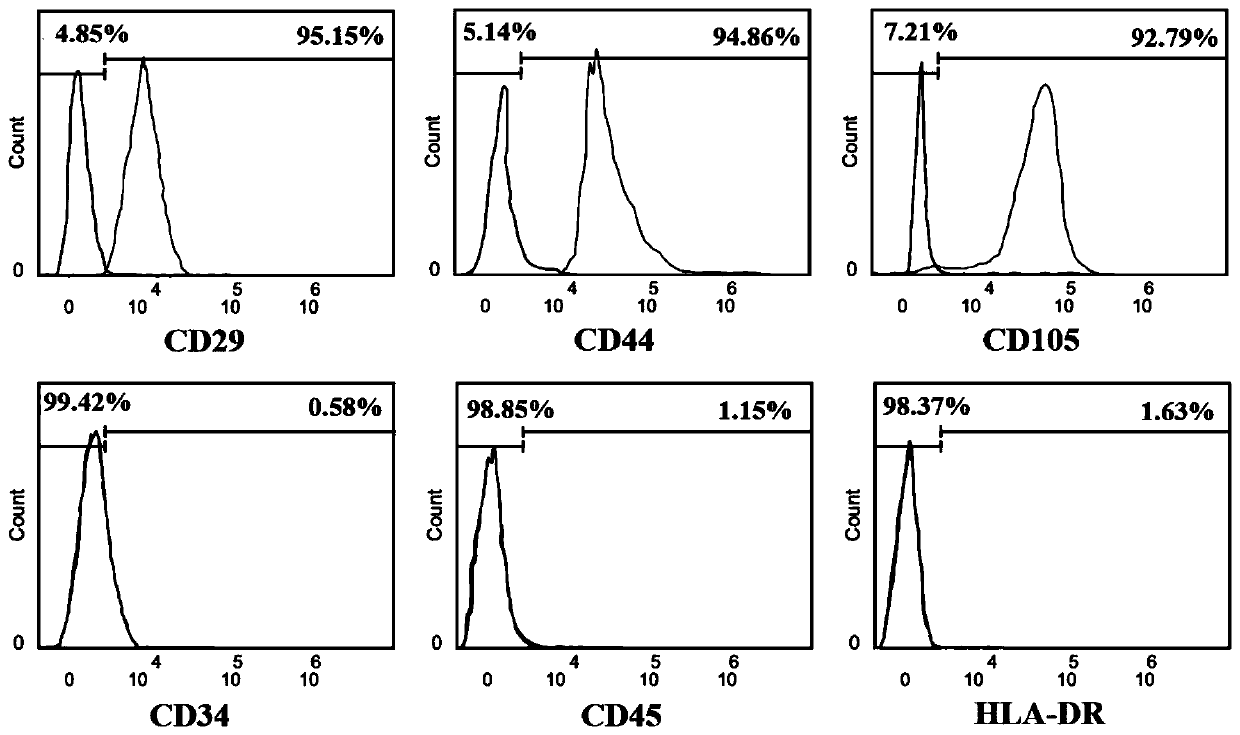
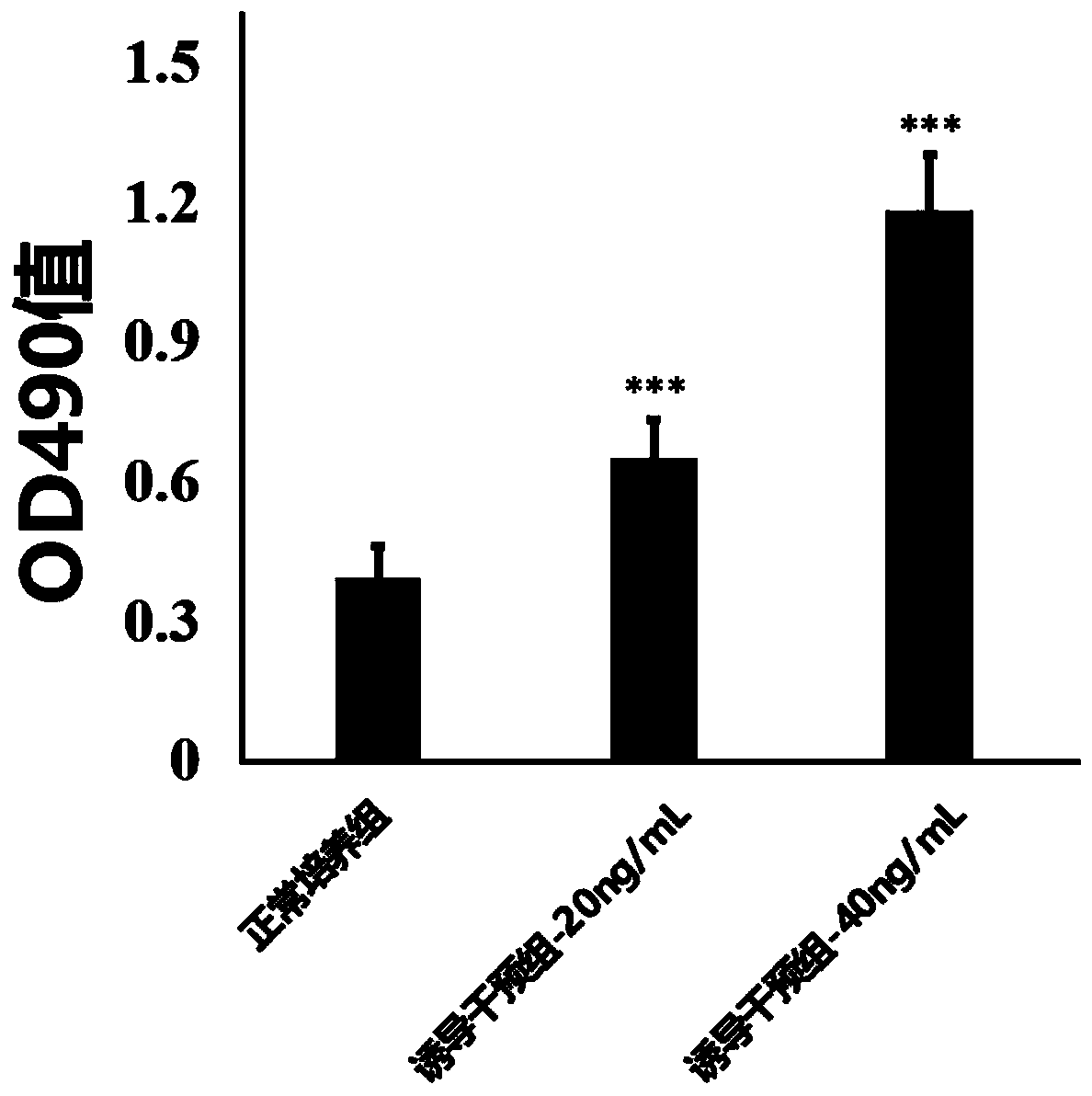
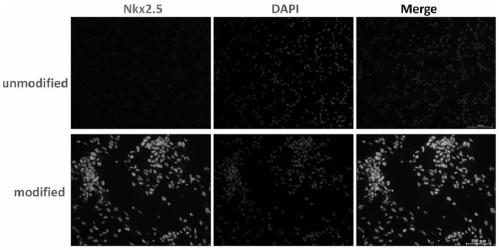
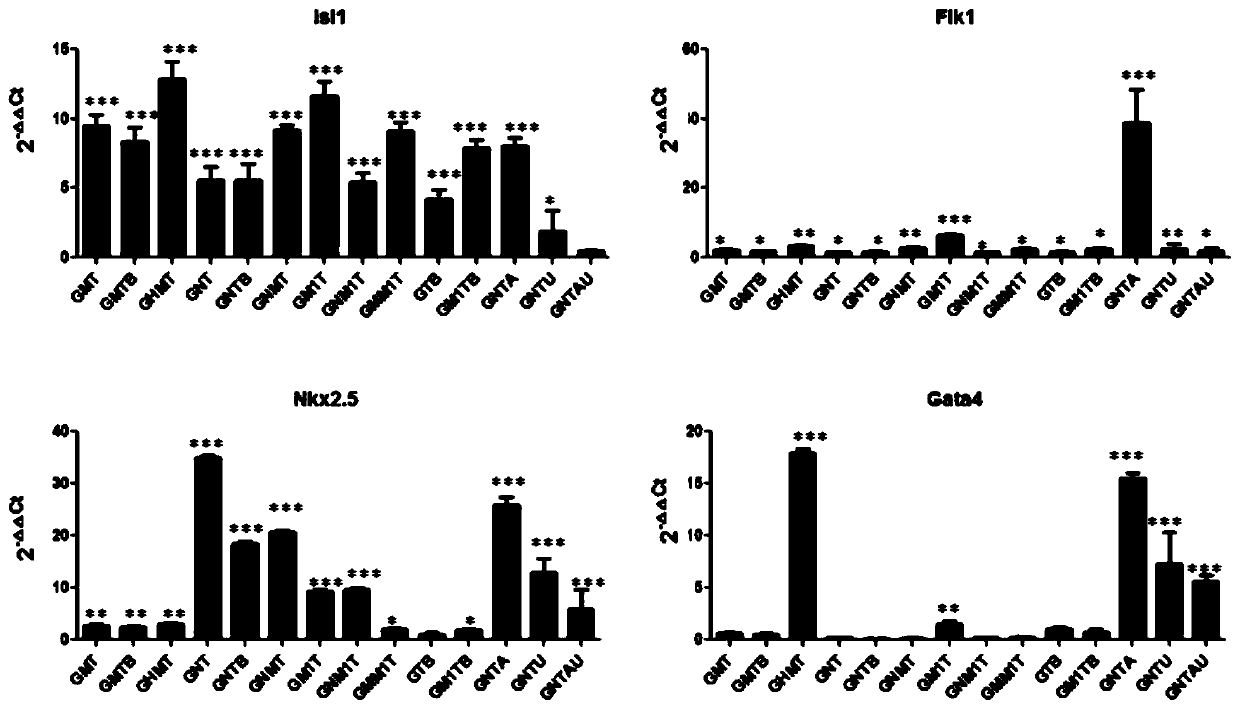
Patents
Literature
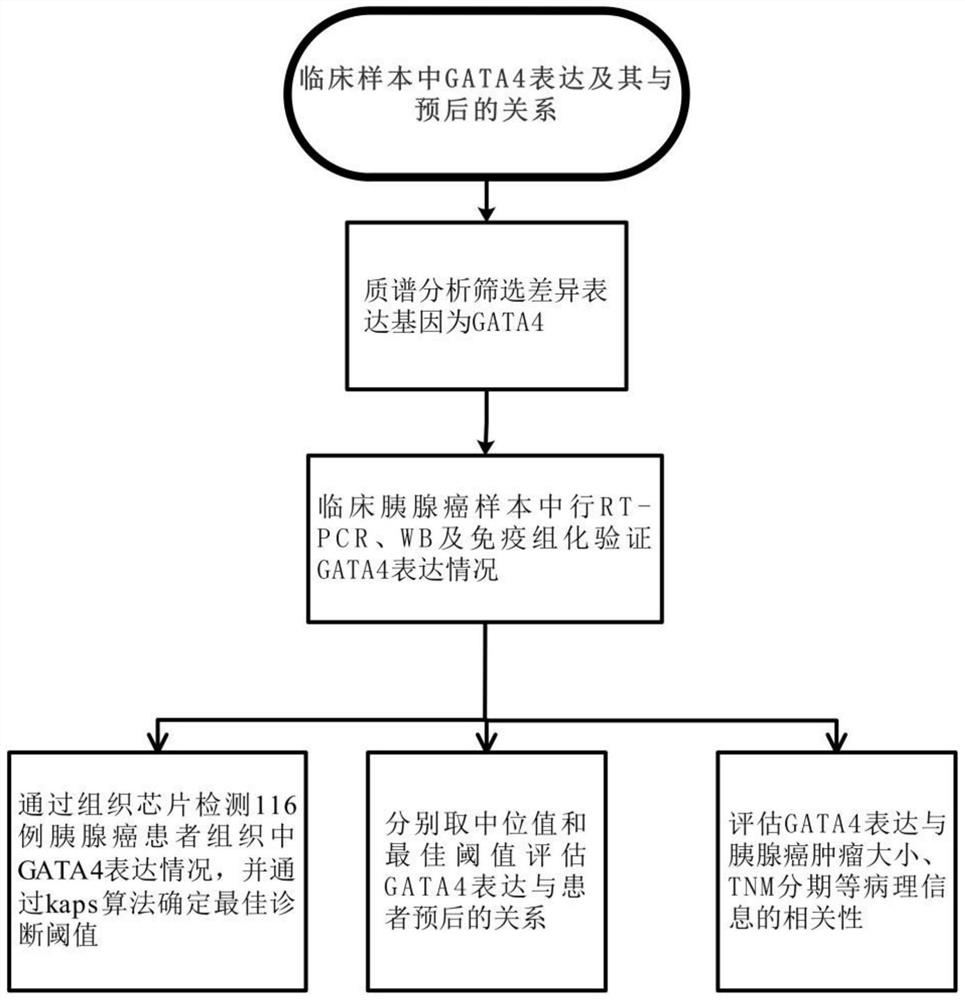
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "GATA4" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transcription factor GATA-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GATA4 gene.
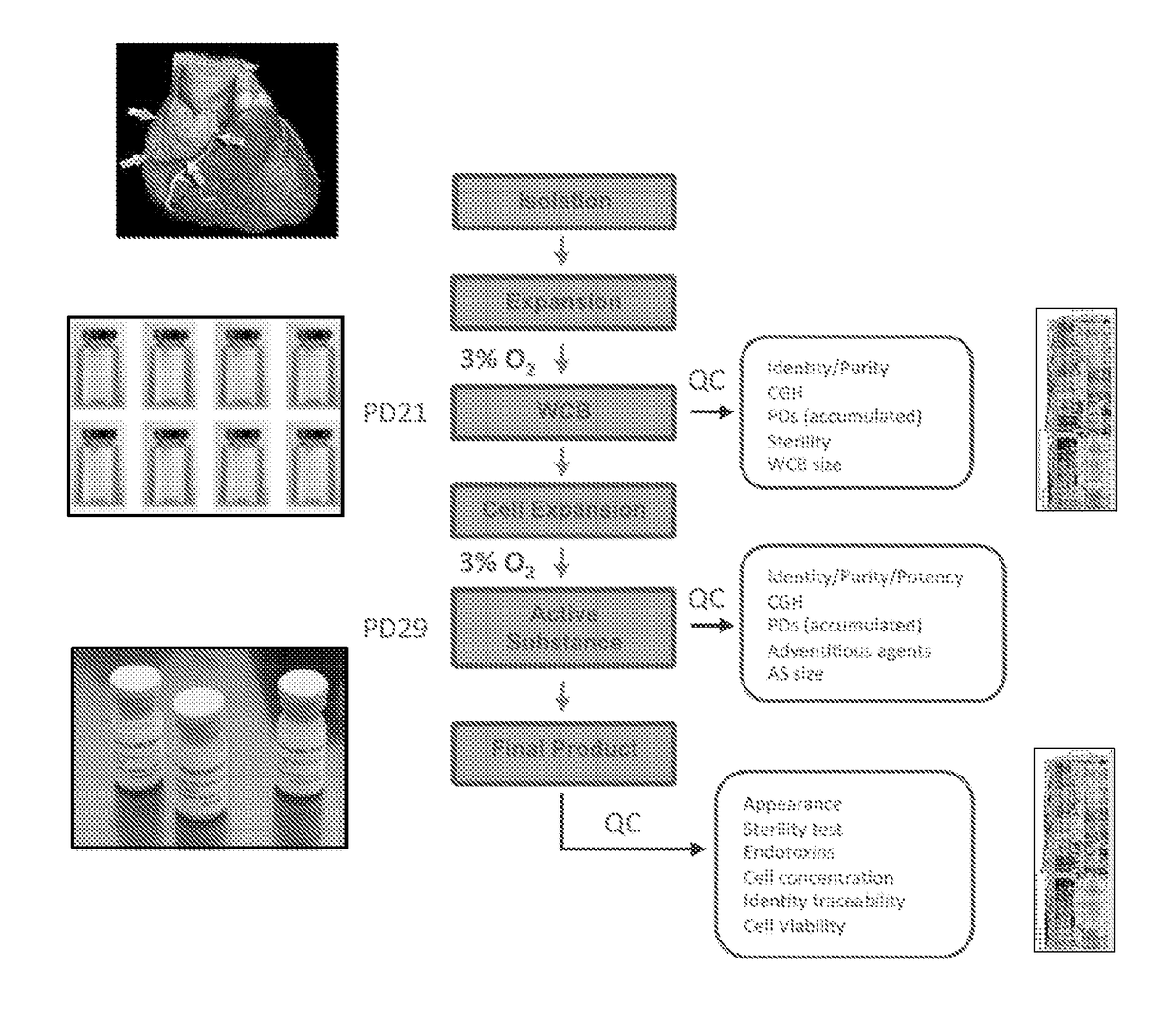
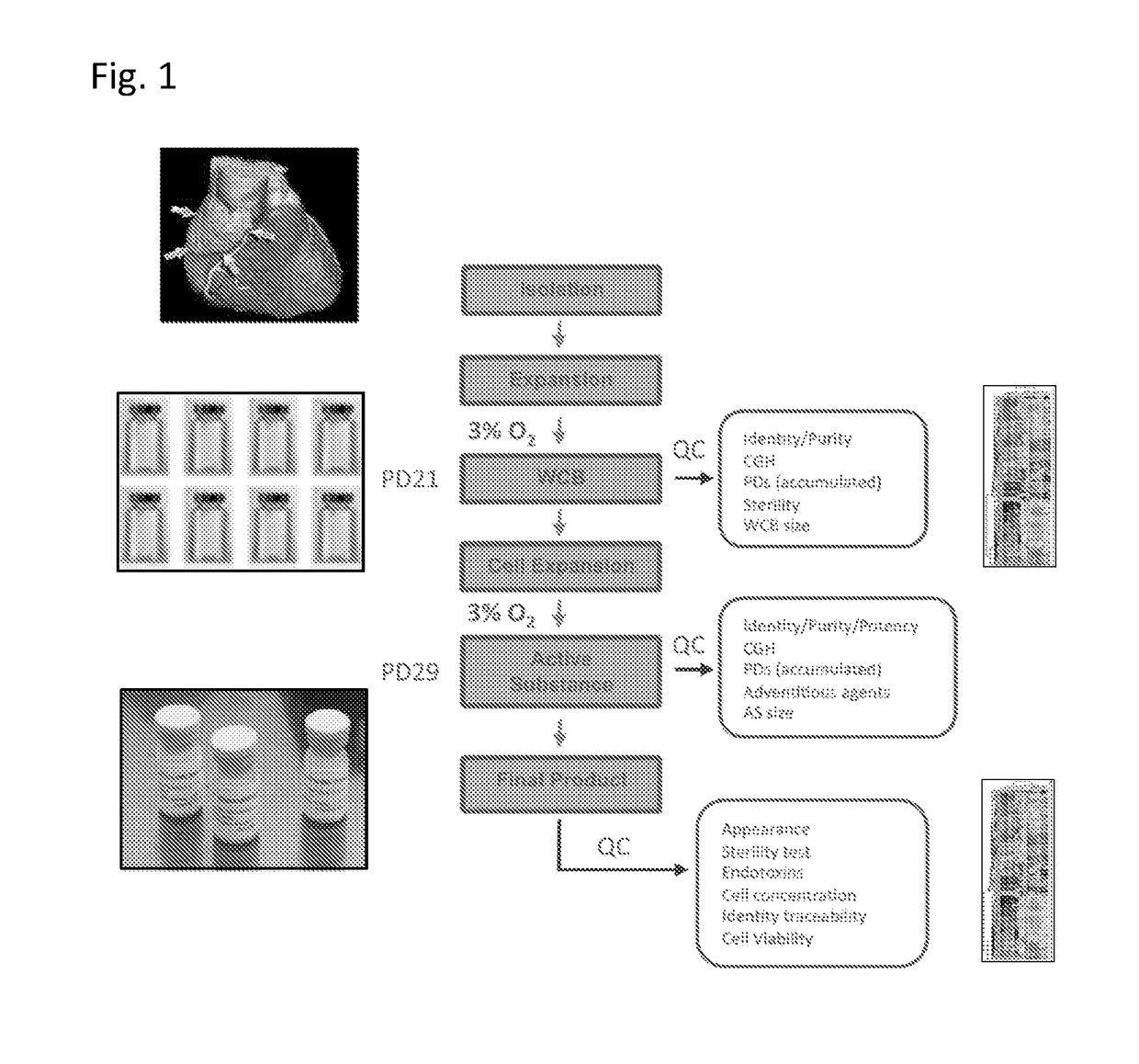
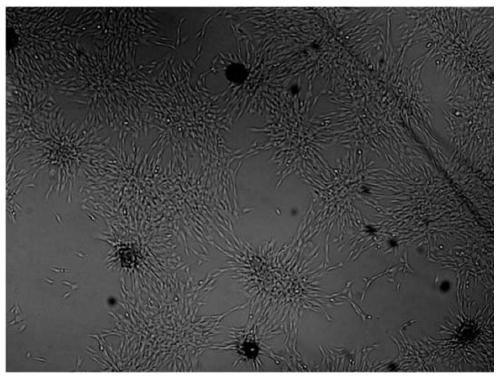
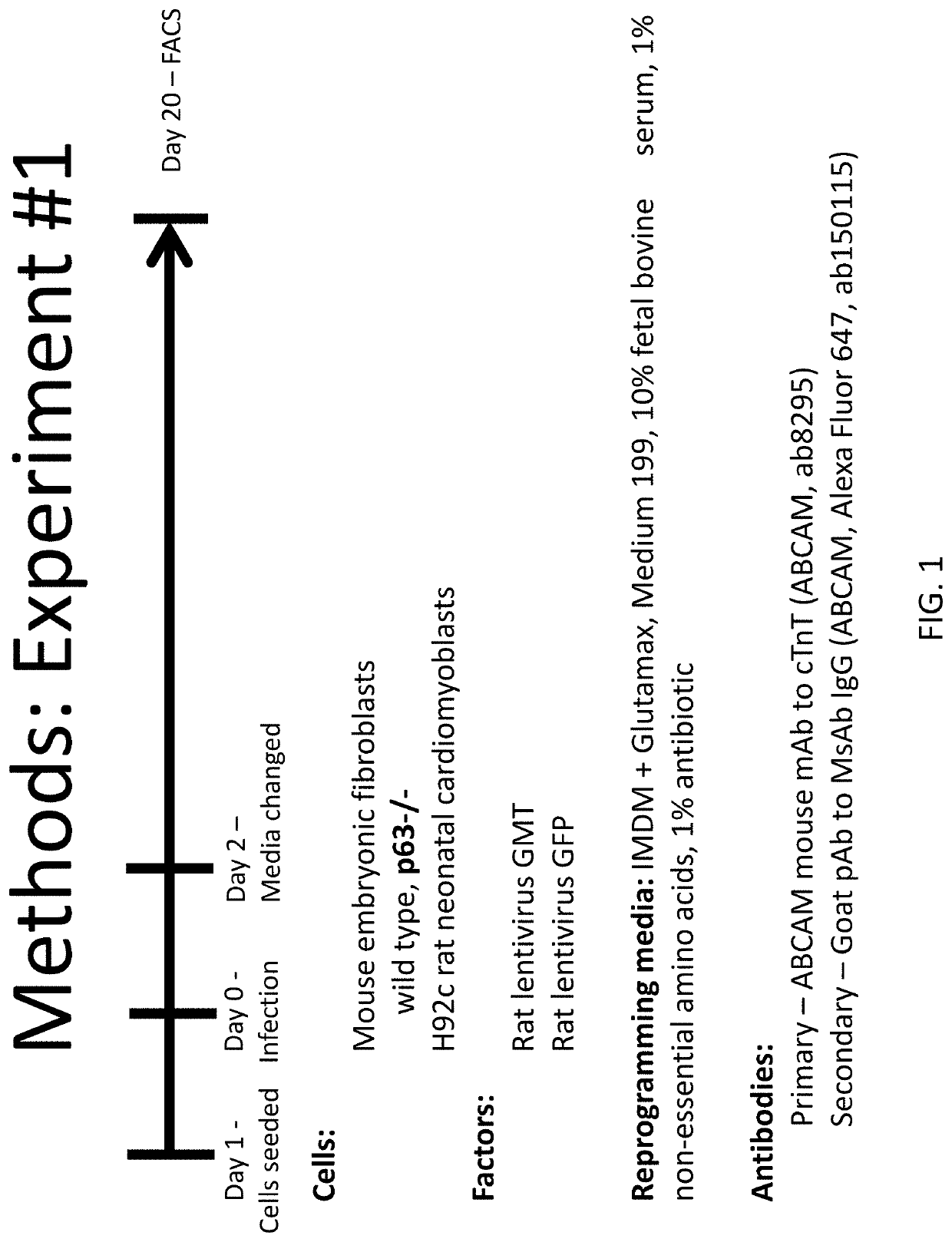
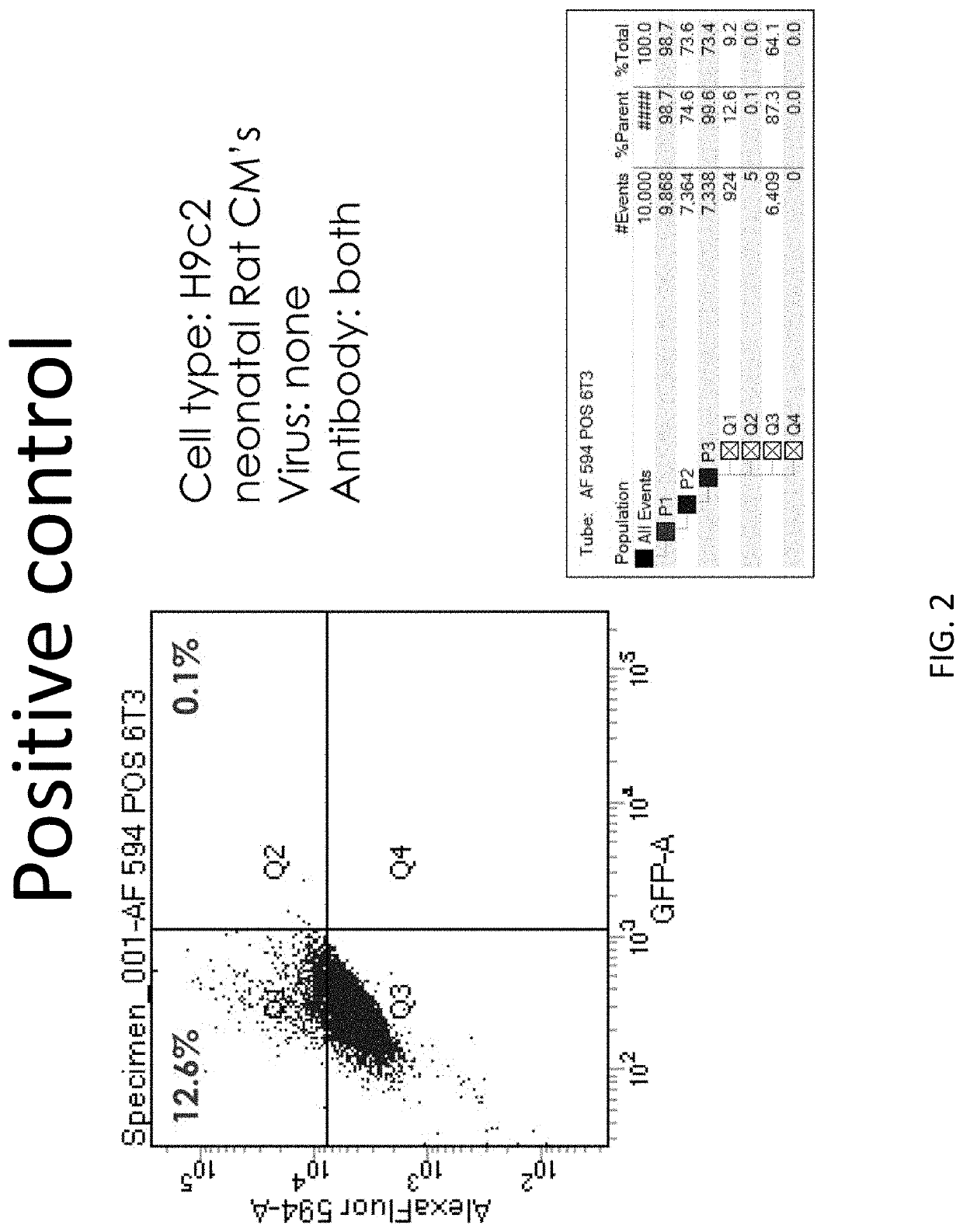
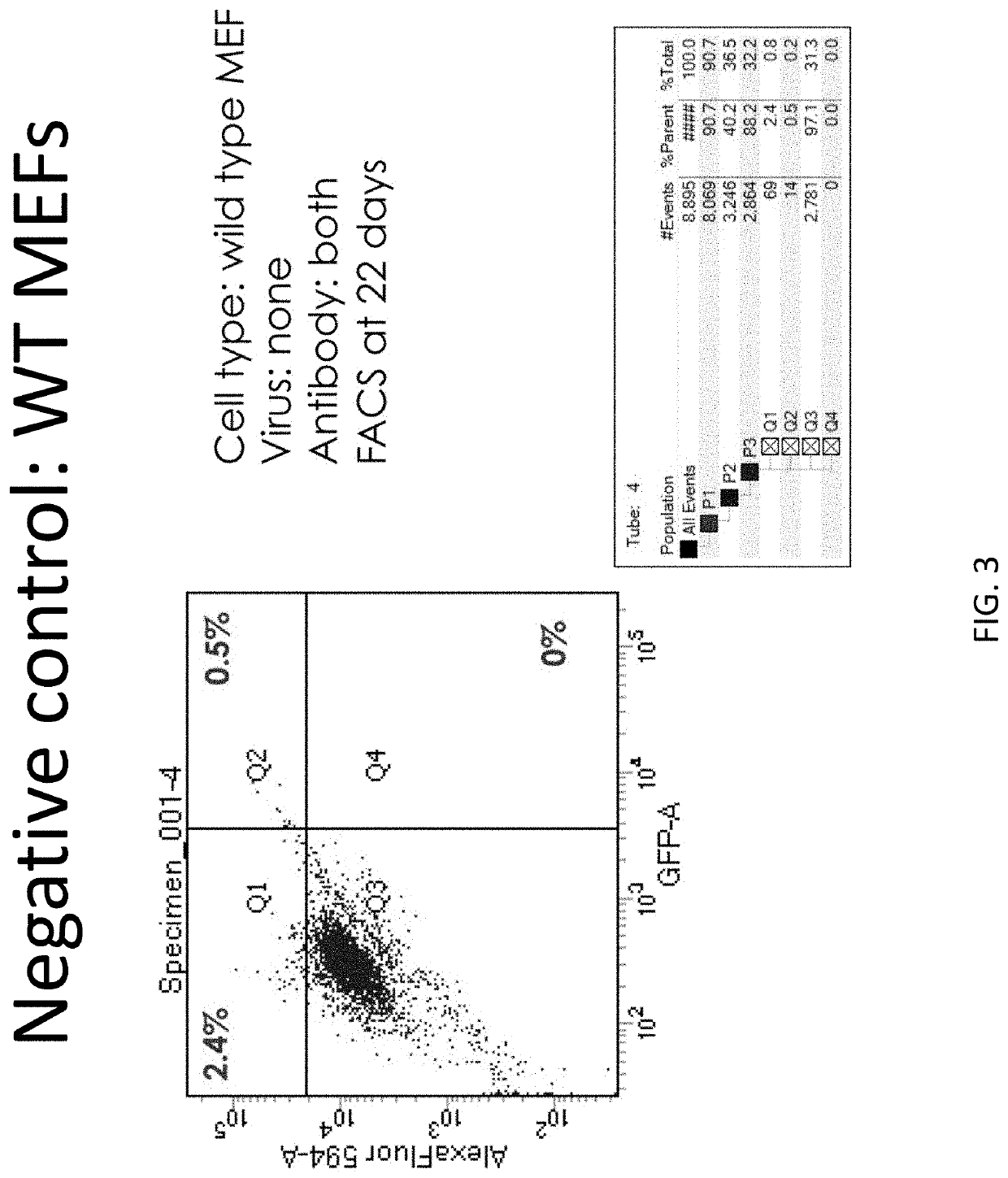
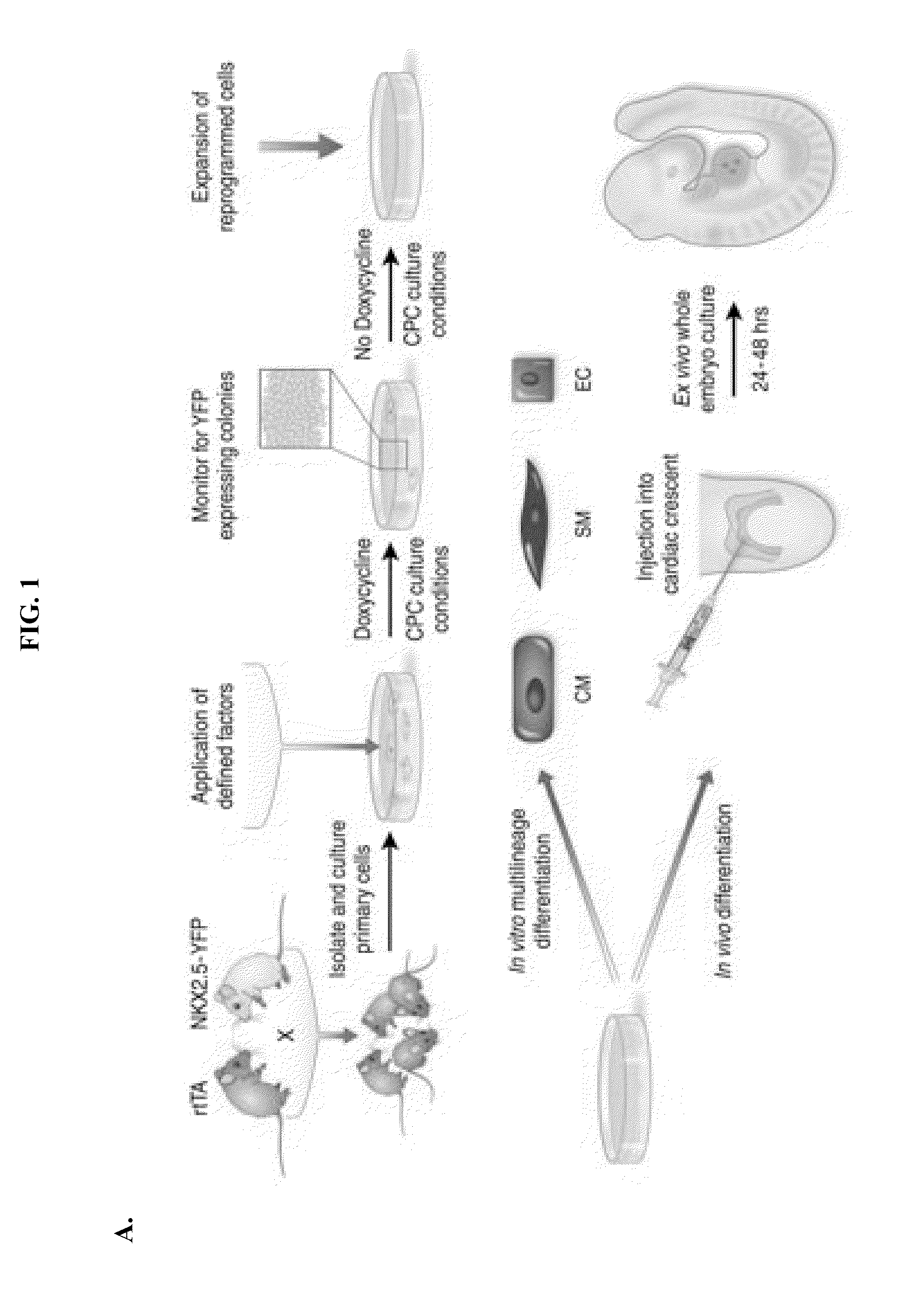
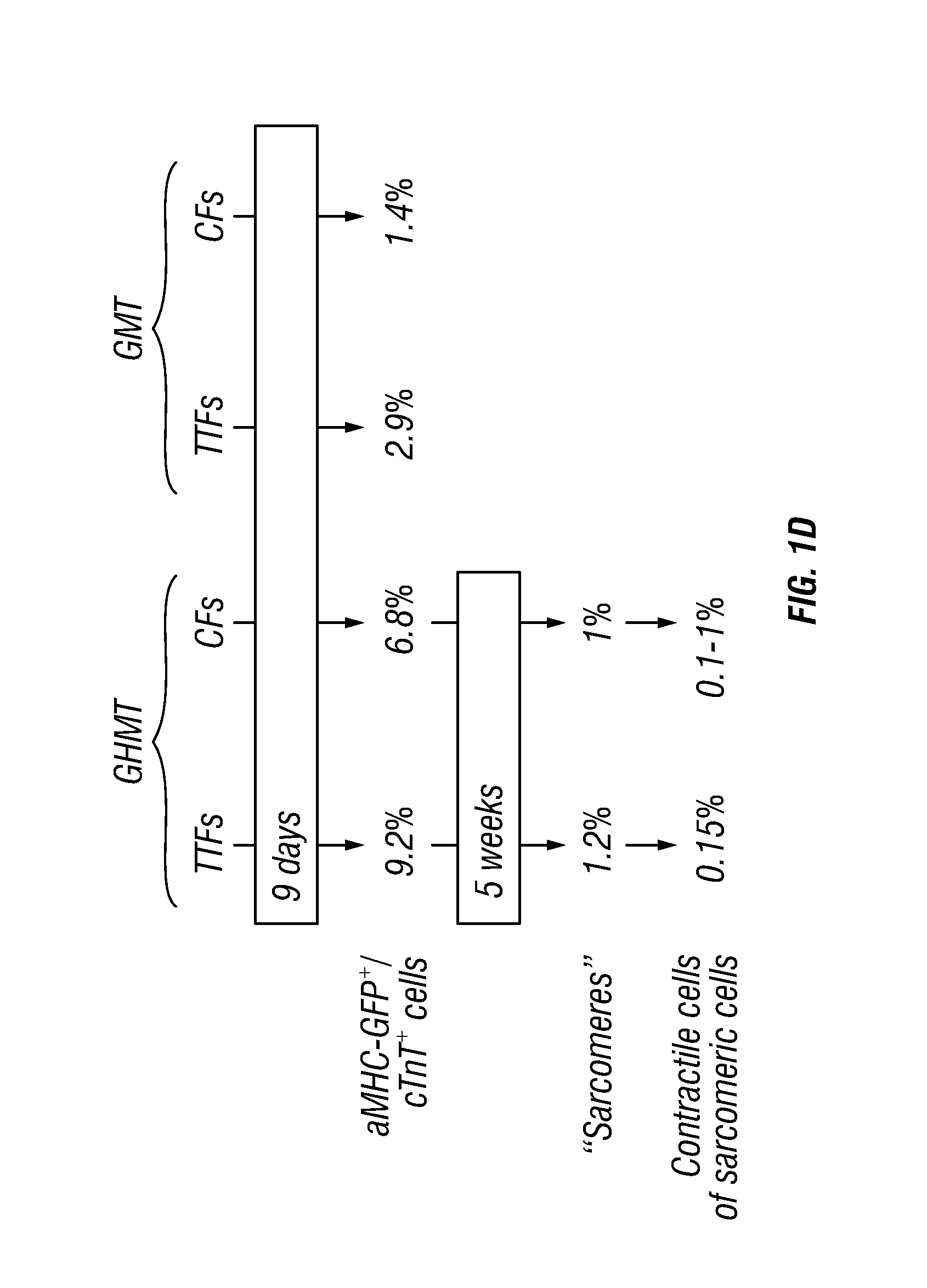
LINEAGE REPROGRAMMING TO INDUCED CARDIAC PROGENITOR CELLS (iCPC) BY DEFINED FACTORS
ActiveUS20150140658A1Facilitated DiffusionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsLineage specificCells heart
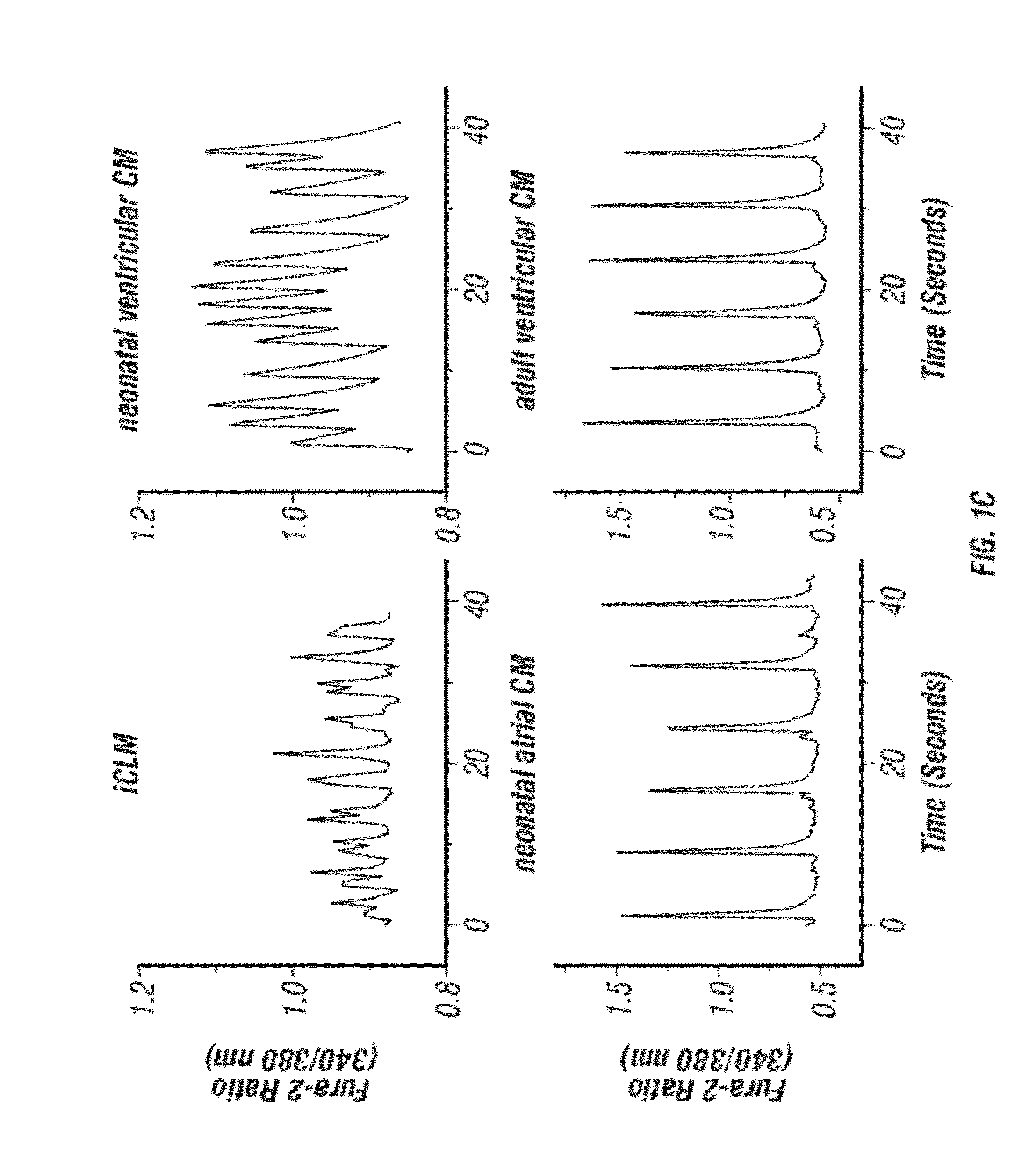
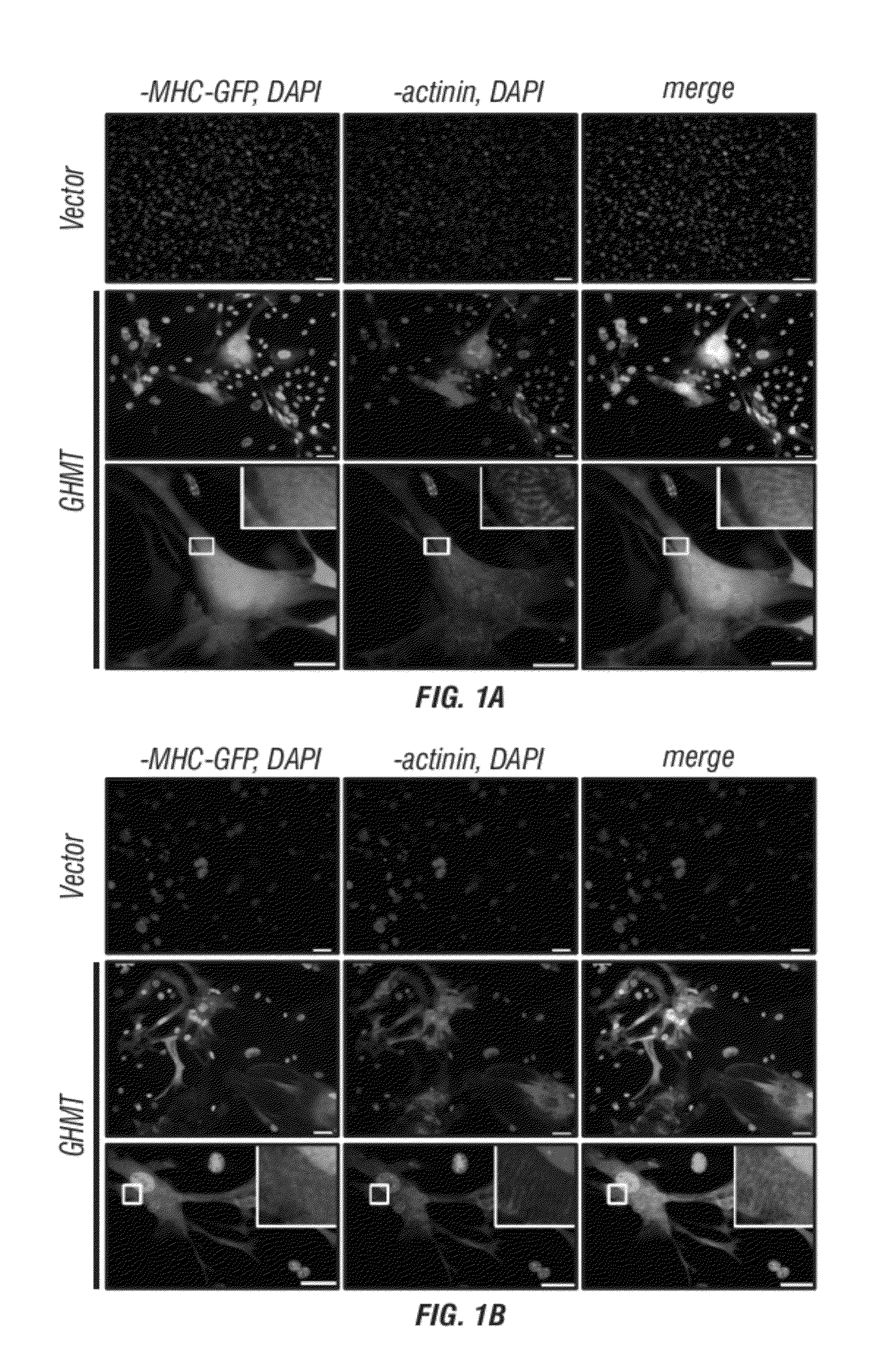
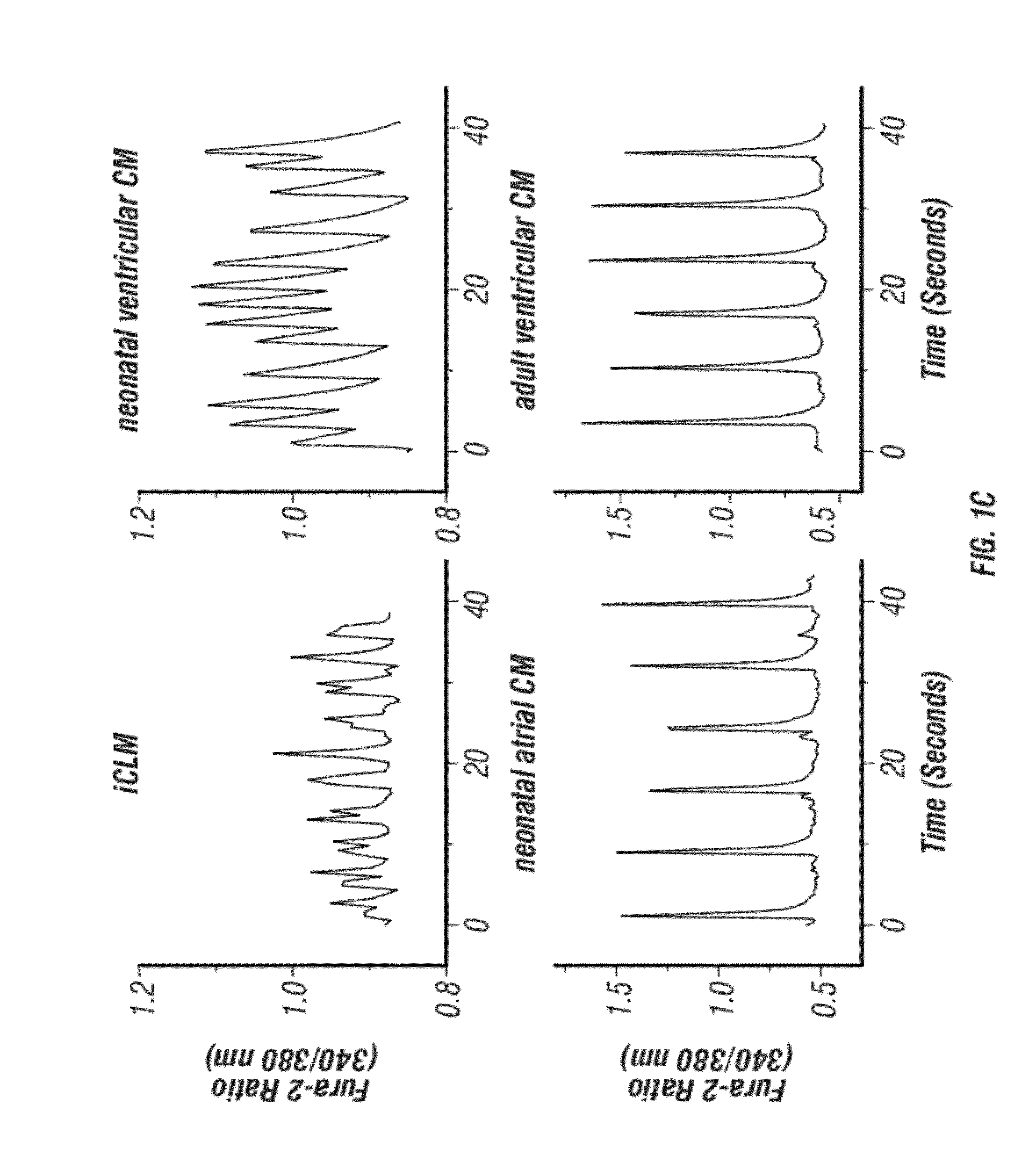
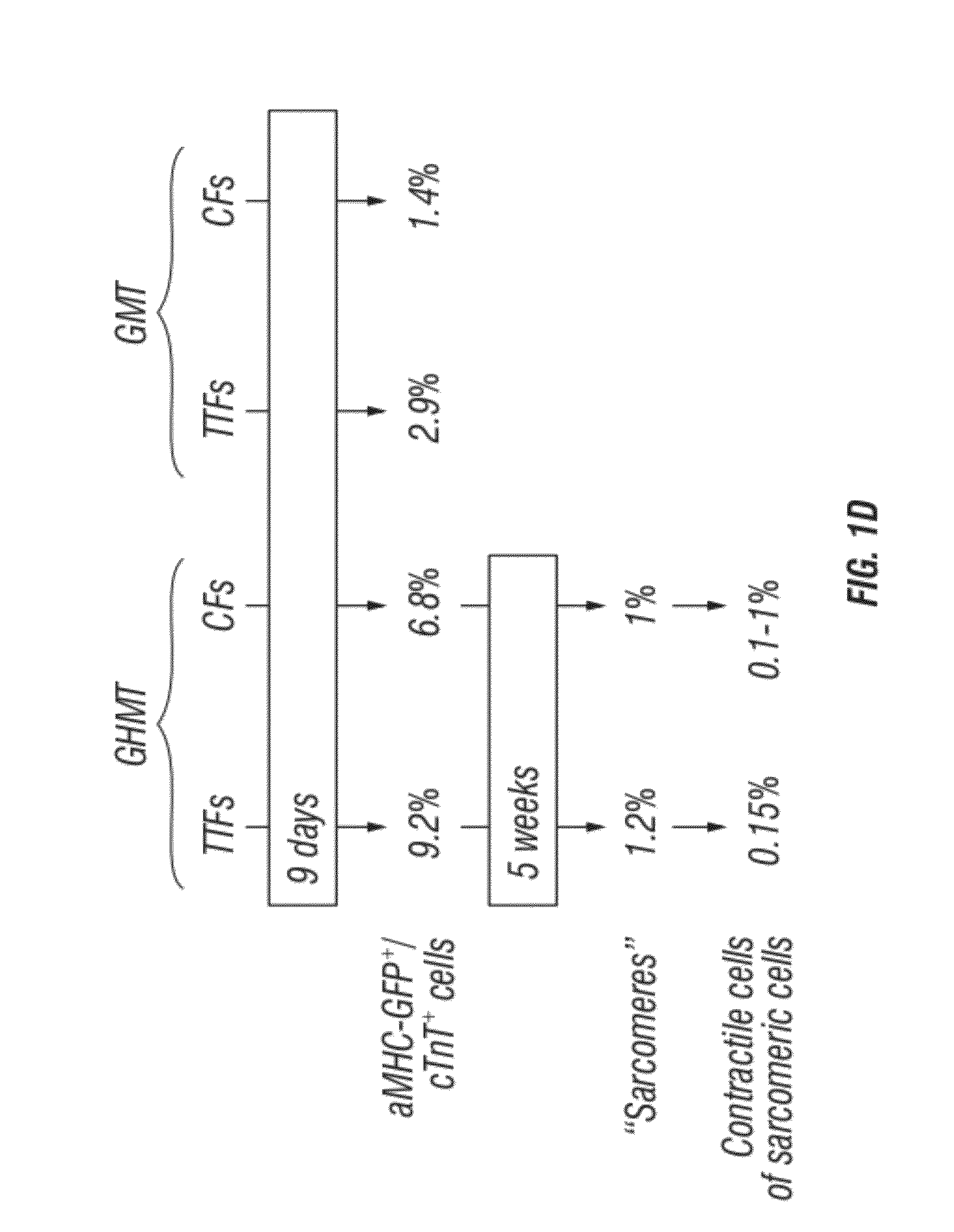
Animal cells, notably adult fibroblasts, are advantageously reprogrammed in direct lineage reprogramming methods using defined factors to produce proliferative and multipotent induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPC). The iCPC thus produced can be differentiated under suitable differentiation conditions to cardiac lineage cells including cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells, as evidenced by expression of lineage specific markers. Sets of factors effective in combination to reprogram the fibroblasts can include a set that includes some or all of 5 factors (Mesp1, Baf60c, Nkx2.5, Gata4, Tbx5), a set that includes some or all of 11 factors (Mesp1, Mesp2, Gata4, Gata6, Baf60c, SRF, Isl1, Nkx2.5, Irx4, Tbx5, Tbx20), a set that includes some or all of 18 factors (T, Mesp1, Mesp2, Tbx5, Tbx20, Isl1, Gata4, Gata6, Irx4, Nkx2.5, Hand1, Hand2, Tbx20, Tbx18, Tip60, Baf60c, SRF, Hey2), and a set that includes some or all of 22 factors (T, Mesp1, Mesp2, Tbx5, Tbx20, Isl1, Gata4, Gata6, Irx4, Nkx2.5, Hand1, Hand2, Tbx20, Tbx18, Tip60, Baf60c, SRF, Hey2, Oct4, Klf4, Sox2, L-myc).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
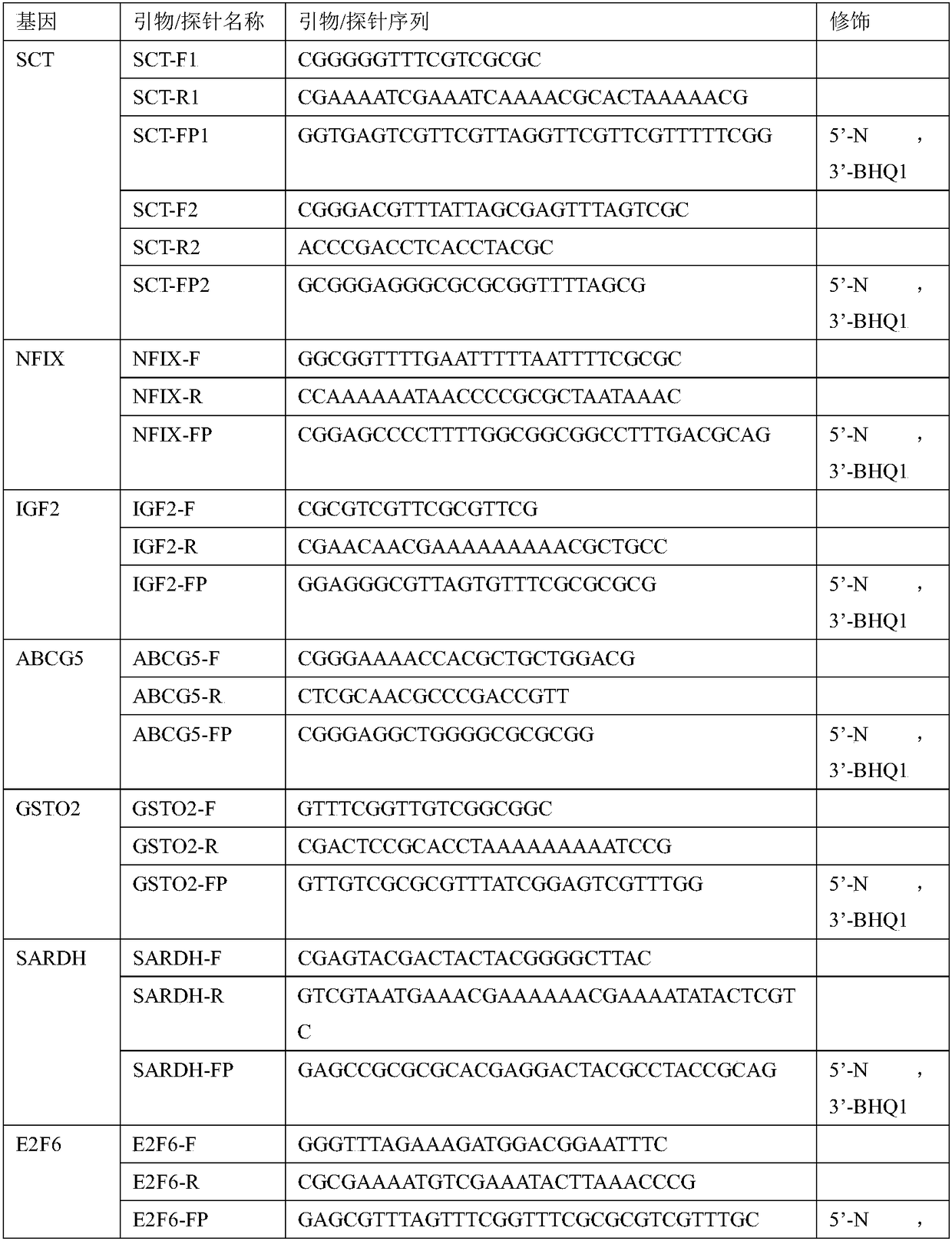
Kit and method for predicting hepatocarcinogenesis risk
InactiveCN108070655AHigh sensitivityNon-invasive testingMicrobiological testing/measurementCvd riskBiology
The invention relates to a kit and a method for predicting a hepatocarcinogenesis risk, relating to the technical field of medical in-vitro diagnosis. Particularly, the invention relates to a kit anda method for predicting a hepatocarcinogenesis risk through the CpG island methylation states of single genes or multiple genes in SCT, NFIX, IGF2, ABCG5, GSTO2, SARDH, E2F6, SHANK2, GATA4, OPLAH, NR2F1 and ZFHX3. According to the combined methylation detection of the multiple genes, the sensitivity is greatly improved; the free nucleic acids of saliva, urine, blood and the like are detected, drawing materials from cancer tissue is not required, the detection is noninvasive, and the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:北京旌准医疗科技有限公司
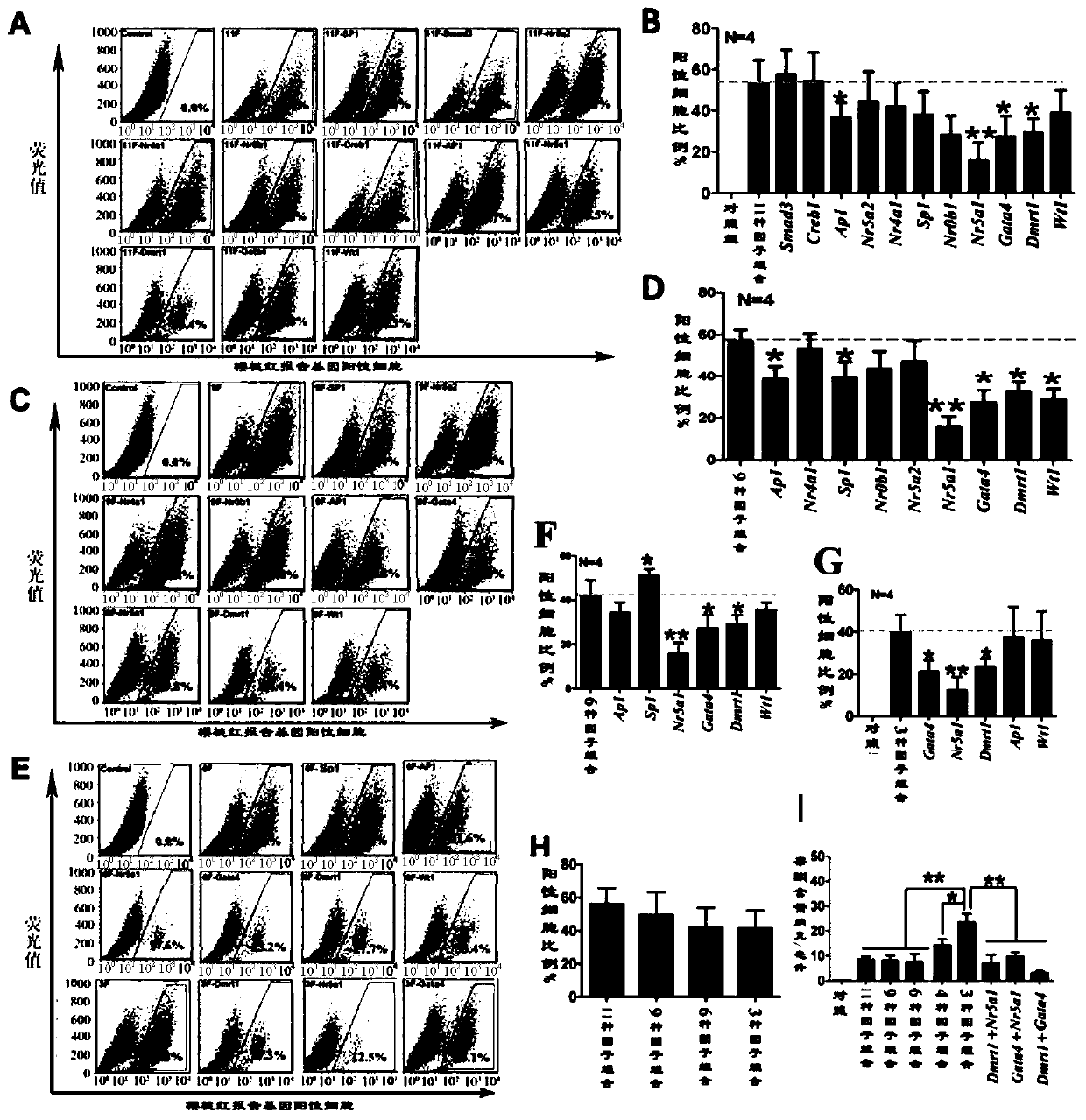
Method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into similar testicular interstitial cells by combination of transcription factors
ActiveCN106636210AReduce riskShort timeGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsTransdifferentiationTesticular Interstitial Cells
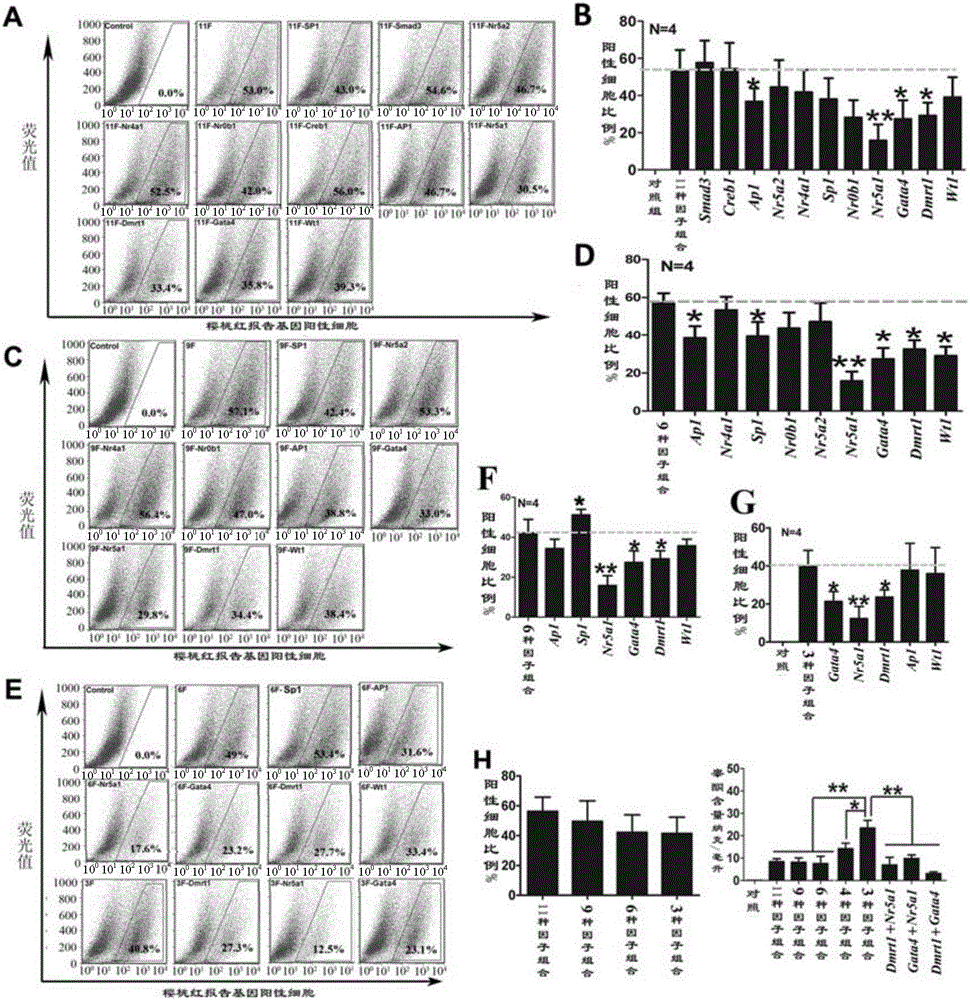
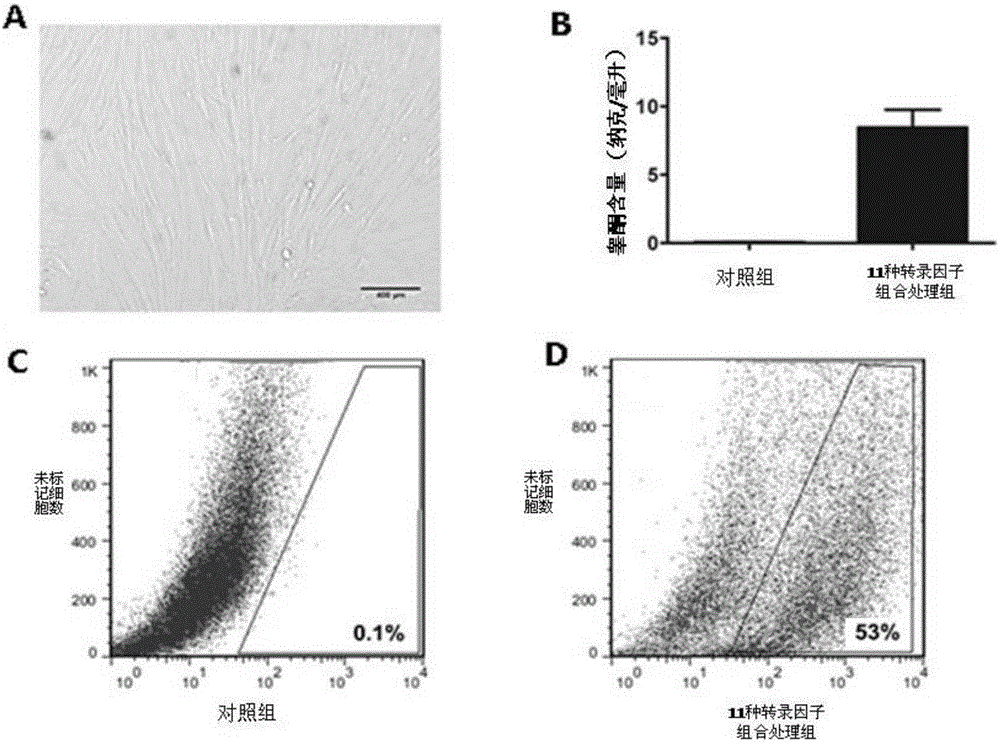
The invention relates to a method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into similar testicular interstitial cells. The method is characterized in that required transcription factors are respectively cloned to lentiviral vectors, and packaged to be virus particles for transfection to fibroblast; by utilizing an overexpression transcription factor method, inducing transdifferentiation of the fibroblast into inducible testicular interstitial cells, wherein the transcription factors are sourced from human beings, mice or rats, and the transcription factors are a part selected from a group of Dmrt1, Nr0b1, Sp1, Wt1, Nr4a1, Nr5a2, AP1, Creb1, Smad3, Nr5a1 and Gata4,or a combination of all transcription factors. The cells after transdifferentiation have the androgen synthesis related gene expression profile similar to that of mature testicular interstitial cells, and can synthesize and secrete testosterone. The similar testicular interstitial cells prepared with the method can be used for treating male hypogonadism syndrome.
Owner:BIOPHARM RES & DEV CENT JINAN
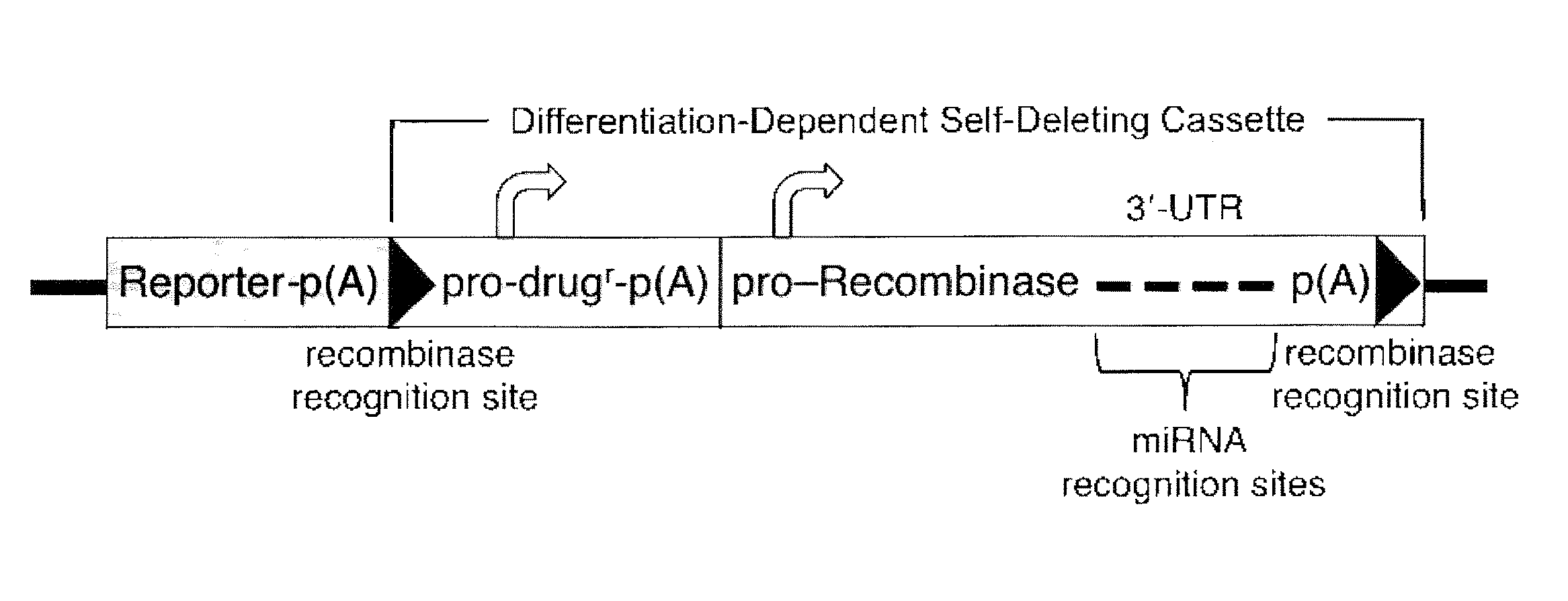
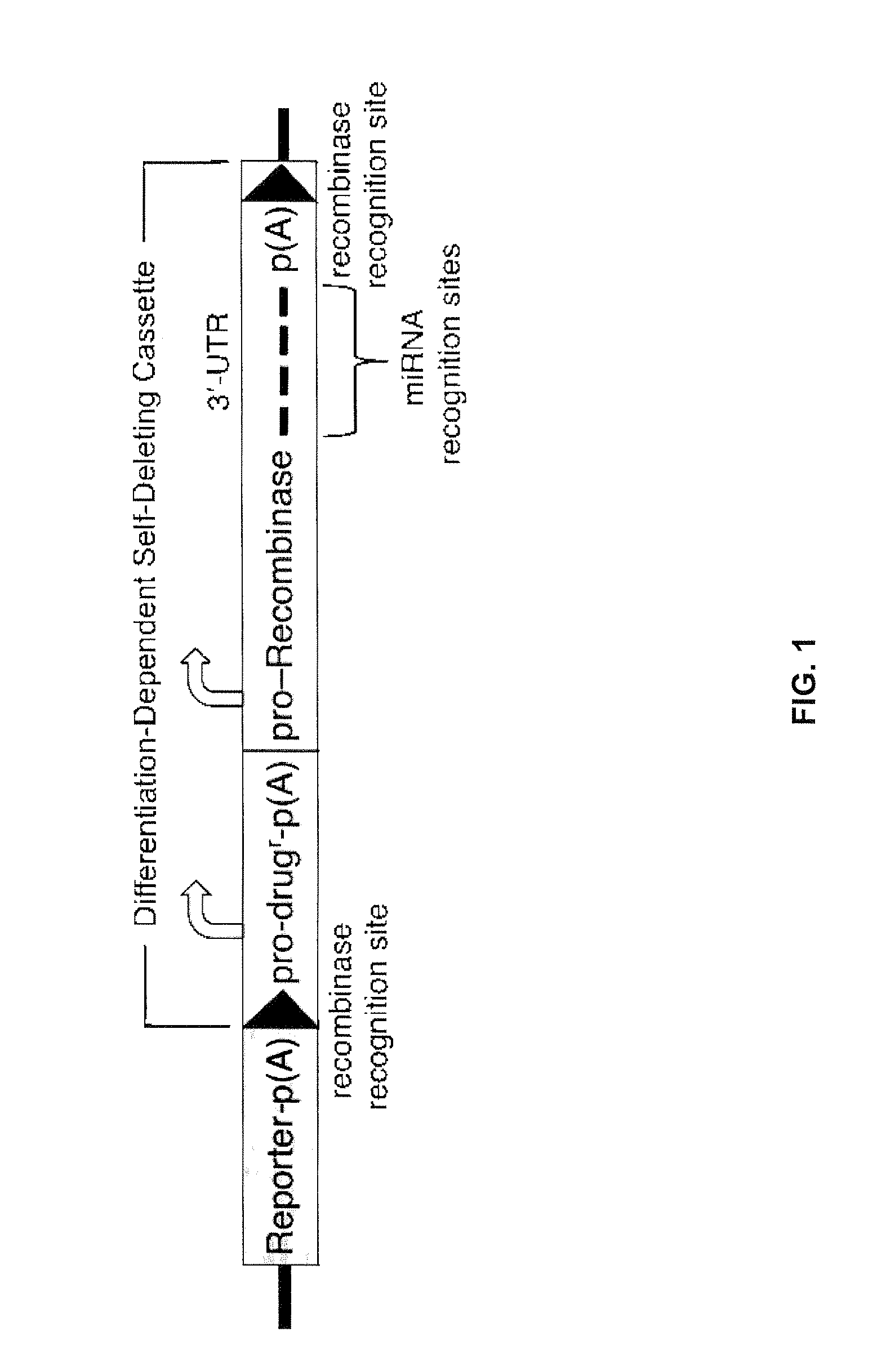
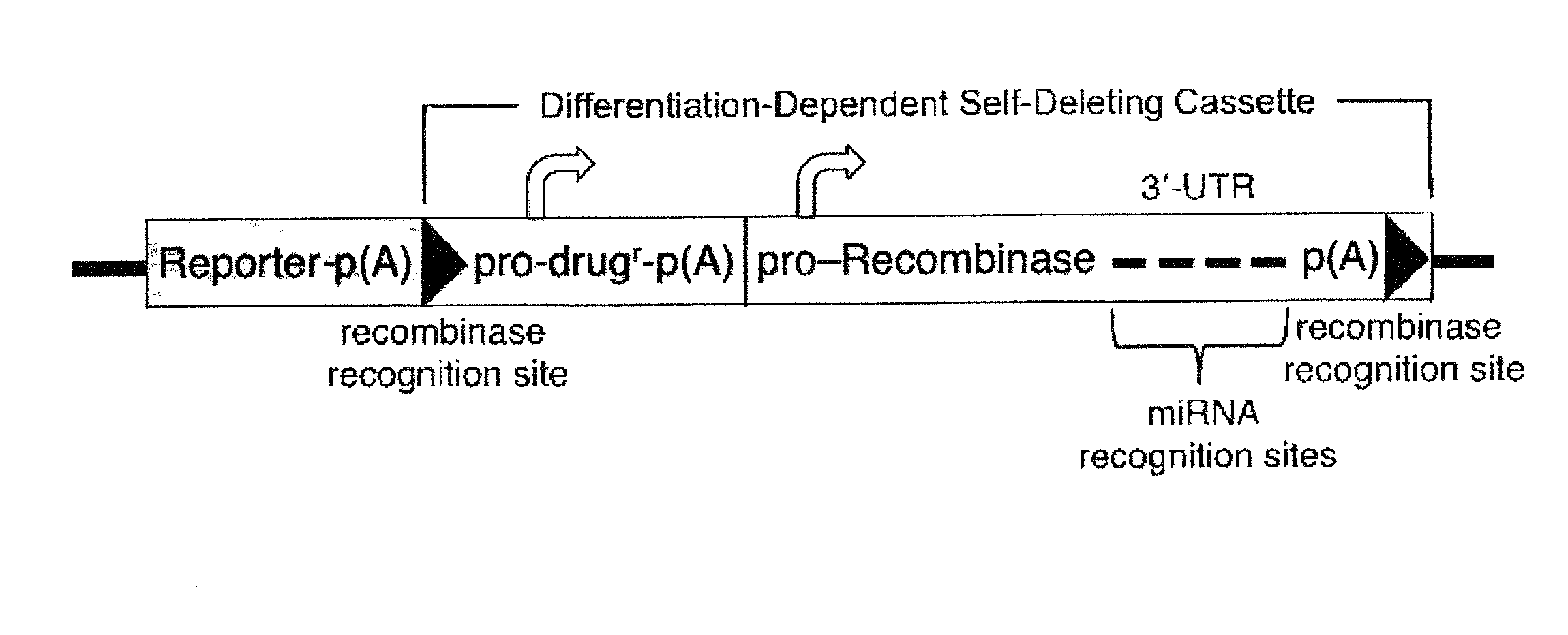
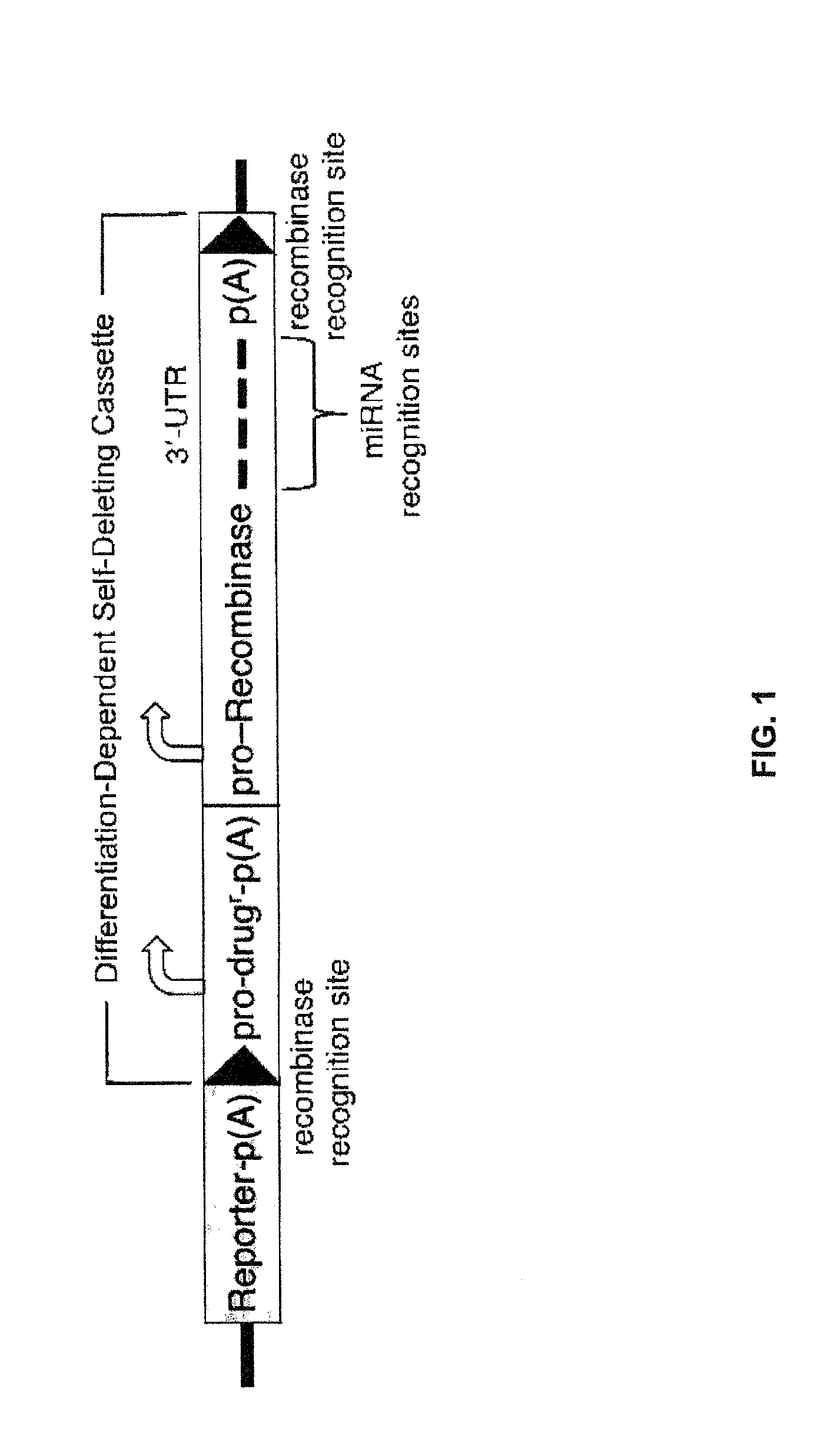
miRNA-Regulated Differentiation-Dependent Self-Deleting Cassette
Targeting constructs and methods of using them are provided for differentiation-dependent modification of nucleic acid sequences in cells and in non-human animals. Targeting constructs comprising a promoter operably linked to a recombinase are provided, wherein the promoter drives transcription of the recombinase in an differentiated cell but not an undifferentiated cell. Promoters include Blimp1, Prm1, Gata6, Gata4, Igf2, Lhx2, Lhx5, and Pax3. Targeting constructs with a cassette flanked on both sides by recombinase sites can be removed using a recombinase gene operably linked to a 3′-UTR that comprises a recognition site for an miRNA that is transcribed in undifferentiated cells but not in differentiated cells. The constructs may be included in targeting vectors, and can be used to automatically modify or excise a selection cassette from an ES cell, a non-human embryo, or a non-human animal.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
miRNA-Regulated Differentiation-Dependent Self-Deleting Cassette
Targeting constructs and methods of using them are provided for differentiation-dependent modification of nucleic acid sequences in cells and in non-human animals. Targeting constructs comprising a promoter operably linked to a recombinase are provided, wherein the promoter drives transcription of the recombinase in an differentiated cell but not an undifferentiated cell. Promoters include Blimp1, Prm1, Gata6, Gata4, Igf2, Lhx2, Lhx5, and Pax3. Targeting constructs with a cassette flanked on both sides by recombinase sites can be removed using a recombinase gene operably linked to a 3′-UTR that comprises a recognition site for an miRNA that is transcribed in undifferentiated cells but not in differentiated cells. The constructs may be included in targeting vectors, and can be used to automatically modify or excise a selection cassette from an ES cell, a non-human embryo, or a non-human animal.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
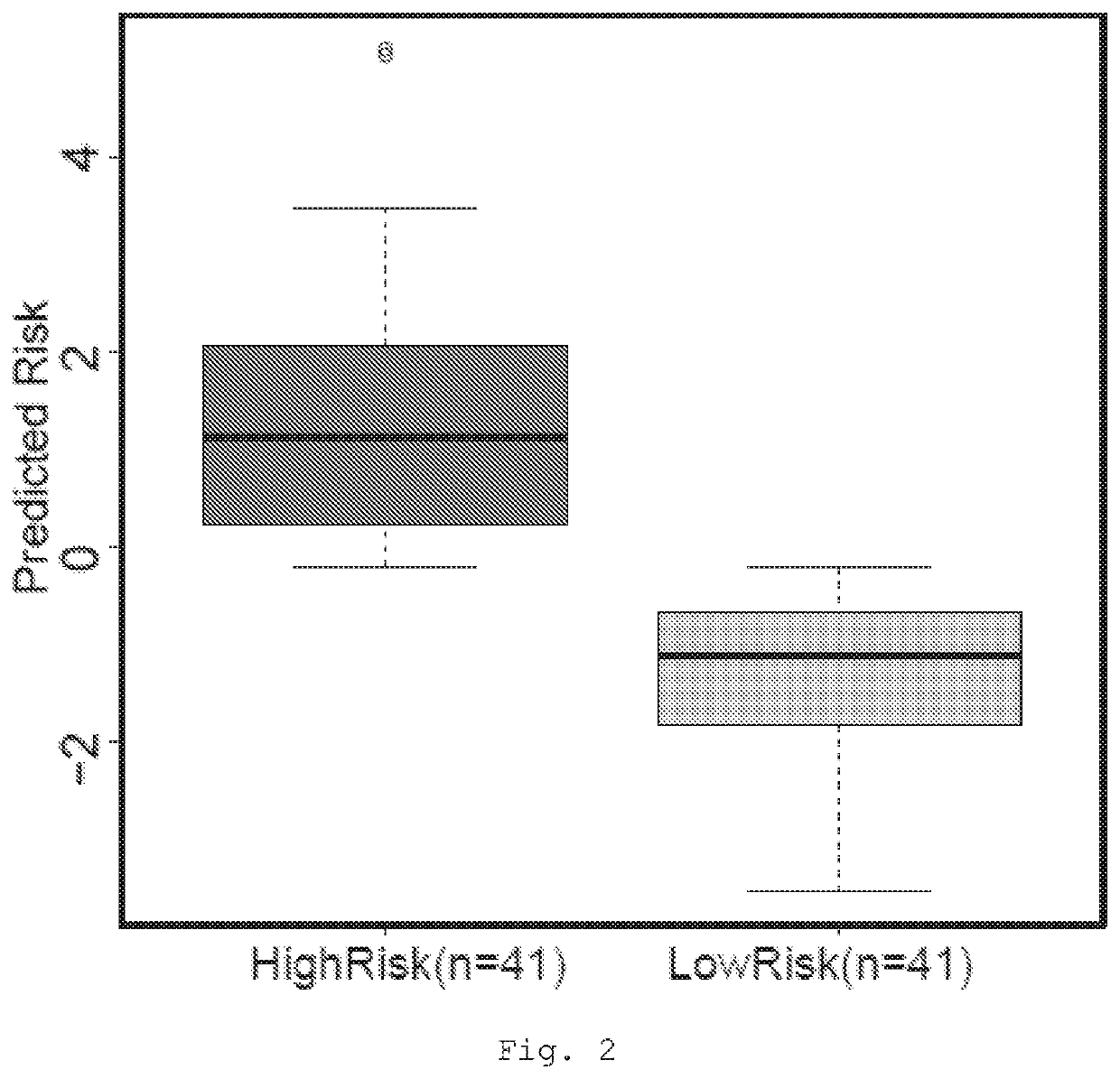
Prognostic and treatment response predictive method
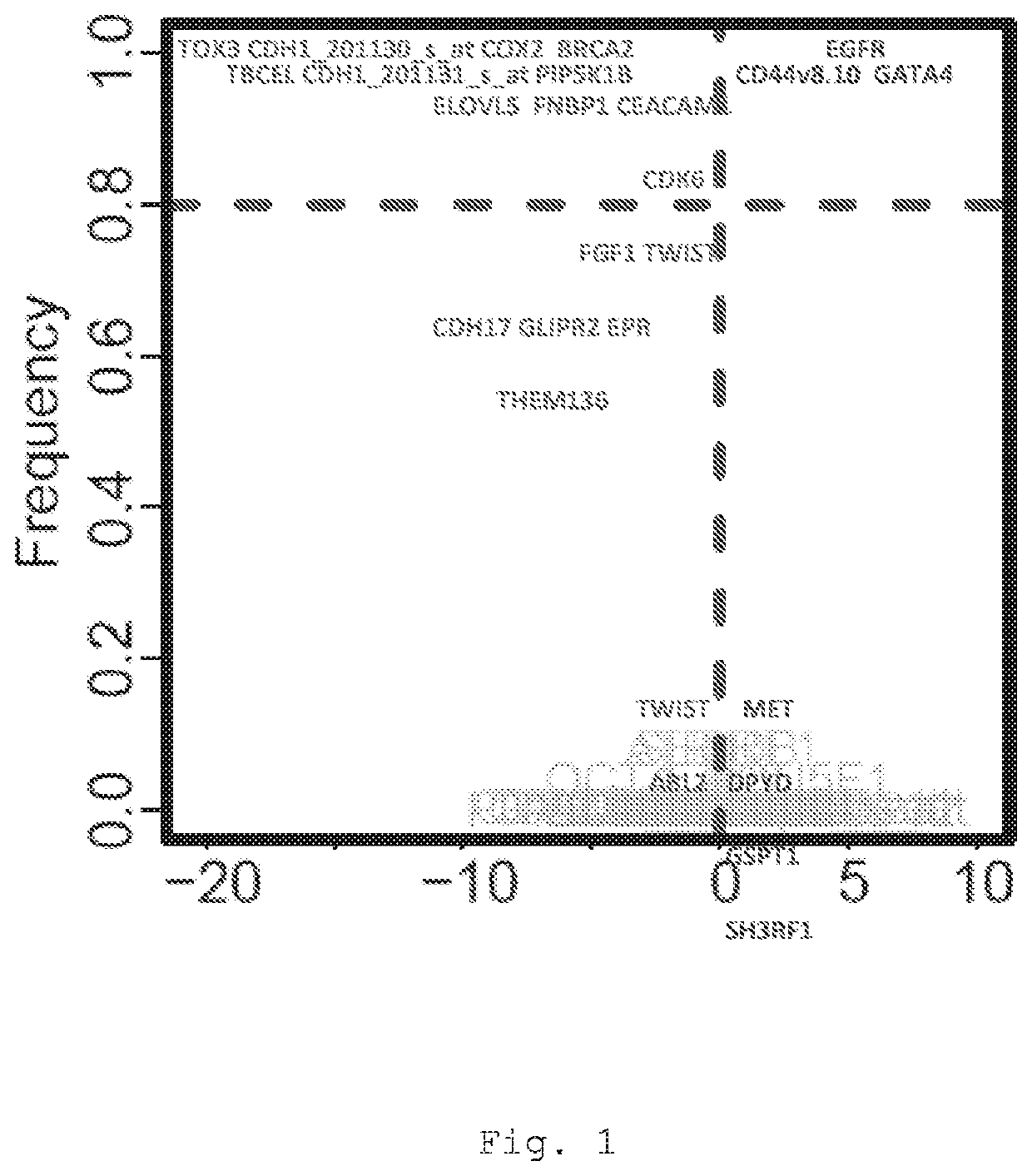
PendingUS20200239968A1Avoiding unwanted side effectAggressive treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDPYDPredictive methods
The present invention provides a method for predicting the treatment response of a human gastroesophageal cancer patient, the method comprising: a) measuring the gene expression of at least 3 of the following genes: CDH1, CDK6, COX2, ELOVL5, GATA4, EGFR, TBCEL, FGF7, CDH17, FNBP1, PIP5K1B, TWIST, CD44, MET, CEACAM1, TOX3, GLIPR2, GSTP1, RON, TMEM136, MYB, BRCA2, FGF1, POU5F1, EPR, DPYD, ABL2 and SH3RF1 in a sample obtained from the gastroesophageal tumour of the patient to obtain a sample gene expression profile of at least said genes; and b) making a prediction of the treatment response and / or prognosis of the patient based on the sample gene expression profile. Also provided are related computer-implemented methods and methods of treatment of gastroesophageal cancer.
Owner:THE INST OF CANCER RES ROYAL CANCER HOSPITAL +2
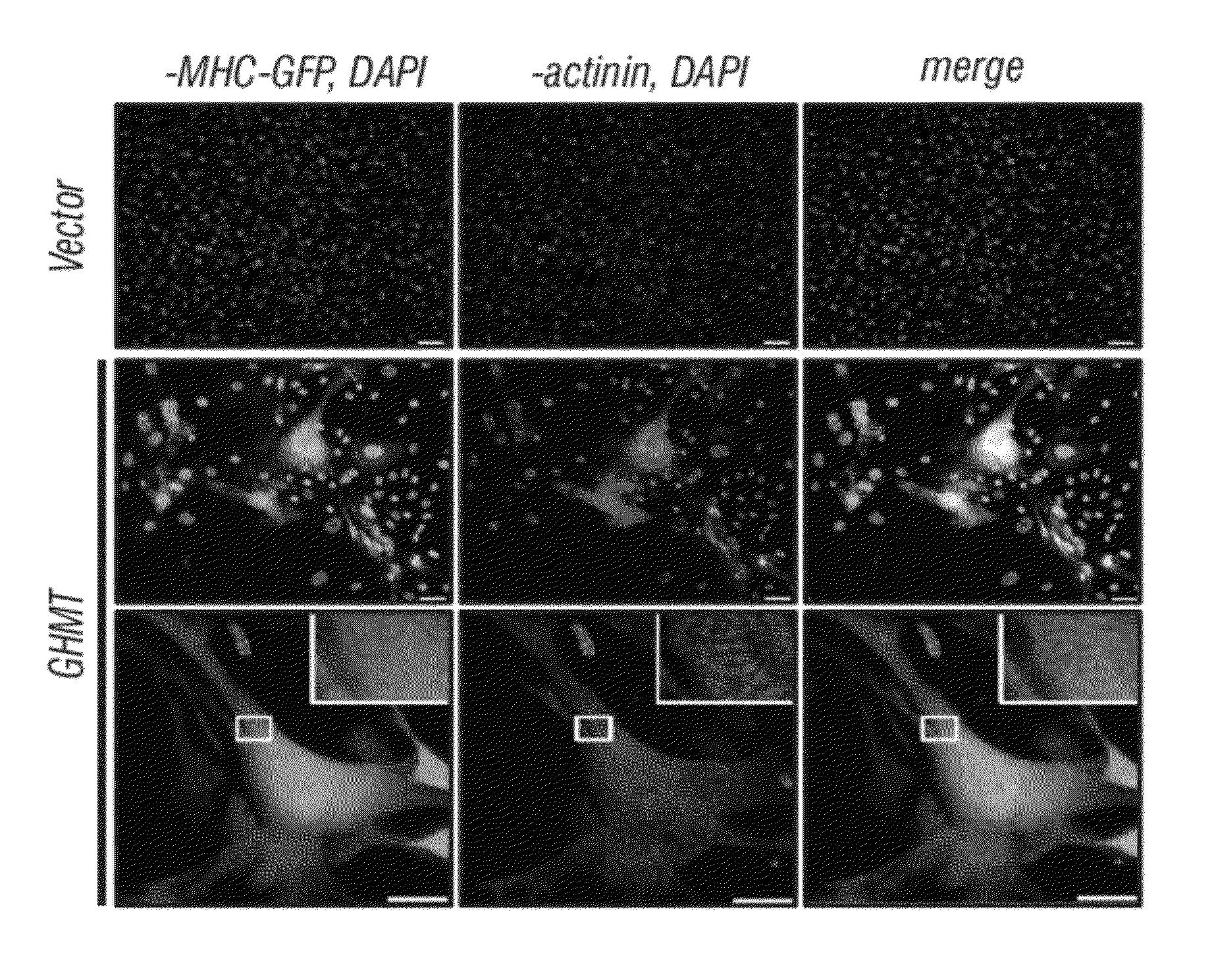
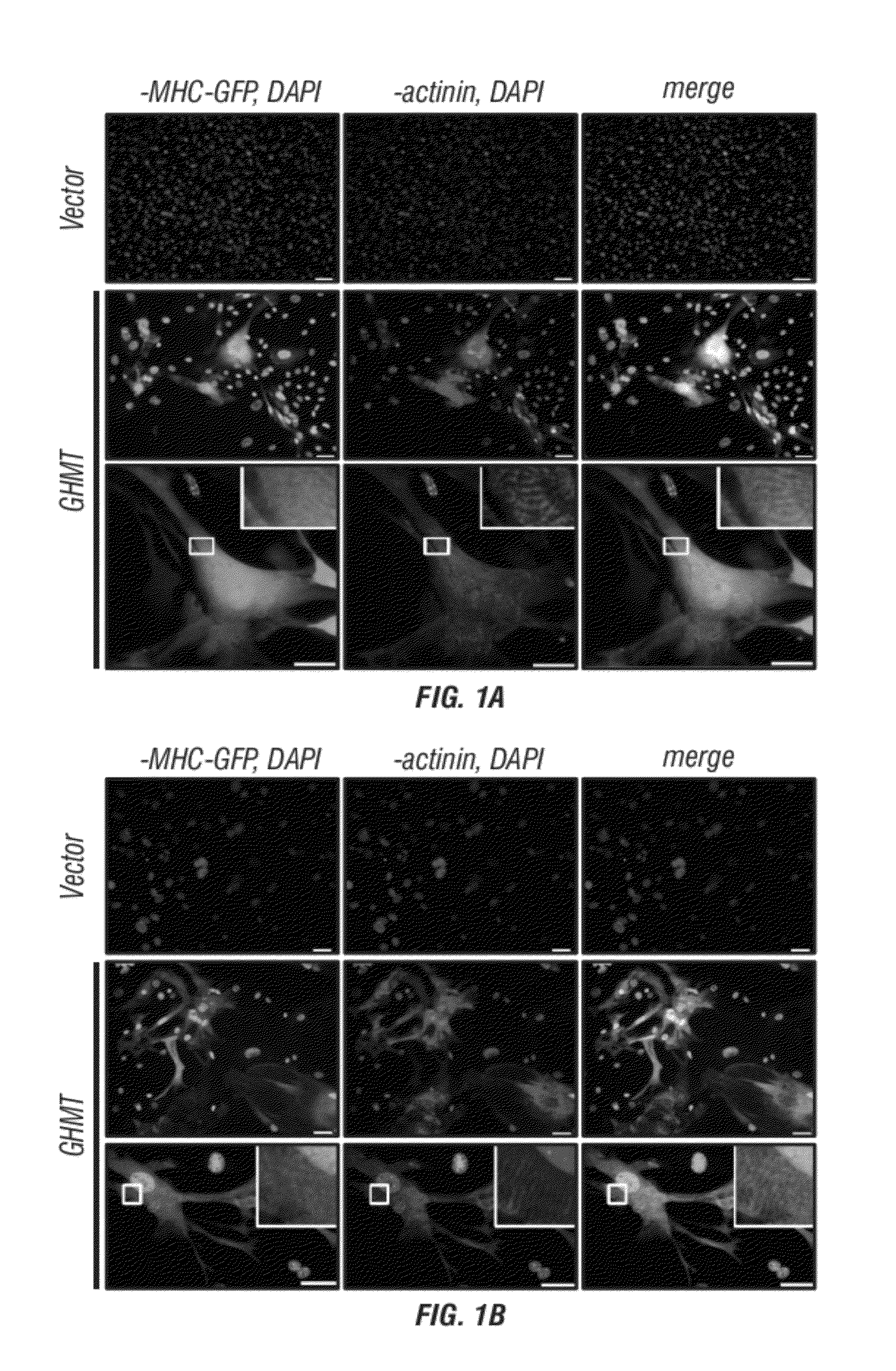
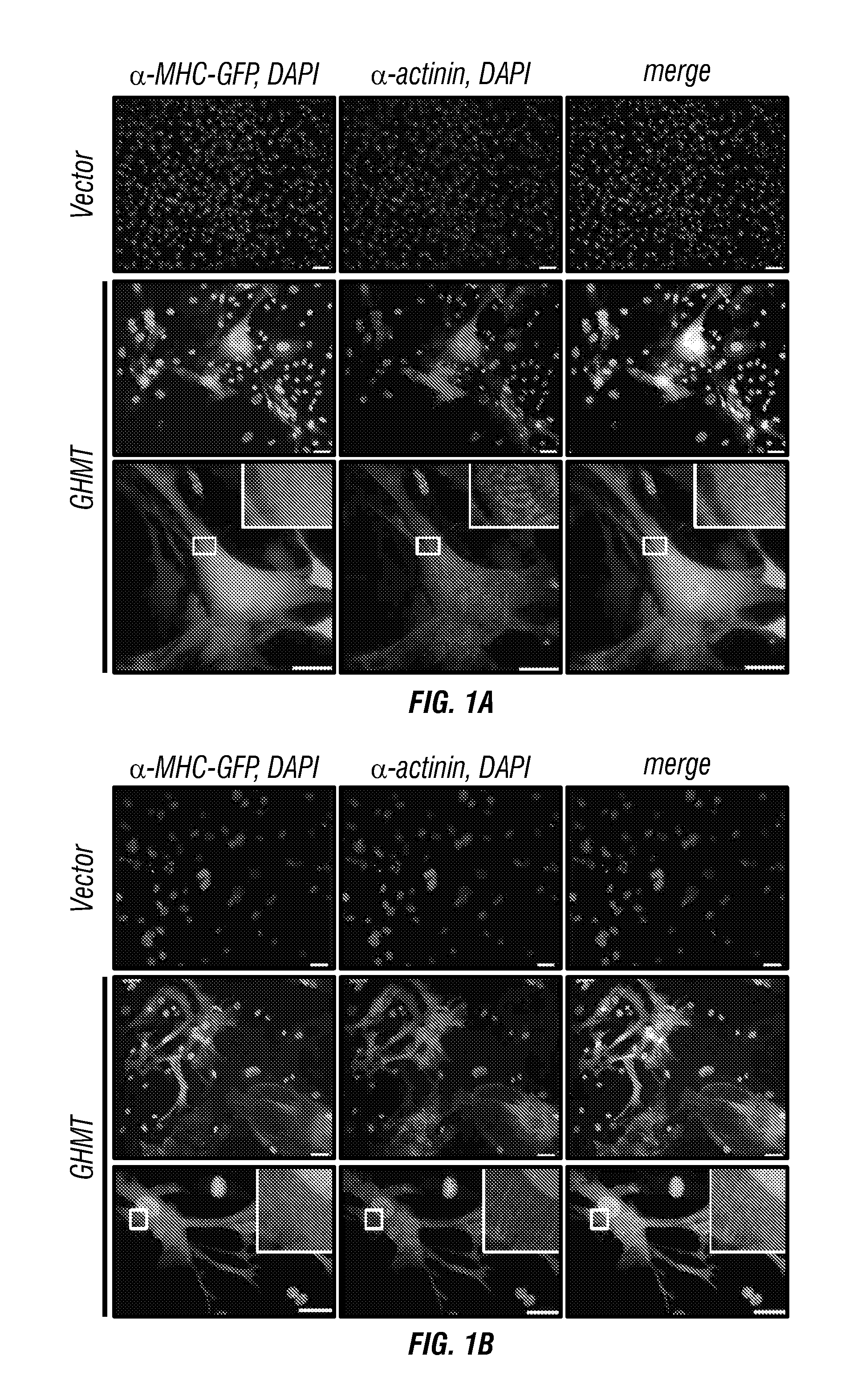
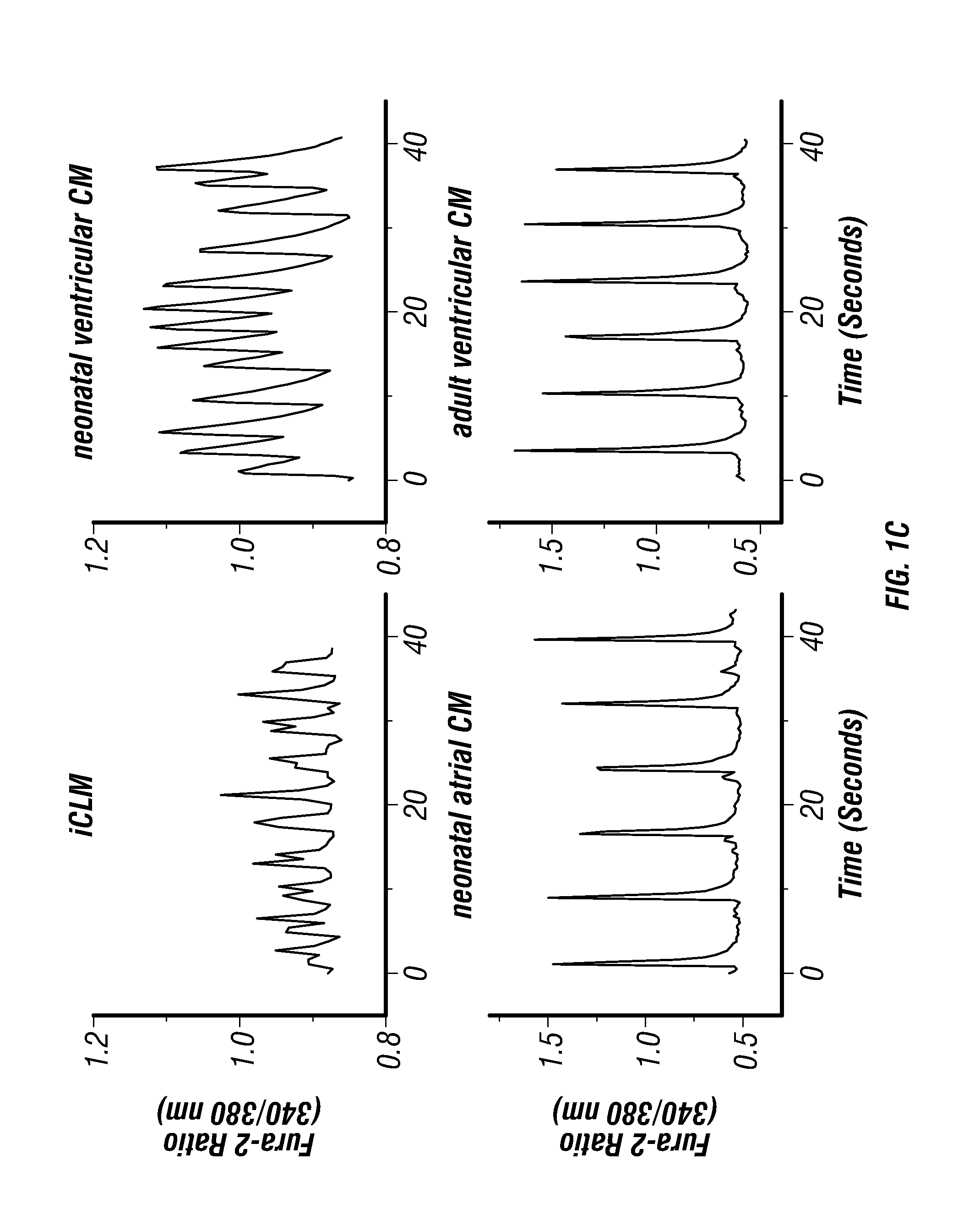
Cardiac Repair By Reprogramming of Cardiac Fibroblasts Into Cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20120213738A1Preventing delaying developmentAvoid delayBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGATA4Reprogramming
The present invention involves the use of transcription factors including Tbx5, Mef2C, Hand2, myocardin and Gata4 to reprogram cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, both in vitro and in vivo. Such methods find particular use in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction to prevent or limit scarring and to promote myocardial repair.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Cardiac repair by reprogramming of cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS9017661B2Preventing delaying developmentAvoid delayOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGATA4Reprogramming
The present invention involves the use of transcription factors including Tbx5, Mef2C, Hand2, myocardin and Gata4 to reprogram cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, both in vitro and in vivo. Such methods find particular use in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction to prevent or limit scarring and to promote myocardial repair.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
p63 INACTIVATION FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEART FAILURE
ActiveUS20180066252A1Increases transdifferentiation efficiencyImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTransdifferentiationReprogramming
Embodiments of the disclosure include methods and compositions for in situ cardiac cell regeneration, including transdifferentiation of cardiac cells to cardiomyocytes. In particular embodiments, in situ cardiac cell regeneration encompasses delivery of p63 shRNA and one or both of Hand2 and myocardin, and in specific embodiments further includes one or more of Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5. In specific aspects of the disclosure, adult cardiac fibroblasts are reprogrammed into cardiomyocytes using viral vectors that harbor p63 shRNA and one or both of the transcription factors Hand2 and myocardin.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Application of TNFR2
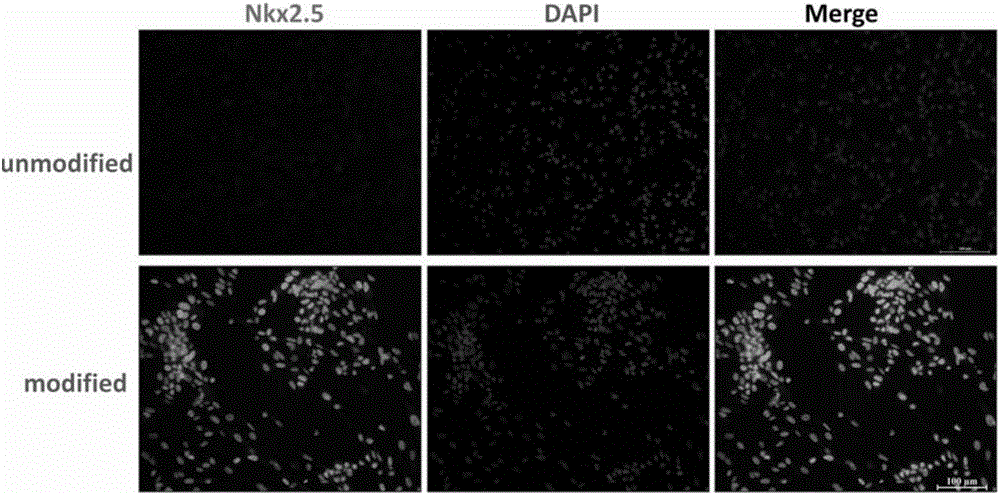
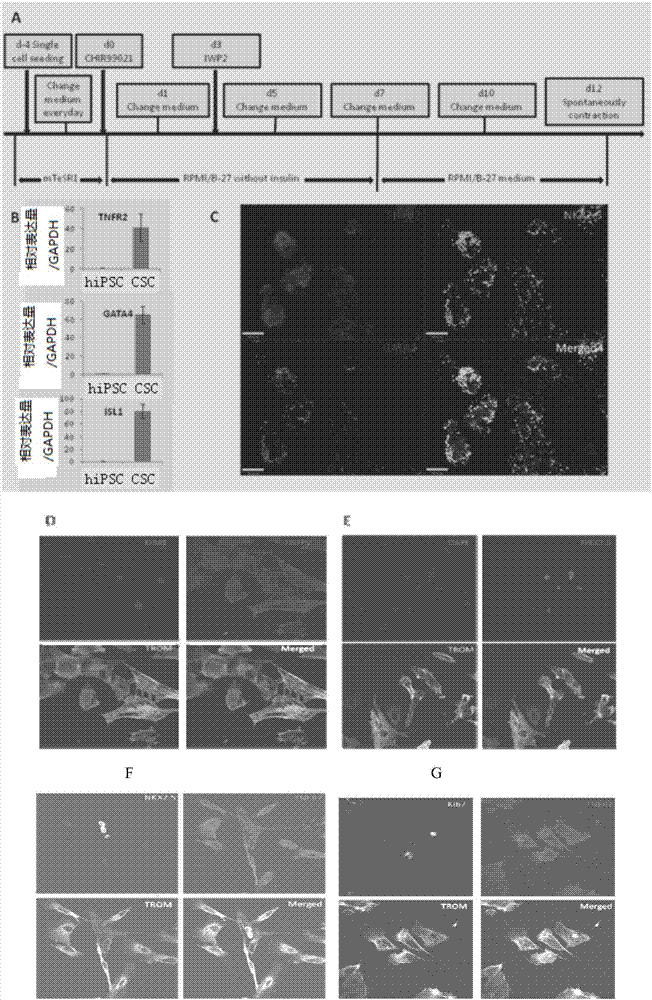
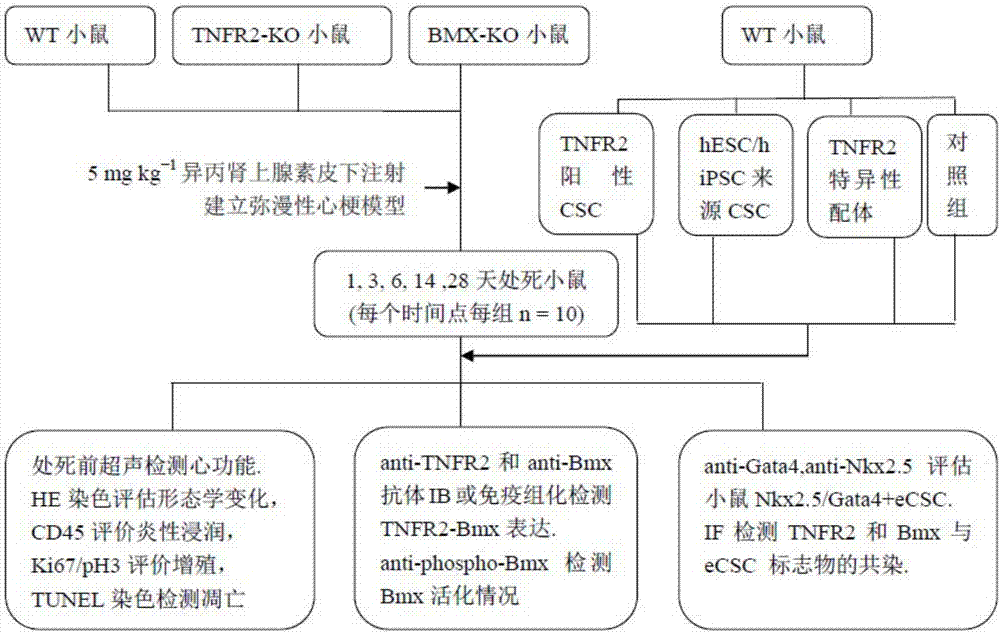
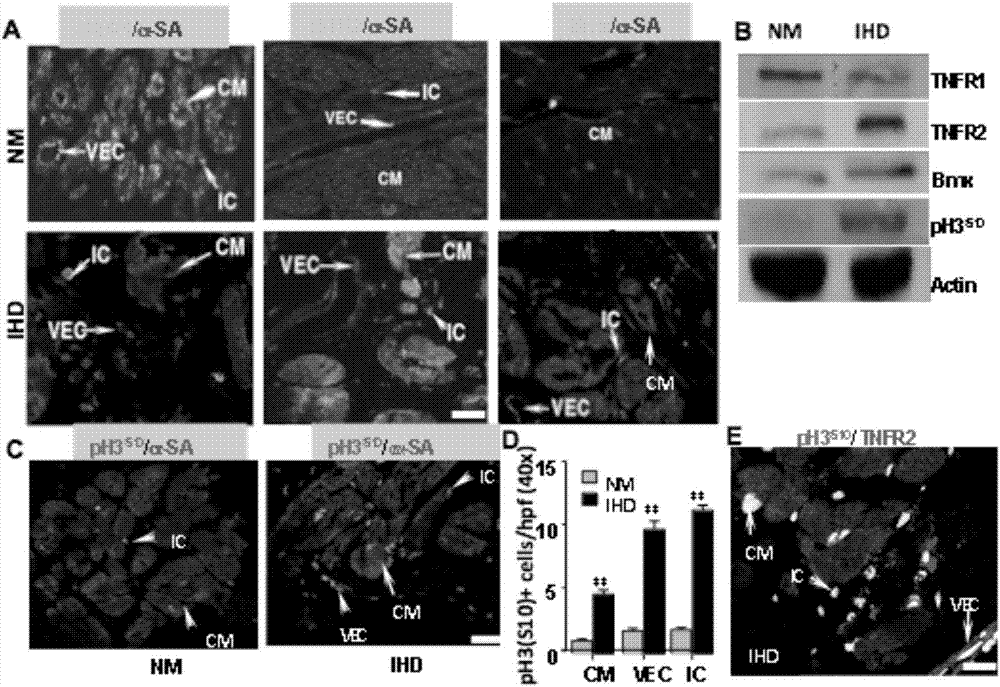
InactiveCN107441491AHigh expressionHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseBiological activation
The invention discloses an application of a TNFR2 activating agent to preparing a drug for promoting activation, migration and survival of cardiac stem cells. The TNFR2 activating agent has the effect of promoting activation of the cardiac stem cells and cardiac repair. The activated TNFR2-Bmx can enhance expression and the activity of Nkx2.5+ / Gata4+, and mediate activation, migration and survival of c-Kit+ endogenous cardiac stem cells (eCSCs). In addition, the activation of the TNFR2 increases the differentiation of cardiac cells of a hESC / hiPSC source. The TNFR2 activating agent activates the TNFR2 through the specificity so that the TNFR2 is beneficial to repairing of myocardial infarction, and a new strategy can be provided for human heart disease treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Application of Guizhou black goat lambing major genes, primer pairs and kit
PendingCN113278709AImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGATA4Fishery
The invention discloses application of Guizhou black goat lambing major genes, primer pairs and a kit. The Guizhou black goat lambing major genes comprise up-regulation genes AMH, CYP19A1, FOXL2, FSHR, GATA4, INHBA, LHB, LHX9 and ZP3, and down-regulation genes CNOT1, DMRTA1, GHRHR, Hox-All, Oviductin, PCYT1B, SLC34A2, WDR19 and Wnt-7A; and the expression quantity of the up-regulation genes and the expression quantity of the down-regulation genes in the lambing Guizhou black goats are up-regulated and down-regulated respectively. Guizhou black goat lambing major genes are mastered, gene individuals with single-lambing property are gradually eliminated in generation breeding, gene individuals with lambing property are selected and reserved, and an important scientific basis is provided for building a new specialized lambing strain of a breeding group of the Guizhou black goats. The Guizhou black goat lambing major genes, the primer pairs and the kit has an important value for researching the polyfetal character of the Guizhou black goats, and has an important significance for improving the production performance, the breeding supply capacity, the economic benefit and the social benefit of the Guizhou local variety goats.
Owner:贵州省种畜禽种质测定中心
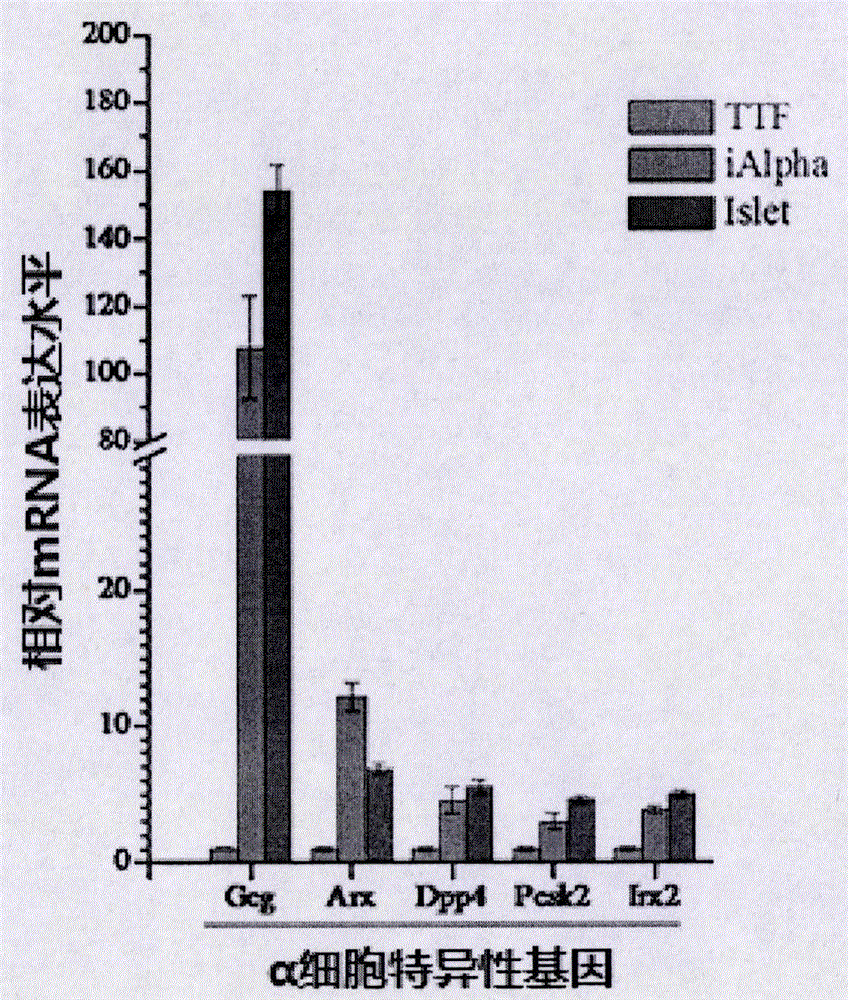
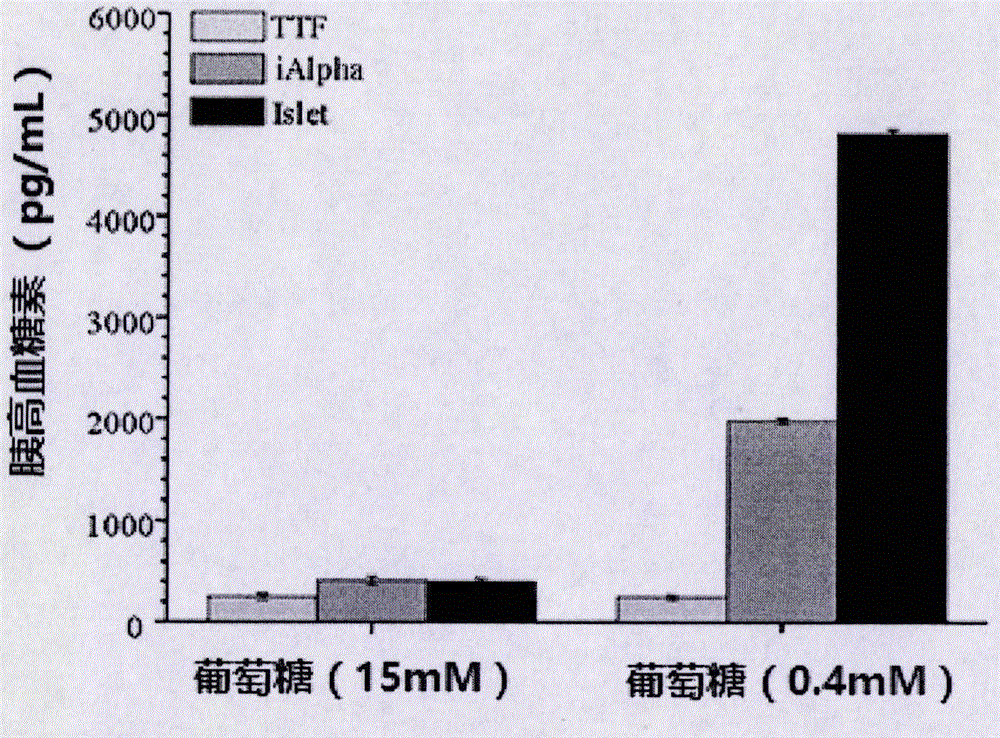
Preparation method, product and application of alpha cell
InactiveCN106754727ALow tumorigenicityBest combinationMetabolism disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGATA4PAX4
The invention provides a preparation method, a product and application of an alpha cell. The preparation method of the alpha cell comprises the following steps of over-expressing the following transcription factors in a somatic cell: Hhex, Foxa3, Gata4, Pdx1 and Pax4. The invention also provides the alpha cell prepared and obtained by the method and the application of the alpha cell. The invention discloses a brand-new method for obtaining the alpha cell; the alpha cell has important effects on the research and the treatment of diabetes mellitus and the application of relevant regenerative medicine; the invention also optimizes a method for preparing the alpha call; the better combination of the transcription factors is found out. The alpha cell prepared and obtained by utilizing the method provided by the invention not only has the function of a natural islet alpha cell, but also is a fungible clinical resource for treating the diabetes mellitus, which is wide in source range and is high-efficiency, stable and safe.
Owner:刘天津
Cardiac repair by reprogramming of cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes
ActiveUS20150307847A1Preventing delaying developmentAvoid delayOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseGATA4Reprogramming
The present invention involves the use of transcription factors including Tbx5, Mef2C, Hand2, myocardin and Gata4 to reprogram cardiac fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes, both in vitro and in vivo. Such methods find particular use in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction to prevent or limit scarring and to promote myocardial repair.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
A method for inducing the transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into Leydig cells by a combination of transcription factors
ActiveCN106636210BReduce riskShort timeGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsTransdifferentiationTesticular Interstitial Cells
The invention relates to a method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into similar testicular interstitial cells. The method is characterized in that required transcription factors are respectively cloned to lentiviral vectors, and packaged to be virus particles for transfection to fibroblast; by utilizing an overexpression transcription factor method, inducing transdifferentiation of the fibroblast into inducible testicular interstitial cells, wherein the transcription factors are sourced from human beings, mice or rats, and the transcription factors are a part selected from a group of Dmrt1, Nr0b1, Sp1, Wt1, Nr4a1, Nr5a2, AP1, Creb1, Smad3, Nr5a1 and Gata4,or a combination of all transcription factors. The cells after transdifferentiation have the androgen synthesis related gene expression profile similar to that of mature testicular interstitial cells, and can synthesize and secrete testosterone. The similar testicular interstitial cells prepared with the method can be used for treating male hypogonadism syndrome.
Owner:BIOPHARM RES & DEV CENT JINAN
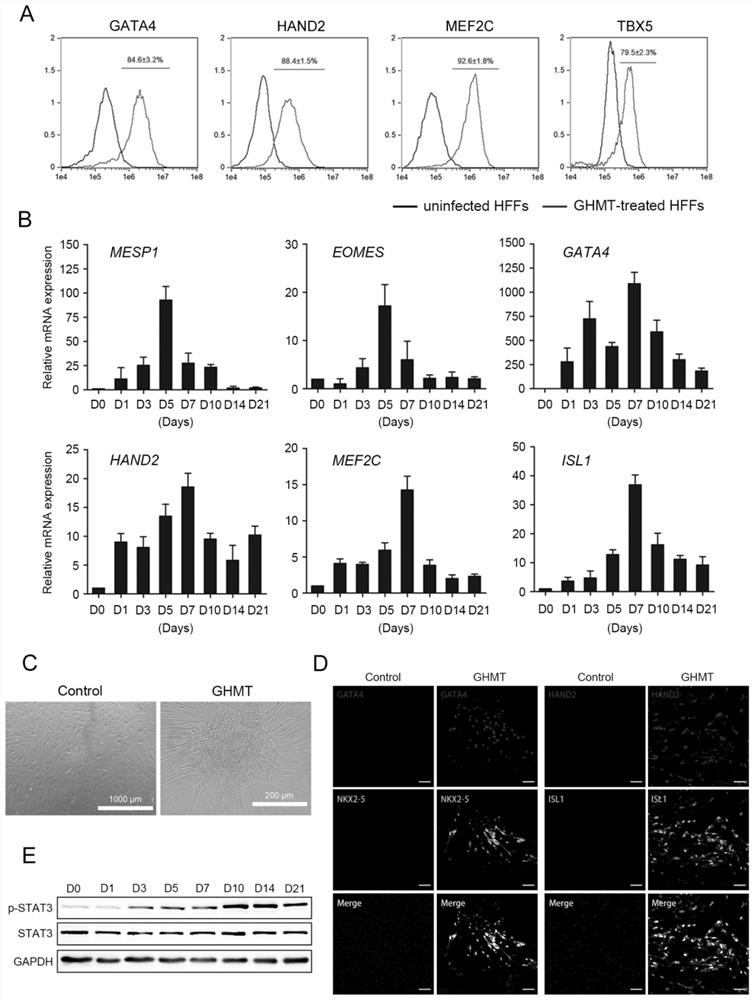
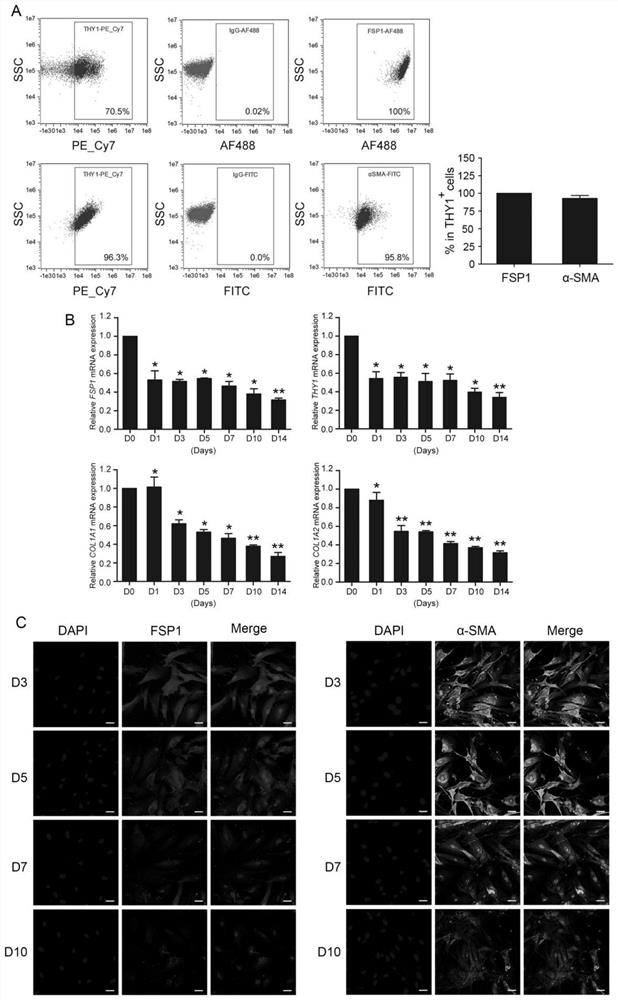
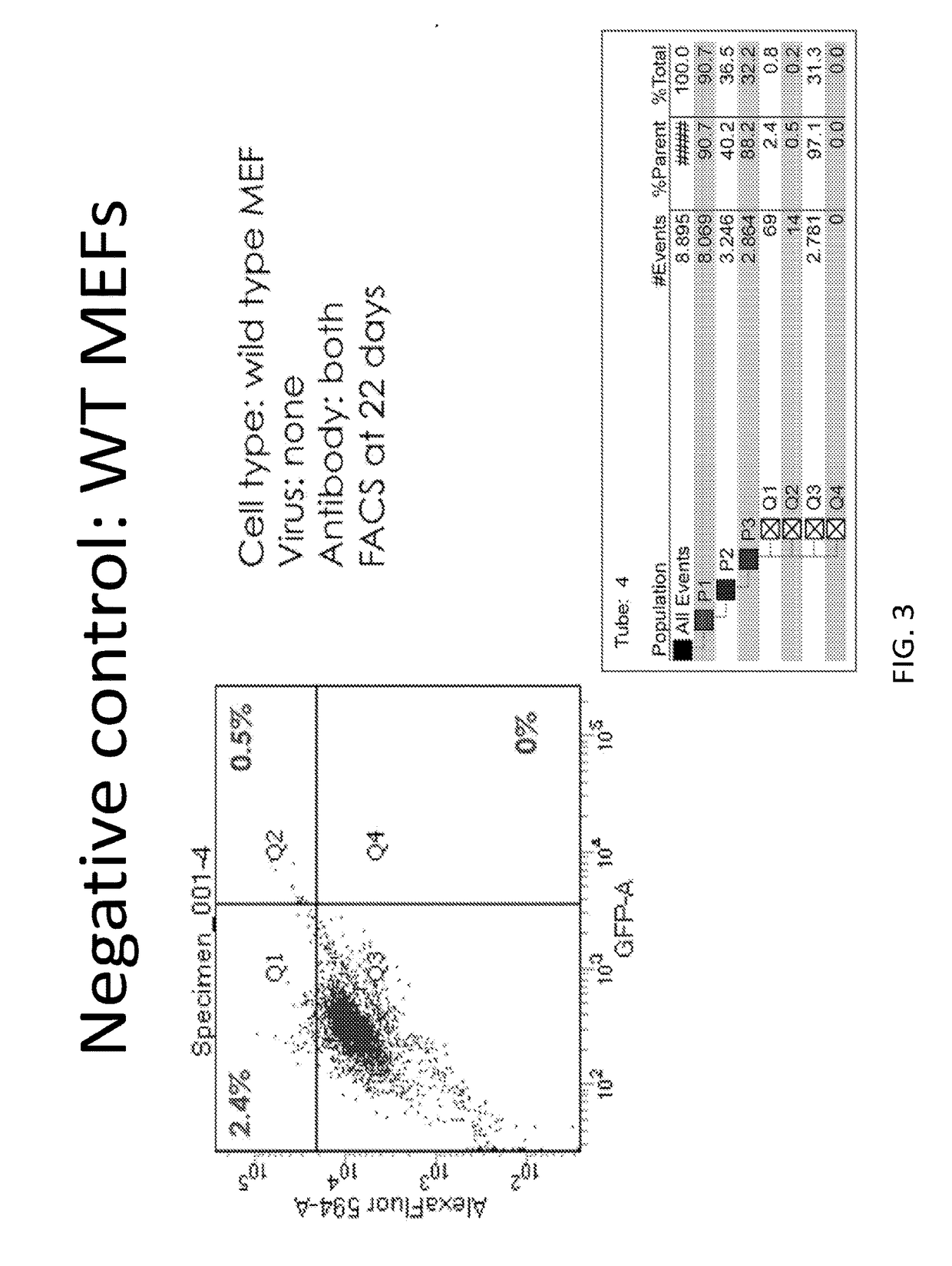
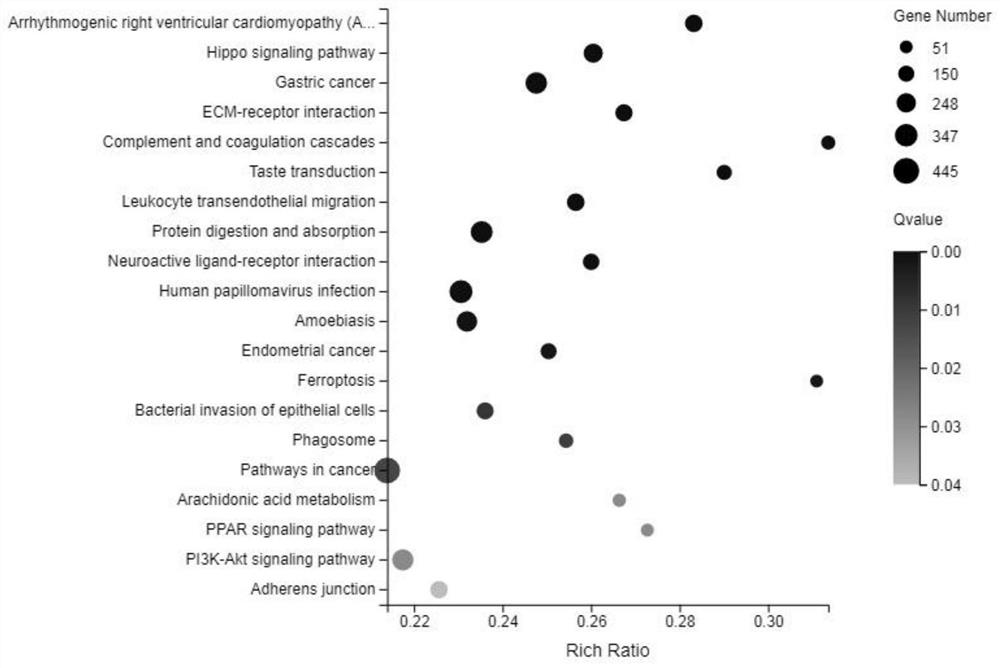
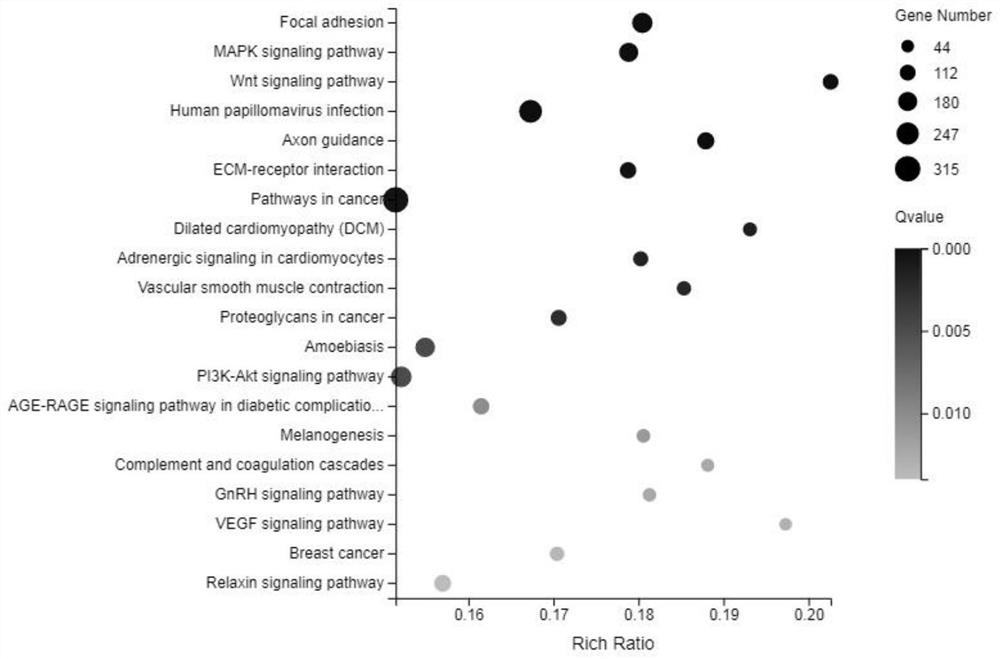
Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel
InactiveCN112604001AExpression up-regulationOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPancreas CancersOncology
The invention relates to an application of a GATA4 inhibitor in inhibiting an NF-[kappa]B / STAT3 signal channel, and according to earlier-stage research, USP28 regulates the stability of MYC through deubiquitination so as to promote up-regulation of the expression quantity of MYC; then a GATA4 promoter region is demethylated, so the expression of GATA4 is up-regulated; The process of 'inflammatory cancer transformation' of pancreas is promoted by activating two inflammation-related signal channels, namely NF-[kappa]B / SASP and Reg3[beta] / STAT3. The application has the advantages that the transcription factor GATA4 is taken as an entry point, the discussion that USP28 / MYC / GATA4 signal axis promotes pancreas inflammatory cancer transformation is taken as the center, the formation cause of pancreas cancer is understood from the new perspective of transformation, and a new method and thought are provided for preventing and treating pancreas cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
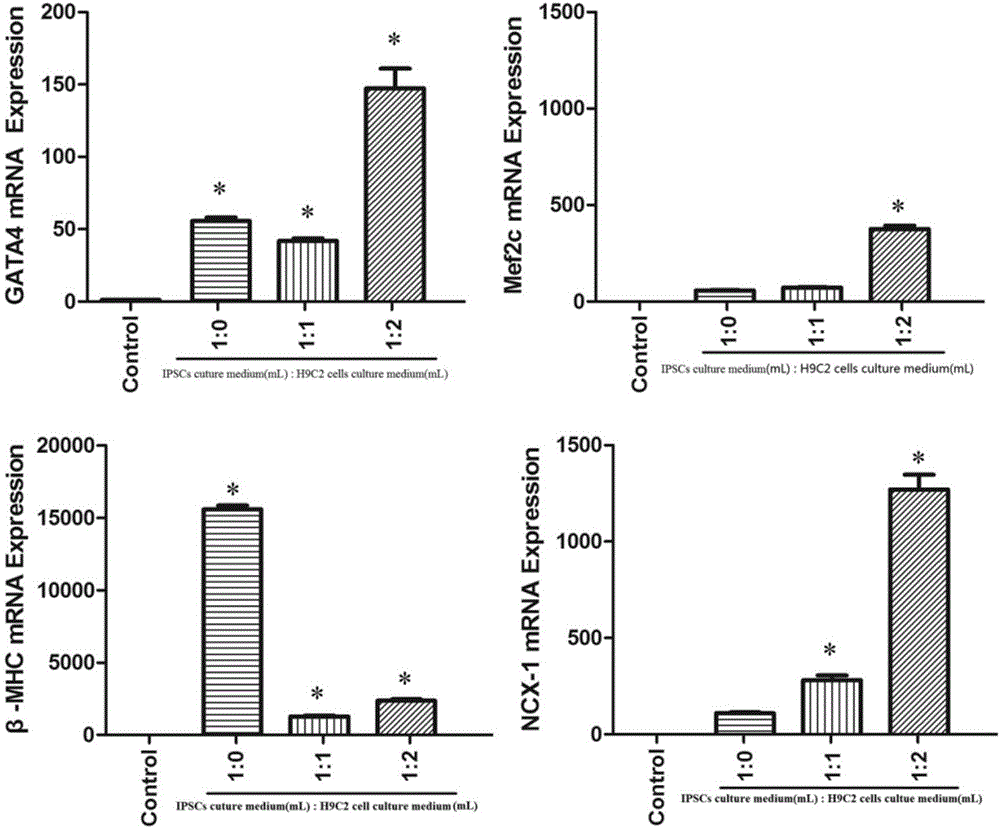
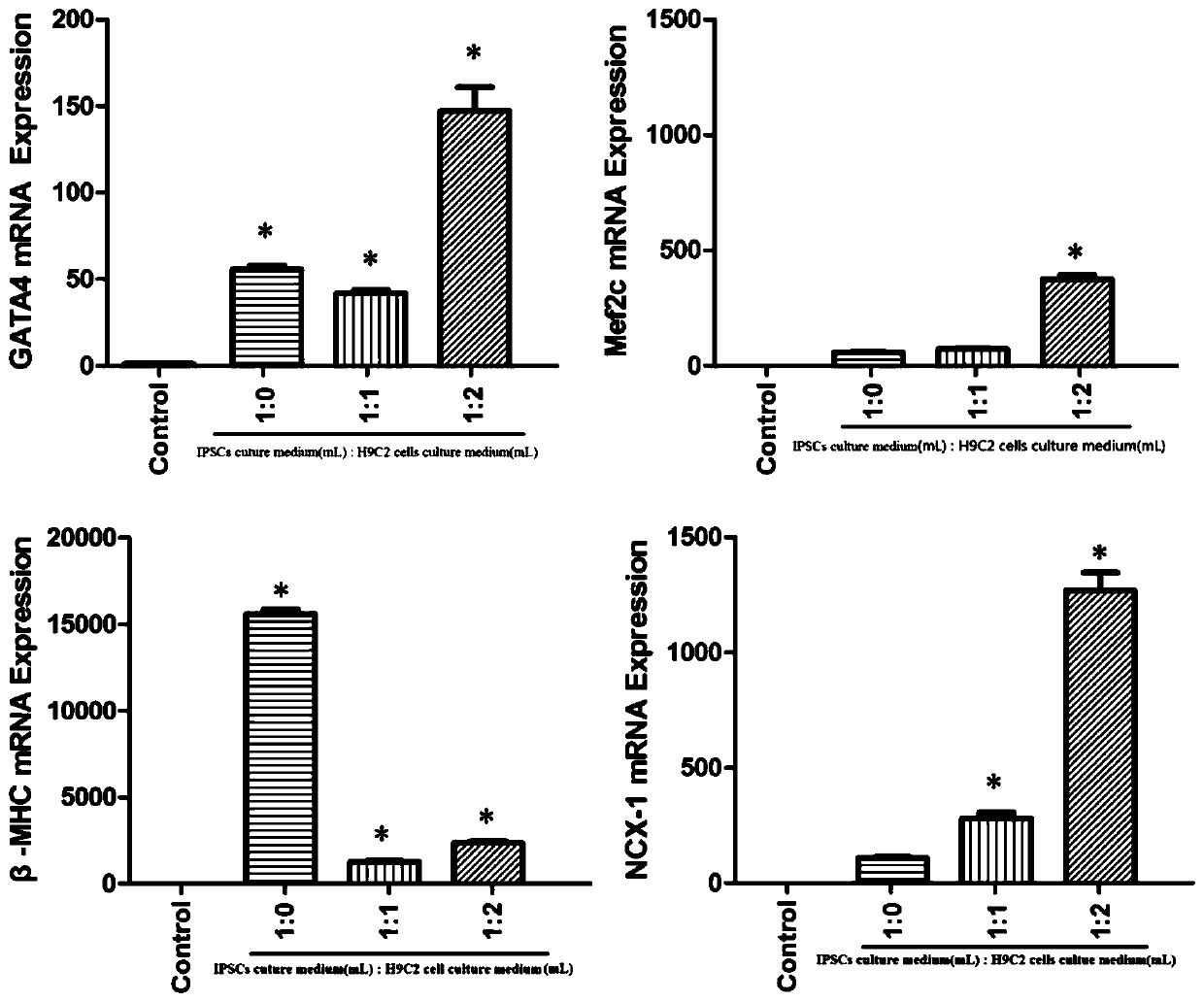
Method for inducing directional myocardiac differentiation of iPSCs (induced Pluripotent Stem Cells) with H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution
ActiveCN107177555APromotes fluorescence quenchingHigh expressionForeign genetic material cellsGATA4Immunofluorescence
The invention discloses a method for inducing directional myocardiac differentiation of iPSCs (induced Pluripotent Stem Cells) with a H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a conventional iPSCs culture solution from which LIF is removed with the H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution; culturing the iPSCs. The method proves that the H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution can effectively induce directional myocardiac differentiation of the iPSCs. Fluorescence quenching of a multi-directional differentiation potential gene OCT-4 is facilitated. As proved by a cell immunofluorescence experiment, the expression of alpha-actinin can be enhanced. As proved by a qPCR result, the expressions of mRNAs (messenger Ribonucleic Acids) such as beta-MHC, GATA4, Mef2C and NCX-1 are increased remarkably.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
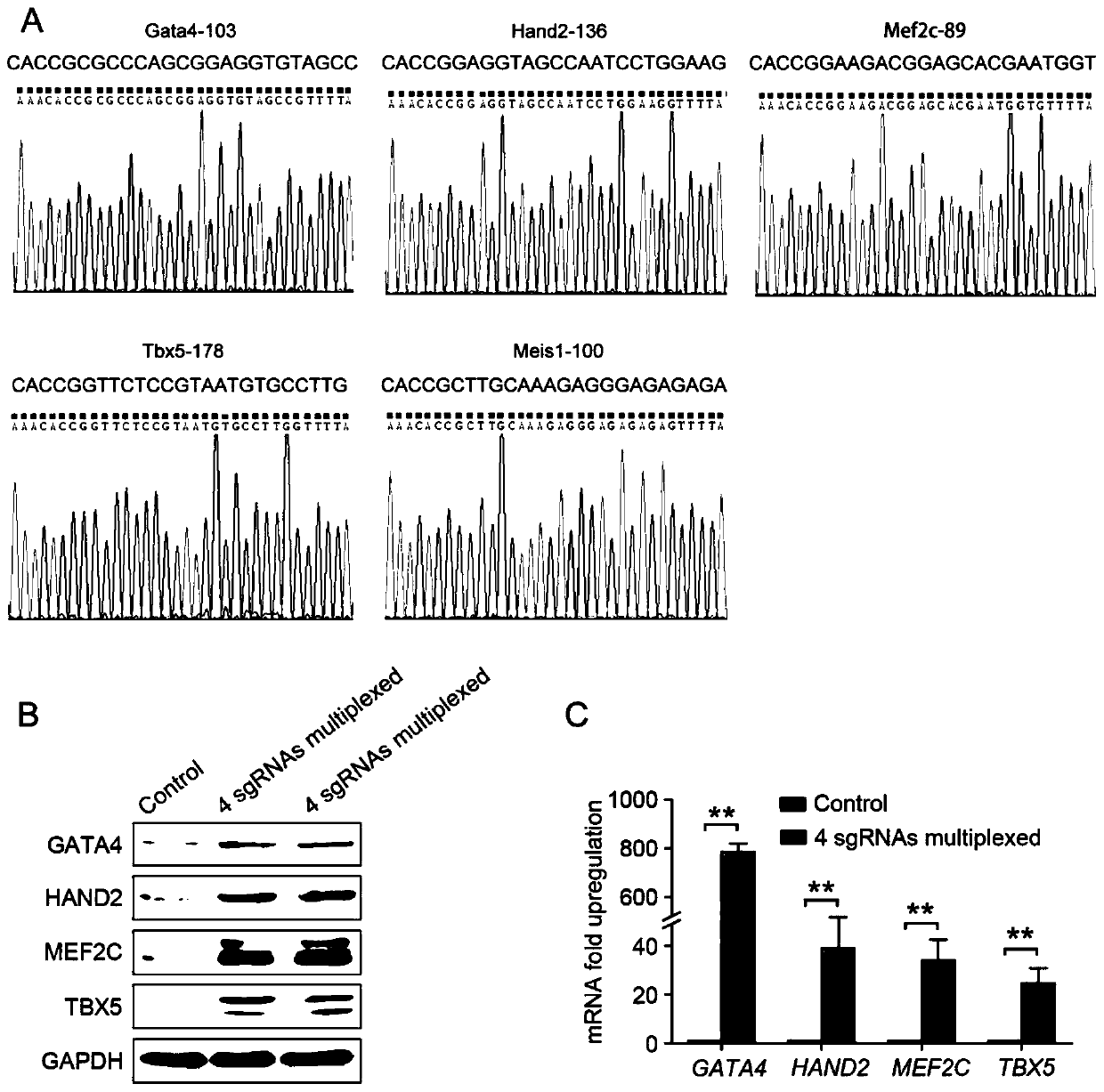
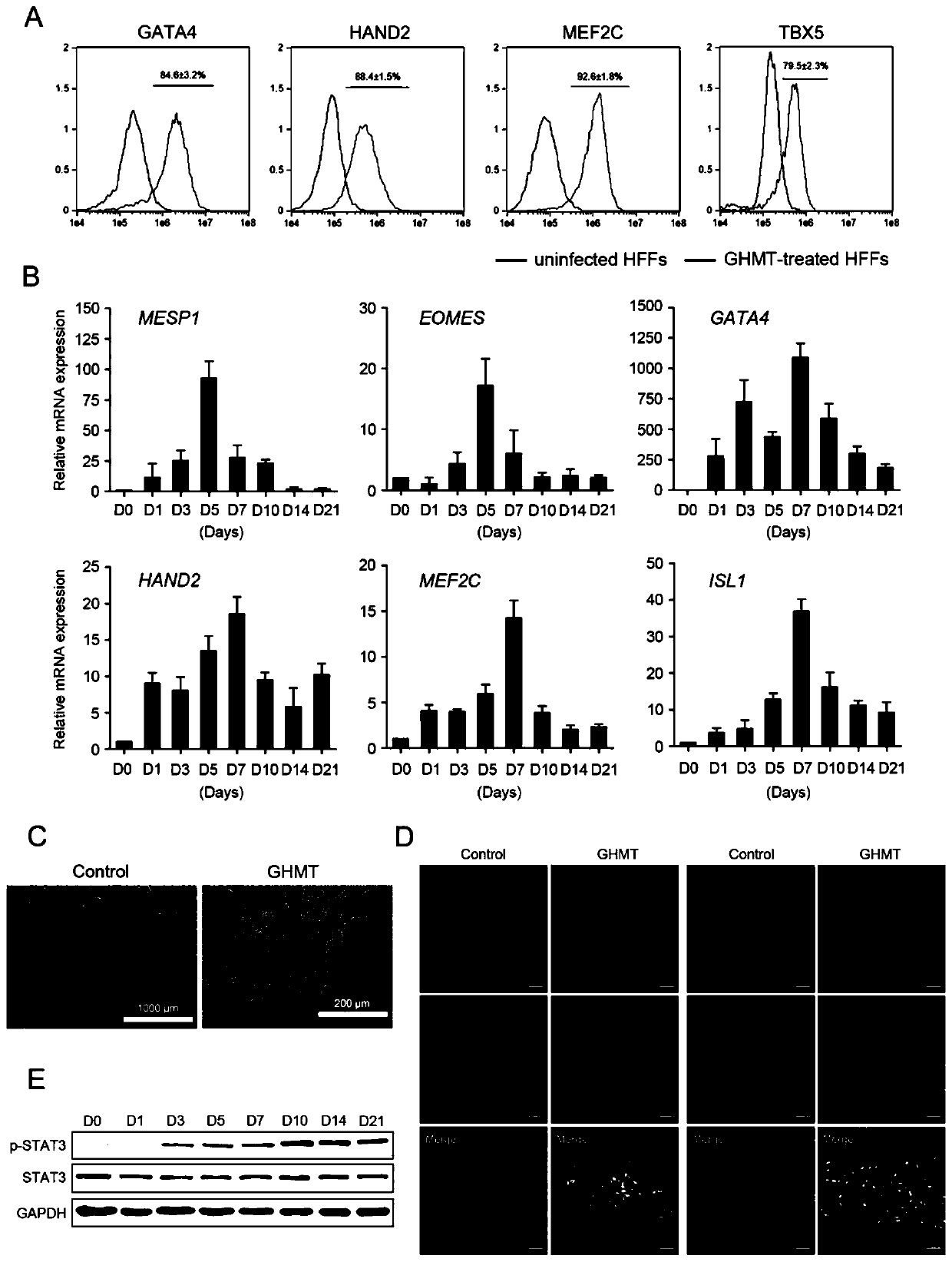
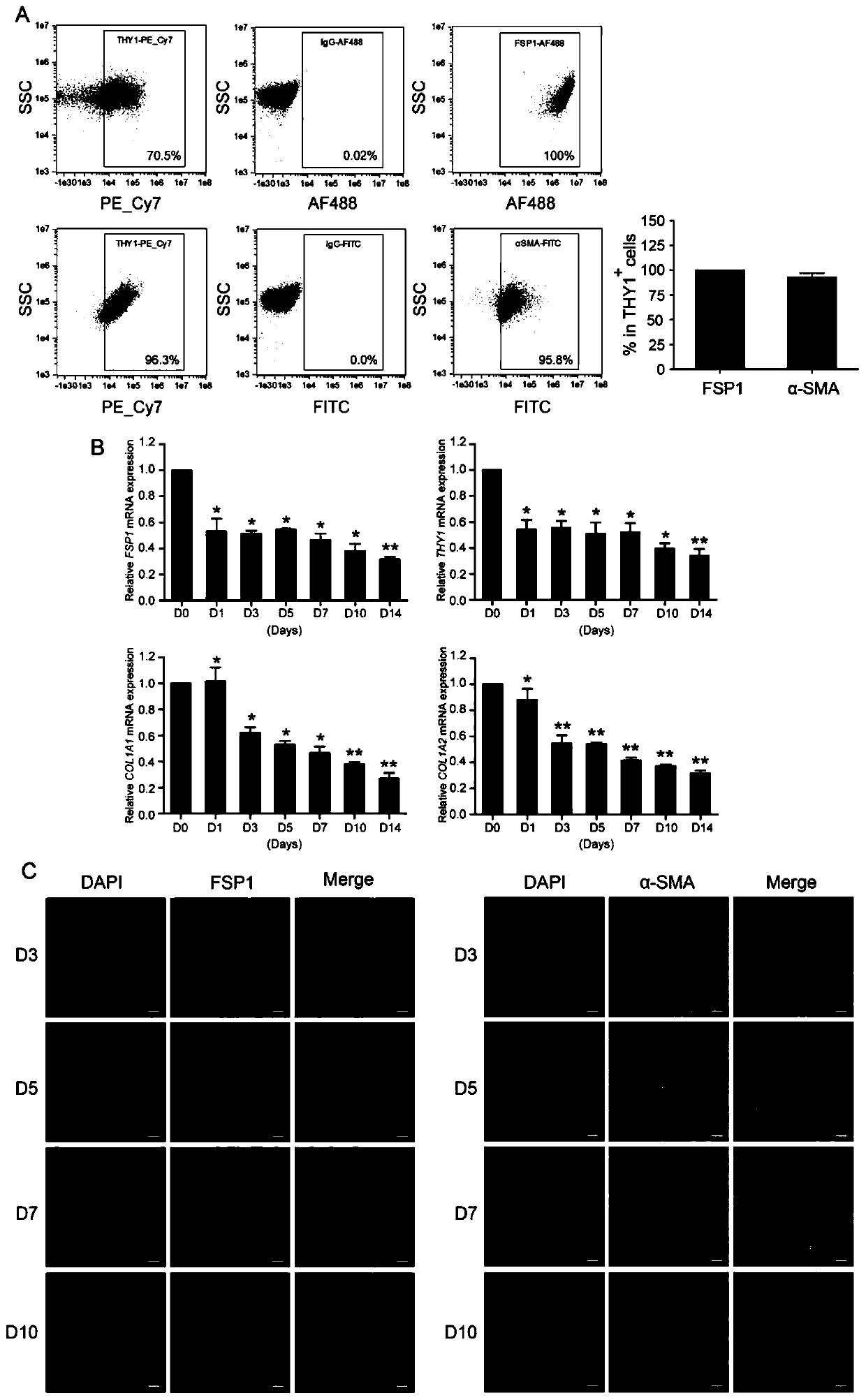
Method for preparing heart progenitor cells
ActiveCN110760546AHigh reprogramming efficiencyInhibit synthesisHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAReprogrammingHeart development
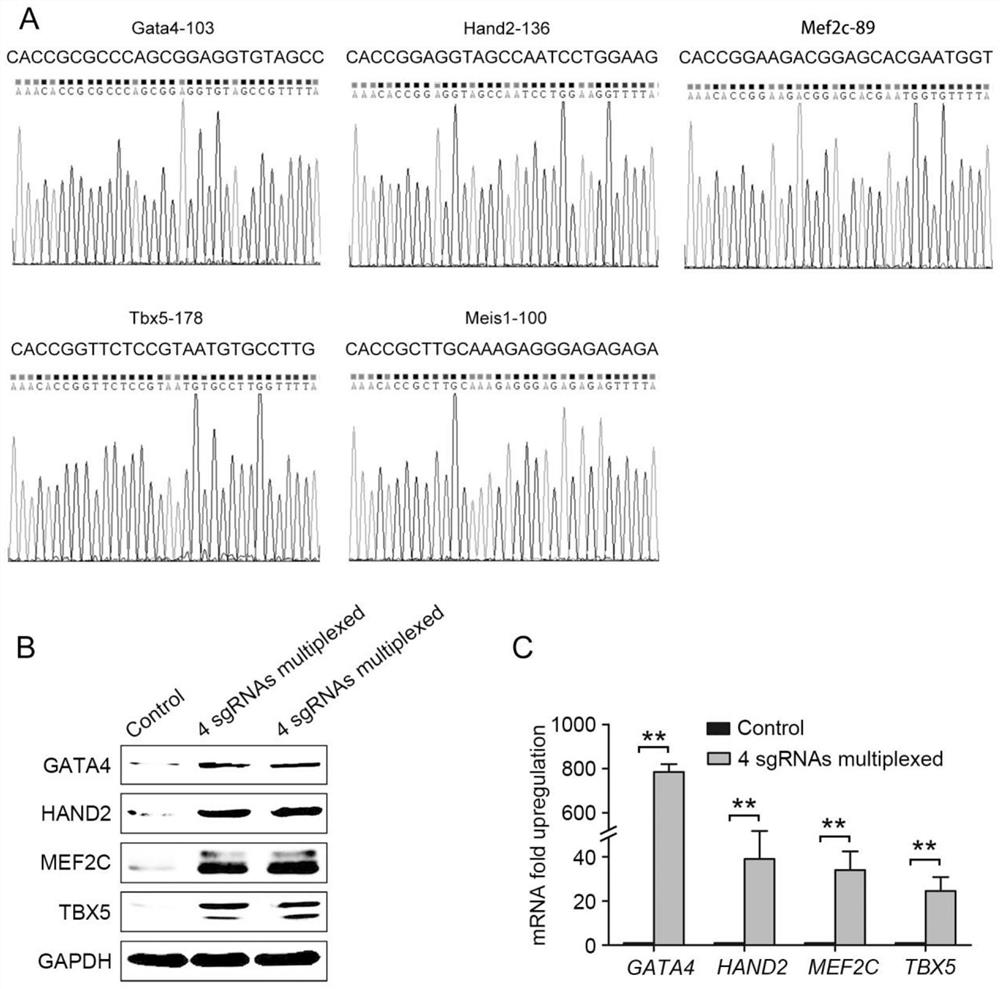
The invention provides a method for directly re-programming heart progenitor cells based on endogenous gene transcriptional activation. The method has better operation feasibility and theory creativity. For the first time, through a CRISPR / Cas9 system, endogenous heart development relevant transcription factors GATA4, HAND2, MEF2C, TBX5 and MEIS1 are activated, human foreskin fibroblasts are induced to be re-programmed into the heart progenitor cells having the potential of being disintegrated towards cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells, a seed cell source is provided for cardiovascular disease model construction, new medicine screening and myocardial regeneration, and besides, a novel apparent cell re-programming theory and connotation are enriched.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Application of diagnostic marker GATA4 in pancreas inflammatory cancer transformation
InactiveCN112626210AImprove accuracyImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemPancreas CancersOncology
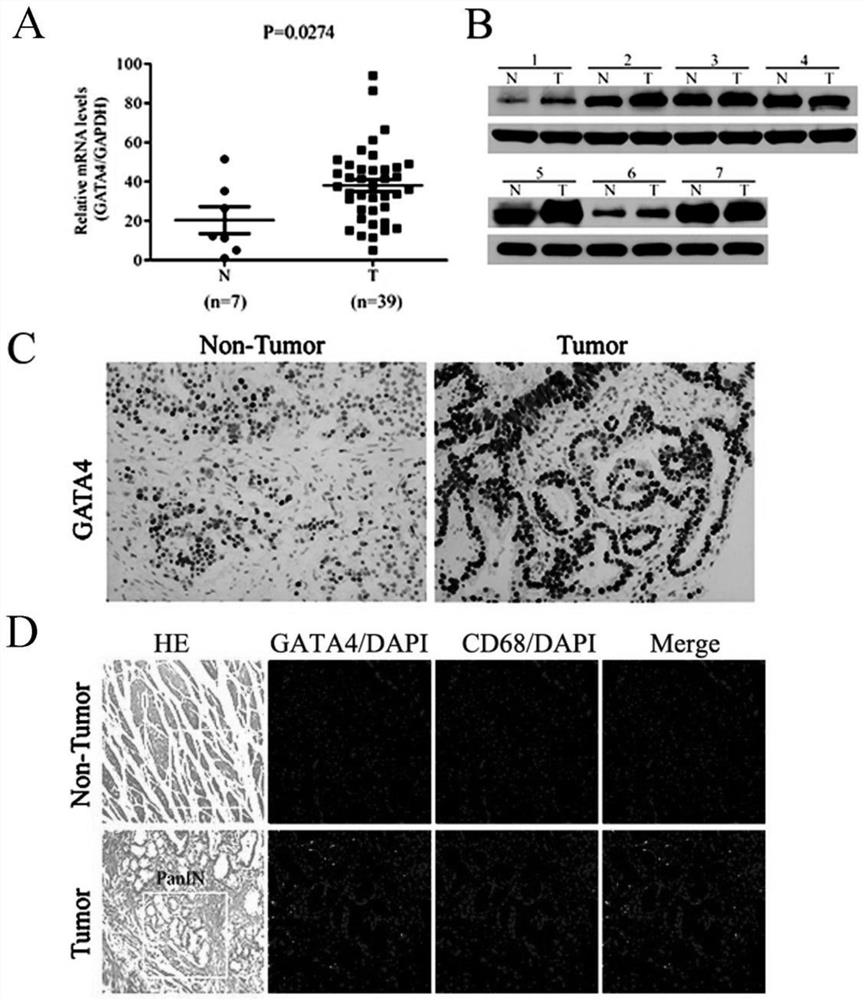
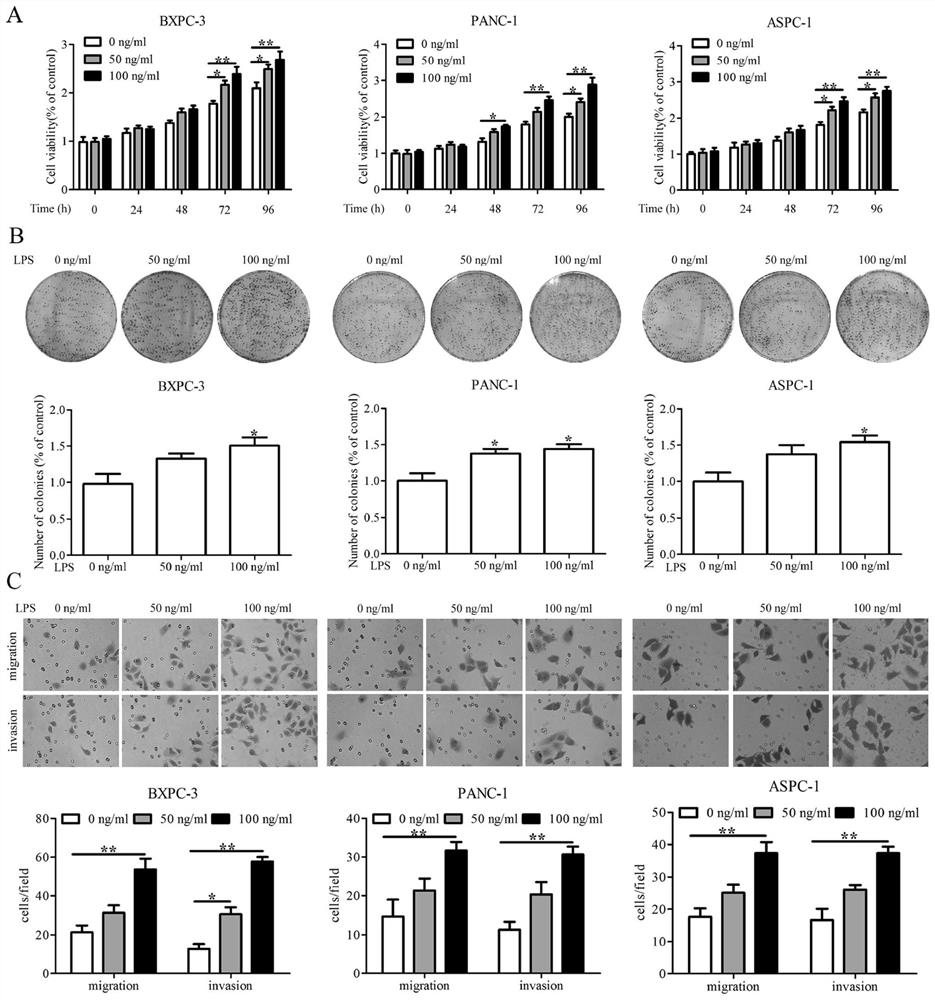
The invention relates to application of a diagnostic marker GATA4 in pancreas inflammatory cancer transformation. According to the invention, immunofluorescence detection finds that the level of the GATA4 is positively correlated with the CD68 level, and prompts that the GATA4 may participate in inflammatory regulation in the pancreatic cancer development process. According to the experiment, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) with different concentrations is added into a macrophage culture medium LMCM for inducing THP-1 differentiation to treat pancreatic cancer cells; the result shows that up-regulation of the GATA4 level in the pancreatic cancer cells can be promoted, and proliferation, migration and invasion of the pancreatic cancer cells can be promoted; and meanwhile, overexpression of the GATA4 can obviously promote proliferation, migration and invasion ability of the pancreatic cancer cells induced by the LMCM with different LPS concentrations. This prompts that the GATA4 may be a key factor in the pancreatitis cancer transformation process. The invention provides a method for diagnosing pancreas inflammatory cancer transformation through molecular detection; the diagnosis speed is high; the cost is low; and the result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for preparing cardiac progenitor cells
ActiveCN110760546BHigh reprogramming efficiencyInhibit synthesisHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAReprogrammingHeart development
The invention provides a method for direct reprogramming of cardiac progenitor cells based on transcriptional activation of endogenous genes. The method has good operational feasibility and theoretical innovation. For the first time, the endogenous cardiac development-related transcription factors GATA4, HAND2, MEF2C, TBX5 and MEIS1 are activated by the CRISPR / Cas9 system to induce the reprogramming of human foreskin fibroblasts with tropism Cardiac progenitor cells with differentiation potential of cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells provide seed cell sources for the construction of cardiovascular disease models, new drug screening and myocardial regeneration, and enrich the theory and connotation of new epigenetic cell reprogramming.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Novel Markers for Bladder Cancer Detection
ActiveUS20120027870A1Raise the possibilityReduce the possibilityBiocideInorganic active ingredientsBladder cancerGATA4
A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from FOXE1 and GATA4. Detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer. The sample comprises nucleic acid molecules from bladder cells. The methods may be used to select treatments and patients for treatment. Related kits include primers allowing the methylation status of the genes to be determined.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
P63 inactivation for the treatment of heart failure
ActiveUS11421229B2Increases transdifferentiation efficiencyImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHeart cellsTransdifferentiation
Embodiments of the disclosure include methods and compositions for in situ cardiac cell regeneration, including transdifferentiation of cardiac cells to cardiomyocytes. In particular embodiments, in situ cardiac cell regeneration encompasses delivery of p63 shRNA and one or both of Hand2 and myocardin, and in specific embodiments further includes one or more of Gata4, Mef2c, and Tbx5. In specific aspects of the disclosure, adult cardiac fibroblasts are reprogrammed into cardiomyocytes using viral vectors that harbor p63 shRNA and one or both of the transcription factors Hand2 and myocardin.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Methylation of the GATA4 gene in urine samples as a marker for bladder cancer detection
ActiveUS9388471B2Loss of gene functionRaise the possibilityBiocideSugar derivativesBladder cancerGATA4
A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from FOXE1 and GATA4. Detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer. The sample comprises nucleic acid molecules from bladder cells. The methods may be used to select treatments and patients for treatment. Related kits include primers allowing the methylation status of the genes to be determined.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
Adult cardiac stem cell population
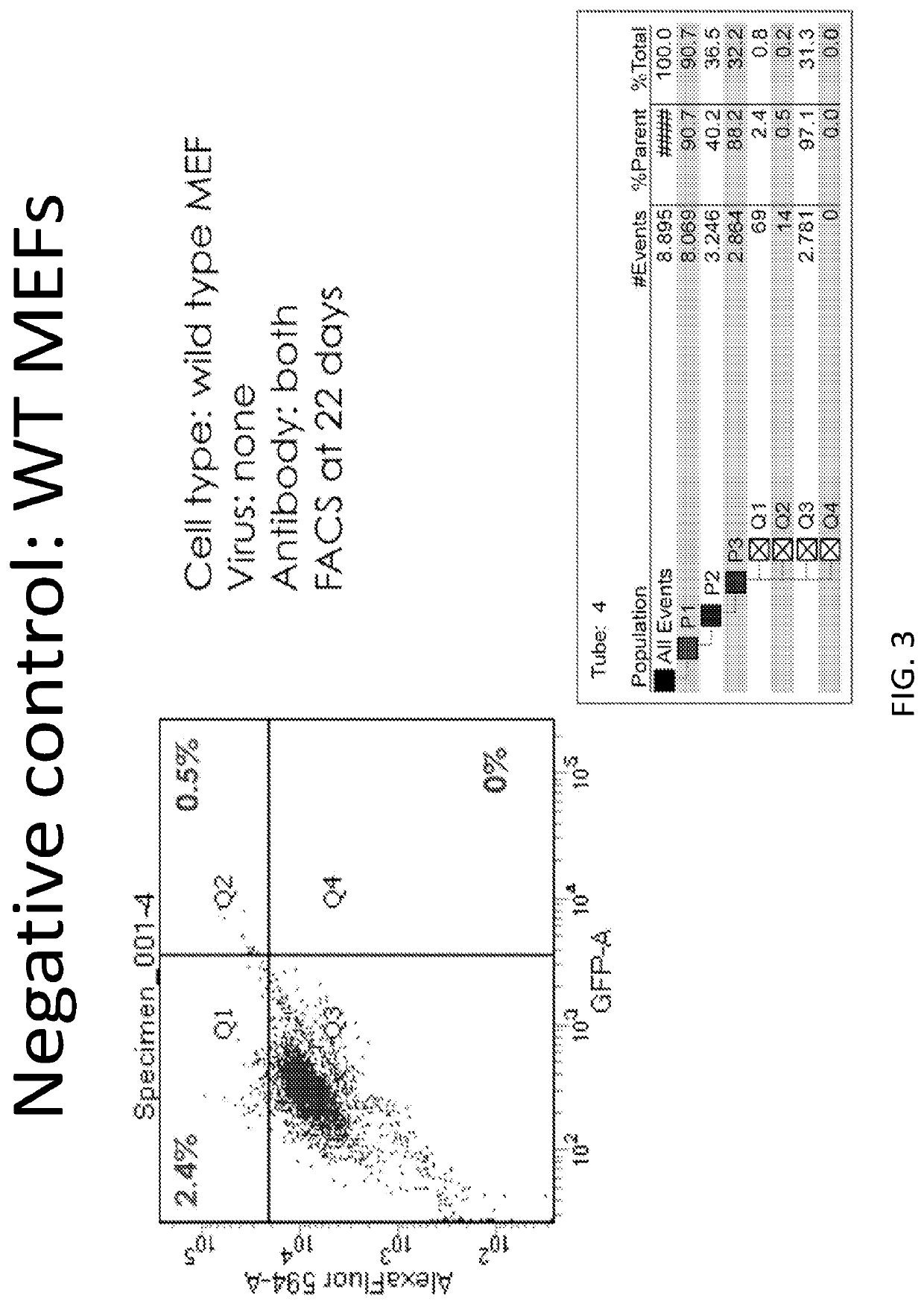
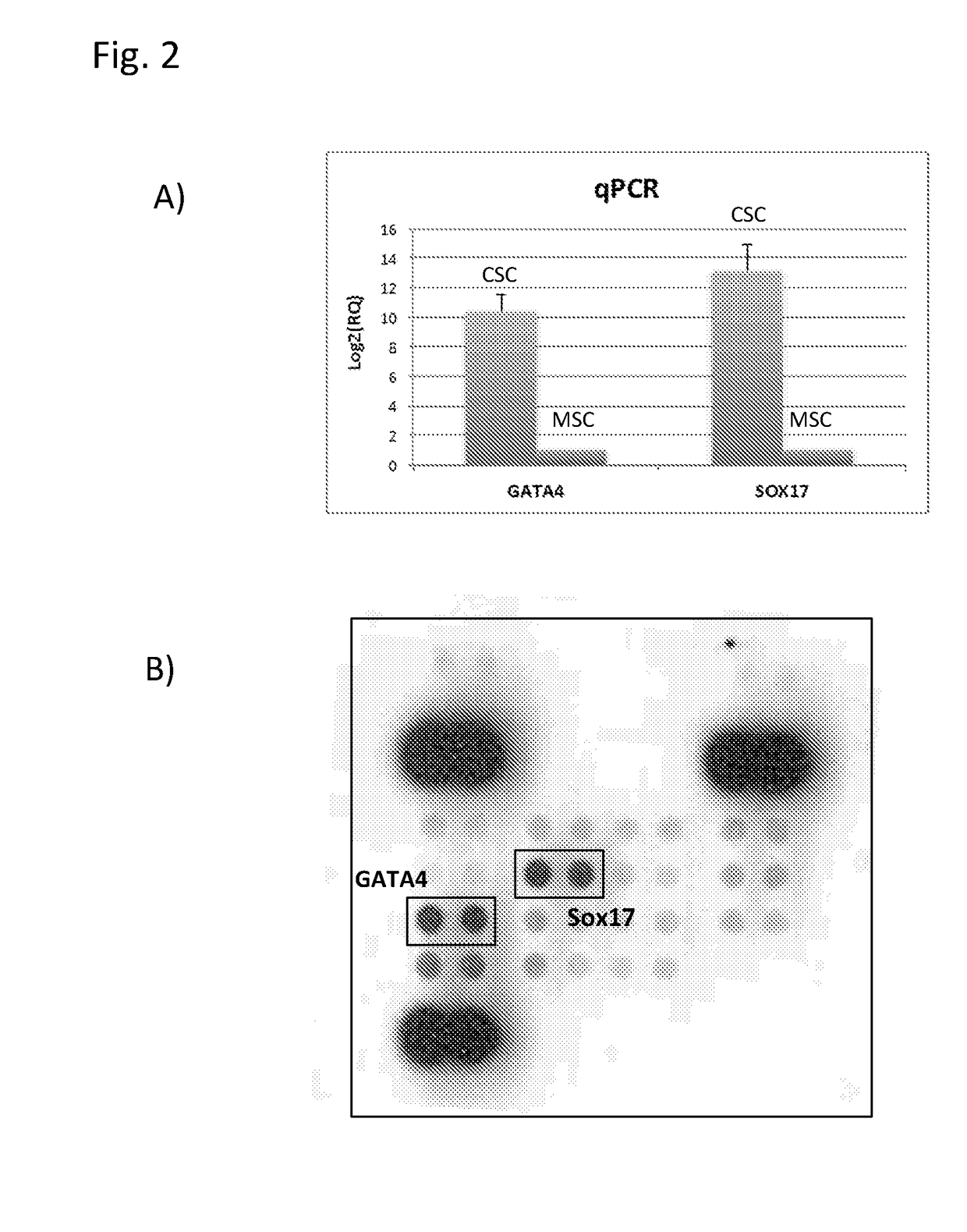
ActiveUS10016462B2Suitable for therapeutic applicationLower capability requirementsBiocideMuscular disorderCells boneReverse transcriptase
The present invention relates to the identification, isolation, expansion and characterization of a specific type of multipotent adult cardiac stem cell. These adult stem cells are characterized in that they naturally express a specific pattern of markers, which can be used to assist with their isolation and expansion. In particular, the cells express SOX17 and GATA4, but do not express Oct4, Nanog, c-kit and telomerase reverse transcriptase. These cells are able to differentiate into one or more of the following cell types: adipocytes, osteocytes, endothelial cells and / or smooth muscle cells. They also display an unprecedented capacity for immunoregulation as well as providing, activating and / or inducing repair of damaged cardiac tissue. These adult stem cells may be used as therapeutic agents including, without limitation, for the regeneration of tissue, particularly for regeneration of damaged cardiac tissue, such as myocardium.
Owner:CORETHERAPIX SLU
Gene methylation as a biomarker in sputum
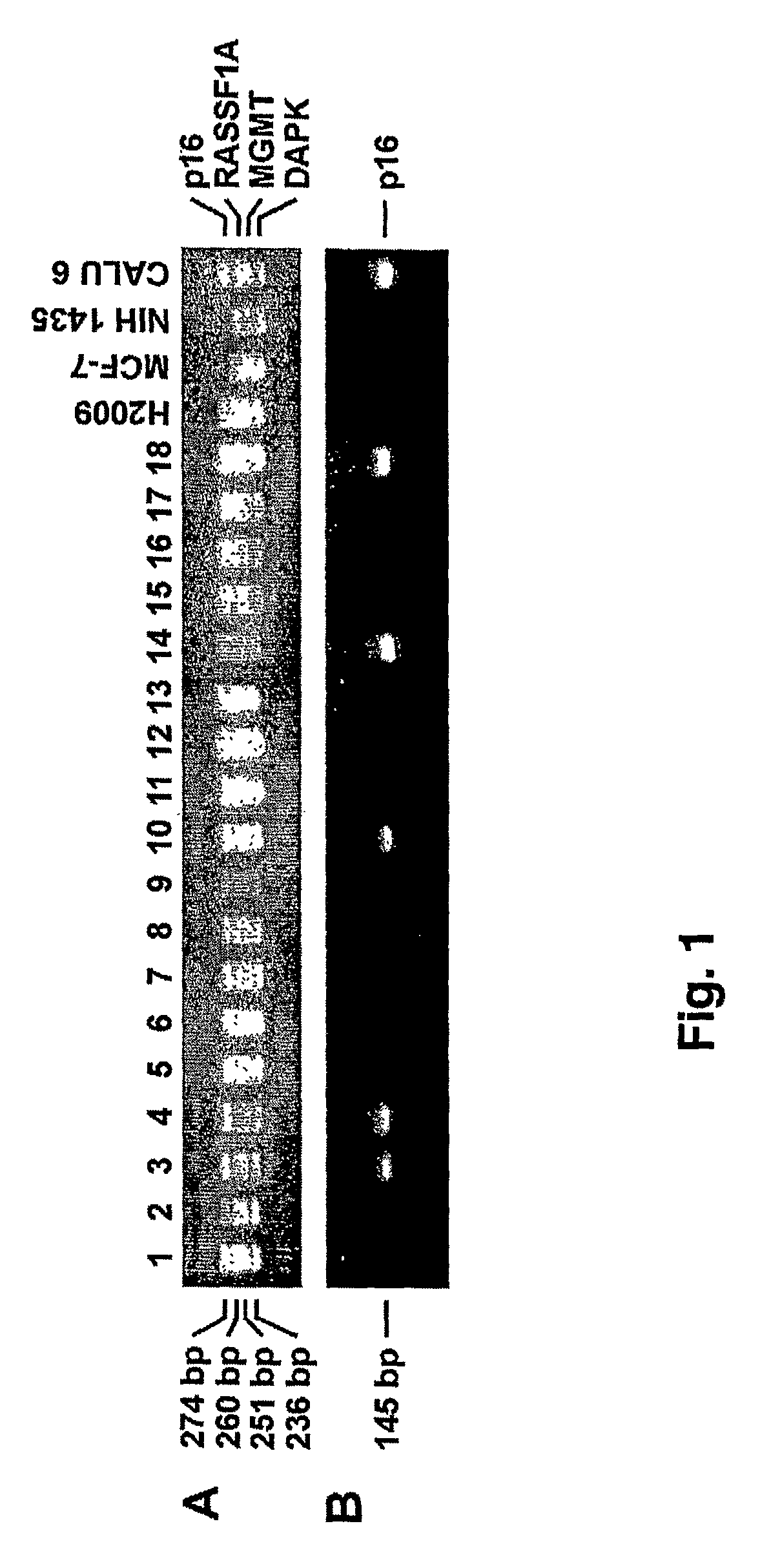
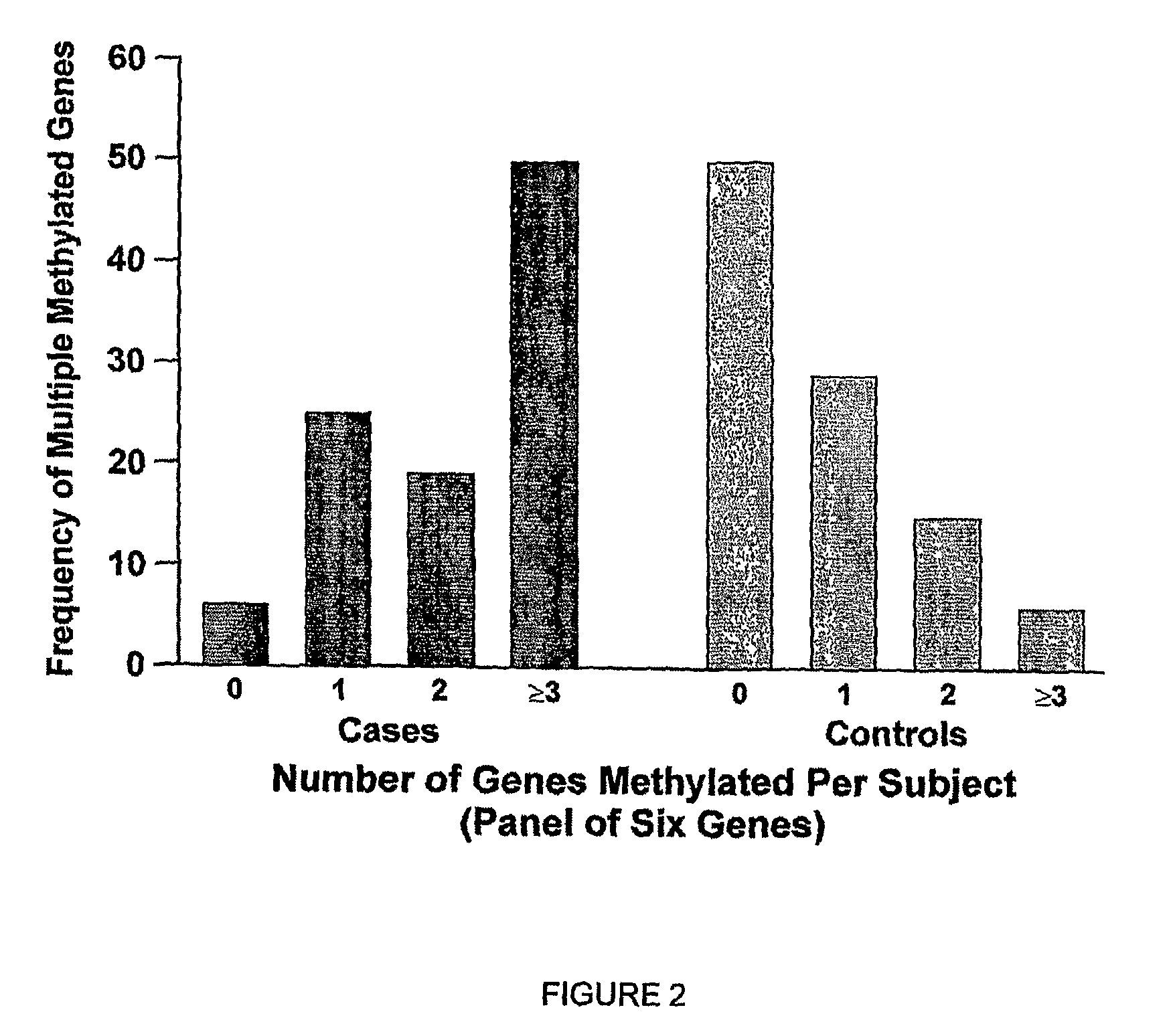
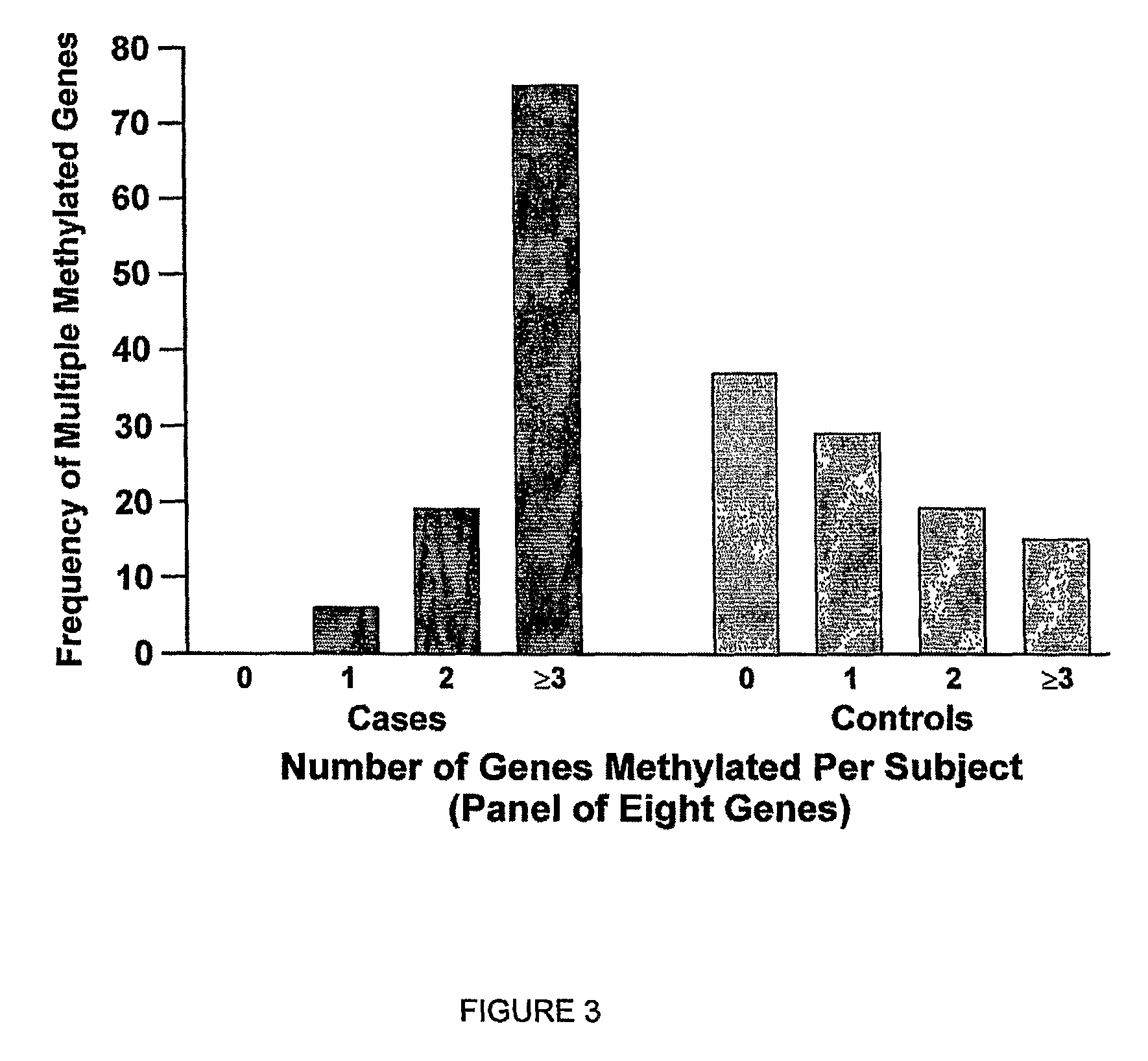
ActiveUS9512483B2Reduce high mortality rateLow recurrence rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIncreased riskPromoter
The present invention provides for a method to monitor the health of a subject. The method includes obtaining a test sample from the patient. A first probe specific for a CpG promoter region of a biomarker selected from p16, MGMT, PAX-α, PAX5-β, RASSF1A, HLHP, GATA4, GATA5, SFRP1, LAMC2, IGFBP3, H-cadherin, BETA 3, HLHP, and DAPK is provided to the sample. The probe contacts the test sample. The DNA of interest from the test sample is isolated. A second stage probe specific for a second CpG promoter region of a biomarker selected from p16, MGMT, PAX-α, PAX5-β, RASSF1A, HLHP, GATA4, GATA5, SFRP1, LAMC2, IGFBP3, H-cadherin, BETA 3, HLHP, and DAPK is provided to the sample to form a second stage PCR product. The DNA is analyzed for hypermethylation of the promoter region for at least one of p16, MGMT, PAX-α, PAX5-β, RASSF1A, HLHP, GATA4, GATA5, SFRP1, LAMC2, IGFBP3, H-cadherin, BETA 3, HLHP, and DAPK. Hypermethylation of the promoter region of at least one of p16, MGMT, PAX-α, PAX5-β, RASSF1A, HLHP, GATA4, GATA5, SFRP1, LAMC2, IGFBP3, H-cadherin, BETA 3, HLHP, and DAPK is an indication that the subject is at increased risk of developing cancer for example, non small cell lung cancer.
Owner:LOVELACE RESPIRATORY RES INST
Method for inducing amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into cardiomyocytes in vitro
InactiveCN110129263AEffective differentiationPromote proliferationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsAmniotic fluidCells heart
The invention discloses a method for inducing amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into cardiomyocytes in vitro. CTnI is a typical protein in ventricular and atrial cells and is an important characteristic protein of cardiomyocytes; GATA4 is an important transcriptional regulatory factor for cardiac gene expression, jointly regulates the normal development of a heart, the expression of functional genes and the pathological process of cardiac hypertrophy through interaction with other transcriptional regulatory factors, and is also an important characteristic protein of the cardiomyocytes. Through mRNA and protein expression levels of the cTnI and GATA4, the human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells can be observed to be obviously differentiated into the cardiomyocytes under induction of propylgallate. Therefore, propylgallate can be used for inducing the human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into the cardiomyocytes in vitro. The method provided by the invention can effectively induce the human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into the cardiomyocytes.
Owner:南京乐扬医药科技有限公司
A method for preparing cardiac progenitor cells
ActiveCN106676062BIncrease positive rateLow immunogenicitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsGATA4Reprogramming
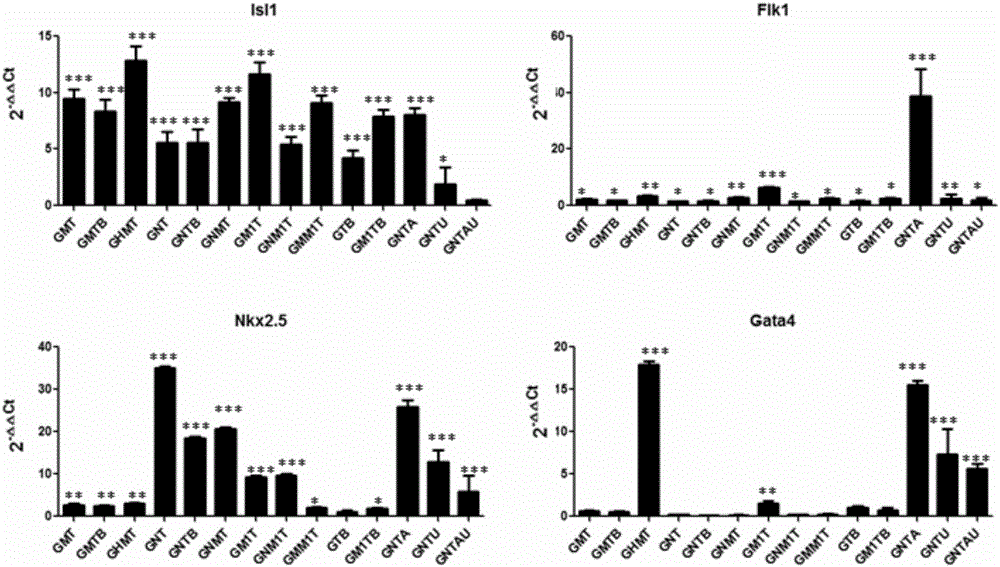
The invention belongs to the field of biopharmaceutical research, and particularly relates to a method for preparing cardiac progenitor cells. The method comprises the following steps: transducing a reprogramming factor into an initial reprogramming object cell, wherein the reprogramming factor is selected from cardiac transcription factors and epigenetic regulation factors; preferably the reprogramming factor can be selected from one of or a combination of a plurality of (i) Gata4, ( / i) (i) Tbx5, Nkx2.5, AF9, Hand2, Mef2C, Mesp1, ( / i) (i) Baf60c and UTX ( / i). By preparing the cardiac progenitor cells with the method, the cardiac progenitor cells can be obtained after about 8 to 10 days, the obtained cardiac progenitor cells are all (i) Isl+ / Tbx5+(i) double positive cells, the positive rate is high, and the immunogenicity is low.
Owner:GMU MEDICAL DRUG DEV CO LTD
p63 INACTIVATION FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEART FAILURE
PendingUS20220348921A1Increases transdifferentiation efficiencyImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHeart cellsTransdifferentiation
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method for preparing cardiac progenitor cells
ActiveCN106676062AIncrease positive rateLow immunogenicitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsGATA4Cardiac progenitors
The invention belongs to the field of biopharmaceutical research, and particularly relates to a method for preparing cardiac progenitor cells. The method comprises the following steps: transducing a reprogramming factor into an initial reprogramming object cell, wherein the reprogramming factor is selected from cardiac transcription factors and epigenetic regulation factors; preferably the reprogramming factor can be selected from one of or a combination of a plurality of (i) Gata4, ( / i) (i) Tbx5, Nkx2.5, AF9, Hand2, Mef2C, Mesp1, ( / i) (i) Baf60c and UTX ( / i). By preparing the cardiac progenitor cells with the method, the cardiac progenitor cells can be obtained after about 8 to 10 days, the obtained cardiac progenitor cells are all (i) Isl+ / Tbx5+(i) double positive cells, the positive rate is high, and the immunogenicity is low.
Owner:GMU MEDICAL DRUG DEV CO LTD
Cardiac stem cell marker and application thereof
The invention provides a cardiac stem cell marker and application thereof. The cardiac stem cell marker contains TNFR2. According to the invention, the cardiac stem cell with positive TNFR2 is induced in ischemic myocardium of a mouse myocardial infarction model to be produced, a TNFR2-Bmx passage has the effect of activating ischemia-induced endogenous cardiac stem cells in the mouse myocardial infarction model, and the TNFR2 in an ischemic heart and a Nkx2.5+ / Gata4+CSC marker perform coexpression. In addition, the invention further provides a composition and a kit for screening the cardiac stem cell. The composition and the kit contain a reagent for detecting the TNFR2. Thereby, the TNFR2 serves as a new biomarker and provides a new molecular marker for separating the endogenous cardiac stem cells.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A method for h9c2 cardiomyocyte culture medium to induce iPSCs directed myocardial differentiation
ActiveCN107177555BPromotes fluorescence quenchingHigh expressionForeign genetic material cellsGATA4Immunofluorescence
The invention discloses a method for inducing directional myocardiac differentiation of iPSCs (induced Pluripotent Stem Cells) with a H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a conventional iPSCs culture solution from which LIF is removed with the H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution; culturing the iPSCs. The method proves that the H9C2 myocardial cell culture solution can effectively induce directional myocardiac differentiation of the iPSCs. Fluorescence quenching of a multi-directional differentiation potential gene OCT-4 is facilitated. As proved by a cell immunofluorescence experiment, the expression of alpha-actinin can be enhanced. As proved by a qPCR result, the expressions of mRNAs (messenger Ribonucleic Acids) such as beta-MHC, GATA4, Mef2C and NCX-1 are increased remarkably.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com













![Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/60405968-723f-4fe9-a2a8-eeff73c11931/HDA0002851170260000011.png)
![Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/60405968-723f-4fe9-a2a8-eeff73c11931/HDA0002851170260000021.png)
![Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel Application of GATA4 inhibitor in inhibition of NF-[kappa]B/STAT3 signal channel](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/60405968-723f-4fe9-a2a8-eeff73c11931/HDA0002851170260000031.png)