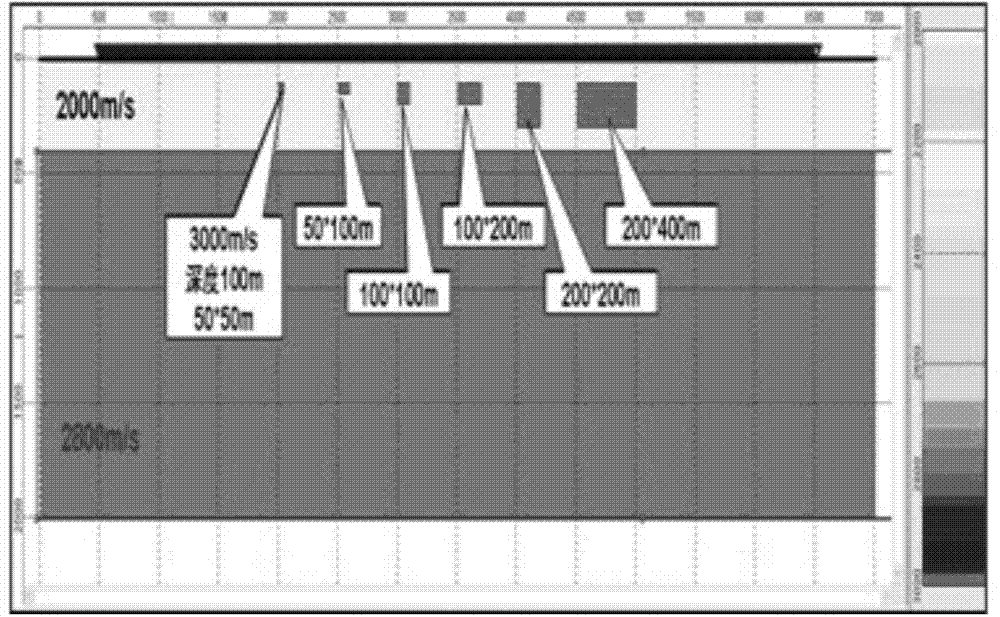
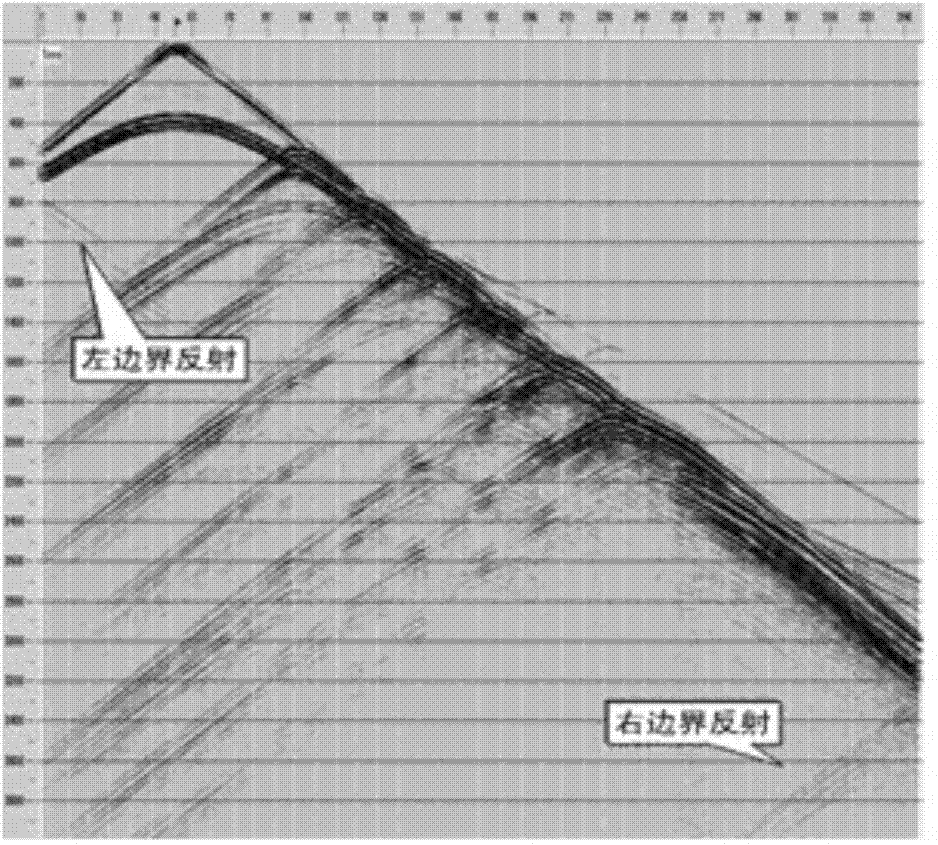
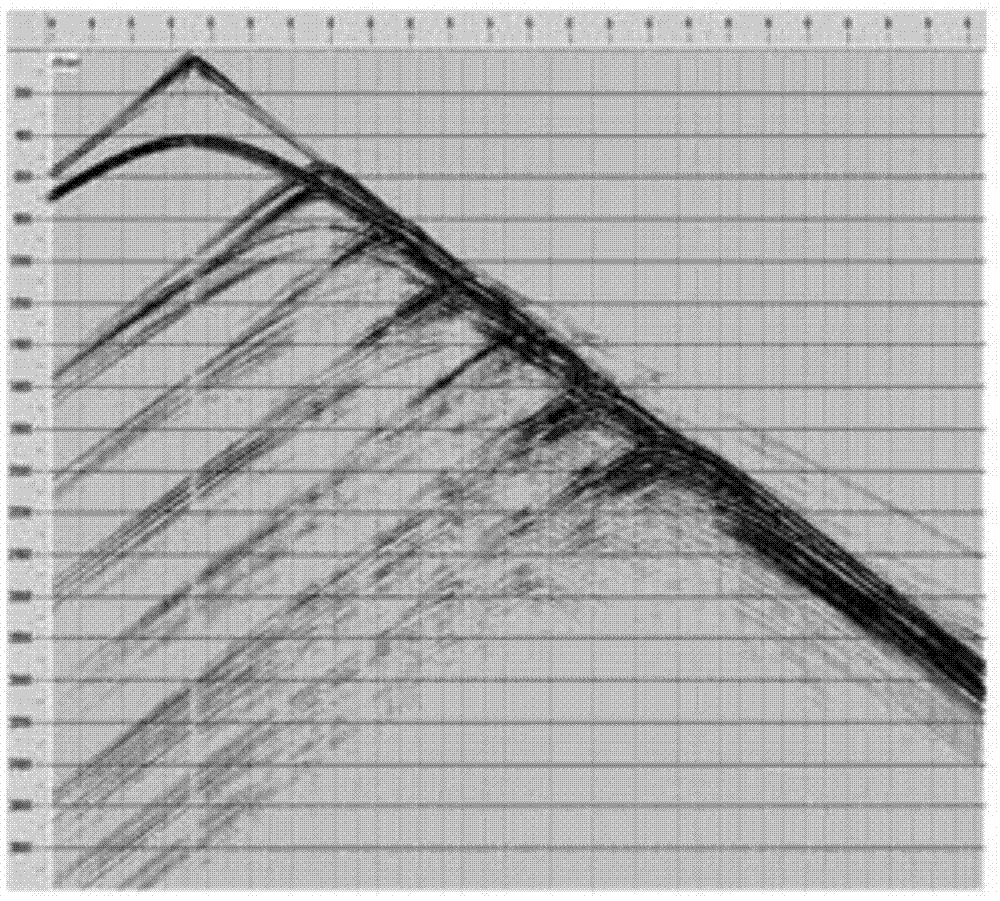
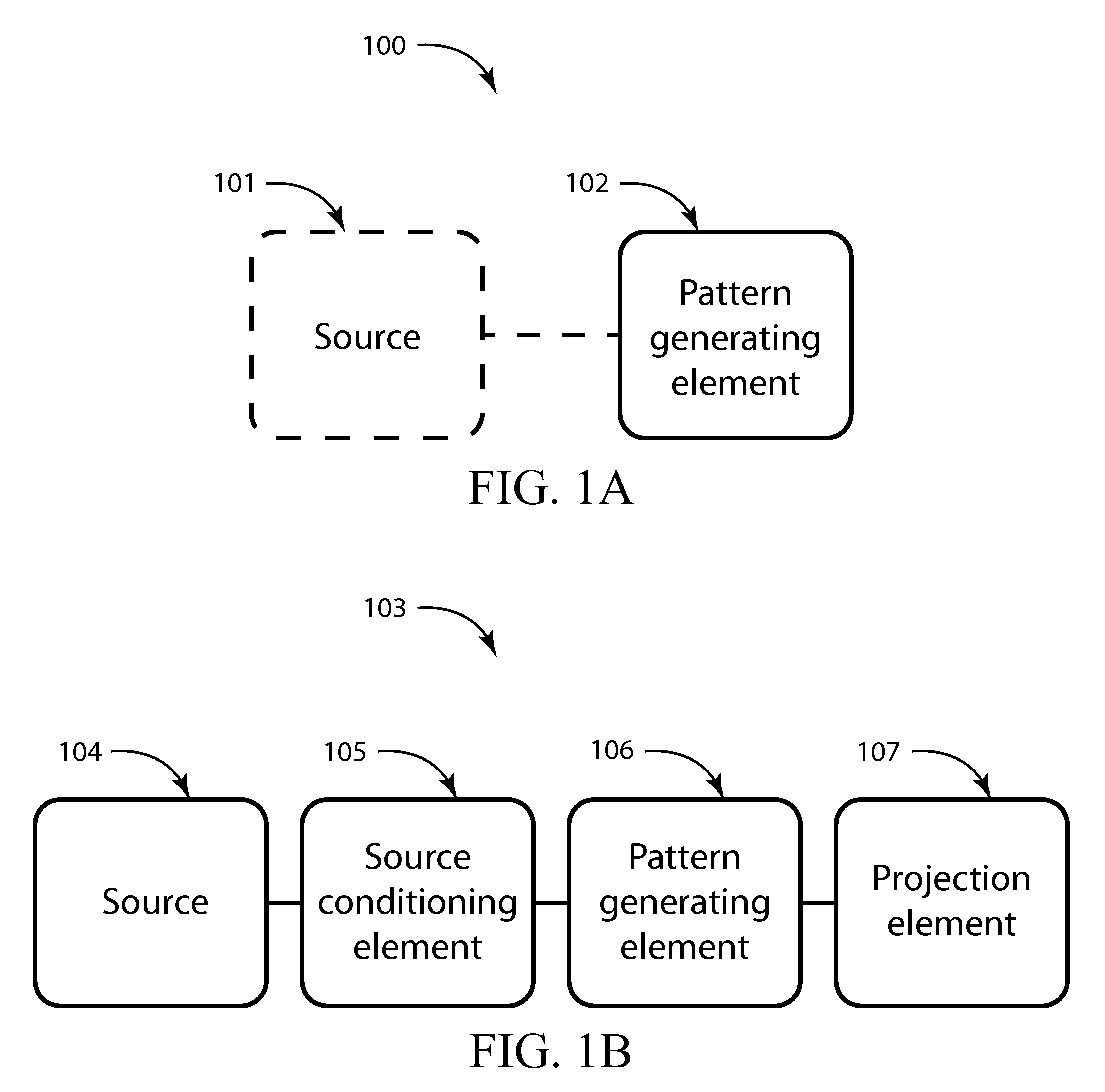
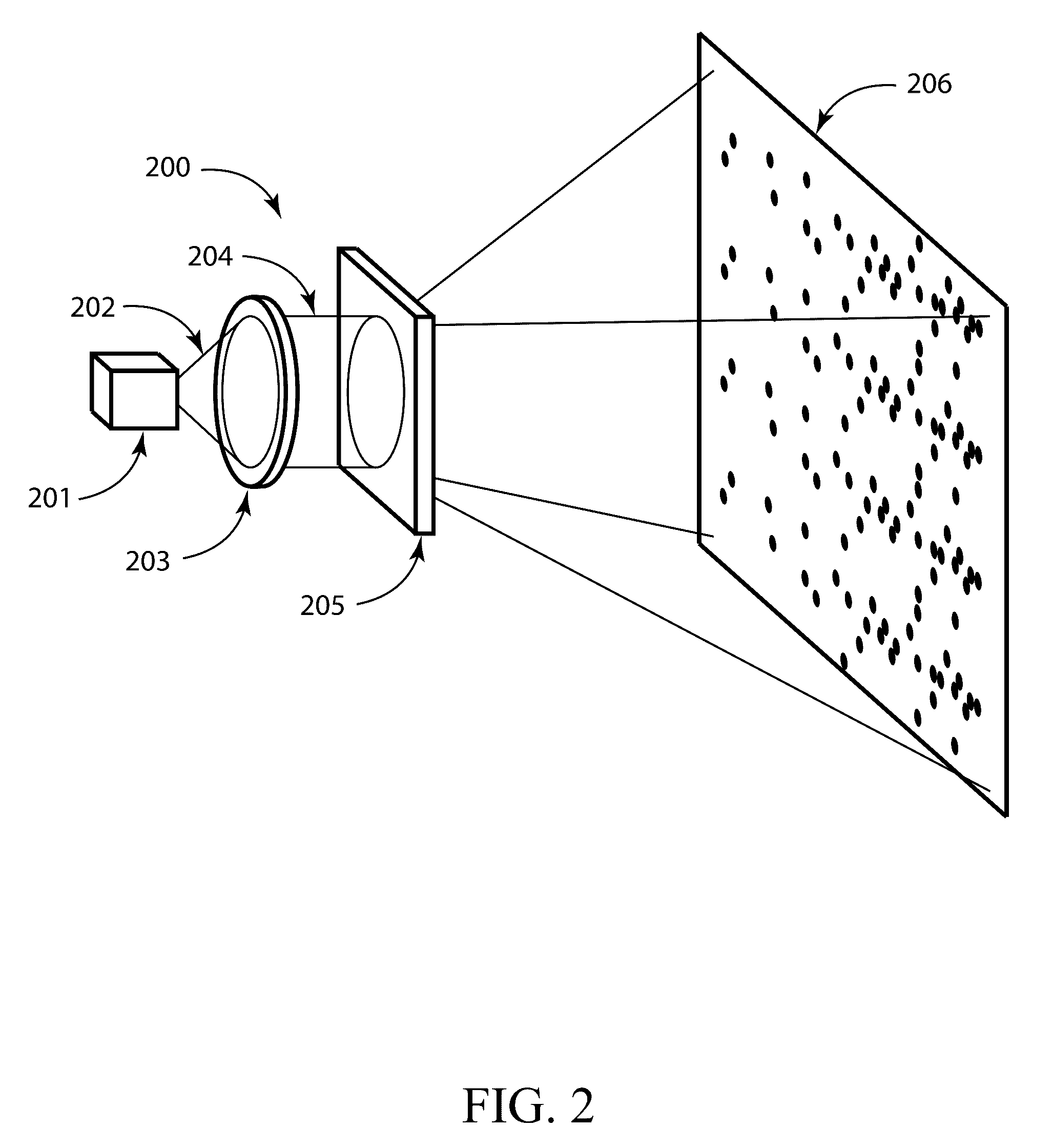
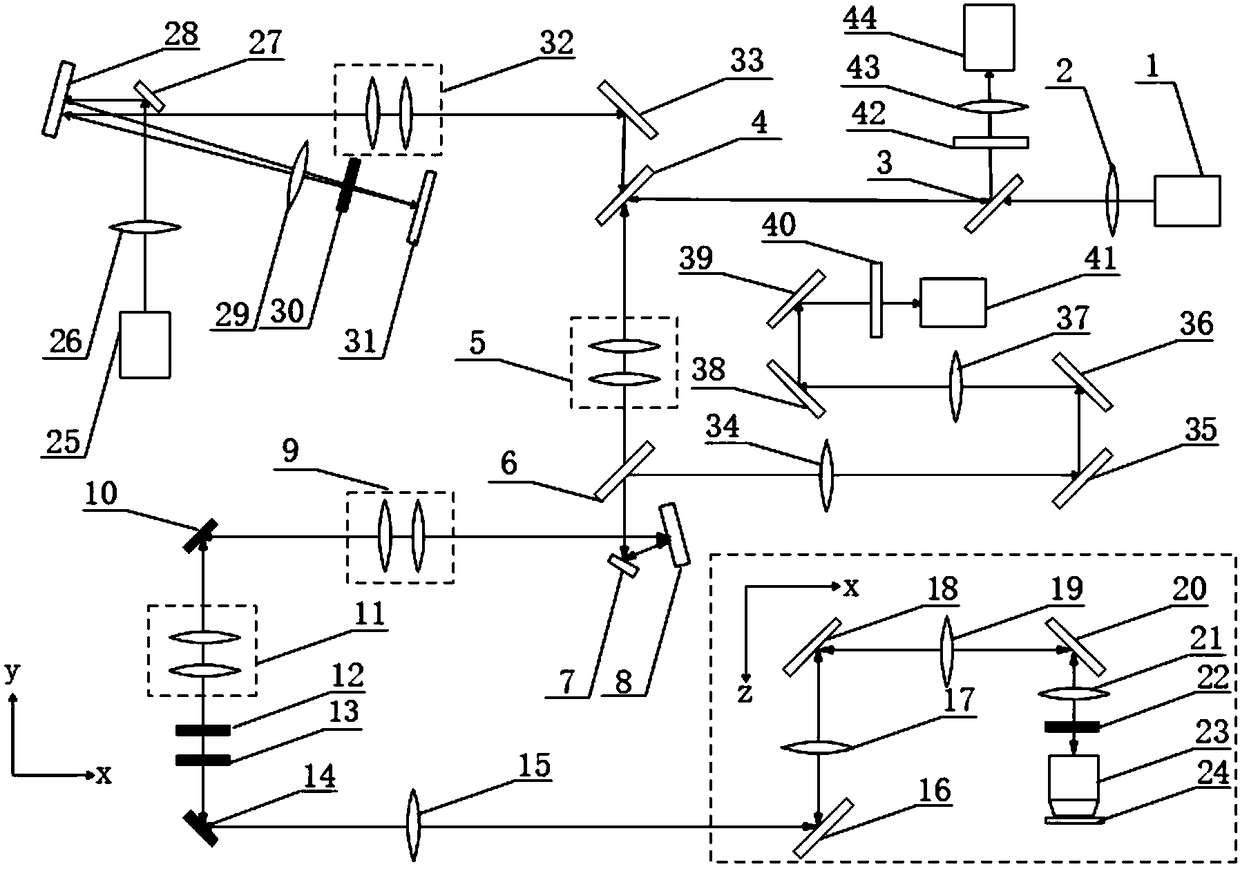
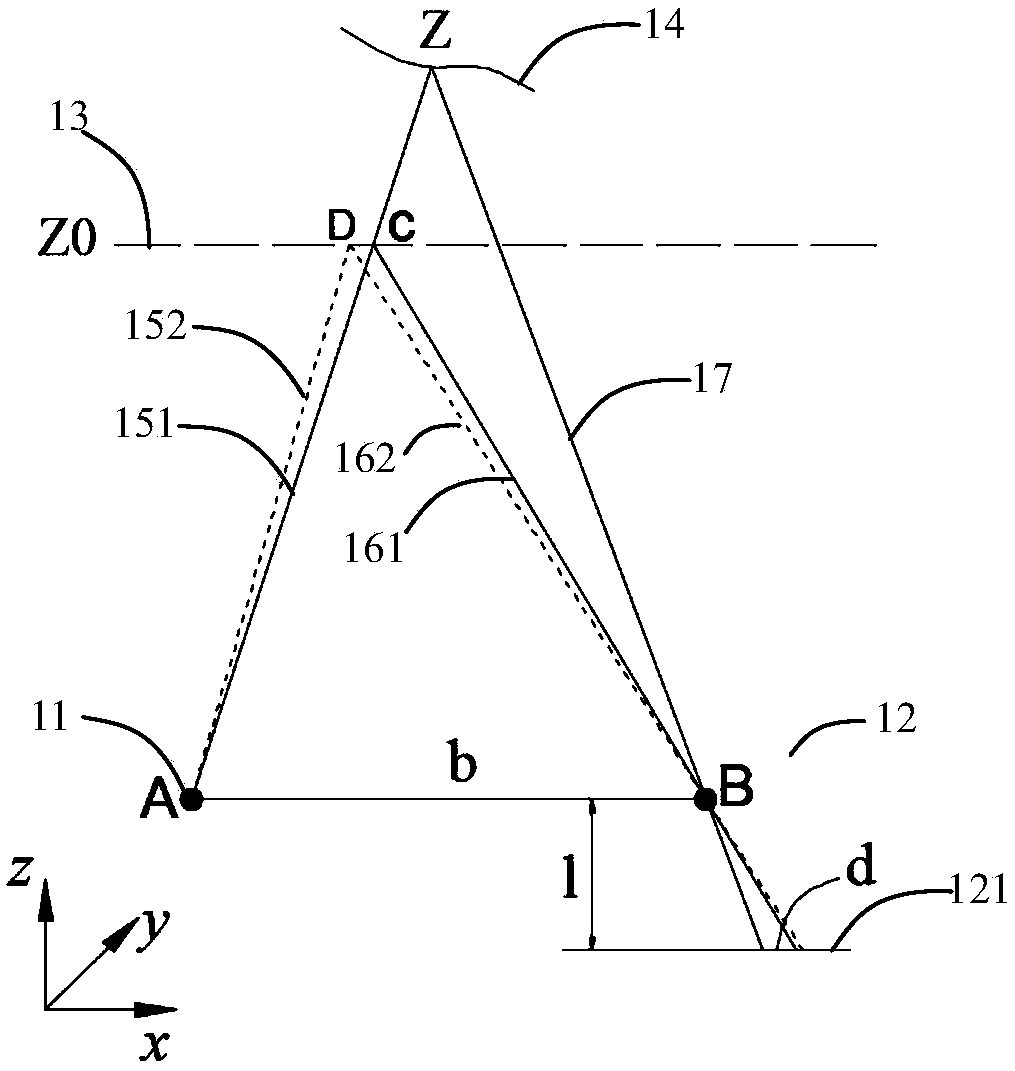
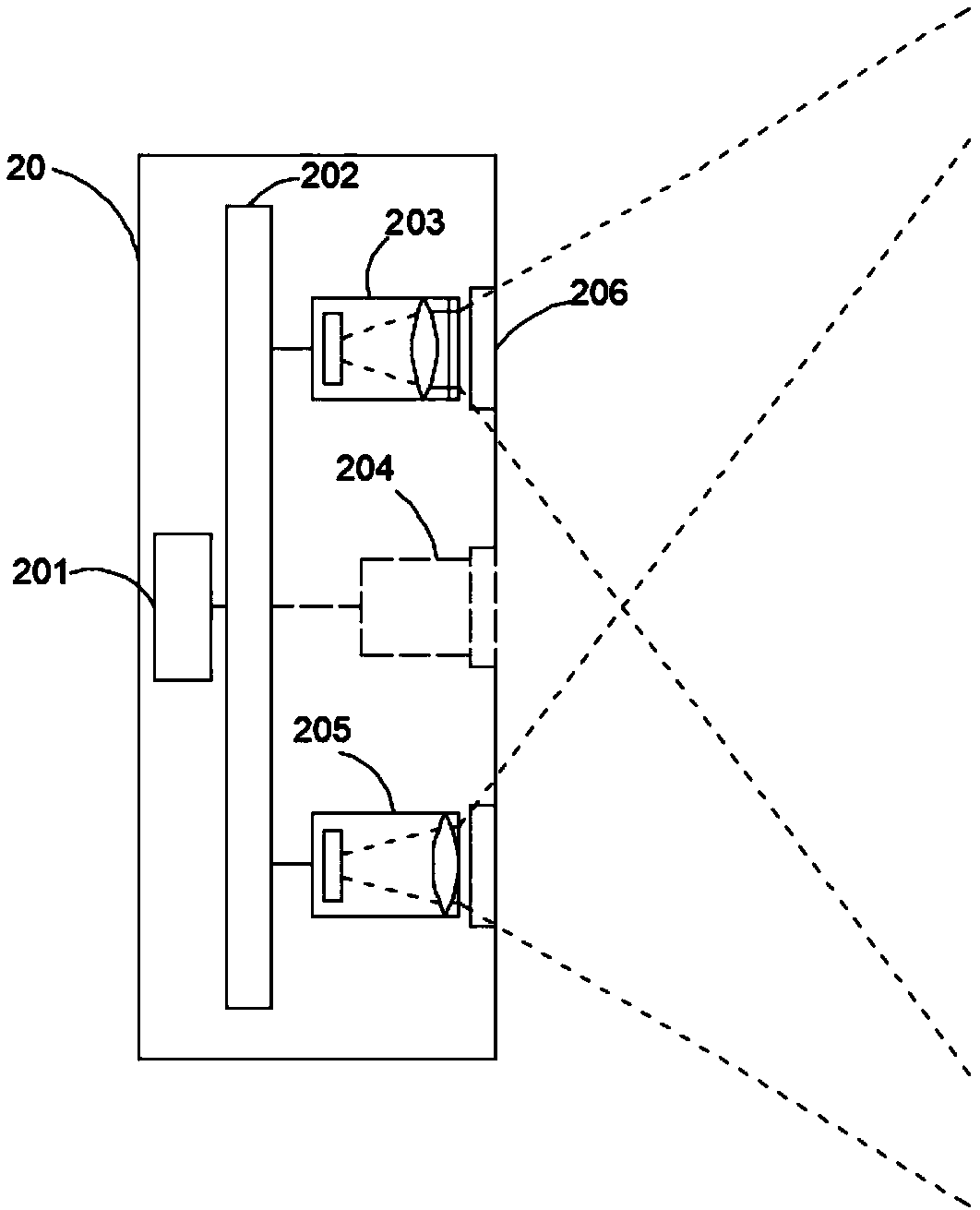
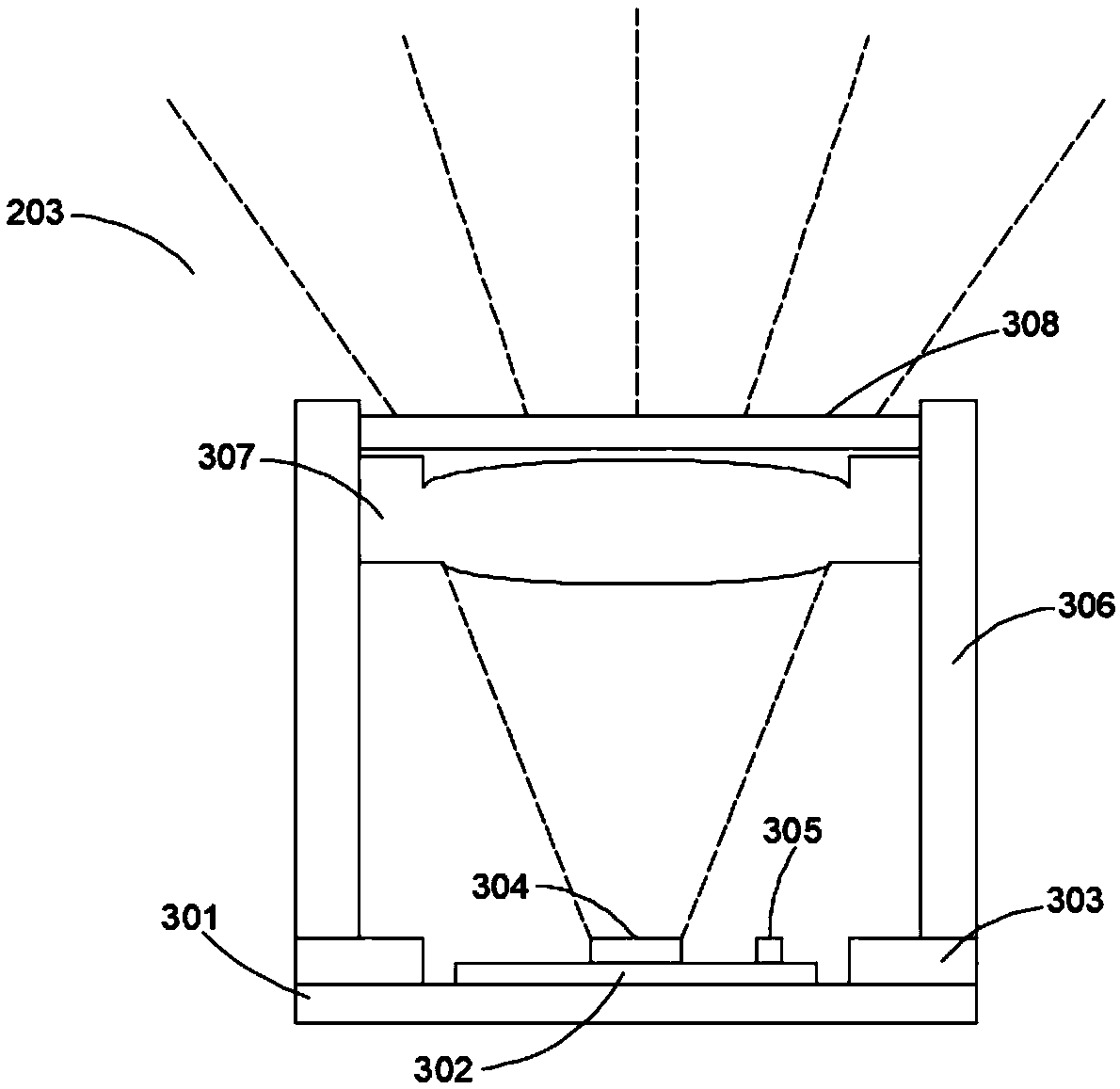
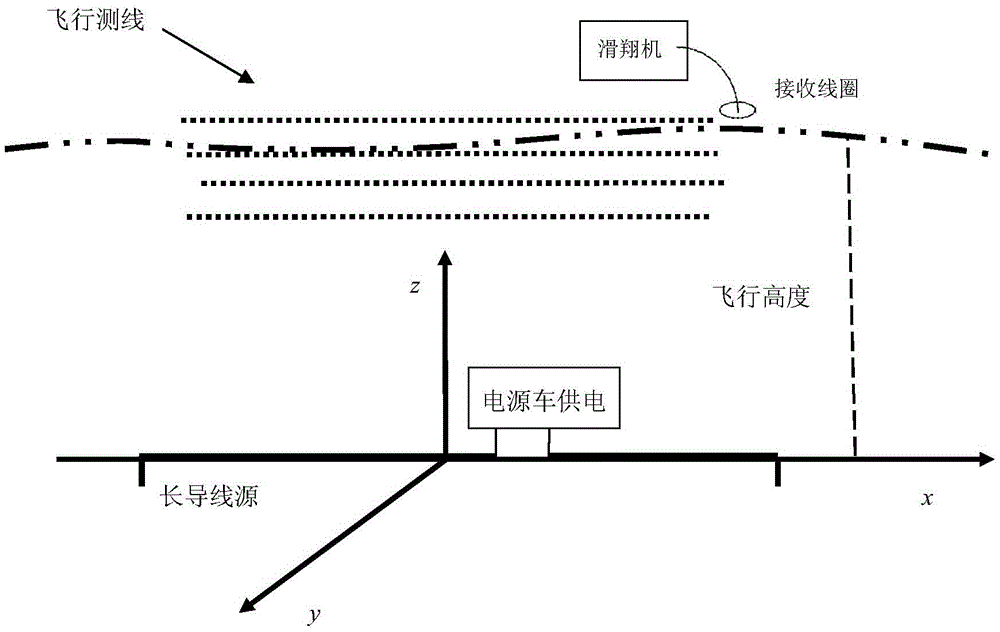
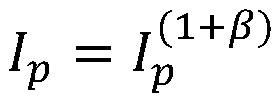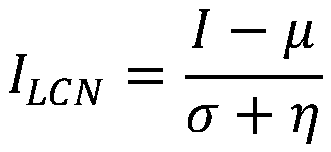Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
229 results about "Depth imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
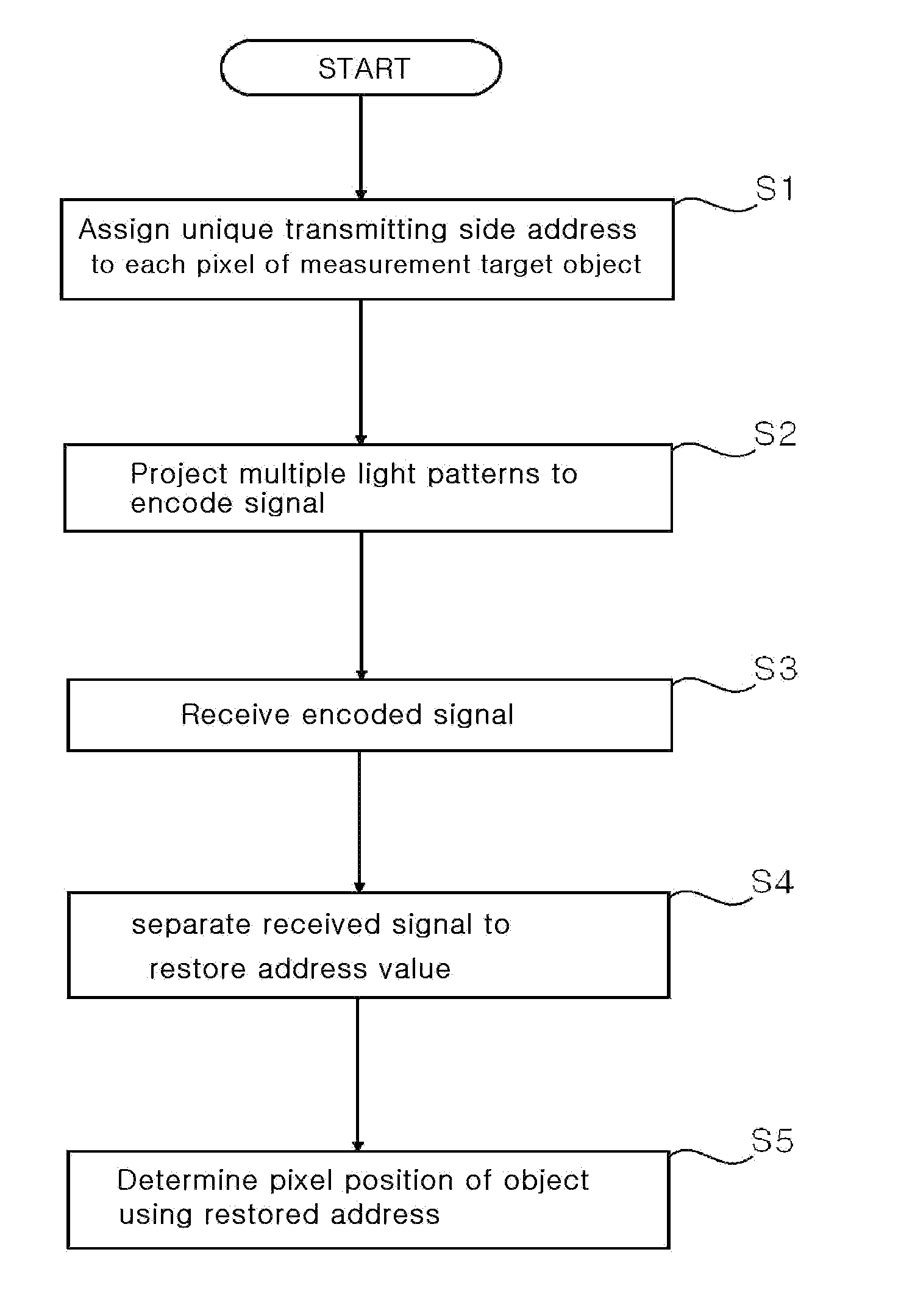
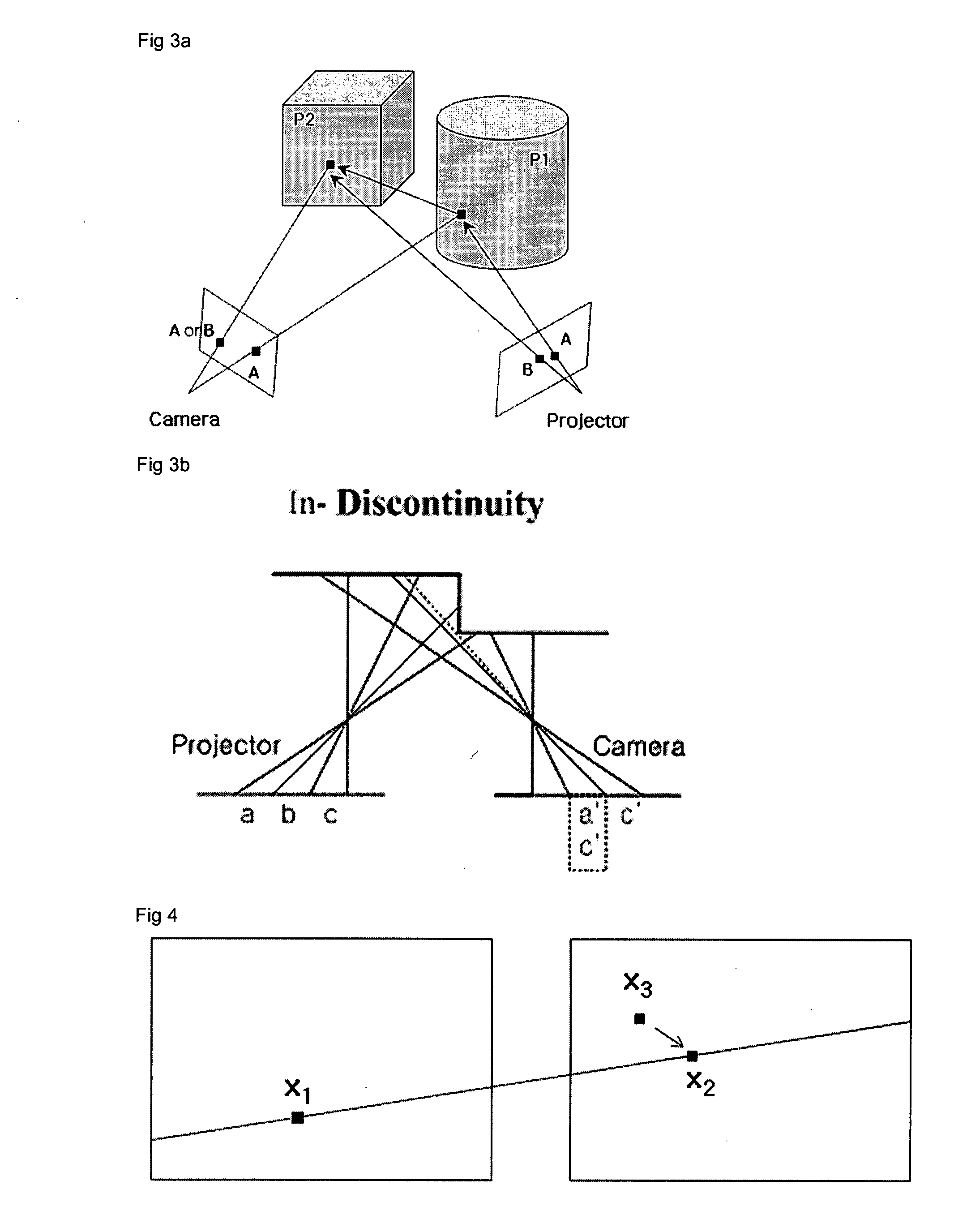
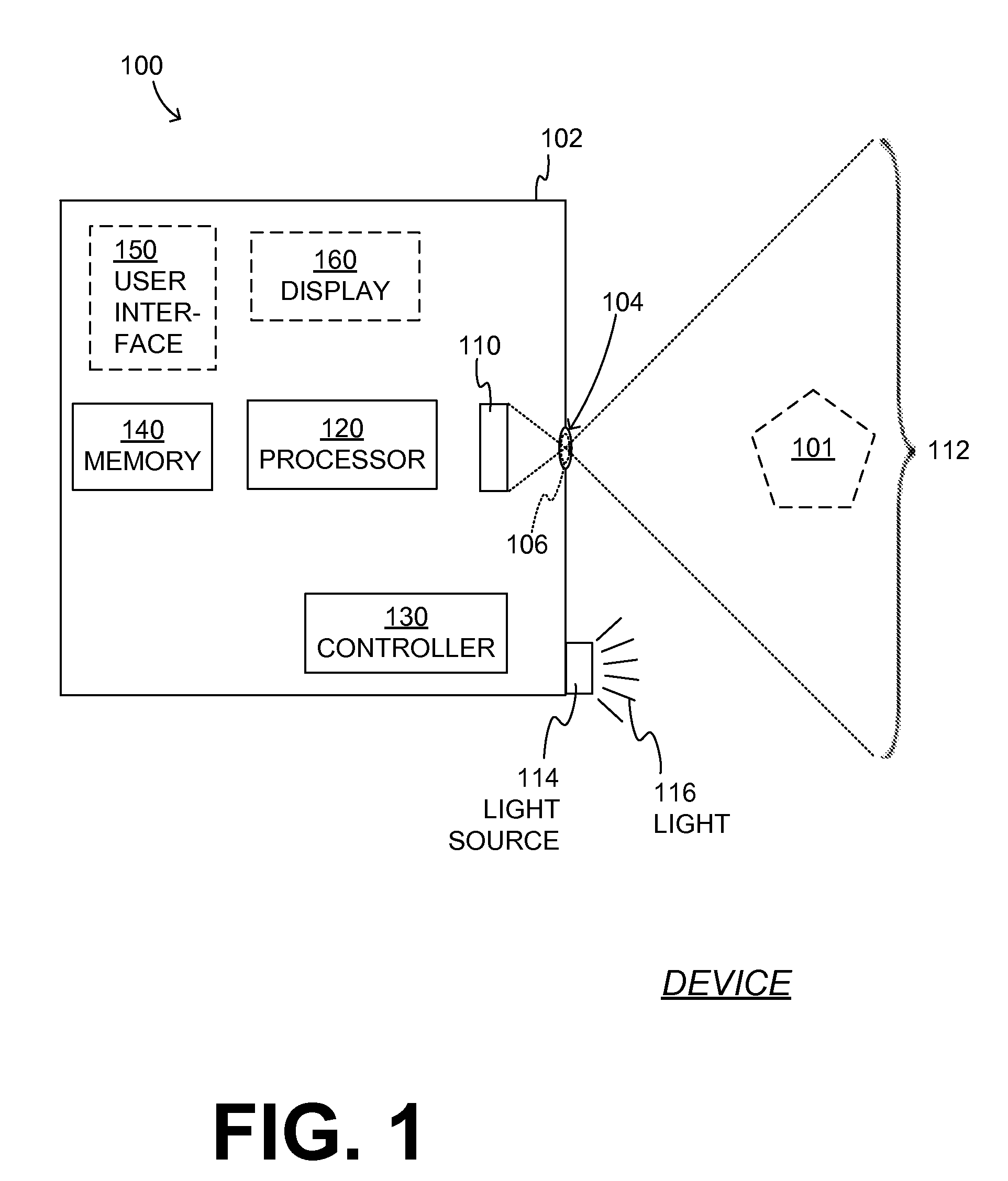
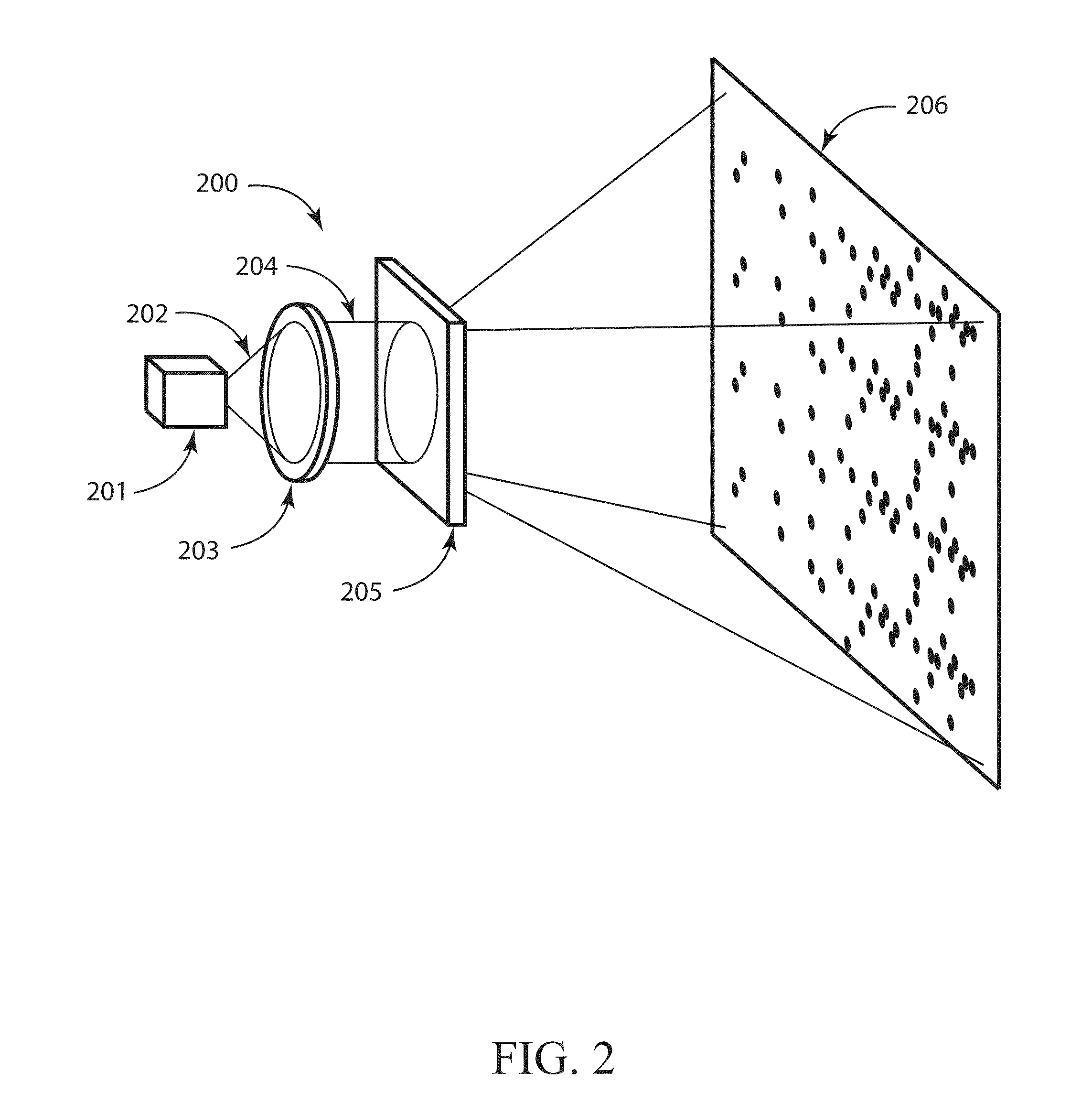
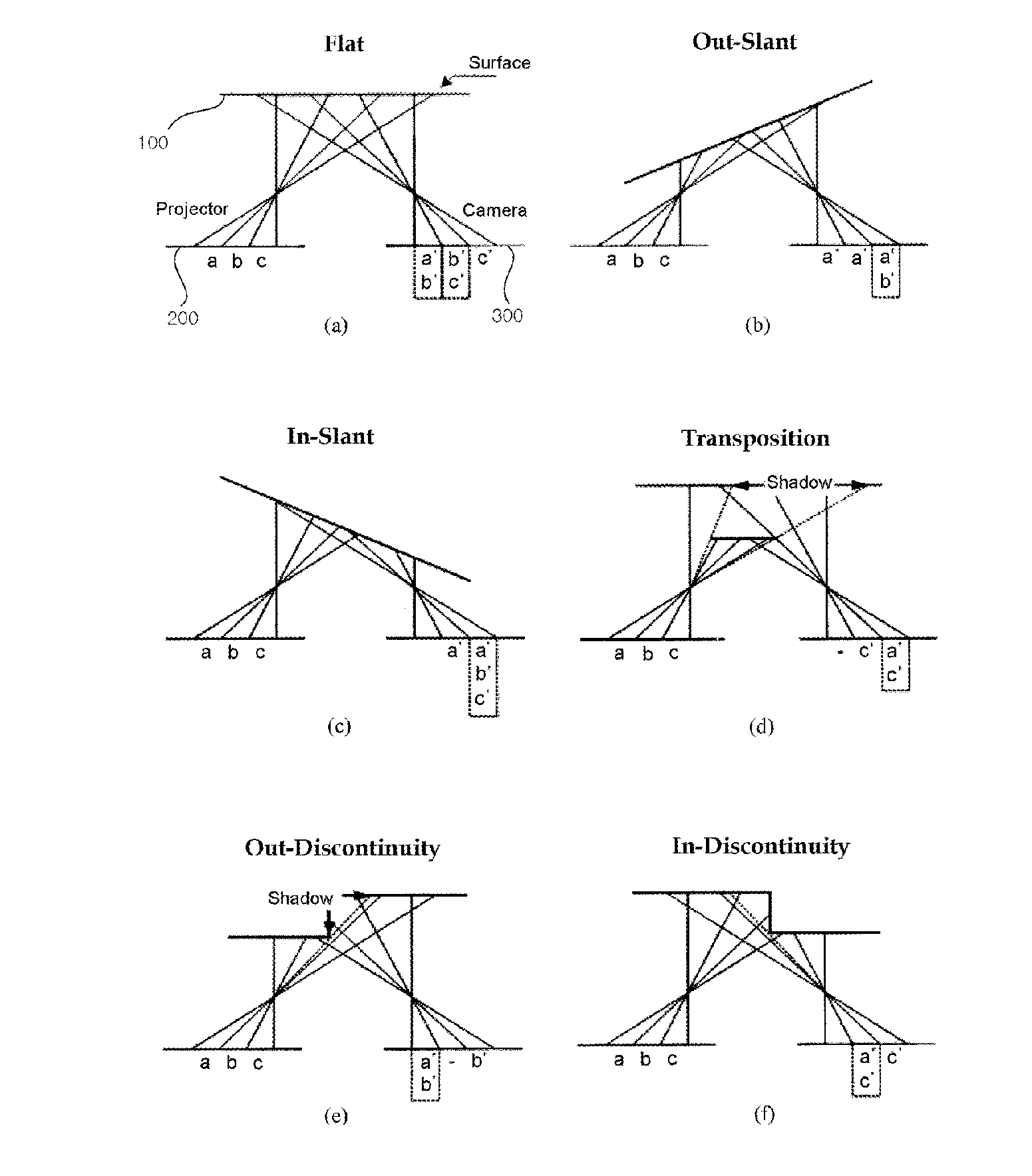
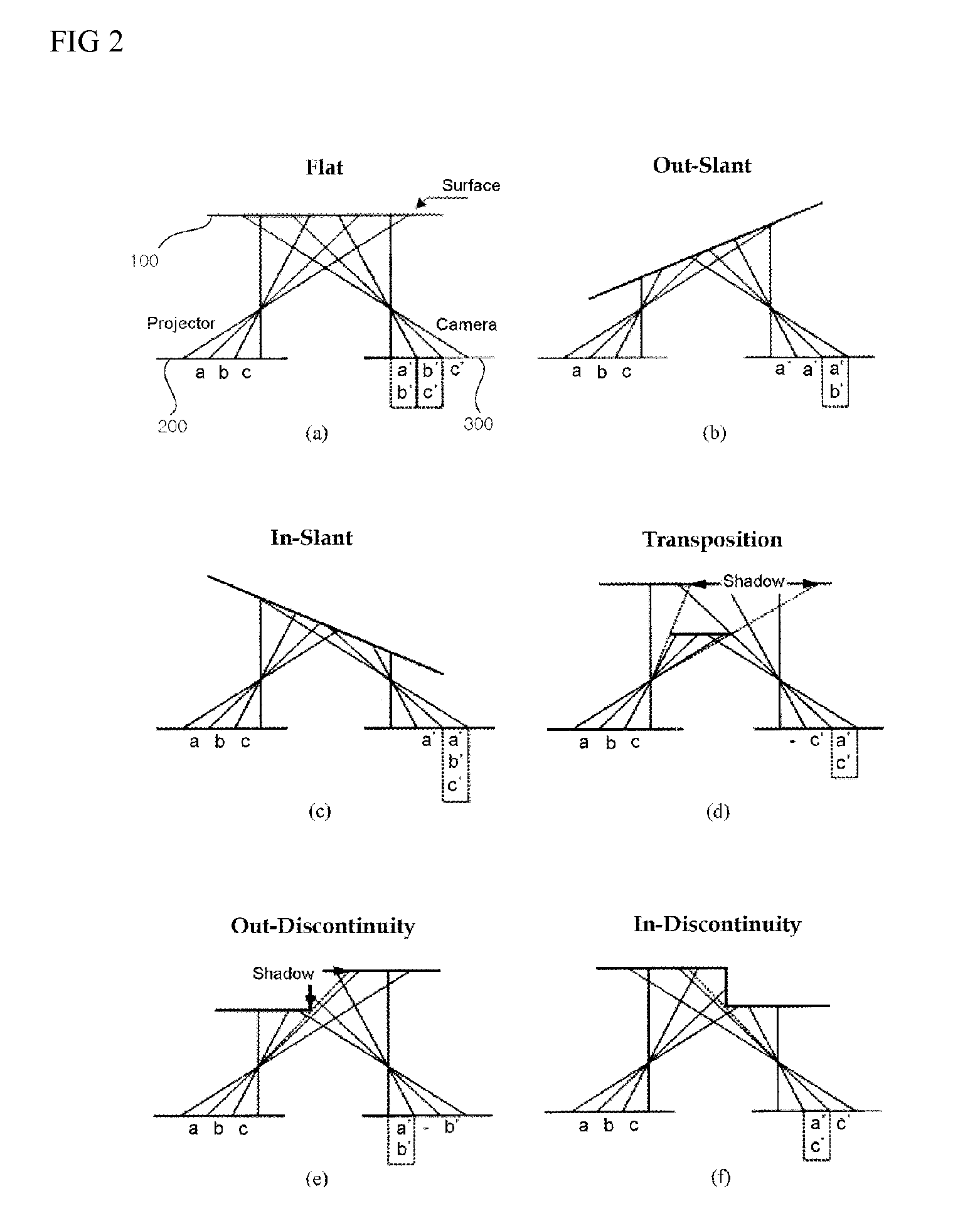
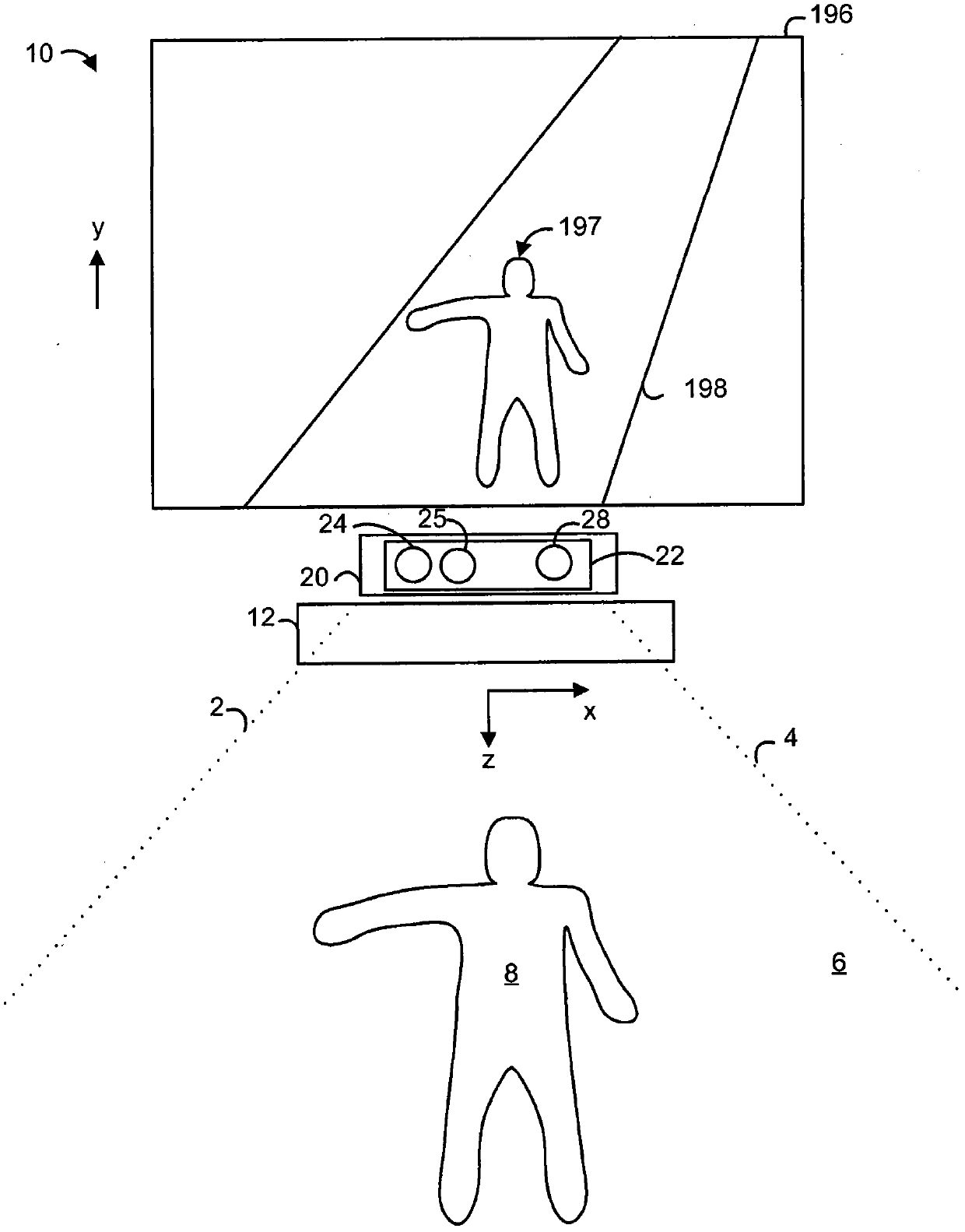
Method and system of structural light-based 3D depth imaging using signal separation coding and error correction thereof
InactiveUS20060210145A1Easy to explainImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionEnvironmental noiseDepth imaging
A 3D depth imaging method and system are disclosed. The 3D depth imaging method involves radiating light at a measurement target object using a projection means and imaging the light using an image receiving means, and includes the steps of assigning a unique transmitting side address to a signal corresponding to each pixel of the projection means to encode the signal; projecting multiple light patterns at the projection means to transmit the signal; receiving the encoded signal at the image receiving means; separating the received signal to restore the address; and determining a pixel position of the object using the transmitting side address and the restored address. With the 3D depth imaging method and system, it is possible to exactly separate signals received by the image receiving means even when the signals are overlap and the geometrical structure of the object varies, and it is also possible to obtain a depth image that is robust against ambient environmental noise.
Owner:ING GROUP NV
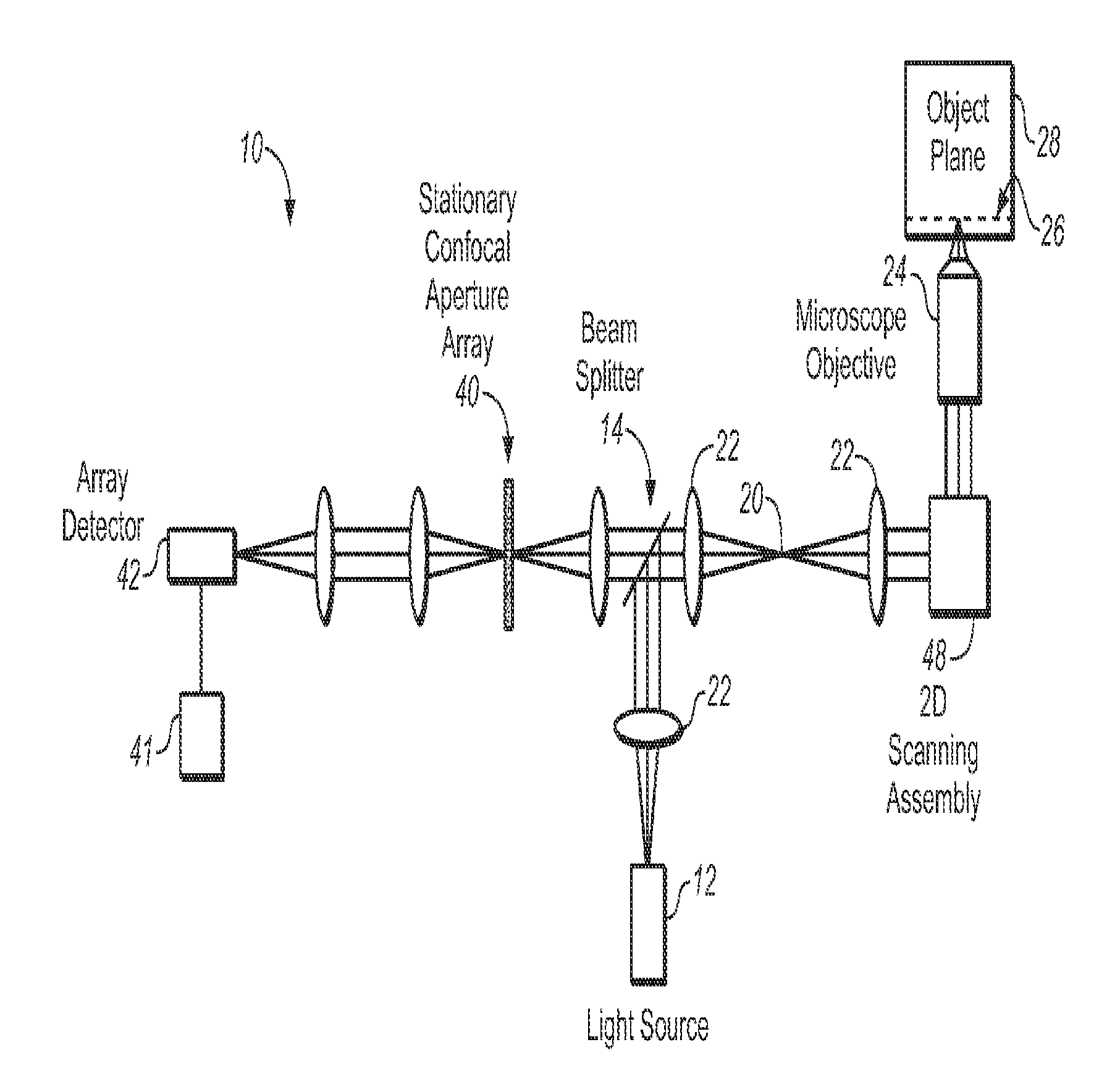
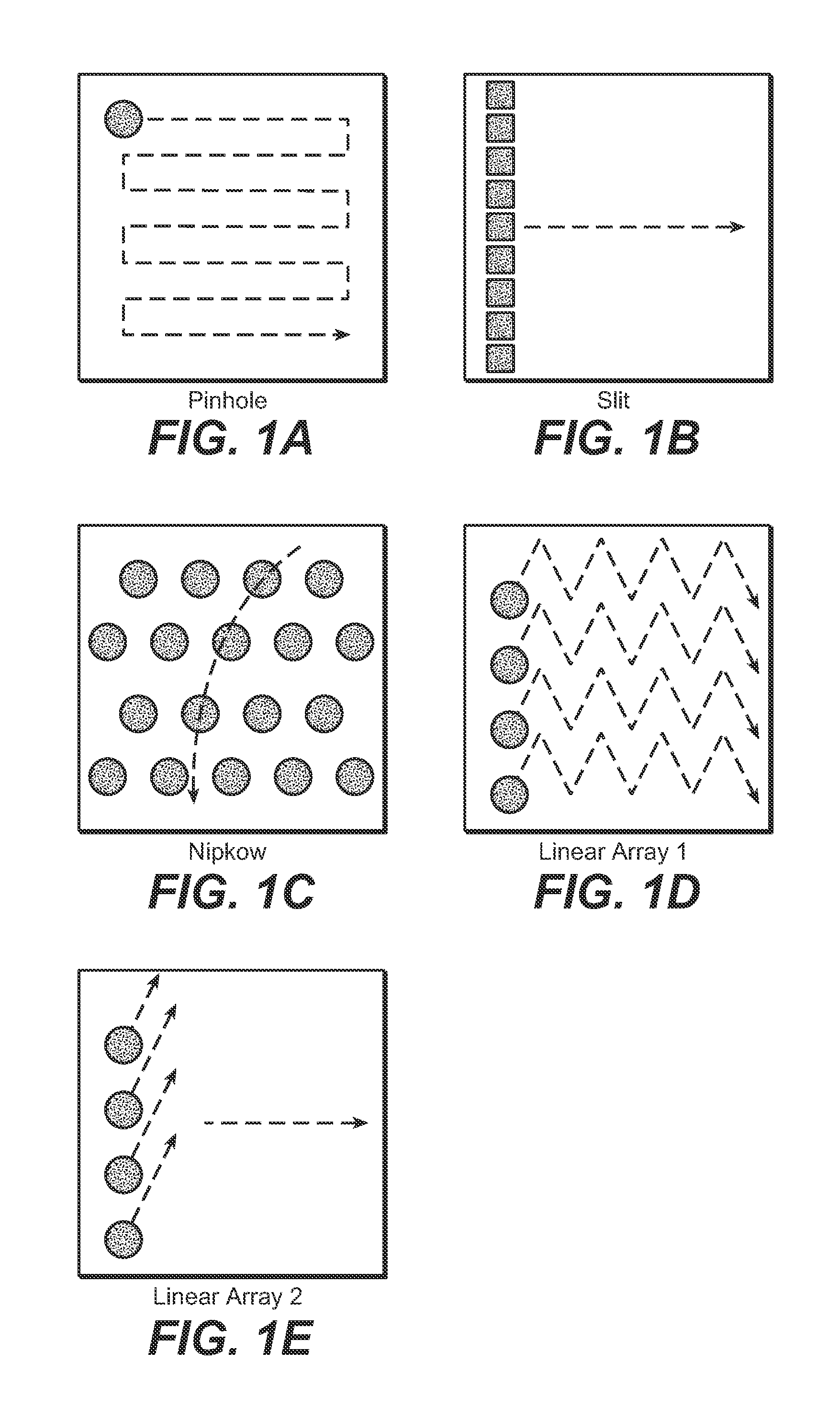
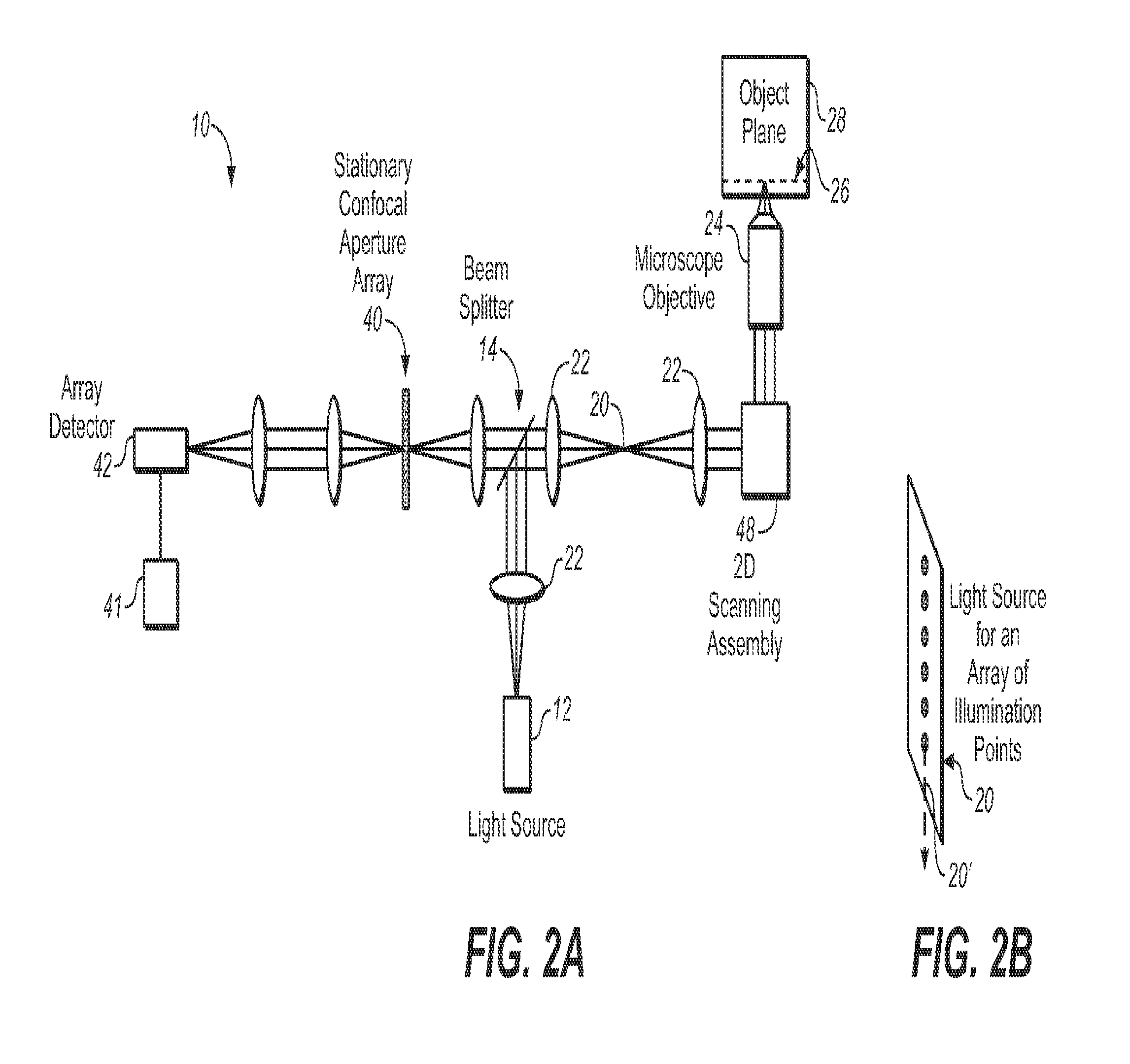
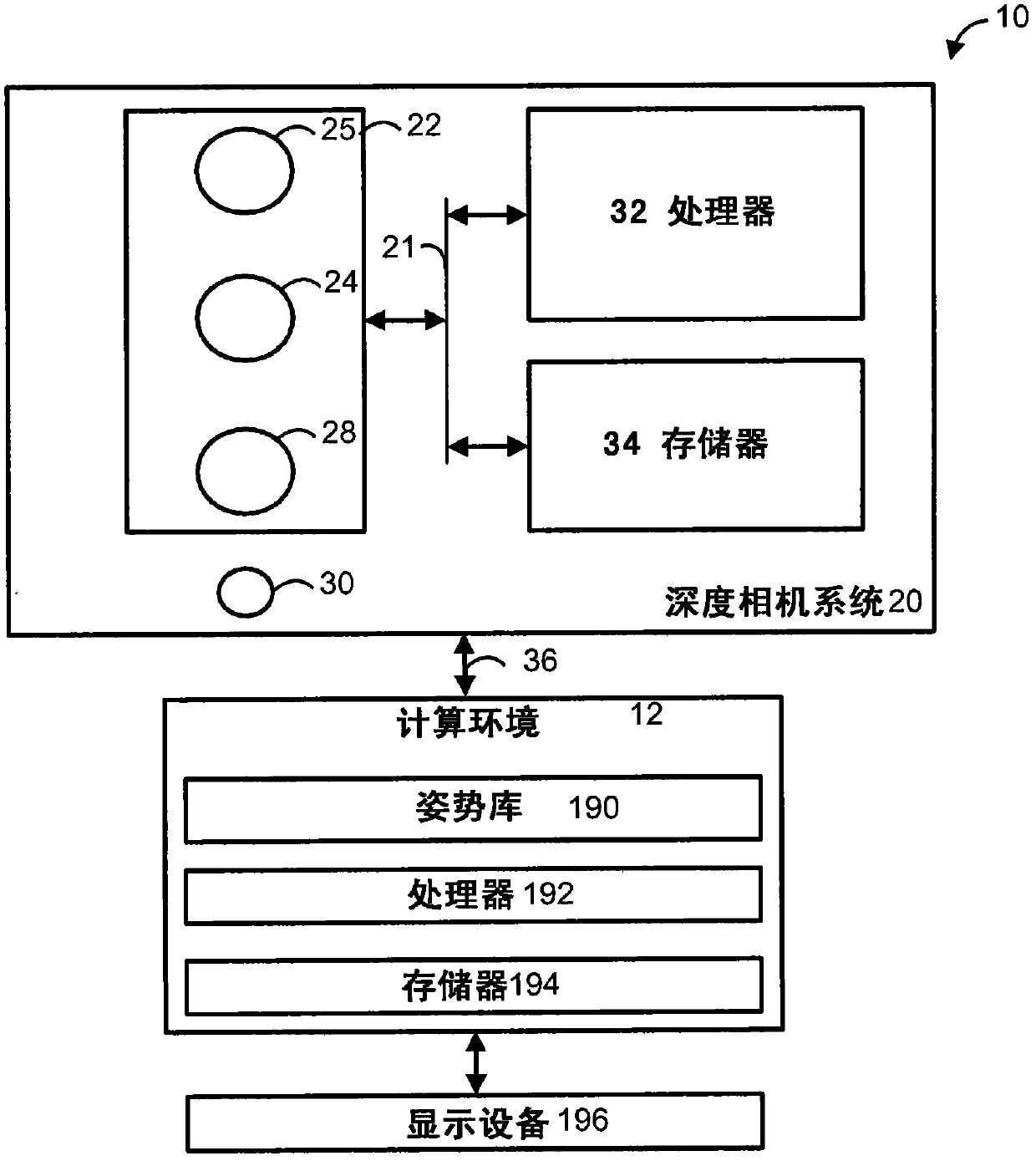
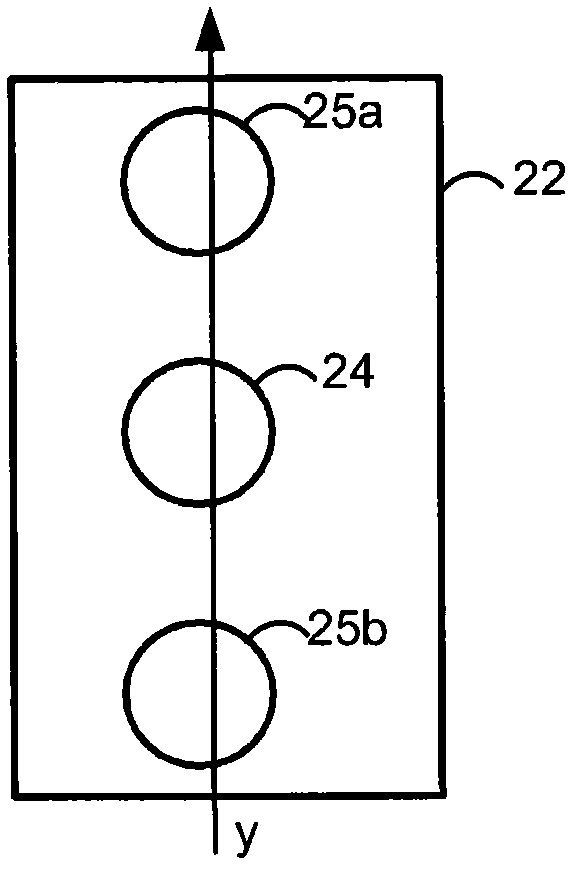
Novel Multi-Point Scan Architecture
ActiveUS20120113506A1Increase frame rateQuick switchPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersHigh frame rateDepth imaging
The embodiments of this invention use a multi-point scanning geometry. This design maintains the high frame rate of the slit-scan system and still allows both grayscale and multi-spectral imaging. In a confocal configuration, the multi-point scanning system's confocal performance is close to that of a single point scan system and is expected to yield improved depth imaging when compared to a slit-scan system, faster imaging than a point scan system, and the capability for multi-spectral imaging not readily achievable in a Nipkow disk based confocal system.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
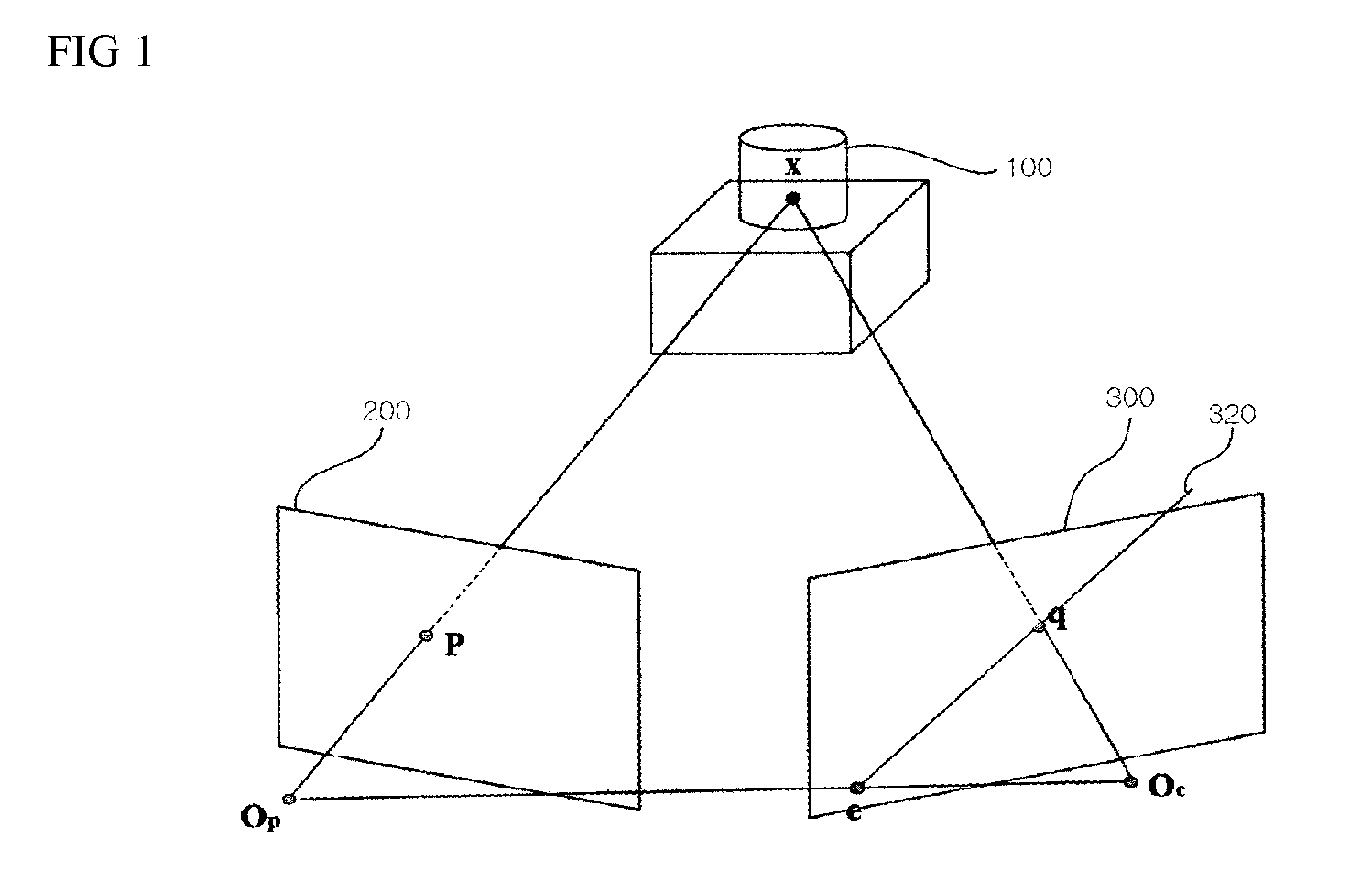
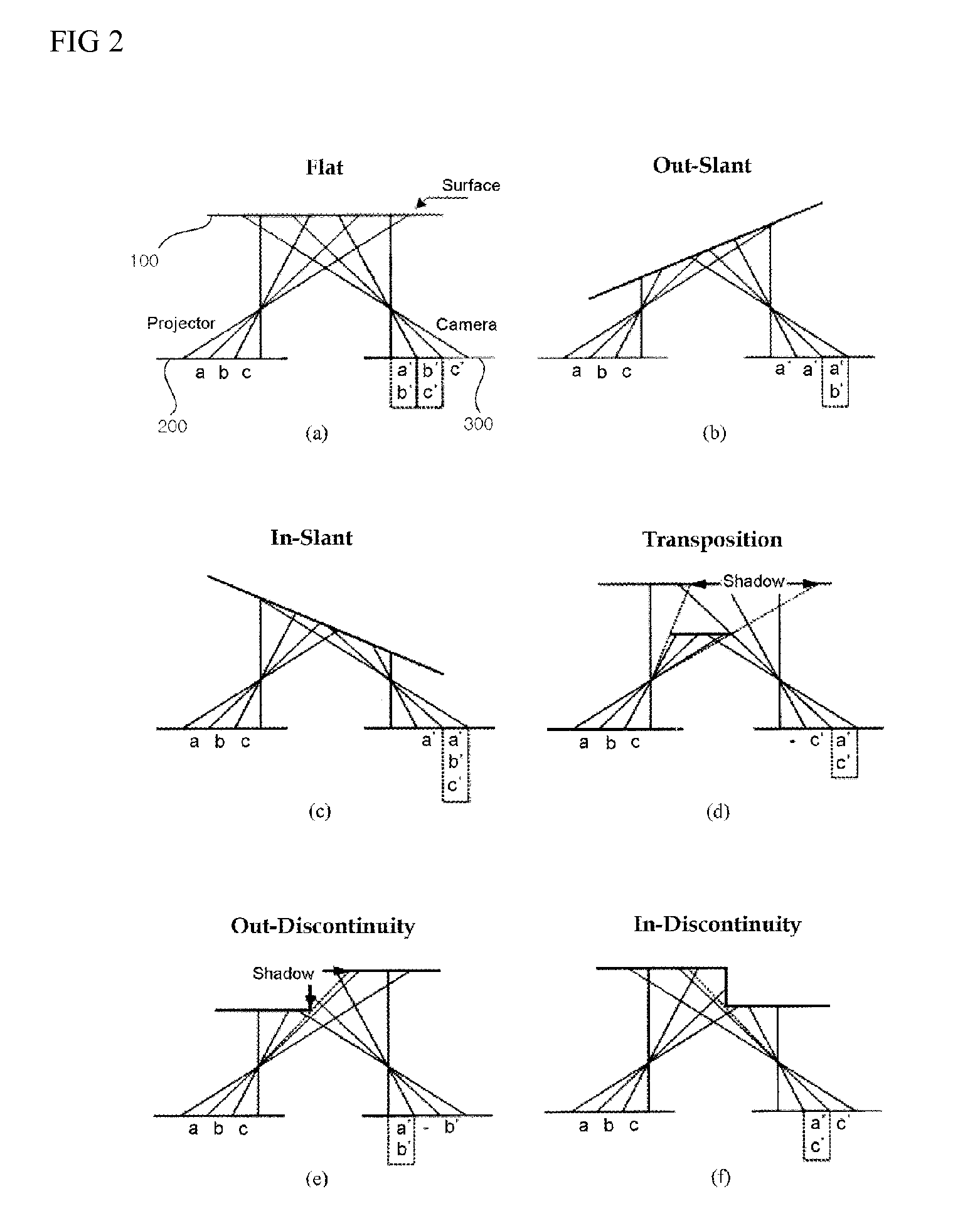
Structural light based depth imaging method and system using signal separation coding, and error correction thereof
ActiveUS20080205748A1Correct distortionCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansDepth imagingComputer science
Provided is a structural light based three-dimensional depth imaging method and system using signal separation coding and error correction thereof capable of detecting, removing and correcting corresponding errors between a projection apparatus and an image photographing apparatus caused by phenomena such as reflection on an object surface, blurring by a focus, and so on, using geometrical constraints between the projection apparatus and the image photographing apparatus. Here, the projection apparatus projects light, and the image photographing apparatus obtains the light. The depth imaging method includes projecting light from a projection apparatus, obtaining the light using an image photographing apparatus, and measuring a distance or a three-dimensional depth image. Therefore, it is possible to provide a structural light based thee-dimensional depth imaging method and system using geometrical conditions capable of precisely obtaining three-dimensional depth information of target environment.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
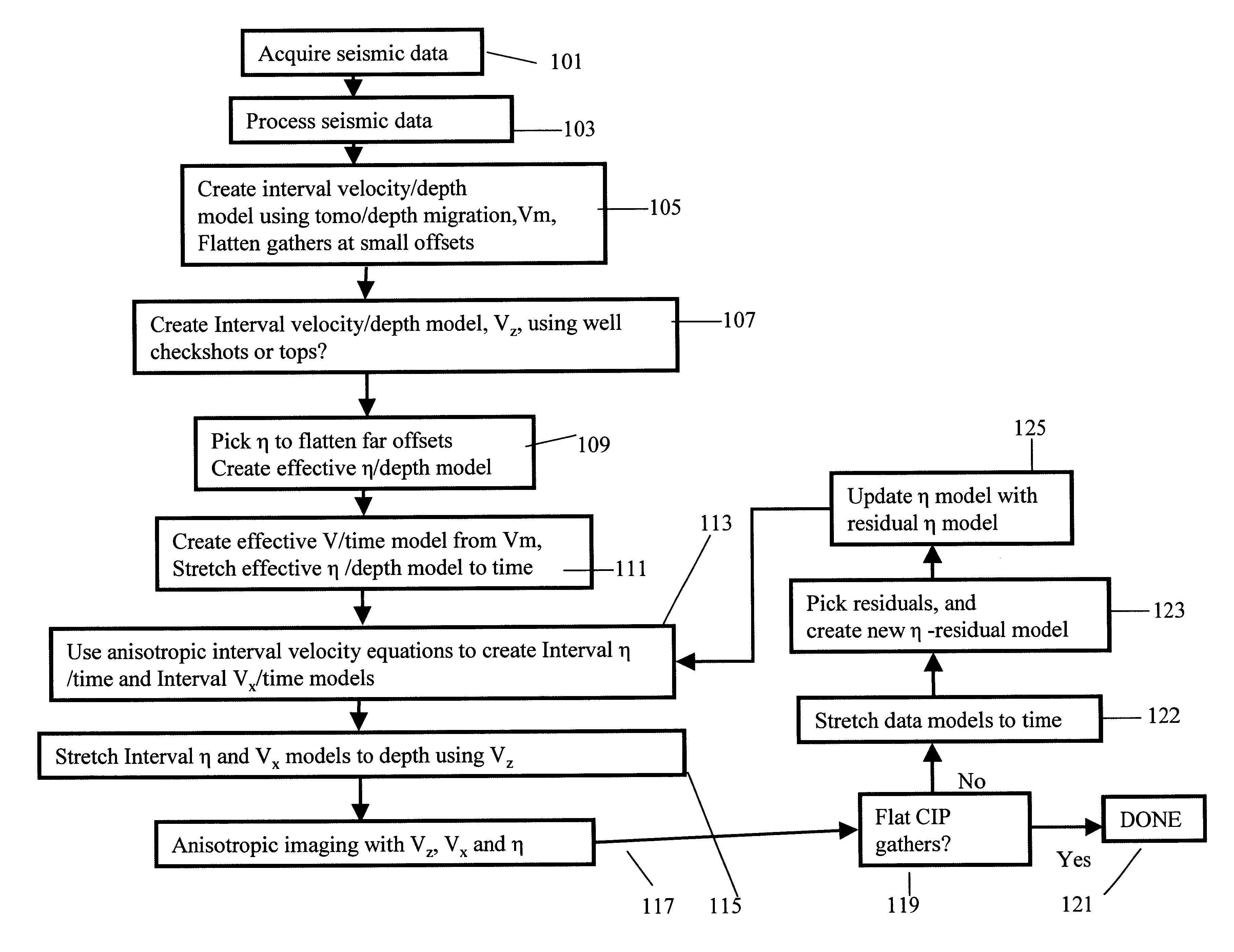
Method of building and updating an anisotropic velocity model for depth imaging of seismic data
InactiveUS6864890B2Drawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDepth imagingClassical mechanics
Conventional migration of short offset seismic data is performed. An interval velocity is obtained using, for example, check shots. An initial model of effective anellipticity parameter as a function of depth is obtained by flattening long offsets within a common image point. From these, interval anellipticity and horizontal velocity are obtained as a function of time. These initial models are used for anisotropic imaging. Any remaining residuals are used to update the interval anellipticity model and the process of migration is repeated until satisfactory results are obtained.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Molecular imaging and nanophotonics imaging and detection principles and systems, and contrast agents, media makers and biomarkers, and mechanisms for such contrast agents
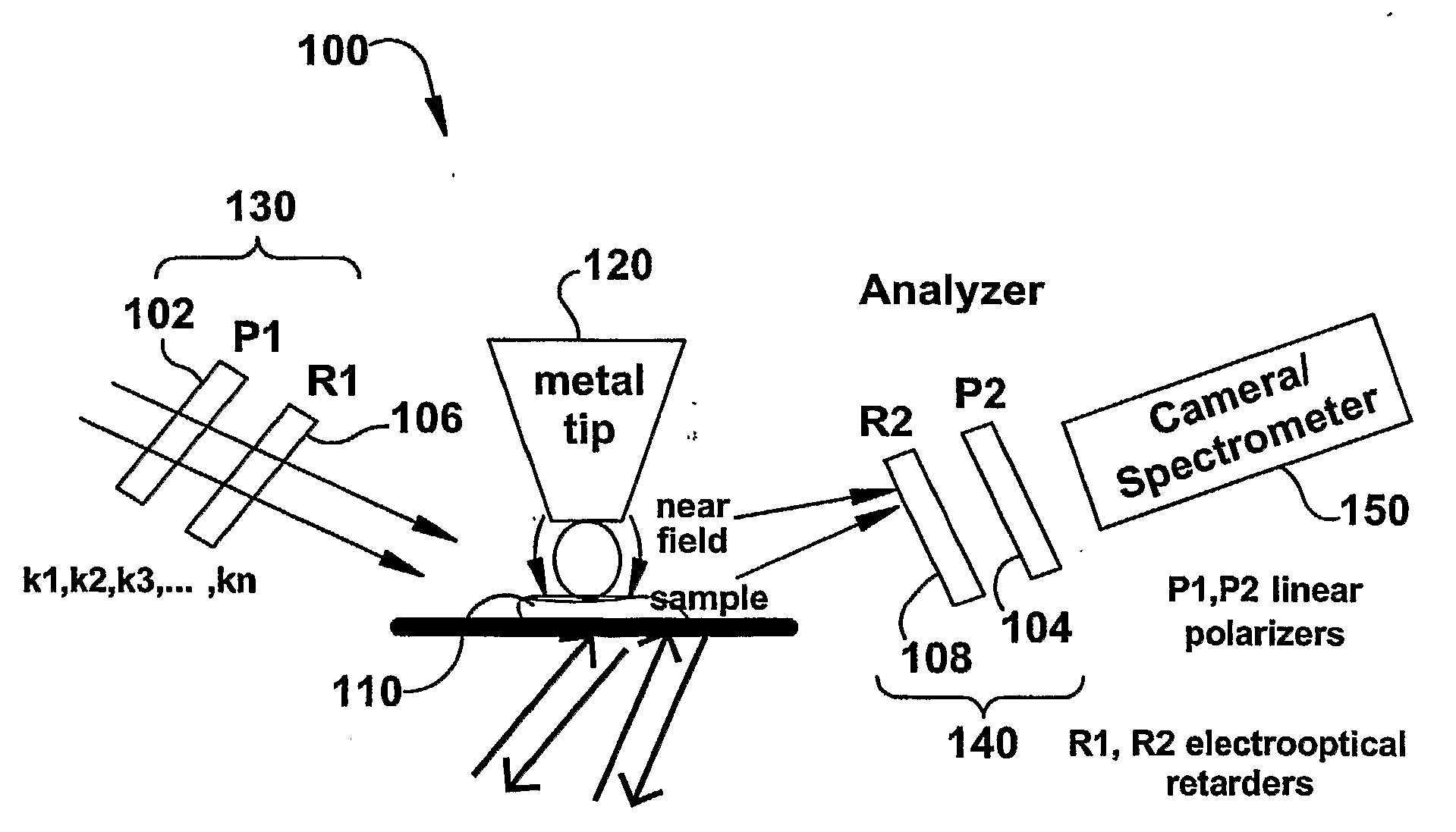
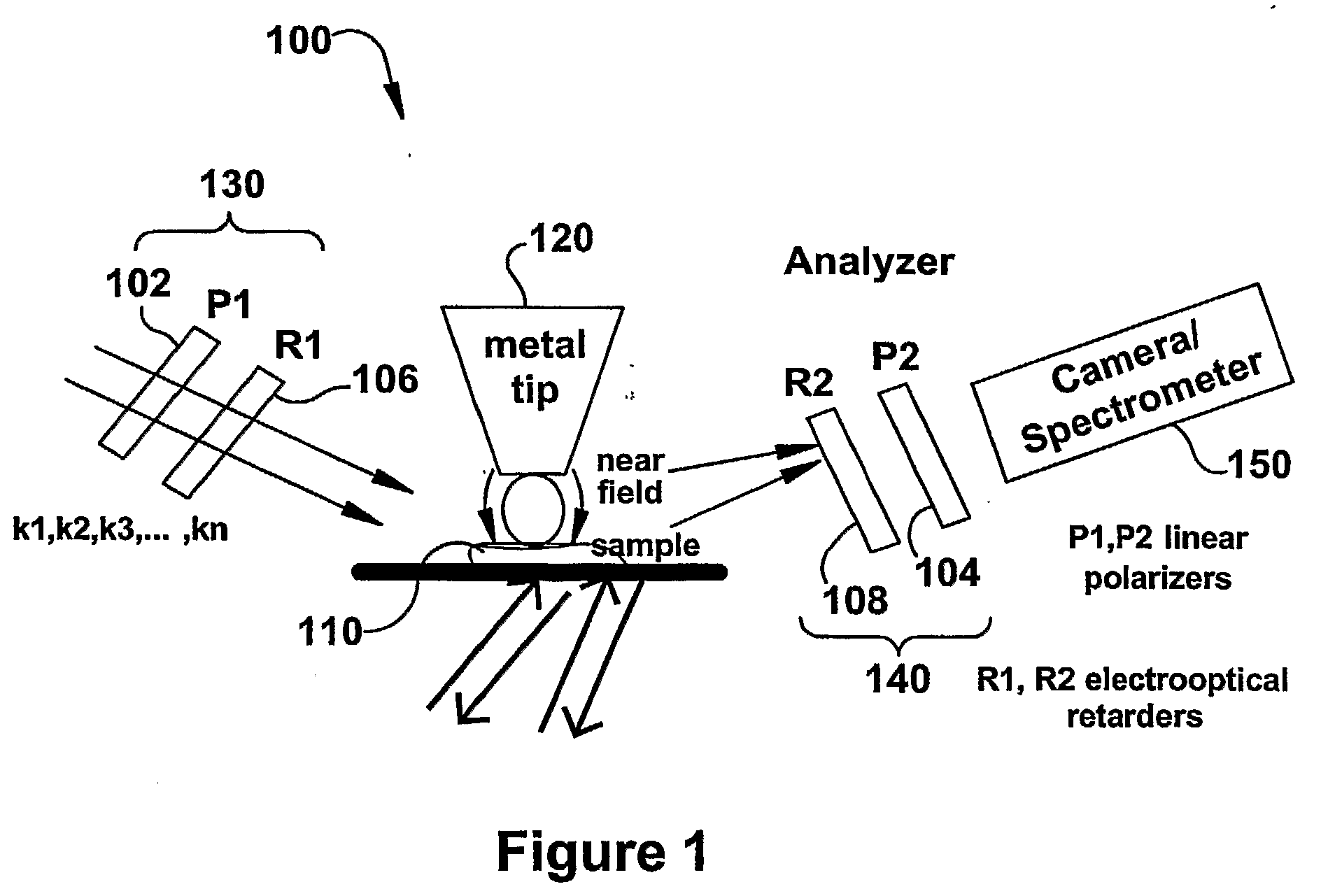
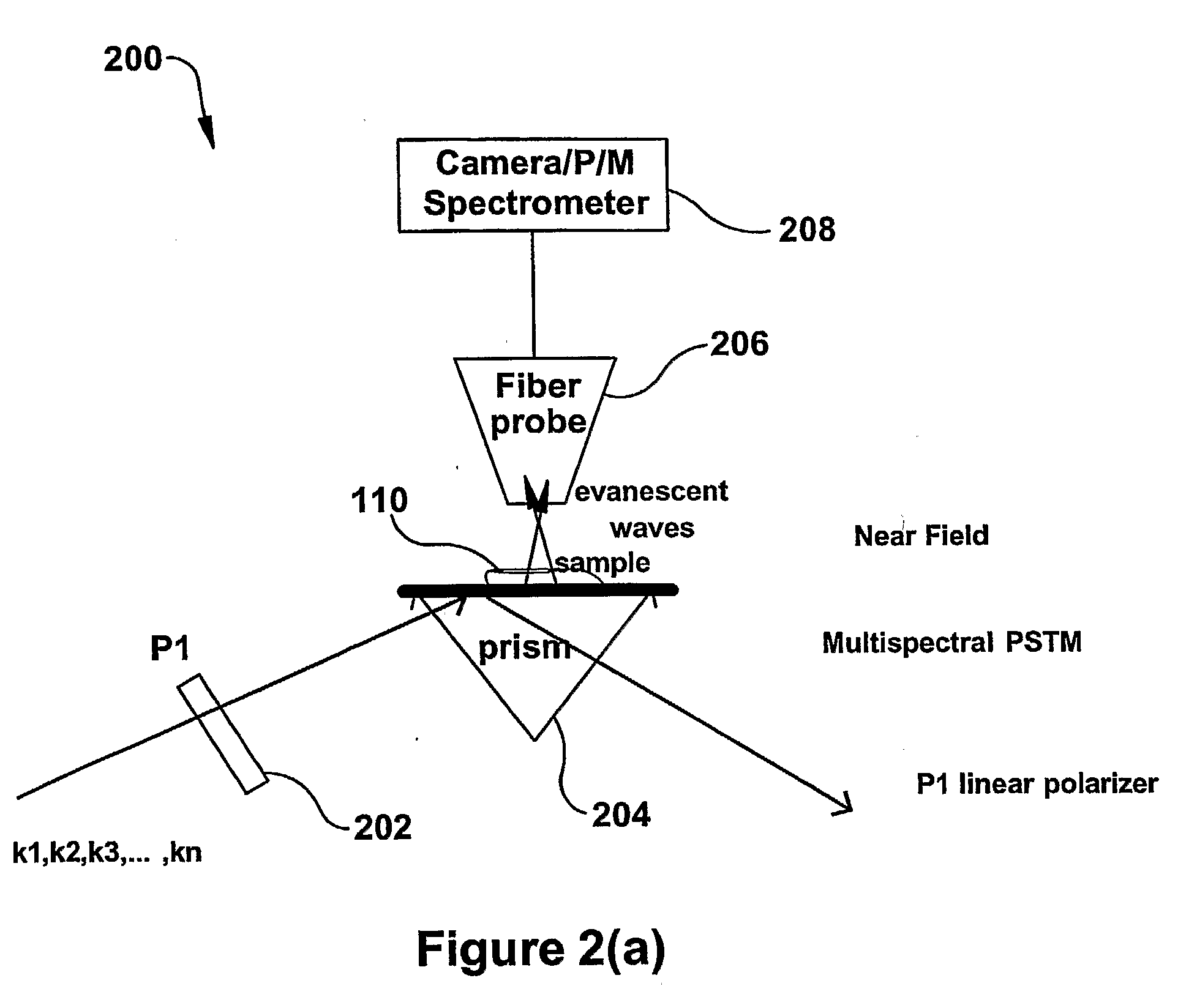
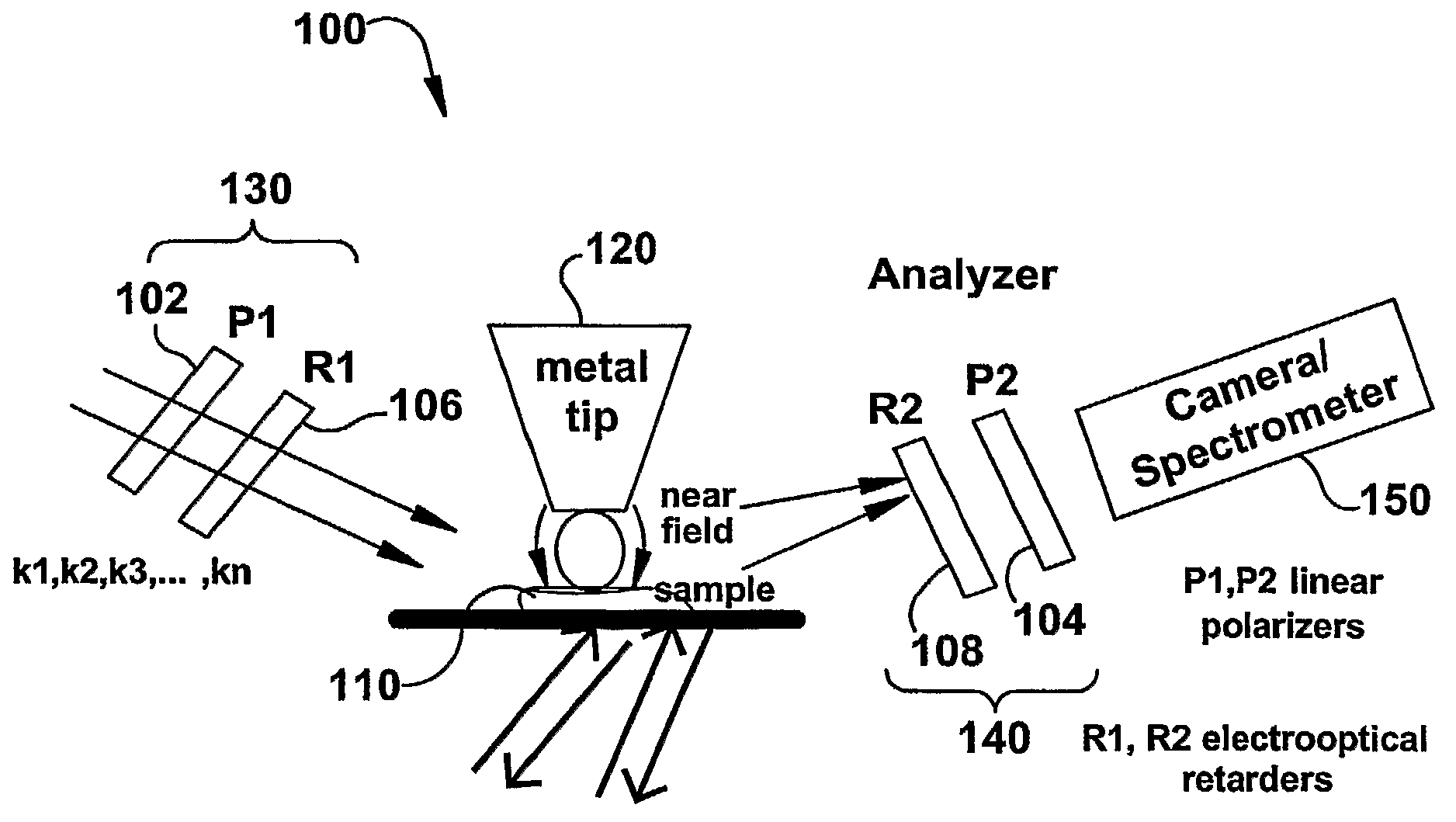
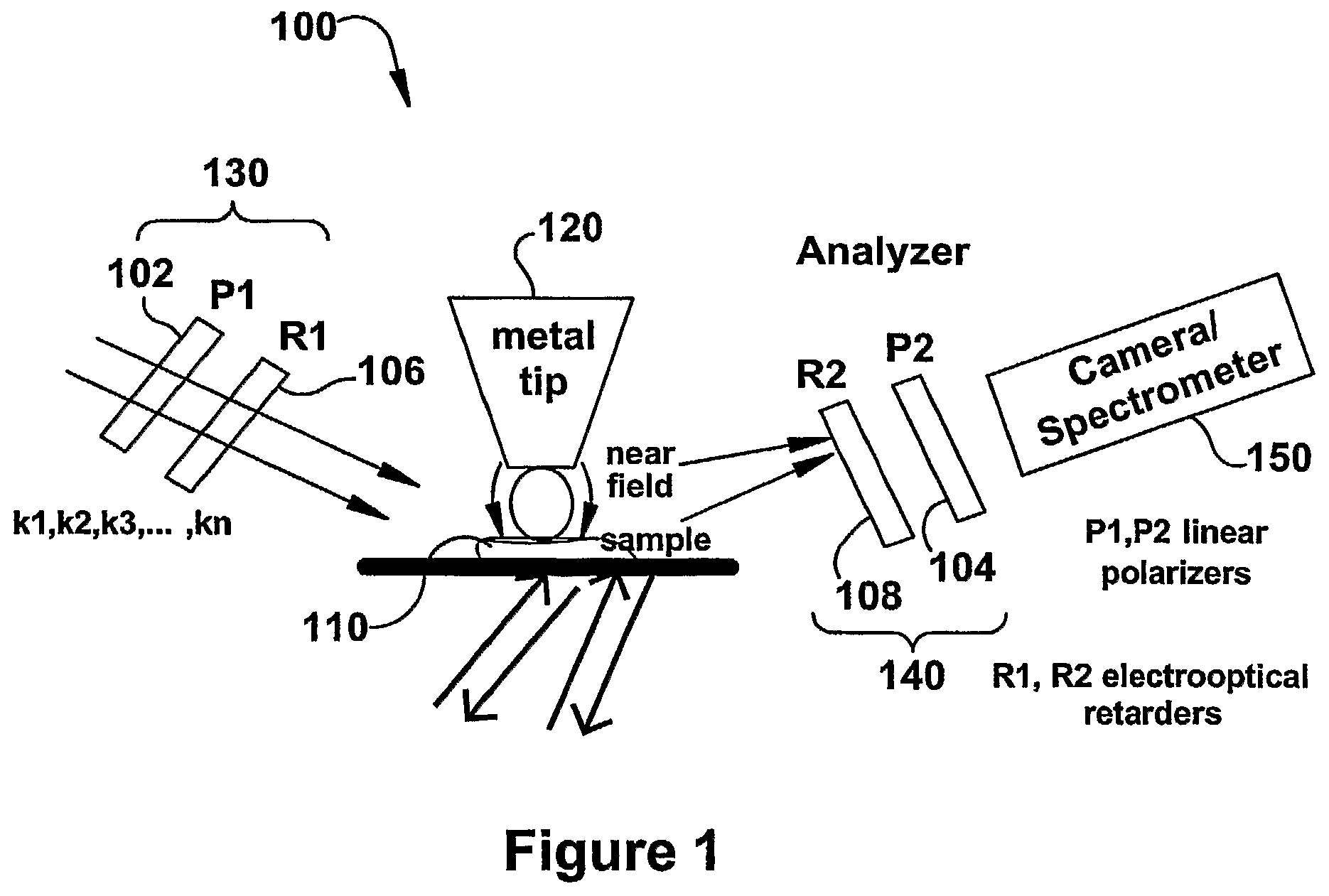
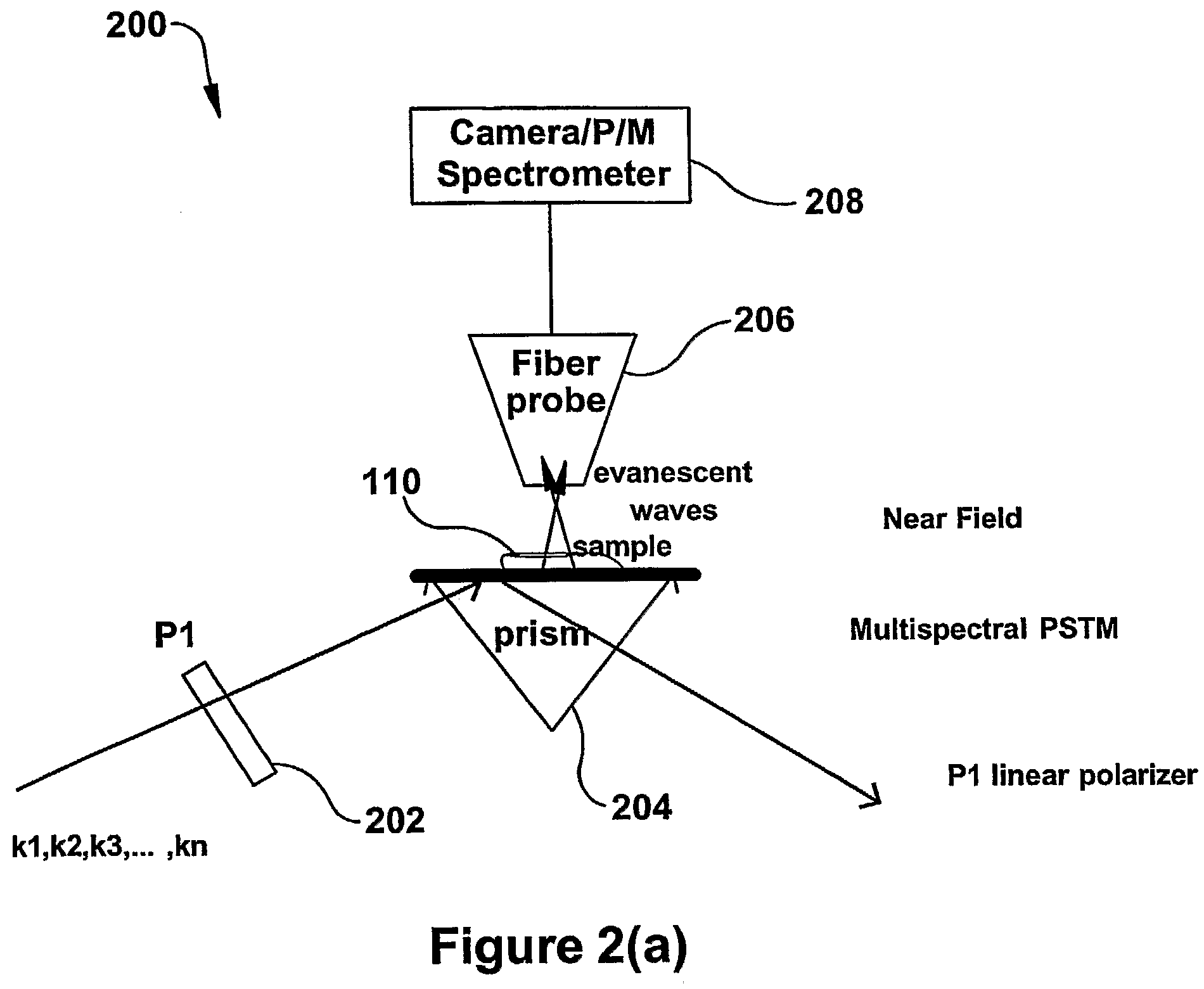
InactiveUS20090119808A1Enhanced sub-surfaceEnhanced in-depth imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesSurface/boundary effectDepth imagingImage resolution
The present invention relates to near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) and near-field / far-field scanning microscopy methods, systems and devices that permit the imaging of biological samples, including biological samples or structures that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the present invention permits the production of multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field microscopy systems that can achieve a spatial resolution of less than 100 nanometers. In another embodiment, the present invention permits the production of a multifunctional, multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field / far-field microscopy that can achieve enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imaging of biological samples. In still another embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of polar molecules as new optical contrast agents for imaging applications (e.g., cancer detection).
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
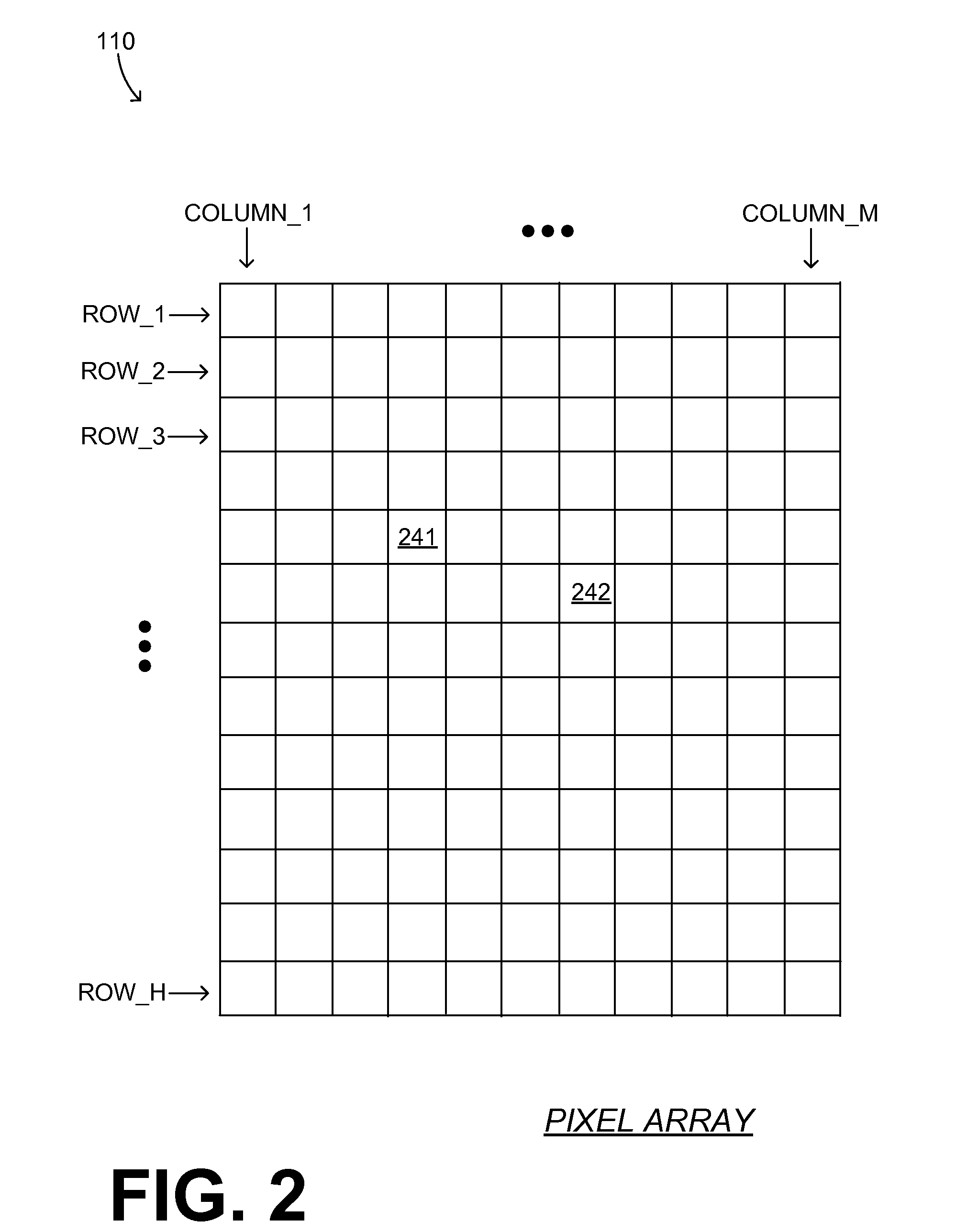
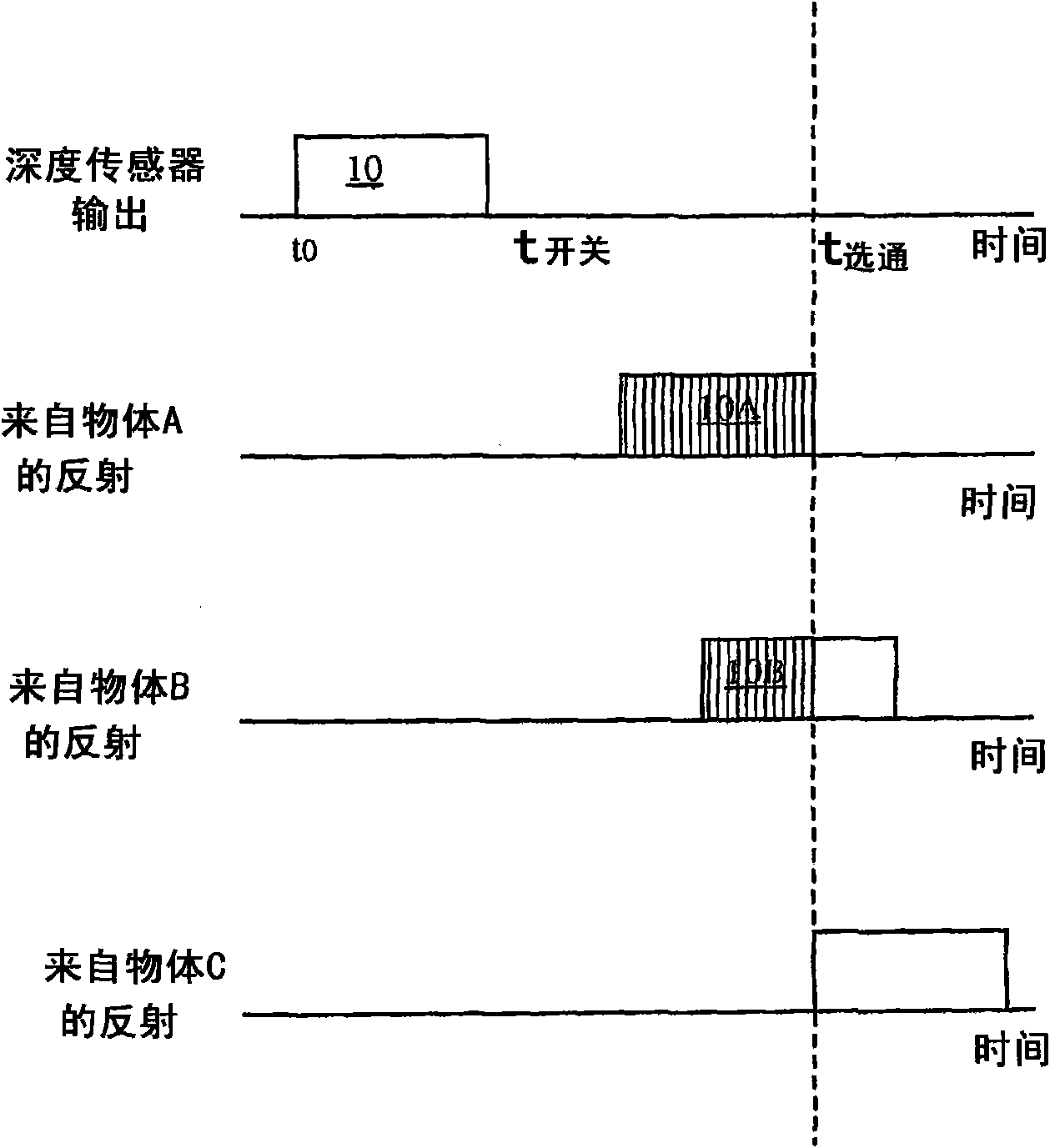
Correction of depth images from t-o-f 3D camera with electronic-rolling-shutter for light modulation changes taking place during light integration
ActiveUS20160198147A1Fast frame rateAvoid inefficiencyElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systemsLight sensingDepth imaging
In embodiments, a T-O-F depth imaging device renders a depth image of an object that has corrected depth values. The device includes a pixel array that uses an Electronic Rolling Shutter scheme. The device also includes a light source that transmits towards the object light that is modulated at an operating frequency, and an optical shutter that opens and closes at the operating frequency. The optical shutter further modulates the light that is reflected from the object, before it reaches the pixel array. The transmission of the light and the operation of the shutter change phase relative to each other while at least one of the pixels is sensing the light it receives, which permits a faster frame rate. Depth is determined by the amount of light sensed by the pixels, and a correction is computed to compensate for the changing phase.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
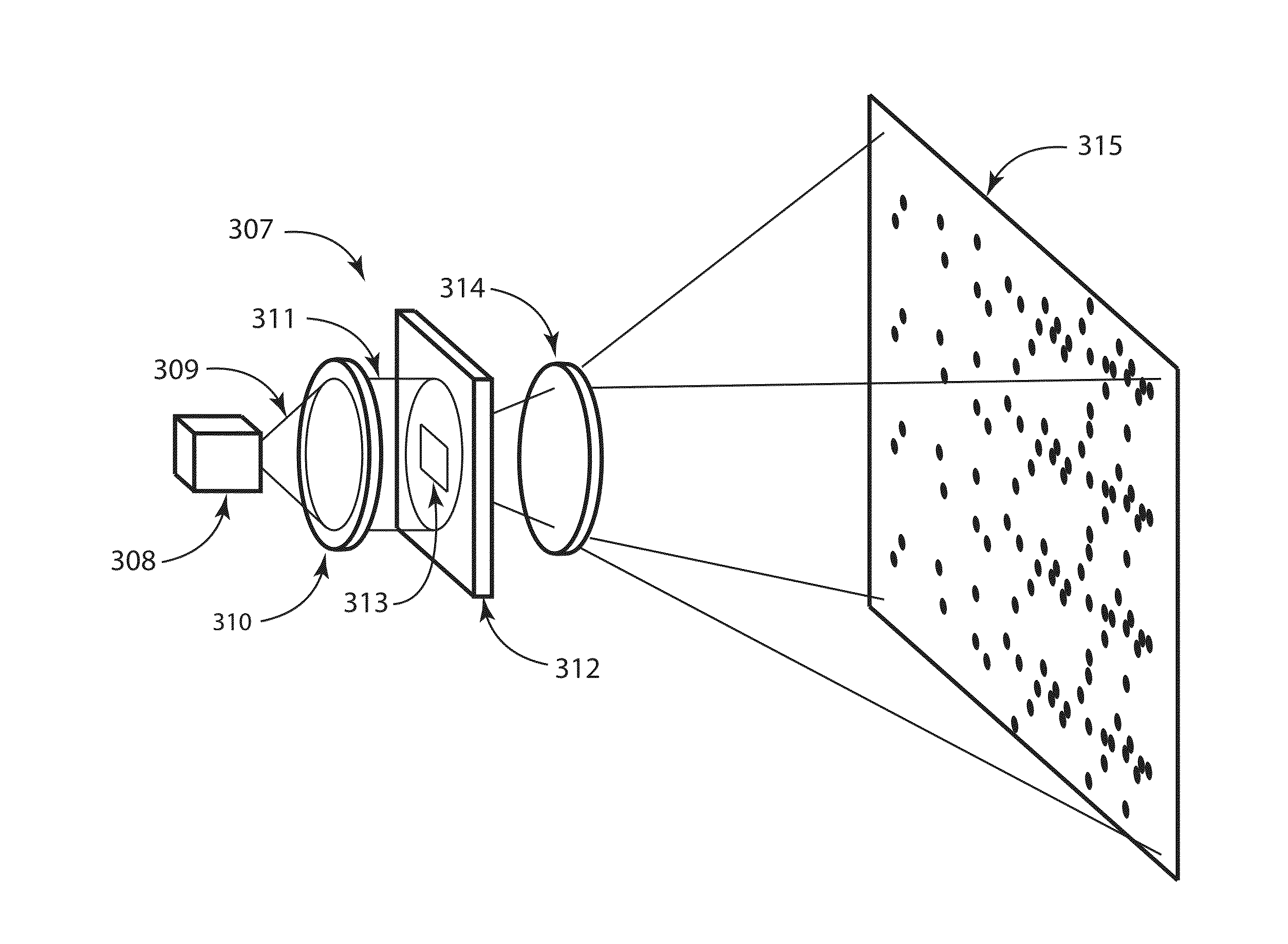
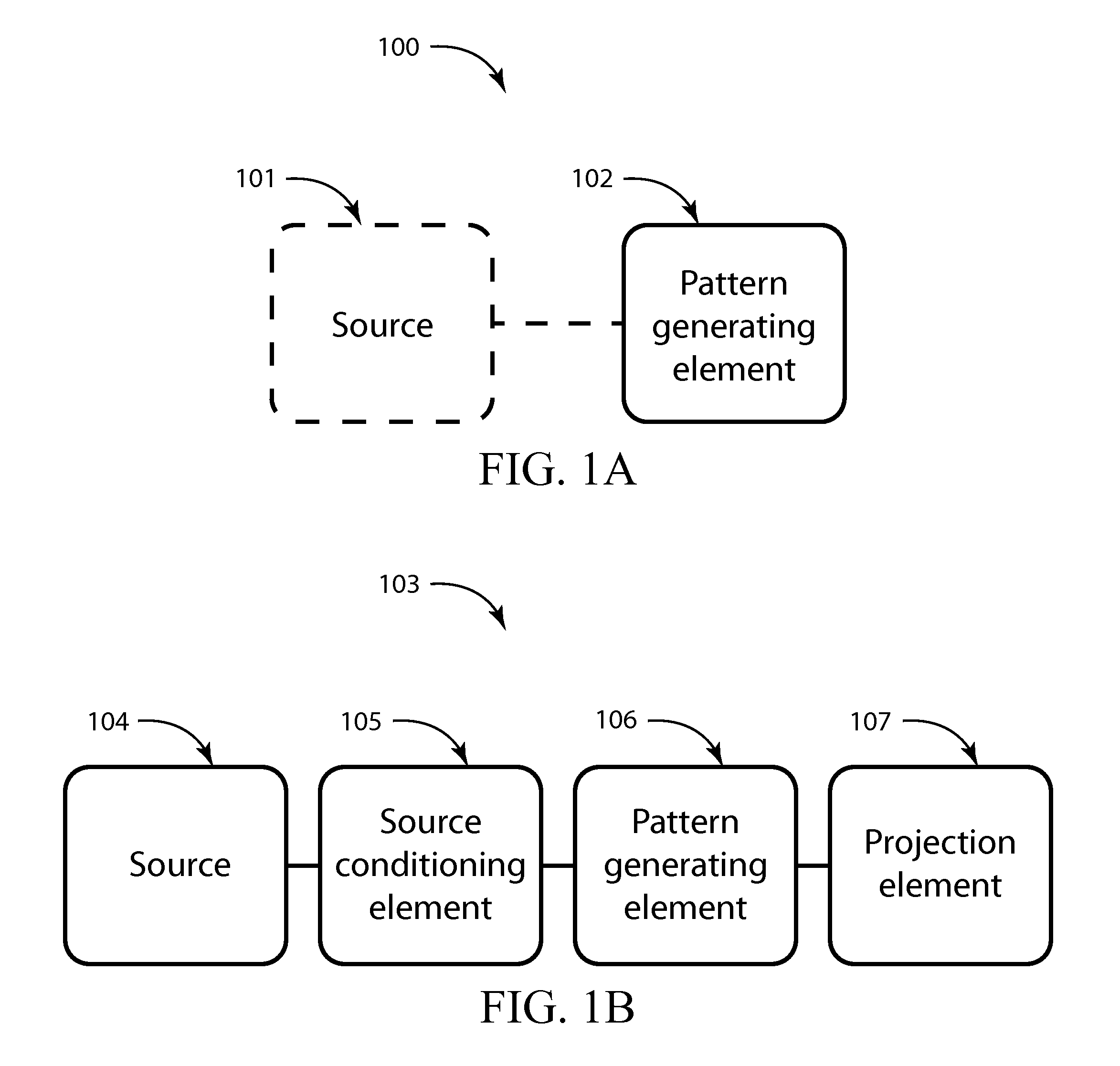
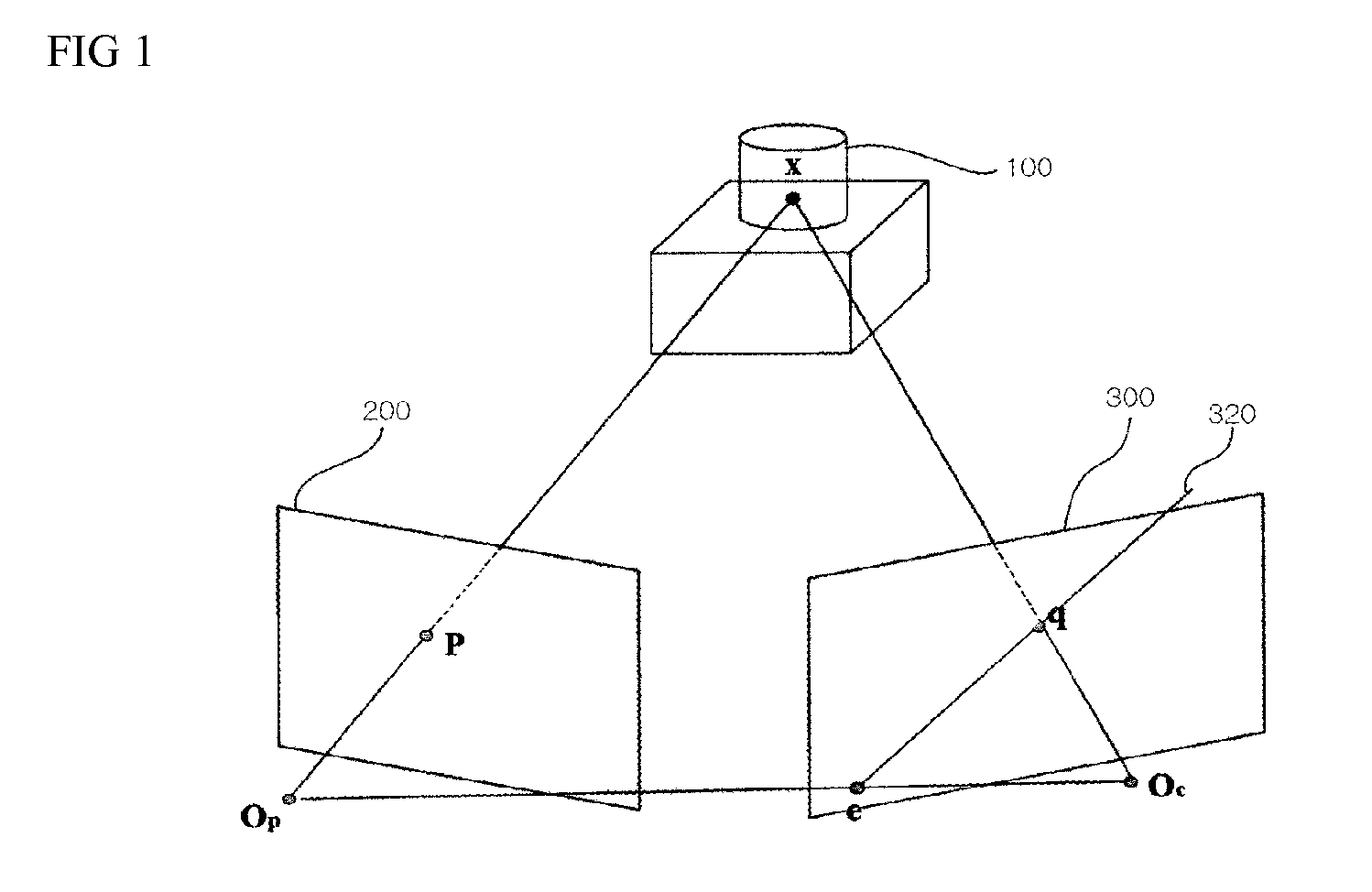
Spatially self-similar patterned illumination for depth imaging
Methods, systems, and devices involving patterned radiation are provided in accordance with various embodiments. Some embodiments include a device for projecting pattern radiation. Some embodiments include a method for estimating coordinates of a location on an object in a 3D scene. Some embodiments include a system for estimating the coordinates of a location on an object in a 3D scene. A variety of radiation patterns are provided in accordance with various embodiments. Some embodiments may relate to the use of patterned illumination to identify the angular information that may be utilized to measure depth by triangulation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Rendered audiovisual communication
ActiveUS9479736B1Television system detailsTelevision conference systemsStereoscopic imagingCommunications system
Systems and approaches are provided to allow for rendered audiovisual communication. An electronic device can be used to capture image information relating to physical features of a user. A model can be generated from the image information, and the model may be used to render audiovisual communication information from image and audio captured in real time. The rendered audiovisual communication data can simulate live video conferencing with substantial performance gains over conventional approaches to video conferencing. When the image capturing component of the electronic device is capable of depth imaging, stereo imaging, or other imaging techniques, the rendered audiovisual communication can be further enhanced with 3-D rendering of the user. Other aspects of audiovisual data, such as speech, background, and lighting conditions can also be rendered or synthesized to improve audiovisual communication.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Method for inverting near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms
The invention discloses a method for inverting a near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms. The method comprises acoustic wave equation-based wave field forward modeling and steepest descent-based waveform inversion technologies, and comprises the following steps of 1, extracting time-domain preliminary waveform records and an initial model; 2, calculating a simulated wave field and a wave field residual by utilizing acoustic wave equation staggered grid finite-difference forward modeling simulation; 3, reversely propagating the wave field residual to obtain a retransmission wave field; 4, calculating a gradient of a target function by utilizing the retransmission wave field and a forward propagation wave field, and calculating an updating step length; 5, updating a speed model; 6, inspecting whether the speed model is consistent with an iteration stopping condition, outputting the speed model if the speed model is consistent with the iteration stopping condition, otherwise returning to the step 2, and continuing iterative updating. According to the method, a wave equation theory-based full-waveform inversion technology is used as reference, and preliminary waves with higher energy and more stable waveforms are used for inversion, so that the multiplicity of solutions of full-waveform inversion is reduced, and the inversion stability and the calculation efficiency are improved; the accuracy of static correction and shallow depth imaging is improved.
Owner:中国石油集团西北地质研究所有限公司
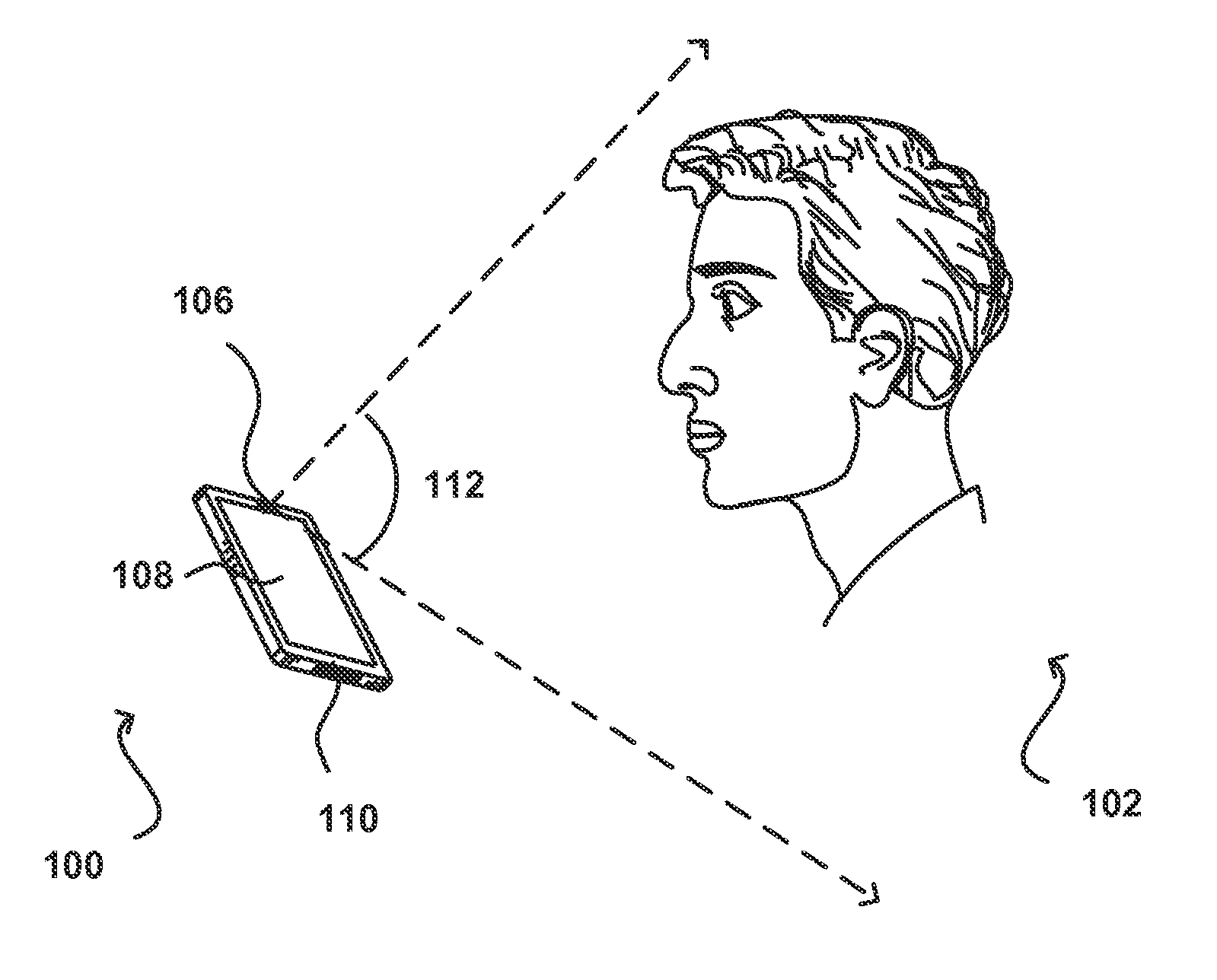
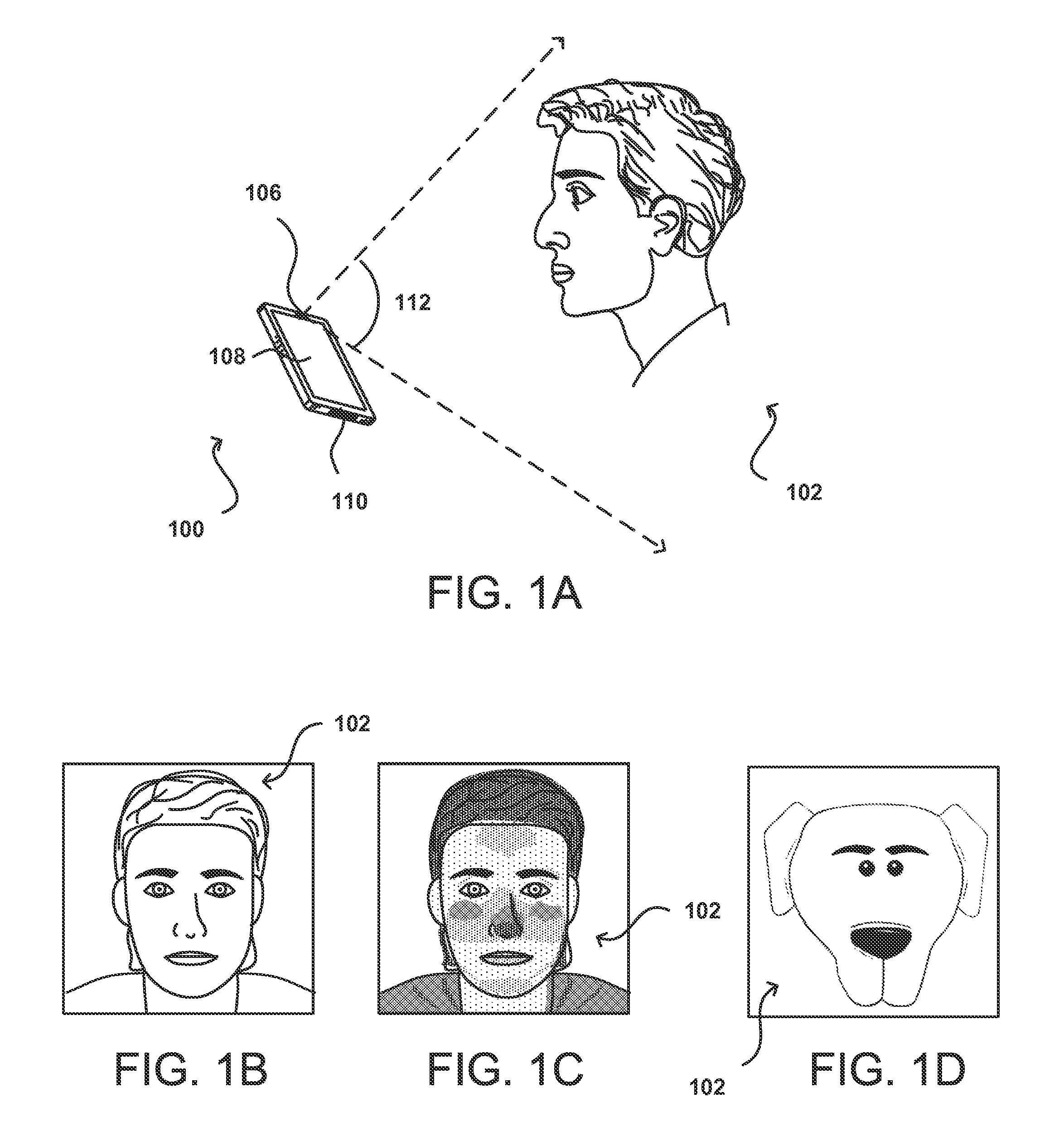
Remote iris intelligent imaging device and method
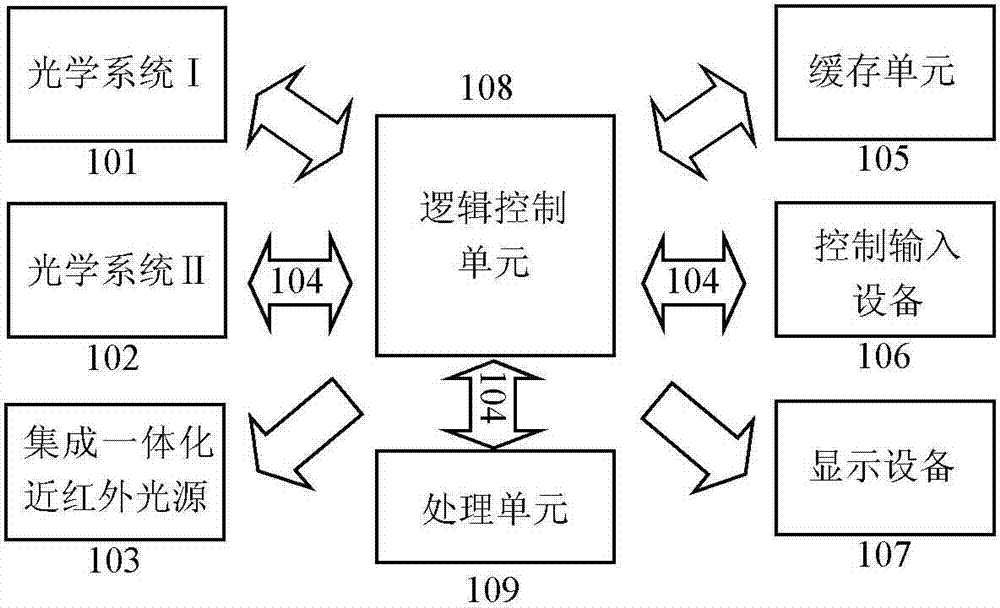
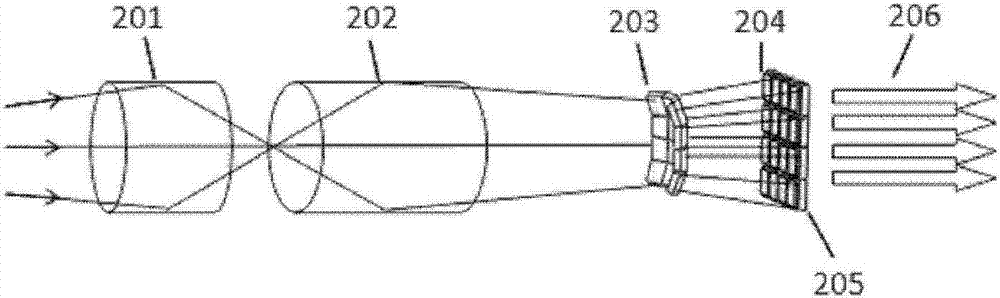
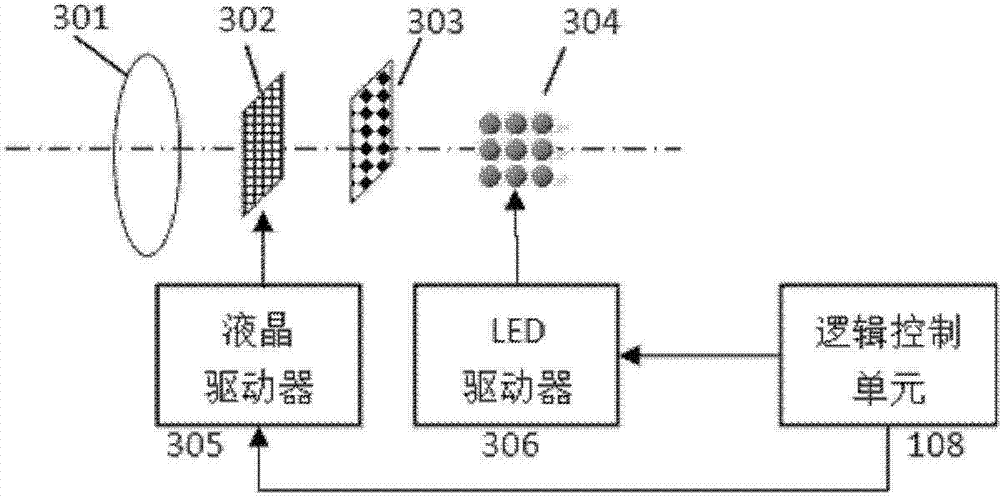
ActiveCN102855471AImprove the level of technologyPromote recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical elementsFace detectionDepth imaging
The invention discloses a remote iris intelligent imaging device and a method. The device comprises an optical system I for depth imaging, an optical system II for obtaining optical field data, an integrated near-infrared source, a data transmission module, a cache unit, a control input device, a display device, a logic control unit and a processing unit. According to the device and the method, lens arrays and multi-sensor optical systems are constructed to obtain the optical field data, head posture estimation, face detection and human eye detection technologies are used for achieving an intelligent man-machine interactive mode, and image processing methods such as image enhancement, mosaic, multiple focusing are combined to achieve remote iris imaging with the large depth of field; and practicability of the iris recognition technology is improved, the application range of the iris recognition system is expanded, and the device and the method play an important role in promoting research and application development of iris biometric recognition.
Owner:TIANJIN IRISTAR TECH LTD
Dual mode depth imaging
A depth imaging system comprising: apparatus operable in first and second modes to provide depth images of a scene; and a processor adapted to selectively control the apparatus to operate in the first or second mode to provide a depth map responsive to at least one predefined threshold.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
T-O-F depth imaging device rendering depth image of object and method thereof
A T-O-F depth imaging device rendering a depth image of an object and a method thereof are provided. In embodiments, a T-O-F depth imaging device renders a depth image of an object that has corrected depth values. The device includes a pixel array that uses an Electronic Rolling Shutter scheme. The device also includes a light source that transmits towards the object light that is modulated at an operating frequency, and an optical shutter that opens and closes at the operating frequency. The optical shutter further modulates the light that is reflected from the object, before it reaches the pixel array. The transmission of the light and the operation of the shutter change phase relative to each other while at least one of the pixels is sensing the light it receives, which permits a faster frame rate. Depth is determined by the amount of light sensed by the pixels, and a correction is computed to compensate for the changing phase.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wide Dynamic Range Depth Imaging
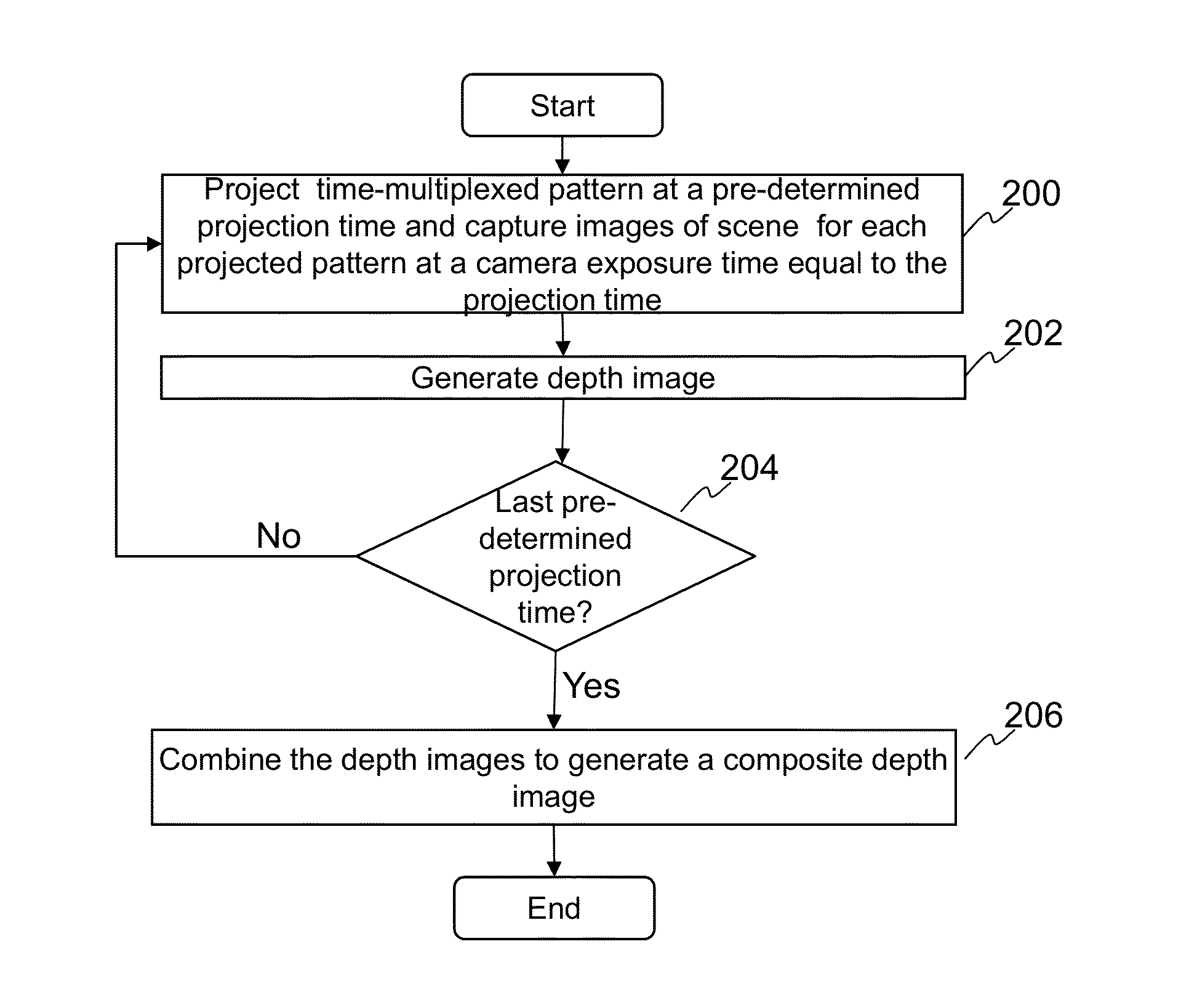
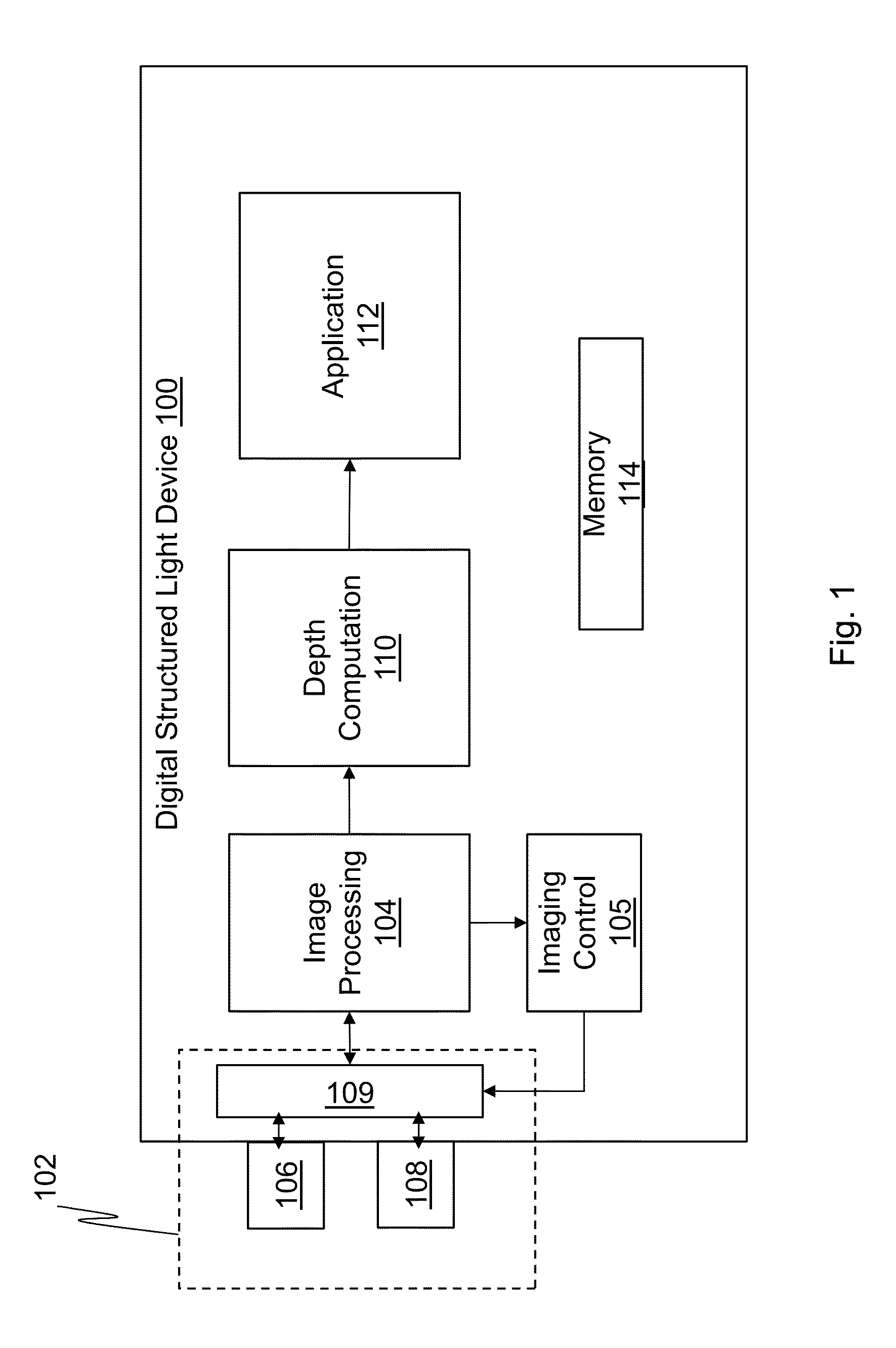
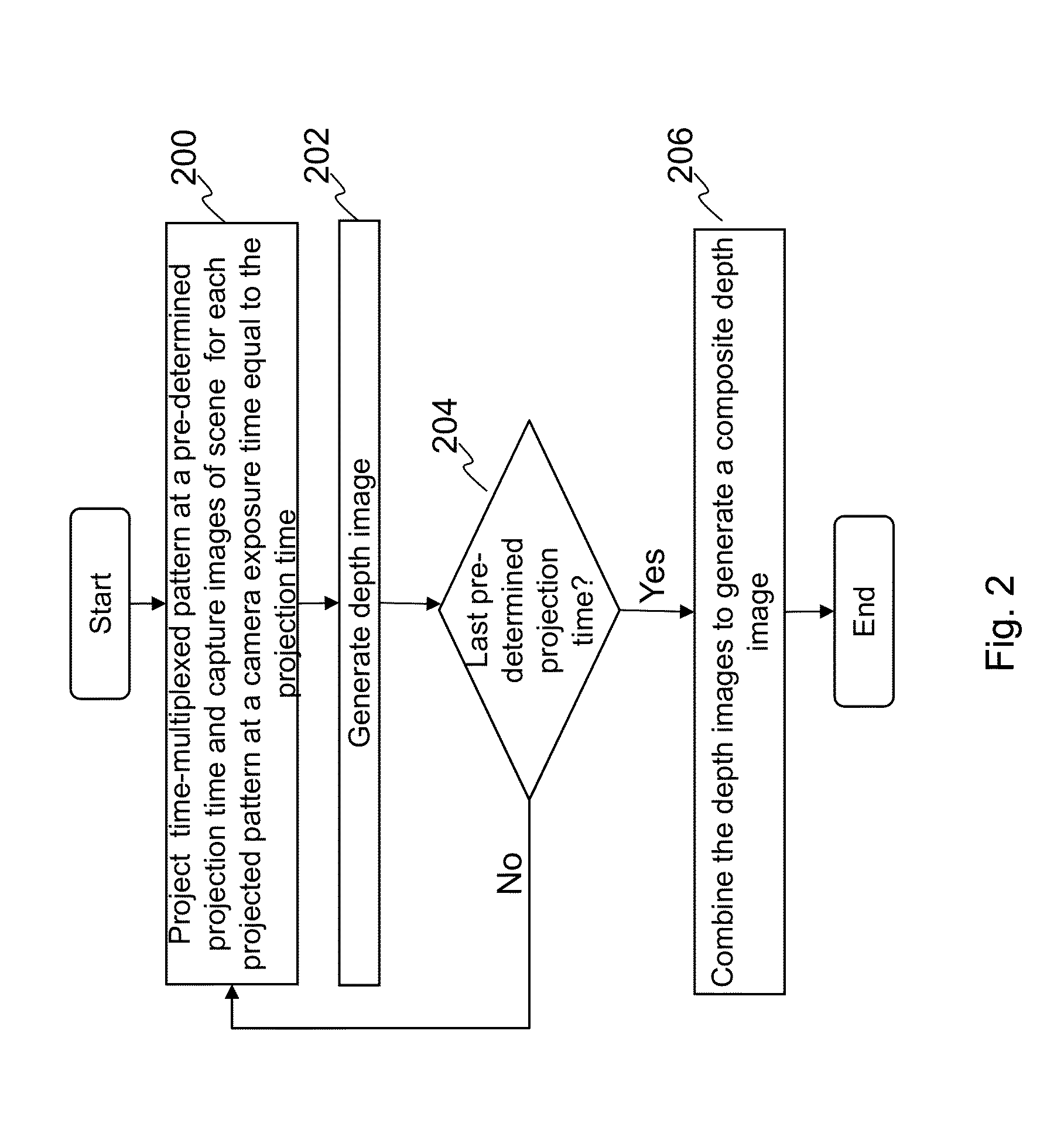
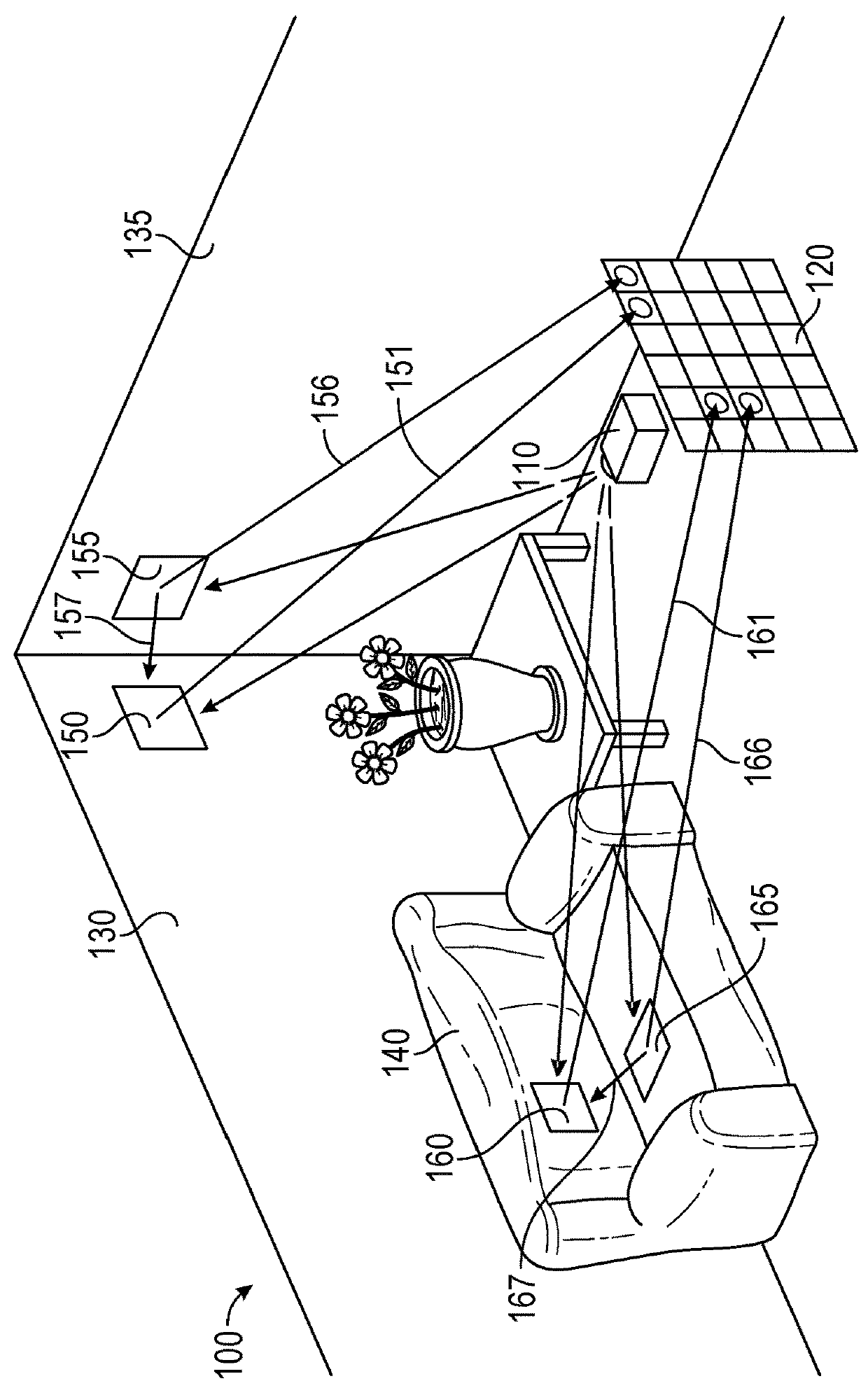
Wide dynamic range depth imaging in a structured light device is provided that improves depth maps for scenes with a wide range of albedo values under varying light conditions. A structured light pattern, e.g., a time-multiplexed structured light pattern, is projected into a scene at various projection times and a camera captures images of the scene for at least the same exposure times as the projection times. A depth image is computed for each of the projection / exposure times and the resulting depth images are combined to generate a composite depth image.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
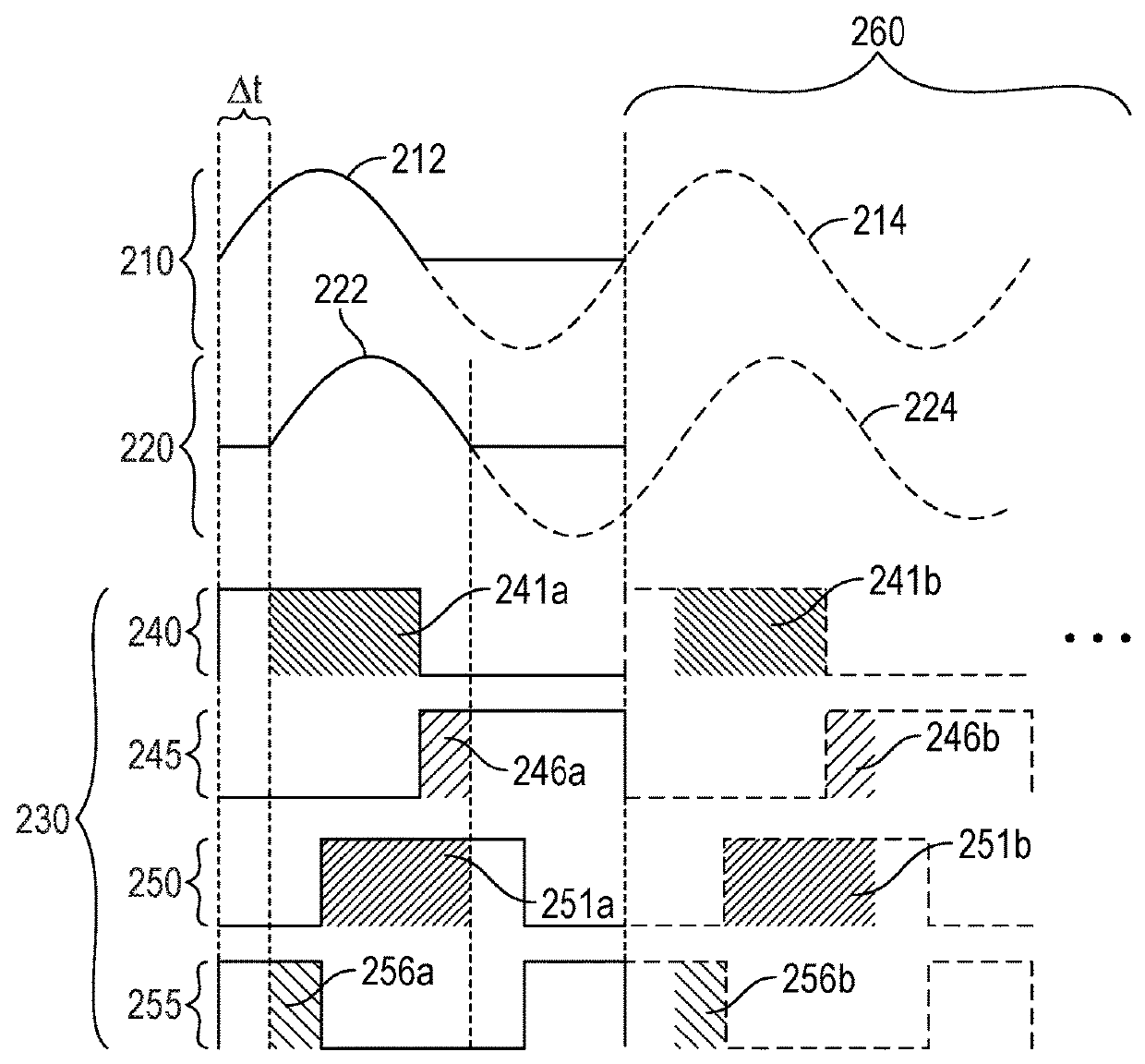
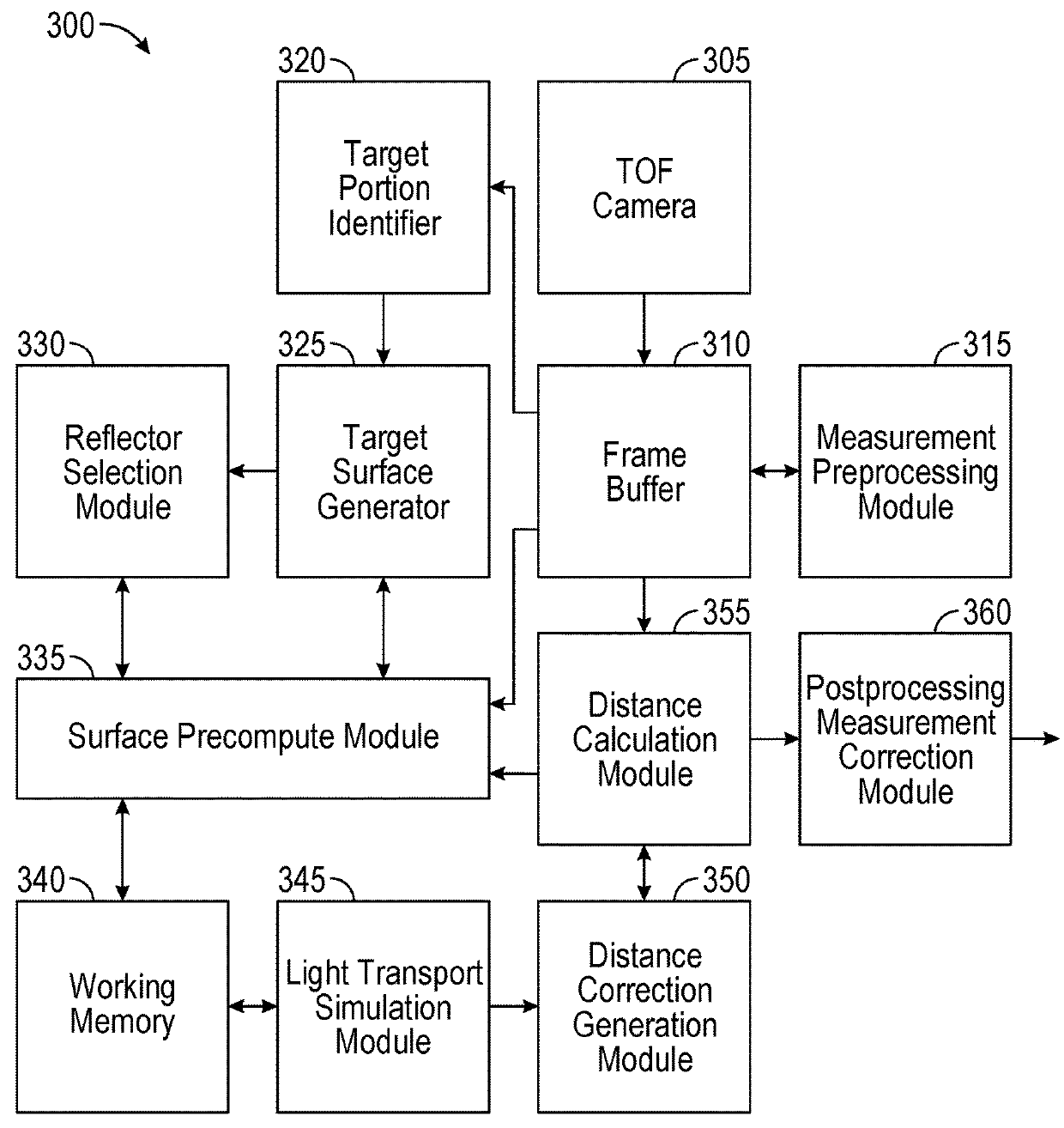
Correction of multipath interference in time of flight camera depth imaging measurements
InactiveUS20180278910A1Well formedElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systemsTarget surfaceDepth imaging
A system for determining distances to features in a scene is disclosed. The system includes, among other features, a target portion identifier module, a target surface generator, a reflector selection module, a light transport simulation module, a depth measurement correction generation module, and a distance calculation module. The target portion identifier module is configured to identify a plurality of target portions of the scene. The target surface generator is configured to simulate a plurality of target surfaces. The reflector selection module is configured to select a first plurality of reflector surfaces from the plurality of target surfaces and a second plurality of reflector surfaces from the first plurality of reflector surfaces. The light transport simulation module is configured to, for each target surface included in the target surfaces, simulate a multipath reflection of light emitted by the camera, reflected by the reflector surface to the target surface, and reflected by the target surface to the camera, to generate a simulated multipath response for the target surface. The depth measurement correction generation module is configured to generate a depth measurement correction for each target surface based on the simulated multipath response. The distance calculation module is configured to determine distances for the pixels based on the depth measurement corrections.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
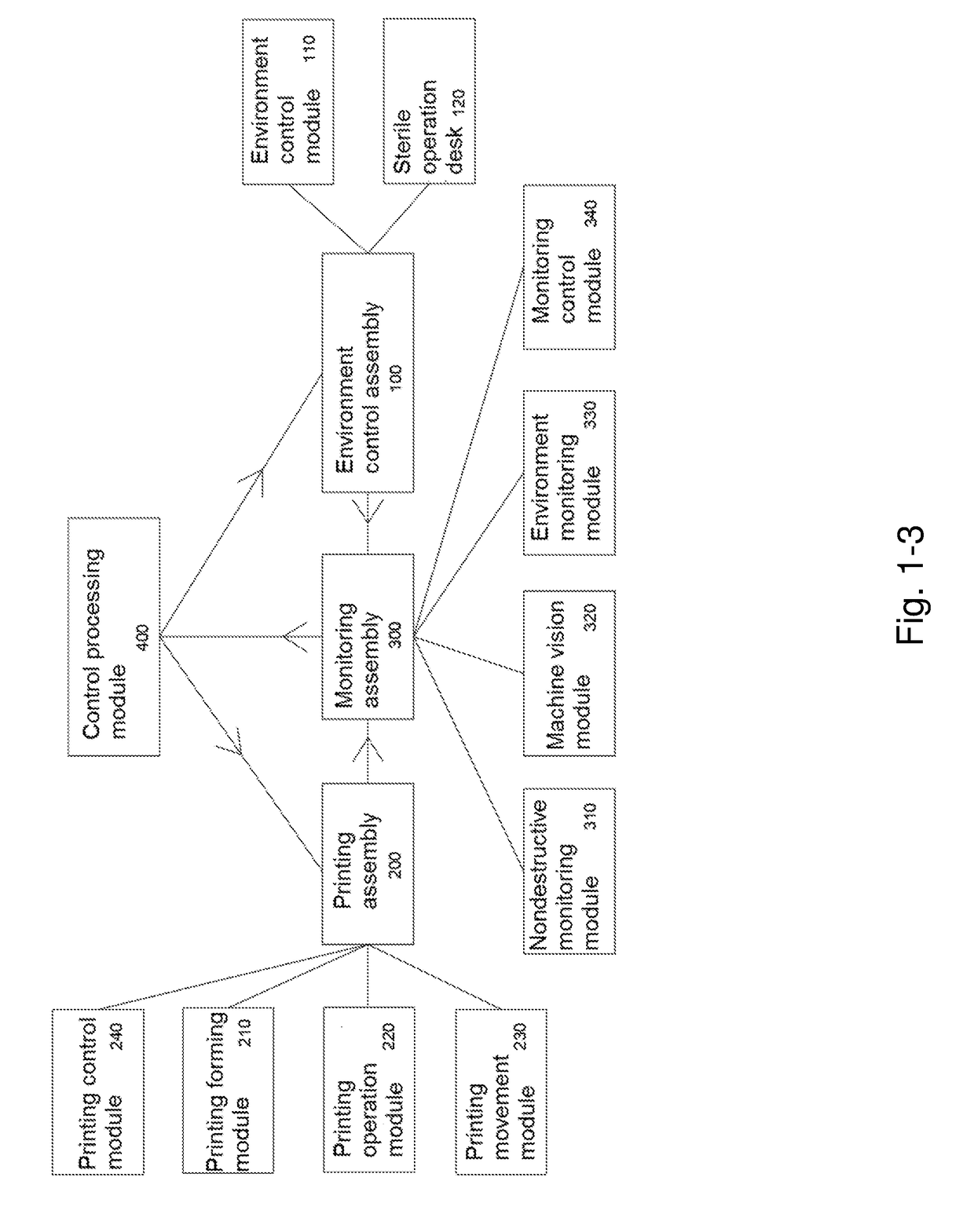
On-line Monitoring Method and System for Three-dimensional Printing
ActiveUS20190086899A1Improve consistencyImprove quality stabilityProgramme controlImage enhancementDepth imagingMonitoring system
Provided are a three-dimensional printing on-line monitoring method and system, relating to the technical field of three-dimensional printing, so as to solve the technical problem that the existing three-dimensional printing on-line monitoring systems are limited in imaging volume and cannot realize full-longitudinal-depth imaging. In the three-dimensional printing on-line monitoring method, full-longitudinal-depth imaging monitoring of the whole printing process is achieved by longitudinal-depth segmented scanning of a printing solidified layer and based on a longitudinal automatic splicing algorithm, and synchronous micro-tomography imaging on-line monitoring of the printing is achieved by guiding printing parameter optimization and control of a next depth-increased segment by using in real time a result feedback of the longitudinal-depth segmented being scanned; and at the same time of completing the manufacturing of the printed product, a three-dimensional high-resolution global image of an internal structure of the printed product is acquired, thereby completing quality control.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
Method and system of structural light-based 3D depth imaging using signal separation coding and error correction thereof
Owner:ING GROUP NV
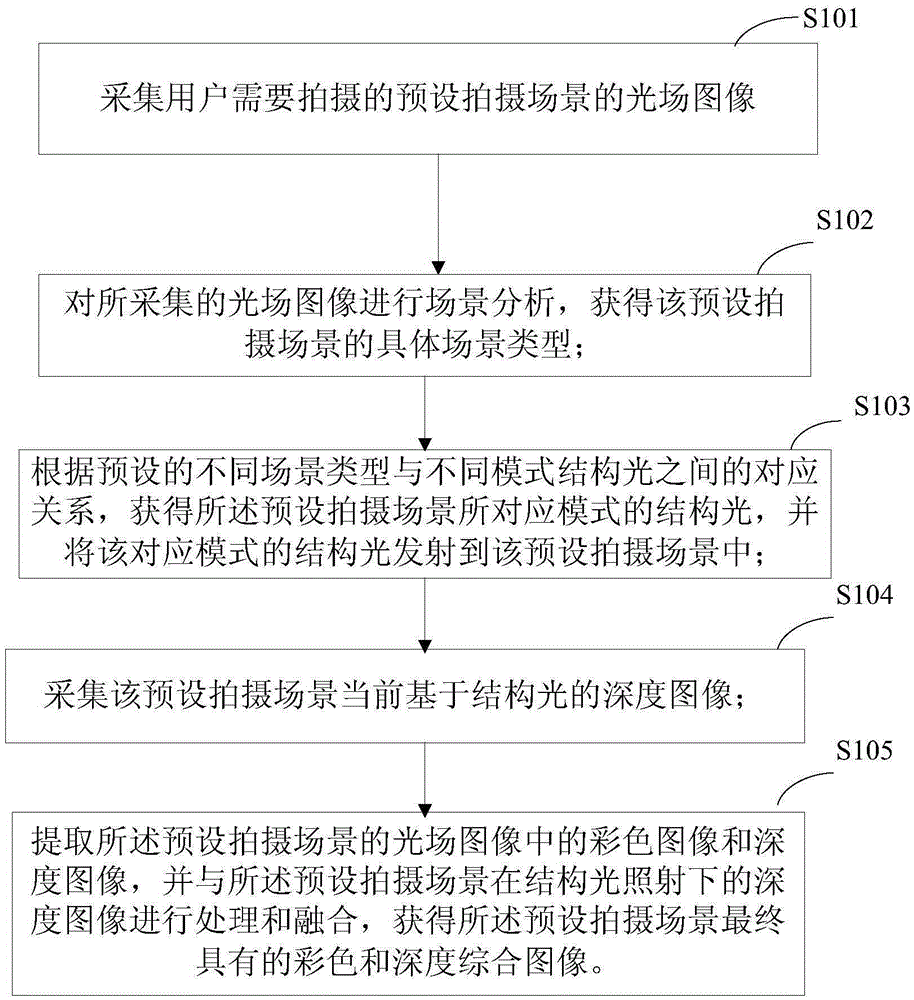
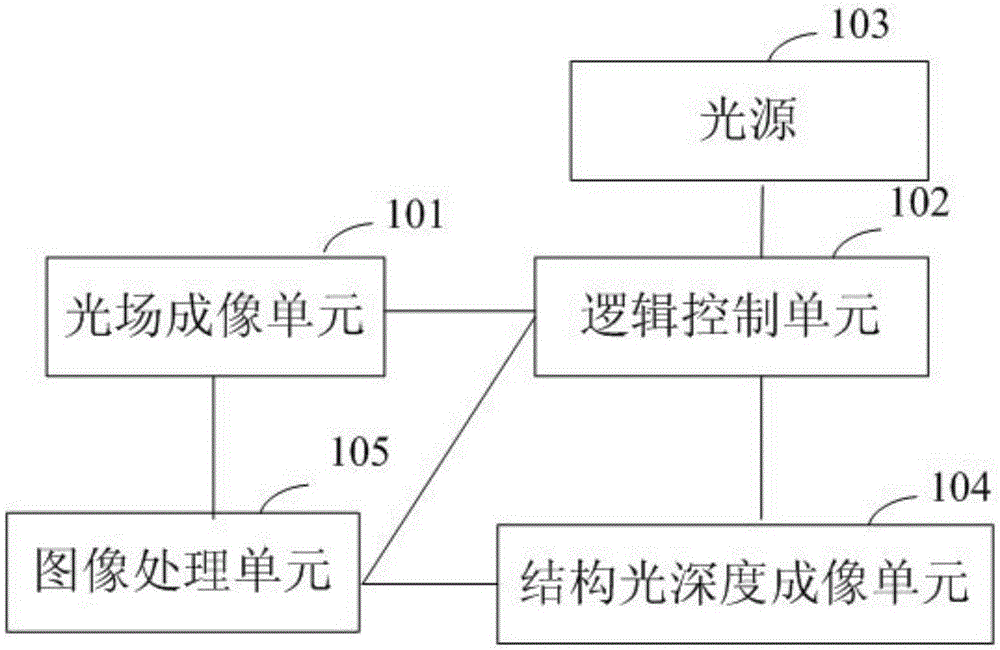
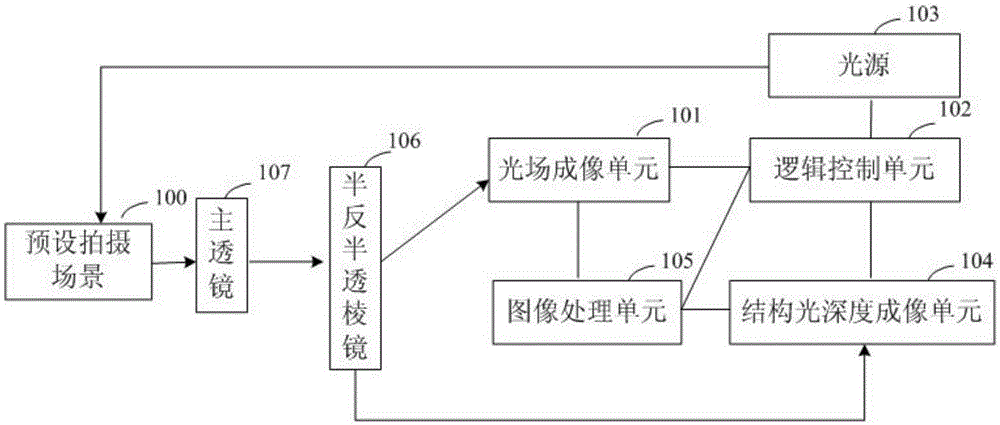
Color and depth imaging method and device based on structured light and light-field imaging
The invention discloses a color and depth imaging method based on structured light and light-field imaging. The method comprises steps as follows: a light field image of a preset shoot scene to be shot by a user is acquired; the acquired light field image is subjected to scene analysis, and a specific scene type of the preset shoot scene is acquired; a corresponding mode of structured light of the preset shoot scene is acquired and shot to the preset shoot scene according to the relation between different preset screen types and structured light in different modes; a depth image of the preset shoot scene under radiation of the structured light is acquired; color images and depth images in the light field image are extracted and processed and fused together with the depth image, and a comprehensive image with color and depth for the preset shoot scene is finally acquired. According to the color and depth imaging method based on structured light and light-field imaging and a device used for the method, an active and inactive combined depth imaging mode is adopted, an active depth imaging mode and an inactive depth imaging mode complement each other's advantages, color and depth imaging is realized, and the imaging quality is guaranteed.
Owner:天津中科智能识别有限公司
Spatially self-similar patterned illumination for depth imaging
Methods, systems, and devices involving patterned radiation are provided in accordance with various embodiments. Some embodiments include a device for projecting pattern radiation. Some embodiments include a method for estimating coordinates of a location on an object in a 3D scene. Some embodiments include a system for estimating the coordinates of a location on an object in a 3D scene. A variety of radiation patterns are provided in accordance with various embodiments. Some embodiments may relate to the use of patterned illumination to identify the angular information that may be utilized to measure depth by triangulation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Depth imaging super-resolution microscopic imaging system
InactiveCN108303806AGood for depth imagingStrong penetrating powerMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceWavefront sensorImaging quality
The invention discloses a depth imaging super-resolution microscopic imaging system. The depth imaging super-resolution microscopic imaging system includes a first laser, a first lens, a first dichroscope, a second dichroscope, a second laser, a sixth lens, a phase modulation assembly, a third dichroscope, a deformation reflector, an X axis scanning vibrating mirror, a phase compensation assembly,a Y axis scanning vibrating mirror, a vertical optical path refraction matching unit, a second quarter wave-plate, a microscopic object lens, a sample table, a horizontal optical path refraction matching unit, a first optical filter, a wavefront sensor, a second optical filter, a tenth lens and an imaging device. By means of the two-photon effect, by compensating the fluorescent wavefront phase change through the wavefront sensor and the deformation reflector, by combining with movement of the sample table in the Z axis direction, the depth imaging super-resolution microscopic imaging systemcan realize three-dimensional depth imaging while correcting the aberration caused by the samples, thus being relatively higher in the imaging quality.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Molecular imaging and nanophotonics imaging and detection principles and systems, and contrast agents, media makers and biomarkers, and mechanisms for such contrast agents
InactiveUS7823215B2Enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesNanoopticsDepth imagingBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) and near-field / far-field scanning microscopy methods, systems and devices that permit the imaging of biological samples, including biological samples or structures that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the present invention permits the production of multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field microscopy systems that can achieve a spatial resolution of less than 100 nanometers. In another embodiment, the present invention permits the production of a multifunctional, multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field / far-field microscopy that can achieve enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imaging of biological samples. In still another embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of polar molecules as new optical contrast agents for imaging applications (e.g., cancer detection).
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Bessel beam generator based on annular Dammann gratings
ActiveCN102495472AImprove conversion efficiencyQuality improvementOptical elementsGratingPhase difference
A bessel beam generator based on an annular Dammann gratings is sequentially formed by the annular Dammam gratings sharing the same optical axis, a first lens, an amplitude type spatial filter, a second lens and a focusing objective lens. The first lens and the second lens are a confocal lens group, each annular Dammam grating is first-ordered and multi-cycle and has the two-value phase difference of pi, and the amplitude type spatial filter is located on a confocal plane of the first lens and the second lens. Diffraction-free light beams with micron dimension or submicron dimension crosswise facula and 10-102 wavelength of axial focal depth can be generated in a focusing backfield of the focusing objective lens. Switch efficiency is as high as 80%. By means of a spatial filtering mode, quality of generated bessel beams is further improved. The micron or submicron diffraction-free bessel beam can be widely used in the fields of optical micro-machining, optical storage, large focus depth imaging, laser grain capture and quickening, a self-focusing servo-system and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
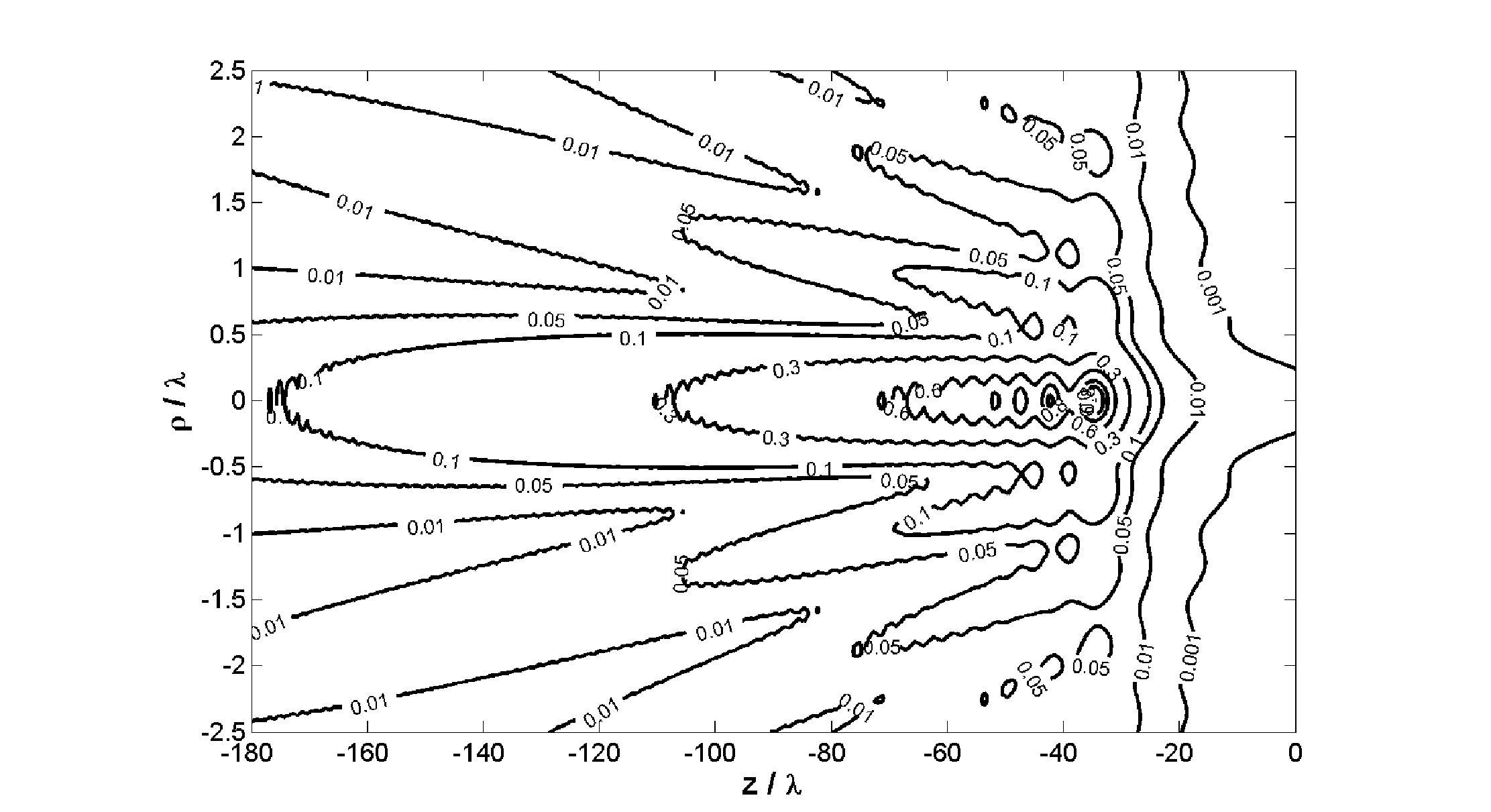
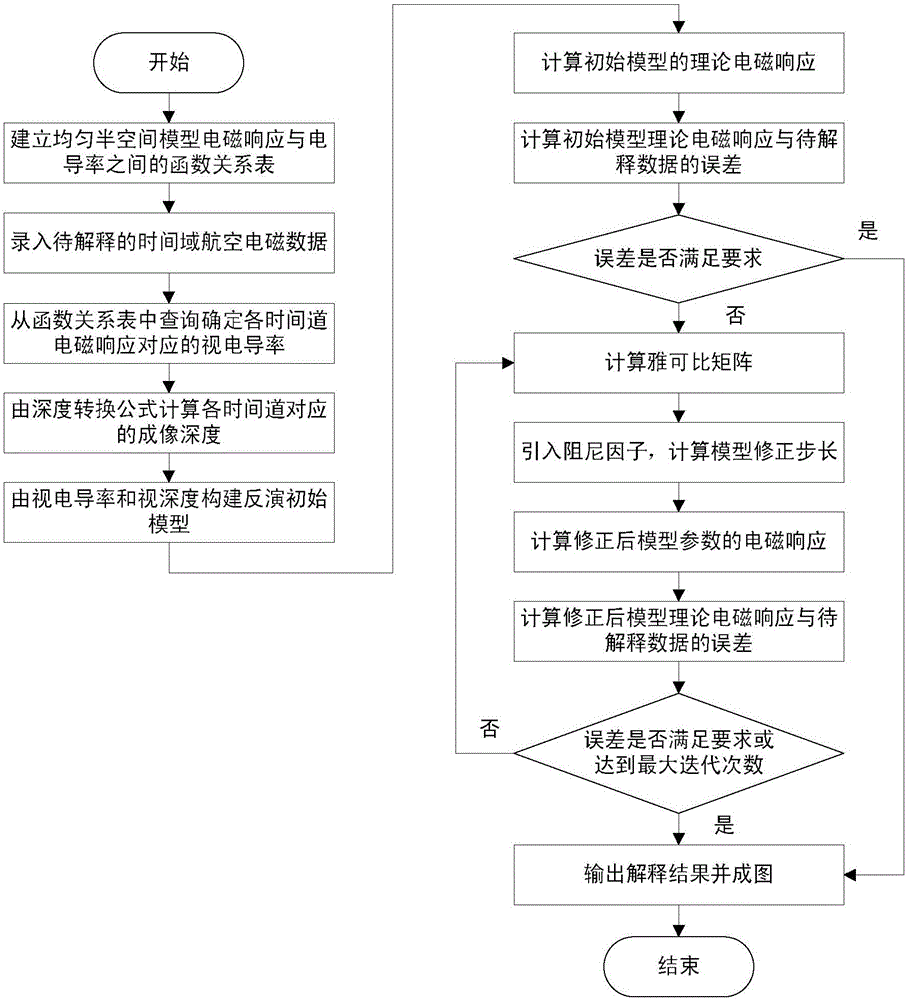
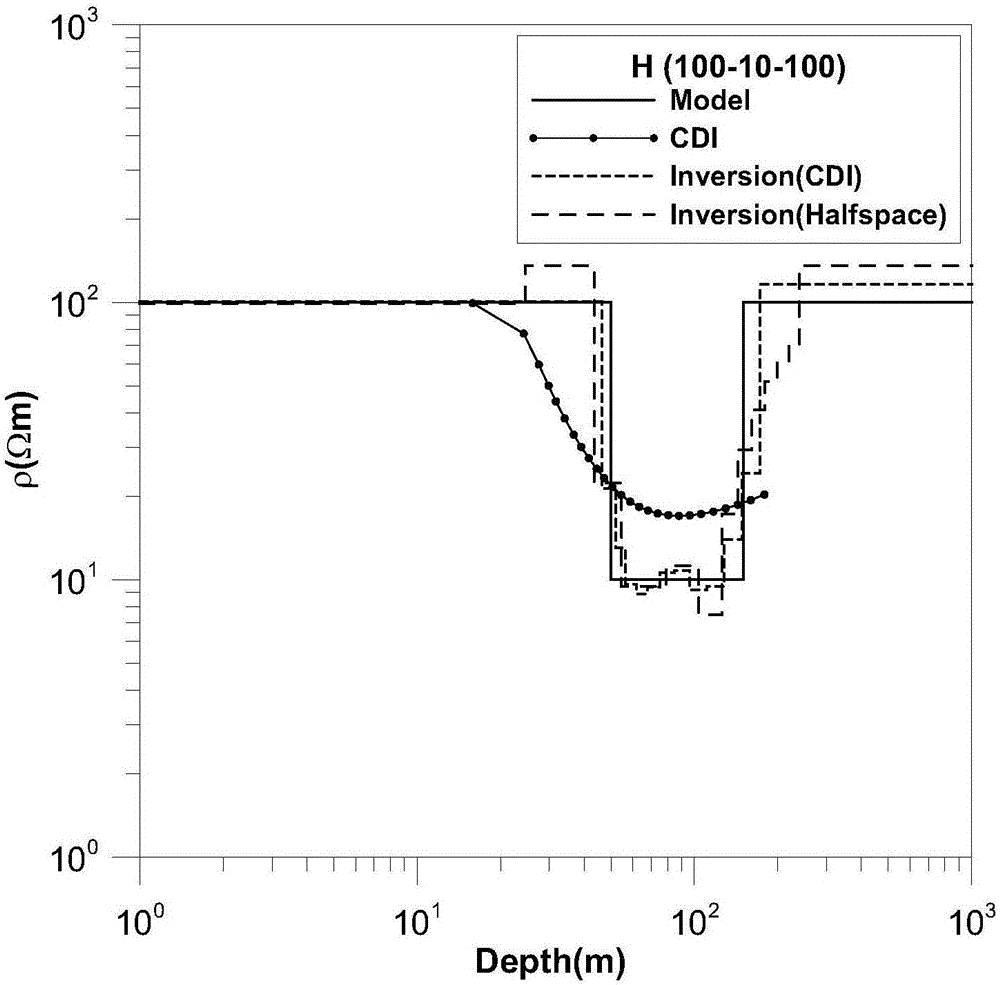
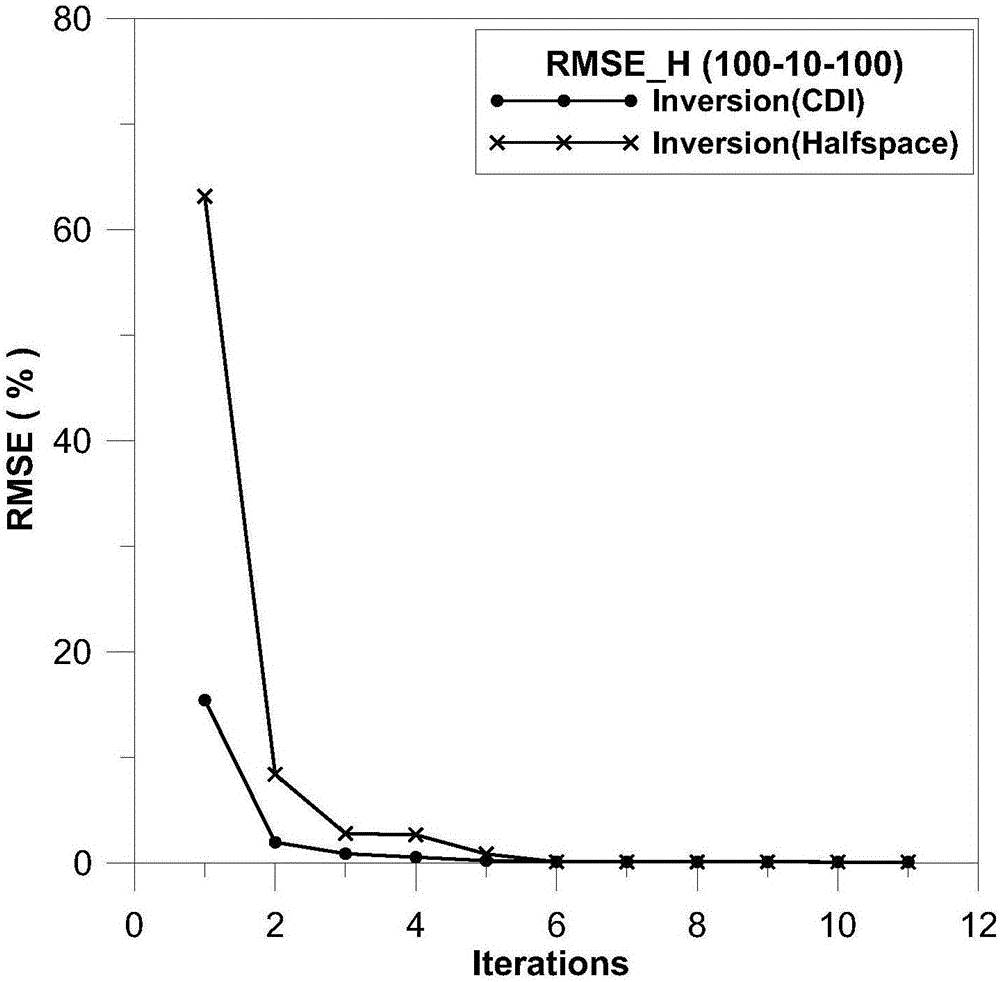
Time domain aero-electromagnetic data inversion method based on conductivity-depth imaging
InactiveCN106338774ASolve the difficulty of choosingIncrease speedElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationTime domainModel selection
The invention discloses a time domain aero-electromagnetic data inversion method based on conductivity-depth imaging. First, the apparent conductivity and apparent depth of an underground medium are obtained by use of a conductivity-depth imaging method based on a tale look-up method; then, an inversion initial model is built based on the apparent conductivity and the apparent depth; and finally, inversion is performed by use of a damping characteristic parameter method to complete combination analysis of time domain aero-electromagnetic data. The problem that it is difficult to choose an inversion initial model is solved. As inversion is performed on the basis of the result of approximate imaging, the inversion method has certain constraints of the inversion result, and inversion is of high convergence rate and imaging precision. The invention provides a quick and stable inversion method for time domain aero-electromagnetic data interpretation.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
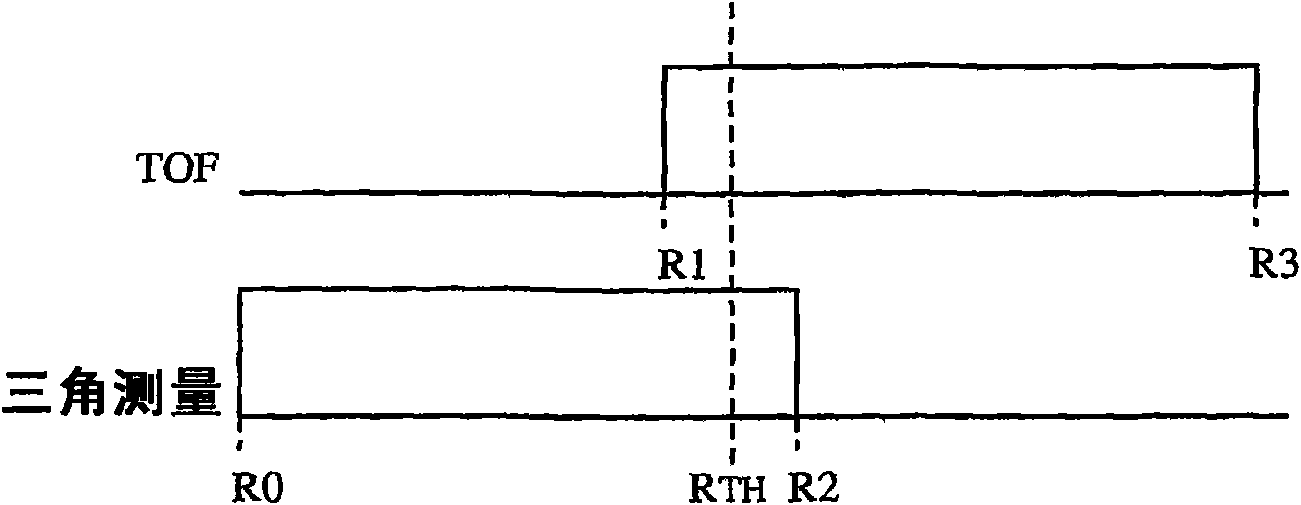
Time-of-flight depth imaging
ActiveCN102520574AAlleviating the need for exact matchesNoise compensationTelevision system detailsImage analysisExact matchDepth imaging
Techniques are provided for determining depth to objects. A depth image may be determined based on two light intensity images. This technique may compensate for differences in reflectivity of objects in the field of view. However, there may be some misalignment between pixels in the two light intensity images. An iterative process may be used to relax a requirement for an exact match between the light intensity images. The iterative process may involve modifying one of the light intensity images based on a smoothed version of a depth image that is generated from the two light intensity images. Then, new values may be determined for the depth image based on the modified image and the other light intensity image. Thus, pixel misalignment between the two light intensity images may be compensated.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
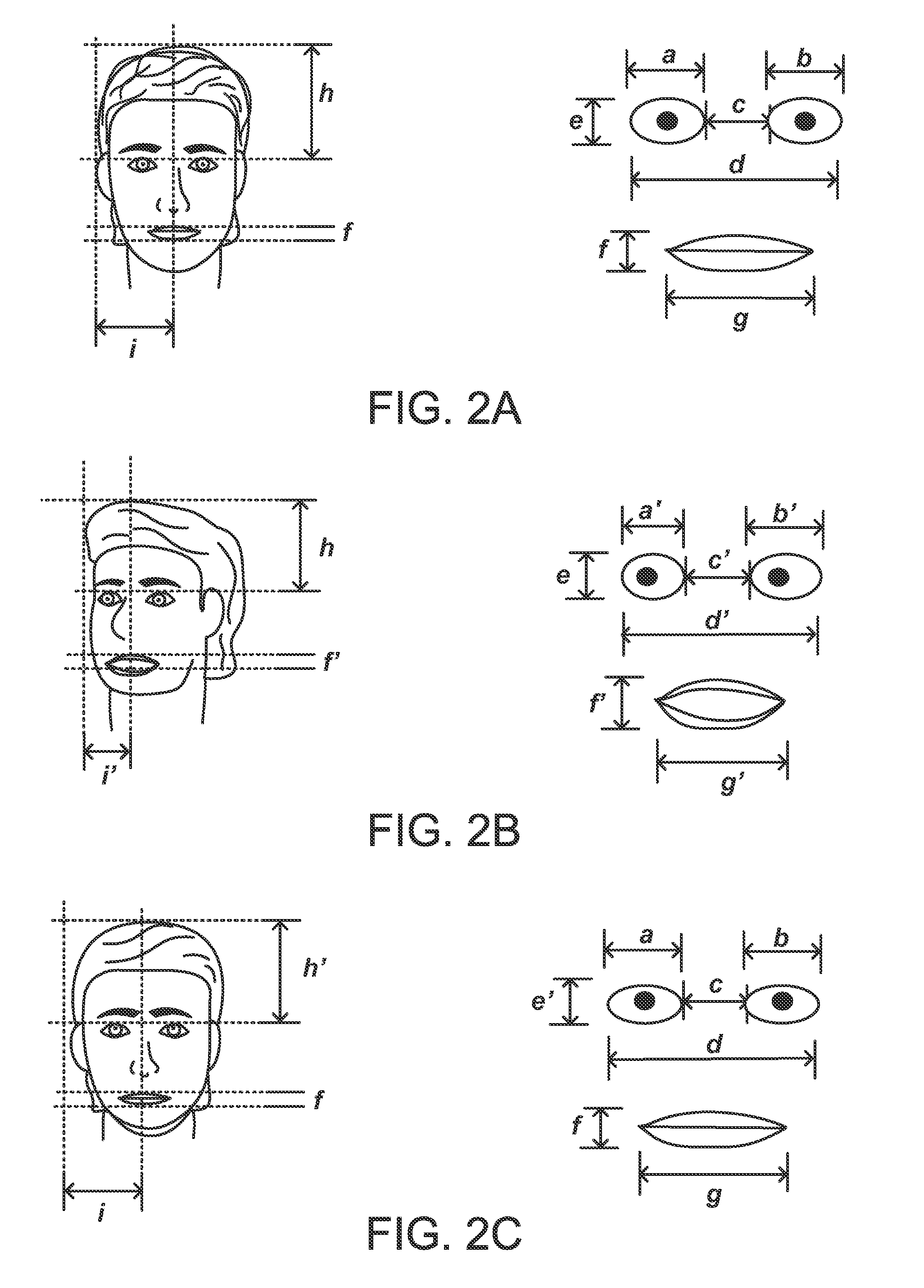
Monocular structured light depth imaging method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111462206ASmall amount of calculationIncrease diversityImage enhancementImage analysisData setImaging quality
The embodiment of the invention provides a monocular structured light depth imaging method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out visual calibration on a monocular structured light imaging hardware system; s2, generating a synthetic training data set; s3, carrying out data augmentation and preprocessing; s4, constructing a convolutionalneural network; s5, determining a loss function; s6, setting an optimizer; s7, training a convolutional neural network; and S8, testing the convolutional neural network. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention is used for training a synthetic training data set of a convolutional neural network, specific optimization and improvement are carried out on face recognition, the imaging effect and the recognition accuracy when monocular structure light depth imaging is adopted for face recognition are improved, the network calculation amount is reduced, and the real-time performance under the imaging quality requirements for high precision and high resolution is improved.
Owner:合肥的卢深视科技有限公司
System and Method for Providing Depth Imaging
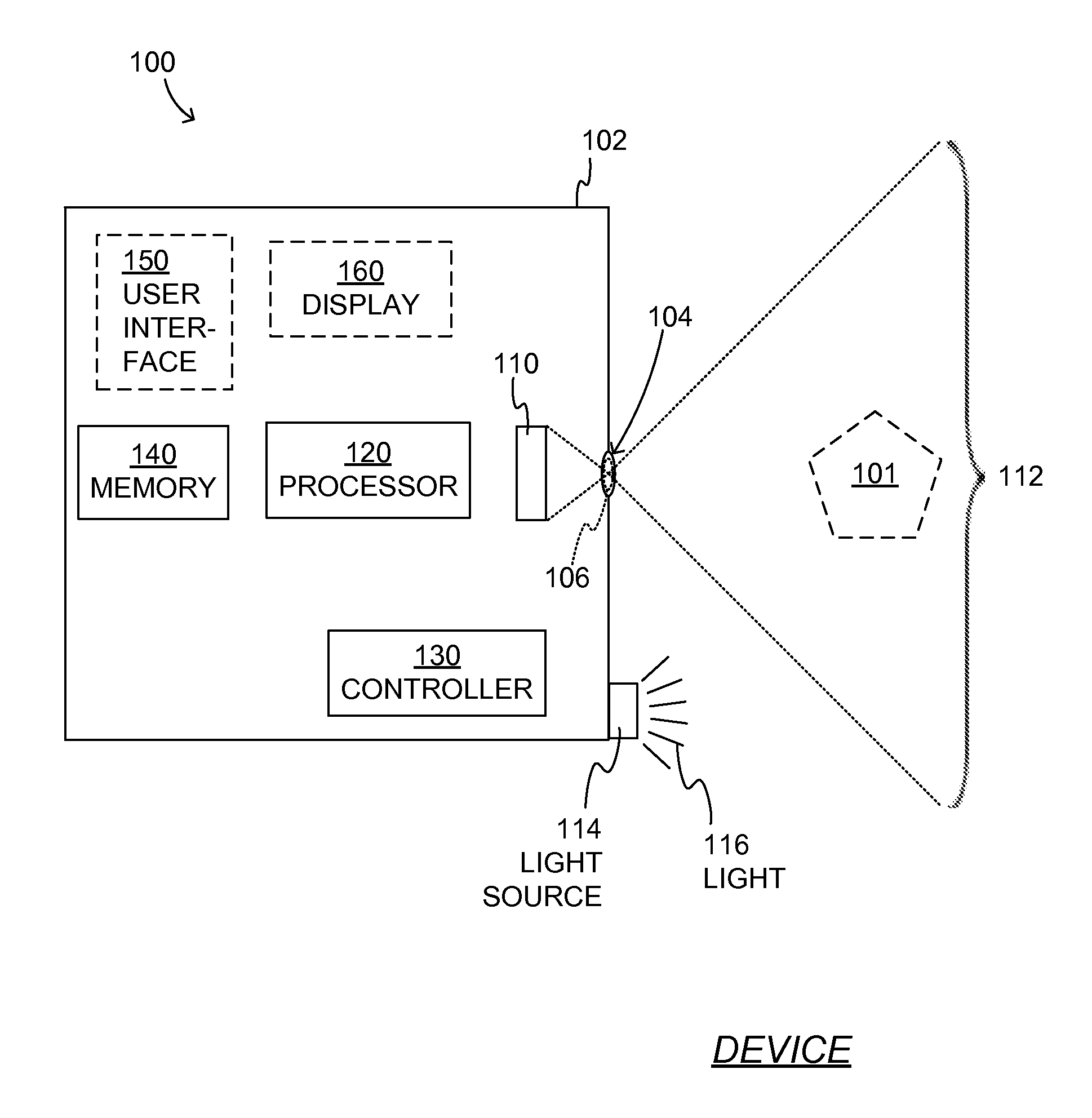
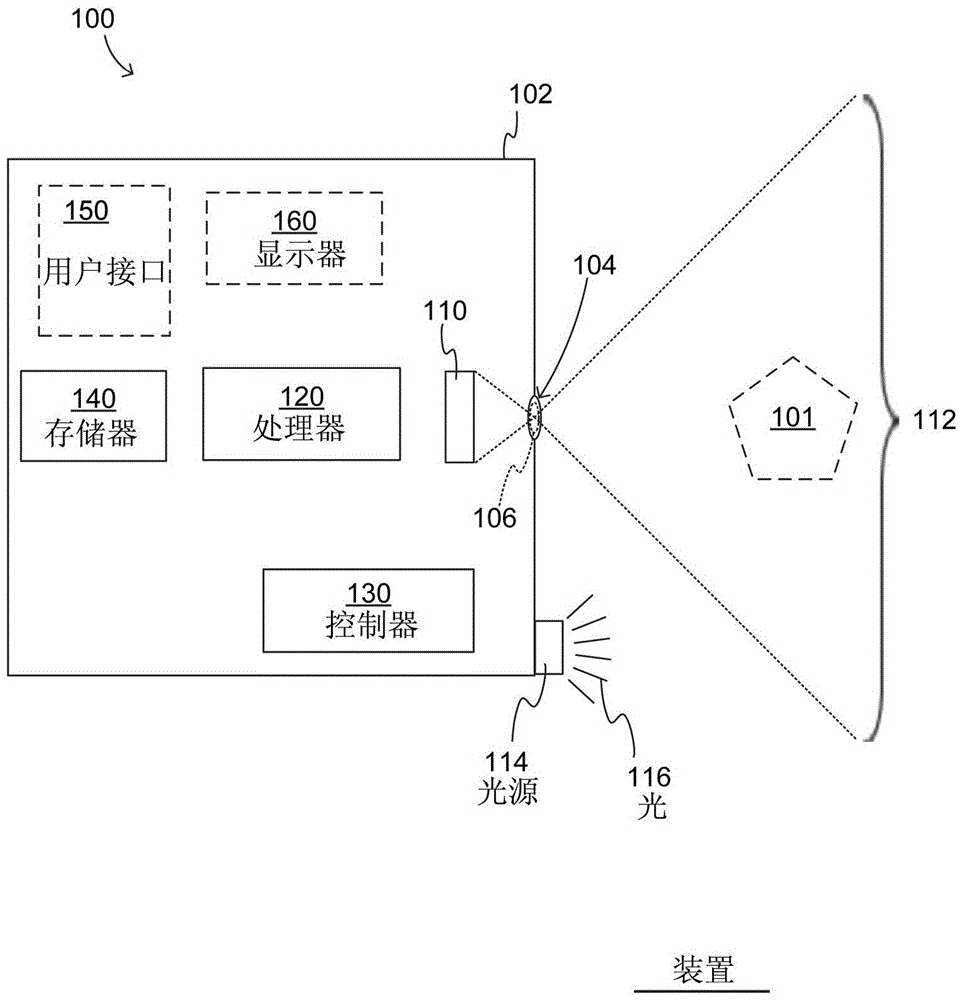
InactiveUS20100315510A1Television system detailsClosed circuit television systemsDepth imagingImage resolution
A device for use with an imaging system that is operable to provide an image signal based on an object disposed at a first distance from the imaging system. The imaging system includes a first camera, a second camera and a display. The first camera is operable to generate a first image signal based on the object and includes a first optics system and a first detector. The first optics system has a focal length, whereas the first detector has a resolution. The second camera is operable to generate a second image signal based on the object. The second camera includes a second optics system and a second detector. The second optics system has the same focal length of the first optics system and the second detector has the same resolution as the first detector. The second camera is separated from the first camera by a second distance. The display is operable to display an image based on a modified image. The device comprises an image processor that is operable to establish a virtual separation membrane and to output a modified image based on the first image signal, the second image signal, the virtual separation membrane, the second distance, the focal length and the resolution.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
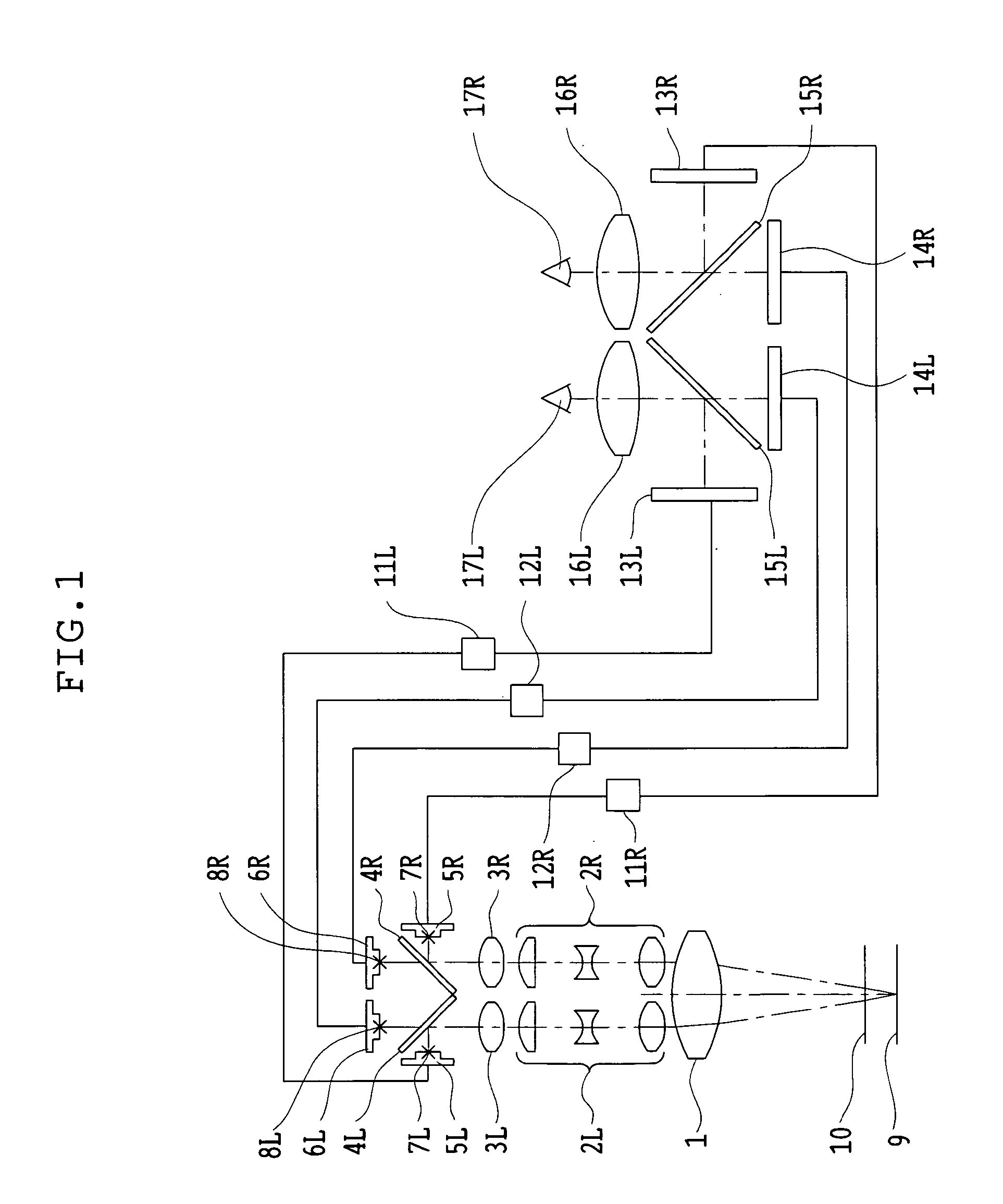
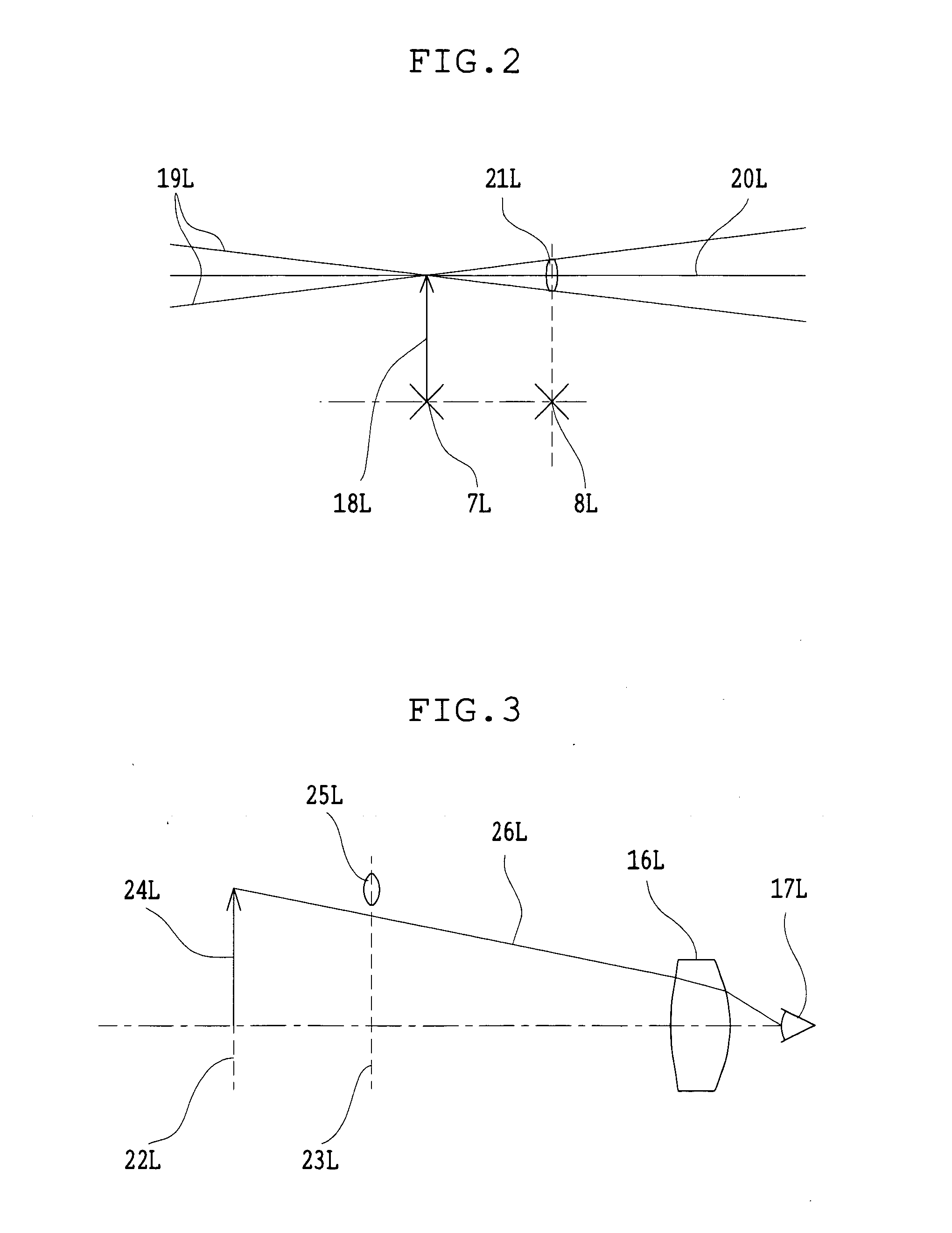
Binocular stereoscopic observation apparatus, electronic image stereomicroscope, electronic image stereoscopic observation apparatus, and electronic image observation apparatus
A binocular stereoscopic observation apparatus includes an imaging section forming left and right images with parallax in at least two directions and an observing section in which the images with parallax are stereoscopically observed with a viewer's eyes. In this case, the imaging section has an imaging lens forming images of an object at imaging positions on each of left and right optical paths and i imaging positions on the optical axis of the imaging lens, satisfying the following conditions: L(j−1)<Lj Ek=Lj−L(j−1) Dd<Ek where Lj is a distance, measured along the optical axis, from the imaging lens to the jth imaging position, Ek is a difference between distances, measured along the optical axis, from adjacent imaging positions to the imaging lens, and Dd is an image-side depth of an optical system of the imaging section. The observing section has an eyepiece optical system and i display devices on each of the left and right optical paths so that an image formed at the jth imaging position from the imaging lens on each optical path of the imaging section is displayed on the jth display device from the eyepiece optical system on a corresponding optical path, satisfying the following condition: Mj<M(j−1) where Mj is a distance, measured along the optical axis, from the eyepiece optical system to the jth display device. The observing section further has means for superimposing i displayed images on a viewer's pupil. Here, i is an integer of 2 or more and j is an integer satisfying conditions, 1≦j≦i and j≧2.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
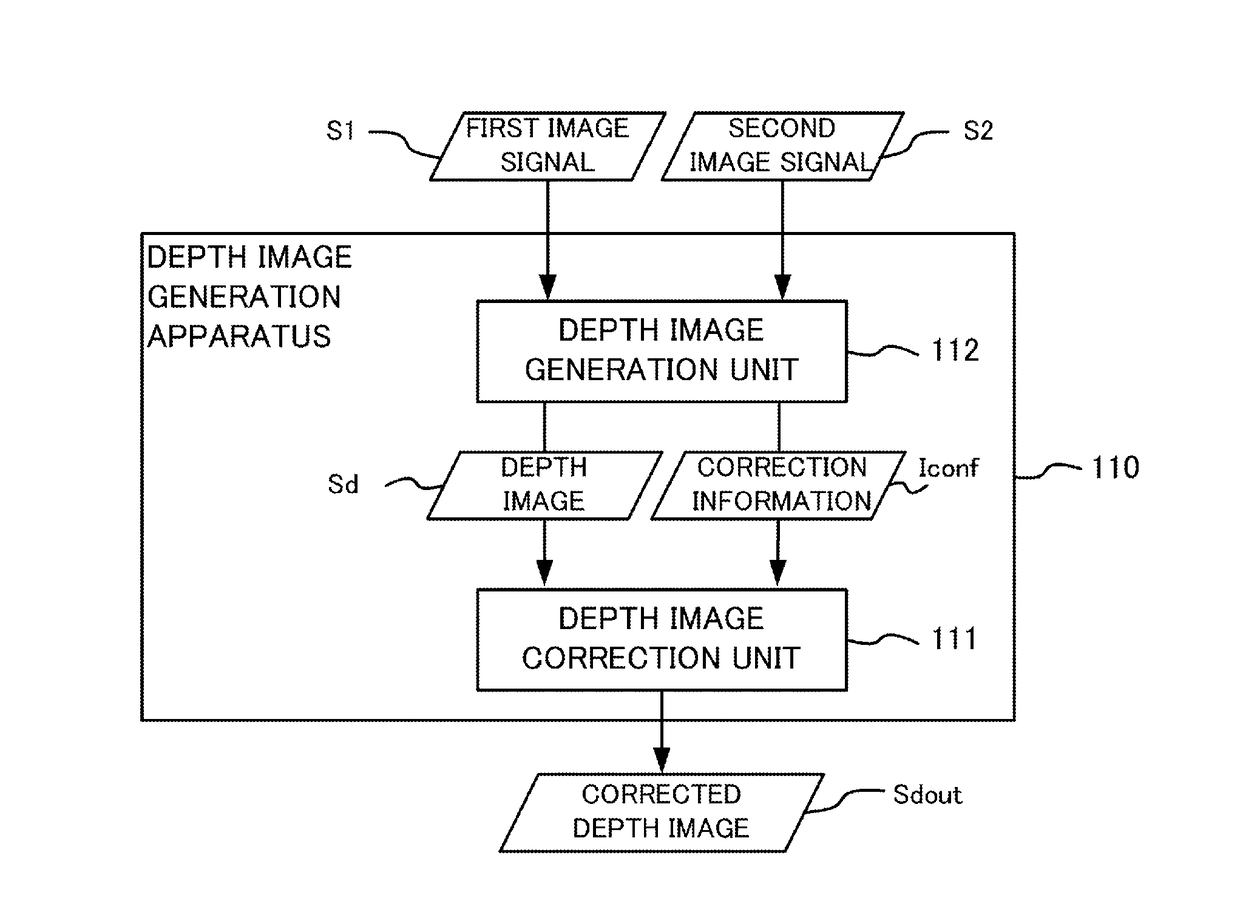
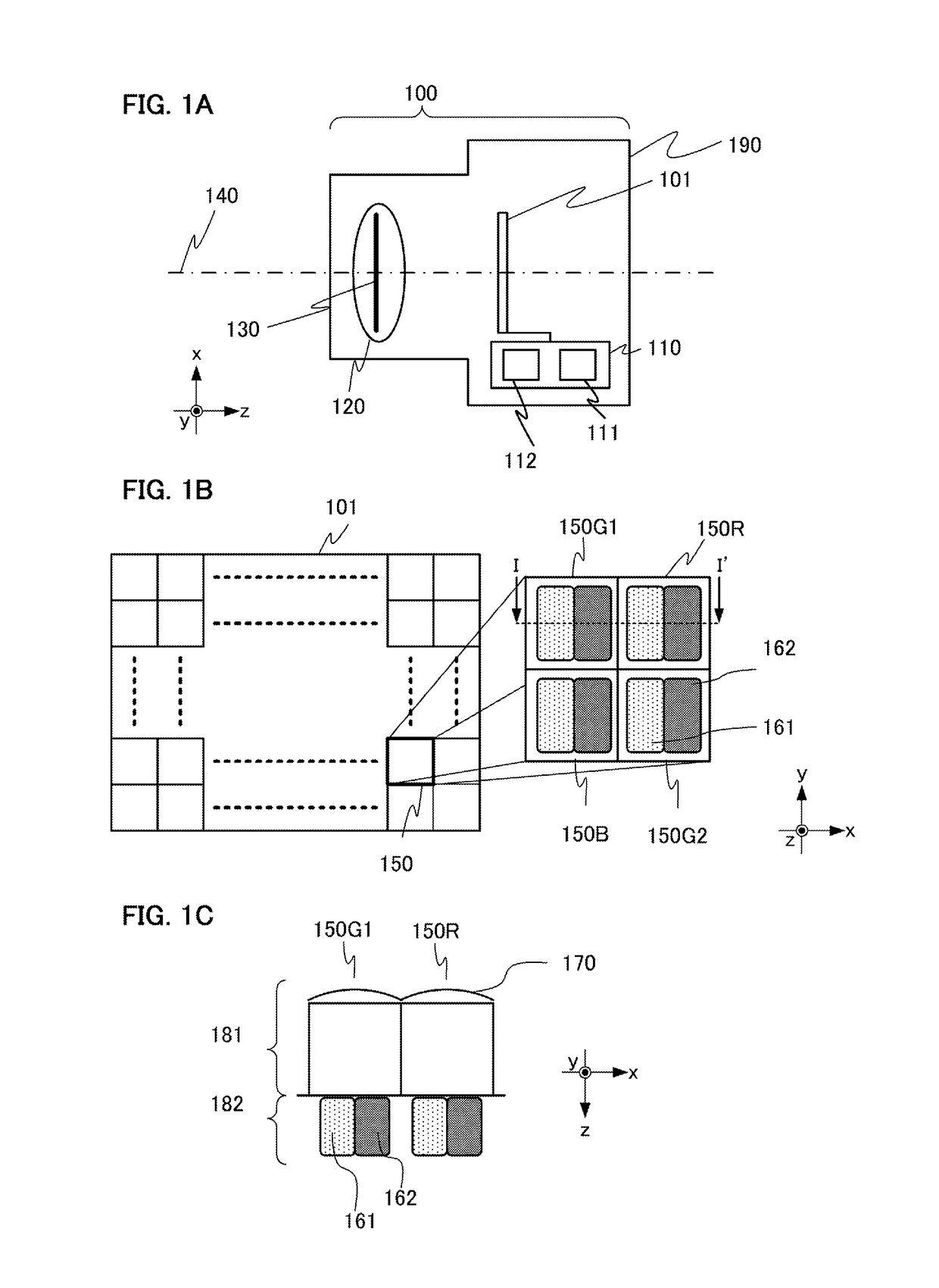
Depth imaging correction apparatus, imaging apparatus, and depth image correction method
ActiveUS20170223334A1Accurate correctionAccurate imagingImage analysisUsing optical meansIn planeDepth imaging
Provided is a depth image correction apparatus to correct depth information in a depth image, which acquires a depth image and correction information, and corrects the depth values of the depth image based on the correction information and generates a corrected depth image. The apparatus acquires, as the correction information, first confidence indicating reliability in the depth values, and second confidence indicating reliability in position in an in-plane direction vertical to the depth direction. The apparatus performs first correction processing of generating a first corrected depth image by correcting the depth image based on the first confidence and similarity of the depth values, and second correction processing of generating the corrected depth image by correcting the first corrected depth image based on the second confidence.
Owner:CANON KK
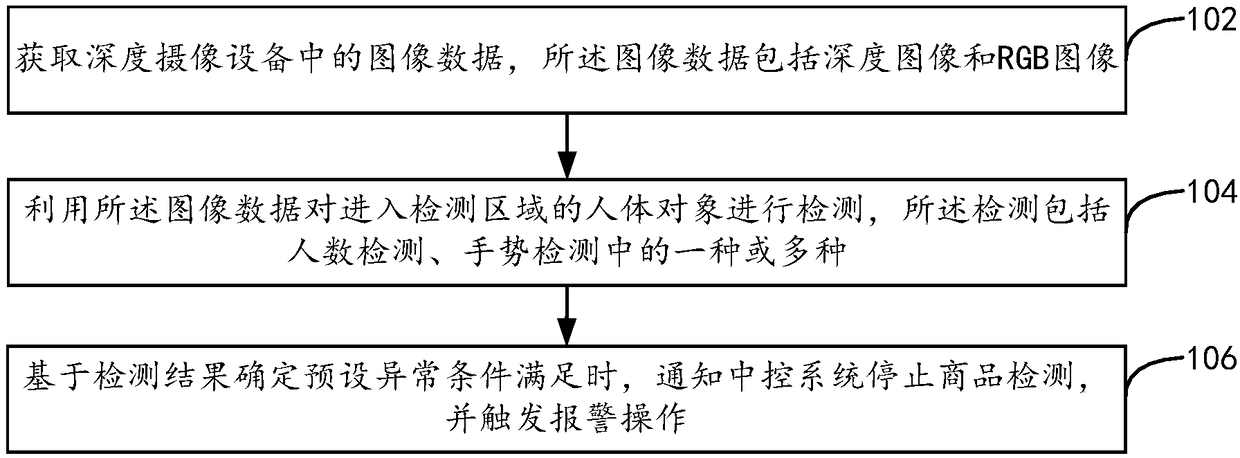
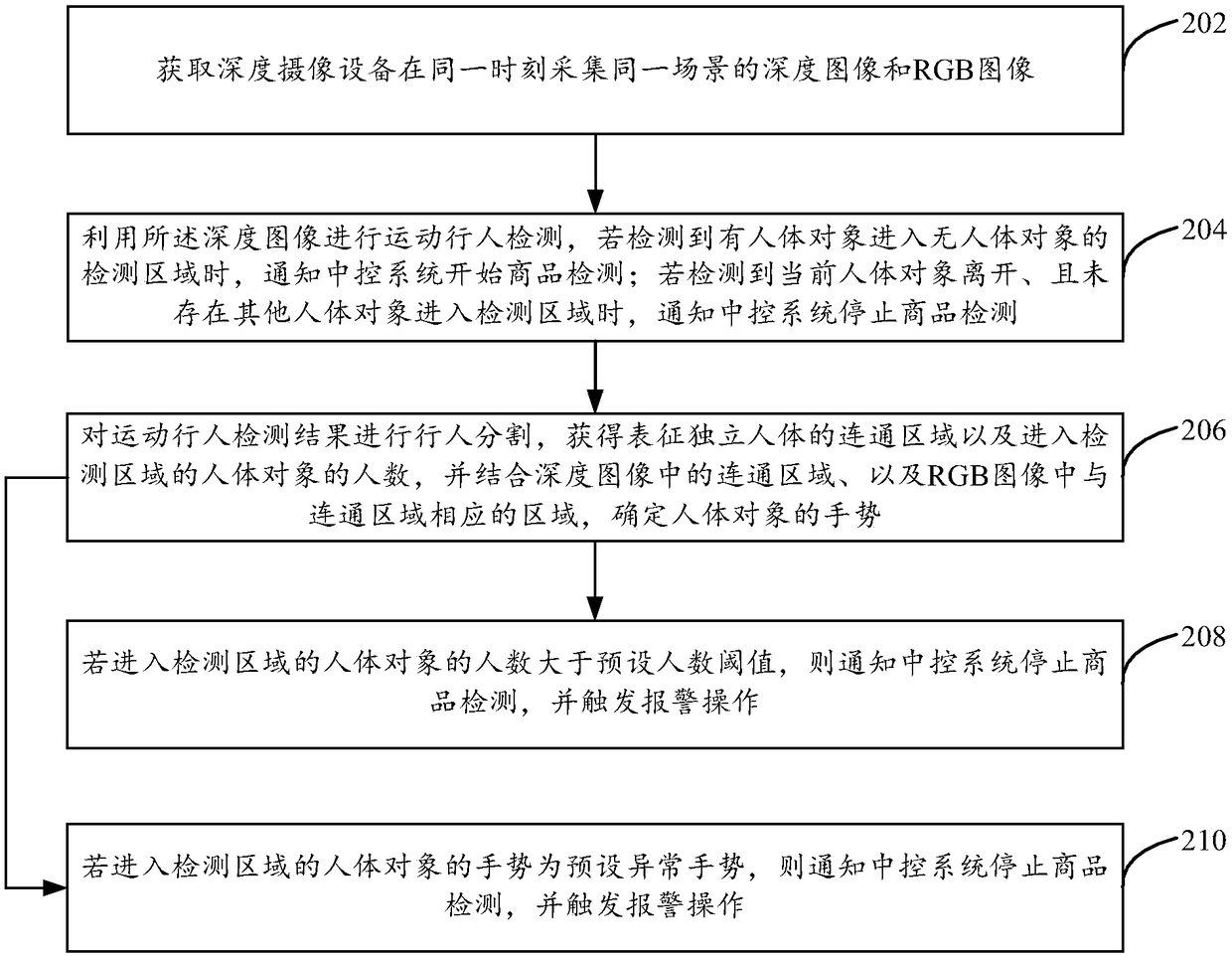
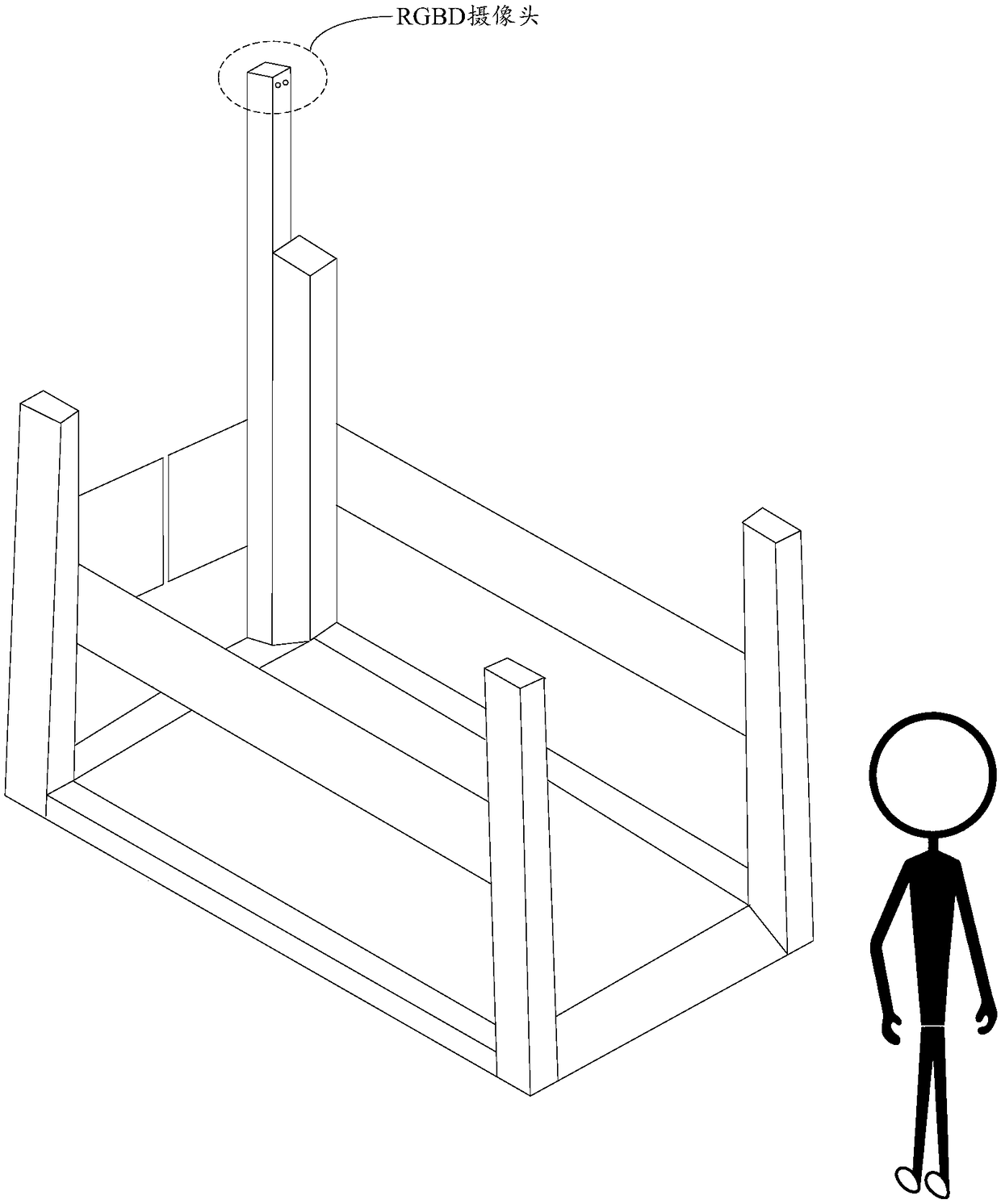
Anomaly detection method, device and apparatus in unattended settlement scenario
The embodiment of that present specification provide an anomaly detection method, device and apparatus in an unattended settlement scenario, by providing a depth imaging apparatus having at least a detection area in a shooting area in an unattended settlement scene, image data acquired from the depth imaging apparatus may be utilized to determine the depth of the image. A human body object entering the detection area is detected, the image data include a depth image and an RGB image, a detection area is an area where goods to be settled are detected prior to settlement, thus, at least the depth image and the RGB image can be used to judge whether the number of people in the detection area is abnormal or whether the human gesture is abnormal, and the central control system can be notified to stop commodity detection and trigger an alarm operation, so as to avoid the loss to customers or businesses caused by the abnormal situation.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
Depth imaging system and temperature error correction method thereof
PendingCN108711167AHigh measurement accuracySimple structureImage analysisDepth imagingReference structure
The application provides a depth imaging system and a temperature error correction method. The method includes the following steps: obtaining a first reference structured light image and a target structured light image; performing matching calculation on the first reference structured light image and the target structured light image to obtain a corresponding pixel pair; performing temperature error correction based on the pixel pair and a temperature error compensation model, and acquiring a second reference structured light image; and performing depth calculation by using the second reference structured light image and the target structured light image to acquire a depth image. According to the above depth imaging system and the temperature error correction method, the error correction of reference structured light can be realized, the error correction of depth measurement can be further realized, and finally, the measurement accuracy of the depth imaging system can be improved; andmeanwhile, the process of measuring the current temperature by using an additional temperature sensor is not required, and the structure of the depth imaging system can be simplified.
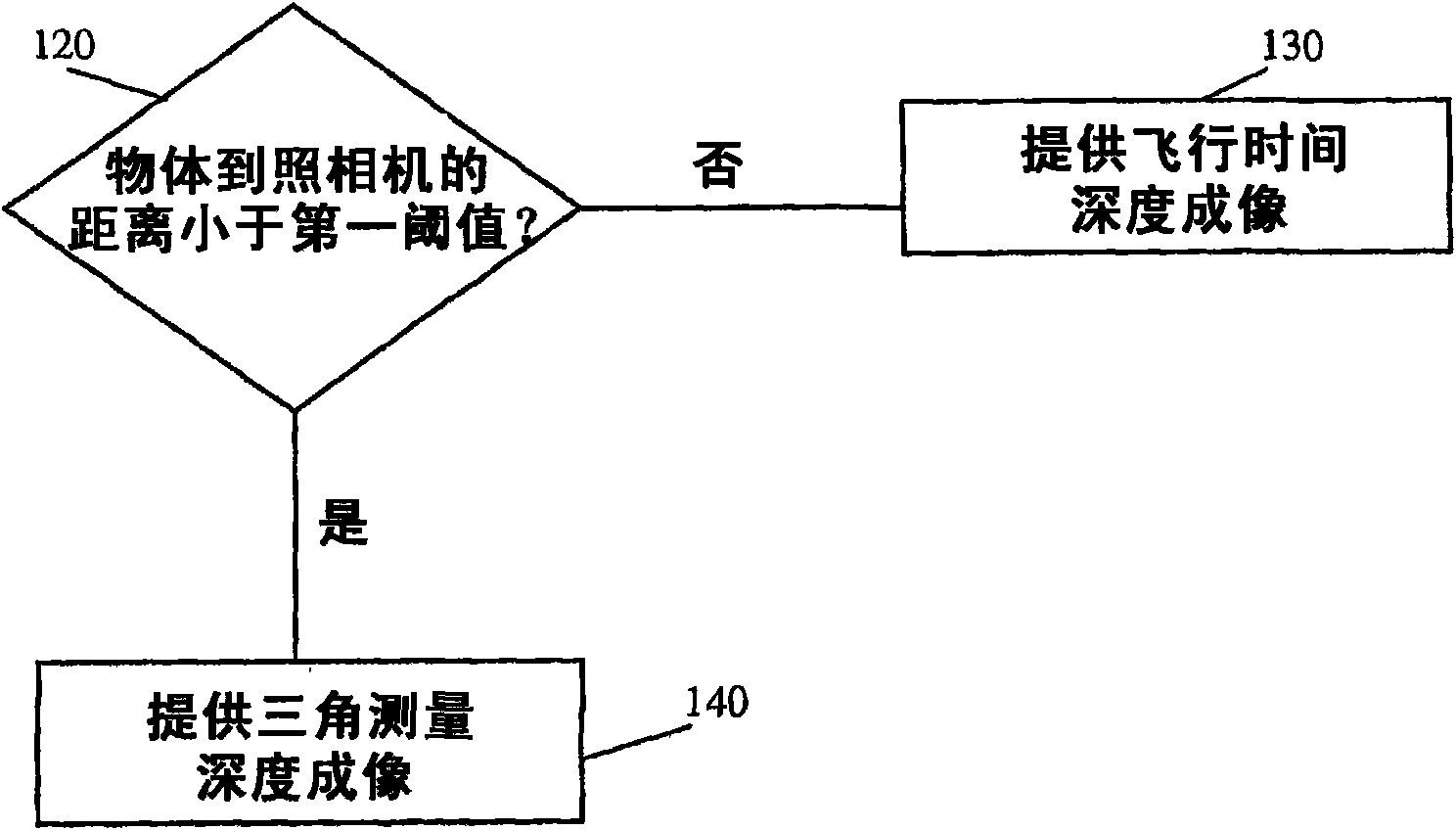
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
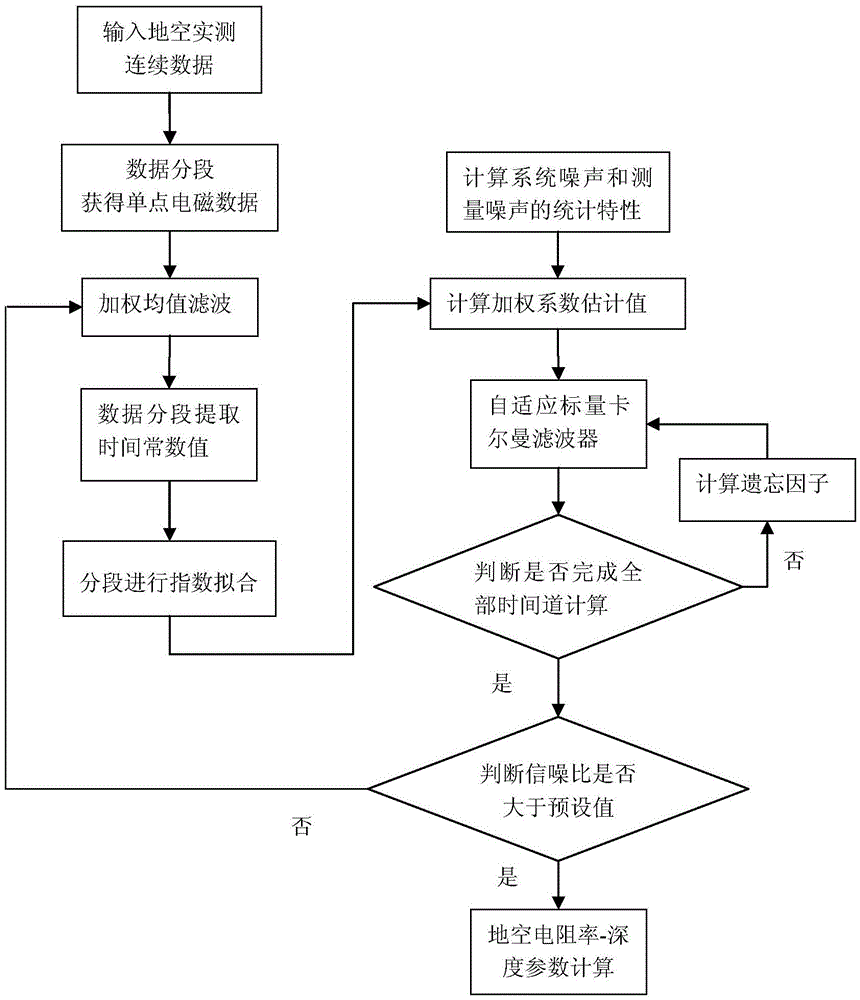
Exponential fit-adaptive Kalman-based ground-air electromagnetic data de-noising method
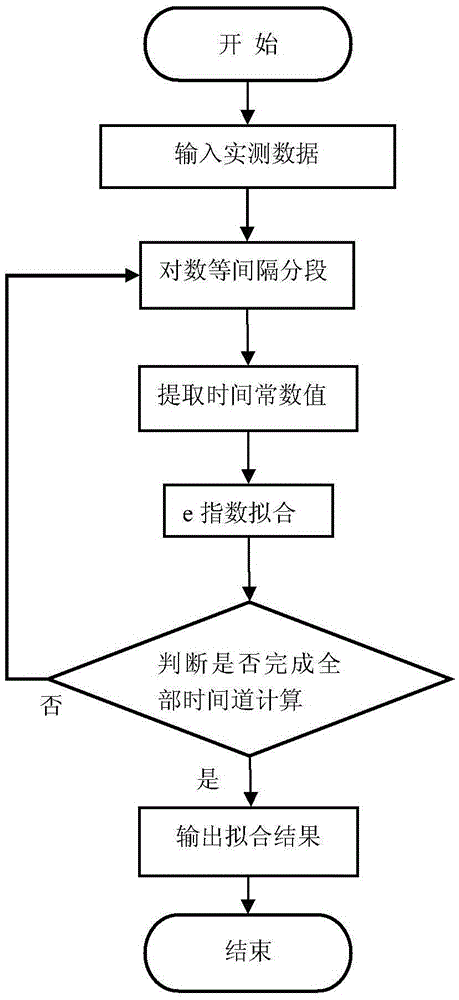
ActiveCN105652325APreserve and enhance valid informationImprove signal-to-noise ratioDetection using electromagnetic wavesDepth imagingSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention relates to an exponential fit-adaptive Kalman-based ground-air electromagnetic data de-noising method. According to the technical scheme of the invention, for single-point electromagnetic data during the ground-air measurement, time windows are determined and then the data are segmented at equal logarithm interval based on the features of electromagnetic data in the ground-air time domain according to the approximate e-index attenuation law, and the time constant value of data in each time frame are extracted as fitting parameters. Meanwhile, the data in each time frame are processed based on the e-exponential fitting method, and fitting output results are adopted as predicted values to be input into a filter. After that, the adaptive scalar Kalman filtering method is applied to filtering the electromagnetic noise in data, and the filtered data are subjected to resistivity-depth imaging. Compared with the existing electromagnetic data filtering method in the ground-air time domain, the above filtering method of the present invention not only effectively suppresses the electromagnetic noise in electromagnetic data in the ground-air time domain, but also fully retains and enhances the effective information in measured data. Therefore, both the signal-to-noise ratio and the quality of electromagnetic data in the ground-air time domain are improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com