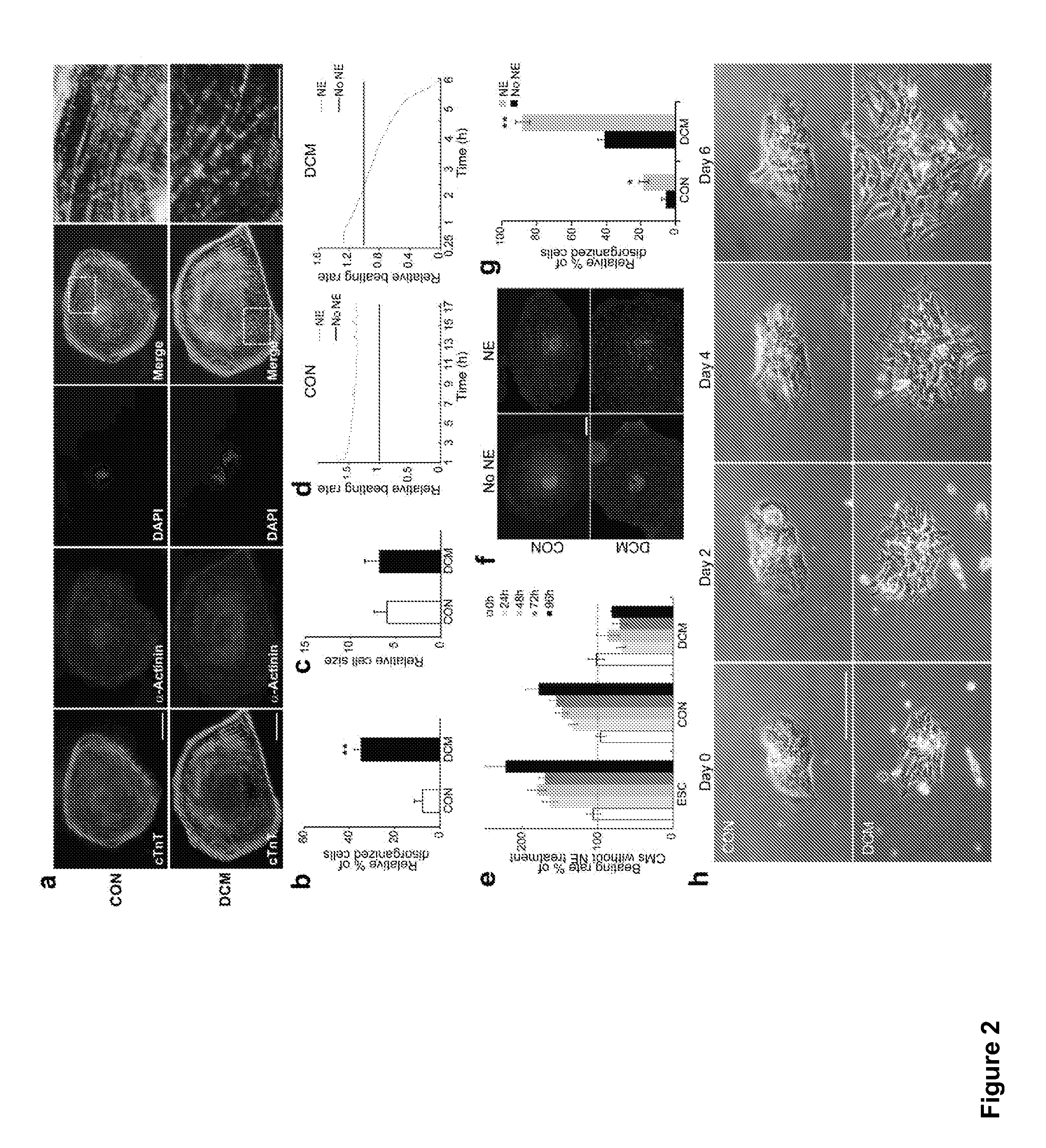
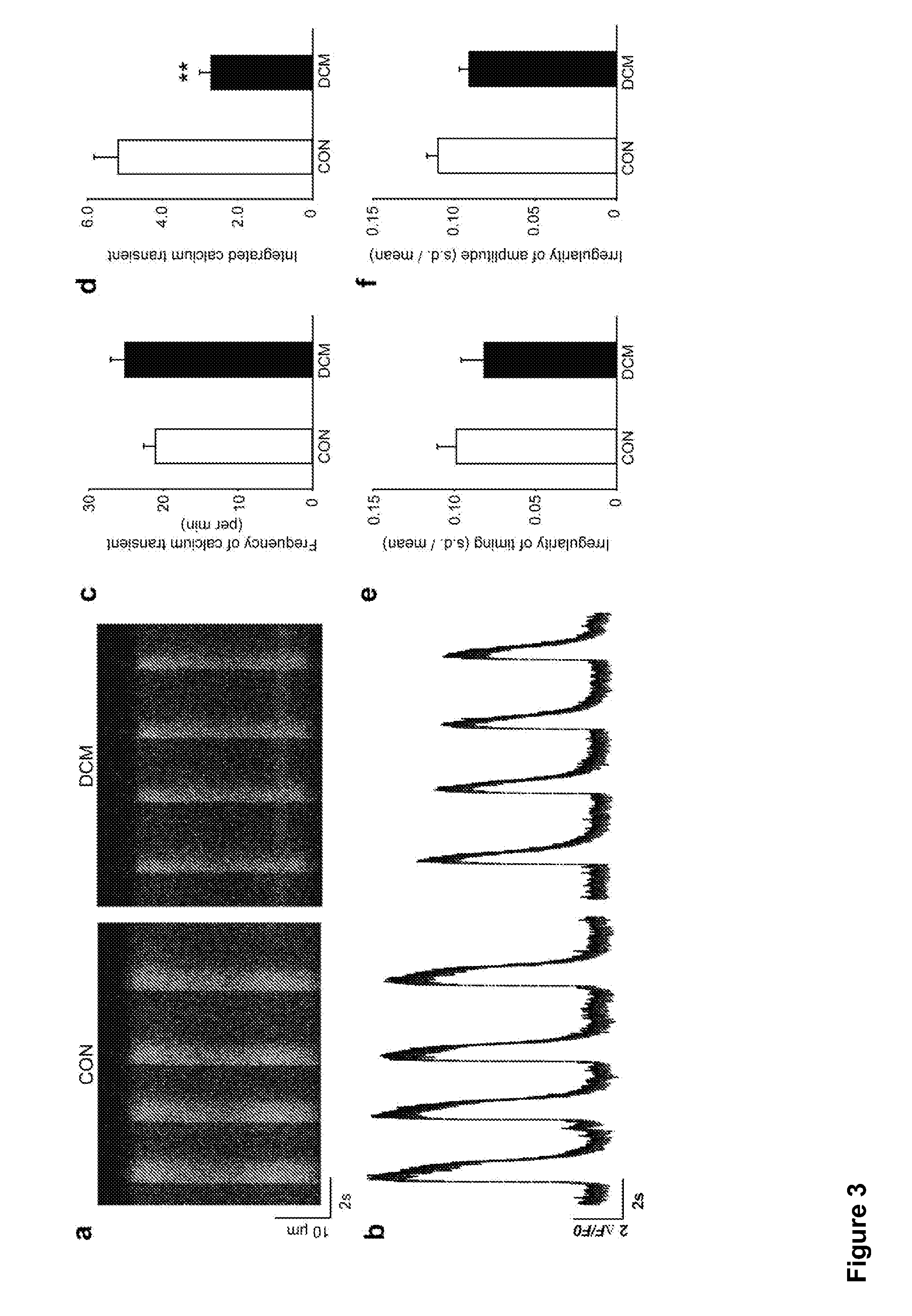
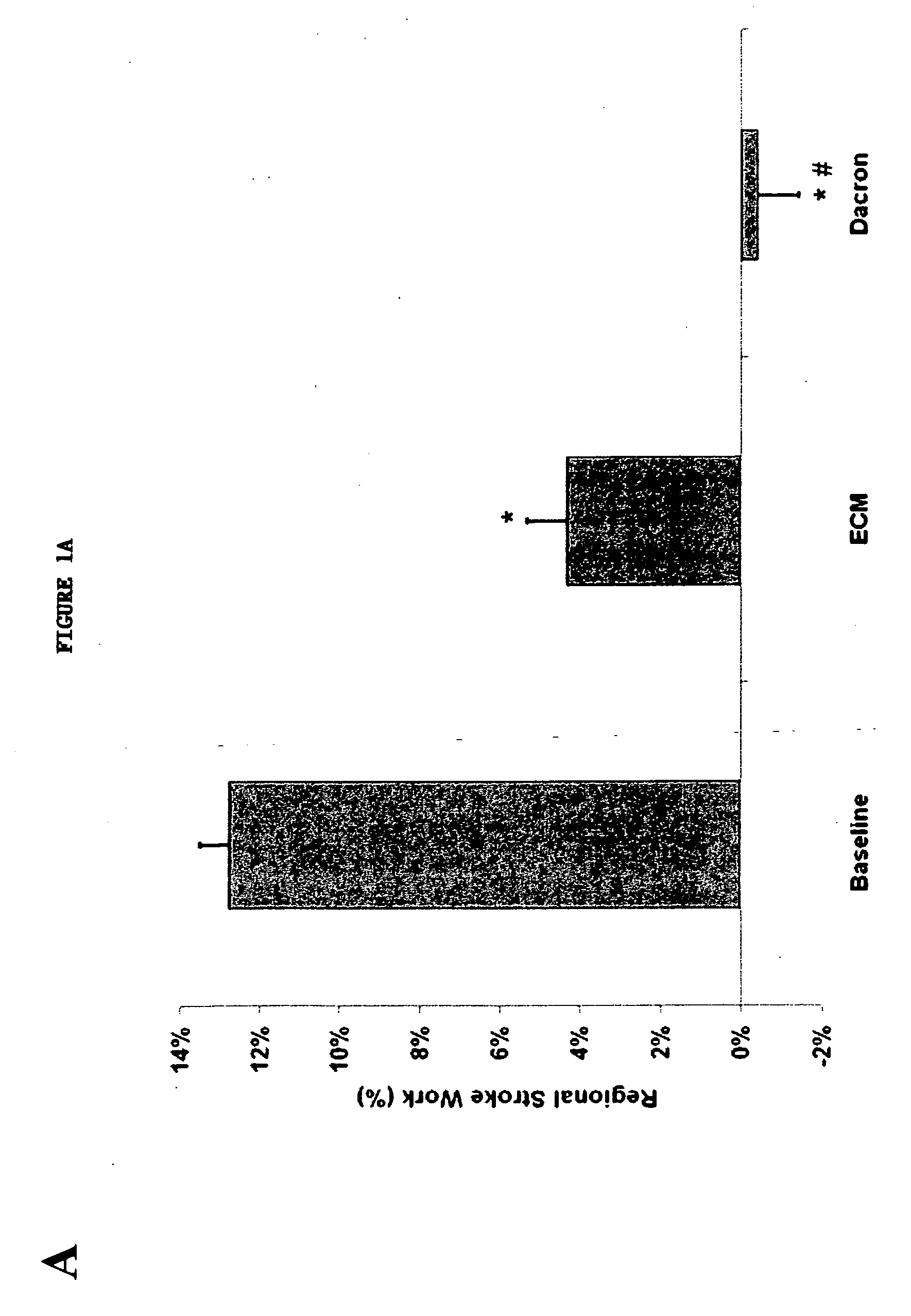
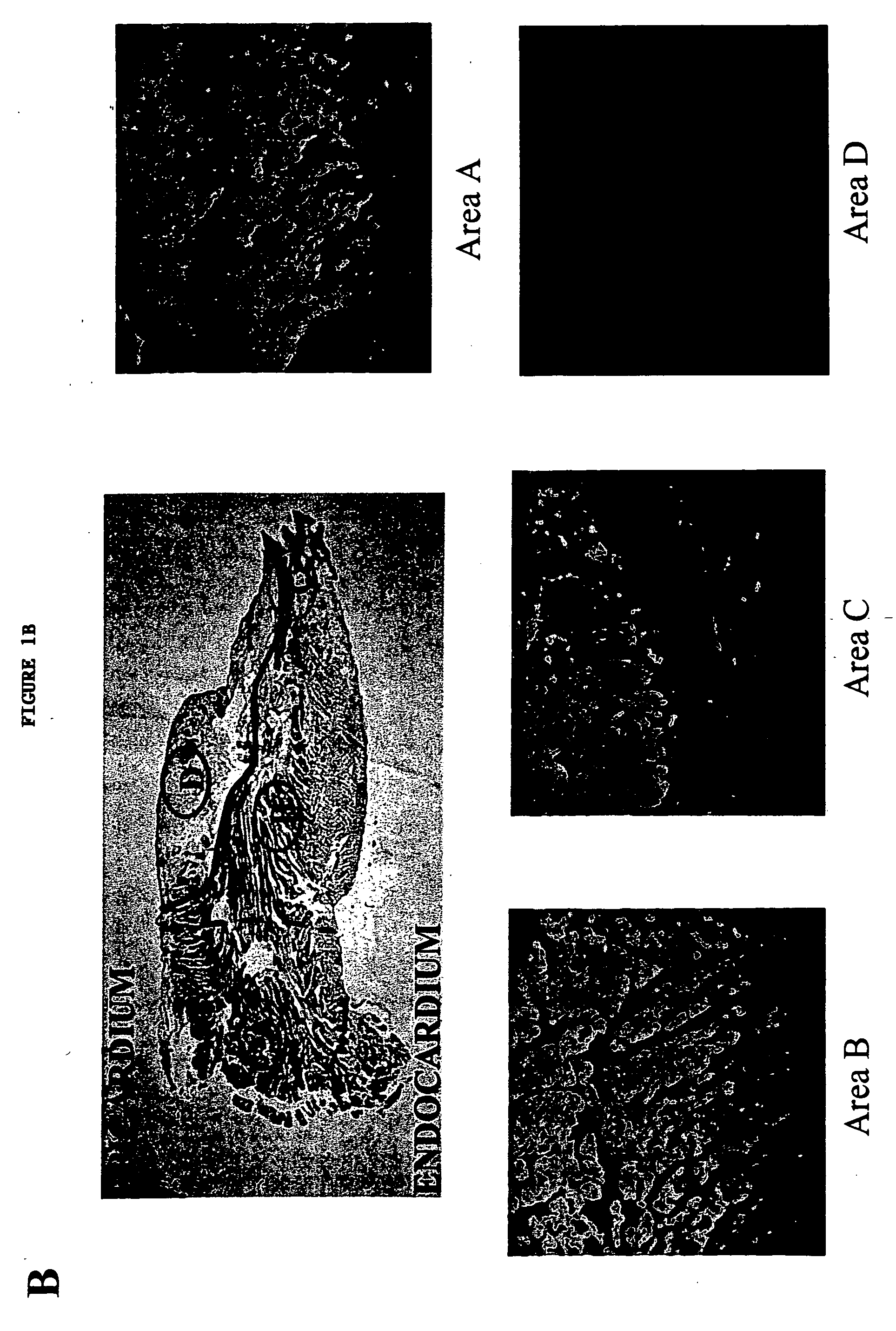
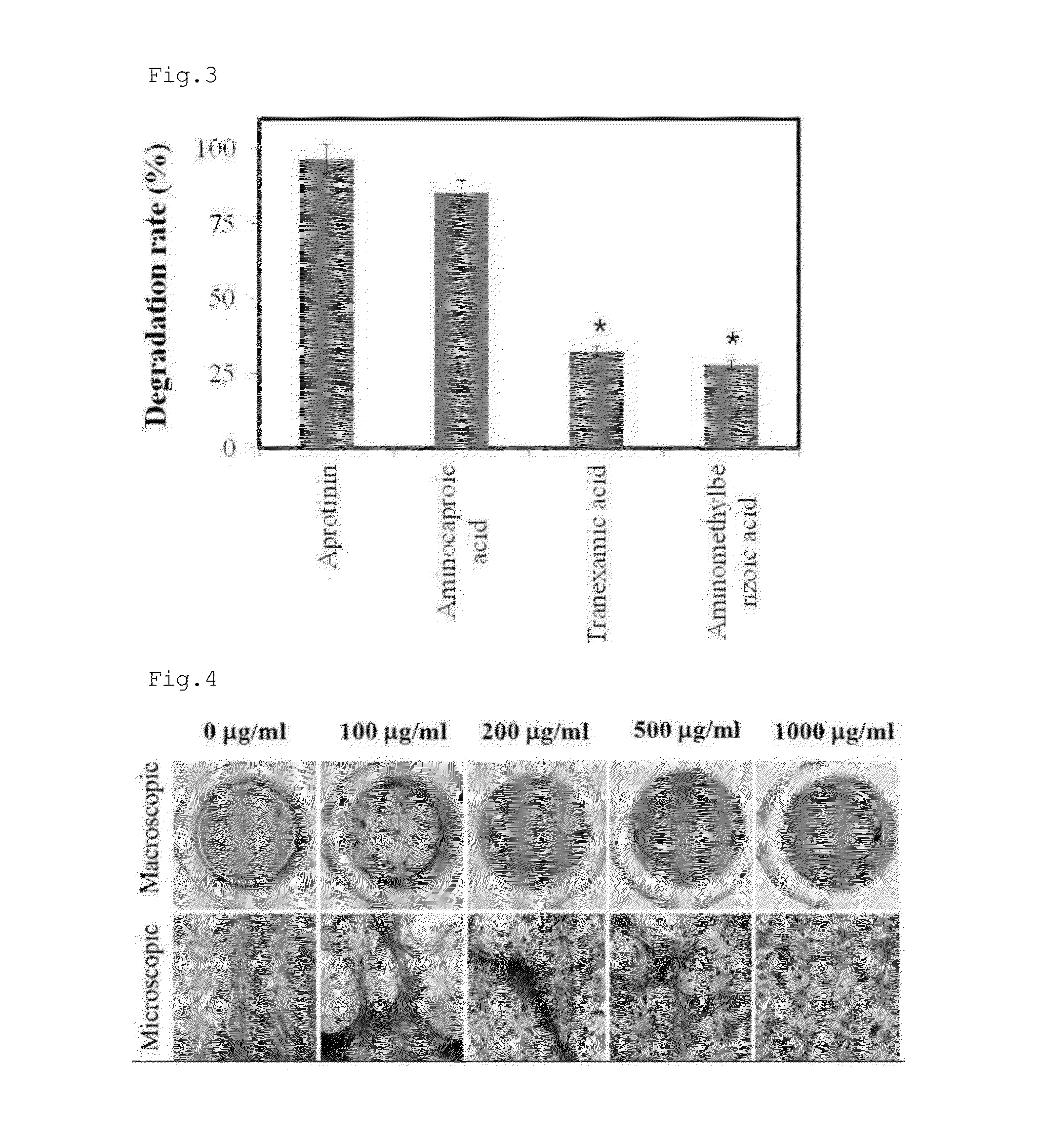
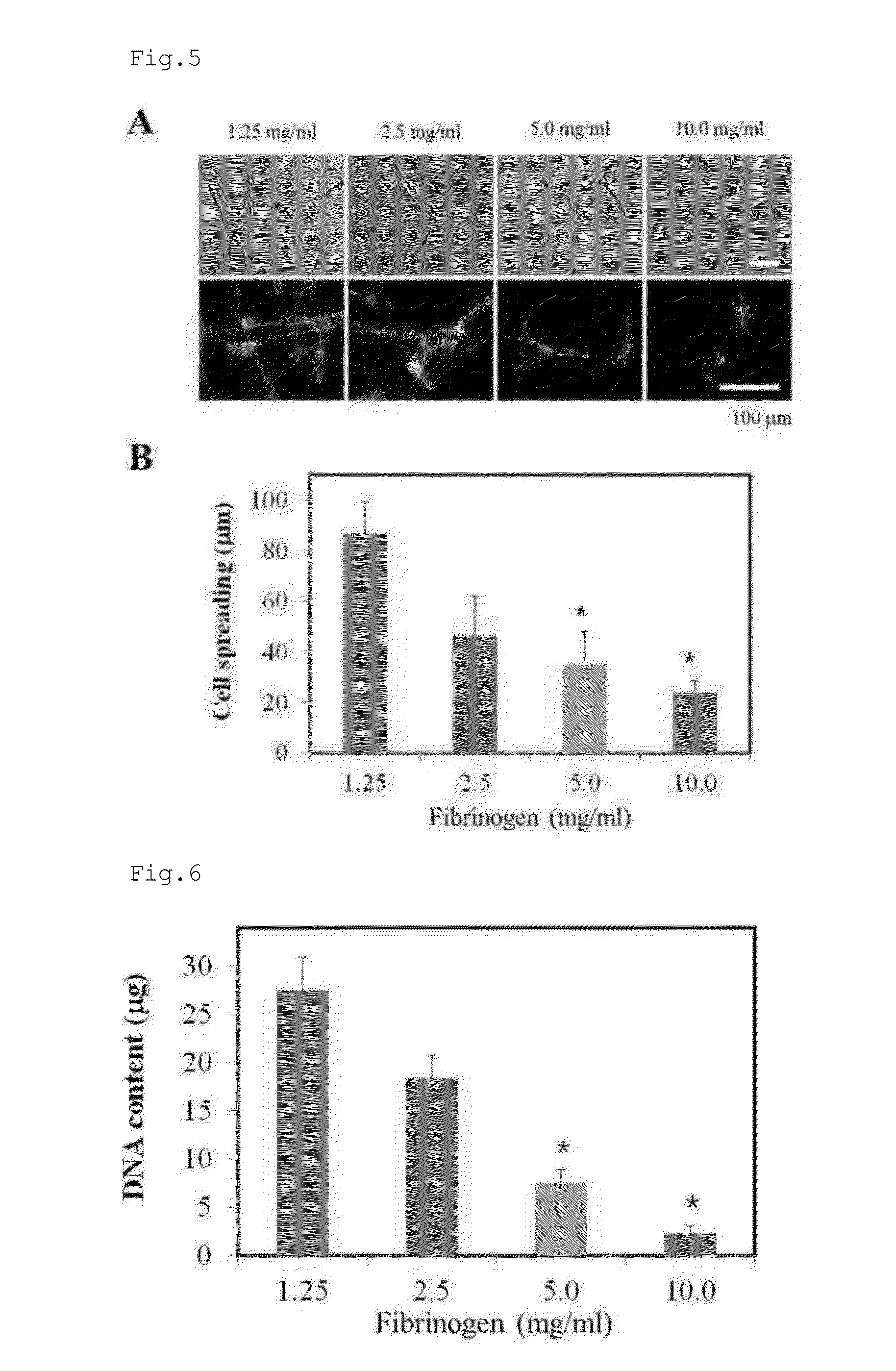
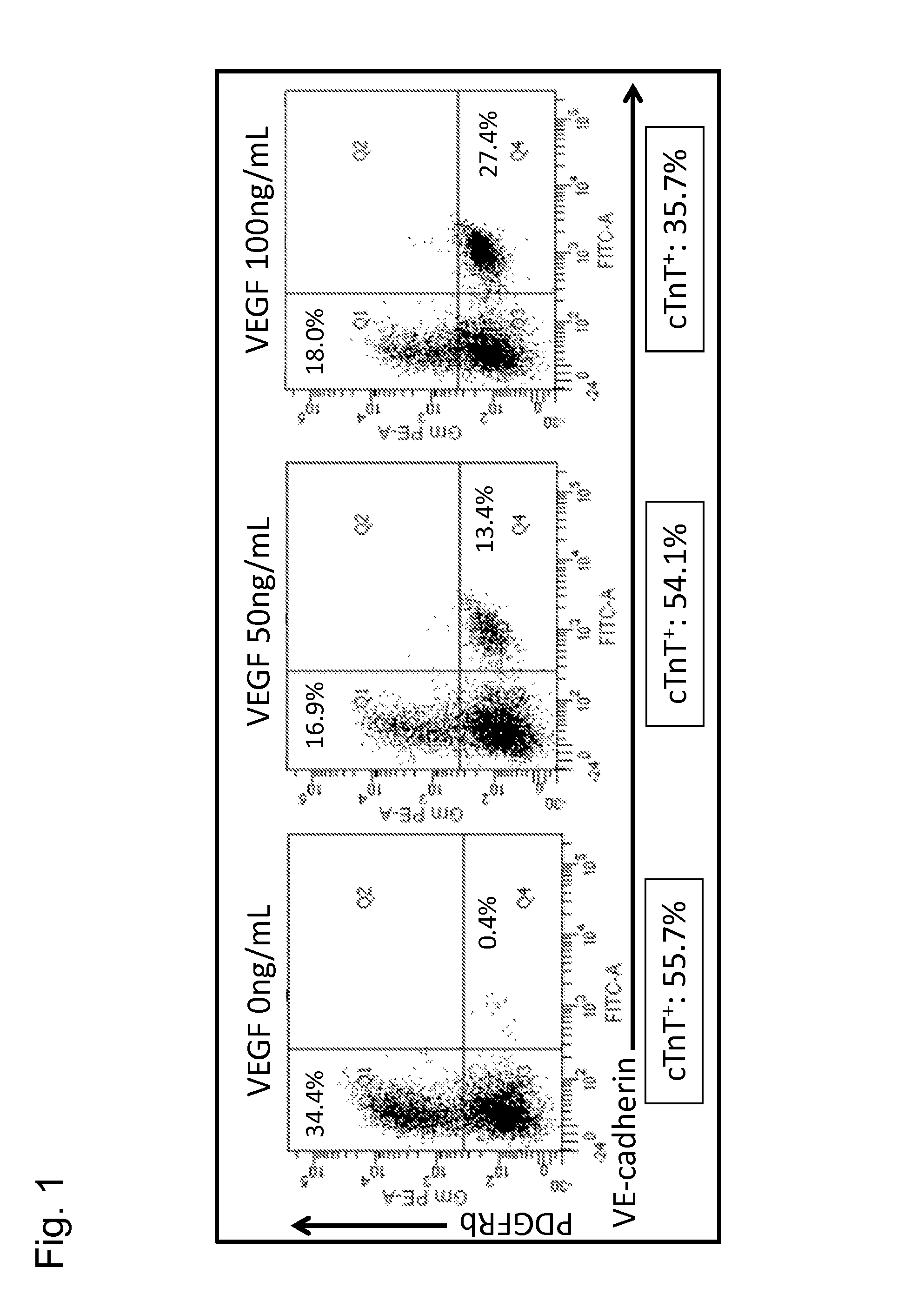
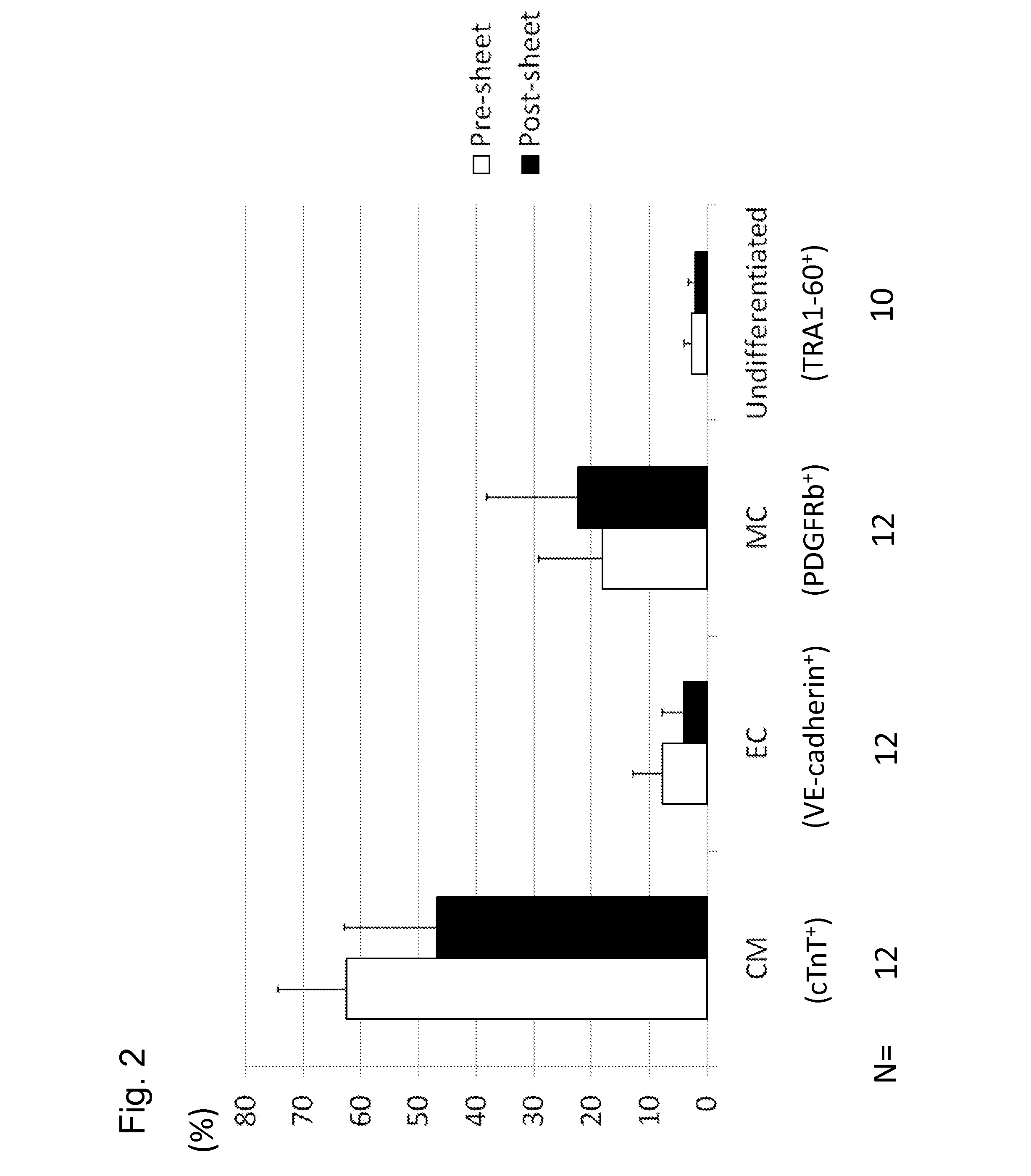
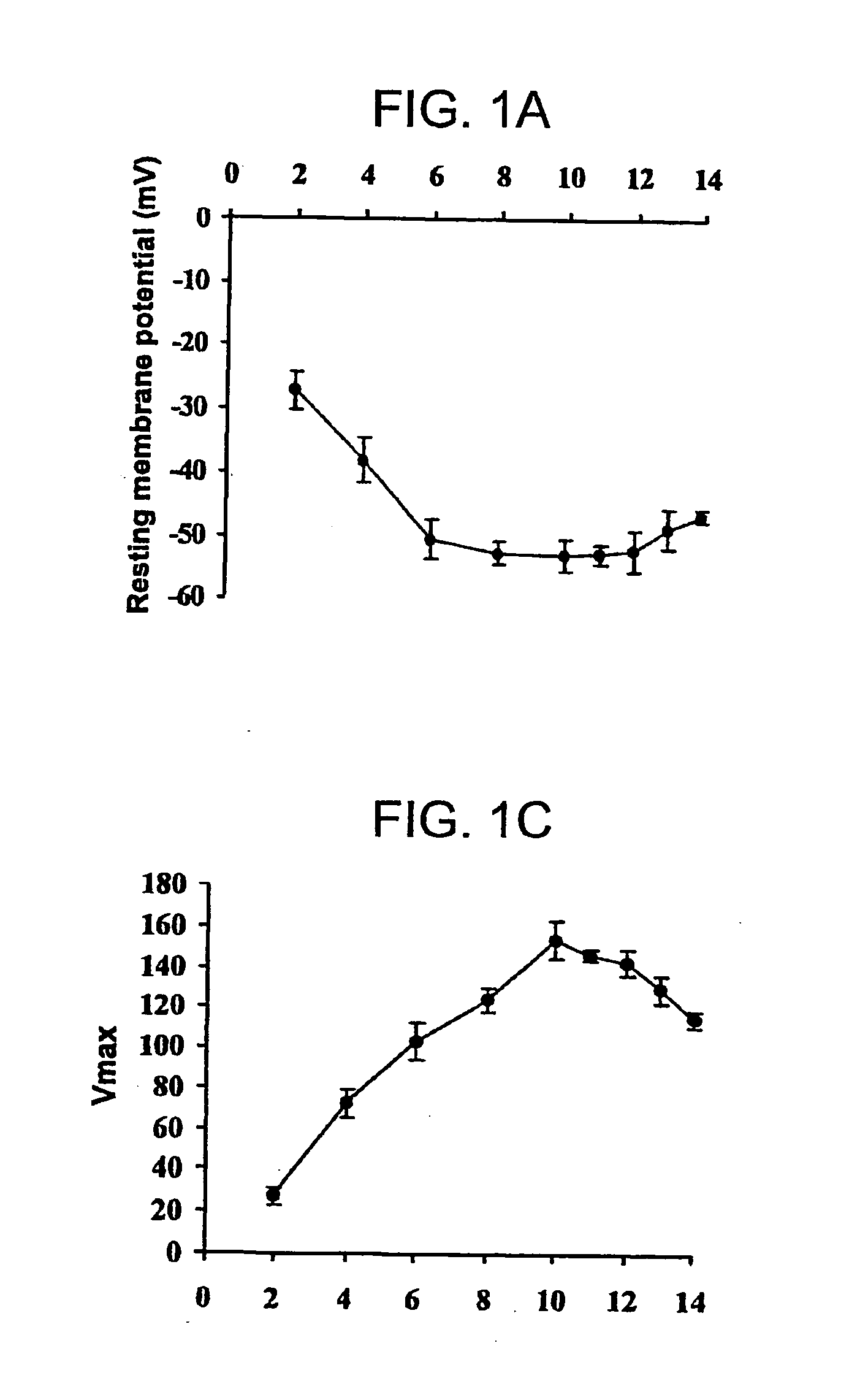
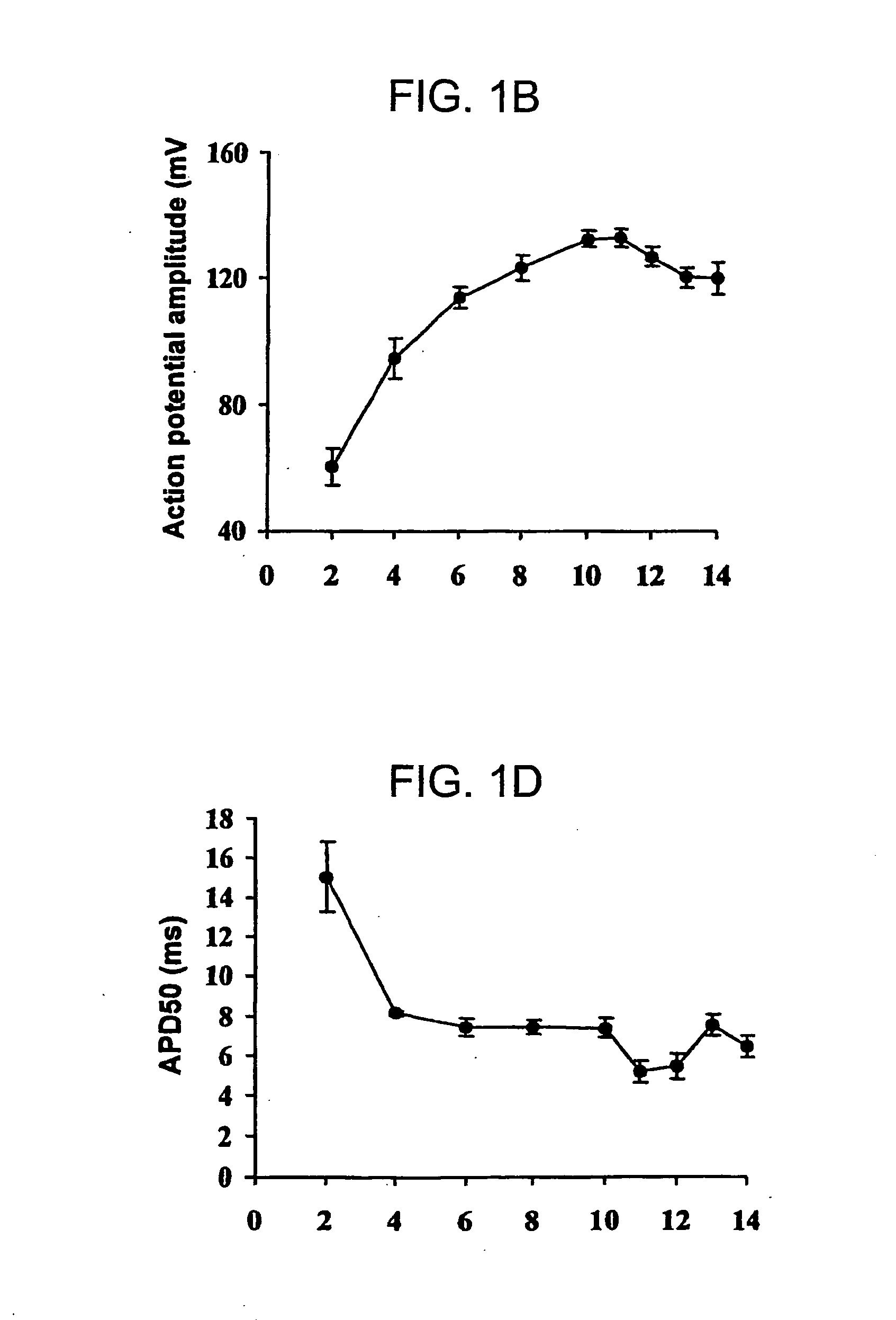
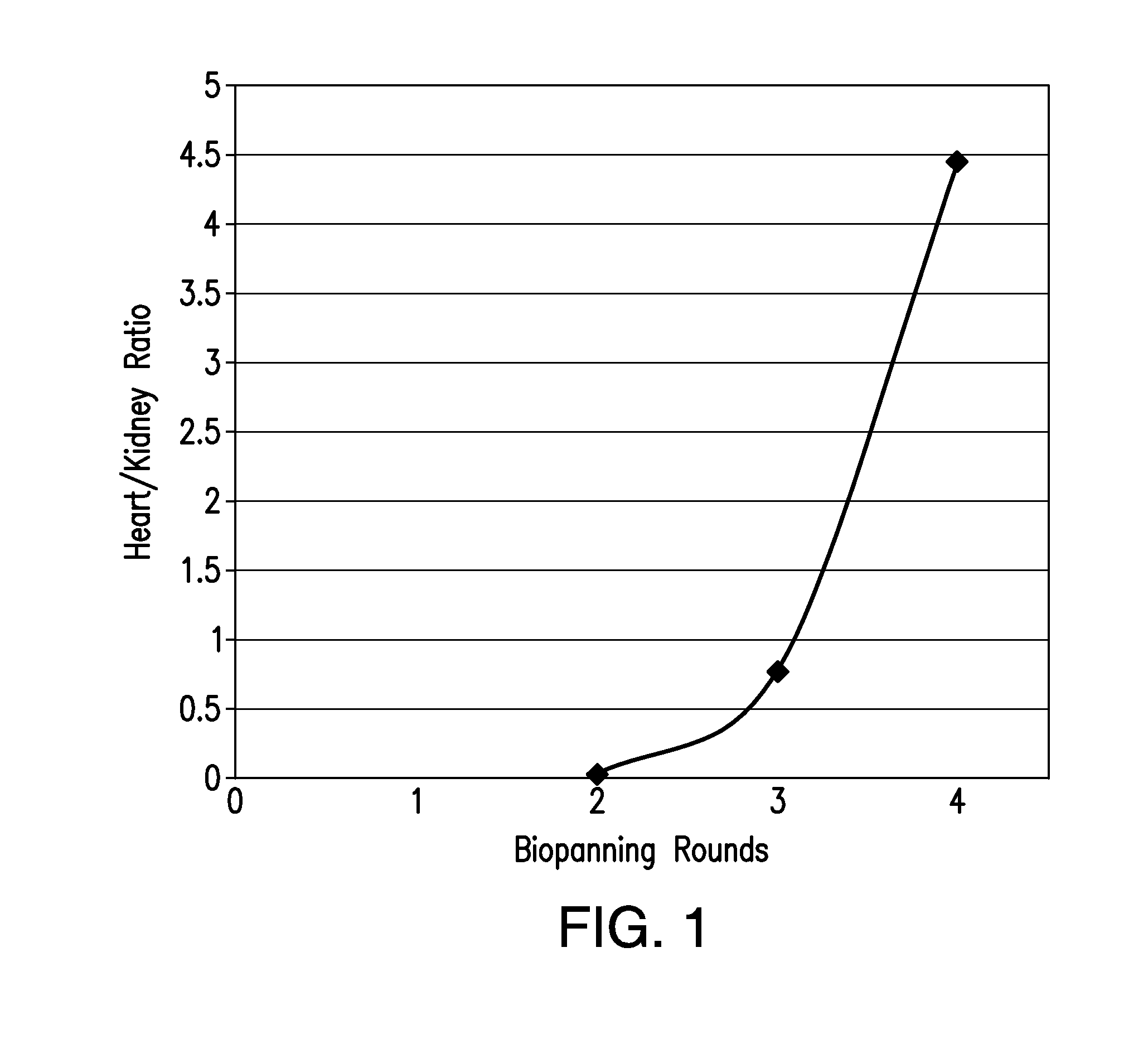
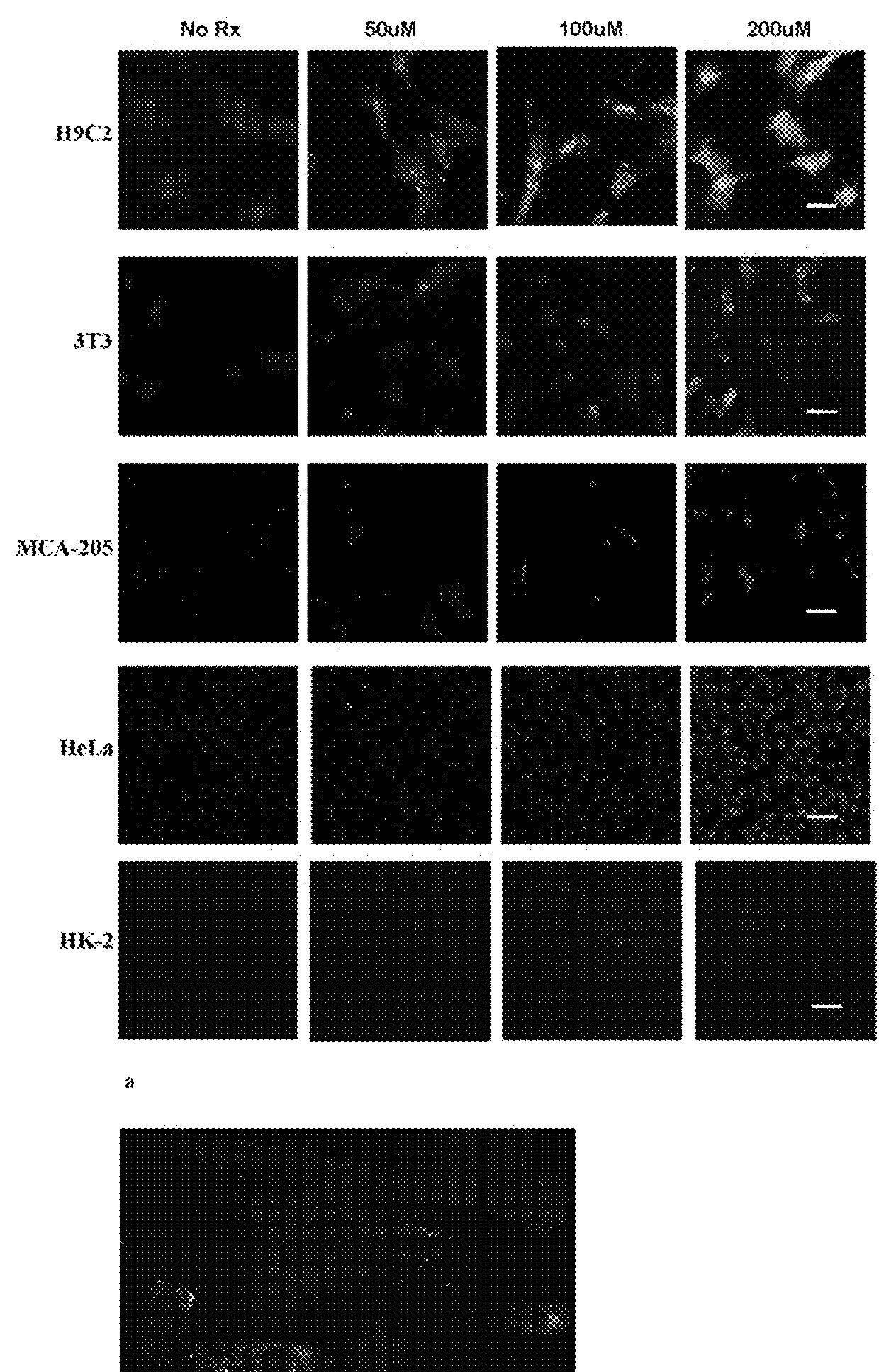
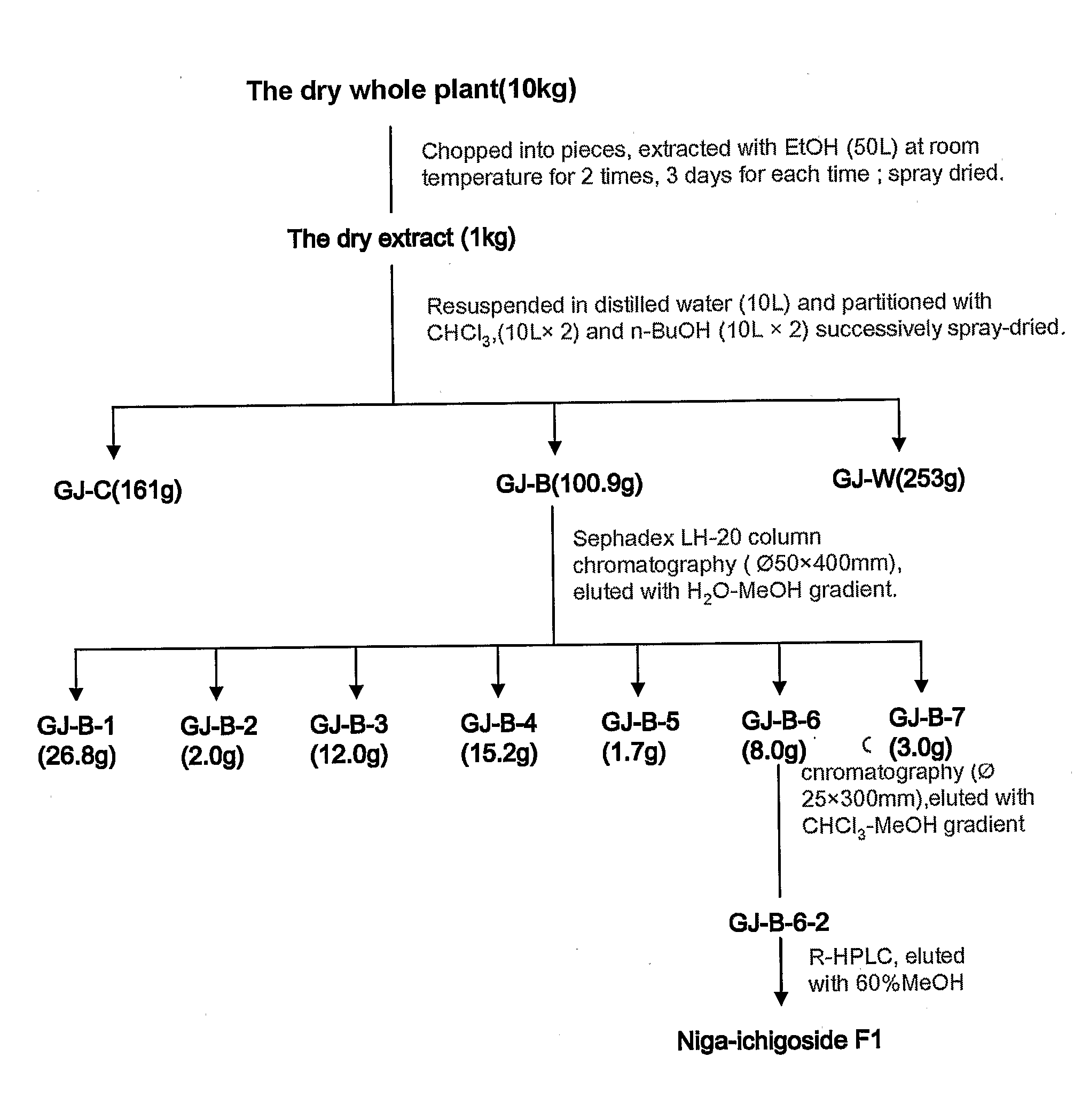
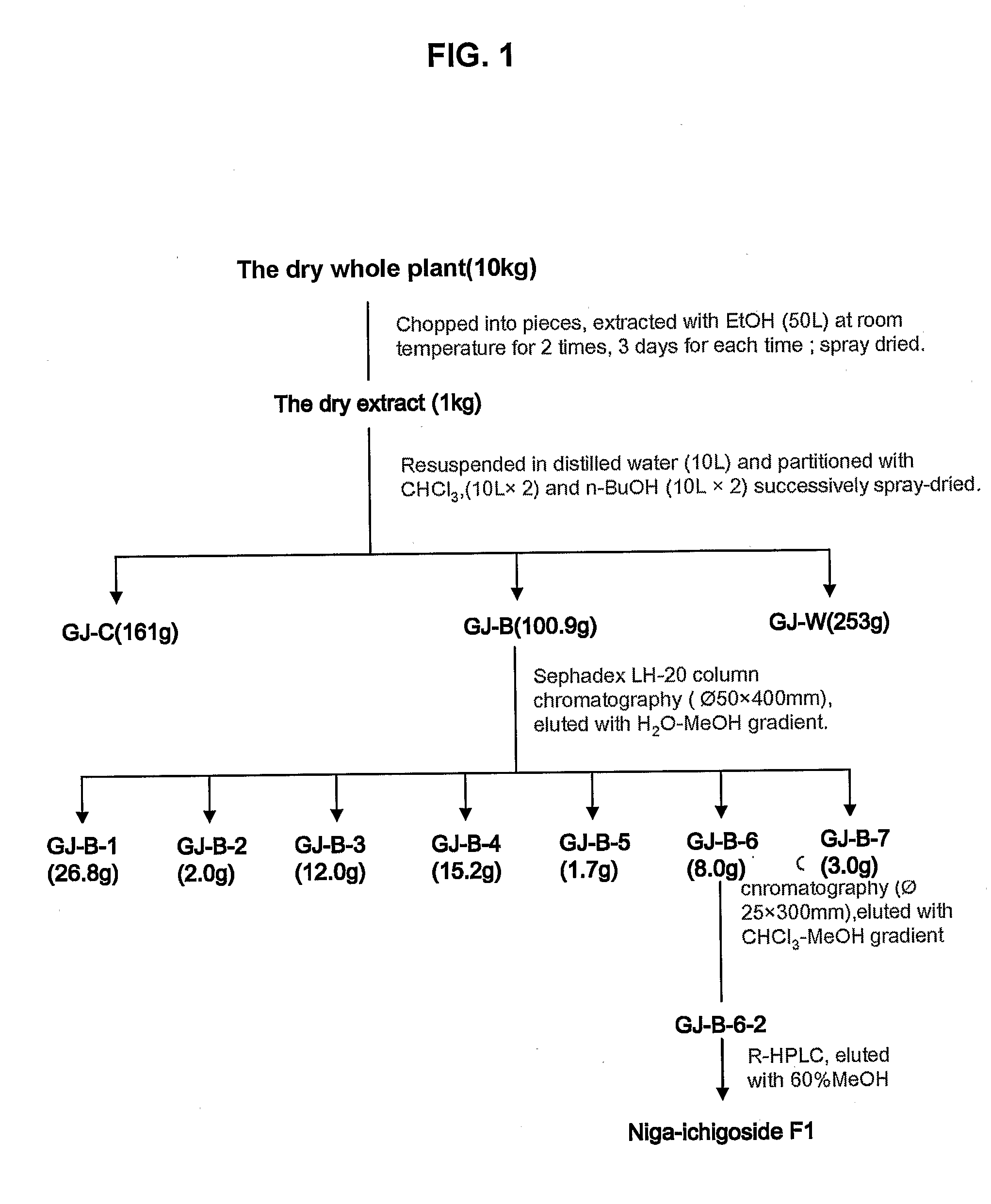
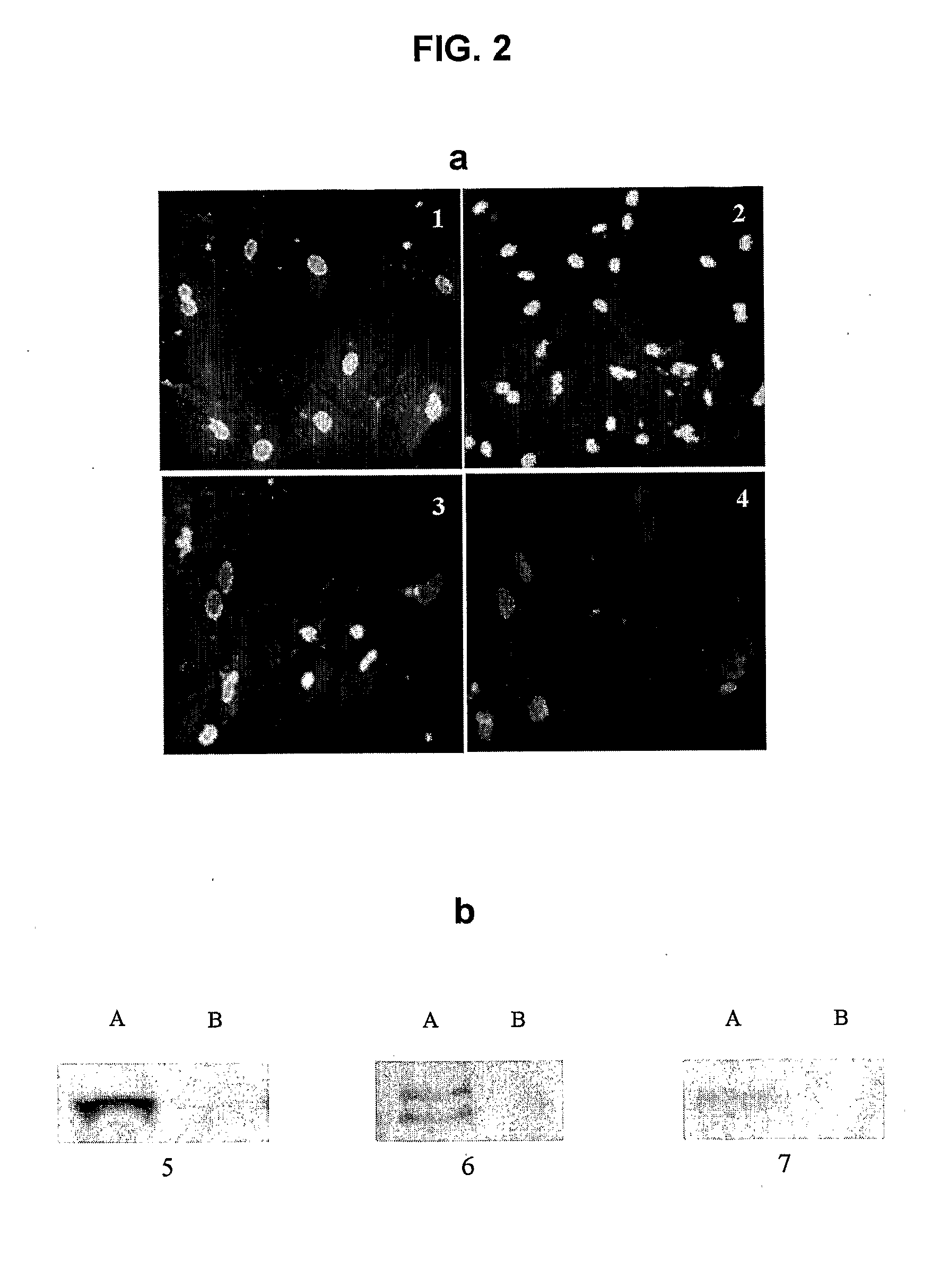
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
231 results about "Cardiac muscle cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
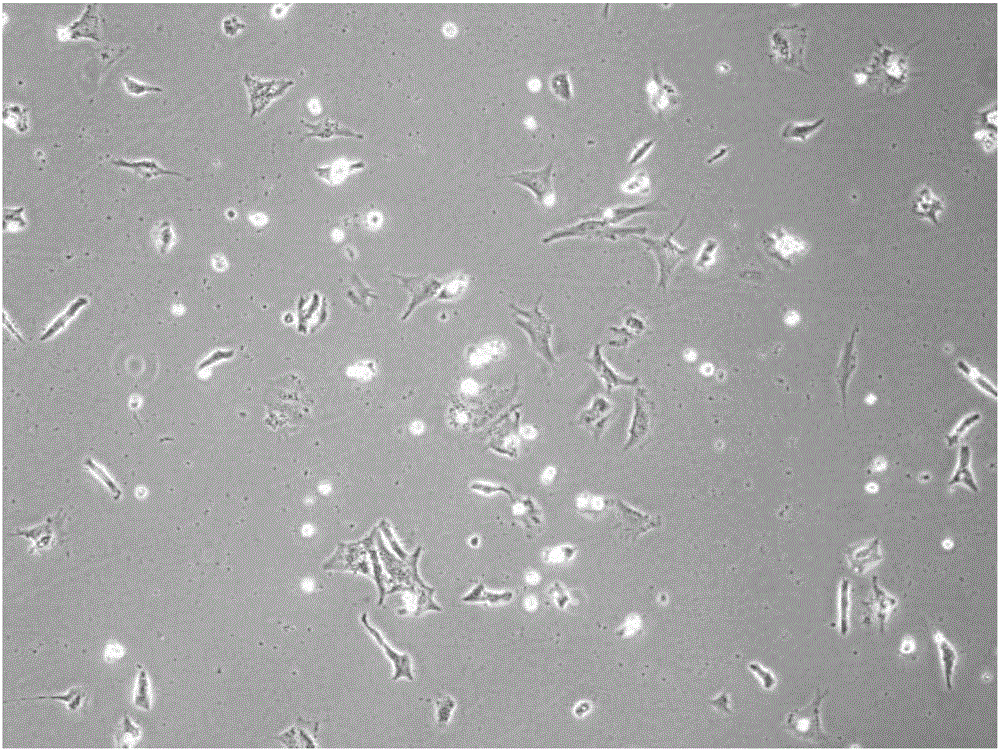
Cardiac muscle cells or cardiomyocytes (also known as myocardiocytes or cardiac myocytes) are the muscle cells (myocytes) that make up the cardiac muscle (heart muscle). Each myocardial cell contains myofibrils, which are specialized organelles consisting of long chains of sarcomeres, the fundamental contractile units of muscle cells.
Cardiac muscle function and manipulation
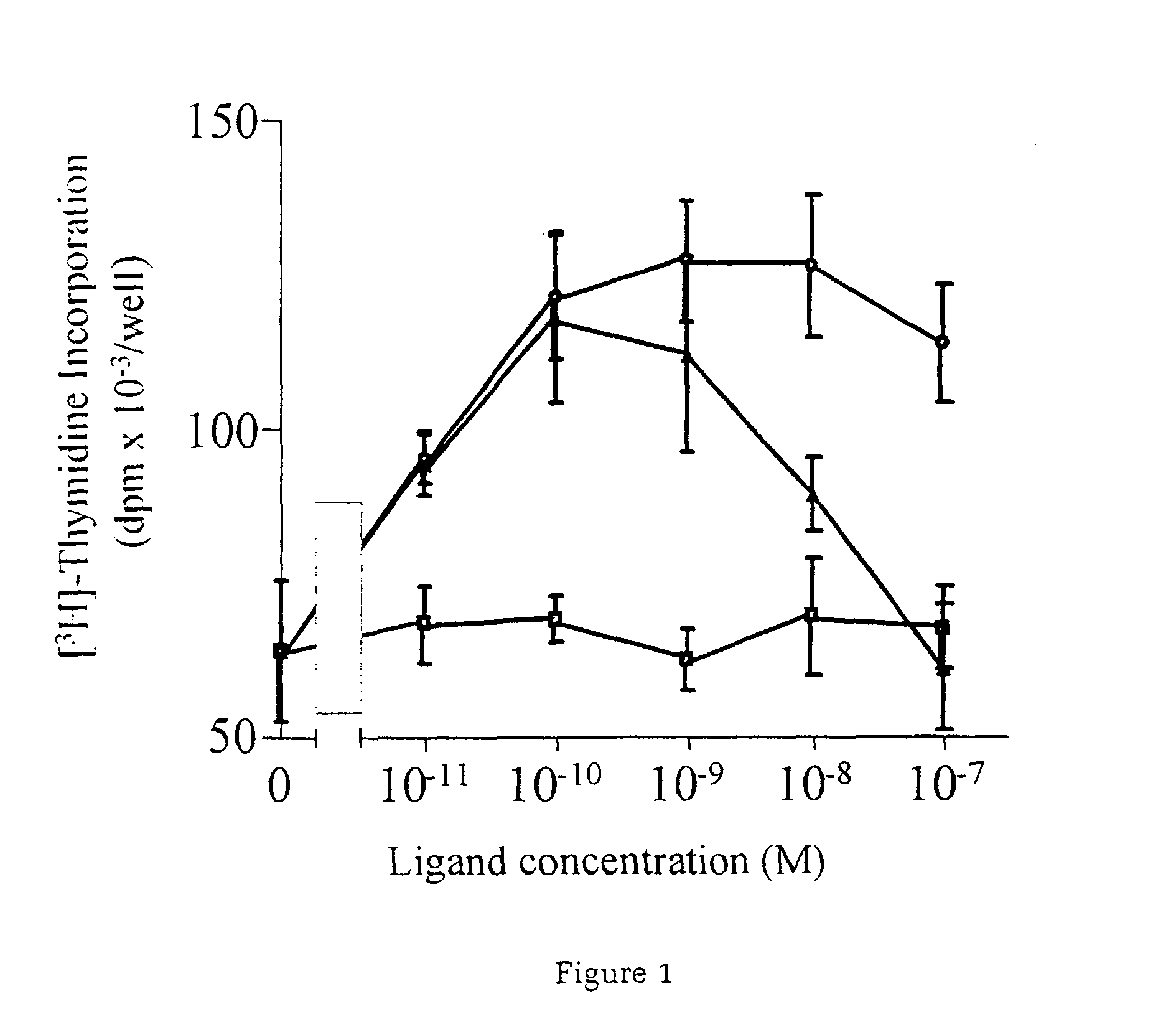
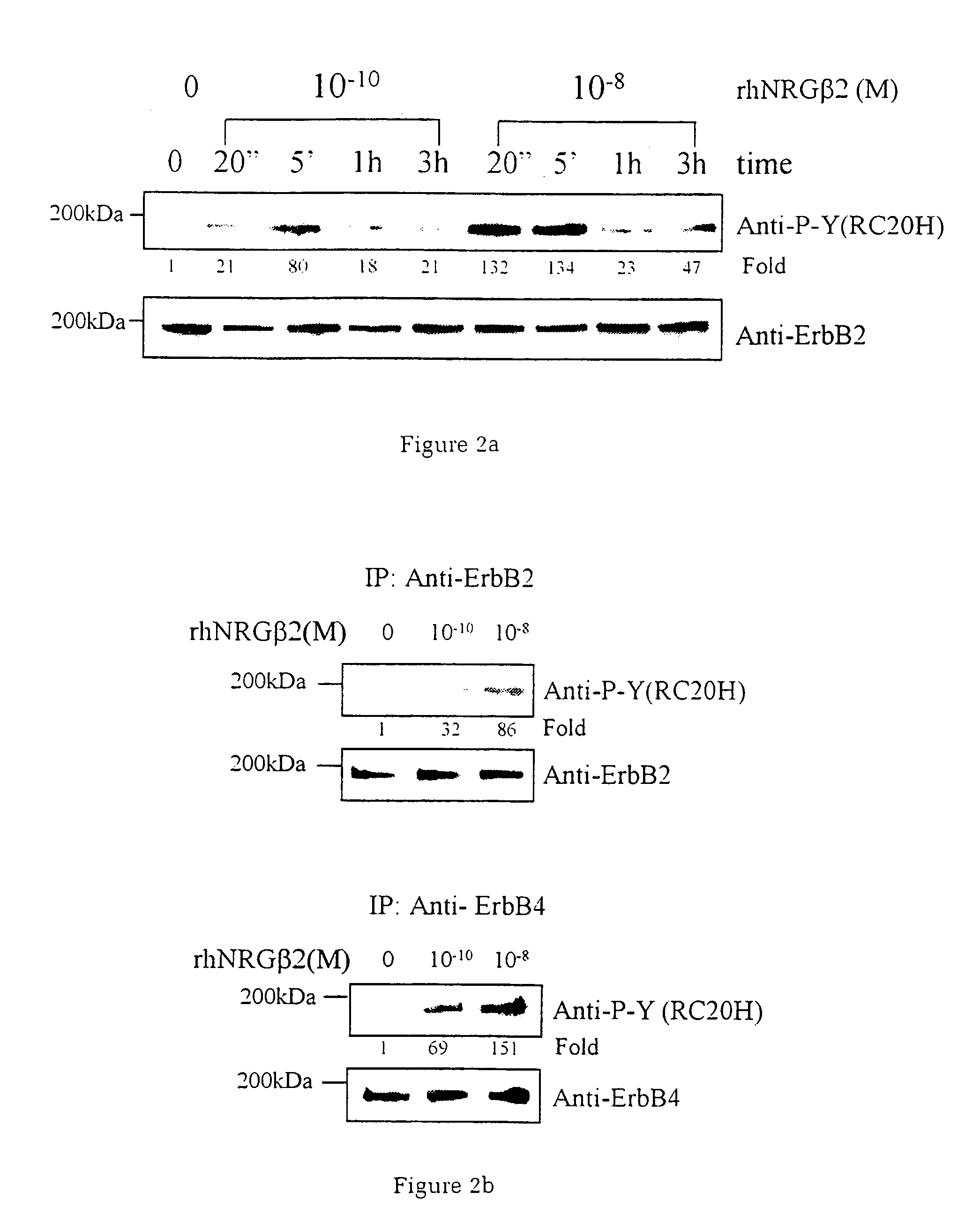
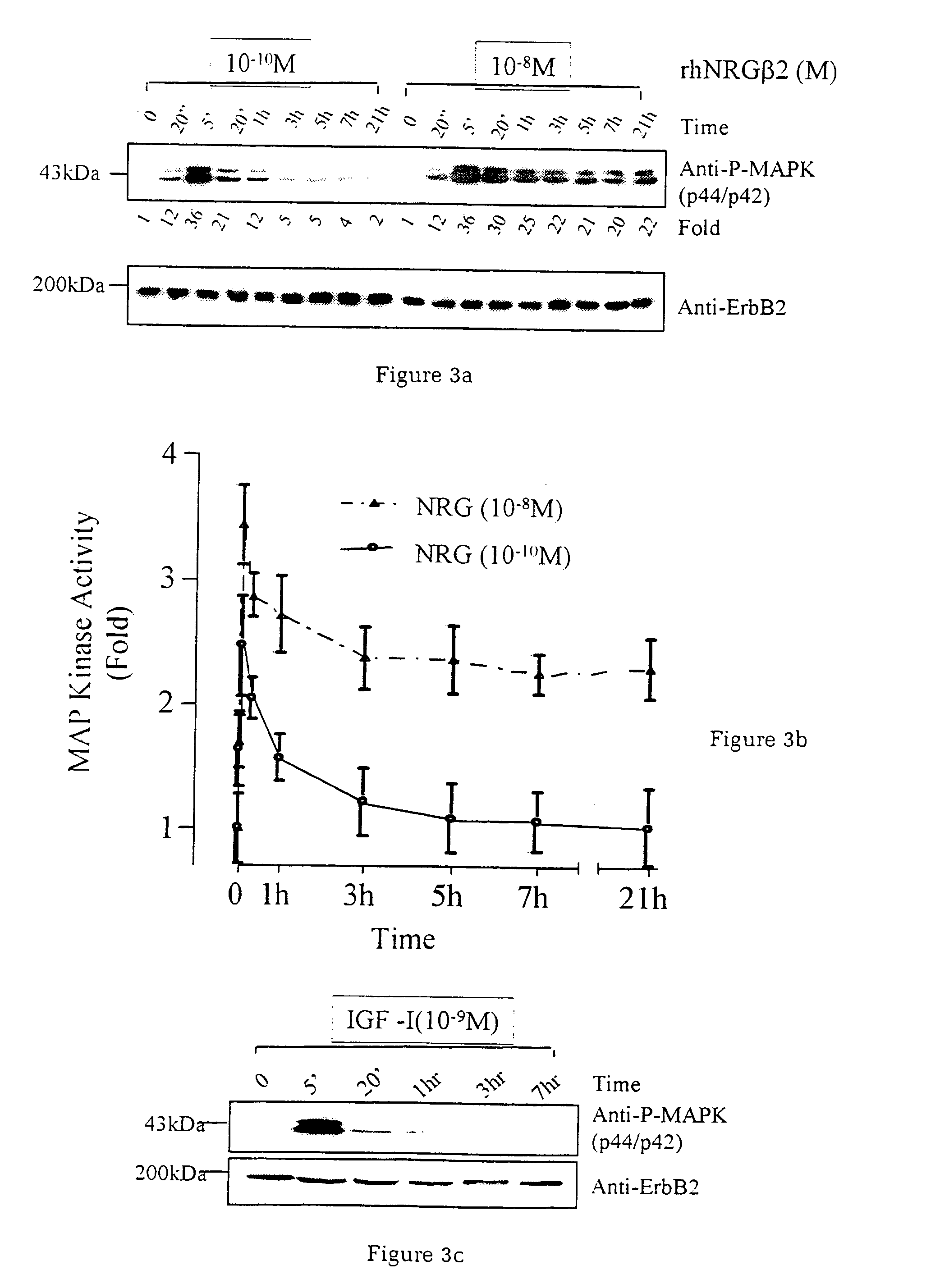
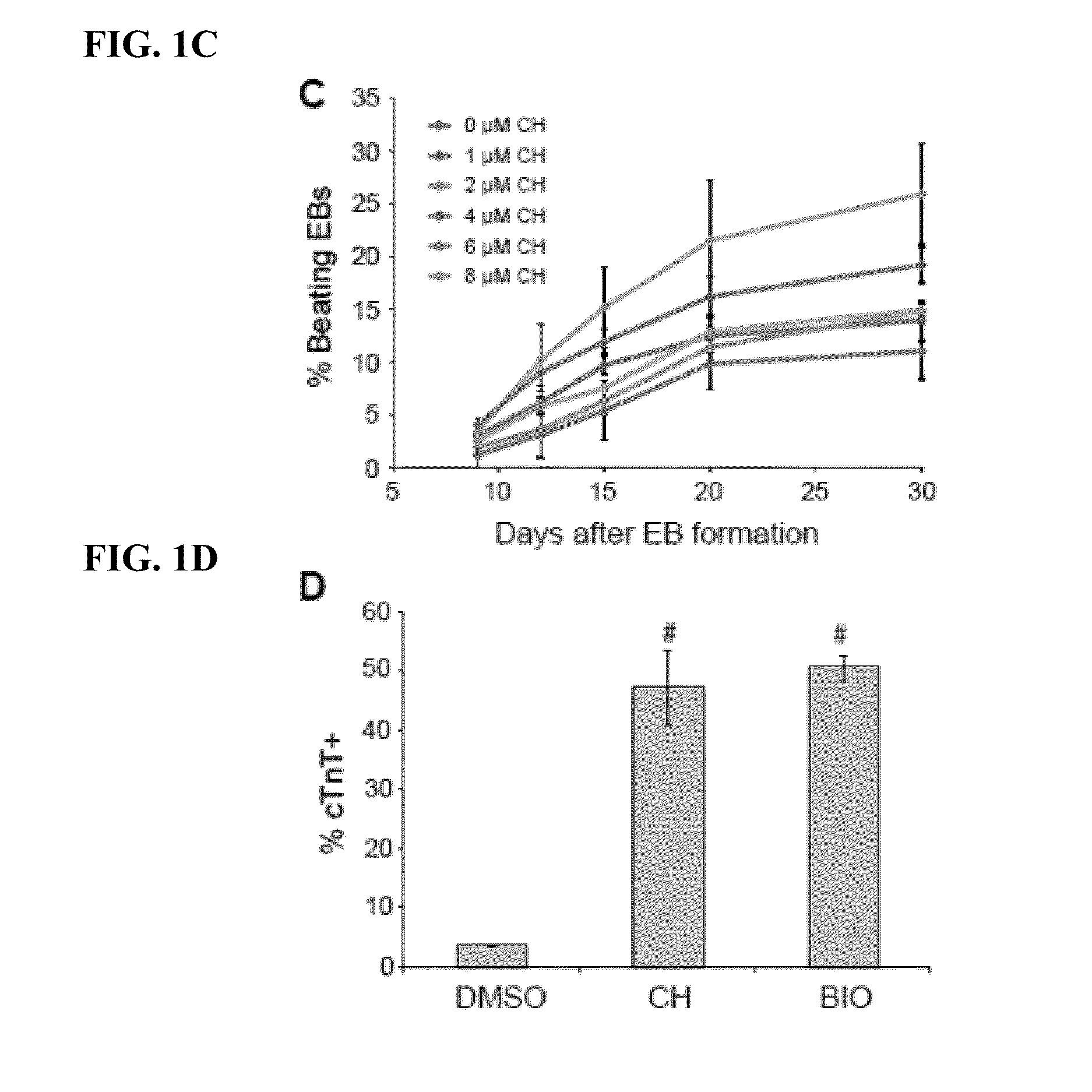
InactiveUS7226907B1Augment PE-mediated cardiac muscle cell differentiationImprove heart functionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCardiomyocyte growthNeuregulin
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
Systems and method for engineering muscle tissue
ActiveUS20150125952A1Accurately recapitulateHigh throughput formatGenetic material ingredientsDrug screeningMuscle tissueNanostructure
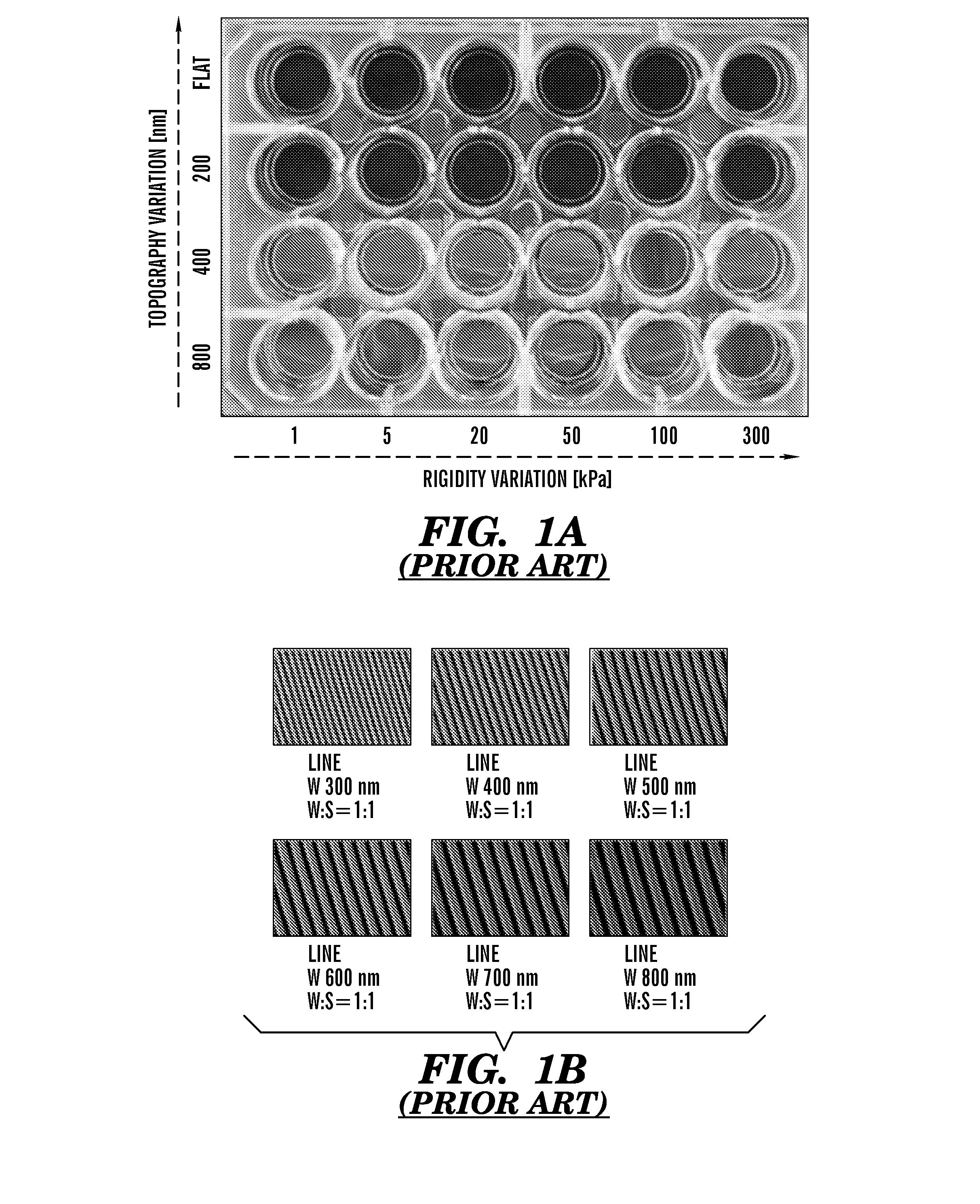
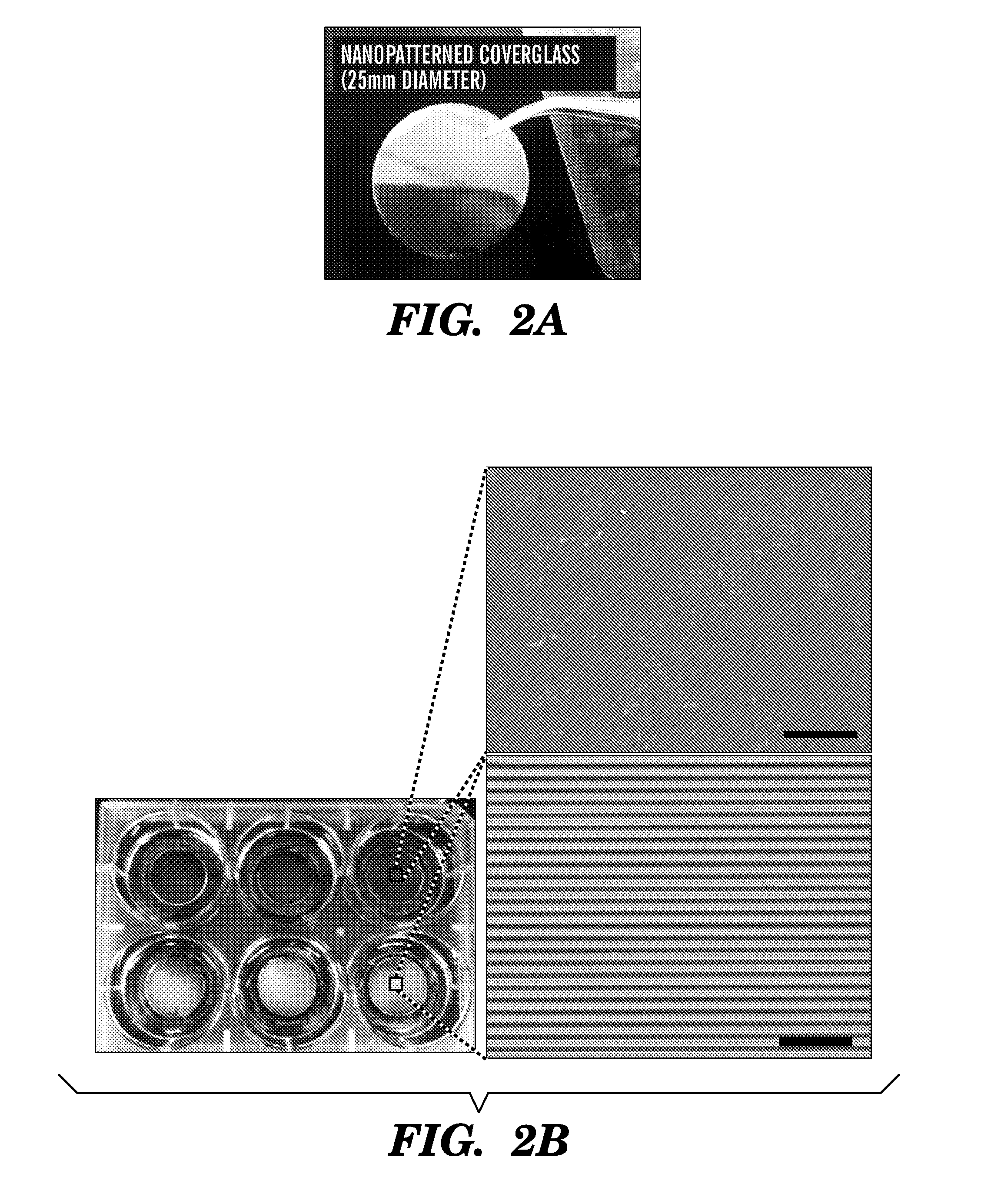
The present invention generally relates to the field of cell growth and tissue engineering, in particular, tissue engineered compositions comprising a nanotextured substrate which is structurally configured for growth of cells in an anatomically correct adult phenotype in vitro. In particular, described herein are nanotextured substrates which are structurally configured for the anisotropic organization, maturation, and growth of in vitro-differentiated muscle cells, such as cardiomyocytes, and methods for the production and use thereof in varying sizes, nanotextures and substrate rigidities. In vitro-differentiated cardiomyocytes grown on the nanotextured substrates described herein are better-differentiated and more closely mimic adult cardiac tissue than the same cells grown on a non-textured substrate of the same composition. The nanotextured substrate / cell constructs provide a platform for screening to predict the effect of test agents or drugs on, for example, human cardiac tissue, including patient-derived tissue, or for the identification of agents that effect various cardiac functional parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Generation of cardiomyocytes from human pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20130189785A1Artificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
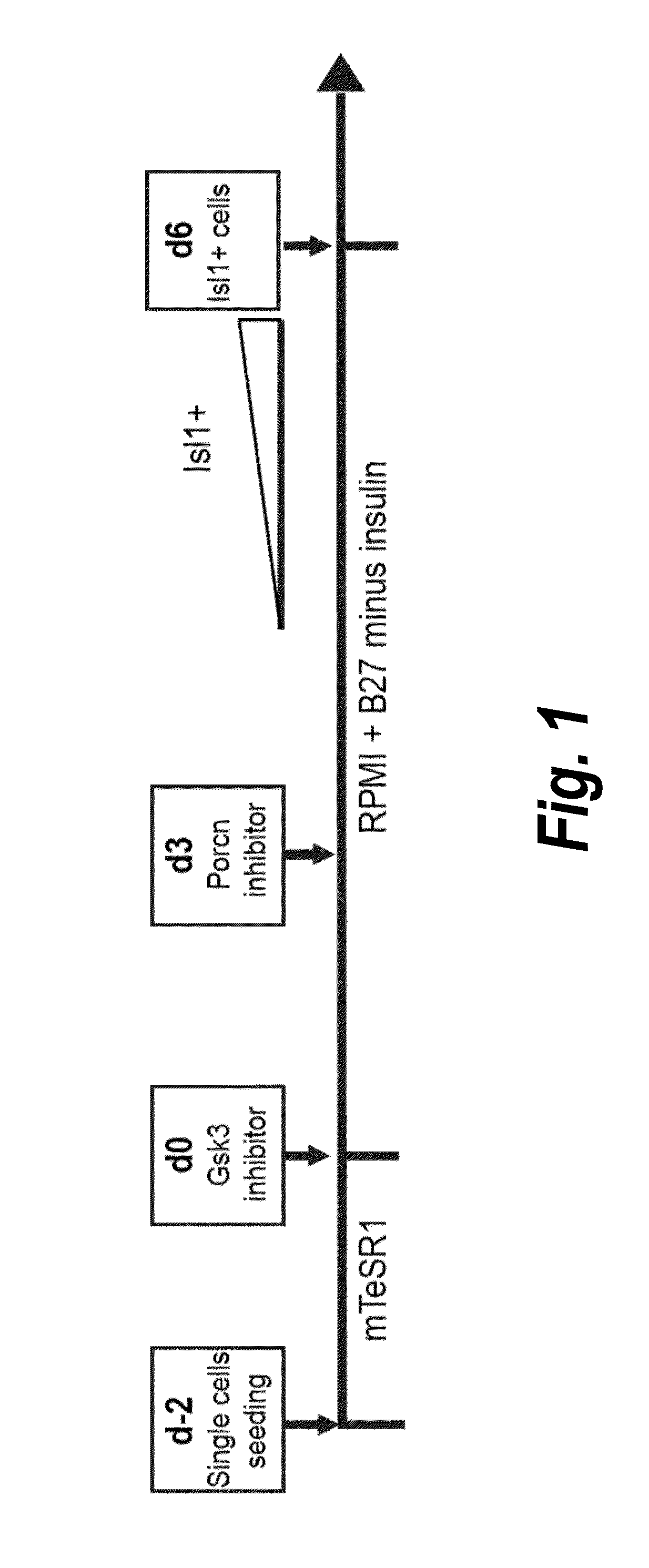
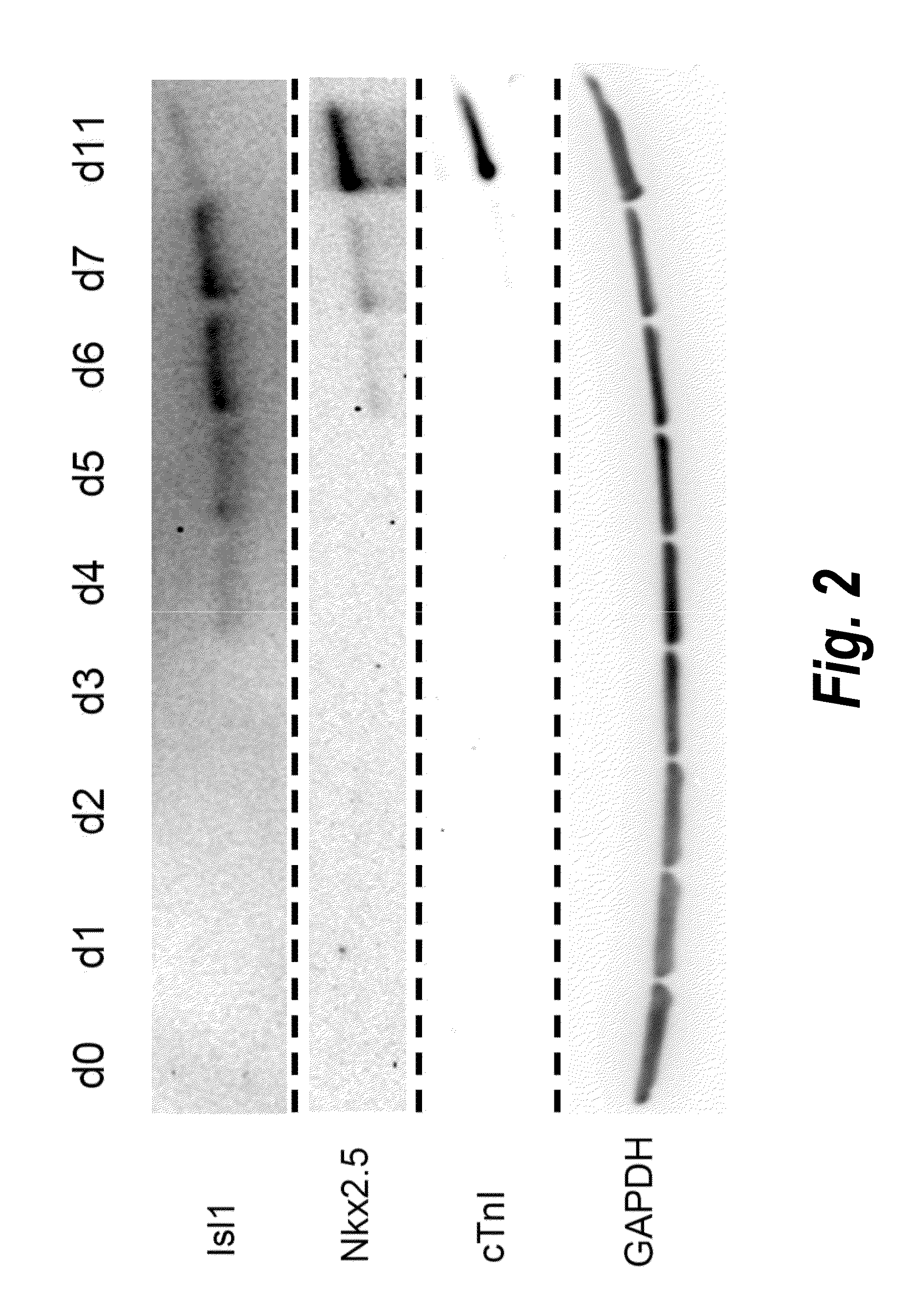
Methods for generating high-yield, high-purity cardiomyocyte progenitors or cardiomyocytes from pluripotent cells are described. Wnt / β-catenin signaling is first activated in pluripotent cells, e.g., by inhibition of Gsk-3 to obtain a first population of cells. Wnt / β-catenin signaling is then inhibited in the first cell population to induce cardiogenesis under fully defined, growth factor free culture conditions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cardiac muscle function and manipulation
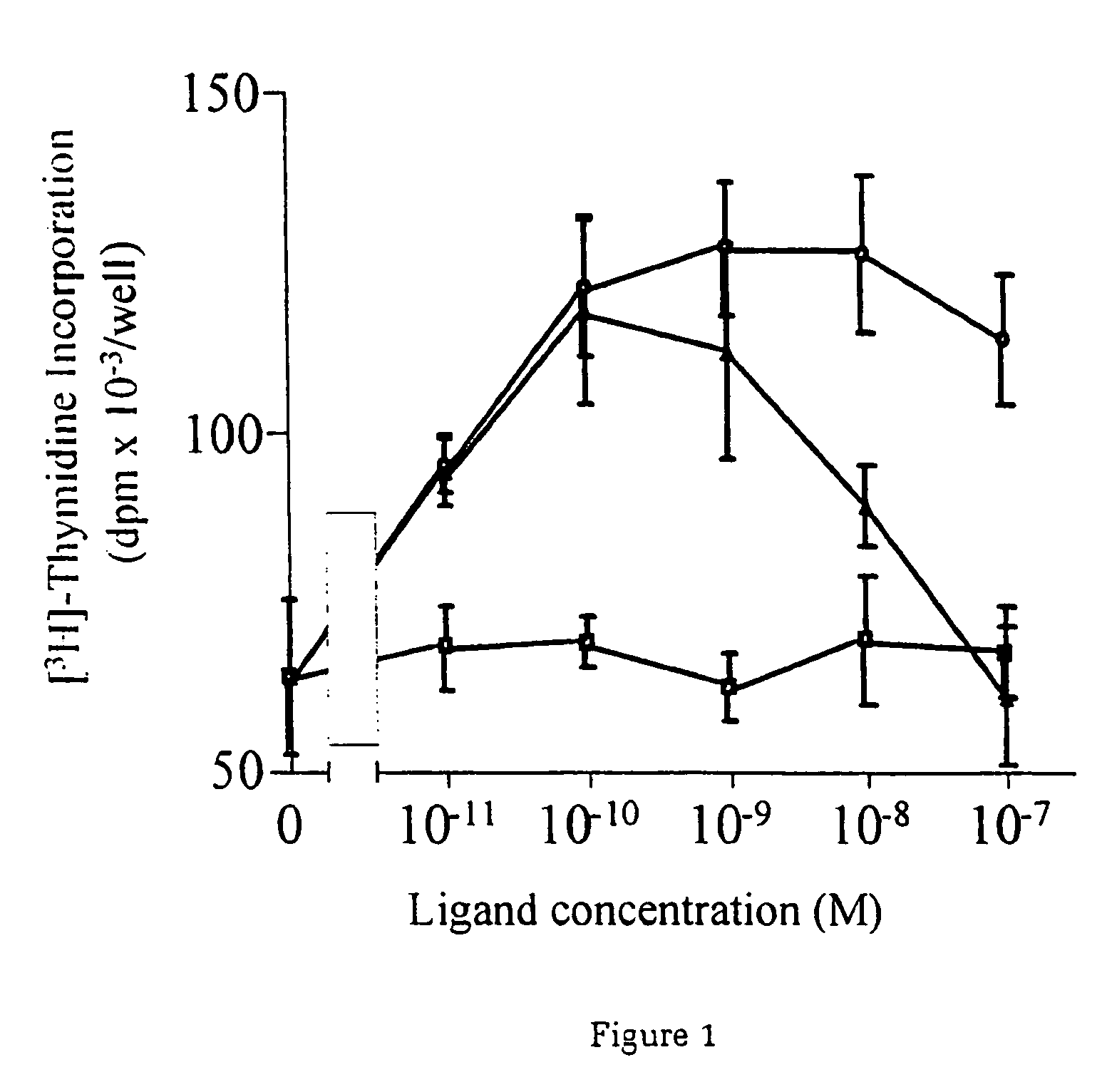
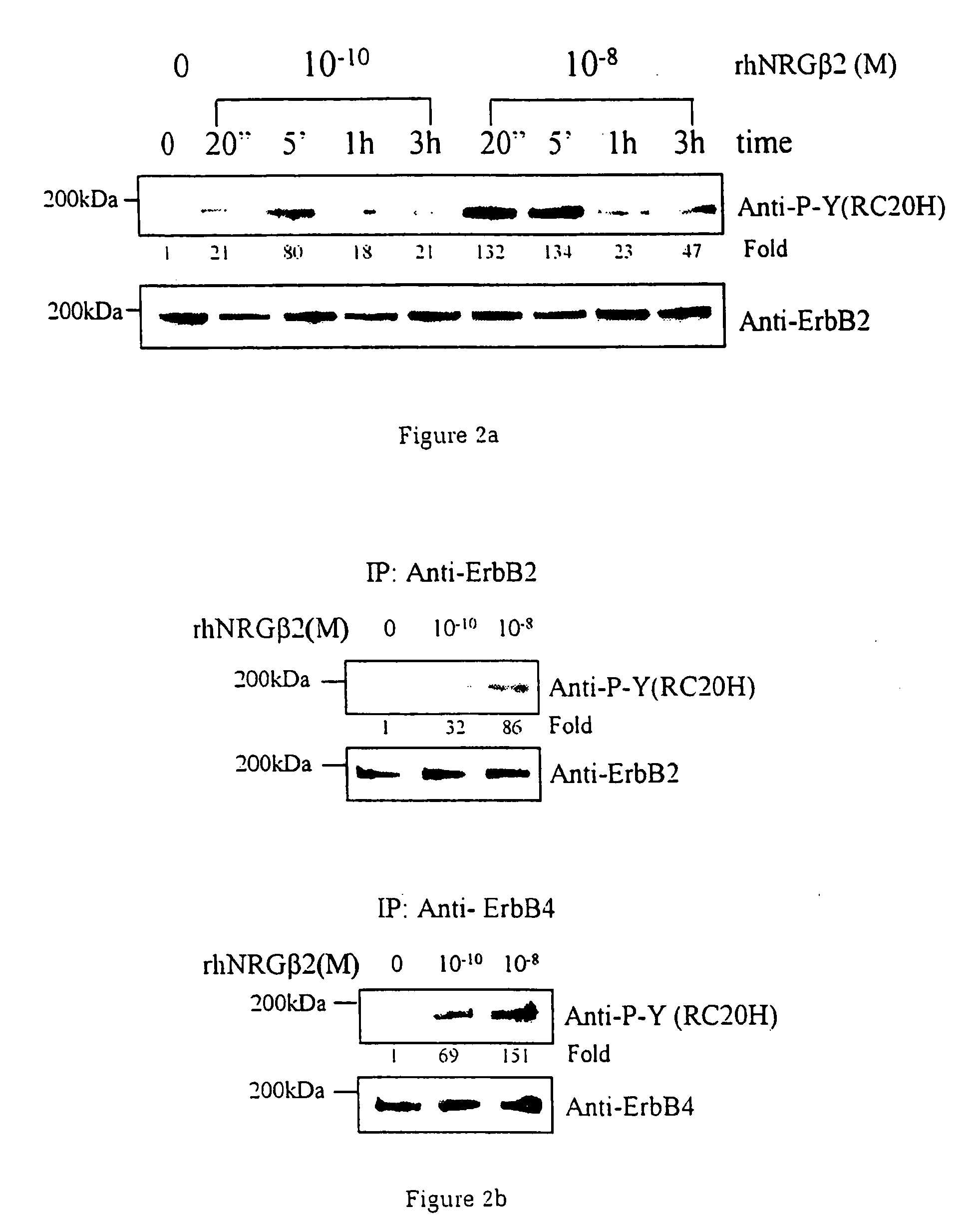
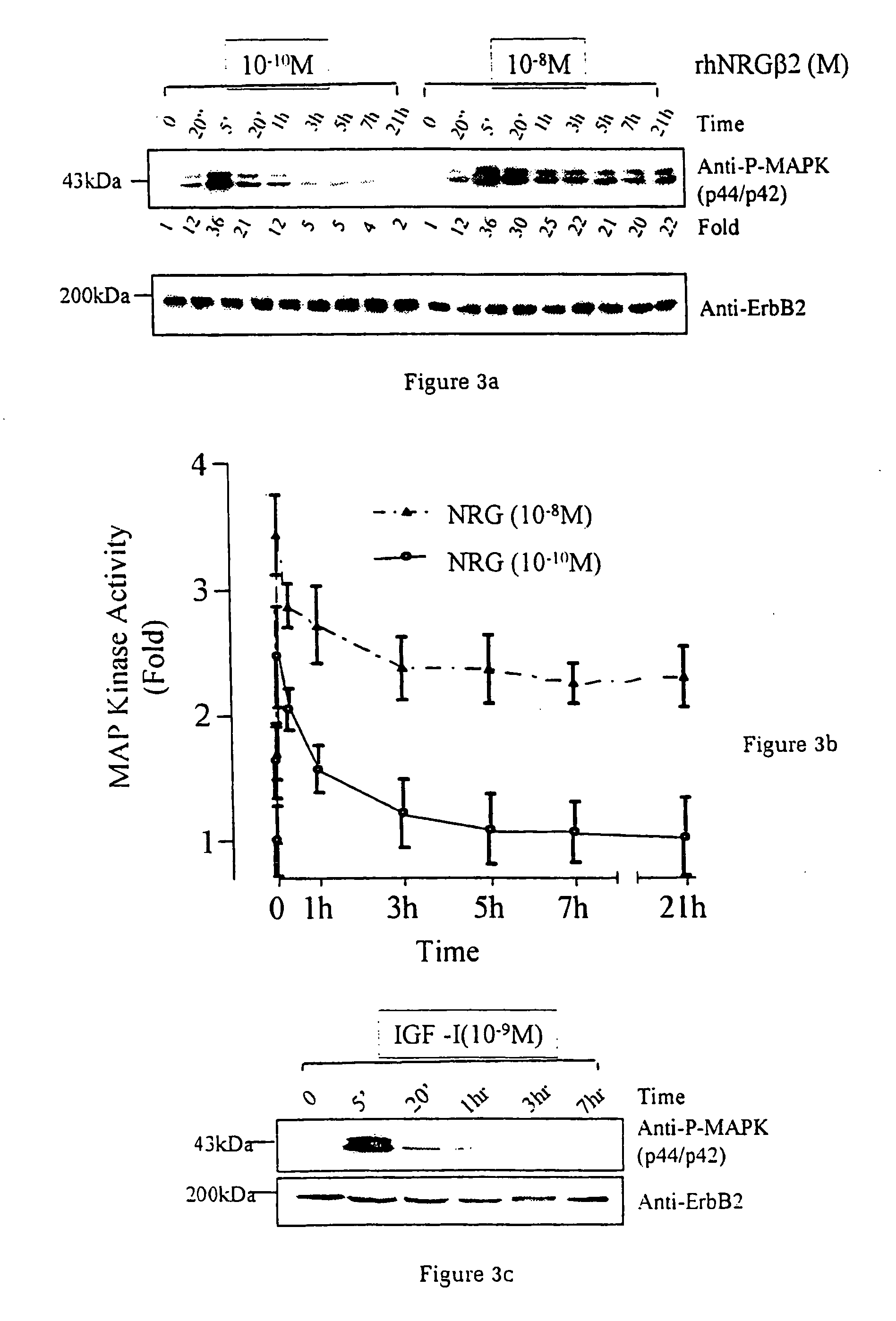
InactiveUS20060199767A1Promote cell differentiationImprove heart functionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticNeuregulinCardiomyocyte growth
A method of causing cardiomyocyte growth and / or differentiation, the method comprising exposing a cardiomyocyte to neuregulin (NRG) thereby activating the MAP kinase pathway in the cardiomyocyte and causing growth and / or differentiation of the cardiomyocyte. Use of neuregulin, neuregulin polypeptide, neuregulin derivatives, or compounds which mimic the activities of neuregulins in the treatment or management of heart disease and heart failure in a mammal.
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
Cardiomyocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients and methods of use thereof
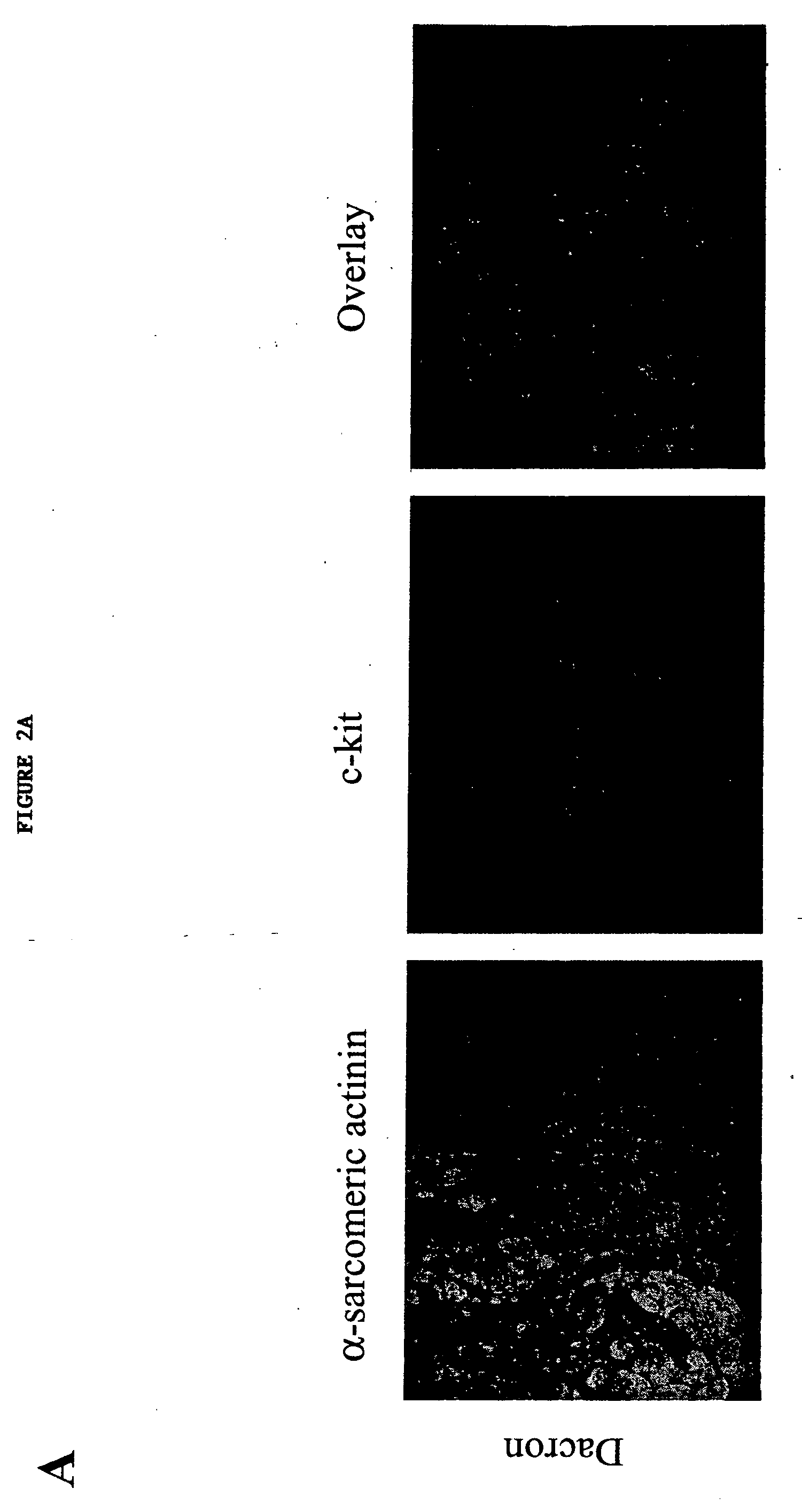
ActiveUS20130029866A1Abnormal sarcomeric α-actinin distributionReduce the probability of jumpingLibrary screeningDrug screeningPluripotential stem cellHuman body
Human somatic cells obtained from individuals with a genetic heart condition are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), and differentiated into cardiomyocytes for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Use of human stem cells and/or factors they produce to promote adult mammalian cardiac repair through cardiomyocyte cell division
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprising (i) producing a solution comprising media conditioned from the culture of cells, in vitro, and (ii) administering the solution of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. Methods for determining whether an agent stimulates or inhibits myocyte proliferation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells and application of inducing culture medium
ActiveCN105861428ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsFibroblastCells fibroblast
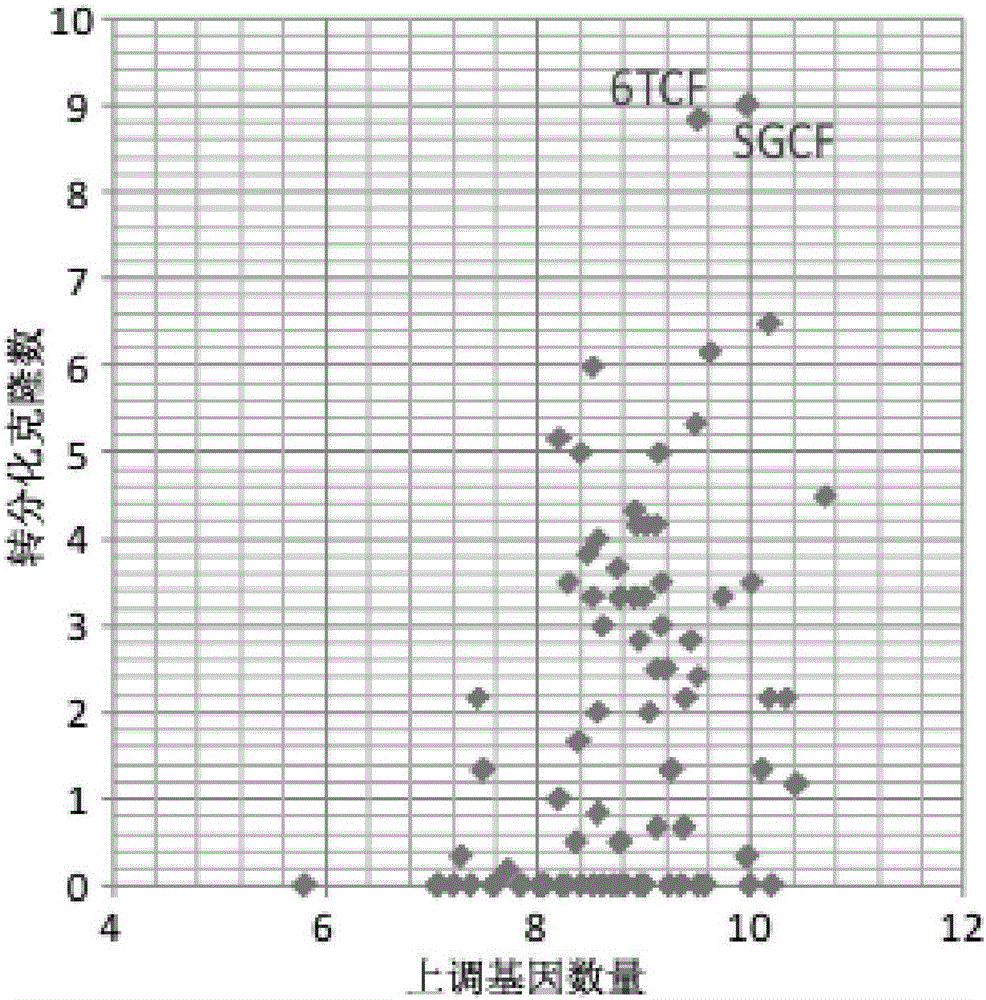
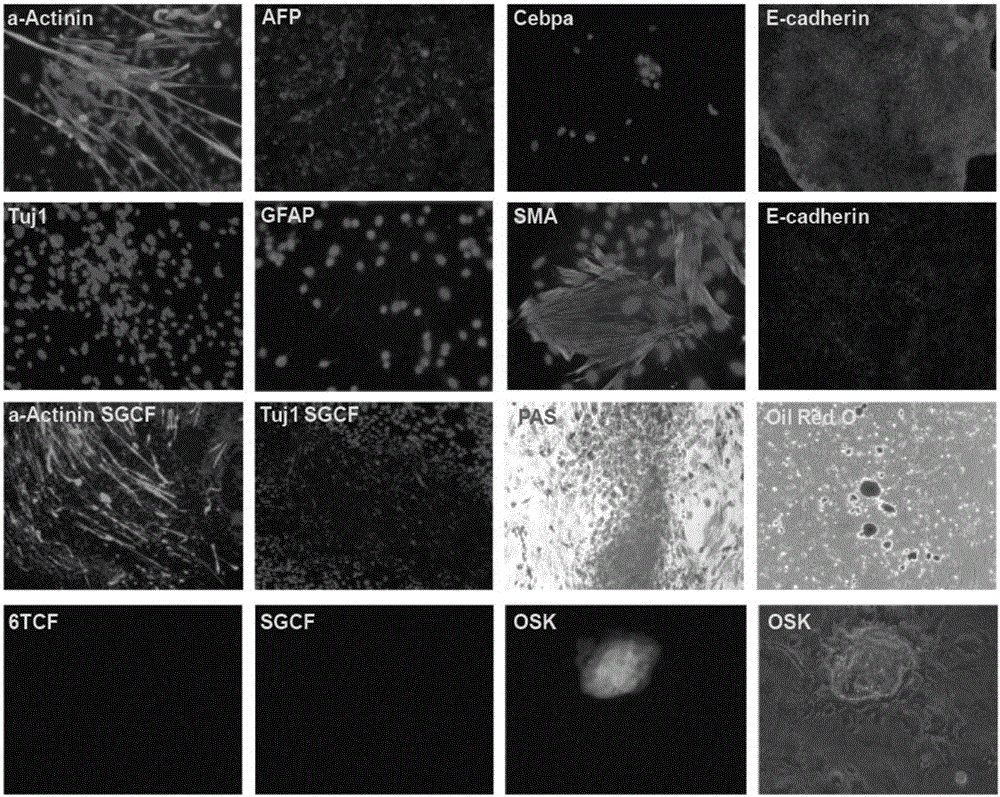
The invention discloses an inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells, a method and an application of the inducing culture medium. The inducing culture medium comprises a basic culture medium and an inducing small molecular assembly which is 6TCFOW or SCFOV, wherein 6 is E61541, T is tranylcypromine, C is CHIR99021, F is forskolin, O is Dorsomorphin, W is IWR-I, S is SB431542, and V is valproic acid. The inducing culture medium can trans-differentiate the fibroblast into the cardiac muscle cells which have normal cardiac muscle cell specific molecular tags and a normal cardiac muscle function, so that a new way is provided for solving the cell source problem of the regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for culturing cardiac progenitor cells and use of cardiac progenitor cells
InactiveUS20130295060A1Robust ex vivo expandabilityHigh yieldBiocideSkeletal/connective tissue cellsNeural cellOsteoblast
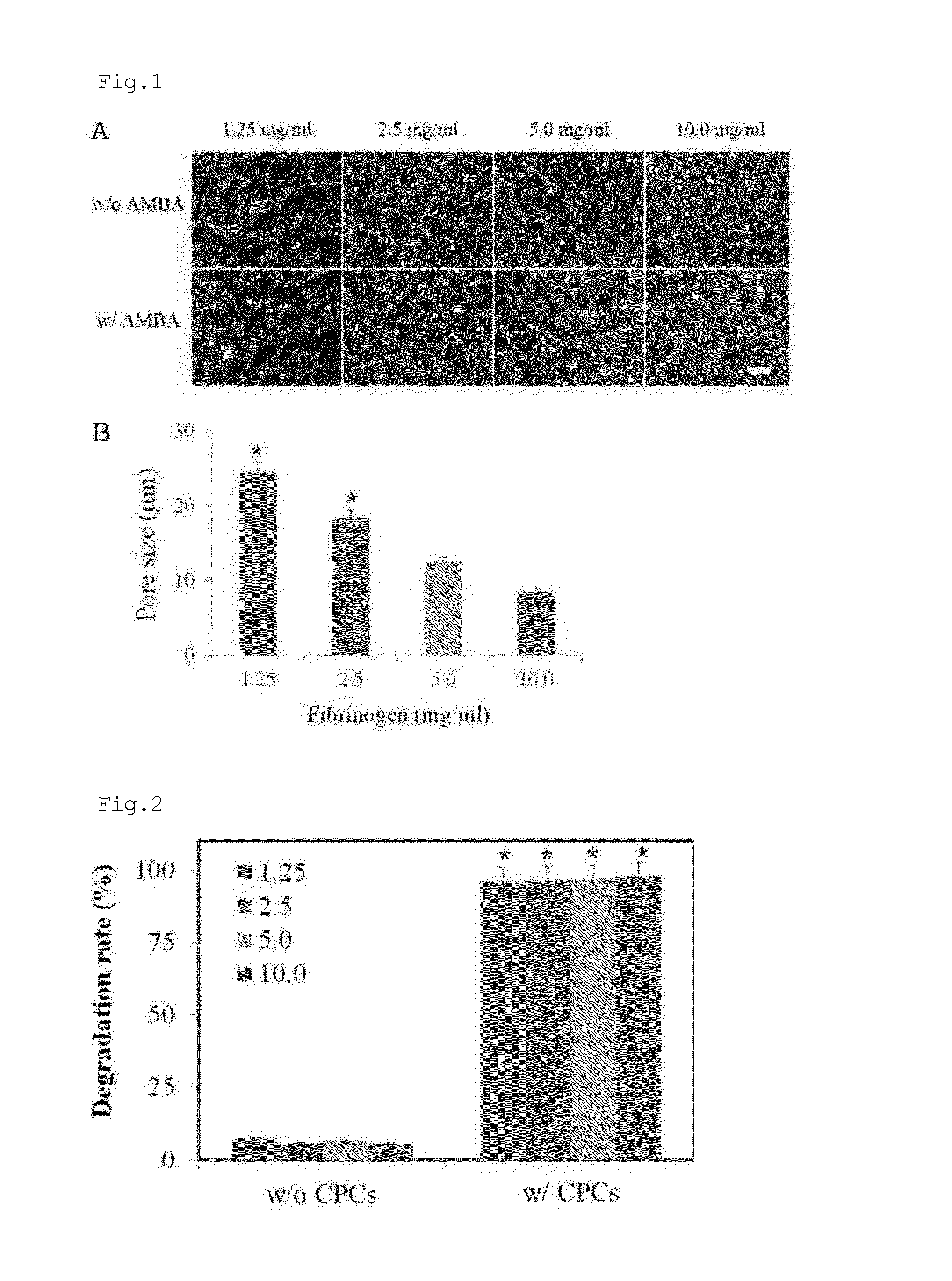
Disclosed is a method for culturing myocardium-resident cardiac progenitor cells, comprising: embedding myocardial fragments into hydrogel; culturing the myocardial fragment into hydrogel; degrading only the hydrogel to recover cardiac progenitor cells grown out of the myocardial fragment to the hydrogel; and amplifying the cardiac progenitor cells in vitro. Also, the cardiac progenitor cells, a method for differentiating the same, and the use thereof as cell therapeutic agent for heart diseases are provided. In addition to possessing the potential to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, osteoblasts, adipocytes, chondrocytes, vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, neural cells, and skeletal muscle cells, the myocardium-resident cardiac progenitor cells can spontaneously differentiate into cardiomyocytes even in the absence of a special differentiation inducing agent. Thus, the cardiac progenitor cells can be used to produce bio-active medicines such as cell therapeutics and tissue engineering therapeutics with high industrial applicability.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Method for producing mixed cell population of cardiomyocytes and vascular cells from induced pluripotent stem cell
ActiveUS20150297794A1Improve heart functionBiocideSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMixed cellMixed Cellular Population
Owner:IHEART JAPAN
Methods for Generating Cardiomyocytes
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Method for Promoting Differentiation of Pluripotent Stem Cells into Cardiac Muscle Cells
ActiveUS20140127807A1Improve efficiencyLow costOrganic chemistrySkeletal/connective tissue cellsInduced pluripotent stem cellMultipotential stem cell
The present invention relates to a composition for promoting differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into cardiac muscle cells, and a method for inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into cardiac muscle cells and a method for preparing cardiac muscle cells
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Methods and compositions for correction of cardiac conduction disturbances
The invention provides methods for establishing electrical coupling between cardionyocytes and recombinant cells which have been genetically engineered to express a gap junction protein, eg., Connexin protein such as Connexin 43 (CX43) protein, n invention is based on the discovery that genetic modification of skeletal muscle cells to express a recombinant connexin, enables the genetically modified cells to establish electrocommunication with cardiac cells via gap junctions. The recombinant connexin-expressing cells can be used for repair of cardiac issue and for treatment of cardiac disease by transplantation into cardiac tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cardiac-Specific Protein Targeting Domain
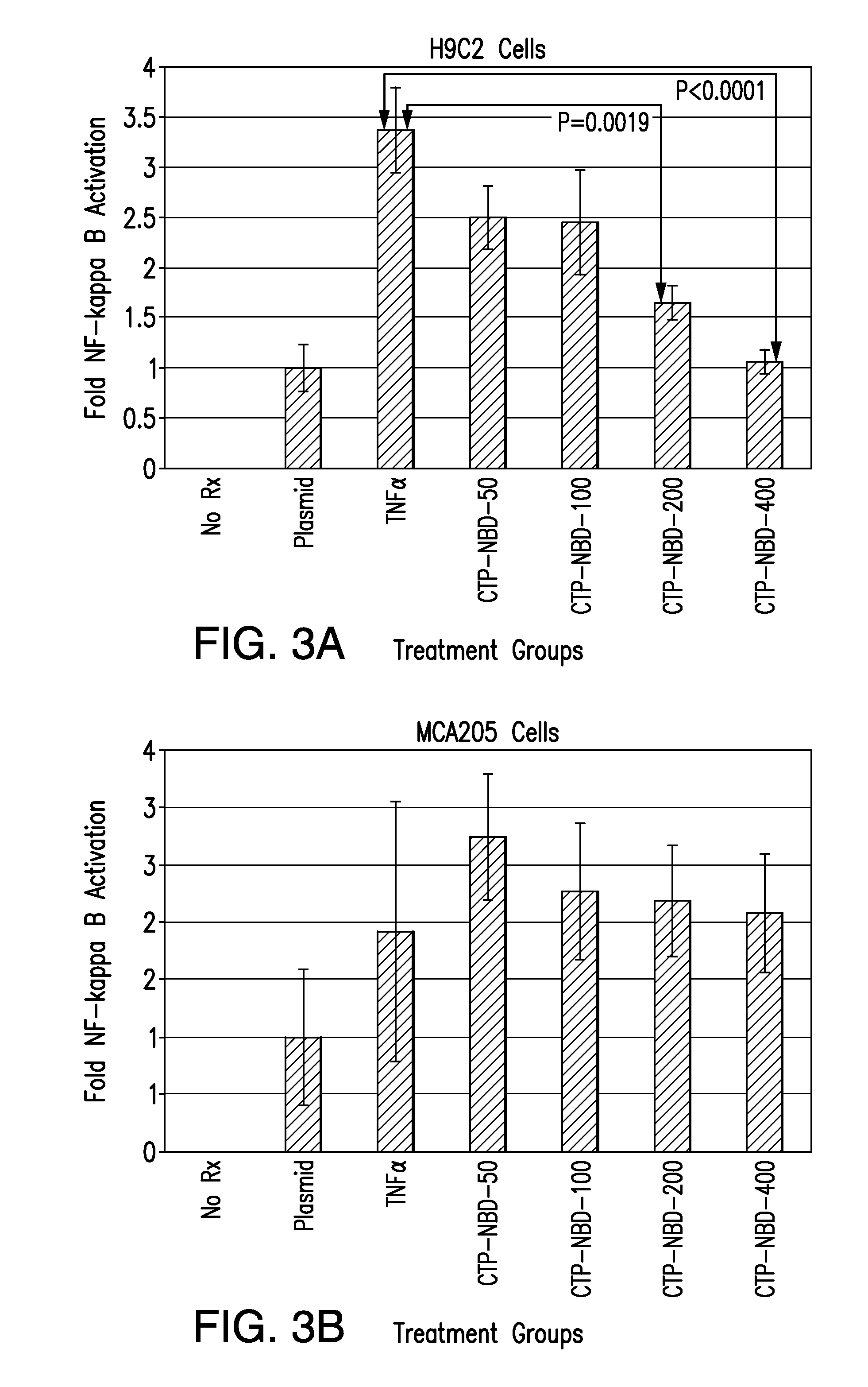
The present invention relates to Cardiac Targeting Peptides or CTPs that are able to transduce cardiomyocytes specifically in culture and in vivo, and to methods for using such peptides and their derivatives to deliver peptides, proteins or nucleic acids specifically to the heart. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that the peptide APWHLSSQYSRT (SEQ ID NO:1) functioned as a cardiac-specific protein targeting peptide and was successful in delivering a number of different cargoes to cardiac muscle cells in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Cardiomyocytes From Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells From Patients and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20170058263A1Abnormal sarcomeric α-actinin distributionReduce the probability of jumpingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsSomatic cellHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Human somatic cells obtained from individuals with a genetic heart condition are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), and differentiated into cardiomyocytes for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
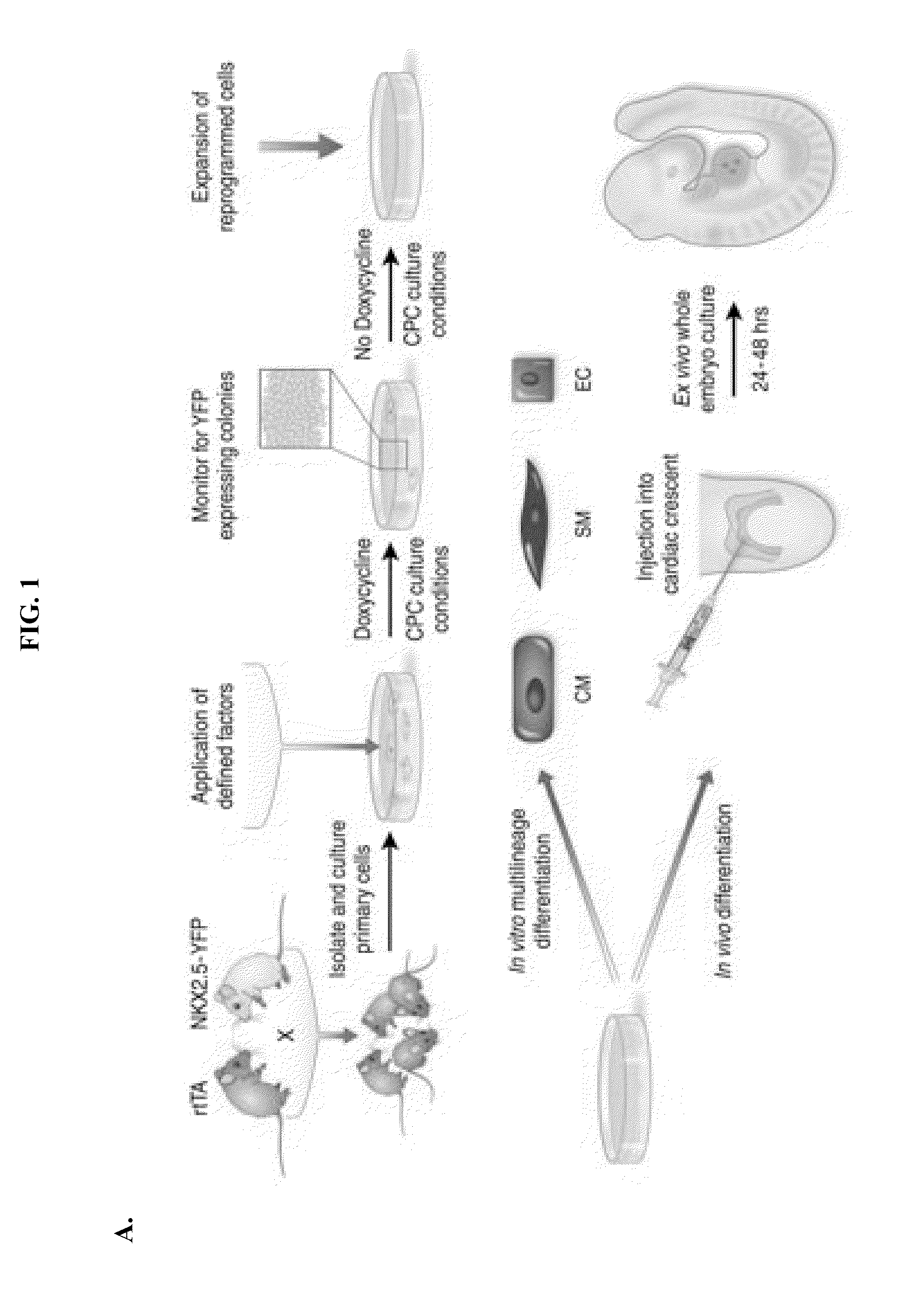
LINEAGE REPROGRAMMING TO INDUCED CARDIAC PROGENITOR CELLS (iCPC) BY DEFINED FACTORS
ActiveUS20150140658A1Facilitated DiffusionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsLineage specificCells heart
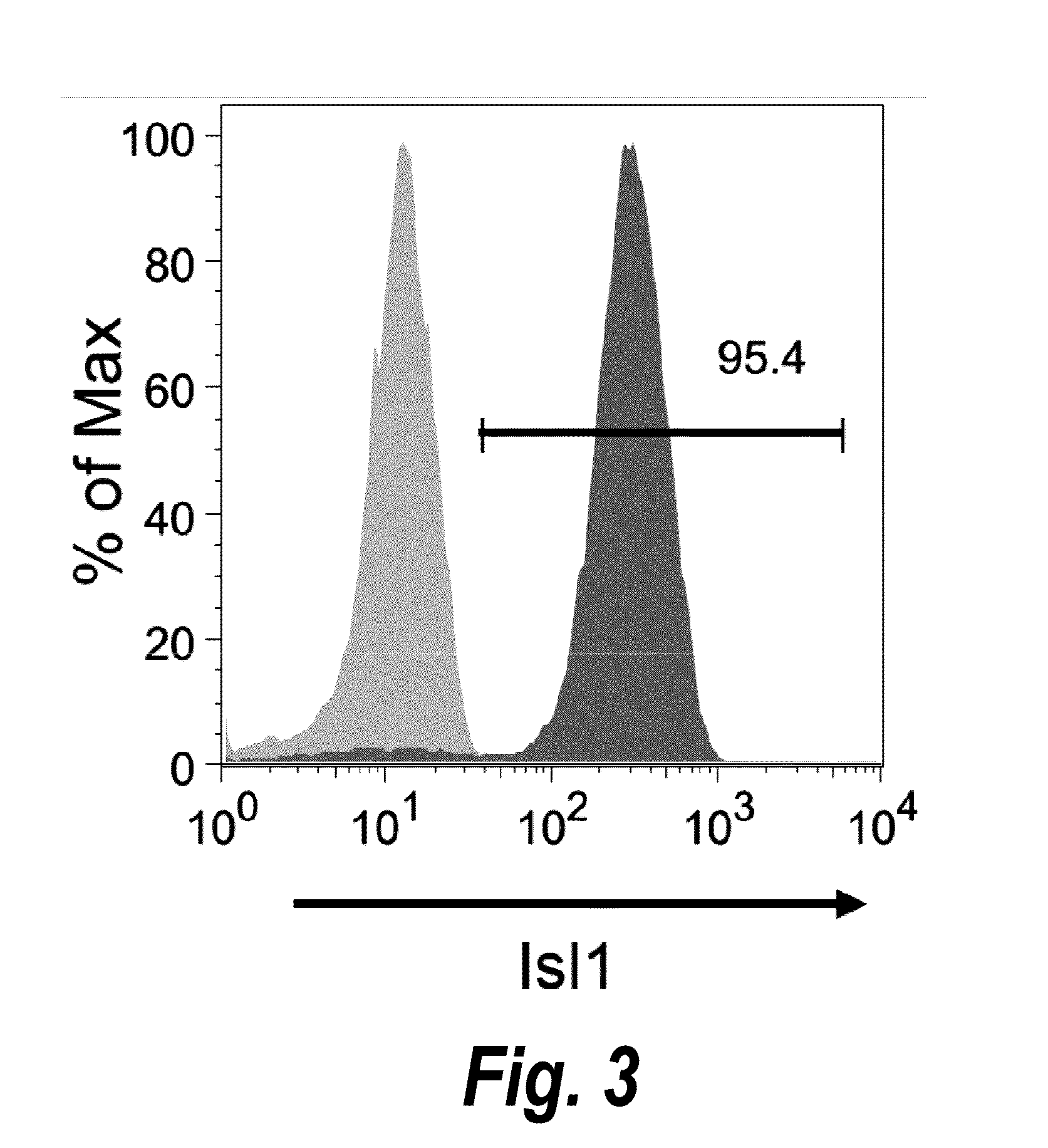
Animal cells, notably adult fibroblasts, are advantageously reprogrammed in direct lineage reprogramming methods using defined factors to produce proliferative and multipotent induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPC). The iCPC thus produced can be differentiated under suitable differentiation conditions to cardiac lineage cells including cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells, as evidenced by expression of lineage specific markers. Sets of factors effective in combination to reprogram the fibroblasts can include a set that includes some or all of 5 factors (Mesp1, Baf60c, Nkx2.5, Gata4, Tbx5), a set that includes some or all of 11 factors (Mesp1, Mesp2, Gata4, Gata6, Baf60c, SRF, Isl1, Nkx2.5, Irx4, Tbx5, Tbx20), a set that includes some or all of 18 factors (T, Mesp1, Mesp2, Tbx5, Tbx20, Isl1, Gata4, Gata6, Irx4, Nkx2.5, Hand1, Hand2, Tbx20, Tbx18, Tip60, Baf60c, SRF, Hey2), and a set that includes some or all of 22 factors (T, Mesp1, Mesp2, Tbx5, Tbx20, Isl1, Gata4, Gata6, Irx4, Nkx2.5, Hand1, Hand2, Tbx20, Tbx18, Tip60, Baf60c, SRF, Hey2, Oct4, Klf4, Sox2, L-myc).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for promoting differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into cardiac muscle cells
ActiveUS20130183753A1Low costHigh differentiation efficiencyOrganic chemistryArtificial cell constructsInduced pluripotent stem cellCells heart
The present invention relates to a composition for promoting differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into cardiac muscle cells, and a method for inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into cardiac muscle cells and a method for preparing cardiac muscle cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Use of lifr or fgfr3 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS20160108363A1Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseBiocideArtificial cell constructsSurface markerProgenitor
The present invention provides LIFR and FGFR3 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ LIFR+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / LIFR+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Cardiac muscle cell detection method based on inverse opal structure hydrogel and application thereof
ActiveCN107655813AGood biocompatibilityUnique and stable optical sensing signalIndividual particle analysisBiocompatibility TestingOptical sensing
The invention discloses a cardiac muscle cell detection method based on inverse opal structure hydrogel and application thereof. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing inverse opal structure hydrogel of biocompatibility; (2) culturing cardiac muscle cells based on inverse opal structure hydrogel; (3) detecting the cardiac muscle cells; (4) analyzing data. The inverse opal structure hydrogel in the invention has good biocompatibility, cells have high activity and phenotype when growing on the surface of the hydrogel, the inverse opal structure hydrogel not only provides a carrier for the growth of the cardiac muscle cells, but also provides a stable optical sensing signal for detecting the cardiac muscle cell shrinking force and hopping frequency. The detection method does not need a complicated detection system, and has the advantages of intuitiveness, high sensitivity, high efficiency and capability of preventing the influence of external conditions; the method can be used for screening and evaluating heart drugs and can screen the drugs by virtue of the variation of the cardiac muscle cell shrinking force and hopping frequency after the drug is added.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
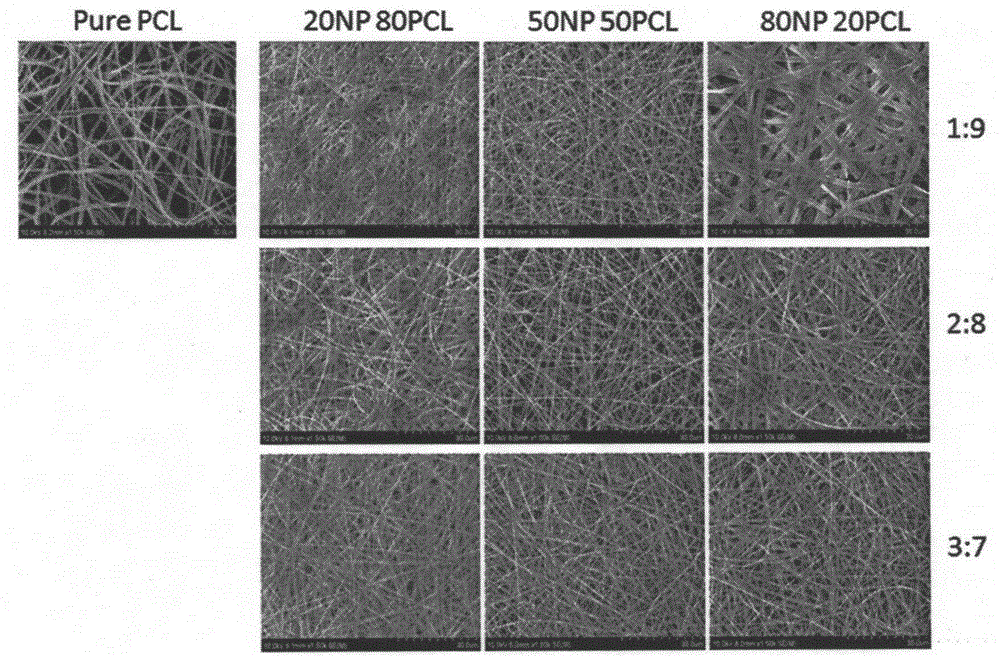
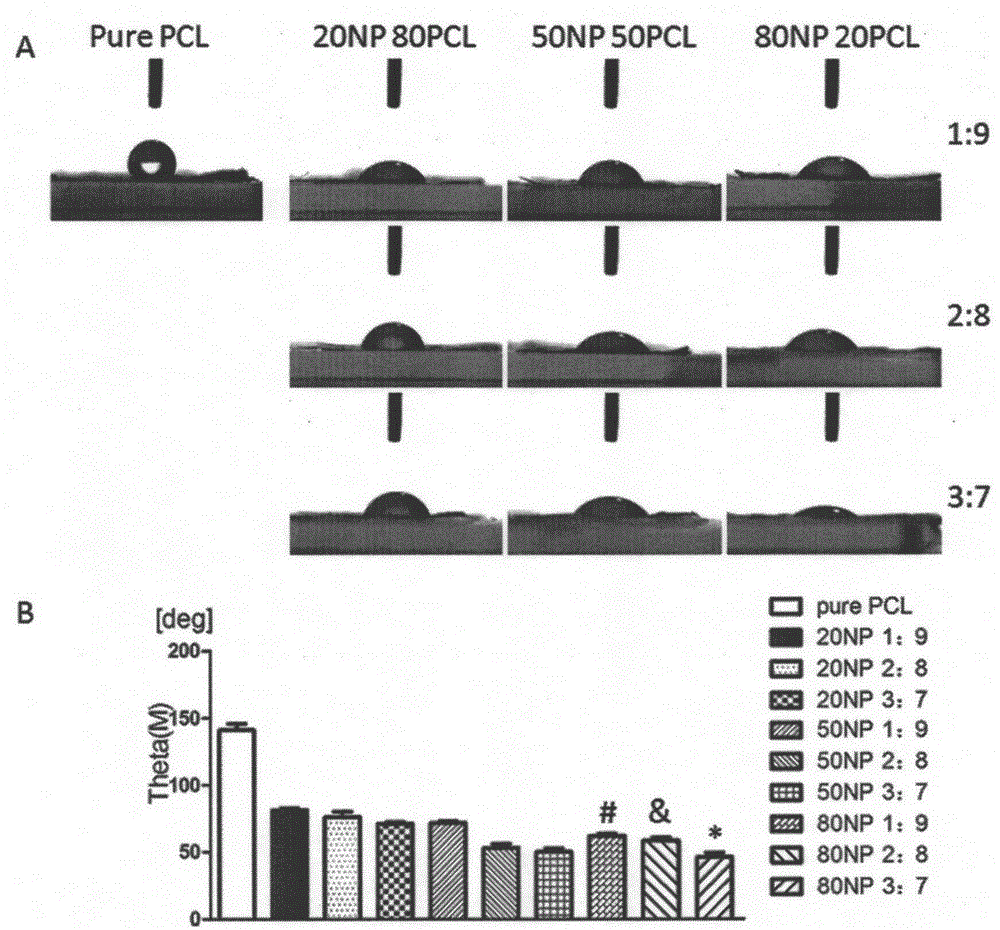
Natural protein/polycaprolactone nanofiber electrospun membrane, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105233345AEasy to operateSimple materialNon-woven fabricsProsthesisCardiac muscle tissueBiological simulation
The invention provides a natural protein / polycaprolactone nanofiber electrospun membrane, and preparation and application thereof. The natural protein / polycaprolactone nanofiber electrospun membrane is obtained by mixing natural protein and polycaprolactone to prepare a spinning solution and performing electrospinning, and the natural protein comprises natural elastin and natural collagen. The natural protein containing cardiac muscle tissue extracellular matrix components is mixed with an artificially synthesized degradable material, and the nanofiber membrane can be prepared quickly and effectively through an electrostatic spinning technically. The natural protein / polycaprolactone nanofiber electrospun membrane has the advantages that preparation is simple, materials are easy to obtain, and preparation cost is low. The natural protein / polycaprolactone nanofiber electrospun membrane not only has a good biomechanical property, but also can fully simulate cardiac muscle tissue extracellular matrix environment. Biological simulation can be carried out in the aspects of the structure and the ingredient, and an effect of treating myocardial infarction by stem cell transplantation is improved. Therefore, the natural protein / polycaprolactone nanofiber electrospun membrane can serve as an extracellular culture medium to provide an extracellular matrix microenvironment for promoting cell adhesion, survival and multiplication.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
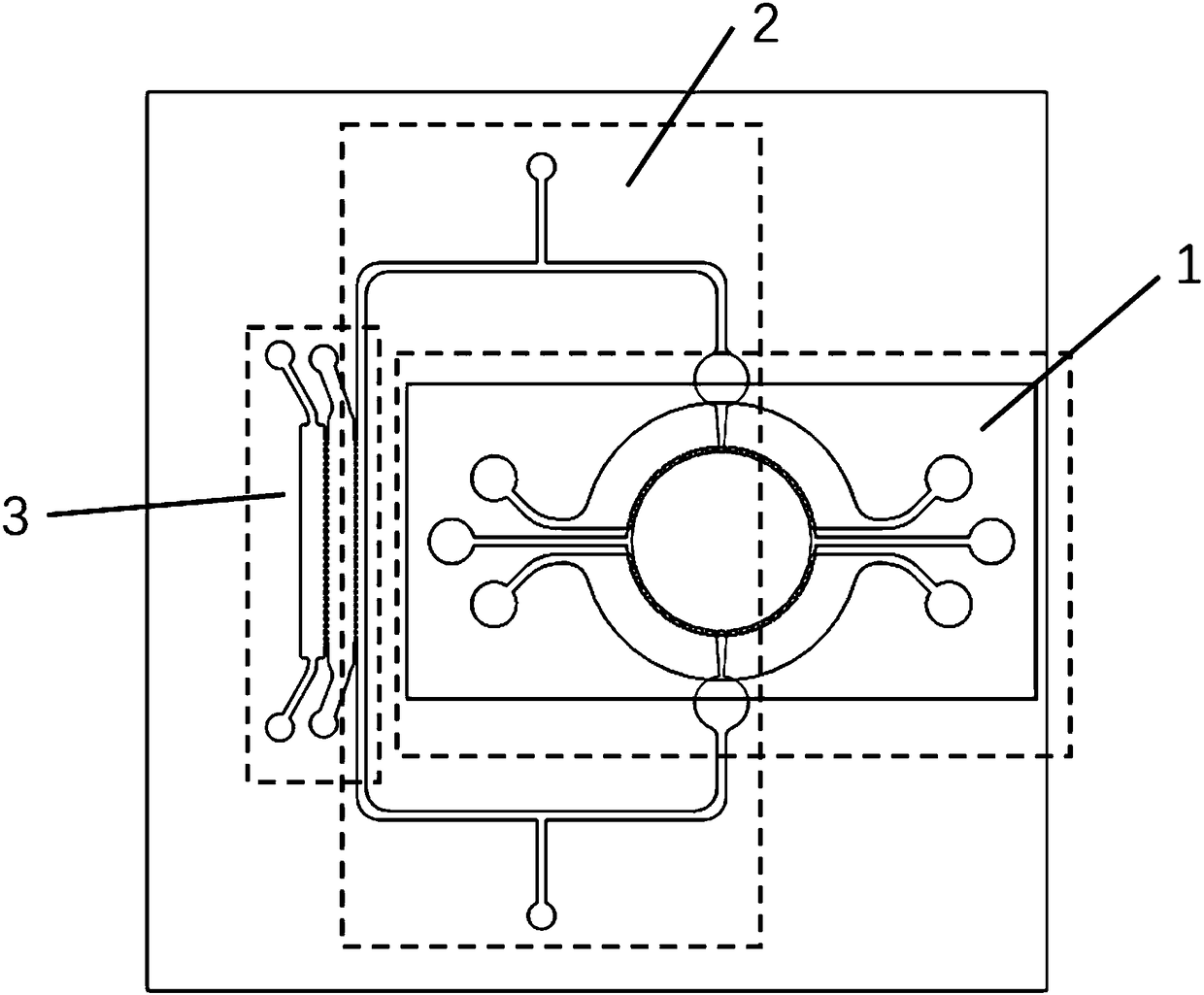
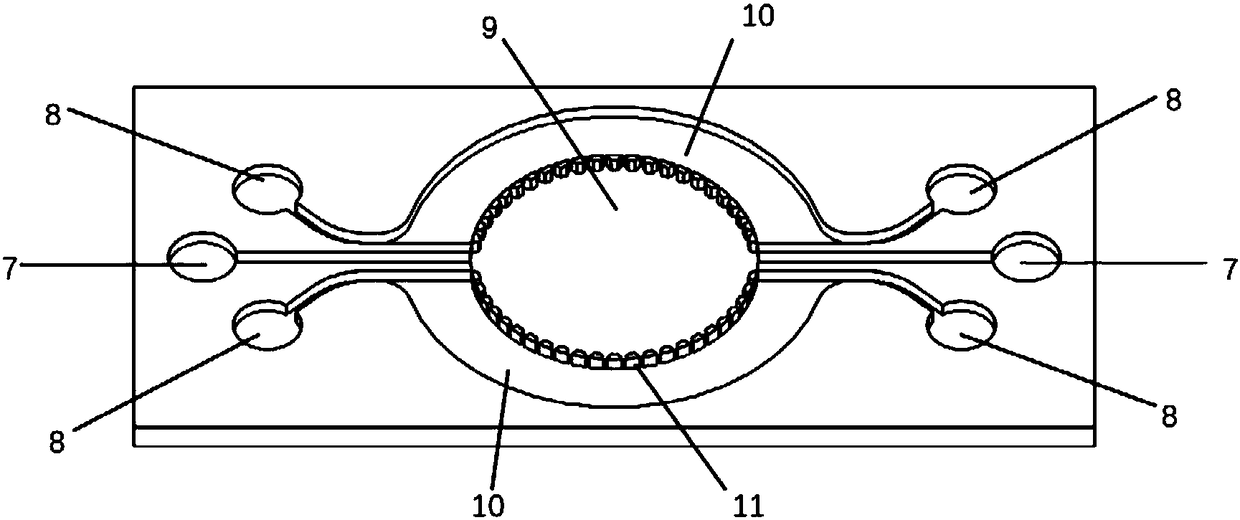
Self circulation organ chip dynamic culture device driven by cardiac muscle cell micro pump
PendingCN108300660ASolve the problem that the drive needs external energy supplyReduce volumeTissue/virus culture apparatusSpecific use bioreactors/fermentersVertical vibrationExternal energy
The invention provides a self circulation organ chip dynamic culture device driven by a cardiac muscle cell micro pump. The device comprises a lower layer chip, a middle film and an upper layer chip in sequential laminated arrangement from bottom to top, wherein the upper layer chip comprises a cardiac muscle cell micro pump module; the lower layer chip comprises a self circulation system module and an organ chip culture module; the self circulation system module is communicated with the organ chip culture module; the cardiac muscle cell micro pump module is used for simulating the blood pumping function of the heart; the self circulation system module is used for simulating the human body blood circulation loop; the organ chip culture module is used for simulating the human body organ function; the vertical vibration of the middle film is driven through the independent beating of the cardiac muscle cells growing in the cardiac muscle cell micro pump module; the self circulation flowing of culture liquid in the self circulation system module is realized; nutrient substances of the organ chip culture module are dynamically supplied. The self circulation organ chip dynamic culture device has the advantages that the external energy supply is not needed; the environment is more similar to the human body biomimetic environment; the size is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
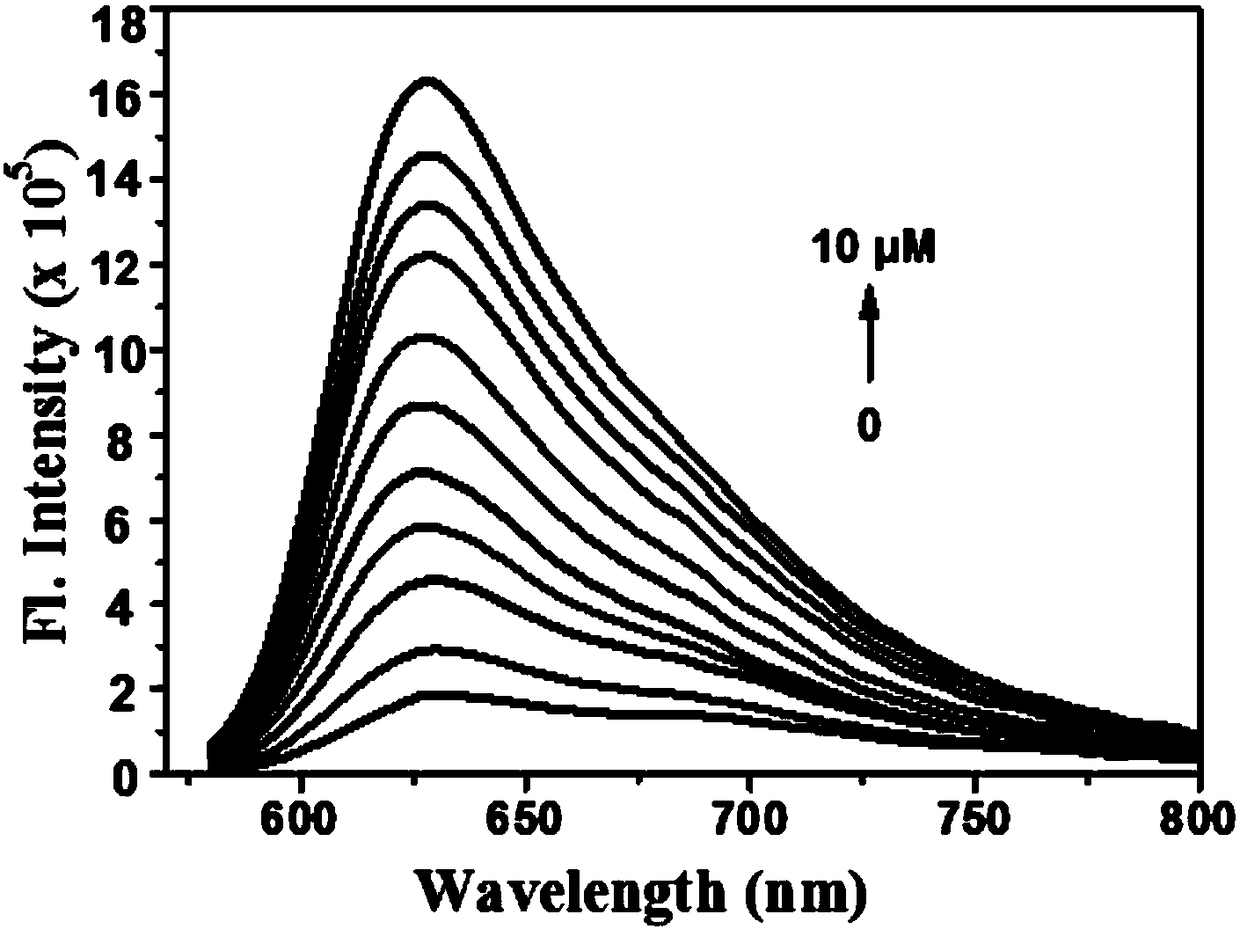
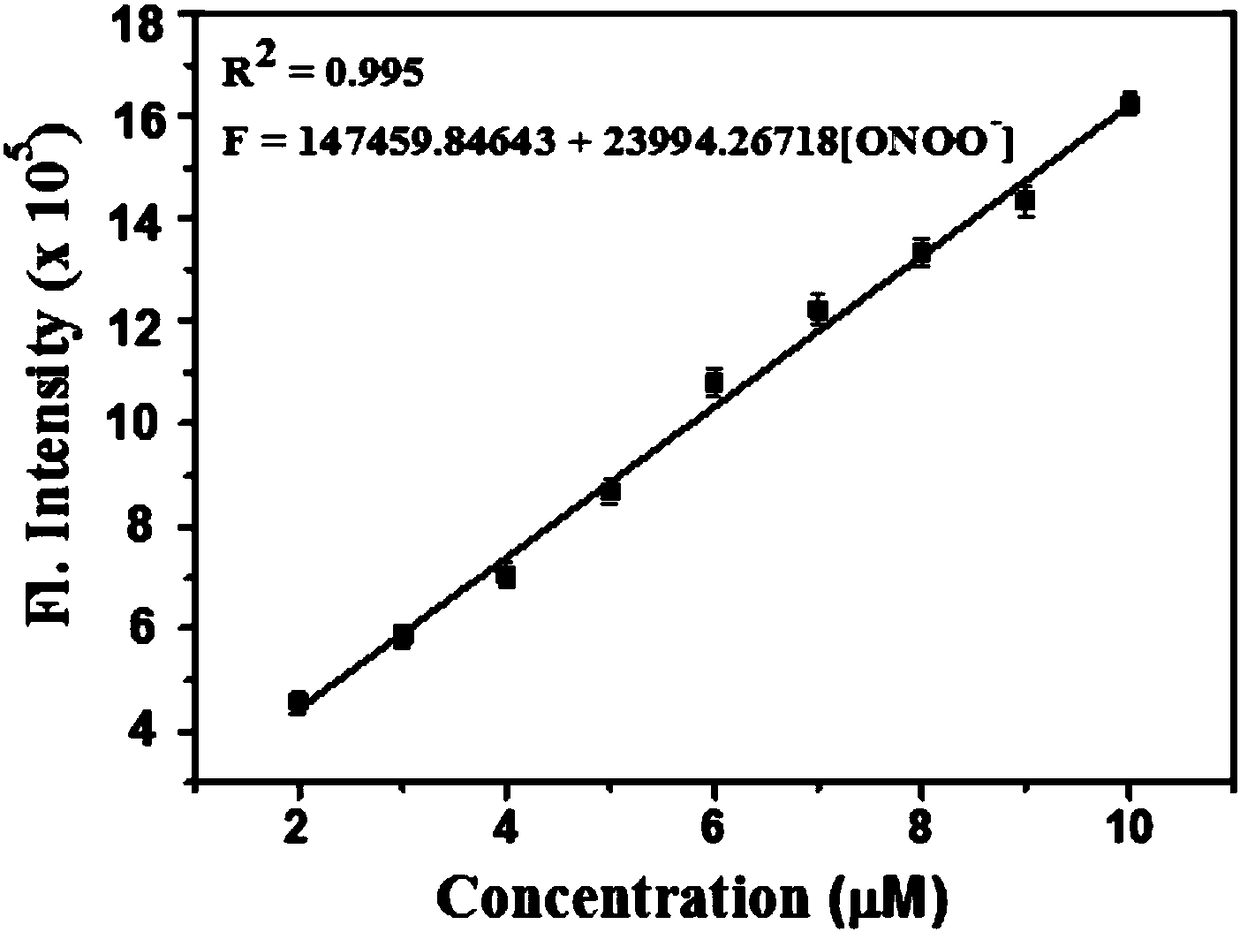
Two-photon fluorescence probe for detecting peroxynitrite as well as preparation method and application of two-photon fluorescence probe
ActiveCN108164494AIncrease penetration depthReduce self-absorptionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescencePeroxynitriteStructural formula
The invention discloses a two-photon fluorescence probe for detecting peroxynitrite as well as a preparation method and application of the two-photon fluorescence probe. The two-photon fluorescence probe has the structural formula as shown in the description. The two-photon fluorescence probe is named as TPNIR-FP. The two-photon fluorescence probe adopts a Nile red derivative as a fluorescent group and an alpha-keto-amide functional group as an ONOO-reaction group, can rapidly respond to ONOO- (within 10 seconds), and in addition is high in sensitivity and good in selectivity. The two-photon fluorescence probe can be applied to imaging research on ONOO- in antharcycline antibiotic induced cardiac muscle cell and cardiac muscle tissue damage.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of nanofiber scaffold for heart tissue engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nanofiber scaffold for heart tissue engineering. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the nanofiber scaffold from poly(glyceroi sebacate) (PGS) / a gelatin nanofiber scaffold material with different components through electrostatic spinning, and crosslinking the nanofiber scaffold in a mixed solution of hydrochlorinated N,N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethyl-carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) to obtain the nanofiber scaffold. The nanofiber scaffold related by the invention can be used for promoting the formation of sarcomere and has wide prospects on the aspect of being used as a material for cardiac muscle cell regeneration and repair.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Cardiac-specific protein targeting domain
The present invention relates to Cardiac Targeting Peptides or CTPs that are able to transduce cardiomyocytes specifically in culture and in vivo, and to methods for using such peptides and their derivatives to deliver peptides, proteins or nucleic acids specifically to the heart. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that the peptide APWHLSSQYSRT (SEQ ID NO:1) functioned as a cardiac-specific protein targeting peptide and was successful in delivering a number of different cargoes to cardiac muscle cells in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
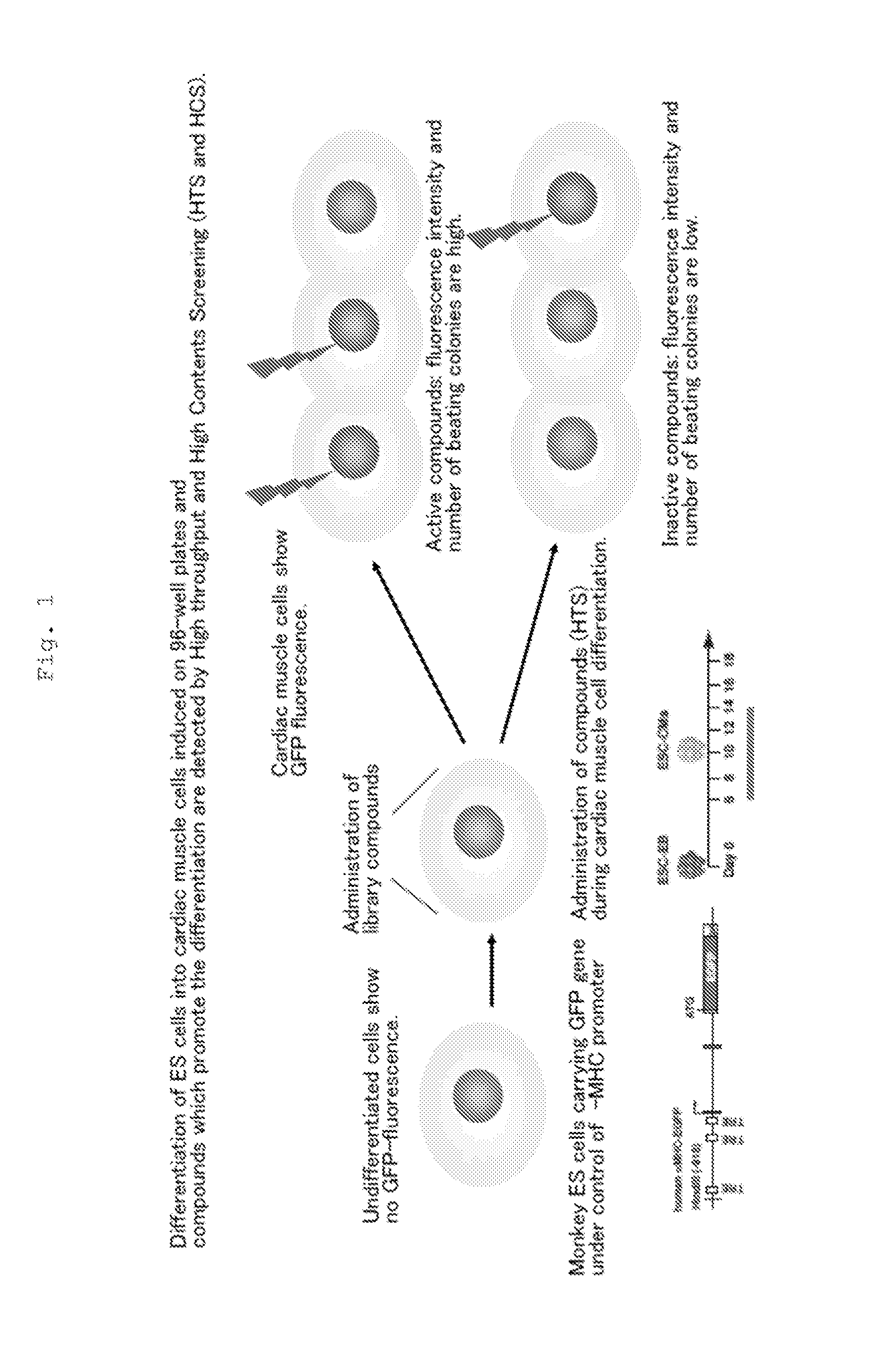
Use of icariin in inducing external oriented differentiation of embryo stem cells
InactiveCN1425763APharmacologically activeSugar derivativesEmbryonic cellsCell Differentiating AgentDirected differentiation
The present invention provides a new use icariin in inducing external oriented differentiation of embryo stem cells into single type of cells. Icariin may be used as the mitogen in stem cell transplanting cardiac muscle regeneration or cardiac muscle cell reconstruction, and in constructing high-efficiency pharmacodynamic screening model for initial screening and estimation of medicine effect. The present invention demonstrates the medicine effect of icariin in cell level and approaches its plentiful biological information. The present invention determines icariin as pharmacological active componnet and this provides Chinese medicine prevention and treatment with substantil foundation. At the same time, the description of the pharmacodynamic mechanism provides reference for modernized development of Chinese medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition and method for regenerating myofibers in the treatment of muscle injuries
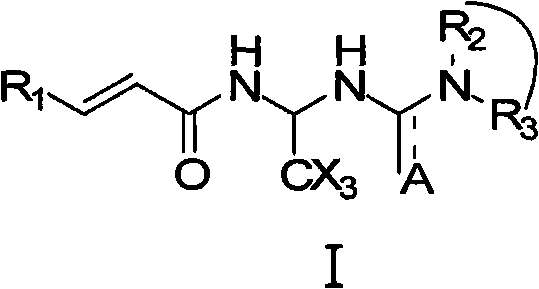
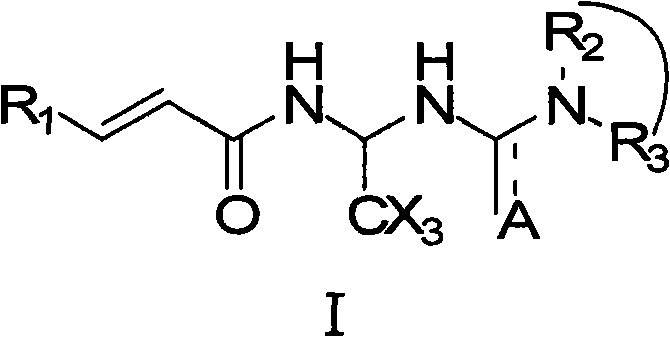
ActiveUS20090028959A1Enhance proliferation and cardiogenic differentiationEfficient discoveringBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A pharmaceutical composition and method for regenerating cardiomyocytes in treating or repairing heart muscle damages or injuries caused by an ischemic disease. The pharmaceutical composition contains an active ingredient compound with a backbone structure of Formula (I). The active ingredient compound is capable of (a) increasing viability of myogenic precursor cells to enable said precursor cells to survive through an absolute ischemic period; (b) reconstituting a damaged blood supply network in said heart region where said injured muscle is located; and (c) enhancing cardiomyogenic differentiation efficiency of said precursor cells down cardiac linage, said steps being performed simultaneously or in any particular order.
Owner:LEAD BILLION
Isolation and culture method for primary mice or rat cardiac muscle cells
InactiveCN105907708AHigh purityHigh activityCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMotilityMicrobiology
The invention discloses an isolation and culture method for primary mice or rat cardiac muscle cells. The isolation and culture method employs specially-prepared compound enzyme for long-term digestion, so the obtained cells are large in gross quantity and high in both isolation degree and motility rate; due to different acquisition manners, pollution and influence of residual blood in a heart are eradicated and the probability of contamination of the acquired cardiac muscle cells by bacteria, fungi and other cells is low; and the method can realize subculturing, so a good cell culture scheme is provided for related research based on culture of cardiac muscles.
Owner:王晓冰 +1
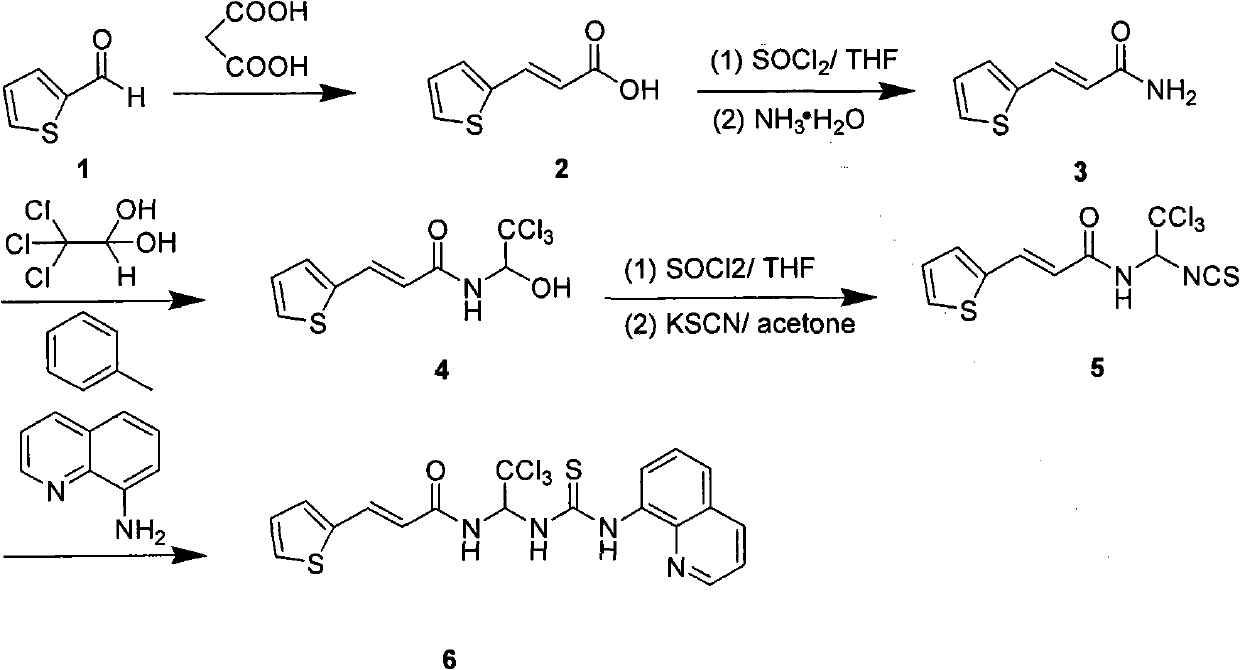
Acrylamide compounds and medicinal uses thereof
The invention relates to compounds of the general formula I, or their isomers, medicinal salts and solvates. The invention also relates to compositions containing the compounds shown of the general formula I, or their isomers, medicinal salts and solvates, and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, excipients or diluents. The invention further relates to uses of the compounds shown of the general formula I, or their isomers, medicinal salts and solvates in resisting cell apoptosis and preventing or treating of diseases or symptoms related to cell apoptosis, and especially in protecting cardiac muscle cells and preventing or treating diseases or symptoms related to cardiac muscle cell apoptosis.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Cardiosphere-derived cells and their extracellular vesicles to retard or reverse aging and age-related disorders
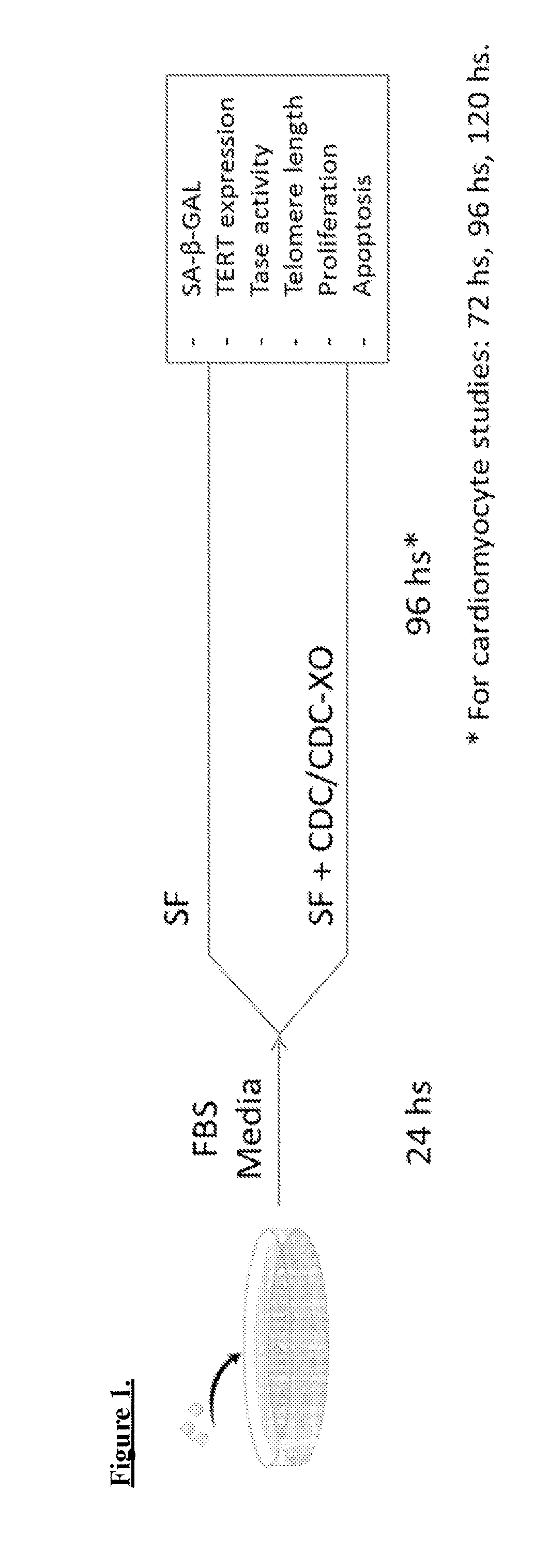
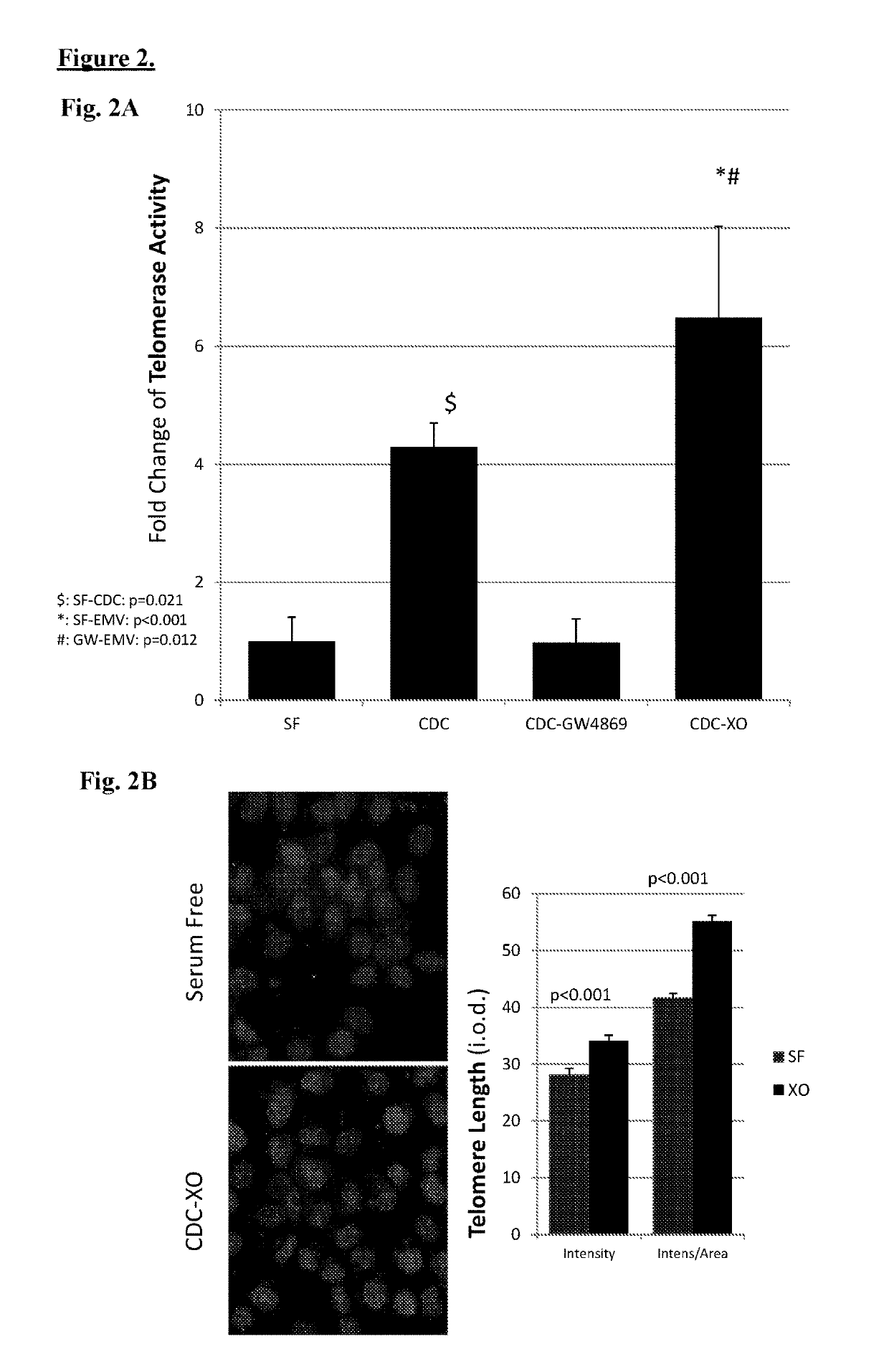
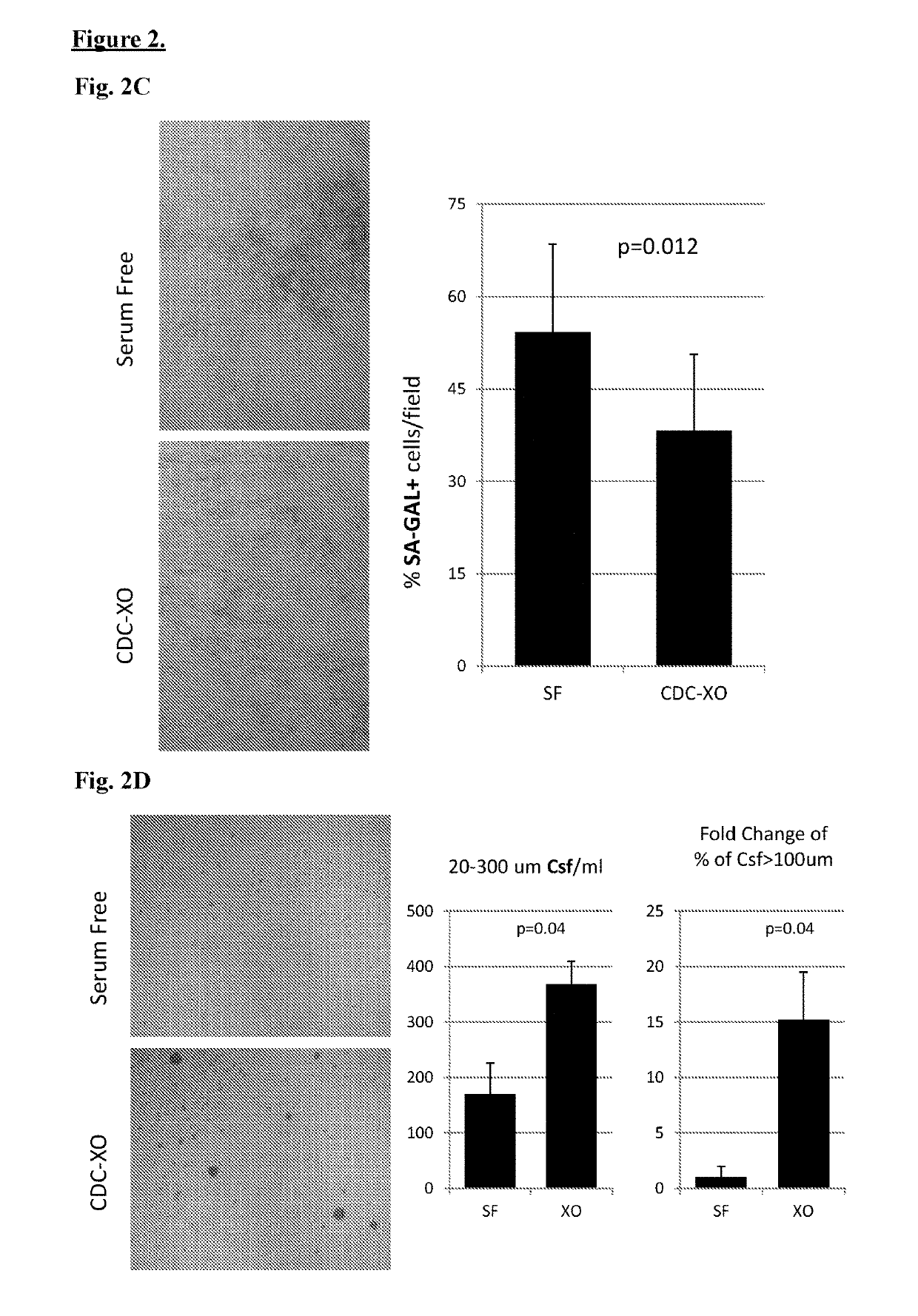
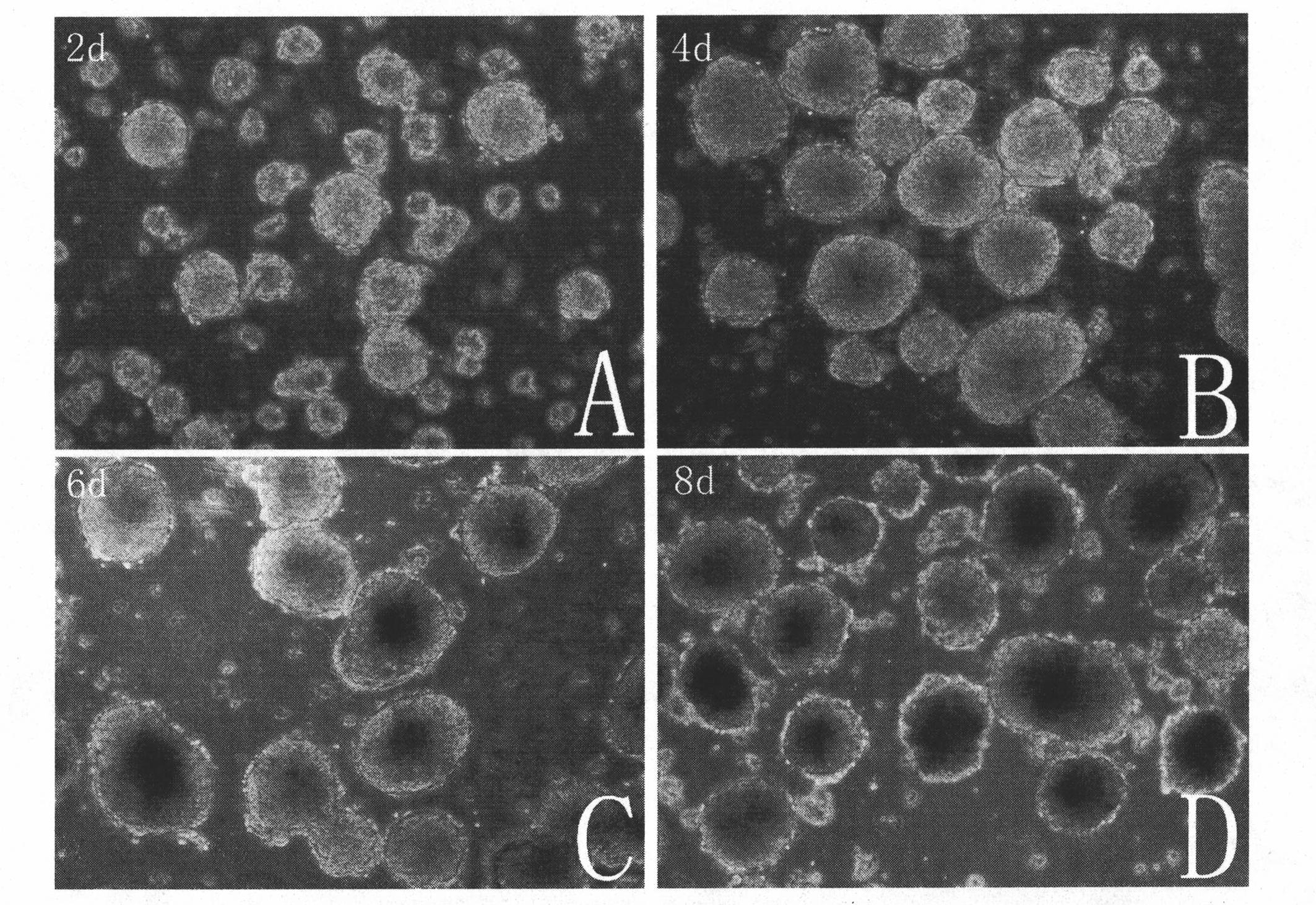
Described herein are compositions and methods related to use of cardiosphere-derived cells and their extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes and microvesicles, for achieving anti-aging and rejuvenation. This includes discoveries for effects on heart structure, function, gene expression, and systemic parameters. For animal studies, intra-cardiac injections of neonatal rat CDCs was compared to in old and young rats including evaluation of blood, echocardiographic, haemodynamic and treadmill stress tests. For in vitro studies, human heart progenitors from older donors, or cardiomyocytes from aged rats were exposed to human CDCs or cardiosphere derived cell (CDC) derived exosomes (CDC-XO) from pediatric donors. CDCs and CDC-XOs were capable of effectuating youthful patterns of gene expression in the hearts of old, along with a variant of physiological and function benefits, including elongation of telomere length. Together, these results indicate capacity of CDCs and CDC-XO to ward off the effects of aging through rejuvenation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Induction factor for inducing differentiation of iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells into cardiac muscle cells and application thereof
InactiveCN102093977APromote differentiationNo side effectsVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsCardiac muscle tissue regenerationSide effect
The invention belongs to the field of regenerative medicine of cardiac muscle tissues, and discloses application of ascorbic acid as an induction factor in inducting differentiation of iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells into cardiac muscle cells and a differentiation-inducing culture medium containing ascorbic acid. The invention also discloses a method for inducing differentiation of iPS cells into cardiac muscle cells by using the differentiation-inducing culture medium, which comprises the following step: inducing an iPS cell derived embryoid body, which has grown in a suspension mode for 5-7 days, to differentiate by utilizing the differentiation-inducing culture medium, thereby obtaining cardiac muscle cells. By using ascorbic acid as the induction factor, the invention obviously enhances the differentiation efficiency of the iPS cells into the cardiac muscle cells, and the differentiation percentage can reach 50-60%; the differentiation-inducing culture medium does not have toxic or side effect on the cells; and in addition, the method provided by the invention is simple, has the advantage of low cost, can be operated in common laboratories, and is suitable for large-scale proceeding.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com