Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Cardiac fibroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
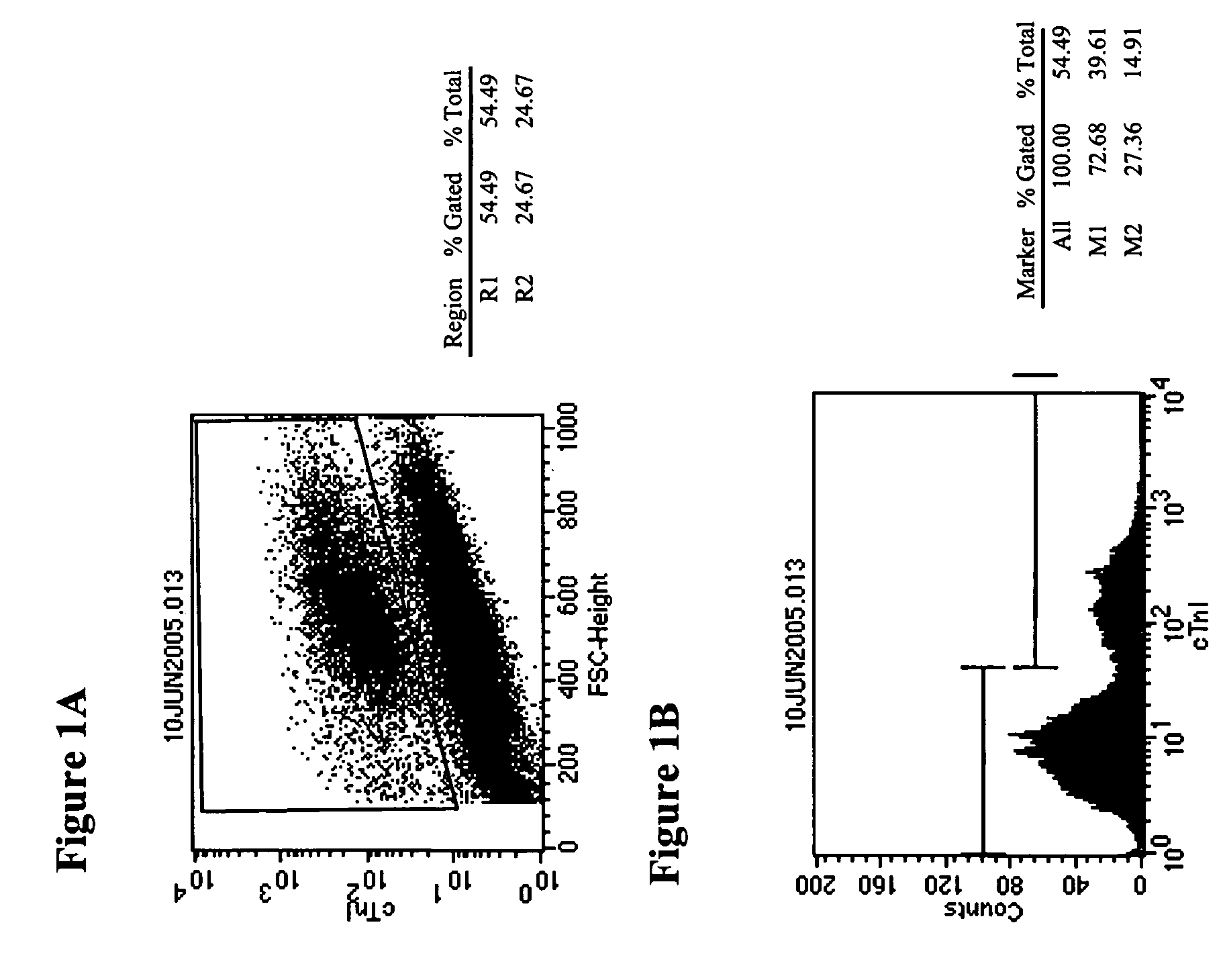
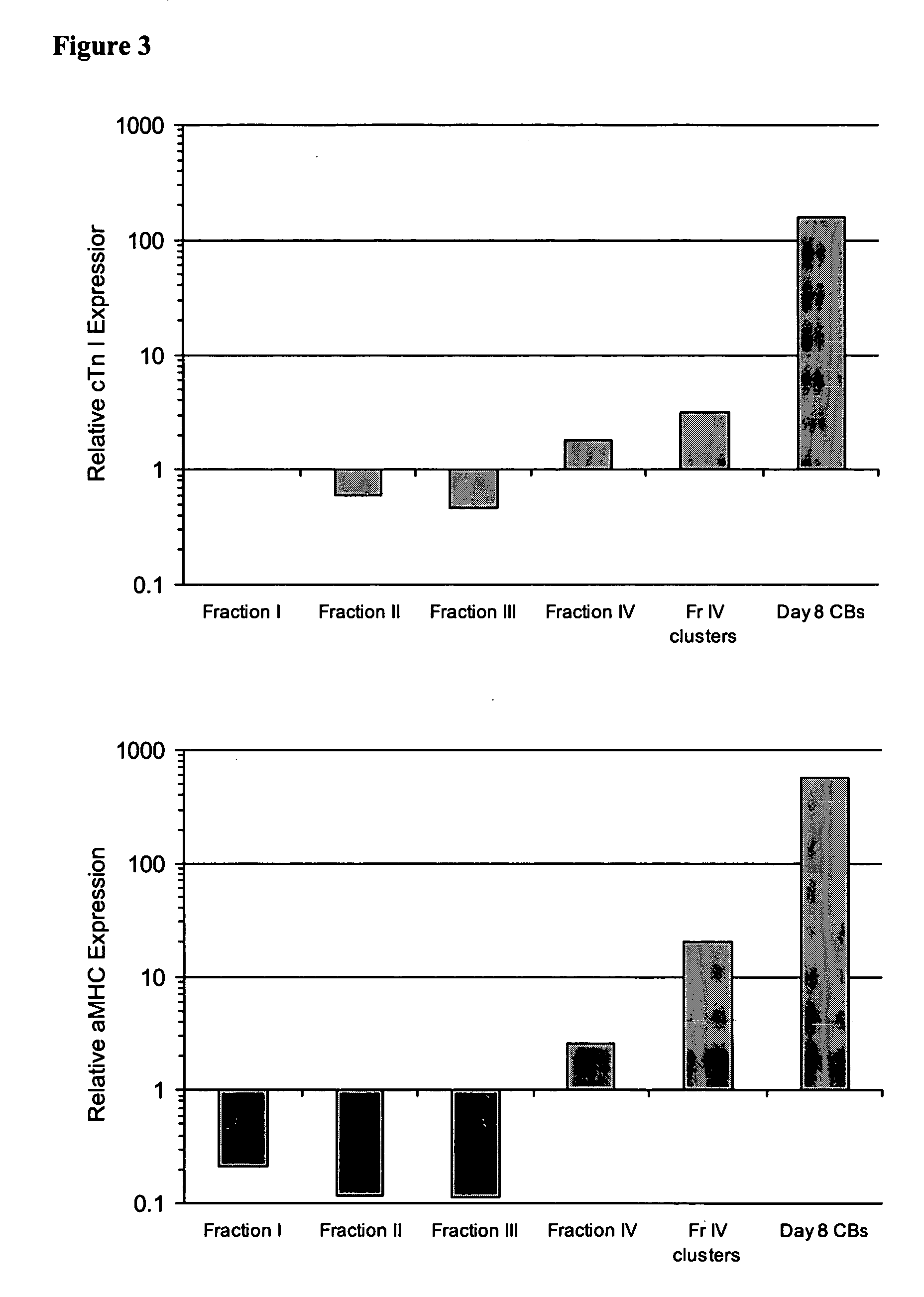
In an adult homeostatic heart, fibroblasts are found in the cardiac skeleton and within the myocardial interstitium (see Fig. 1). The cardiac skeleton is a connective tissue structure that forms the valvular components of the heart and also connects them to the septa.
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Adult Human Cardiac-Derived Progenitor Cells
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that cardiac progenitor cells are present in and can be isolated from adult human heart. Accordingly, a cell of the present invention comprises a human adult cardiac-derived progenitor cell capable of differentiating into a cardiac myocyte where said cell is isolated according to the expression of specific biomarkers, identified elsewhere herein. The present invention also includes methods of use of an adult cardiac-derived progenitor cell in the treatment of heart disease.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
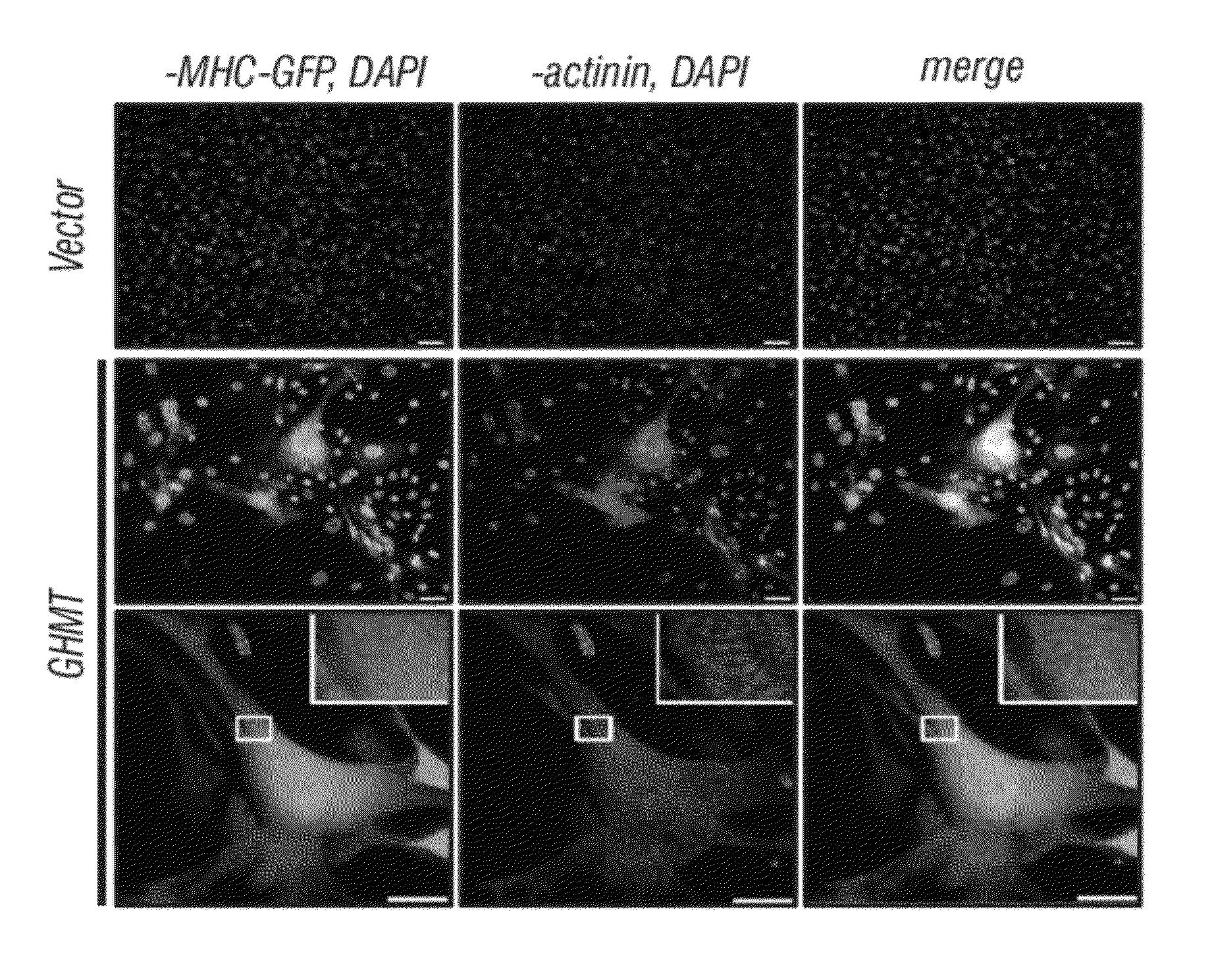
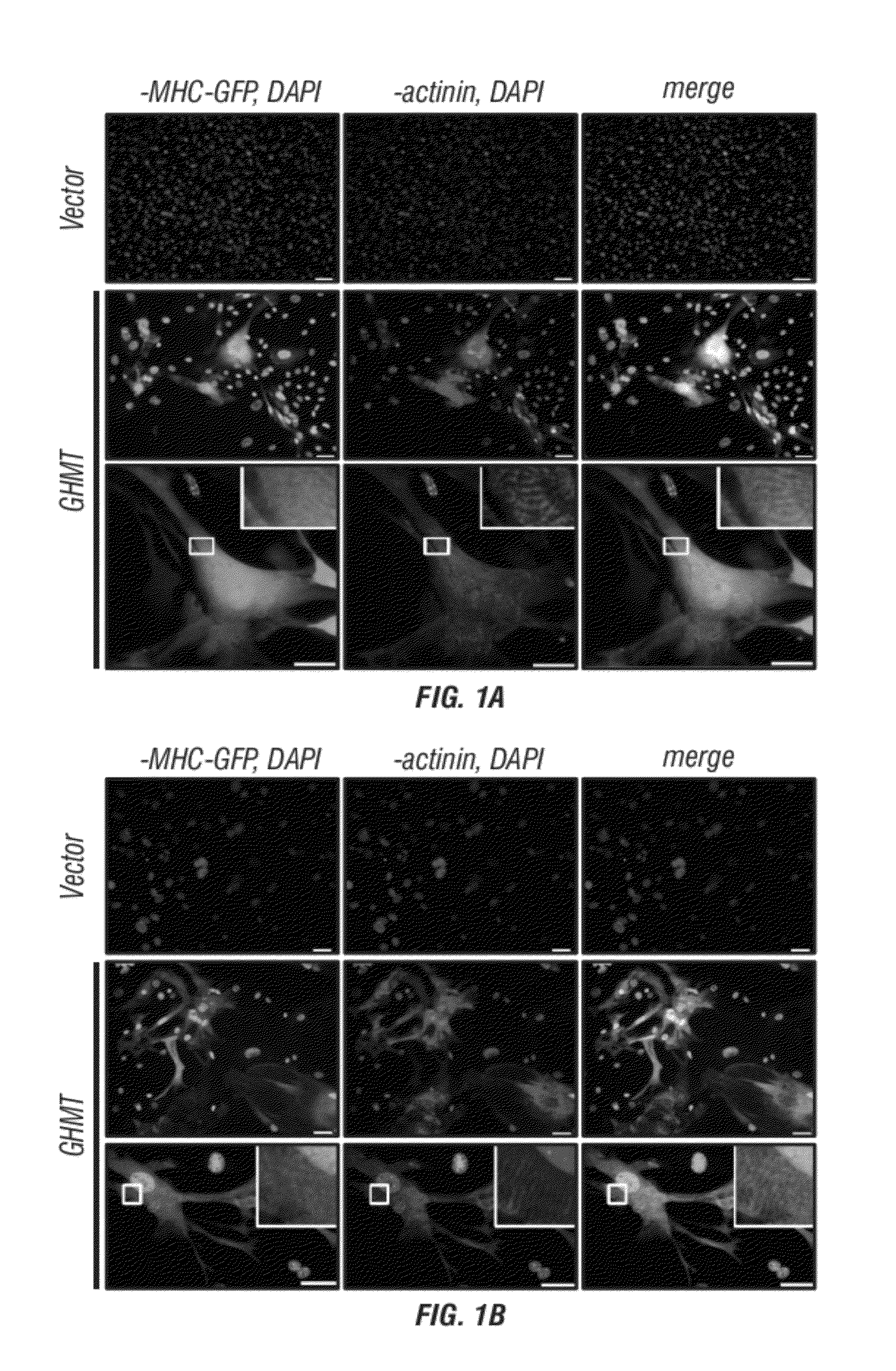
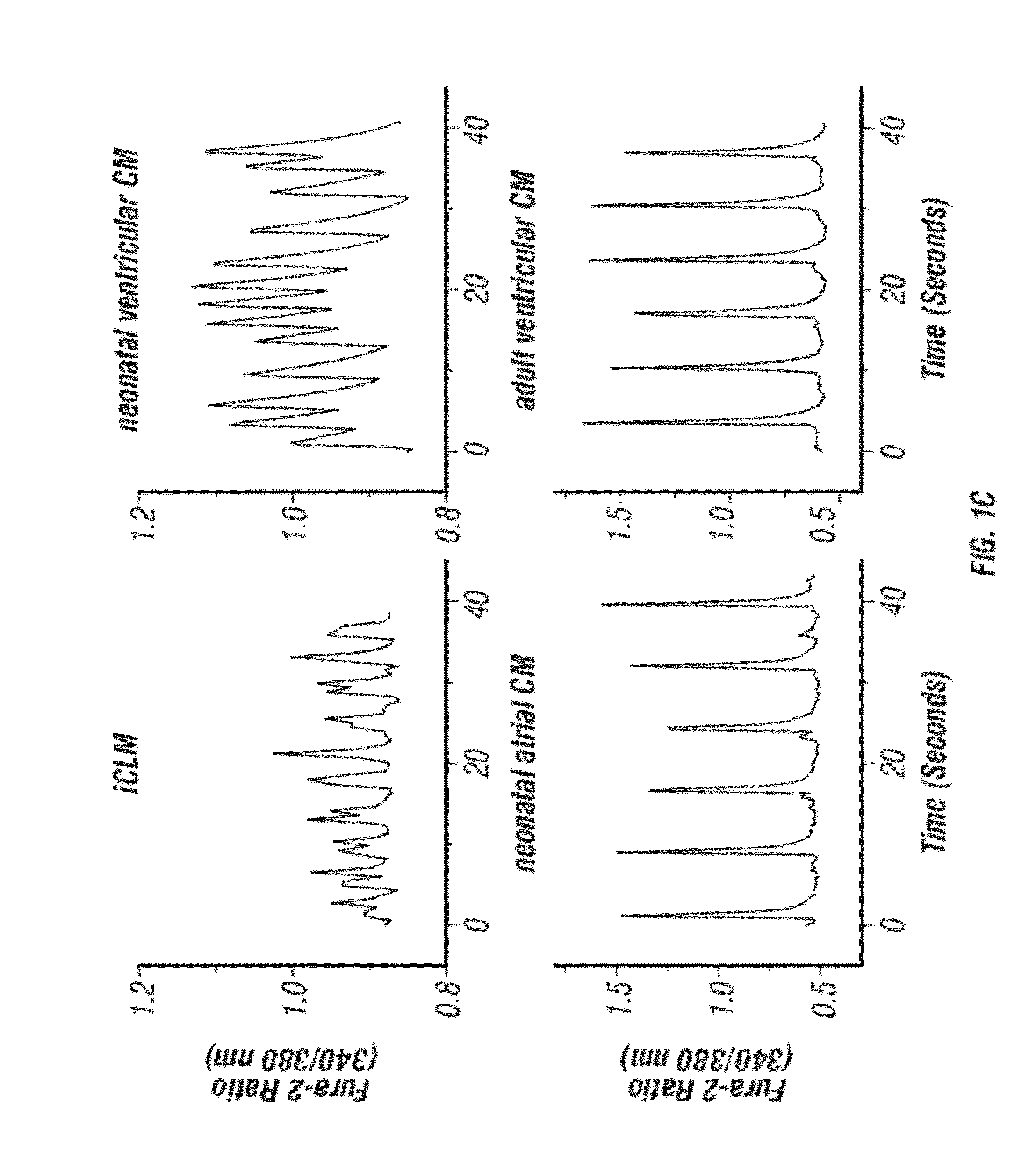
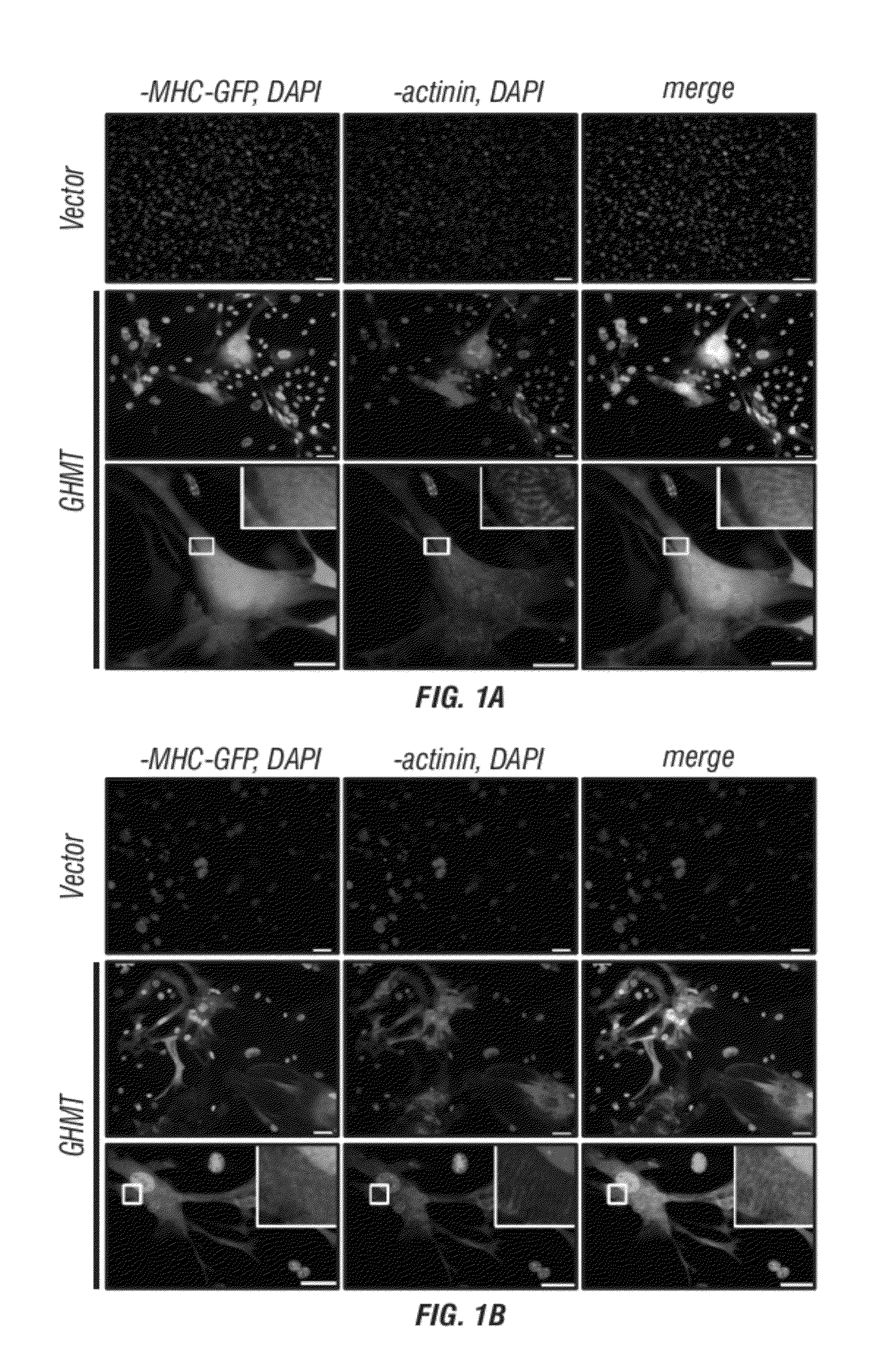
Cardiomyocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients and methods of use thereof
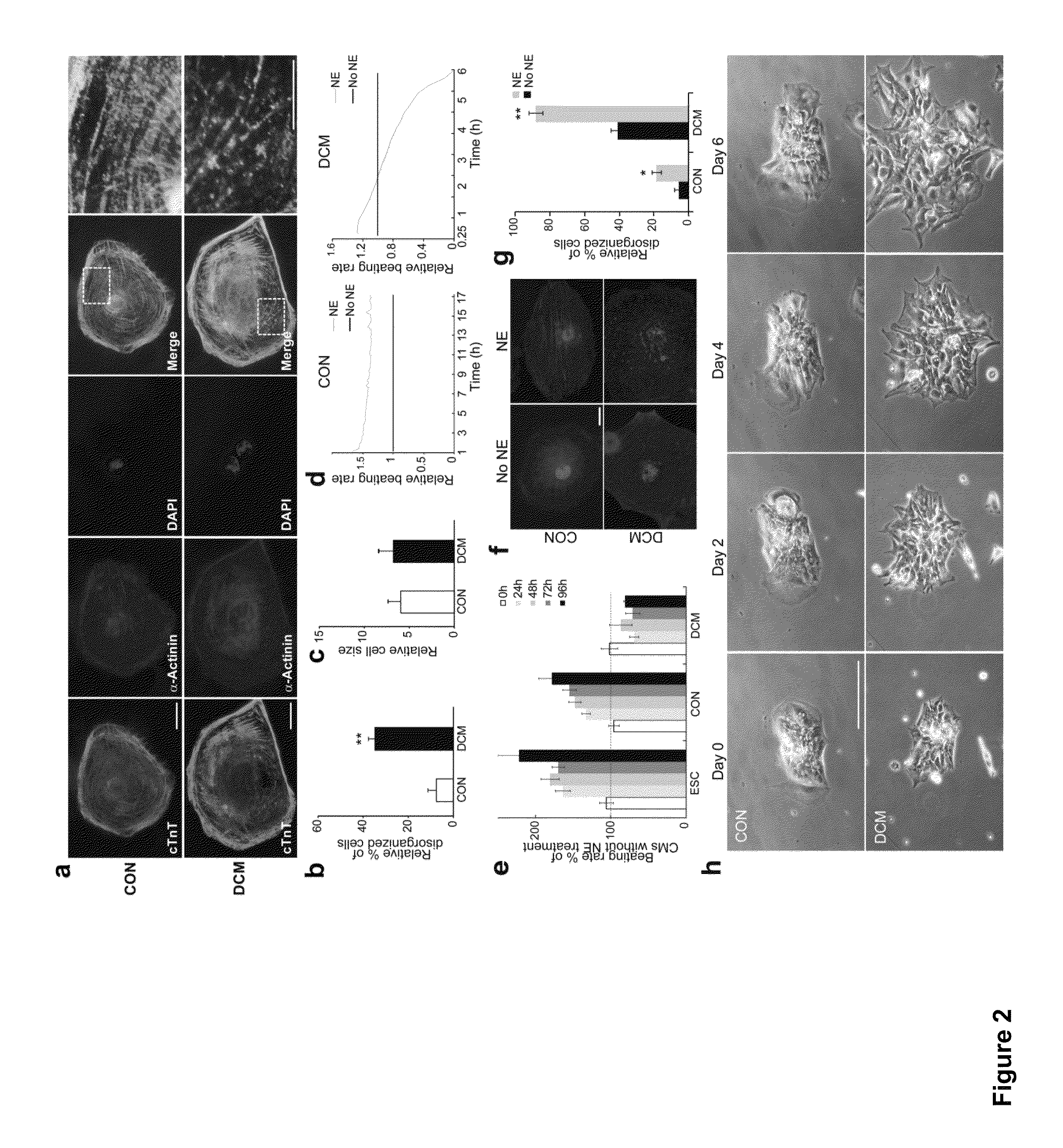
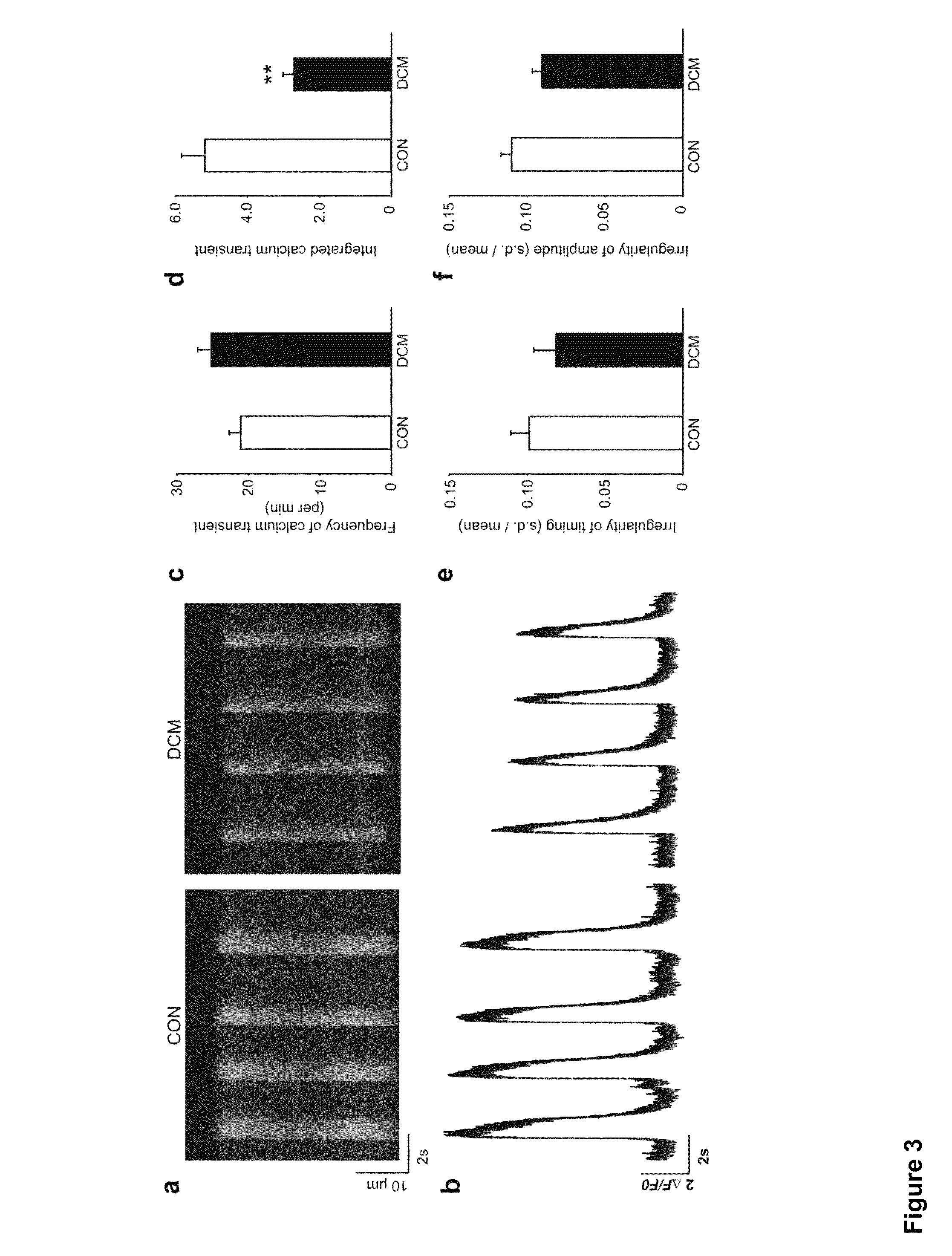
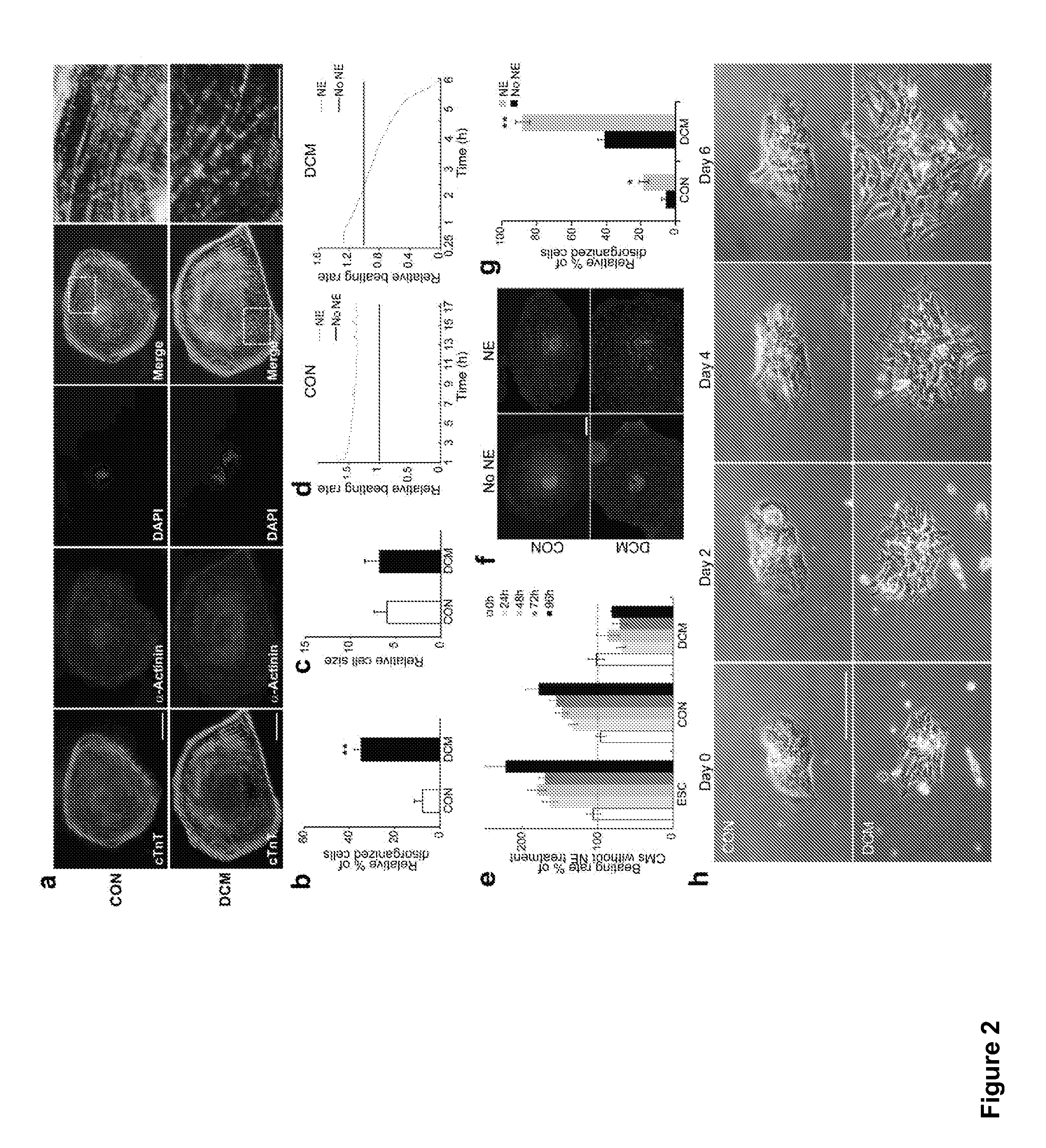
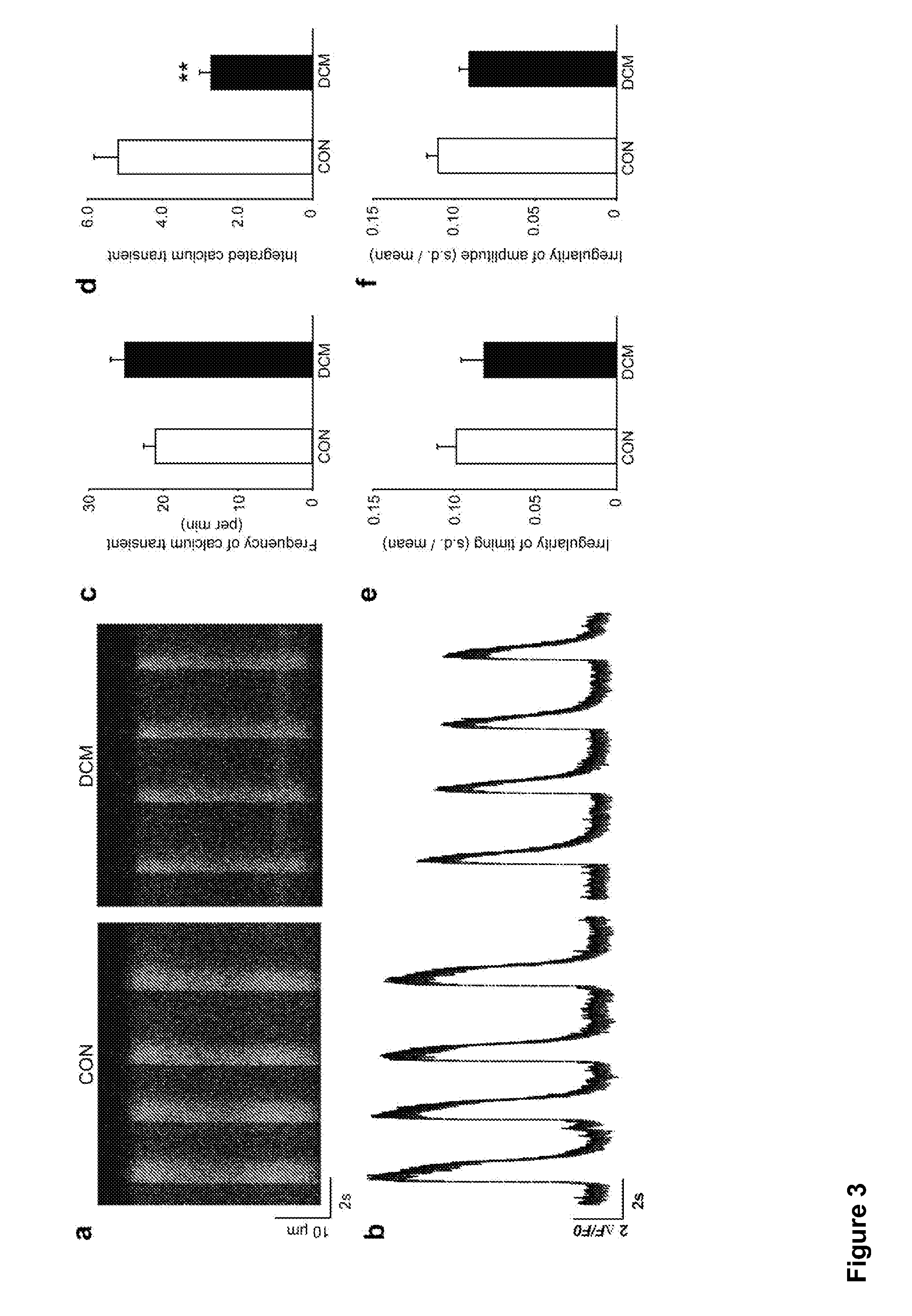
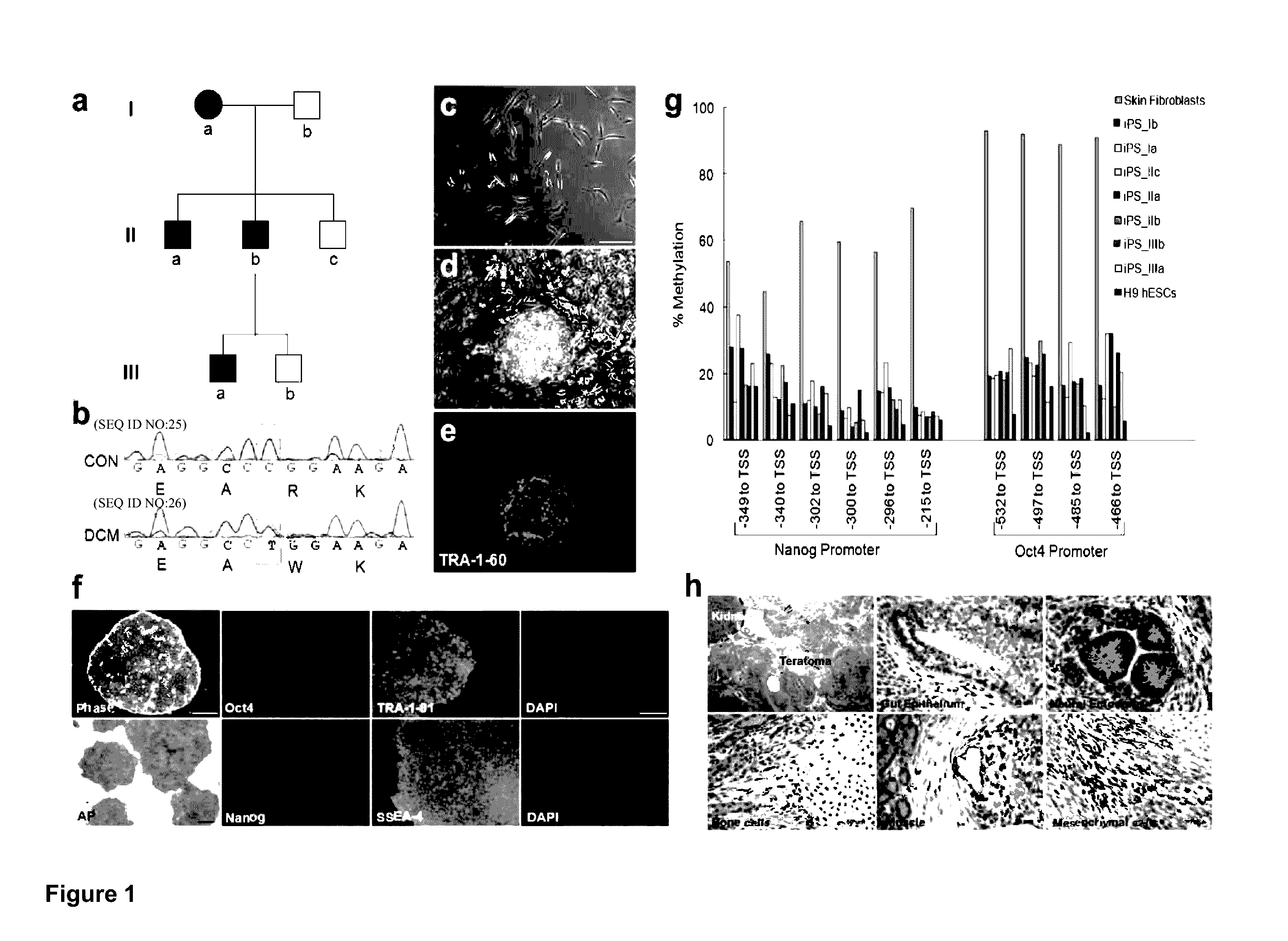
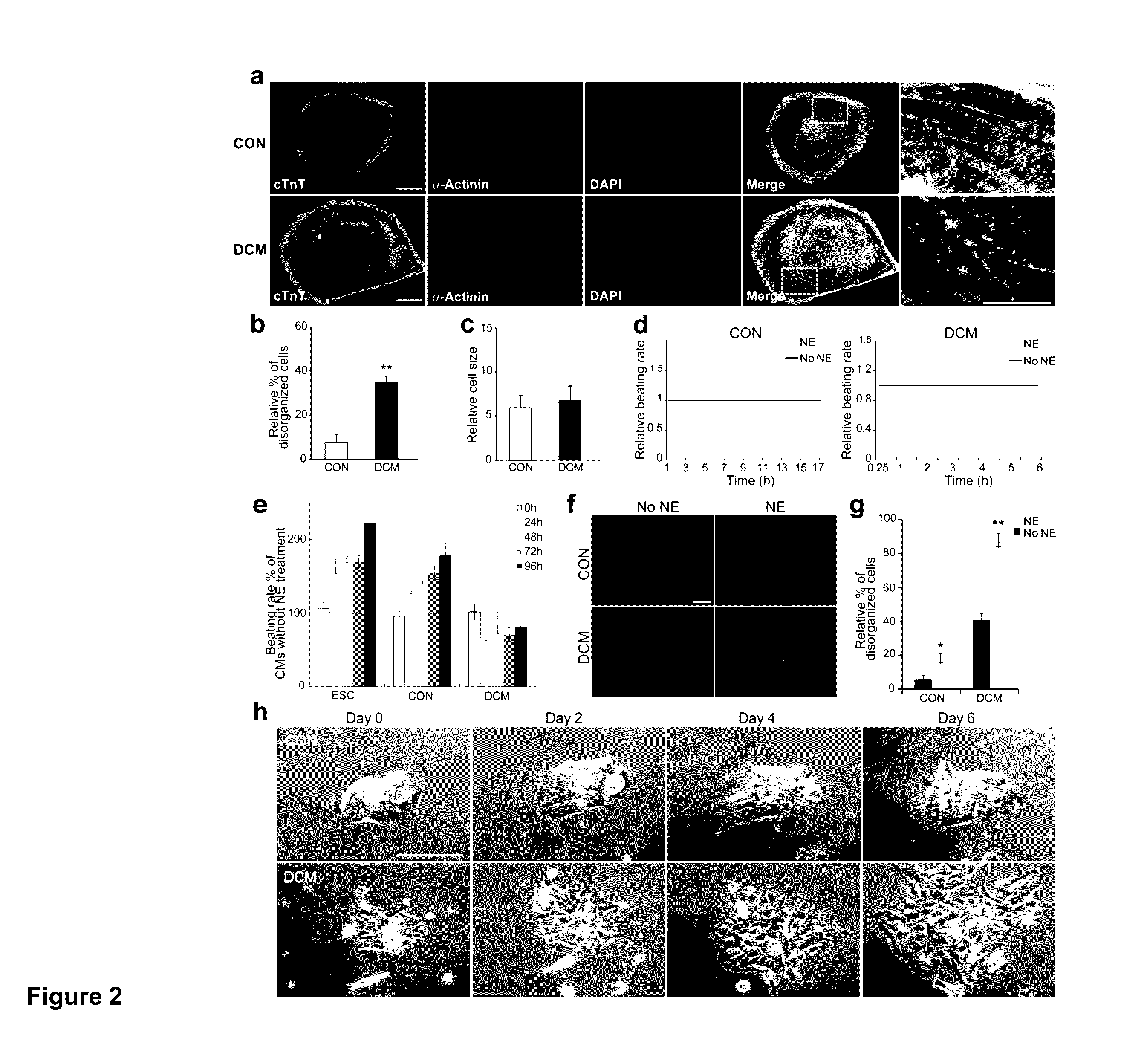
ActiveUS20130029866A1Abnormal sarcomeric α-actinin distributionReduce the probability of jumpingLibrary screeningDrug screeningPluripotential stem cellHuman body
Human somatic cells obtained from individuals with a genetic heart condition are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), and differentiated into cardiomyocytes for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cardiomyocytes From Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells From Patients and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20170058263A1Abnormal sarcomeric α-actinin distributionReduce the probability of jumpingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsSomatic cellHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Human somatic cells obtained from individuals with a genetic heart condition are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), and differentiated into cardiomyocytes for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
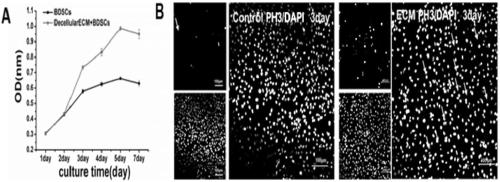
3-dimensional cardiac fibroblast derived extracellular matrix
ActiveUS20130059006A1Reduce deliveryFlexible movementPowder deliveryBiocideCell-Extracellular MatrixCardiac muscle
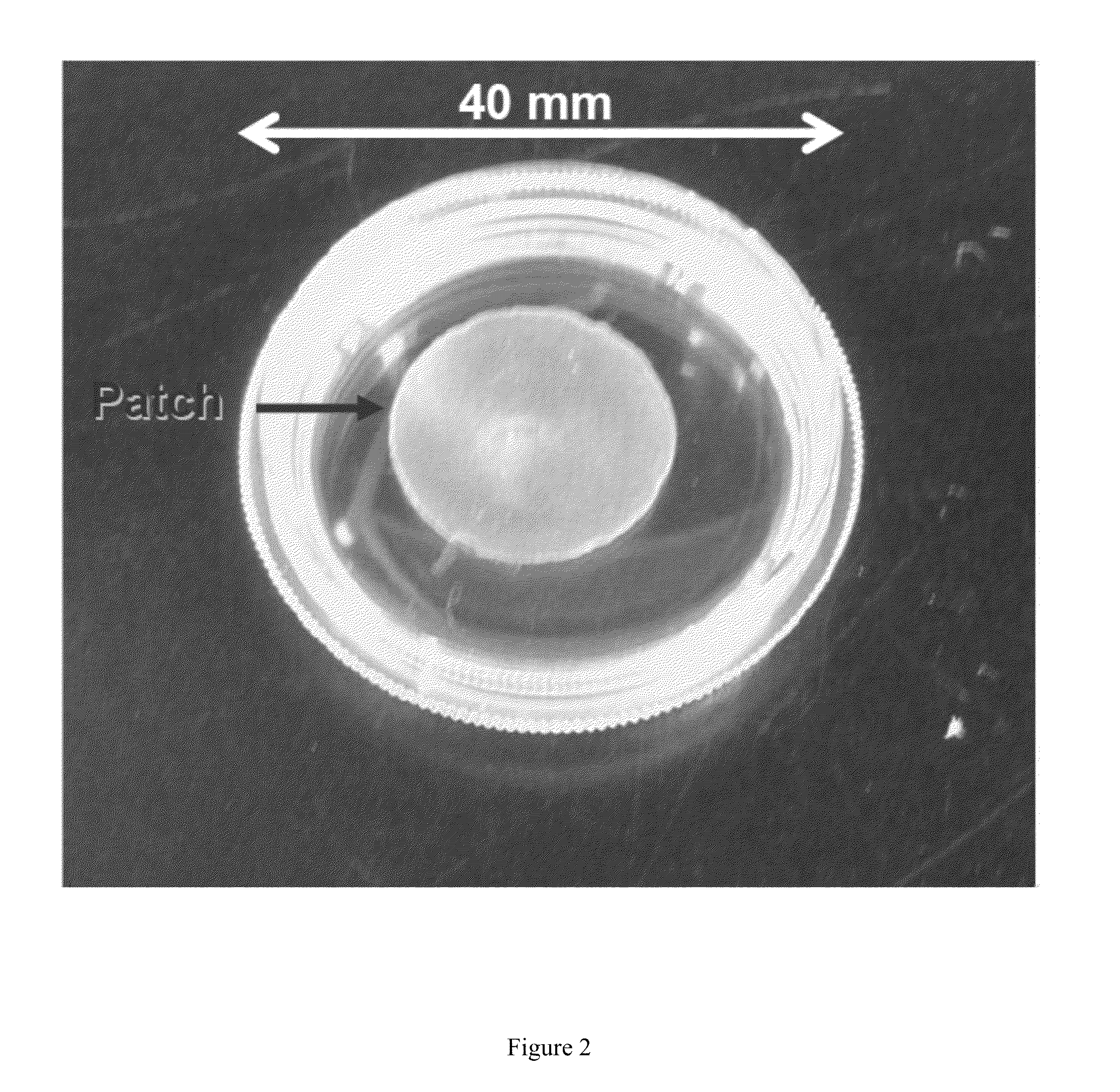
A bioscaffold made from an isolated cardiac fibroblast-derived 3-dimensional extracellular matrix (ECM) is disclosed. The bioscaffold can be used as an epicardial patch for the delivery of therapeutic cells into myocardial tissue. Methods of making the 3-dimensional extracellular matrix using cultured cardiac fibroblasts are also disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cardiac fibroblast-derived extracellular matrix and injectable formulations thereof for treatment of ischemic disease or injury
InactiveUS20160354447A1Effective treatmentReduce injuriesAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseExtremity injury
Compositions and methods using an engineered cardiac fibroblast-derived 3-dimensional extracellular matrix (ECM) are disclosed. The ECM includes the structural proteins fibronectin, collagen type I, collagen type III, and elastin, and from 60% to 90% of the structural proteins present in the engineered extracellular matrix are fibronectin. The compositions, which can be used to treat cardiac disease or ischemic disease or injury, are injectable compositions, where the ECM is diced into small fragments or lyophilized into a powder. The disclosed methods include a method of treating ischemic disease or injury by contacting a cell free patch made from the ECM with the injured tissue, without the concomitant delivery of therapeutic cells, and a method of treating ischemic limb injury by contacting a patch, either by itself or seeded with therapeutic cells, with the injured limb tissue.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
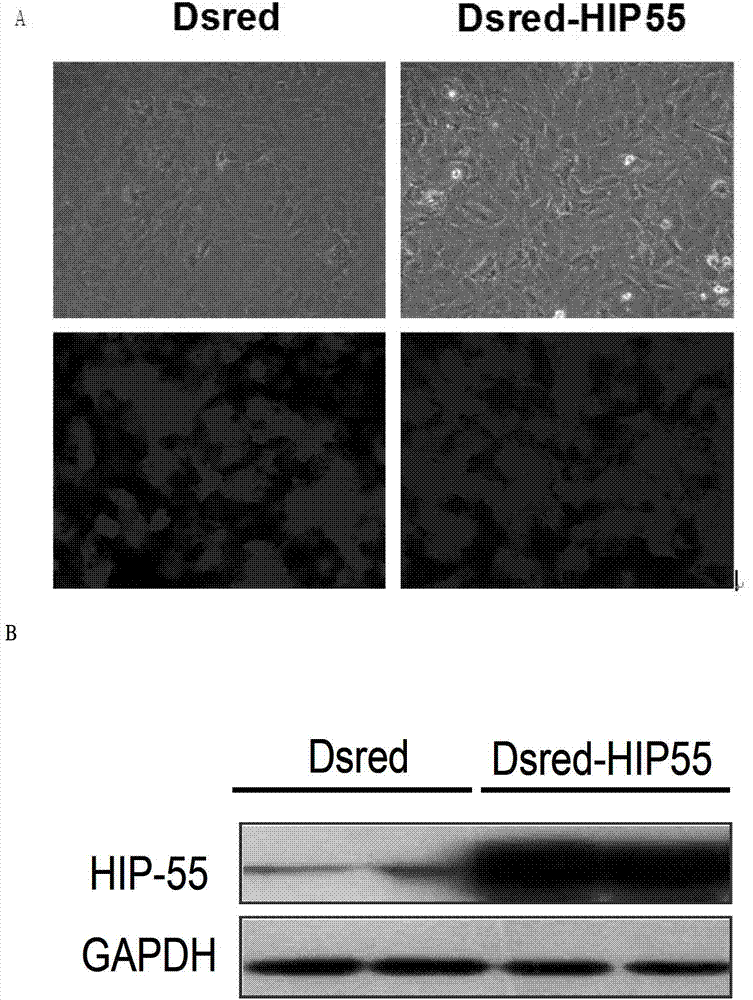
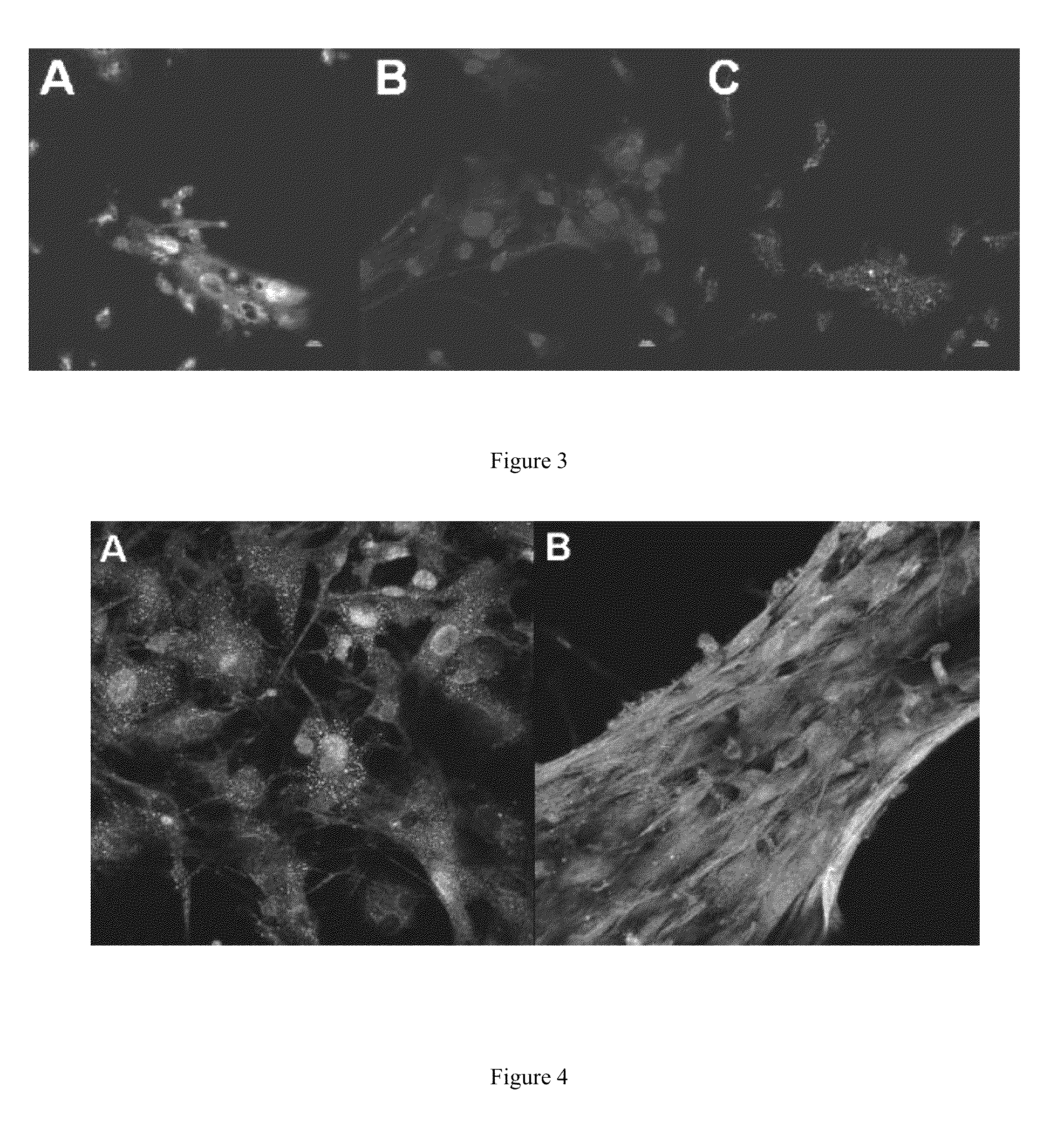
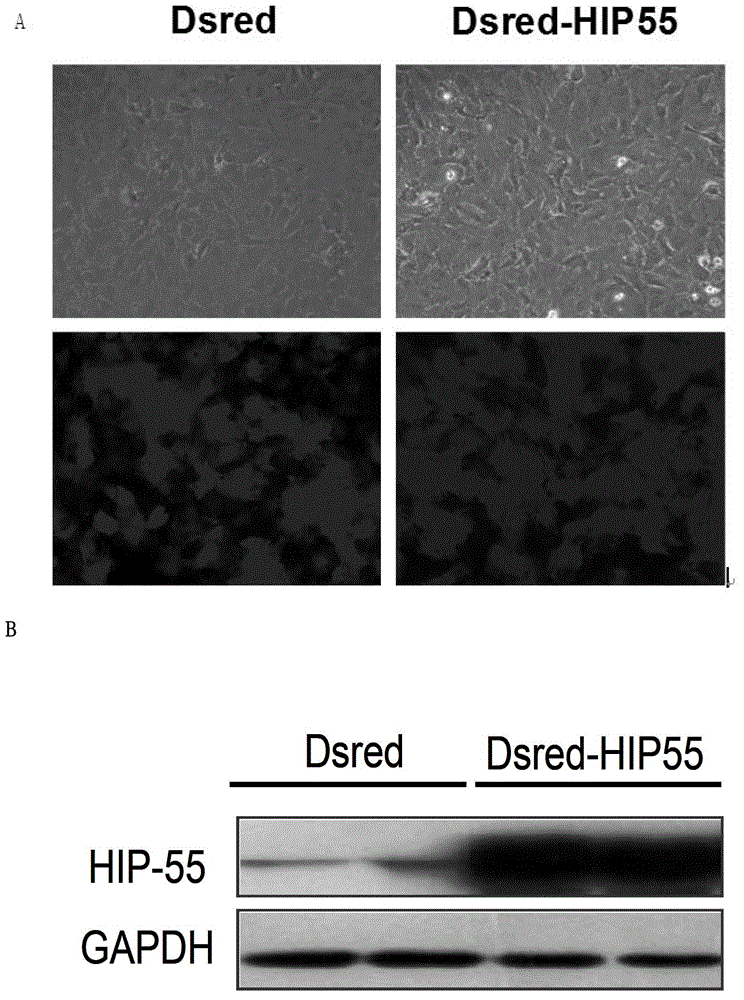
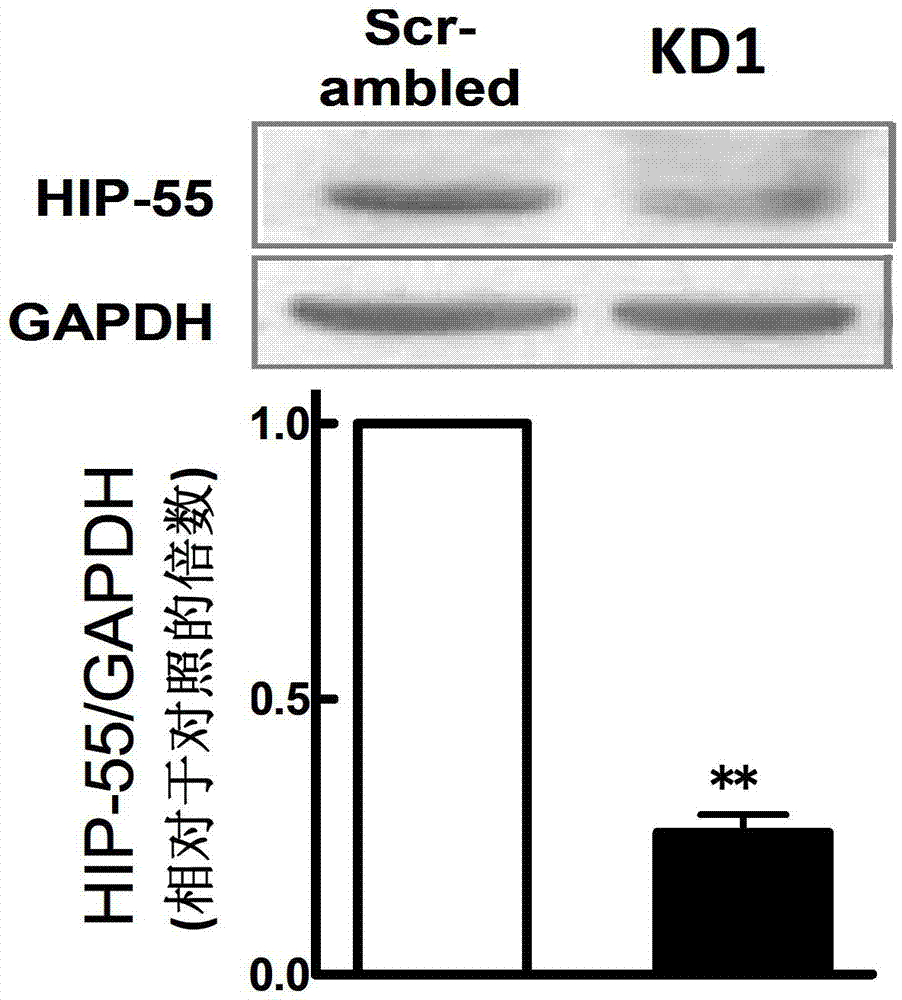
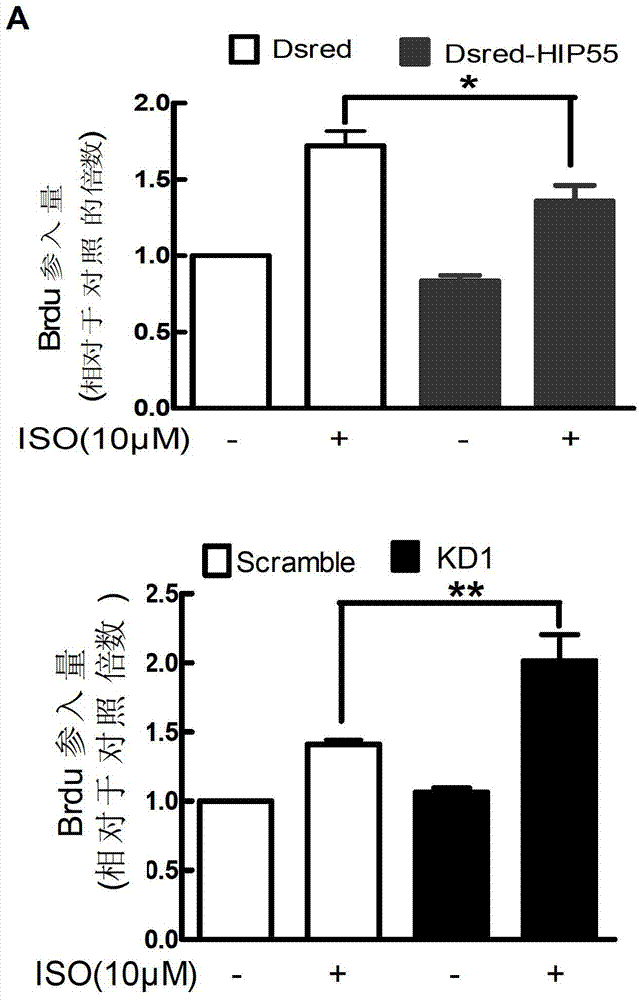
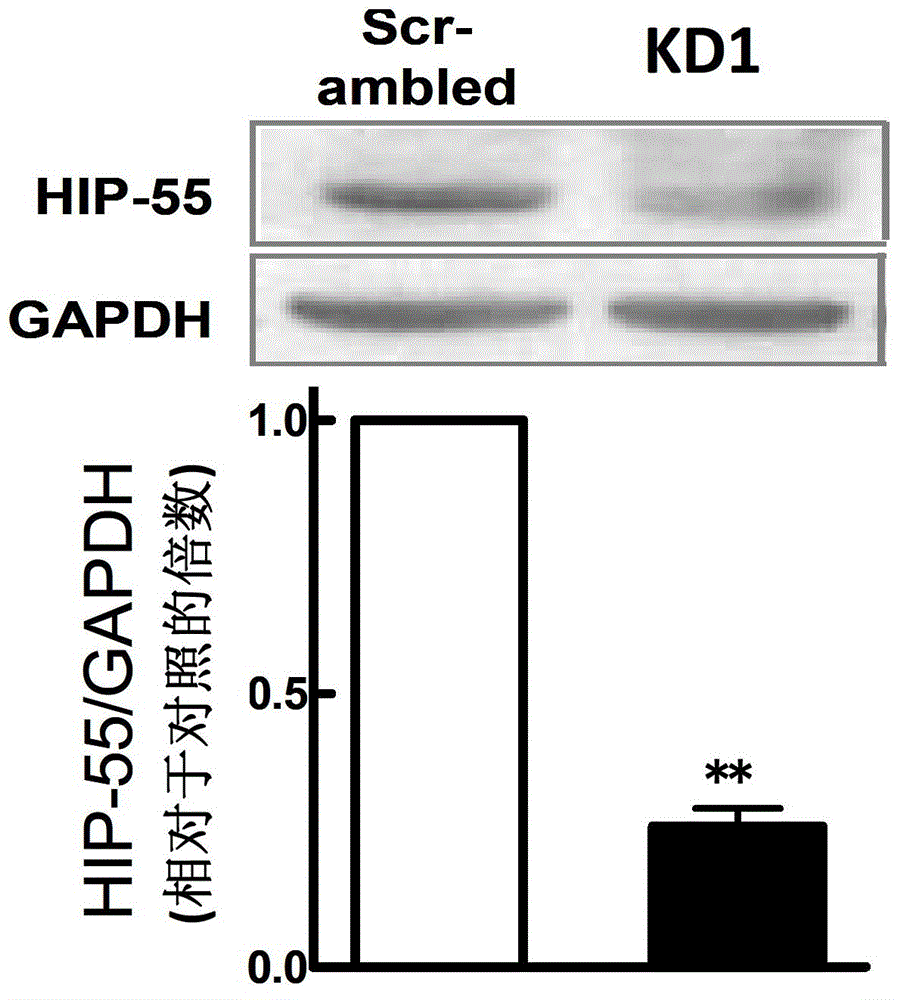
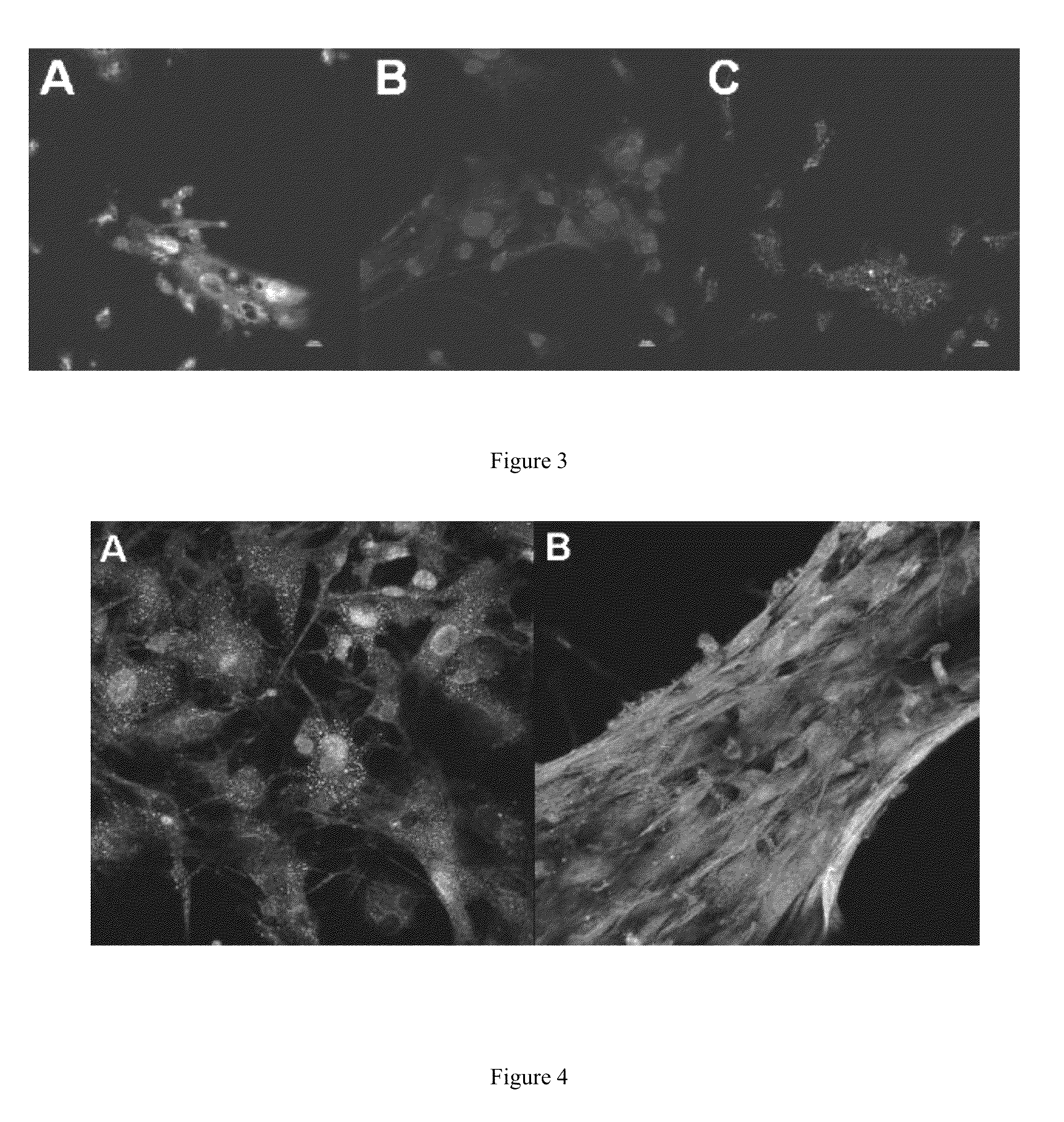
Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa)
InactiveCN103110932APrevent proliferationPromote proliferationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh level expressionBiological activation
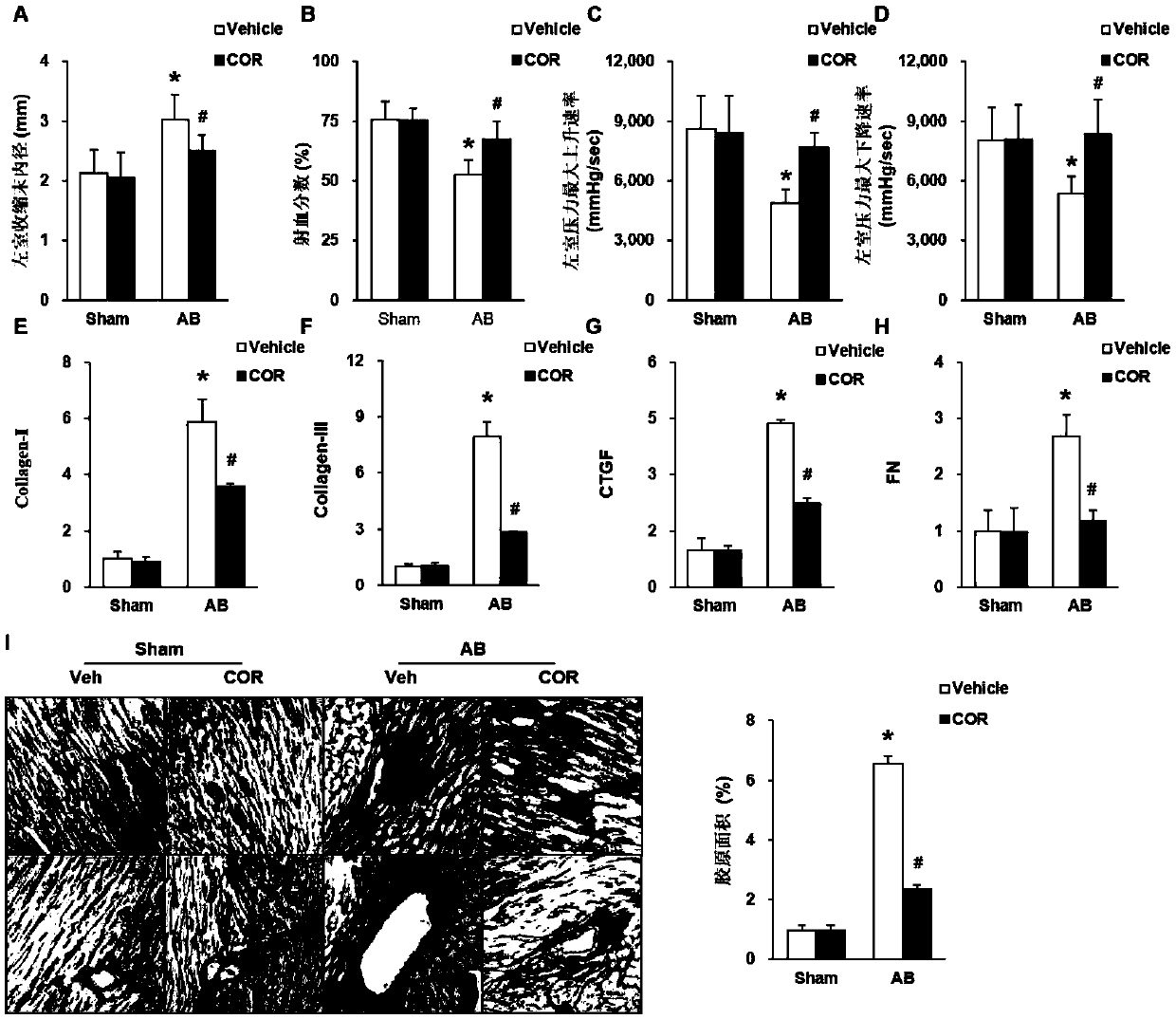
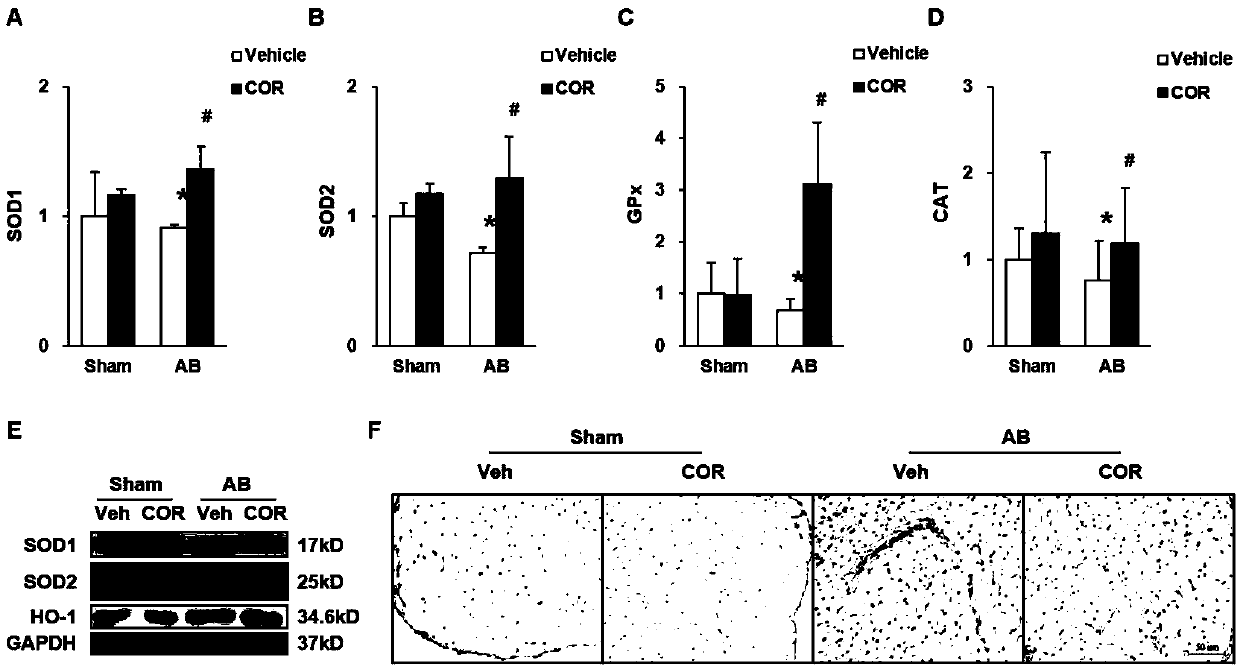
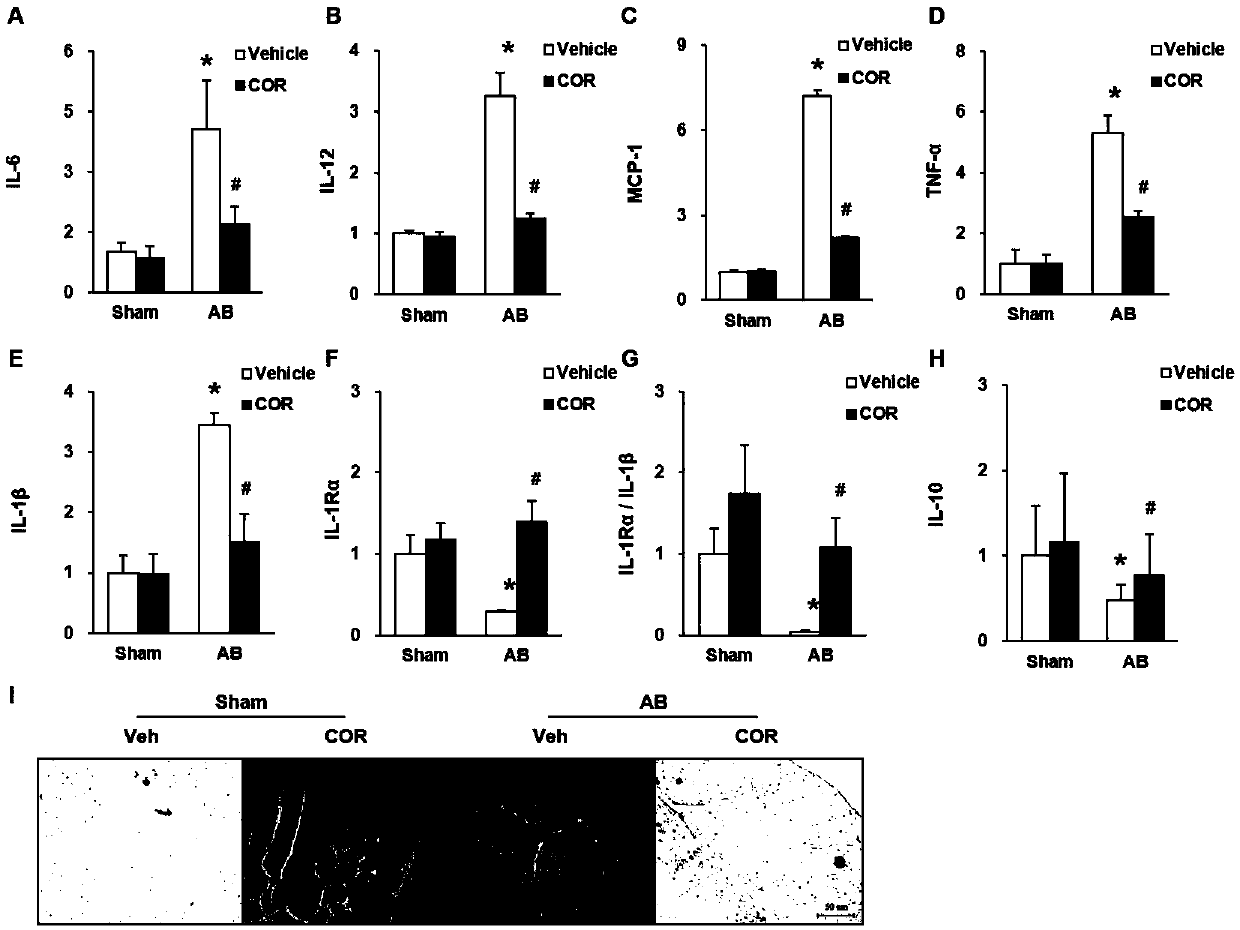
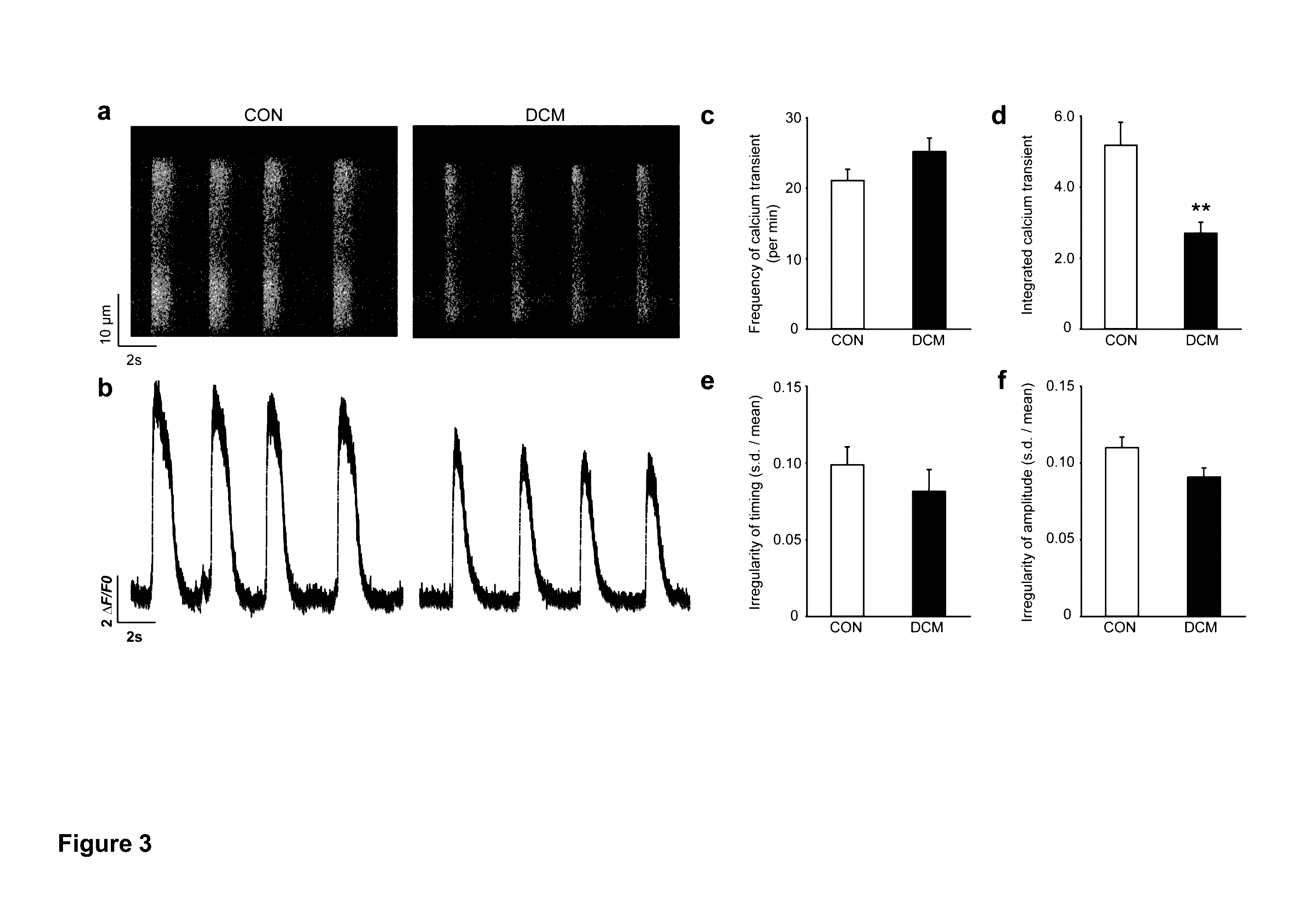
The invention discloses a novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa). The invention provides an application of an HIP-55 protein, an HIP-55 protein coding gene or a recombinant vector containing the HIP-55 protein coding gene or adenovirus containing the HIP-55 protein coding gene to preparation of products with the function (1) or (2): (1) suppression of cardiac fibroblasts proliferation; and (2) suppression of P38MAPK (P38 mitogen activated proteinkinase) activity; and an amino acid sequence of the HIP-55 protein is a sequence 2 in a sequence table. Experiments prove that the HIP-55 has expressions in different organs of a rat, especially has a high-level expression in the heart and further has an overexpression in cardiac fibroblasts of a small rat under the induction of ISO (isoprenaline), and therefore the HIP-55 can be used for remarkably suppressing the cardiac fibroblast proliferation; and the HIP-55 can be used for suppressing P38MAPK activation induced by ISO and the kinase activity in the overexpression of HIP-55 cardiac fibroblasts.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Differentiation of primate pluripotent stem cells to cardiomyocyte-lineage cells
ActiveUS9062289B2Culture processArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
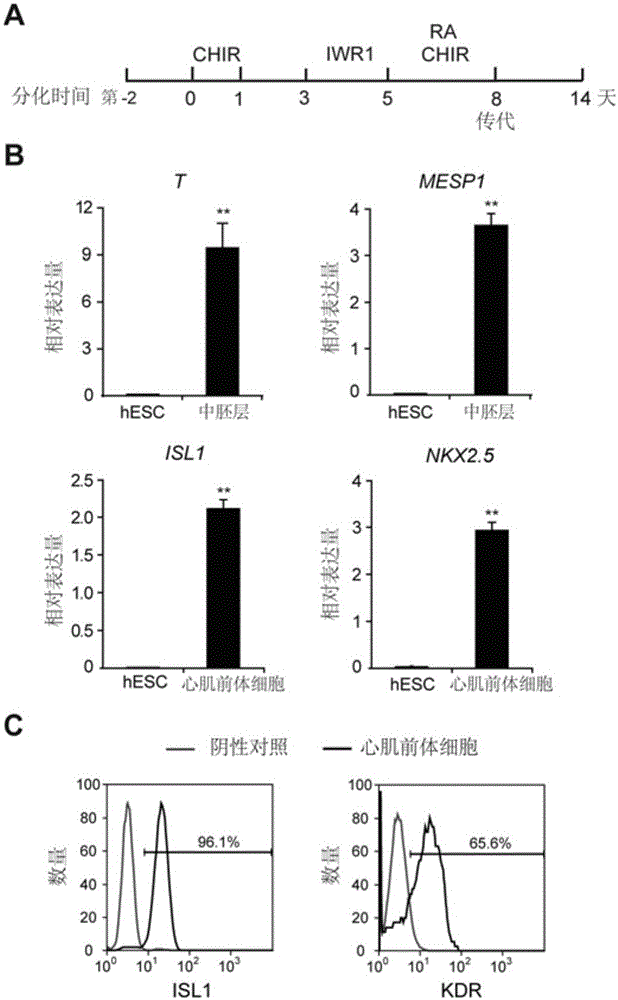
The present application describes the new methods for the differentiation of primate pluripotent stem cells into cardiomyocyte-lineage cells. The methods utilize sequential culturing of the primate pluripotent stem cells in certain growth factors to produce cardiomyocyte-lineage cells. In certain embodiments of the invention, the population of cells produced by the sequential culturing is further enriched for cardiomyocyte-lineage cells so as to produce a higher percentage of those cells.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
RNA(Ribonucleic Acid)and application thereof in diseases of cardiovascular system
InactiveCN103114087APrevent proliferationPromote proliferationGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesDiseaseCardiac fibrosis
The invention discloses RNA and application of RNA in diseases of a cardiovascular system. According to RNA, the nucleotide sequence of RNA is a sequence 3 in a sequence table. The invention further provides a gene,encoding RNA. The nucleotide sequence of the gene of RNA is a sequence 4 in the sequence table. The experiment of the invention shows that RNA and the application of RNA in the diseases of the cardiovascular system find that by an induction of isoproterenol (ISO), RNAi method Knock down IHP-55 is used in neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts to obviously promote proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts; ISO induced activation and kinase activity of P38MAPK can be enhanced in the Knock-down HIP-55 cardiac fibroblasts; and HIP-55 is a new protein which has a protective effect on cardiac fibrosis, and provides a new target for clinical diagnosis, treatment and new medicament development.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
3-dimensional cardiac fibroblast derived extracellular matrix
ActiveUS8802144B2Reduce deliveryFlexible movementBiocidePowder deliveryCell-Extracellular MatrixCardiac muscle
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for culturing adult mouse cardiac fibroblasts
PendingCN110358723AReduced Possibility of ContaminationSimplify the experimental processCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsFiberCervical dislocation
The invention discloses a method for culturing adult mouse cardiac fibroblasts. The method comprises the following steps: taking SPF grade 8-12 weeks-old mice, and sterilizing the material after cervical dislocation; taking out the heart of the mice and placing the mice in a culture dish containing pre-cooled calcium-free HBSS, extruding the residual blood in the heart, removing the heart atrium,left and right auricula, and pericardium, preserving the ventricle, transferring the material to a new culture dish containing the pre-cooled calcium-free HBSS, cutting the heart, transferring the material to a centrifuge tube, and after the cardiac tissue is precipitated, sucking the HBSS by a pipette; adding a collagenase digestion solution in the centrifuge tube for digestion, and then resuspending the material to obtain a cell suspension; spreading the material into a first culture dish and performing standing culture; resuspending the cells, discarding a supernatant by centrifugation, spreading the resuspended cells in the medium to a second culture dish, and adding the original first culture dish to the new medium. The culture method is simple and easy, has good stability, high repeatability and uniform morphology, and the obtained fibroblasts grow well.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of epicardial cells from stem cells
InactiveCN106635969ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsGerm layerAdventitial cell
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Method for inducing differentiation of multipotent stem cells into myocardial cells by biogenic amine and application
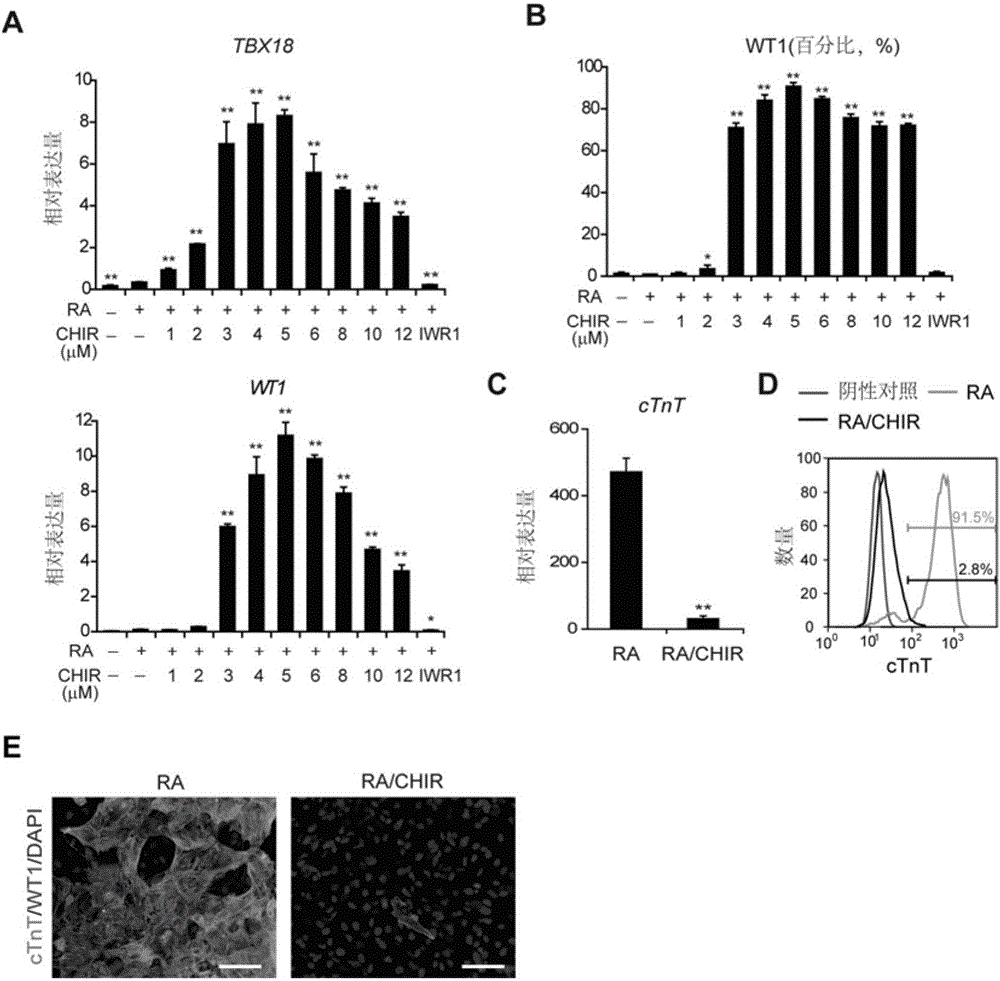
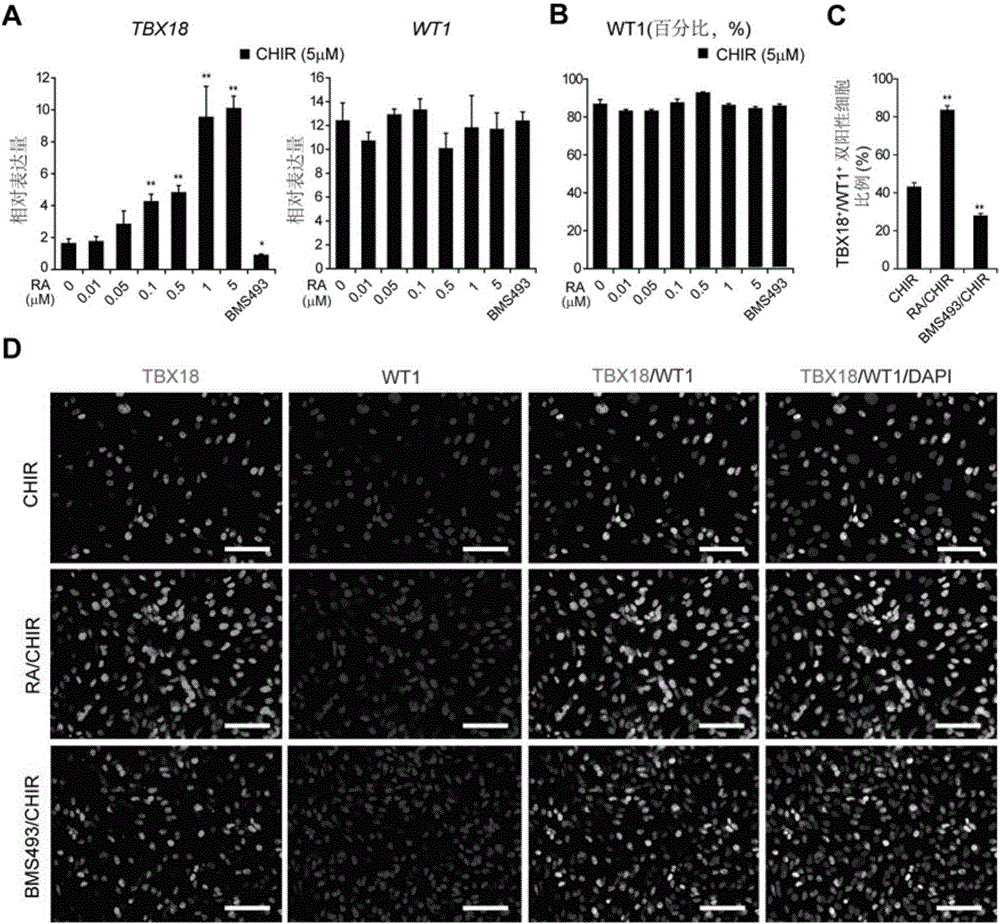
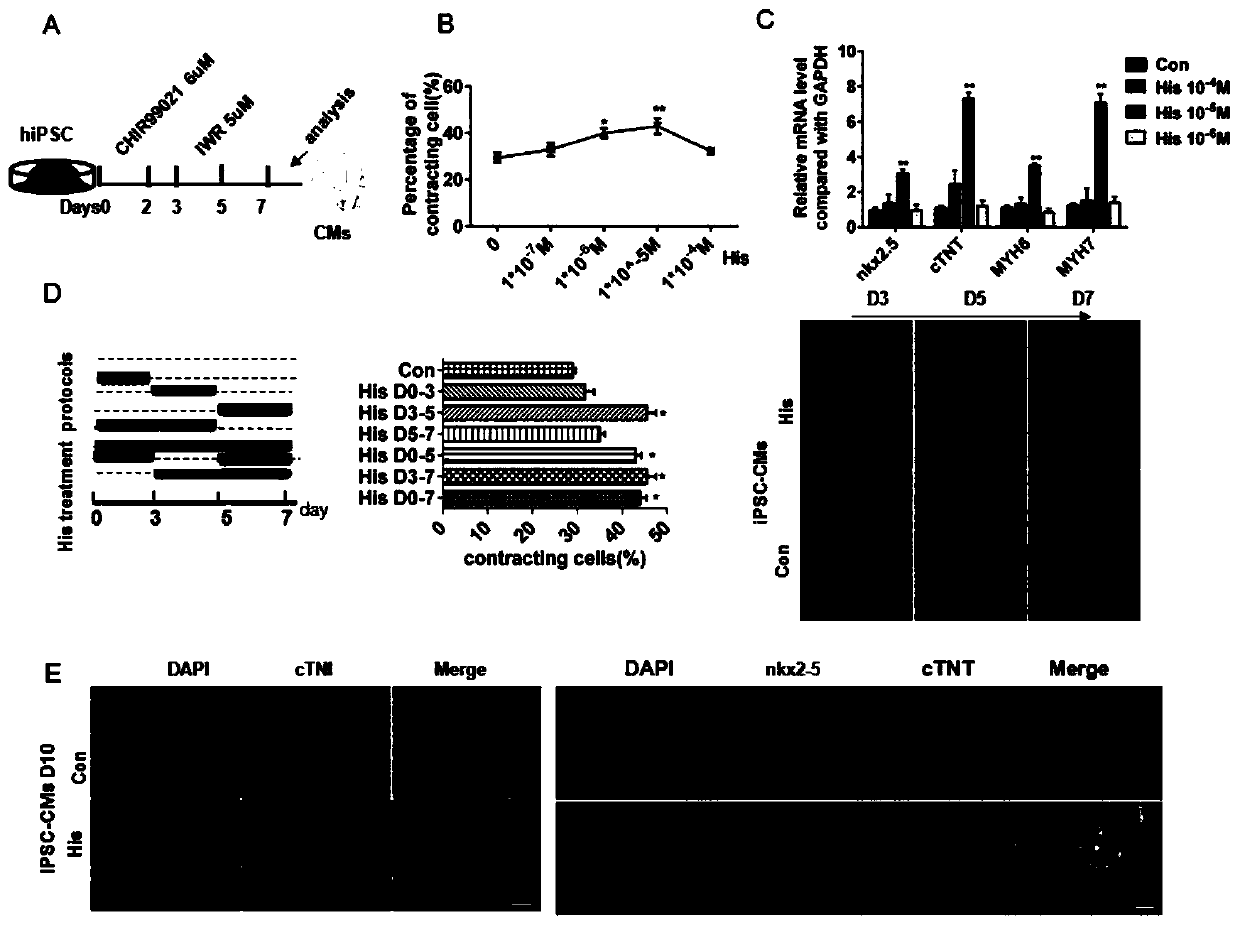
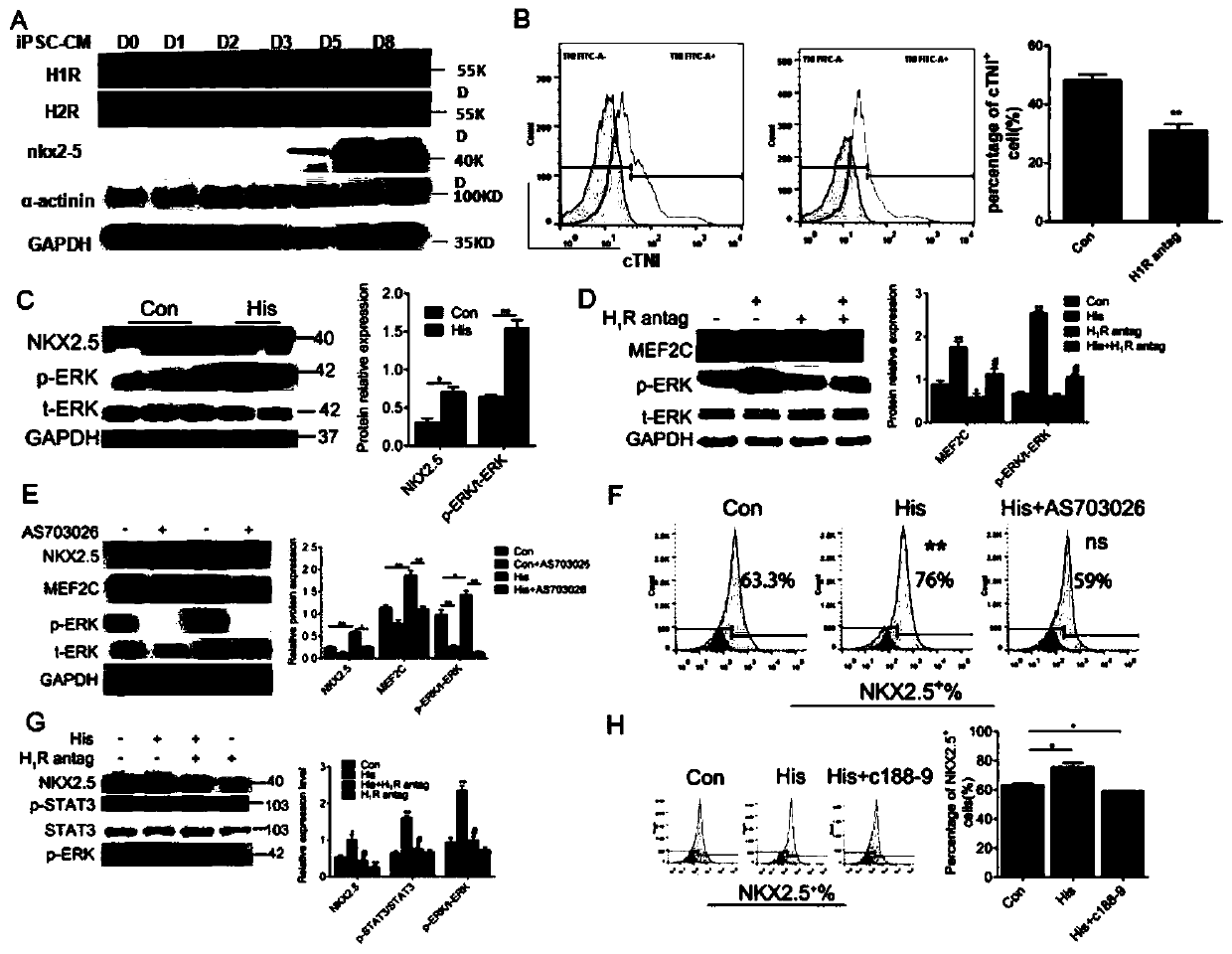
ActiveCN111187750AHigh differentiation maturityPromote differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHeart diseaseBiochemistry
The invention provides a method for promoting and inducing differentiation and maturation of multipotent stem cells into myocardial cells by using biogenic amine and application. According to the method, histamine is added into an in-vitro culture for inducing differentiation of the multipotent stem cells into the myocardial cells at a fixed time point so as to induce differentiation and maturation of the multipotent stem cells into the myocardial cells. The invention also provides a method for detecting the time that the histamine promotes ips to differentiate into the myocardial cells, and the concentration of the myocardial cells. The method is mature, simple to operate and environmentally friendly. The cells obtained by the method have characteristic cell surface markers and morphological markers of the myocardial cells, can spontaneously and periodically contract, and are suitable for various applications such as heart disease research, drug screening, cell treatment and the like.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
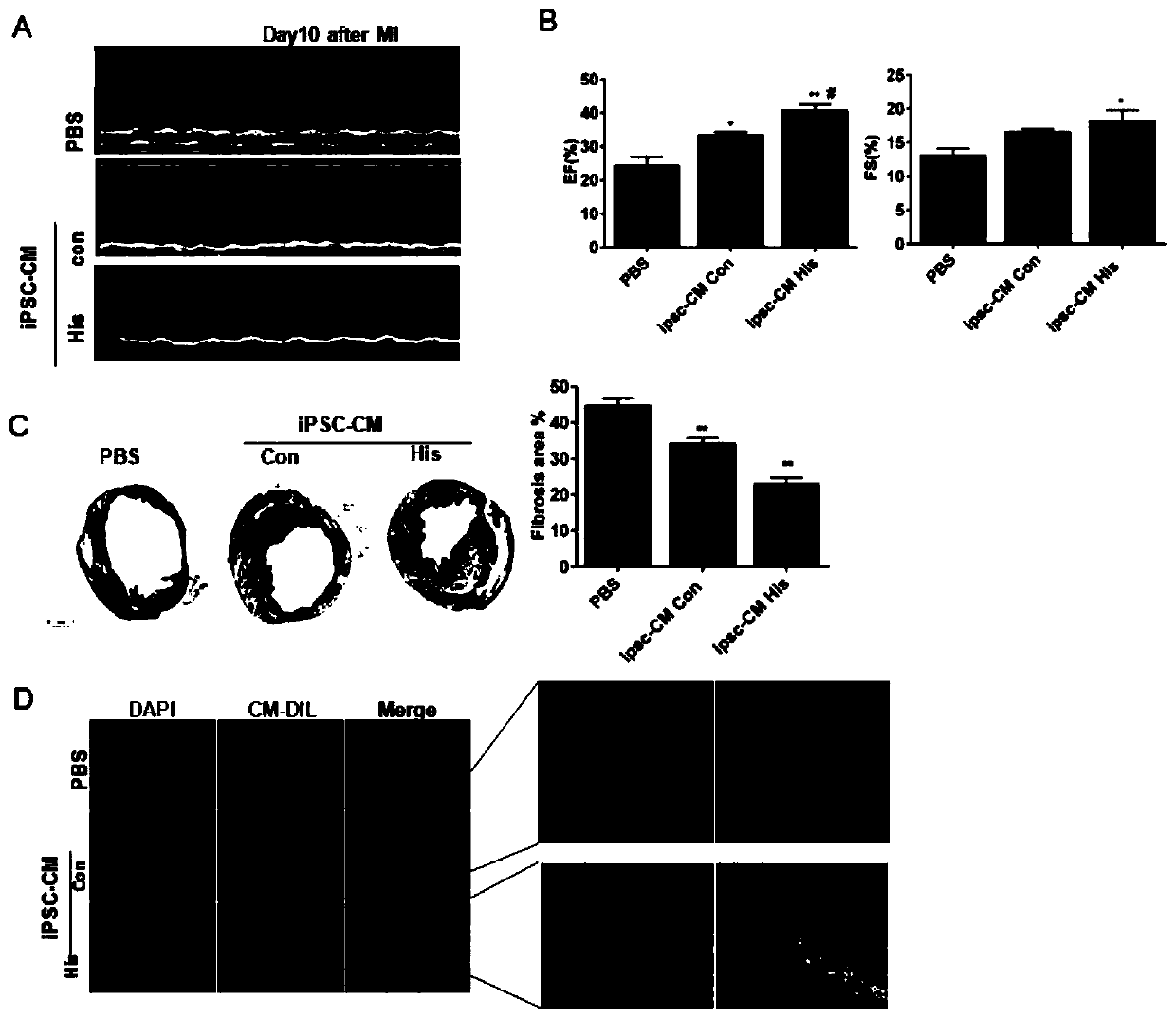
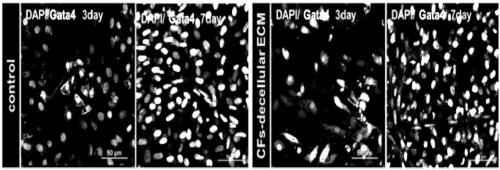
Cardiac Repair By Reprogramming of Cardiac Fibroblasts Into Cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20120213738A1Preventing delaying developmentAvoid delayBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGATA4Reprogramming
The present invention involves the use of transcription factors including Tbx5, Mef2C, Hand2, myocardin and Gata4 to reprogram cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, both in vitro and in vivo. Such methods find particular use in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction to prevent or limit scarring and to promote myocardial repair.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for cardiac fibroblast differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20180094245A1Cell differentiationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInduced pluripotent stem cellEndocrinology
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of using stem cells to prepare epicardial cells
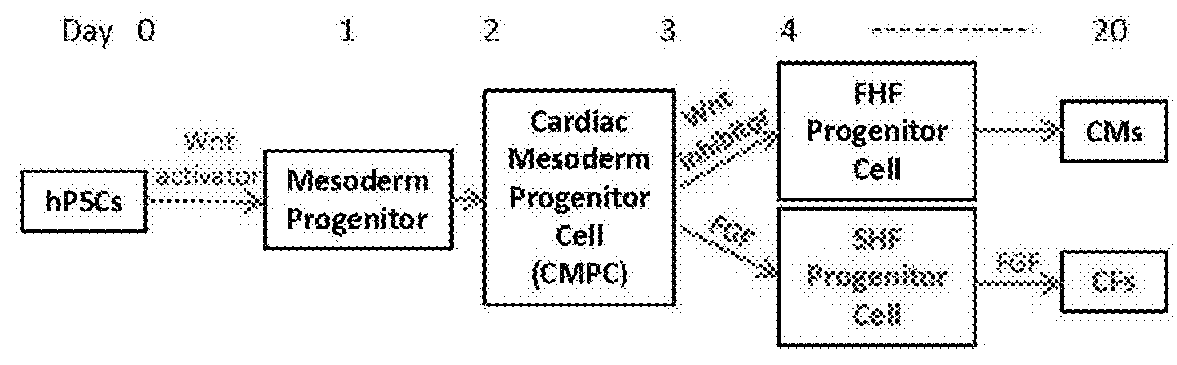
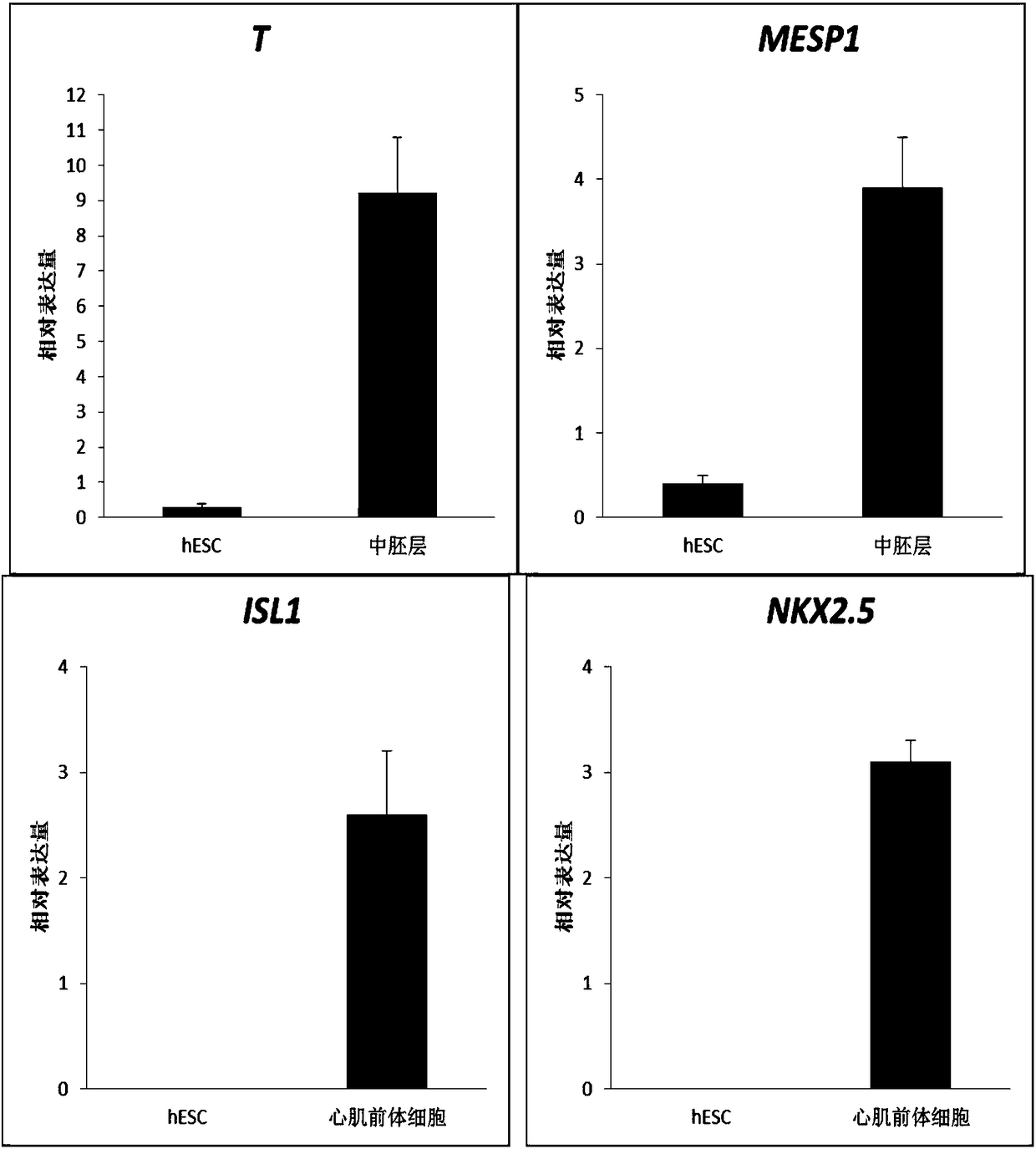
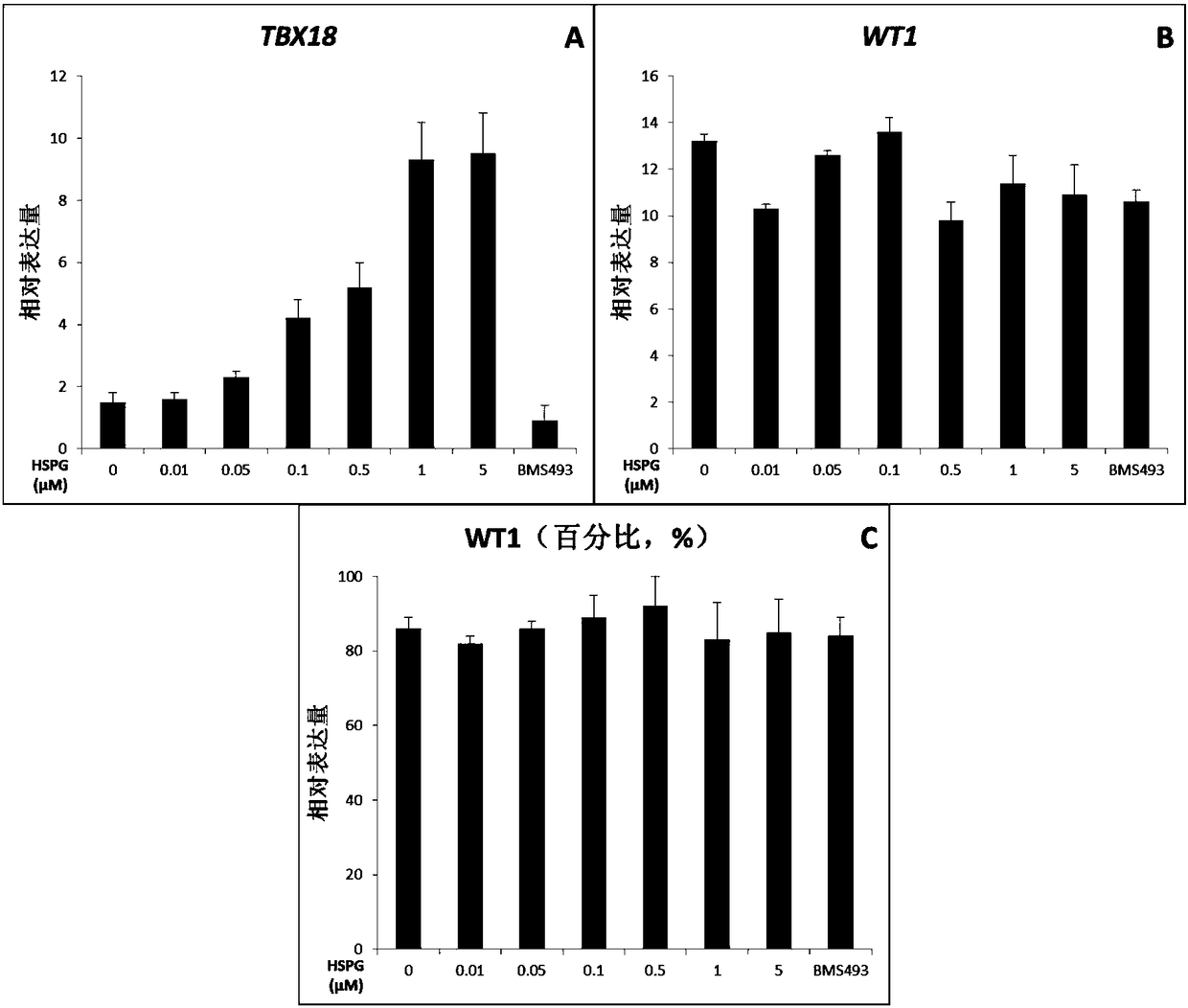
The invention provides a method of using multipotent stem cells to prepare epicardial cells, comprising: 1) inducing multipotent stem cells to differentiate into mesodermal cells by activating a WNT signal pathway; 2) converting the mesodermal cells in step 1) into myocardial precursor cells by inhibiting the WNT signal pathway; 3) converting the myocardial precursor cells in step 2) into preliminary epicardial cells by activating a fibroblast growth factor signal pathway and the WNT signal pathway; preparing pericardial cells with the preliminary epicardial cells of step 3). The invention also relates to: a method of using multipotent stem cells to prepare vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac fibroblasts; epicardial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac fibroblasts all of which are prepared through the above method; and their application.
Owner:重庆斯德姆生物技术有限公司
Cardiac repair by reprogramming of cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS9017661B2Preventing delaying developmentAvoid delayOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGATA4Reprogramming
The present invention involves the use of transcription factors including Tbx5, Mef2C, Hand2, myocardin and Gata4 to reprogram cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, both in vitro and in vivo. Such methods find particular use in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction to prevent or limit scarring and to promote myocardial repair.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Culture solution for differentiating adipose-derived stromal cells into myocardial cells and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102140436AHigh Application Security StandardsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPenicillinStreptomycin
The invention discloses a method for preparing culture solution for differentiating adipose-derived stromal cells into myocardial cells. 1L of culture solution comprises the following components: 10g of Gibco DMEM(Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium) high glucose medium, 2.3g of NaHCO3, 2.6g of N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N-ethane-sulphonicacid (HEPES), 15 to 25 volume percent of Gibco fetal calf serum, 5*104U of penicillin, 5*104U of streptomycin and 75 to 85 volume percent of deionized water. A simple and definite culture solution system for differentiating the adipose-derived stromal cells into the myocardial cells is obtained, and meets higher application security standard.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Truncated growth differentiation factor 11 with biological activity and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a truncated growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) with biological activity and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. The truncated growth differentiation factor 11 comprises 95 amino acids, wherein the amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 The biological activity of the obtained truncated growth differentiation factor 11 is researched, and the result shows that the truncated GDF11 is capable of stimulating collagen secretion of fibroblasts and has the activity of promoting phosphorylation of cardiac fibroblasts Smad2 / 3 and activating a passage of the cardiac fibroblasts Smad2 / 3. Therefore, the truncated growth differentiation factor 11 has a wide application prospect in treatment or prevention of irreversible senile diseases such as a diastolic heart failure and alzheimer disease.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Cardiomyocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9395354B2Abnormal sarcomeric α-actinin distributionReduce the probability of jumpingLibrary screeningDrug screeningBiotechnologySomatic cell
Human somatic cells obtained from individuals with a genetic heart condition are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), and differentiated into cardiomyocytes for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
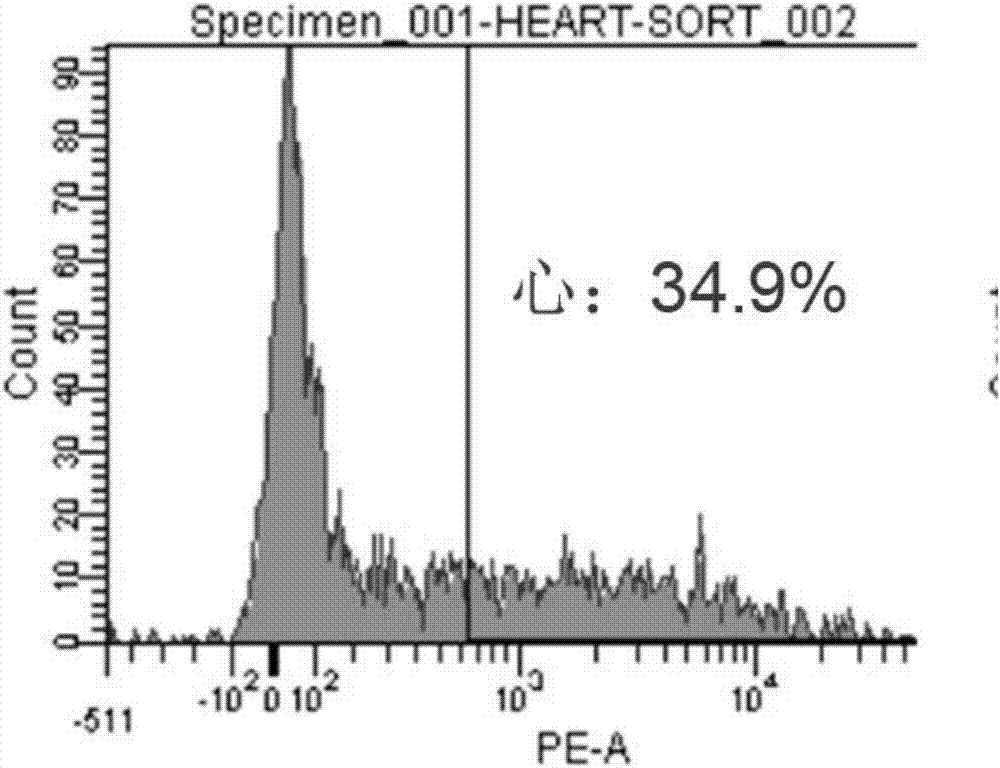
Method for sorting cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets of mice and application of cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets
The invention belongs to the animal cell culture techniques and relates to a method for sorting cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets of mice and application of the cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out recovery and enlarged culture on mice cardiac fibroblast cell strains; sorting cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets by virtue of a PE-marked CD90 antibody; collecting the sorted cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets, carrying out centrifugation to remove supernatant so as to obtain precipitates, inoculating the precipitates into a culture bottle, carrying out enlarged culture, so as to finish the sorting of the cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets of the mice. The sorted cardiac fibroblast CD90<+> subsets are taken as preponderant subsets for sorting cardiac fibroblasts and are used for triggering the myocardium repair potential of the cardiac fibroblasts, so that the experimental basis and theoretical support are provided for the efficient utilization of the cardiac fibroblasts.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Use of corilagin in preparation of anti-myocardial fibrosis medicines
ActiveCN109674804AInhibit myocardial fibrosisAlleviate deterioration of heart functionOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderSide effectIn vivo
The invention discloses use of corilagin in preparation of anti-myocardial fibrosis medicines, belonging to the technical field of biological medicine. By constructing an in-vivo myocardial fibrosis model induced by a mouse aortic ligation operation and an in-vitro myocardial fibrosis model of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta-induced rat suckling CFs for performing experimental study, the results show that the corilagin can regulate macrophage polarization so as to inhibit inflammation, also can down-regulate an interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor so as to avoid excessive production of TGF-beta, and inhibits the expression of a TGF-beta receptor so as to reduce the activation of cardiac fibroblasts, thereby reducing collagen content and relieving myocardial fibrosis. The corilagin providedby the invention can reduce the myocardial fibrosis caused by long-term stress load, protect heart tissues and inhibit or delay deterioration of heart functions; the corilagin has a significant effectin the aspect of anti-myocardial fibrosis, is little in side effects, and can be used for preparing the anti-myocardial fibrosis medicines.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
p63 INACTIVATION FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEART FAILURE
ActiveUS20180066252A1Increases transdifferentiation efficiencyImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTransdifferentiationReprogramming
Embodiments of the disclosure include methods and compositions for in situ cardiac cell regeneration, including transdifferentiation of cardiac cells to cardiomyocytes. In particular embodiments, in situ cardiac cell regeneration encompasses delivery of p63 shRNA and one or both of Hand2 and myocardin, and in specific embodiments further includes one or more of Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5. In specific aspects of the disclosure, adult cardiac fibroblasts are reprogrammed into cardiomyocytes using viral vectors that harbor p63 shRNA and one or both of the transcription factors Hand2 and myocardin.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
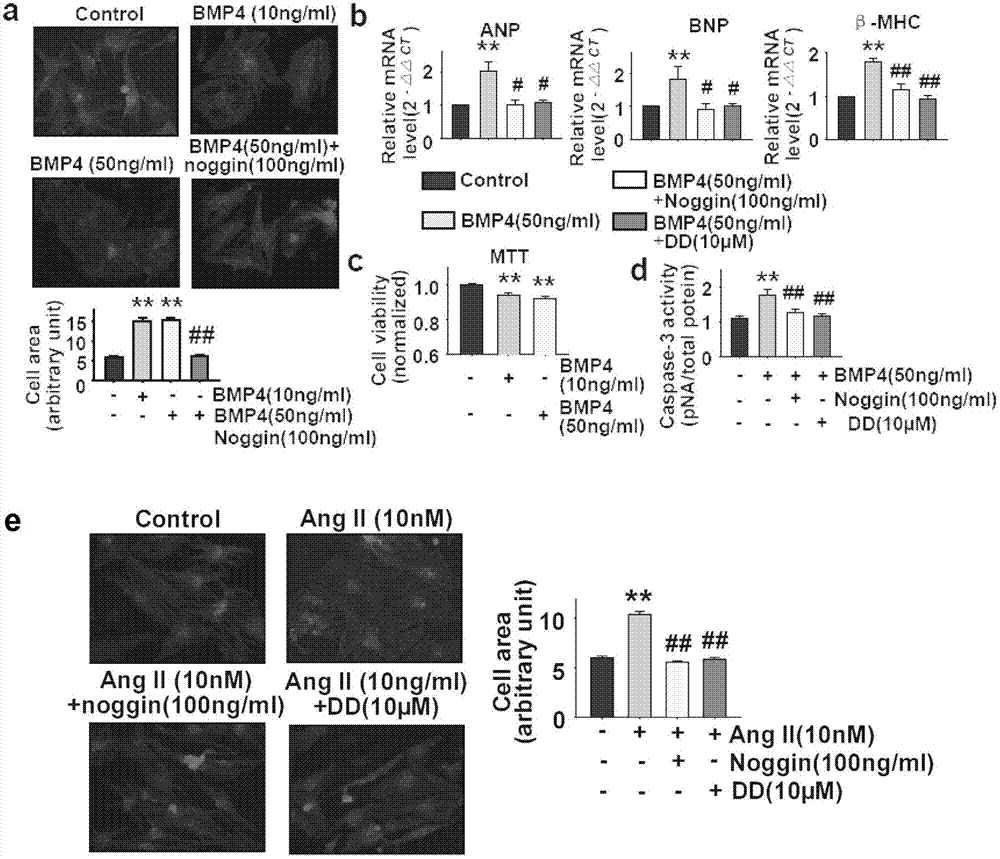
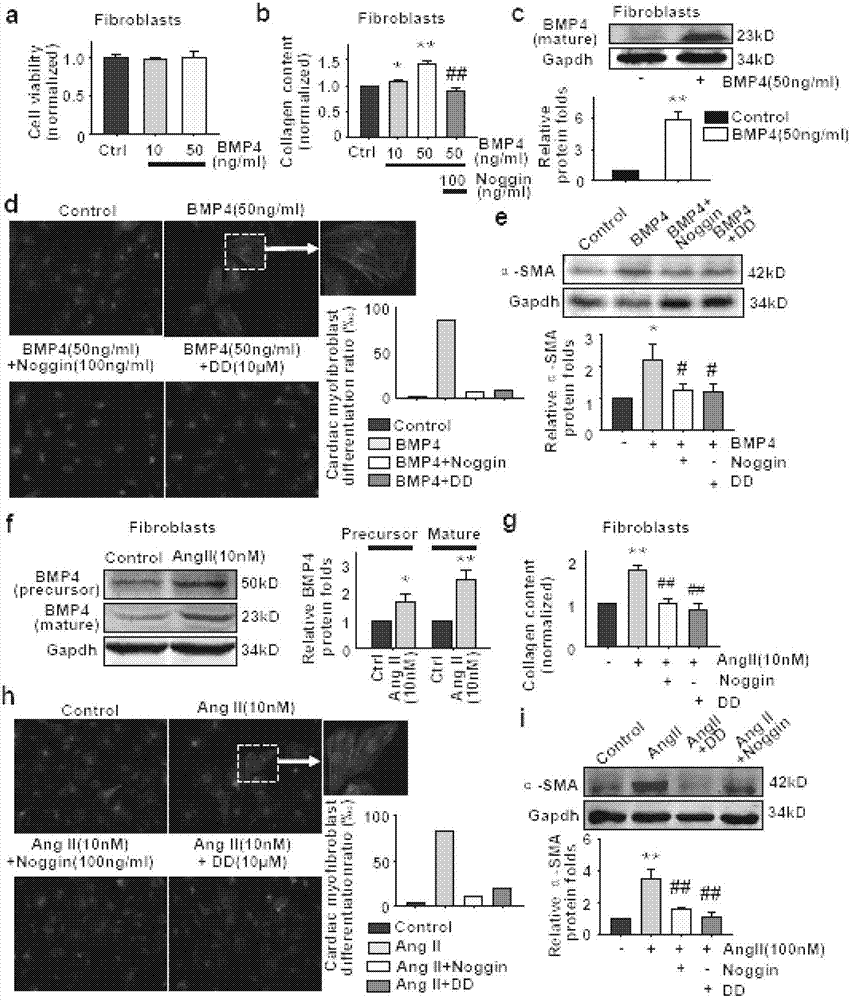
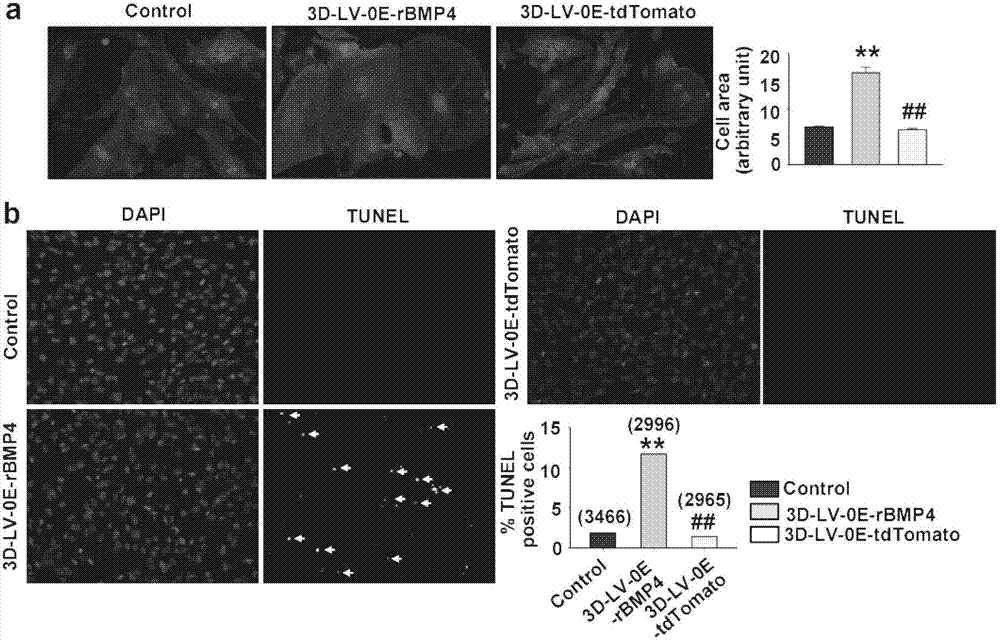
Application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in screening drugs for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure or cardiac fibrosis
The invention discloses an application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in screening drugs for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure or cardiac fibrosis and belongs to the field of biomedicine. Screened drug types comprise: bone morphogenetic protein-4 formation inhibitor, bone morphogenetic protein-4 antagonistic, bone morphogenetic protein-4 receptor antagonists and bone morphogenetic protein-4 downstream signal antagonistic. The invention also relates to an application of the drugs in preparation of medicines for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure and arrhythmia. Researches have found that bone morphogenetic protein-4 can induce myocardial hypertrophy, apoptosis and cardiac fibroblast collagen secretion increase, lead to occurrence of cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure and arrhythmia. However, drugs for antagonism of bone morphogenetic protein-4 and its cell signaling pathway can be used to inhibit occurrence of cardiac hypertrophy, inhibit cardiac fibrosis and minimize occurrence of cardiac cell death and arrhythmia. The invention provides a theoretical basis for realizing high-flux medicine screening, and is of practical guiding significance.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Myoblast treatment of diseased or weakened organs
InactiveUS20070009499A1Increase blood flowImprove bindingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterograftsWeakness
Bioengineering the regenerative heart or other body organ in need of greater muscle mass or improved blood perfusion provides a novel treatment for organ weakness or failure. In the case of cardiac failure treatment, on May 14, 2002, a 55-year-old man suffering ischemic myocardial infarction received 25 injections carrying 465 million cGMP-produced pure myoblasts into his myocardium after coronary artery bypass grafting. Three myogenesis mechanisms were elucidated with 17 human / porcine xenografts using cyclosporine as immunosuppressant. Some myoblasts developed to become cardiomyocytes. Others transferred their nuclei into host cardiomyocytes through natural cell fusion. As yet others formed skeletal myofibers with satellite cells. De novo production of contractile filaments augmented heart contractility. Human myoblasts transduced with VEGF165 gene produced six times more capillaries in porcine myocardium than placebo. Xenograft rejection was not observed for up to 20 weeks despite cyclosporine discontinuation at 6 weeks.
Owner:LAW PETER
Method for establishing heart disease drug screening model
The invention provides a method for establishing a heart disease drug screening model, which comprises the following steps of A) establishing a virus vector comprising four transcription factors: Oct3 / 4, Sox2, c-Myc and klf4; B) transfecting the virus vector in the step A) with a virus packaging cell to obtain virus liquid; C) infecting the virus liquid in the step B) with the fibroblast of the beta adrenergic receptor wild-type gene knockout mouse; D) screening the clone similar to the mouse embryonic stem cell, and subculturing to obtain the induced pluripotent stem cells with beta adrenergic receptor wild-type gene defect; E) establishing a virus vector containing the beta adrenergic receptor mutant gene; F) transfecting the virus vector in the step E) with the virus packaging cell to obtain virus liquid; G) infecting the virus liquid in the step F) with the induced pluripotent stem cells with beta adrenergic receptor wild-type gene defect; H) selecting positive clone and performing induced differentiation into myocardial cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI BODE BIOTECH
Method for improving efficiency of differentiating brown adipose-derived stem cells into cardiomyocytes
InactiveCN109666633ARich sourcesLarge amount of collected cellsCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention discloses a method for improving the efficiency of differentiating brown adipose-derived stem cells into cardiomyocytes and belongs to the technical field of cell engineering. Cardiac stem cells from which brown adipose tissue comes are rich in source, the quantity of collected cells is large, and the cells are easily accepted by a patient; by means of the method, an extracellular matrix derived from cardiac fibroblasts is utilized for improving the differentiation of the brown adipose-derived stem cells into the cardiomyocytes, and the problem that a current isolation culture method is low in efficiency of differentiating brown adipose-derived stem cells into cardiomyocytes is solved.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
RNA(Ribonucleic Acid)and application thereof in diseases of cardiovascular system
InactiveCN103114087BPrevent proliferationPromote proliferationGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesCardiac fibrosisDisease
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
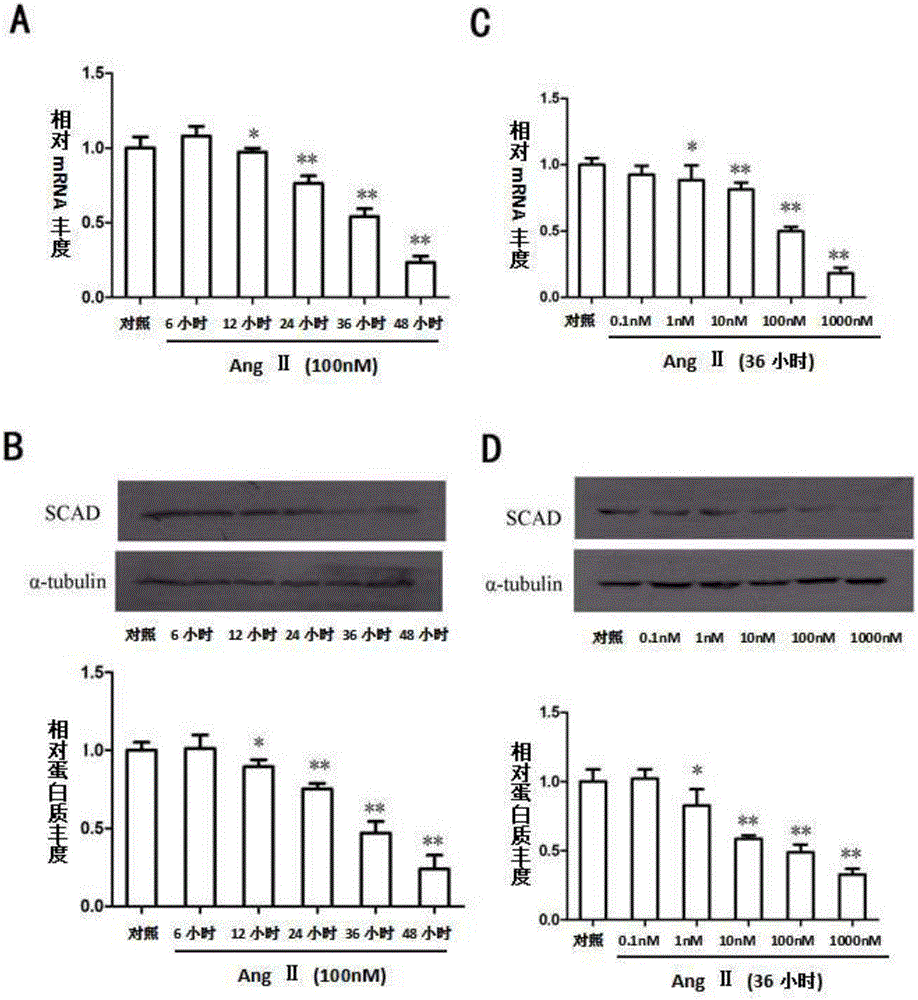
Application of SCAD gene or SCAD protein
InactiveCN106540272AIncrease drug targetsPeptide/protein ingredientsGene therapyDiseaseCardiac myofibroblasts
The invention discloses application of an SCAD gene or SCAD protein and particularly discloses the application of the SCAD gene and the SCAD protein or an expression accelerator or activator of the SCAD protein in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating myocardial fibrosis or medicine for preventing cardiac fibroblasts from being activated or converted into myofibroblasts or medicine for preventing cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis. Through establishment of animal and cell models, the important role of the SCAD in myocardial fibrosis and / or cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis is disclosed for the first time, a theoretical foundation and a feasible basis are provided for addition of new medicine research and development of related diseases of myocardial fibrosis and cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, and the SCAD gene or the SCAD protein can be used as a new medicine effect target spot for addition of the related diseases of myocardial fibrosis and cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Cardiac repair by reprogramming of adult cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20210180023A1Reduced exercise toleranceReduction in hospitalizationPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCardiac muscleRat heart
The present disclosure involves the use of reprogramming factors including AKT1, GATA4, TBX5, MEF2C, HAND2 and either ZNF281 or AS-CL1 to reprogram adult non-cardiomyocytes, such as cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, both in vitro and in vivo. Such methods find particular use in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction to prevent or limit scarring and to promote myocardial repair.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com








![Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa) Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa)](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b2691f1d-0226-4f4c-a97a-8161bb327d14/HDA00002773508400011.PNG)
![Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa) Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa)](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b2691f1d-0226-4f4c-a97a-8161bb327d14/HDA00002773508400021.PNG)
![Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa) Novel application of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 [HPK1]-interacting protein of 55kDa)](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b2691f1d-0226-4f4c-a97a-8161bb327d14/HDA00002773508400031.PNG)