Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Heart structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
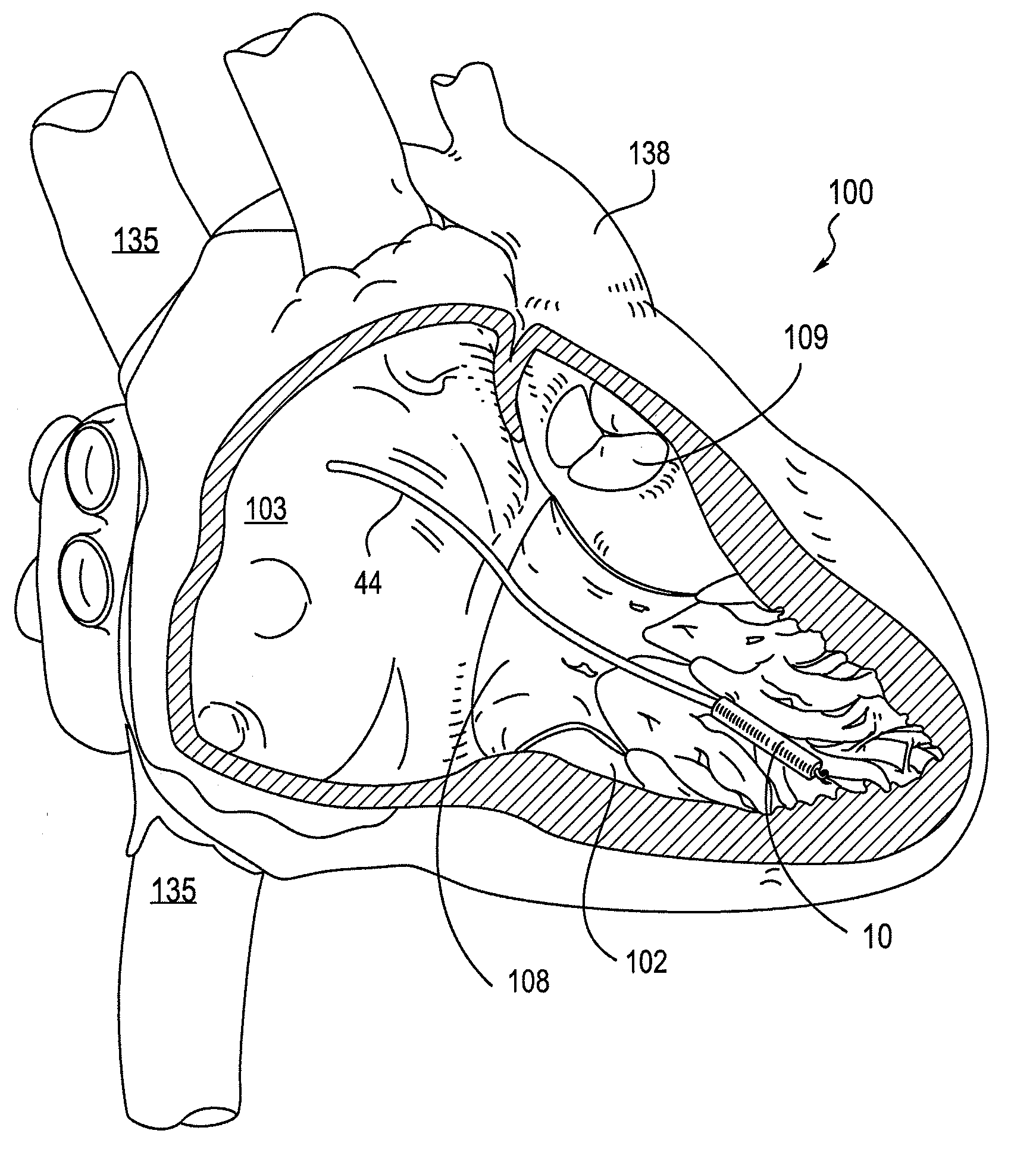
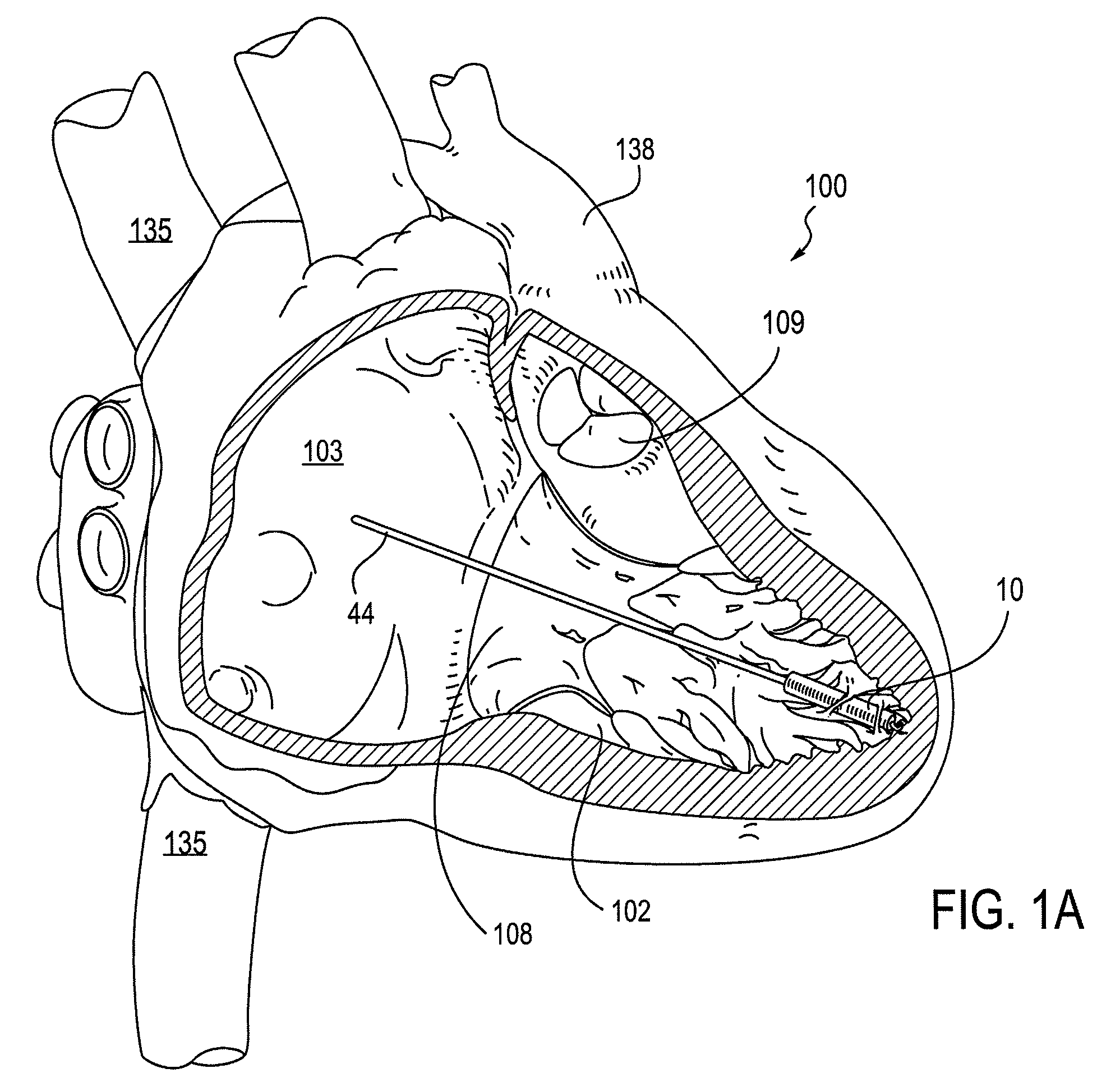
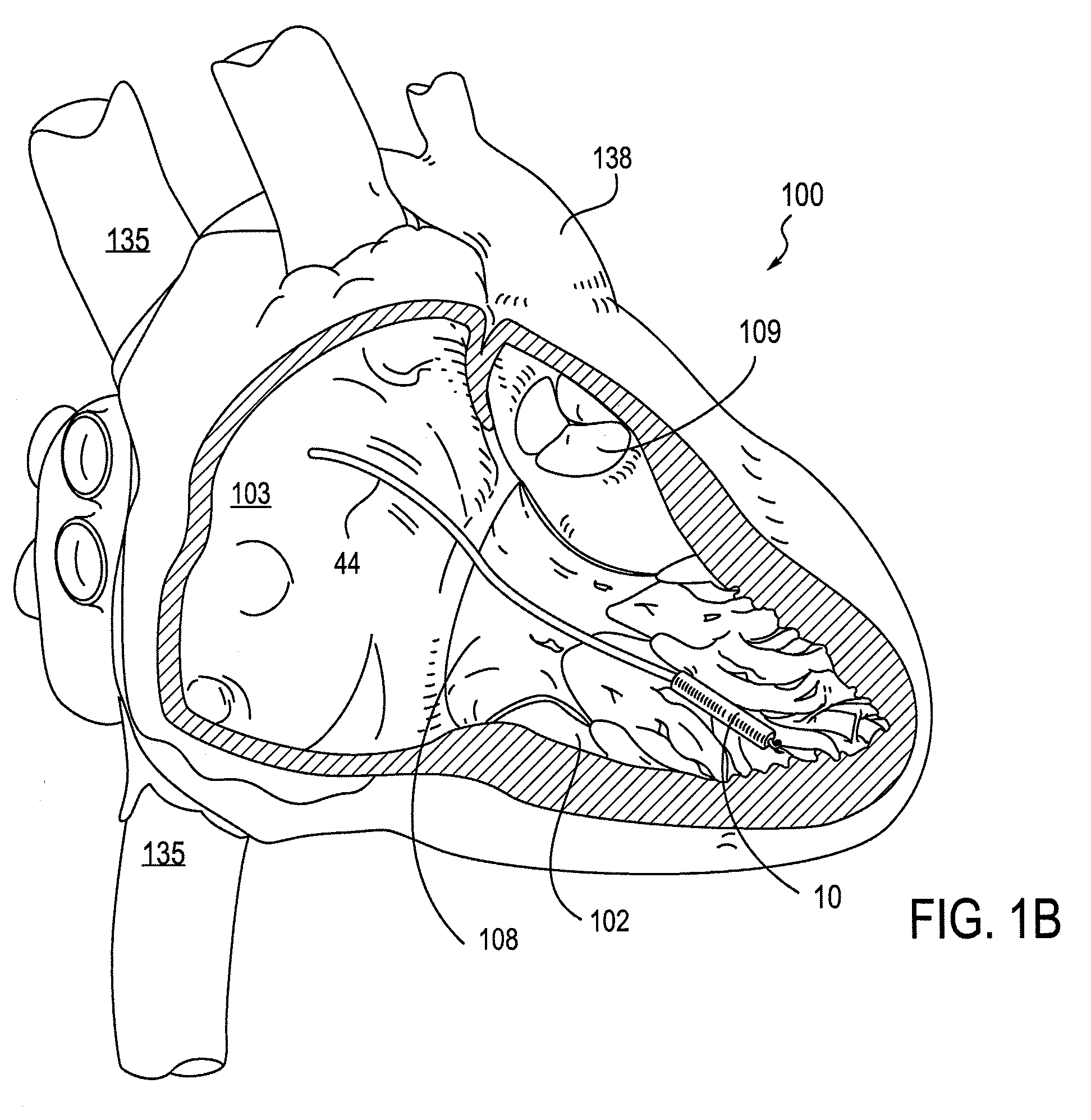
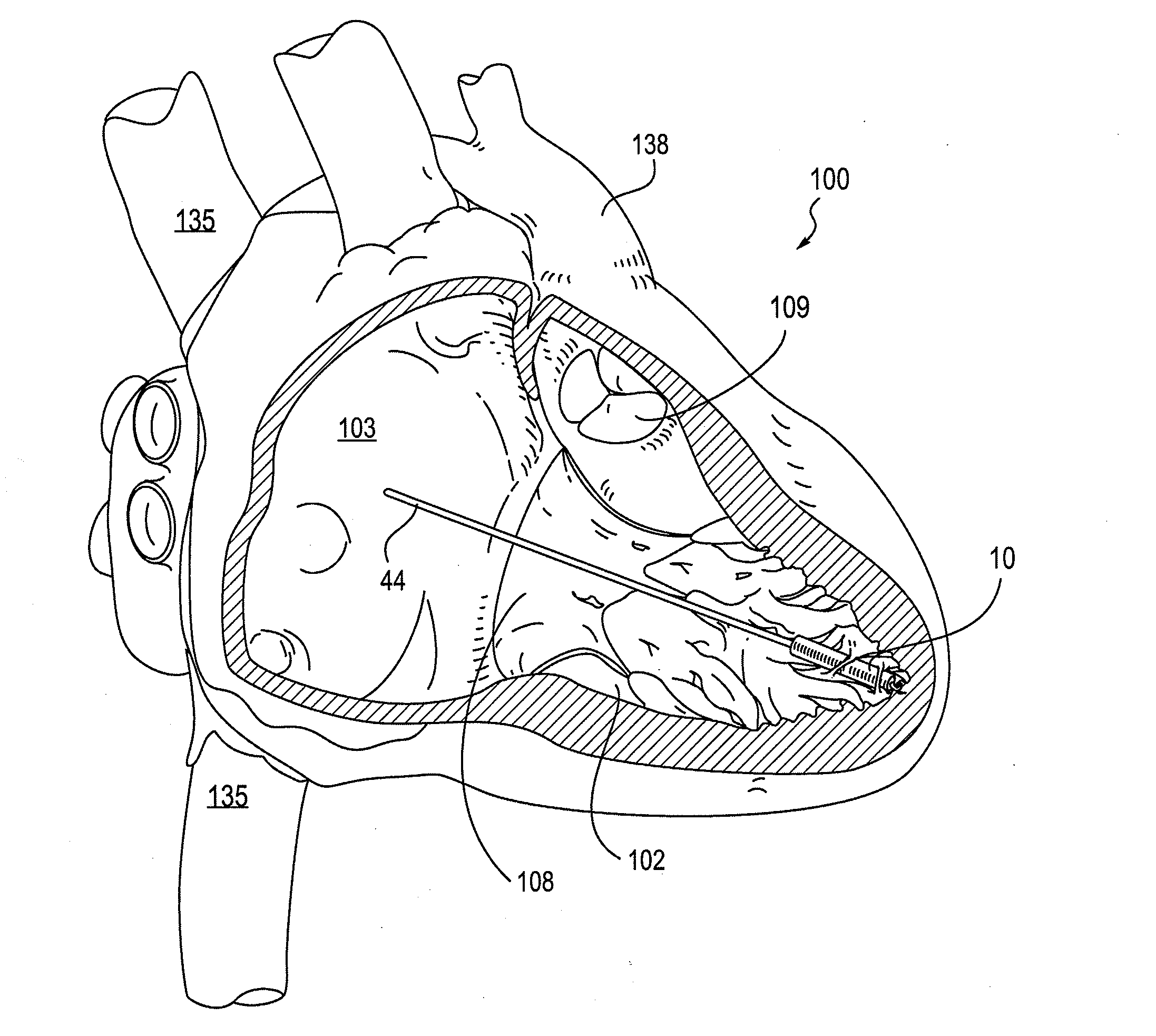
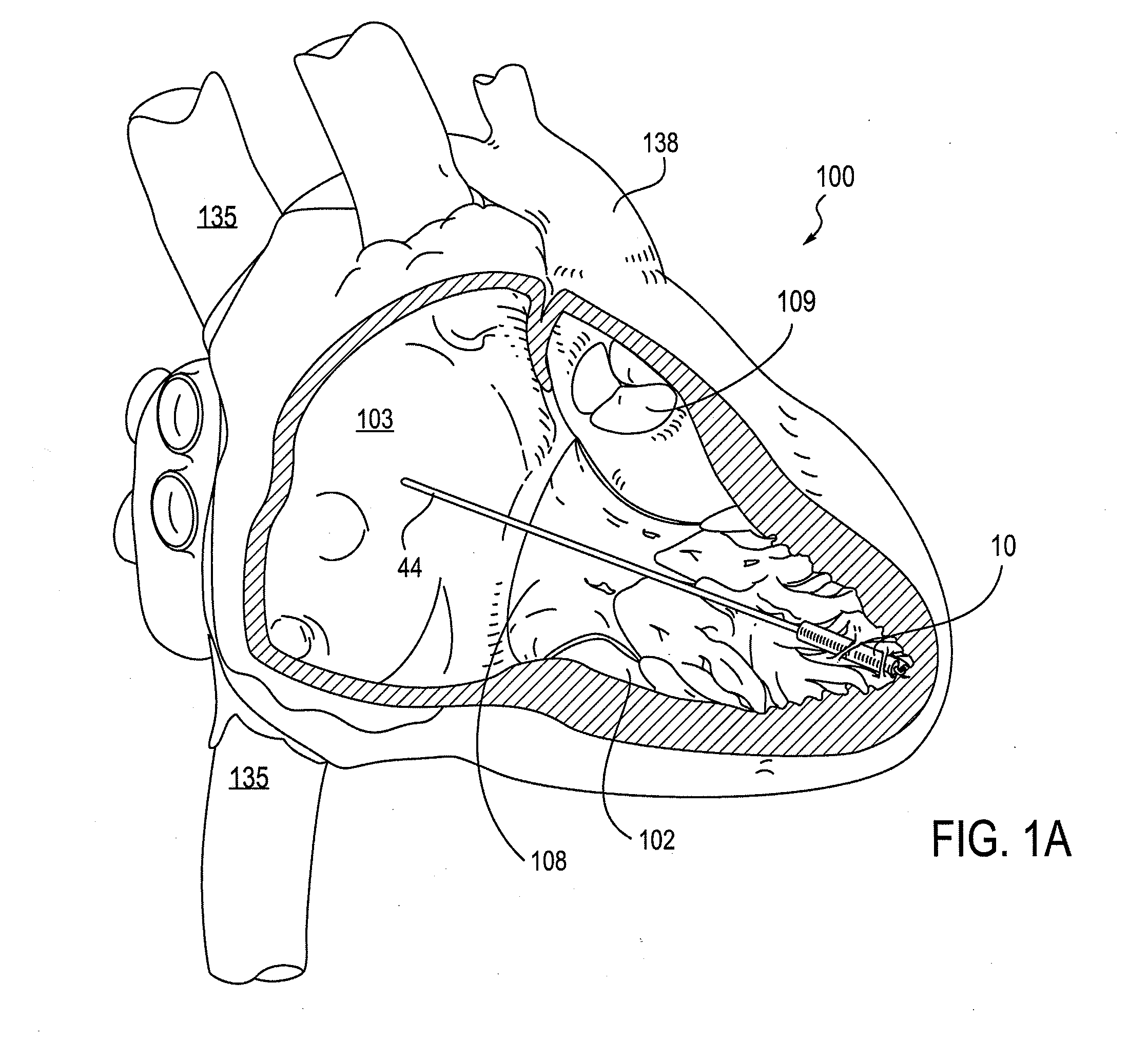
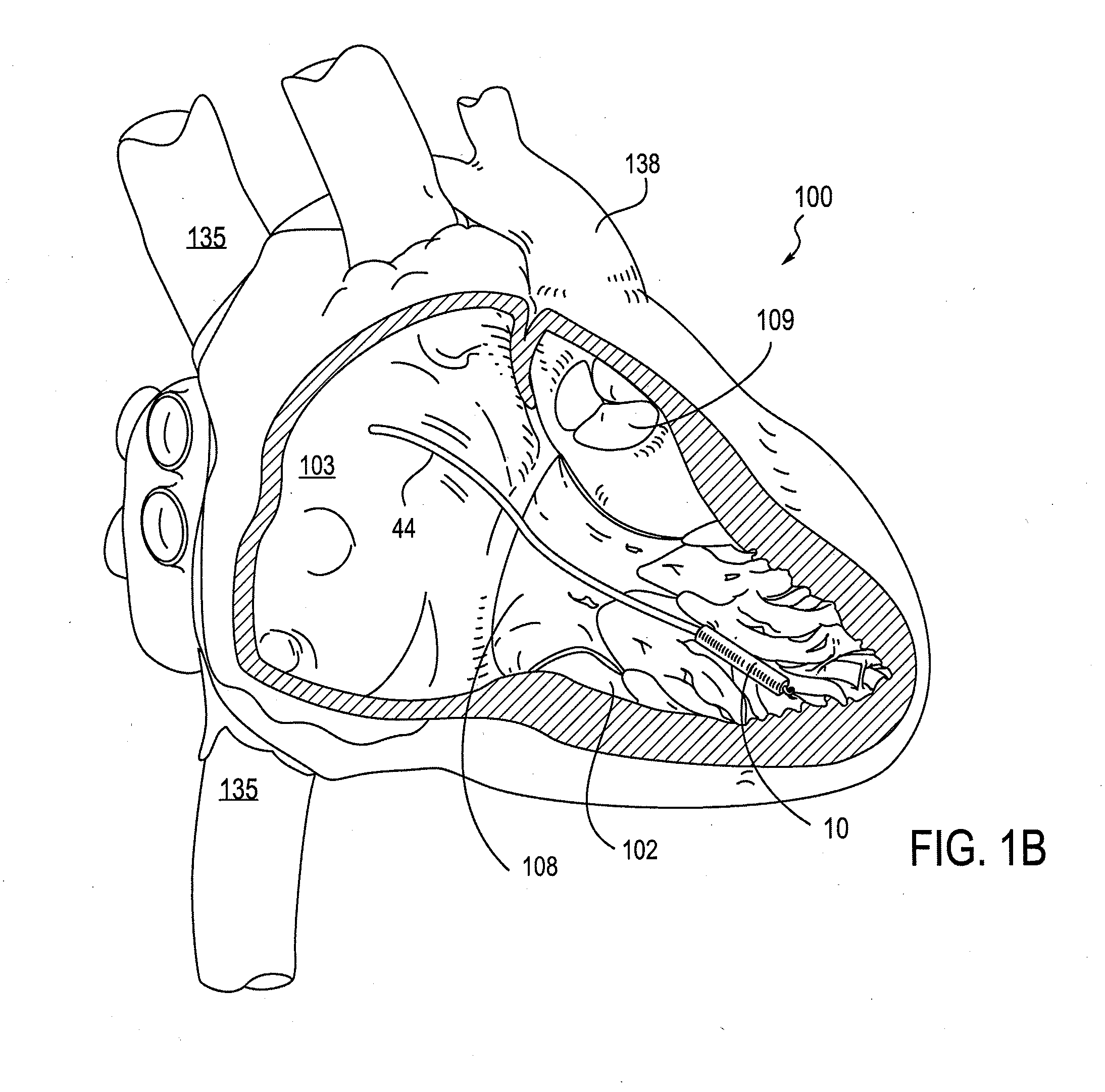
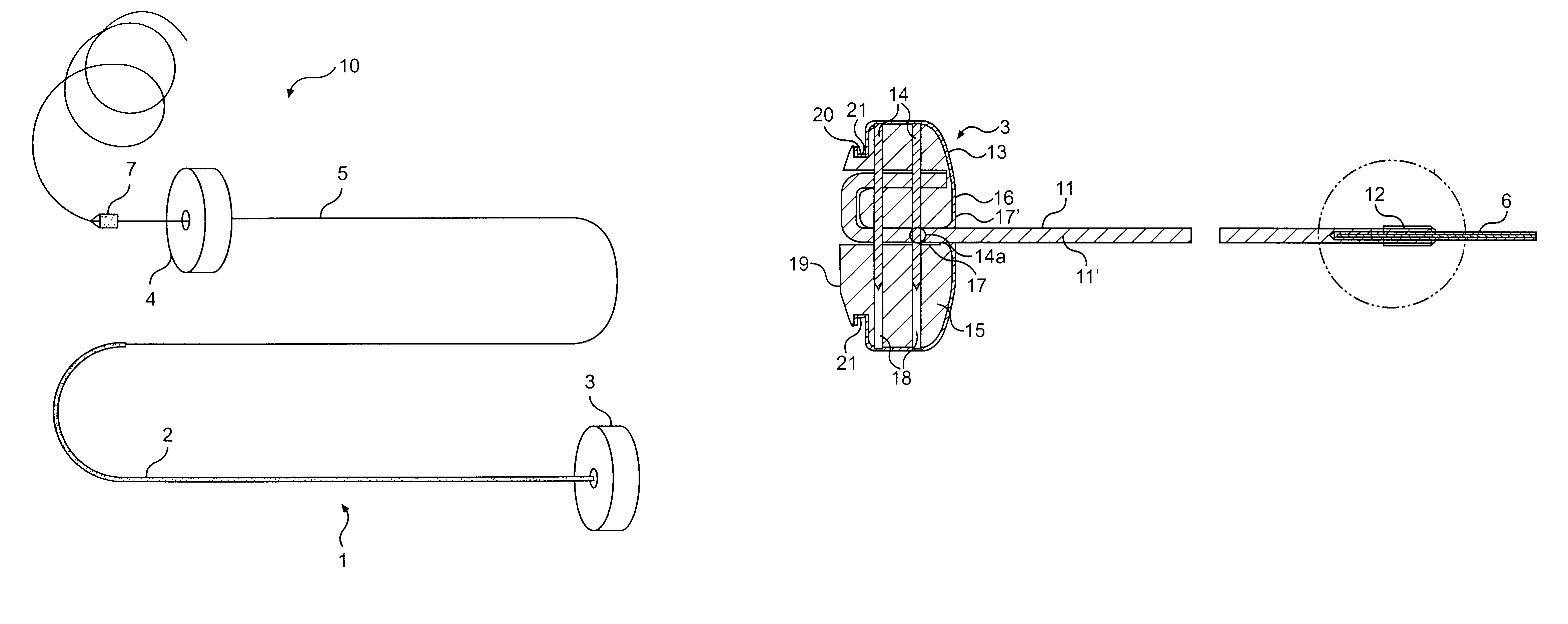
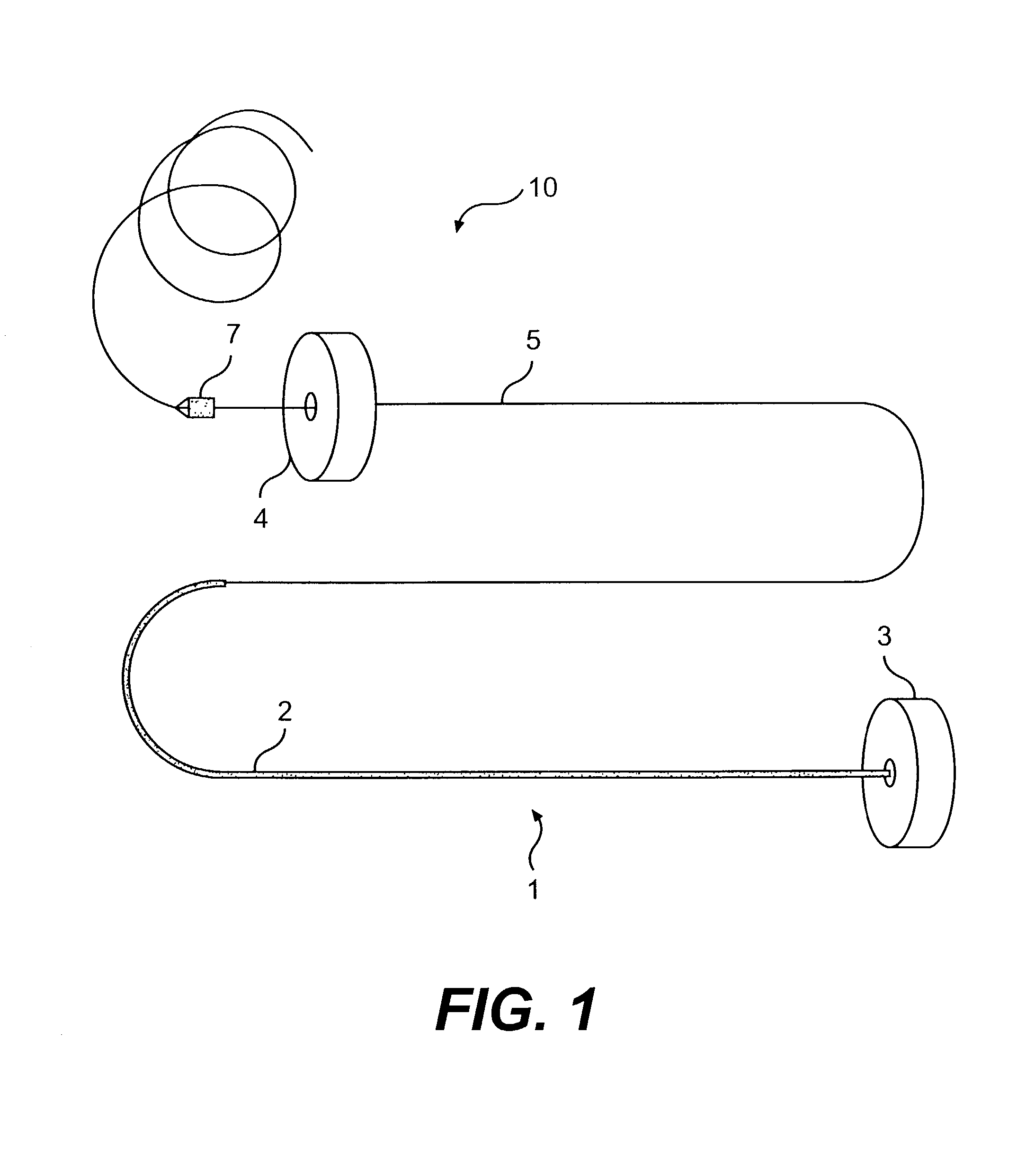
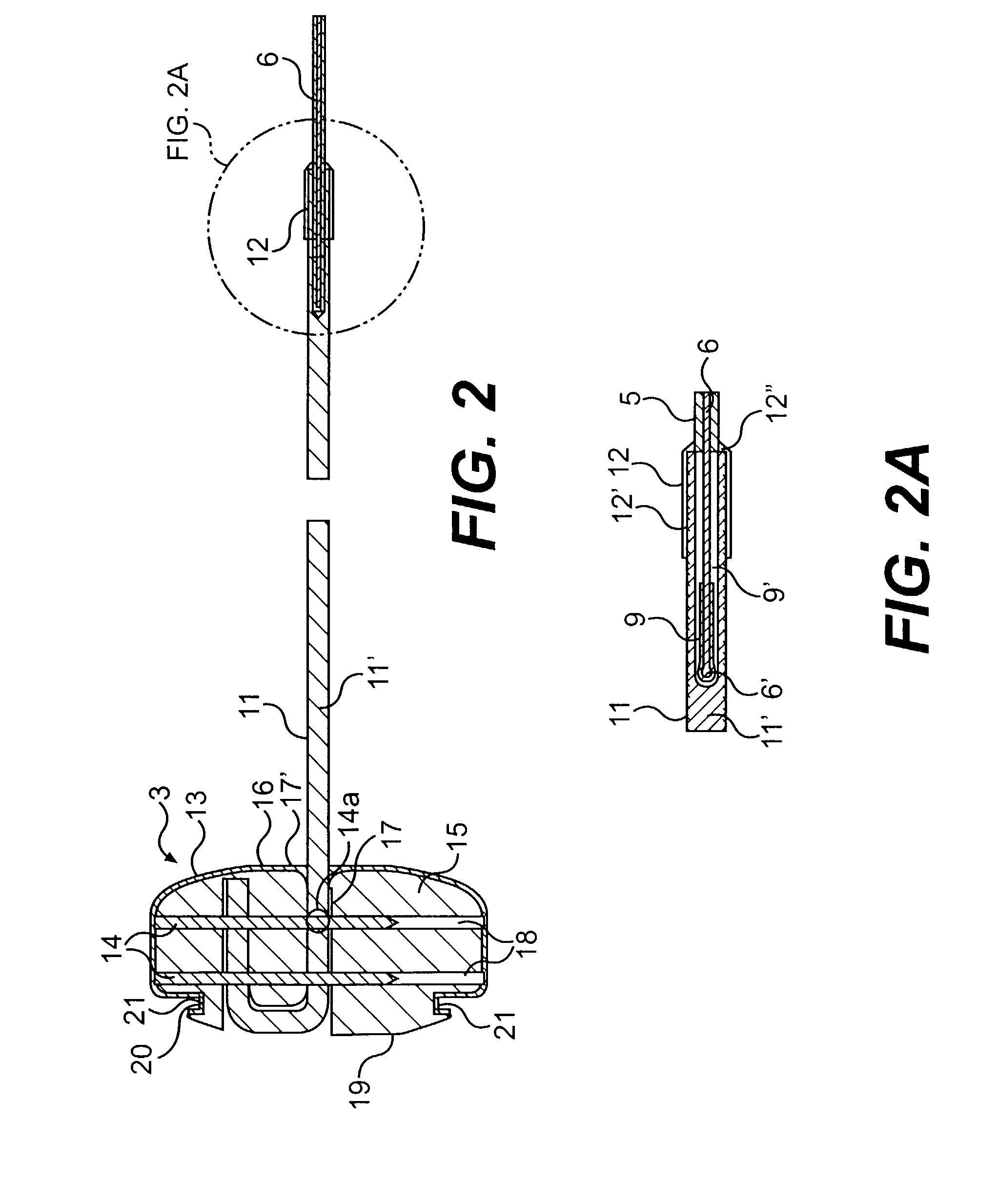
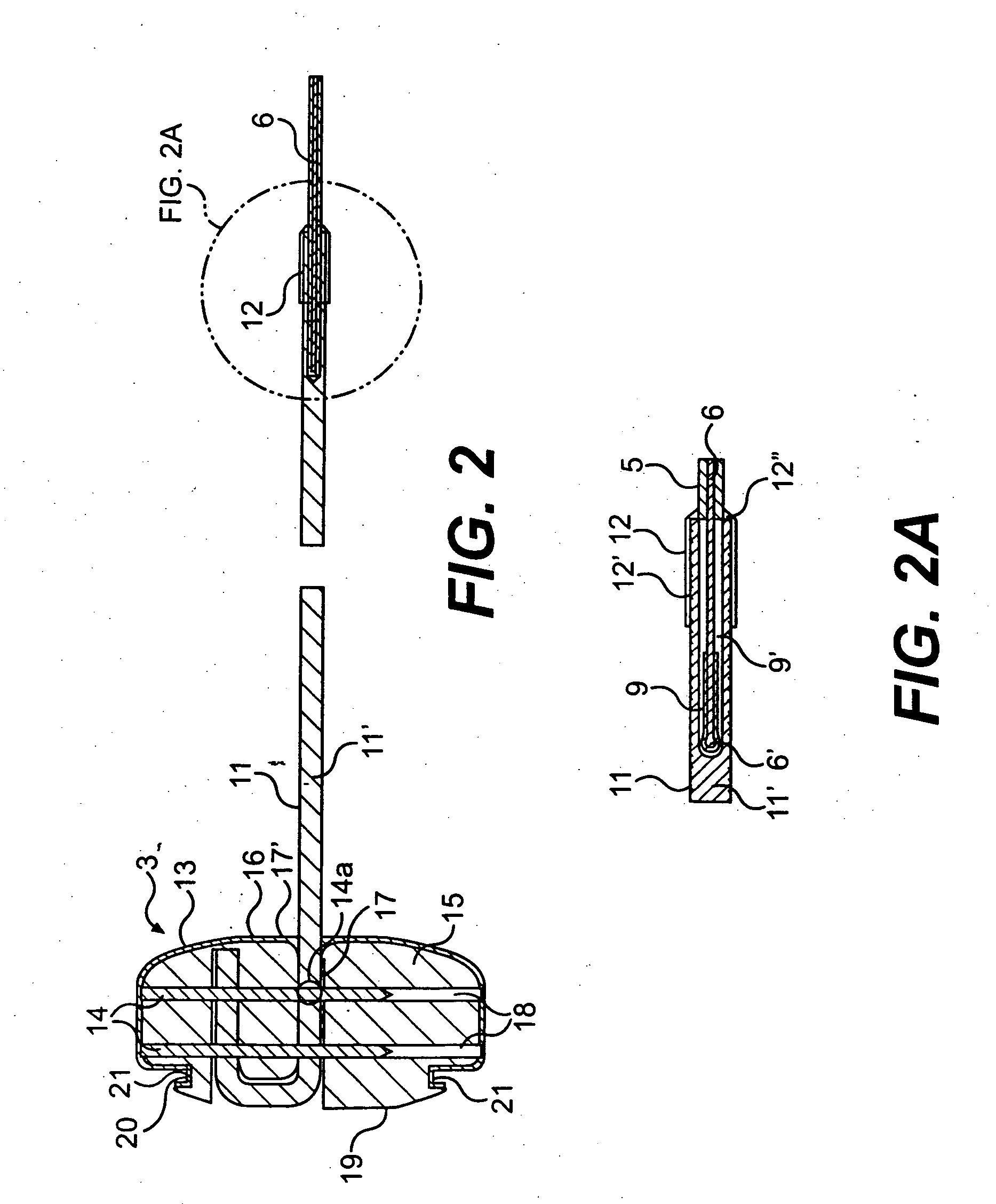
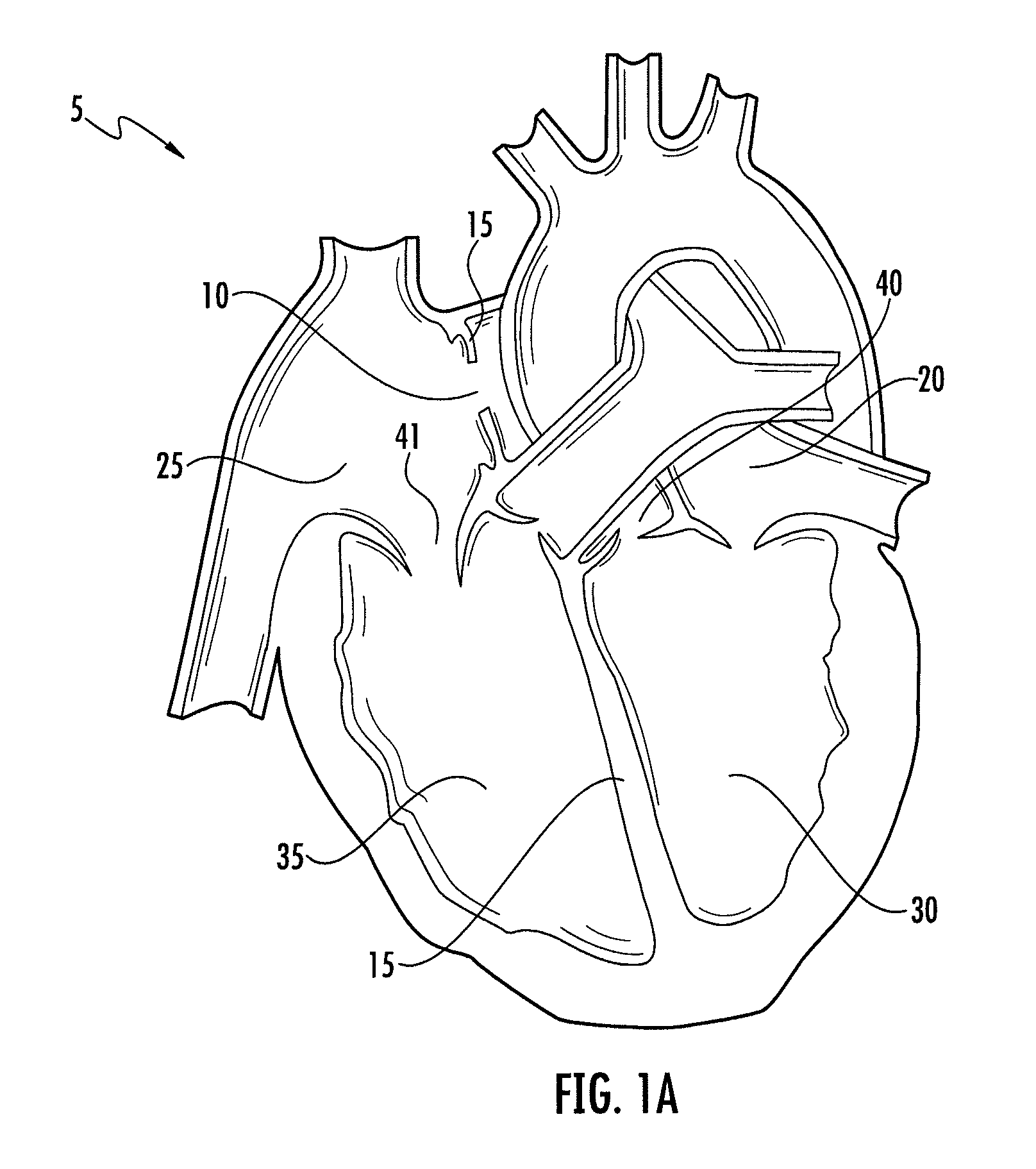
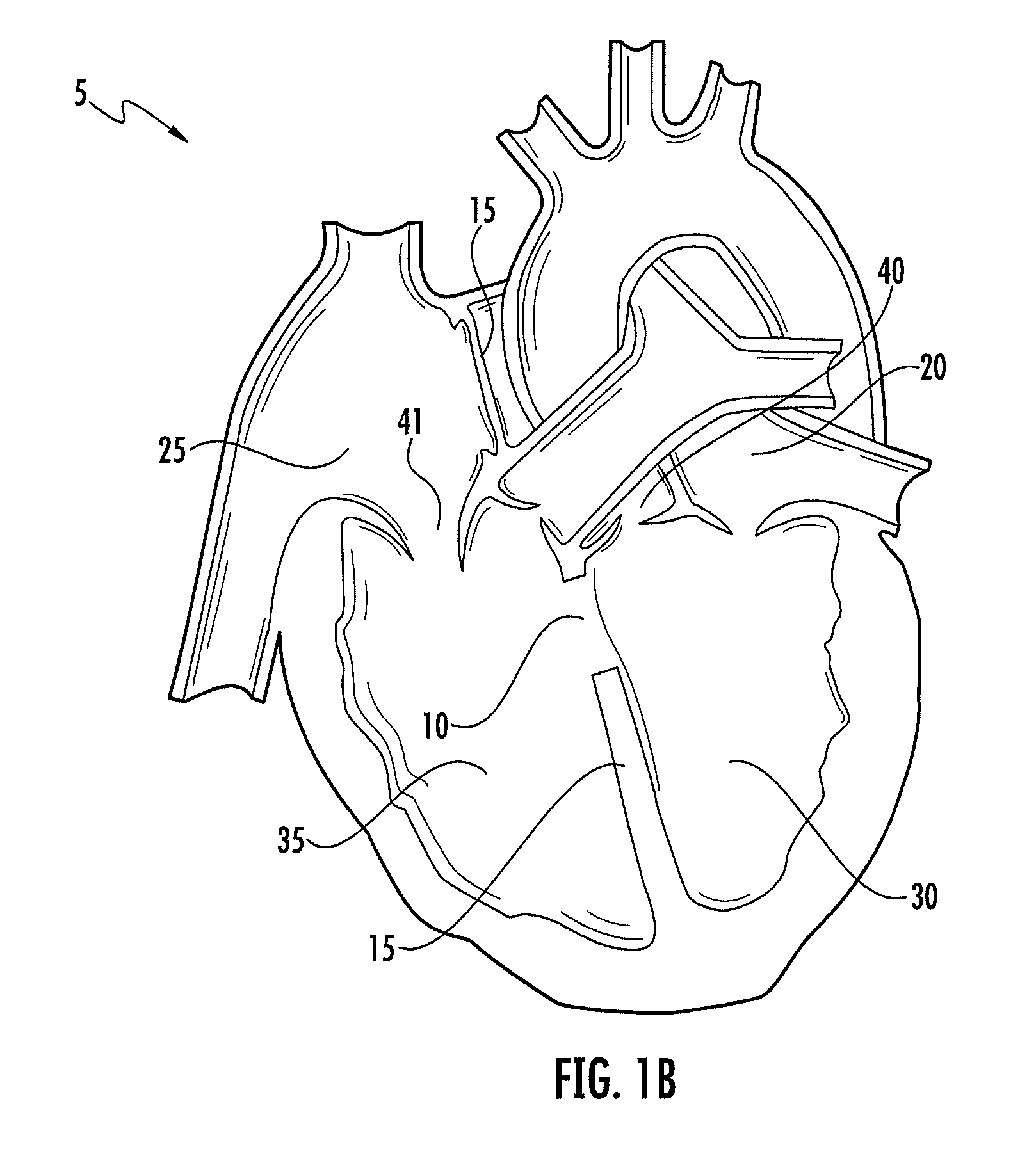
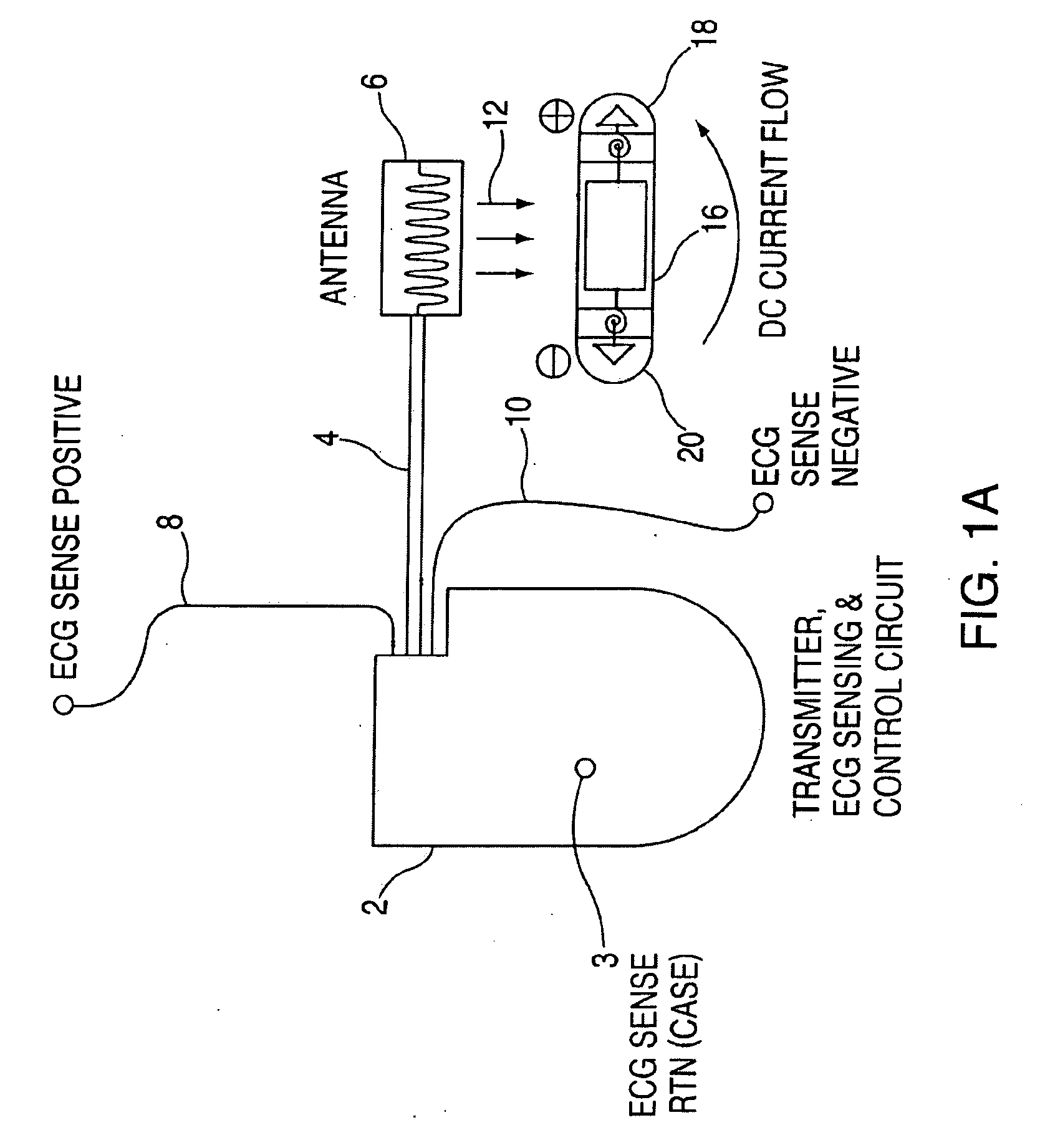
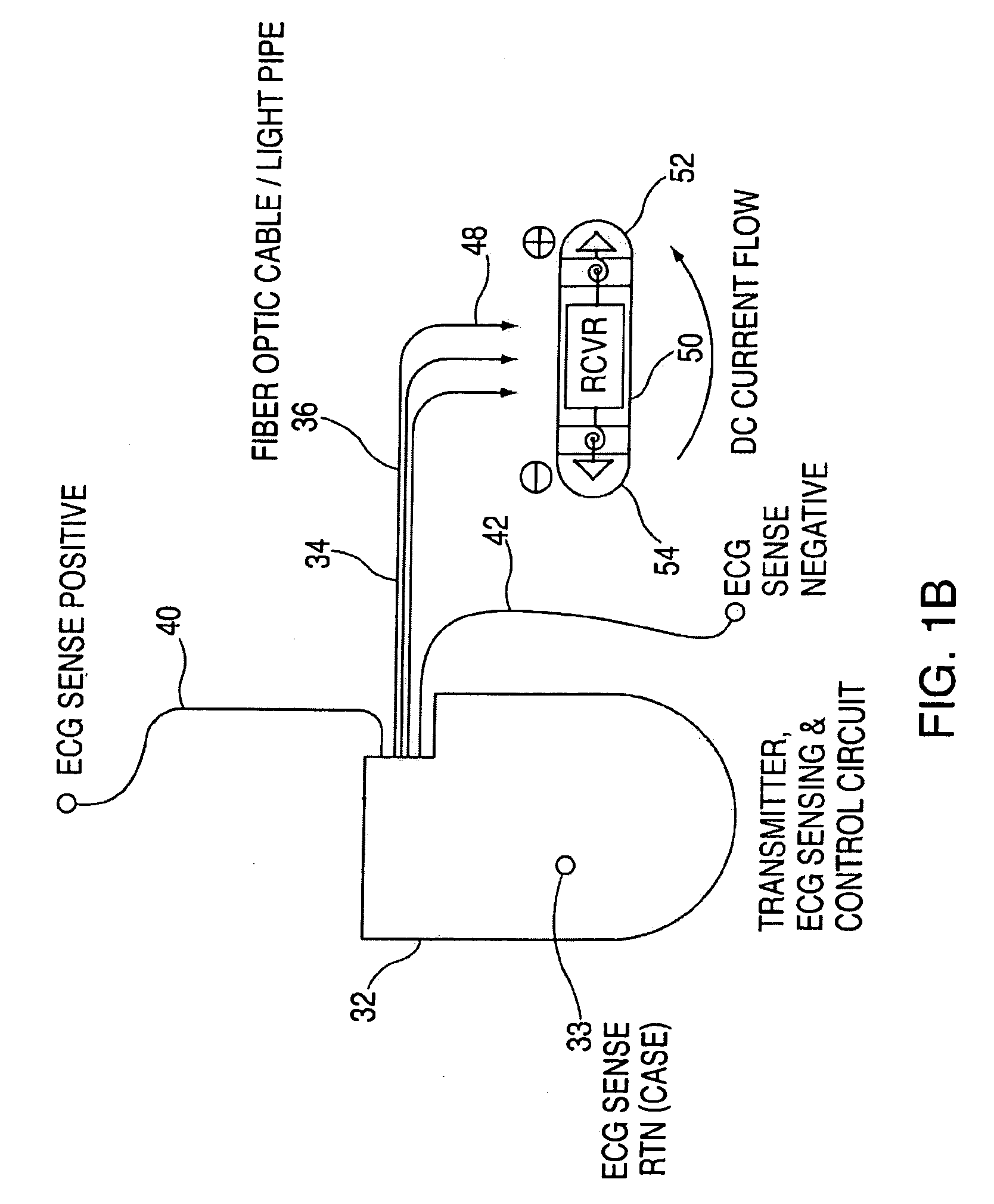
Leadless cardiac pacemaker with secondary fixation capability
ActiveUS8527068B2Discourage attachment and colonization of surfaceImprove capture abilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationTrabeculae carneaeCardiac pacemaker electrode
The invention relates to leadless cardiac pacemakers (LBS), and elements and methods by which they affix to the heart. The invention relates particularly to a secondary fixation of leadless pacemakers which also include a primary fixation. Secondary fixation elements for LBS's may passively engage structures within the heart. Some passive secondary fixation elements entangle or engage within intraventricular structure such as trabeculae carneae. Other passive secondary fixation elements may engage or snag heart structures at sites upstream from the chamber where the LBS is primarily affixed. Still other embodiments of passive secondary fixation elements may include expandable structures.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker with Secondary Fixation Capability
ActiveUS20100198288A1Discourage attachment and colonization of surfaceImprove capture abilityHeart stimulatorsTrabeculae carneaeCardiac pacemaker electrode
The invention relates to leadless cardiac pacemakers (LBS), and elements and methods by which they affix to the heart. The invention relates particularly to a secondary fixation of leadless pacemakers which also include a primary fixation. Secondary fixation elements for LBS's may passively engage structures within the heart. Some passive secondary fixation elements entangle or engage within intraventricular structure such as trabeculae carneae. Other passive secondary fixation elements may engage or snag heart structures at sites upstream from the chamber where the LBS is primarily affixed. Still other embodiments of passive secondary fixation elements may include expandable structures.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Splint assembly for improving cardiac function in hearts, and method for implanting the splint assembly
InactiveUS7044905B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberTension member
A splint assembly for placement transverse a heart chamber to reduce the heart chamber radius and improve cardiac function has a tension member formed of a braided cable with a covering. A fixed anchor assembly is attached to one end of the tension member and a leader for penetrating a heart wall and guiding the tension member through the heart is attached to the other end. An adjustable anchor assembly can be secured onto the tension member opposite to the side on which the fixed pad assembly is attached. The adjustable anchor assembly can be positioned along the tension member so as to adjust the length of the tension member extending between the fixed and adjustable anchor assemblies. The pad assemblies engage with the outside of the heart wall to hold the tension member in place transverse the heart chamber. A probe and marker delivery device is used to identify locations on the heart wall to place the splint assembly such that it will not interfere with internal heart structures. The device delivers a marker to these locations on the heart wall for both visual and tactile identification during implantation of the splint assembly in the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Splint assembly for improving cardiac function in hearts, and method for implanting the splint assembly
InactiveUS20060149123A1Reduce tensionReduce consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberCardiac wall
A splint assembly for placement transverse a heart chamber to reduce the heart chamber radius and improve cardiac function has a tension member formed of a braided cable with a covering. A fixed anchor assembly is attached to one end of the tension member and a leader for penetrating a heart wall and guiding the tension member through the heart is attached to the other end. An adjustable anchor assembly can be secured onto the tension member opposite to the side on which the fixed pad assembly is attached. The adjustable anchor assembly can be positioned along the tension member so as to adjust the length of the tension member extending between the fixed and adjustable anchor assemblies. The pad assemblies engage with the outside of the heart wall to hold the tension member in place transverse the heart chamber. A probe and marker delivery device is used to identify locations on the heart wall to place the splint assembly such that it will not interfere with internal heart structures. The device delivers a marker to these locations on the heart wall for both visual and tactile identification during implantation of the splint assembly in the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Method and apparatus for occluding a physiological opening
InactiveUS20120010644A1Avoid suture related injuryInvention is often bulkyBalloon catheterDilatorsAdhesiveBiological activation
A method and apparatus for suture-less placement of an occluding patch in which release of the device can be accelerated. In one embodiment, an inactive form of an adhesive is applied on the area of the patch that will come into contact with cardiac tissue; this allows for the introduction and necessary manipulation of the catheter system until activation of the adhesive occurs. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, the adhesive properties of certain polymeric materials are relied upon rather than their ability to cure or harden into a specific shape. In another embodiment, the patch is immediately released utilizing a detaching mechanism on the balloon or the balloon catheter which supports the patch; the patch along with the inflated balloon remain on the cardiac structure occluding the opening.
Owner:SIDERIS ELEFTHERIOS B +1
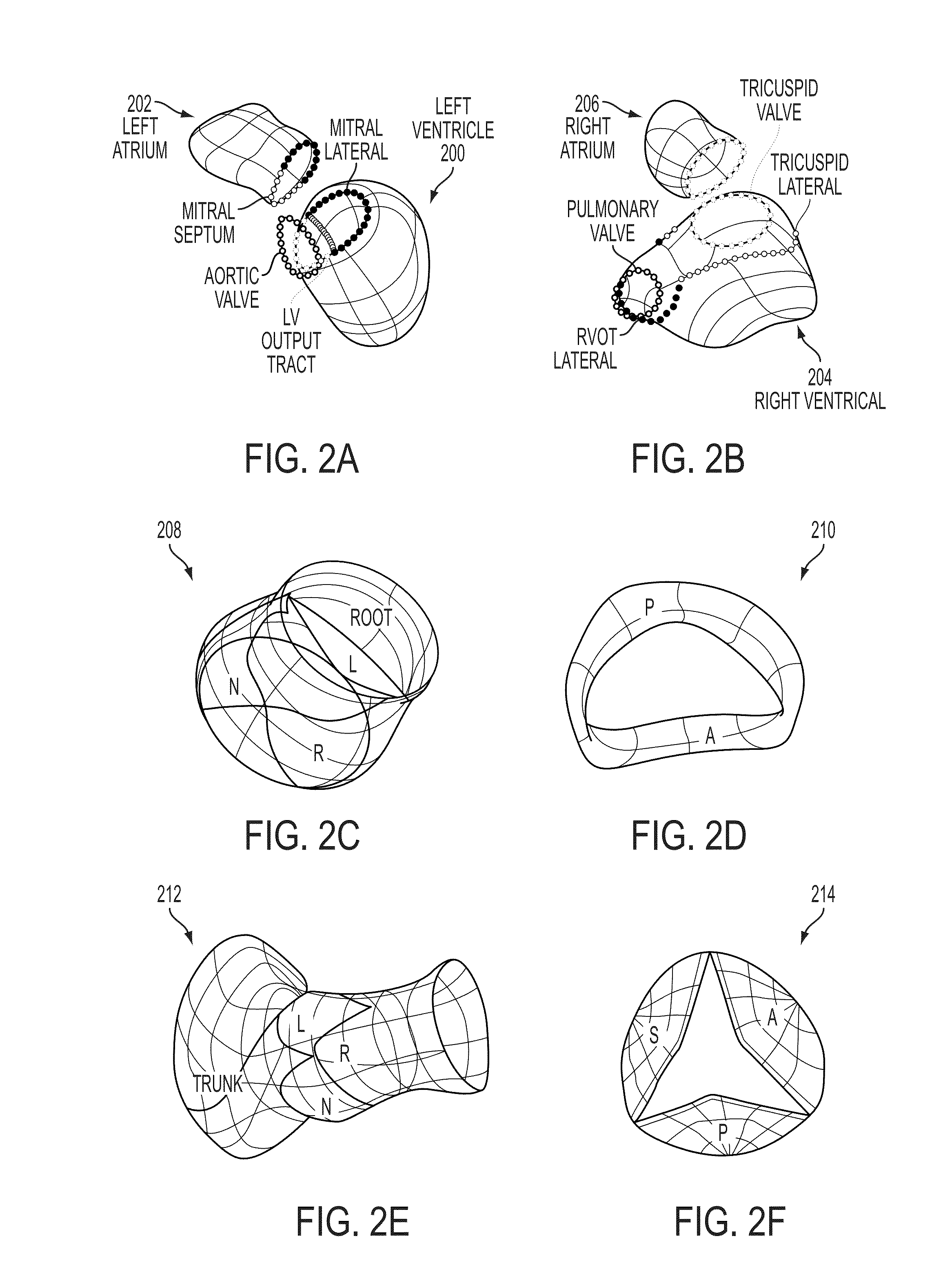
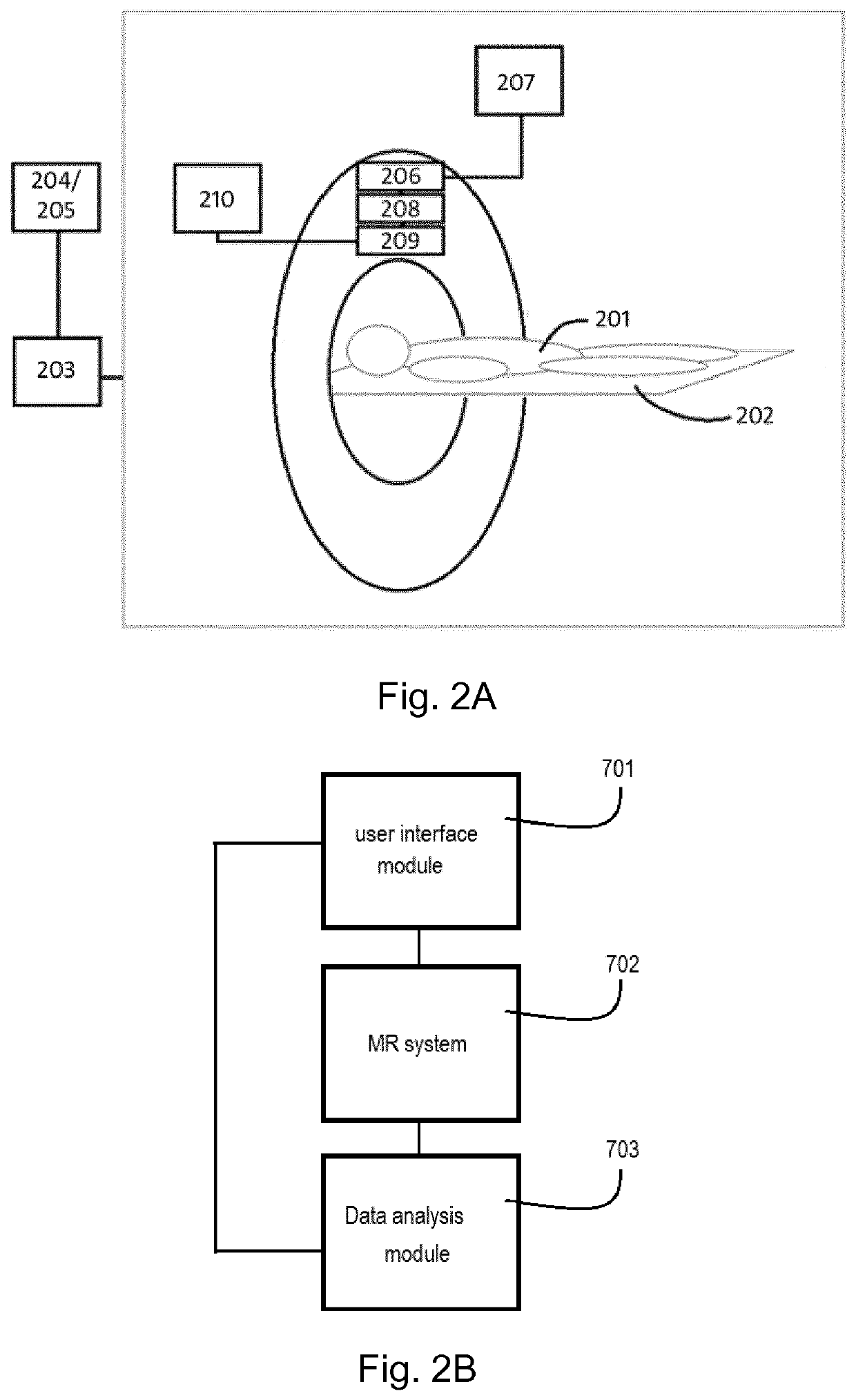
Method and system for comprehensive patient-specific modeling of the heart
ActiveUS8682626B2Medical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesAnatomical structuresEntire heart
A method and system for patient-specific modeling of the whole heart anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction from 4D medical image data is disclosed. The anatomy and dynamics of the heart are determined by estimating patient-specific parameters of a physiological model of the heart from the 4D medical image data for a patient. The patient-specific anatomy and dynamics are used as input to a 3D Navier-Stokes solver that derives realistic hemodynamics, constrained by the local anatomy, along the entire heart cycle. Fluid structure interactions are determined iteratively over the heart cycle by simulating the blood flow at a given time step and calculating the deformation of the heart structure based on the simulated blood flow, such that the deformation of the heart structure is used in the simulation of the blood flow at the next time step. The comprehensive patient-specific model of the heart representing anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction can be used for non-invasive assessment and diagnosis of the heart, as well as virtual therapy planning and cardiovascular disease management. Parameters of the comprehensive patient-specific model are changed or perturbed to simulate various conditions or treatment options, and then the patient specific model is recalculated to predict the effect of the conditions or treatment options.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
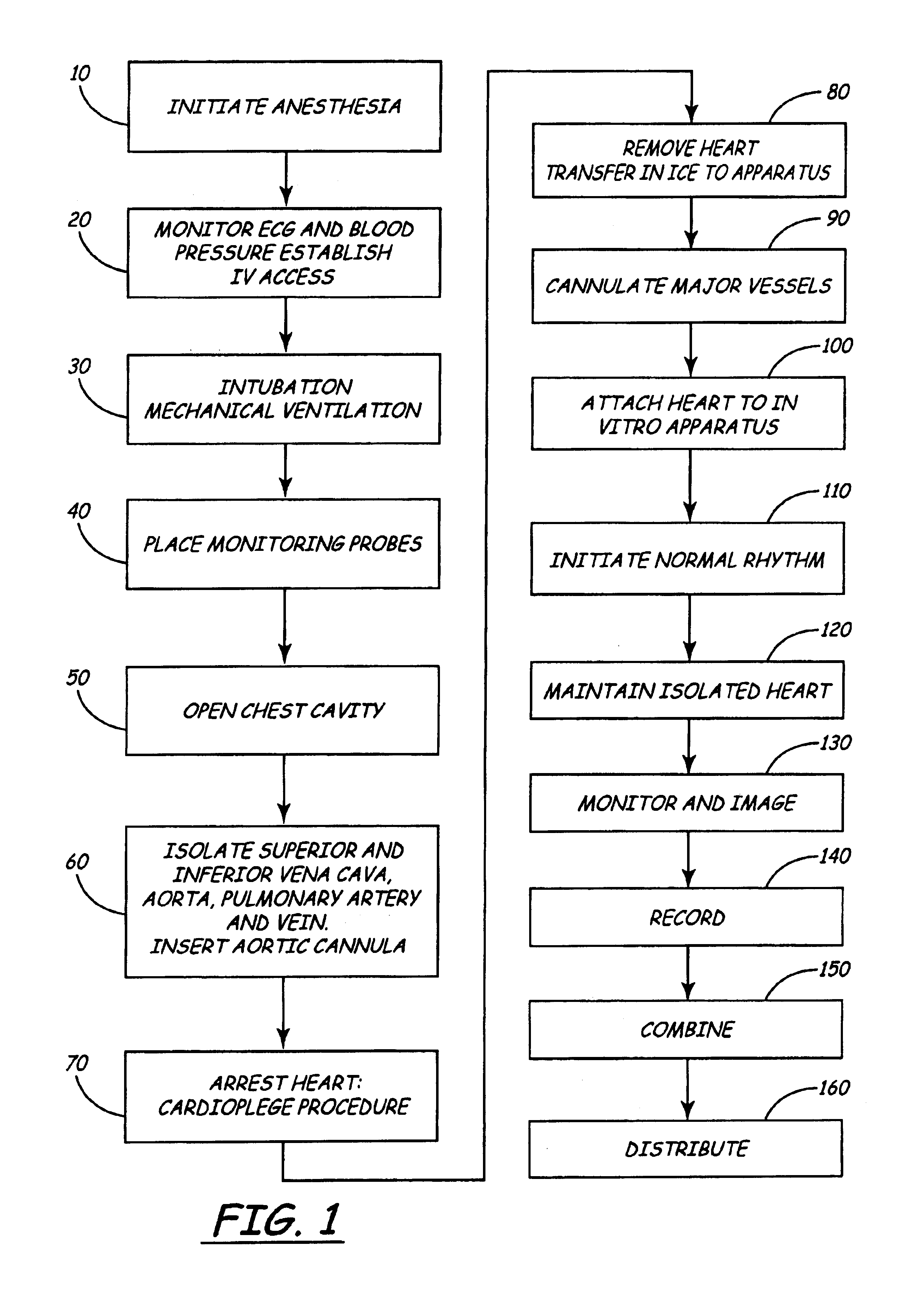
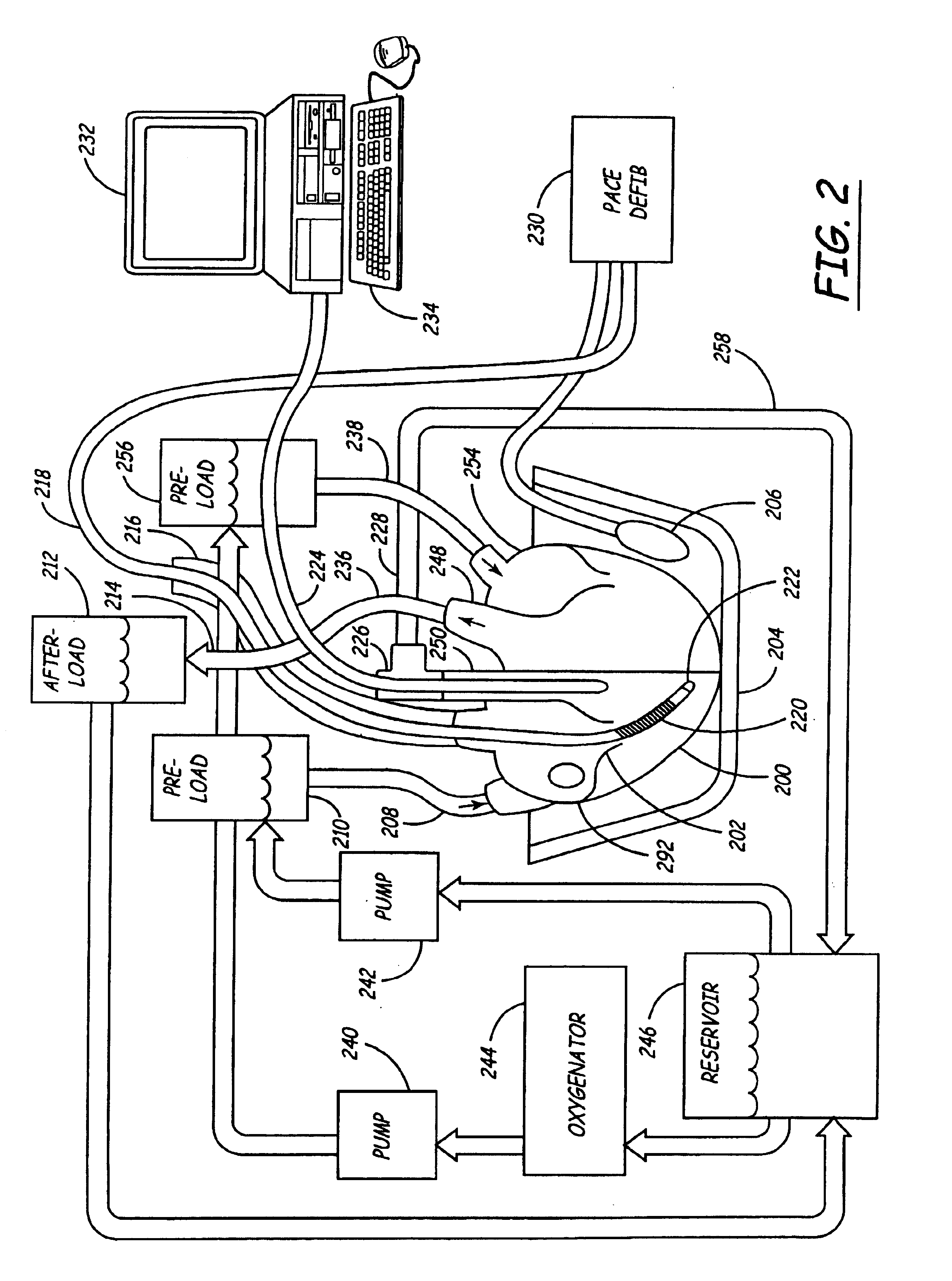
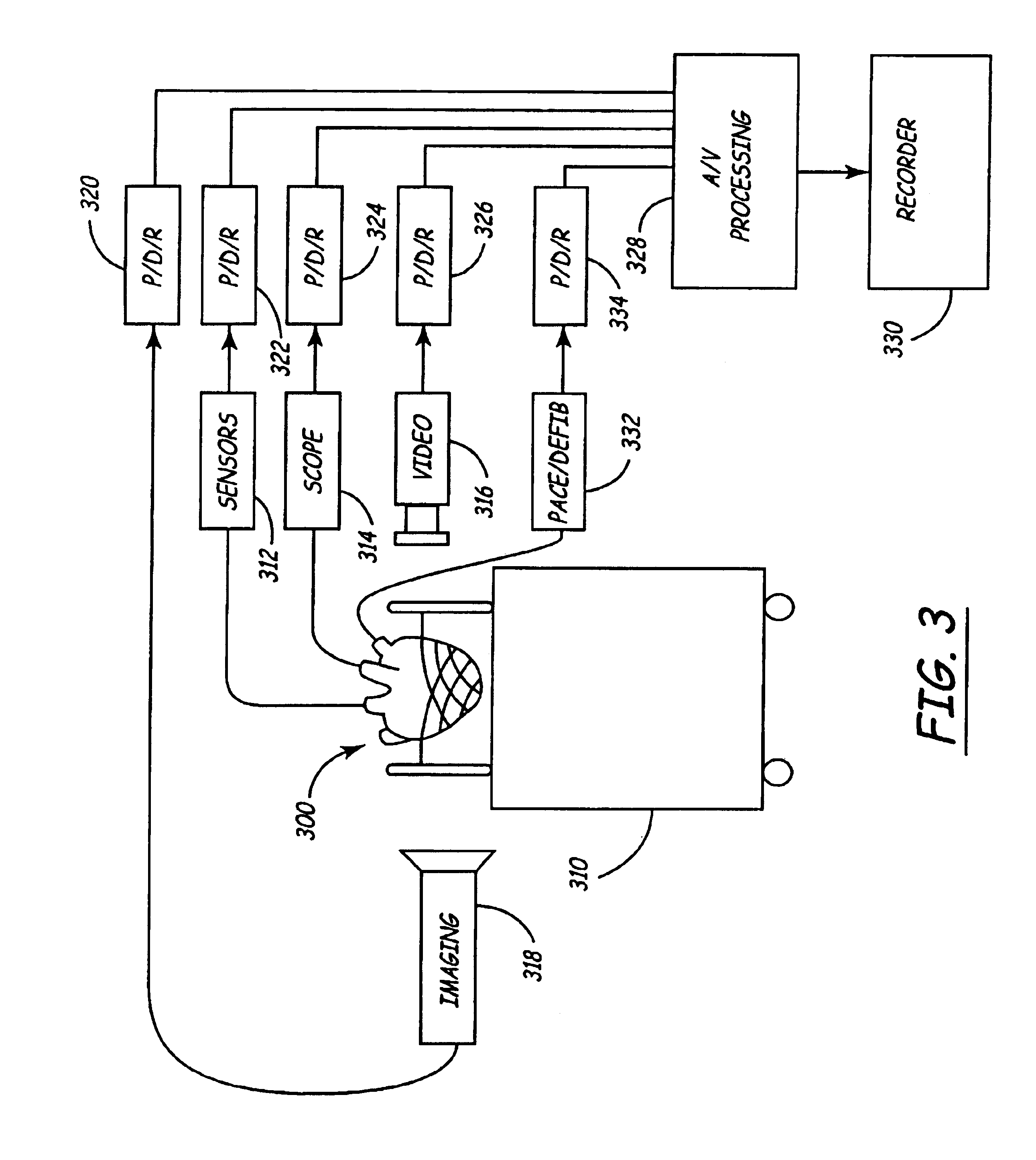
Isolated perfused heart preparation and method of use
InactiveUS7045279B1Easy to produceMaintain activityDead animal preservationCatheterKrebs bufferMedical treatment
An isolated heart preparation in which essentially normal pumping activity of all four chambers of the heart is preserved, allowing for the use of the preparation in conjunction with investigations of electrode leads, catheters, cardiac implants and other medical devices intended to be used in or on a beating heart. The preparation may also be employed to investigate heart functions, in the presence or absence of such medical devices. In order to allow for visualization of heart structures and devices located within the chambers of the heart, a clear perfusate such as a modified Krebs buffer solution with oxygenation is circulated through all four chambers of the heart and the coronary vasculature. The preparation and recordings of the preparation may be used in conjunction with the design, development and evaluation of devices for use in or on the heart, as well as for use as an investigational and teaching aid to assist physicians and students in understanding the operation of the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for comprehensive patient-specific modeling of the heart
ActiveCN102346811ADescription of measurement accuracySpecial data processing applicationsTreatment optionsEntire heart
A method and system for patient-specific modeling of the whole heart anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction from 4D medical image data is disclosed. The anatomy and dynamics of the heart are determined by estimating patient-specific parameters of a physiological model of the heart from the 4D medical image data for a patient. The patient-specific anatomy and dynamics are used as input to a 3D Navier-Stokes solver that derives realistic hemodynamics, constrained by the local anatomy, along the entire heart cycle. Fluid structure interactions are determined iteratively over the heart cycle by simulating the blood flow at a given time step and calculating the deformation of the heart structure based on the simulated blood flow, such that the deformation of the heart structure is used in the simulation of the blood flow at the next time step. The comprehensive patient-specific model of the heart representing anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction can be used for non-invasive assessment and diagnosis of the heart, as well as virtual therapy planning and cardiovascular disease management. Parameters of the comprehensive patient-specific model are changed or perturbed to simulate various conditions or treatment options, and then the patient specific model is recalculated to predict the effect of the conditions or treatment options.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
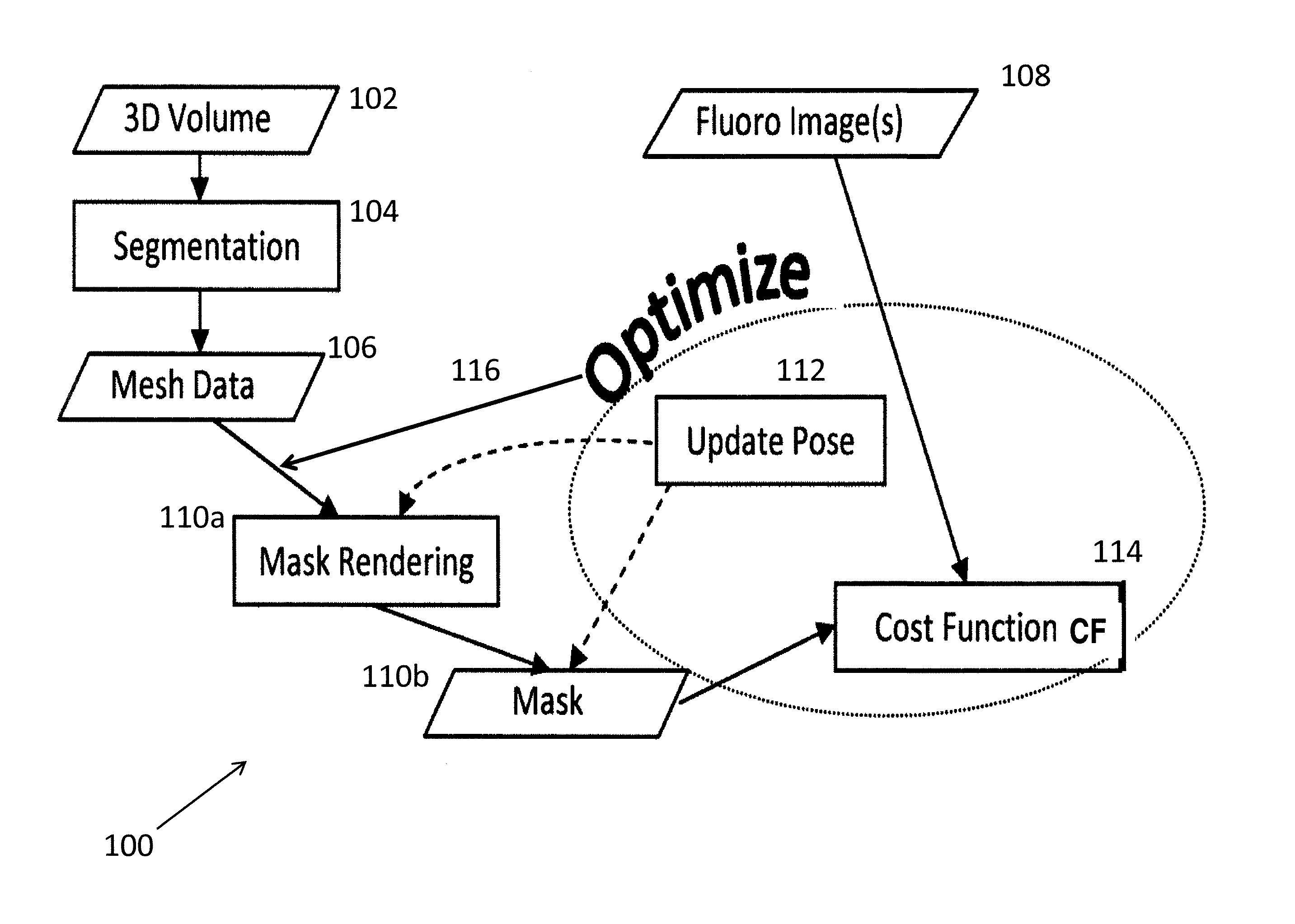
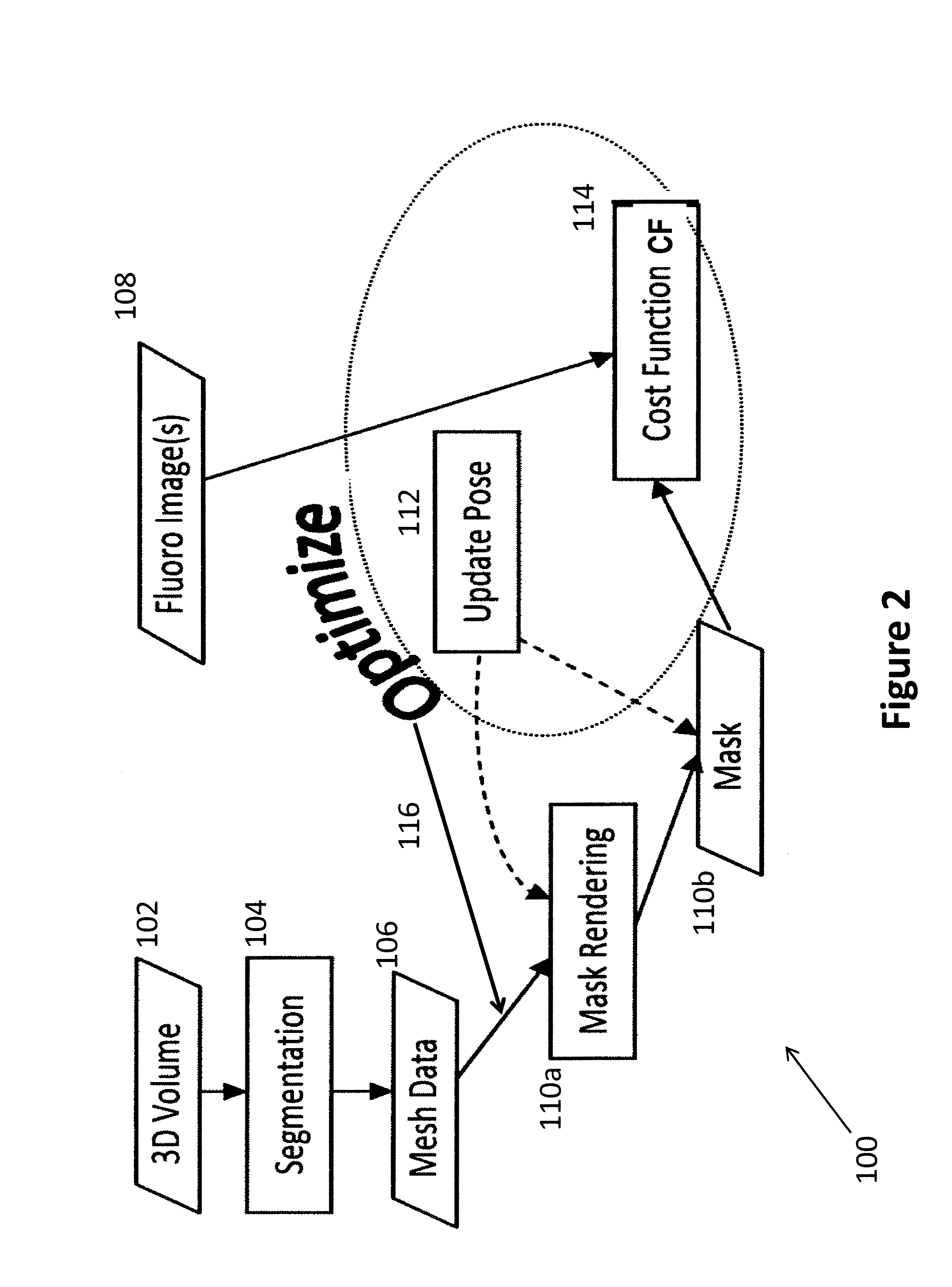
2d/3d image registration method
ActiveUS20130070995A1Minimize the differenceEasy to operateImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic image3d image
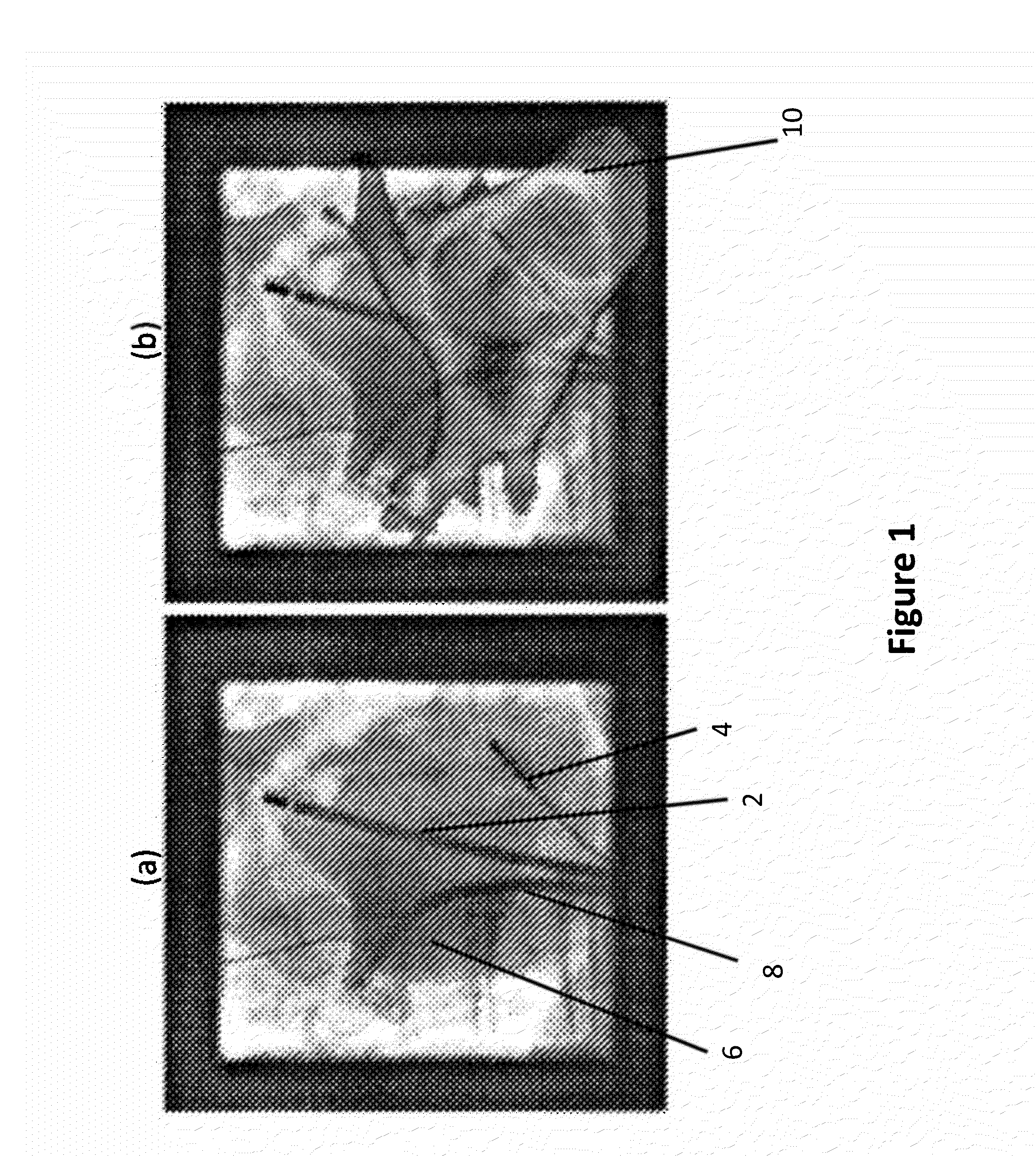
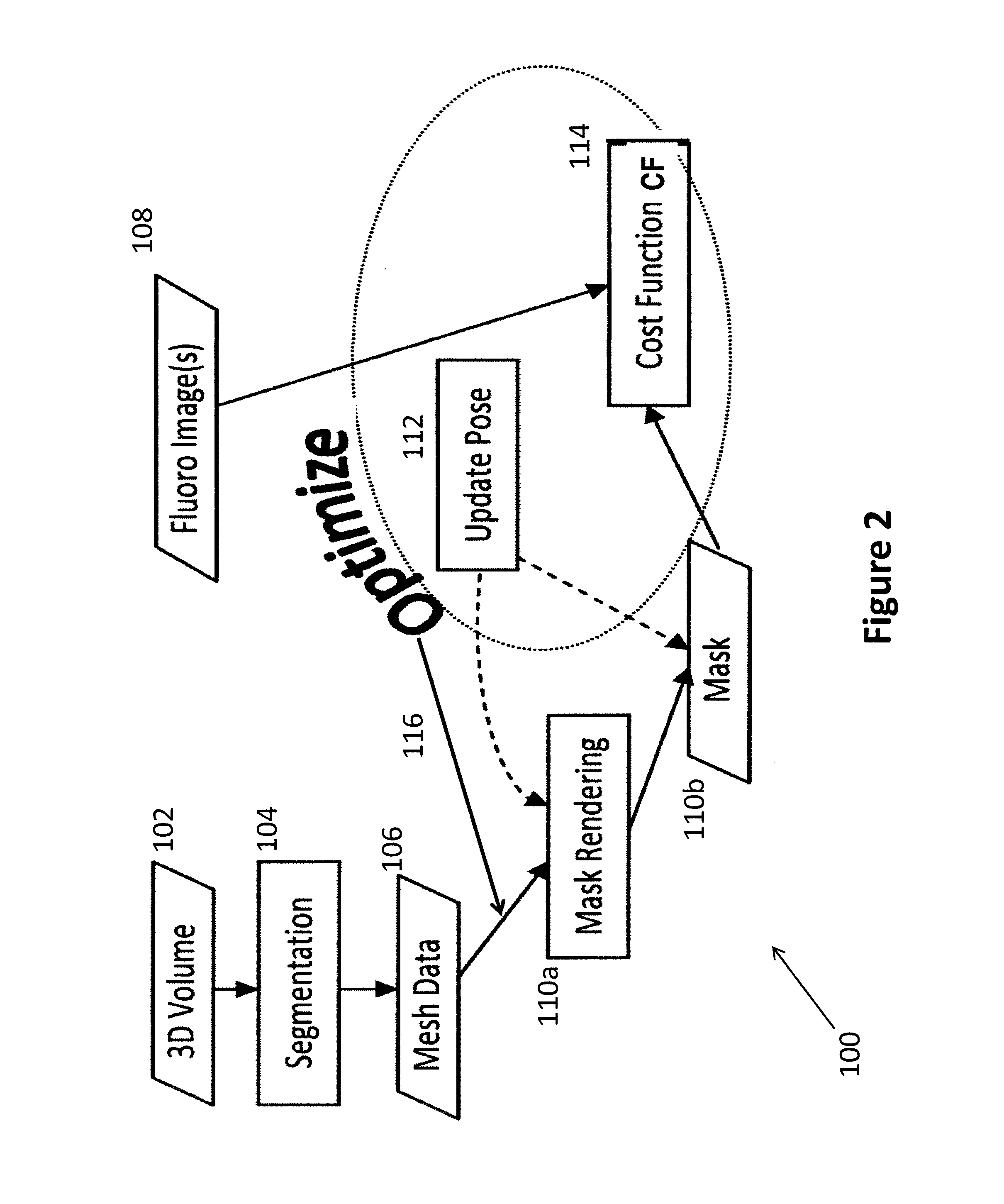
A method (100) that registers a 3D heart volume (112, 114) obtained from either a pre-operative MR image or CT image (102) to an intra-operative fluoroscopic image using a mesh of the heart structure (106) as the basis for the registration.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Intracardiac device for restoring the functional elasticity of the cardiac structures, holding tool for the intracardiac device, and method for implantation of the intracardiac device in the heart
ActiveCN102215784AGood reliability levelThe exchange force is smallAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsDevice implantCardiac cycle
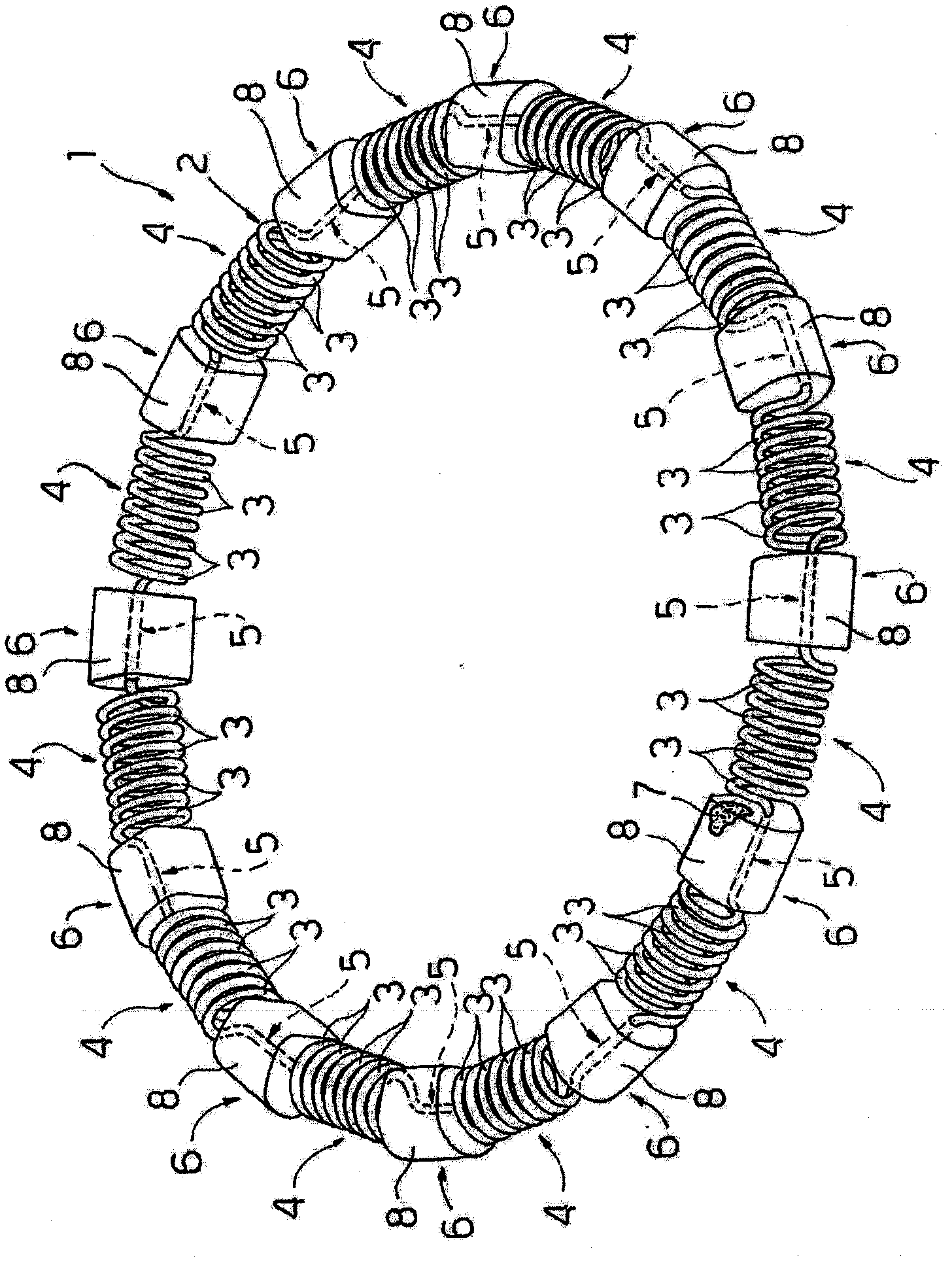
An intracardiac device (101) for restoring the functional elasticity of the cardiac structures, in particular for the treatment of cardiomyopathies and or valvulopathies, by storing energy from the cardiac structures and ceding energy to the cardiac structures during the cardiac cycle, has an elongated shape, is at least partially wound in coils (83) and is attachable to a cardiac structure; the coils (83) are selected in material, number and dimension so as to allow an elastic elongation of the intracardiac device (101) higher than 10% of the rest length of the intracardiac device (101) and are exposed, in use, to the blood flow.
Owner:COBO LTD
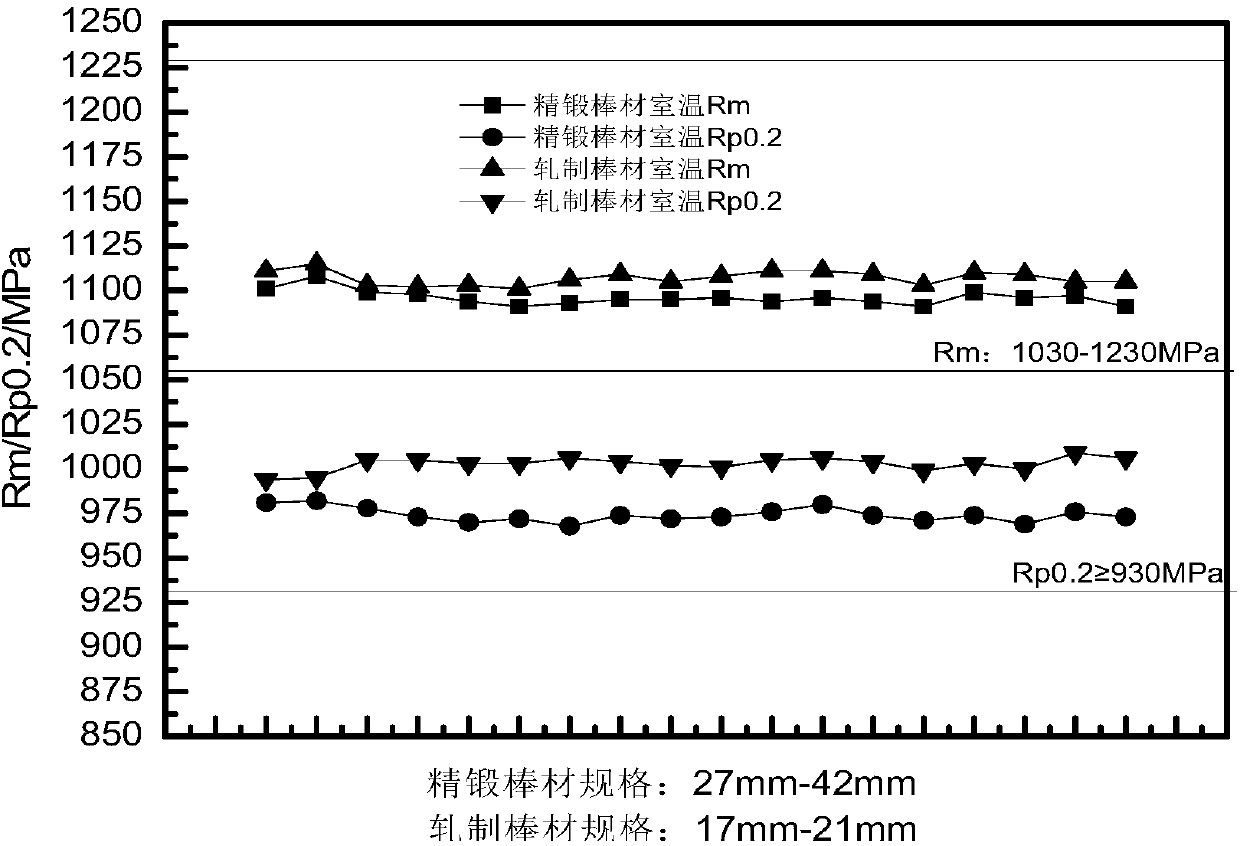
Forging method of TC4 titanium alloy large-specification rods
ActiveCN108097852AReduce lossIncrease the degree of deformationMetal-working apparatusIngotTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a forging method of TC4 titanium alloy large-specification rods. TC4 cast ingots are selected; TC4 are drawn to deform according to a deformation of 40-60%, and are broken to obtain multiple forgings; second heating-number forging and third heating-number forging are performed on each forging; one-upsetting and one-drawing deformation is performed on each forging in secondheating-number forging and third heating-number forging; fourth heating-number forging is performed on each forging; one-upsetting and one-drawing deformation is performed; the forgings are rounded asrods of phi 200-phi 220 mm; fifth heating-number forging is performed on each rod of phi 200-phi 220 mm; and the rods are drawn to deform according to a deformation of 40-60%, and are rounded to formrods of phi 120 mm. The one-upsetting and one-drawing operation is adopted to replace traditional three-upsetting and three-drawing operation, so that the operation is simplified, the production costand the material loss are reduced, the material deformation degree is increased, the heart structures can be crushed more sufficiently, and the equiaxial property is achieved; and the blank forging temperature is gradually lowered along with the operation, crushing of grain particles and transformation of morphologies are facilitated, and the structure uniformity of the TC4 alloy large-specification rods is improved.
Owner:西安赛特思迈钛业有限公司
Device and method for occluding a septal defect
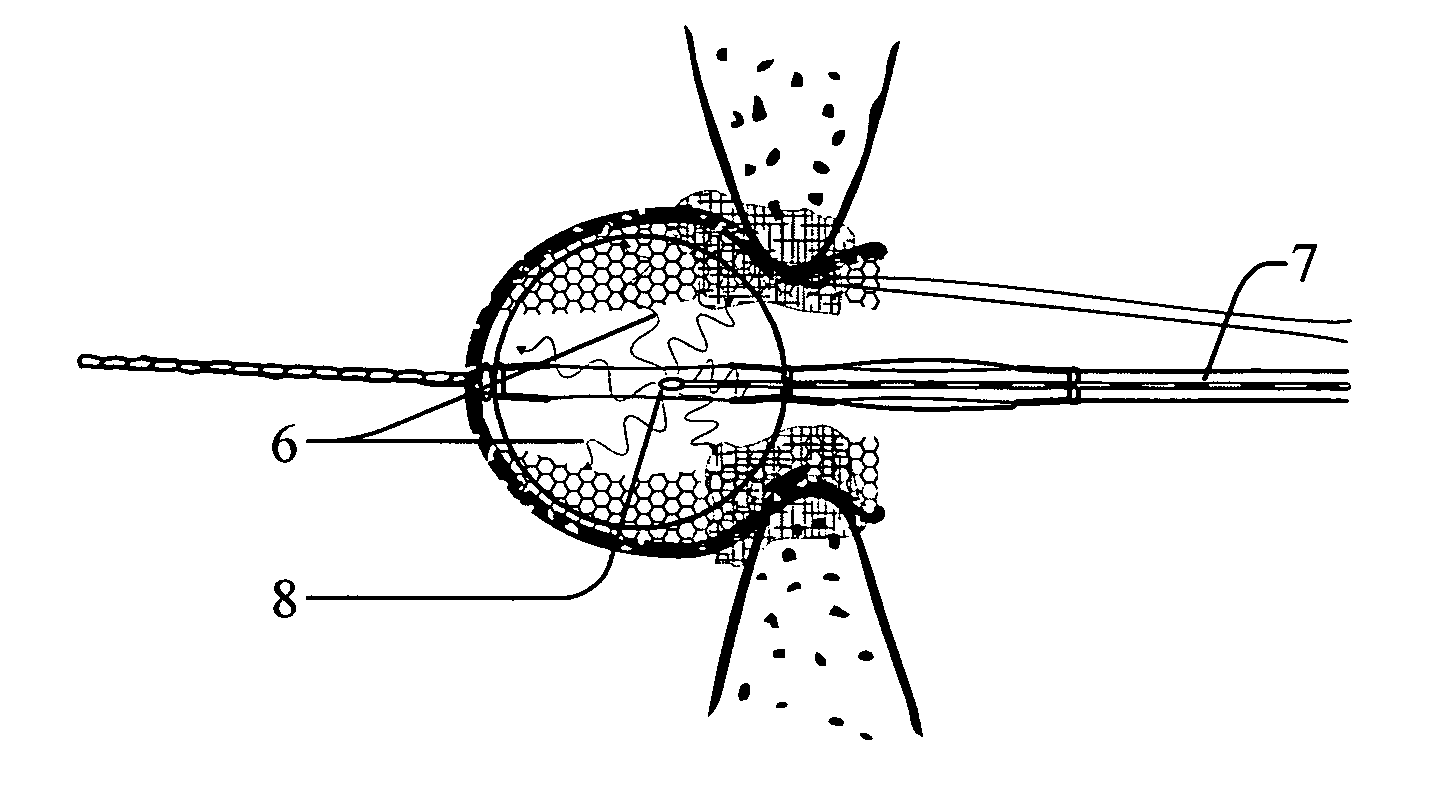
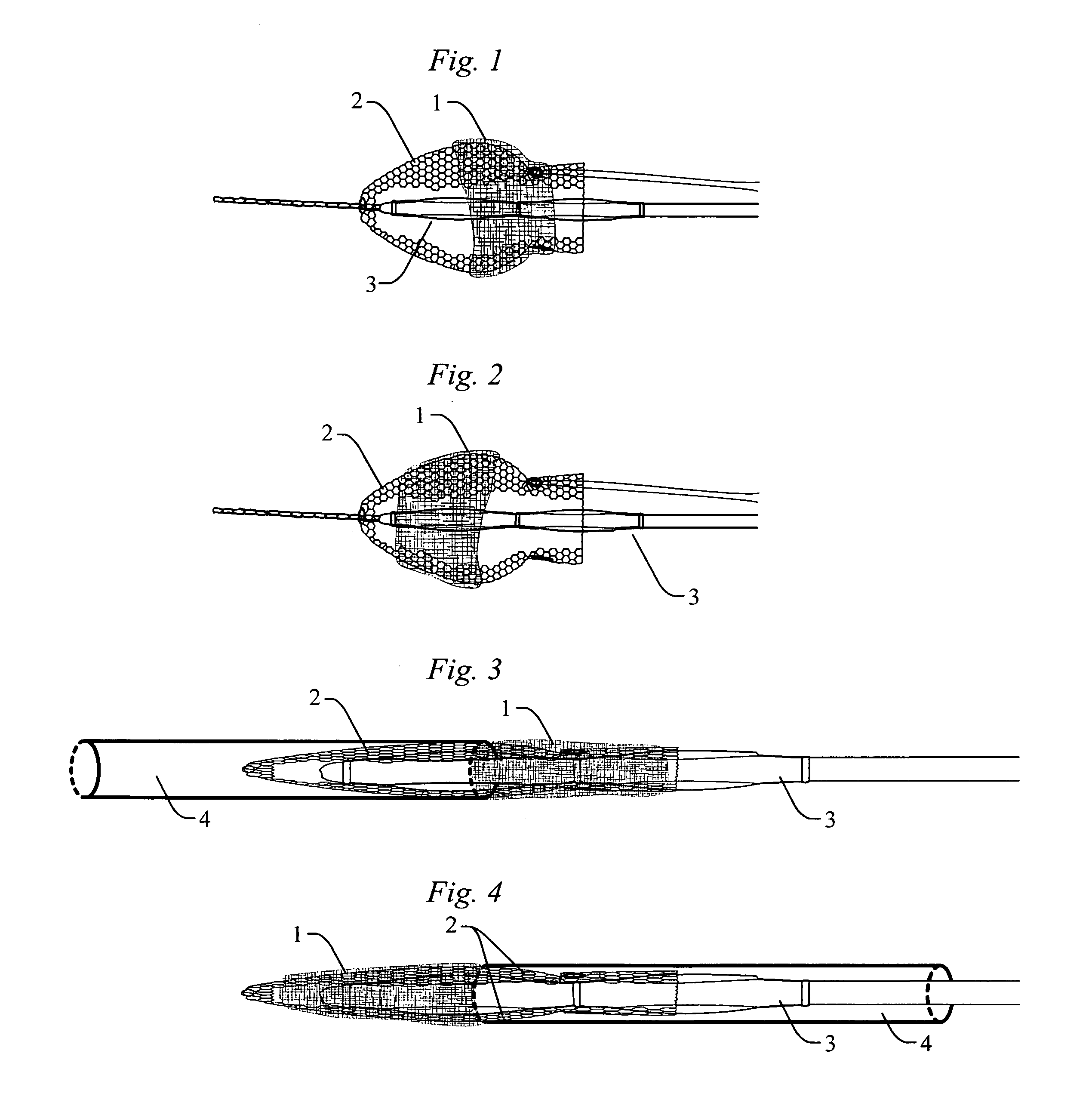
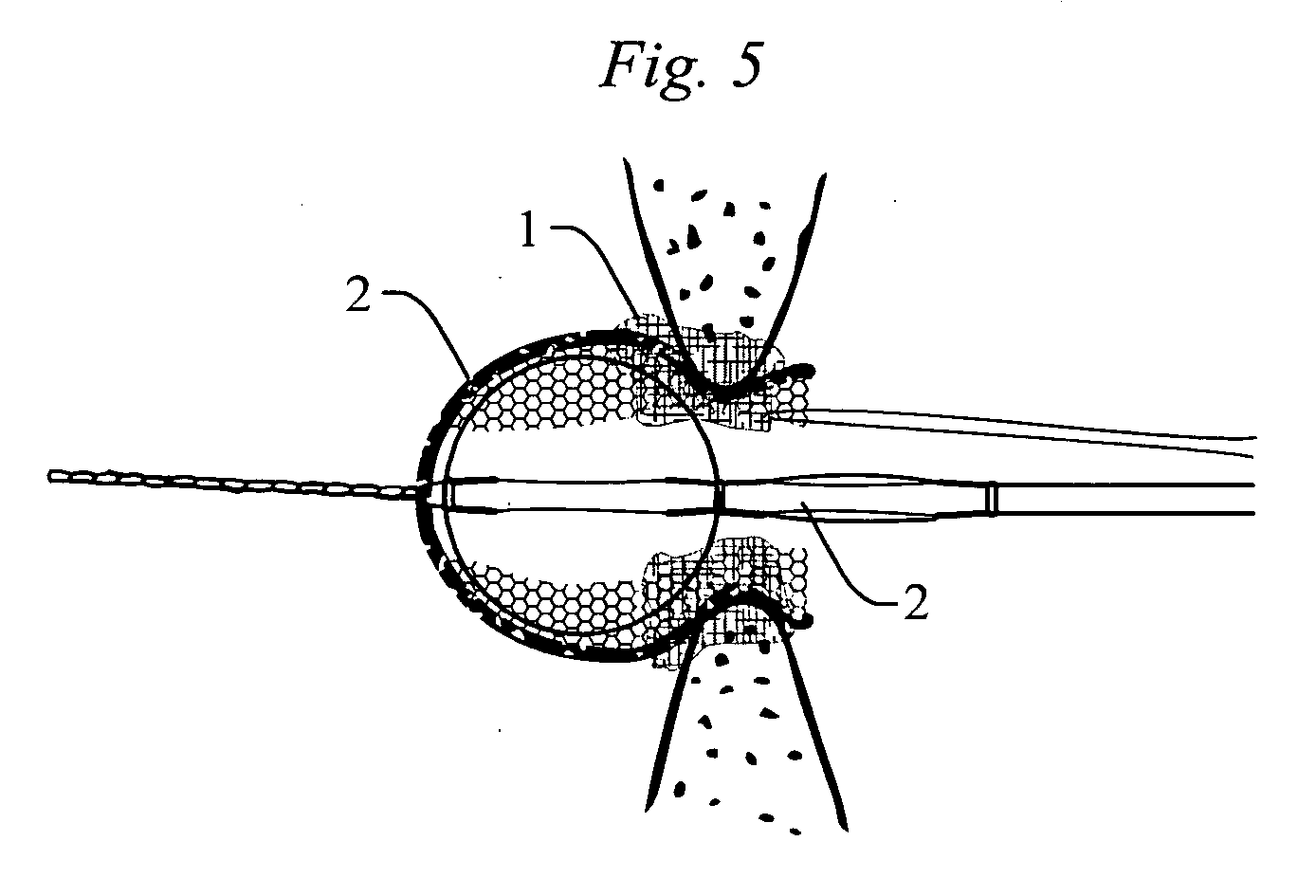
A device for occluding a septal defect is provided. In general, the occluding device has a contracted state that allows the occluding device to be received within a delivery device for deployment to the site of the defect and an expanded state that is achieved when the occluding device is deployed from the delivery device. The occluding device has a proximal portion, which may be substantially circular, a distal portion, which may be substantially ovaloid, and a connecting portion extending between the two. The distal portion may define first and second outer parts at opposite ends of the major axis, which may be bent or curved. The configuration of the proximal and distal portions allow the occluding device to securely engage the septal wall and be kept in position at the septal defect without causing substantial interference with the functioning of adjacent heart structures.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
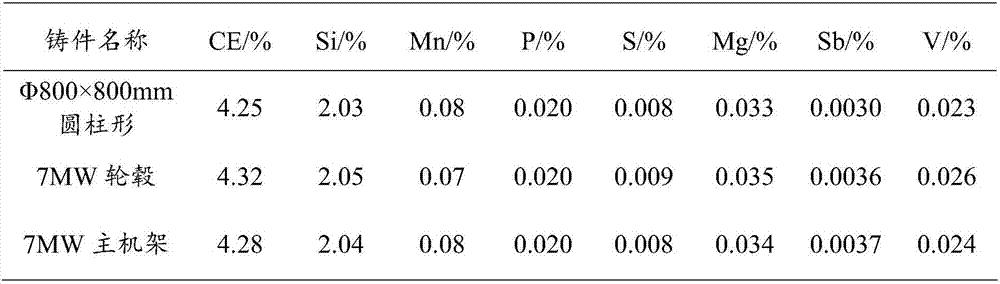
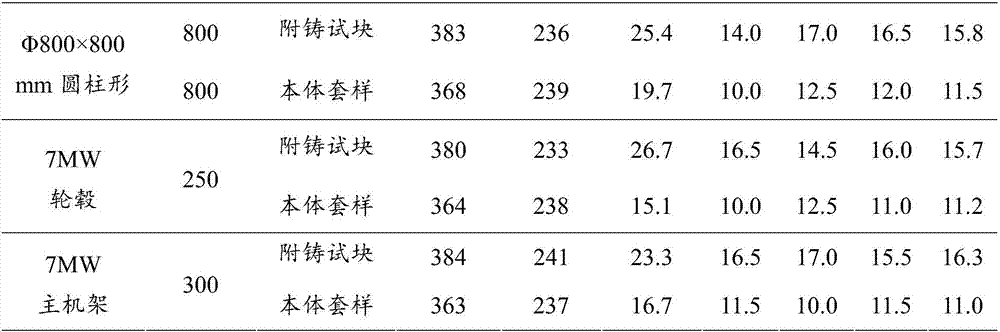
Ultrathick large low-temperature ductile cast iron and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses ultrathick large (wall thickness not less than 200 mm) low-temperature ductile cast iron. The ultrathick large low-temperature ductile cast iron comprises the following components: 4.2-4.4 wt% of CE, 1.9-2.1 wt% of Si, Mn not more than 0.15 wt%, P not more than 0.025 wt%, 0.006-0.012 wt% of S, 0.030-0.045 wt% of Mg, 0.003-0.005 wt% of Sb, 0.02-0.03 wt% of V, and the balance of Fe and impurities carried in the preparation process. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the ultrathick large low-temperature ductile cast iron. The ultrathick large low-temperature ductile cast iron is excellent in heart structure, generates no such special-shaped graphite as fragment graphite, satisfies -20 DEG C impact requirements when satisfying the tensile strength, the yield strength and the ductility, and satisfies the material requirements by high-power development of wind power castings.
Owner:JIANGSU JIXIN WIND ENERGY TECH
Electrocardio ultrasonic signal fusion computed tomography imaging system and method
InactiveCN104068845ARealize synchronous acquisitionDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyMyocarditisCardiac arrhythmia
The invention relates to a medical examination and diagnosis method and instrument, in particular to a multi-dimensional electrocardio ultrasonic signal fusion computed tomography imaging system and method based on anatomical orientation. A multi-dimensional ultrasonic cardiac structure and a perfusion image technology are further integrated on the basis of a multi-dimensional electrocardiosignal imaging system and method, and a novel non-invasive platform is provided for recording and evaluating the electro-mechanical signal characteristic and myocardial perfusion characteristic of heart. The method is a unique electrocardio-mechanical function and perfusion synchronized computed tomography imaging method based on anatomical orientation, and the technology is a non-invasive imaging technology for detecting transmural cardiac electrical activity information and mechanical signals. By adopting the medical examination and diagnosis method and instrument, the diagnosis of myocardial diseases such as cardiac hypertrophy, cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction and myocarditis, the determination of the origin of arrhythmia, and the like can be enhanced, and a brand-new diagnosis and guide treatment tool is provided for rapid real-time diagnosis of heart diseases.
Owner:镇郁琼 +1
Apparatus and method for treating atrial fibrillation and atrial tachycardia
InactiveUS20090216290A1Minimize and eliminate useEliminates severe DC shocksHeart stimulatorsElectrical ProblemAtrial cavity
A method and device for treating an electrical problem in an organ, especially a heart, of a human or animal patient comprises atraumatically blocking the transmission of one or more electrical signals external to the organ. Nerve cell membranes near a cathode are depolarized while nerve cell membranes near an anode are hyperpolarized, inducing a DC conduction block. The method and device are especially suitable for treating atrial tachycardia where unwanted signals from at least one pulmonary vein and / or at least one fat pad are blocked within the construct of the heart.
Owner:HAK CONSULTING
2D/3D image registration method
ActiveUS8942455B2Minimize the differenceEasy to operateImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic image3d image
A method (100) that registers a 3D heart volume (112, 114) obtained from either a pre-operative MR image or CT image (102) to an intra-operative fluoroscopic image using a mesh of the heart structure (106) as the basis for the registration.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Forging method capable of improving structure uniformity of titanium alloy forging stock
ActiveCN108057829AClear grain boundariesGuarantee organizationMetal-working apparatusTitanium alloyTransition temperature
The invention discloses a forging method capable of improving structure uniformity of a titanium alloy forging stock. Differential thermal analyzing is used for measuring the phase transformation temperature beta t of a titanium alloy blank to be forged; under the temperature from (beta t+100) DEG C to (beta t+150) DEG C, heat preservation is carried out for 4 hours to 6 hours, and the blank to beforged is forged into a square blank; the obtained square blank is subject to heat preservation for 2 hours to 4 hours at the temperature from (beta t-20) DEG C to (beta t-10) DEG C, second-heating forging is carried out, the obtained square blank is subject to free drawing until the deformation amount reaches 50% to 60% of the total deformation amount, and the square blank obtained after free drawing is obtained; the obtained square blank obtained after free drawing rotates by 45 degrees around the center axis of the length direction of the square blank, pressing is carried out, and the final square blank is obtained; and the macrostructure of the cross section of the forge blank obtained after machining is uniform, the grain boundary is clear, no special-shaped piebald defects exist, the microstructure is uniform and consistent, the whole is of a net basket structure or equal-axis structure, and the edge and heart structures have no difference.
Owner:西安赛特思迈钛业有限公司
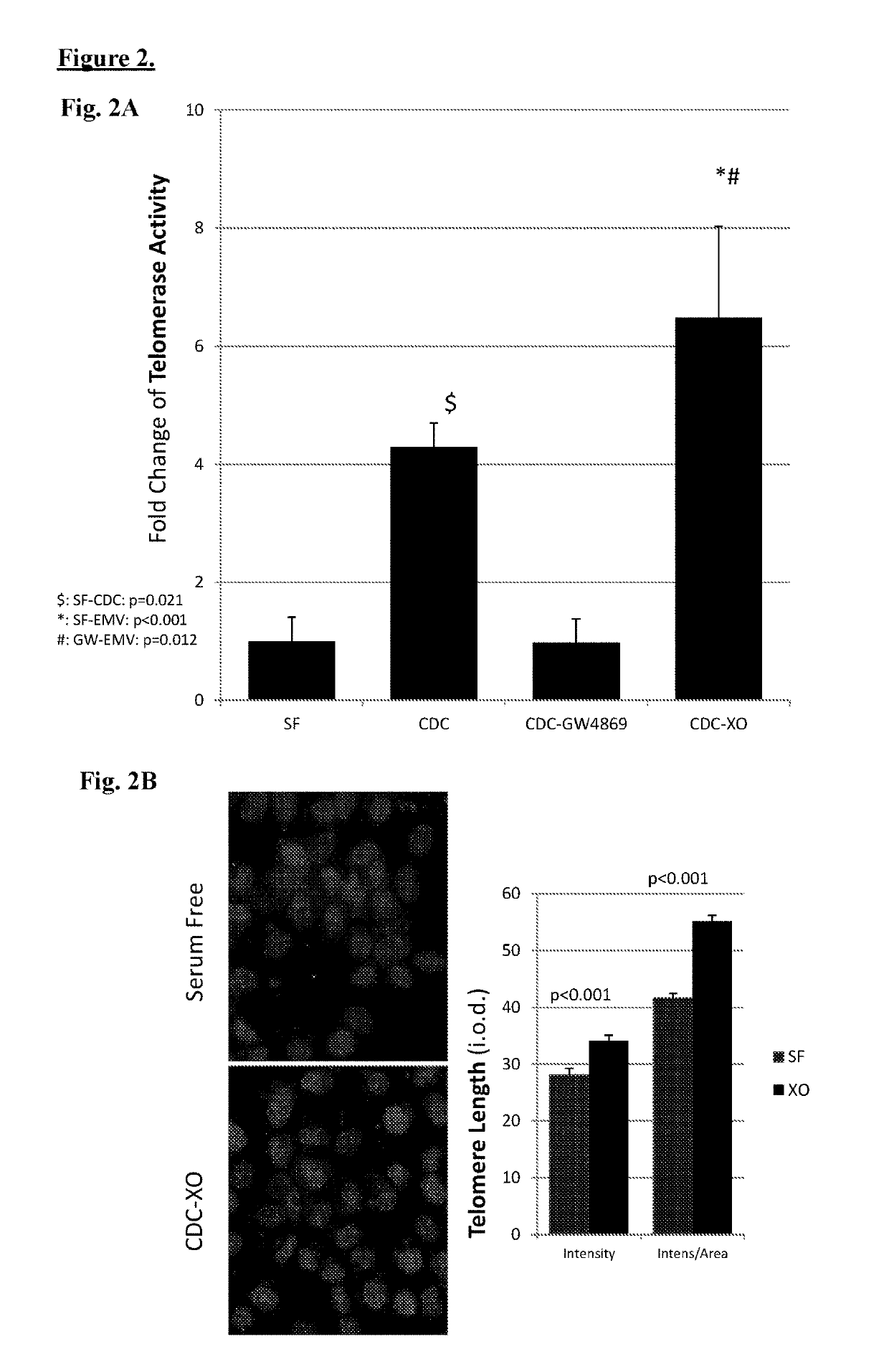
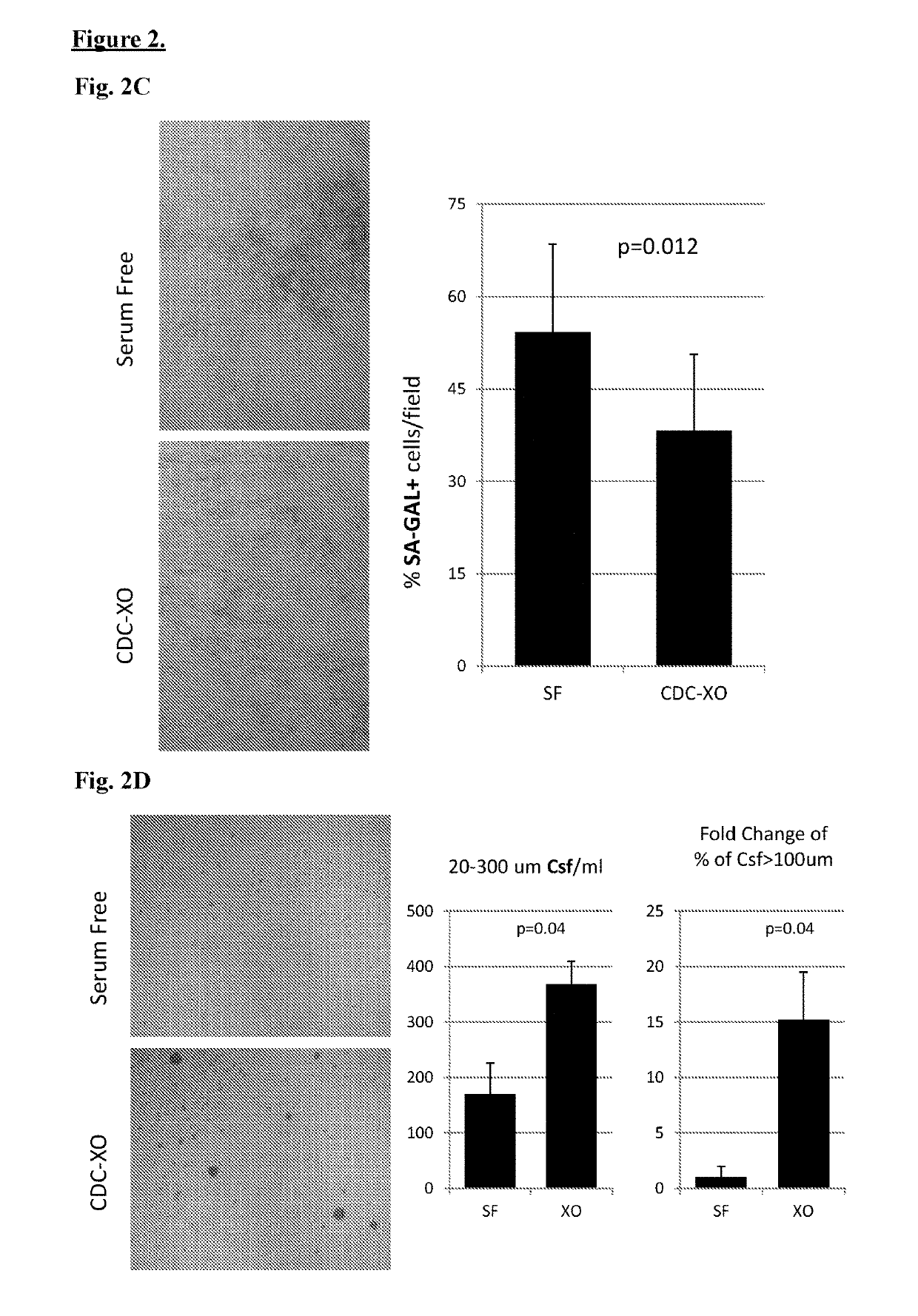
Cardiosphere-derived cells and their extracellular vesicles to retard or reverse aging and age-related disorders
Described herein are compositions and methods related to use of cardiosphere-derived cells and their extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes and microvesicles, for achieving anti-aging and rejuvenation. This includes discoveries for effects on heart structure, function, gene expression, and systemic parameters. For animal studies, intra-cardiac injections of neonatal rat CDCs was compared to in old and young rats including evaluation of blood, echocardiographic, haemodynamic and treadmill stress tests. For in vitro studies, human heart progenitors from older donors, or cardiomyocytes from aged rats were exposed to human CDCs or cardiosphere derived cell (CDC) derived exosomes (CDC-XO) from pediatric donors. CDCs and CDC-XOs were capable of effectuating youthful patterns of gene expression in the hearts of old, along with a variant of physiological and function benefits, including elongation of telomere length. Together, these results indicate capacity of CDCs and CDC-XO to ward off the effects of aging through rejuvenation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
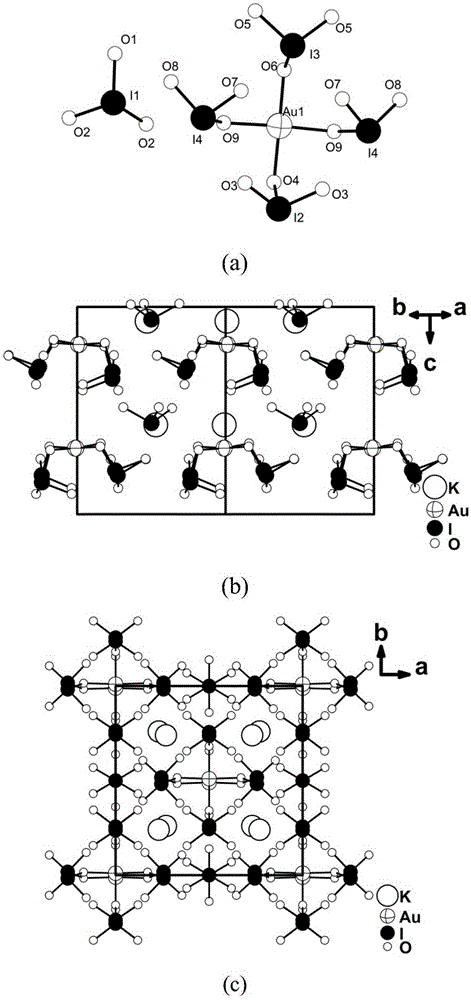
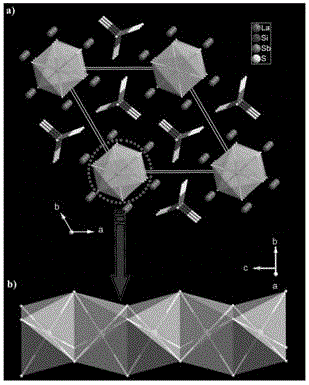
Inorganic compound K2Au(IO3)5 with non-heart structure, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105350079AStrong frequency doubling effectWide transmittance rangePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNonlinear optical crystalSpace group
The invention relates to an inorganic compound with a non-heart structure, and a preparation method and an application thereof as a nonlinear optical crystal. The crystal has a chemical formula of K2Au(IO3)5, belongs to an orthorhombic crystal system, has a space group of C[mc]2[1], and has crystal cell parameters of a=11.5949(8) angstroms, b=11.6905(6) angstroms, c=11.4716(6) angstroms, alpha=beta=gamma=90 DEG and Z=4. The yellow K2Au(IO3)5 crystal is prepared by a hydrothermal method. The powder frequency-doubling effect of the K2Au(IO3)5 crystal is 1.0 time that of KTiOPO4.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
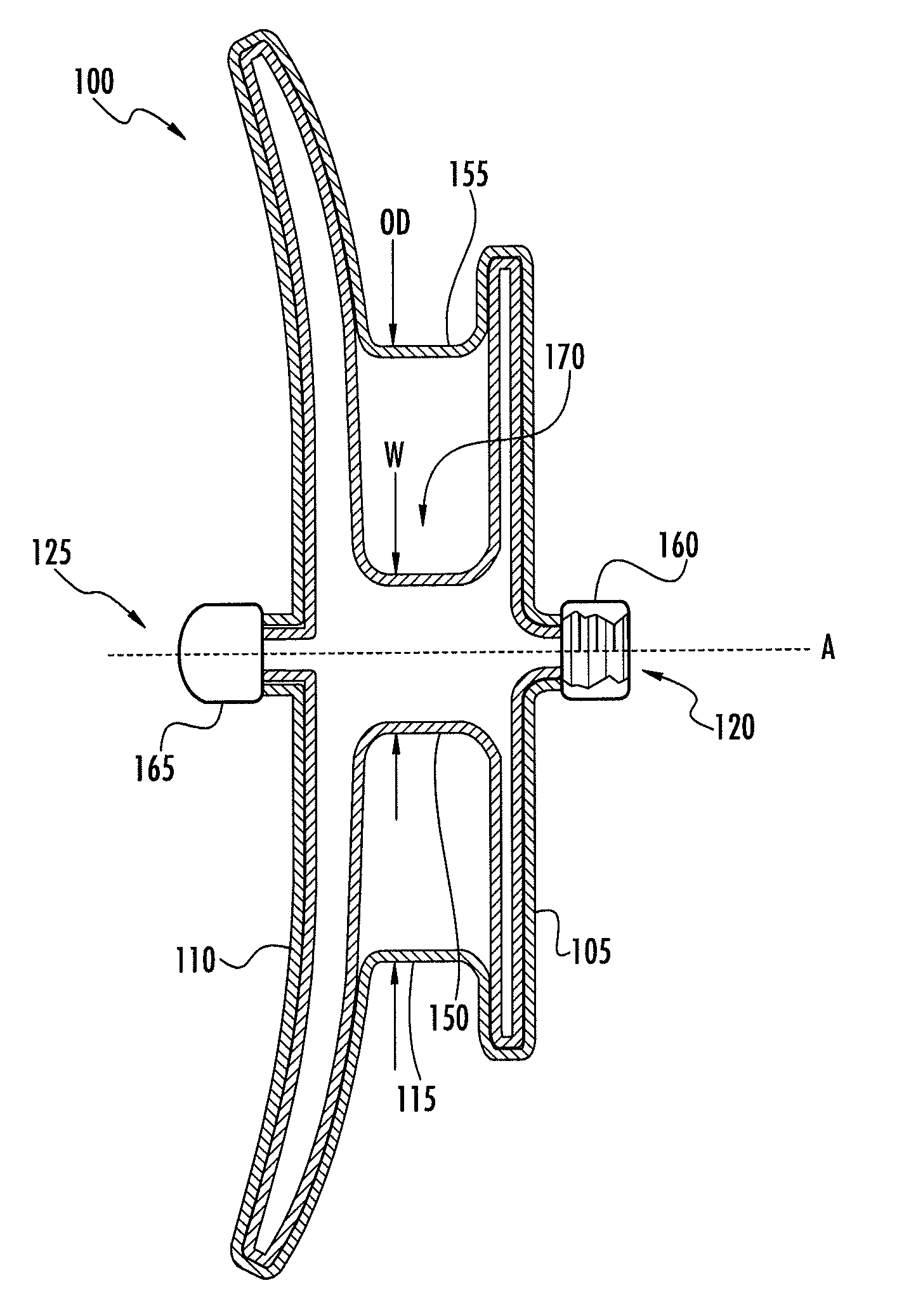
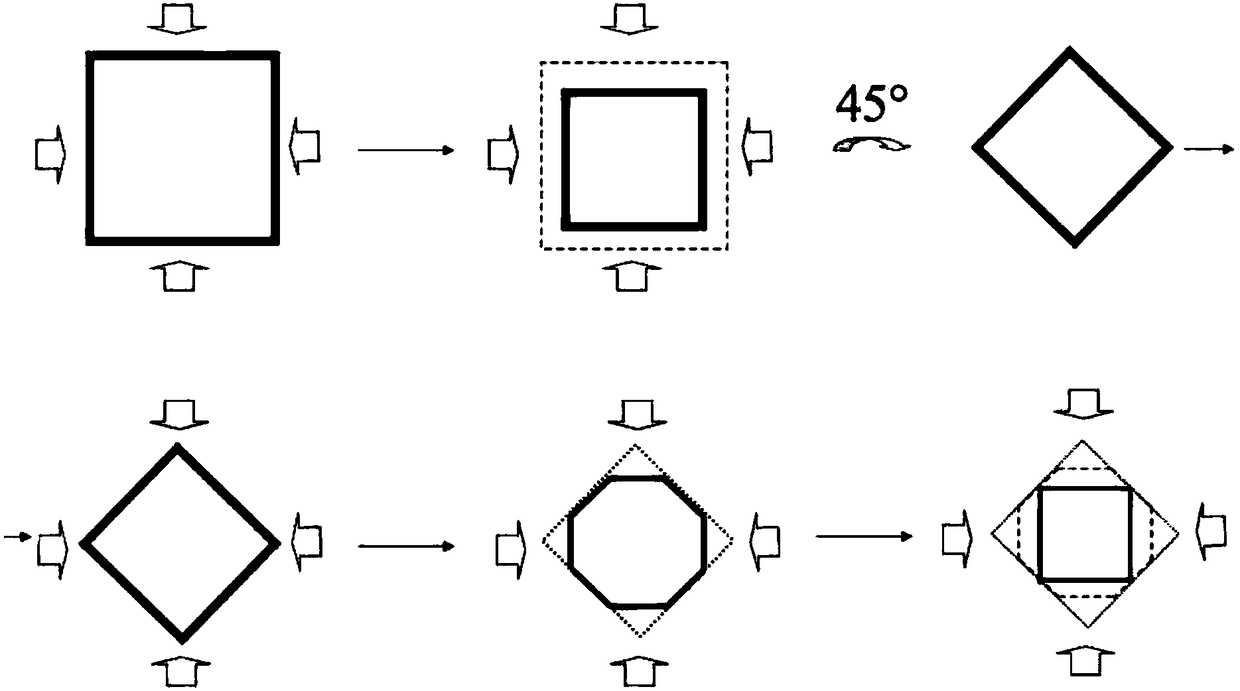
Left heart assisting device
ActiveCN105597172ADestruction will notConform to the physiological anatomyBatteries circuit arrangementsControl devicesLap jointEngineering
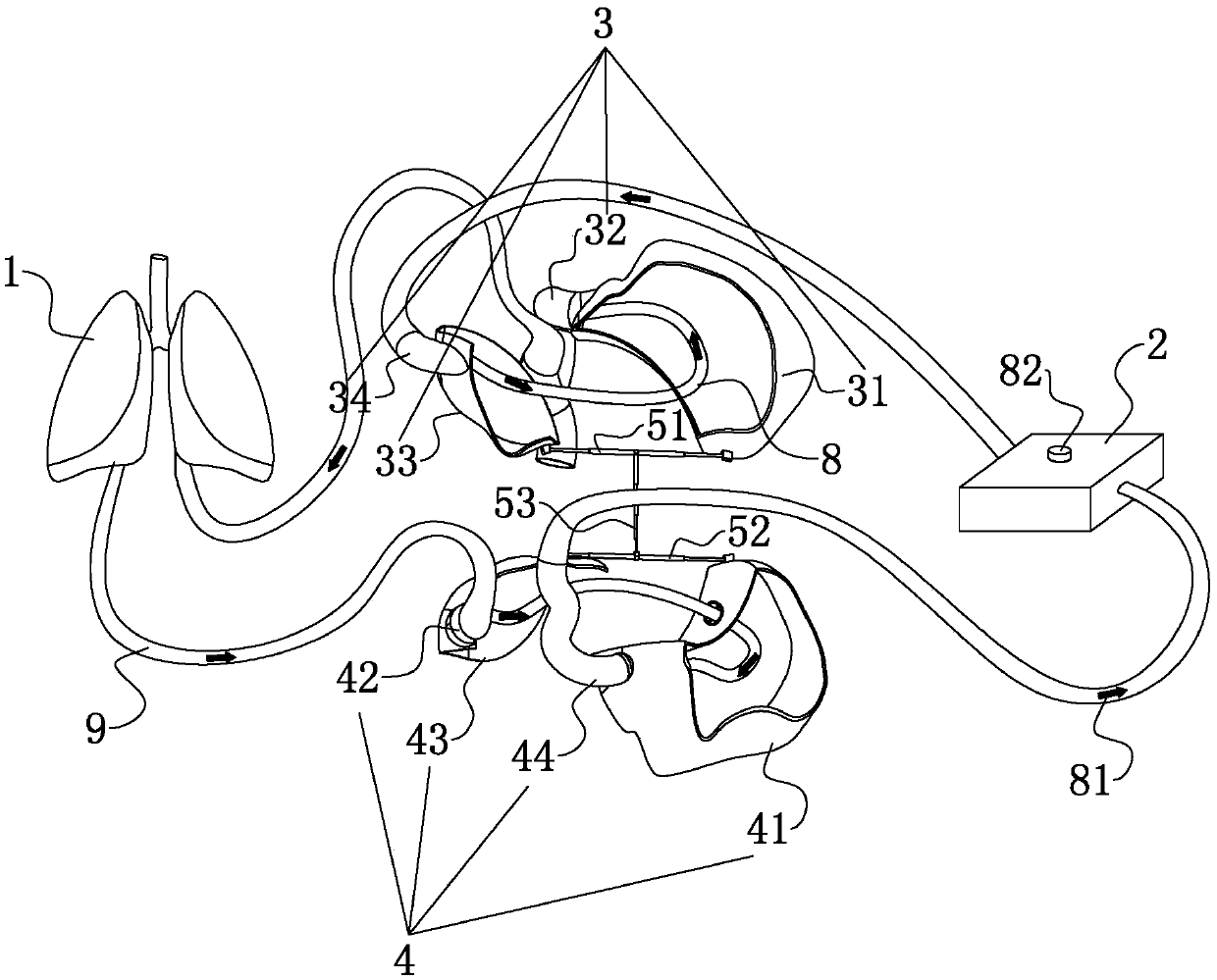
The invention discloses a left heart assisting device which comprises communicated first pipeline and second pipeline, a blade and a drive device, wherein the first pipeline comprises communicated flow-in part and flow-out part; an angle of 5-45 degrees is formed between the first center vertical line of the flow-in end surface of the flow-in part and the second center vertical line of the flow-out end surface of the flow-out part; the second pipeline comprises a flow-in port, a flow-out port and a lap-joint part between the flow-in port and the flow-out port; the flow-in port is detachably connected with the flow-out end surface; the flow area of the lap-joint part is larger than or equal to the flow area of the flow-out port; the blade is rotatably connected with the inside of the flow-out part; the flow-out part comprises a bottom wall opposite to the flow-out end surface; the blade and the drive device are arranged on the two sides of the bottom wall respectively; and the drive device is used for driving the blade to rotate. The left heart assisting device can be arranged in the heart cavity without damaging the heart structure.
Owner:深圳市华畅医疗创新有限公司
Preparing method of high-uniformity TC11 alloy bar for blade
The invention discloses a preparing method of a high-uniformity TC11 alloy bar for a blade. A TC11 titanium alloy precision forging blank subject to blooming forging and two-phase area forging is taken and heated below the phase change point, precision forging machine-fire multi-pass precision forging is adopted to obtain a medium precision forging blank; the medium precision forging blank is heated and subject to empty burning under the phase change point, and the structural uniformity of the medium precision forging blank is improved; the medium precision forging blank with the uniform structure is heated below the phase change point, and precision forging machine-fire multi-pass precision forging is adopted to form a finished product bar or the precision forging blank is subject to endcutting and discharging to prepare a rolled blank; the precision forging finished product bar is heated and subject to empty burning below the phase change point, and preparing of the high-uniformityTC11 precision forging bar for the blade is achieved or the rolled blank is heated below the phase change point; transverse column type hot rolling machine-fire multi-pass rolling is adopted to obtainthe high-uniformity TC11 rolled bar for the blade. The finally-obtained TC11 alloy precision forging and rolling bar for the blade is uniform and consistent in transverse high-power side and heart structure, the performance is stable, the corresponding material standard needs are met, the batch consistency is good, and the high-quality needs of an engine for the blade TC11 alloy bar are met.
Owner:西部超导材料科技股份有限公司
Method and system for pericardium based model fusion of pre-operative and intra-operative image data for cardiac interventions
A method and system for model based fusion pre-operative image data, such as computed tomography (CT), and intra-operative C-arm CT is disclosed. A first pericardium model is segmented in the pre-operative image data and a second pericardium model is segmented in a C-arm CT volume. A deformation field is estimated between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. A model of a target cardiac structure, such as a heart chamber model or an aorta model, extracted from the pre-operative image data is fused with the C-arm CT volume based on the estimated deformation field between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. An intelligent weighted average may be used improve the model based fusion results using models of the target cardiac structure extracted from pre-operative image data of patients other than a current patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Infrared nonlinear optical crystal La3Sb0.33SiS7 and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104674349AHas nonlinear optical propertiesPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsCrystal systemNonlinear optical crystal
The invention discloses an infrared nonlinear optical crystal La3Sb0.33SiS7 and a preparation method thereof. The crystal is a non-heart structure sulfide, the crystal system is a hexagonal system, and the space group is P63. The preparation method comprises the solid-phase reaction of elemental lanthanum, elemental antimony, elemental silicon and elemental sulfur under vacuum. Under the irradiation of laser with the wave length of 2.05 [mu]m, the nonlinear effect of the infrared nonlinear optical crystal La3Sb0.33SiS7 corresponds to that of commercial nonlinear optical material potassium titanium phosphate (KTP).
Owner:ZUNYI NORMAL COLLEGE
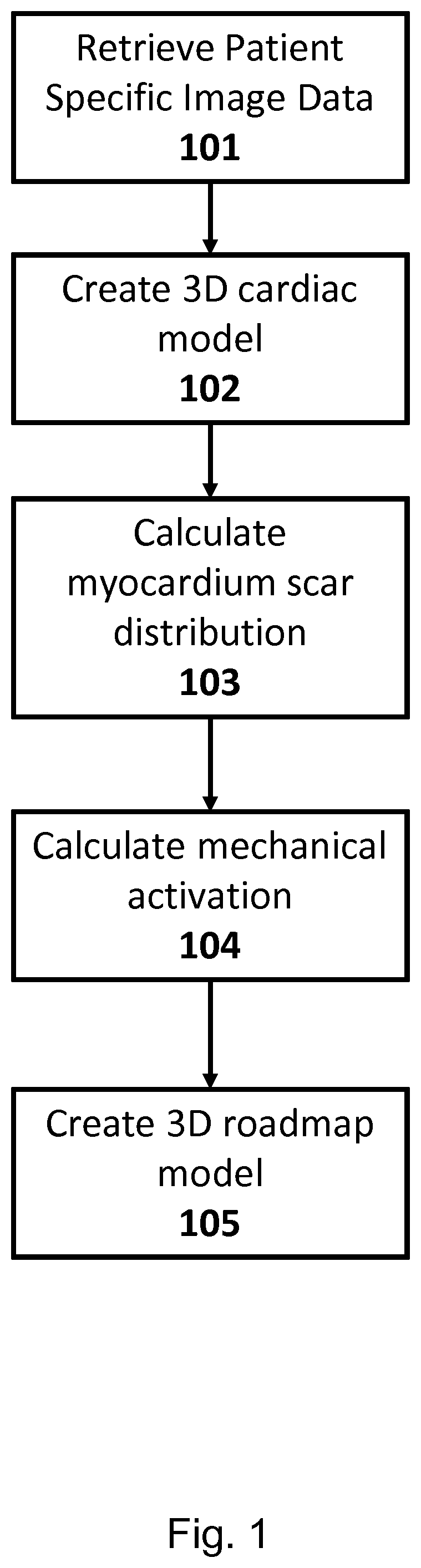
Methods and systems for guidance in cardiac resynchronization therapy
A method for providing guidance in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) comprising: a) providing image data sets of the heart of a patient; b) creating a three-dimensional (3D) anatomical model of the cardiac structures; c) calculating myocardium infarct scar distribution; d) calculating heart mechanical activation data; e) superimposing the scar distribution and the mechanical activation data on the 3D anatomical model to obtain a 3D roadmap model including anatomical geometry and mechanical activation data. A corresponding device and computer program are also model disclosed.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Electrophysiologic catheter with multilevel adjustable bends
PendingCN109498151AGood adhesive performanceFacilitate surgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringCatheter
The invention provides an electrophysiologic catheter with multilevel adjustable bends. The electrophysiologic catheter comprises a first-level adjustable bend section, a second-level adjustable bendsection, a handle, a first pull wire, a second pull wire and a plurality of guide wires, the first-level adjustable bend section comprises a first pipeline and a head electrode arranged at a far end of the first pipeline, two passageways are arranged in the first pipeline along the length direction of the same, the second-level adjustable bend section comprises a second pipeline, a far end of thesecond pipeline is connected with a near end of the first pipeline, three passageways are arranged in the second pipeline along the length direction of the same, two of the three passageways of the second pipeline are communicated with the two passageways of the first pipeline, and at least one ring electrode is arranged on an outer wall of each of the first pipeline and the second pipeline. The electrophysiologic catheter with multilevel adjustable bends is capable of adapting to all heart structures in one specification, so that operation is enabled to be more convenient.
Owner:KOSSEL MEDTECH SUZHOU
left ventricular assist device
ActiveCN105597172BDestruction will notConform to the physiological anatomyBatteries circuit arrangementsControl devicesLeft ventricular sizeLap joint
The invention discloses a left ventricular assist device, which comprises a connected first pipeline and a second pipeline, blades and a driving device; the first pipeline includes a connected inflow part and an outflow part, and the first An angle of 5° to 45° is formed between a central vertical line and the second central vertical line of the outflow end face of the outflow portion; the second pipeline includes an inflow port, an outflow port, and The overlapping portion between the outflow ports, the inflow port is detachably connected to the outflow end surface, the flow area of the lap joint portion is greater than or equal to the flow area of the outflow port; the blade is rotatably connected to the outflow portion inside; the outflow portion includes a bottom wall opposite to the outflow end surface, the blades and the driving device are respectively arranged on both sides of the bottom wall, and the driving device is used to drive the blades to rotate. The left heart assist device can be built into the heart cavity without damaging the heart structure.
Owner:深圳市华畅医疗创新有限公司
Detachable heart model for teaching show
The invention discloses a detachable heart model for teaching show. The detachable heart model comprises a simulated lung, a simulated body, a left heart model and a right heart model, wherein the left heart model comprises a left ventricle model, an aorta model, a left atrium model and a pulmonary vein model; the right heart model comprises a right ventricle model, a suprahepatic vena cava model,a right atrium model and a pulmonary artery model; one side of the left heart model is hinged with one side of the right heart model by virtue of a connector; the connector comprises a left heart connecting shaft, a right heart connecting shaft and an intermediate connecting shaft; the intermediate connecting shaft is connected between the left heart connecting shaft and the right heart connecting shaft; and light strips are arranged in the heart model, the simulated lung and the simulated body according to blood circulation. According to the detachable heart model disclosed by the invention,sorting of the heart structures can be changed according to the blood circulation process in the teaching process, and the flow sequence of blood in the heart is intuitively shown. Meanwhile, the structure of each part of the heart can be independently displayed, and the teaching efficiency is improved.
Owner:陈琼
Deep learning atrial septal defect detection method and device
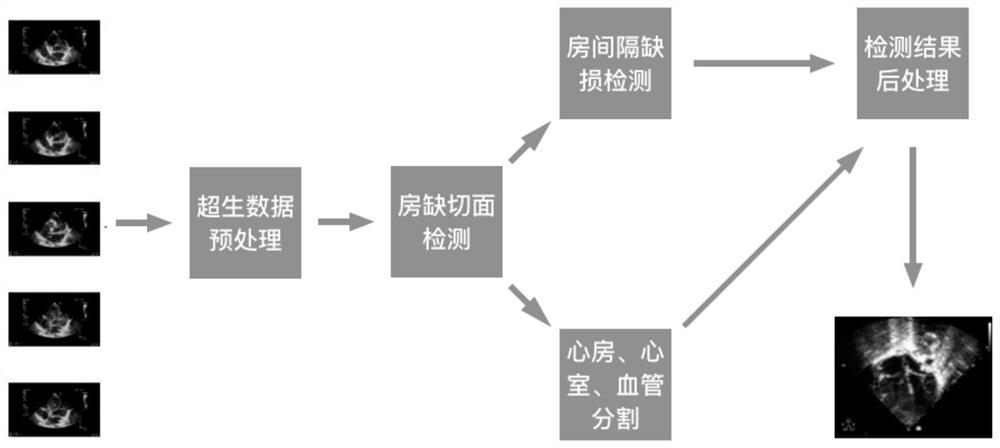
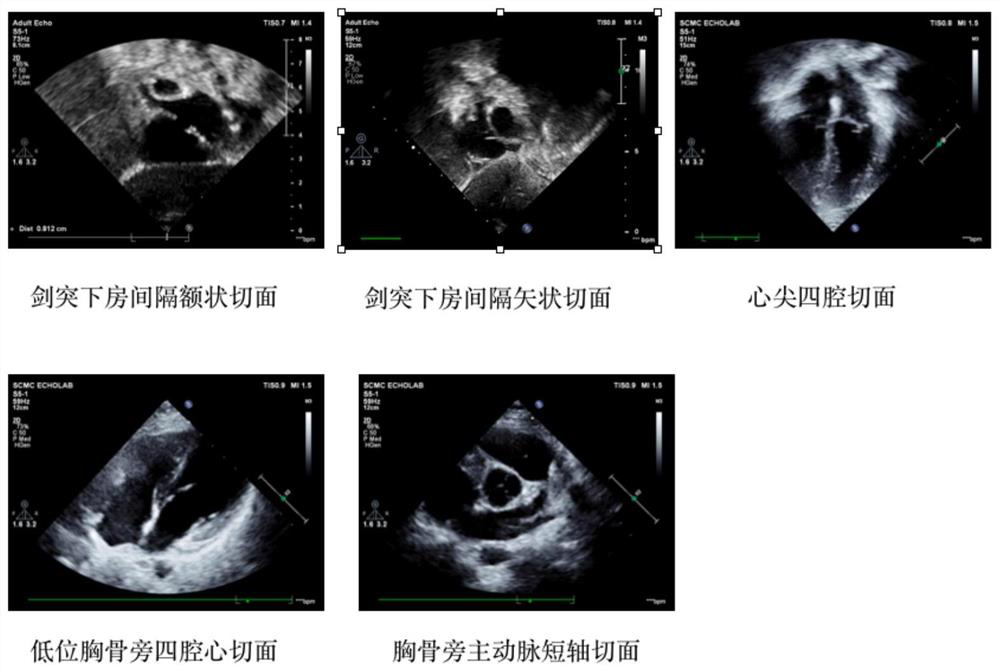
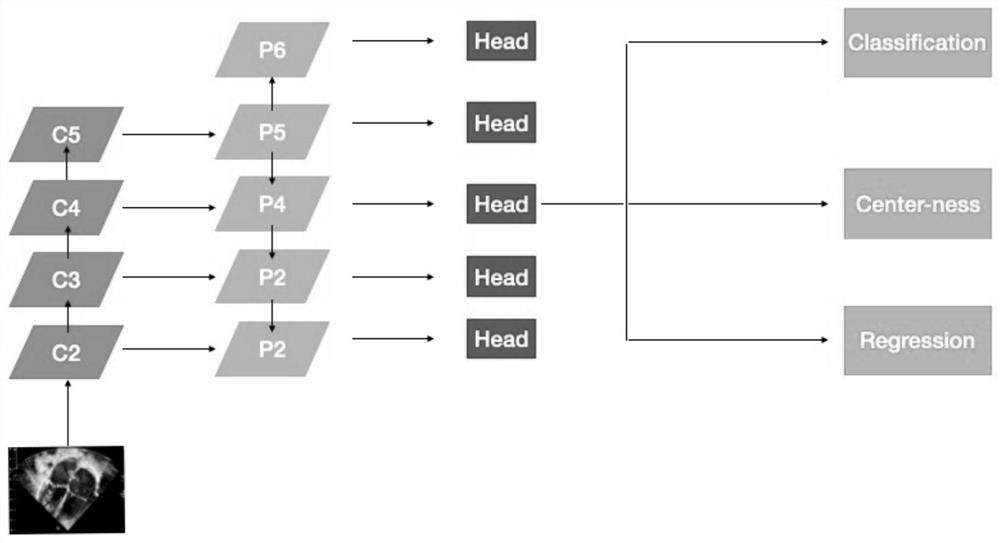
PendingCN111915557AAvoid detection processImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHeart apexRight atrium
The invention provides a deep learning atrial septal defect detection method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an ultrasonic cardiogram, preprocessing the ultrasonic cardiogram, and extracting a region of interest; carrying out feature extraction on the region of interest, and identifying a subsword process atrial septal frontal section, a subsword process atrial septal sagittal section, a cardiac apex four-cavity cardiac tangent plane, a low-position paracarpal four-cavity cardiac tangent plane and a paracarpal aorta short-axis tangent plane; detecting the minimum distance point of the atrial septal defect; segmenting heart structures of a subsword atrial septal frontal section, a subsword atrial septal sagittal section, a cardiac apex four-cavity cardiac tangent plane, a low paracardial four-cavity cardiac tangent plane and a paracardial aorta minor axis section to obtain segmentation results, the heart structures including a left atrium, a right atrium, a left ventricle, a right ventricle, an aorta and pulmonary arteries; and according to the segmentation results, filtering the detected minimum distance point bounding box of the atrial septal defect, andtaking the filtered result as an atrial septal defect detection result.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +2
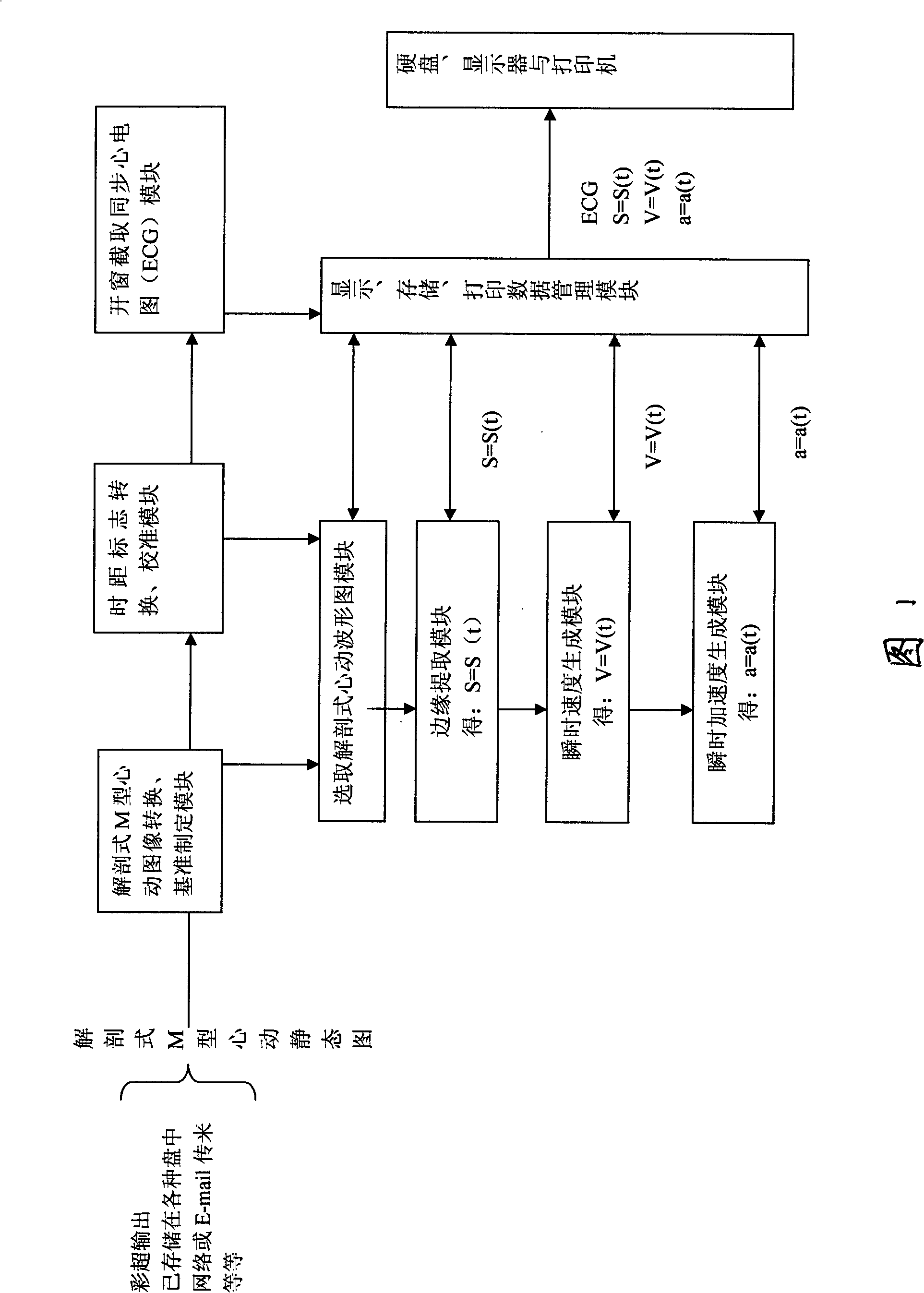
Method for testing instantaneous speed and accelerated speed of dissection type M type kinetocardiogram
InactiveCN101297763AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesDiseaseHemodynamics
This invention relates to a detection method for an instantaneous speed and an instantaneous acceleration of an anatomic M-typed kinetocardiogram, which is characterized by comprising an edge extracting module, a speed generating module and an acceleration generating module, wherein, the edge extracting module comprises a linear template, the invention chooses waveform of the anatomic M-typed kinetocardiogram of a certain part of a certain structure randomly in the anatomic M-typed kinetocardiogram, time discrete function differentiation is made for the waveform after the edge extracting is made so as to obtain the motion speed of every moment of the part, and then the time discrete function differentiation is made for the waveform again, thus obtaining the motion acceleration of every moment of the part (a repeating part). The invention can detect the motion speed and the motion acceleration of of every moment of every part of every heart structure accurately, thus disclosing the motion information of every part of the heart further in a noninvasive mode and providing important scientific evidences for the study of the diagnosis of the heart disease and the hemodynamics.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
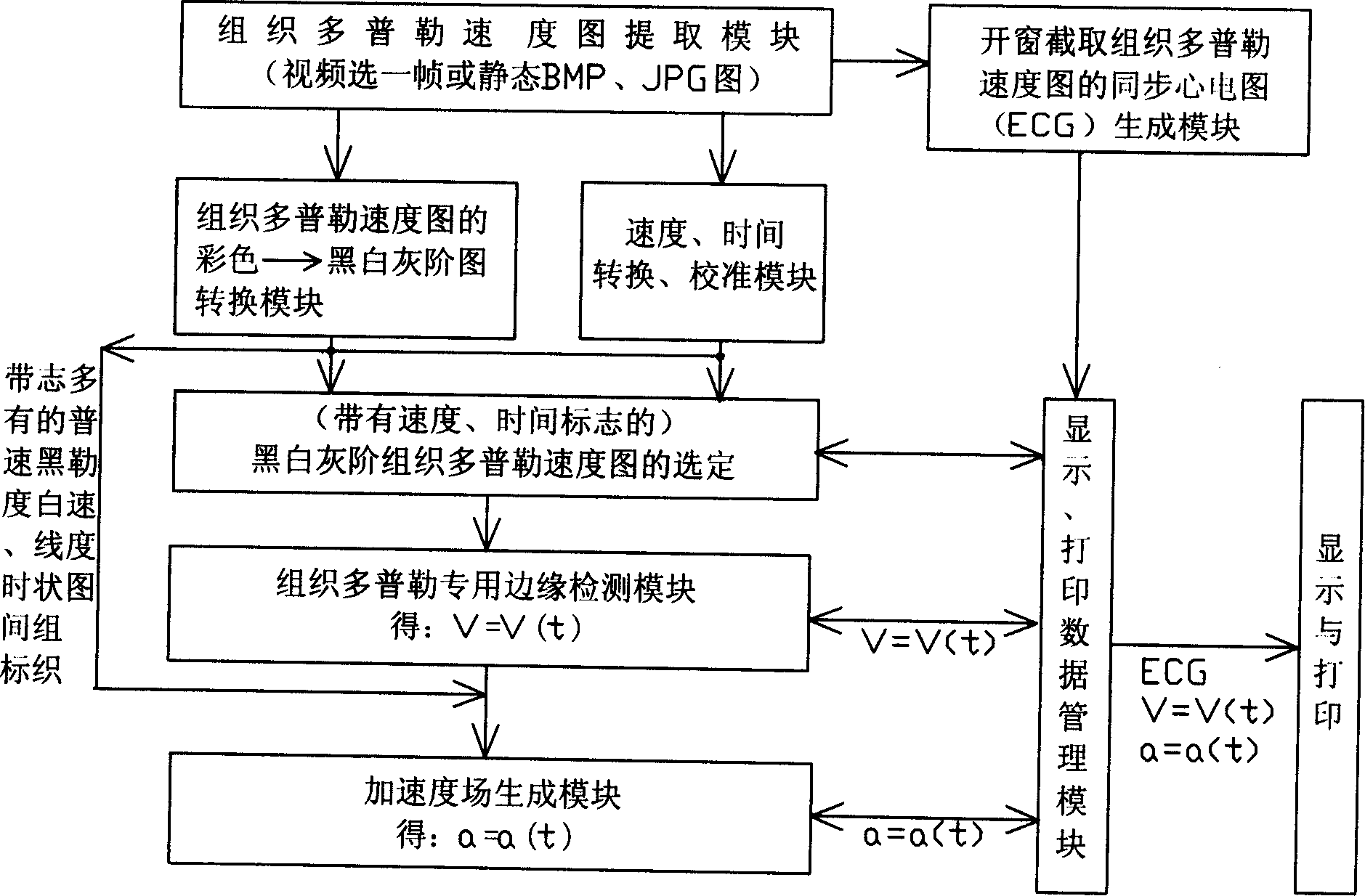
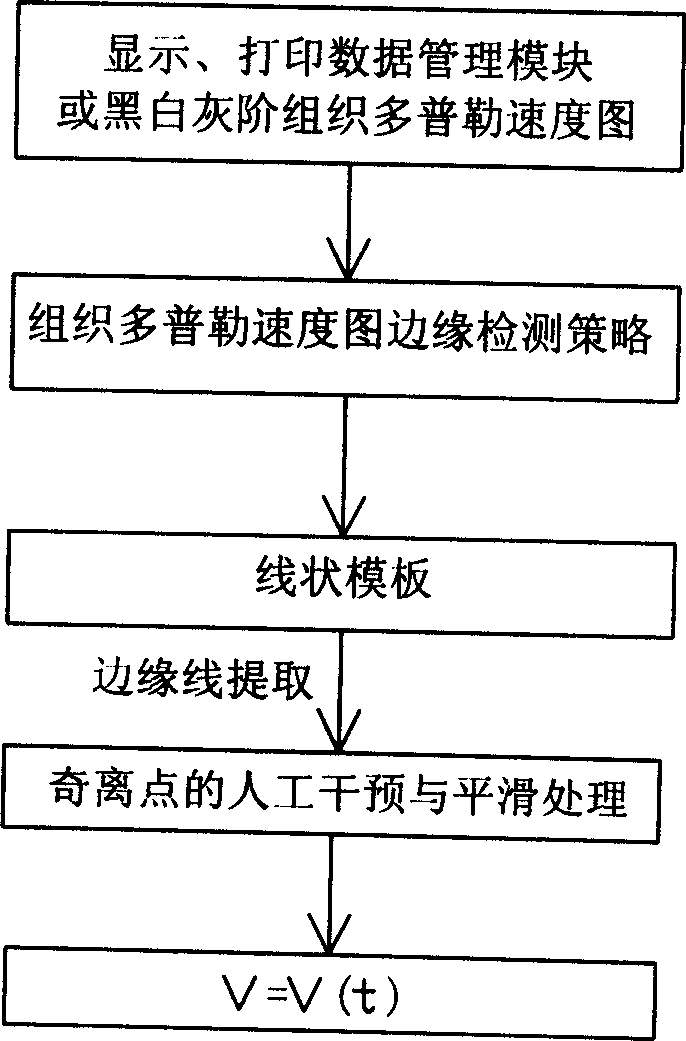
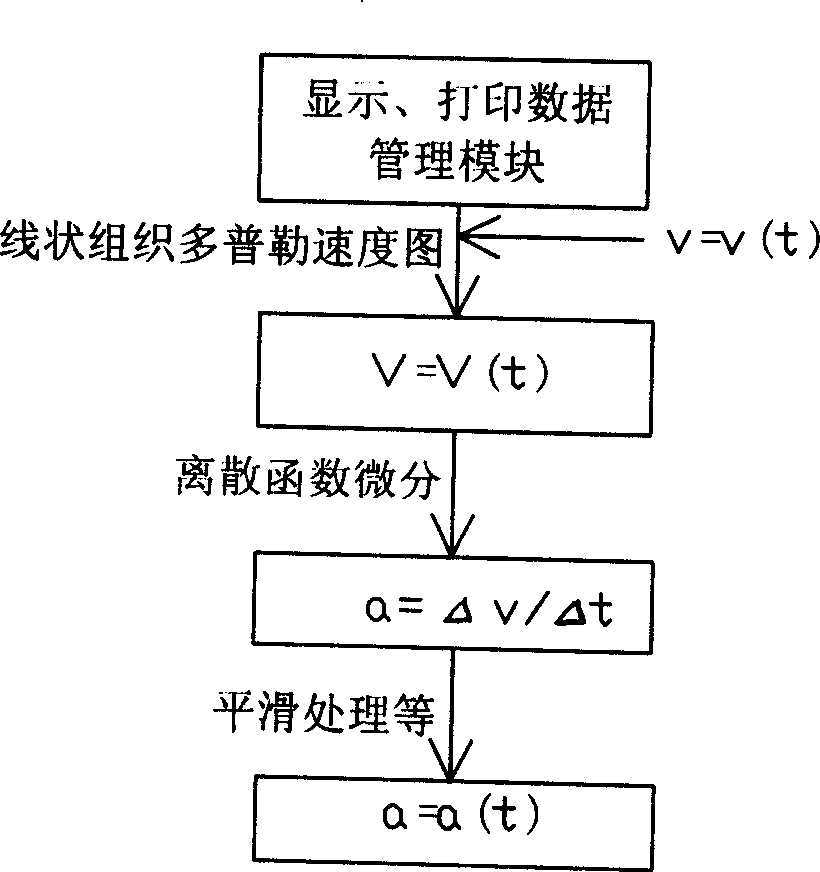
Method and apparatus for detecting acceleration field of tissue image of colorful Doppler ultrasonography
InactiveCN1732852AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcceleration measurementUltrasonography dopplerClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a detecting method of tissue Doppler acceleration field and its device in color super technique, it is about abstracting rate curve V=V(t) in some position of the heart constructions from tissue Doppler velocity diagram, doing first-order differentiation to it and getting the detection of acceleration field of the acceleration a=a(t) in said position of the heart conditions. Said invention and its device could detect the acceleration field while moving in said potion at the base of getting the velocity diagram of heart constructions in some position in color super new tech tissue Doppler detection. According to Newton's second law F=ma, the detection of acceleration offers very important information to the forced situation in said position, therefore, it has very important values to homodynamic research in different positions of the heart construction and the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com