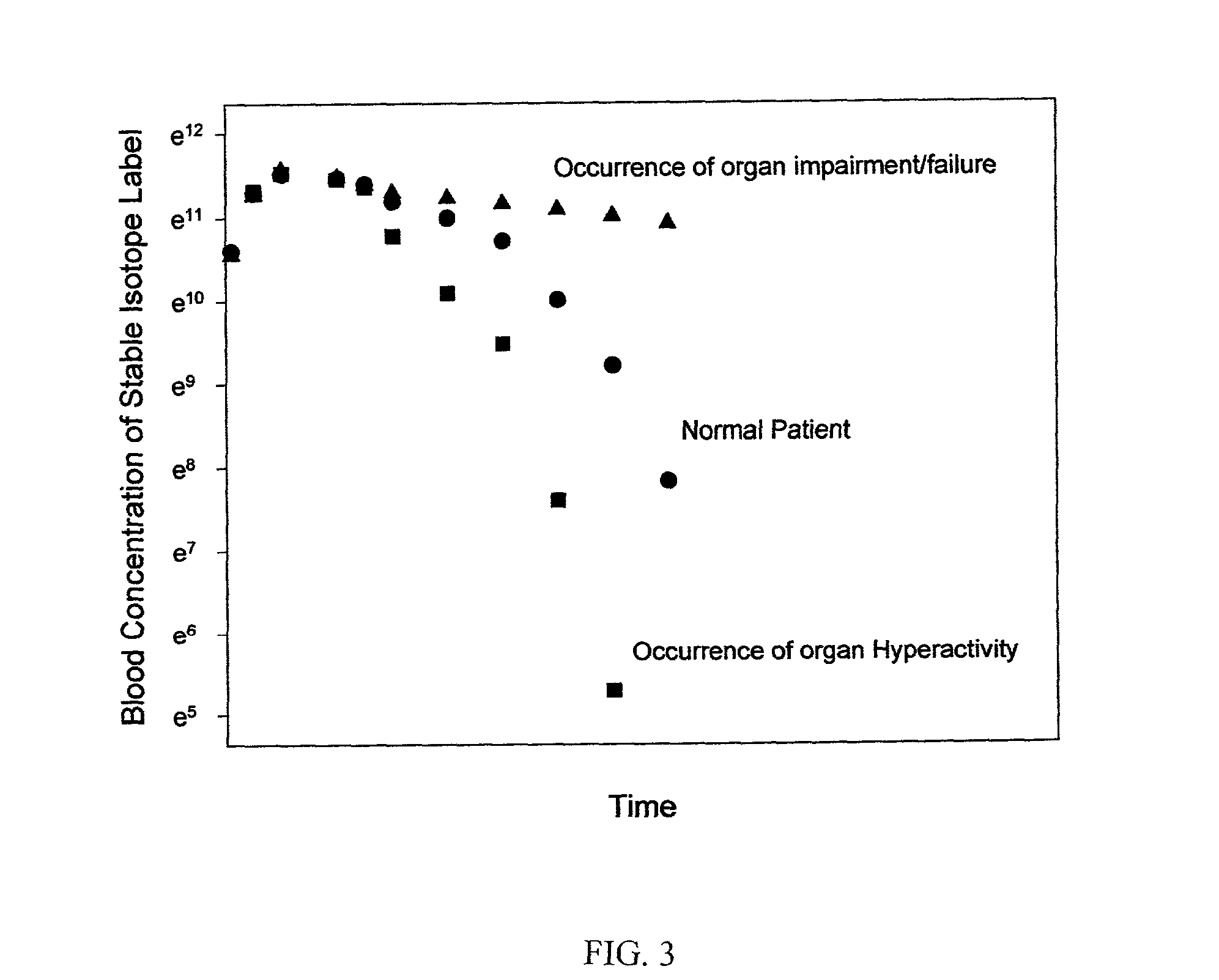
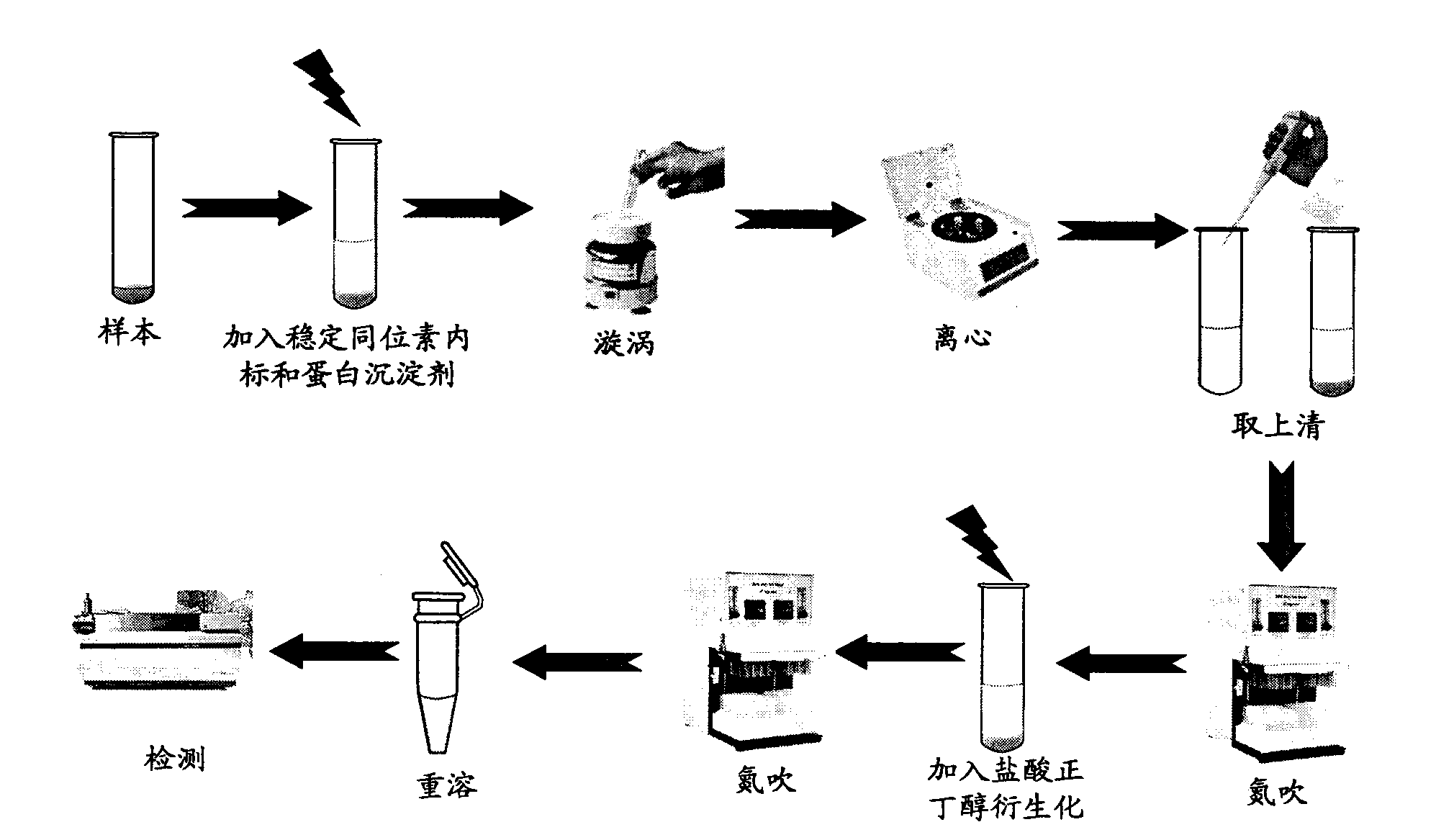
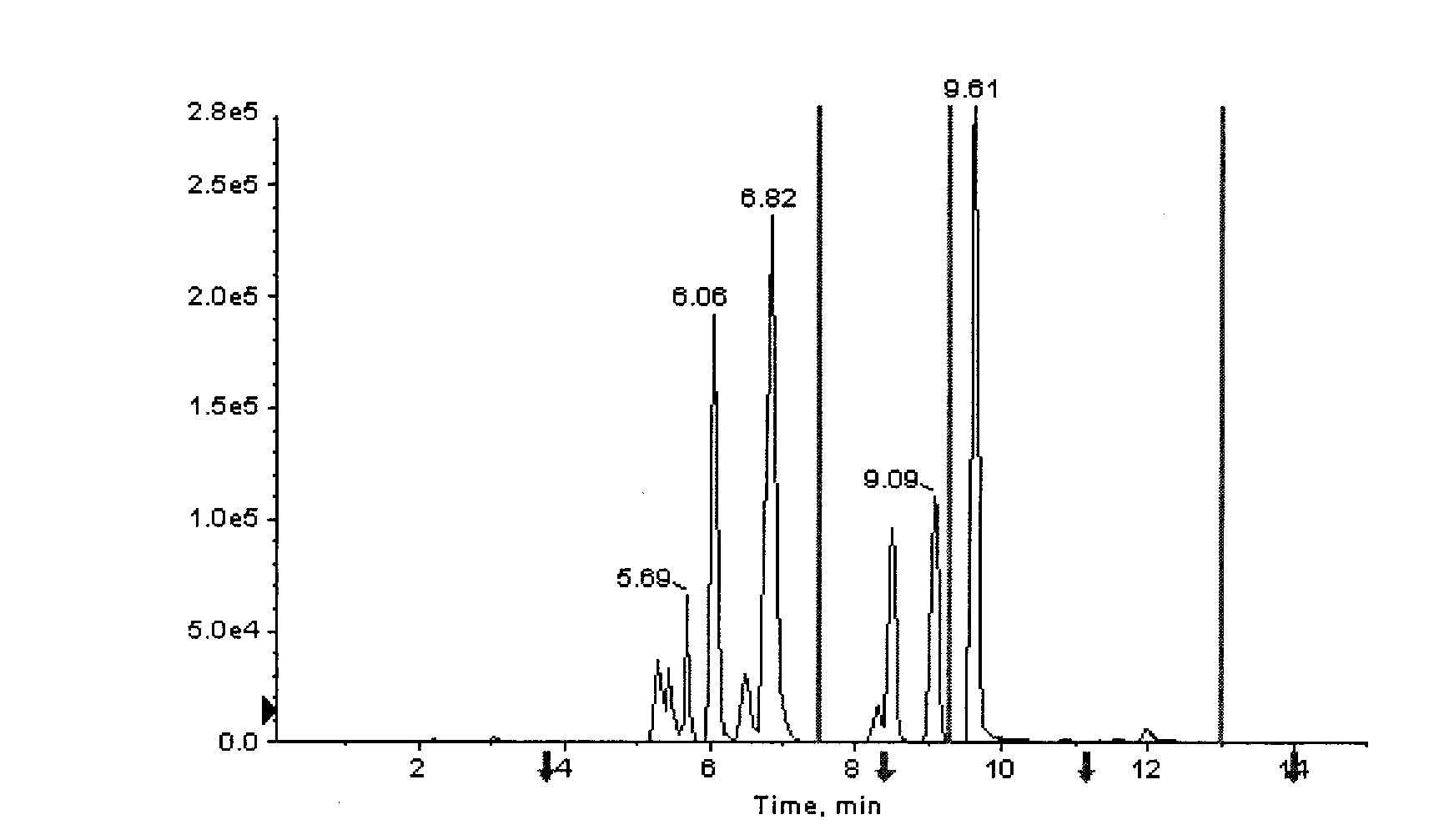
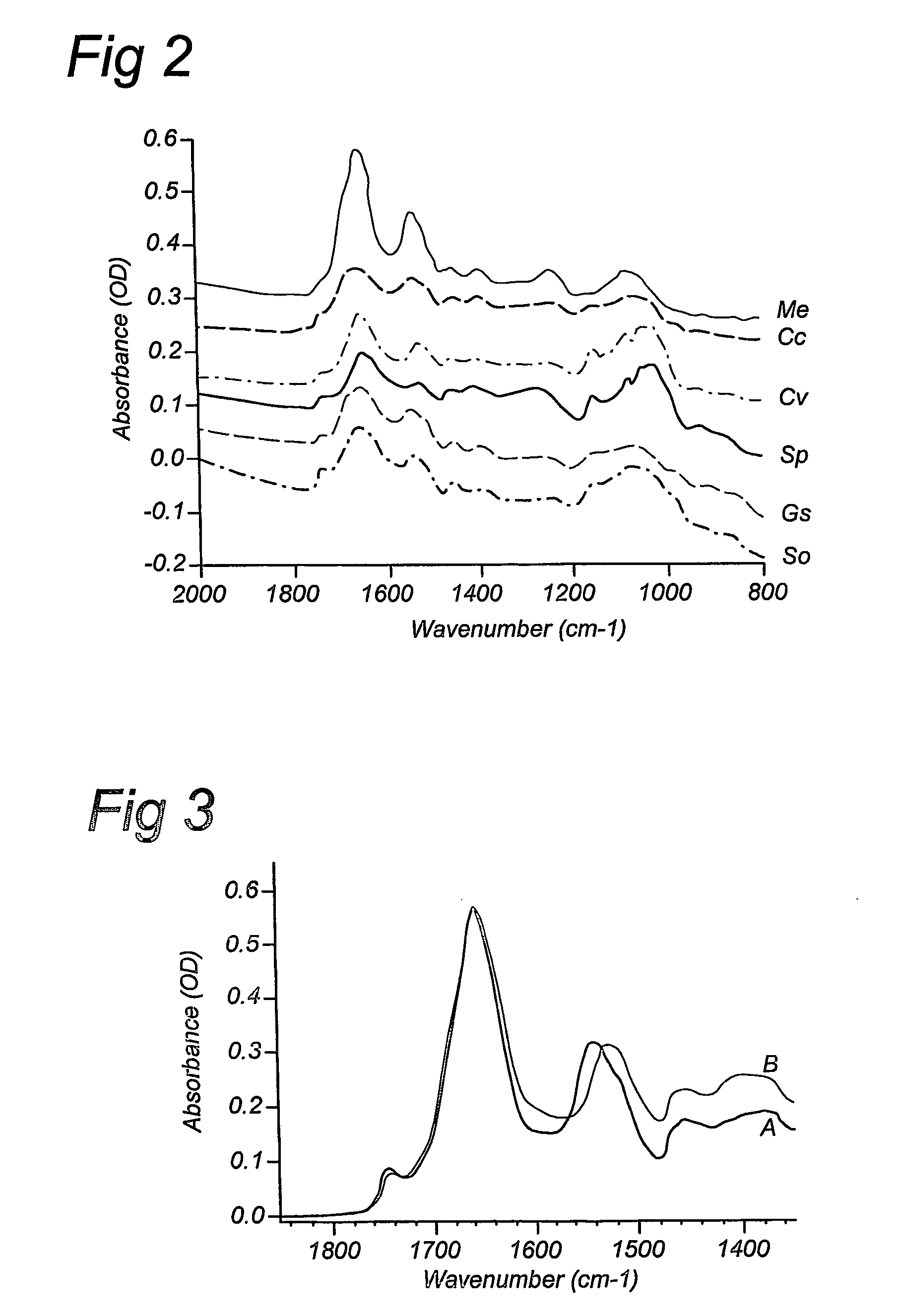
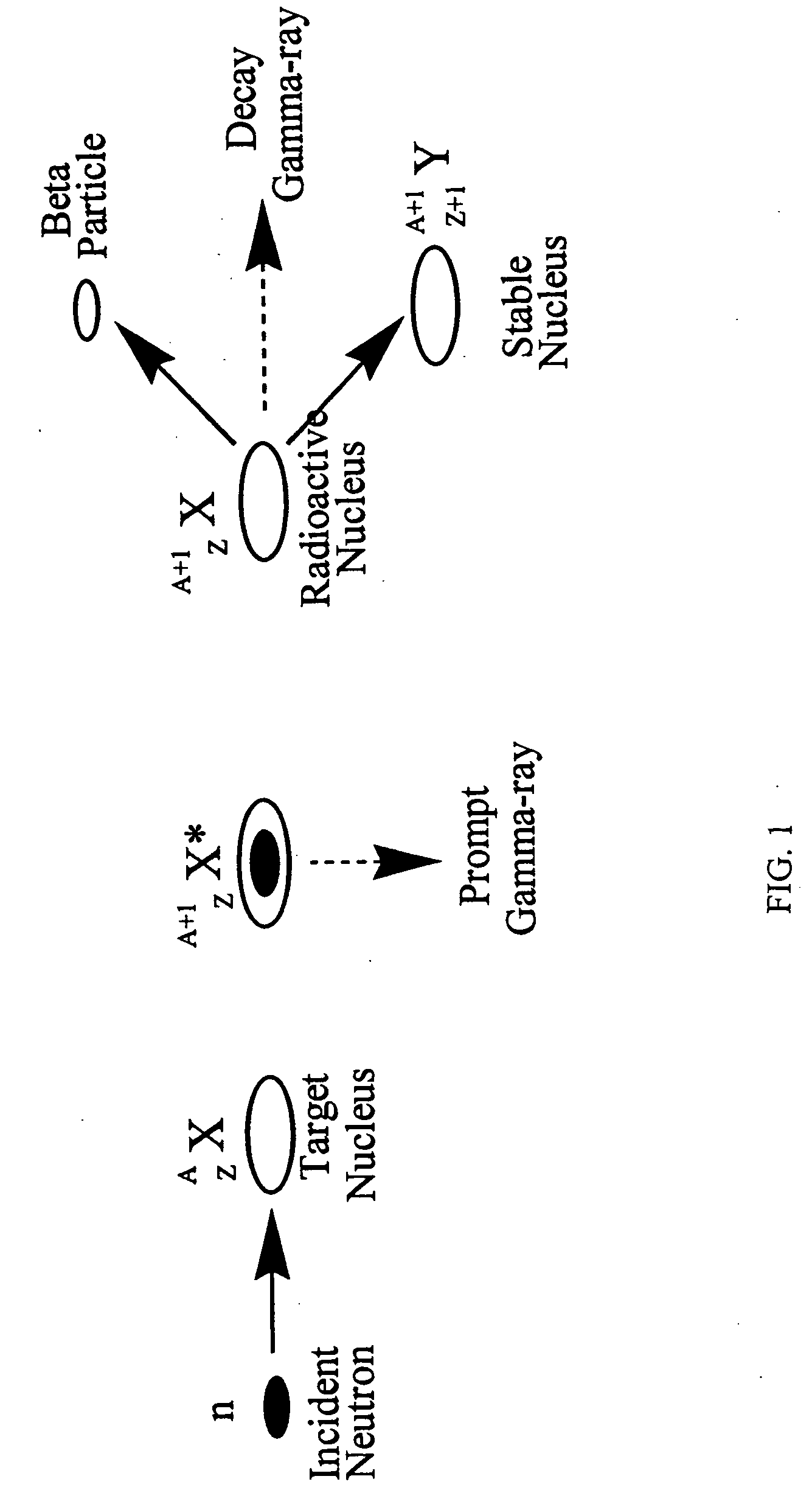
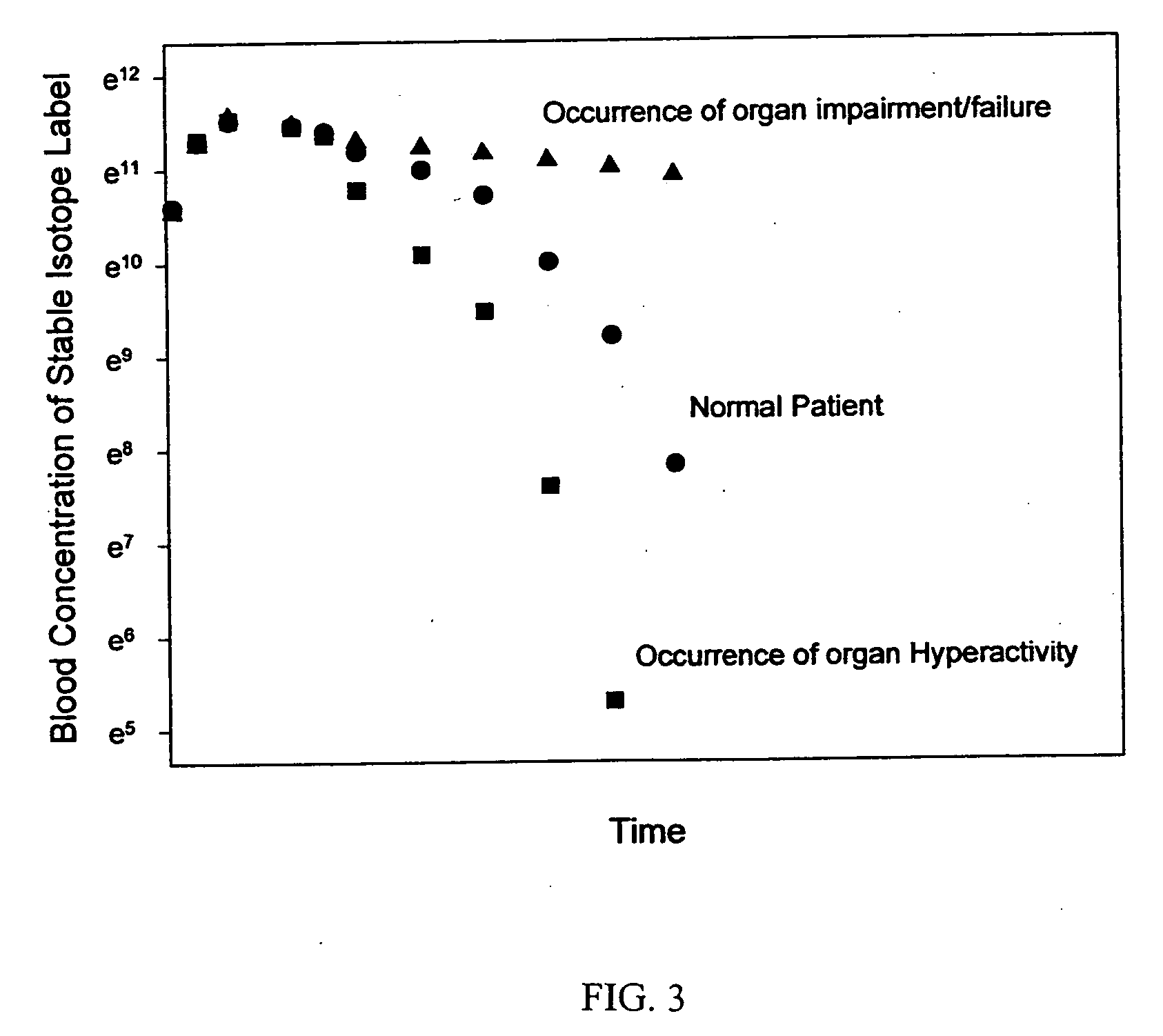
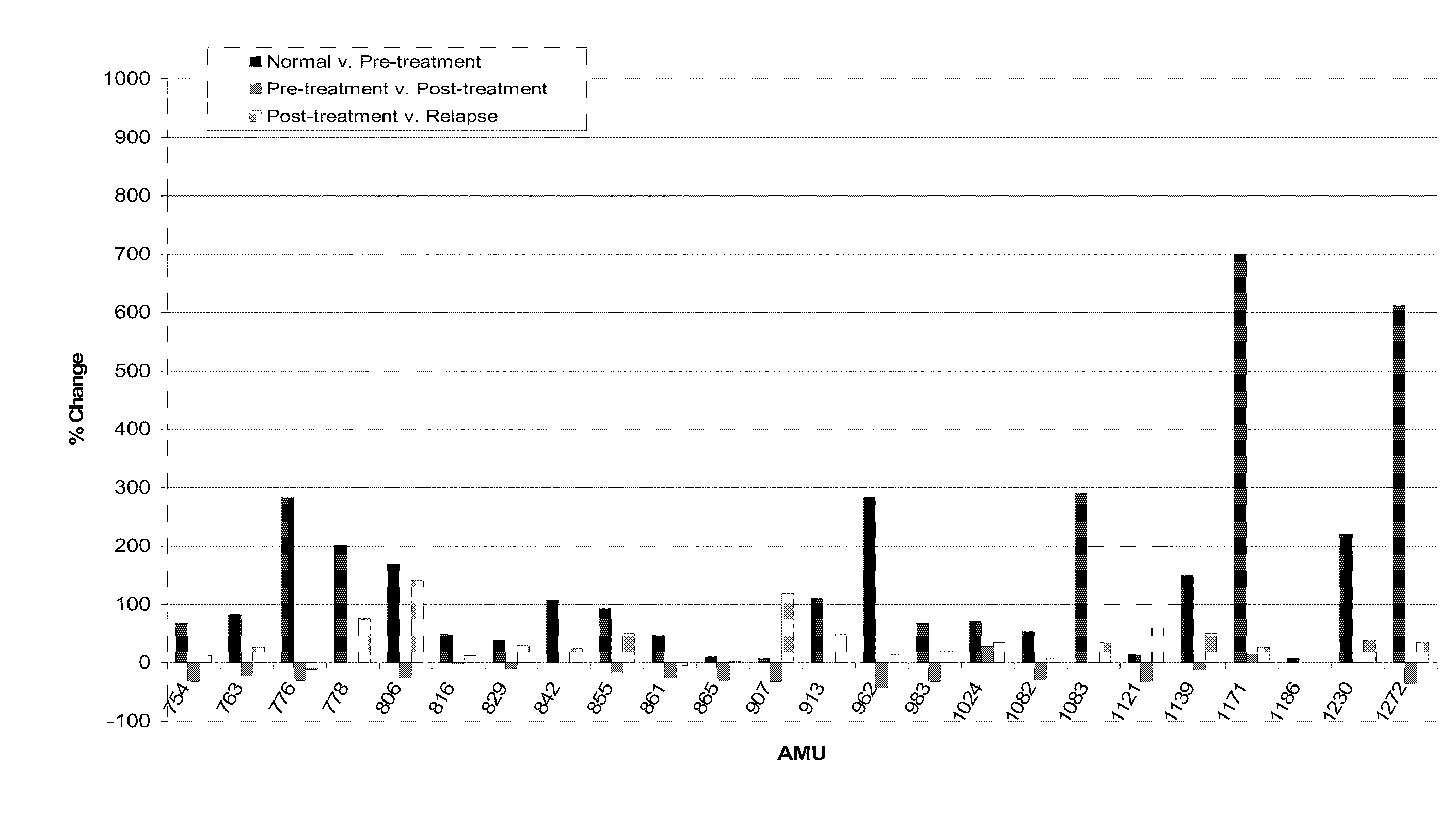
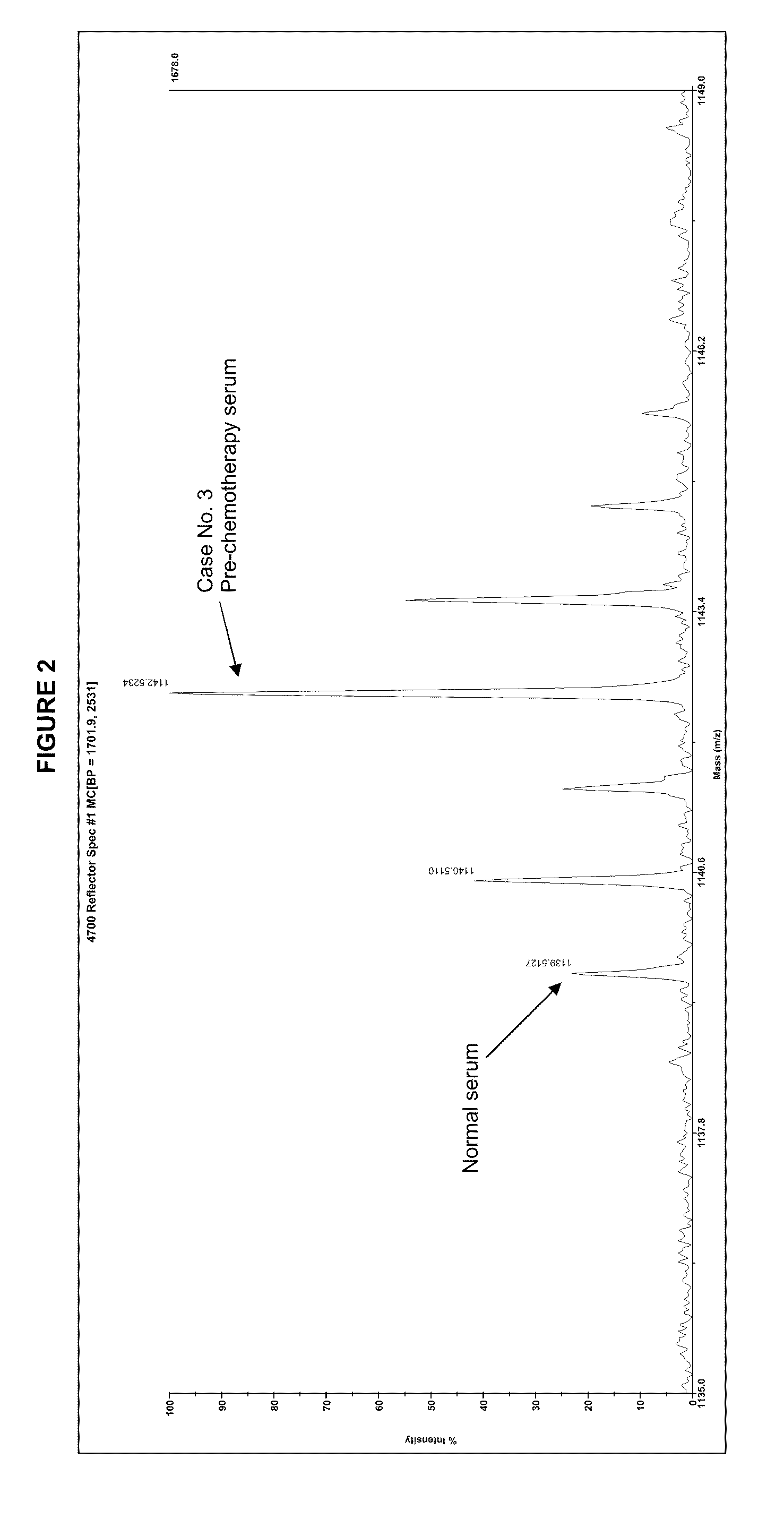
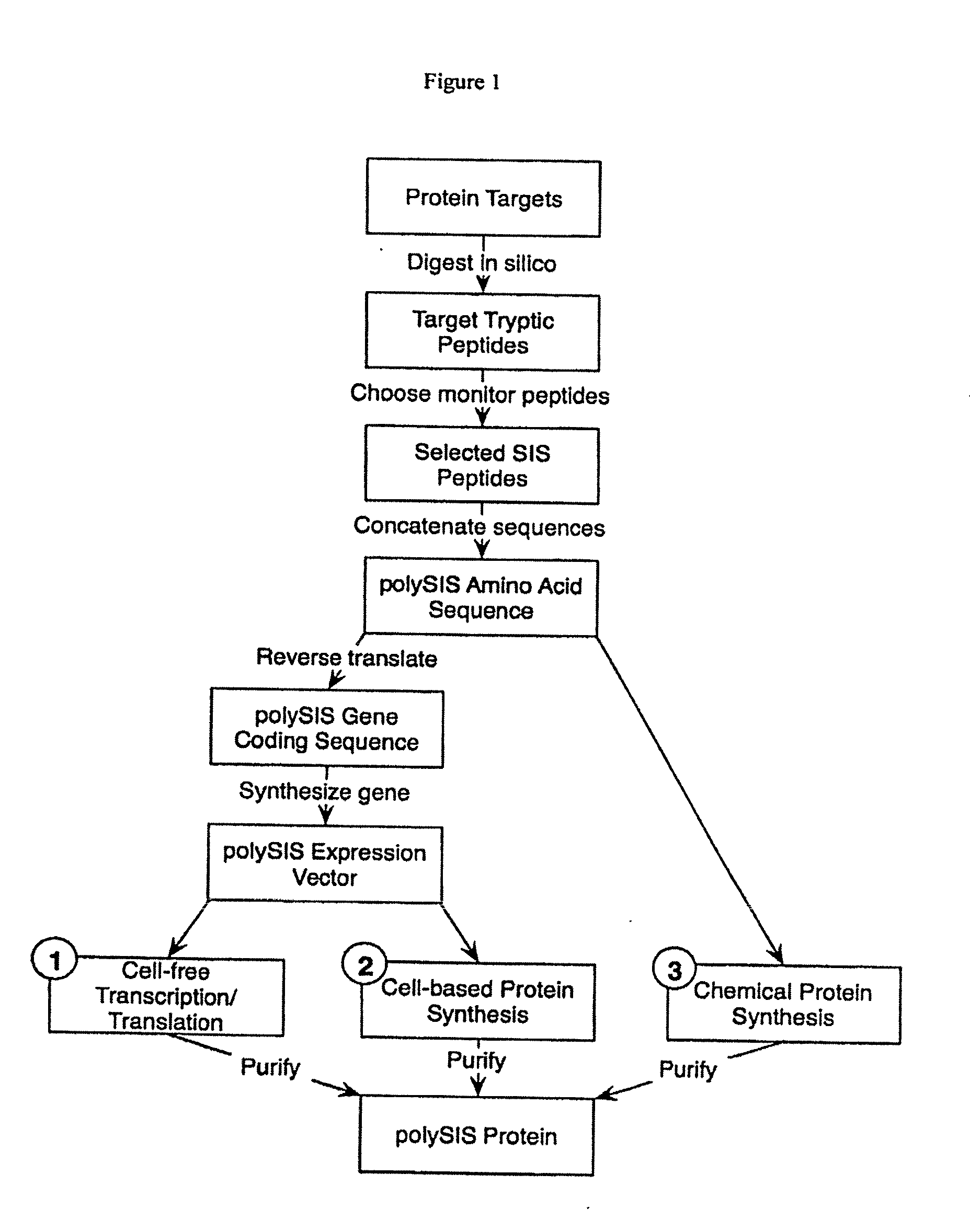
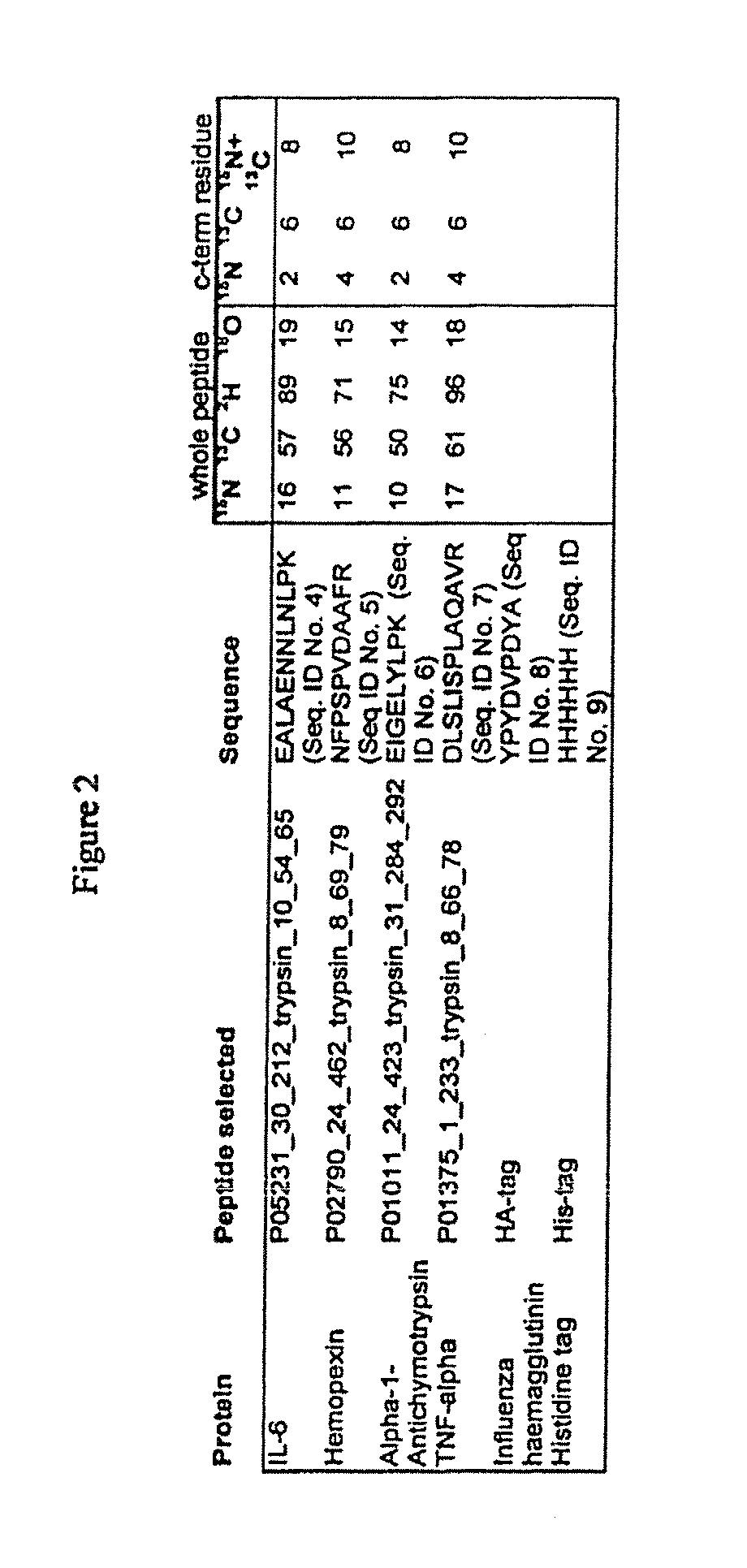
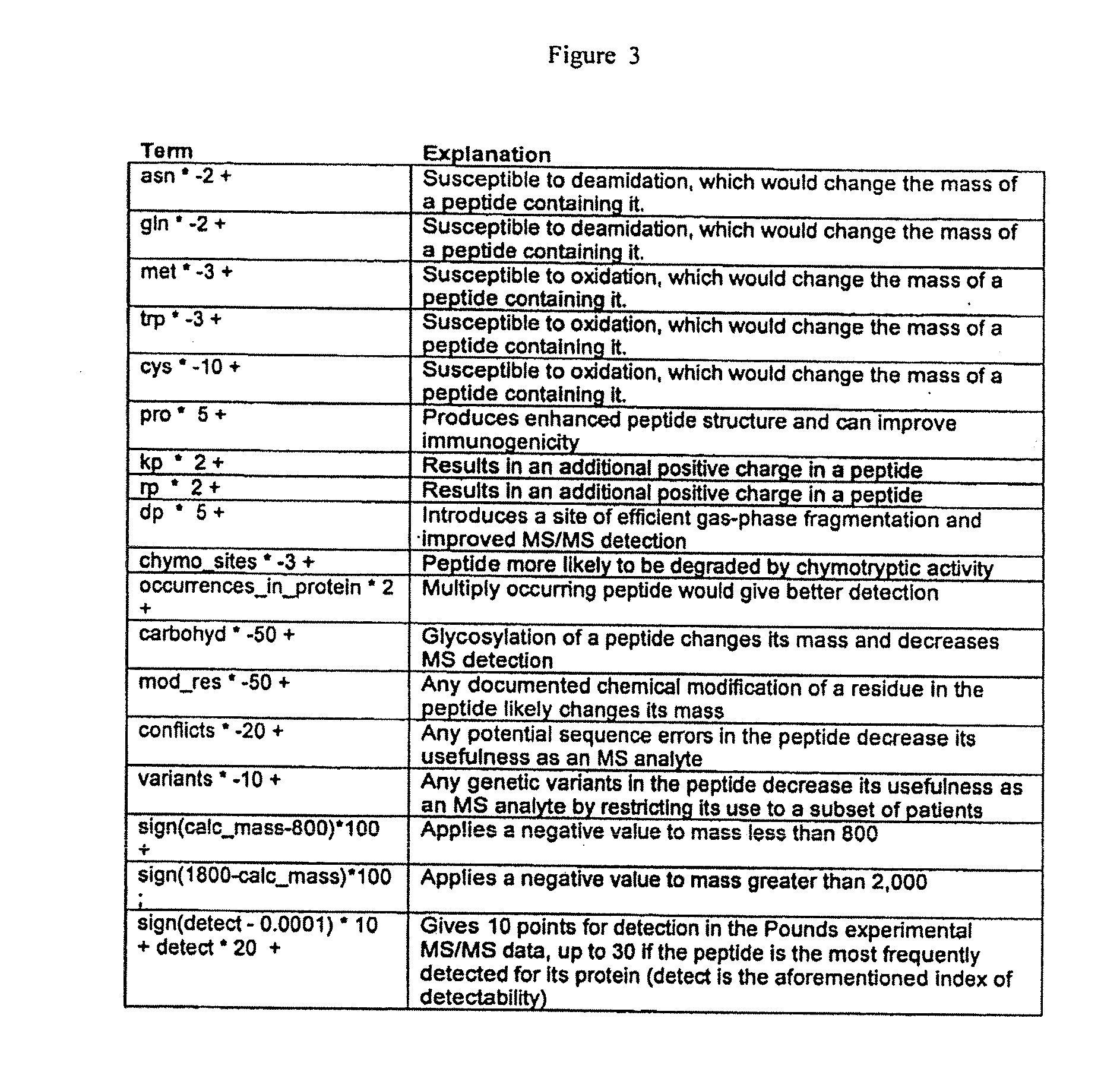
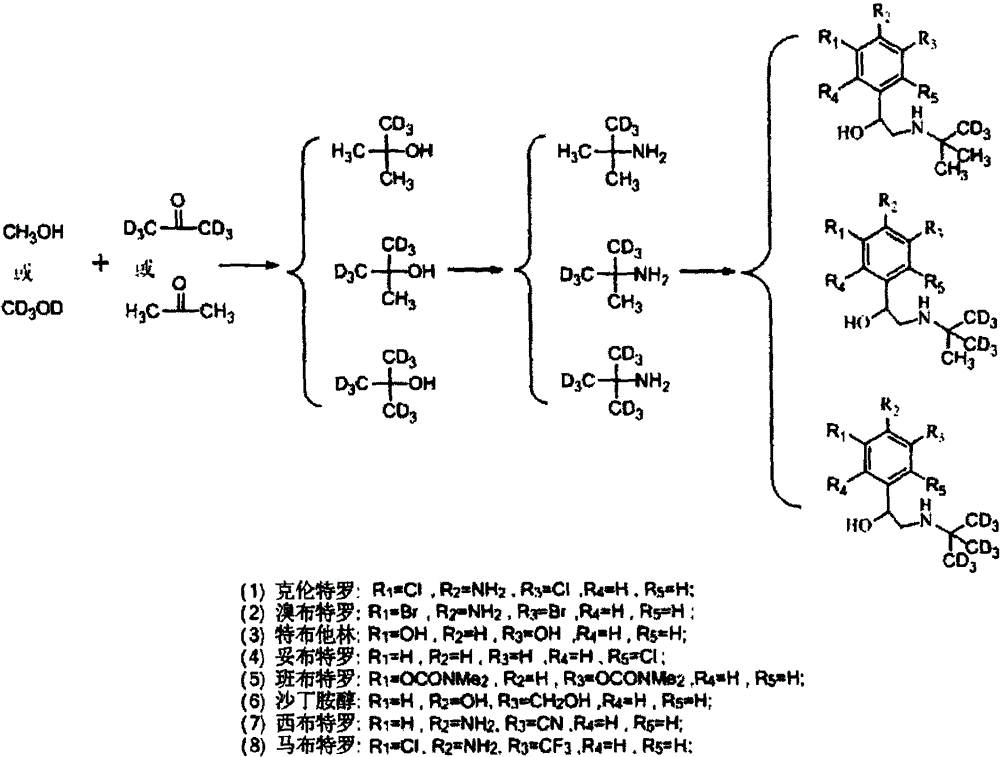
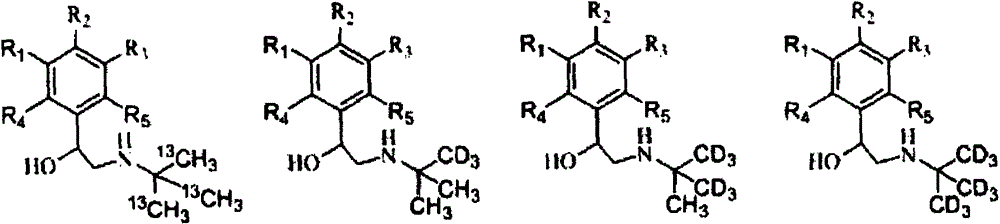
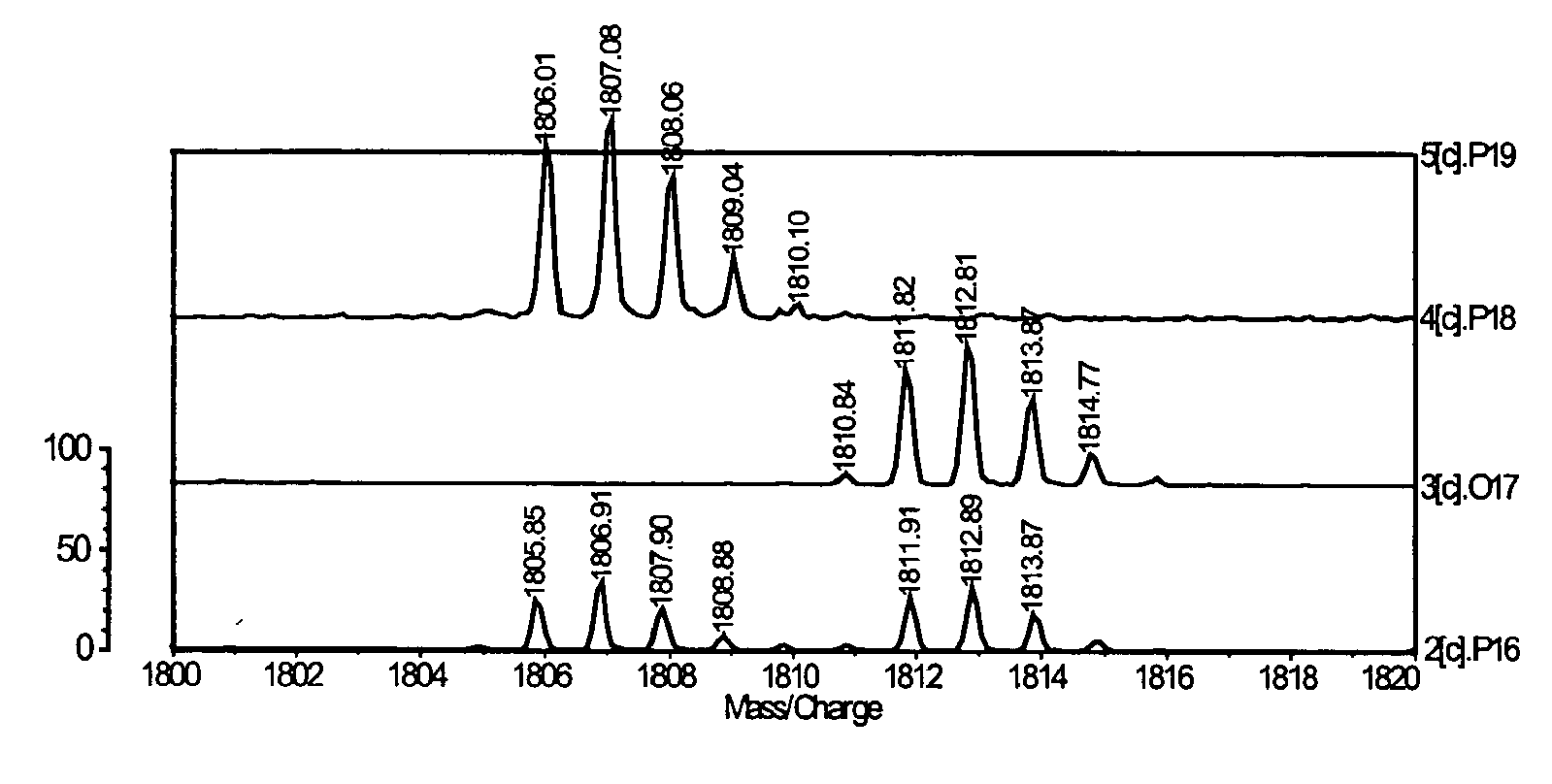
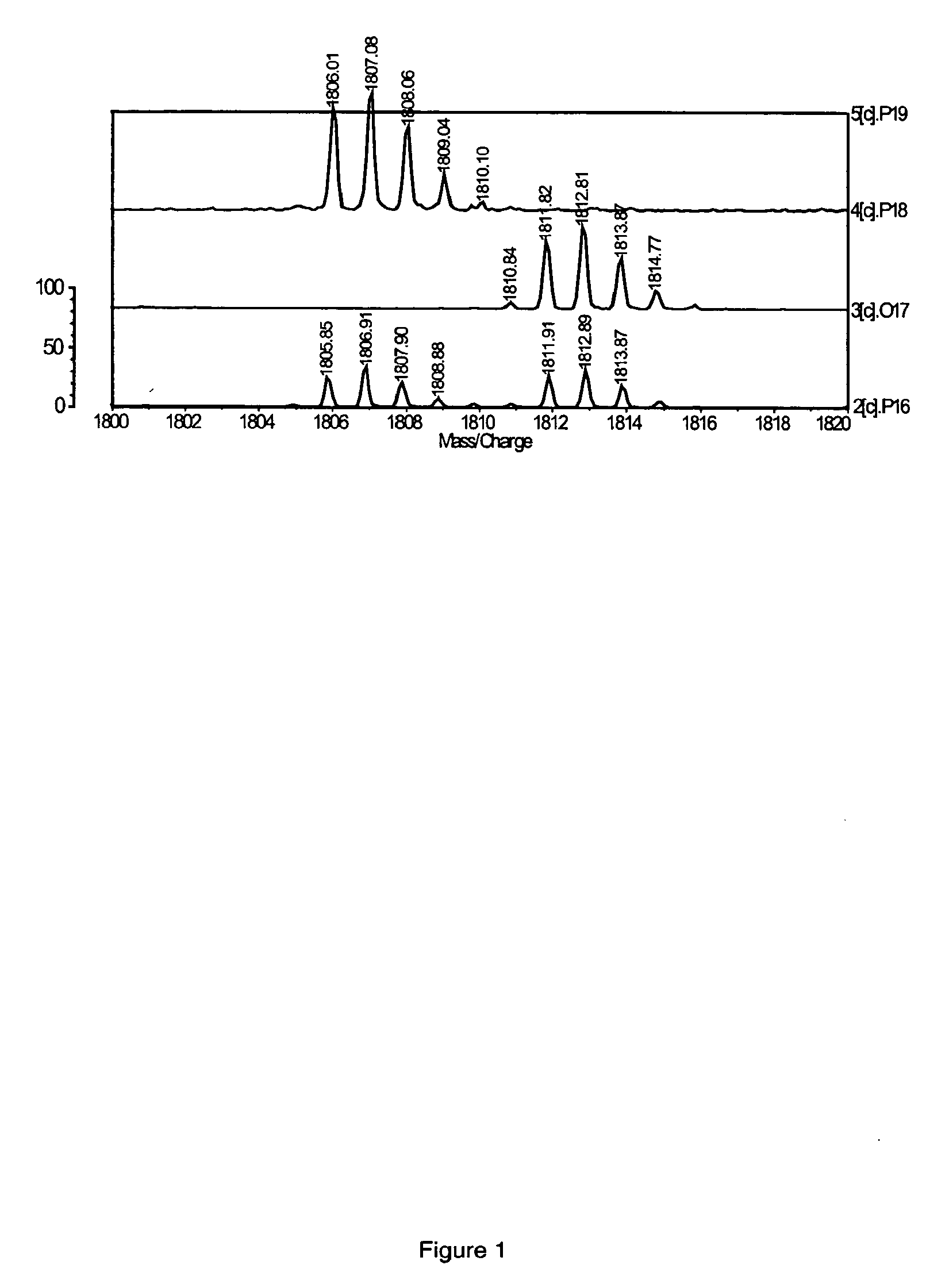
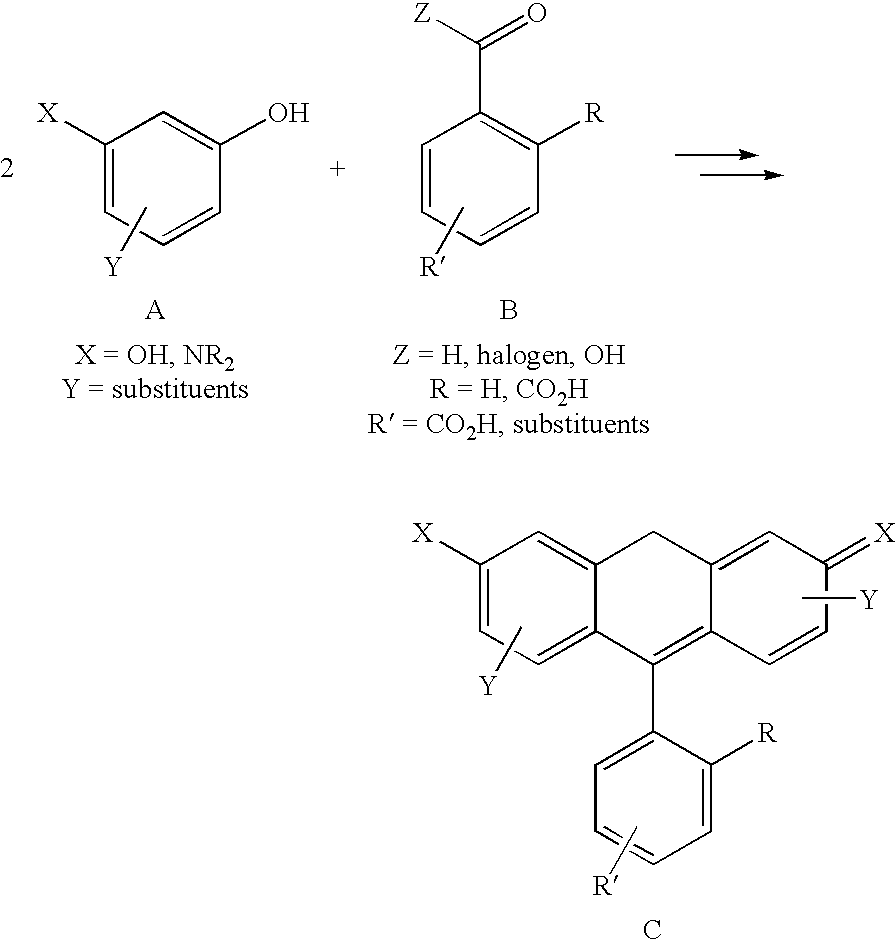
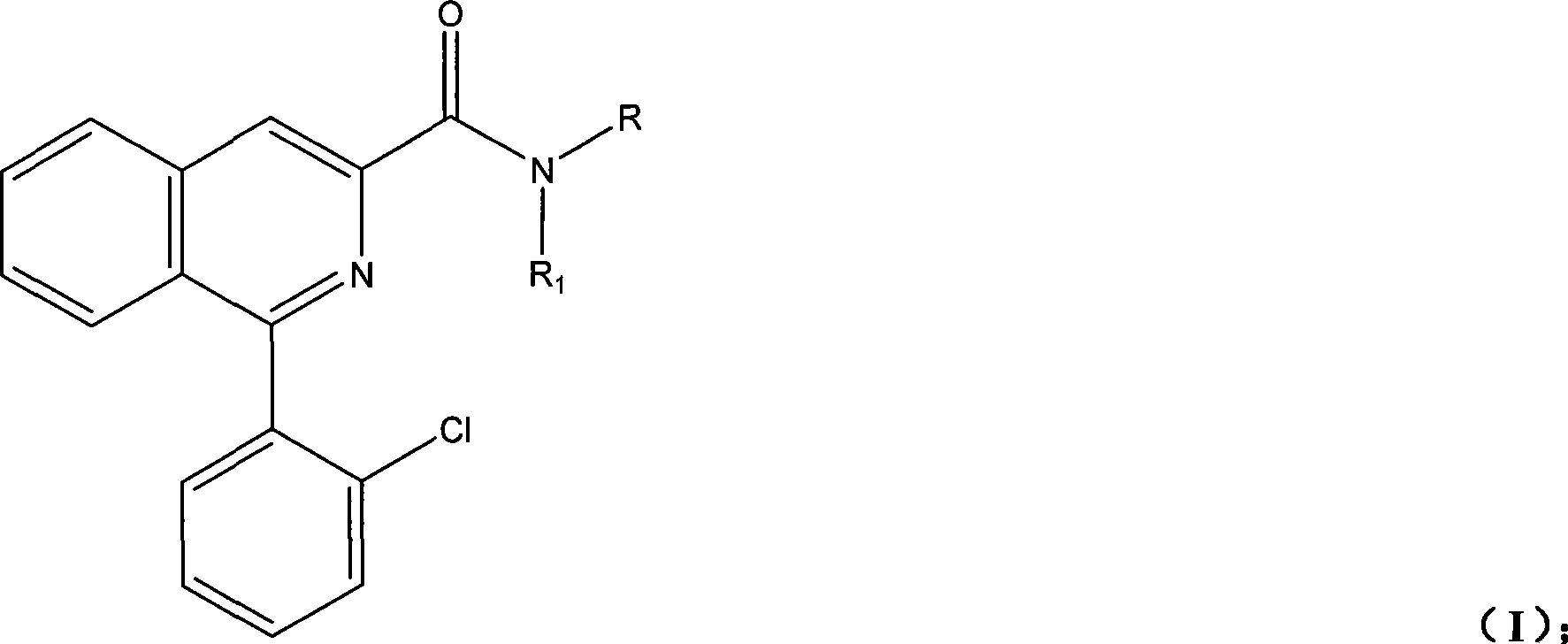
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
241 results about "Stable Isotope Labeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope ... Stable isotope labeling involves the use of non-radioactive isotopes that can act as a tracers used to model several chemical and biochemical systems.
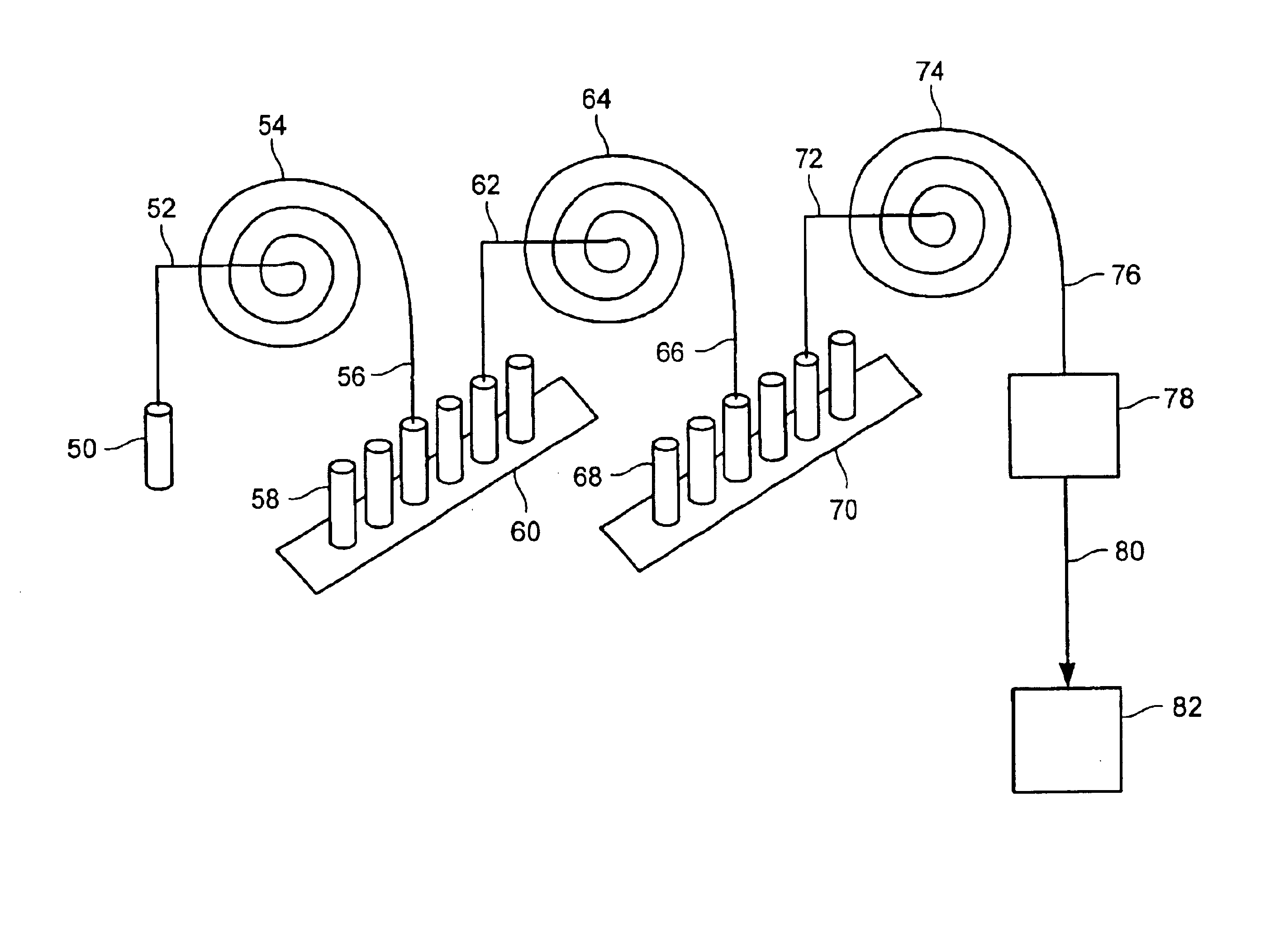
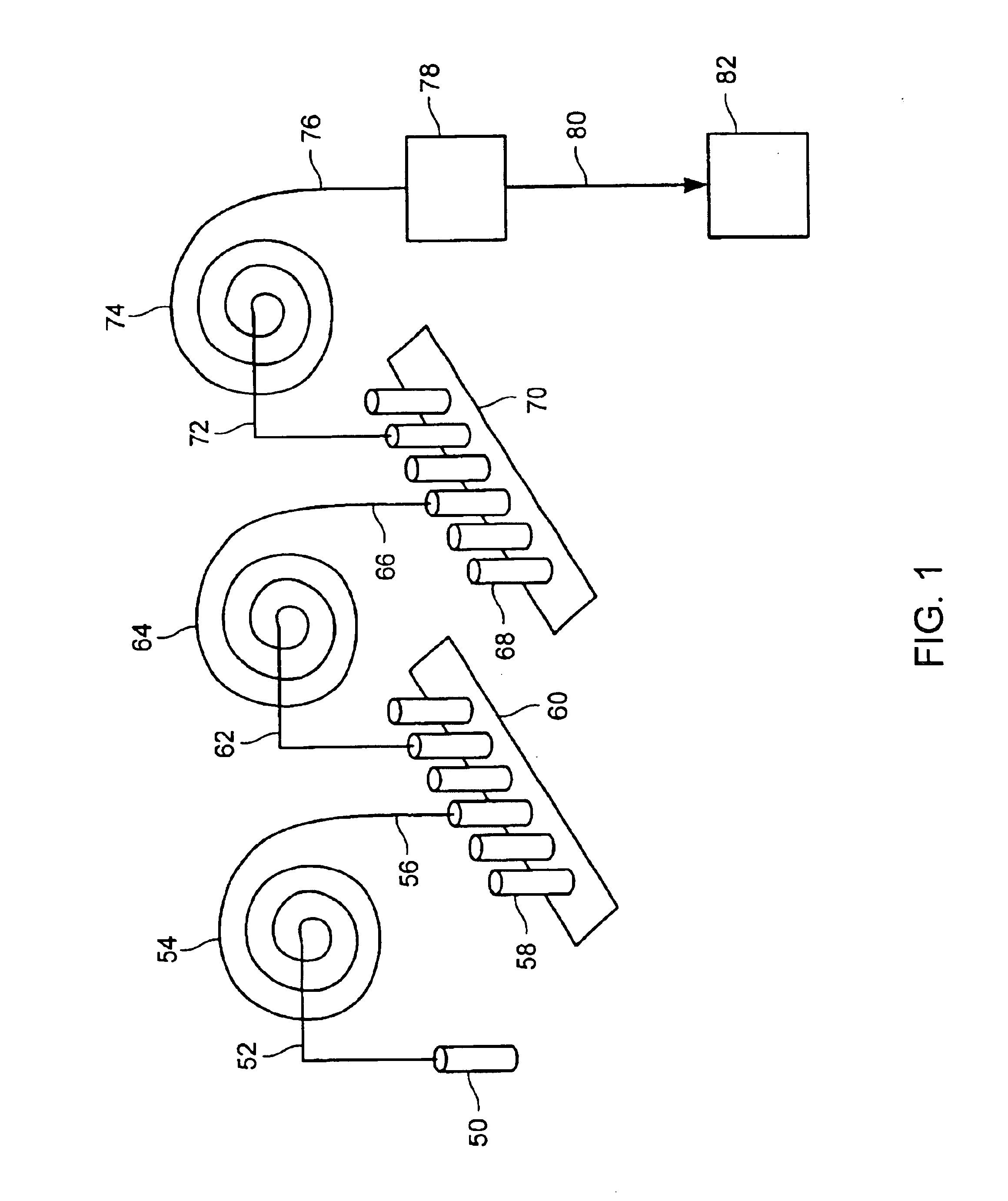
Methods for conducting metabolic analyses
InactiveUS6849396B2Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementStable Isotope LabelingAnalyte
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for purifying metabolites of interest and conducting metabolic analyses. The methods generally involve determining metabolic flux values for a plurality of target analytes by monitoring the relative isotope abundance of a stable isotope in a substrate labeled with the stable isotope and / or one or more target metabolites formed through metabolism of the labeled substrate. Certain methods utilize multiple electrophoretic methods to separate the target analytes from other components within the sample being analyzed. The methods can be used in a variety of applications including screens to identify metabolites that are correlated with certain diseases and diagnostic screens for identifying individuals having, or susceptible to, a disease.
Owner:TARGET DISCOVERY
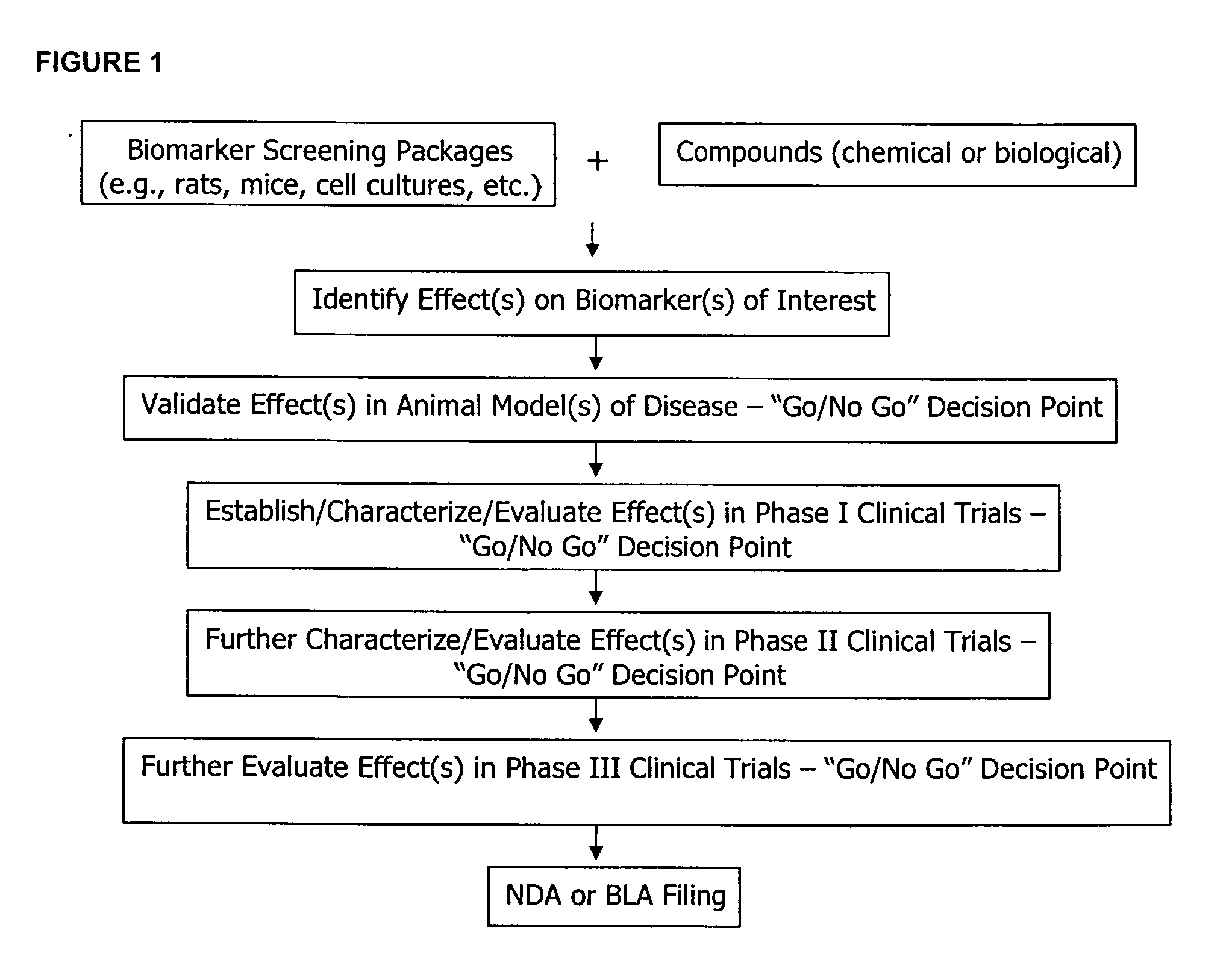
Molecular flux rates through critical pathways measured by stable isotope labeling in vivo, as biomarkers of drug action and disease activity
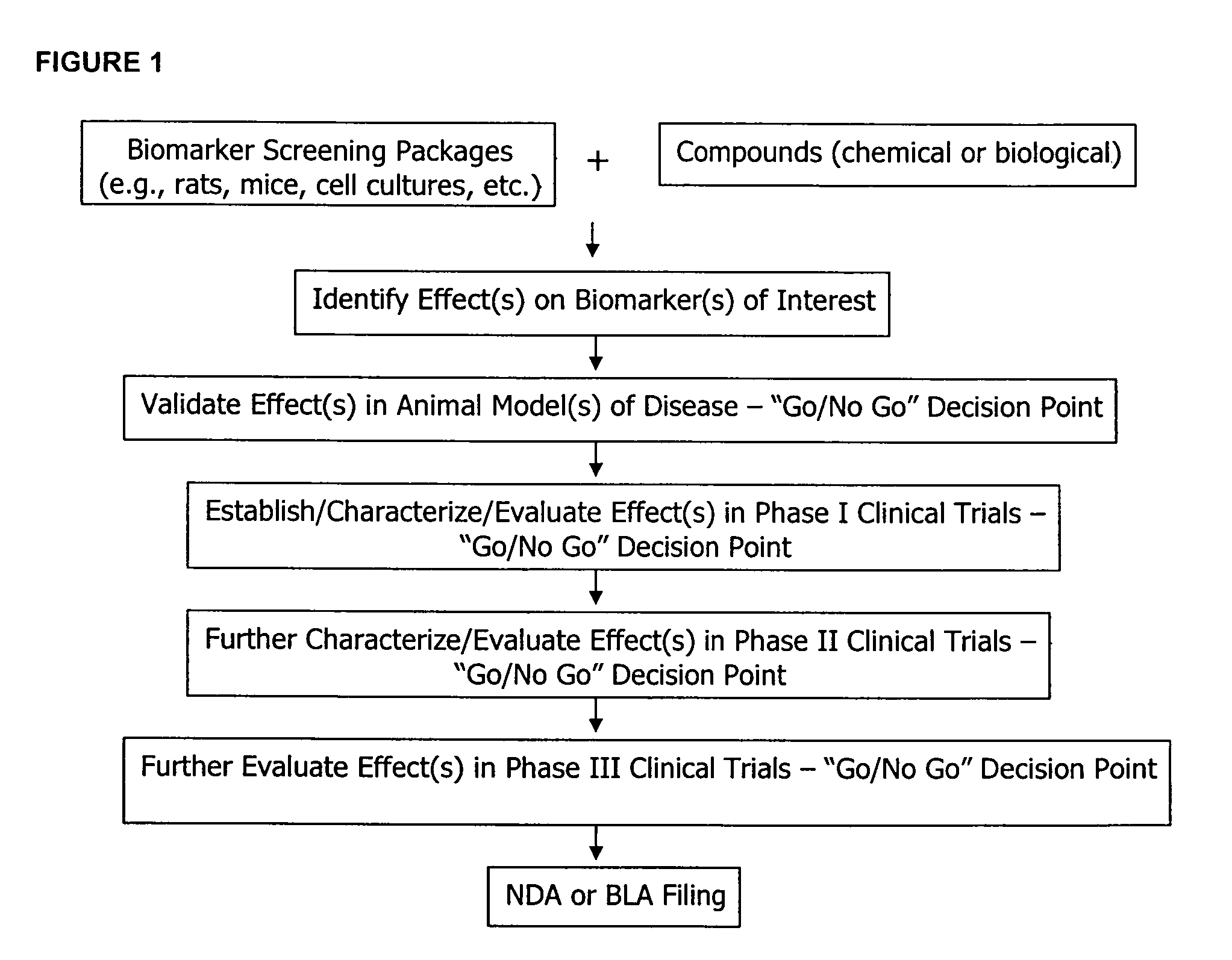
The methods described herein enable the evaluation of compounds on subjects to assess their therapeutic efficacy or toxic effects. The target of analysis is the underlying biochemical process or processes (i.e., metabolic process) thought to be involved in disease pathogenesis. Molecular flux rates within the one or more biochemical processes serve as biomarkers and are quantitated and compared with the molecular flux rates (i.e., biomarker) from control subjects (i.e., subjects not exposed to the compounds). Any change in the biomarker in the subject relative to the biomarker in the control subject provides the necessary information to evaluate therapeutic efficacy of an administered drug or a toxic effect and to develop the compound further if desired. In one aspect of the invention, stable isotope-labeled substrate molecules are administered to a subject and the label is incorporated into targeted molecules in a manner that reveals molecular flux rates through one or more metabolic pathways of interest. By this method, a comparison between subjects and control subjects reveals the effects of the chemical entity or entities on the biomarkers. This, in turn, allows for the identification of potential therapeutic uses or toxicities of the compound. Combinations of compounds can also be systematically evaluated for complementary, synergistic, or antagonistic actions on the metabolic pathways of interest, using the methods of the present invention as a strategy for identifying and confirming novel therapeutic or toxic combinations of compounds.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
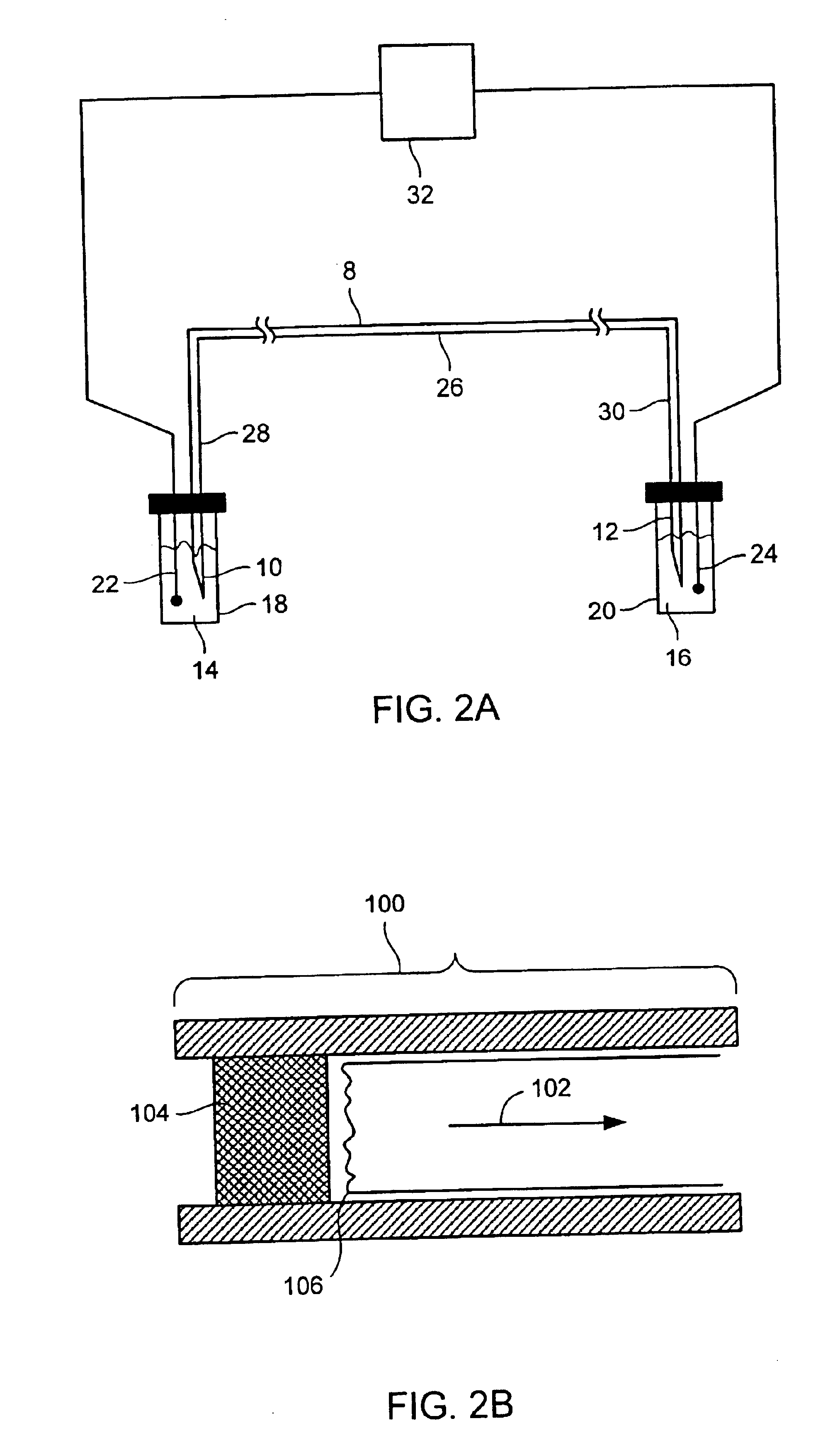
Methods for measuring cellular proliferation and destruction rates in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS6461806B1Organic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsStable Isotope LabelingDisease
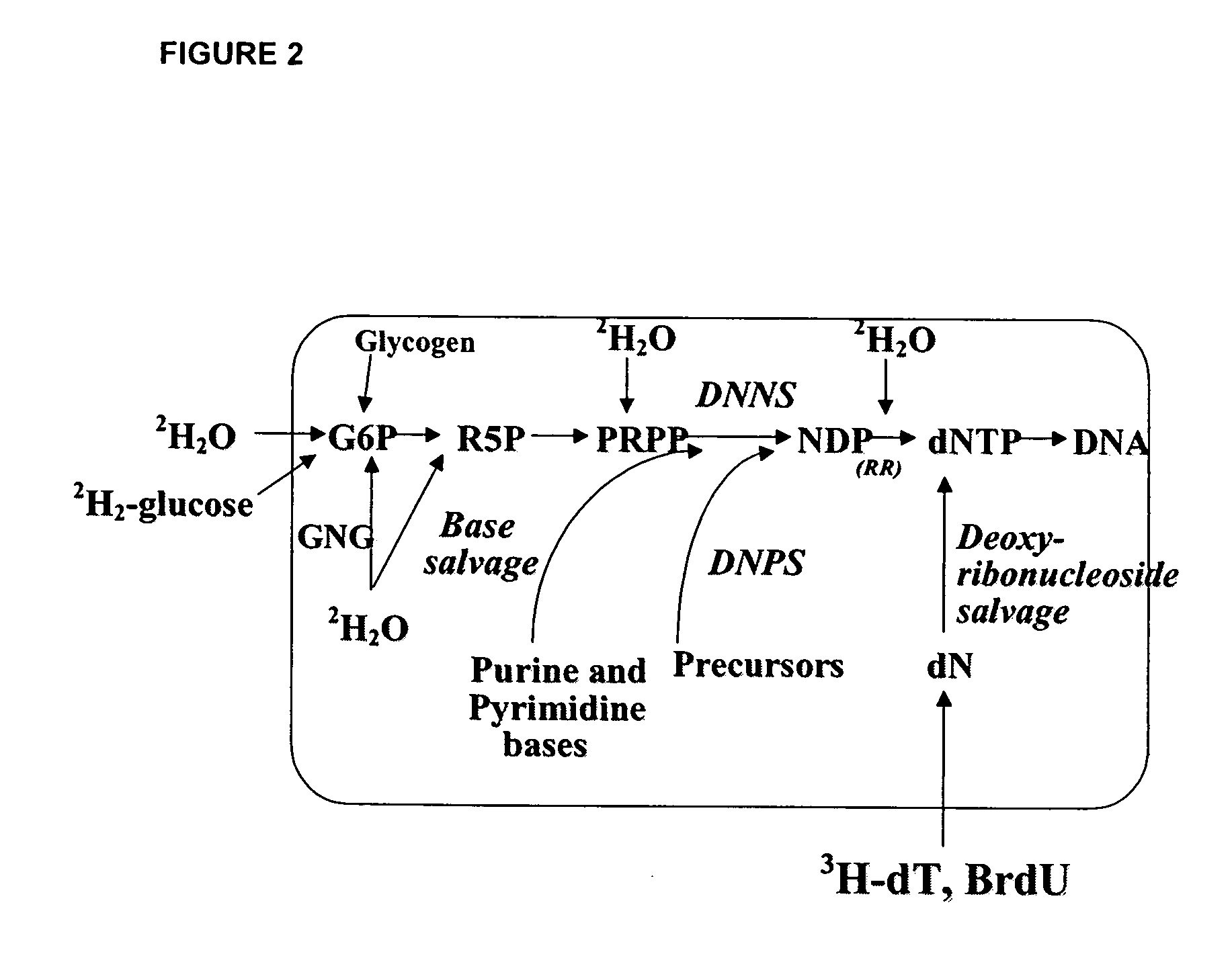
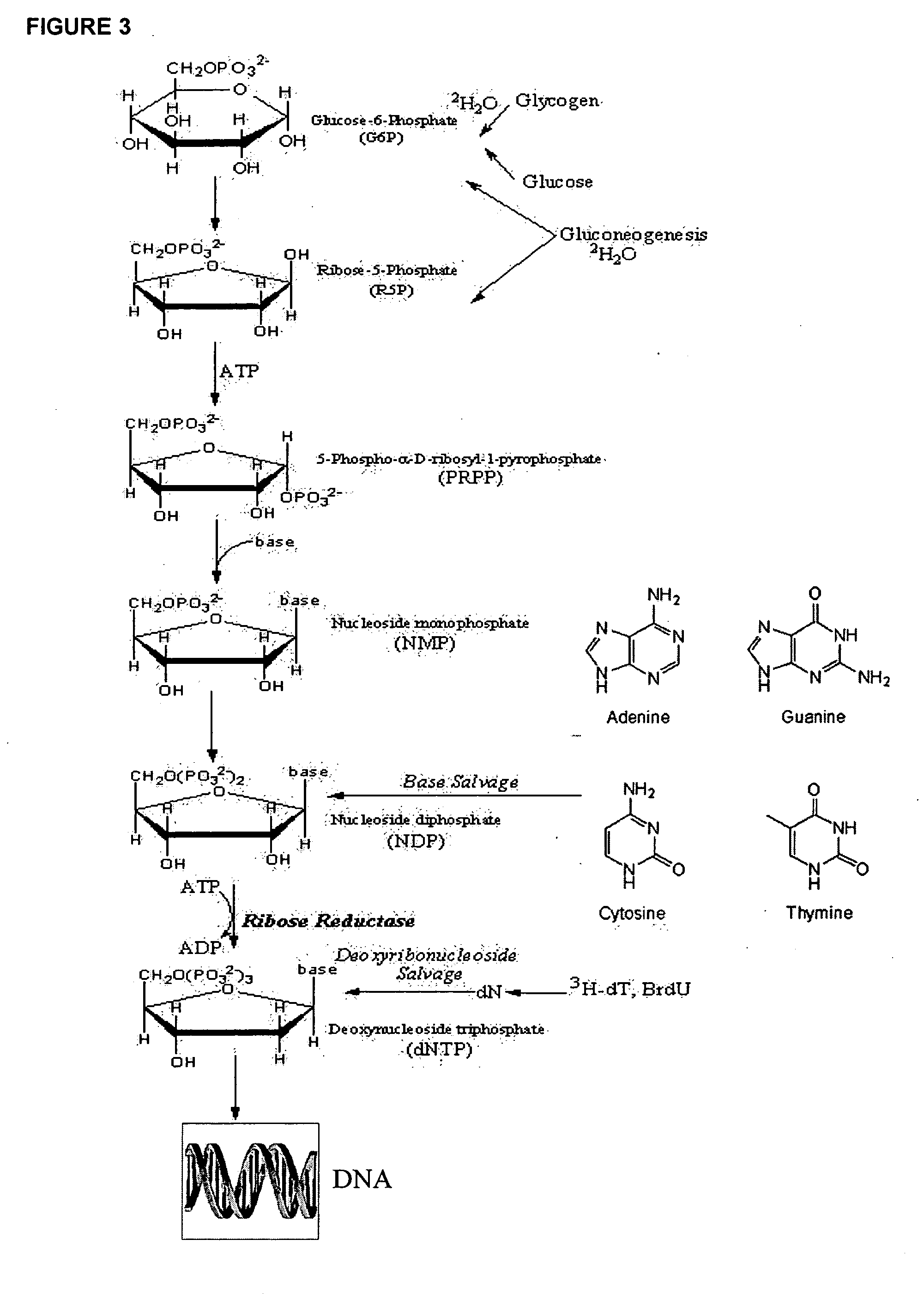
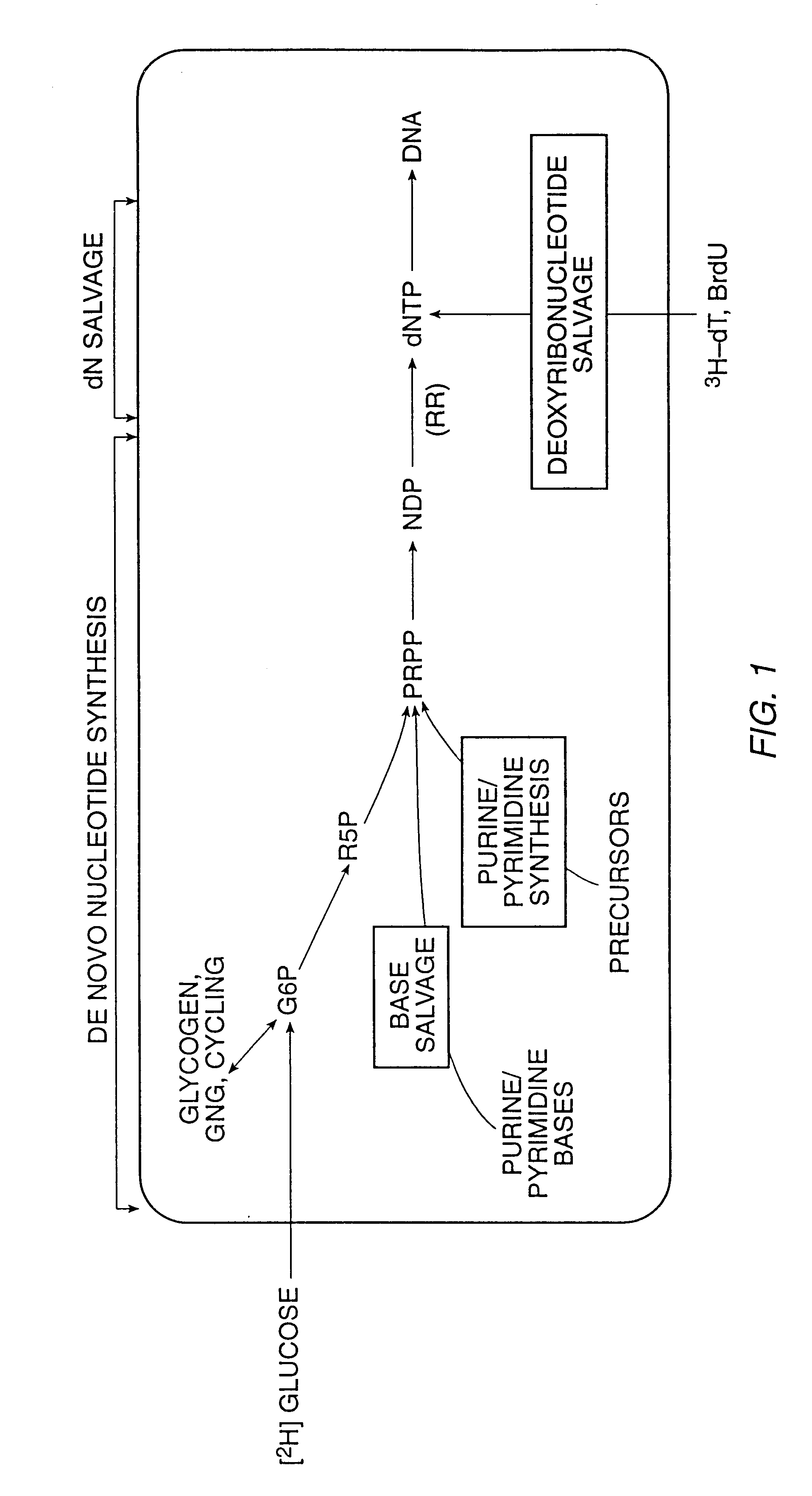
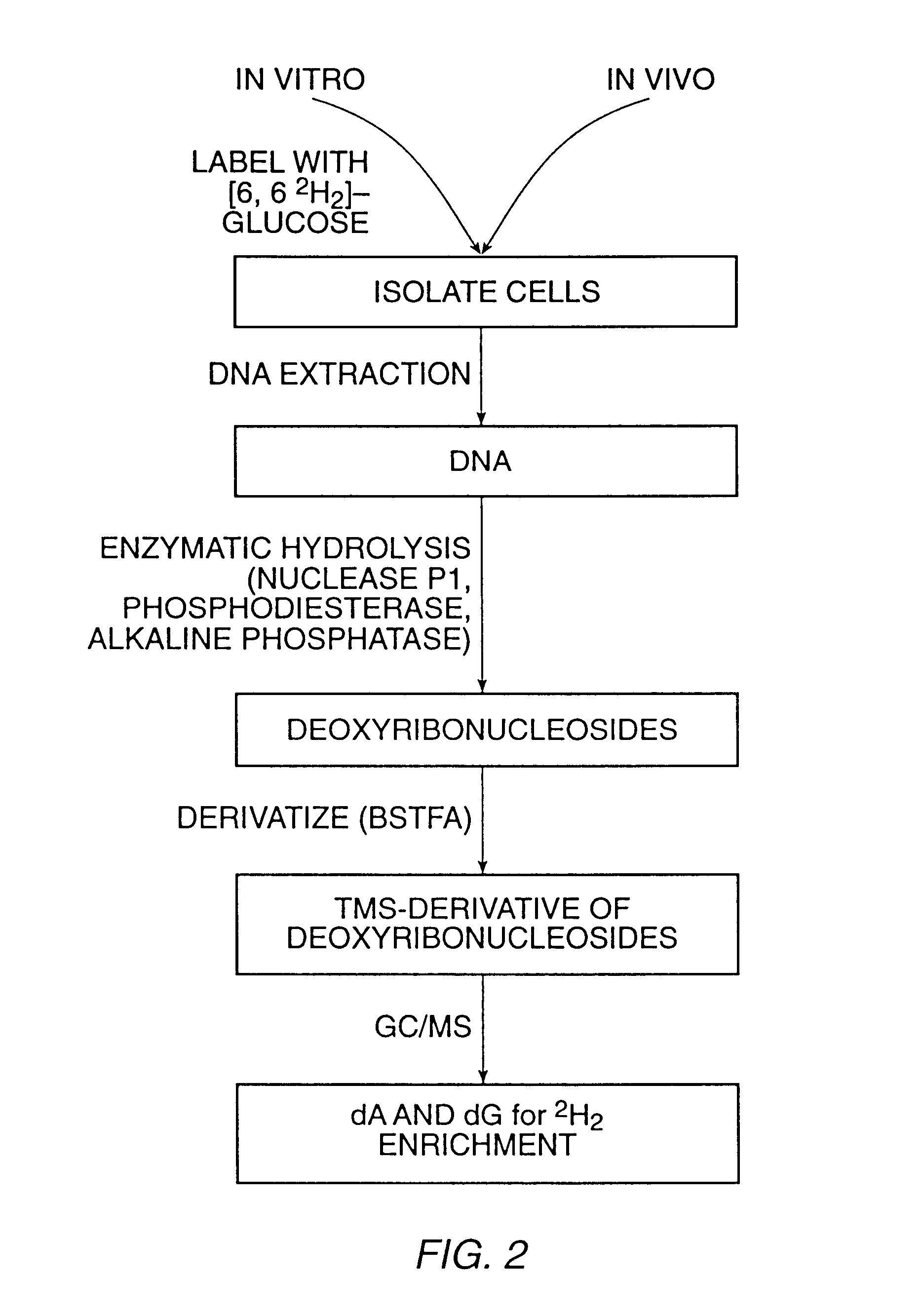
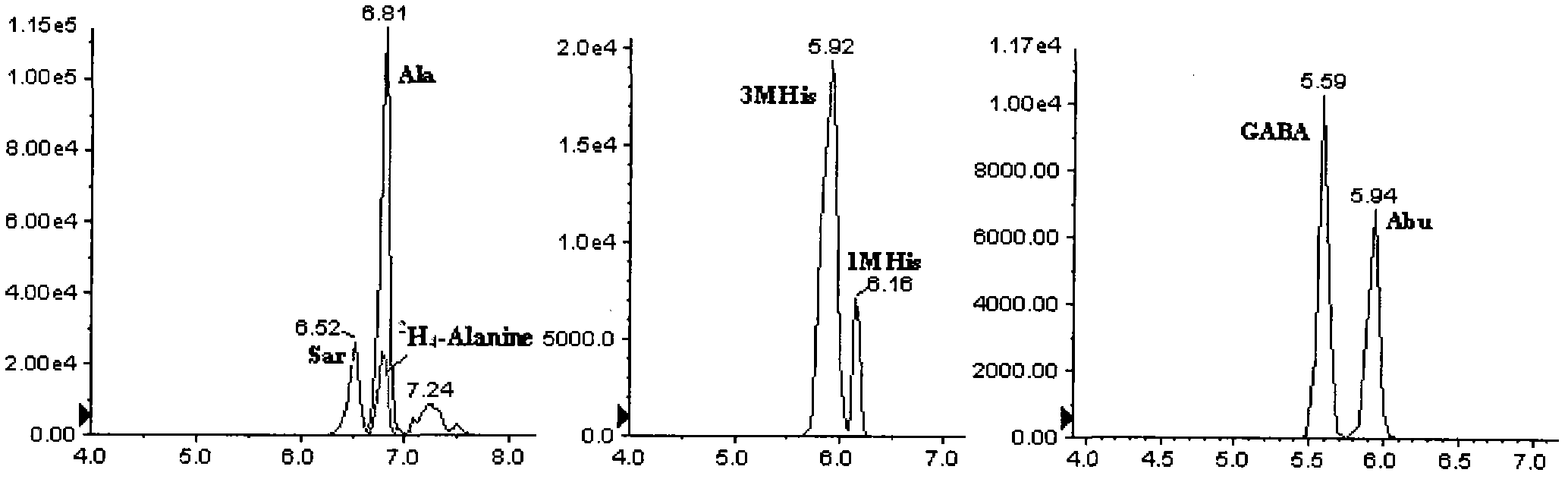
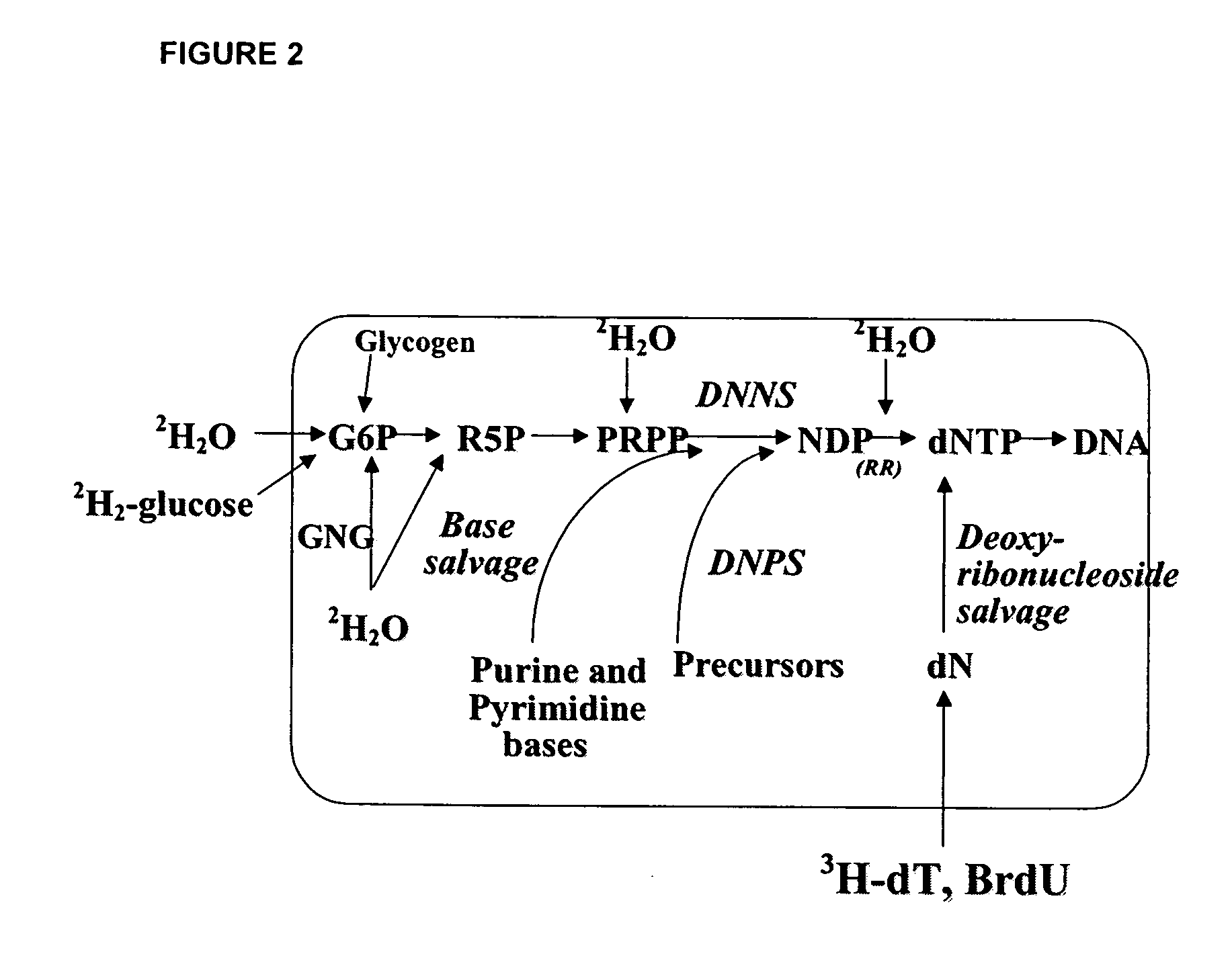
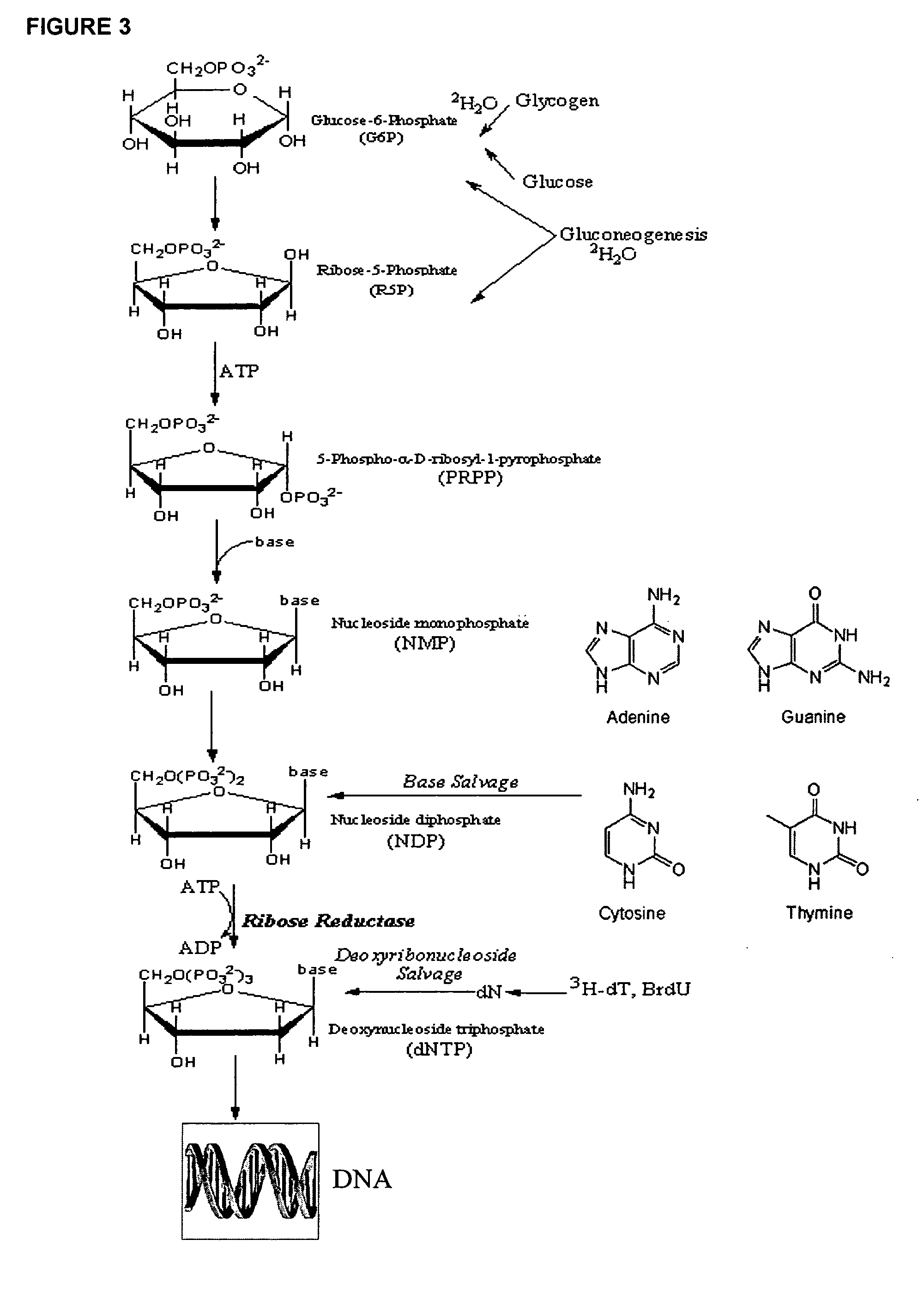
The present invention relates to methods for measuring the proliferation and destruction rates of cells by measuring deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis and / or destruction. In particular, the methods utilize non-radioactive stable isotope labels to endogenously label DNA synthesized through the de novo nucleotide synthesis pathway in a cell. The amount of label incorporated in the DNA is measured as an indication of cellular proliferation. The decay of labeled DNA over time is measured as an indication of cellular destruction. Such methods do not involve radioactivity or potentially toxic metabolites, and are suitable for use both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, the invention is useful for measuring cellular proliferation or cellular destruction rates in humans for the diagnosis, prevention, or management of a variety of disease conditions in which cellular proliferation or cellular destruction is involved. The invention also provides methods for measuring proliferation or destruction of T cells in a subject infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and methods of screening an agent for a capacity to induce or inhibit cellular proliferation or destruction. In addition, the invention provides methods for measuring cellular proliferation in a proliferating population which utilize both radioactive isotope labels and stable isotopes to endogenously label DNA through the de novo nucleotide synthesis pathway.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
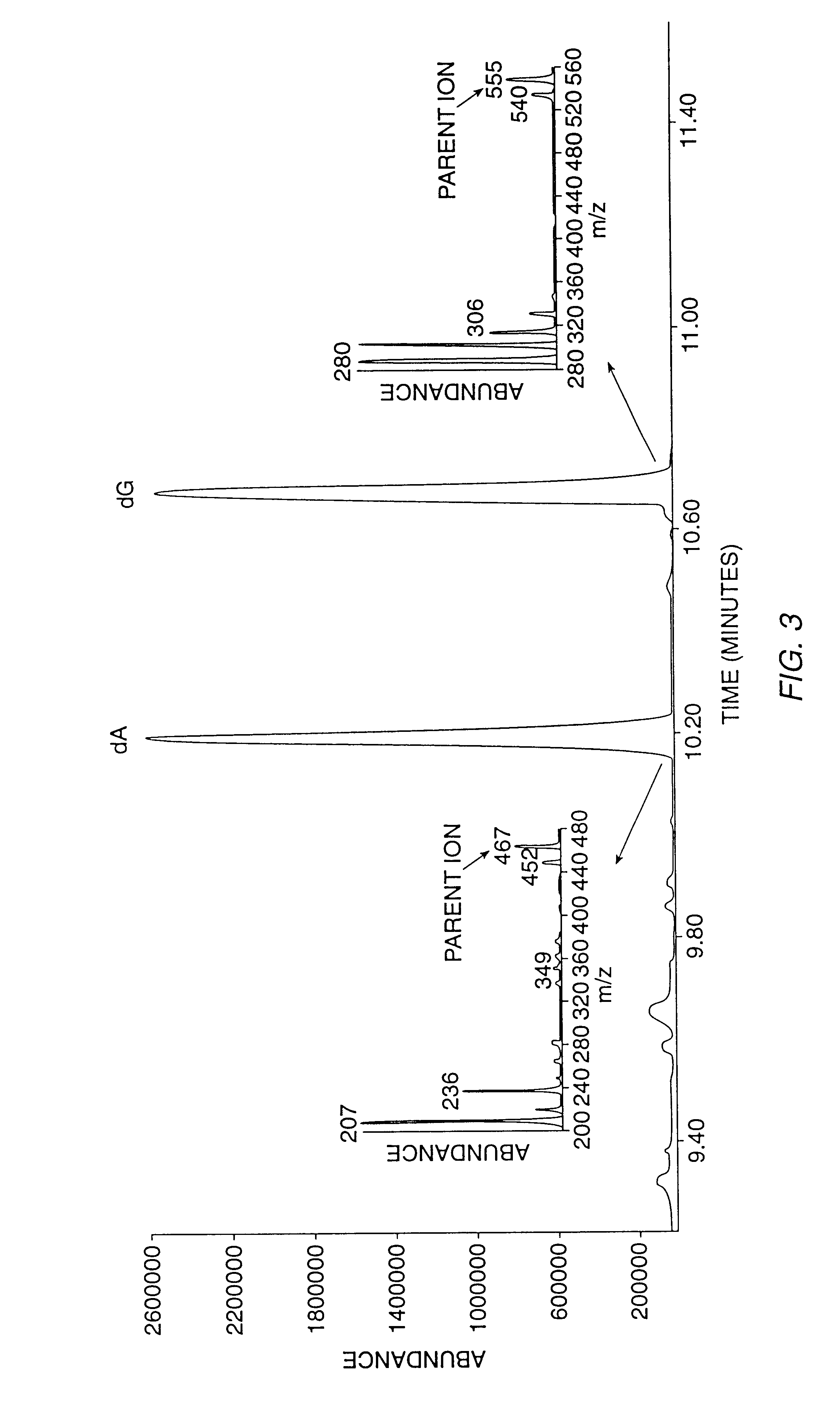
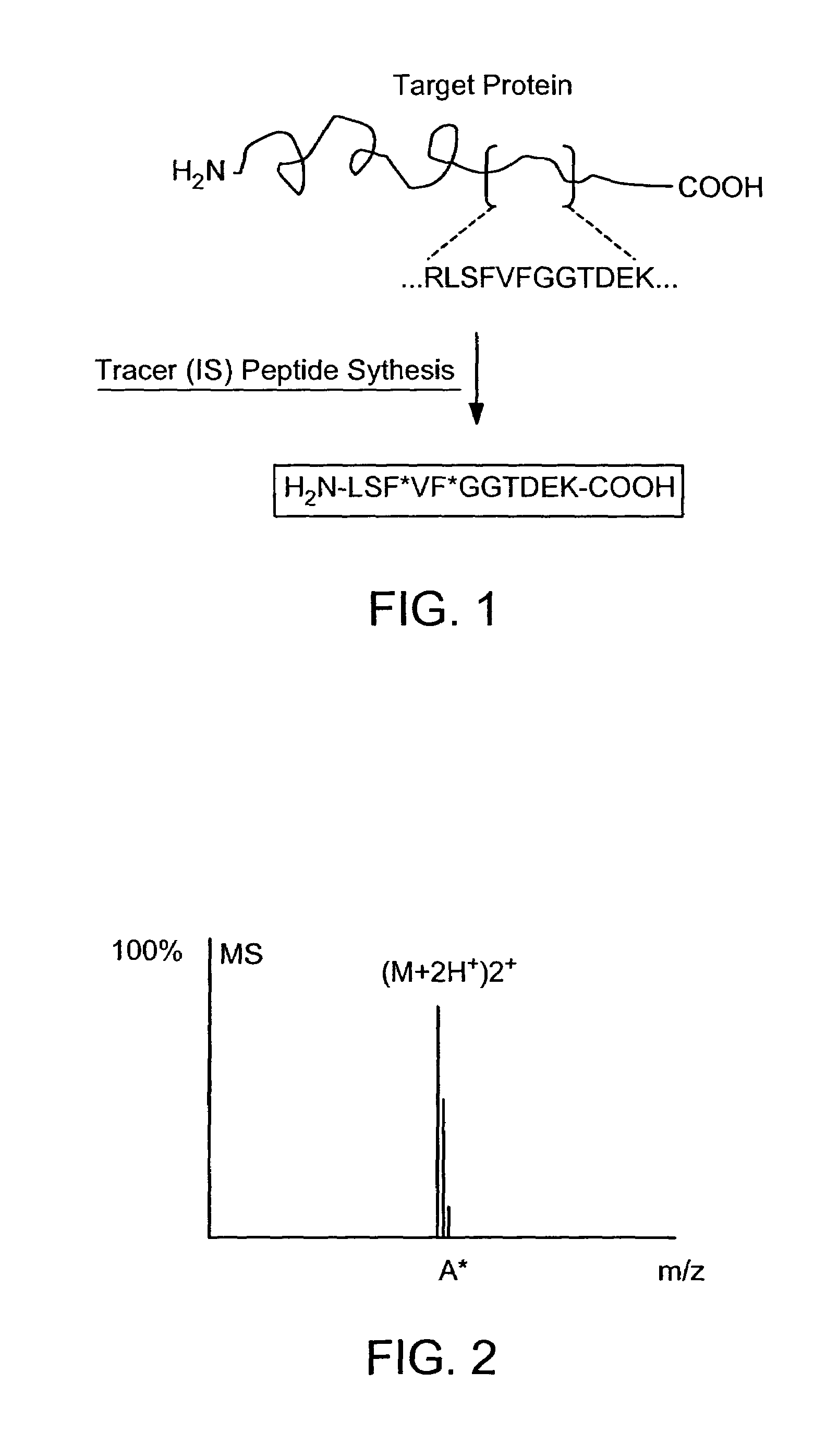
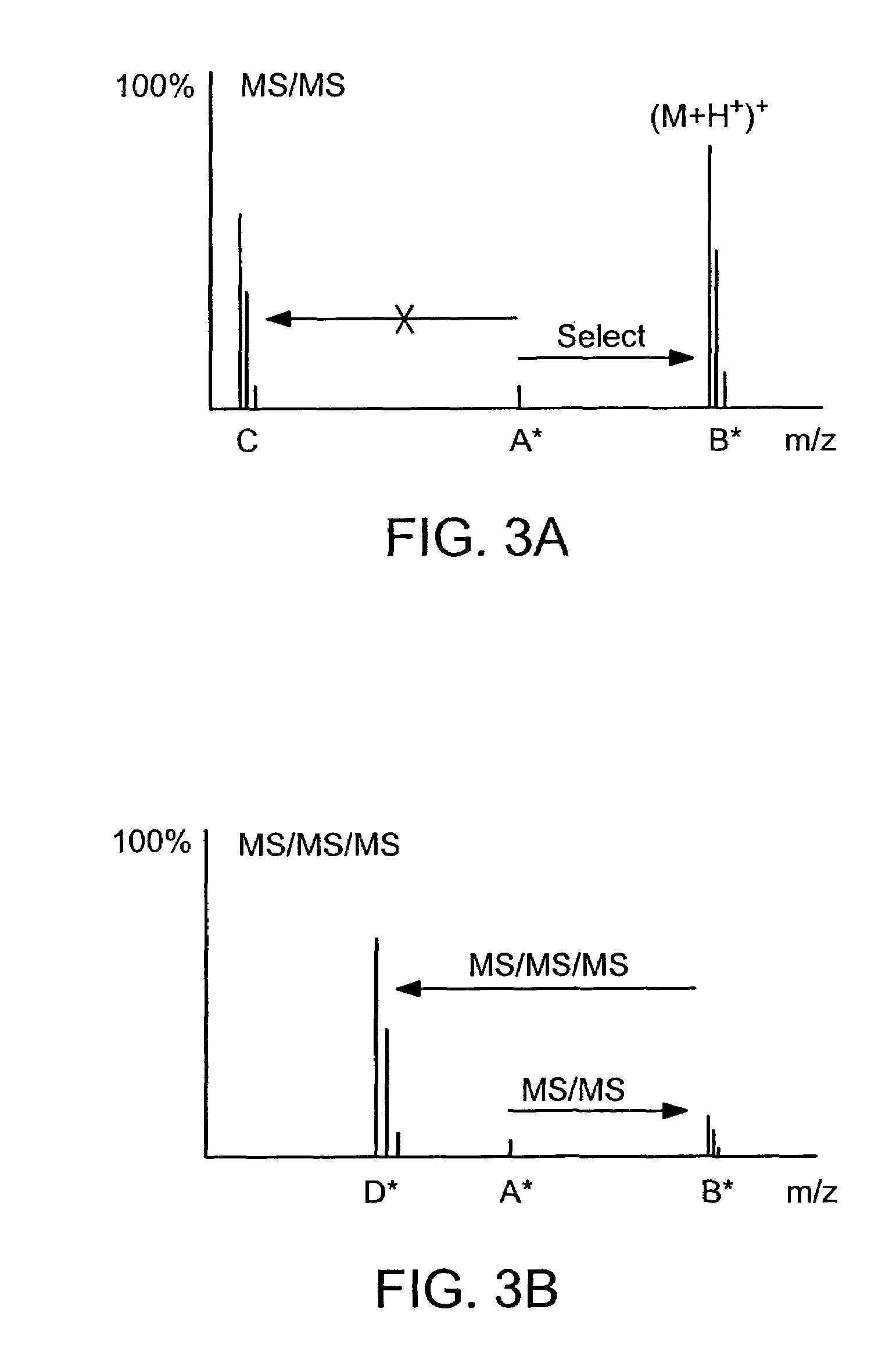
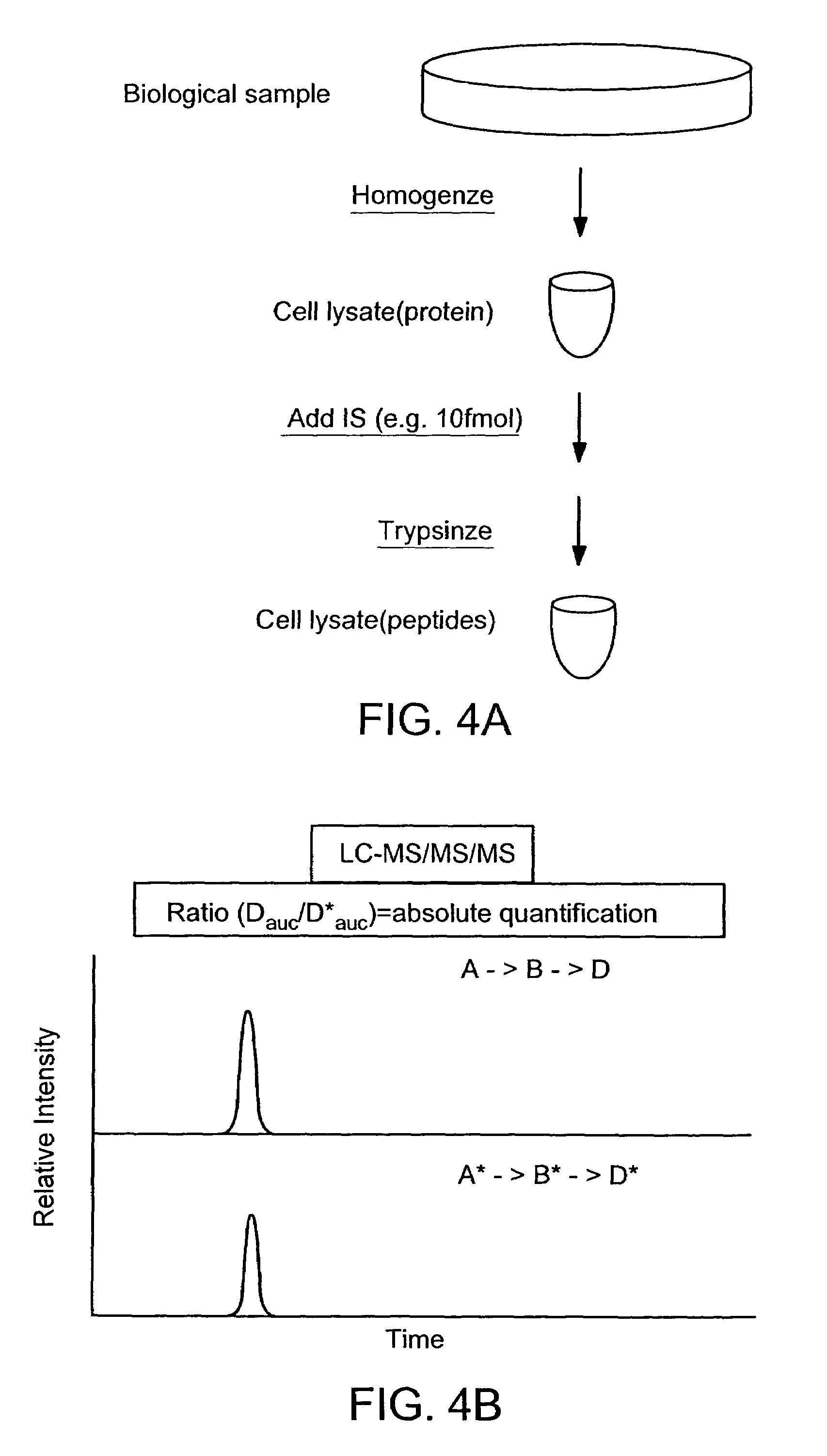
Absolute quantification of proteins and modified forms thereof by multistage mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7501286B2Rapid and high throughput analysisQuantitative precisionDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsStable Isotope LabelingIsotope
The invention provides reagents, kits and methods for detecting and / or quantifying proteins in complex mixtures, such as a cell lysate. The methods can be used in high throughput assays to profile cellular proteomes. In one aspect, the invention provides a peptide internal standard labeled with a stable isotope and corresponding in amino acid sequence to the amino acid sequence of a subsequence of a target polypeptide. In another aspect, the peptide internal standard is labeled at a modified amino acid residue and is used to determine the presence of, and / or quantitate the amount of a particular modified form of a protein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for conducting metabolic analyses
InactiveUS20050153346A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementStable Isotope LabelingMetabolite
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for purifying metabolites of interest and conducting metabolic analyses. The methods generally involve determining metabolic flux values for a plurality of target analytes by monitoring the relative isotope abundance of a stable isotope in a substrate labeled with the stable isotope and / or one or more target metabolites formed through metabolism of the labeled substrate. Certain methods utilize multiple electrophoretic methods to separate the target analytes from other components within the sample being analyzed. The methods can be used in a variety of applications including screens to identify metabolites that are correlated with certain diseases and diagnostic screens for identifying individuals having, or susceptible to, a disease.
Owner:TARGET DISCOVERY
Synthesis, compositions and methods for the measurement of the concentration of stable-isotope labeled compounds in life forms and life form excretory products
Stable isotope labeling and neutron activation to measure biological functions are provided, as are the use and method of adding a chemical monitor to correct for neutron flux to sample vials prior to the addition of sample is presented, and the use of stable isotopes as a chemical bar code for vials and other items. Methods are provided also for measuring glomerular filtration rate and glomerular sieving function in a subject, and for measuring other physiological functions.
Owner:BIOPAL
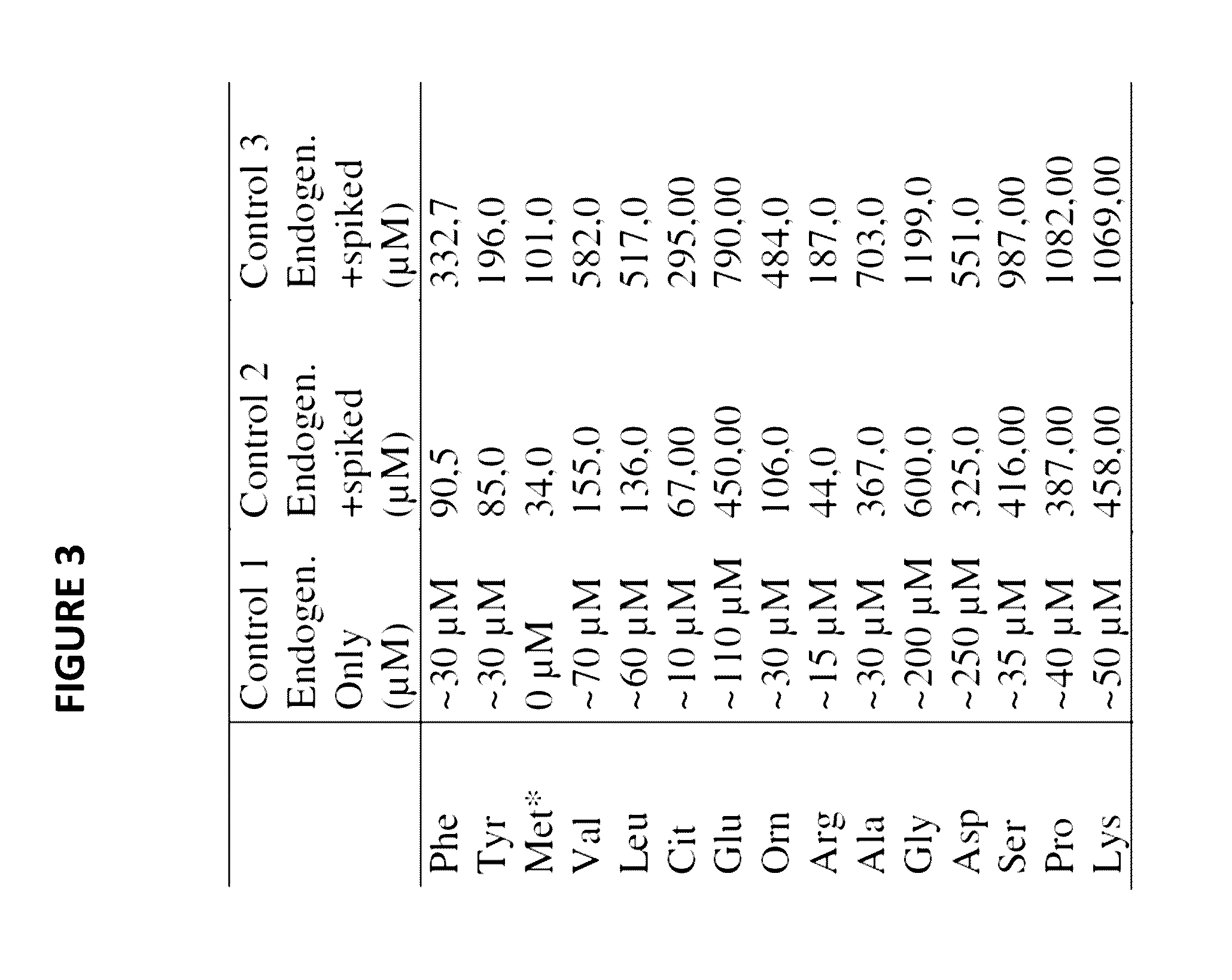
A simultaneous quantitative detection method of 30 amino acids and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103163226AImprove detection qualityRealize localizationComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansStable Isotope LabelingReversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography
The invention provides a high-sensitivity and high-throughput kit for simultaneous quantitative detection of 30 amino acids and a preparation method thereof. According to the kit, after extraction treatment of amino acids in a complex sample by using organic solvents, precipitating by using methanol, adding stable isotope-labeled amino acid internal labels, performing derivatization treatment by using hydrochloric acid and n-butanol, drying and redissolving, carrying out reversed-phase chromatography gradient separation by adopting C18 bonded phase silica gel as a stationary phase and acetonitrile-water containing heptafluorobutyric acid and formic acid as a mobile phase, and carrying out quantitative detection by adopting a mass spectrometer. The kit of the invention has the advantages that detection sensitivity can reach 10ng / ml, and all methodological indexes can meet the requirements of quantitative detections of amino acids in clinical examinations, industrial productions and scientific researches.
Owner:刘丽宏 +2
Molecular flux rates through critical pathways measured by stable isotope labeling in vivo, as biomarkers of drug action and disease activity
The methods described herein enable the evaluation of compounds on subjects to assess their therapeutic efficacy or toxic effects. The target of analysis is the underlying biochemical process or processes (i.e., metabolic process) thought to be involved in disease pathogenesis. Molecular flux rates within the one or more biochemical processes serve as biomarkers and are quantitated and compared with the molecular flux rates (i.e., biomarker) from control subjects (i.e., subjects not exposed to the compounds). Any change in the biomarker in the subject relative to the biomarker in the control subject provides information to evaluate therapeutic efficacy of an administered drug or a toxic effect and to develop the compound further if desired. In one aspect of the invention, stable isotope-labeled substrate molecules are administered to a subject and the label is incorporated into targeted molecules in a manner that reveals molecular flux rates through metabolic pathways of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
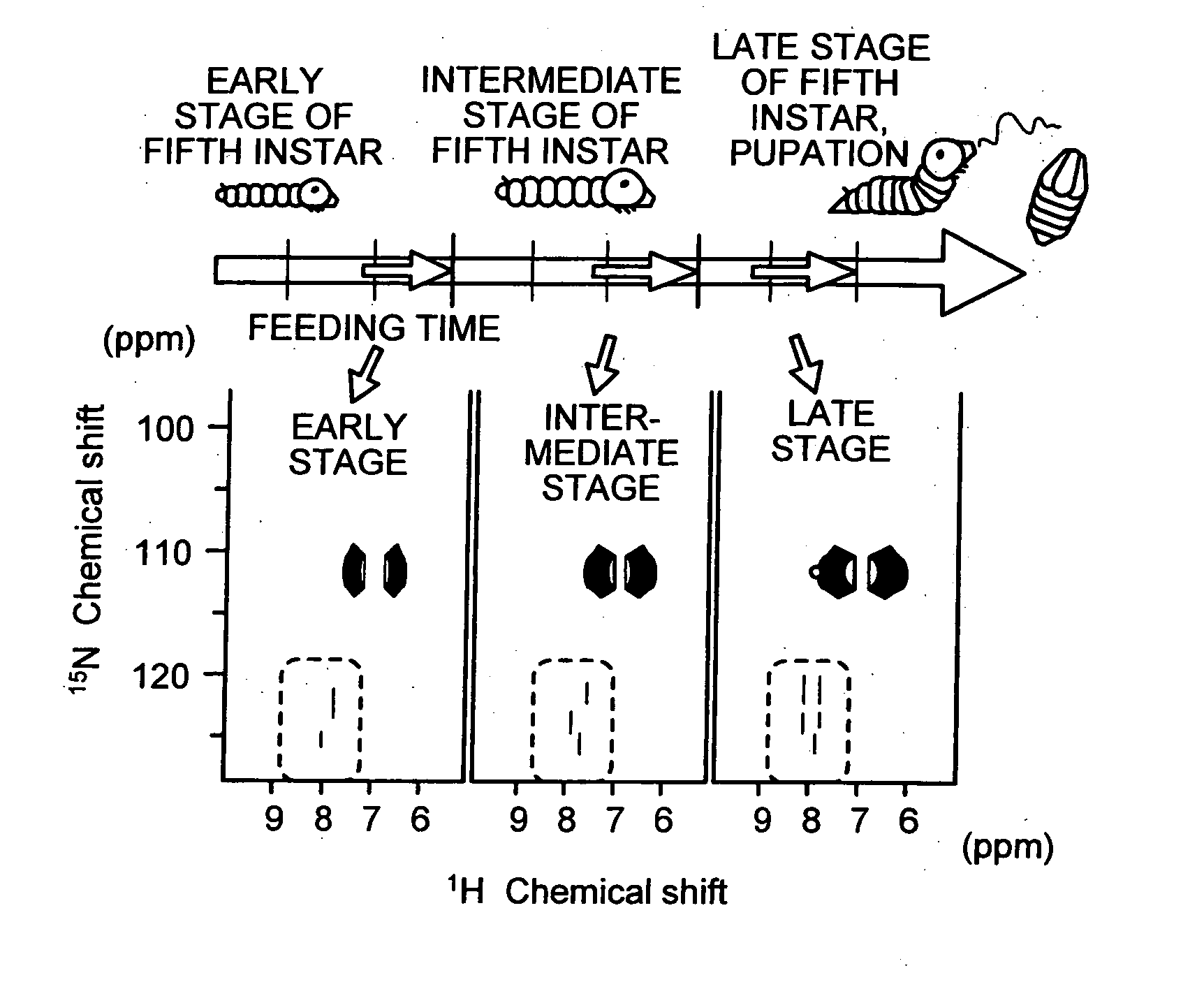
Method of analyzing metabolism for animal, method of producing labeled animals, labeled animals and method of measuring NMR for animals
InactiveUS20060035382A1Magnetic measurementsVertebrate cellsStable Isotope LabelingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention provides a novel NMR metabolomics method for observing an animal by labeling the animal itself. A labeled animal labeled with a stable isotope is produced by feeding an animal a labeled food labeled with the stable isotope. Metabolism of a biological substance in the animal is analyzed based on nuclear magnetic resonance data of the biological substance containing the stable isotope. The nuclear magnetic resonance data is acquired by performing NMR measurement on a body of the labeled animal, a portion of the body, or an extract.
Owner:RIKEN
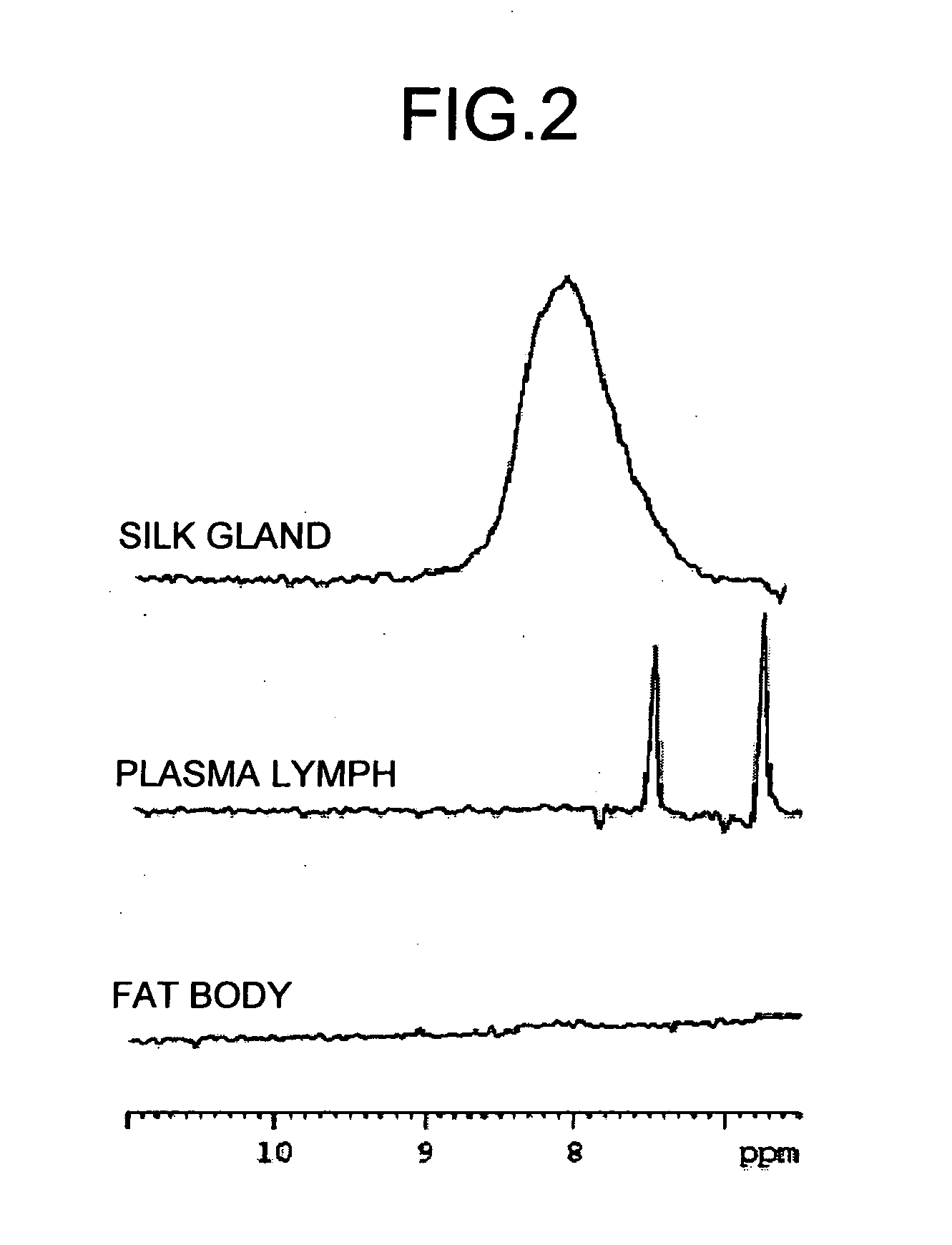
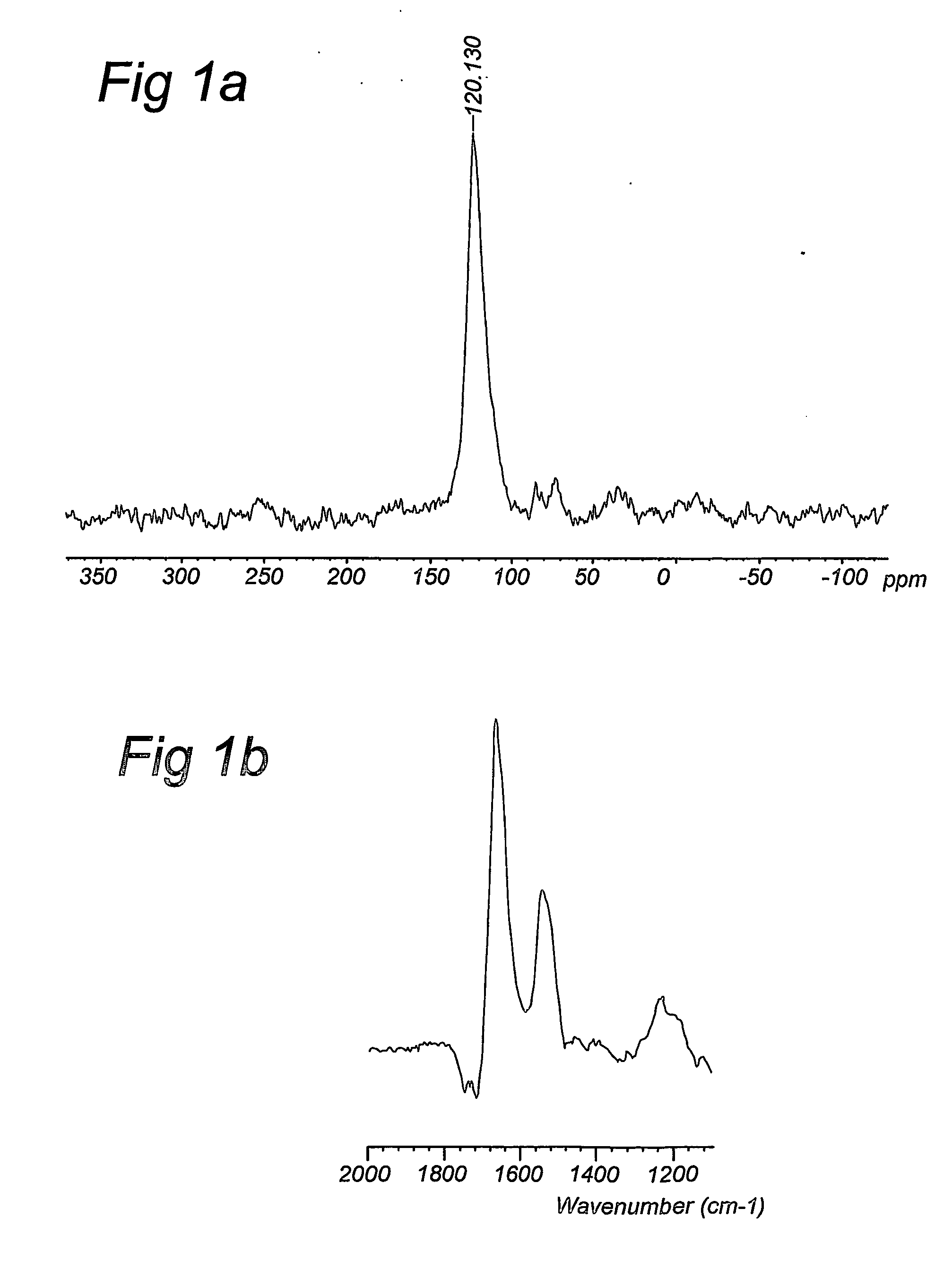
Compositions and method for stable isotope labelling of biological compounds
InactiveUS20070082399A1Meaningful NMR spectralEnhanced and good resolvedMicroorganism lysisDepsipeptidesStable Isotope LabelingSpectroscopy
The present invention is concerned the labelling of biological compounds with stable isotopes such that the three-dimensional structure of the biological compounds may be analysed by e.g. NMR spectroscopy. The invention employs microorganisms that are grown on mineral media comprising carbon and nitrogen sources that contain stable isotopes to produce biomass that is uniformly labelled with stable isotopes. The biomass may be autolysed to produce an autolysate. The biomass may further be extracted with organic solvent to produce lipids. The (delipidised) biomass is hydrolysed to produce labelled amino acids and other nutrients, which are used together with the autolysate, extracted lipids and further components to compose a culture medium for a mammalian or insect host cells for the production of biological compounds that are uniformly labelled with stable isotopes. The biological compound preferably is a biological acromolecule, such as e.g. a mammalian membrane protein. Data supplied from the esp@cenet database—Worldwide
Owner:TATIANA A EGOROVA ZACHERNYUK
Synthesis, compositions and methods for the measurement of the concentration of stable-isotope labeled compounds in life forms and life form excretory products
InactiveUS20060067881A1Powder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsStable Isotope LabelingChemical compound
Stable isotope labeling and neutron activation to measure biological functions are provided, as are the use and method of adding a chemical monitor to correct for neutron flux to sample vials prior to the addition of sample is presented, and the use of stable isotopes as a chemical bar code for vials and other items. Methods are provided also for measuring glomerular filtration rate and glomerular sieving function in a subject, and for measuring other physiological functions.
Owner:BIOPHYSICS ASSAY LAB
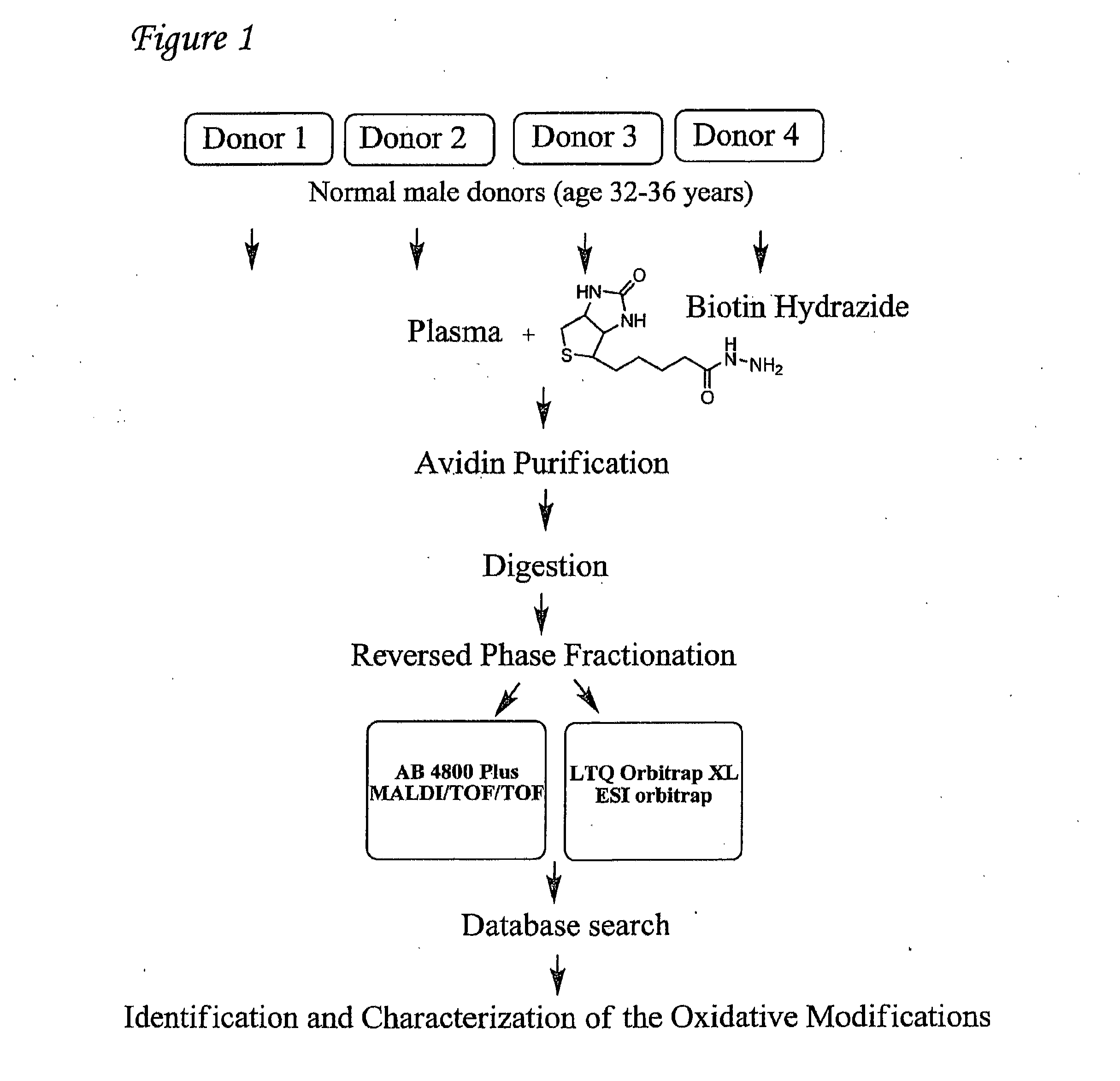
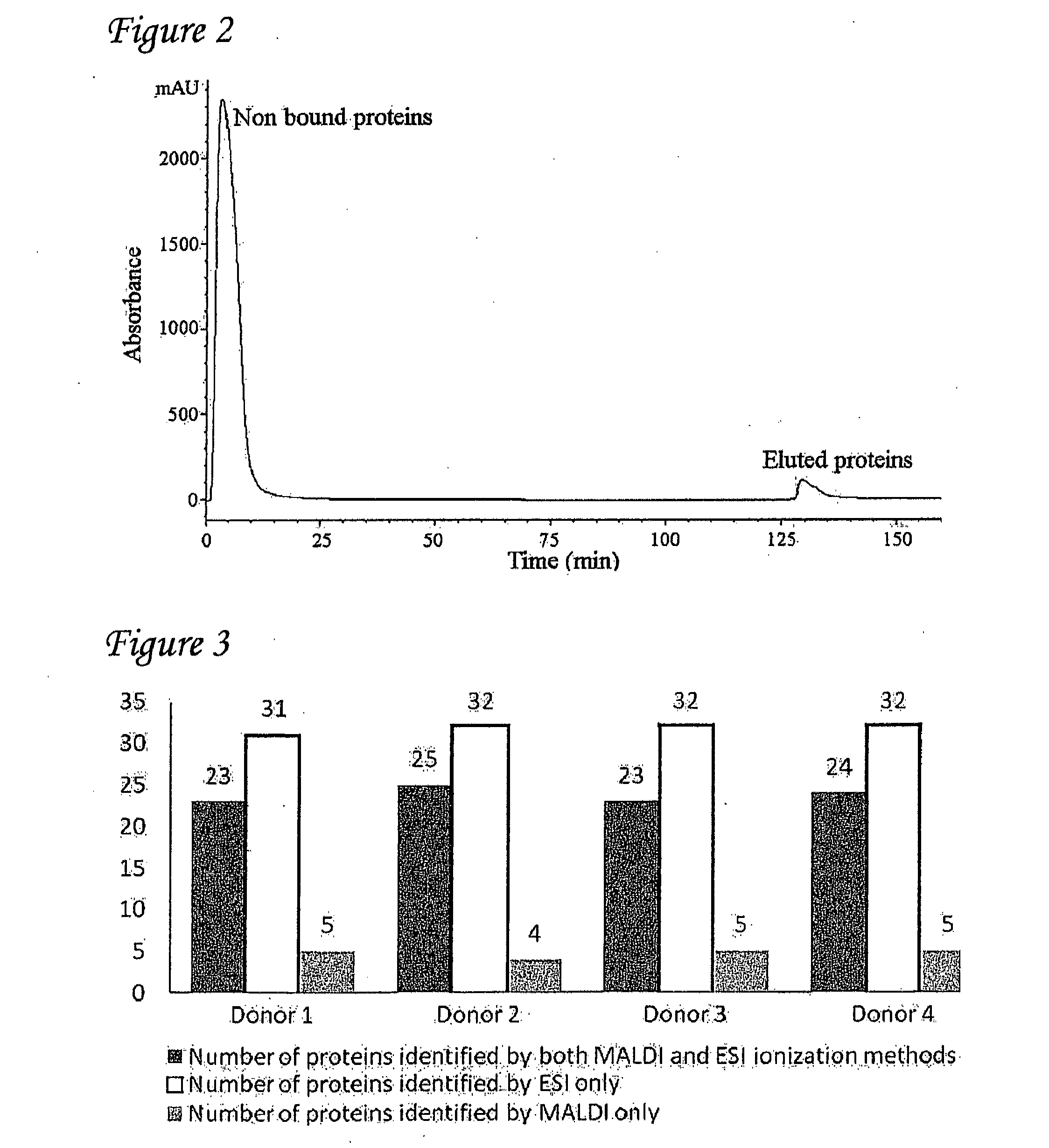
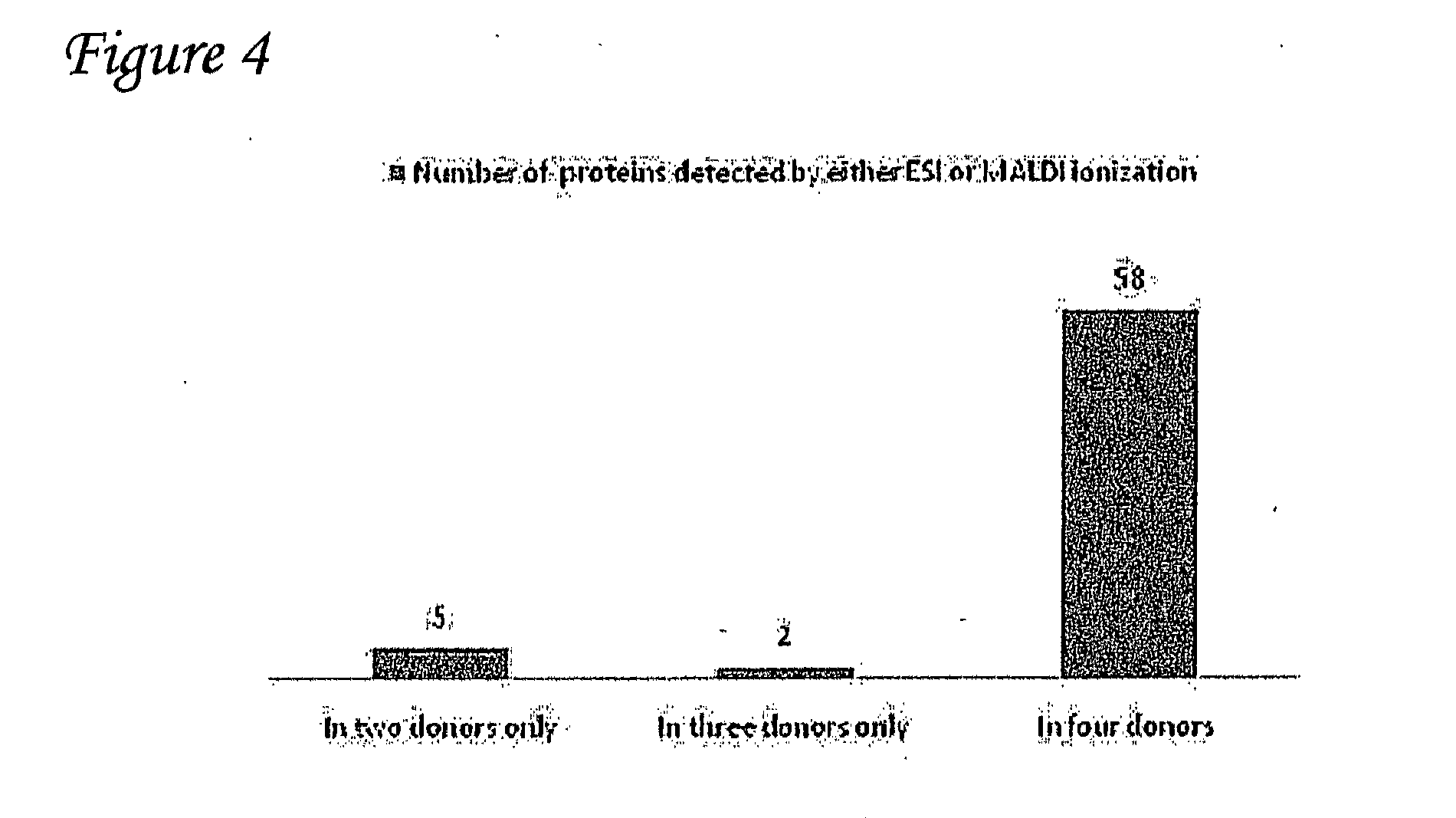
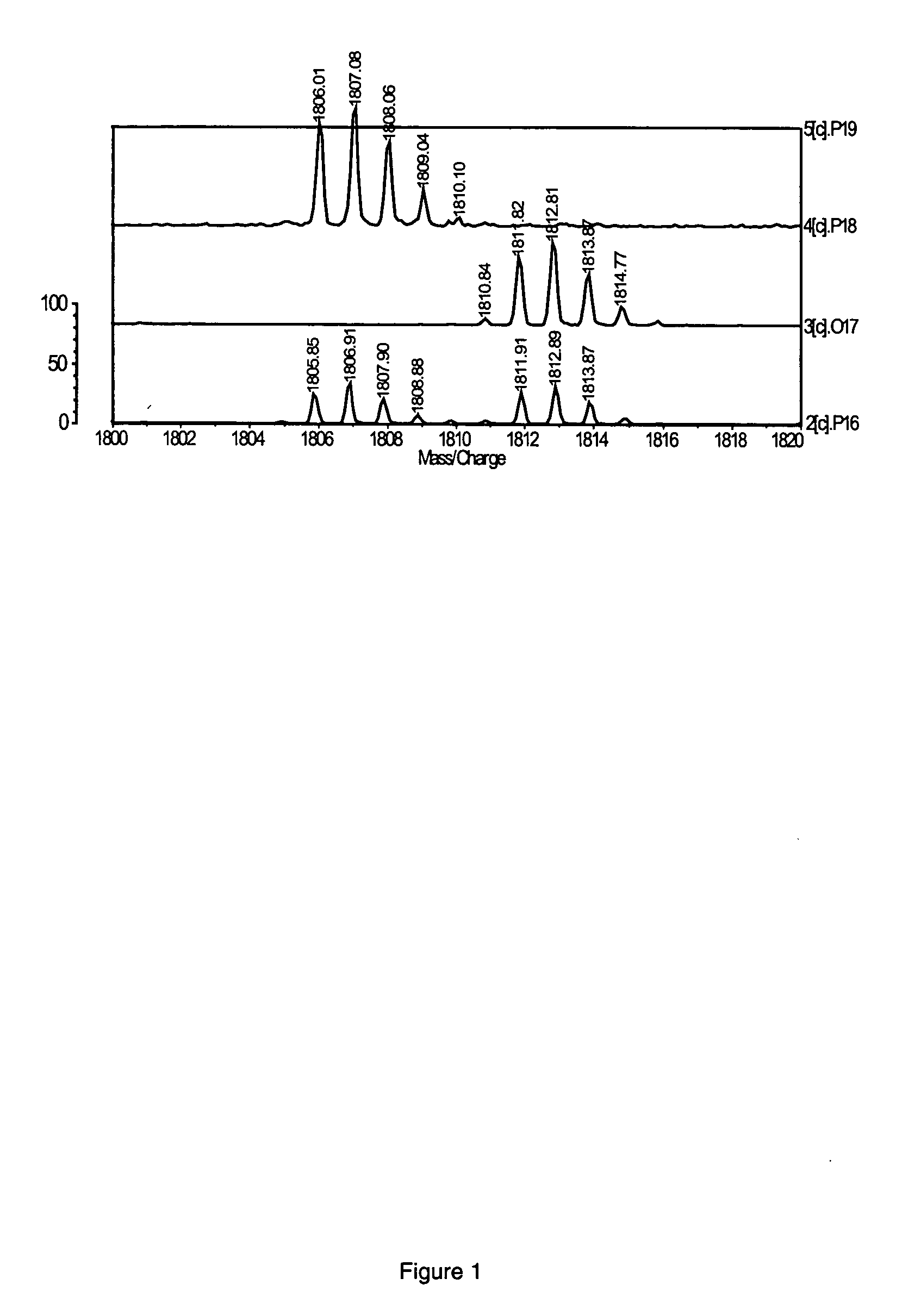
Detection of oxidized polypeptides
ActiveUS20120309040A1Improve the level ofModify susceptibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsStable Isotope LabelingAntioxidant
A diagnostic method for determining the absence or presence of a disease is provided. The method generally includes assaying the amount and / or types of oxidized peptides in a sample from a subject, and comparing these to the amount and types of reference oxidized polypeptides. The method may include the use of stable isotope label, affinity selection, to identify and quantify changes in oxidized peptides or oxidized proteins associated with diseases such as type II diabetes mellitus, breast cancer, and Parkinson's disease, to monitor a patient's response to a therapeutic agent (e.g., an antioxidant), and / or to monitor disease recurrence.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Fluorescent isotope tags and their method of use
InactiveUS20060063269A1High sensitivityFlexible multiplexingAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionStable Isotope LabelingMetabolite
The present invention provides novel reactive fluorescent compounds that incorporate stable isotopic (deuterium, 13-carbon, 15-nitrogen, 18-oxygen) substitutions. The invention includes the use of these compounds, in combination with non-isotopically substituted analogs, for the purification, identification and relative quantification of proteins, peptides, saccharides, metabolites, and other biologically important compounds by combining liquid chromatography (LC) and mass spectrometry (MS). Fluorescent labeling of target compounds in this manner provides orders-of-magnitude sensitivity enhancement over traditional stable isotope labels, and also affords the possibility of simultaneous multiplexed analysis due to the multiwavelength nature of different fluorophores.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
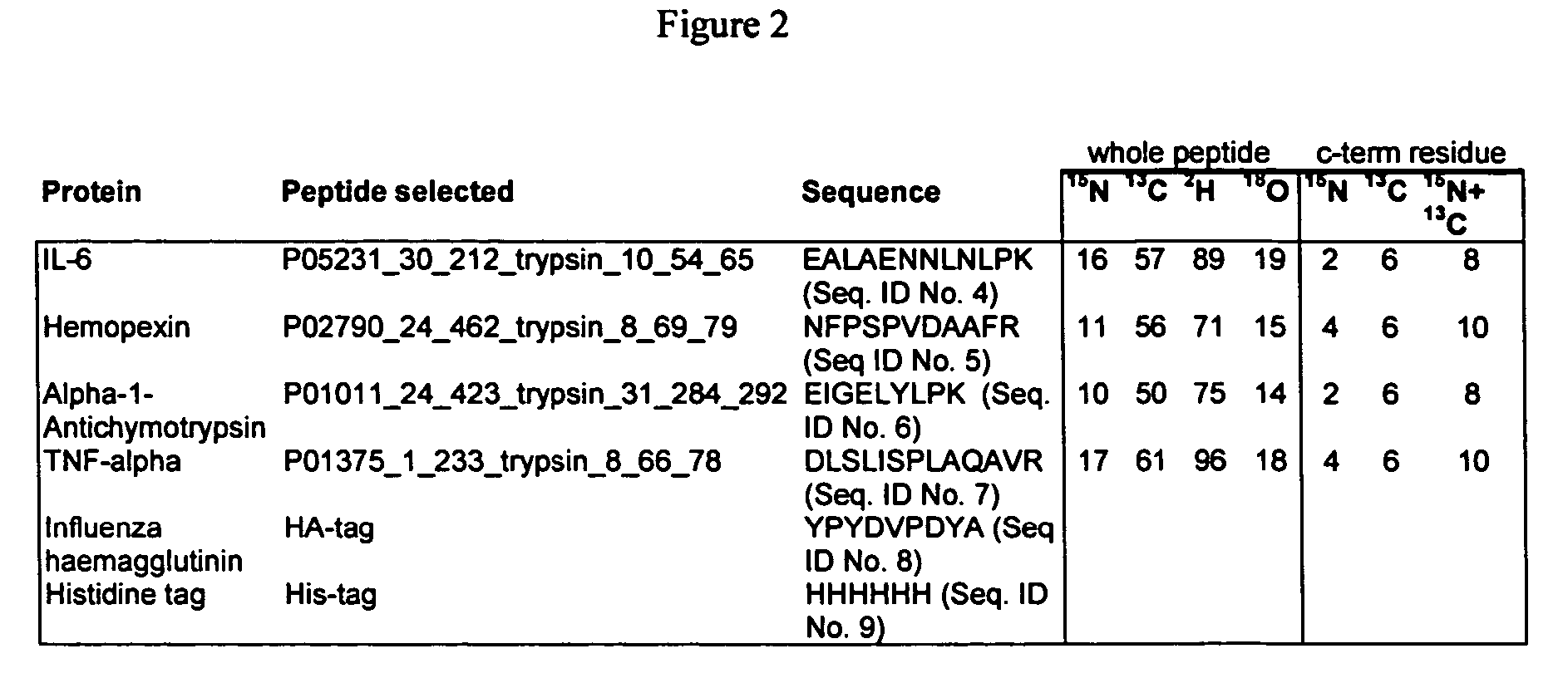
Stable isotope labeled polypeptide standards for protein quantitation
InactiveUS20060154318A1Increase heightDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsStable Isotope LabelingProtein target
This invention relates to proteins having an amino acid sequence containing several amino acid subsequences found in nature and wherein at least two different subsequences act as monitor sequences, said subsequences being part of at least one natural protein which is a target protein, wherein the end of each of said two different subsequences have a cleavage site that will be cleaved by the same site-specific proteolytic treatment to release said subsequences.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Polypeptide analyses using stable isotope labeling
InactiveUS7052916B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationComponent separationStable Isotope LabelingProtein level
Methods for incorporating a stable isotope into a protein or peptide fragment are disclosed. The methods include providing isolated isotope-labeled protein or peptide fragments and analyzing the isolated labeld fragments. In another aspect of the invention, methods for quantitatively comparing peptides in two protein or peptide fragment mixtures are provided. In these methods, protein levels are measured using stable-isotope coded protein or peptide fragments.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
Detection of glycopeptides and glycoproteins for medical diagnostics
ActiveUS20090053828A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStable Isotope LabelingMalignant lymphoma
A diagnostic method for determining the absence or presence of a disease is provided. The method includes assaying the amount and / or types of glycopeptides in a sample from a subject, and comparing these to the amount and types of reference glycopeptides. The method may include the use of a stable isotope label, affinity selection, immunoaffinity chromatography, and glycoproteomics techniques, to identify and quantify changes in glycosylated peptides or glycosylated proteins associated with cancers such as malignant lymphoma or breast cancer, to monitor patient's response to therapy, and to monitor disease recurrence.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Stable isotope labeled polypeptide standards for protein quantitation
InactiveUS20100311097A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementStable Isotope LabelingProtein target
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Synthesis method of stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist type compound
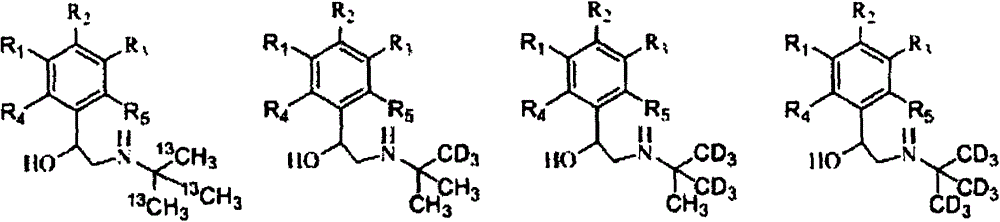
ActiveCN104478740AEasy to synthesizeSimple process routeCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationStable Isotope LabelingTert-Butylamine
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist type compound. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: (1) by taking stable isotope-labeled methanol as a raw material, reacting with acetone or stable isotope-labeled acetone, and ammonifying to obtain stable isotope-labeled tert-butylamine; and (2) by taking a bromoketone type compound as a precursor of the beta receptor agonist type compound, reacting with stable isotope-labeled tert-butylamine to prepare the stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist type compound. Compared with the prior art, the method for preparing the stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist, provided by the invention, is simple, safe and reliable, the chemical purity of the product after separation and purification is above 99.0%, the isotopic abundance is above 98.0% atom, and the product can fully meet the requirements of residual detection in the field of food safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
Method of analysis of amine by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20070010026A1Quick and efficient synthesisHigh throughput analysisParticle separator tubesBiological testingStable Isotope LabelingIsotopic labeling
Method of identification and quantitative analysis of primary and / or secondary amine(s) in a sample by mass spectrometry using stable isotope labeled internal standard is provided. Said internal standard is prepared by reaction of an authentic sample of said amine with a stable isotope labeled reagent, and is added to a sample containing said amine. Said amine in said sample is then quantitatively converted to a chemical compound of identical structure, except the stable isotope atoms, as that of said internal standard using a non-labeled reagent. Said sample is then extracted and the extract is analyzed by mass spectrometry. Identification and quantification of said amine are made from a plot of ion ratio of said converted amine to said internal standard versus amine concentration.
Owner:NGUYEN HOA DUC +2
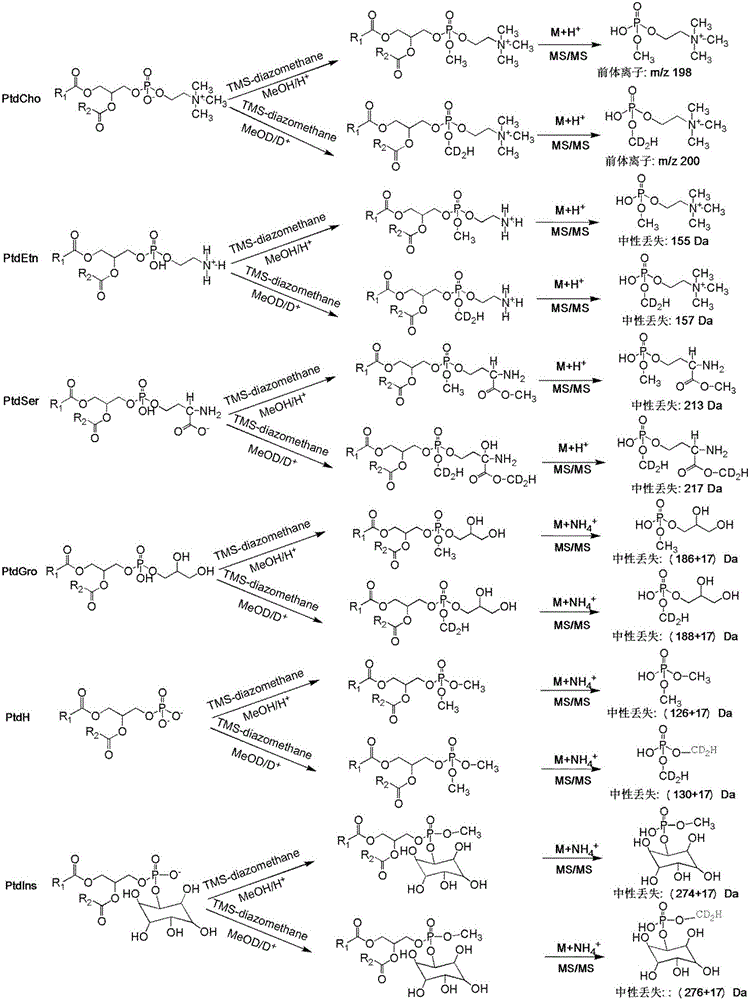
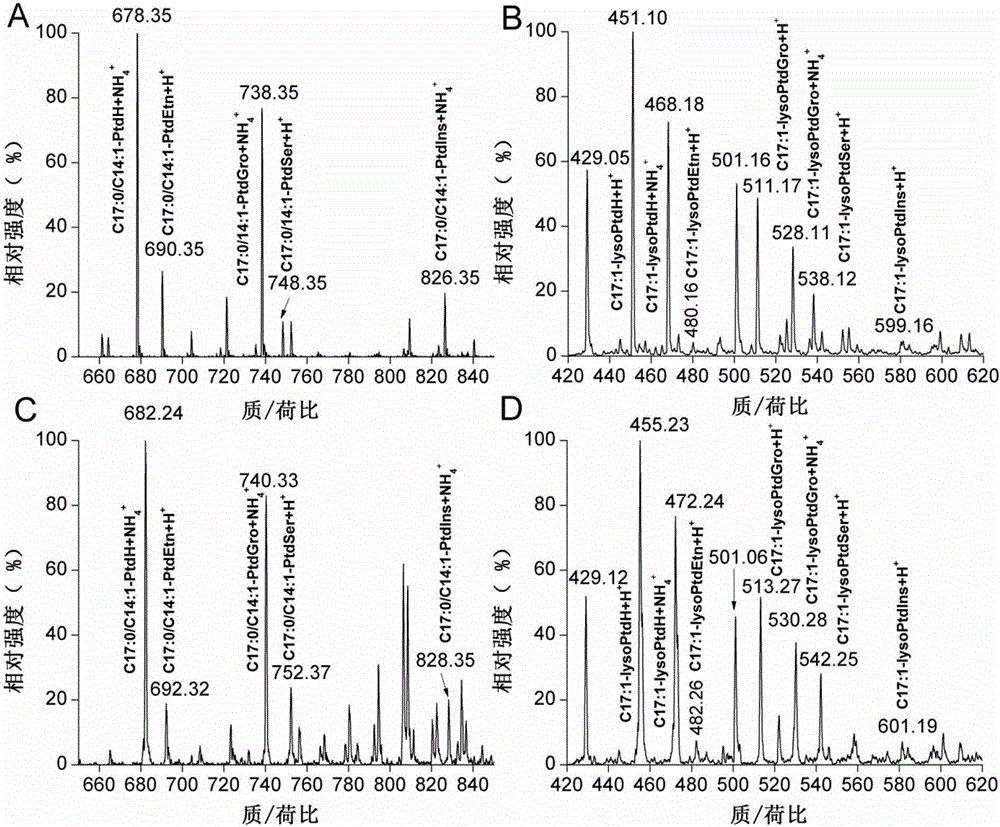
Phospholipid classification detection and quantification method based on stable isotope labeling
ActiveCN105067697AHigh sensitivityComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansStable Isotope LabelingPhosphoric acid
The present invention discloses a phospholipid classification detection and quantification method based on stable isotope labeling, and belongs to the technical field of phospholipid quantification detection methods. According to the method, mainly trimethylsilyl diazomethane is used to respectively generate diazomethane and deuterium-labeled diazomethane in a methyl tert-butyl ether / methanol / 1N hydrochloric acid solution system and a methyl tert-butyl ether / deuteromethanol / 1N deuterium chloride solution system in an in-situ manner so as to further respectively carry out methyl esterification on the phosphoric acid group or carboxylic acid group in the phospholipid molecule to generate the light isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative and the heavy isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative, wherein the light isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative and the heavy isotope labeled-phospholipid methyl esterification derivative have the same physical and chemical properties and different molecular weights; and the relative intensity of the light isotope labeled-mass spectrum peak signal and the heavy isotope labeled-mass spectrum peak signal are compared to associate with the phospholipid molecule amount in the sample so as to achieve the relative quantification on the phospholipid. The method of the present invention has characteristics of enhanced sensitivity and completion within a shor time.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
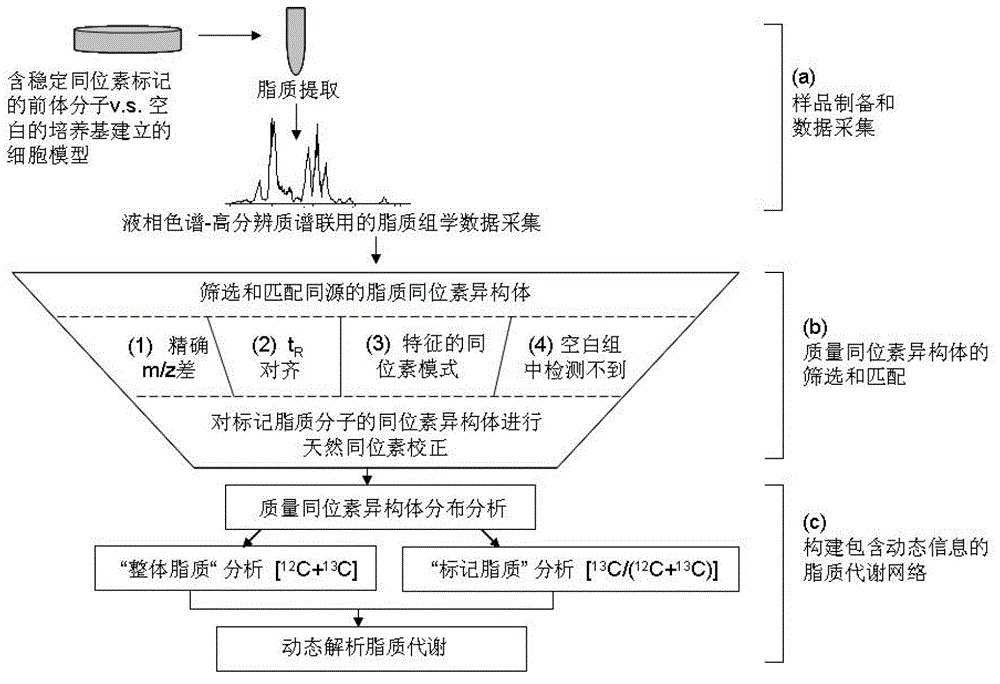
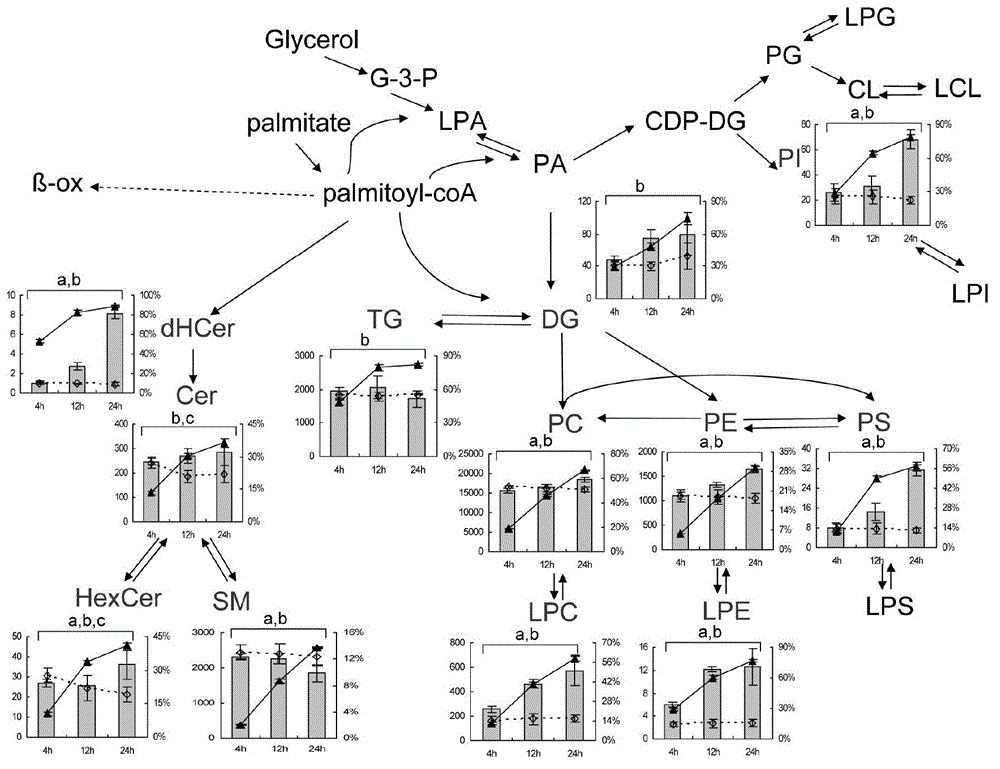
Network dynamic researching method for lipid metabolism
ActiveCN104063570AWide coverageHigh molecular specificitySpecial data processing applicationsLipidomeStable Isotope Labeling
The invention discloses a network dynamic searching method for lipid metabolism. The method is based on stable isotope labeling assisted lipidomics and combined with non-target isotope isomer screening. The network dynamic searching method is characterized in that stable isotope labeling cell, animal or human experiments, high resolution UHPLC-MS lipidomics analysis and the non-target isotope isomer screening are combined; the dynamic metabolism processes, such as synthesis, conversion and decomposition of lipid molecules in the lipid metabolism fingerprint acquisition can be captured while the lipid metabolism fingerprint in a static state is acquired. The network dynamic searching method for the lipid metabolism has high molecule specificity and extensive network coverage capability; the method is repeatable, steady and reliable. The method develops a new idea for deeply searching lipid metabolism and aims to gain more profound and comprehensive understanding in pathological process, physiological process and metabolism perturbation in the biosystem.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of analysis of aldehyde and ketone by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7309608B2Quick and efficient synthesisHigh throughput analysisSamplingLiquid carbonaceous fuelsStable Isotope LabelingHydrazone
A method of identification and quantitative analysis of aldehydes and / or ketones in a sample by mass spectrometry using stable isotope labeled oxime internal standards or stable isotope labeled hydrazone internal standards is provided. Stable isotope labeled oxime internal standards are synthesized by reaction of an authentic sample of aldehydes and / or ketones with a stable isotope labeled alkoxylamine reagent while stable isotope labeled hydrazone internal standards are synthesized by reaction of an authentic sample of aldehydes and / or ketones with a stable isotope labeled alkylhydrazine reagent. A non labeled version of the stable isotope labeled reagent is used to convert aldehydes and / or ketones in the sample to the non labeled version of the stable isotope labeled oxime or hydrazone internal standards.
Owner:NGUYEN HOA DUC +2
Peptide for use in simultaneous protein quantification of metabolizing enzymes using mass spectrometric analysis apparatus
InactiveUS20110177491A1Achieved conveniently and rapidlyImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesStable Isotope LabelingIsotope
There are provided a peptide consisting of an amino acid sequence for simultaneously quantifying absolute amounts of metabolizing enzyme proteins in a biological sample at high sensitivity and a method for using the same. A peptide which can be detected at high sensitivity with a mass spectrometer that enables highly sensitive simultaneous quantification of metabolizing enzymes, intracellular proteins, is selected, and the amino acid sequence thereof is identified. Using a stable-isotope-labeled peptide having the same amino acid sequence as the amino acid sequence of this peptide to be quantified, a mass spectrometry by LC-MS / MS is performed at predetermined concentration levels of the stable-isotope-labeled peptide to create a calibration curve. The stable-isotope-labeled peptide is added to a peptide fragment obtained by fragmenting metabolizing enzyme proteins to be quantified in a sample with trypsin, amass spectrometry by LC-MS / MS is performed to calculate amass spectrum area ratio of the metabolizing enzyme protein peptides to be quantified and the stable-isotope-labeled peptide, and a quantitative value is obtained from the area ratio using the calibration curve.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Fluorescent isotope tags and their method of use
InactiveUS20090017546A1High sensitivityFlexible multiplexingOrganic chemistryBiological testingStable Isotope LabelingMetabolite
The present invention provides novel reactive fluorescent compounds that incorporate stable isotopic (deuterium, 13-carbon, 15-nitrogen, 18-oxygen) substitutions. The invention includes the use of these compounds, in combination with non-isotopically substituted analogs, for the purification, identification and relative quantification of proteins, peptides, saccharides, metabolites, and other biologically important compounds by combining liquid chromatography (LC) and mass spectrometry (MS). Fluorescent labeling of target compounds in this manner provides orders-of-magnitude sensitivity enhancement over traditional stable isotope labels, and also affords the possibility of simultaneous multiplexed analysis due to the multiwavelength nature of different fluorophores.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
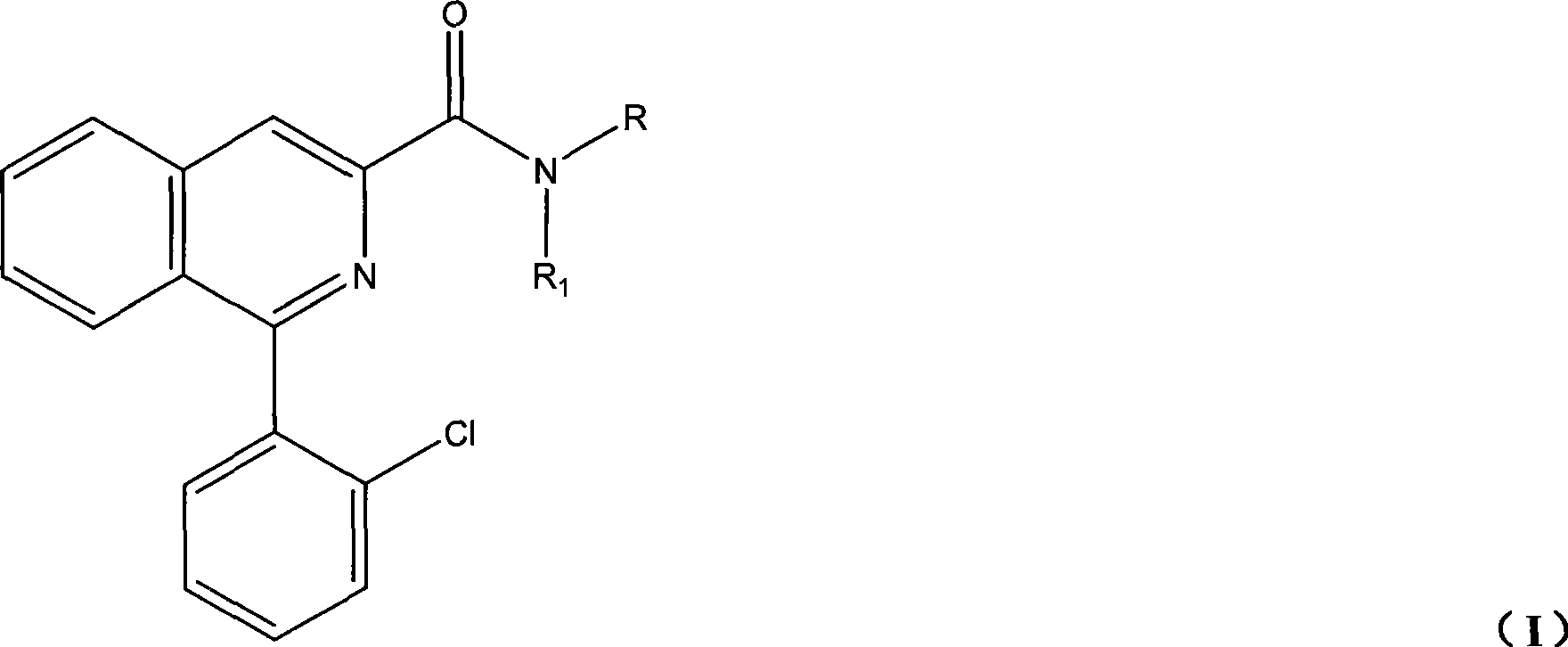
Synthesis of PET imaging agent prosome isoquinoline methanamide derivant
InactiveCN101429161AReduce pollutionSimple processOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersStable Isotope LabelingBenzaldehyde
The invention discloses a synthetic method for an isoquinoline formamide derivative of PET developer precursor, and belongs to the field of synthesis of stable isotope labeled precursor. The method is as follows: a) glycin and o-chlorobenzoyl chloride with proper molar ratio are subjected to acylation reaction under alkaline environment to obtain 2-chloro hippuric acid; b) the 2-chloro hippuric acid obtained in step a) and benzaldehyde are subjected to cyclization reaction under appropriate temperature, and proper amount of catalyst is added into the mixture for molecule rearrangement to obtain 1-(2-chlorpheyl)isoquinoline-3-methanoic acid; and c) the 1-(2-chlorpheyl) isoquinoline-3-methanoic acid reacts with halogeno reagent and then is ammonolyzed to obtain a compound as general formula (I). The synthetic method has the advantages that the synthetic method shortens synthetic route, reduces synthetic cost, is simple, convenient and practical, and has higher yield.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
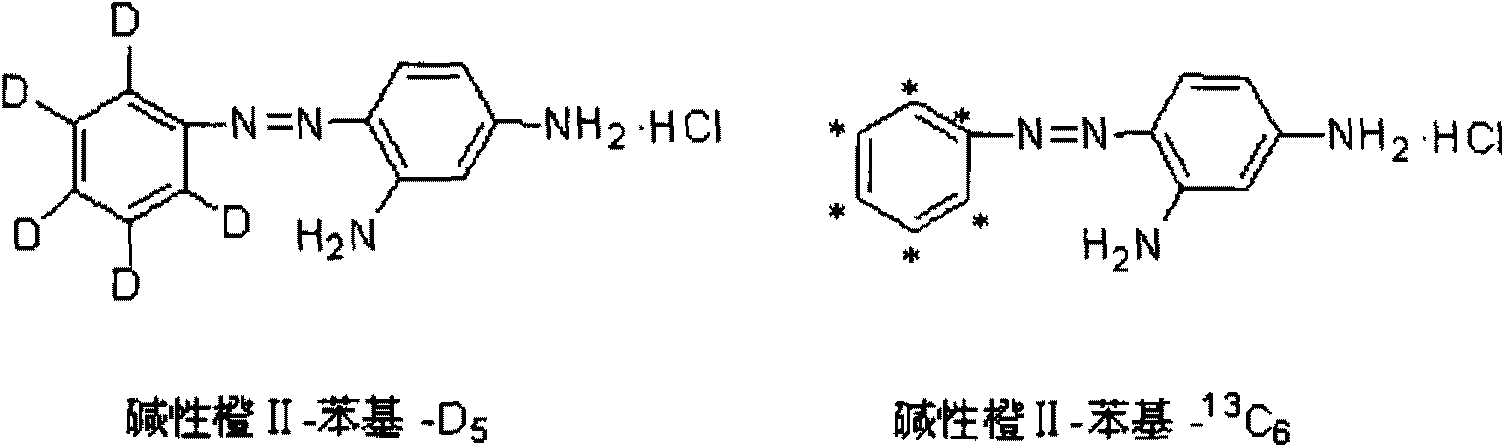
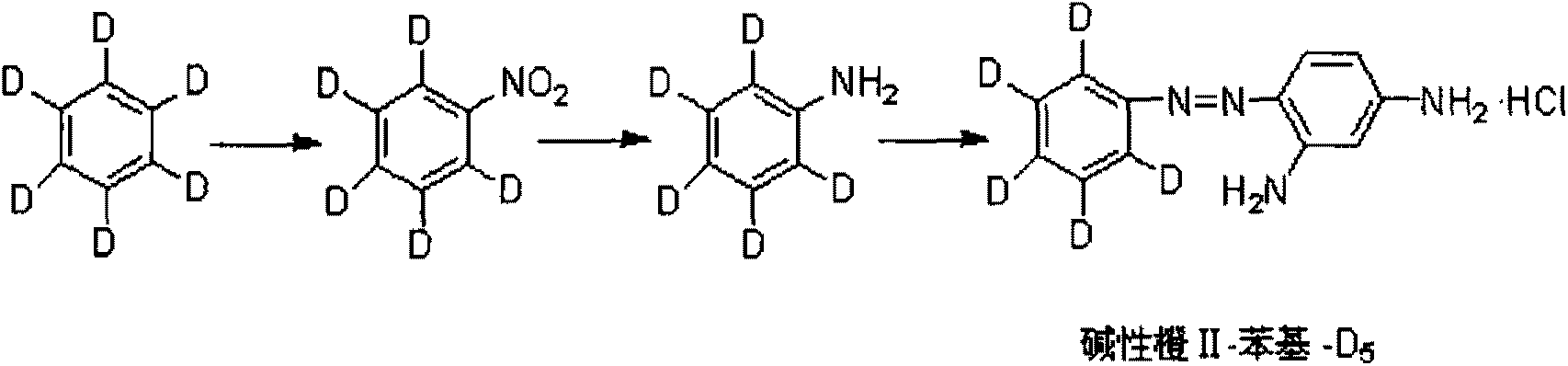
Synthetic method for stable isotope labeling basic orange II
ActiveCN103254096AReduce manufacturing costConform to the detection reagent requirementsOrganic chemistryStable Isotope LabelingBenzene
The invention relates to a synthetic method for a stable isotope labeling basic orange II. The synthetic method comprises the steps of: carrying out nitration reaction by taking stable isotope labeling benzene as a raw material to generate stable isotope labeling nitrobenzene; then, subjecting the stable isotope labeling nitrobenzene and a reducing agent to reaction to obtain stable isotope labeling phenylamine; and finally, carrying out diazotization and m-phenylenediamine coupling transposition to obtain the stable isotope labeling basic orange II. After being separated and purified, the stable isotope labeling basic orange II prepared by the invention has the chemical purity of over 98% and the isotope abundance of over 98% and can sufficiently meet the requirement for detecting prohibited dyes in the field of food safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
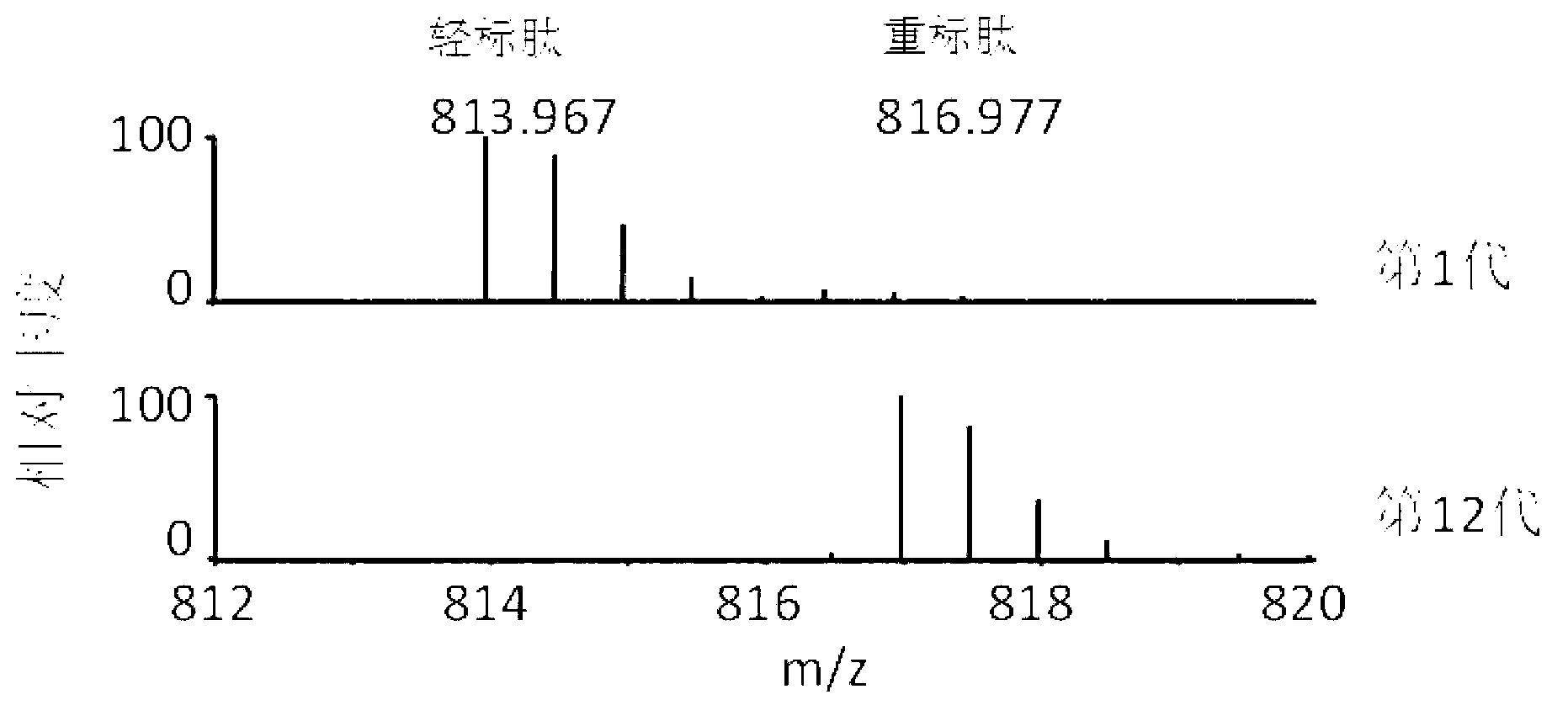
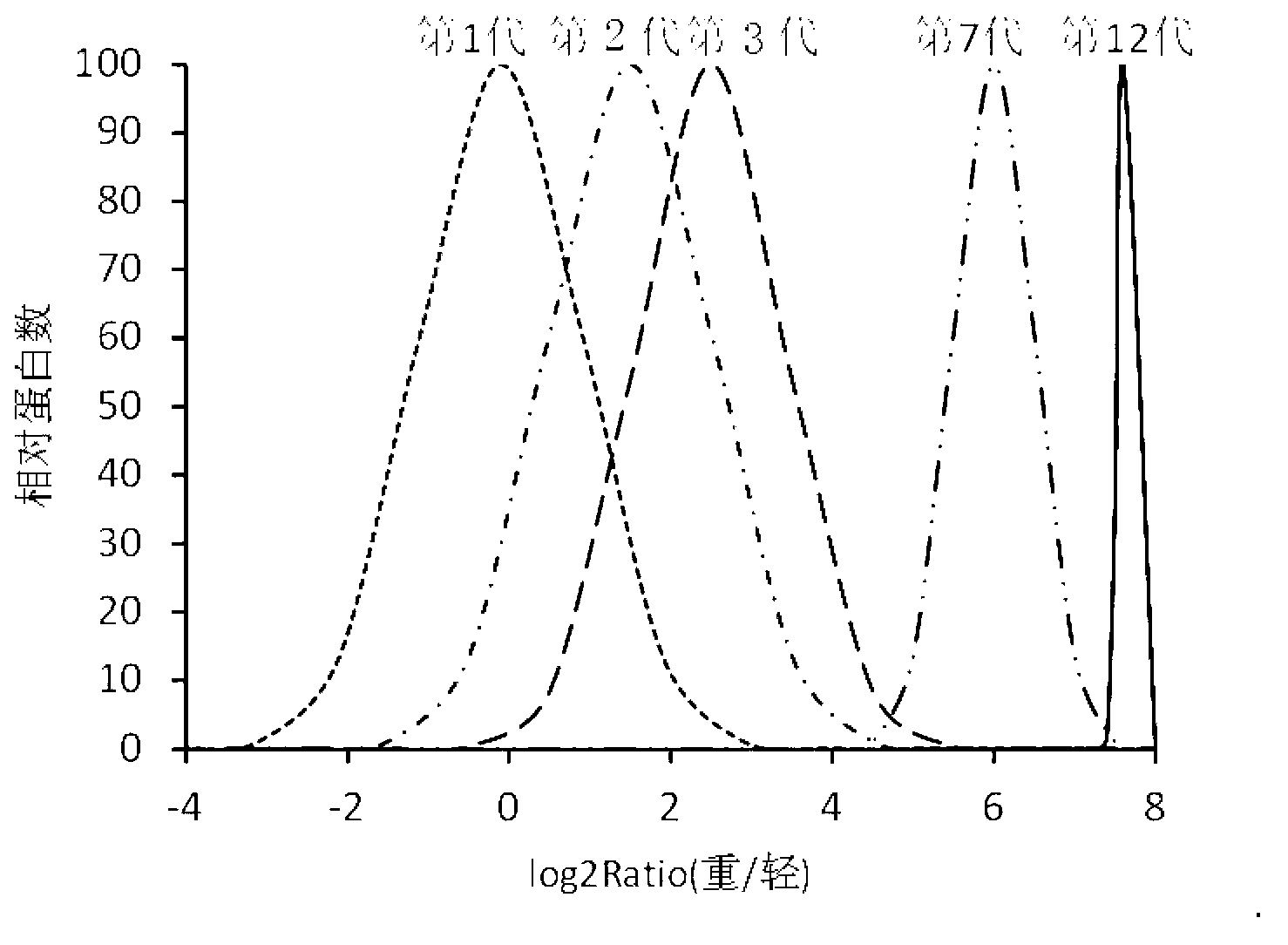
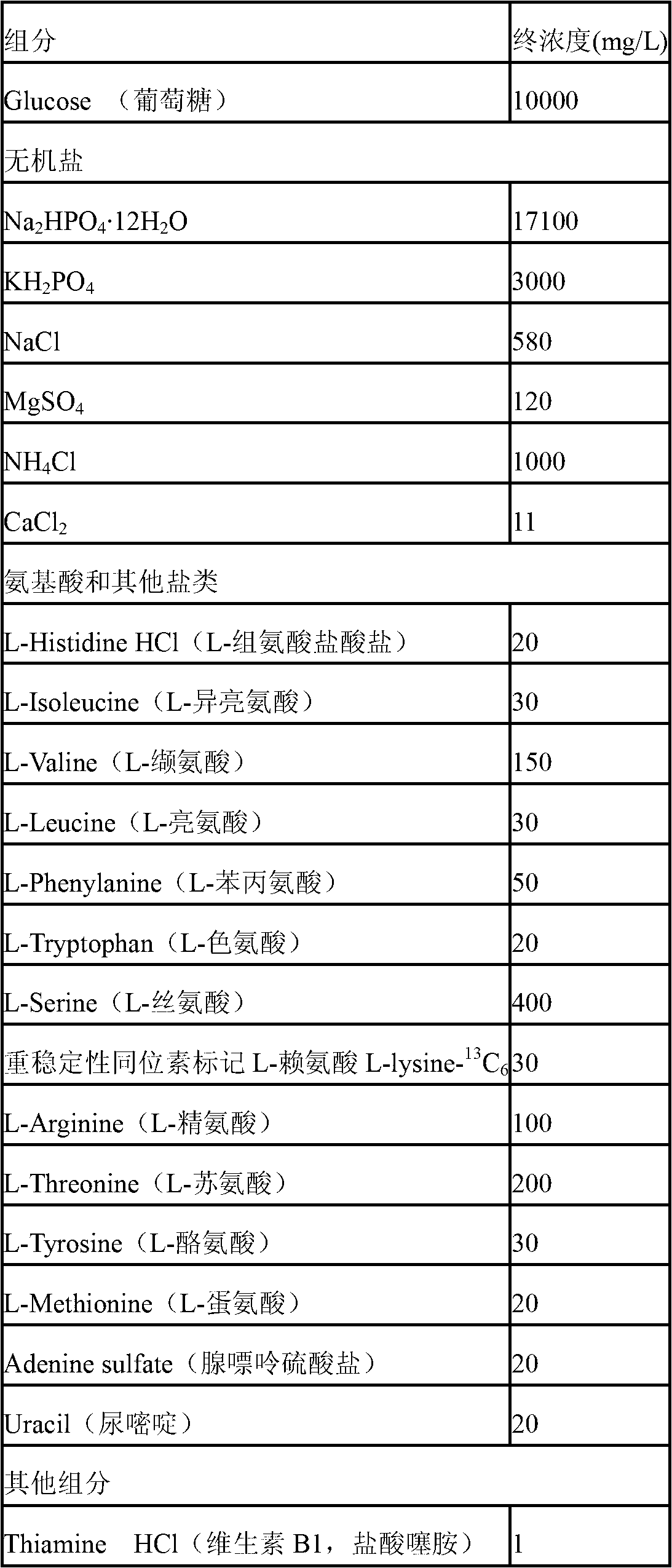
Method for labeling escherichia coli proteome by using SILAC (Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Cultures) and special culture medium
ActiveCN102796682ASave cumbersome stepsOmit conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliStable Isotope Labeling
The invention discloses a method for labeling escherichia coli proteome by using SILAC (Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Cultures) and a special culture medium. The invention provides a special culture medium for the SILAC-labeled escherichia coli. The special culture medium comprises inorganic salt, histidine hydrochloride, isoleucine, valine, leucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, serine, heavy stable isotope labeled lysine, arginine, threonine, tyrosine, methionine, adenine sulfate, uracil, vitamin B1 and glucose; and the inorganic salt is Na2HPO4.12H2O, KH2PO4, NaCl, MgSO4, NH4Cl and CaCl2. Experiments prove that, the special culture medium for the SILAC-labeled escherichia coli, disclosed by the invention, creates a condition for researches of labeling the escherichia coli proteome, preparing a quantitative internal label and highly-precisely quantifying the escherichia coli proteome.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Method of analysis of amine by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050014279A1Quick and efficient synthesisParticle separator tubesBiological testingStable Isotope LabelingIsotopic labeling
Method of identification and quantitative analysis of primary and / or secondary amine(s) in a sample by mass spectrometry using stable isotope labeled internal standard is provided. Said internal standard is prepared by reaction of an authentic sample of said amine with a stable isotope labeled reagent, and is added to a sample containing said amine. Said amine in said sample is then quantitatively converted to a chemical compound of identical structure, except the stable isotope atoms, as that of said internal standard using a non-labeled reagent. Said sample is then extracted and the extract is analyzed by mass spectrometry. Identification and quantification of said amine are made from a plot of ion ratio of said converted amine to said internal standard versus amine concentration.
Owner:NGUYEN HOA DUC +2
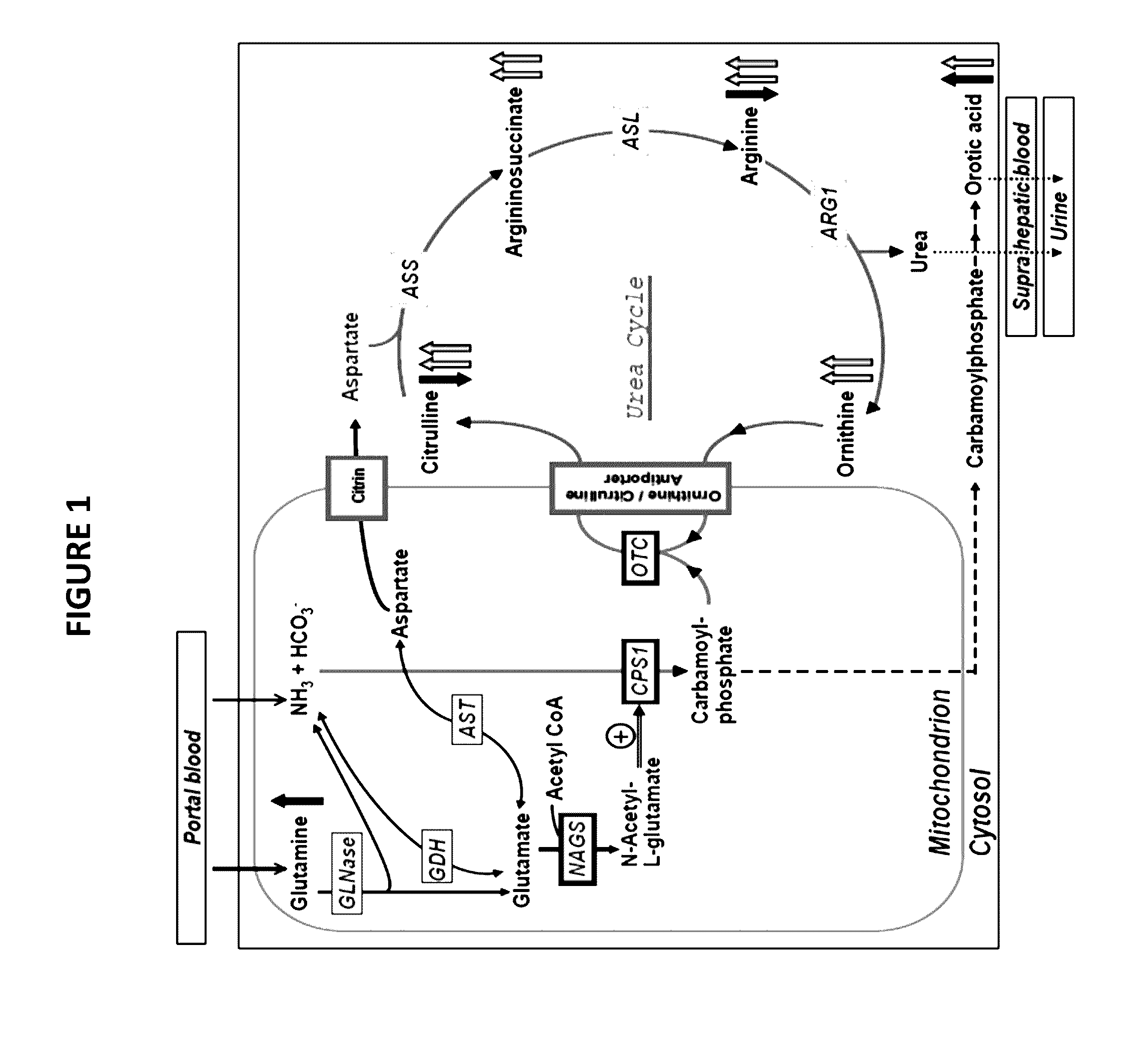
Novel methods and kits for detecting of urea cycle disorders using mass spectrometry
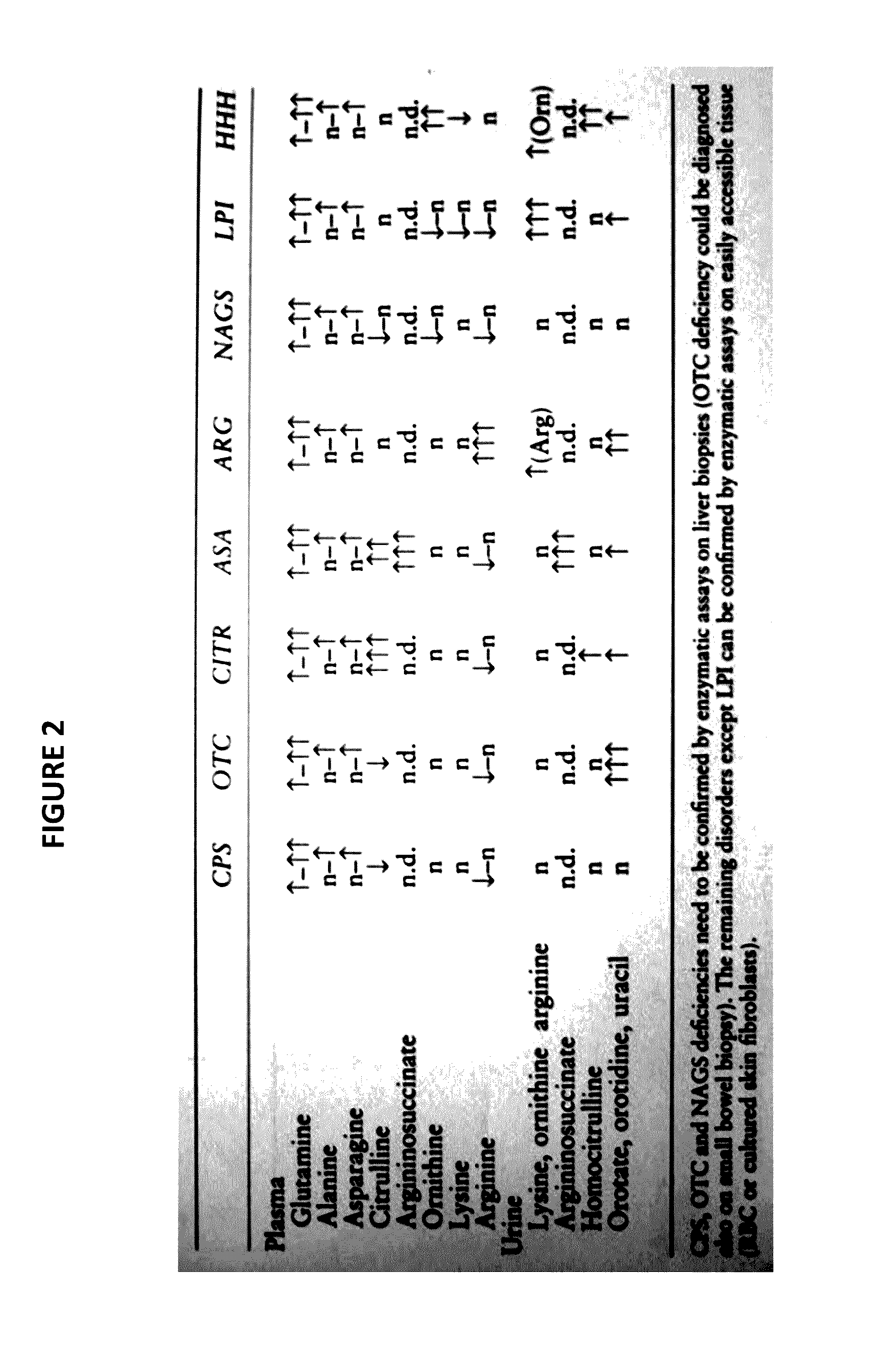
InactiveUS20170059535A1Component separationBiological testingStable Isotope LabelingHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention relates to newborn screening kits, methods, stable isotopically-labeled internal standards or internal standard solution for high throughput screening and analysis of metabolic disorders using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) are provided. The metabolic disorders can be amino acid, organic acid or fatty acid oxidation disorders, and particularly urea cycle disorders or deficiencies, hyperammonemia, Hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria (HHH), and / or argininosuccinic aciduria. The newborn screening kits, methods, stable isotopically-labeled internal standards or internal standard solution are particularly useful for newborn screening (NBS) of metabolic disorders.
Owner:LABSYST DIAGNOSTICS OY
Method for detecting carboxylic acid metabolites in plasma by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry based on stable isotope labeling
InactiveCN108931603AImprove efficiencyHigh sensitivityComponent separationStable Isotope LabelingMetabolite
The invention relates to a method for detecting carboxylic acid metabolites in plasma by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry based on stable isotope labeling. The method overcomes the problemsof low ionization efficiency and insufficient sensitivity in mass spectrometric detection of carboxylic acid metabolites through signal recognition of differentially labeled plasma samples, realizes non-targeted analysis of carboxyl-containing compounds in the samples and can be used for stable relative quantification.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com