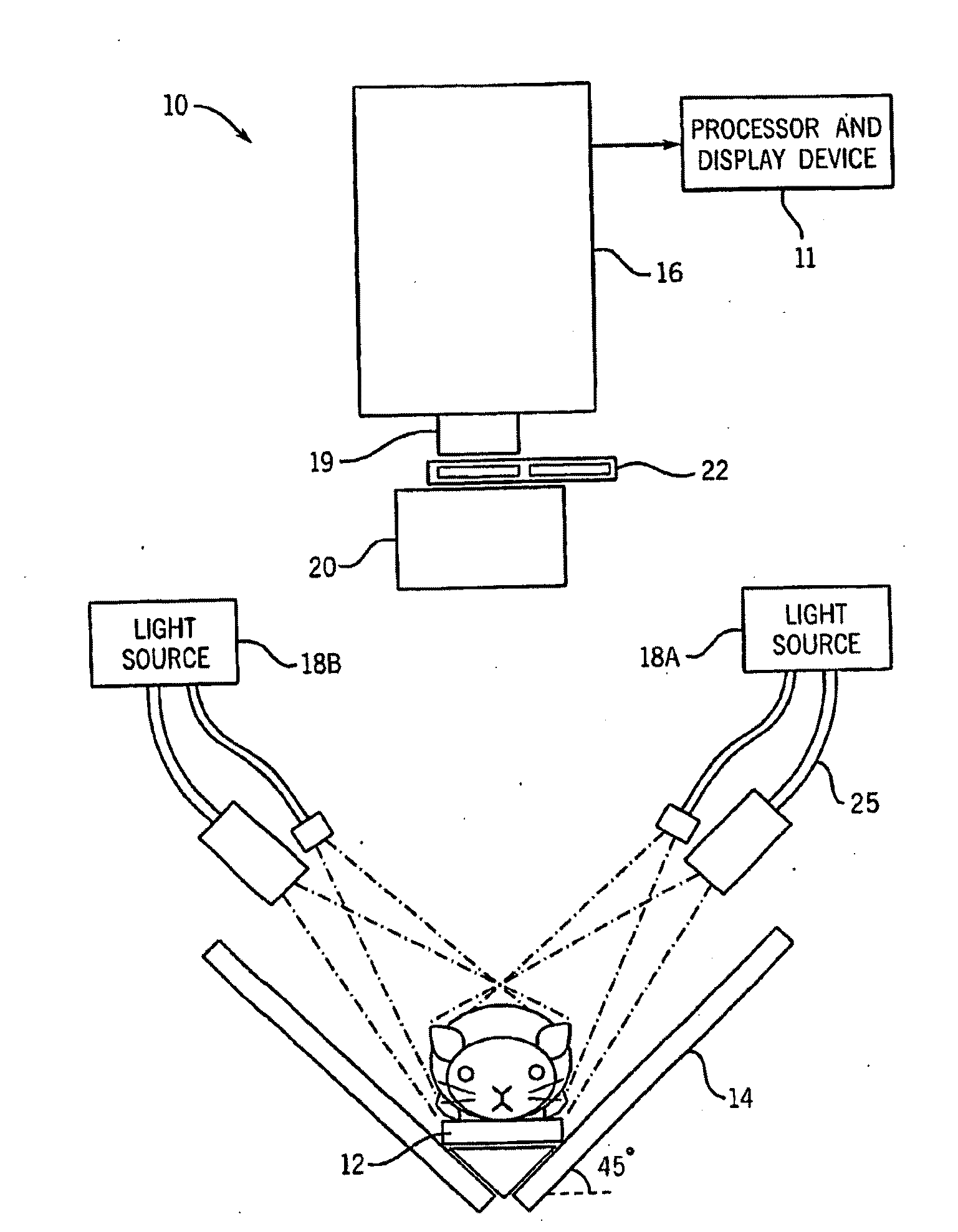
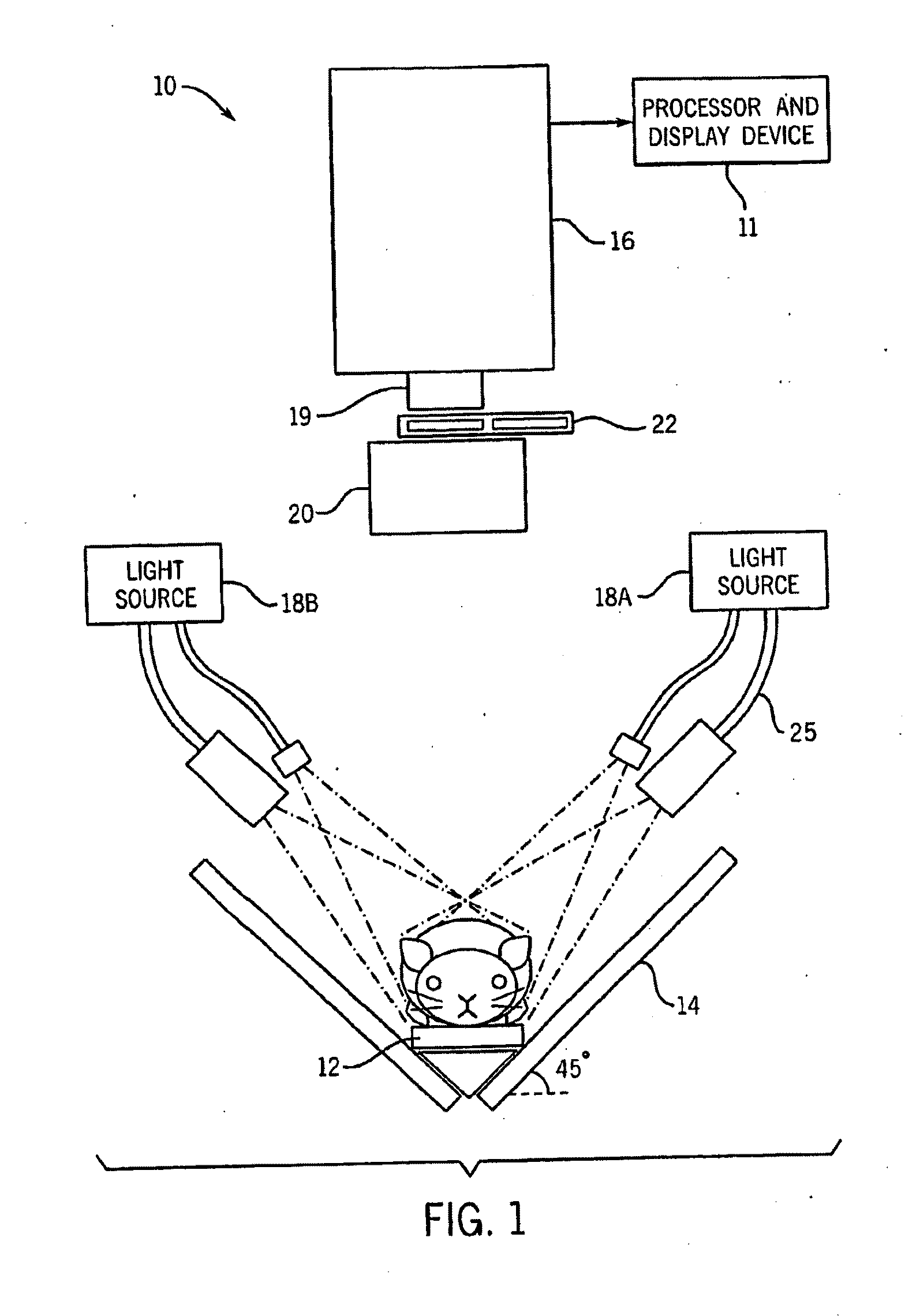
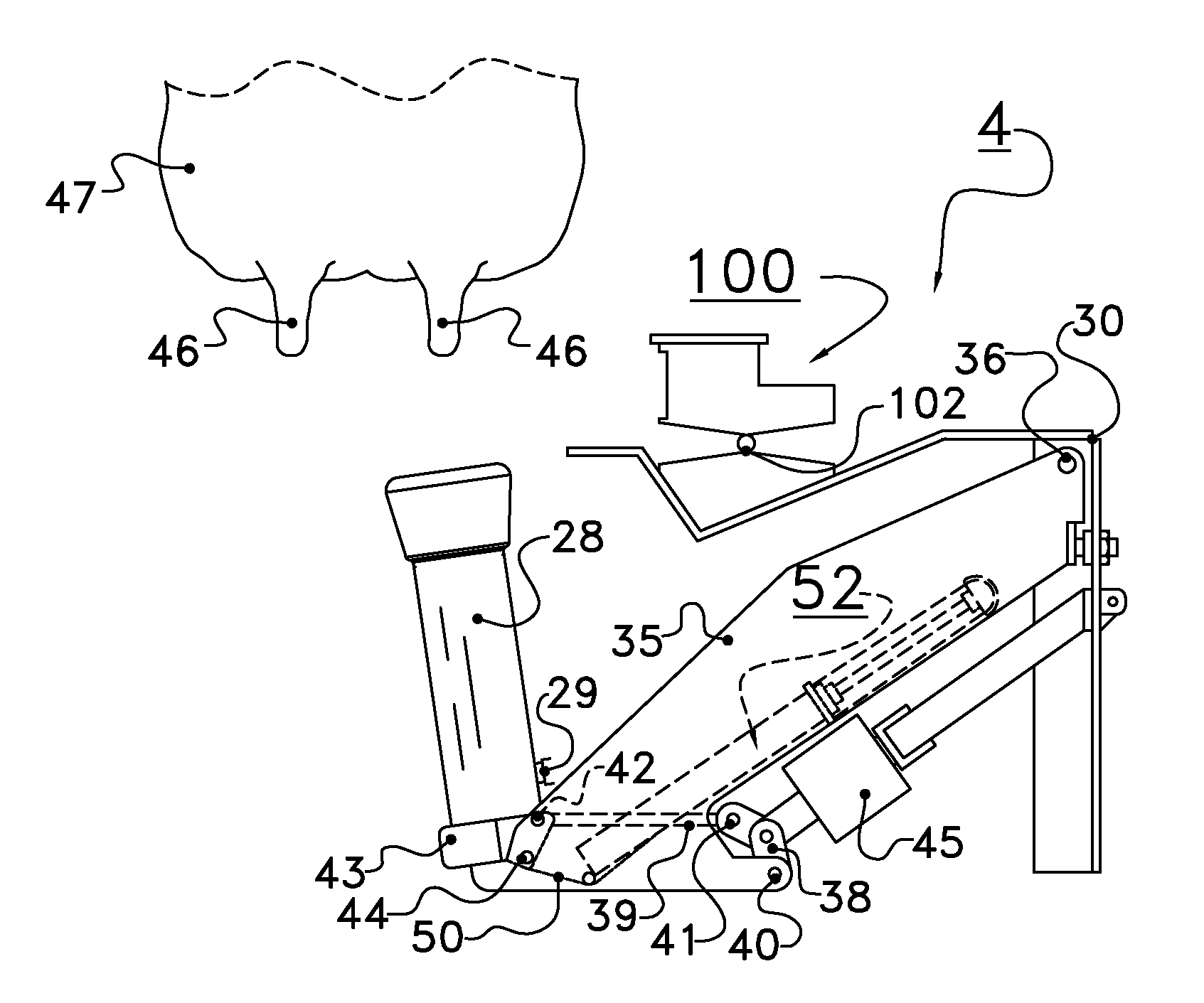
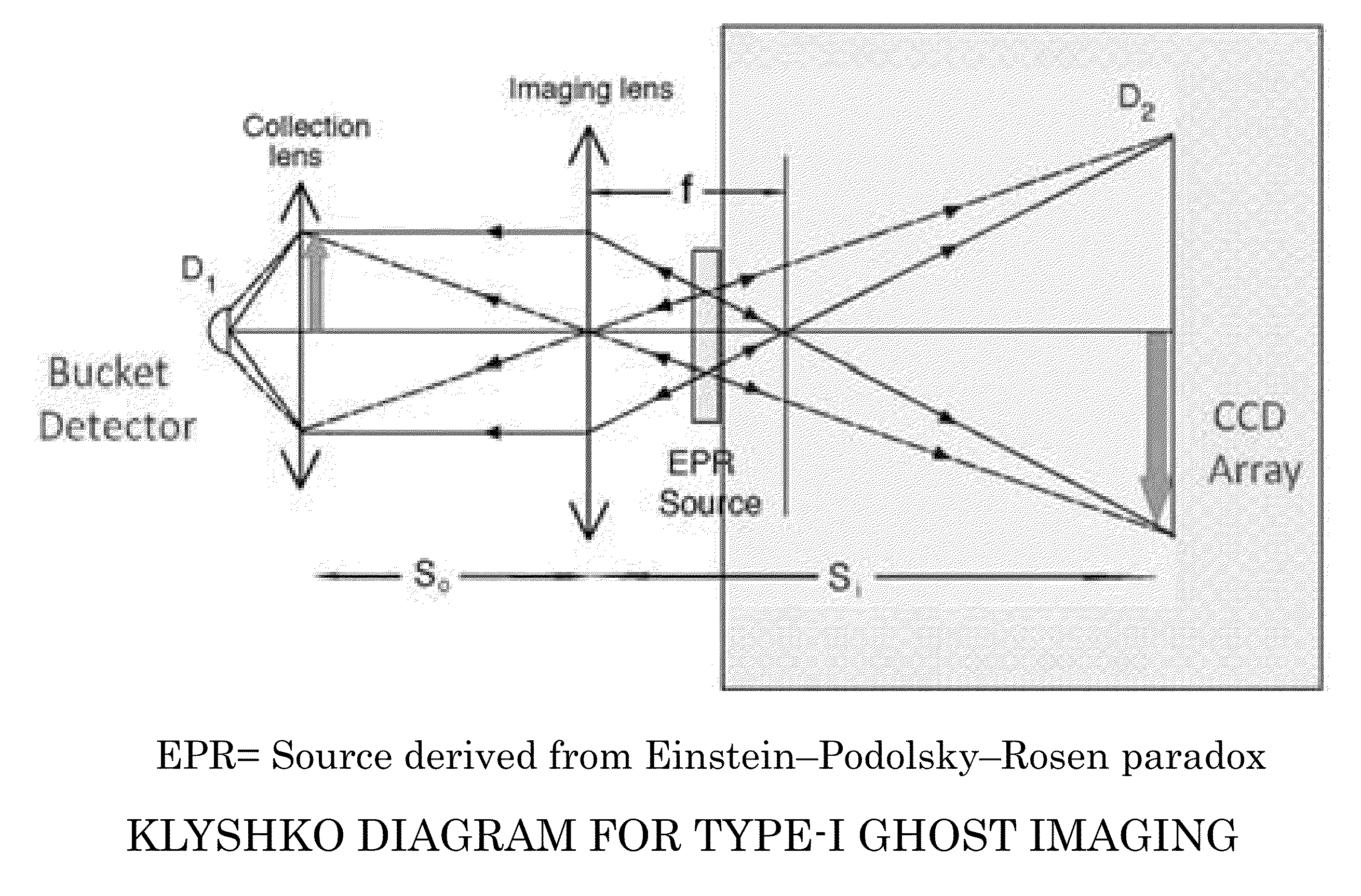
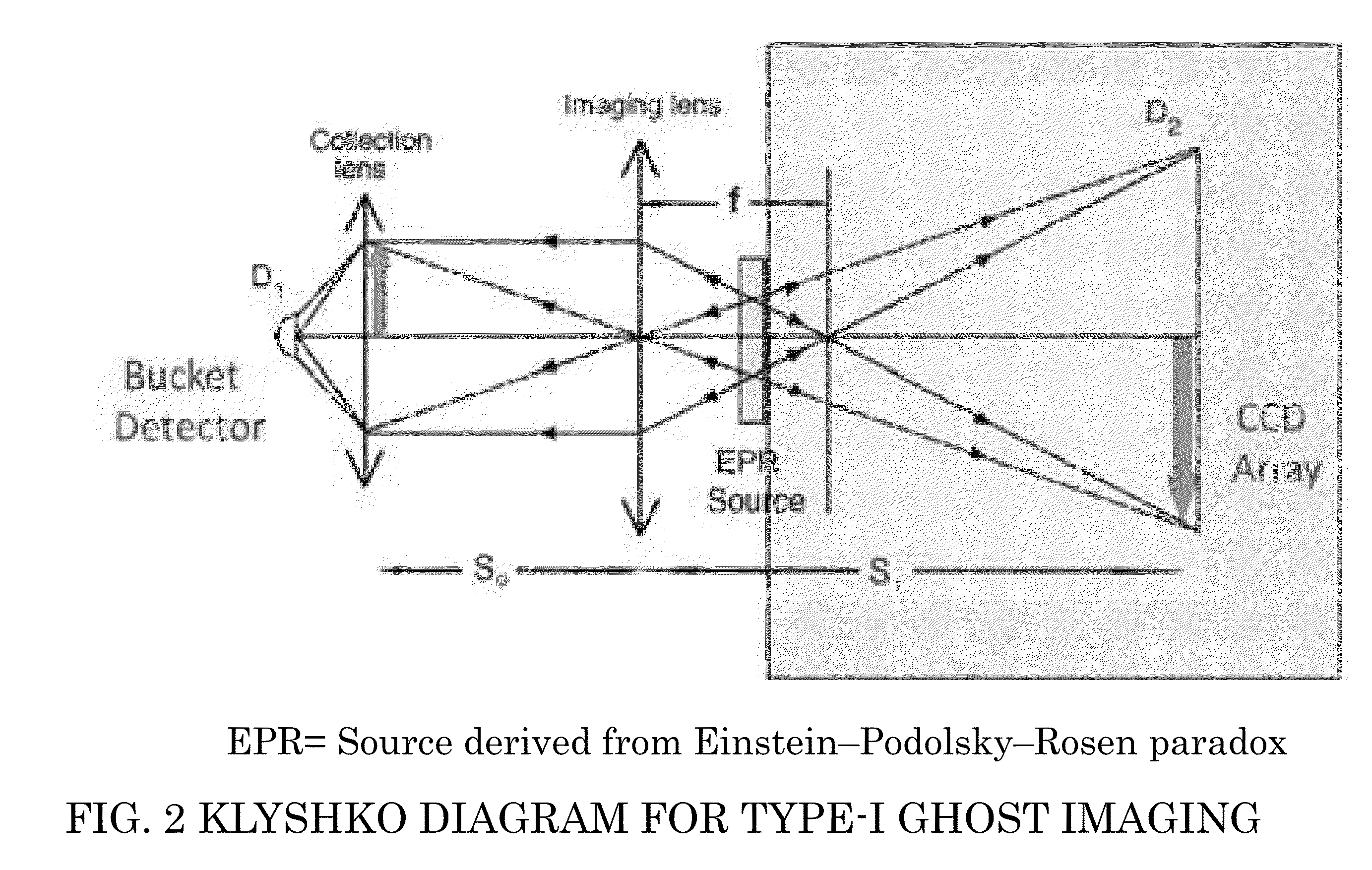
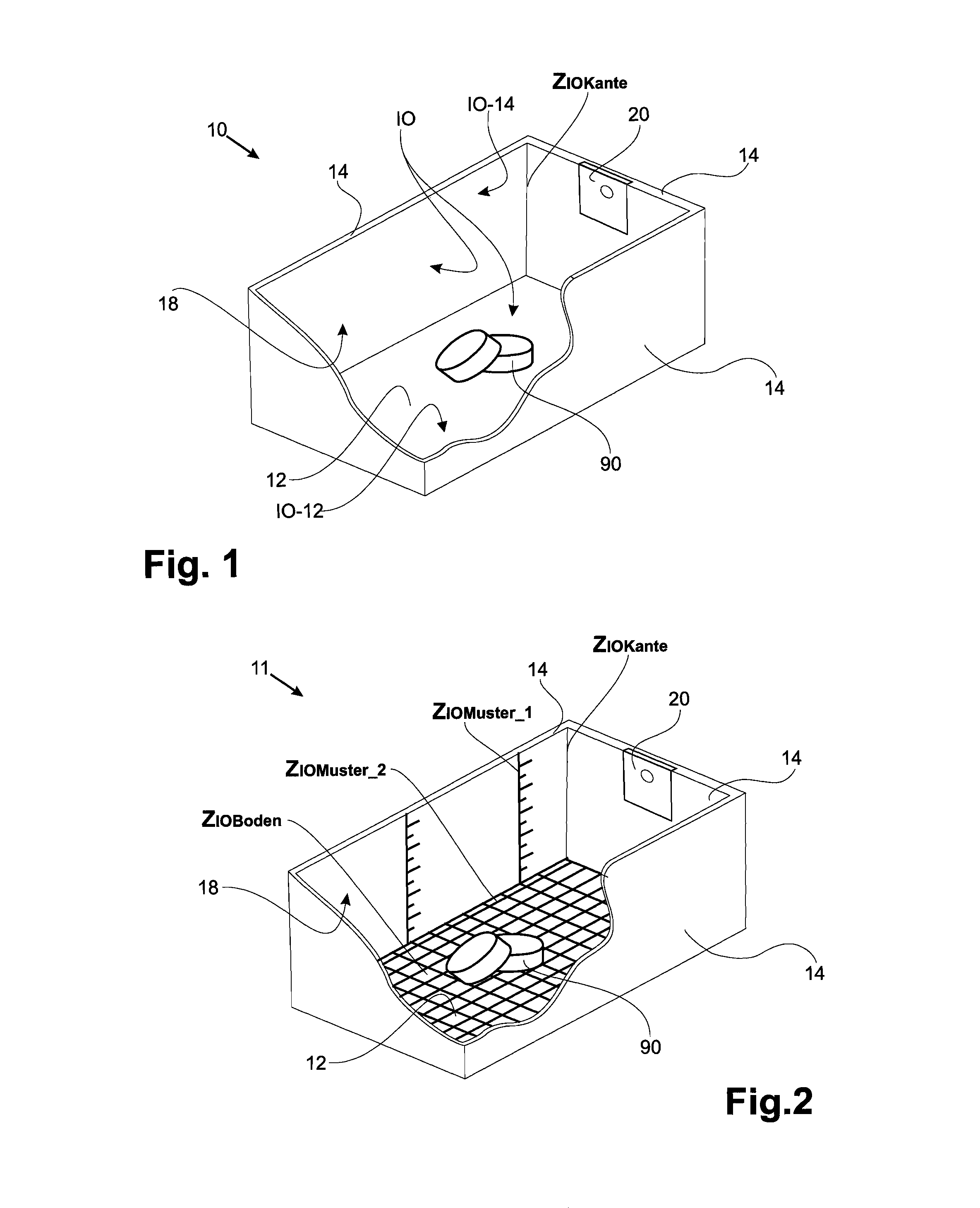
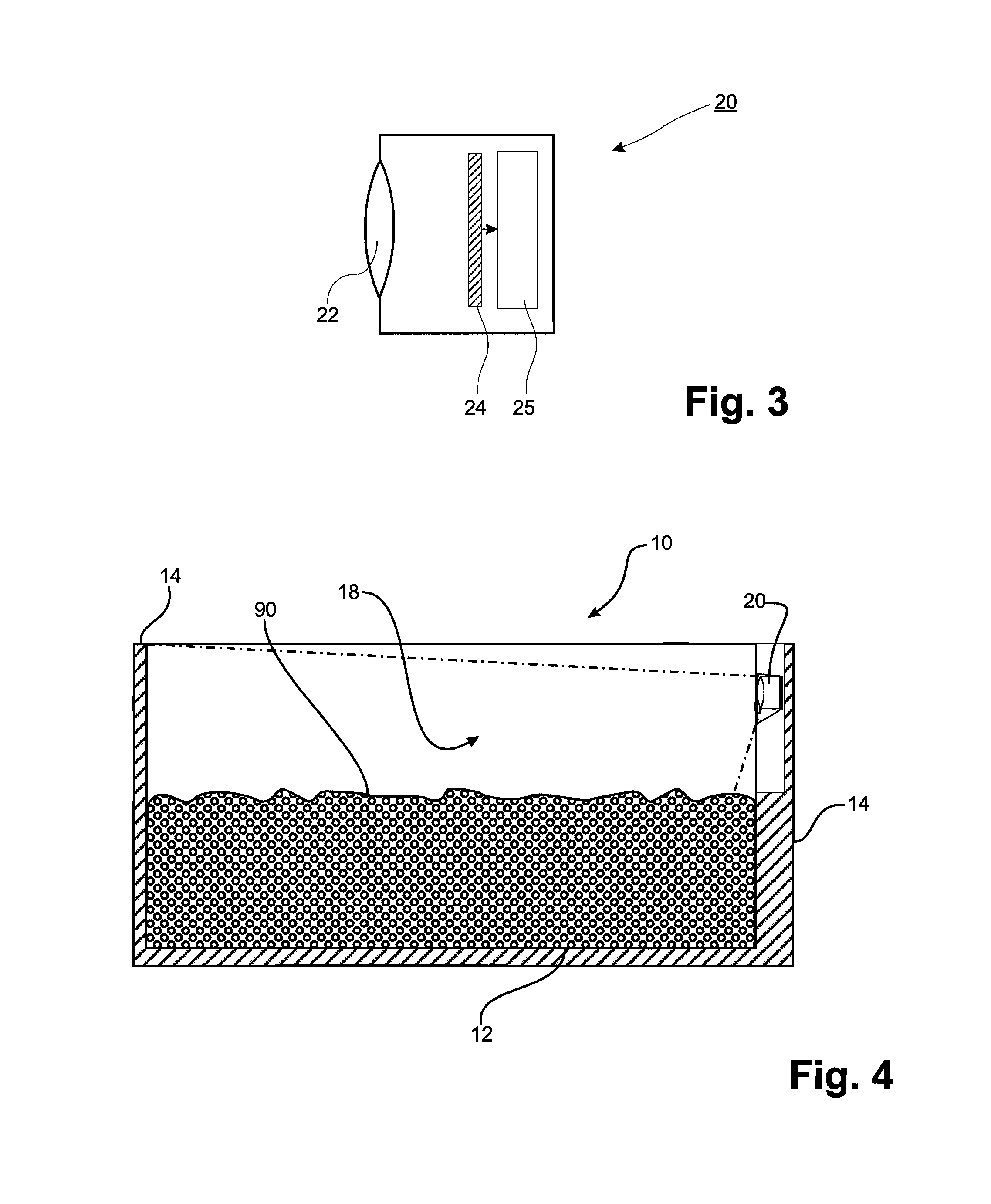
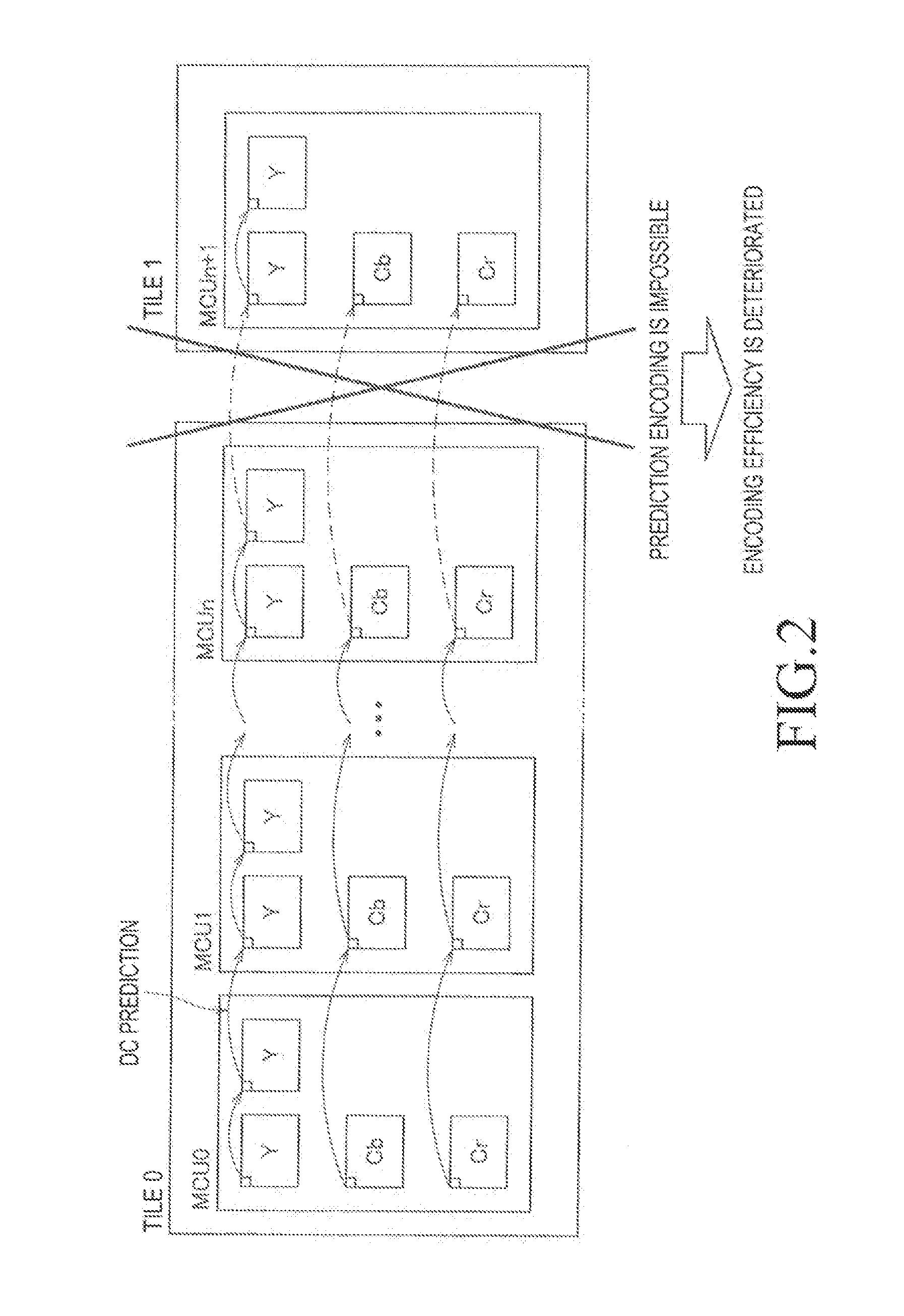
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Generate image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
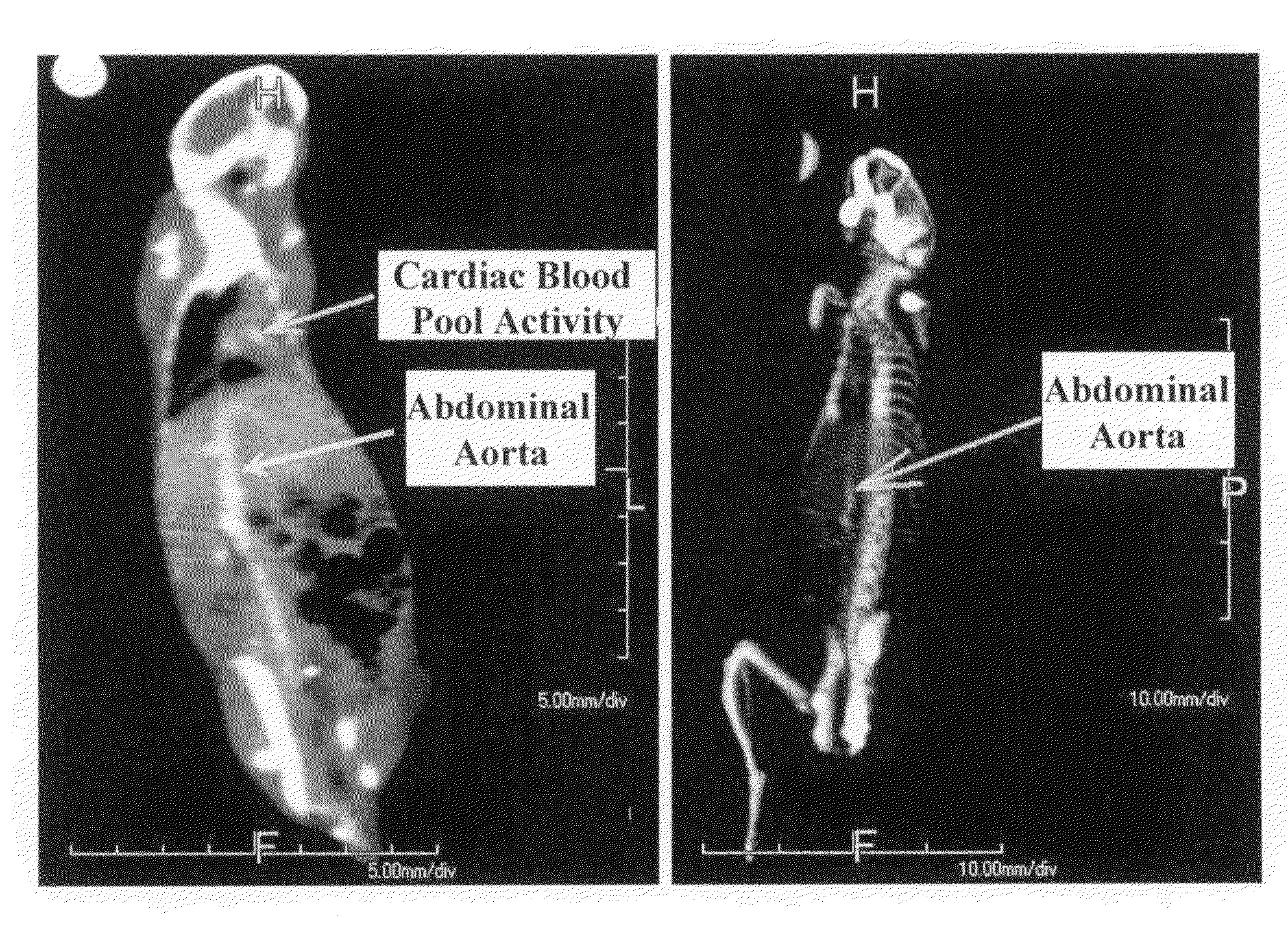
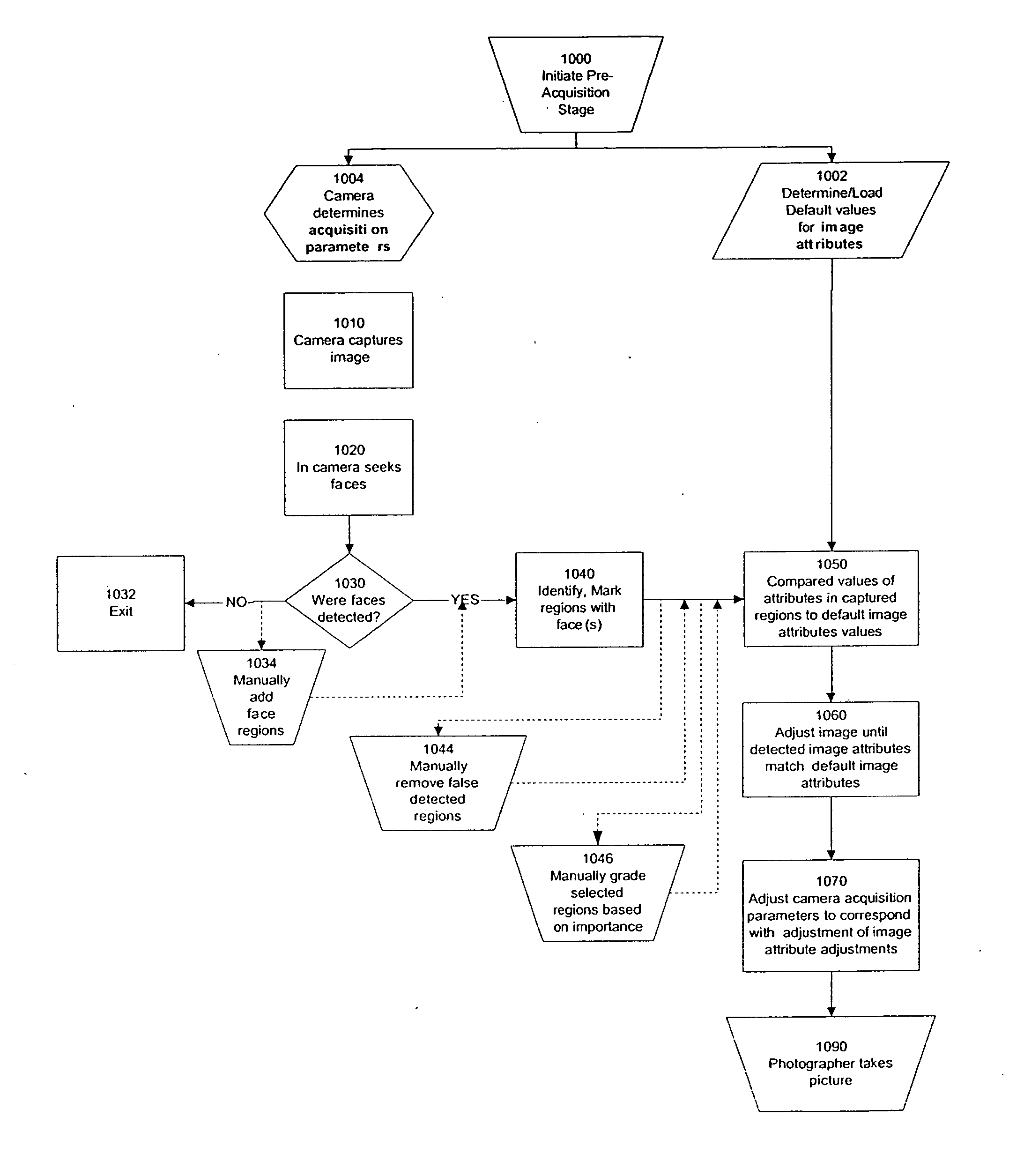
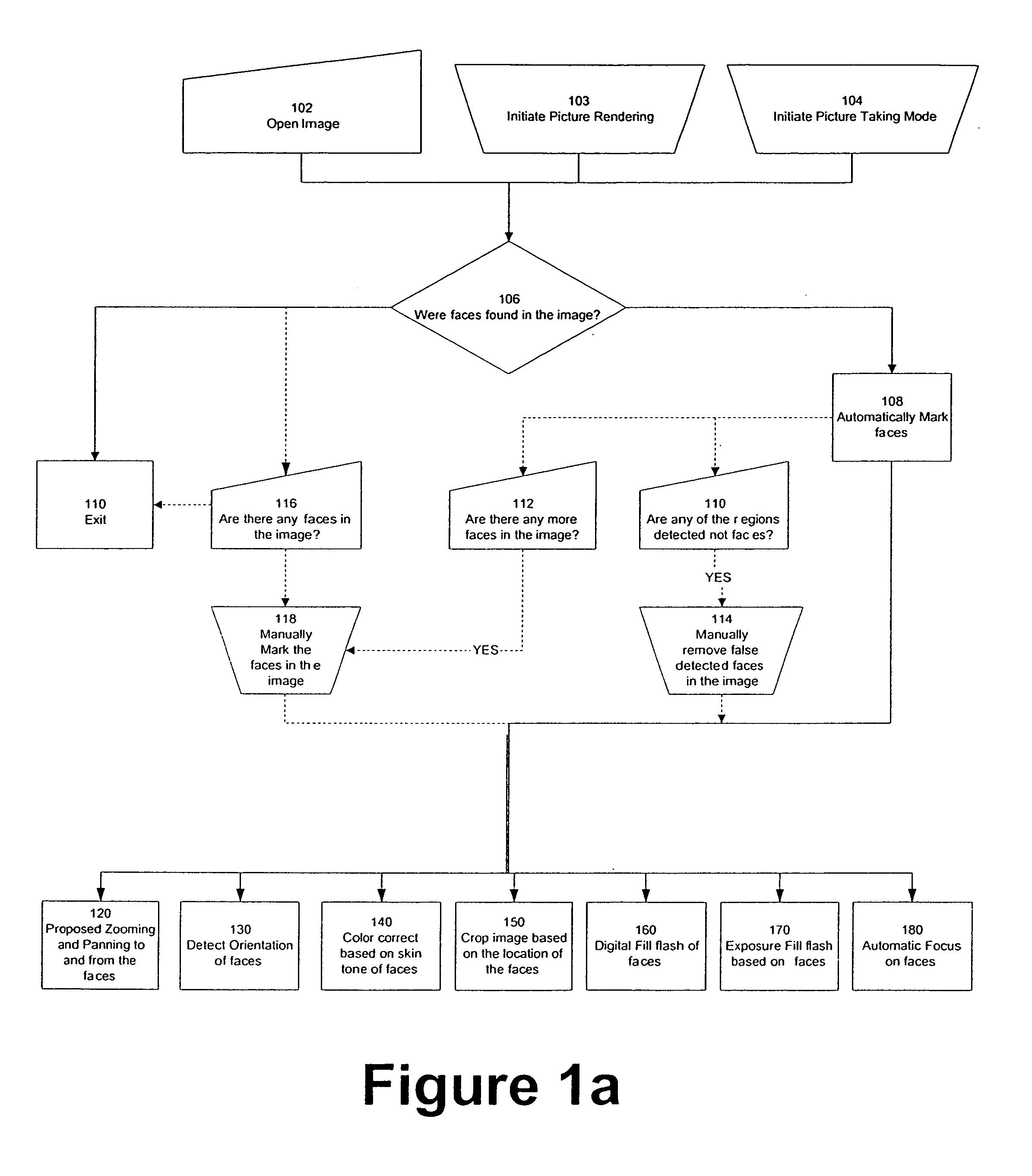
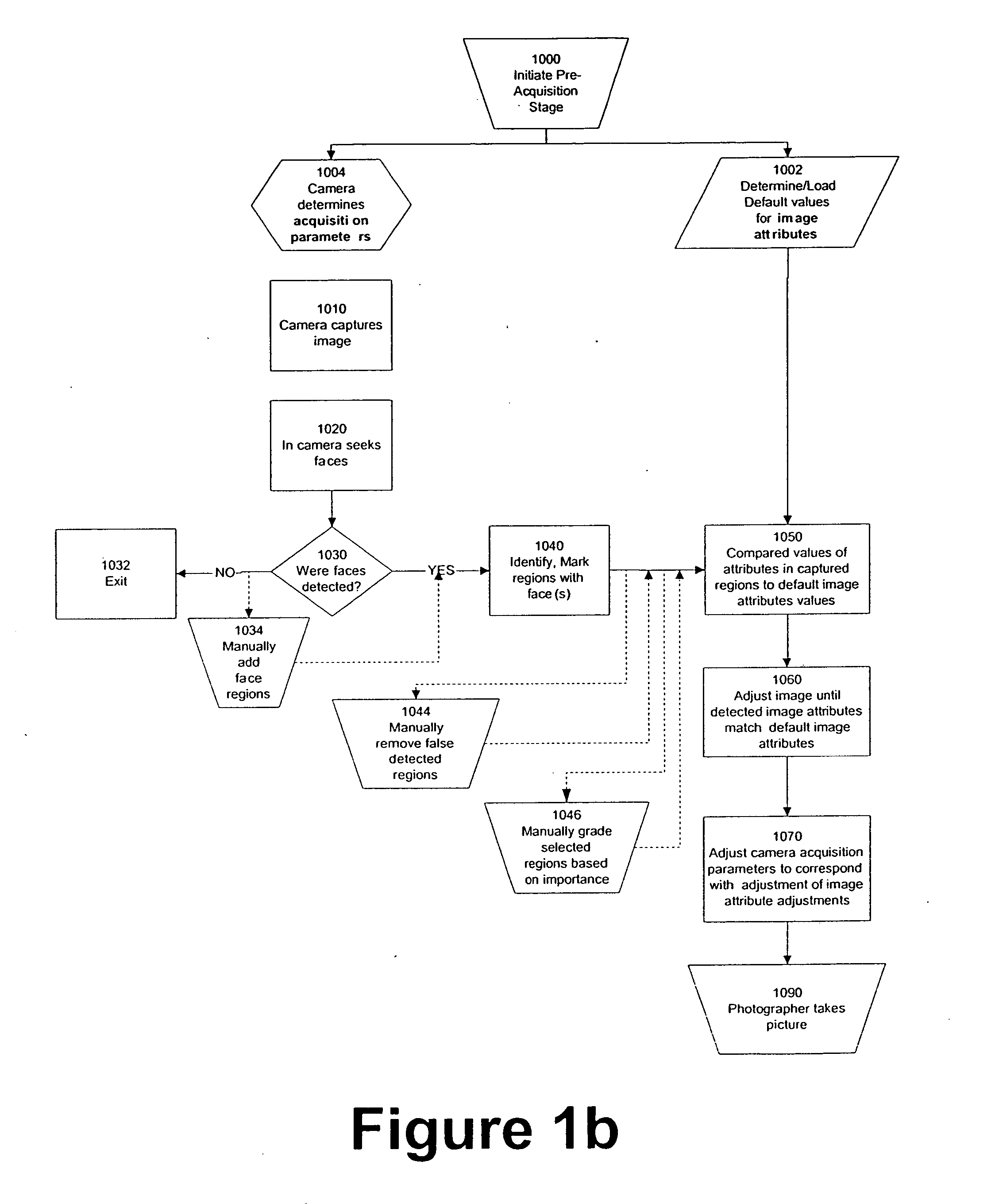
Modification of viewing parameters for digital images using face detection information
ActiveUS20060204034A1Generate imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsFace detectionAnimation
A method of modifying the viewing parameters of digital images using face detection for achieving a desired spatial parameters based on one or more sub-groups of pixels that correspond to one or more facial features of the face. Such methods may be used for animating still images, automating and streamlining application such as the creation of slide shows and screen savers of images containing faces.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
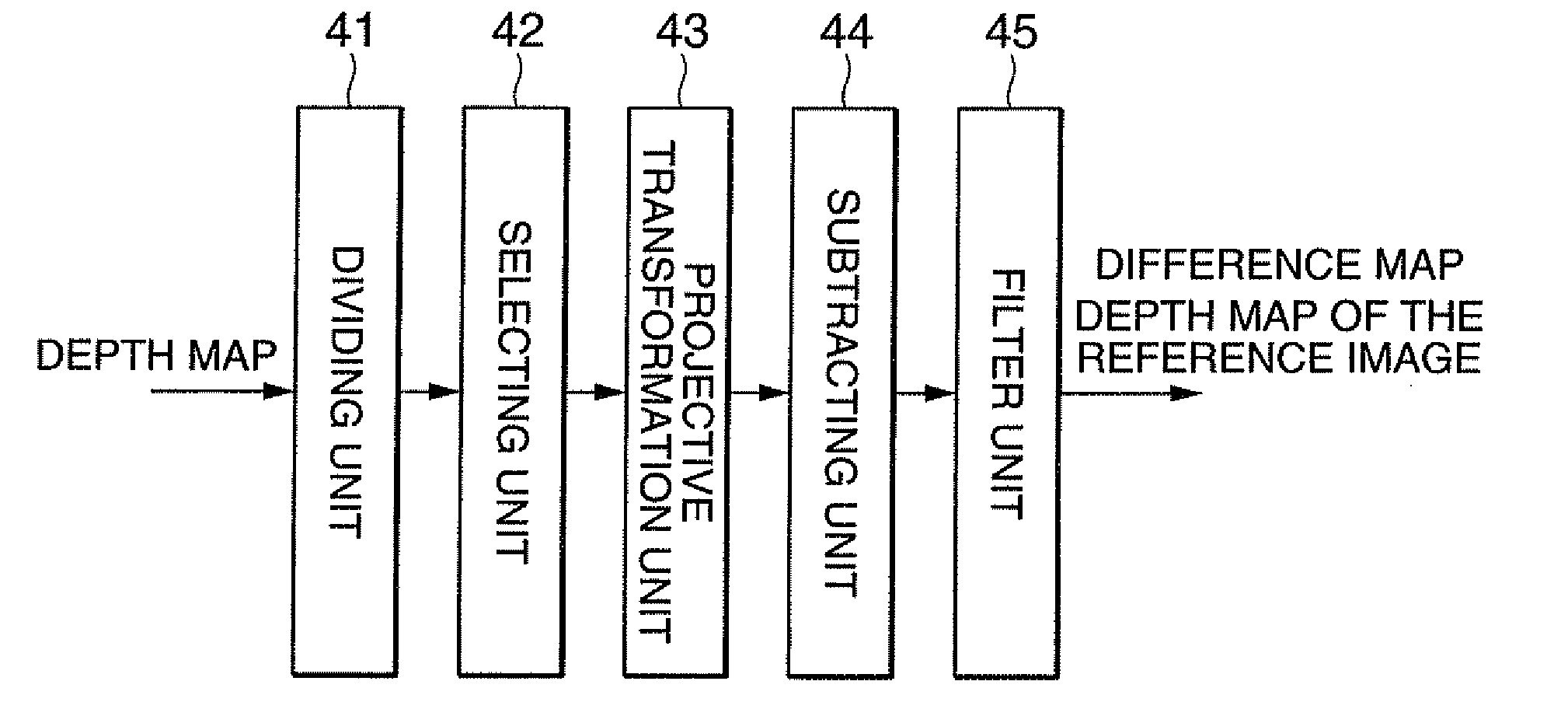
Image processing apparatus and c0mputer program
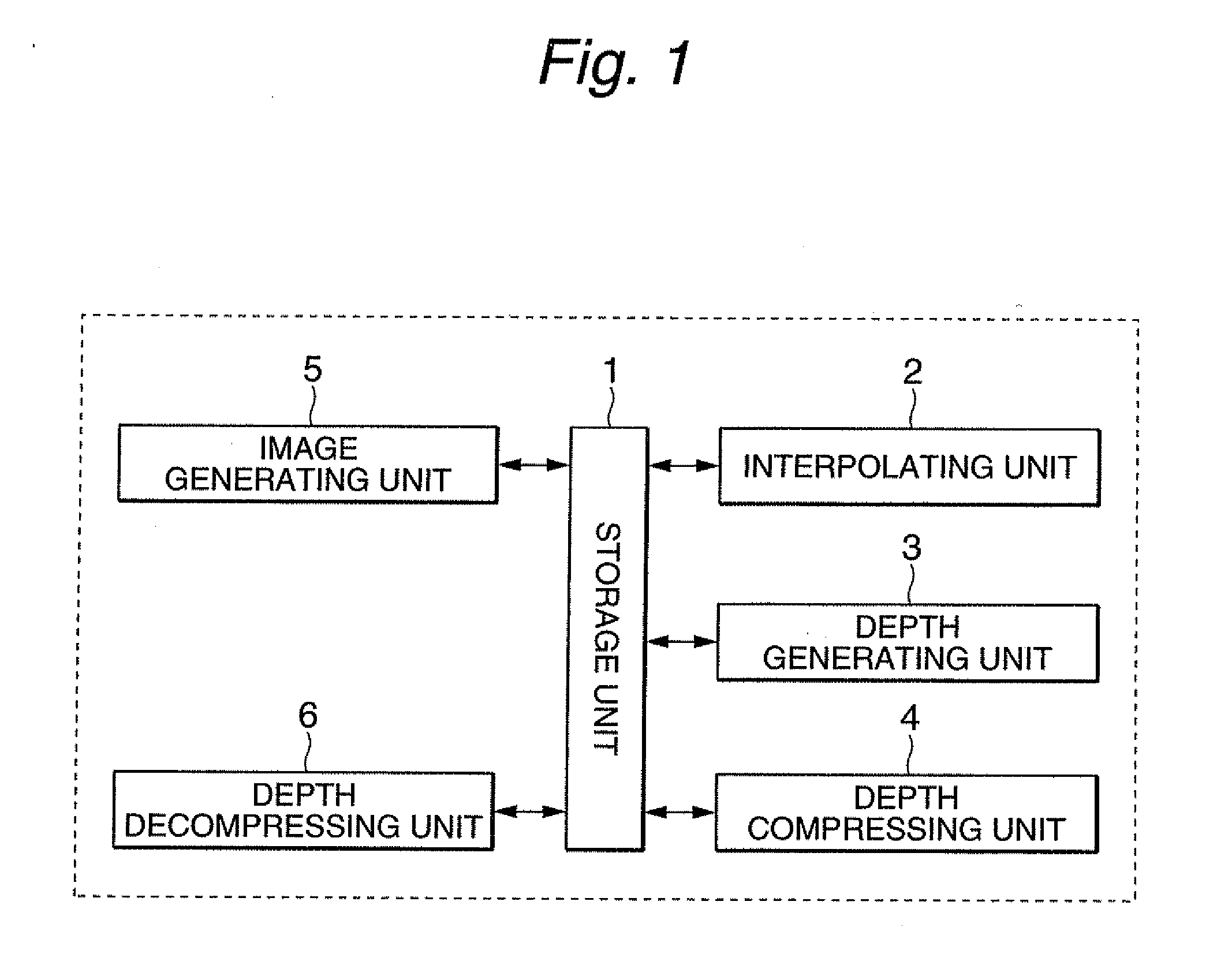
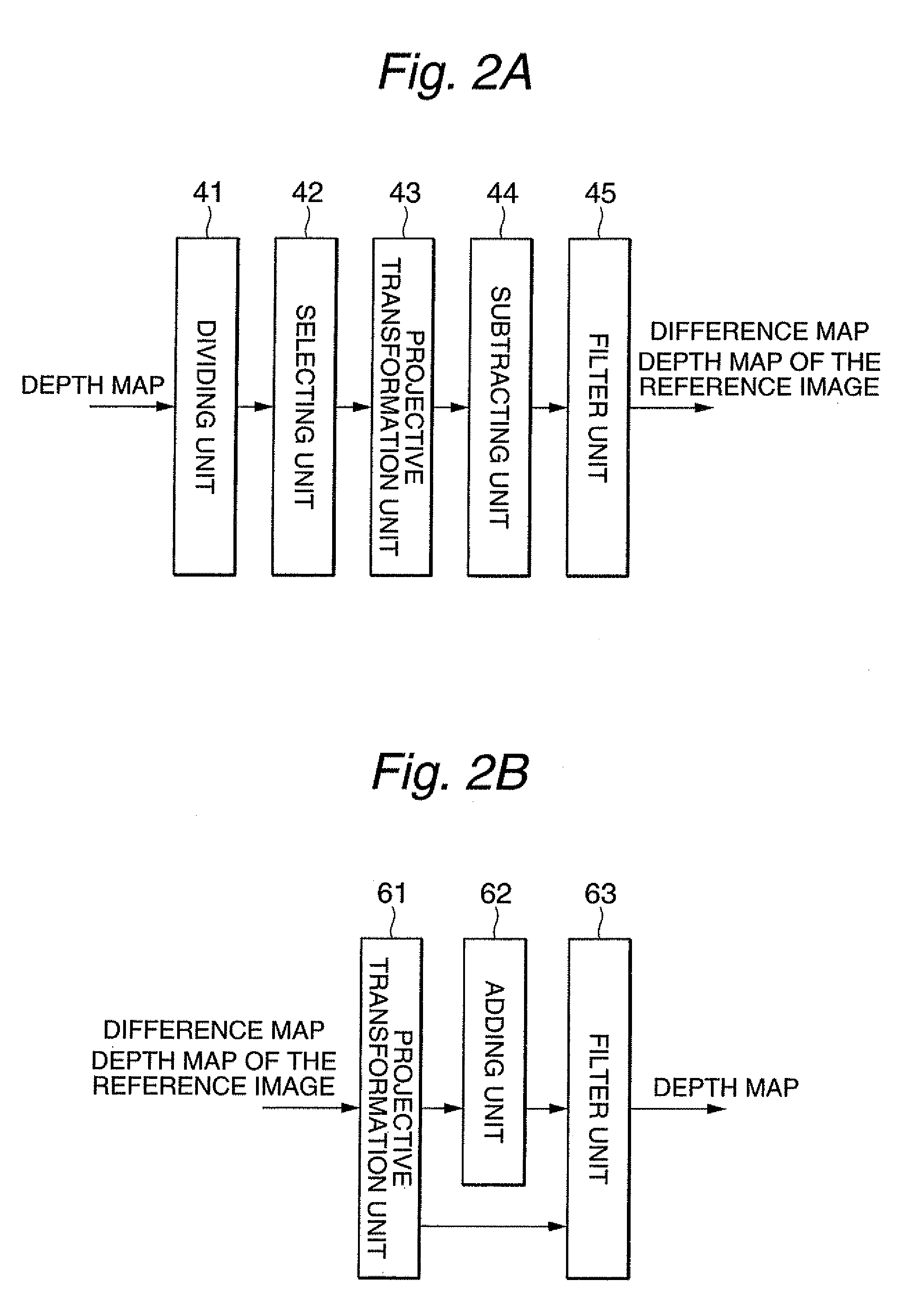
ActiveUS20100254627A1Reduce amount of dataReduce amountImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsDepth map
The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus for compressing image data used in an image generating apparatus for generating a free-viewpoint image. According to the invention, the apparatus has a selecting unit that selects one image as a first image, and defines other images as second images, a projective transformation unit that generates a projected depth map of a second image from a depth map of the first image, a subtracting unit that creates a difference map of the second image, and a storage unit that stores the depth map of the first image and the difference map of the second image. Here, the difference map is a difference between a depth map of the second image and the projected depth map of the second image, and the depth map indicates a depth value of each pixel of a corresponding image.
Owner:KDDI CORP
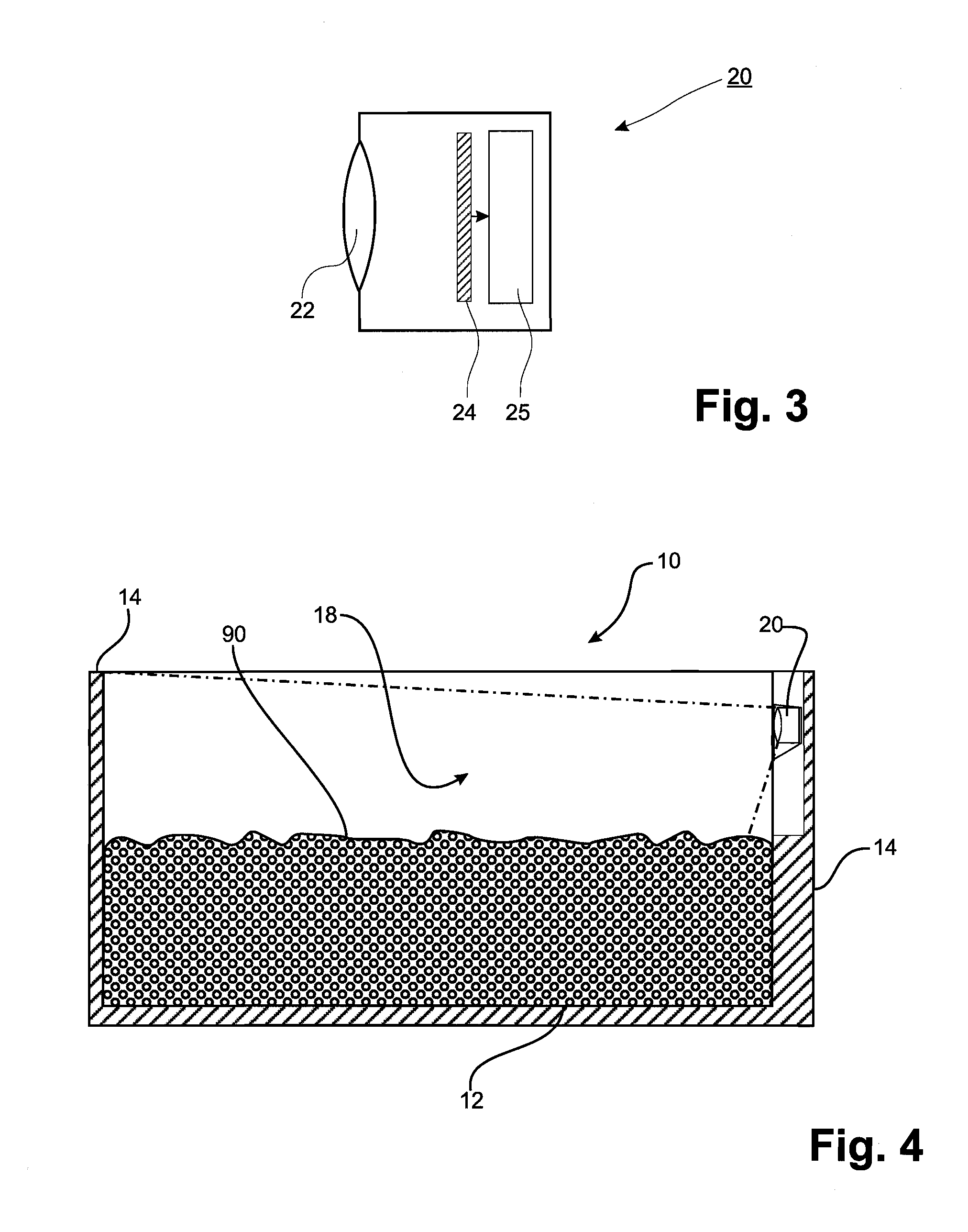
Method for dynamically detecting the fill level of a container, container therefor, and system for dynamically monitoring the fill level of a plurality of containers
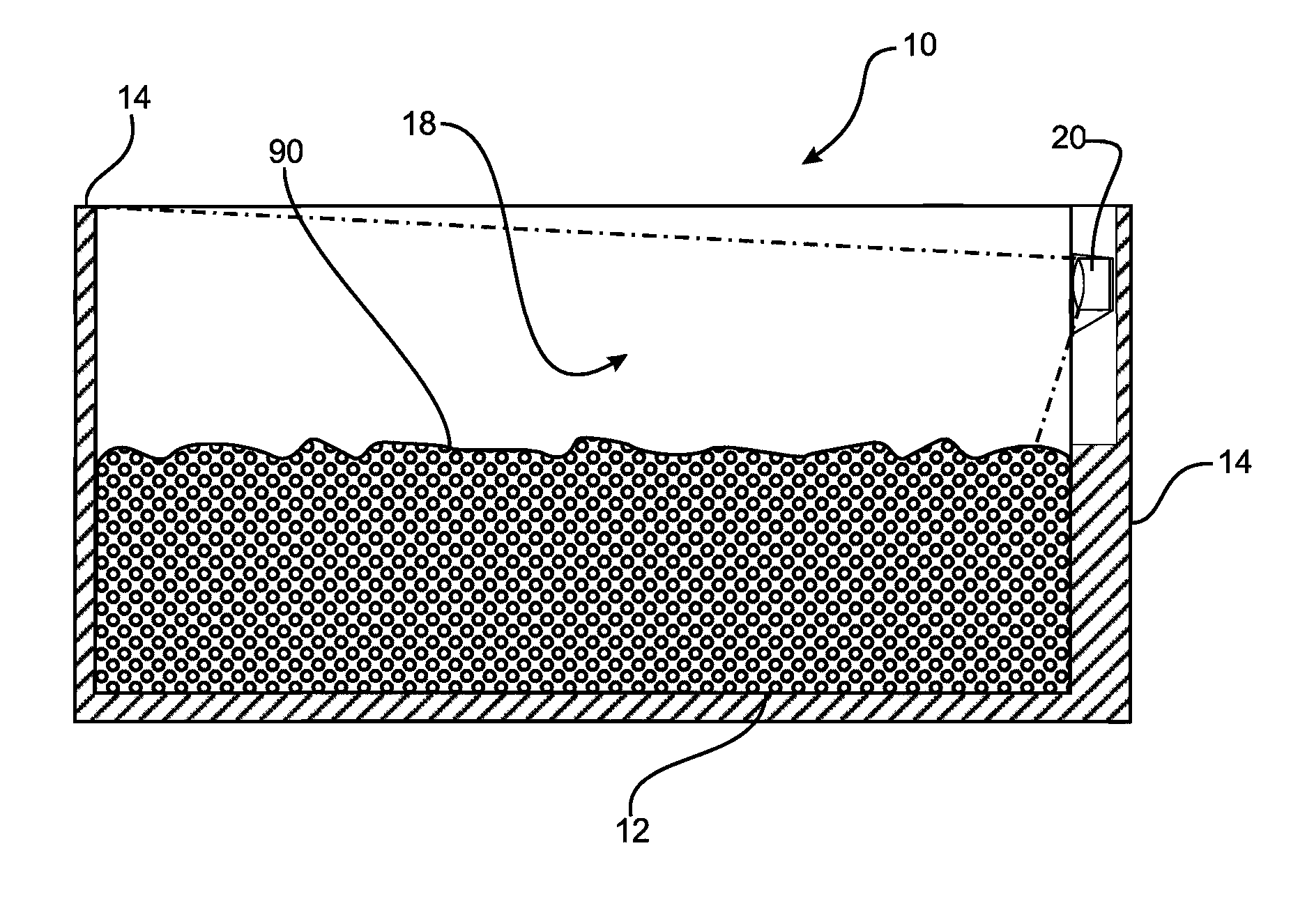
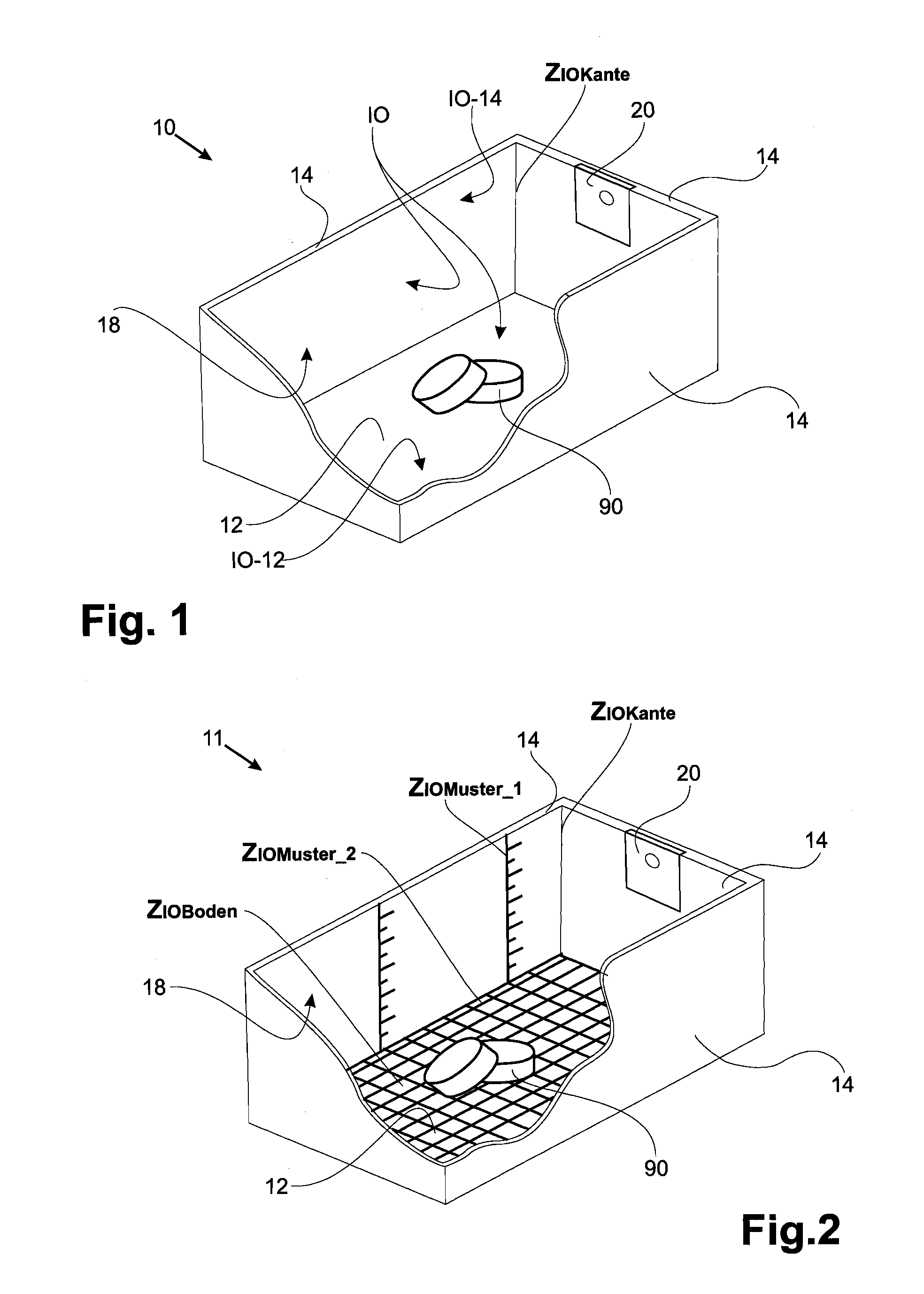
InactiveUS20120314059A1Efficient detectionAccurate measurementImage enhancementImage analysisEMPTY CONTAINER
The application pertains to detecting the fill level of a container for transporting and / or storing objects. This is achieved by determining an estimate of the number of objects in the container with the aid of a value of the container volume occupied by the objects or the already emptied container volume, on the basis of an average object volume of one or of a predetermined number of the objects, as long as the container bottom is covered by objects situated in the container. When a predetermined portion of the container bottom is visible, the objects in the container are counted, by identifying the individual objects on the container bottom. In addition, a container that is particularly suitable for the proposed methods and a system with a plurality of such containers are proposed.
Owner:WUERTH IND SERVICE +1
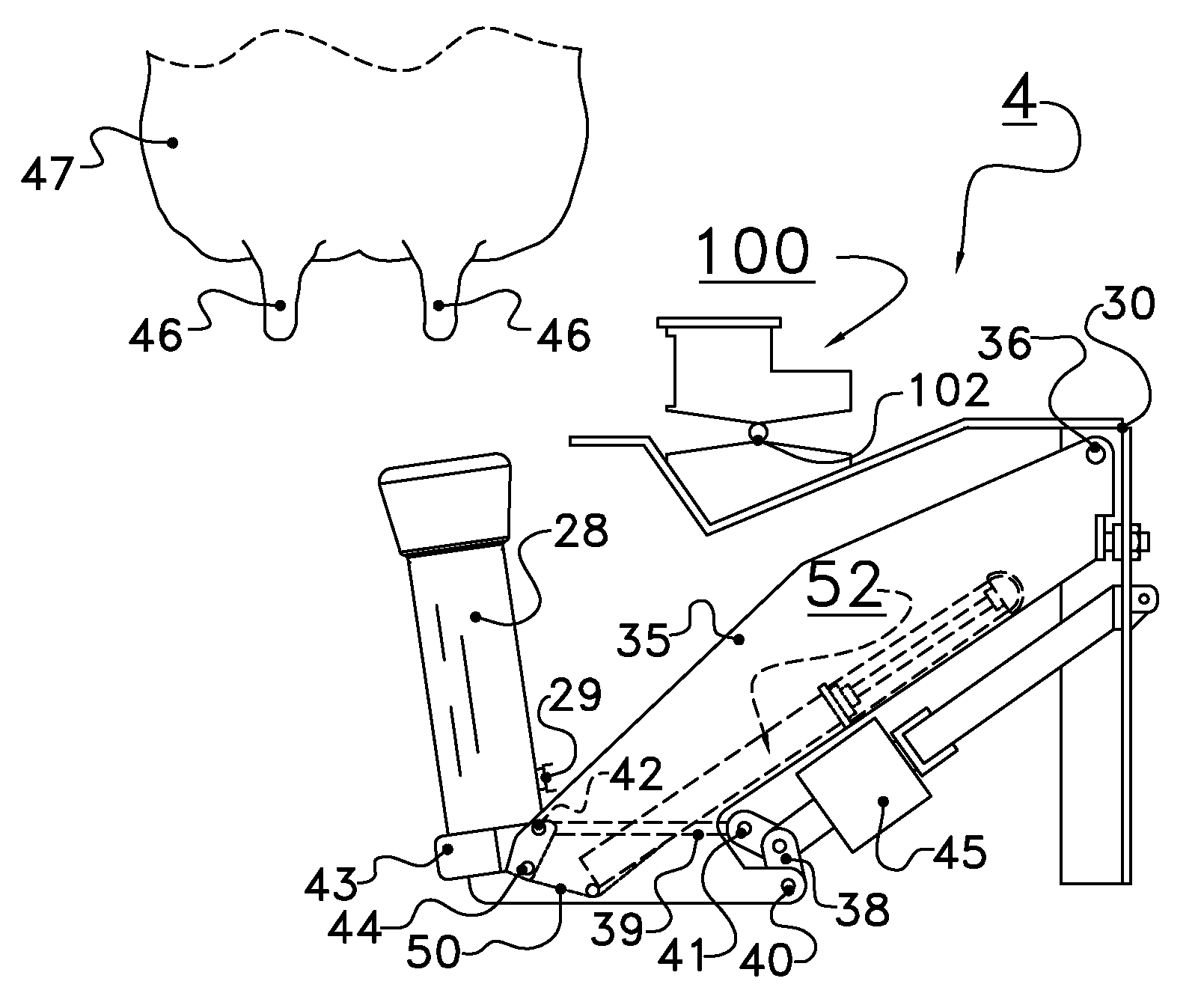
Method of controlling a milking implement, a software program for and an implement performing the method
ActiveUS8286583B2Testing is superfluousOrientation of the teat cup relative to the udder can be improvedCathetersObstetricsMilk cow's
A method of controlling a milking implement for automatically milking a dairy animal with an udder, such as a cow, which milking implement includes a camera and a teat cup. More particularly, the method includes attaching the teat cup to a teat of the udder, followed by producing by the camera an image of at least a part of the udder and of at least a part of the teat cup, making an analysis of the image of the udder with the teat cup, and performing at least one control action by the milking implement, based on the analysis.
Owner:MAASLAND
In-vivo optical imaging method including analysis of dynamic images
ActiveUS20090252682A1Enhance the imageGenerate imageImage analysisDiagnostics using lightAnatomical structuresData set
In-vivo optical molecular imaging methods for producing an image of an animal are described. A time series of image data sets of an optical contrast substance in the animal is acquired using an optical detector Each image data set is obtained at a selected time and has the same plurality of pixels, with each pixel having an associated value. The image data sets are analyzed to identify a plurality of distinctive time courses, and respective pixel sets are determined from the plurality of pixels which correspond to each of the time courses. In one embodiment, each pixel set is associated with an identified anatomical or other structure, and an anatomical image map of the animal can be generated which includes one or more of the anatomical structures.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method of controlling a milking implement, a software program for and an implement performing the method
ActiveUS20110048329A1Testing is superfluousOrientation of the teat cup relative to the udder can be improvedCathetersComputer scienceSoftware
Method of controlling a milking implement for automatically milking a dairy animal with an udder, such as a cow, which milking implement comprises a camera and a teat cup, which method comprises the following steps:attaching the teat cup to a teat of the udder, followed byproducing by means of the camera an image of at least a part of the udder and of at least a part of the teat cup,making an analysis of the image of the udder with the teat cup, and performing at least one control action by means of the milking implement, based on the analysis.
Owner:MAASLAND
Image generating device, image generating method, and non-transitory information storage medium
Provided is an image generating device for generating an image of an object including a plurality of elements connected to one another. The image generating device includes: a calculating section for iteratively calculating a motion of each element of the plurality of elements based on a physical constraint condition of the each element with respect to another connected element; a parent-child information acquiring section for acquiring parent-child information corresponding to a connection between the each element and the another element based on information indicating an element having a predetermined relationship with another object; a correcting section for correcting a position of a child element with respect to a parent element based on the parent-child information and the motion of the each element; and an image generating section for generating information on the image of the object based on the corrected position of the each element.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Assistant monitor apparatus and the method of controlling the same
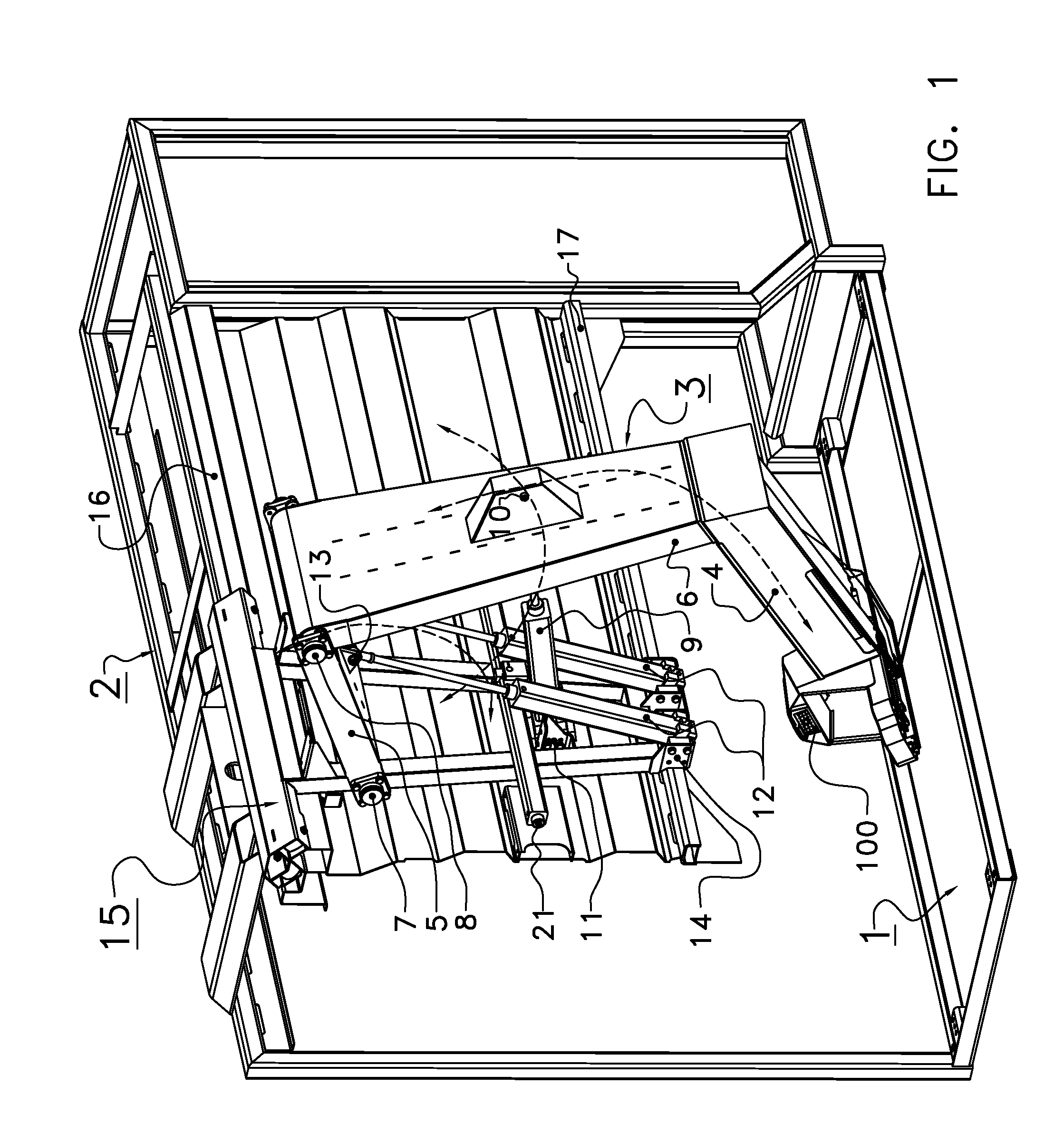
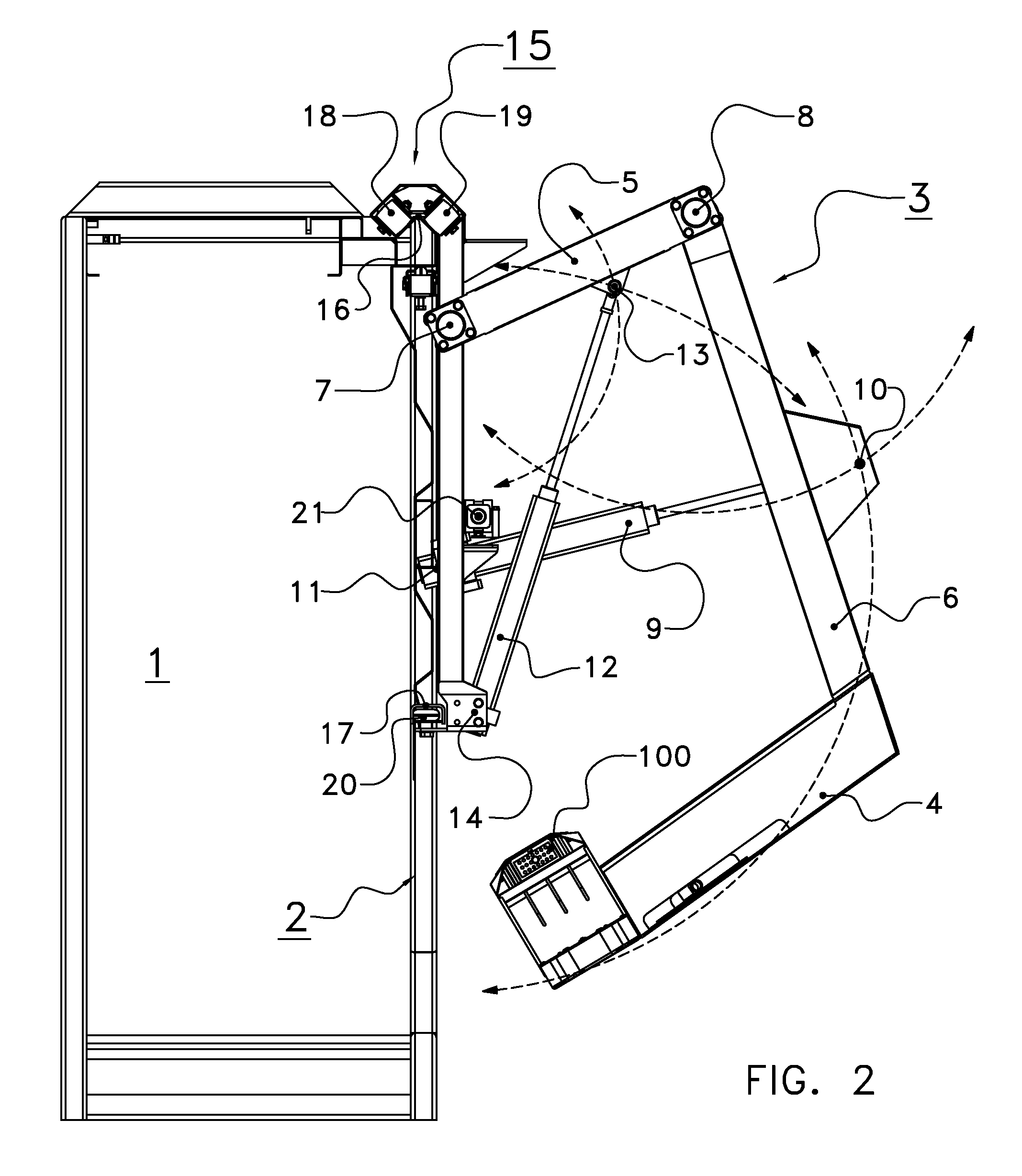
ActiveUS7188014B1Generate imageEnsure safetyDigital data processing detailsPower-operated mechanismDriver/operatorControl signal
The present invention relates to an assistant monitor method for vehicle, comprising steps of: projecting a light beam to illuminate objects surrounding a transportation means; receiving the reflected light of the light beam so as to generate an electric image signal accordingly; generating a status signal by detecting and sensing the status of the transportation means; processing the status signal so as to correspondingly generate a control signal; and adjusting the projecting angle of the light beam and the receiving angle to receive the reflected light beam according to the control signal. Moreover, according to the method, the present invention also provides an assistant monitor apparatus of for vehicle to implement the foregoing method. By means of the aforesaid apparatus provided in the present invention, the projecting direction of the light projector and a sensing angle of the image sensor for receiving the reflected light can be controlled to reduce blind spots of a rear mirror of the transportation means while avoiding the whitening effect to be generated on the rear mirror, such that safety of the driver driving the transportation mean along with the ambient vehicles and pedestrians can be ensured.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and Apparatus for Non-line-of-sight Imaging
A system and method for obtaining an image of an object out of line of sight, the method comprising directing a chaotic light beam at a first area containing the object; measuring the light from the chaotic light beam at a plurality of instances in time; using a photon detector, detecting light from a second area over a plurality of instances in time; the photon detector not being in the line of sight with the first area but in line-of-sight with a second area; using a processor, correlating the information received by the photon detector with the measurement of light from the chaotic light beam at specific instances in time; and producing an image of the object. The system for imaging information comprising a spatial receiver, a chaotic photon light source for producing light; the light comprising a first beam adapted to be directed at a first predetermined area containing an object, and a second beam which is received by the spatial receiver and measured at specific intervals in time; at least one processor operatively connected to the spatial receiver, the spatial receiver operating to transmit spatial information correlated to specific intervals of time to the processor; and a first receiver operatively connected to the at least one processor and operative to detect the influence of the object on the first portion of the light beam; the first receiver not being in the line of sight with the first predetermined area and adapted to detect light from a second predetermined area spaced from and coplanar with the first predetermined area, the at least one processor operating to correlate the outputs of the first receiver with spatial information derived from the spatial receiver at correlating intervals of time to create an image of the object.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Electromagnetic Radiation Detector
InactiveUS20100321501A1Easy to changeLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInfraredRainbow
A device implemented with the present invention senses and converts unseeable electromagnetic (EM) energy such as high frequency radio, infrared, ultraviolet, etc. to an image in the human visual spectrum (red to violet—i.e. the rainbow). The size of the image and quality of the image is improved by rotating or oscillating the sensors in order to scan a broader array of electrometric energy.The electromagnetic radiation detector (EMR) comprises: a sensor circuit that generates EMR signals of the scanned electromagnetic energy of the desired band of electromagnetic spectrum. The EMR detector further comprises processors that convert the EMR signals into image data that is used to generate the visible image of the scanned electromagnetic energy; and a motor that allows the sensor circuit to scan the electromagnetic energy. The sensor circuit may be a plug-in PCB module to allow ready selection of the desired frequency band.
Owner:ARNDT DONALD J
Method for dynamically detecting the fill level of a container, container therefor, and system for dynamically monitoring the fill level of a plurality of containers
InactiveUS9019367B2Efficient detectionAccurate measurementImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringEMPTY CONTAINER
The application pertains to detecting the fill level of a container for transporting and / or storing objects. This is achieved by determining an estimate of the number of objects in the container with the aid of a value of the container volume occupied by the objects or the already emptied container volume, on the basis of an average object volume of one or of a predetermined number of the objects, as long as the container bottom is covered by objects situated in the container. When a predetermined portion of the container bottom is visible, the objects in the container are counted, by identifying the individual objects on the container bottom. In addition, a container that is particularly suitable for the proposed methods and a system with a plurality of such containers are proposed.
Owner:WUERTH IND SERVICE +1
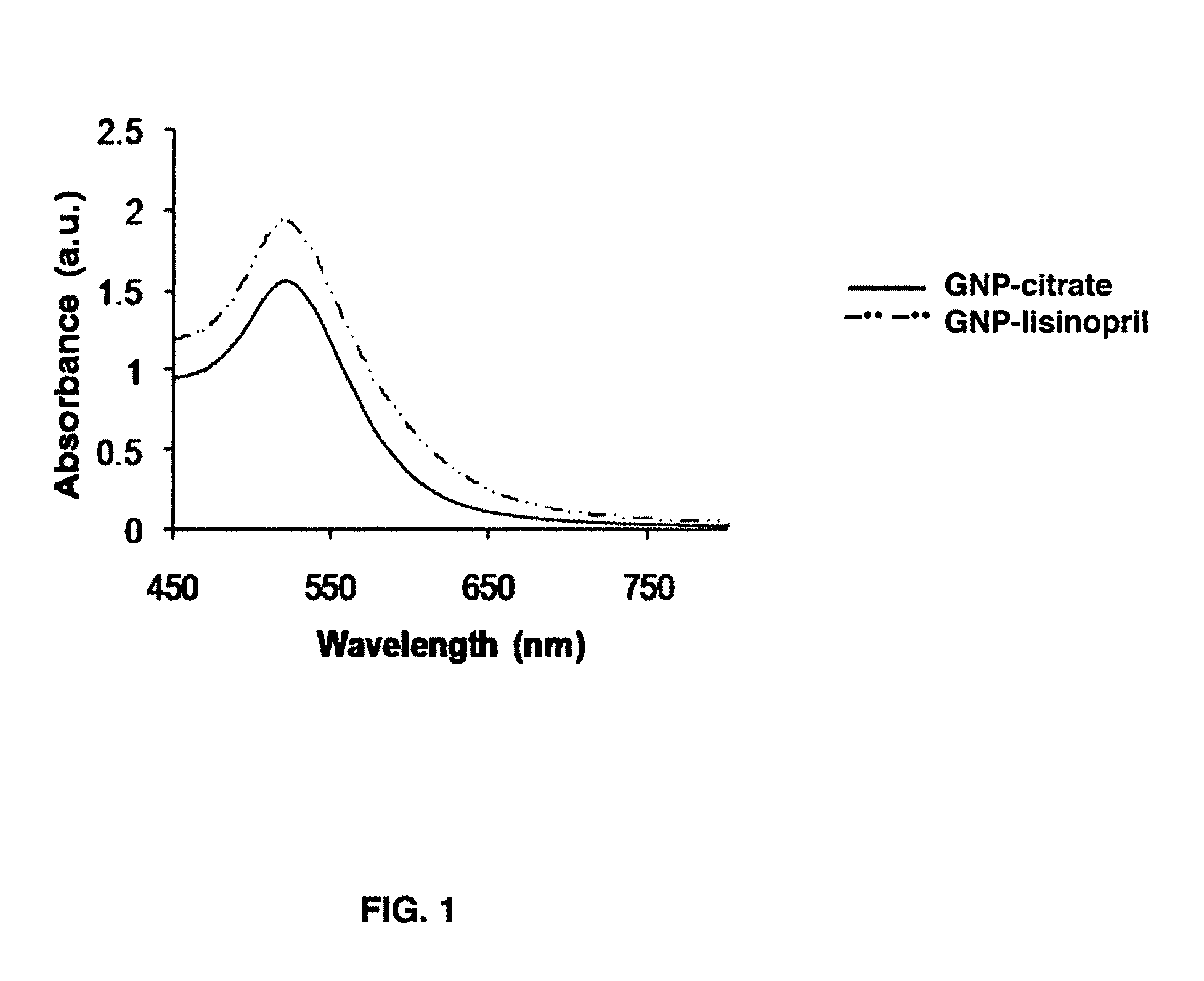
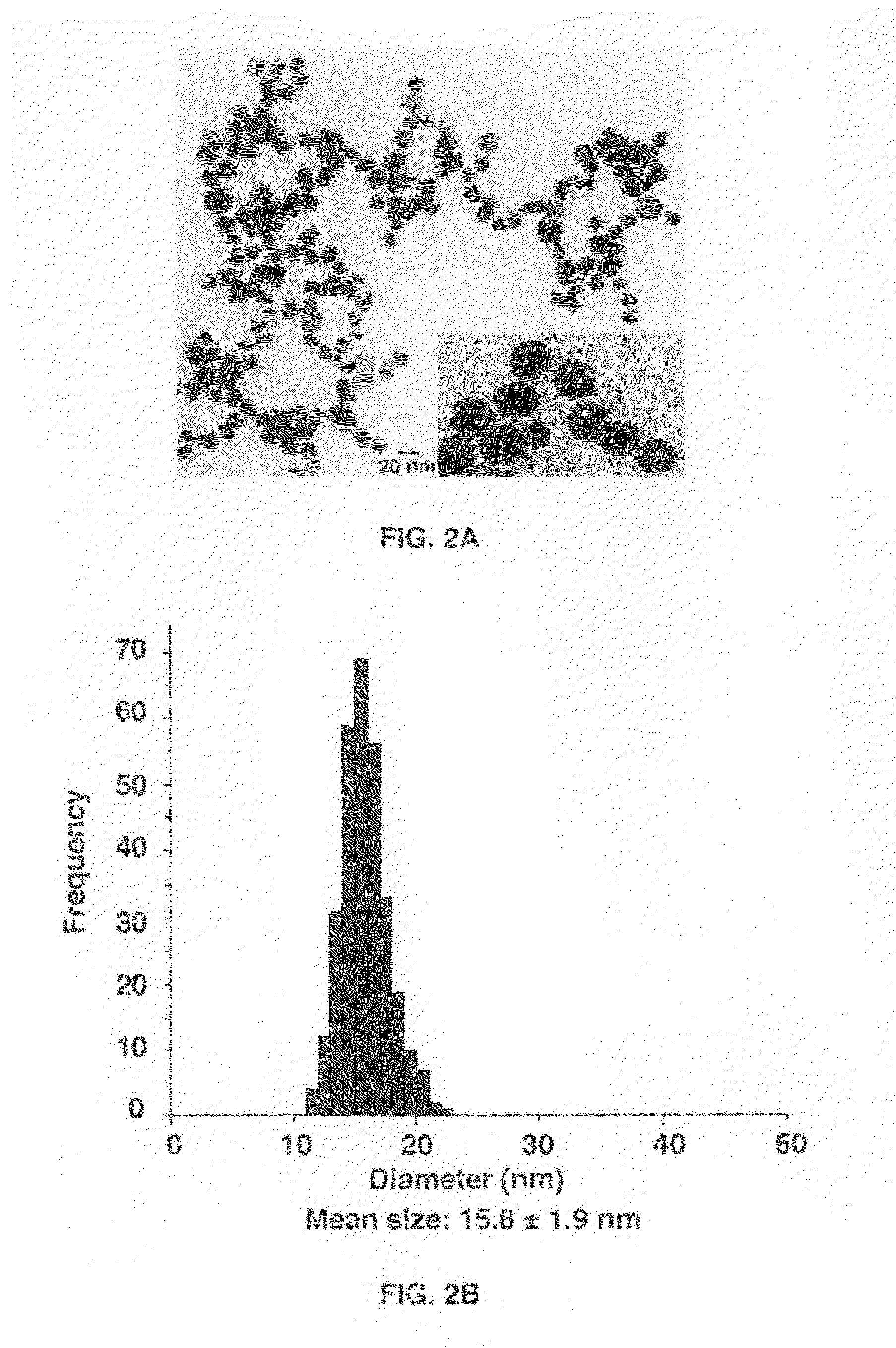
Gold nanoparticle imaging agents and uses thereof
Overexpression of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) has been associated with a number of pathophysiologies, including those associated with cancer and the cardiovascular system. Thus, targeted imaging of ACE is of crucial importance for monitoring tissue ACE activity as well as treatment efficacy. To this end, lisinopril-coated gold nanoparticles were prepared to provide a new type of probe for targeted molecular imaging of ACE by tuned K-edge computed tomography (CT) imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
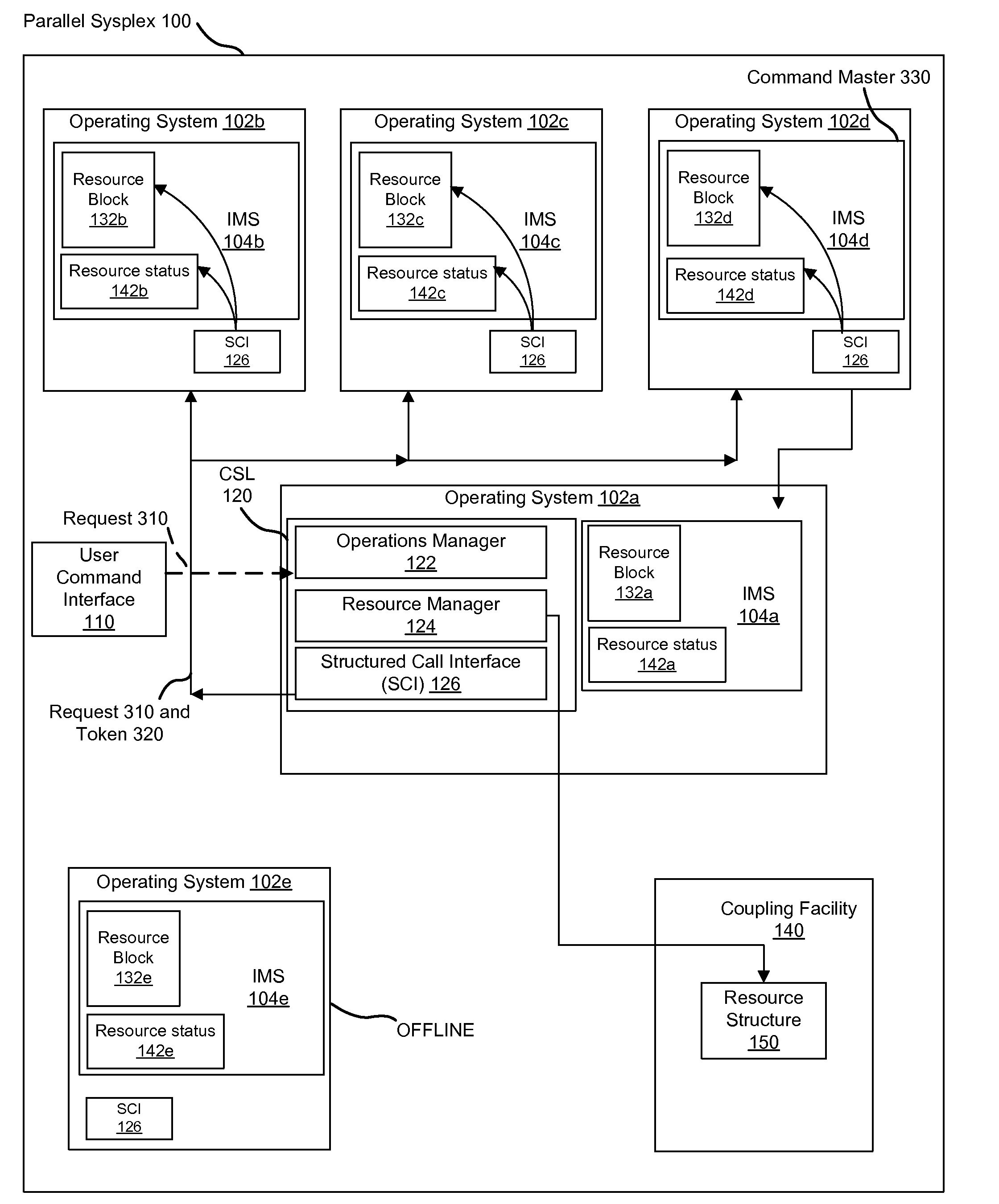
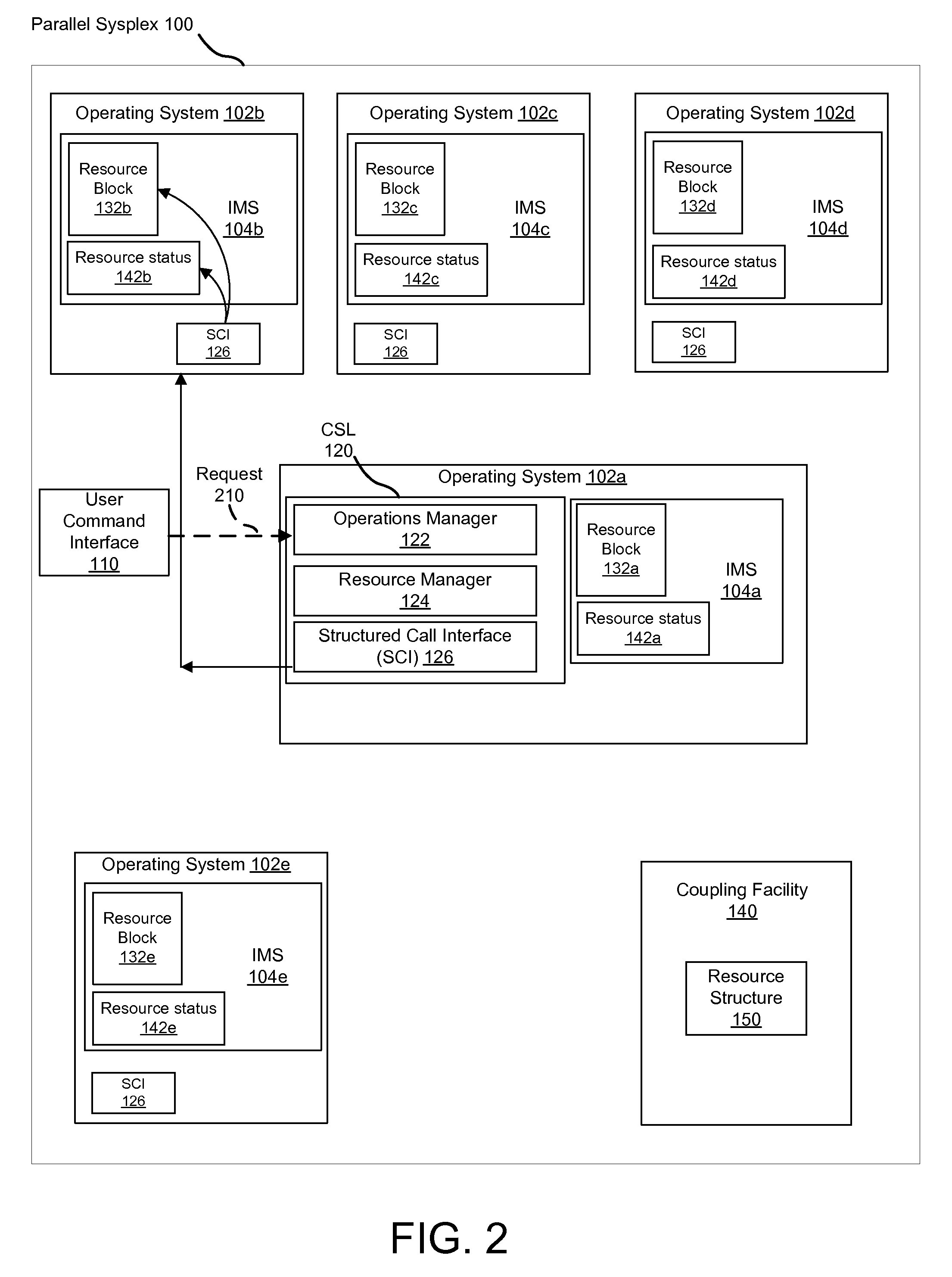
Apparatus, system, and method for autonomously maintaining a single system image in a parallel systems complex
InactiveUS20080307429A1Generate imageBootstrappingSoftware deploymentShared mediumResource information
An apparatus, system, and method for autonomously maintaining a single system image in a parallel systems complex. A computer program product causes the relevant systems in a parallel systems complex to receive requests with a global scope from a user. The request is sent to each IMS system in the sysplex, and each IMS system applies the resource information and logs the resource information for recovery. The request is written to a shared medium which IMS sysplex members can access. When an IMS member is brought online, the IMS member restores status information first from local recovery logs. The IMS member then checks the information against the global medium to determine if requests were issued while the IMS was offline. If so, the IMS inherits the information in the global medium before processing work. An IMS added into the sysplex applies the information from the global medium before processing work.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Generating an erosion image utilizing parallel pixel processing
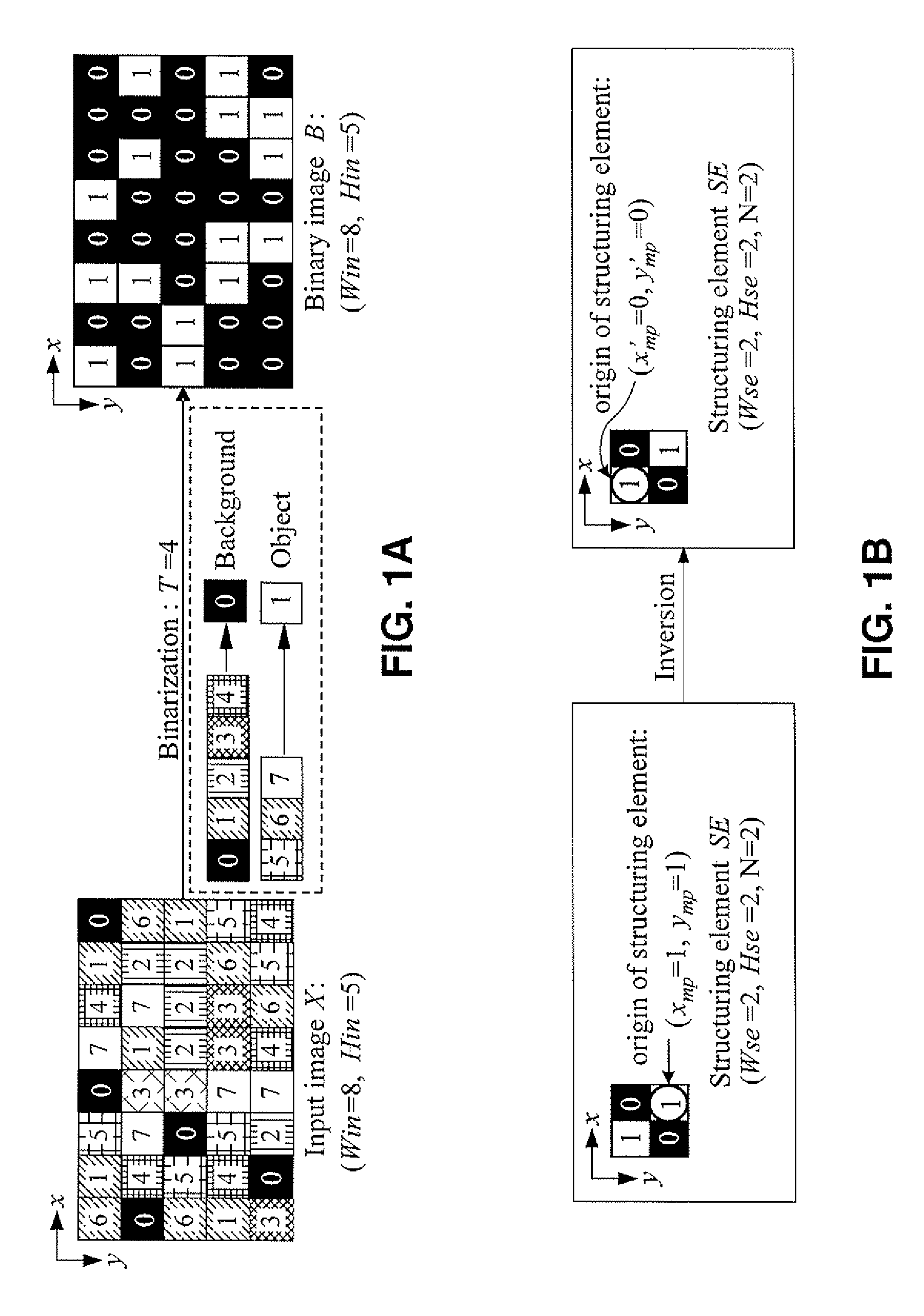
InactiveUS20100177980A1Generate imageImage enhancementImage analysisStructuring elementComputer vision
An erosion image is generated from an original digital image utilizing a processing image (b) and a target image (T), where each pixel in the target image is processed in parallel. The process entails, for each target pixel, i) determining coordinate values for the target pixel, ii) determining a surrounding pixel area for the target pixel, iii) and processing each pixel in the surrounding pixel area to determine whether or not to updated the value of the target pixel. In processing each surrounding pixel, a determination is made whether the pixel has a value of 1. If not, then the next surrounding pixel is processed. If so, then a determination is made which pixel element of a structuring element overlays the target pixel, and whether that SE pixel has a value of 1. If so, then the value of the target pixel is updated. If not, then the next pixel in the surrounding pixel area is processed. Once the target pixel has been updated a set number of times to a predetermined value (e.g., 2), the processing of the remaining surrounding pixels is terminated. After all target pixels have been processed, an output image is obtained by setting target pixels having a value of 2 to a binary value of 1, and setting the other pixels to a binary value of 0. The resultant output image is an erosion image that is then output.
Owner:CANON KK
Device and method for recording and representing images of a test object
ActiveUS20070179382A1Reduced light stressReduce expenditureAudiometeringRadiation diagnosticsFunctional imagingTest object
It is the object of an arrangement and a method for the recording and reproduction of images of an object to be examined to record the images of the object to be examined with reduced light stress and lower expenditure on adjustments and to generate secondary images which are substantially independent from brightness, are highly suitable for spectrometric studies of metabolism and microcirculation at the eye as well as for functional imaging, and can be adapted to the medical inquiry and make it possible to provide complex secondary image information while also enabling simple, practicable and extremely economical constructional variants. An illumination system contains at least one beam path with a device for simultaneous illumination of the object to be examined by at least one reference wavelength region and at least one information wavelength region, each of which is adapted, respectively, to a color channel of an image-generating recording system. While the at least one reference wavelength region is at least approximately invariant with respect to medically relevant information, the at least one information wavelength region is provided for detecting the medically relevant information. The method according to the invention combines the image values of evaluation windows or individual image points of simultaneously recorded images to form secondary images and image sequences while generating spatially-resolved dynamic characteristic values which are combined to form functional images.
Owner:IMEDOS INTELLIGENTE OPTISCHE SYST DER MEDIZIN & MESSTECHNIK GMBH
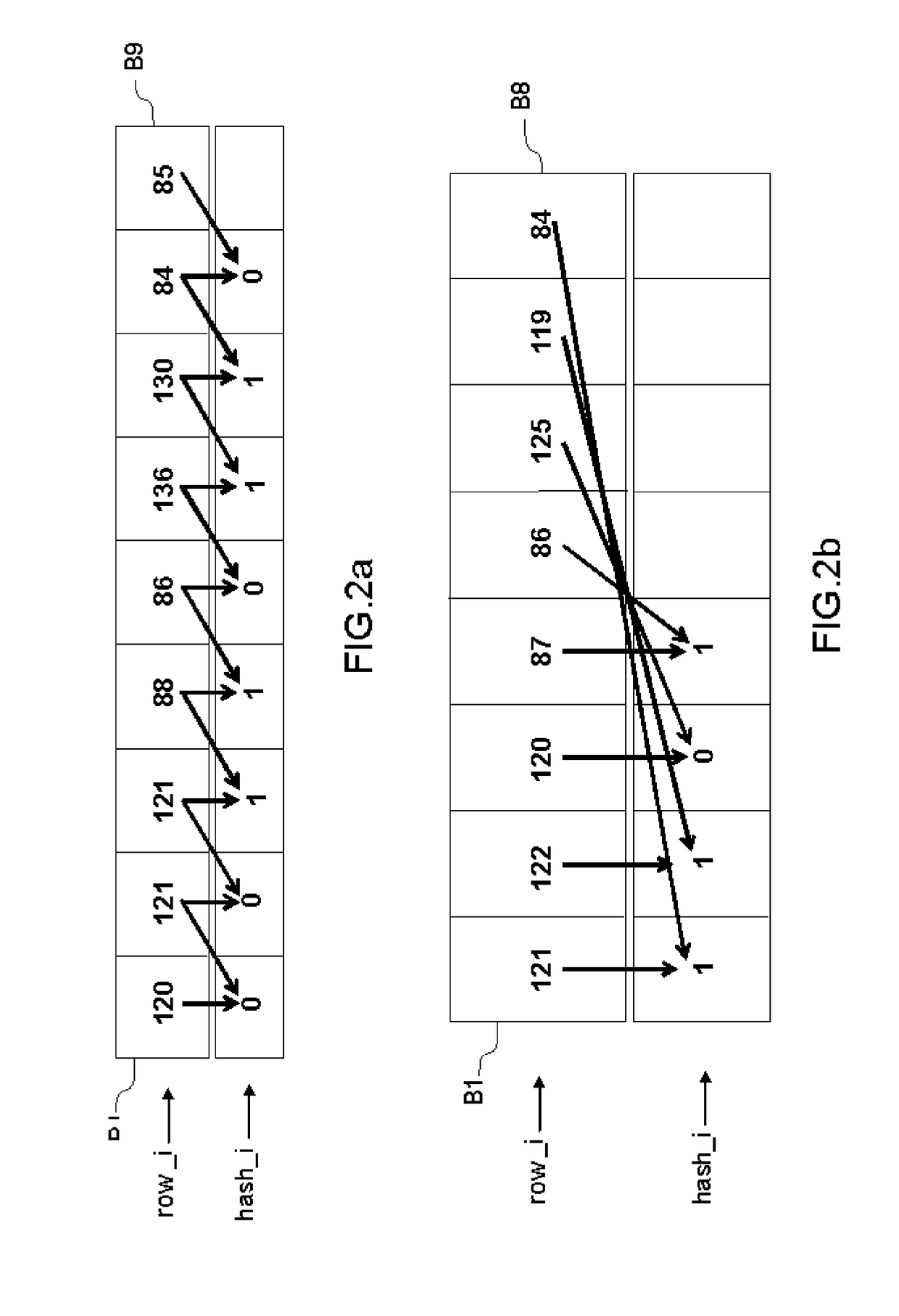
Image processing apparatus
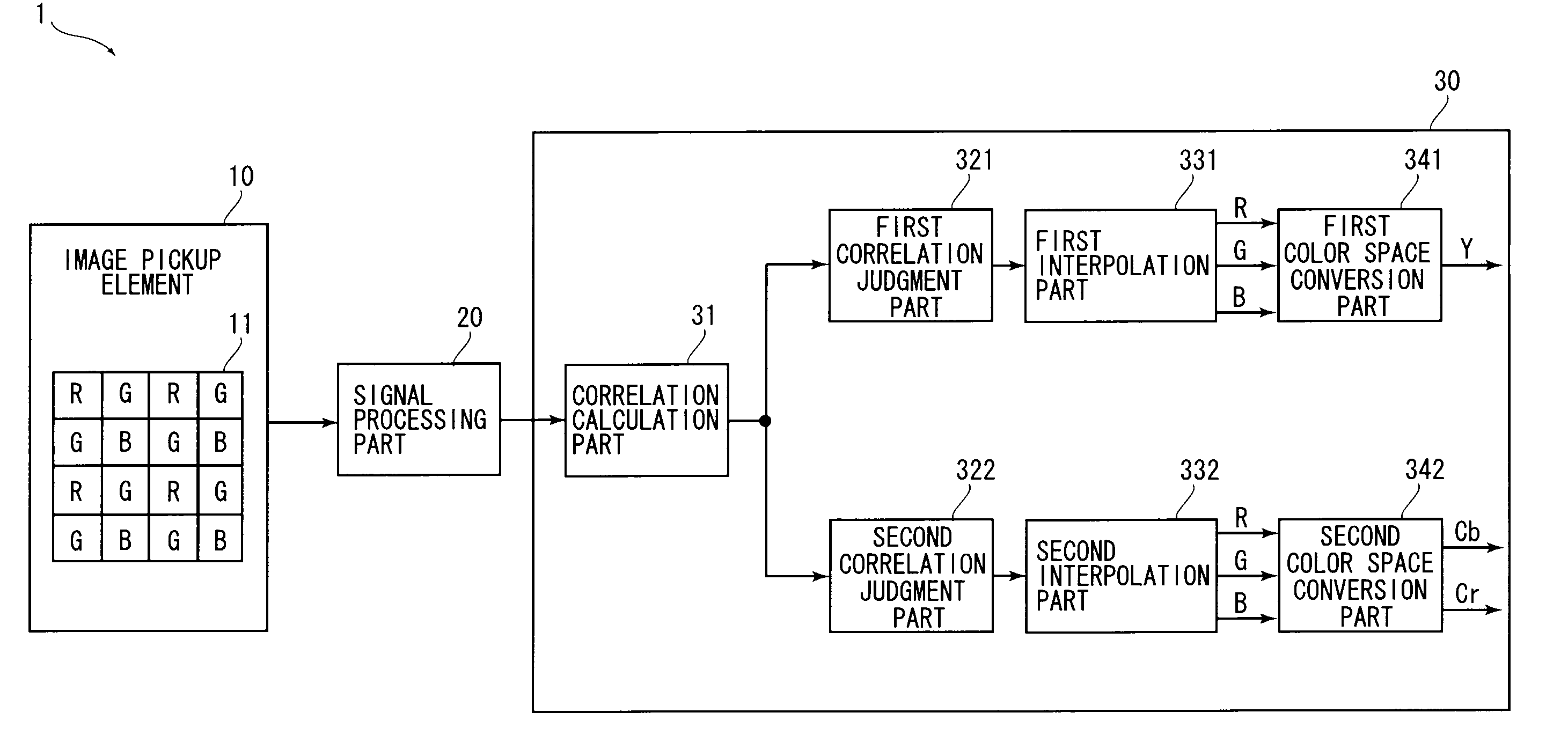
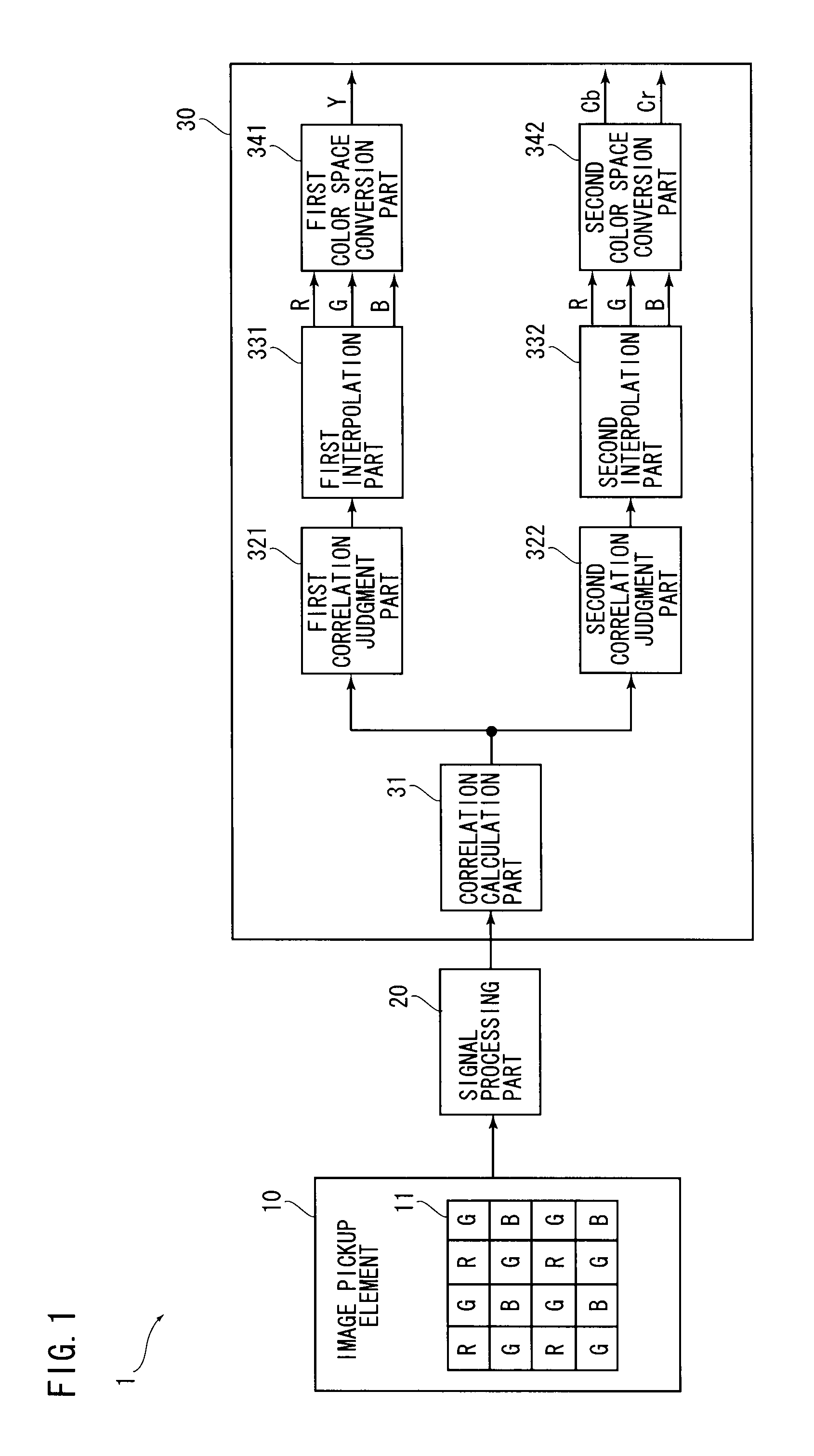
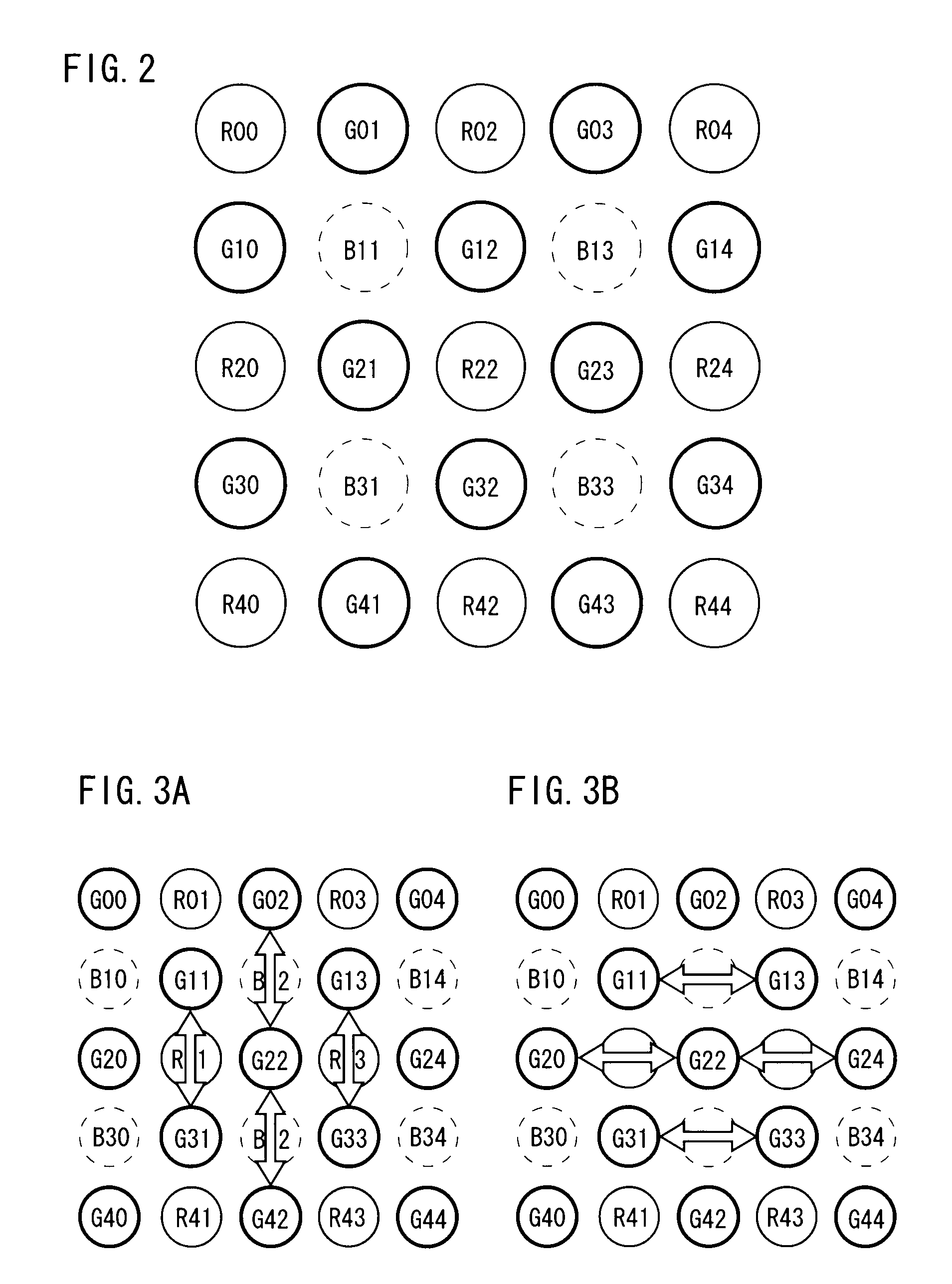
InactiveUS20090060389A1Suppress color noise componentAvoid lostCharacter and pattern recognitionSolid-state device signal generatorsImaging processingLightness
From an image pickup element, pixel signals of Bayer array are outputted. A correlation calculation part calculates correlation values with respect to a specified pixel in vertical and horizontal directions. A first interpolation part performs a pixel interpolation process while evaluating the correlation highly. A second interpolation part performs a pixel interpolation process while evaluating the correlation relatively low. A complete signal of RGB outputted from the first interpolation part is converted into a luminance signal in a first color space conversion part, and a complete signal of RGB outputted from the second interpolation part is converted into a color difference signal in a second color space conversion part.
Owner:MEGACHIPS
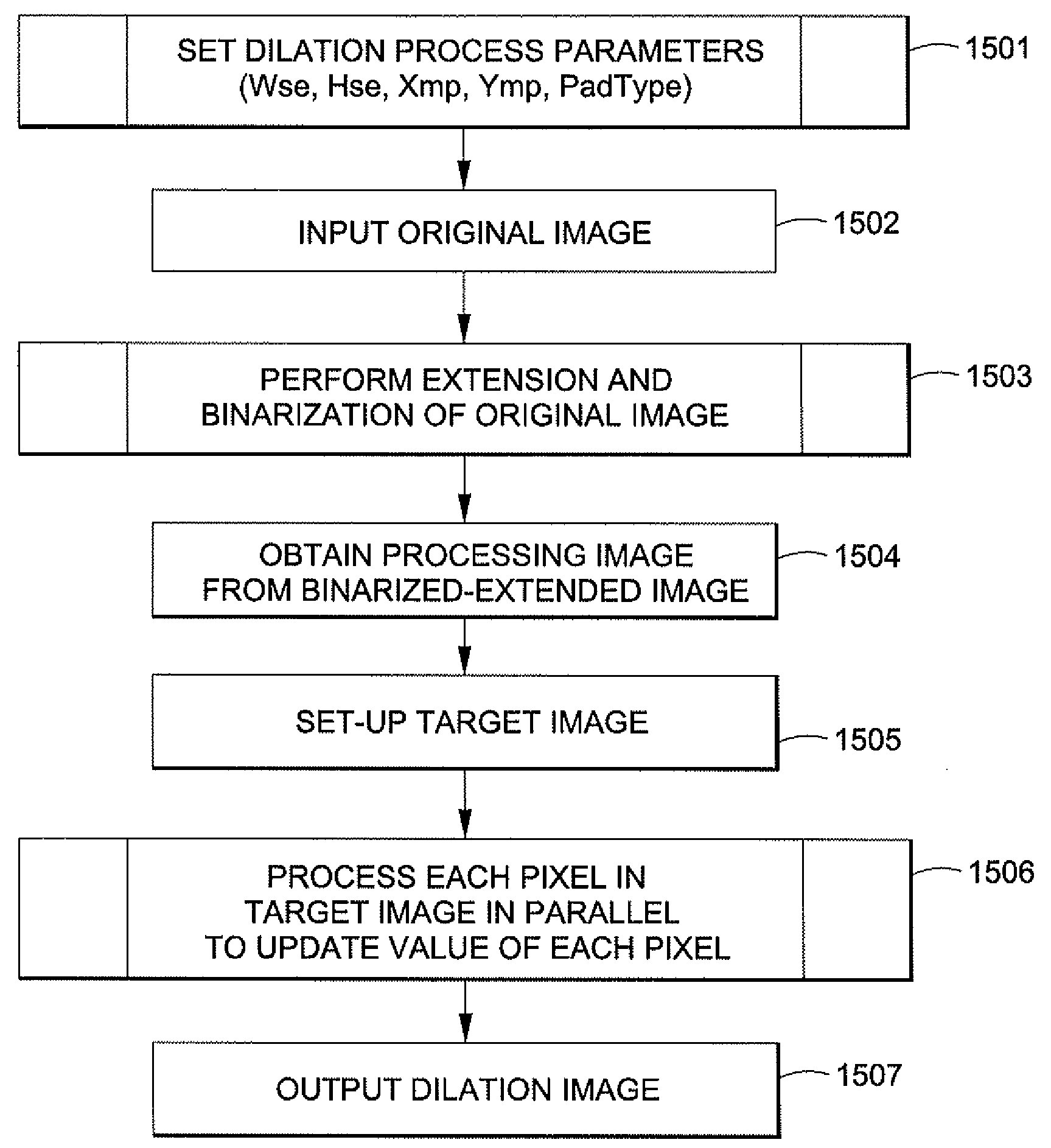
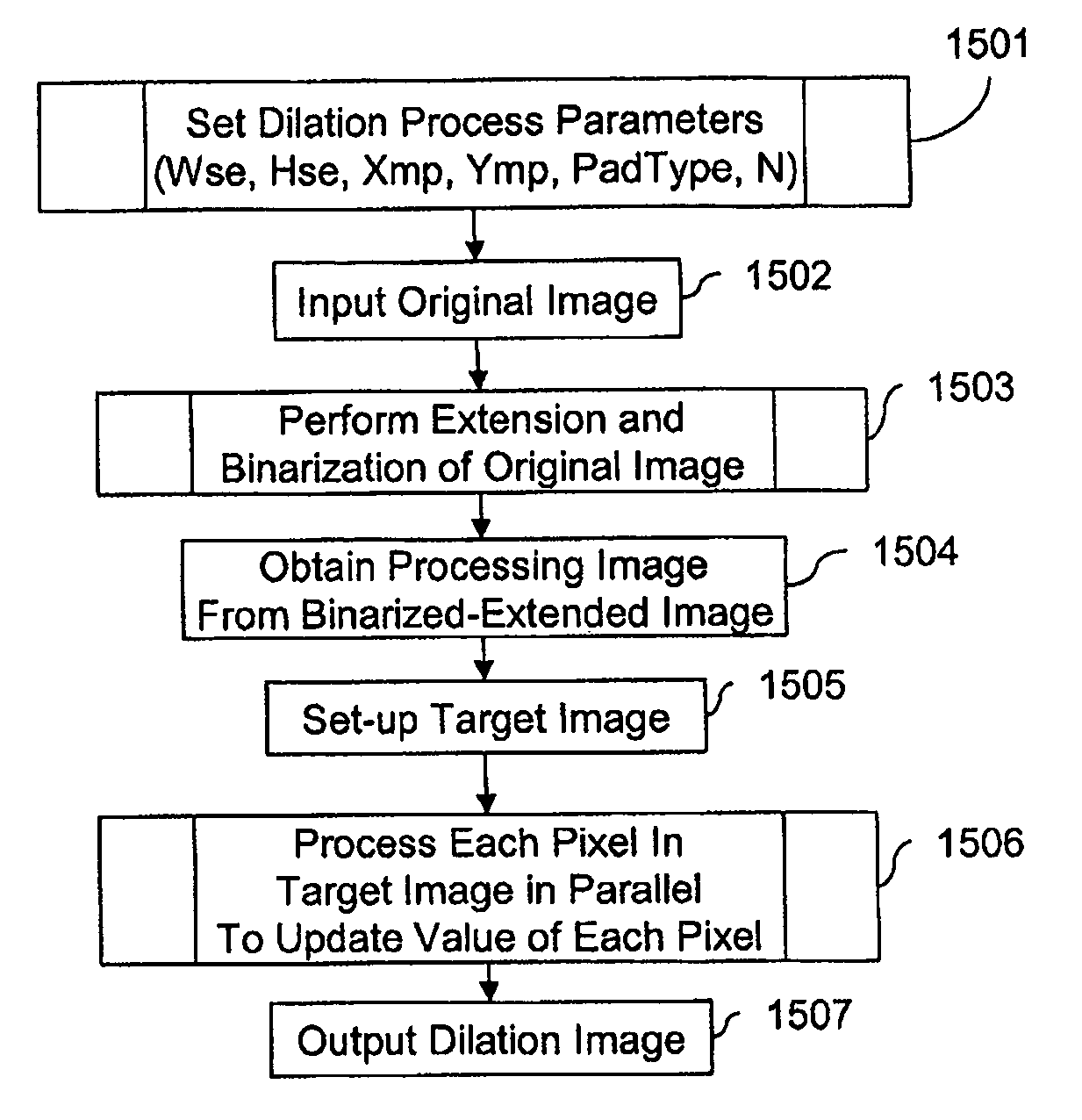
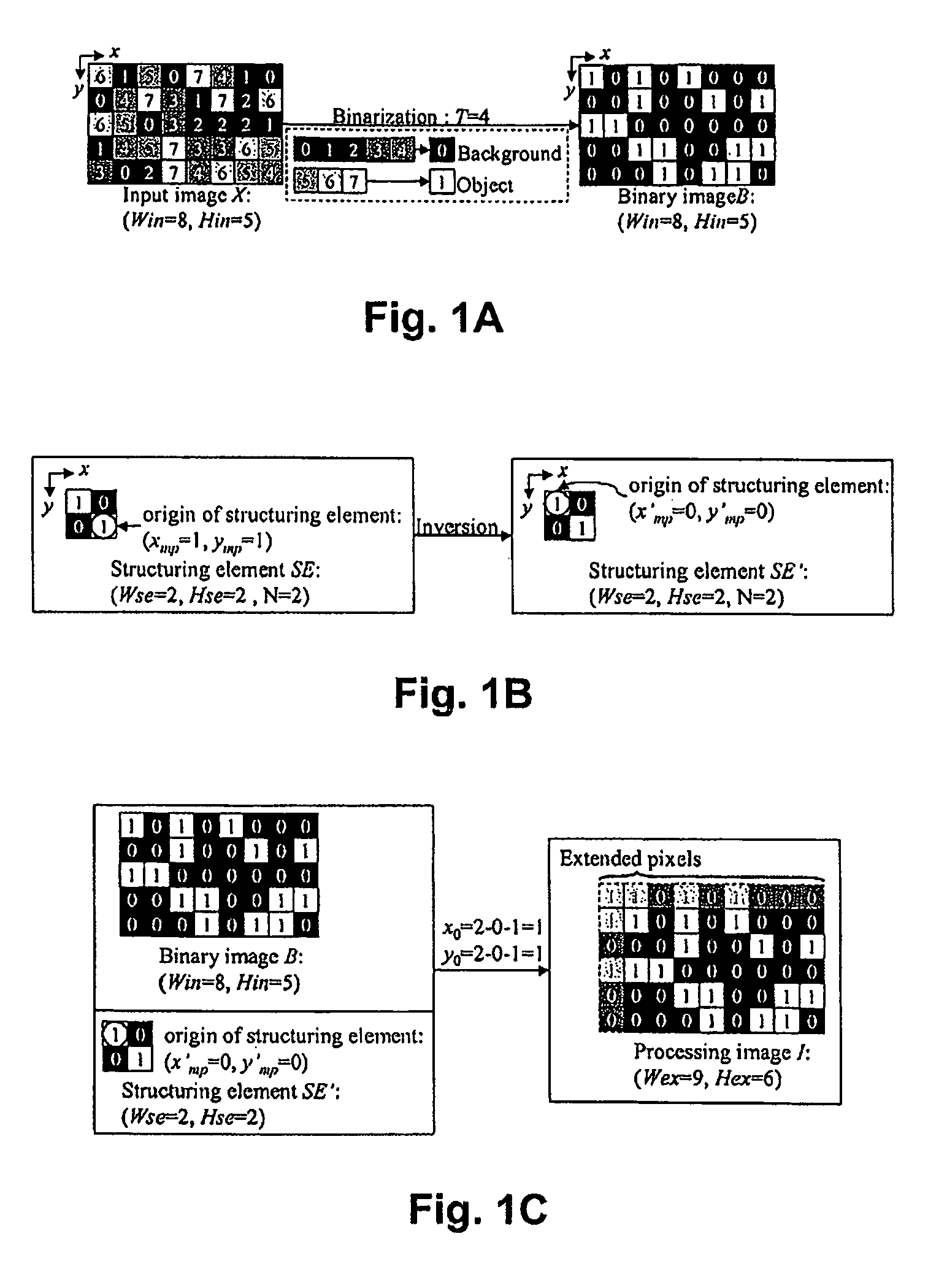
Generating a dilation image utilizing parallel pixel processing
A dilation image is generated from an original digital image utilizing a processing image (b) and a target image (T), where each pixel in the target image is processed in parallel. The process entails, for each target pixel, i) determining coordinate values for the target pixel, ii) determining a surrounding pixel area for the target pixel, iii) and processing each pixel in the surrounding pixel area to determine whether or not to updated the value of the target pixel. In processing each surrounding pixel, a determination is made whether the pixel has a value of 1. If not, then the next surrounding pixel is processed. If so, then a determination is made which pixel element of the structuring element overlays the target pixel, and whether that pixel has a value of 1. If so, then the value of the target pixel is updated. If not, then the next pixel in the surrounding pixel area is processed. Once the target pixel has been updated one time, the processing of the remaining surrounding pixels is terminates. If processing of all surrounding pixels results in no update to the target pixel, then the target pixel is not updated. After all target pixels have been processed, the resultant image is output as the dilation image.
Owner:CANON KK
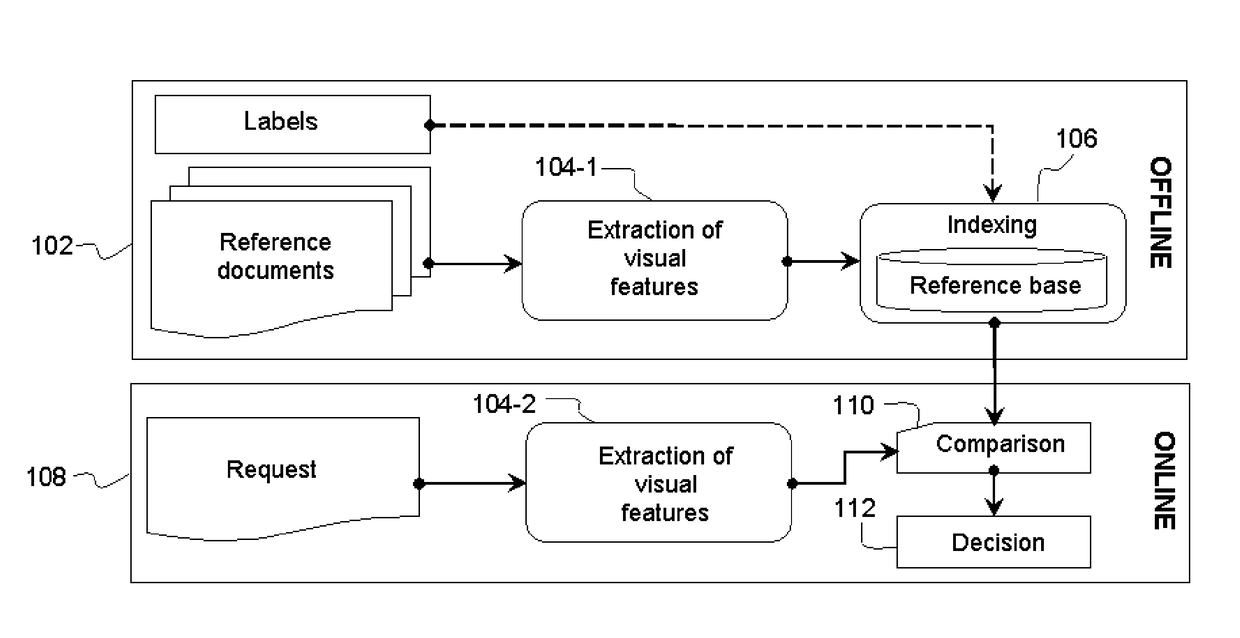
Method and device for detecting copies in a stream of visual data
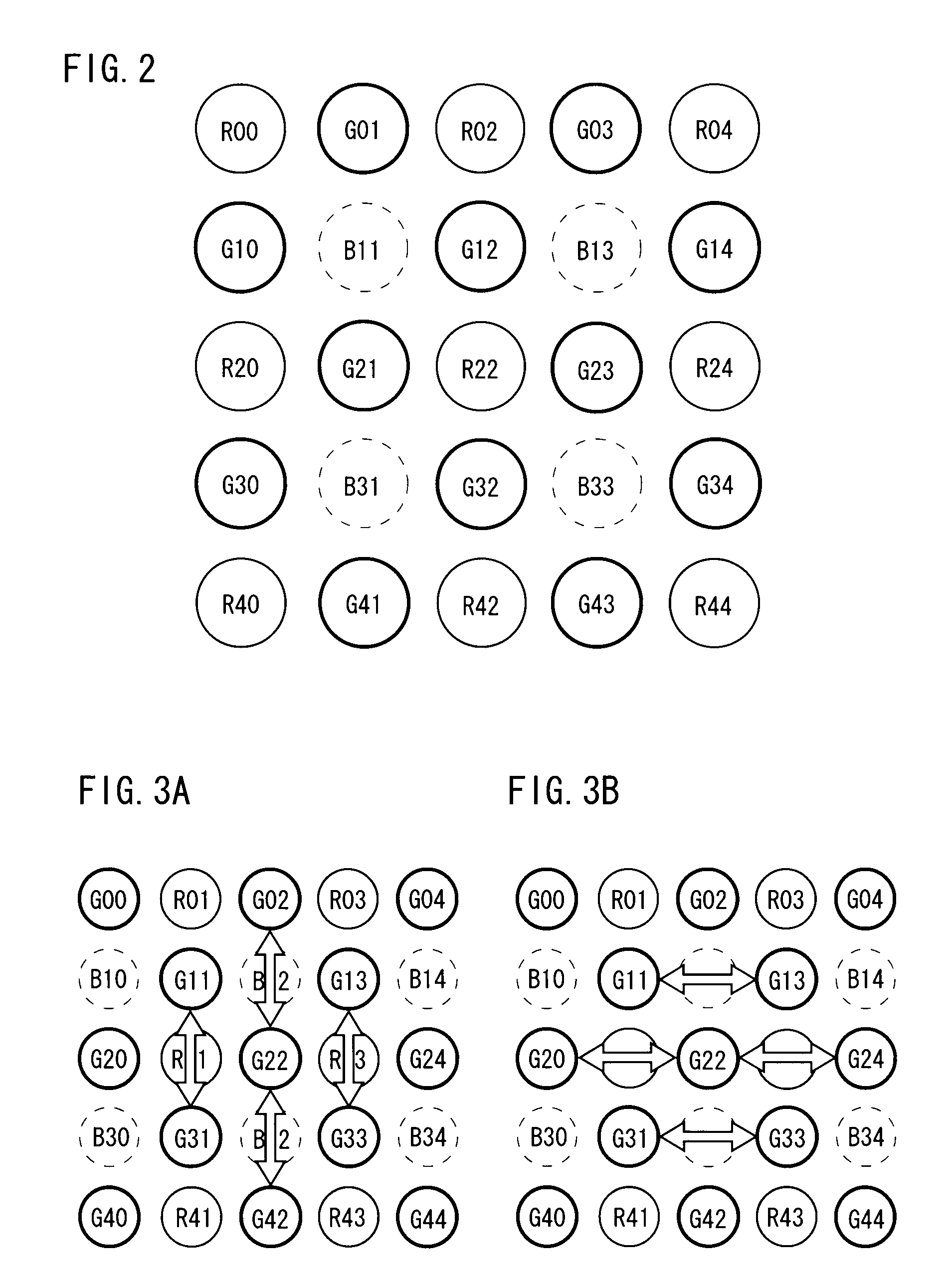
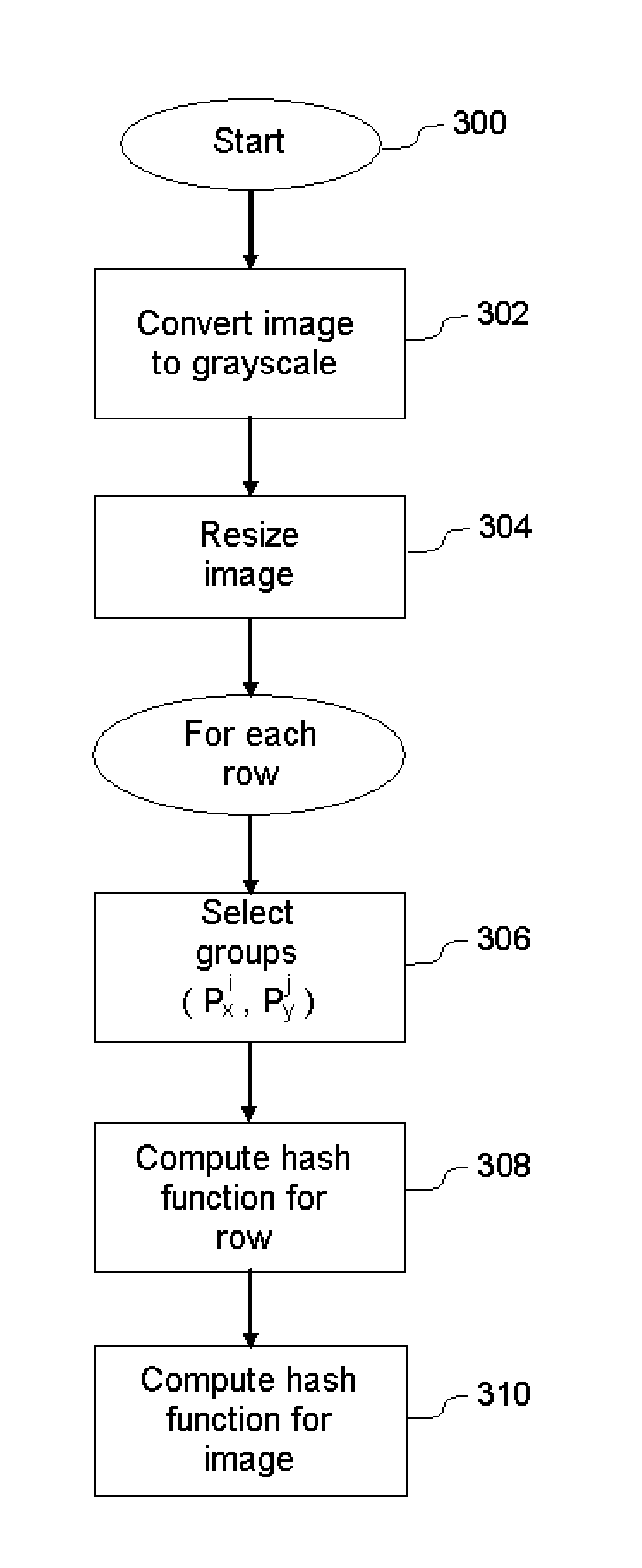
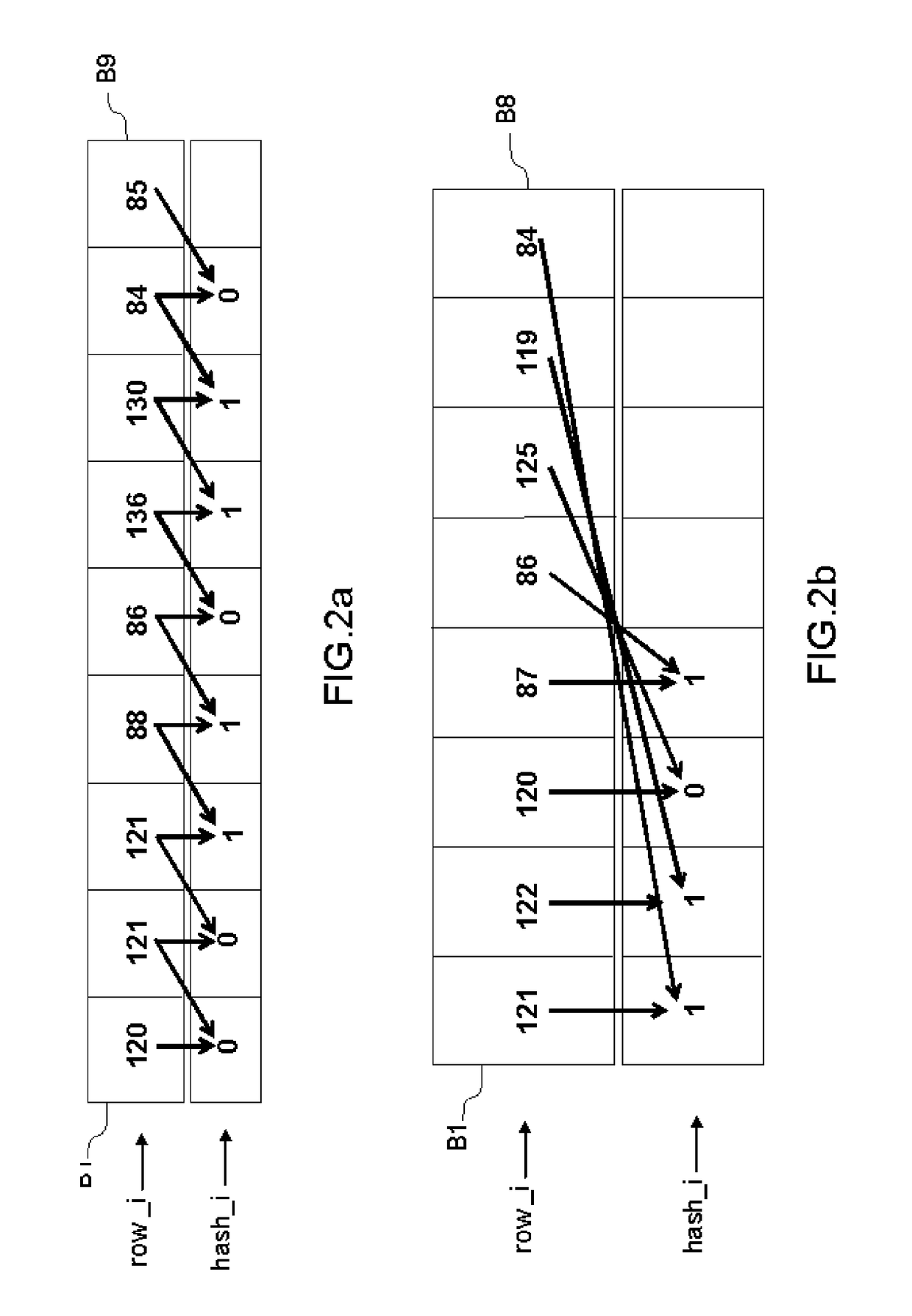
InactiveUS20180293461A1Generate imageQuick buildGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionData stream
A method and a device for detecting copies or near-copies of images, comprises receiving an initial image, converting the initial image to grayscale, resizing the grayed image to a reduced image having a plurality of rows and an even number of columns, computing an overall signature for the reduced image, and determining whether the initial image is a copy or near-copy of an image according to the result of a comparison between the overall signature of the reduced image and reference image signatures. The step of computing the overall signature comprises the steps of computing a row signature for each row of the reduced image, the computation being based on a comparison of values obtained statistically across subsets of symmetrical pixels in each row, and concatenating the row signatures in order to obtain an overall signature.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Imaging flow cytometer
An imaging flow cytometer includes at least one flow channel through which an observation target flows, a light source which irradiates the flow channel with sheet-like excitation light, an imaging unit which images a specific cross-section of the observation target by imaging fluorescence from the observation target having passed through a position irradiated with the excitation light, and a three-dimensional image generation unit which generates a three-dimensional image of the observation target as a captured image on the basis of a plurality of captured images obtained by cross-sectional imaging by the imaging unit.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Image processing apparatus
InactiveUS8798398B2Generate imageMaintain resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionSolid-state device signal generatorsImaging processingColor difference
From an image pickup element, pixel signals of Bayer array are outputted. A correlation calculation part calculates correlation values with respect to a specified pixel in vertical and horizontal directions. A first interpolation part performs a pixel interpolation process while evaluating the correlation highly. A second interpolation part performs a pixel interpolation process while evaluating the correlation relatively low. A complete signal of RGB outputted from the first interpolation part is converted into a luminance signal in a first color space conversion part, and a complete signal of RGB outputted from the second interpolation part is converted into a color difference signal in a second color space conversion part.
Owner:MEGACHIPS
Method and device for detecting copies in a stream of visual data
InactiveUS20170103285A1Generate imageQuick buildImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData stream
A method and a device for detecting copies or near-copies of images, comprises receiving an initial image, converting the initial image to grayscale, resizing the grayed image to a reduced image having a plurality of rows and an even number of columns, computing an overall signature for the reduced image, and determining whether the initial image is a copy or near-copy of an image according to the result of a comparison between the overall signature of the reduced image and reference image signatures. The step of computing the overall signature comprises the steps of computing a row signature for each row of the reduced image, the computation being based on a comparison of values obtained statistically across subsets of symmetrical pixels in each row, and concatenating the row signatures in order to obtain an overall signature.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Radiographic image capturing system
InactiveUS20160296189A1Generate imageRadiation diagnostic device controlImaging processingComputer science
A radiographic image capturing system includes the following. A capturing stand includes a holder which can hold a plurality of radiographic image capturing devices. A radiation irradiator is able to apply radiation to the radiographic image capturing devices loaded in the holder at once. A console carries out image processing on image data acquired by the radiographic image capturing devices. The console carries out the image processing through application of a parameter applied to image data acquired by a radiographic image capturing device assigned with a predetermined number to image data acquired by the other radiographic image capturing devices. The predetermined number is a number from multiple numbers assigned to the radiographic image capturing devices loaded in the holder in an ascending order from a head to toe of a patient.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Liquid crystal display cell
InactiveUS7609340B2Reduce reflectionPrevent leakageNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
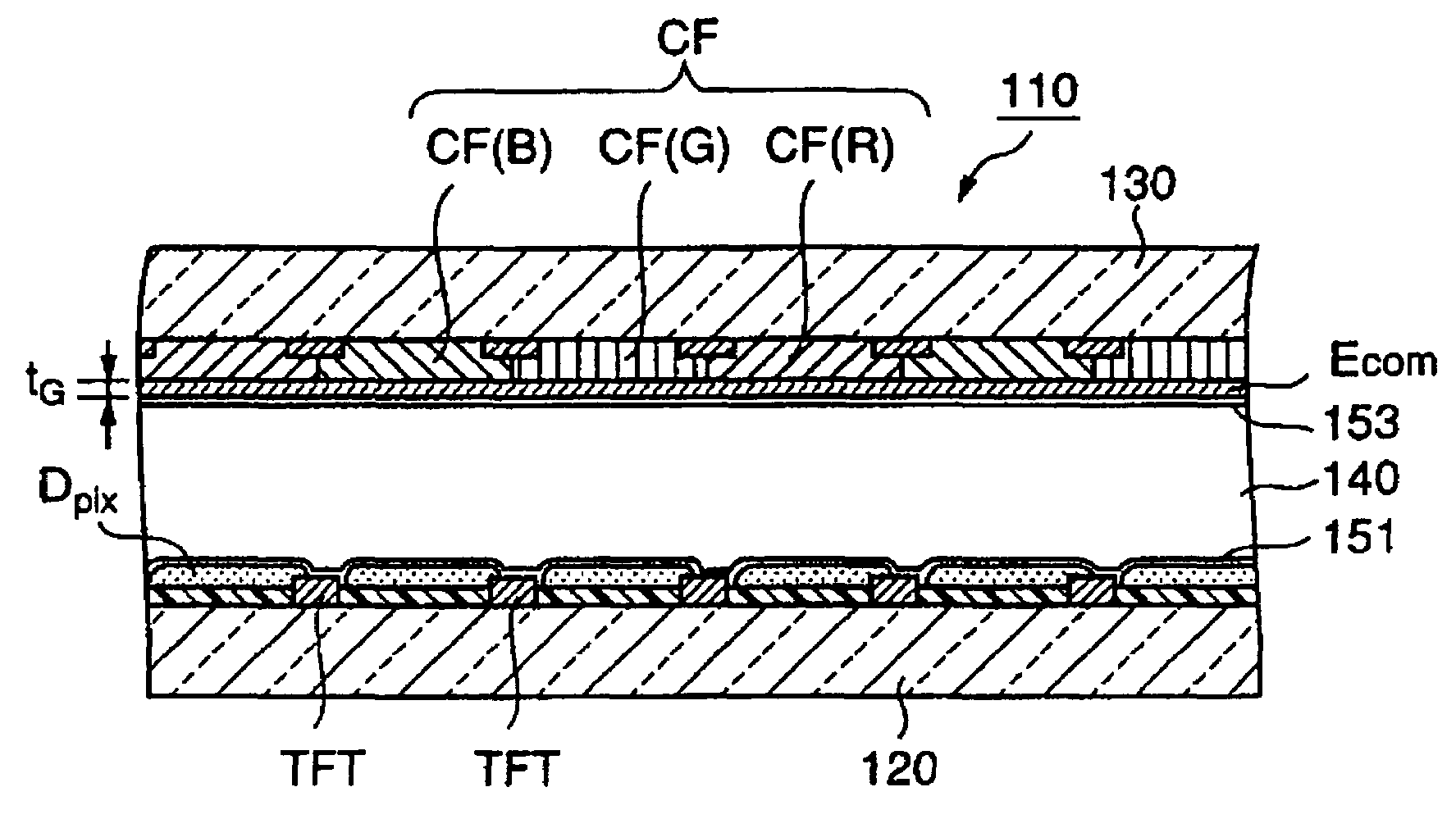
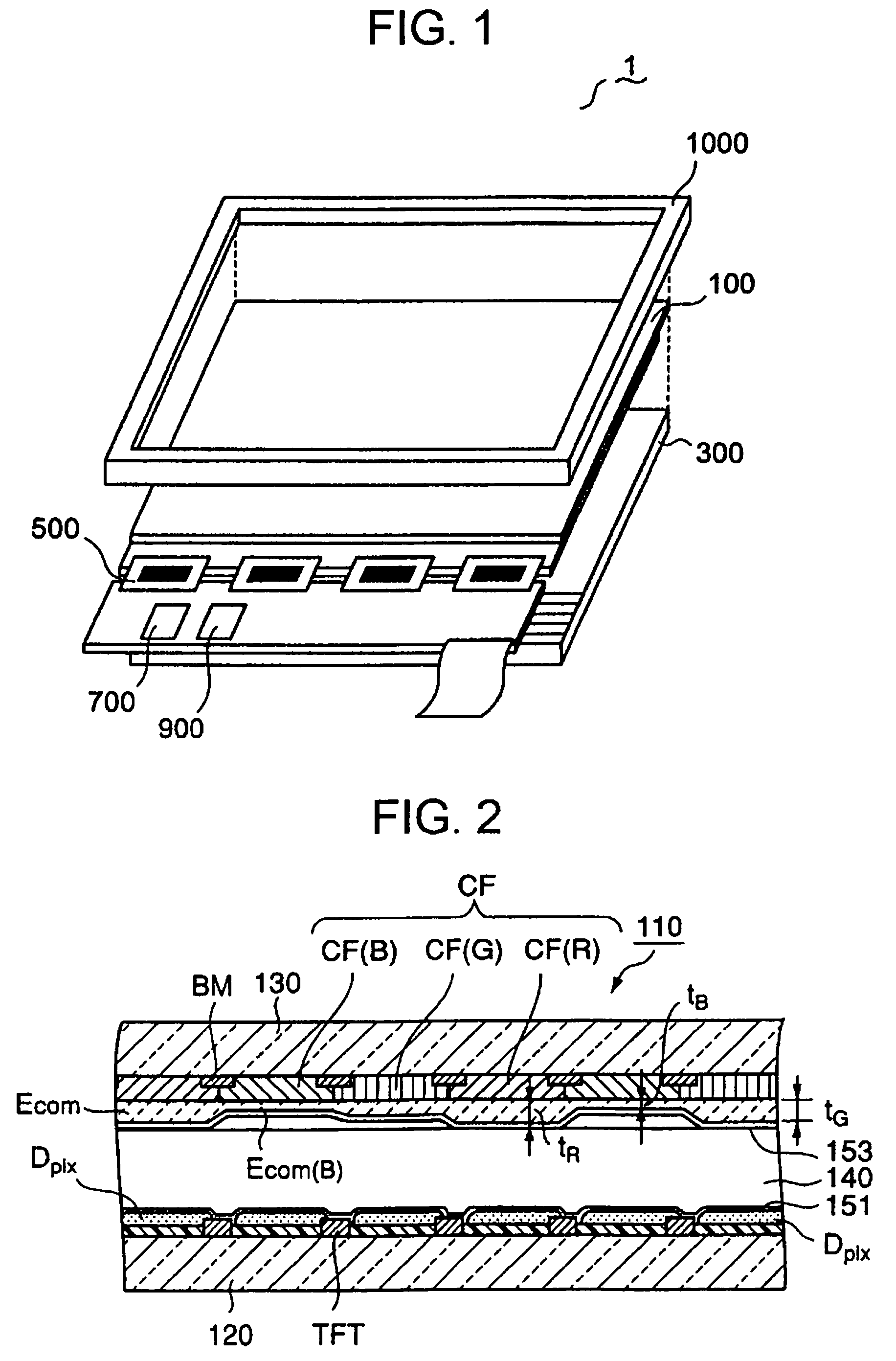
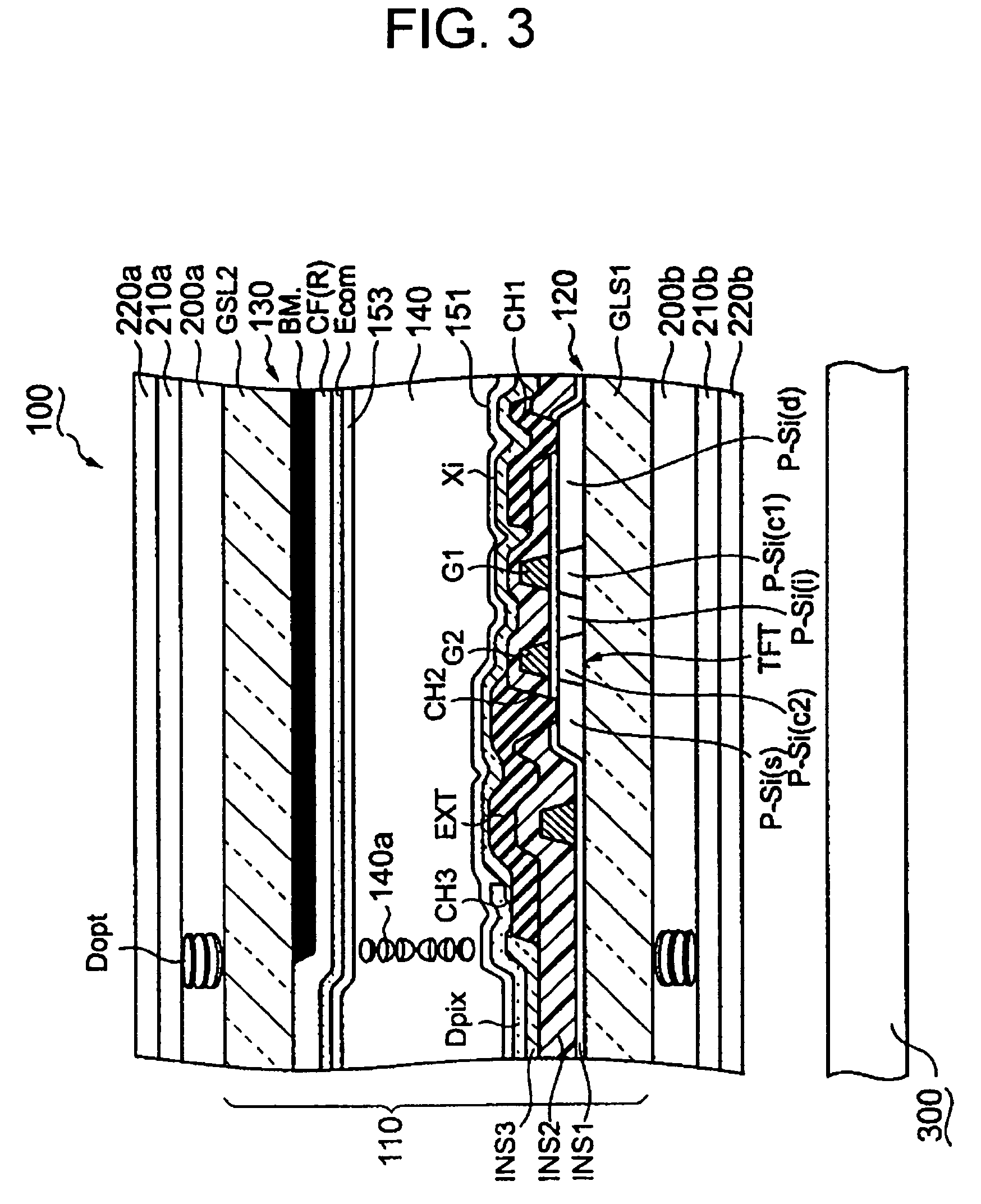
To reduce the blue tone in the black display of the OCB liquid crystal display device. A liquid crystal display cell (11) includes: an opposing substrate (130) having an opposing electrode (Ecom); an array substrate (120) having a pixel electrode Dpix for each color; a liquid crystal layer (140) arranged in a bend arrangement located between the opposing substrate (120) and the array substrate (120); and red, green, and blue filter layers arranged on one of the substrates. The opposing electrode has a film thickness tB of the portion Ecom (B) corresponding to the blue filter layer, which thickness is set so as to have the minimum value in the range 380 nm to 480 nm in the spectrum of the front reflectance and satisfy the following: 100 nm<tB≦140 nm.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENTRAL CO LTD
Generating a dilation image utilizing parallel pixel processing
A dilation image is generated from an original digital image utilizing a processing image (b) and a target image (T), where each pixel in the target image is processed in parallel. The process entails, for each target pixel, i) determining coordinate values for the target pixel, ii) determining a surrounding pixel area for the target pixel, iii) and processing each pixel in the surrounding pixel area to determine whether or not to updated the value of the target pixel. In processing each surrounding pixel, a determination is made whether the pixel has a value of 1. If not, then the next surrounding pixel is processed. If so, then a determination is made which pixel element of the structuring element overlays the target pixel, and whether that pixel has a value of 1. If so, then the value of the target pixel is updated. If not, then the next pixel in the surrounding pixel area is processed. Once the target pixel has been updated one time, the processing of the remaining surrounding pixels is terminates. If processing of all surrounding pixels results in no update to the target pixel, then the target pixel is not updated. After all target pixels have been processed, the resultant image is output as the dilation image.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus and computer program
ActiveUS8548227B2Generate imageQuick buildImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsImaging processing
Owner:KDDI CORP
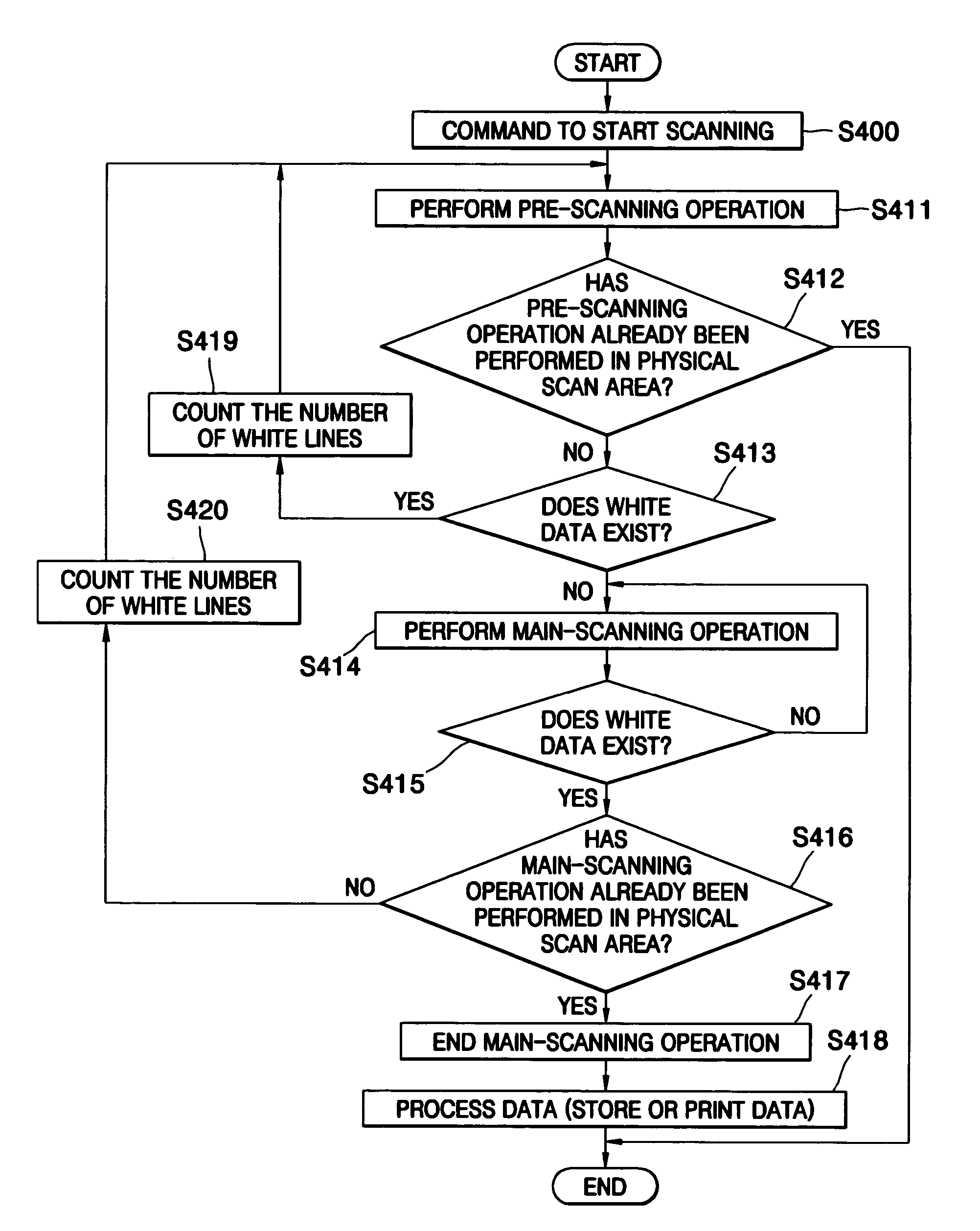
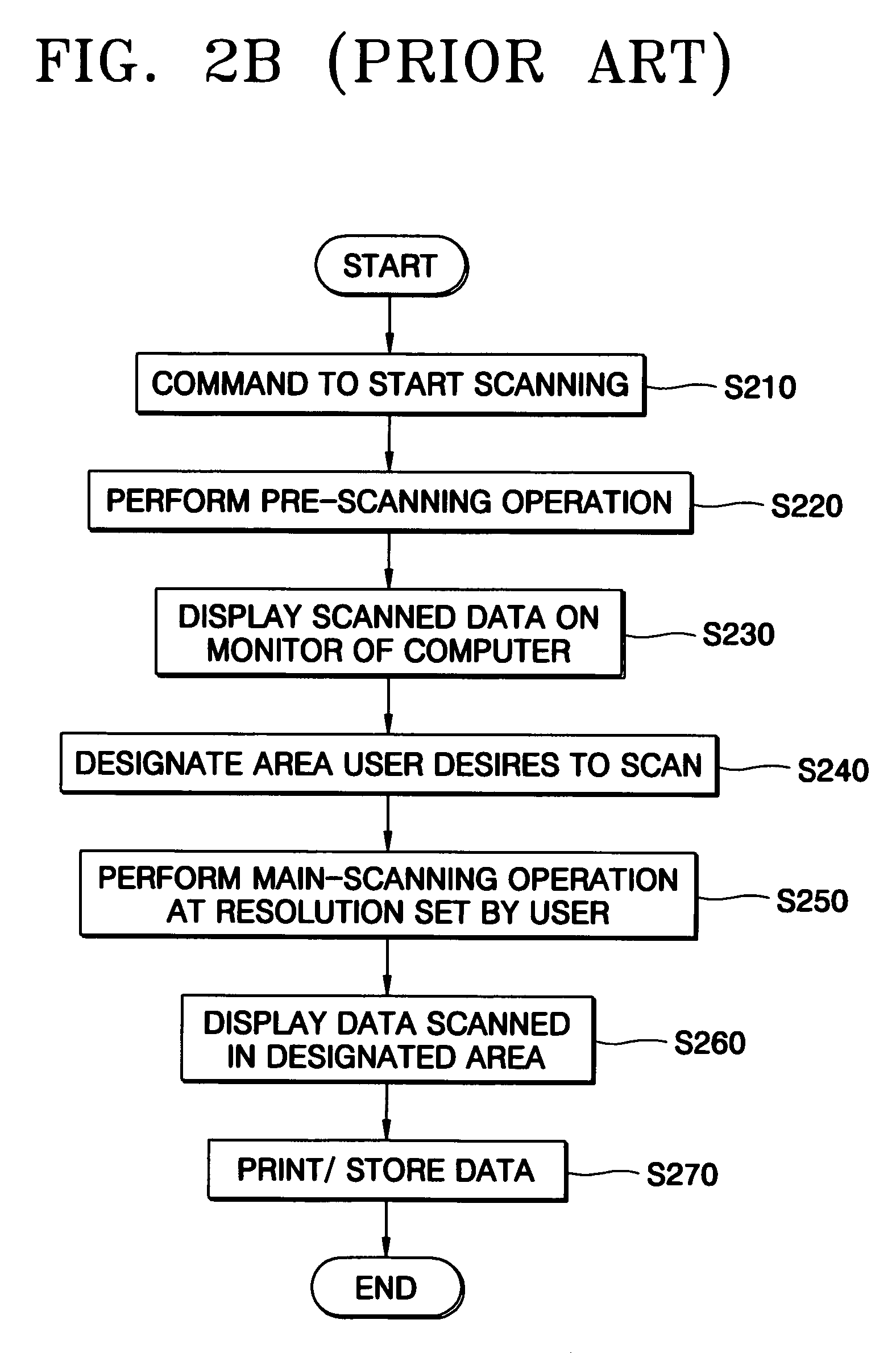
Method of scanning a document using a pre-scanning operation
InactiveUS7734120B2Unnecessary amount of dataGenerate imageCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrographic process apparatusImage resolutionComputer science
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
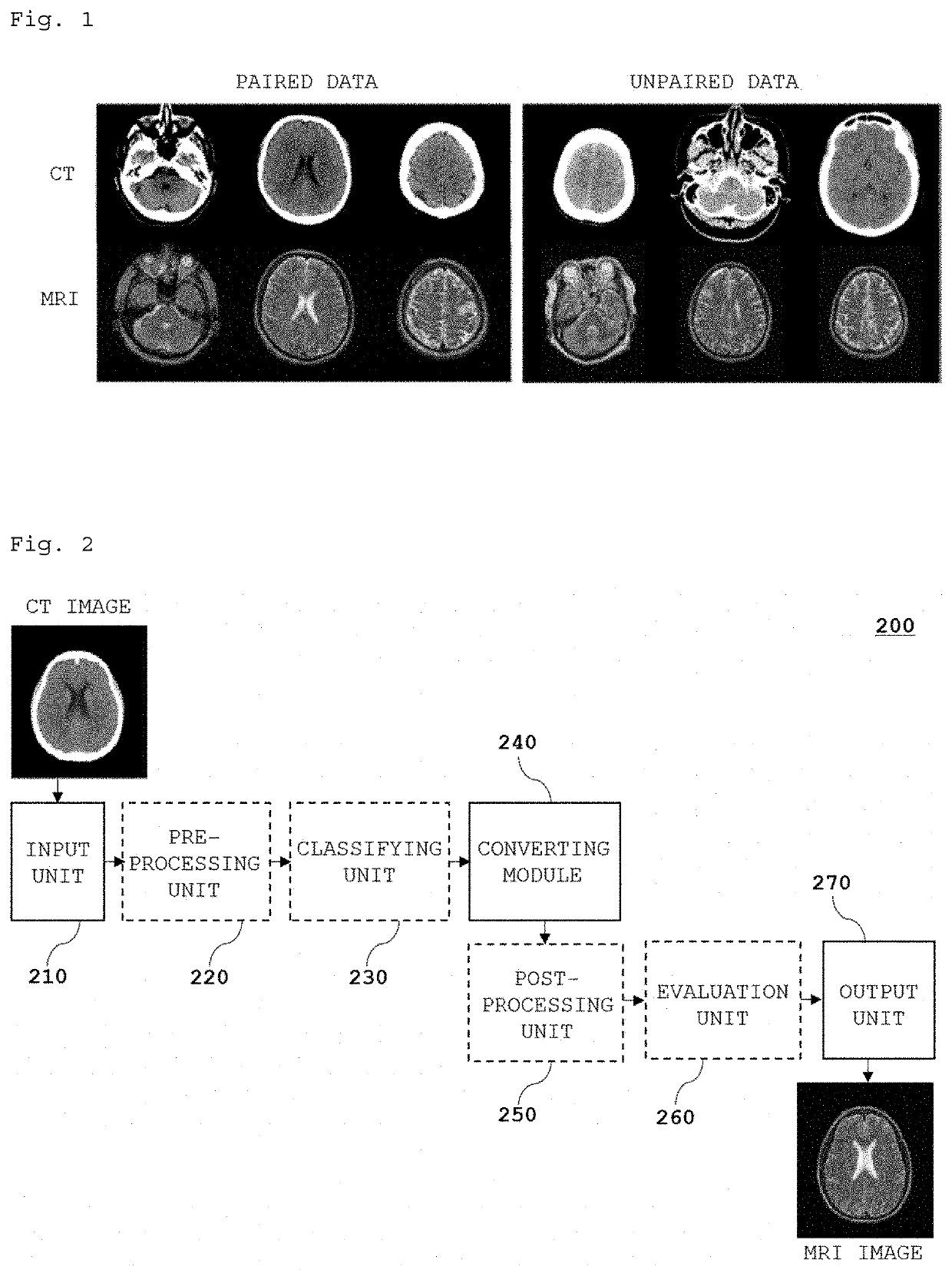
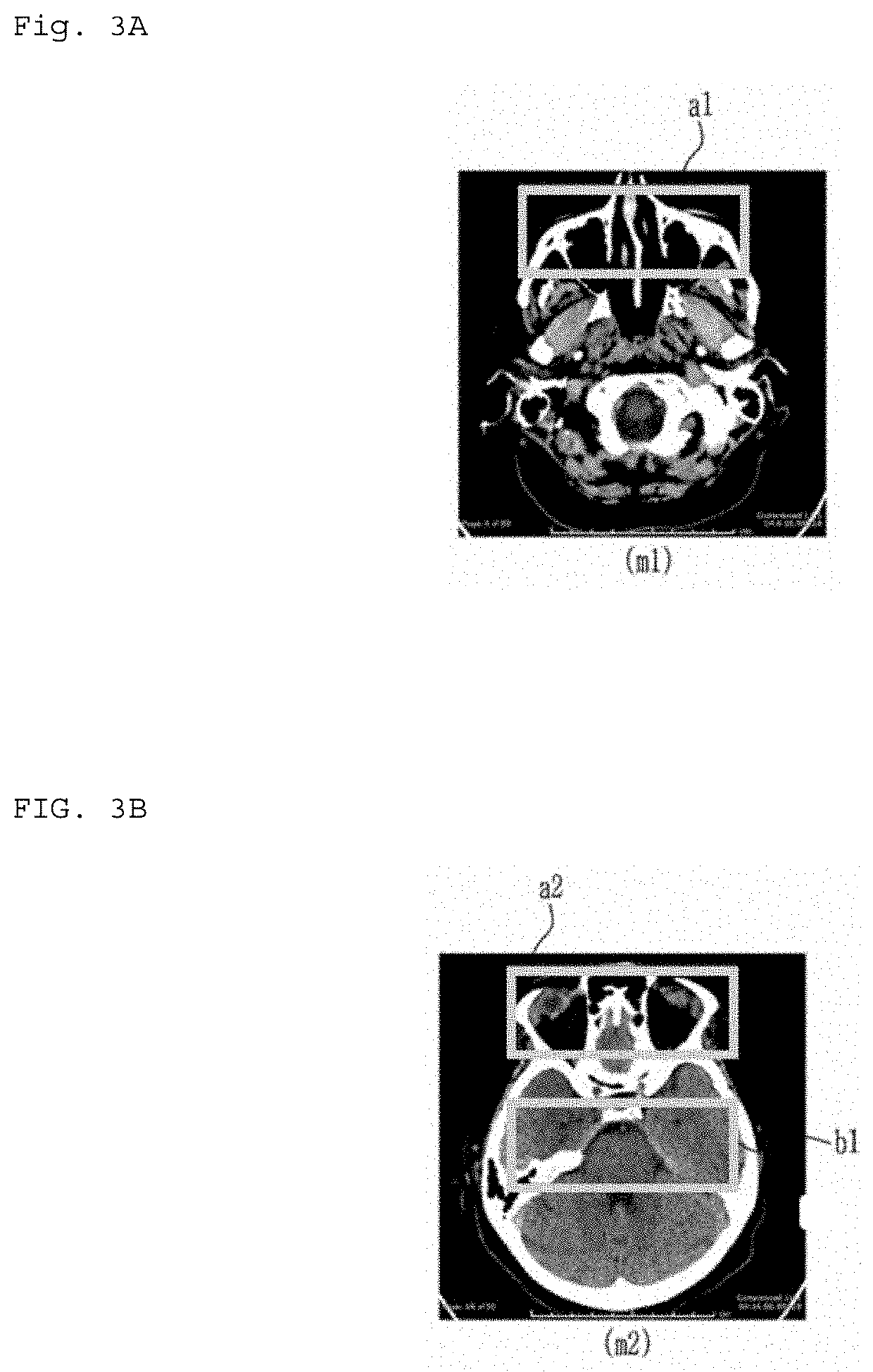
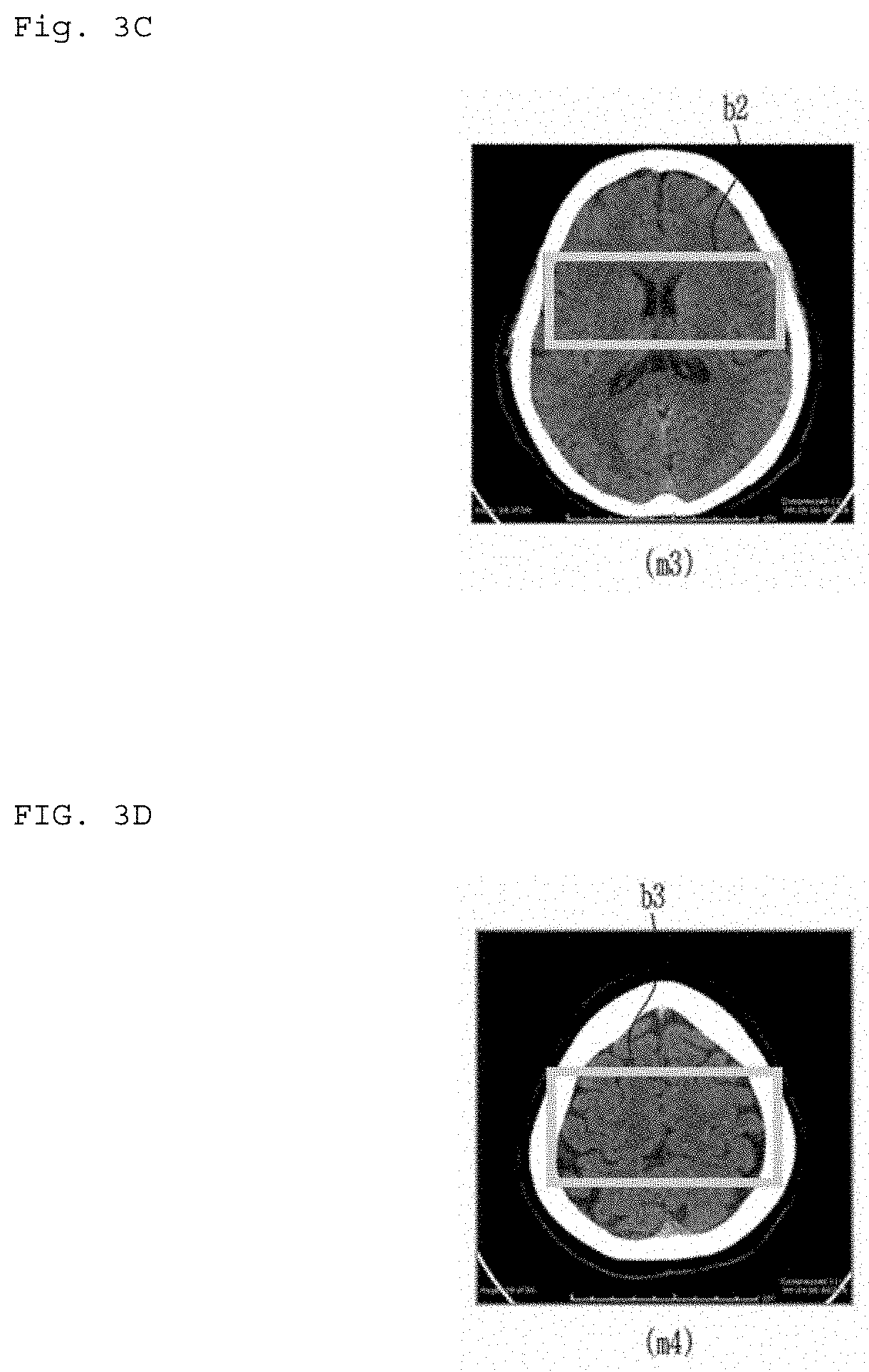
Diagnostic image converting apparatus, diagnostic image converting module generating apparatus, diagnostic image recording apparatus, diagnostic image converting method, diagnostic image converting module generating method, diagnostic image recording method, and computer recordable recording medium
InactiveUS20210225491A1Efficiently providedGenerate imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage recordingNuclear medicine
An apparatus for converting a diagnostic image according to some embodiments of the present invention includes an input unit for inputting a CT image, a converting module configured to convert the CT image inputted via the input unit into an MRI image, and an output unit configured to output the MRI image converted by the converting module.
Owner:AHN YEONG SAEM
Cleaning of a front of an optical instrument of a milking parlor
An arrangement and a corresponding method for cleaning a front of an optical instrument using a movable cap for directing a cleaning fluid to the front of the optical instrument.
Owner:GEA FARM TECH
Imaging apparatus and image processing method
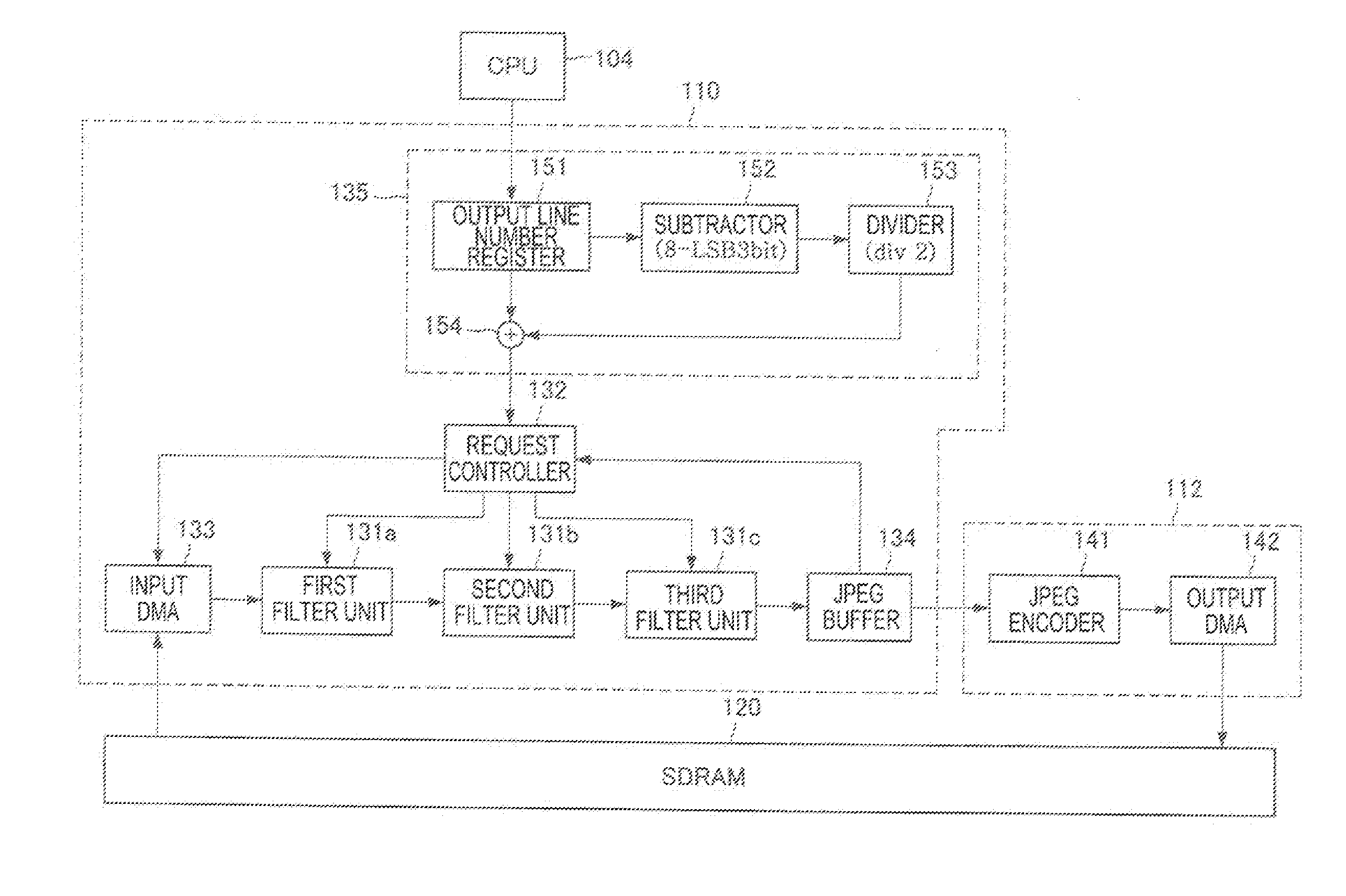
InactiveUS20130155284A1Efficient JPEG compression encodingGenerate imageTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImaging processingImaging equipment
Disclosed is an imaging apparatus which performs efficient JPEG compression encoding by dividing an image after an image processing into a plurality of blocks and then performing JPEG compression, and also generates a natural compressed image. The imaging apparatus includes an image processor for generating image data from a light input into an imaging device, an encoder for encoding the image data to generate encoded image data, and a storage unit for storing the encoded image data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Generating an erosion image utilizing parallel pixel processing
An erosion image is generated from an original digital image utilizing a processing image (b) and a target image (T), where each pixel in the target image is processed in parallel. The process entails, for each target pixel, i) determining coordinate values for the target pixel, ii) determining a surrounding pixel area for the target pixel, iii) and processing each pixel in the surrounding pixel area to determine whether or not to updated the value of the target pixel. In processing each surrounding pixel, a determination is made whether the pixel has a value of 1. If not, then the next surrounding pixel is processed. If so, then a determination is made which pixel element of a structuring element overlays the target pixel, and whether that SE pixel has a value of 1. If so, then the value of the target pixel is updated. If not, then the next pixel in the surrounding pixel area is processed. Once the target pixel has been updated a set number of times to a predetermined value (e.g., 2), the processing of the remaining surrounding pixels is terminated. After all target pixels have been processed, an output image is obtained by setting target pixels having a value of 2 to a binary value of 1, and setting the other pixels to a binary value of 0. The resultant output image is an erosion image that is then output.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com