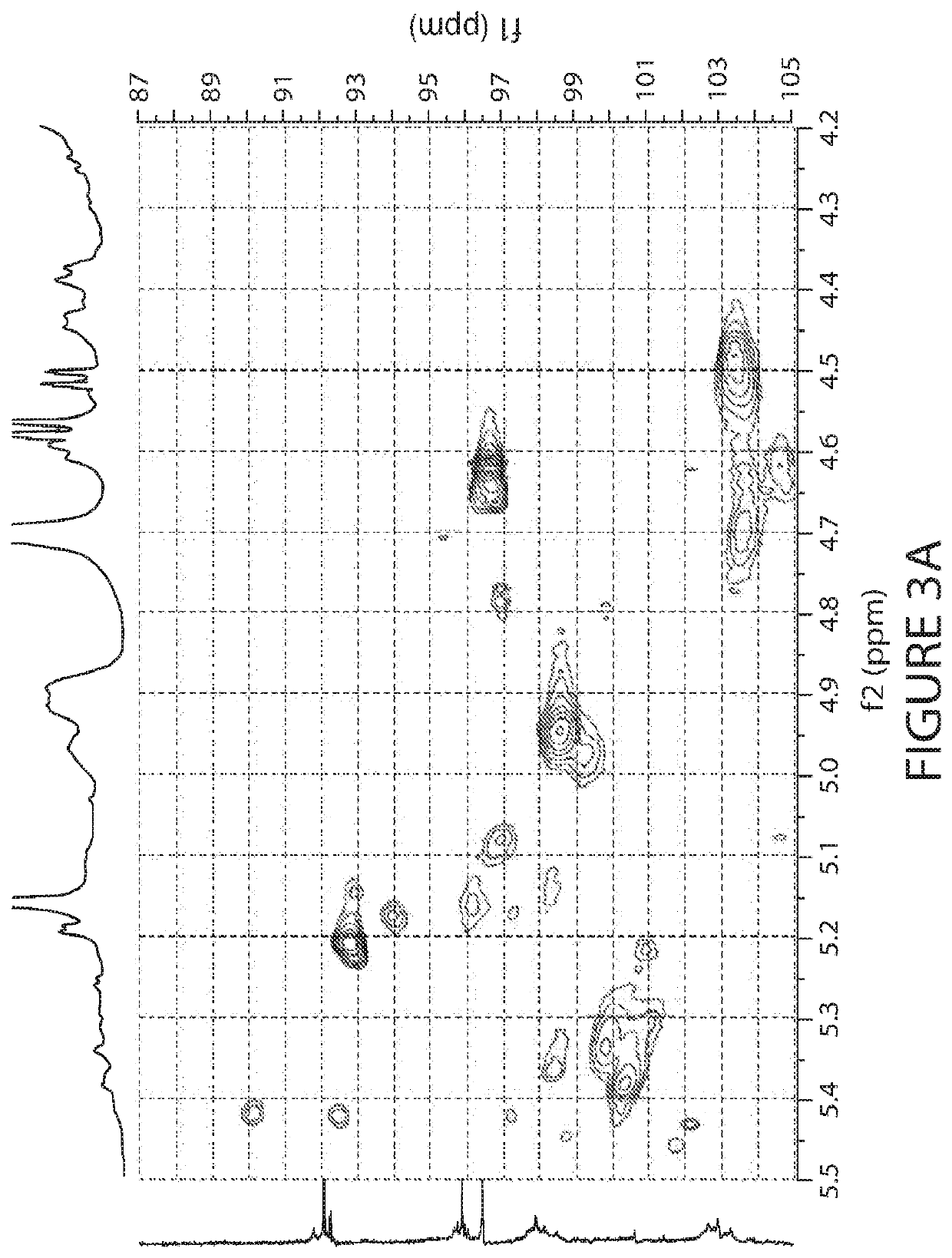
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Hyperammonemia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hyperammonemia is a metabolic disturbance characterised by an excess of ammonia in the blood. It is a dangerous condition that may lead to brain injury and death. It may be primary or secondary. Ammonia is a substance that contains nitrogen. It is a product of the catabolism of protein. It is converted to the less toxic substance urea prior to excretion in urine by the kidneys. The metabolic pathways that synthesize urea involve reactions that start in the mitochondria and then move into the cytosol. The process is known as the urea cycle, which comprises several enzymes acting in sequence.
Novel methods and kits for detecting of urea cycle disorders using mass spectrometry
InactiveCN106483208AComponent separationBiological testingIsotopic labelingHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention relates to newborn screening kits, methods, stable isotopically-labeled internal standards or internal standard solution for high throughput screening and analysis of metabolic disorders using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) are provided. The metabolic disorders can be amino acid, organic acid or fatty acid oxidation disorders, and particularly urea cycle disorders or deficiencies, hyperammonemia, Hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria (HHH), and / or argininosuccinic aciduria. The newborn screening kits, methods, stable isotopically-labeled internal standards or internal standard solution are particularly useful for newborn screening (NBS) of metabolic disorders.
Owner:LABSYST DIAGNOSTICS OY
Compositions useful in treatment of ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency
Viral vectors comprising engineered hOTC DNA and RNA sequences are provided which when delivered to a subject in need thereof are useful for treating hyperammonemia, ornithine transcarbamylase transcarbamylase deficiency and symptoms associated therewith. Also provided are methods of using hOTC for treatment of liver fibrosis cirrhosis in OTCD patients by administering hOTC.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
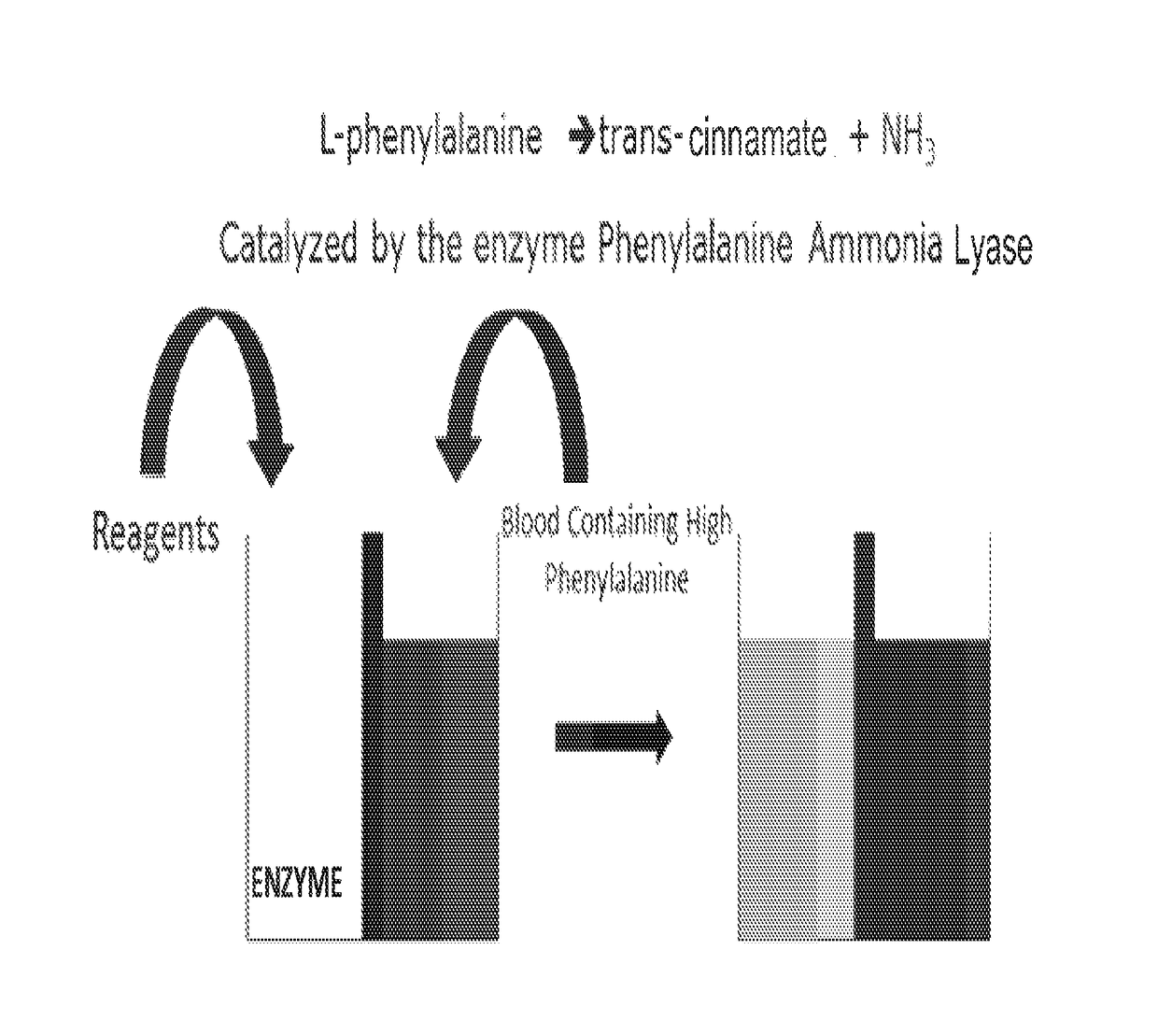
Device And Methods Of Using Device For Detection Of Hyperammonemia
ActiveUS20160231310A1Spectrum investigationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorIonomerHyperammonemia
The present disclosure relates to a bio-sensor capable of measuring the total concentration of one or a plurality of ammonia or ammonium ions with the use of indophenol reagents in the presence of an ionomer. In some embodiments, the biosensor comprises a perflurinated membrane that comprises an ionomer in contact with an alkaline buffer in a vessel configured to receive a sample, such as whole blood. The disclosure also relates to a method of detecting or quantifying the ammonia or ammonium ion concentration in whole blood in a point of care biosensor without reliance on gas chromatography or any measurement that takes more than about twenty minutes.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +2
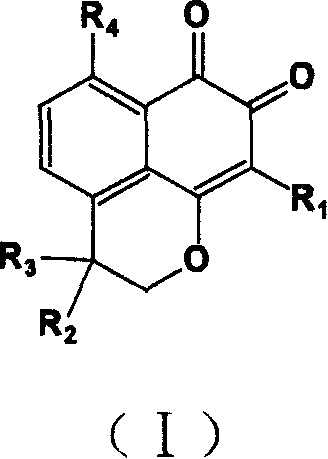
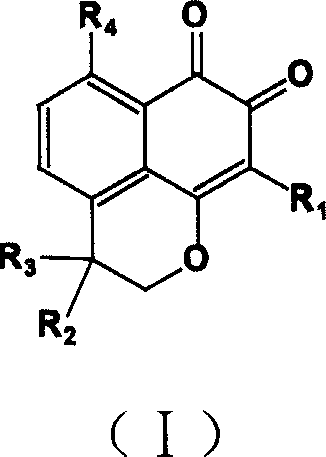
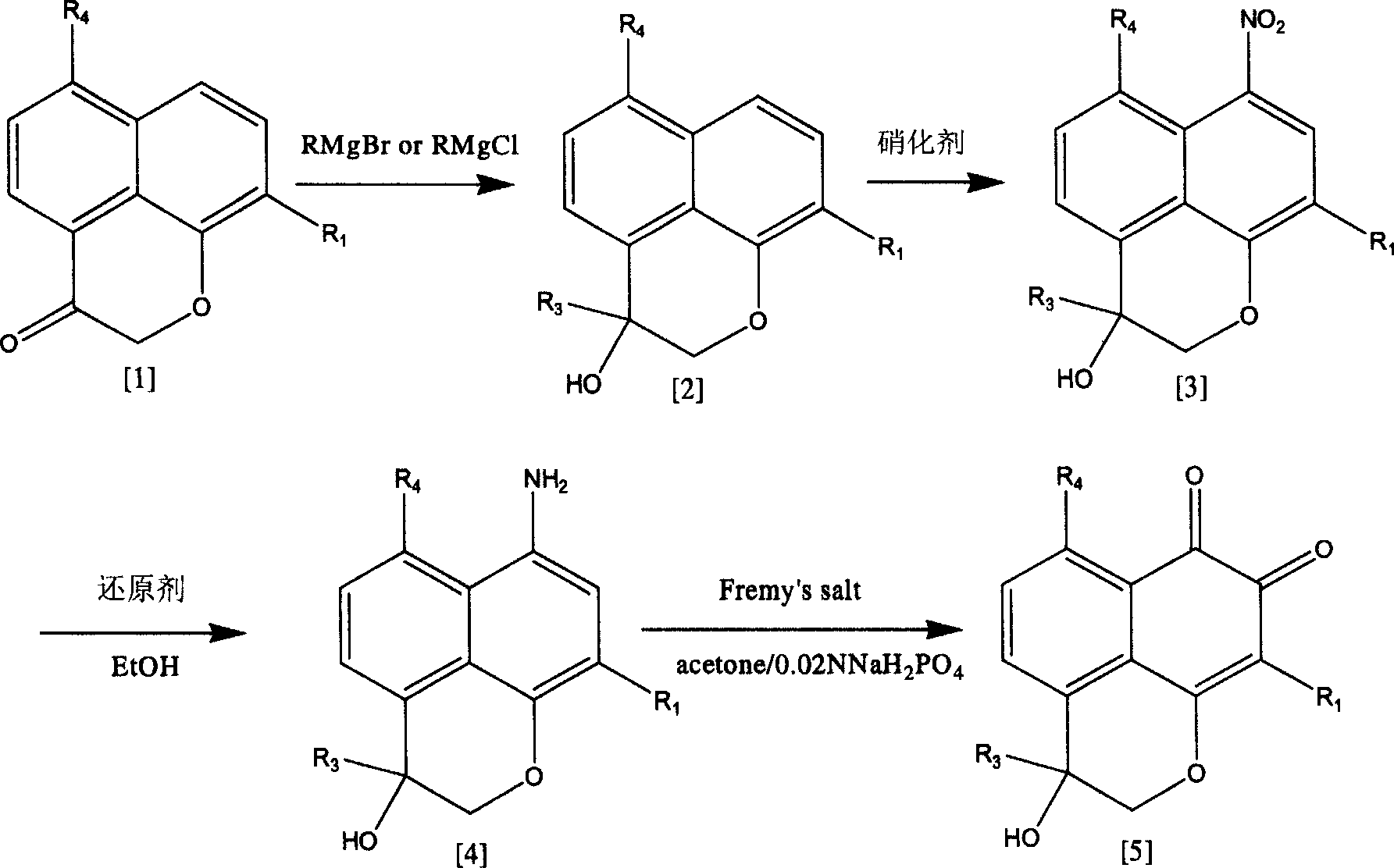
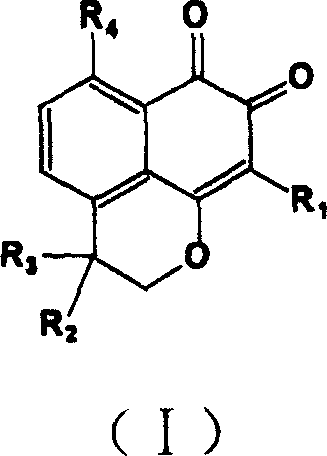
Compound containing structure of o-naphthaquinone and application
InactiveCN1660833AHigh speedImprove convenienceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderQuinoneHyperammonemic encephalopathy
A compound containing o-naphthalene quinone structure for preparing medicines to prevent and treat hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy is prepared from natural Masonate F through structure reformation and optimization.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Pharmaceutical preparation containing arginine glutamic acid
The invention relates to the medicament preparation of arginine glutamic acid and the preparation method and the application thereof. Through long-term experimental study, the personnel of the invention develops the medicament preparation of the arginine glutamic acid, the preparation takes the arginine glutamic acid as raw material medicine, which prepares the preparation with proper medicinal auxiliary material. The operating process of the medicament preparation of the invention is simple, the environmental pollution is small, and the invention is suitable for the production of a great industry. A pharmacological test shows that the medicament preparation of arginine glutamic acid has a very obvious pharmacological function on the aspect of the remedy of the hyperammonemia caused by acute liver disease and chronic liver disease such as hepatocirrhosis, fatty liver and hepatitis.
Owner:BEIJING JIASHILIANBO PHARM SCI & TECH
Compositions and methods comprising a defined microbiome and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10058576B2Minimal urease activityReduce bacteria countPowder deliveryBacteriaHyperammonemic encephalopathyGut microbiome
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Glycan preparations and methods of use for hyperammonemia
PendingUS20220233577A1Reduce riskReduce severityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyDisease
Compositions, e.g., pharmaceutical compositions, nutritional compositions, medical foods, and food ingredients, as well as their methods of use, are provided, for treating diseases associated with hyperammonemia, e.g., urea cycle disorders (UCD) and hepatic encephalopathy (HE), e.g., minimal HE (MHE) and overt HE (OHE), and modulating enzyme activities and levels of microbes and taxa, and metabolites (e.g., ammonia) in the microbiome of a subject.
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD
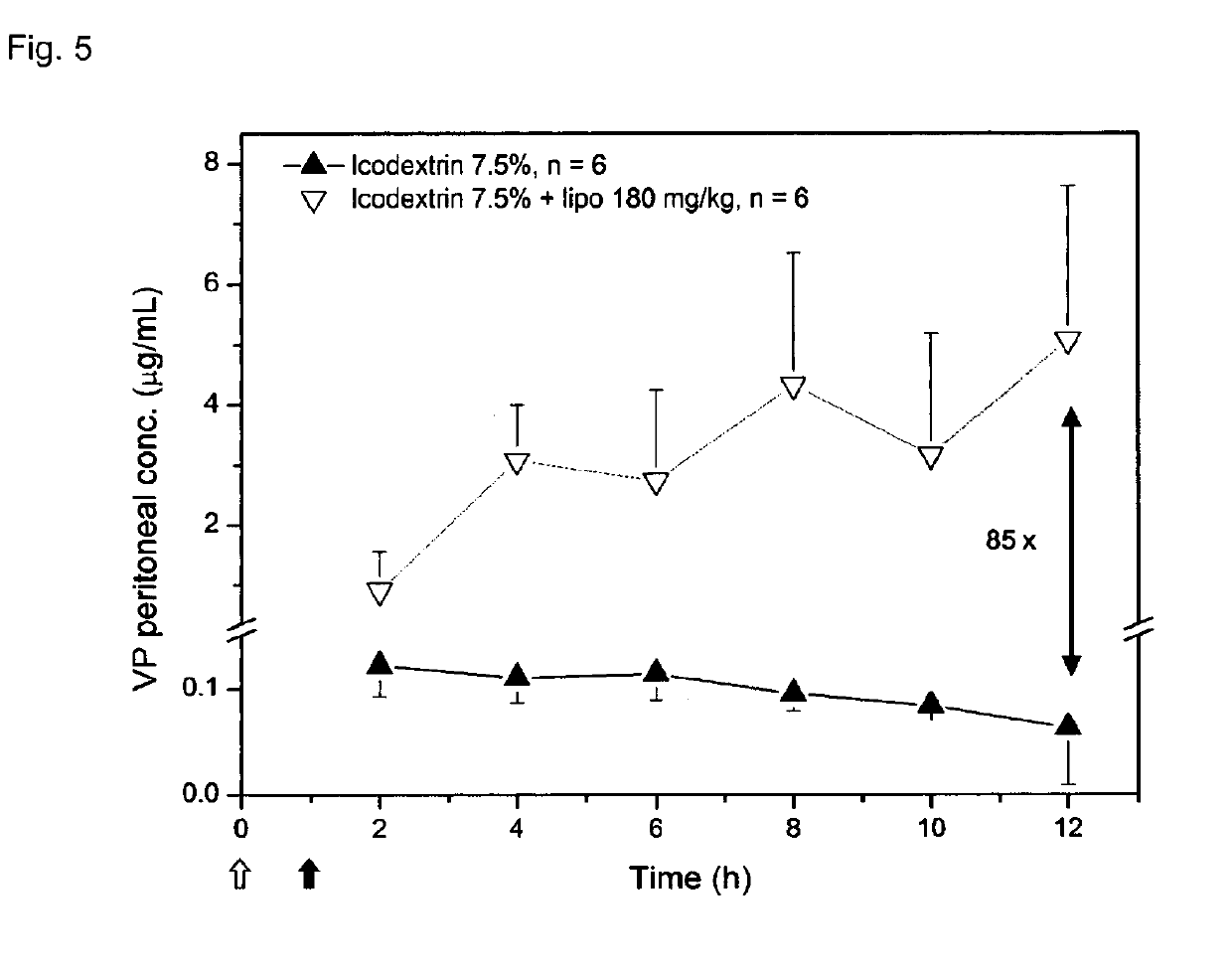
Liposome composition for use in peritoneal dialysis
InactiveUS20190105270A1Metabolism disorderAntinoxious agentsPeritoneal dialysis catheterPeritoneal space
The present invention is directed to a liposome composition for use in the peritoneal dialysis of patients suffering from endogenous or exogenous toxicopathies, wherein the pH within the liposomes differs from the pH in the intraperitoneal cavity and wherein the pH within the liposome results in a liposome-encapsulated charged toxin. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising said liposomes. A further aspect of the present invention relates to a method of treating patients suffering from endogenous or exogenous toxicopathies, preferably selected from drug, metabolite, pesticide, insecticide, toxin, and chemical warfare toxicopathies, more preferably hyperammonemia, comprising the step of administering liposomes of the invention in a therapeutically effective amount into the peritoneal space of a patient in need thereof. Next to human, the present invention is particularly suitable to veterinary aspects.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Amino acid compositions for the treatment of liver disease
PendingCN111295187AImprove the level ofLower levelPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHyperammonemia
Disclosed are compositions comprising branched chain amino acids, urea cycle amino acids and essential amino acids for use in treating or preventing liver diseases and disorders with hyperammonemia ormuscle wasting in a subject.
Owner:AXCELLA HEALTH INC
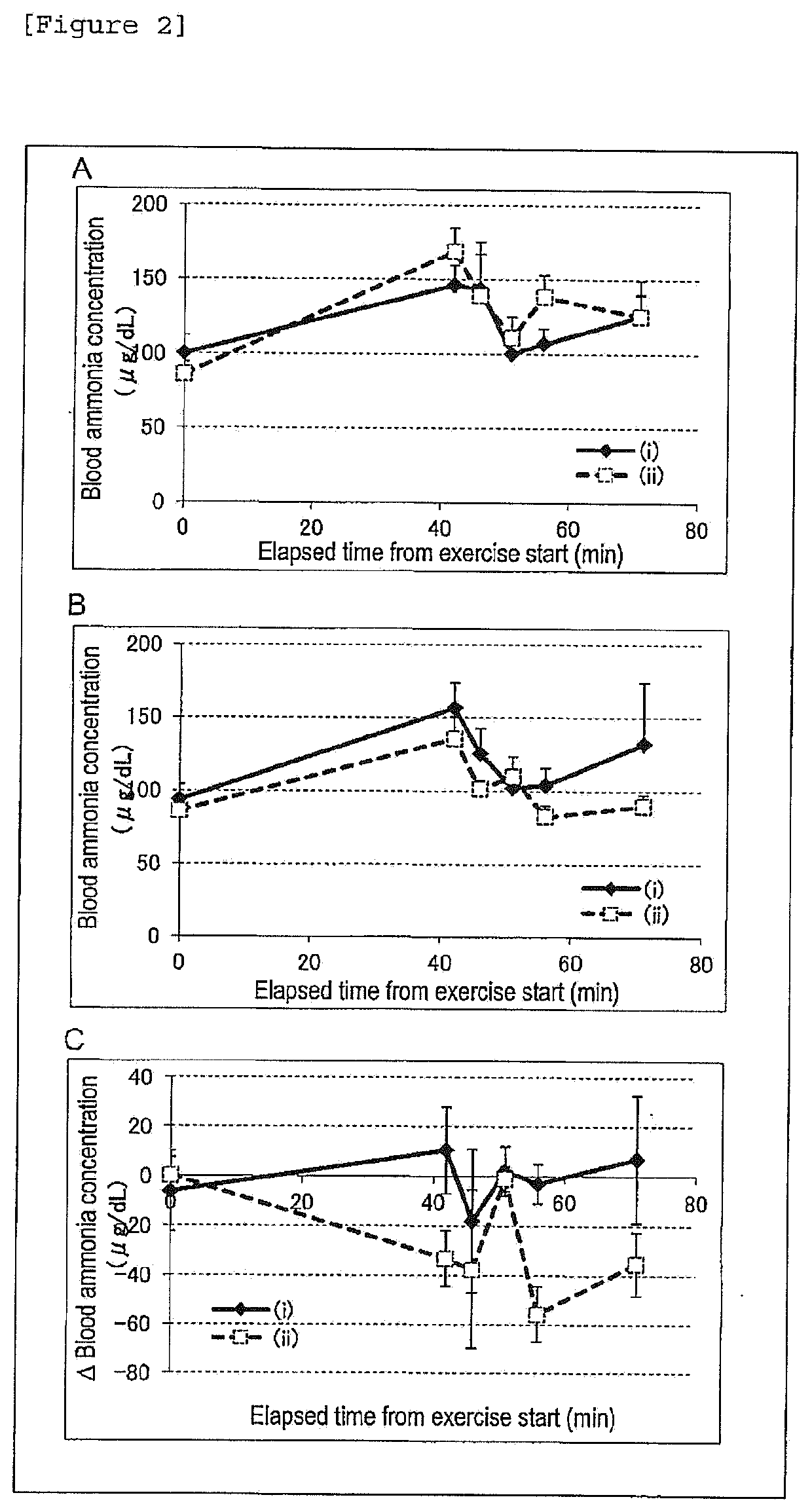
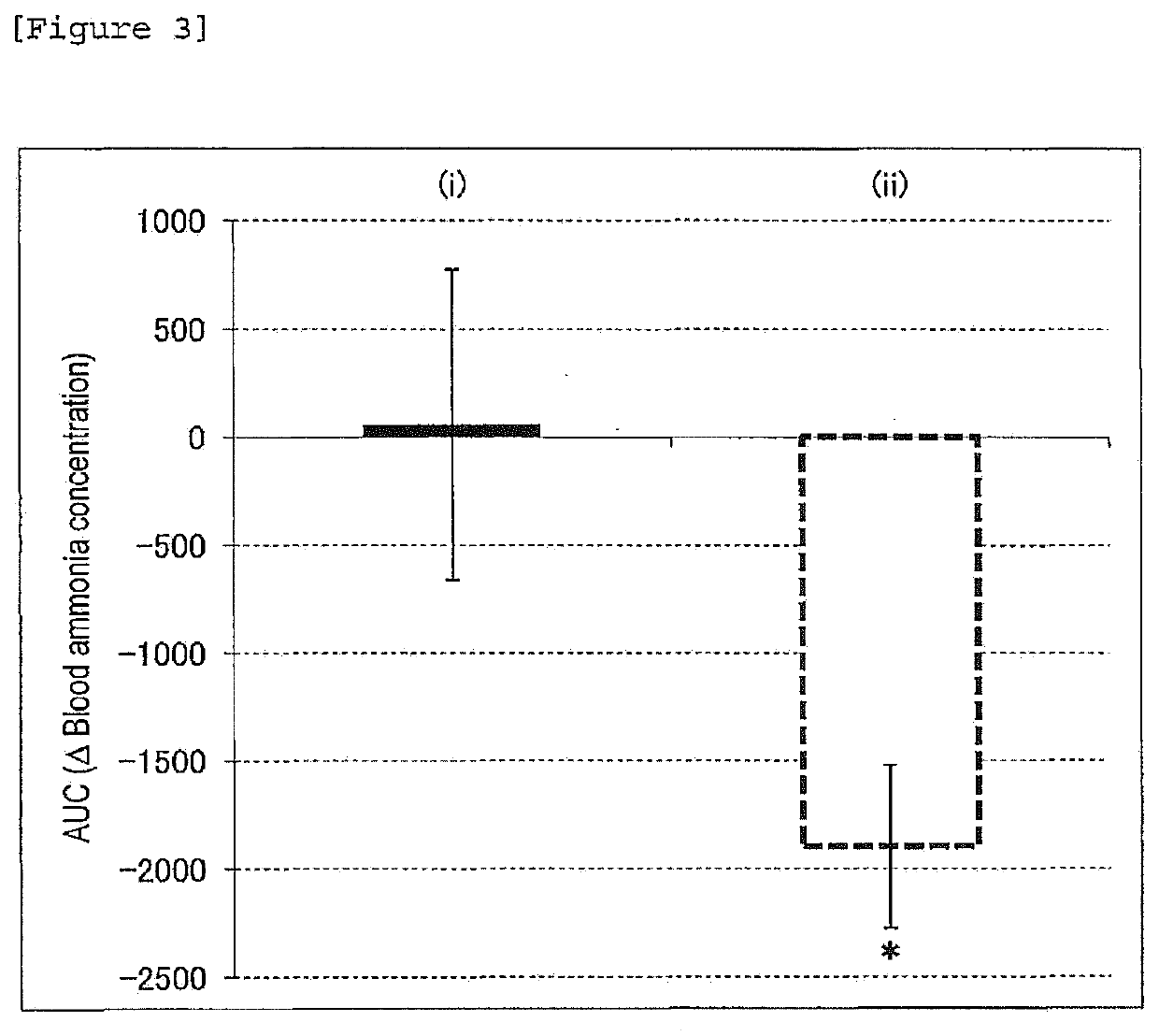
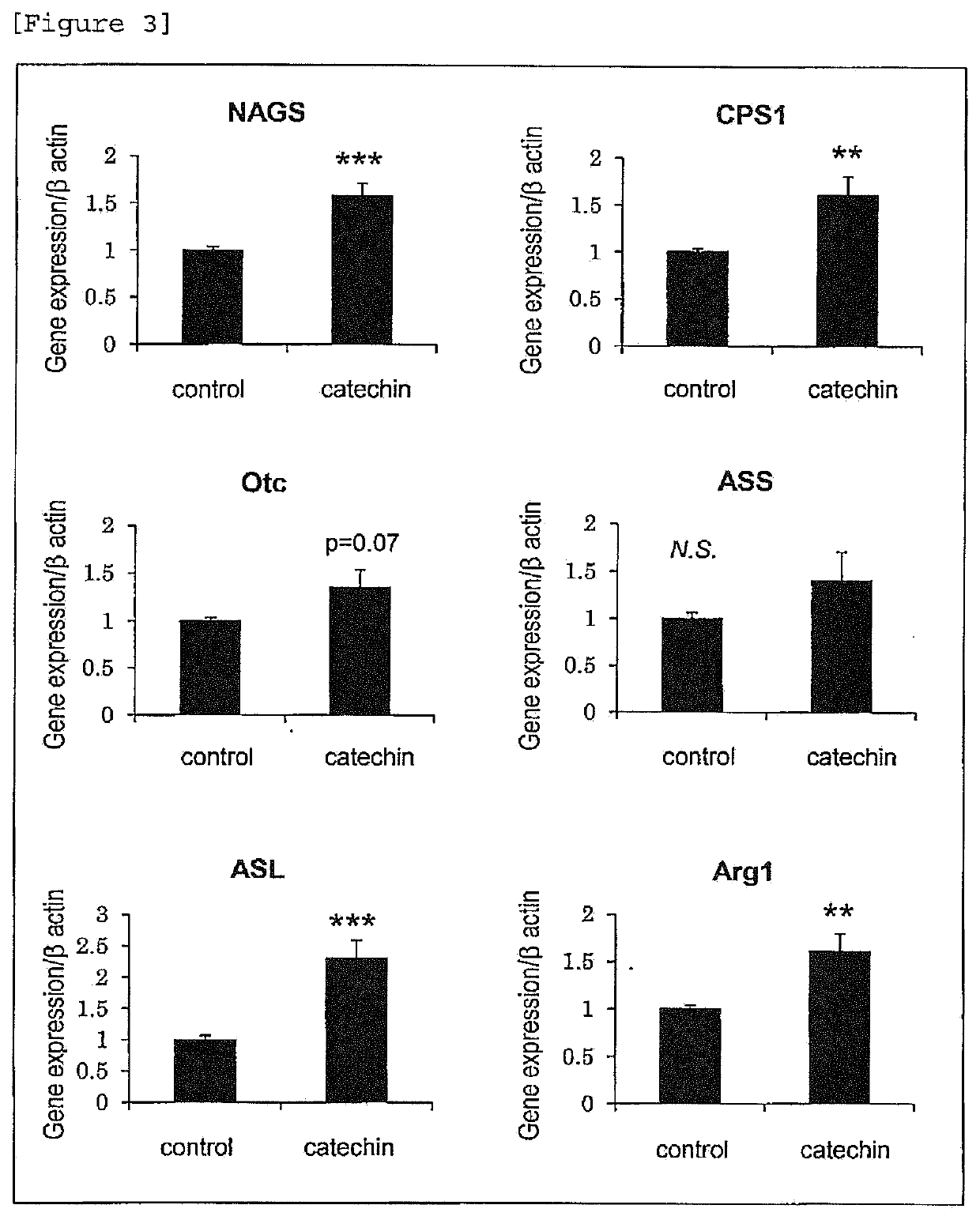
Ammonia Metabolism Promoter
ActiveUS20200197361A1Inhibition decreasedOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDecreased glycogenHyperammonemia
A material which has excellent ammonia metabolism improving effect and is effective for endurance enhancement, anti-fatigue or the like is provided. An ammonia metabolism promoting agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An endurance enhancing agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An anti-fatigue agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for suppressing a reduction in blood glucose level by exercise, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for promoting recovery from reduced blood glucose level by exercise, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for suppressing a reduction in muscle glycogen by exercise, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. A muscle endurance enhancing agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for preventing or ameliorating hyperammonemia, hepatic encephalopathy or chronic fatigue syndrome, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients.
Owner:KAO CORP
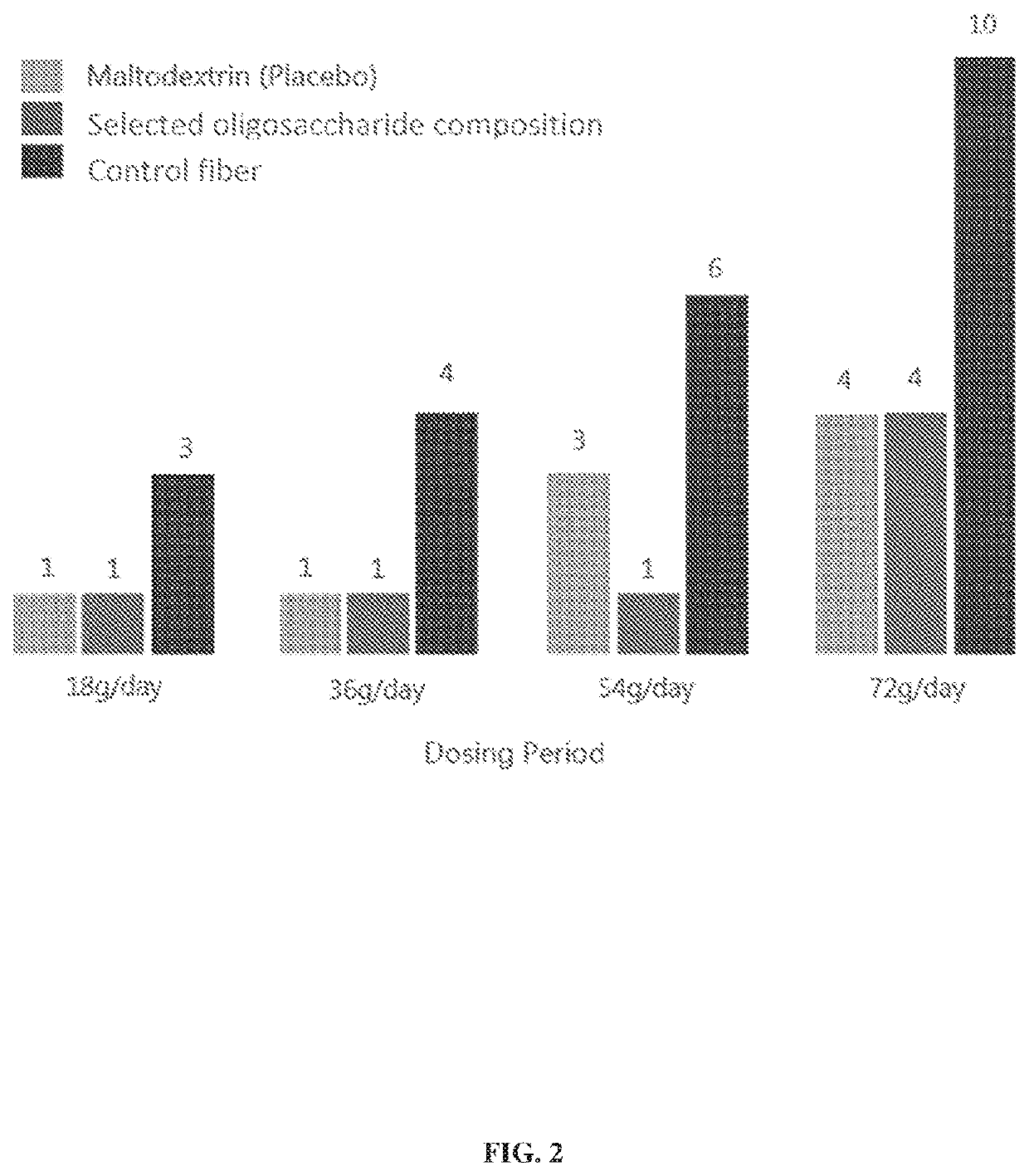
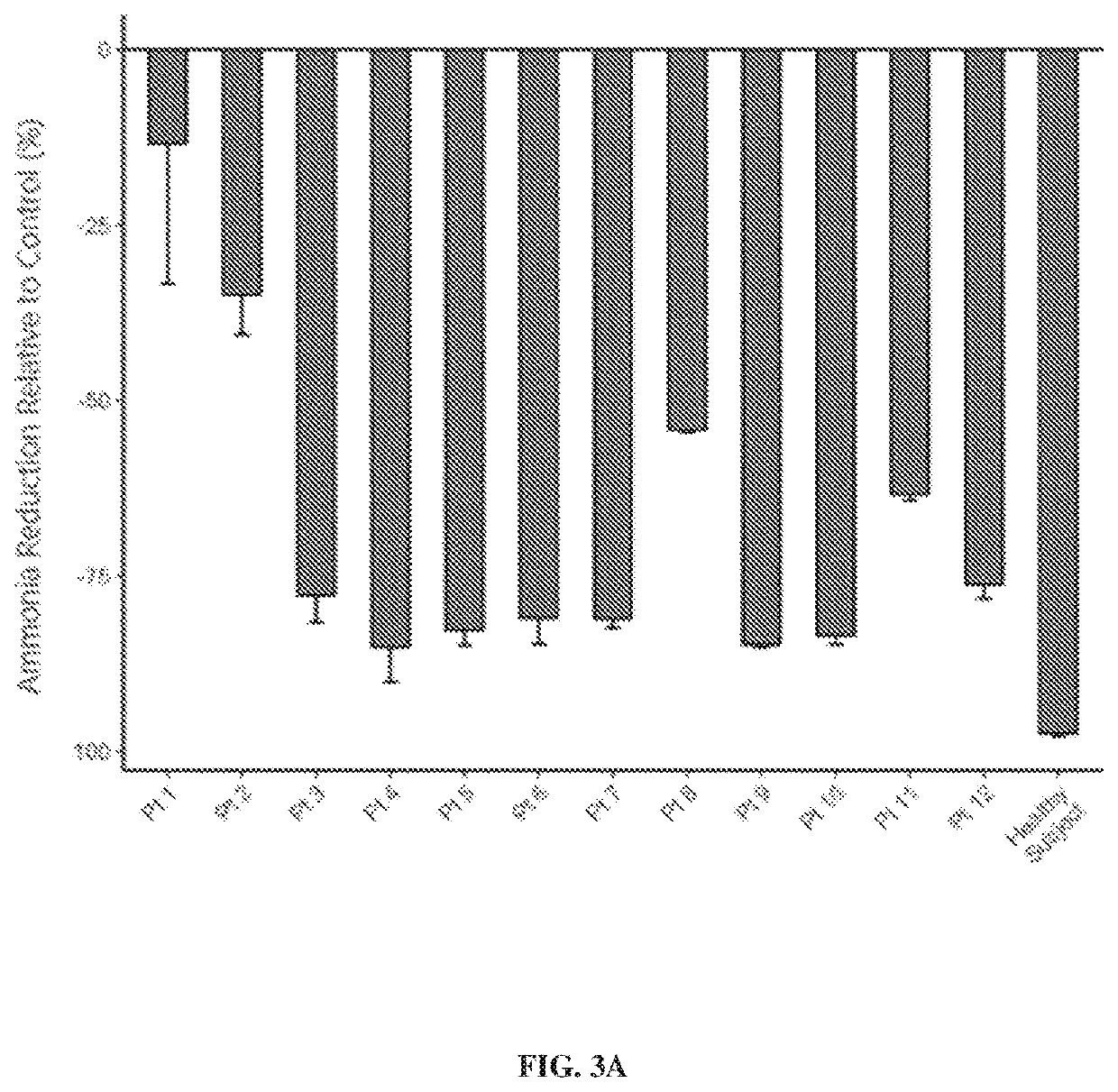
Oligosaccharide compositions and methods of use thereof for reducing ammonia levels
PendingUS20210198302A1Reduce ammonia levelsGood for healthSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderDiseaseMicroorganism
Aspects of the disclosure relate to oligosaccharide compositions and methods of making the same. Also provided are methods of using oligosaccharide compositions as microbiome metabolic therapies for reducing ammonia levels and for the treatment of hyperammonemia-related diseases (e.g., urea cycle disorders and hepatic encephalopathy).
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD
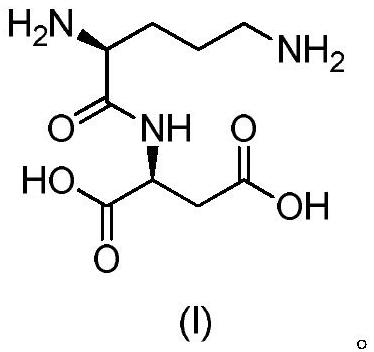
Active salt of dipeptide compound of ornithine and aspartic acid and application thereof
InactiveCN107573404BLower blood ammonia levelsImprove memory impairmentDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseDipeptide
The present invention provides active salts of ornithine and aspartate dipeptide compounds, preparation methods thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the active salts, and preparation of the dipeptide compounds or their active salts for preventing or treating hyperemia Use in the medicament of ammonia disease or liver disease, especially hepatic encephalopathy. The test results clearly show that the ornithine and aspartate dipeptide compounds and their active salts of the present invention can significantly reduce blood ammonia concentration after administration, and can significantly improve the memory secondary to TAA-induced liver injury in rats. It means that the dipeptide compound and its active salt have a certain therapeutic effect on hyperammonemia or liver disease, especially hepatic encephalopathy.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +3
Device and methods of using device for detection of hyperammonemia
ActiveUS9952199B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIonomerHyperammonemia
The present disclosure relates to a bio-sensor capable of measuring the total concentration of one or a plurality of ammonia or ammonium ions with the use of indophenol reagents in the presence of an ionomer. In some embodiments, the biosensor comprises a perflurinated membrane that comprises an ionomer in contact with an alkaline buffer in a vessel configured to receive a sample, such as whole blood. The disclosure also relates to a method of detecting or quantifying the ammonia or ammonium ion concentration in whole blood in a point of care biosensor without reliance on gas chromatography or any measurement that takes more than about twenty minutes.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +2
Application of L-arabinose to preparation of medicine or health care products for preventing or curing hyperammonemia
The invention discloses the application of L-arabinose to the preparation of medicine or health care products for preventing or curing hyperammonemia, and particularly discloses the application of L-arabinose to the preparation of medicine or health care products for reducing blood ammonia and / or endotoxin. The applicant finds, in experiments, that L-arabinose can effectively reduce the level of blood ammonia and endotoxin of a mouse (1 to 4 grams / kg / day), and body health is not damaged while the function is achieved.
Owner:唐传生物科技(厦门)有限公司
Active salt of dipeptide compound of ornithine and aspartic acid as well as application thereof
ActiveCN107573404ALower blood ammonia levelsImprove memory impairmentDipeptide ingredientsMetabolism disorderBlood ammoniaChemistry
The invention provides active salt of a dipeptide compound of ornithine and an aspartic acid, a preparation method of the active salt, a pharmaceutical composition including the active salt, and application of the dipeptide compound or the active salt thereof in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating hyperammonemia or liver diseases, in particular to hepatic encephalopathy. A test result clearly indicates that after the dipeptide compound of the ornithine and the aspartic acid and the active salt of the dipeptide compound are administered, the concentration of blood ammonia can beobviously reduced, and secondary memory disorder after TAA(tumor-associated antigen)-induced liver injury in rats can be obviously improved, indicating that the dipeptide compound and the active saltof the dipeptide compound have a certain treatment effect on hyperammonemia or liver diseases, in particular to the hepatic encephalopathy.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +3
Methods of treating urea cycle disorders by interfering with glucagon receptor signaling
PendingUS20210130480A1Reduce the amount requiredInhibit bindingOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Provided herein are methods of treating a subject with hyperammonemia or a urea cycle disorder. The methods comprise administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutic amount of a glucagon signaling pathway inhibitor, such that ammonia levels are lowered or that amino acid metabolism enzymes are down-regulated, or a condition or disease characterized by hyperammonemia is mediated, or at least one symptom or complication associated with the condition or disease is alleviated or reduced in severity. The glucagon signaling pathway inhibitor can be a small molecule inhibitor of the signaling pathway, an antisense inhibitor of the signaling pathway, shRNA, siRNA, a GCG neutralizing monoclonal antibody, a GCGR antagonist, a peptide inhibitor of the signaling pathway, a DARPin, a Spiegelmer, an aptamer, engineered Fn type-III domains, etc. The therapeutic methods are useful for treating a human suffering from hyperammonemia or a urea cycle disorder.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Oligosaccharide compositions and methods of use thereof for reducing ammonia levels
Aspects of the disclosure relate to oligosaccharide compositions and methods of making the same. Also provided are methods of using oligosaccharide compositions as microbiome metabolic therapies for reducing ammonia levels and for the treatment of hyperammonemia-related diseases (e.g., urea cycle disorders and hepatic encephalopathy).
Owner:DSM营养产品有限责任公司
Use of dihydroartemisinin in the preparation of drugs for the prevention and treatment of hyperammonemia
The invention proposes the use of dihydroartemisinin in the preparation of medicines, and the medicines are used for preventing or treating hyperammonemia. Therefore, it provides theoretical basis and application value for human or animal hyperammonemia treatment or auxiliary treatment medicine.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Device and methods of using device for detection of hyperammonemia
The present disclosure relates to a biosensor capable of measuring the total concentration of one or a plurality of ammonia or ammonium ions with the use of indophenol reagents in the presence of an ionomer. In some embodiments, the biosensor comprises a perflurinated membrane that comprises an ionomer in contact with an alkali buffer in a vessel configured to receive a sample, such as whole blood. The disclosure also relates to a method of detecting or quantifying the ammonia or ammonium ion concentration in whole blood in a point of care bio sensor without reliance on gas chromatography or any measurement that takes more than about twenty minutes.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
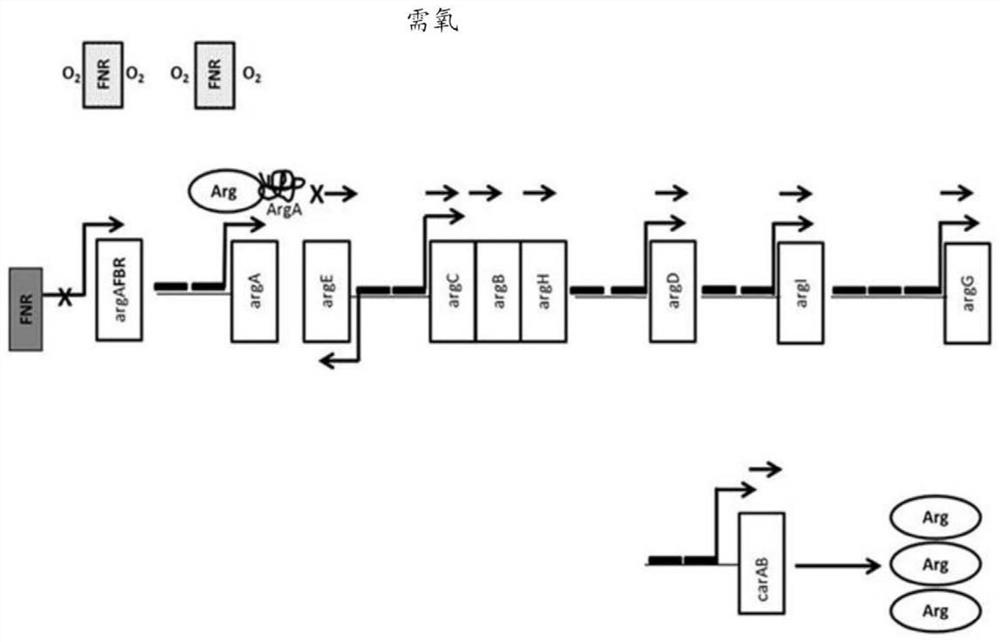
Bacteria engineered to treat diseases associated with hyperammonemia
Genetically engineered bacteria, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of modulating and treating disorders associated with hyperammonemia are disclosed.
Owner:SYNLOGIC OPERATING CO INC
Food for improving clinical conditions capable of lowering the concentration of low-molecular weight nitrogen-containing compounds in blood
The object of the present invention is to provide a new improvement capable of preventing or delaying the transfer to hemodialysis therapy or reducing the number of implementations of the therapy in the case of renal dysfunction, and preventing or reducing the occurrence of hyperammonemia in the case of liver dysfunction Disease with food. In order to achieve this object, the disease-modifying food of the present invention is characterized by containing indigestible polysaccharides as the main component and limiting the addition of protein components. Thus, by using the energy generated by the absorption of indigestible polysaccharides, the urea or ammonia secreted into the intestines is used as the N source to synthesize bacterial protein, and the proliferated bacterial cells are excreted as feces to reduce the amount of nitrogen in the blood. Low-molecular nitrogen compounds, as a result, can improve renal dysfunction and liver dysfunction.
Owner:CHEIRON JAPAN CO
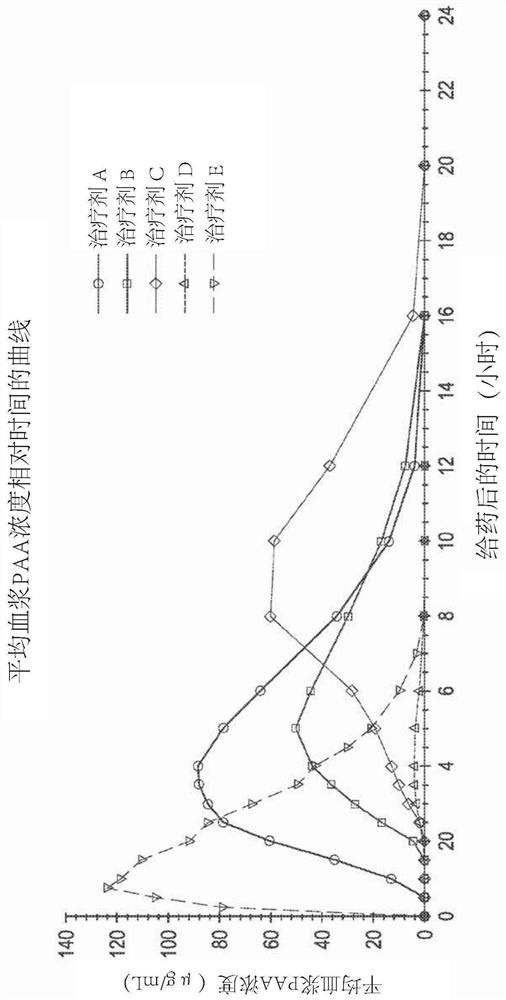
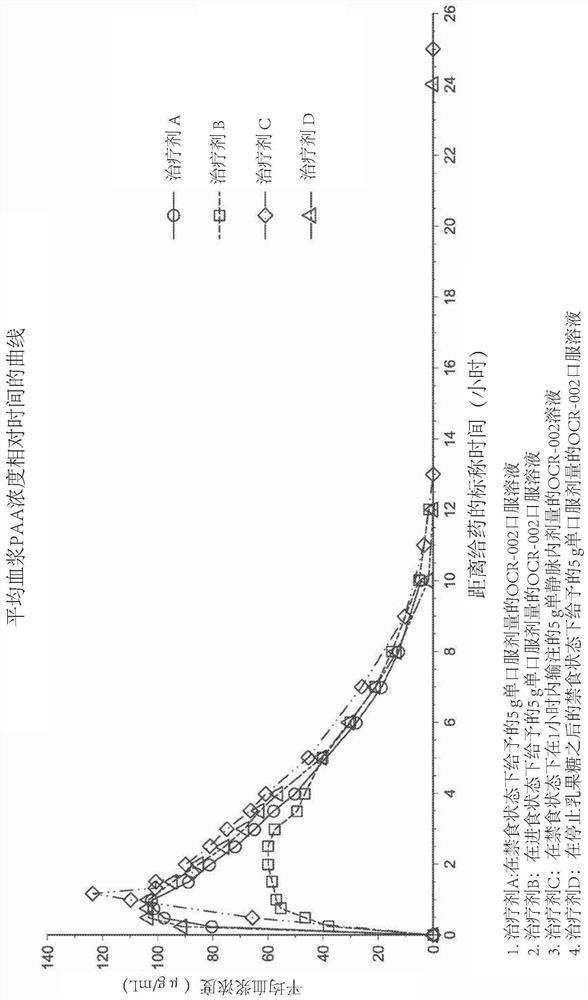
Dosage and use of ornithine phenylacetate for treating hyperamminemia
Embodiments of the present disclosure relate to doses of ornithine phenylacetate for use in treating or ameliorating hyperammonemia and methods of administering such doses of ornithine phenylacetate in patients suffering from chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis. In some embodiments, the patient also has hepatic encephalopathy as a complication of the liver disease.
Owner:OCERA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Acylated derivatives of ornithine and aspartic acid dipeptide compounds and their application
ActiveCN107619428BLower blood ammonia levelsQuick effectNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsDipeptideHyperammonemia
The invention provides an acylated derivative for an ornithine and aspartate dipeptide compound or an officinal salt thereof, a preparation method thereof, a medicine composition containing the derivative or the officinal salt thereof, and the application of the derivative or the officinal salt thereof for preparing medicines for preventing or curing hyperammonemia or liver diseases, particularlyhepatic encephalopathy. Experimental results definitely indicate that the concentration of blood ammonia can be obviously reduced after administration for the acylated derivative for the ornithine andaspartate dipeptide compound, the acylated derivative takes effect quickly by preferably compared with LOLA, subsequent dysmnesia after TAA-induced rat liver injury can be obviously improved, and theacylated derivative for the dipeptide has a certain treatment effect on hyperammonemia or liver diseases, particularly hepatic encephalopathy.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +3
Transmembrane ph-gradient polymersomes and their use in the scavenging of ammonia and its methylated analogs
The present invention provides polymersomes comprising non-biodegradable amphiphilic block-copolymers and their enteral (e.g., oral) or topical use in the treatment of an ammonia or ammonia methylated analog-associated disease or disorder or symptom thereof (e.g., hyperammonemia or trimethylaminuria). More particularly, it provides a polymersome comprising (a) a membrane, which comprises a block copolymer of poly(styrene) (PS) and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), wherein the PS / PEO molecular weight ratio is higher than 1.0 and lower than 4.0; and (b) a core which encloses an acid. It also provides a method of making the polymersome comprising mixing the copolymer-containing organic solvent phase with an aqueous phase containing the acid.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
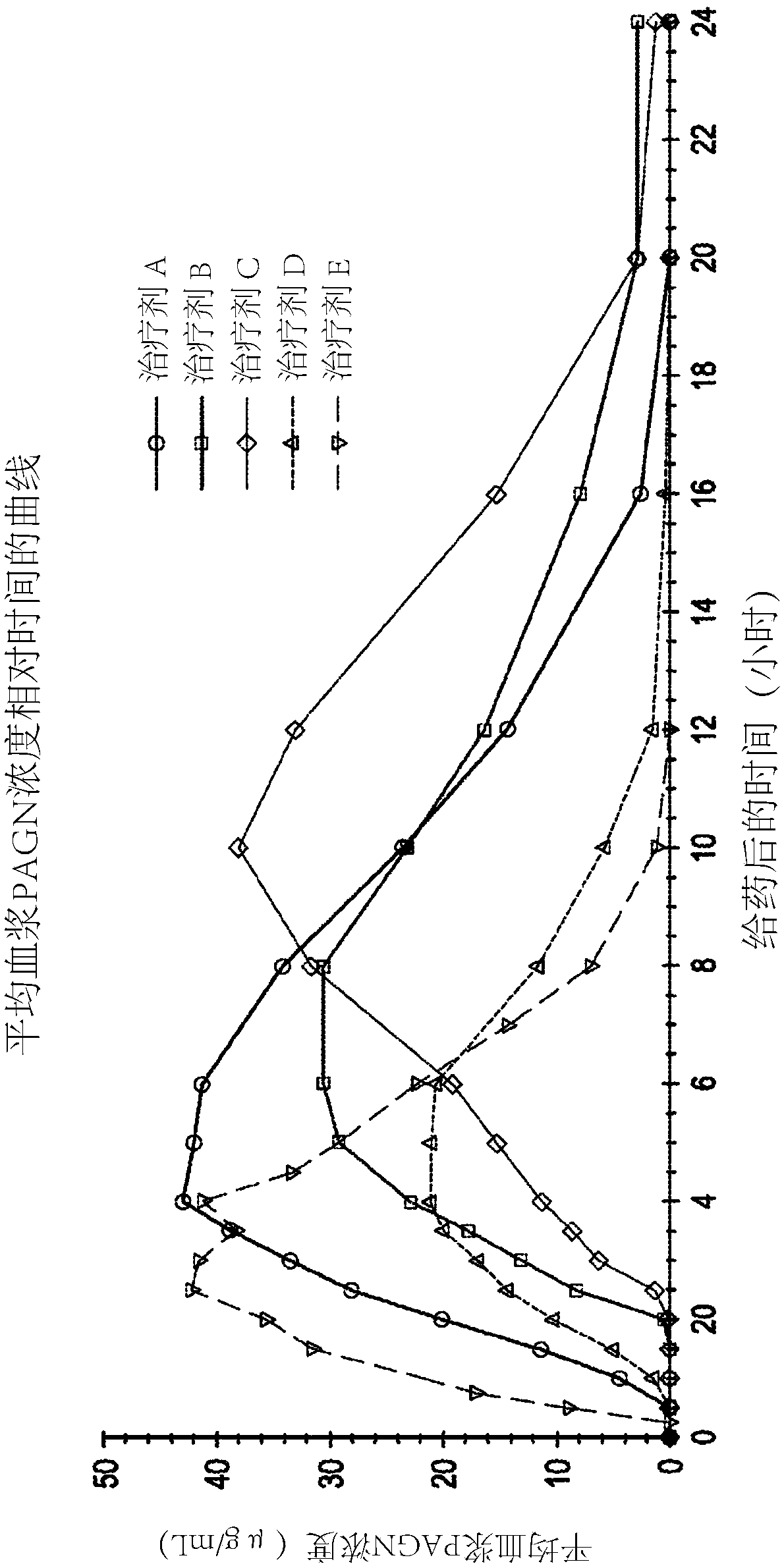
Ammonia metabolism promoter
A material which has excellent ammonia metabolism improving effect and is effective for endurance enhancement, anti-fatigue or the like is provided. An ammonia metabolism promoting agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An endurance enhancing agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An anti-fatigue agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for suppressing a reduction in blood glucose level by exercise, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for promoting recovery from reduced blood glucose level by exercise, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for suppressing a reduction in muscle glycogen by exercise, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. A muscle endurance enhancing agent, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients. An agent for preventing or ameliorating hyperammonemia, hepatic encephalopathy or chronic fatigue syndrome, comprising catechins and ornithine as active ingredients.
Owner:KAO CORP
Formulation of l-ornithine phenylacetate
Some embodiments of the present application are directed to oral formulations of L- ornithine phenylacetate and methods of using the same. These oral formulations offer alternative administration route than the standard intravenous administration of L-ornithine phenylacetate for treating hyperammonemia in patients having various acute and chronic liver diseases and disorders, for example, acute liver failure, liver cirrhosis, liver decompensation, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy, or patients with urea cycle disorders.
Owner:OCERA THERAPEUTICS INC
Compound containing structure of o-naphthaquinone and application
InactiveCN1318414CHigh speedImprove convenienceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderQuinoneNatural product
A compound containing o-naphthalene quinone structure for preparing medicines to prevent and treat hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy is prepared from natural Masonate F through structure reformation and optimization.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Formulation of l-ornithine phenylacetate
Some embodiments of the present application are directed to oral formulations of L-ornithine phenylacetate and methods of using the same. These oral formulations offer alternative administration routethan the standard intravenous administration of L-ornithine phenylacetate for treating hyperammonemia in patients having various acute and chronic liver diseases and disorders, for example, acute liver failure, liver cirrhosis, liver decompensation, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy, or patients with urea cycle disorders.
Owner:OCERA THERAPEUTICS INC
Application of dihydroartemisinin in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating hyperammonemia
The invention provides application of dihydroartemisinin in preparation of a medicine. The medicine is used for preventing or treating hyperammonemia. Therefore, a theoretical basis and application value are provided for human or animal hyperammonemia treatment or adjuvant therapy drugs.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Ammonia Metabolism Promoter
ActiveUS20210228537A1Preventing and ameliorating hyperammonemiaPreventing and ameliorating hepatic encephalopathyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCitrullineHyperammonemia
A material which promotes ammonia metabolism in the body, as well as a material which has excellent ammonia metabolism improving effect and is effective for endurance enhancement and anti-fatigue are provided. An ammonia metabolism promoting agent, comprising catechins as an active ingredient. An agent for preventing or ameliorating hyperammonemia, hepatic encephalopathy or chronic fatigue syndrome, comprising catechins compound as an active ingredient. An ammonia metabolism promoting agent, an endurance enhancing agent and an anti-fatigue agent, comprising catechins, citrulline and arginine as active ingredients.
Owner:KAO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com