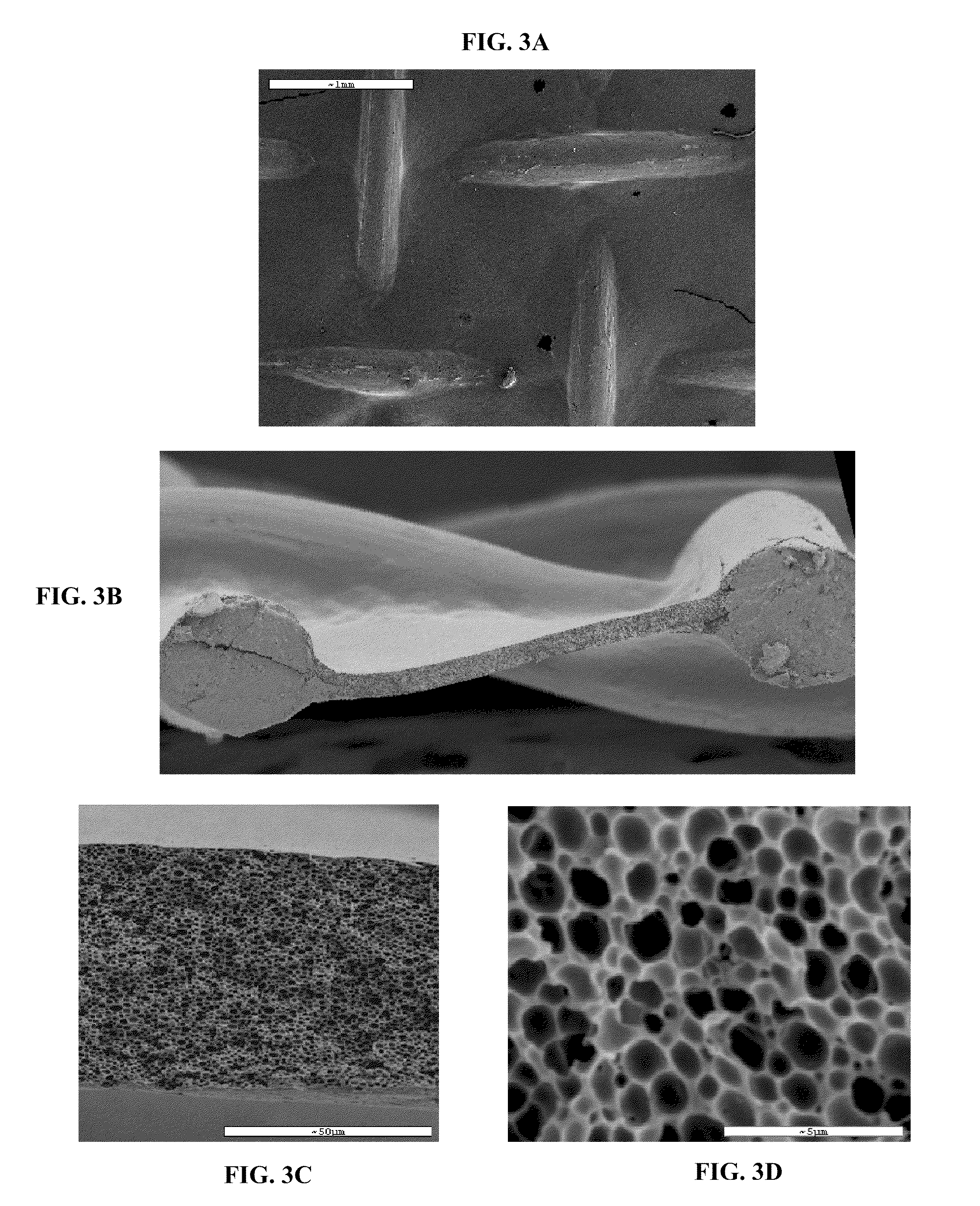
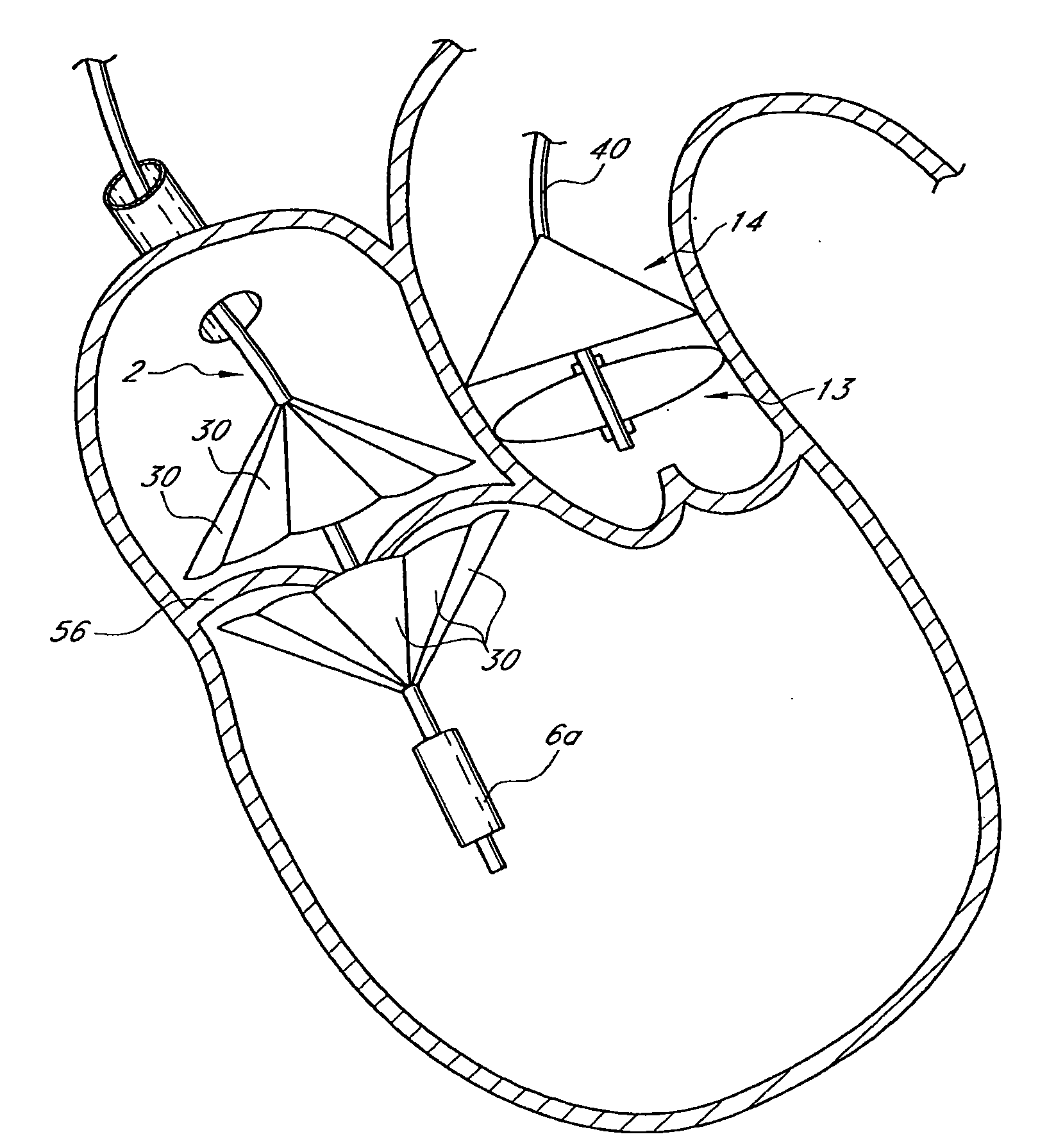
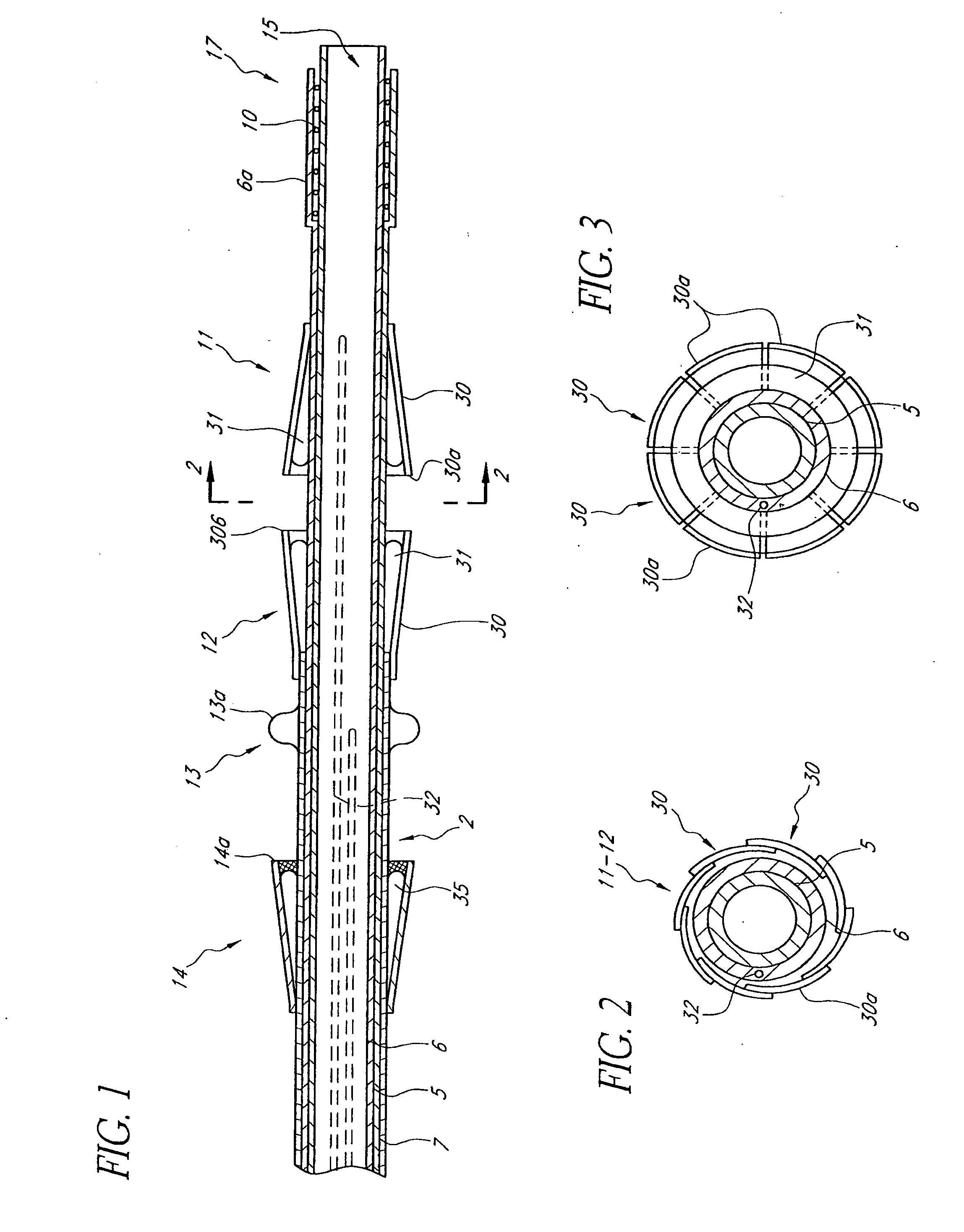
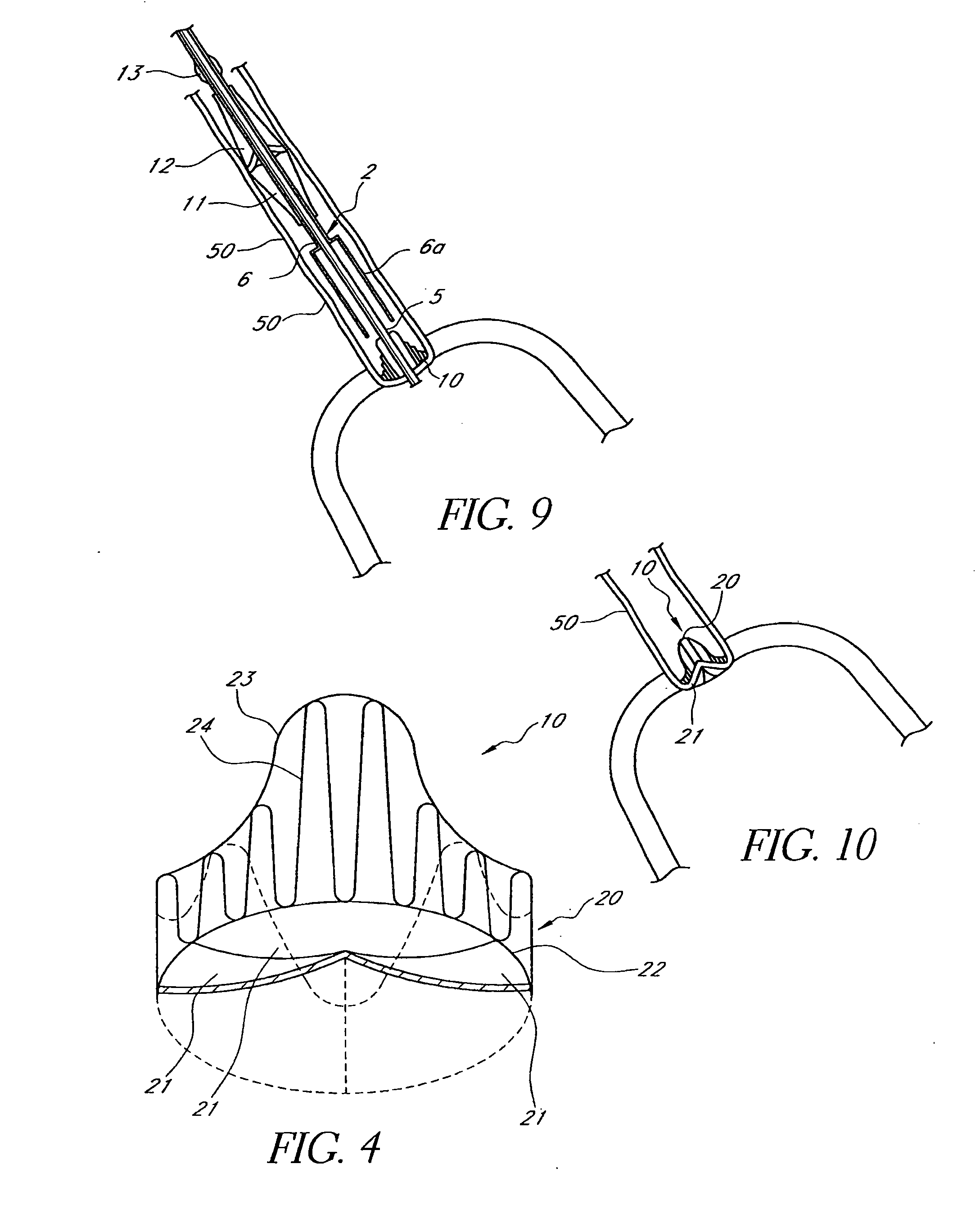
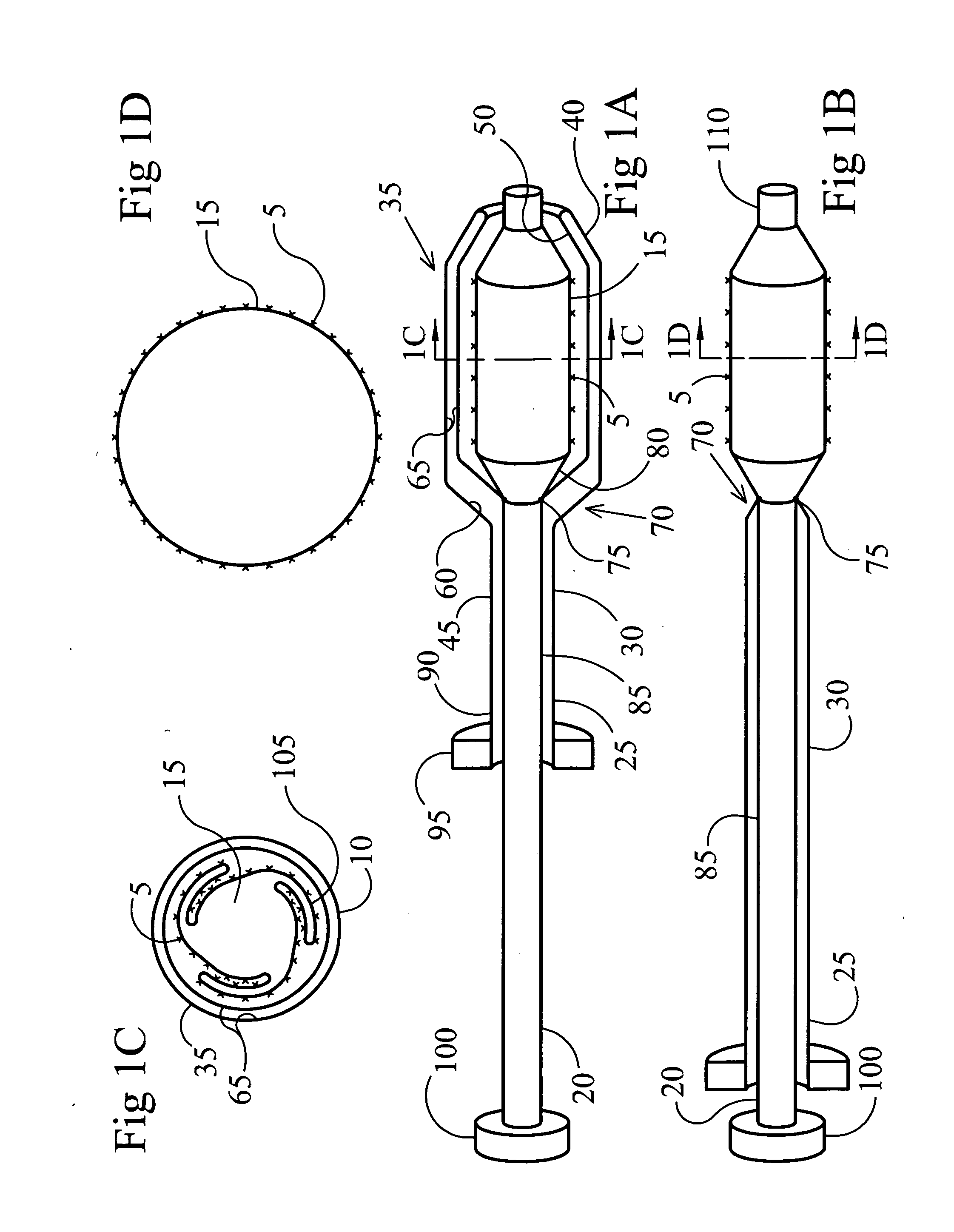
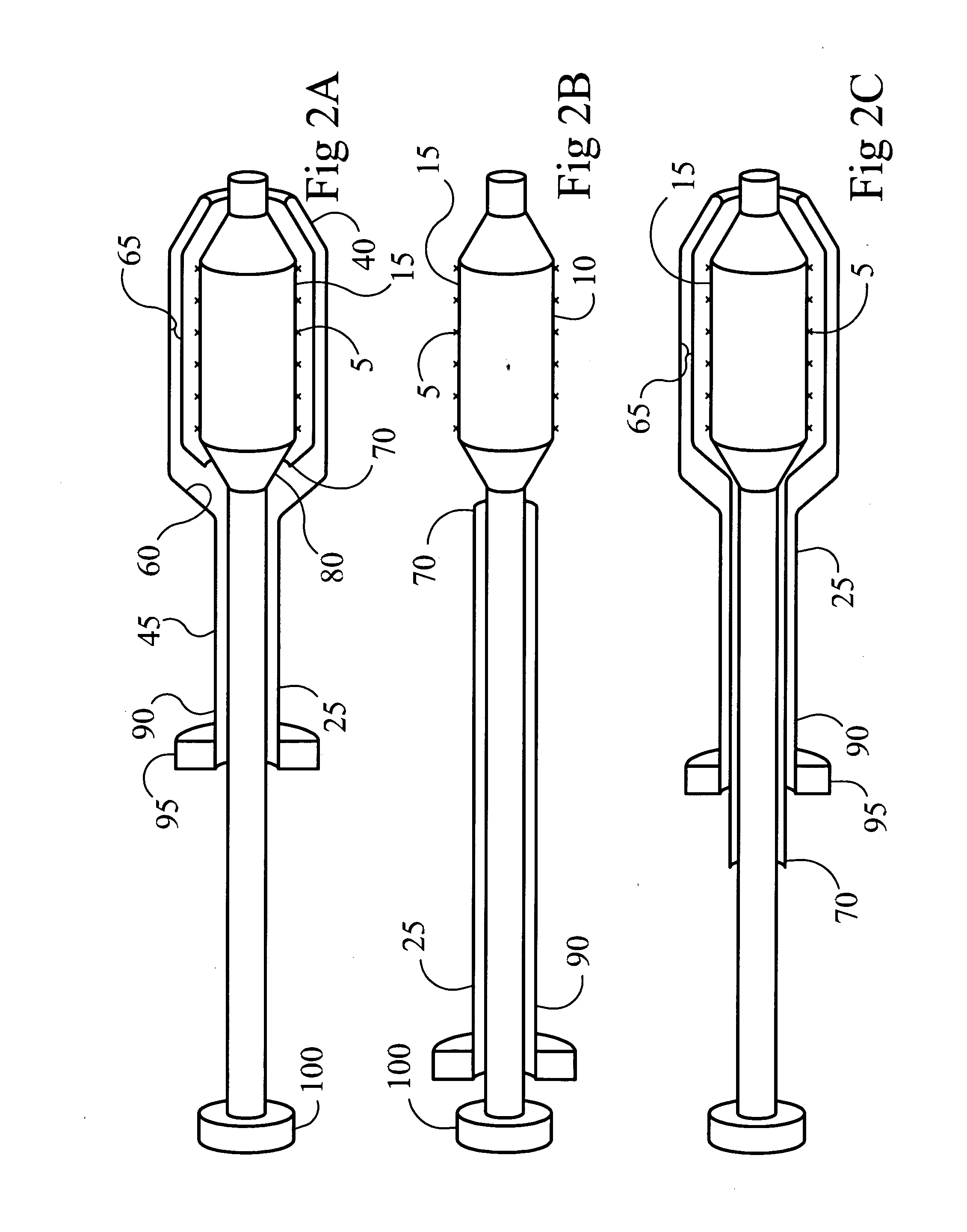
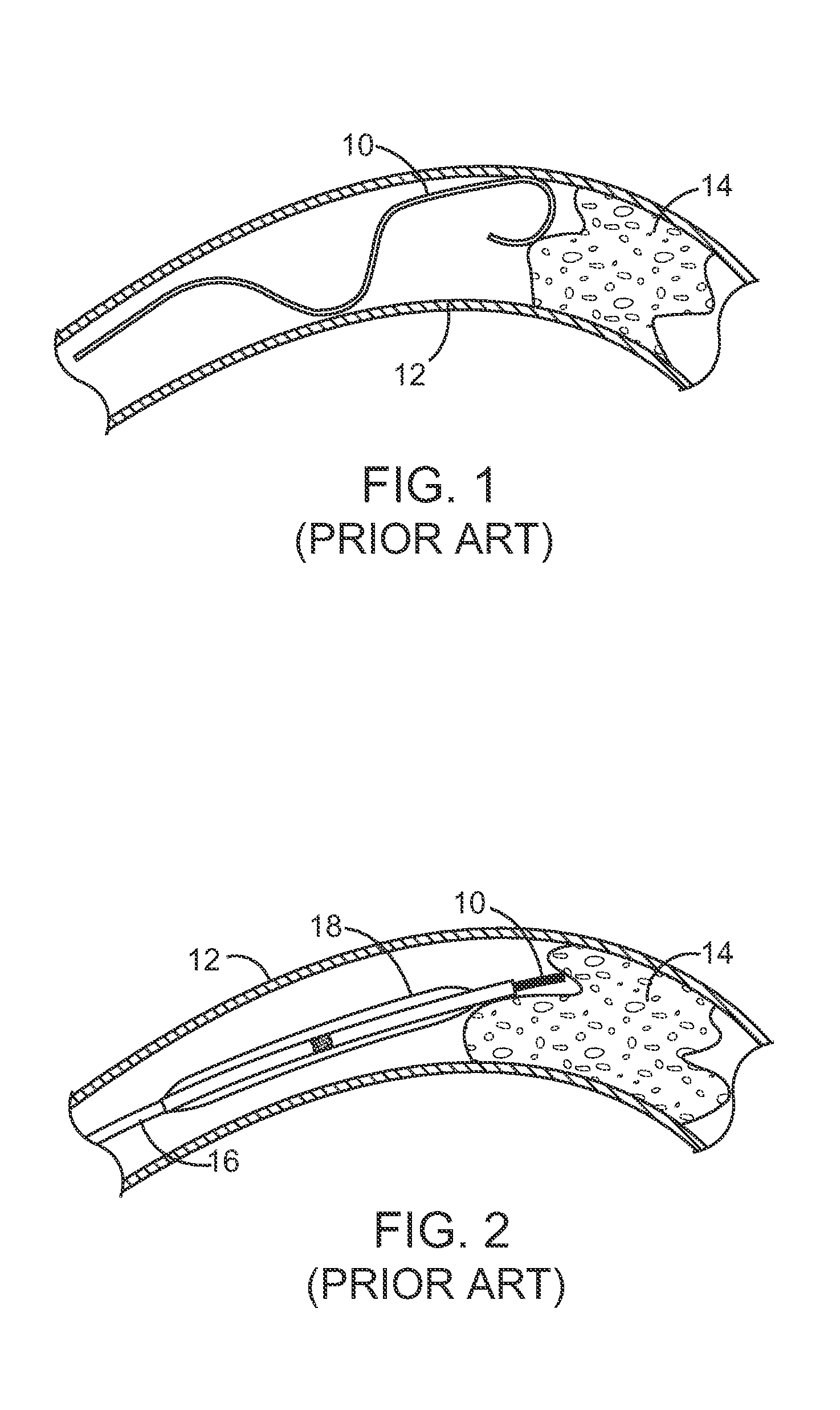
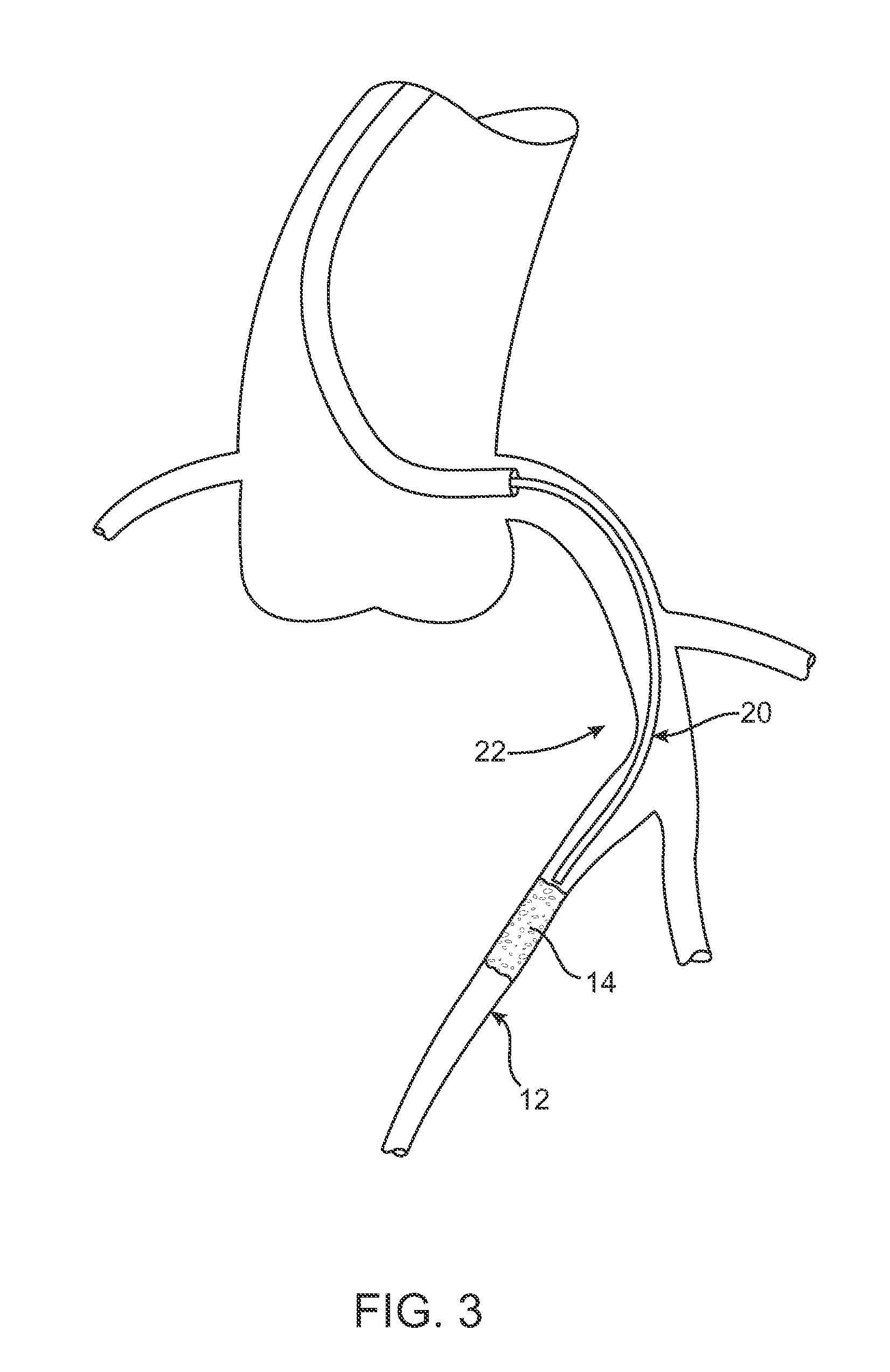
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
202 results about "Drug elution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
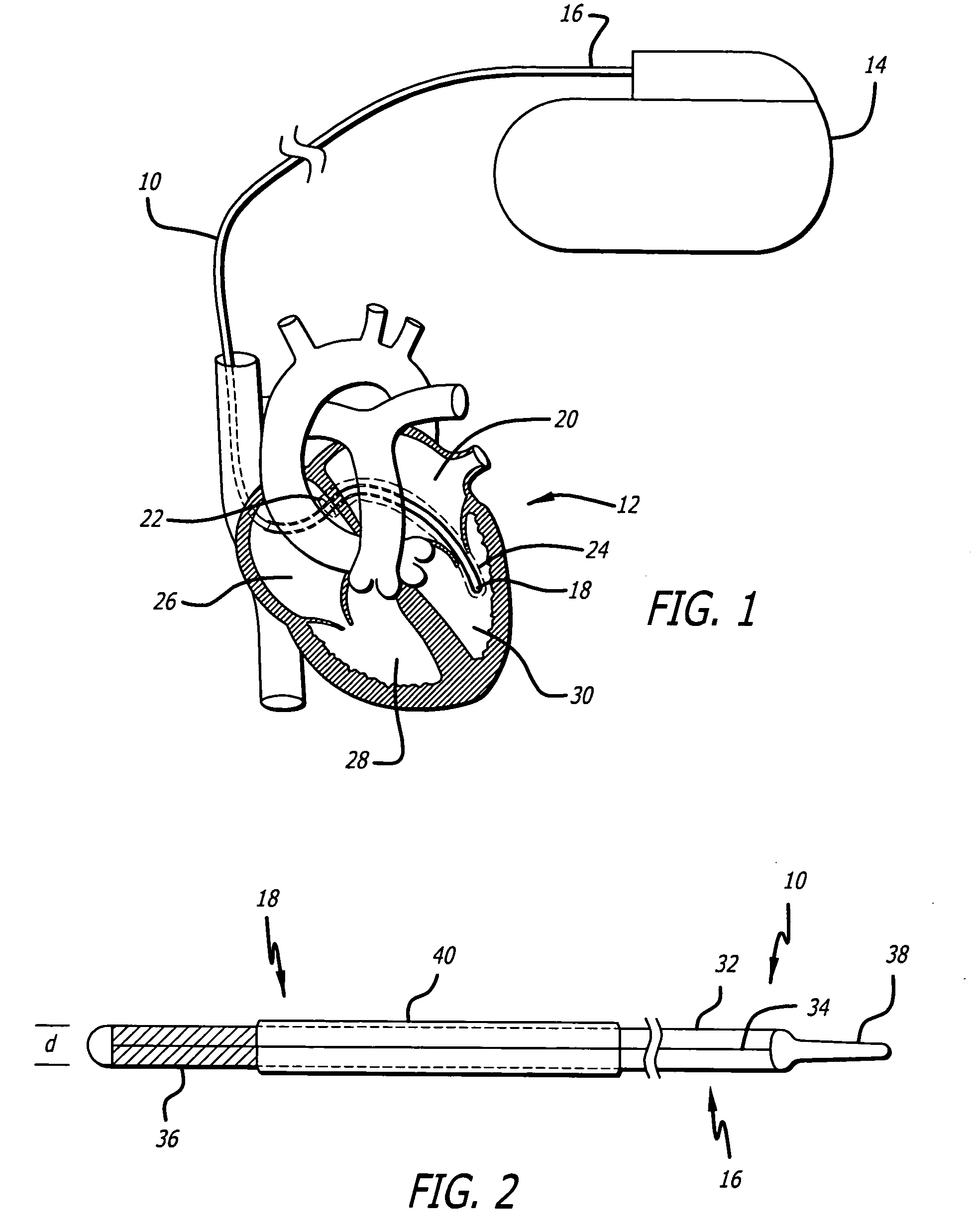
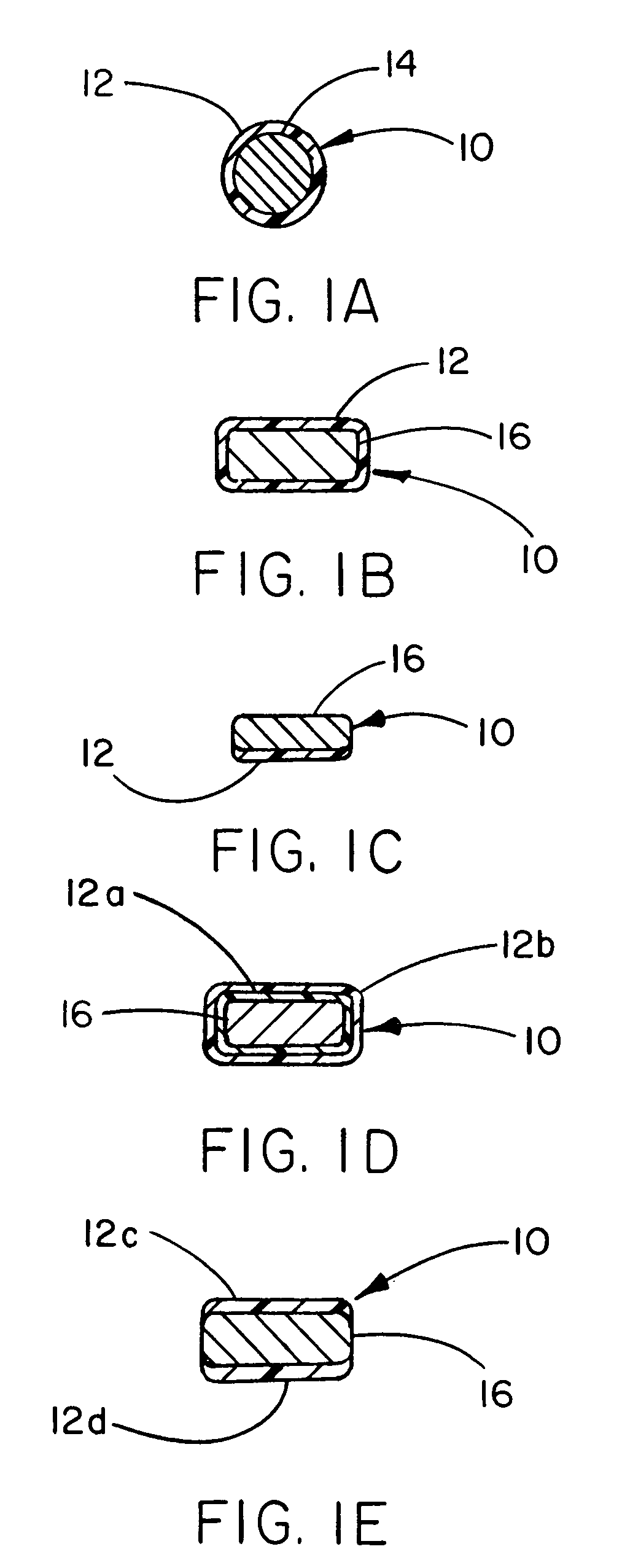
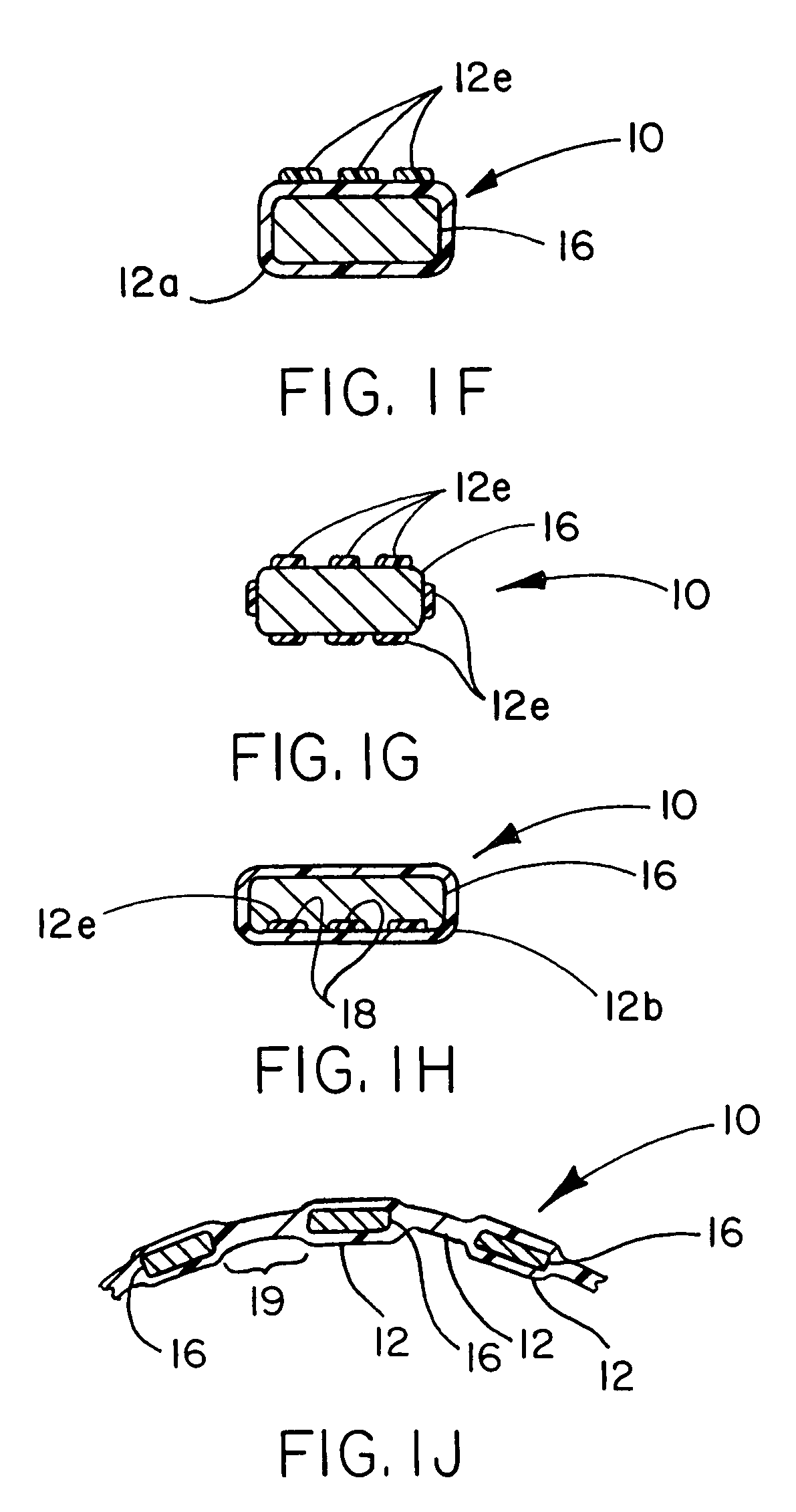
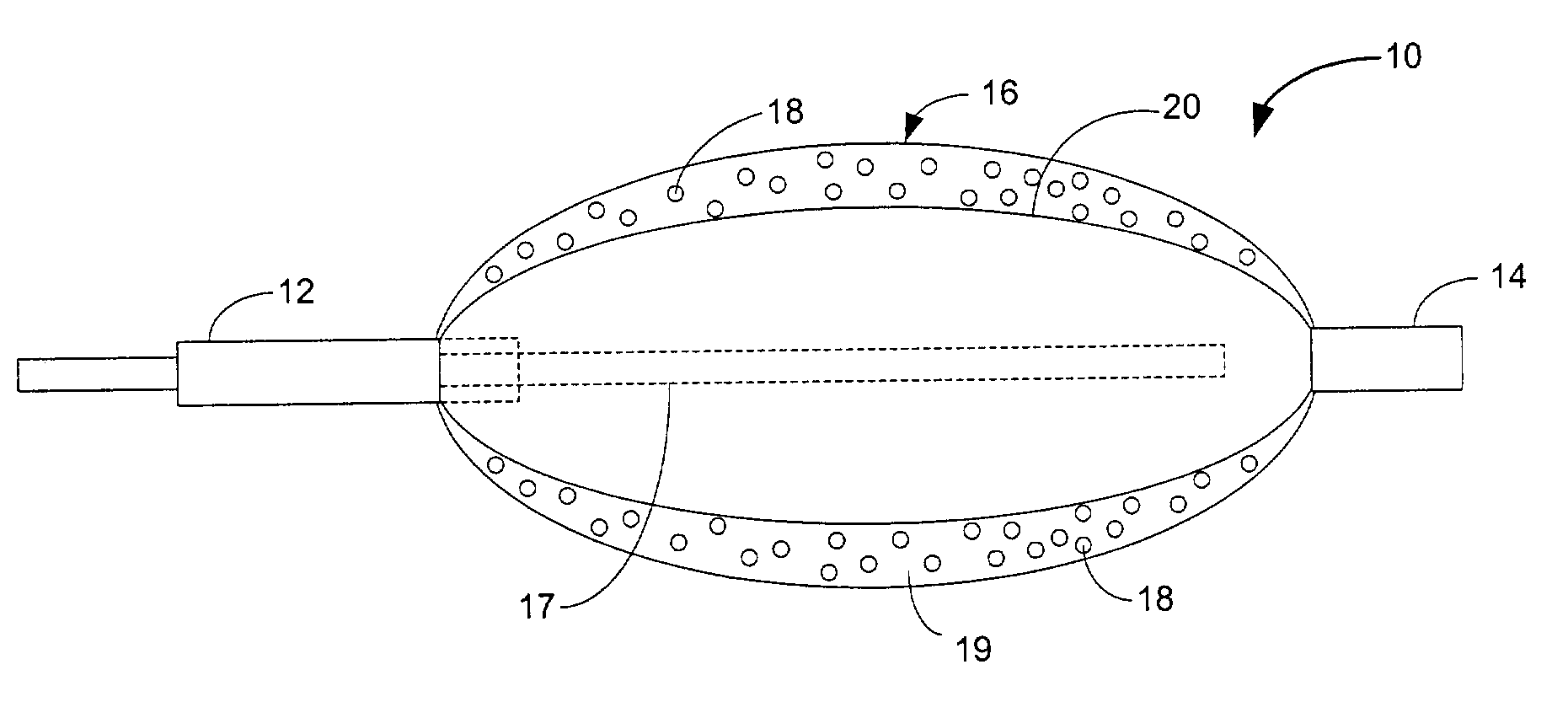
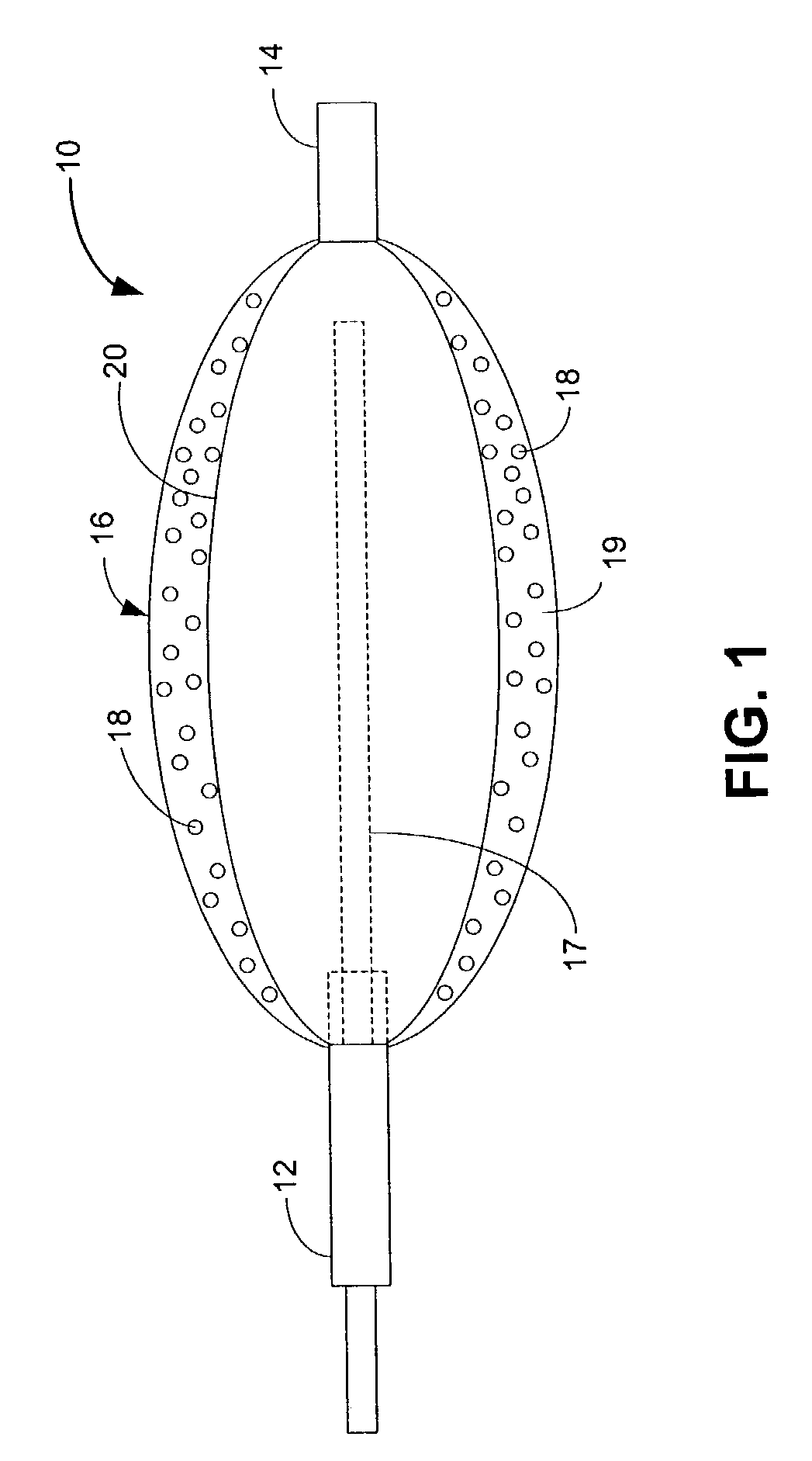
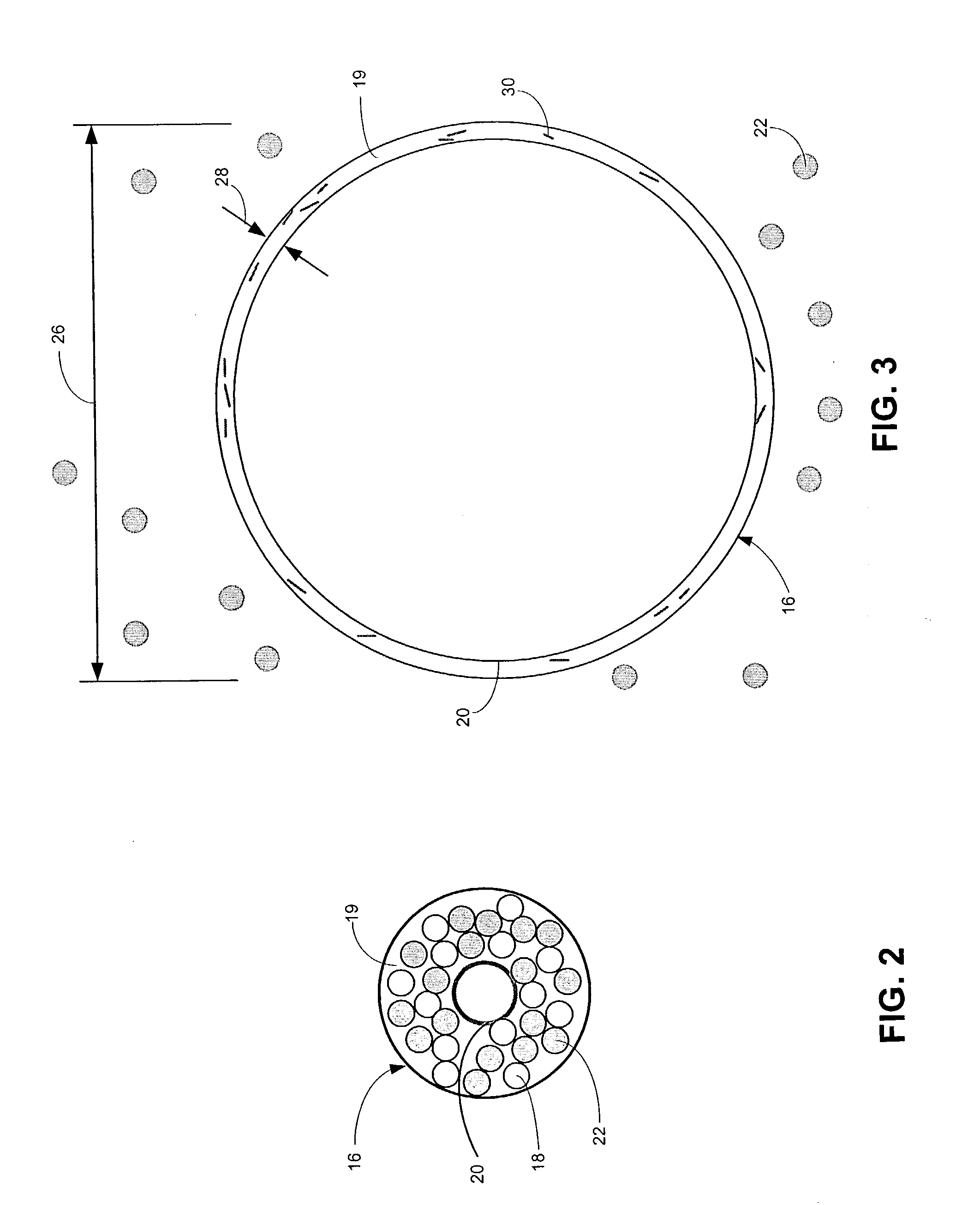
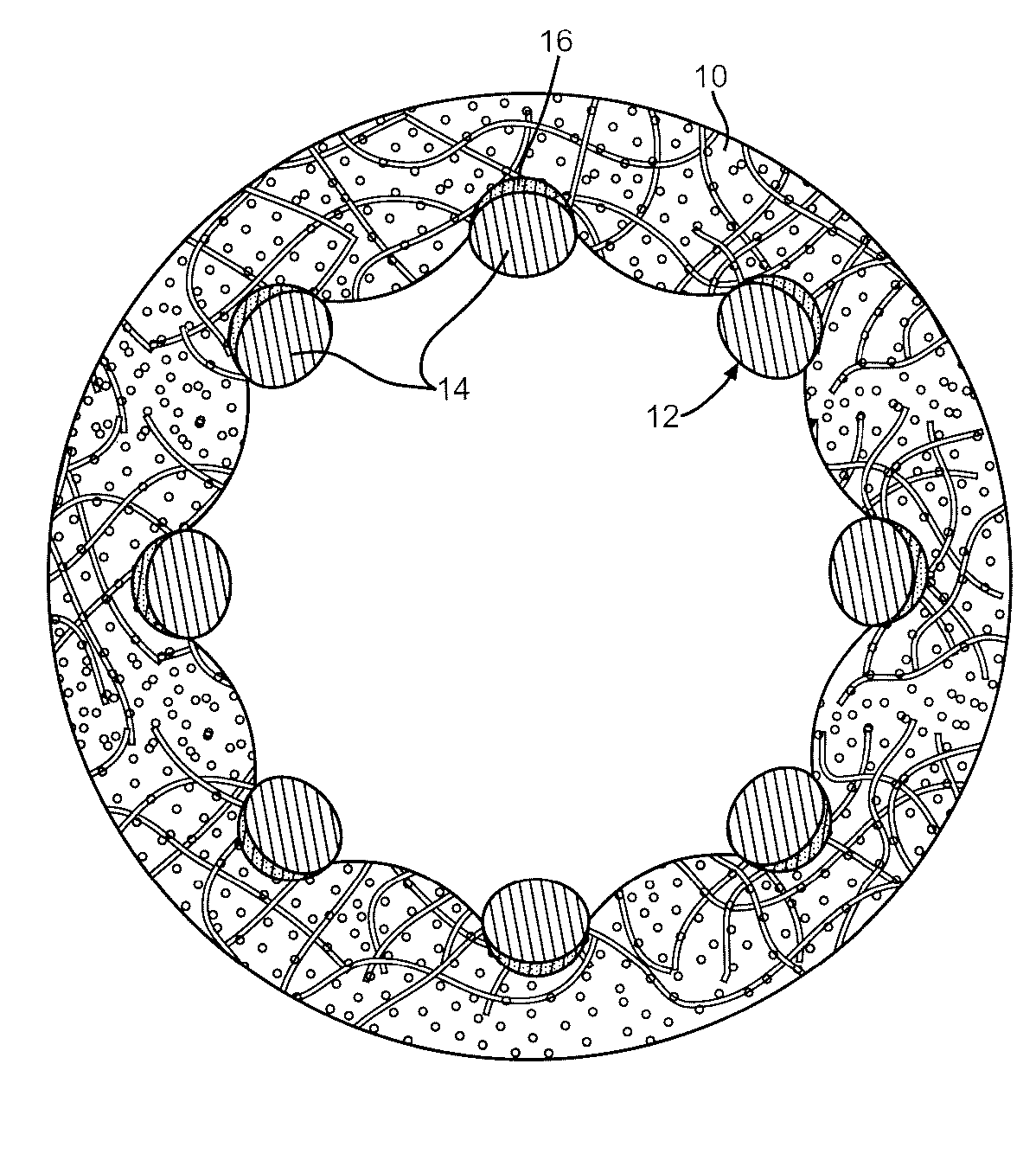
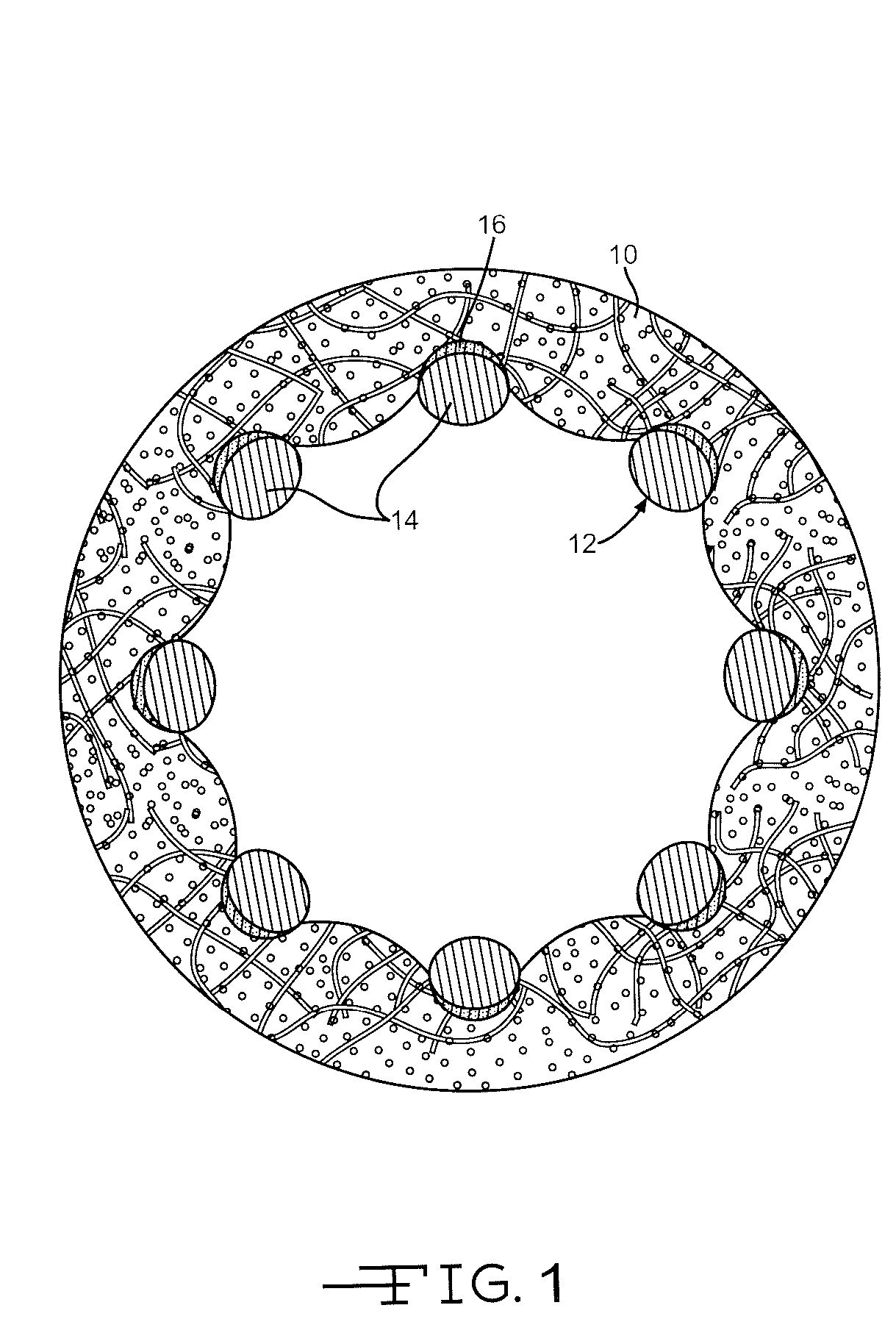
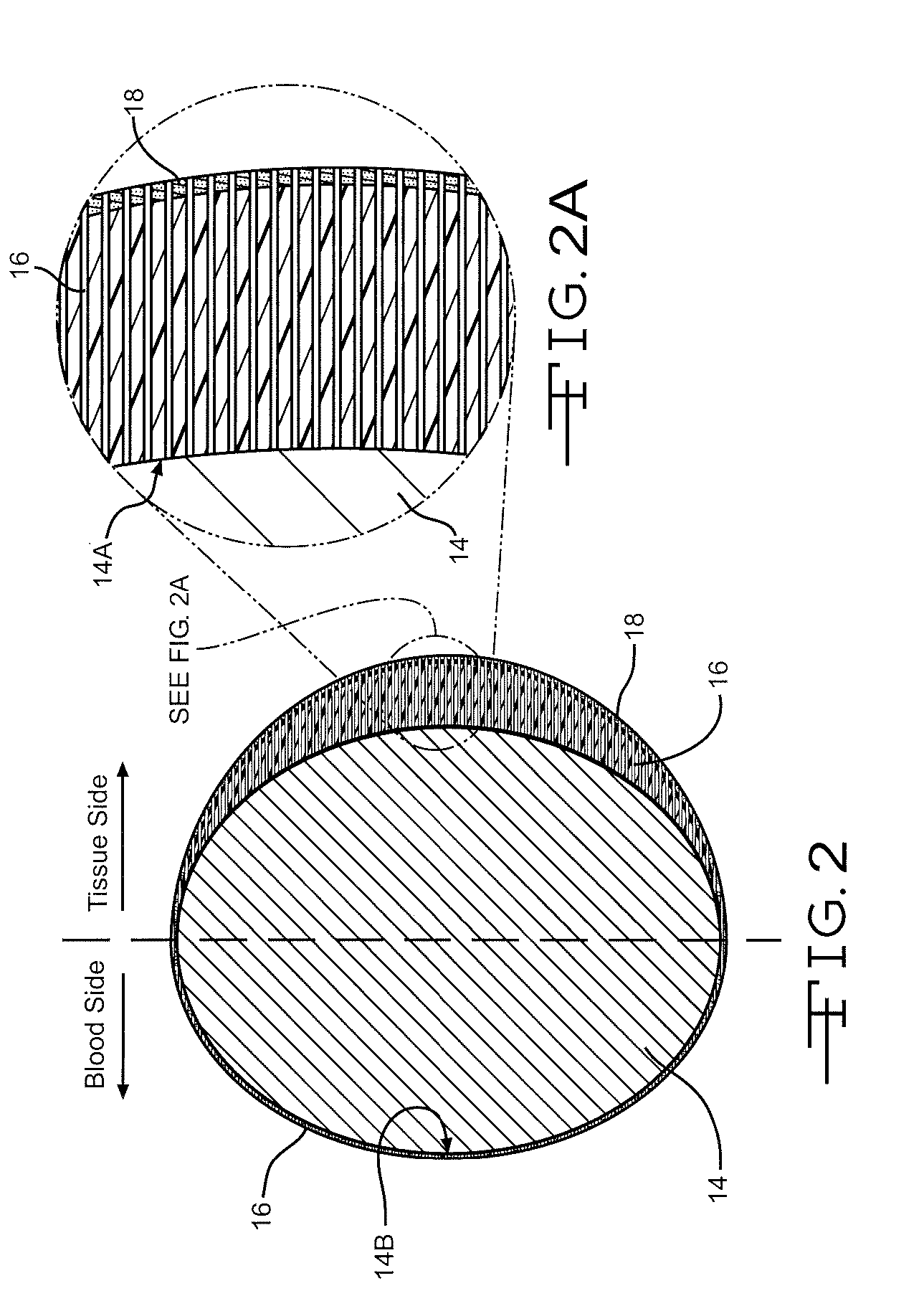
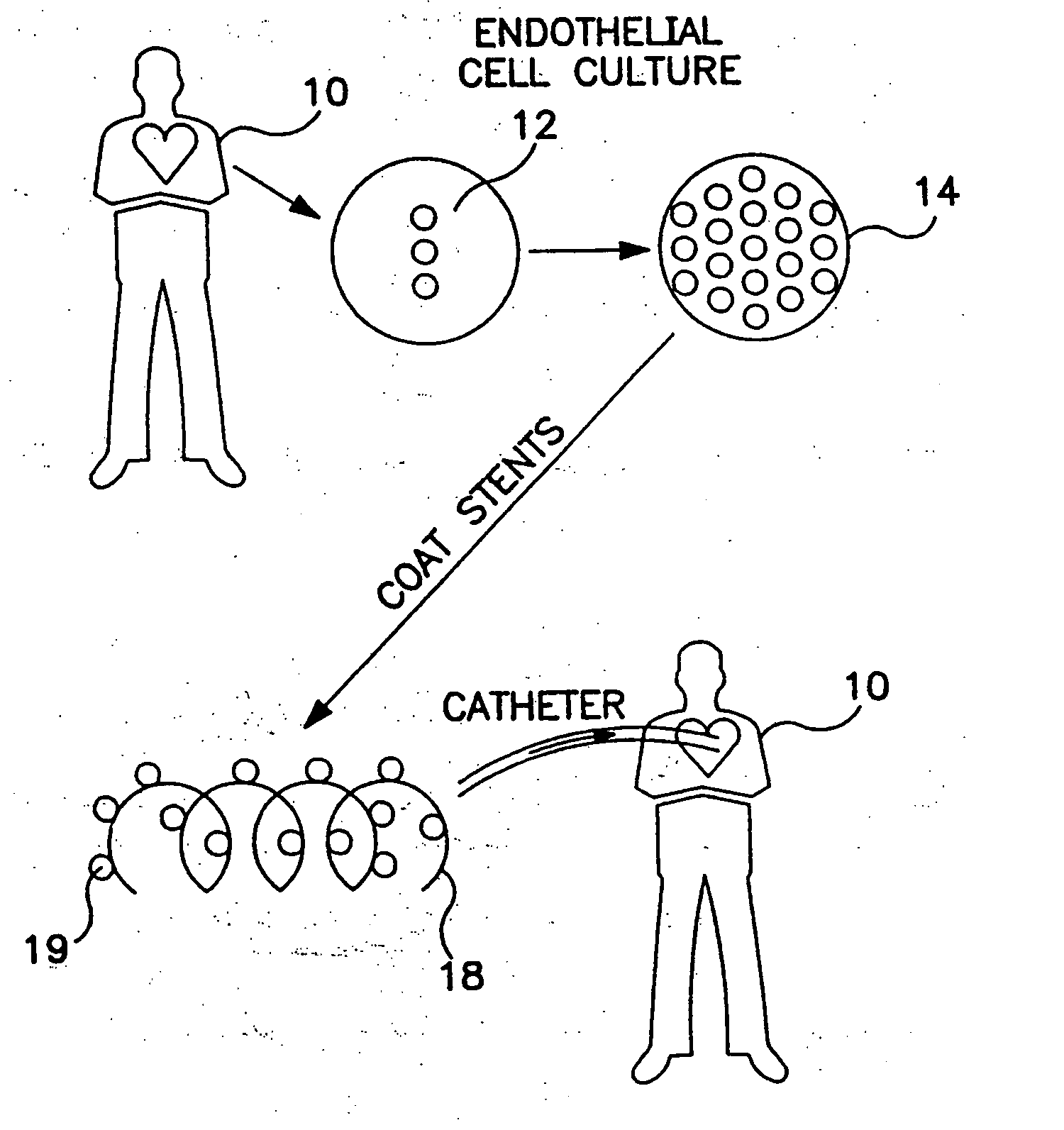
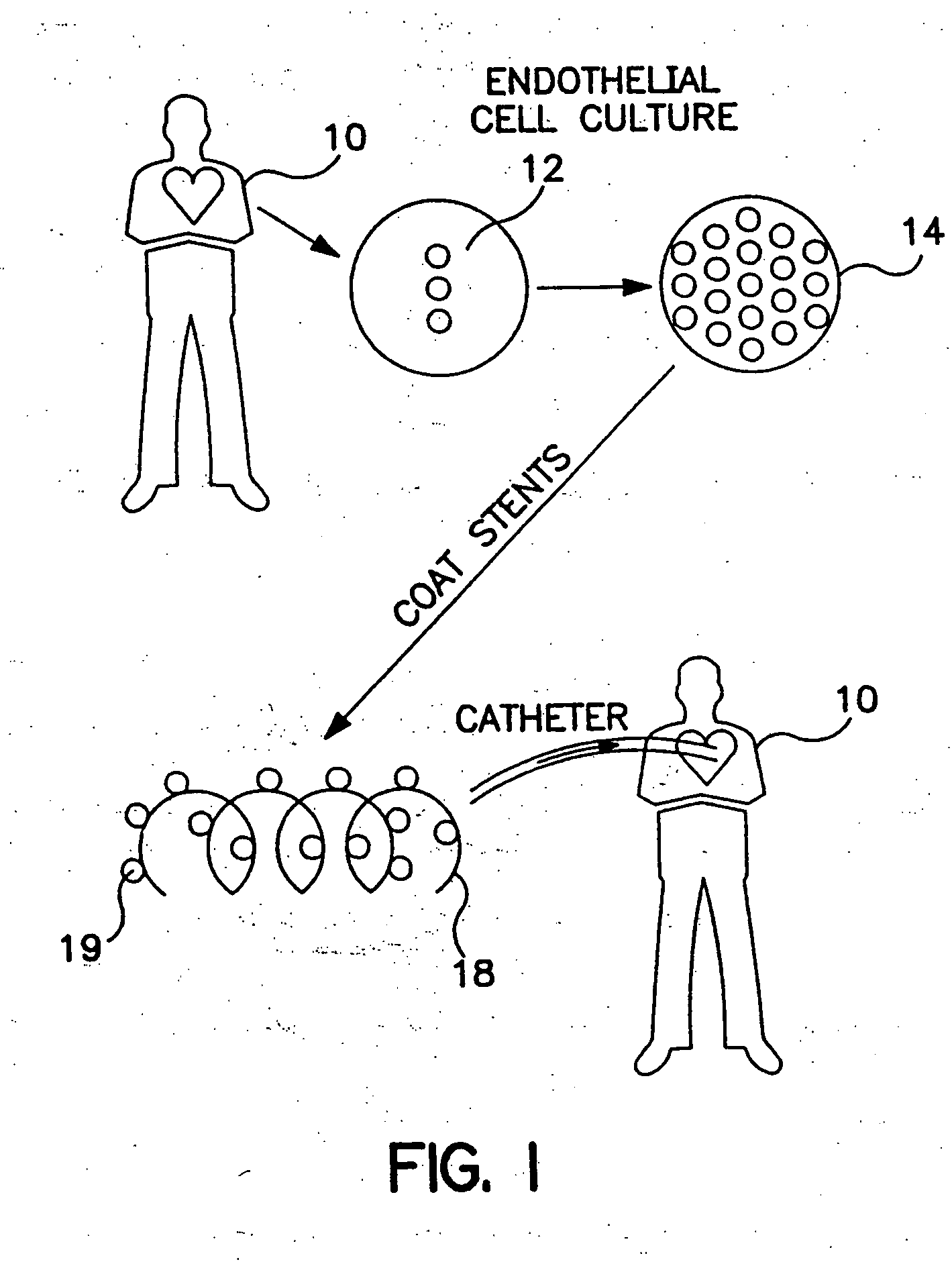
Drug-eluting stents (DES) are a standard metallic coronary stent with a polymer coating and an antiproliferative drug, which allows drug elution into the coronary wall for weeks to months after stent implantation.
Drug-eluting medical devices
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Drug-eluting medical devices
Composite structures composed of a device as a core structure, being a medical device or article, and a porous polymeric coat and designed capable of encapsulating bioactive agents while retaining the activity of these agents are disclosed. Further disclosed are processes of preparing such composite structures.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Prosthetic Valve for Transluminal Delivery
InactiveUS20100004740A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesVenous accessImplantation Site
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchors may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. A radial restraint, comprising a wire, thread or cuff, may be used to ensure expansion does not exceed the preset diameter. The valve support may optionally comprise a drug elution component. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. A blood pump may be inserted into the catheter to ensure continued blood flow across the implantation site during implantation procedure. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. Insertion of the catheter may optionally be performed over a transseptally delivered guidewire that has been externalized through the arterial vasculature. Such a guidewire provide dual venous and arterial access to the implantation site and allows additional manipulation of the implantation site after arterial implantation of the prosthetic valve. Additional expansion stents may be delivered by venous access to the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Drug eluting implants to prevent cardiac apoptosis
Implantable devices are configured to be positioned in or near the heart and to carry and deliver an anti-apoptotic drug to a treatment site in or near the heart. The implantable devices include, but are not limited to, leads, stents, heart valves, atrial septal defect devices, cardiac patches and ventricular restraint devices. Depending on the composition of the device, the drug may be carried by the device through a coating applied to the device, or may be included in the device during the device manufacturing process. The drug may also be included in microparticles, such a microspheres, that are delivered locally through a conduit, such as a catheter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Drug eluting implantable medical device
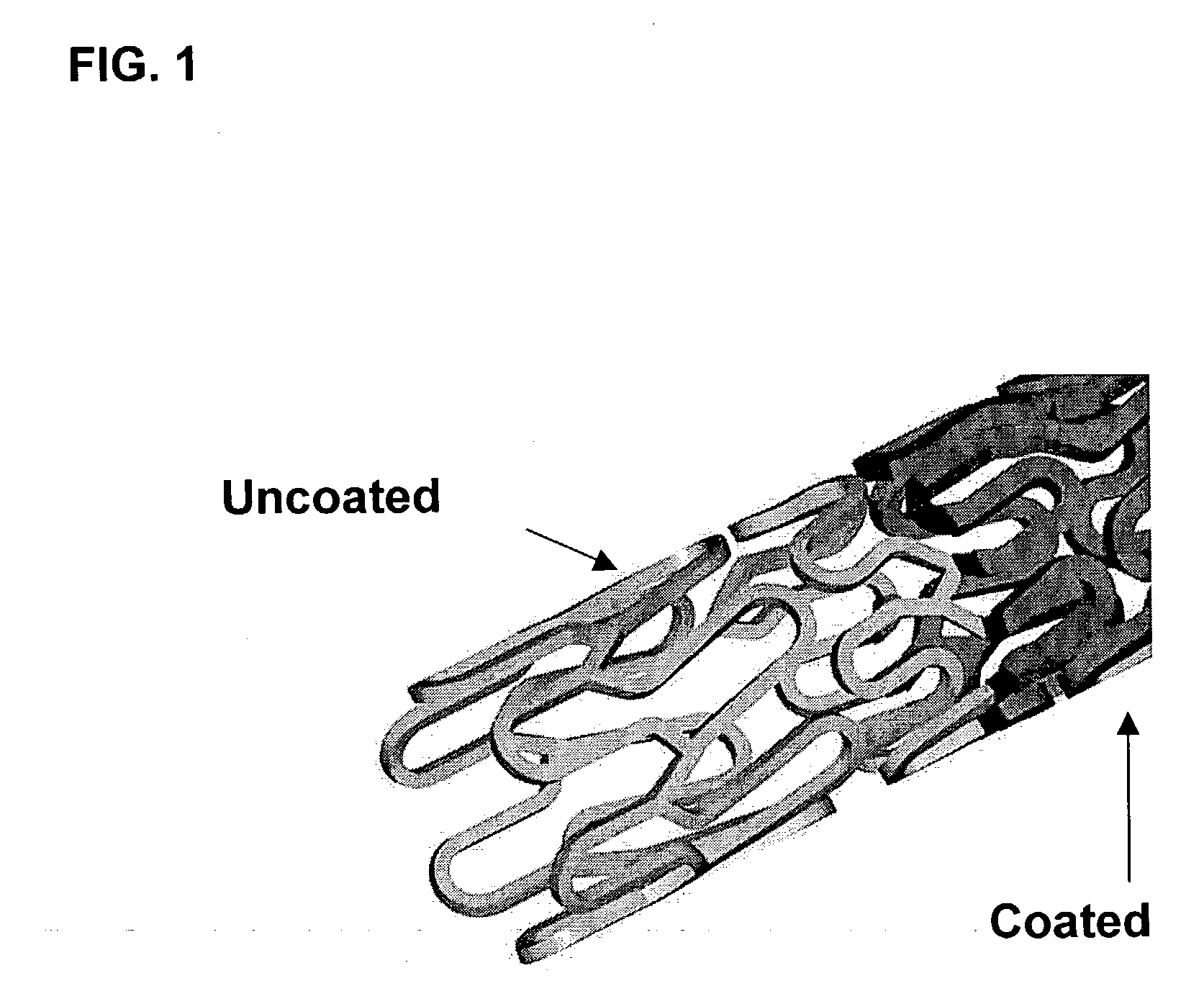
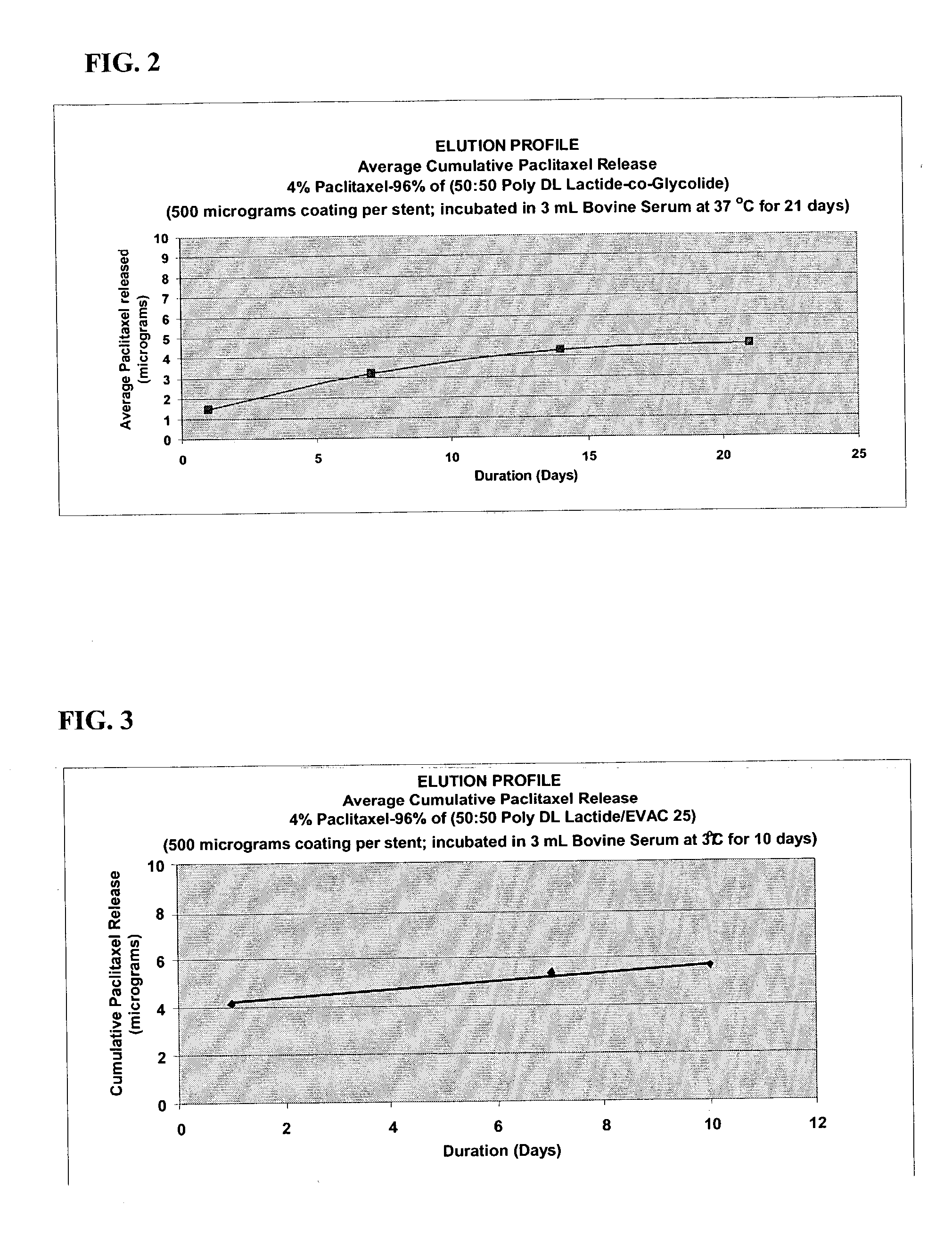
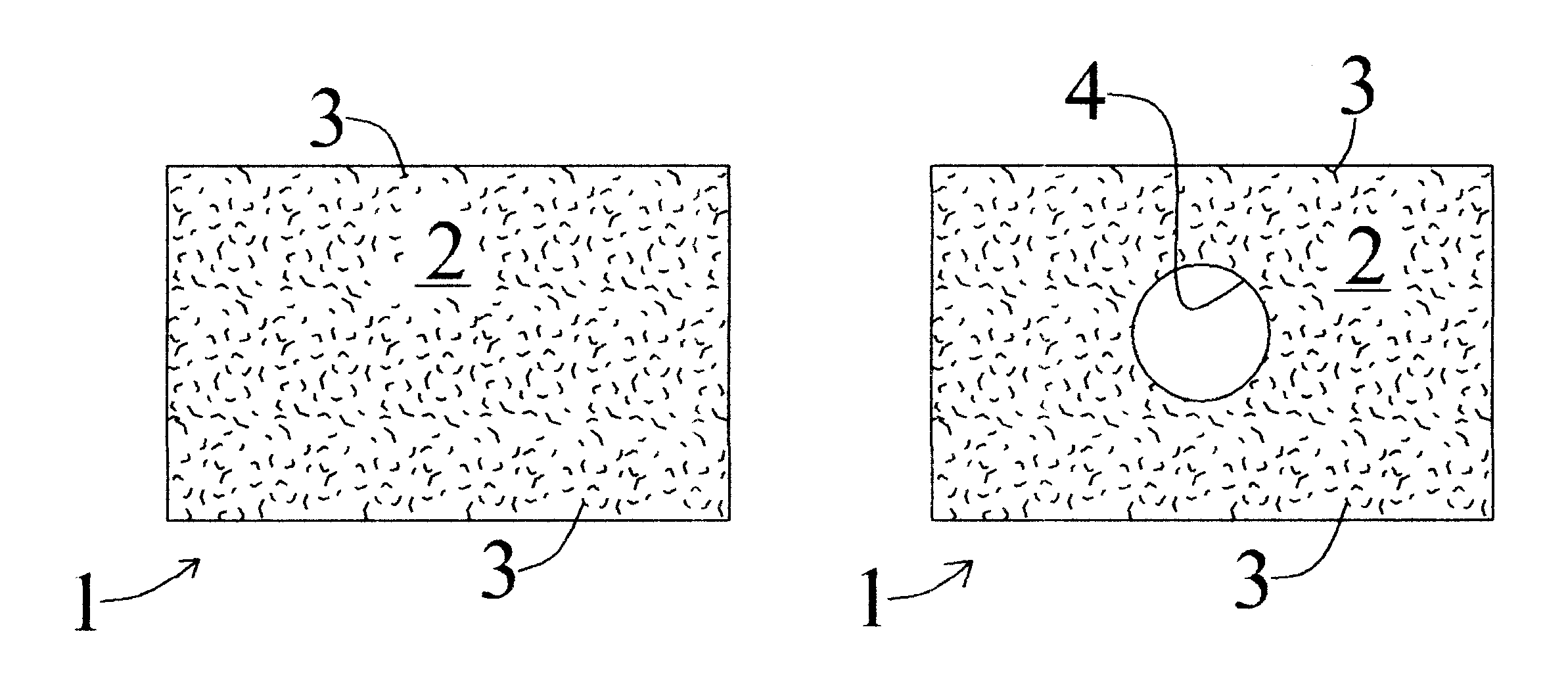
A drug eluting medical device is provided for implanting into vessels or luminal structures within the body of a patient. The coated medical device, such as a stent, vascular, or synthetic graft comprises a coating consisting of a controlled-release matrix of a bioabsorbable, biocompatible, bioerodible, biodegradable, nontoxic material, such as a Poly(DL-Lactide-co-Glycolide) polymer, and at least one pharmaceutical substance, or bioactive agent incorporated within the matrix or layered within layers of matrix. In particular, the drug eluting medical device when implanted into a patient, delivers the drugs or bioactive agents within the matrix to adjacent tissues in a controlled and desired rate depending on the drug and site of implantation.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Apparatus and methods for preventing or treating failure of hemodialysis vascular access and other vascular grafts
InactiveUS6726923B2Reduce calcificationInhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferationBiocideOrganic chemistryVascular graftBlood vessel
Owner:VASCULAR THERAPIES INC
Drug-eluting Biodegradable Stent and Delivery Means
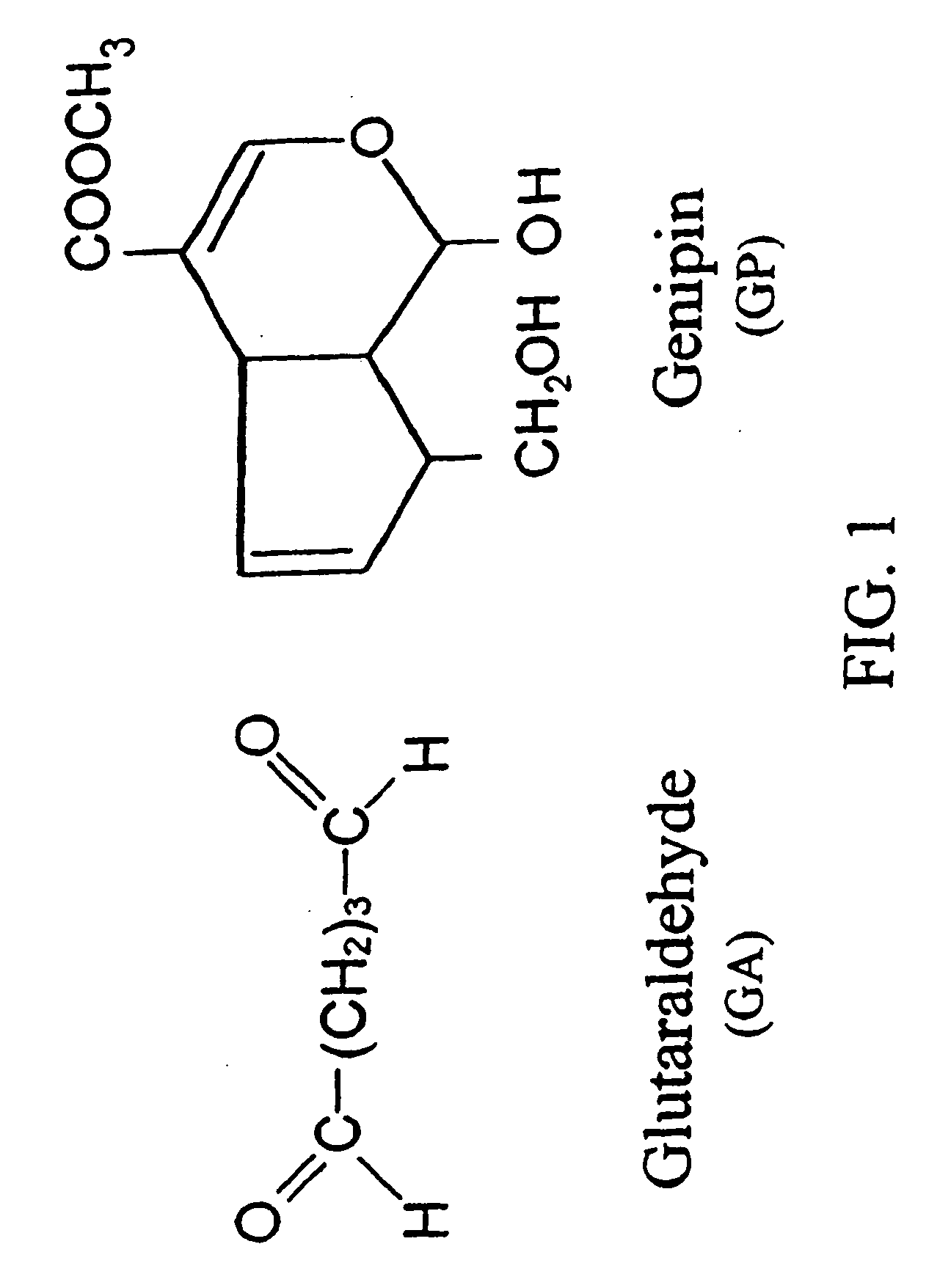
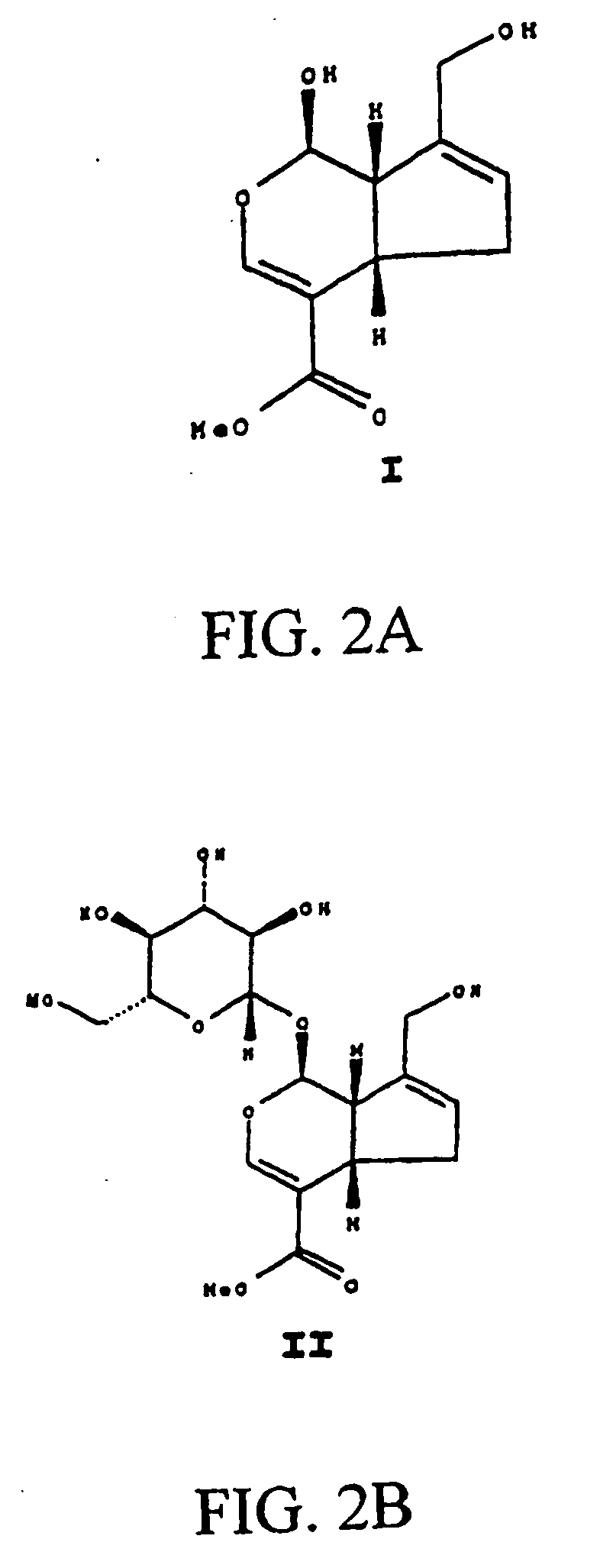
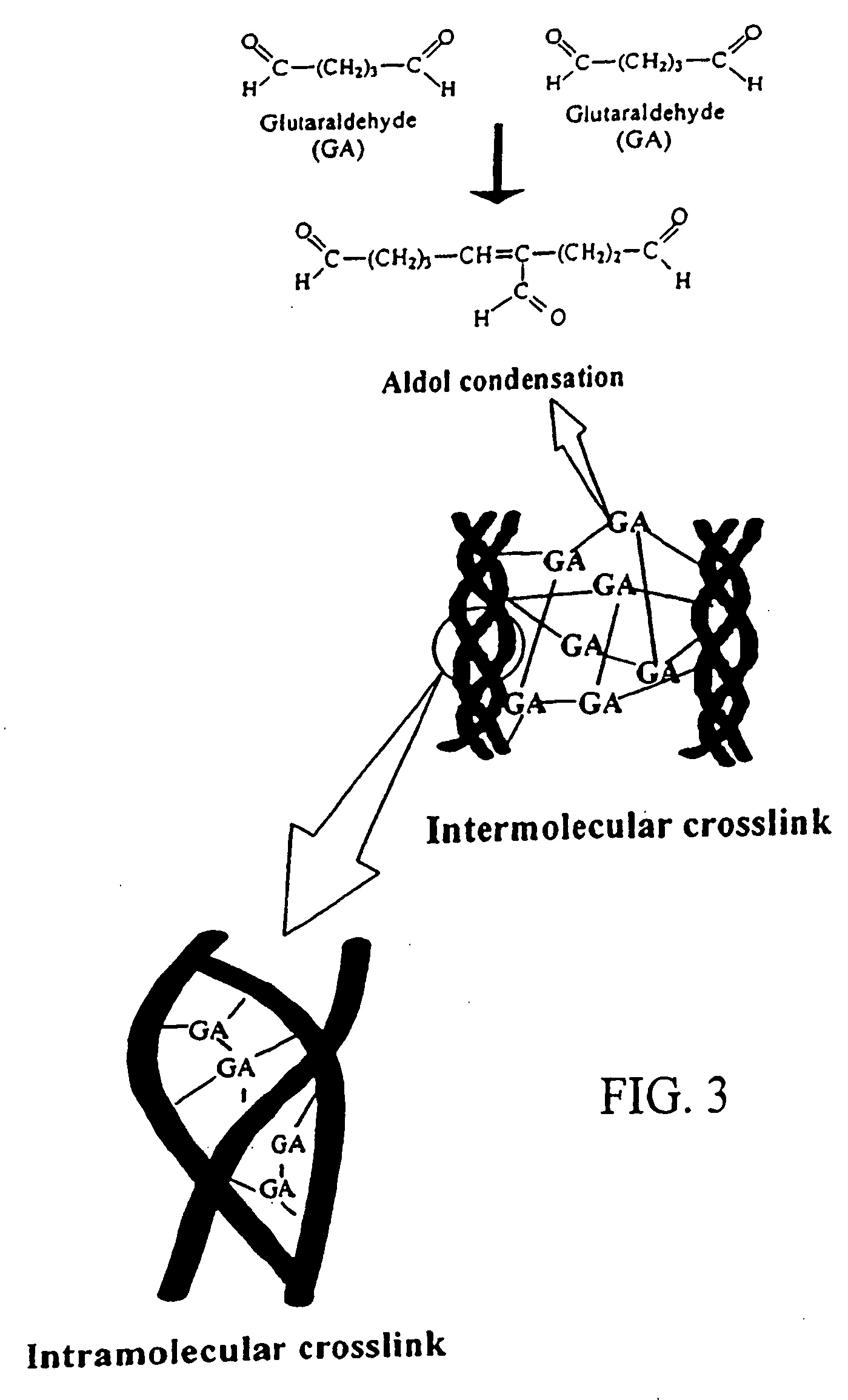
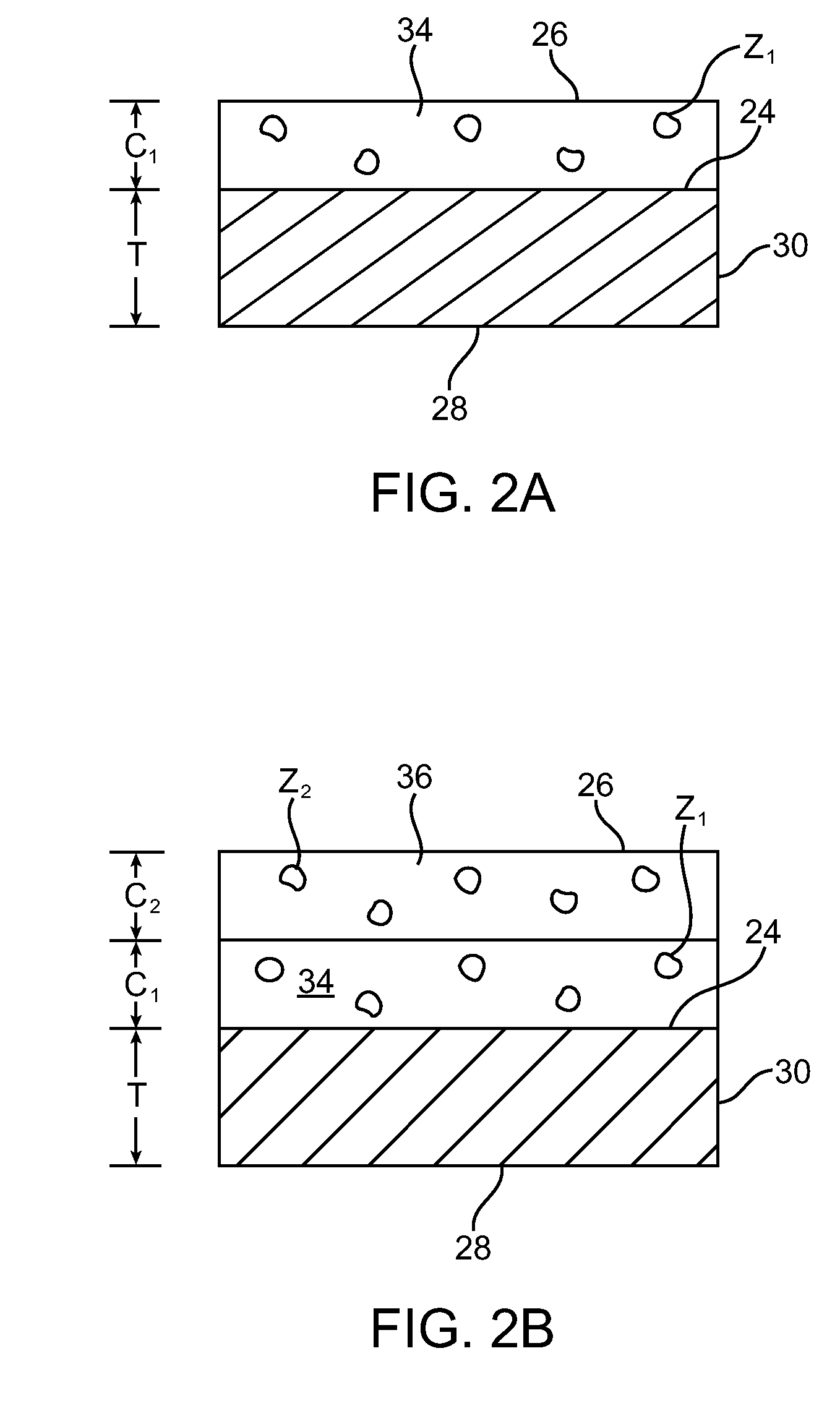
A biodegradable stent comprising a luminal surface portion with a second degree of crosslink, an outer surface portion with a first degree of crosslink, and a body between the luminal and outer surface portions, wherein the body comprises a crosslinked material characterized by the first degree of crosslink not less than the second degree of crosslink.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Drug-eluting biodegradable stent
The present invention relates to a drug-loaded biodegradable stent and methods for treating vulnerable plaques of a patient comprising a plurality of layers or zones, each layer or zone comprising its own specific biodegradation rate and its specific drug loading characteristics. In one embodiment, the layers and zones are configured and arranged, in combination, radially, circumferentially and longitudinally.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Stents with drug eluting coatings
The present invention relates generally to medical devices, preferably a stent, having a drug eluting surface coated or covered with a coating of particles comprising at least an outer layer, an inner layer, and a core comprising a therapeutic agent. Specifically, the invention relates to medical devices having a hydrophilic coating comprising particles with a hydrophilic outer layer, a hydrophobic inner layer, and a core comprising a hydrophobic therapeutic agent, as well as medical devices having a hydrophobic coating comprising particles with a hydrophobic outer layer, a hydrophilic inner layer, and a core comprising a hydrophilic therapeutic agent. The coating, outer layer, and inner layer are preferably biodegradable and capable of providing sustained release of the therapeutic agent over a time period. The invention also relates to methods of making and methods of using the coated or covered medical device.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST +1
Drug eluting structurally variable stent
The present invention provides a stent including a tubular body having a plurality of reservoirs disposed therein and a therapeutic agent located in the reservoirs or located in the reservoirs and on a surface portion of the tubular body, wherein the stent is free of polymeric material. The invention also provides a drug-eluting stent made from the process of providing a polymer-free stent body having a plurality of reservoirs disposed therein, diluting a therapeutic agent in a polymer-free solvent to form an agent-solvent mixture, coating the stent with the agent-solvent mixture, and allowing the solvent to dissipate from the stent thereby leaving the agent disposed on the stent.
Owner:VASCULAR CONCEPTS HLDG
Drug-eluting medical device
The present invention relates to a drug-eluting medical device, in particular a balloon for angioplasty catheters with drug elution to prevent the restenosis of the vessel subjected to angioplasty. More particularly, the present invention relates to a catheter balloon completely or partially coated with paclitaxel in hydrated crystalline form or in hydrated solvated crystalline form, having an immediate release and bioavailability of a therapeutically effective amount of paclitaxel at the site of intervention. The balloon can be made of a polyether-polyamide block copolymer, or a polyester amide, or polyamide-12.
Owner:INVATEC TECH CENT
Drug eluting coatings for medical implants
ActiveUS20040037886A1Minimizing restenosisMinimizing thrombosisSuture equipmentsBiocideEverolimusCyclosporins
Drug eluting coating compositions are composed of at least one therapeutic agent dispersed in modified, biologically active binders. The therapeutic agents included in the coating composition are paclitaxel, sirolimus, tacrolimus, everolimus, actinomycin-D, dexamethasone, mycophenolic acid, cyclosporins, estradiol, and derivatives and analogs thereof. These therapeutic agents are applied to the surface of the medical device by a modified, biologically active binders. By using these biologically active binders, the therapeutic agents can be applied to at least one surface of a medical implant without using inert polymer carriers.
Owner:BIOVENTION INC
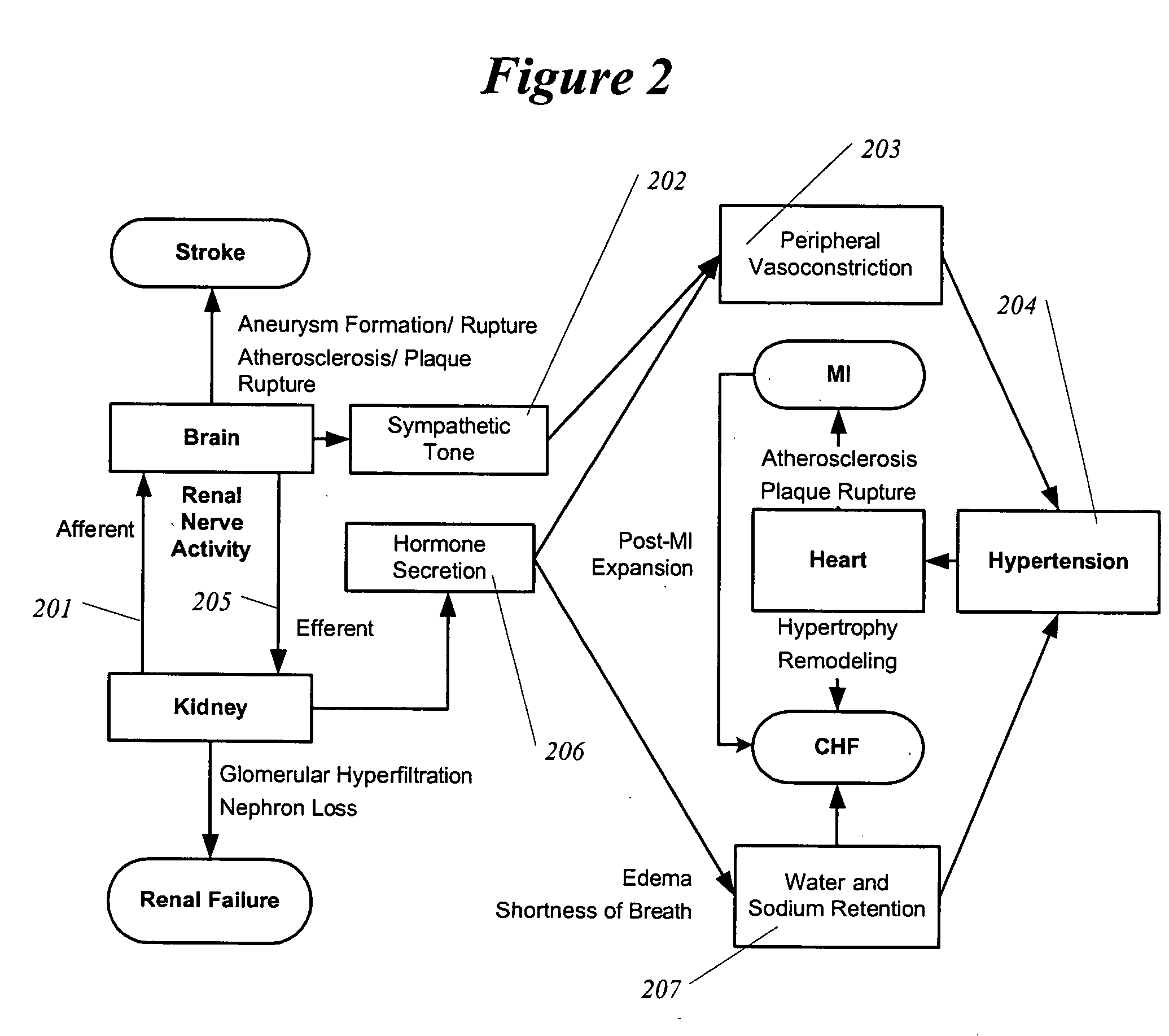
Methods and devices for renal nerve blocking
InactiveUS20050192638A1Shorten the progressResolution of overloadPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImplantable neurostimulatorsRenal nerveImplanted device
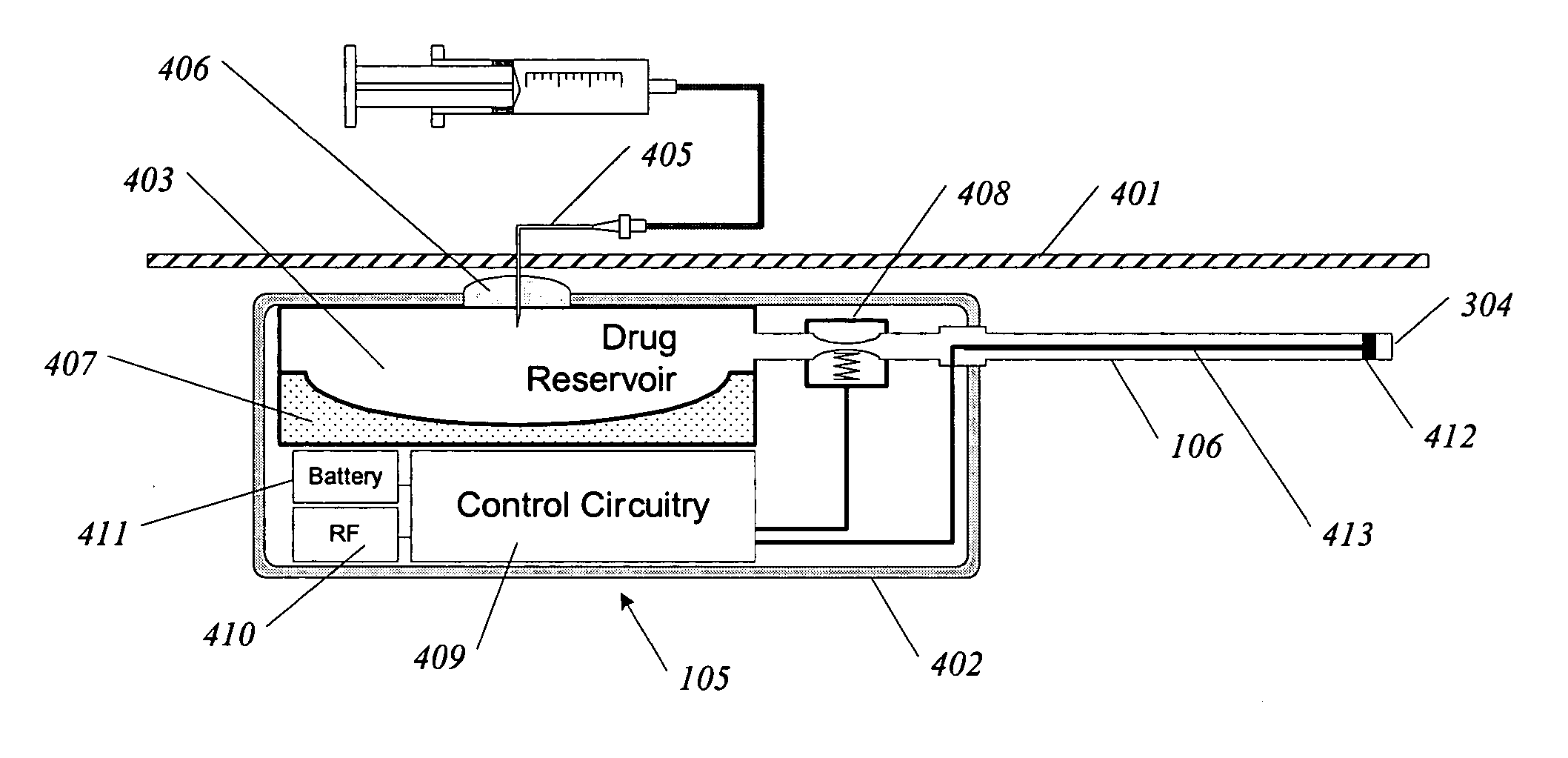
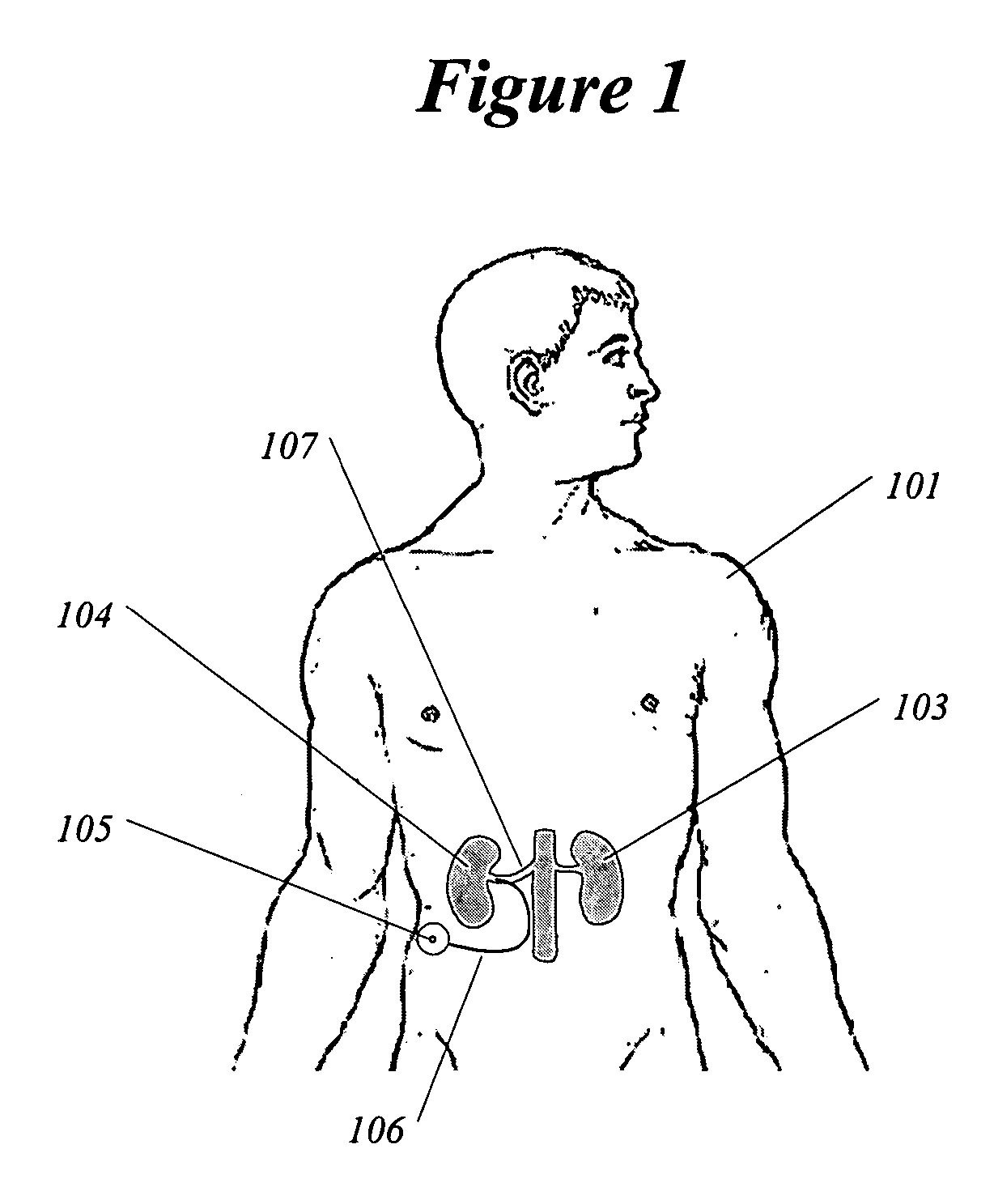
A method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac and renal diseases associated with the elevated sympathetic renal nerve activity by implanting a device to block the renal nerve signals to and from the kidney. The device can be a drug pump or a drug eluding implant for targeted delivery of a nerve-blocking agent to the periarterial space of the renal artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
Methods and apparatus for treatment of aneurysmal tissue
Methods and apparatus for aiding aneurysm repair are provided. Such apparatus is constructed to support or bolster the aneurysmal site initially, while contracting if the aneurysmal site shrinks or contracts. The apparatus also supplies a pharmaceutical agent to aid in healing the surrounding aneurysmal tissue. The apparatus may comprise a drug eluting polymer or may have a passive coating which can be selectively deployed by adding an activation agent after deployment. The device can be used alone or in conjunction with a AAA stent graft that isolates the aneurysmal sac from the vascular system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
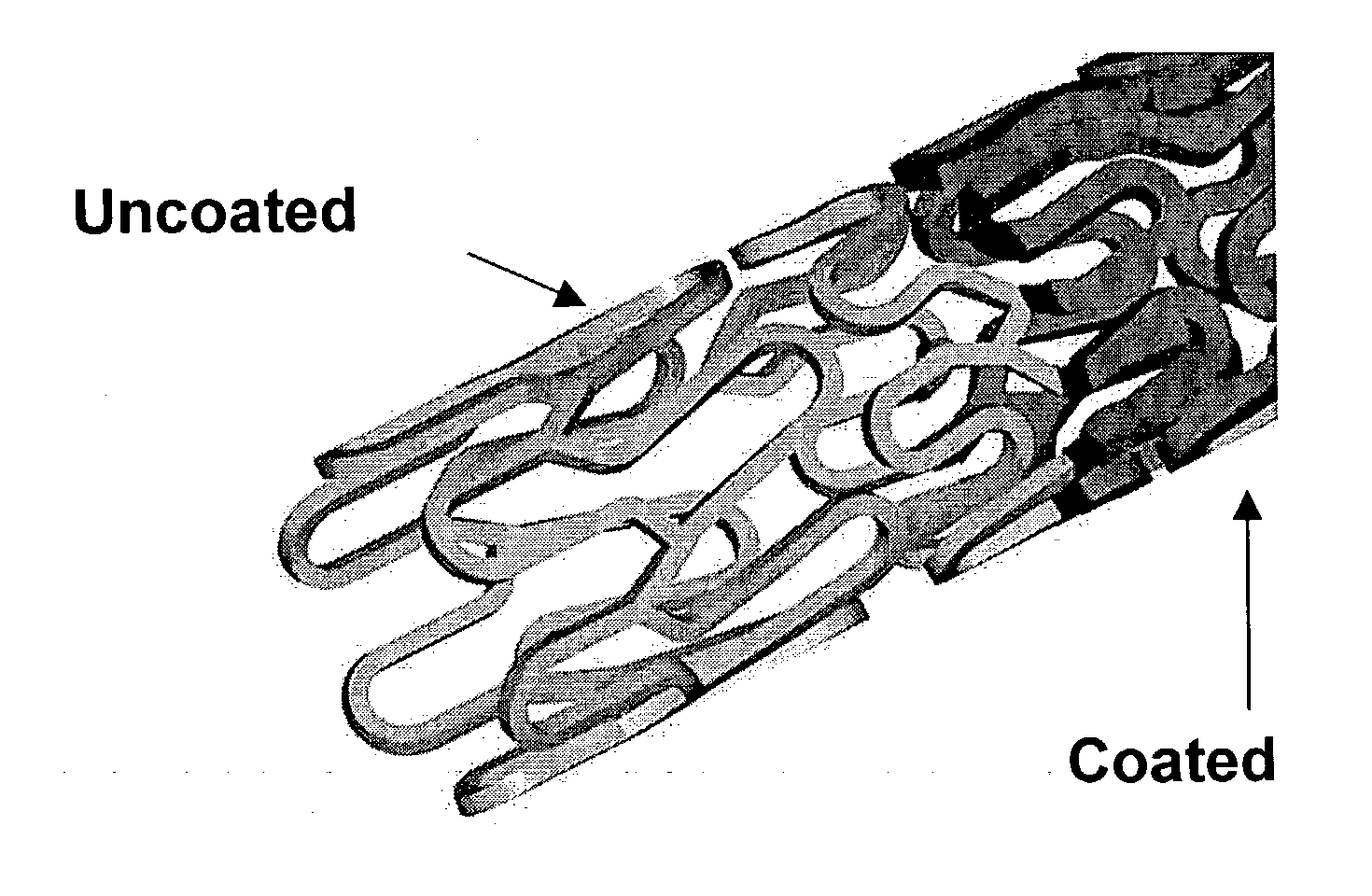
Thermoplastic fluoropolymer-coated medical devices
A medical device provided with at least a partial surface coating of a thermoplastic copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoroalkylvinylether that is free of cross-linking monomers and curing agents. The fluoropolymer coating is preferably an amorphous thermoplastic, is highly inert and biocompatible, has elastomeric characteristics that provide desirable mechanical properties such as good flexibility and durability. These characteristics allow the coating to be considered “functionally transparent” because it withstands mechanical deformations required for the assembly, deployment, expansion, and placement of medical devices, without any adverse effect on the mechanical and biological functionality of the coated device. Further, its inertness, derived from the perfluorocarbon structure, contributes to its functionally transparent nature. The coating can be provided with various liquid or solid additives, can be loaded with large quantities of additives including a wide range of therapeutic agents, and has excellent drug elution characteristics when elutable additives are used. The desirable mechanical characteristics are surprising given the absence of cross-linking monomers and curing agents that would otherwise render such materials inadequately biocompatible. The perfluoroalkylvinylether may be perfluoromethylvinylether, perfluoroethylvinylether or perfluoropropylvinylether.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Drug eluting medical device with an expandable portion for drug release
The present invention relates to a medical device and a method of delivering a drug to a target circulation or tissue. The medical device has an expandable portion which is fabricated from a porous elastomeric material with a plurality of voids therein. The voids are loaded with drugs in various formulations. Upon inflation of the expandable portion, the overall diameter increases, the wall thickness decreases and, consequently, the voids are stretched to cause the drug to be expelled from the voids and into the bodily lumen or tissue adjacent to the medical device. The voids include any open volume within the expandable portion capable of containing the drug.
Owner:ZULI HLDG LTD
Stent Coating For Eluting Medication
InactiveUS20060200231A1Good biocompatibilityPrevention and therapyStentsSurgeryPorosityDiamond-like carbon
A vascular stent comprising a drug-eluting outer layer of a porous sputtered columnar metal having each column capped with a biocompatible carbon-containing material is described. This is done by placing the stent over a close-fitting mandrel and rotating the assembly in a sputter flux. The result is a coating that is evenly distributed over the outward-facing side of the stent's wire mesh while preventing the sputtered columnar coating from reaching the inward facing side where a smooth hemocompatible surface is required. The stent is then removed from the mandrel, exposing all surfaces, and finally coated with a layer of carbon such as amorphous carbon or diamond-like carbon. The carbonaceous coating enhances biocompatibility without preventing elutriation of a therapeutic drug provided in the porosity formed between the columnar structures. The result is a stent that is adapted to both the hemodynamic and the immune response requirements of its vascular environment.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
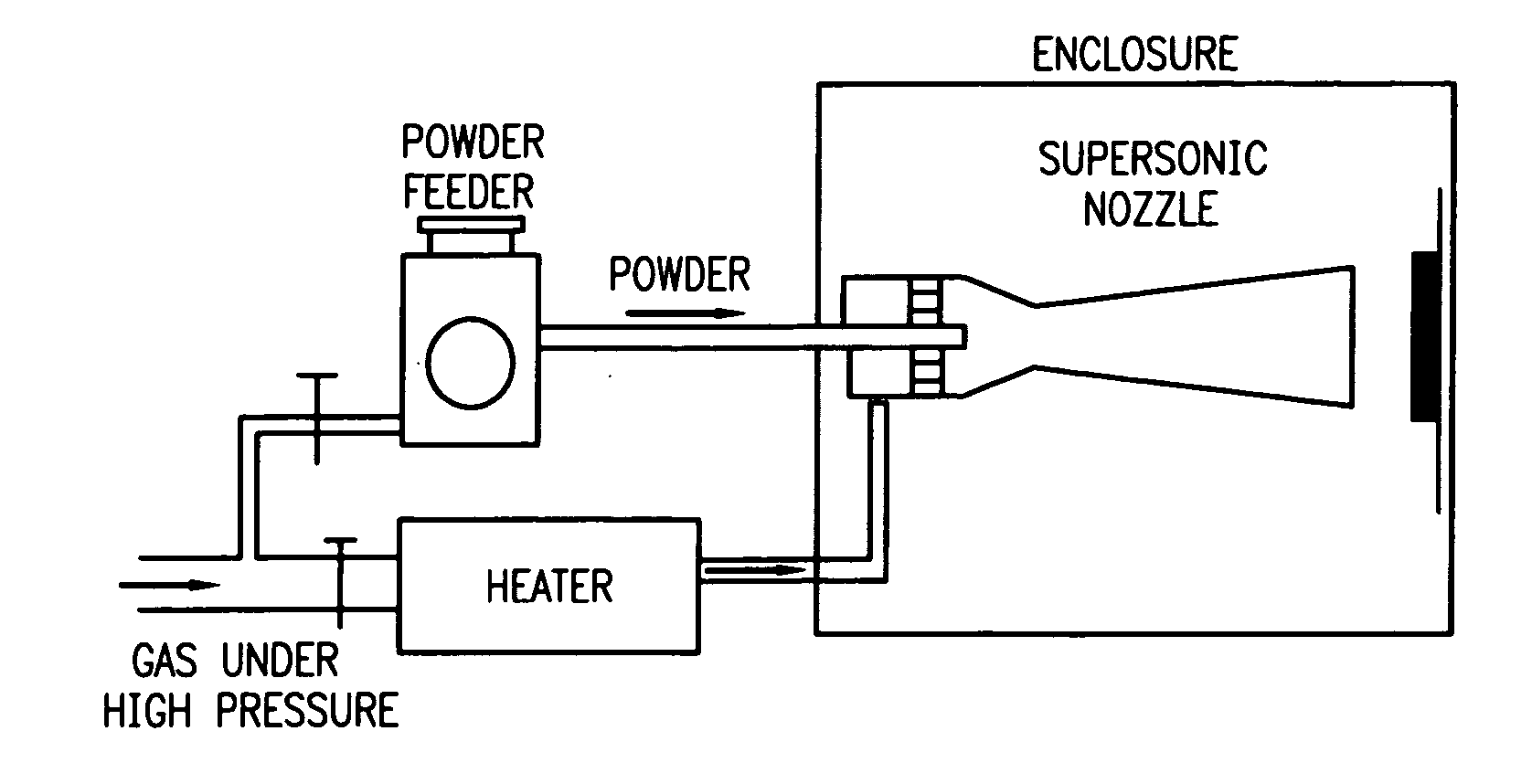
Method and apparatus for spray processing of porous medical devices
InactiveUS20070036905A1Minimize contaminationMinimize oxidationMolten spray coatingPretreated surfacesPorous substrateThermal spraying
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Drug eluting surface covering
InactiveUS20100228333A1Provide protectionImprove permeabilityStentsBalloon catheterBalloon dilatation catheterLesion site
A thin-walled sheath is placed over a balloon having an antirestenotic drug placed on the balloon of a balloon dilatation catheter. The sheath protects the drug from dissolution into the blood and allows improved delivery to the lesion site. A rolling action of the sheath prevents the drug from loss due to shearing motion. The sheath can also provide a protected surface for carrying the drug and providing exposure to the lesion site for delivery of the drug. The sheath can also serve as a delivery sheath for providing delivery of a stent via a single catheter introduction for drug delivery and stent delivery.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM JOSEPH +1
Drug-Eluting Device for Treatment of Chronic Total Occlusions
A drug-eluting medical device and method for treating a chronic total occlusion. The drug-eluting medical device is implanted into the chronic total occlusion and elutes a drug that softens or dissolves the plaque of the occlusion over a period of time. After the medical device has resided in the occlusion for an appropriate period of time such that at least a portion of the chronic total occlusion has been softened or dissolved, a guidewire can cross the occlusion and a procedure such as PTCA can be performed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Fluid management flow implants of improved occlusion resistance
ActiveUS20060074388A1Reduce probabilityMaterial is expensiveWound drainsSurgeryDrugCerebrospinal fluid
This invention relates to achieving or improving uniform distribution of fluid flow in medical devices such as when combined with antibiotics impregnated in a catheter and / or with a drug-eluting catheter to further inhibit the catheter from becoming occluded by debris in the CSF or by bacterial biofilm formation or tissue proliferation in the catheter.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Drug-eluting biodegradable stent
The present invention relates to a biodegradable stent comprising a luminal surface portion with a second degree of crosslink, an outer surface portion with a first degree of crosslink, and a wall between the luminal and outer surface portions, wherein the wall comprises a crosslinked material characterized by the first degree of crosslink not less than the second degree of crosslink.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Medical Device Having Coating With Zeolite Drug Reservoirs
A medical device having a drug-eluting coating that includes a pharmaceutical compound or, more generally, a therapeutic material housed within pores of a zeolite carrier. The zeolite carrier has an open porous structure with reservoirs for holding the therapeutic material. The therapeutic material loaded zeolites may be suspended or dispersed within a bioerodible polymer matrix to provide controlled delivery of the therapeutic material. Zeolite drug carriers may have enhanced or optimally engineered pore sizes for a particular therapeutic material and release profile. Along with a therapeutic material, reservoirs of a zeolite drug delivery system may include a release agent. The release agent may be used to entrap the therapeutic material until such time as a triggering condition is met that prompts the release agent to activate and thereby release the therapeutic material from the zeolite reservoir.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Drug-eluting biodegradable stent
The present invention relates to a drug-loaded biodegradable stent and methods for treating vulnerable plaques of a patient comprising a plurality of layers or zones, each layer or zone comprising its own specific biodegradation rate and its specific drug loading characteristics. In one embodiment, the layers and zones are configured and arranged, in combination, radially, circumferentially and longitudinally.
Owner:GP MEDICAL
Thermoplastic fluoropolymer-coated medical devices
A medical device provided with at least a partial surface coating of a thermoplastic copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoroalkylvinylether that is free of cross-linking monomers and curing agents. The fluoropolymer coating is preferably an amorphous thermoplastic, is highly inert and biocompatible, has elastomeric characteristics that provide desirable mechanical properties such as good flexibility and durability. These characteristics allow the coating to be considered “functionally transparent” because it withstands mechanical deformations required for the assembly, deployment, expansion, and placement of medical devices, without any adverse effect on the mechanical and biological functionality of the coated device. Further, its inertness, derived from the perfluorocarbon structure, contributes to its functionally transparent nature. The coating can be provided with various liquid or solid additives, can be loaded with large quantities of additives including a wide range of therapeutic agents, and has excellent drug elution characteristics when elutable additives are used. The desirable mechanical characteristics are surprising given the absence of cross-linking monomers and curing agents that would otherwise render such materials inadequately biocompatible. The perfluoroalkylvinylether may be perfluoromethylvinylether, perfluoroethylvinylether or perfluoropropylvinylether.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Oscillation assisted drug elution apparatus and method
An apparatus includes a base and a coating disposed on the base. A therapeutic agent is disposed on at least one of the base or the coating. A vibration device is coupled to the base. The vibration device is configured to cause movement of the base such that at least a portion of the therapeutic agent is released from the base or the coating. A method includes inserting a stent into a body lumen of a patient. The stent has a base, a coating disposed on at least a portion of the base, and a therapeutic agent carried by at least one of the base or the coating. The stent is vibrated such that at least a portion of the therapeutic agent is released from the stent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Implantable system with drug-eluting cells for on-demand local drug delivery
An implantable system that includes a carrier and eukaryotic cells, which produce and release a therapeutic agent, and a stimulating element for stimulating the release of the therapeutic agent. The system can also include a sensing element for monitoring a physiological condition and triggering the stimulating element to stimulate the delivery device to release the therapeutic agent. Alternatively, the patient in which the system is implanted can activate the stimulating element to release the therapeutic agent.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
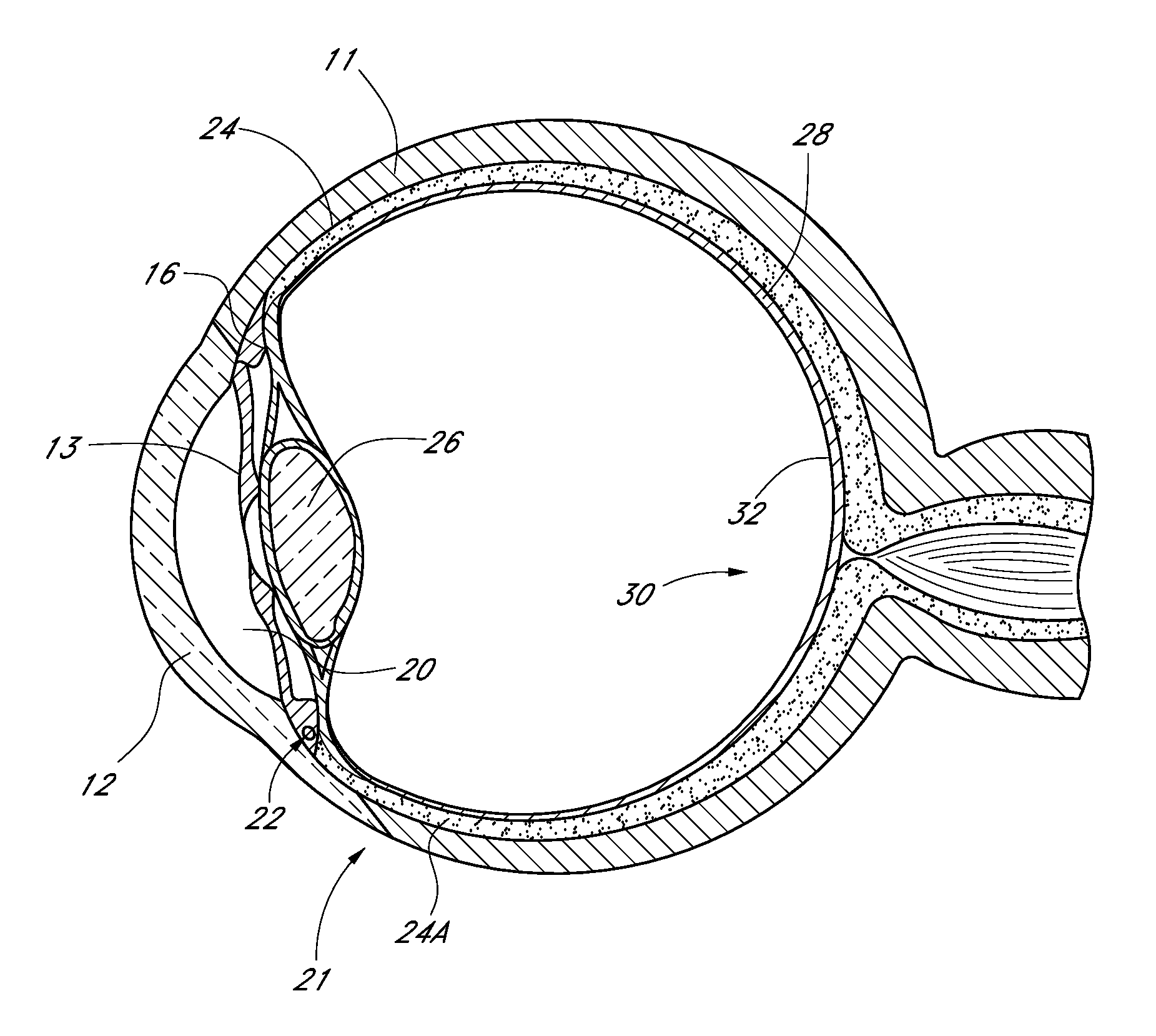
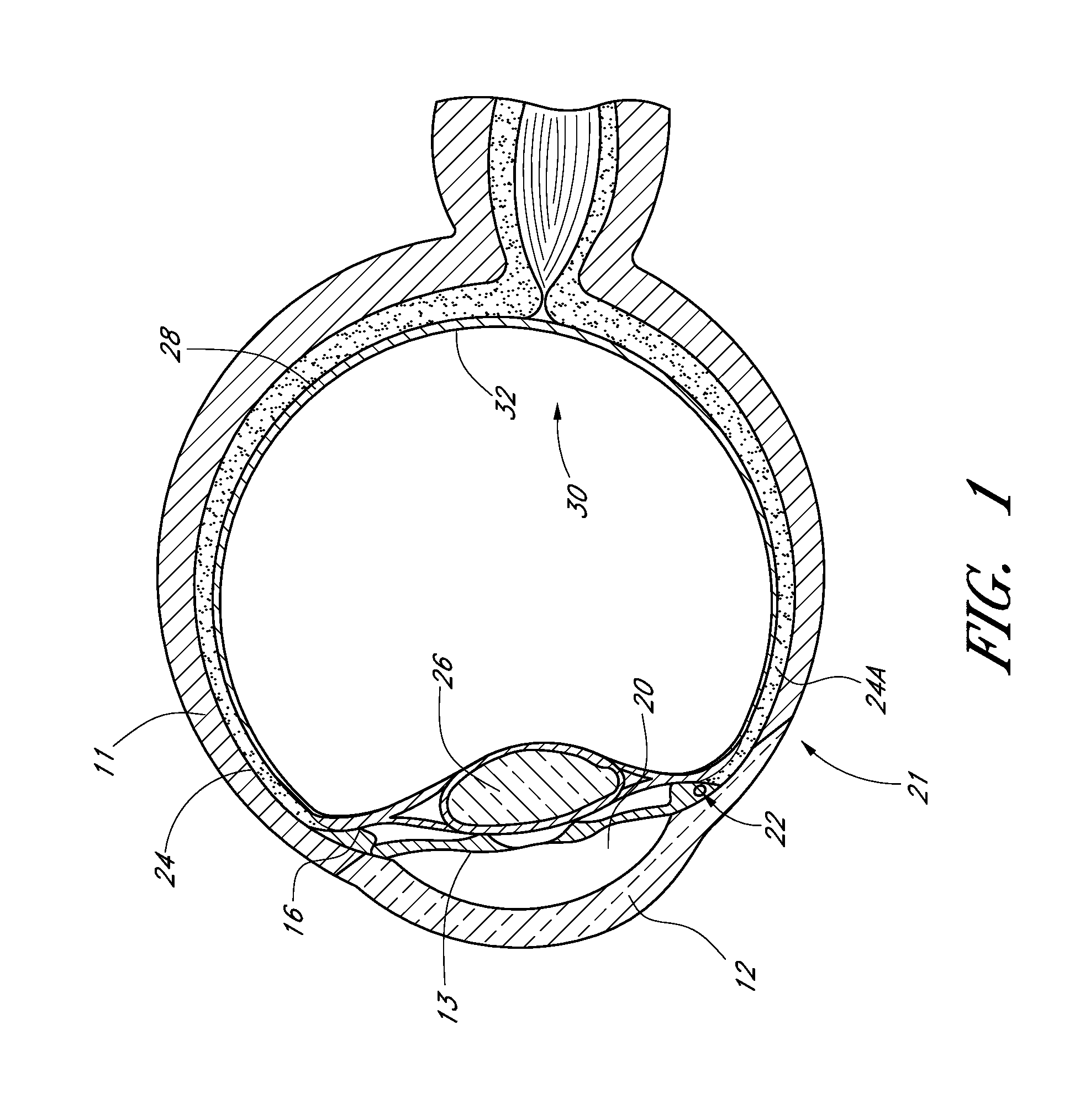
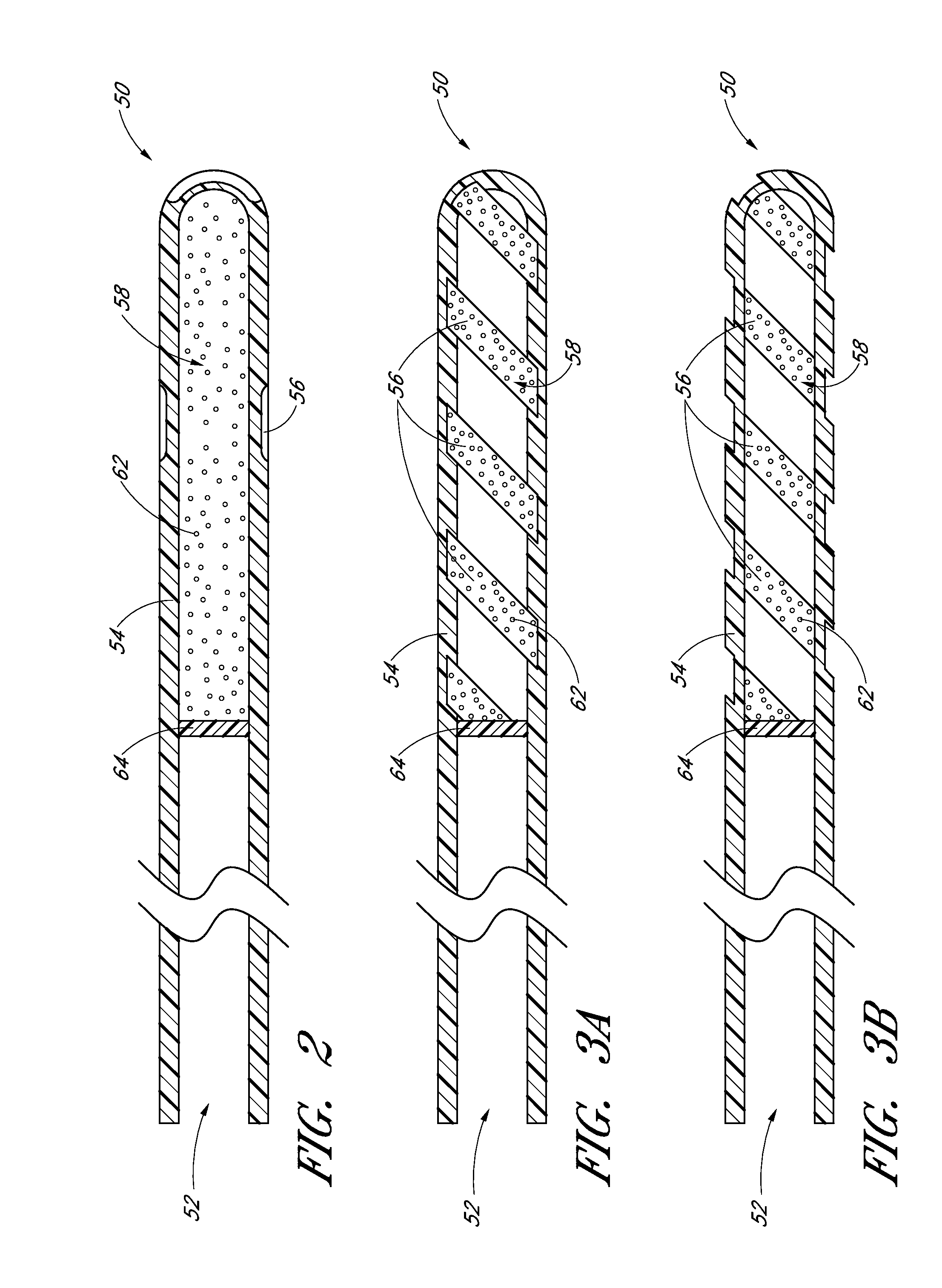
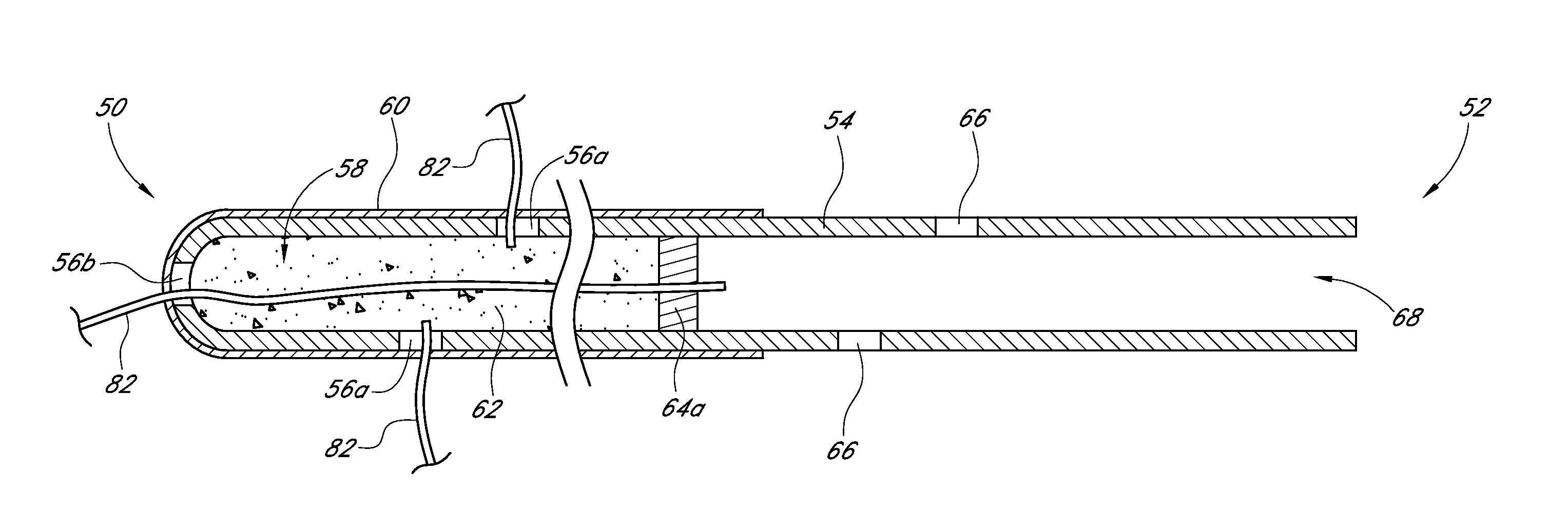
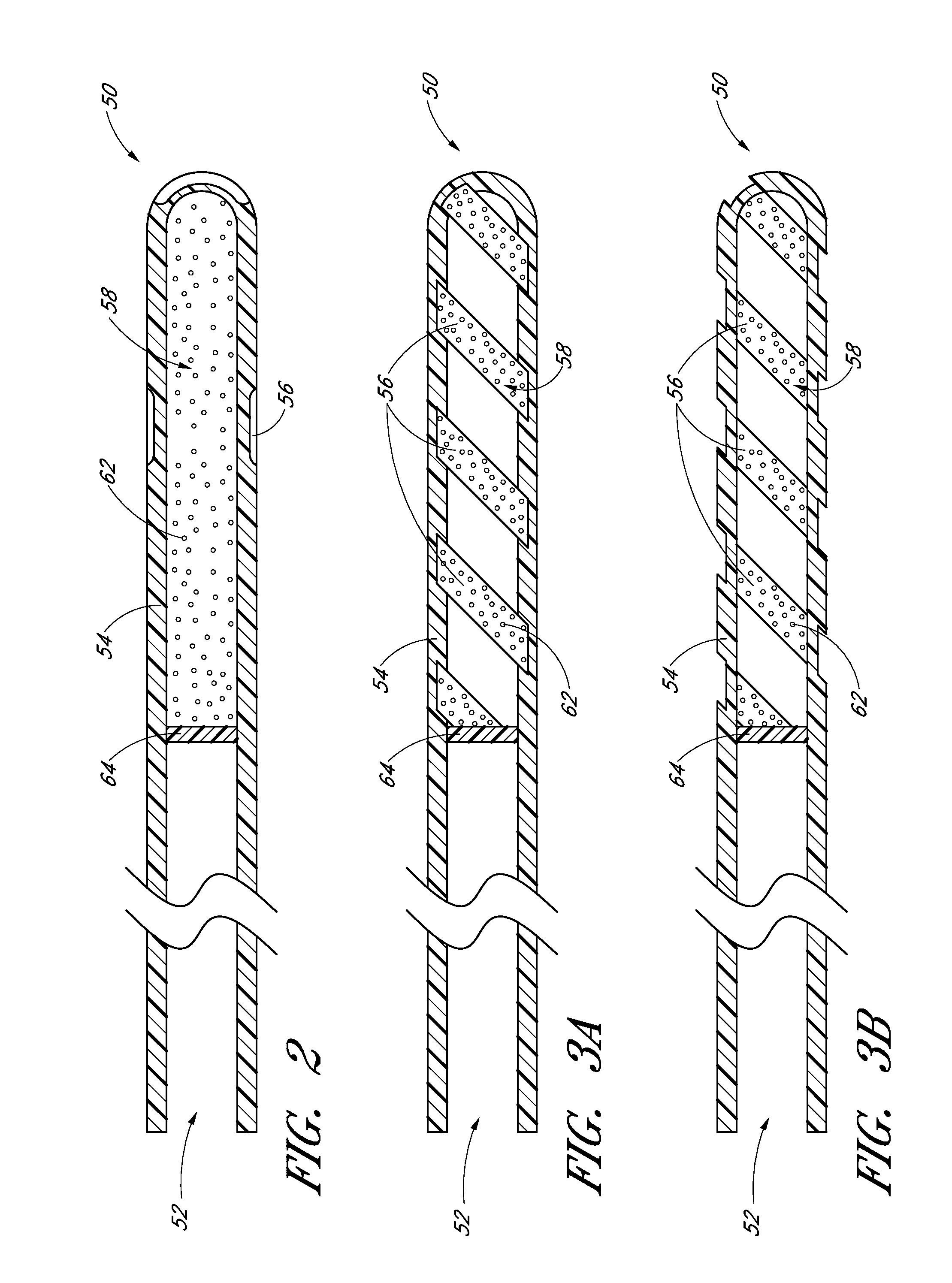
Drug eluting ocular implant
InactiveUS20120078362A1Improve elutionImprove permeabilityEye surgeryMedical devicesAqueous humorControl release
Disclosed herein are drug delivery devices and methods for the treatment of ocular disorders requiring targeted and controlled administration of a drug to an interior portion of the eye for reduction or prevention of symptoms of the disorder. The devices are capable of controlled release of one or more drugs and may also include structures which allows for treatment of increased intraocular pressure by permitting aqueous humor to flow out of the anterior chamber of the eye through the device.
Owner:DOSE MEDICAL CORP
Drug eluting ocular implant
ActiveUS20130289467A1Limited abilityLimits treatment-associated side-effectsEye surgeryMedical applicatorsDrug deliveryDrug
Disclosed herein are drug delivery devices and methods for the treatment of ocular disorders requiring targeted and controlled administration of a drug to an interior portion of the eye for reduction or prevention of symptoms of the disorder. The devices are capable of controlled release of one or more drugs and may also include structures which allow for treatment of increased intraocular pressure by permitting aqueous humor to flow out of the anterior chamber of the eye through the device.
Owner:DOSE MEDICAL CORP
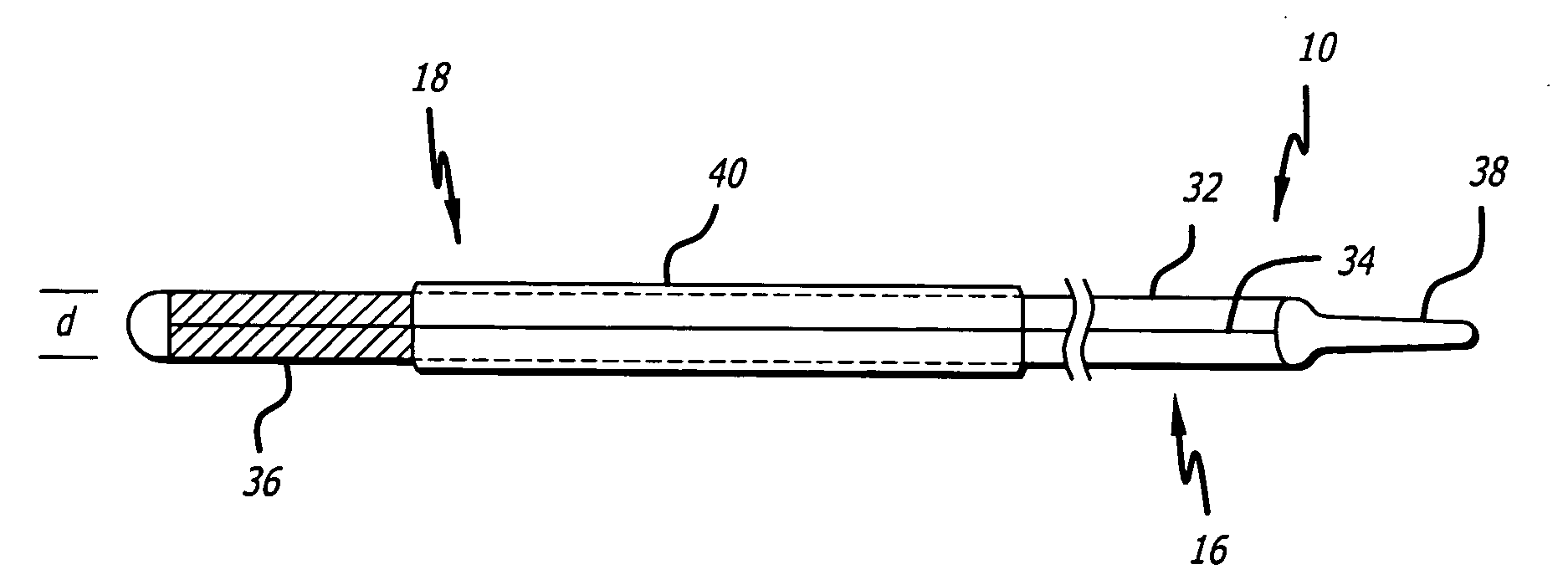
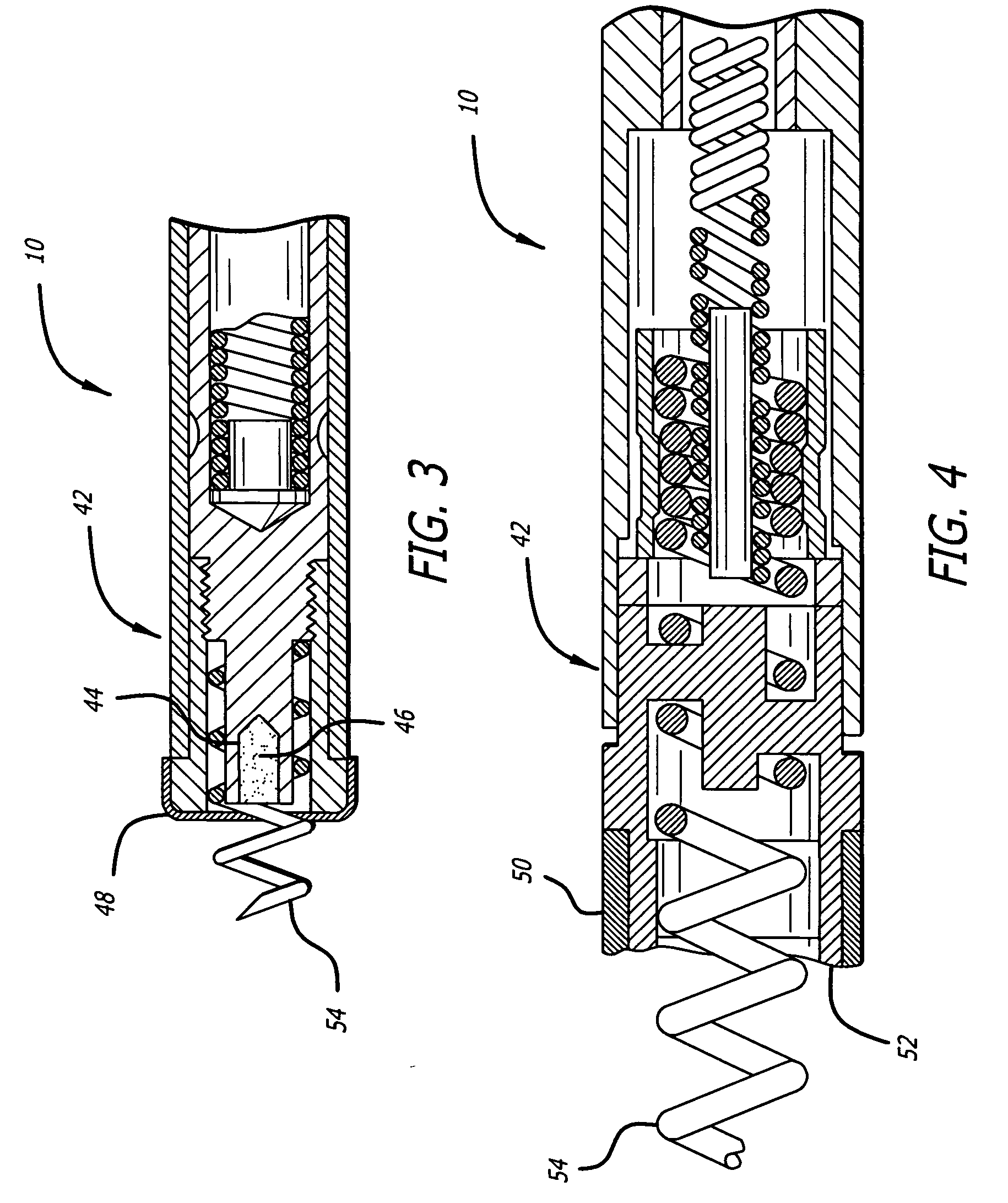
Drug-eluting electrode
An apparatus includes an electrical lead comprising a lead body and an electrical conductor, and an electrode coupled to the electrical conductor, wherein the electrode includes a coating on at least a portion of a surface of the electrode, the coating including two or more layers, with a first layer adjacent the surface of the electrode comprising an insulative material and a second layer adjacent the first layer comprising at least one pharmacological agent.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com