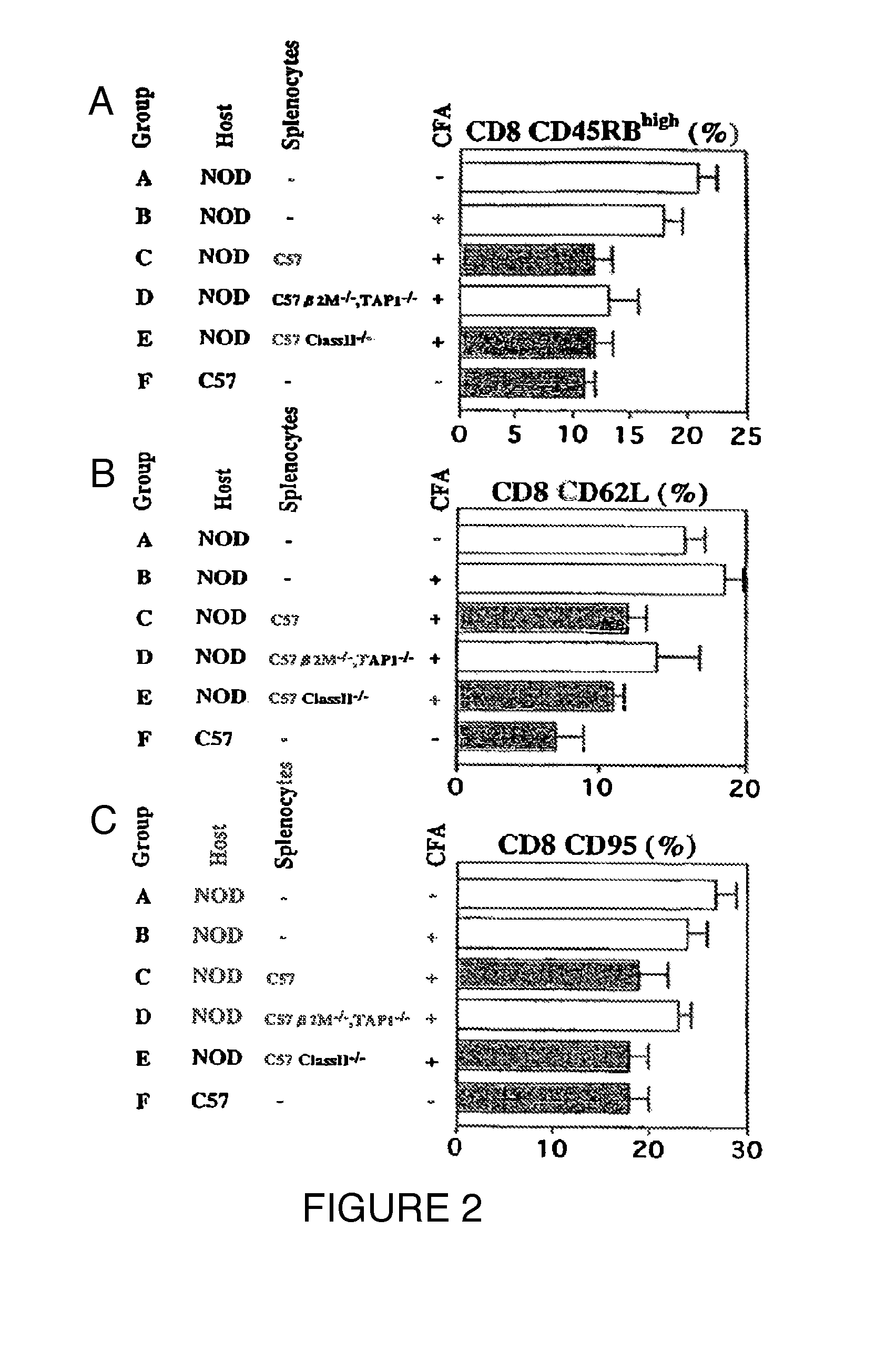
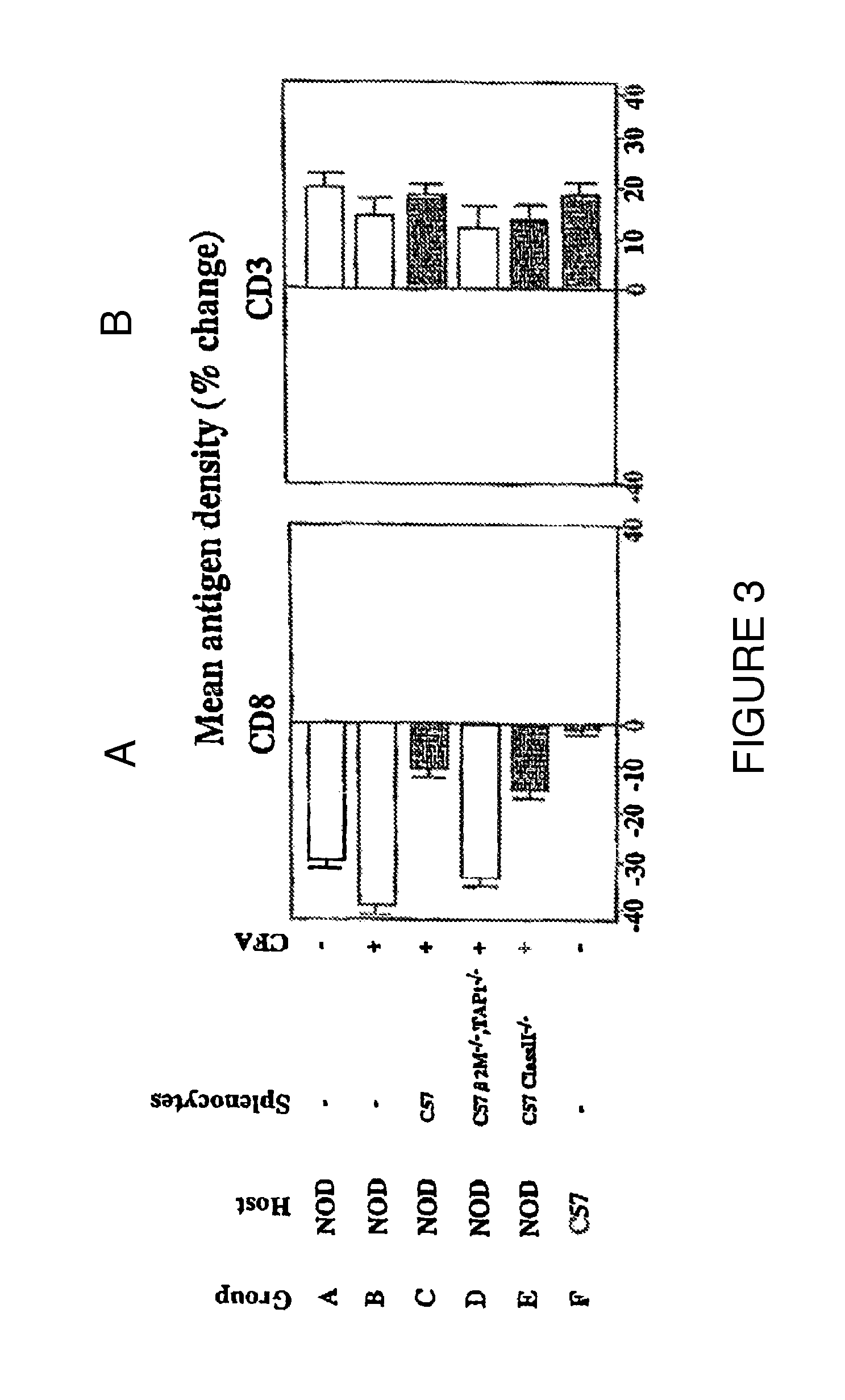
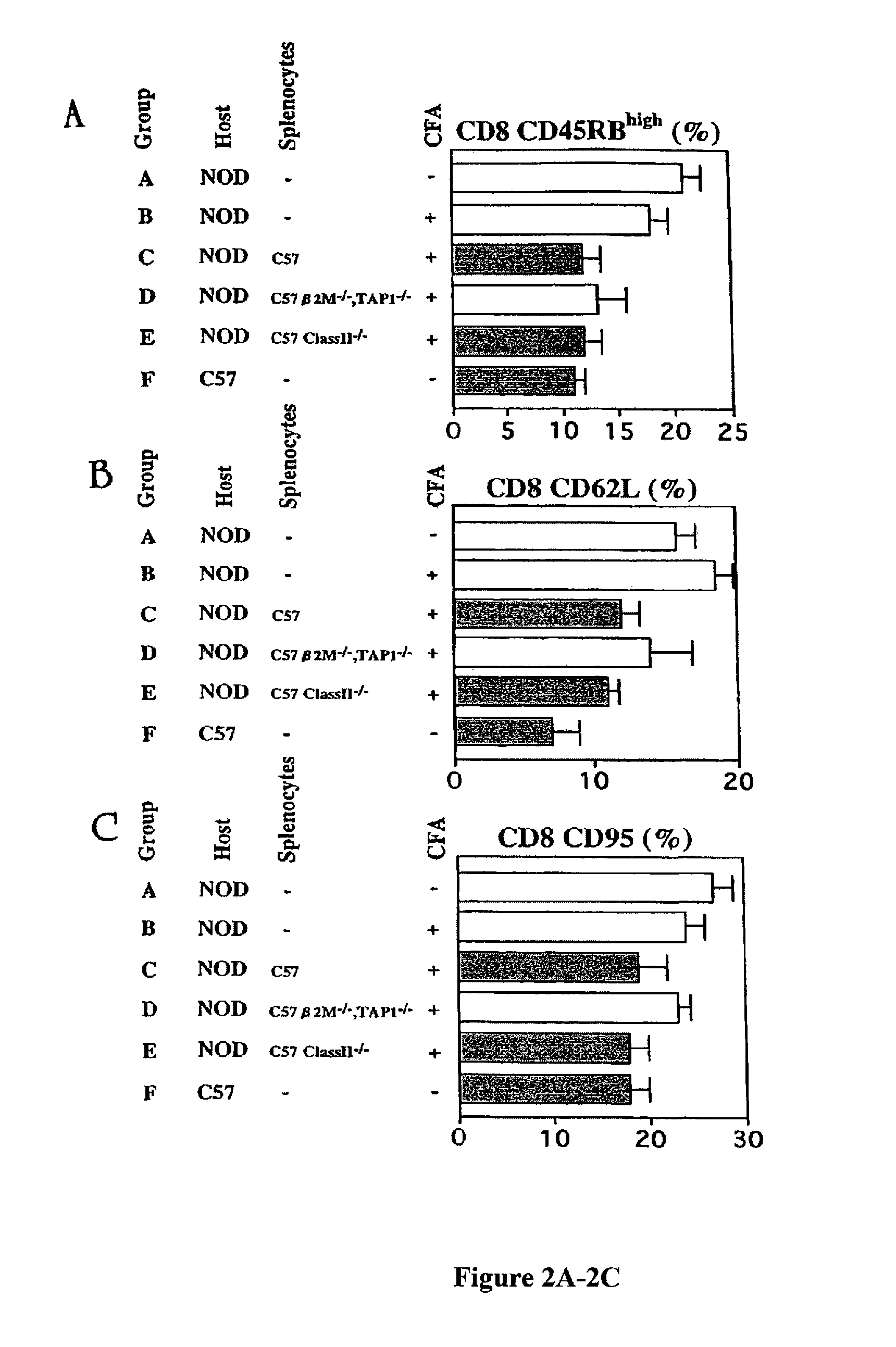
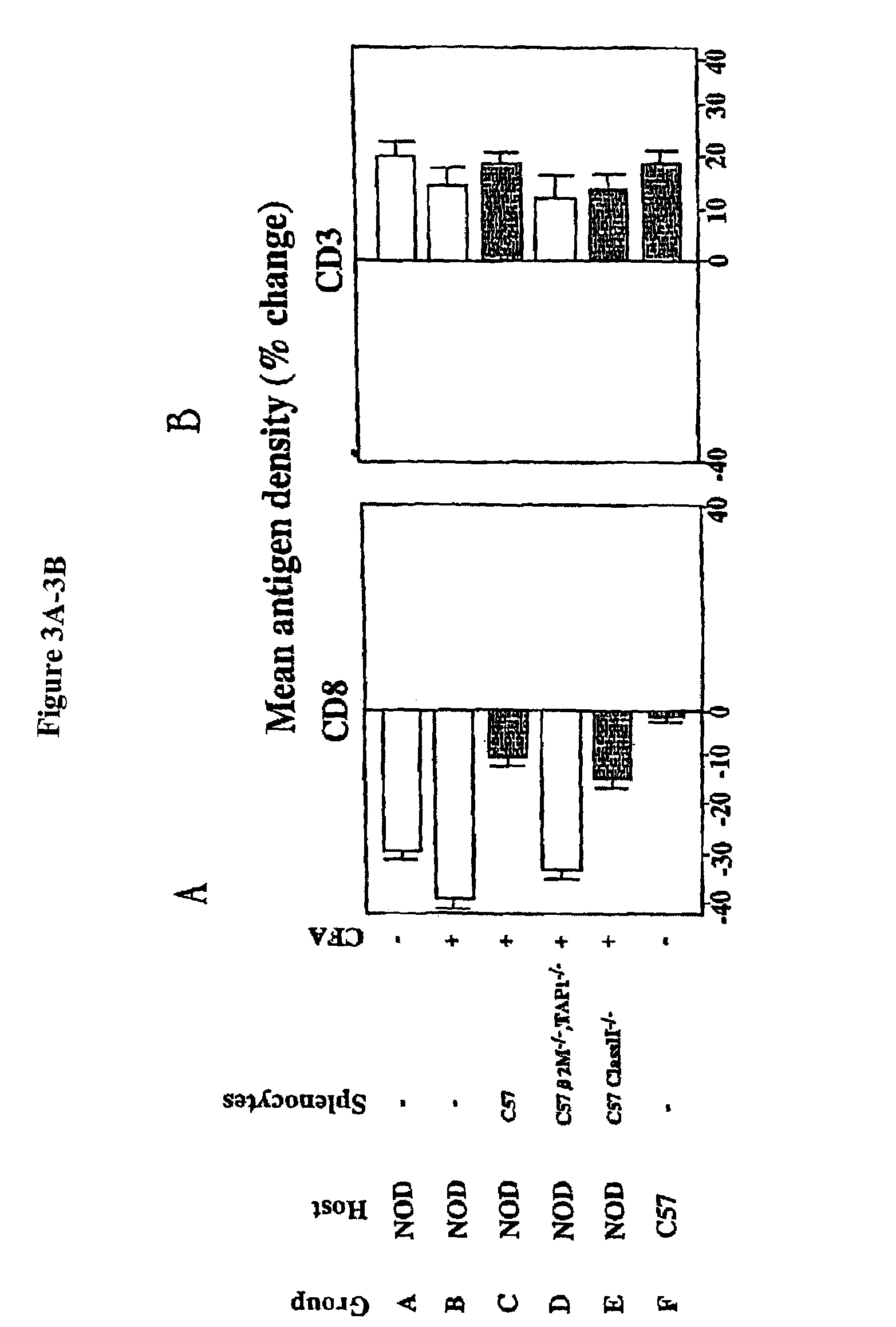
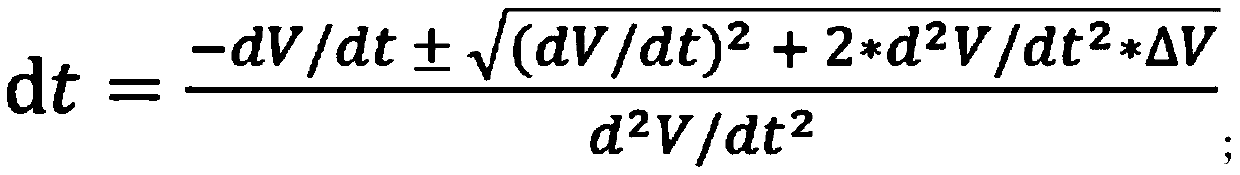Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Heart cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
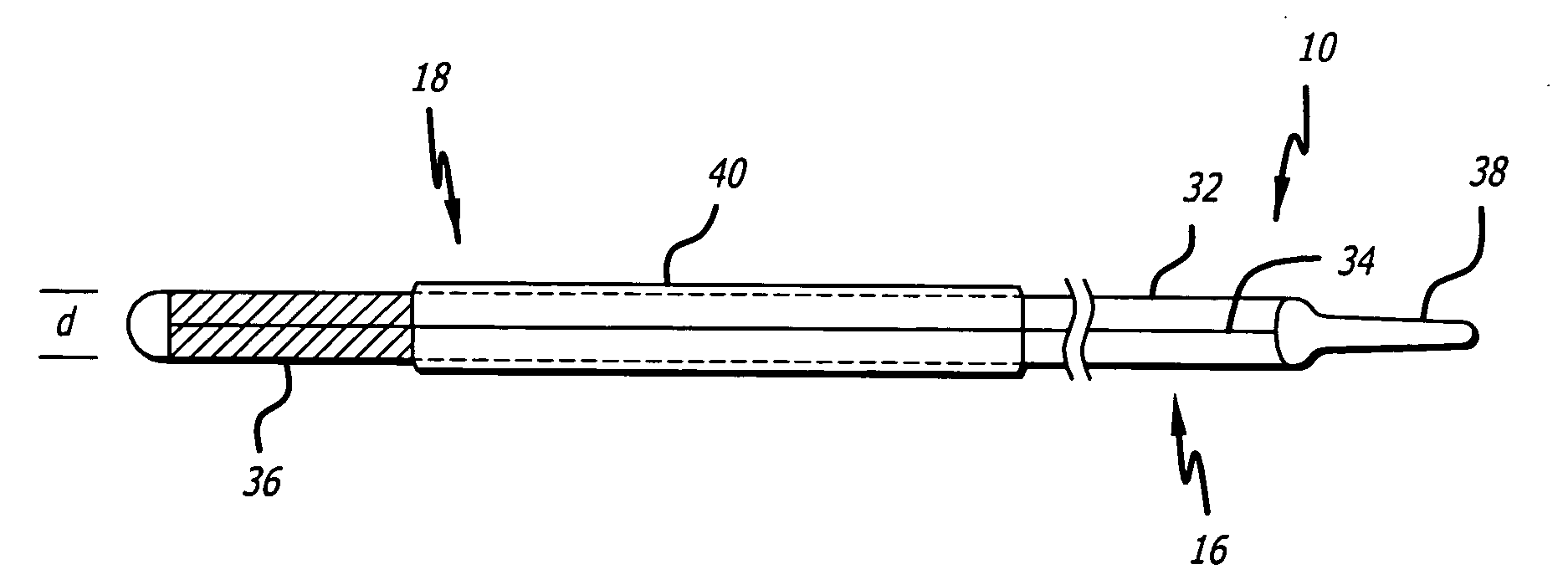
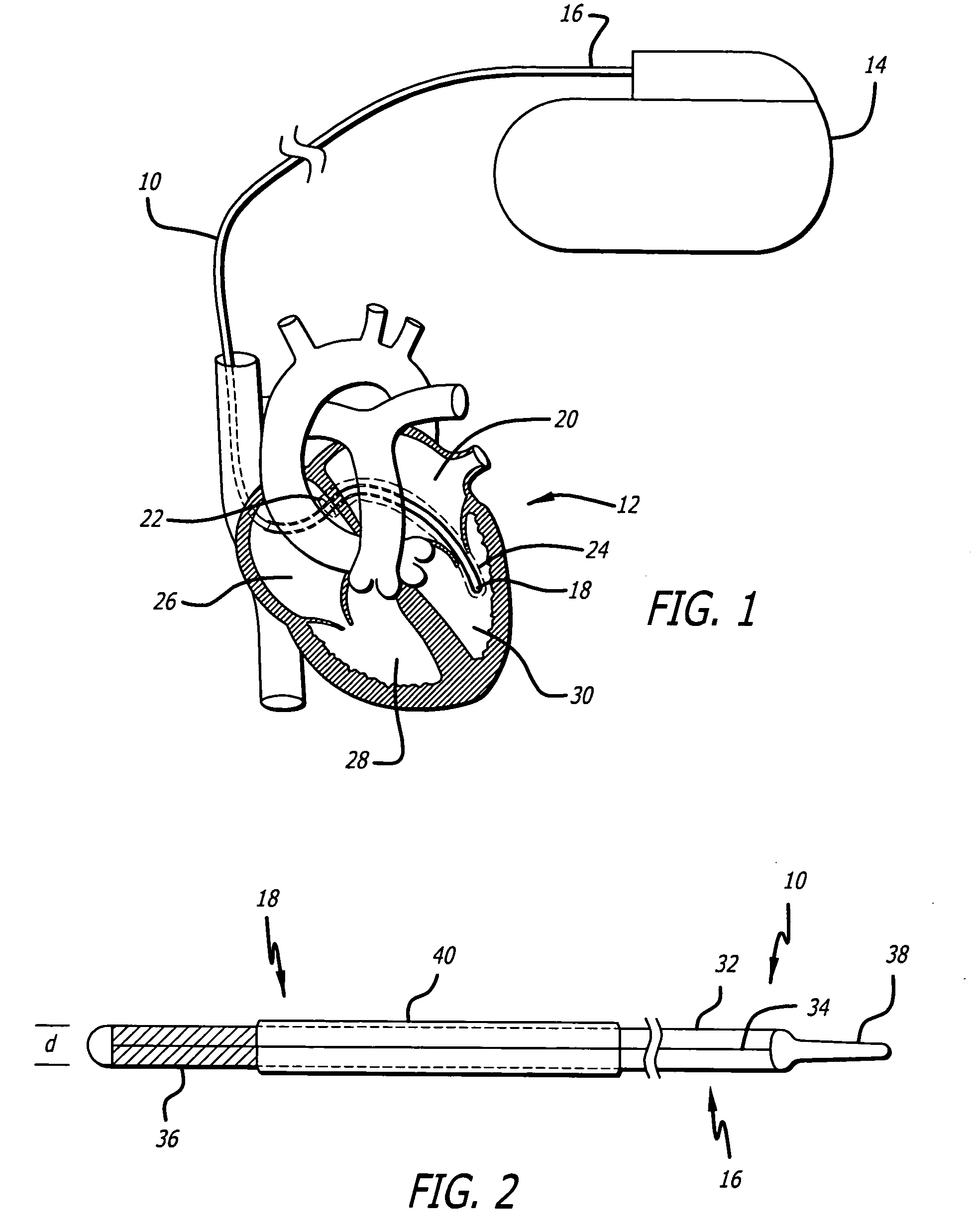
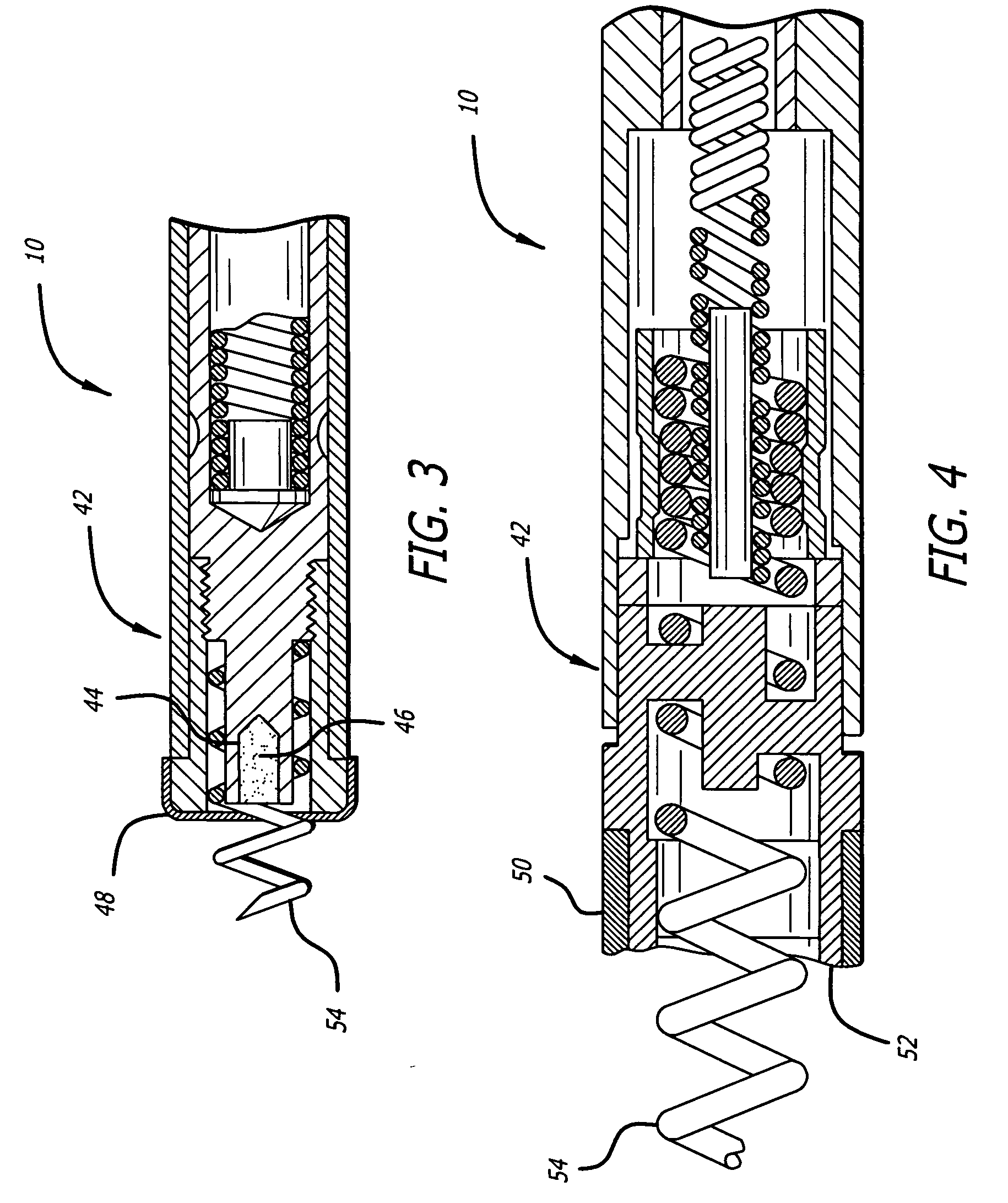
Drug eluting implants to prevent cardiac apoptosis
Implantable devices are configured to be positioned in or near the heart and to carry and deliver an anti-apoptotic drug to a treatment site in or near the heart. The implantable devices include, but are not limited to, leads, stents, heart valves, atrial septal defect devices, cardiac patches and ventricular restraint devices. Depending on the composition of the device, the drug may be carried by the device through a coating applied to the device, or may be included in the device during the device manufacturing process. The drug may also be included in microparticles, such a microspheres, that are delivered locally through a conduit, such as a catheter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Treating heart failure
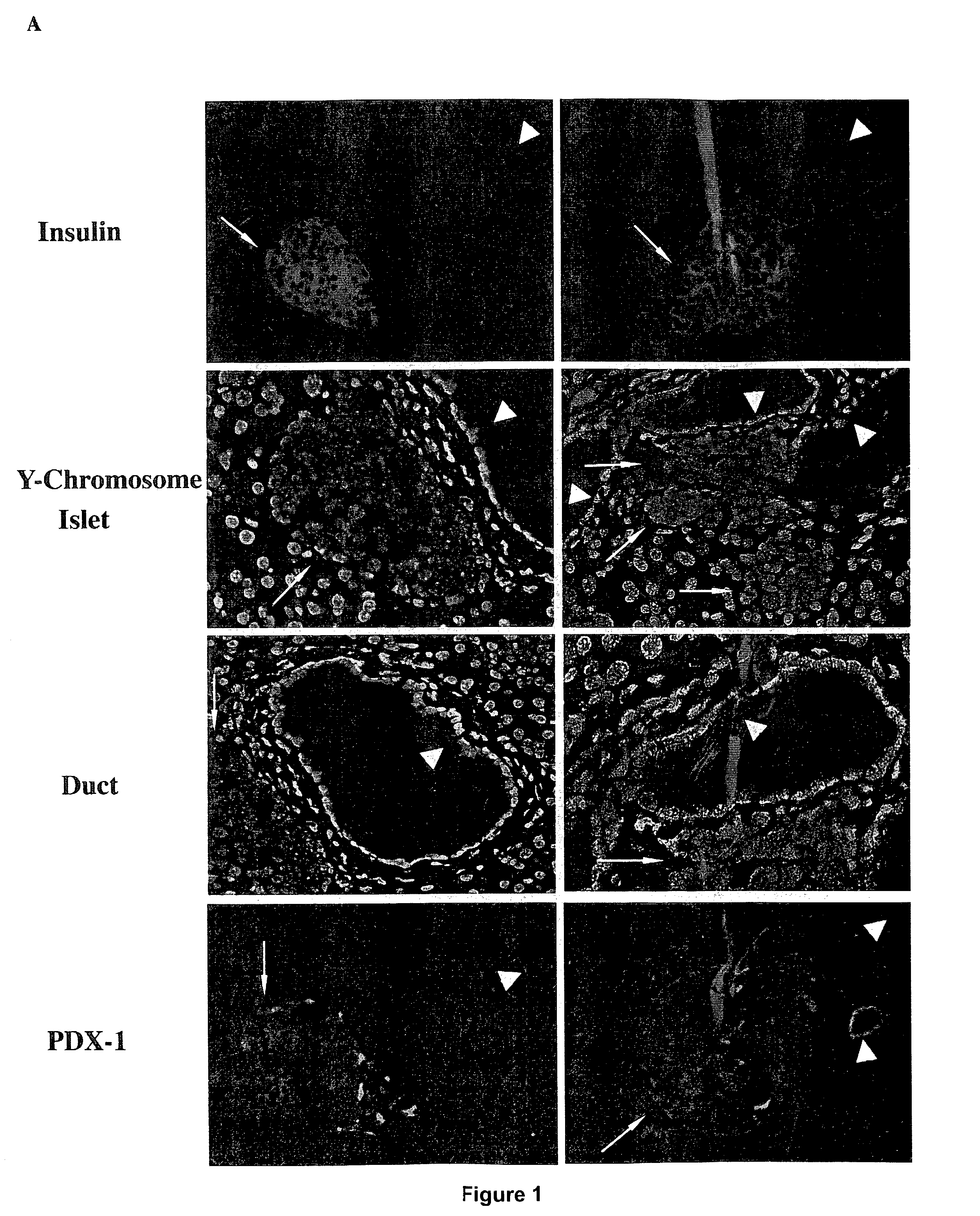
Heart cells in a subject can be treated, for example, by introducing, into the heart of the subject, an adeno-associated virus subtype 6 (AAV6) viral delivery system that includes a functional nucleic acid. For example, the functional nucleic acid encodes a non-viral therapeutic protein, thereby treating the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
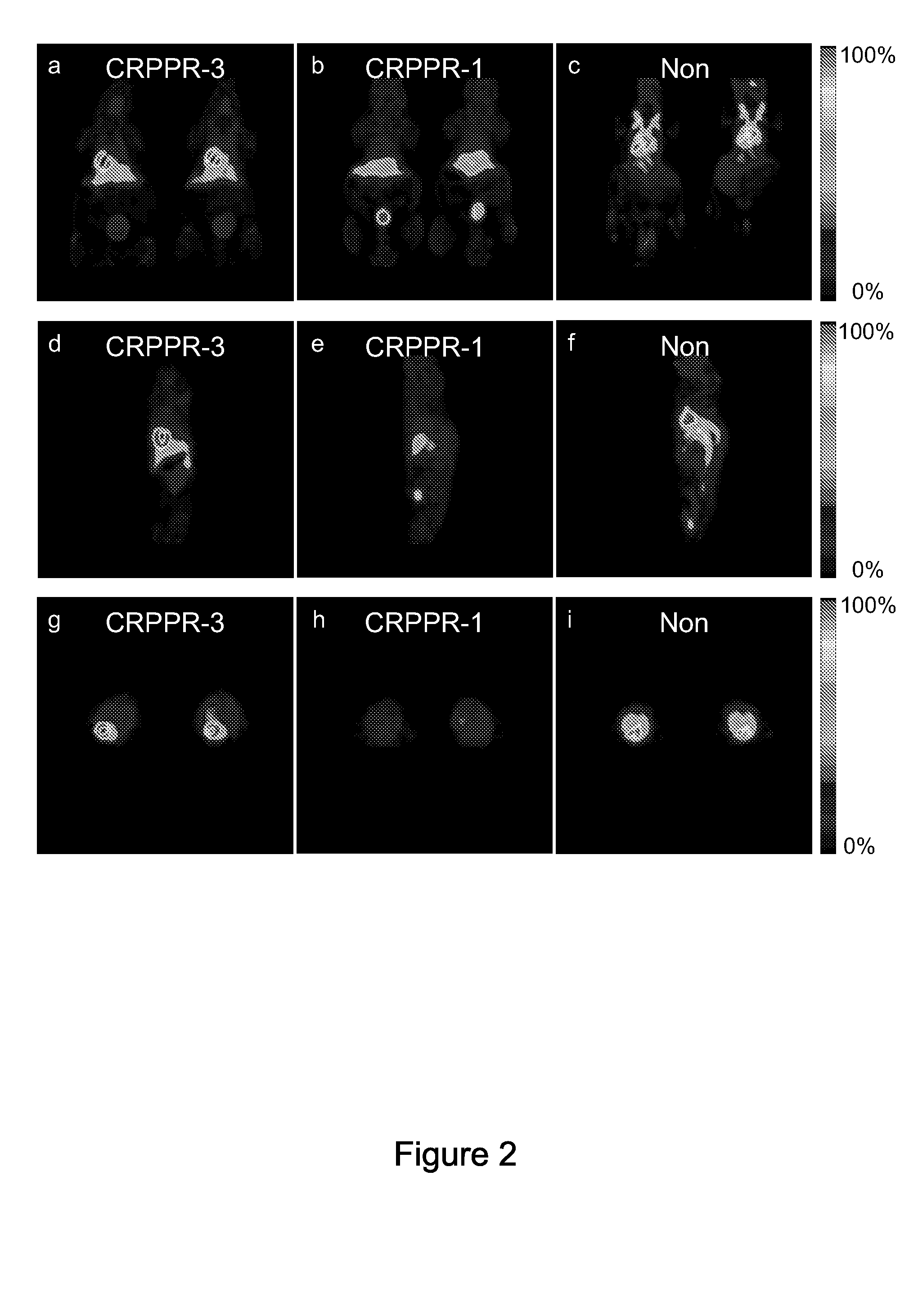
Methods and compounds for targeting tissues
The present invention relates to peptides which home to cells, e.g. heart cells, with high selectivity and which can be useful in the form of compositions. Such compositions can be used, e.g., for selectively targeting a systemically administered therapeutic agent or imaging agent to a cell or tissue in a subject. The present invention further relates to methods of using the compositions for imaging, e.g. PET imaging, and targeting cells, e.g. for delivering a therapeutic agent to one or more target cells in a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
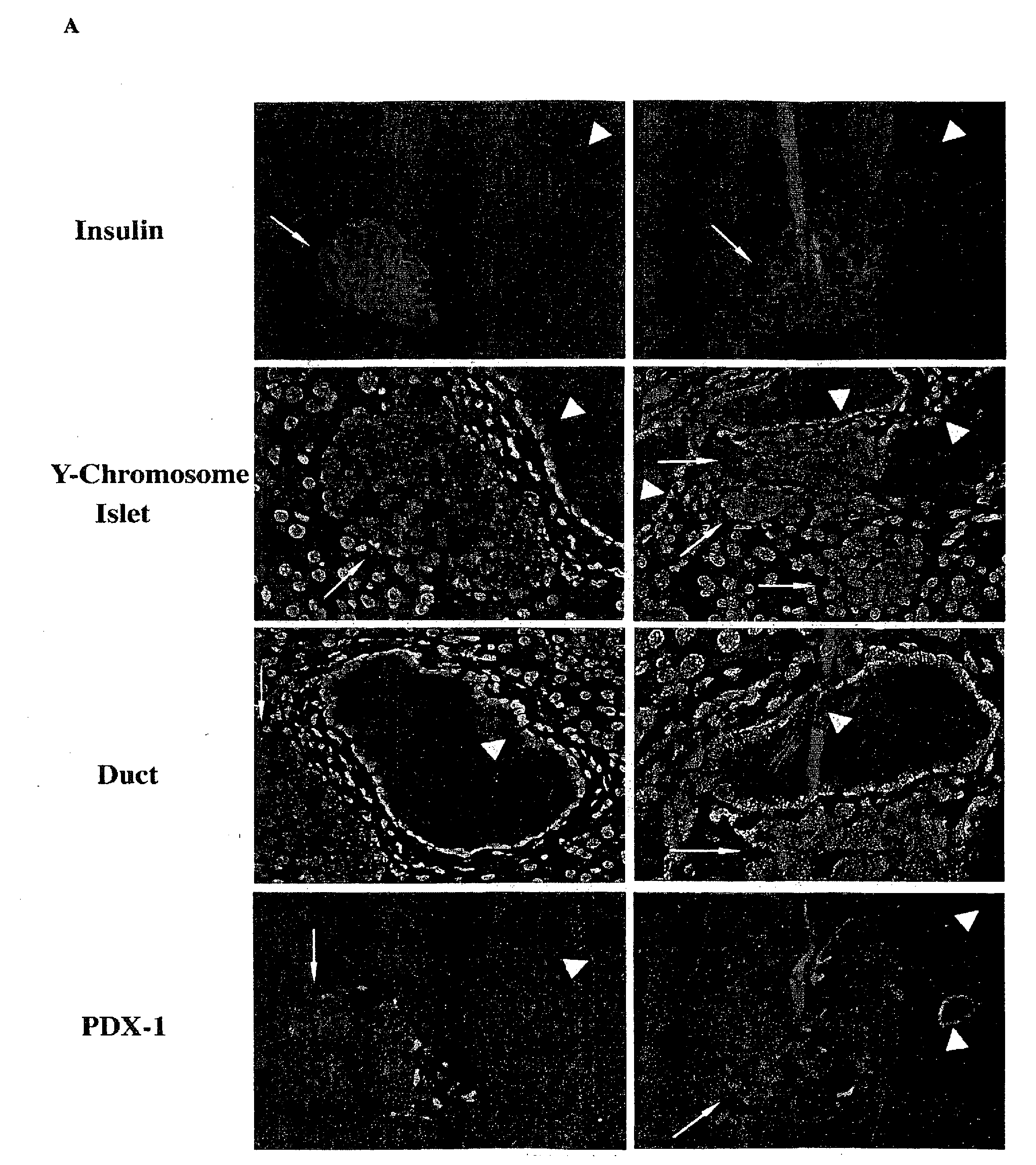
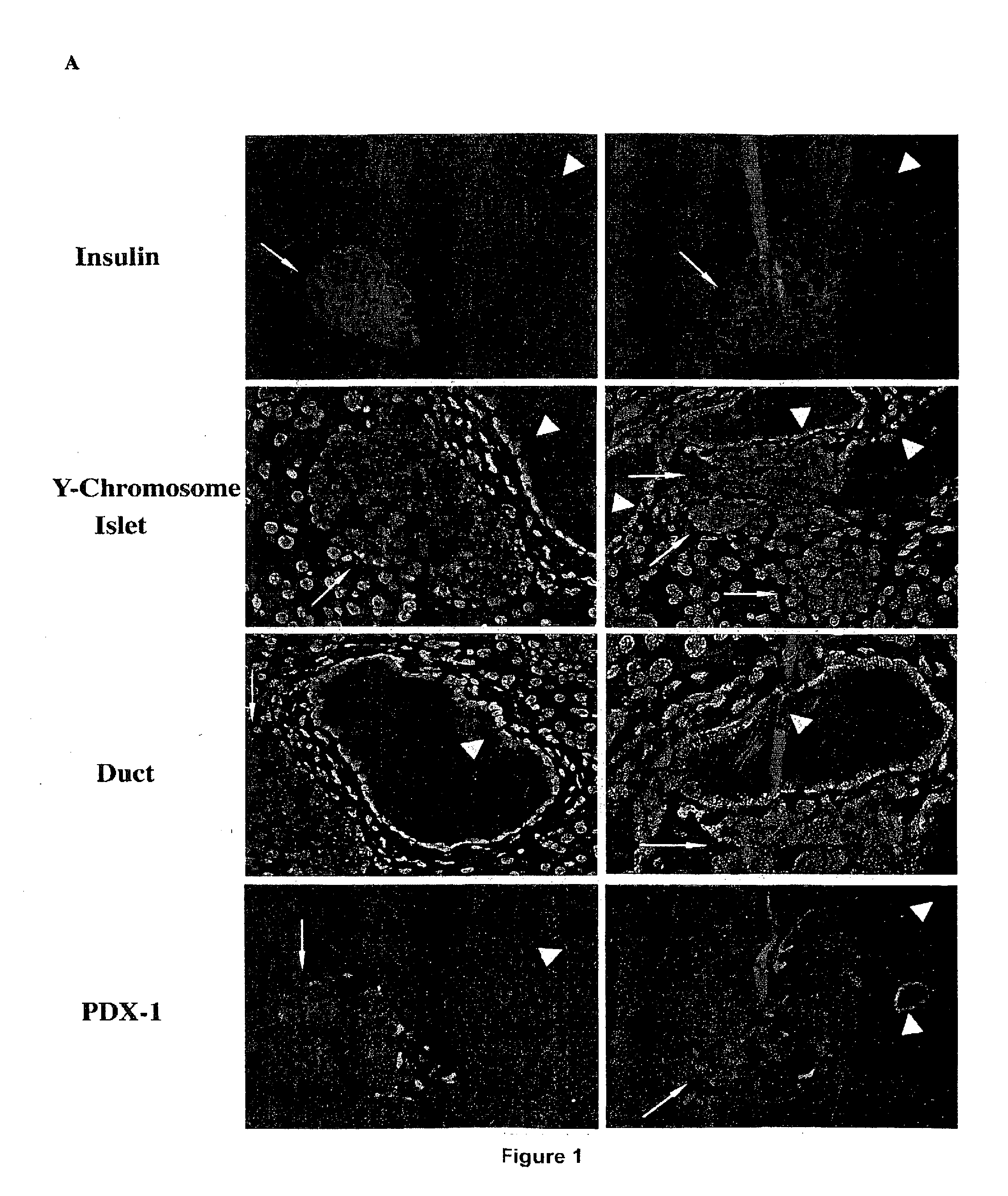
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods and compositions for treating autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS8173129B2Increasing and maintaining numberTreating and stabilizing and preventing autoimmuneSenses disorderNervous disorderHeart cellsDisease
The invention features methods for increasing or maintaining the number of functional cells of a predetermined type, for example, insulin producing cells of the pancreas, blood cells, spleen cells, brain cells, heart cells, vascular tissue cells, cells of the bile duct, or skin cells, in a mammal (e.g., a human patient) that has injured or damaged cells of the predetermined type.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods and compositions for treating type 1 diabetes
ActiveUS7628988B2Increase secretionImprove bioavailabilitySenses disorderNervous disorderHeart cellsVascular tissue
The invention features methods for increasing or maintaining the number of functional cells of a predetermined type, for example, insulin producing cells of the pancreas, blood cells, spleen cells, brain cells, heart cells, vascular tissue cells, cells of the bile duct, or skin cells, in a mammal (e.g., a human patient) that has injured or damaged cells of the predetermined type.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation method of composite vegetable protein peptide
InactiveCN110037163ARaise the gradeImprove market competitivenessMulti-step food processesVegetable proteins working-upBiotechnologyHeart cells
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite vegetable protein peptide. Soybean protein, walnut protein, sesame protein, wheat protein and corn protein are mixed according to a certainproportion to prepare a solution, and then enzymolysis is carried out to prepare the composite vegetable protein peptide. After enzymolysis, the vegetable proteins have different biological activities: the soybean peptide provides continuous nutritional power for heart cells and removes blood fat in cardiovascular blood vessels; the corn oligopeptide protects liver cells from being damaged; the wheat oligopeptide has good effect on spleen deficiency; the walnut peptide has the function of clearing lung; and the sesame peptide can nourish the kidney.
Owner:王书敏
System and method for photodynamic cell therapy
The invention can be characterized as method for stimulating or inhibiting gene expression by photomodulating living cells using a source of narrowband multichromatic electromagnetic radiation. The cells may include, among others, nerve cells, skin cells, retinal cells, heart cells, stem cells, brain cells, cells found in human organs, cells found in hair follicles, and cells found in the human eye or retina. Photomodulation may be enhanced using topically or orally administered compositions. The source of narrowband multichromatic electromagnetic radiation may include at least one light emitting diode (LED) that can emit radiation having a wavelength of from about 300 nm to about 1600 nm.
Owner:GENTLEWAVES
Molecules for targeting compounds to various selected organs or tissues
The invention provides conjugates, comprising an organ, tissue or tumor cell homing molecule linked to a moiety. Such a moiety can be, for example, an oligonucleotide, small interfering RNA, gene, virus, protein, pharmaceutical or detectable agent. In addition the invention provides methods to diagnose or treat a pathology of the muscle or heart, by administrating to a subject having or suspected of having a pathology a molecule or conjugate that homes to, binds to and is taken up by the muscle cells or heart cells.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
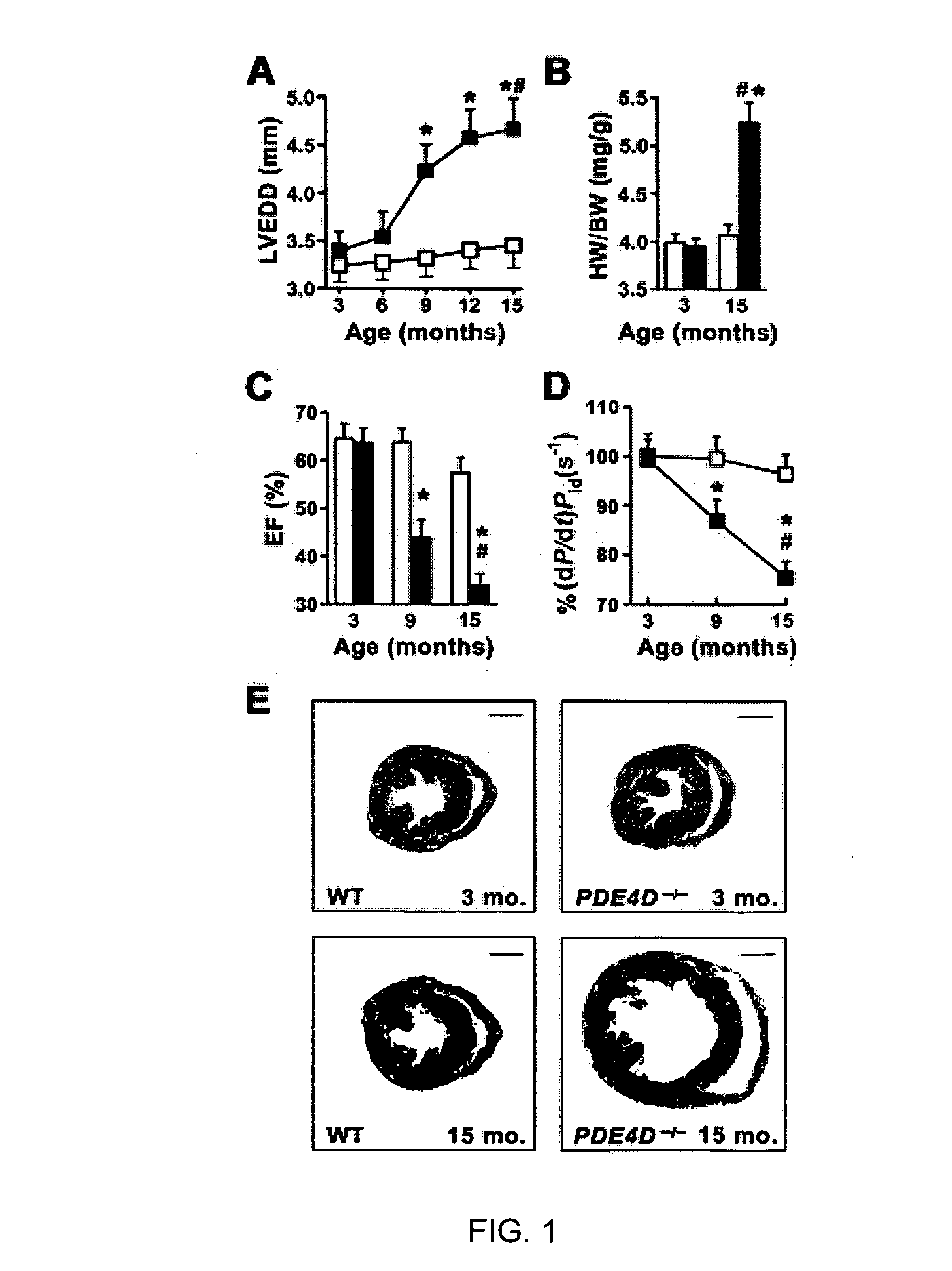
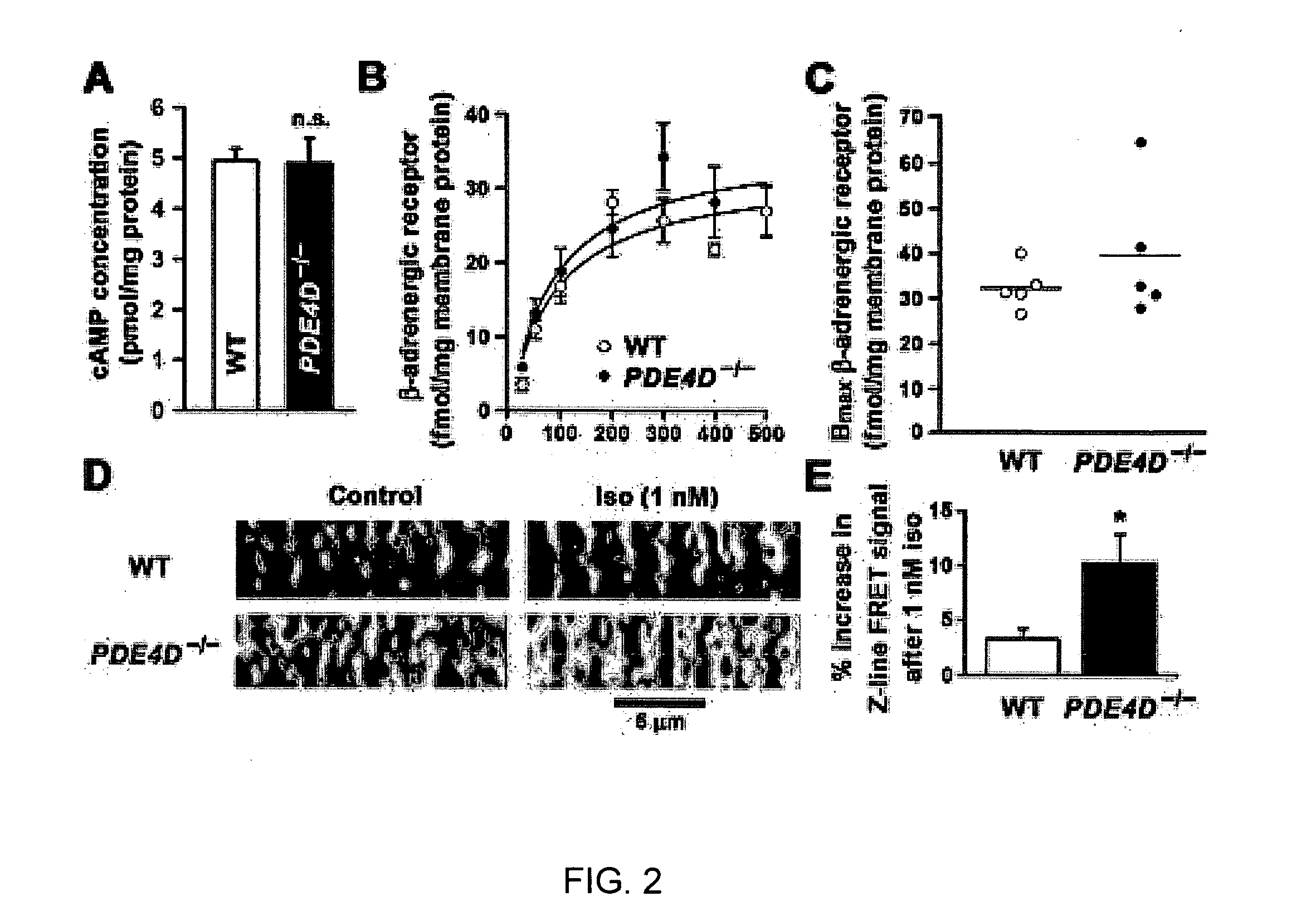
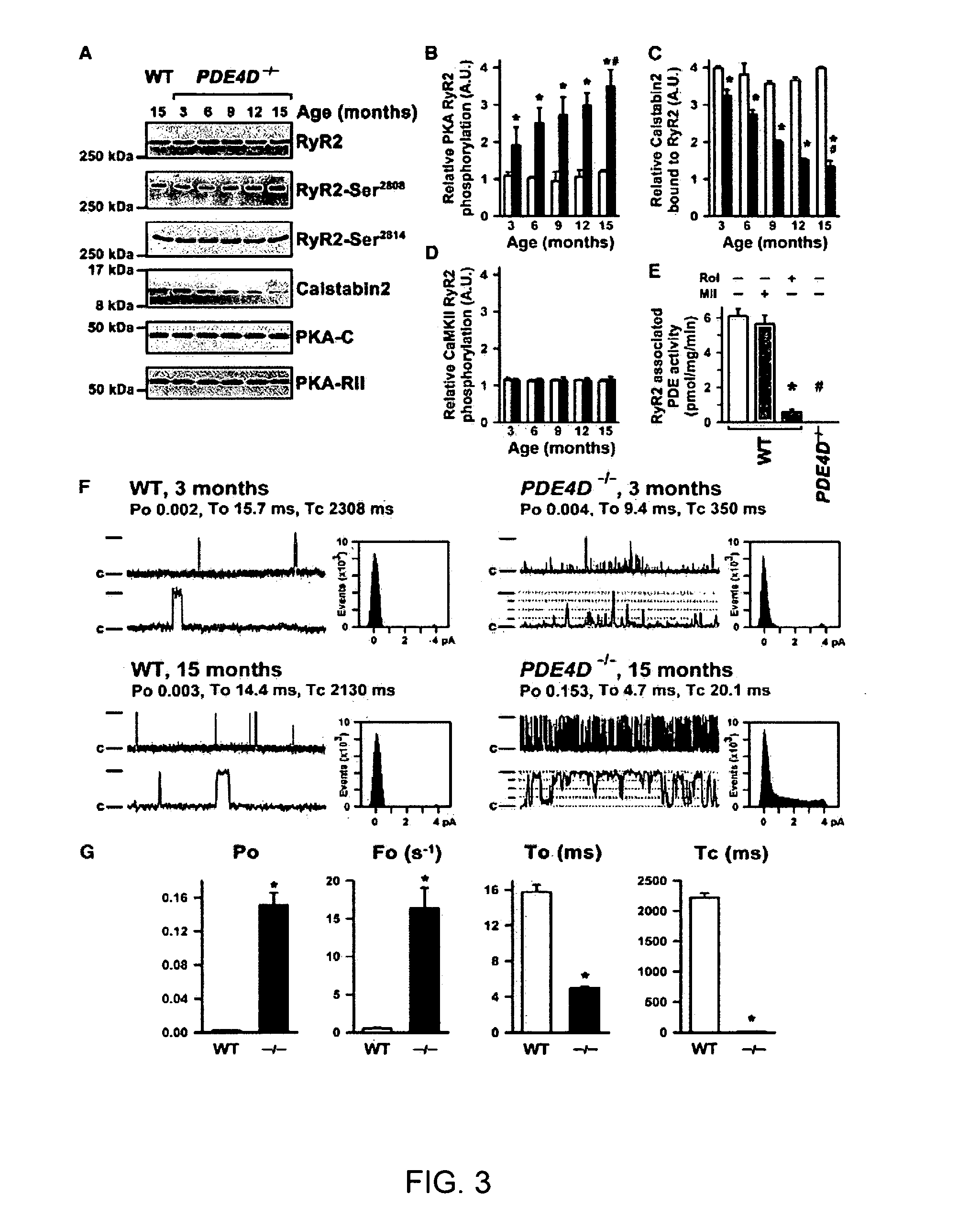
Phosphodiesterase 4D in the ryanodine receptor complex protects against heart failure
InactiveUS20060293266A1Effective treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPhosphodiesteraseRyanodine receptor complex
The present invention provides compositions useful for treating and preventing ryanodine receptor associated disorders comprising a PDE-associated agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides methods for treating or preventing ryanodine receptor associated disorders including cardiac disorders and diseases, skeletal muscular disorders and diseases, cognitive disorders and diseases malignant hyperthermia, diabetes and sudden infant death syndrome. The present invention further provides methods for regulating PKA phosphorylation of a ryanodine receptor as well as methods for regulating Ca+2 release and reuptake in cells. Also provided are kits for use in delivering a PDE-associated agent to cardiac cells in a subject, comprising the composition of the present invention and a catheter.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
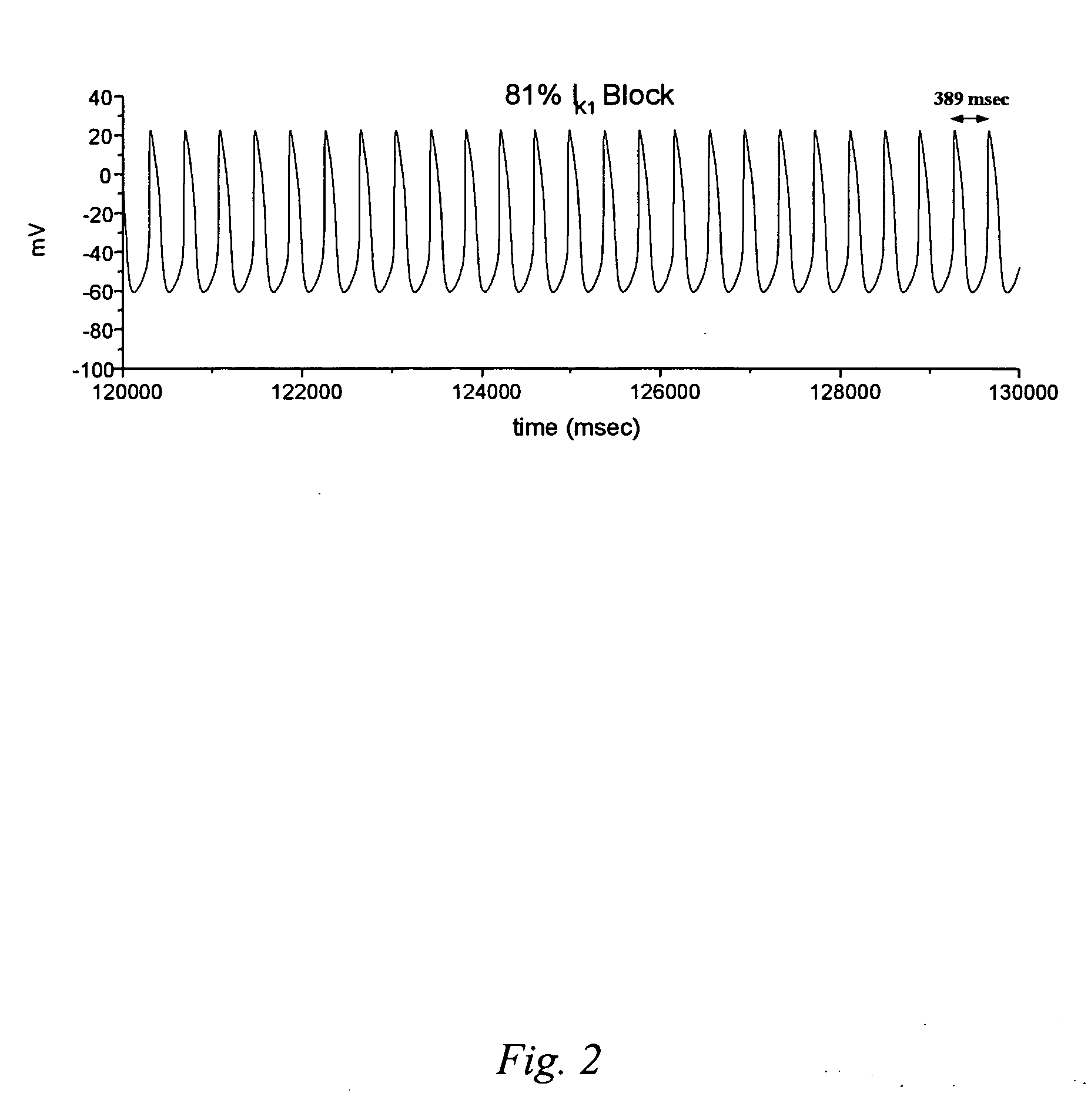
Methods of treating cardiac disorders by suppressing the expression of the potassium inwardly-rectifying channel
The present invention is directed toward methods for regulating biological pacemaking activity and devices used in such regulation. Such regulation can be accomplished by introducing genetic material to the heart by transfecting heart cells of the atrium or ventricle with an oligonucleotide, small interfering RNA, that silence KCNJ2, and suppress the IK1 current. Suppression (or silencing) of KCNJ2 subsequently induces pacemaker-like activities in previously regular myocytes. This invention provides for methods of targeted delivery using a fluid delivery catheter. Such a catheter allows the targeting of a specific area in the atrium or the ventricle of the heart. Also, combination methods of treating arrhythmia with traditional device-based therapies (e.g., pacemakers and defibrillators) and an oligonucleotide of the subject invention.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
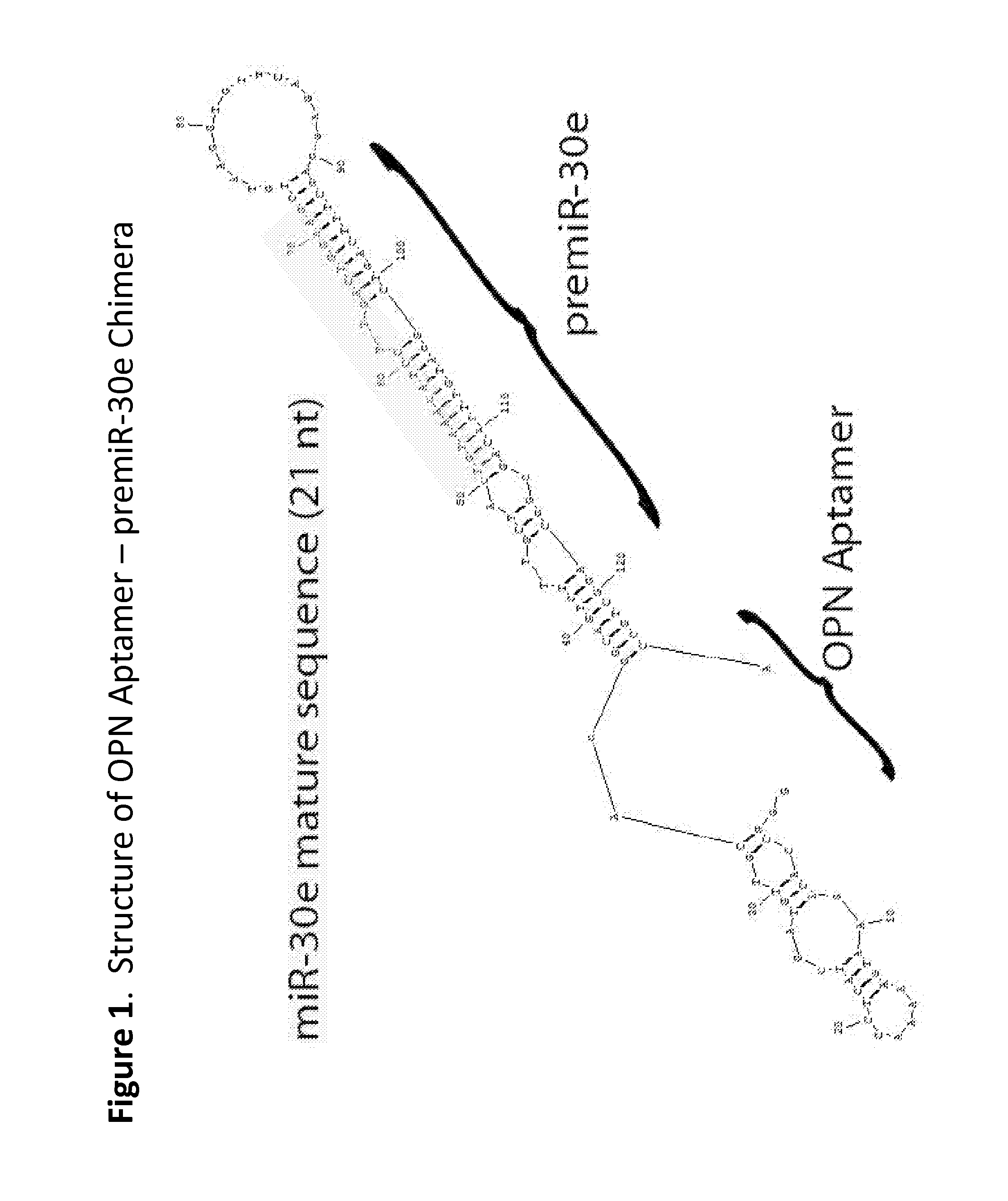
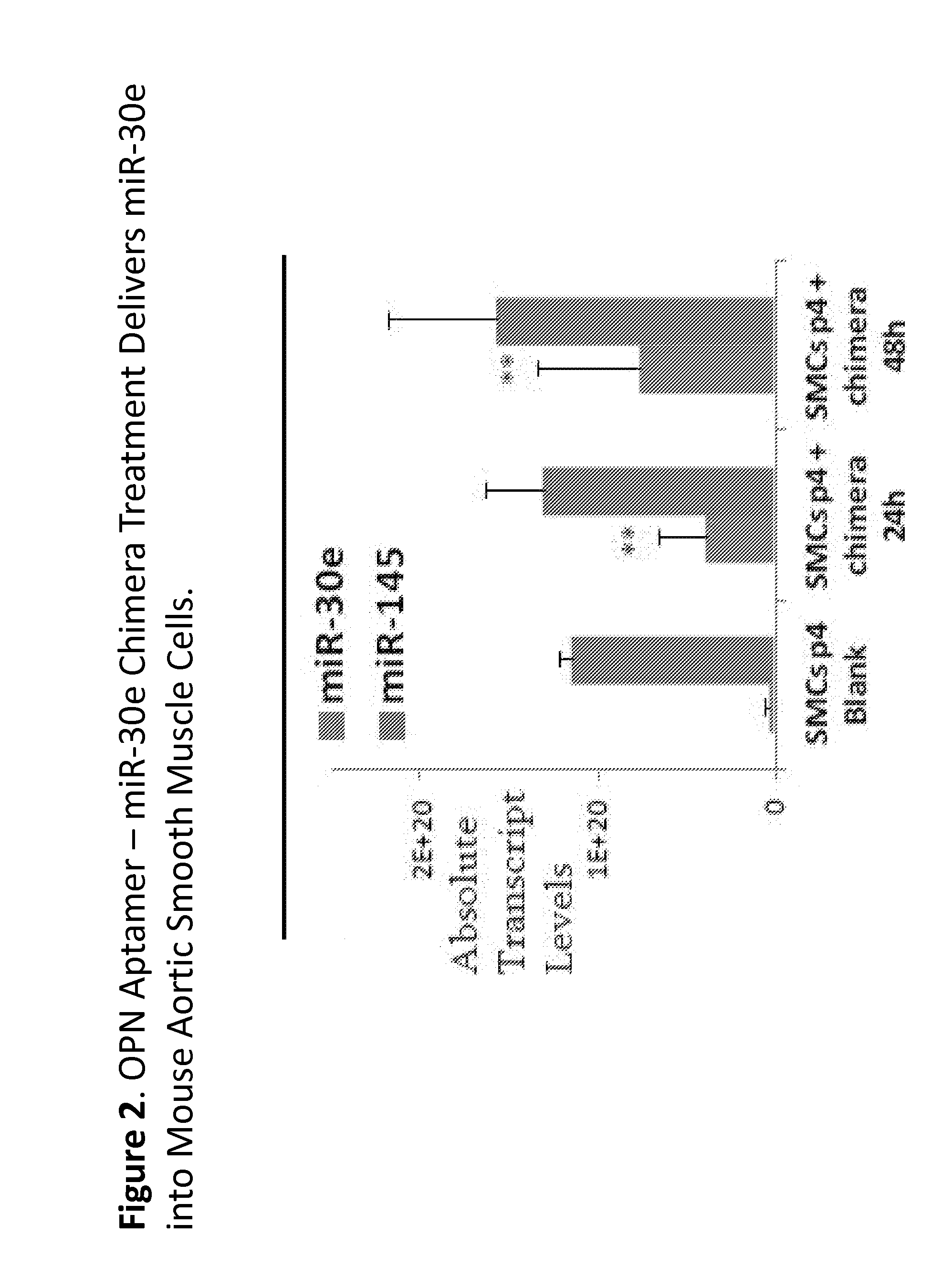
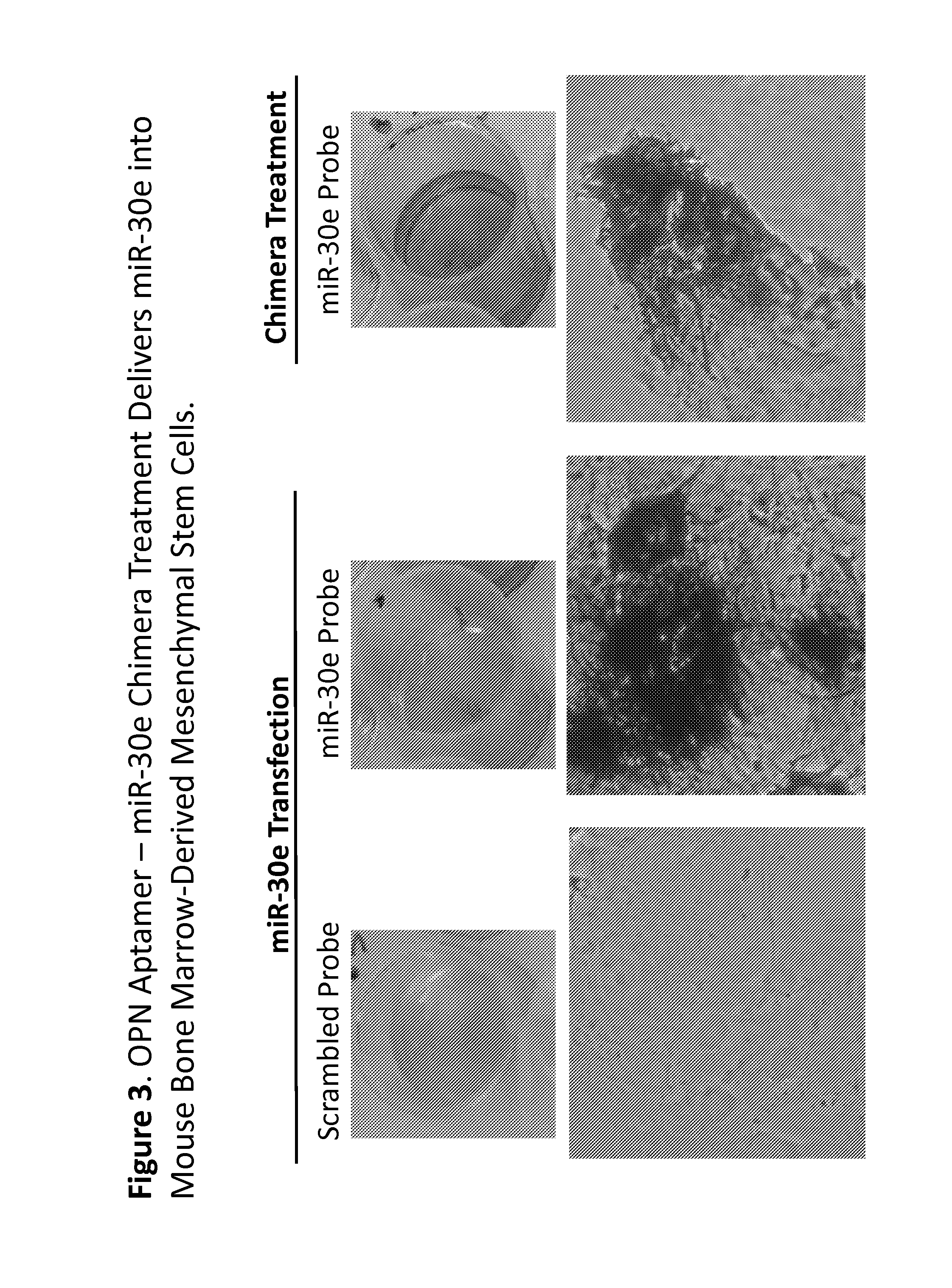
Methods and compositions employing an osteopontin aptamer to deliver nucleic acids into smooth muscle, endothelial, cardiac and progenitor/stem cells
ActiveUS20160272973A1Reduce inflammationRelieve symptomsSpecial deliveryGenetic material ingredientsProgenitorHeart cells
Various therapeutic polynucleotides are provided along with their use to treat a variety of disease states. The chimeric polynucleotides disclosed herein comprise an OPN aptamer linked to an OPN-specific therapeutic oligonucleotide in order to deliver the OPN-specific therapeutic polynucleotide to the site of OPN expression. Thus, the specificity of OPN aptamers allows delivery of therapeutic molecules to the site of unhealthy tissue. Accordingly, the chimeric polynucleotides disclosed herein can reduce at least one symptom of a disease or unhealthy condition by delivering an OPN-specific therapeutic oligonucleotide that interferes with a disease promoting factor.
Owner:SHEHADEH LINA A
Methods And Compounds For Targeting Tissues
The present invention relates to peptides which home to cells, e.g. heart cells, with high selectivity and which can be useful in the form of compositions. Such compositions can be used, e.g., for selectively targeting a systemically administered therapeutic agent or imaging agent to a cell or tissue in a subject. The present invention further relates to methods of using the compositions for imaging, e.g. PET imaging, and targeting cells, e.g. for delivering a therapeutic agent to one or more target cells in a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods of organ regeneration
InactiveUS20100150893A1Increasing and maintaining numberTreating and stabilizing and preventing autoimmuneBiocideSenses disorderHeart cellsPhysiology
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for establishing schizothorax wangchiachii heart cell line and performing ultralow temperature cryopreservation on schizothorax wangchiachii heart cell line
ActiveCN103409365AEasy to operateAvoid damageDead animal preservationVertebrate cellsHeart cellsEnzyme digestion
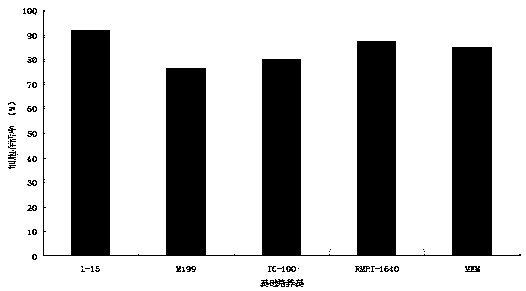
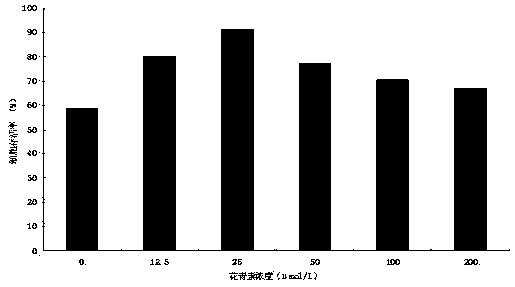
The invention relates to a method for establishing a schizothorax wangchiachii heart cell line and performing ultralow temperature cryoprservation on the schizothorax wangchiachii heart cell line, belonging to the technical field of freshwater aquatic organism cell culture and ultralow temperature cryopreservation. The method comprises the following steps of taking heart tissues of schizothorax wangchiachii as materials, and culturing the materials in an M199 culture solution by adopting a tissue block method and a two-enzyme digestion method, wherein the M199 culture solution contains fetal calf serum and cell growth factors and the pH value of the M199 culture solution is 7.0-7.2; and performing secondary culture by adopting a trypsase digestion method. The method specifically comprises the steps of preparing a cell culture solution, performing primary culture and performing secondary culture. The method has the beneficial effects as follows: 1, the operation is simple and convenient; 2, damages caused by a pure tissue block method to heart cells are reduced; 3, the form of the established schizothorax wangchiachii heart cell line is in the shape of fibroblasts, and the established schizothorax wangchiachii heart cell line grows well, can realize continuous passage culture, can be directly applied to biological characteristic researches, and meets requirements for storage, theoretical study and application of genetic resources of the schizothorax wangchiachii; and 4, the establishing method is also suitable for establishing heart cell lines of other types of fishes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating pediatric viral myocarditis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102847061AEasy to prepareLess excipientsPowder deliveryAntipyreticHeart cellsViral Myocarditis
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating pediatric viral myocarditis. The preparation comprises raw materials of Radix Ophiopogon, therootofred-rootedsalvia, cassia twig, alliummacrostemon, rootofcommonpeony, Schisandra chinensis, pseudo-ginseng, Astragalusmongholicus, Fructus Trichosanthis, Fructus Forsythiae, Semen Platycladi, Rhizoma Atractylodis, luffa vegetable sponge, angelica, Ligusticumwallichii, curcuma zedoary, ginger processed pinellia, the root of large-flowered skullcap, polygala root, earthworm, and Radix aucklandiae. The invention aims to prepare a medicine for treating myocarditis from selected traditional Chinese medicines. The prepared medicine not only can improve the metabolism of myocardium and myocardial nutrition, protect the heart cells and improve myocardial disease resistance, but also can directly kill virus, reduce the damage of virus on myocardium, and realize combination of antivirus and overall regulation; and the medicine can reduce deputy effects caused by long-term application of Western medicine on the human body, and is an ideal medicine for treating myocarditis. In addition, the medicine prepared by the invention contains a large amount of active ingredients, employs cheap raw materials and simple preparation method, and can be widely used in clinical practice.
Owner:张萍
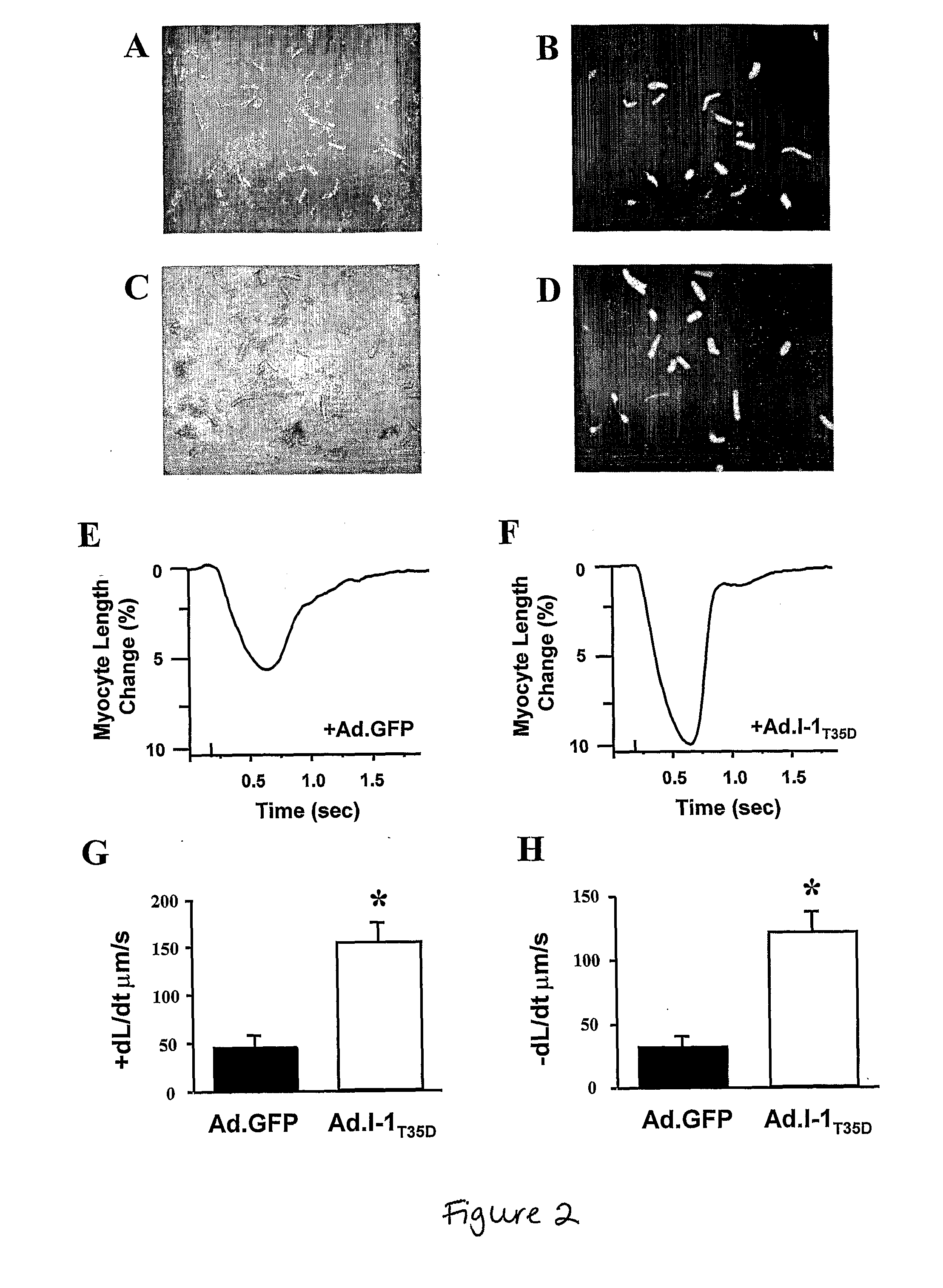
Modulating Phosphatase Activity In Cardiac Cells
ActiveUS20080125385A1Improve responsivenessDecreasing phosphatase activityVirusesMetabolism disorderHeart cellsCardiac disorders
Expression of a phosphatase inhibitor in heart cells can be used to treat cardiac disorders, e.g., heart failure. Decreasing phosphatase activity can improve β-adrenergic responsiveness.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI +1
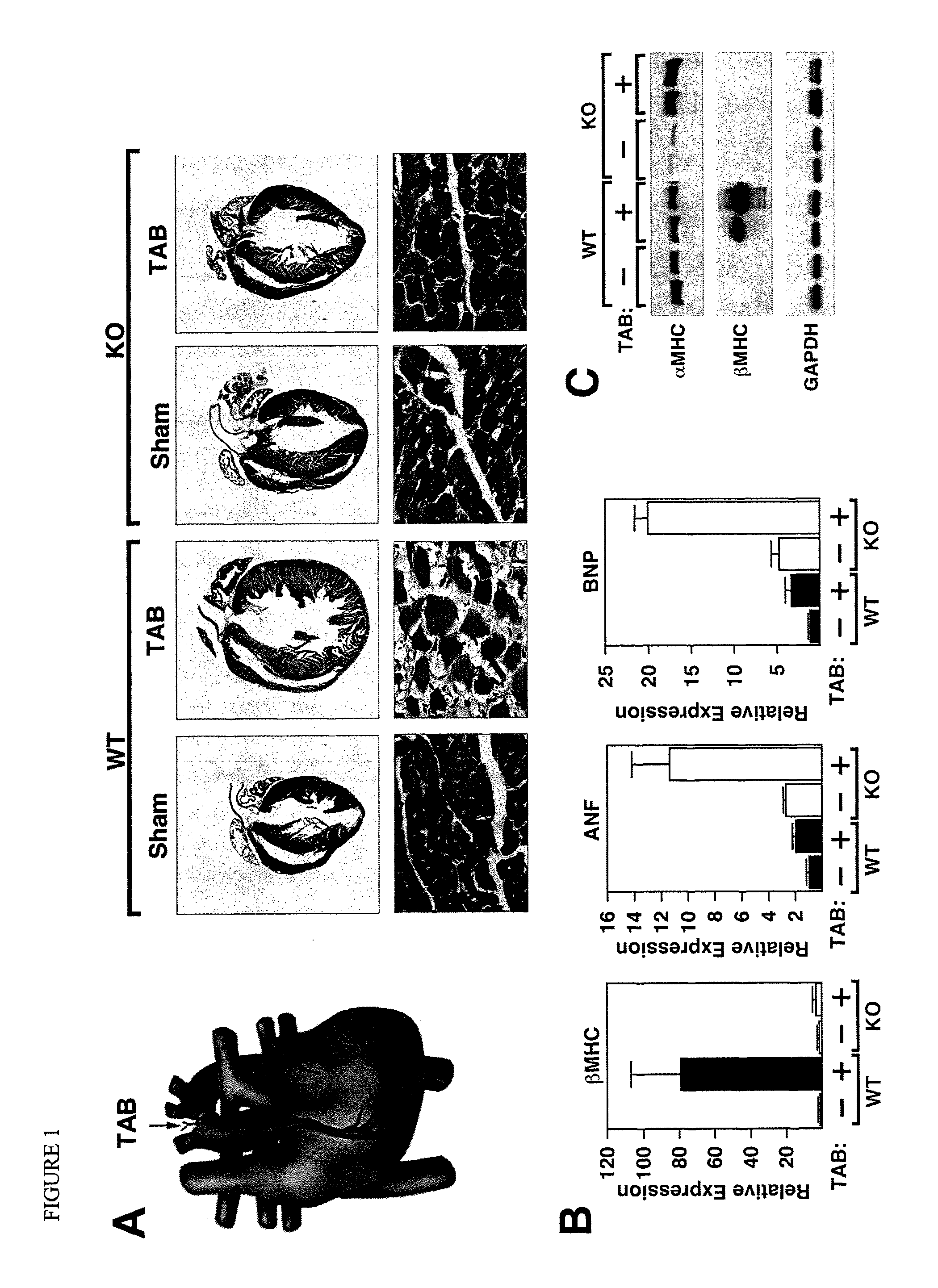
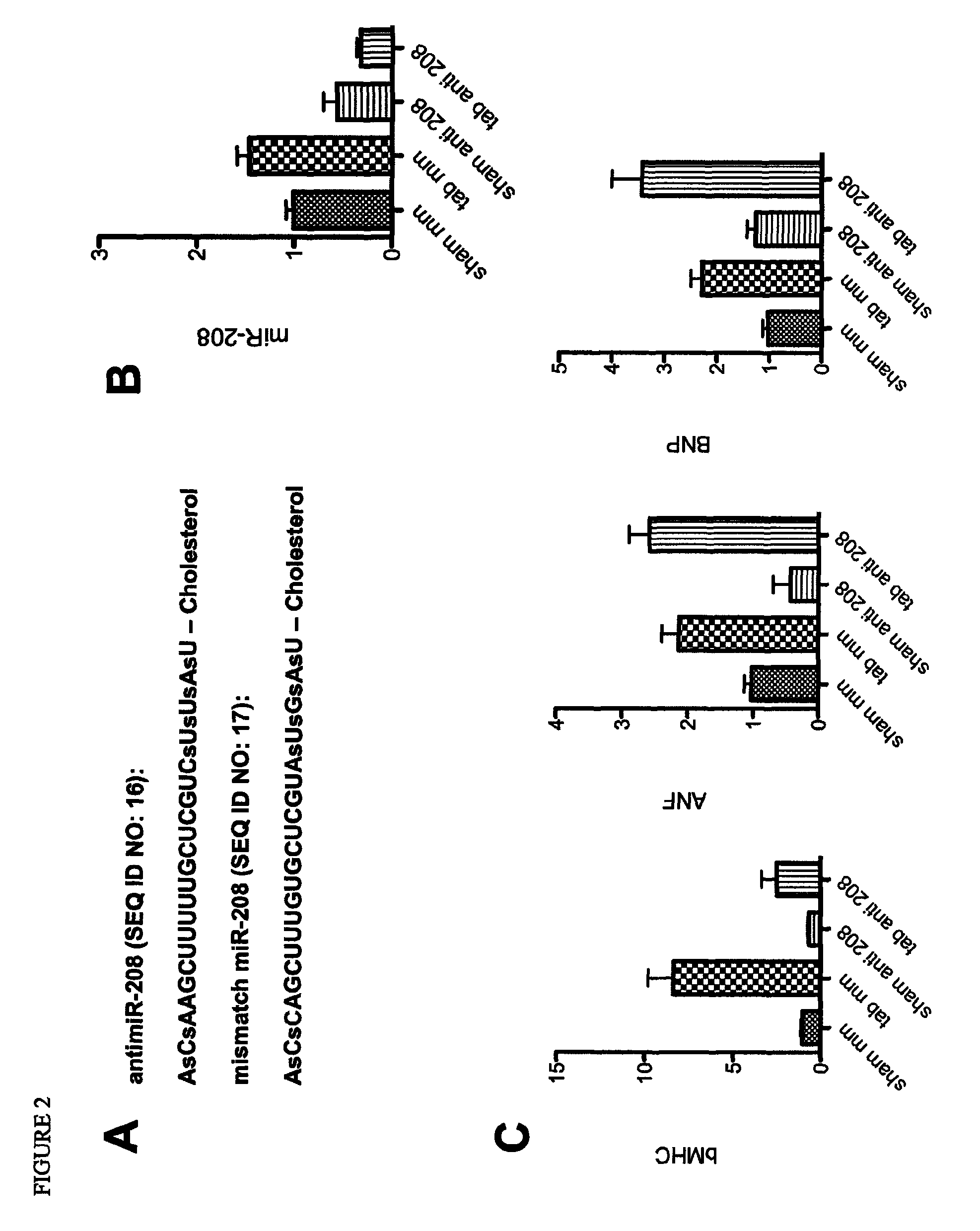
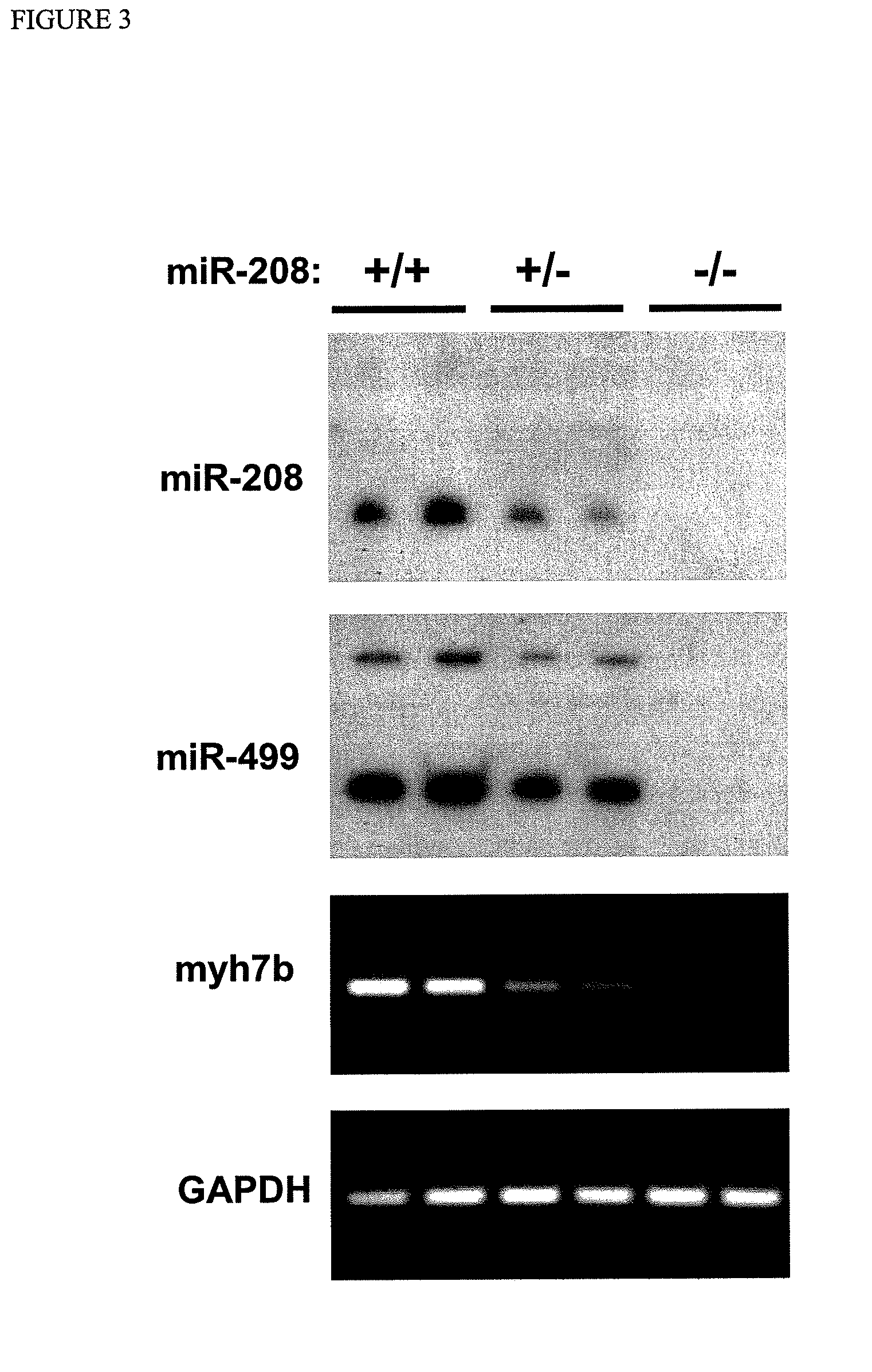
Dual targeting of mir-208 and mir-499 in the treatment of cardiac disorders
InactiveUS20120035243A1Increase contractilityTime period for regulating expression of stress-related genesOrganic active ingredientsActivity regulationDiseaseHeart cells
The present invention provides a method of treating or preventing cardiac disorders in a subject in need thereof by inhibiting the expression or function of both miR-499 and miR-208 in the heart cells of the subject. In particular, specific protocols for administering inhibitors of the two miRNAs that achieve efficient, long-term suppression are disclosed. In addition, the invention provides a method for treating or preventing musculoskeletal disorders in a subject in need thereof by increasing the expression or activity of both miR-208 and miR-499 in skeletal muscle cells of the subject.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Construction method of Epinephelus fuscoguttatus heart cell line
InactiveCN101451121AIdeal for in vitro studiesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin-like growth factorLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method for constructing a heart cell system of blotchy rockcod, which comprises: taking a heart tissue of the blotchy rockcod as a material, adopting a trypsin digestion method to start primary culture, and culturing the heart tissue in a DMEM / F12 liquid medium which contains fetal calf serum, basic fibroblast growth factors, I-type insulin-like growth factors, chondroitin sulfate and culture supernatant of fin cells of the blotchy rockcod in the log phase and has a pH value of between 7.0 and 7.4; and adopting the trypsin digestion method for subculturing. The heart cell system of the blotchy rockcod constructed by the method is subcultured for 70 generations currently. The technology is scientific and reasonable, is hopeful to be applied to separation and breeding of fish viroids, preparation of virus vaccines and research in the aspects of interaction of viruses and host cells, and so on, can also be taken as a model for researching environmental pollutants in environmental toxicology, and performs pollution monitoring and safety evaluation on various environmental pollutants in the sea such as genic toxins, mutagen, carcinogens, environmental hormones and endocrine disruptors.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Construction method for anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line
ActiveCN102766595AGood growthEasy to operateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAnabarilius grahamiFresh water organism
The invention relates to a construction method for a anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line and belongs to the technical field of freshwater organism cell culture. The method includes using anabarilius grahami heart tissue as a material, washing and shearing the heart tissue, using hyaluronidase and II type collagenase to perform a joint digestion to obtain free heart cells and loose tissue blocks, inoculating the free heart cells and the loose tissue blocks in a culture flask of 25 square centimeters, adding an L-15 culture solution containing fetal calf serum, human basic fibroblast growth factor and chondroitin sulfate in the culture flask, and placing the culture flask in a culture box of 28 DEG C to culture. The culture solution is replaced at an interval of three and half days, and when cells grow into monolayers, a trypsin digestive method is utilized to perform cell passage. The construction method for the schizothorax taliensis cardiac cell line has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the cell growth state of the constructed anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line is good, the cells are fibroblast-like, more than 40 generations can be continuously achieved during the cell passage, the constructed anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line can be directly used for models of an environmental toxicology for studying environmental pollutants to perform pollution detection and safety evaluation, and the method is also suitable for the construction of cardiac cell lines of other fishes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecules for targeting compounds to various selected organs or tissues
The invention provides conjugates, comprising an organ, tissue or tumor cell homing molecule linked to a moiety. Such a moiety can be, for example, an oligonucleotide, small interfering RNA, gene, virus, protein, pharmaceutical or detectable agent. In addition the invention provides methods to diagnose or treat a pathology of the muscle or heart, by administrating to a subject having or suspected of having a pathology a molecule or conjugate that homes to, binds to and is taken up by the muscle cells or heart cells.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
Dual targeting of MIR-208 and MIR-499 in the treatment of cardiac disorders
InactiveUS8629119B2Increase contractilityTime period for regulating expression of stress-related genesOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesHeart cellsDisease
The present invention provides a method of treating or preventing cardiac disorders in a subject in need thereof by inhibiting the expression or function of both miR-499 and miR-208 in the heart cells of the subject. In particular, specific protocols for administering inhibitors of the two miRNAs that achieve efficient, long-term suppression are disclosed. In addition, the invention provides a method for treating or preventing musculoskeletal disorders in a subject in need thereof by increasing the expression or activity of both miR-208 and miR-499 in skeletal muscle cells of the subject.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Construction method of Epinephelus fuscoguttatus swim bladder cell line
The invention relates to a method for constructing an air bladder cell system of blotchy rockcod, which comprises: taking an air bladder tissue of the blotchy rockcod as a material to start primary culture, and culturing the air bladder tissue in a DMEM / F12 liquid medium which contains fetal calf serum, carboxymethyl chito-oligosaccharide, basic fibroblast growth factors, I-type insulin-like growth factors, N-acetyl glucose hydrochloride and culture supernatant of heart cells of the blotchy rockcod in the log phase and has a pH value of between 7.0 and 7.4; and adopting a trypsin digestion method for subculturing. The air bladder cell system of the blotchy rockcod constructed by the method is subcultured for 62 generations currently. The technology is scientific and reasonable, is hopeful to be applied to ecotoxicological research, performs pollution monitoring and safety evaluation on various environmental pollutants in the sea, and can also be applied to separation, identification and in vitro breeding of fish viroids, and research in the aspects of interaction of viruses and host cells, and so on.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Pelodiscus sinensis heart cell continuous cell line and establishing method and ultra-low-temperature cryopreservation method thereof
ActiveCN105039241AMaintain biological propertiesMeet resourcesDead animal preservationArtificial cell constructsHeart cellsGermplasm
The invention relates to a pelodiscus sinensis heart cell continuous cell line which is preserved in the common microorganism center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.10597, and further relates to an establishing method and ultra-low-temperature cryopreservation method of the pelodiscus sinensis heart cell continuous cell line. The establishing method includes the following steps of firstly, conducting primary culture, wherein a pelodiscus sinensis heart is cut into tissue small pieces after being preprocessed, trypsin is inoculated into a culture bottle after being digested at the room temperature, and subculture is not started until cells are fully laid on 90% or more of the bottle bottom; secondly, conducting subculture, wherein air is blown on the bottle bottom through a trypsin digesting method to make adherent cells fall down so that subculture can be conducted. By means of the established pelodiscus sinensis heart cell continuous cell line, the research on viral diseases of pelodiscus sinensis and other turtle animals and the research on related therapy drugs for instance the analysis of chromosome and the research of iridescent virus can be conducted on the level of molecular cells, and the requirements for pelodiscus sinensis germplasm resource conservation and theoretical research and application can be met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Haliotis discus hannai cell culture medium and construction method of cell line
ActiveCN110684709AMaintain activityEasy maintenanceInvertebrate cellsCulture processHeart cellsCell culture media
The invention provides a haliotis discus hannai cell culture medium, which is based on an L-15 culture medium and is added with inorganic salt, growth factors, L-glutamine, astaxanthin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, carboxymethyl glucan, taurine, hydrocortisone, a haliotis discus hannai shell aqueous extract, fetal calf serum, antibiotics and other components. The invention also provides a constructionmethod of the haliotis discus hannai cell line, which comprises the following steps: by using haliotis discus hannai heart tissues as a material, obtaining single cells by a mechanical dissociation method, and resuspending the single cells in the cell culture medium for primary culture, thereby successfully constructing the haliotis discus hannai heart cell line. The culture medium and the methodprovided by the invention can well maintain survival and growth of haliotis discus hannai heart cells in vitro, and the constructed cell line has continuous passage capacity. According to the method,the survival rate of the haliotis discus hannai heart cells in-vitro culture is remarkably increased, the in-vitro culture time is prolonged, and the method has the characteristics of quickness, easiness in operation, stability and easiness in repetition.
Owner:福建罗屿岛食品有限公司
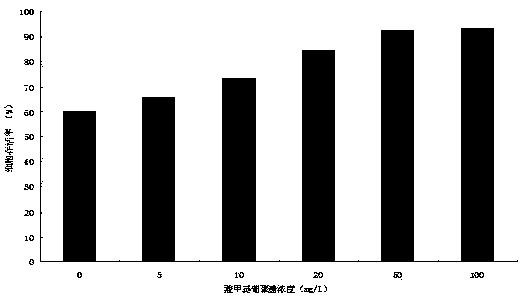
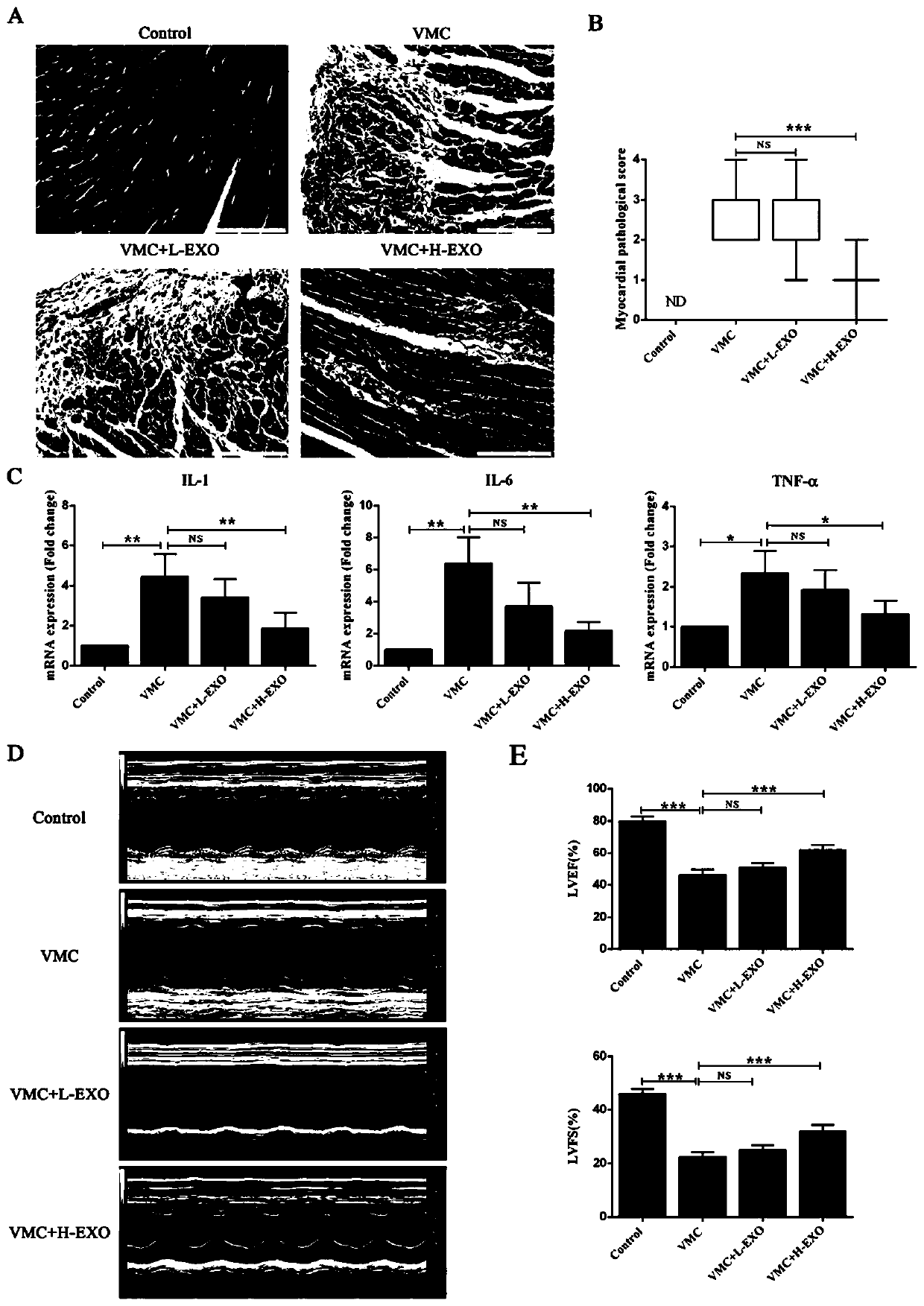
Exosome derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, and identification method and application of exosome
ActiveCN111471650AImprove heart functionInhibit apoptosisCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsHeart cellsViral Myocarditis
The invention relates to an exosome derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, and an identification method and application of the exosome. The present invention finds that the exosomesecreted by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can be ingested by myocardial cells, and can effectively improve the cardiac function of coxsackie B3 (CVB3) induced viral myocarditis mice (VMC), inhibit apoptosis of cardiac cells of the myocarditis mice, and inhibited inhibit apoptosis of human cardiac muscle cells (HCMs) cultured in vitro under induction of CVB3. According to the application disclosed by the invention, the exosome derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can act on a VMC mouse model, so that the effect of improving diseases is achieved to a certain extent, and a new method is provided for treating viral myocarditis by adopting the stem cell-derived exosome in the future.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
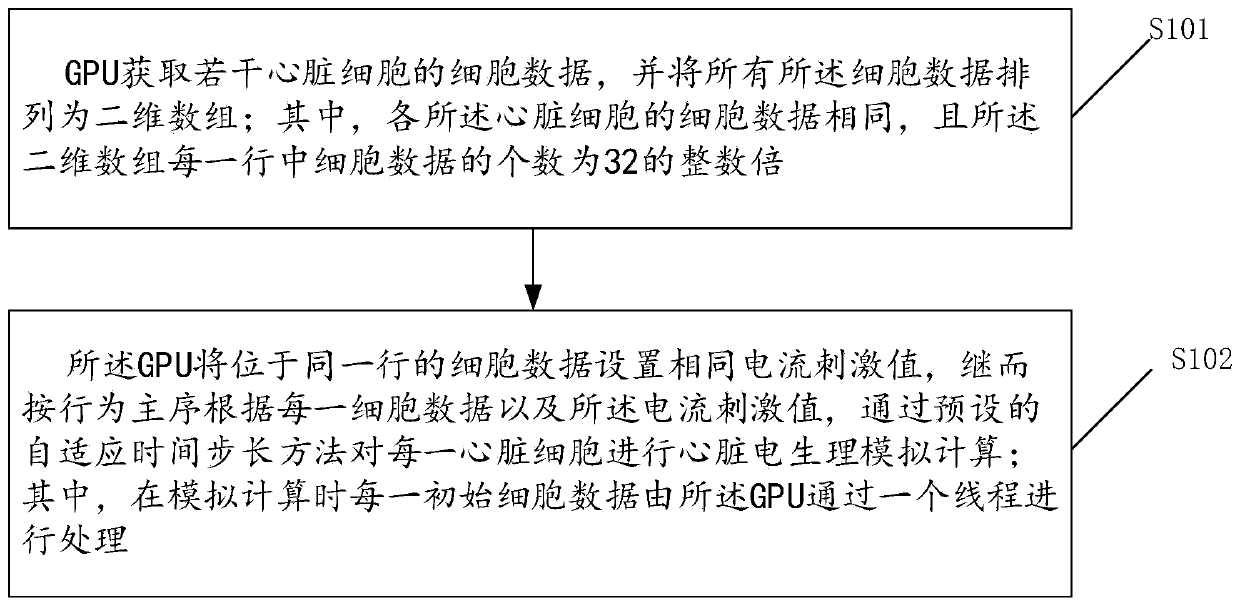
Heart electrophysiology simulation method based on GPU
ActiveCN111091912AImprove accelerationMedical simulationProcessor architectures/configurationHeart cellsAnalogue computation
The invention discloses a heart electrophysiology simulation method based on a GPU. The method comprises the steps that the GPU acquires the cell data of a plurality of heart cells, and arranges all the cell data into a two-dimensional array, wherein the cell data of each heart cell is the same, and the number of the cell data in each row of the two-dimensional array is integral multiples of 32; and the GPU sets the same current stimulation value for the cell data in the same row, and then heart electrophysiological simulation calculation is performed on each heart cell through a preset adaptive time step method according to each piece of cell data and the current stimulation value by taking the row as a main sequence, wherein each piece of initial cell data is processed by the GPU throughone thread during analog computation. By implementing the embodiments of the invention, the problem that heart electrophysiology simulation acceleration effect is weakened when the adaptive time stepmethod is executed on the GPU can be solved, and the acceleration effect during heart electrophysiology simulation is further improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fluorescence-based assay for detecting compounds for modulating the sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX) in "forward mode"
Transporters are an emerging target family with enormous potential, offering scientific and economic opportunities. The Sodium / Calcium exchanger is an important mechanism for removing Ca2+ from diverse cells. In heart, it extrudes Ca2+ that has entered through Ca2+ channels to initiate contraction, while Na+ enters the heart cell. It is of considerable interest to identify compounds that modulate the activity of Sodium / Calcium exchangers.The present invention is directed to a fluorescence-based assay for detecting NCX “forward mode” modulating compounds. It further refers to a kit of parts comprising cells expriming NCX and the use of the kit of parts to test a compound for activity as an agonist or antagonist of NCX.
Owner:SANOFI SA
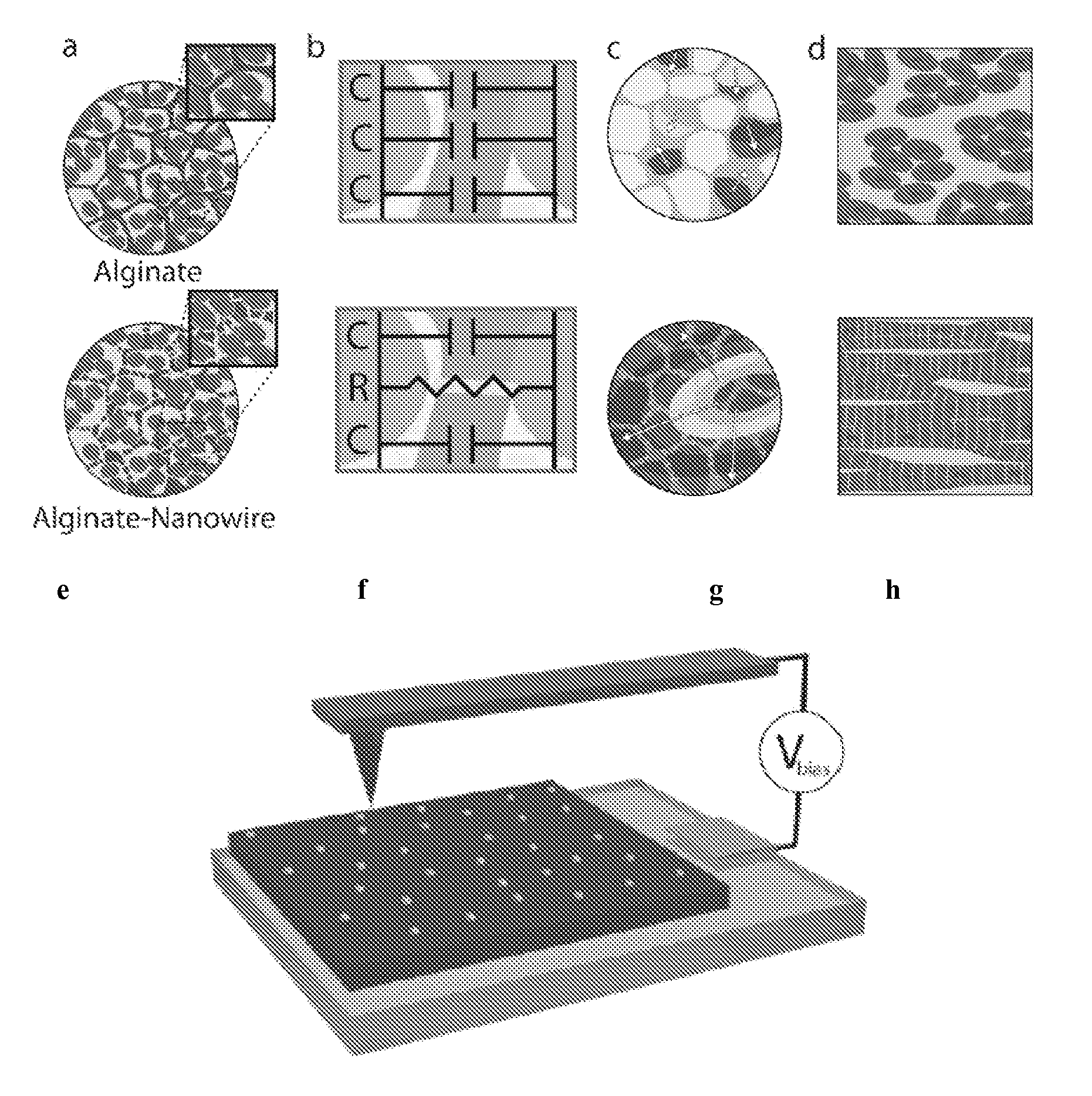
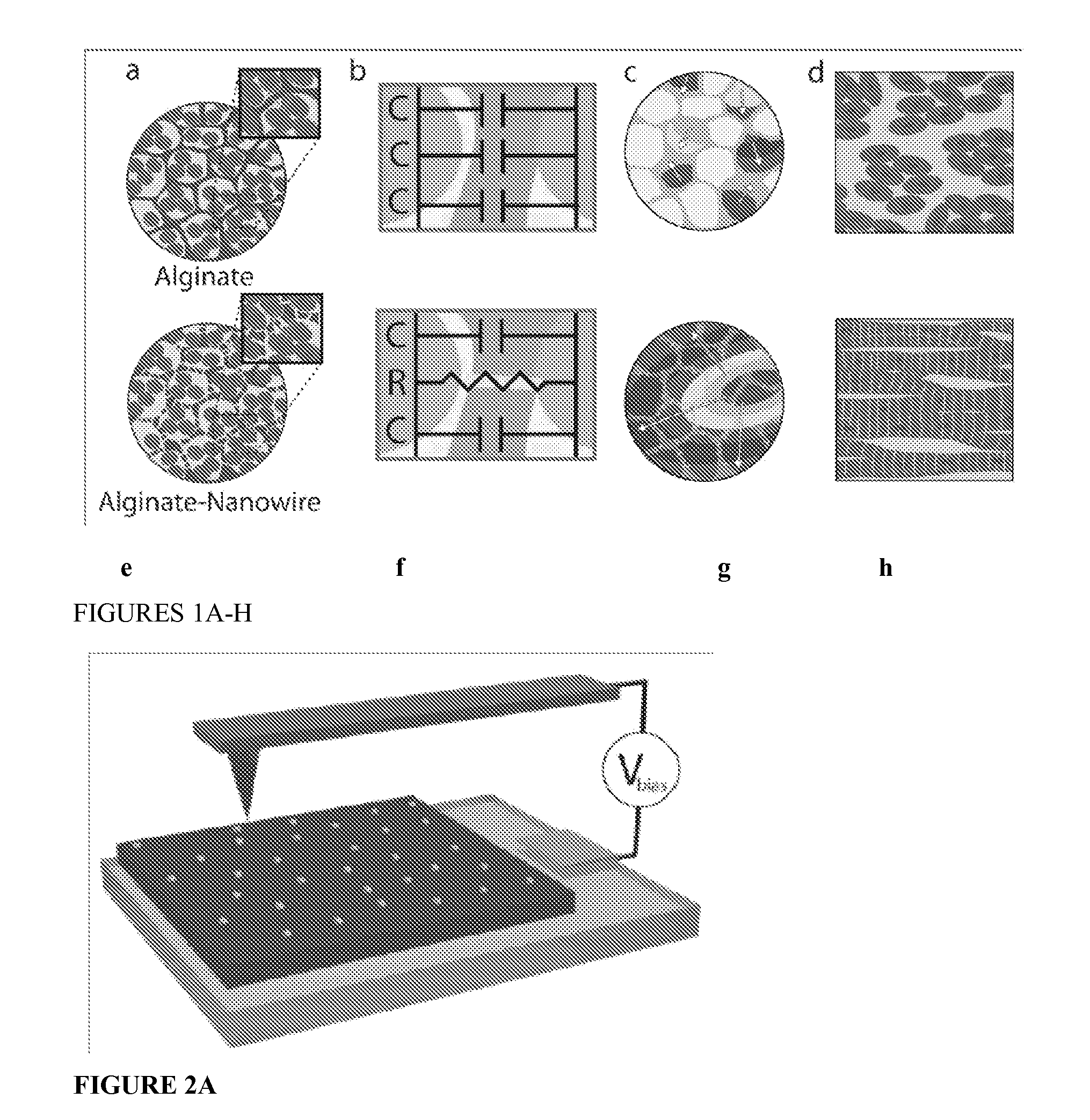
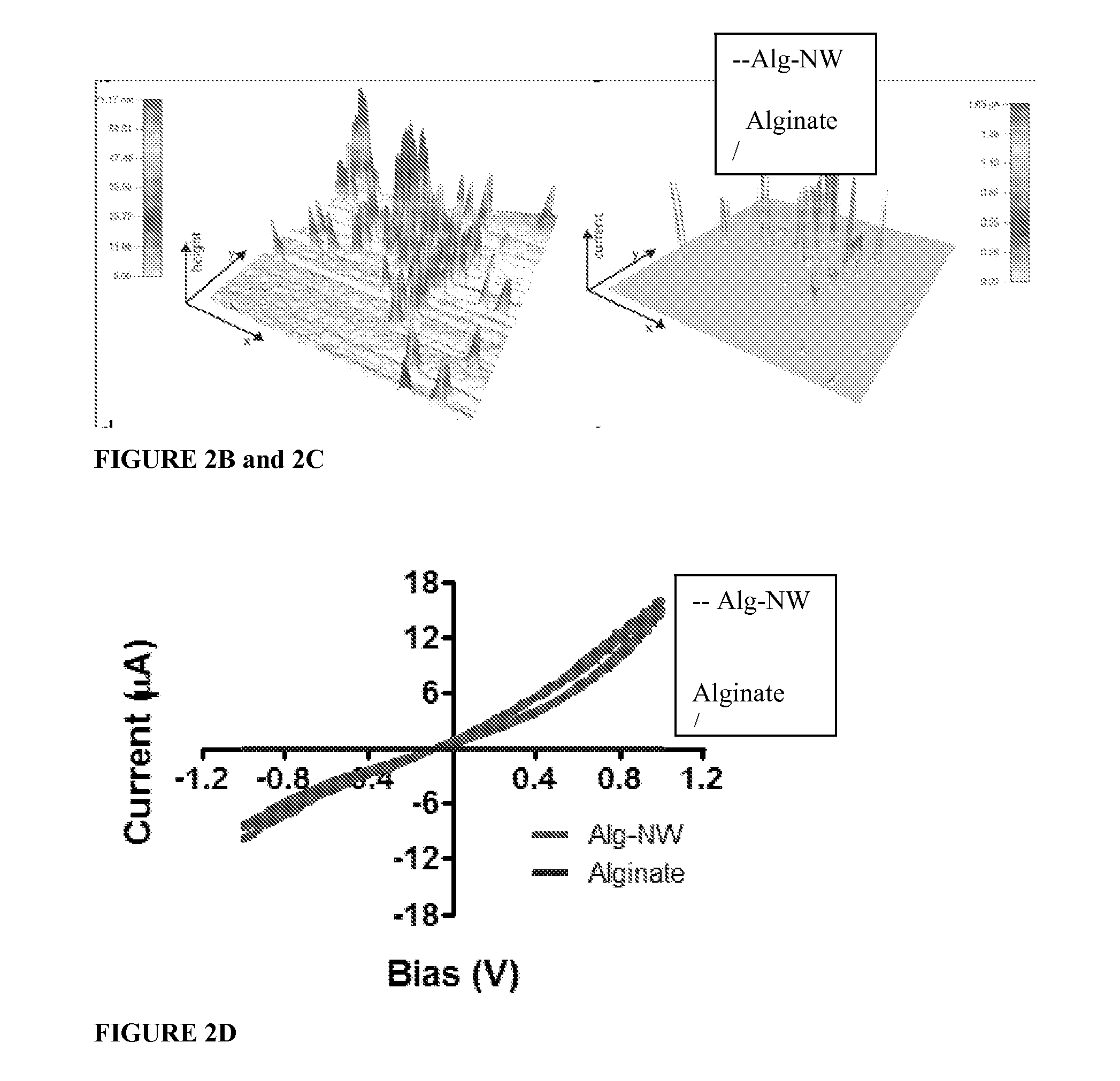
Nanowired three dimensional tissue scaffolds
ActiveUS9114009B2Promote tissue growthImprove electrical communicationEpicardial electrodesHeart valvesNanowireCardiac muscle
Electrically conductive nanowires incorporated within scaffolds enhance tissue growth, bridge the electrically resistant pore walls and markedly improve electrical communication between adjacent cardiac cell bundles. Integration of conducting nanowires within 3D scaffolds should improve the therapeutic value of cardiac patches. Examples demonstrate efficacy of gold nanowires in alginate matrices seeded with cardiomyocytes.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
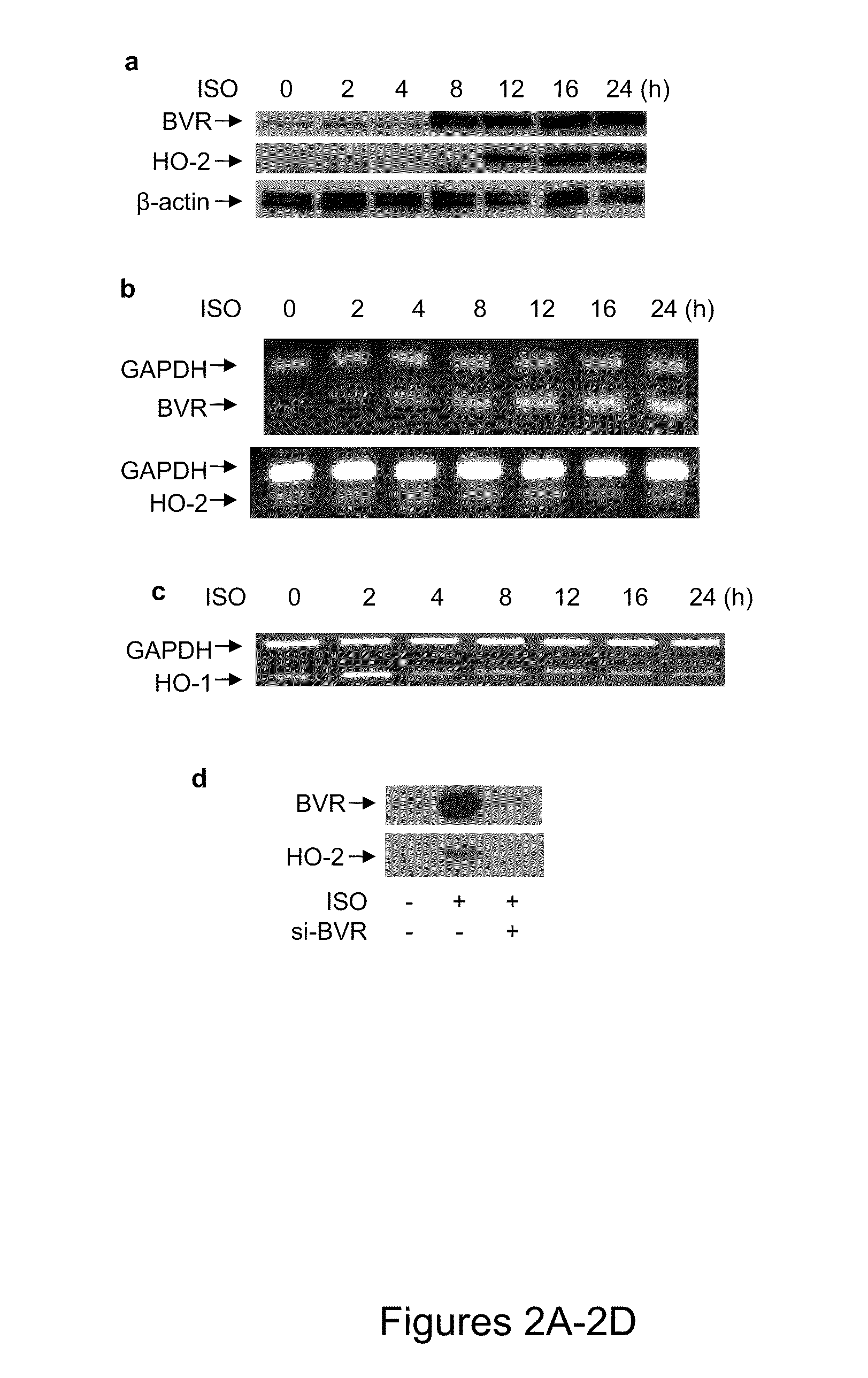
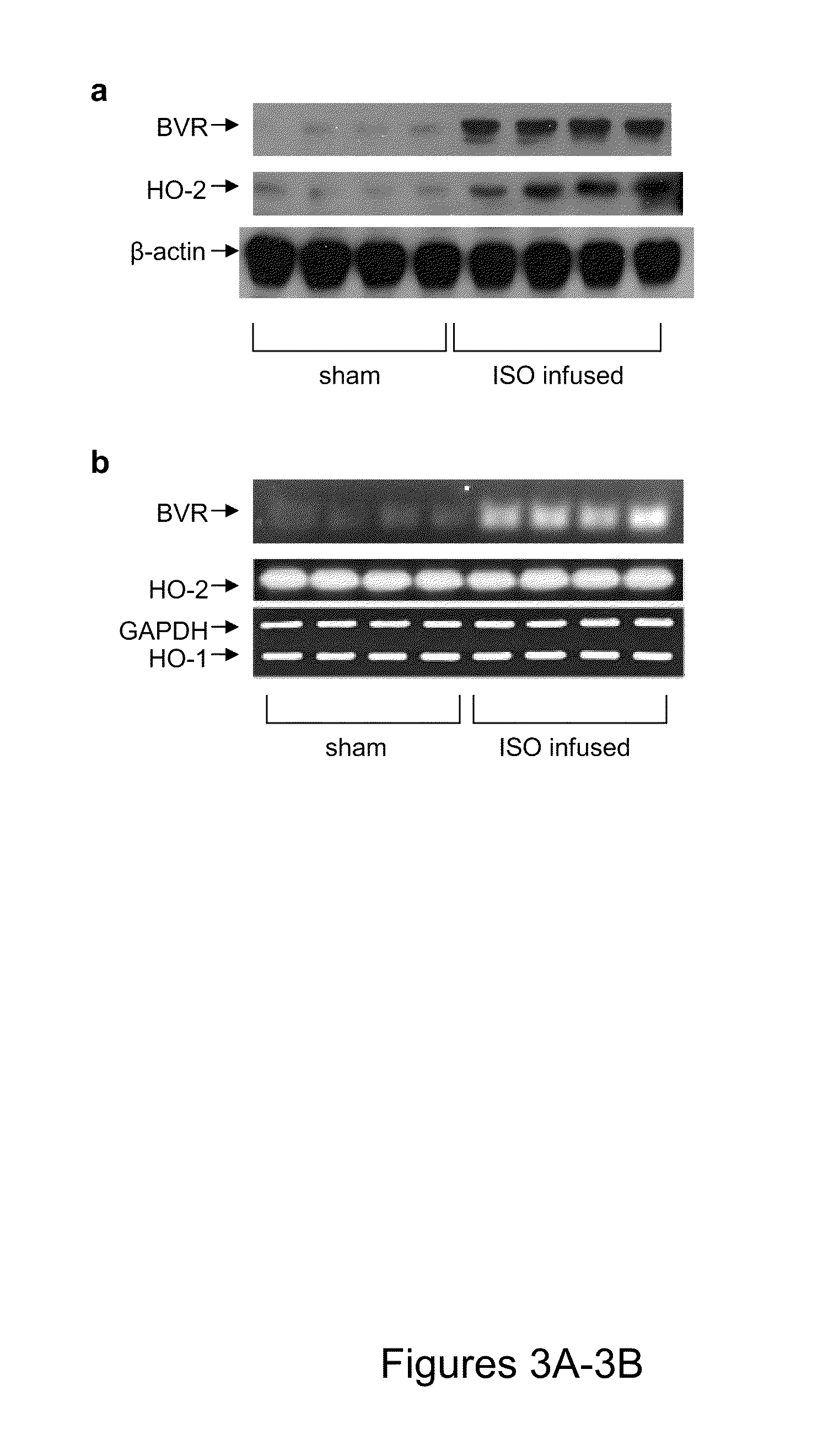
Use of biliverdin reductase (BVR) and bvr peptide fragments to treat coronary disorders
InactiveUS20100303790A1Facilitate HO- mediated cardiac cell protectionInhibit progressOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellCoronary artery disease
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treating coronary disorders and preventing cardiac cell death that involve the use of biliverdin reductase (“BVR”) or BVR peptides to stabilize the expression and activity of intracellular HO-2 in cardiac cells. The present invention also relates to methods and compositions for inducing cancer cell death in a patient having cancer that involve the use of inhibitory BVR peptides to destabilize intracellular HO-2 expression and activity, thereby augmenting cell death.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com