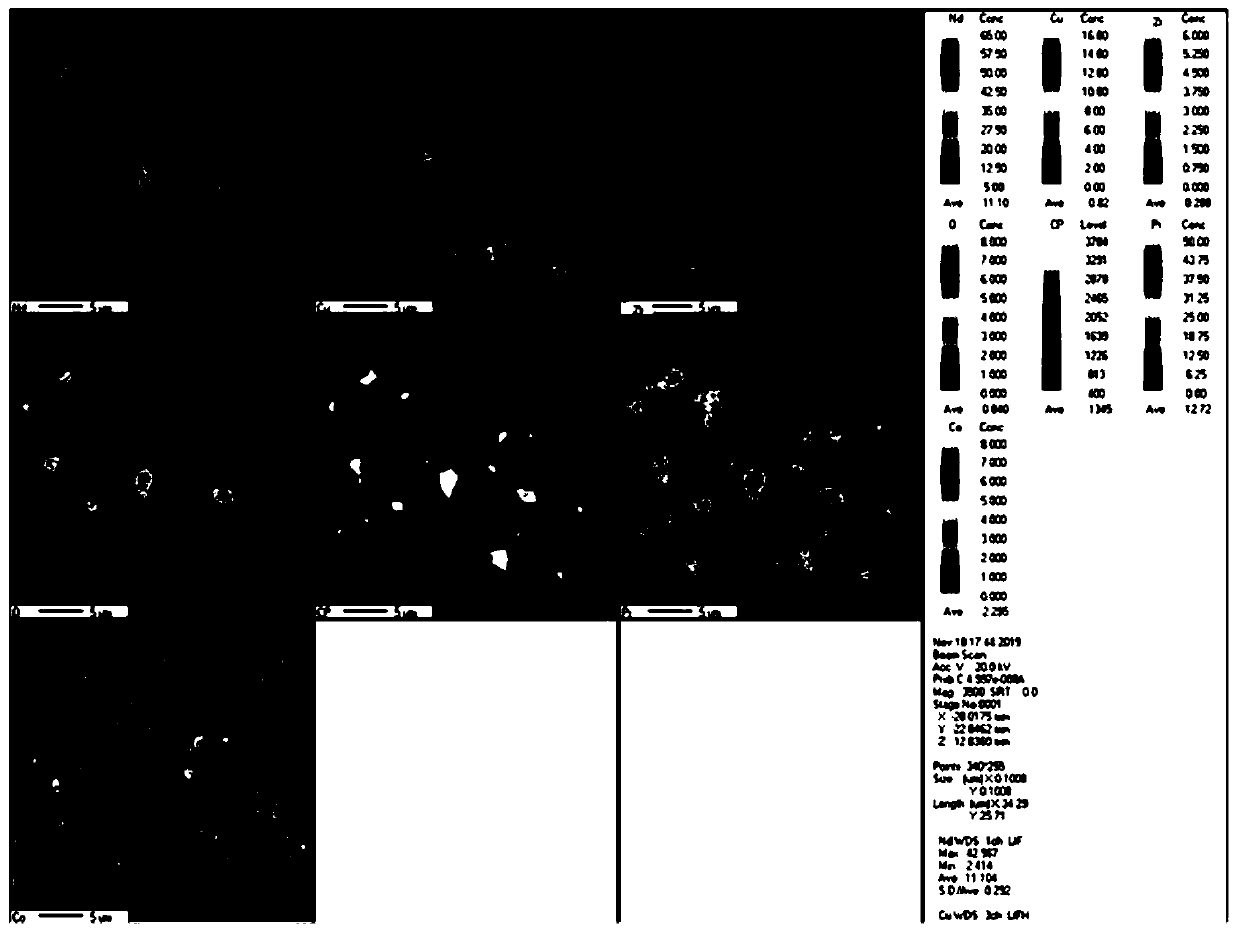
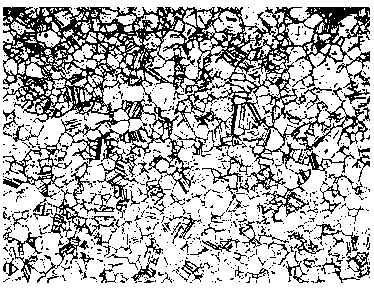
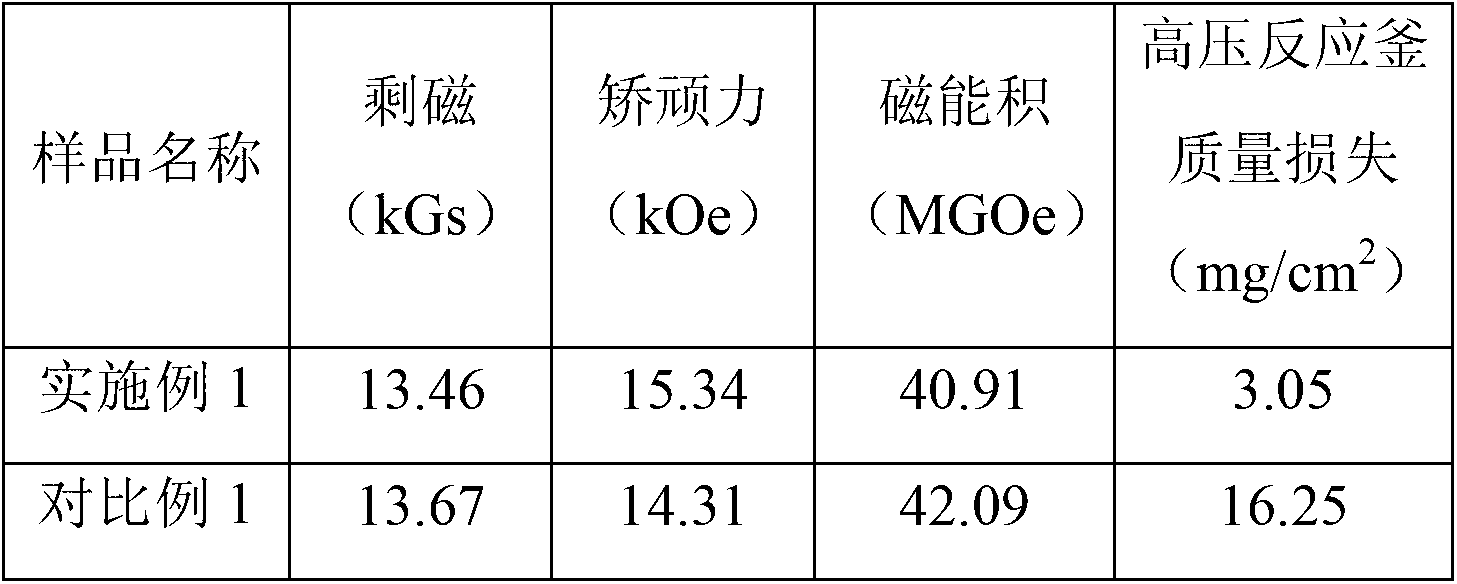
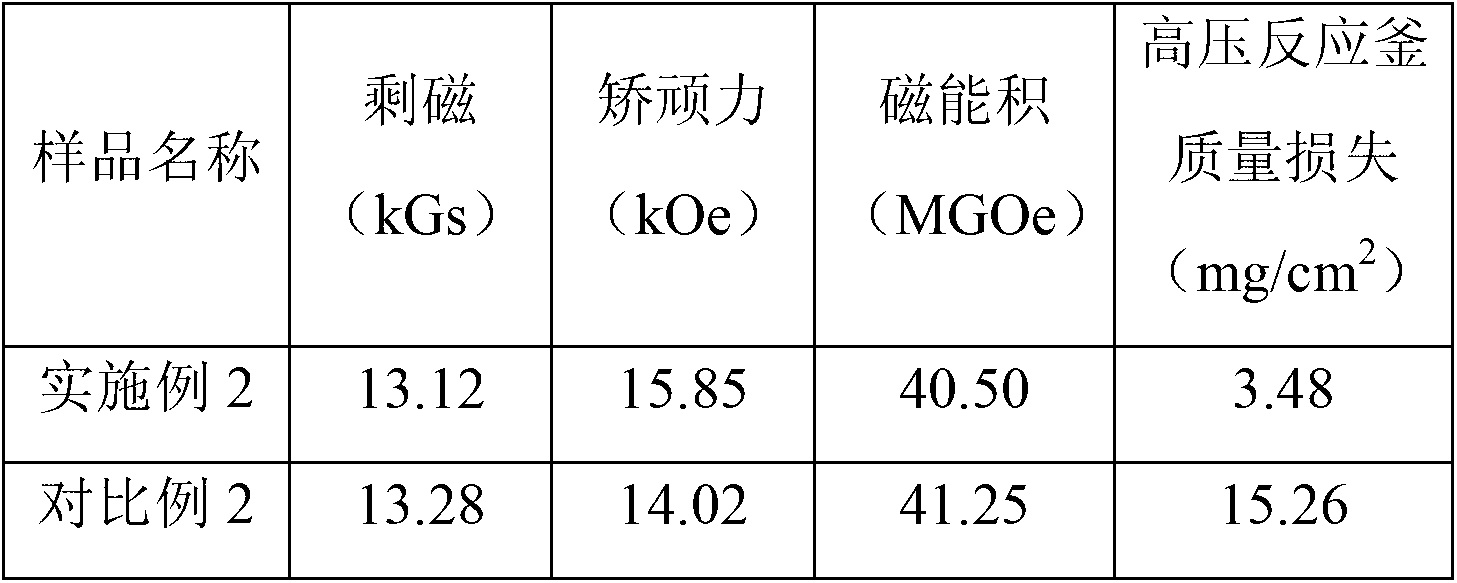
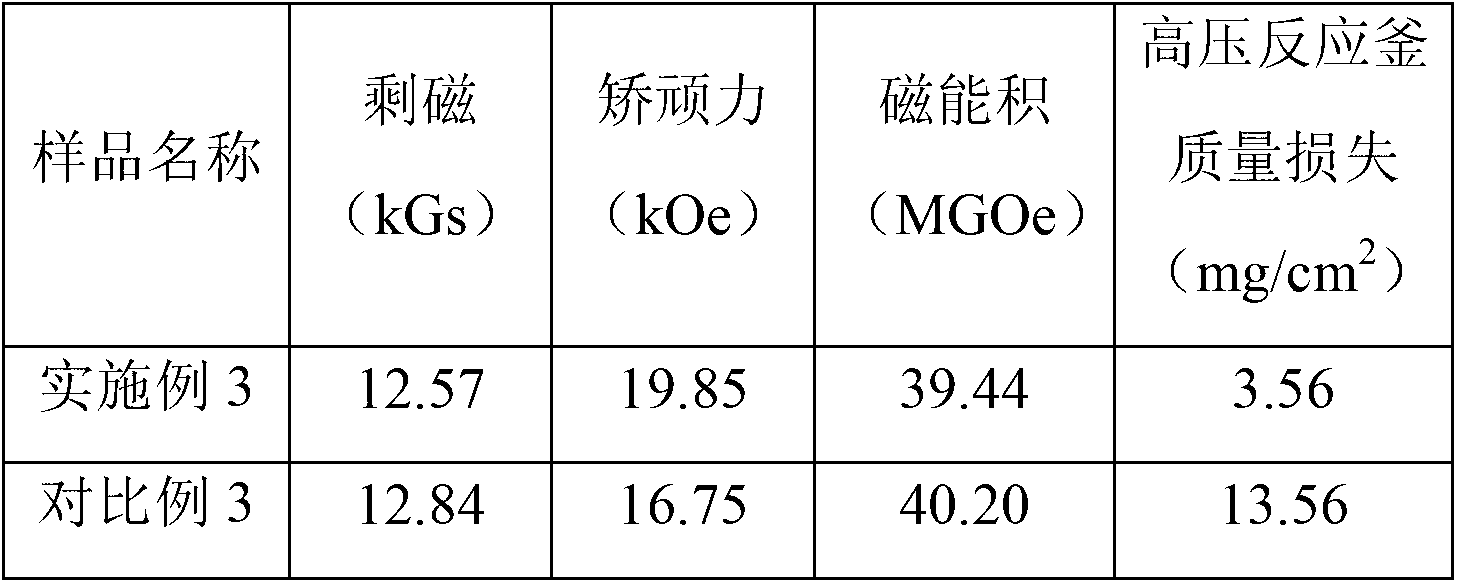
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80results about How to "Clear grain boundaries" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neodymium-iron-boron magnet material and raw material composition thereof, and preparation method and application of neodymium-iron-boron magnet material
ActiveCN110828089AImprove remanenceImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementMetallurgy
The invention discloses a neodymium-iron-boron magnet material and a raw material composition thereof, and a preparation method and application of a neodymium-iron-boron magnet material. The raw material composition of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet material is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 29.5-32% of R' which is a rare earth element and comprises Pr and Nd, wherein Pr>=17.15%; Cu being not less than 0.35%; 0.9-1.2% of B; and Fe: 64-69.2%, wherein the percentage refers to the mass percentage of the total mass of the raw material composition of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet material. According to the neodymium-iron-boron magnet material disclosed by the invention, the residual magnetism and the coercive force of the obtained neodymium-iron-boron magnet material are still relatively high under the condition that heavy rare earth elements are not added.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Metallographic etchant and metallographic etching method for pure titanium and beta titanium alloy
InactiveCN102808179AAccelerated corrosionFast corrosionPreparing sample for investigationHydrofluoric acidEtching
The invention relates to the field of metallographic etching of titanium and titanium alloy and discloses metallographic etchant and a metallographic etching method for pure titanium and beta titanium alloy. The metallographic etchant and the metallographic etching method are mainly used for metallographic etching of the pure titanium and the beta titanium alloy. The etchant consists of 10 to 40 volume parts of nitric acid, 5 to 10 volume parts of hydrofluoric acid, and 30 to 100 volume parts of water. The method comprises the following steps of: soaking a ground and polished metallographic specimen in the etchant for a certain period of time, then placing the metallographic specimen in warm absolute ethanol at the temperature of between 30 and 50 DEG C for a moment, polishing again to ensure that the etching layer is polished completely, and etching the metallographic specimen for the second time by using etchant which is similar to the etchant used in the first-time etching to obtain a single-phase metallographic structure. By the method, processing-state and annealing-state pure titanium and beta titanium alloy bars, wires and plates are subjected to metallographic etching, and the obtained single-phase metallographic structure is clear and complete in crystal boundary, and abnormal etching pits or plaques in a single crystal grain can be avoided.
Owner:西安赛特新材料科技股份有限公司
Metallographic etchant and erosion method of austenitic stainless steel
ActiveCN102517585AClear grain boundariesErosion is slowPreparing sample for investigationSS - Stainless steelAustenite
The invention relates to a metallographic etchant and an erosion method of austenitic stainless steel, which are especially suitable for metallographic erosion of 316 / 316L / 316H / 317 / 317L austenitic stainless steels. The metallographic etchant of the invention is composed of the following ingredients in percentage by volume: 30-35% of hydrochloric acid with mass percent concentration of 40%, 15-20%of nitric acid with mass percent concentration of 68%, 30-35% of propanetriol, and 15-20% of hydrogen peroxide solution with mass percent concentration of 30%. The metallographic etchant of the invention has the advantages of reasonable design, good erosion effect, good tissue display effect of eroded sample, non-pollution and slow and stable erosion reaction.
Owner:ZHENSHI GROUP EASTERN SPECIAL STEEL
Nickel-chromium alloy metallographic corrosion solution and corrosion method
InactiveCN104513985AGrain contrast is obviousFast corrosionPreparing sample for investigationAcetic acidAlcohol
The invention relates to a nickel-chromium alloy metallographic corrosion solution and a corrosion method. The corrosion solution is a mixed solution of concentrated nitric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid, glacial acetic acid and water in a volume ratio of 1:1:1:1. The concrete steps include: (1) preparing the corrosion solution, firstly adding water into a container, then adding concentrated nitric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid and glacial acetic acid respectively, conducting stirring and then performing standing for 10-20min; (2) dripping the corrosion solution on the corrosion surface of a ground and polished nickel-chromium alloy metallographic sample, immersing the sample into the corrosion solution to a depth of 1-2mm, and controlling the corrosion time at 10s-10min; (3) flushing the sample surface with distilled water for more than 2min; and (4) flushing the sample surface with alcohol, and then wiping the sample surface with alcohol-carrying absorbent cotton. According to the invention, the corroded metallographic sample has obvious grain contrast and clear grain boundary line, and at the same time, the defects of under-corrosion and over-corrosion can be avoided. The corrosion solution can rapidly and efficiently corrode the metallographic structure of the sample.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Low-temperature sintered high-permeability NiCuZn ferrite material
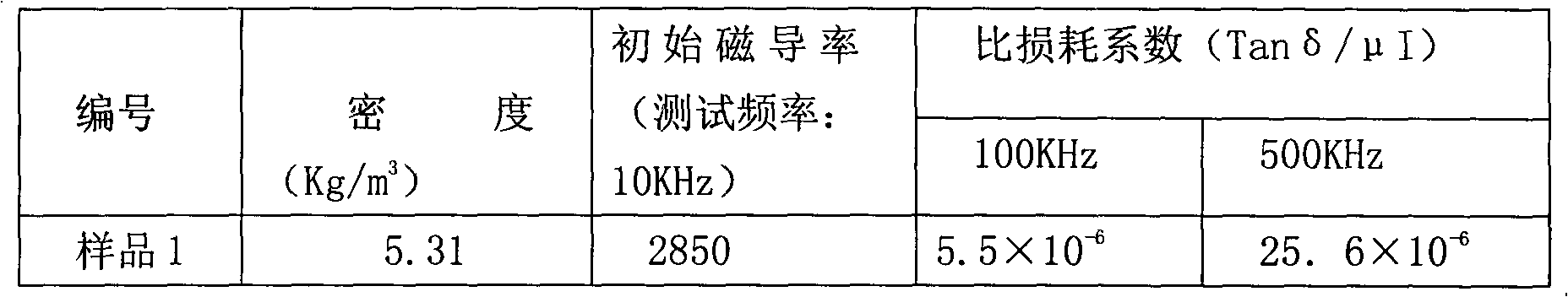
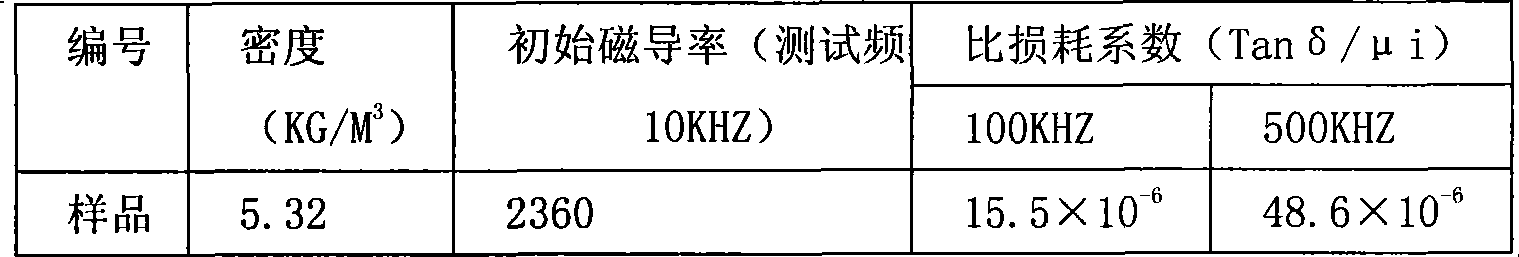
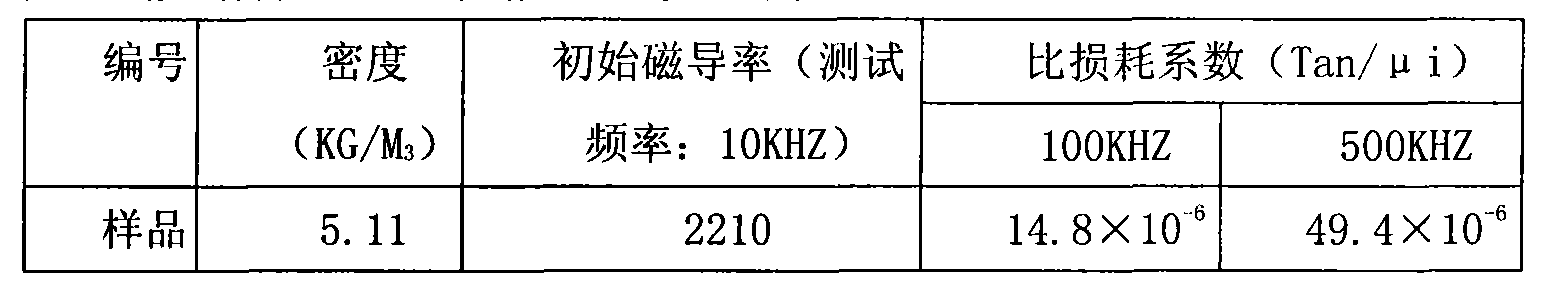
The invention discloses a low-temperature sintered high-permeability NiCuZn ferrite material for a wire wound chip inductor and a preparation method of the ferrite material. The ferrite material comprises the following main components based on oxide content: 40.5 to 49.6 moles percent of Fe2O3, 30 to 47 moles percent of ZnO, 5 to 20 moles percent of CuO and the balance of NiO. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing raw materials, (2) performing primary sanding, (3) performing primary spray drying and granulation, (4) pre-sintering, (5) adding trace elements, (6) performing secondary sanding, (7) performing secondary spray drying and granulation, (8) molding and (9) sintering. By adding auxiliary components such as NaCO3, B2O3, Ta2O5 and the like, the sintering temperature is greatly reduced, the sintering temperature is below 900 DEG C, the high-frequency electromagnetic performance of the material is greatly improved, the sintering density of the material is improved, the mechanical strength of the material is improved, and the manufacturing process requirement of the wire wound chip inductor is met; and on the other hand, energy is saved, and the producing and manufacturing costs are greatly reduced. The initial permeability of the material is 2,850; the specific loss coefficient of the material is less than 5.5*10<-6> under the test conditions of 100 kHz and 0.25mT; and the specific loss coefficient of the material is less than 25.6*10<-6> under the test conditions of 500 kHz and 0.25mT.
Owner:TAIXING ZHONGHENG BUILDING DECORATION ENGCO
High aluminum zinc alloy etching agent and use method thereof
InactiveCN101880881AClear grain boundariesEasy to distinguishPreparing sample for investigationPicric acidCorrosion
The invention relates to a high aluminum zinc alloy etching agent, which can be used for preparing the metallurgical sample of cast and solution treated high aluminum zinc alloy, and is especially suitable for the high aluminum zinc alloy modified by adding zirconium, rare earth and the like. The etching agent comprises hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, glacial acetic acid, picric acid, anhydrous ethanol and water. The corrosion method of the metallic phase of high aluminum zinc alloy using the etching agent is as follows: (1) corrosion, the high aluminum zinc alloy sample after grinding and polishing treatment is immersed in the etching agent at a temperature of 15-30 DEG C, is corroded for 3-15 seconds under the swing condition and taken out; (2) cleaning, the high aluminum zinc alloy sample taken out of the etching agent is immersed in the anhydrous ethanol, and is taken out after ultrasonic cleaning; and (3) drying, the cleaned high aluminum zinc alloy sample is dried by cold wind at room temperature. The metallurgical etching agent of the invention is adopted, so that the metallurgical structure grain boundary is clear, and a second phase is easy to distinguish; and the etching agent has the advantages of short corrosion time of the sample, simple preparation process of the etching agent and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical metallographic etching method universal for nickel-based alloys
InactiveCN101655426AFlat surfaceClear grain boundariesPreparing sample for investigationGlycerolPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses an electrochemical metallographic etching method universal for nickel-based alloys and relates to the electrochemical etching of the metallographic structure of a metal material. The method adopts the electrochemical metallographic etching method and takes an etching solution as a conducting medium, a metallographic specimen to be observed as an anode and a platinum electrode as cathode; the etching-control conditions comprise: the constant etching voltage: 2V / cm<2>-8Vcm<2>, the etching time: 1min-5min, the etching solution thereof contains in percentage by weight, 65%-85% of phosphoric acid, 5%-15% of sulfuric acid, 8%-15% of chromic acid and 3%-8% of glycerol, the prepared high-temperature corrosion-proof nickel-based alloys such as G-3, 825, X750 and the like have flat surface of metallograph, clear crystal boundary and clear crystal grain. Compared with chemical etching method, the electrochemical metallographic etching method has easily-controlled experimental conditions, good experimental repeatability and high experimental efficiency and is suitable for Ni-Fe-Cr alloys.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Metallurgical phase corrosive agent
The invention relates to a metallurgical phase corrosive agent, in particular to a metallurgical phase corrosive agent suitable to be used for beta titanium alloy at the aging state. The corrosive agent comprises the following components in percentage by volume: 5 to 10 percent of hydrofluoric acid (the mass percentage concentration is 40 percent), 10 to 20 percent of nitric acid(the mass percentage concentration is 65 percent), 20 to 30 percent of ethanol(absolute ethyl alcohol) and the balance of water. By using the metallurgical phase corrosive agent, the metallurgical phase observing surface is smooth and bright, the crystal boundary of the metallurgical structure is clear, and the alpha phase, dispersively precipitated, or other precipitated phases can be easily identified, so that the metallurgical phase corrosive agent is particularly suitable to be used as the metallurgical phase corrosive agent of the beta titanium alloy at the aging state.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
High magnetic conductive low temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrite material
InactiveCN101388268AUniform grain sizeClear grain boundariesInorganic material magnetismOxideMaterials science
The invention relates to a NiCuZn ferrite material with high magnetic permeability and low-temperature sintering, whose main phase is a spinel structure, the compositions which are calculated through oxide content are that Fe2O3 is 41-52.8mol%, ZuO is 20-45mol%, and CuO is 1-14mol%, NiO is 2-15mol%. MoO3 and In2O3 are used as additive based on the above materials, MoO3: 0.15wt%-0.25wt% is added, and In2O3: 0.12wt%-0.45wt% is added. Ferrite blanks which are prepared are put in a furnace to be sintered, the sintering temperature is 910-950 DEG C, the sintering time is 6-20 hours, and the temperature is kept for 2-4 hours.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGRUI ELECTRONICS
Metallographic etching agent
The invention discloses a corrosive for metallography, which is composed of hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid, acetone, acetic anhydride and water. With the inventive corrosive, the metallographic observation surface is bright, the grain boundary of metallurgical structure is clear, and the alpha phase or other phases precipitated by diffusion are easy to distinguish. The invention is particularly suitable for the use as a corrosive for approximate beta Ti alloys and metastable beta Ti alloys.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Metallographical corrosive liquid and preparation method thereof and 2205 duplex stainless steel metallographical display method
InactiveCN103924246AResponse is smooth and safeEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationMicroscopic observationDistilled water
The invention discloses a metallographical corrosive liquid and a preparation method thereof and a 2205 duplex stainless steel metallographical display method. The metallographical corrosive liquid is composed of potassium metabisulfite, hydrochloric acid and distilled water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving potassium metabisulfite with distilled water at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C, then adding hydrochloric acid and uniformly stirring, so that the metallographical corrosive liquid is prepared. The 2205 duplex stainless steel metallographical display method comprises the following steps: polishing, cleaning and drying a 2205 duplex stainless steel sample, so that a sample to be detected is obtained; corroding for 10-20 minutes by adopting the metallographical corrosive liquid until the metallographical surface of the sample turns black, so that a sample for observation is obtained, and observing by adopting a metallographical microscope. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages and characteristics that the corrosive liquid is simple to prepare and pollution-free; the preparation method is simple and rapid, and black ferrite crystal particles and white austenite crystal particle tissue can be observed more obviously.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel metallography corrosion agent and austenitic stainless steel metallography display method
InactiveCN104532242AEasy to getReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationAcetic acidHydrofluoric acid
The invention provides an austenitic stainless steel metallography corrosion agent with good erosion effect, and an austenitic stainless steel metallography display method. The corrosion agent has the advantages of simple preparation, convenient operation and small pollution, and the display method had the advantages of good stability and reappearance, and rapid, uniform and clear display of the microstructure. The display method comprises the following steps: mixing 1 part by volume of nitric acid with the mass concentration of 65-68% with 3 parts by volume of hydrochloric acid with the mass concentration of 36-38%, 1.5-3 parts by volume of acetic acid with the mass concentration of 36% and 1 part by volume of hydrofluoric acid with the mass concentration of 40% or more, slightly stirring by using a stirring bar for 20s, standing for 30min to prepare the corrosion agent; immersing a polished austenitic stainless steel sample in the corrosion agent, making the corrosion surface of the sample vertical to the surface of the corrosion agent during immersion, slightly stirring the sample, and allowing the sample to be immersed for 35-60s until the corrosion surface is argenteous; and taking out the immersed sample, flushing by using clear water, carrying out spray washing by using anhydrous ethanol, and carrying out blow drying to obtain the austenitic stainless steel structure to be observed.
Owner:ZHENSHI GROUP EASTERN SPECIAL STEEL
Mg-Cu grain boundary modified high-magnetism sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN103971875AClear grain boundariesLower sintering temperatureInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementCerium
The invention discloses an Mg-Cu grain boundary modified high-magnetism sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet and a preparation process thereof. The Mg-Cu grain boundary modified high-magnetism sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet is represented by (RE<x>Fe<100-x-y>B<y>)<100-u> (Mg<100-z>Cu<z>), wherein RE comprises one or two of Nd, Pr, Ce and La. By adopting the mode of adding magnesium copper alloy into a grain boundary in primary alloy RE<x>Fe<100-x-y>B<y>, Mg and Cu do not diffuse into a principle phase of the magnet and can offer help to improving an organization structure of the grain boundary, improvement on H<c> and BH<max> without doping Dy / Tb is achieved, and comprehensive magnetic performance of the Mg-Cu grain boundary modified high-magnetism sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet satisfies the formula of (BH)<max>(MG0e)+ H<c>(K0e) >= 65. According the preparation method, the primary alloy RE<x>Fe<100-x-y>B<y> and auxiliary alloy Mg<100-z>Cu<z> are prepared through smelting methods, and powder preparation, and powder mixing, orientation forming, sintering and processing are performed on the primary alloy RE<x>Fe<100-x-y>B<y> and auxiliary alloy Mg<100-z>Cu<z> to obtain the permanent magnet. The preparation process is simple, and large-scale industrial production can be achieved by means of the preparation process.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Forging method capable of improving structure uniformity of titanium alloy forging stock
ActiveCN108057829AClear grain boundariesGuarantee organizationMetal-working apparatusTitanium alloyTransition temperature
The invention discloses a forging method capable of improving structure uniformity of a titanium alloy forging stock. Differential thermal analyzing is used for measuring the phase transformation temperature beta t of a titanium alloy blank to be forged; under the temperature from (beta t+100) DEG C to (beta t+150) DEG C, heat preservation is carried out for 4 hours to 6 hours, and the blank to beforged is forged into a square blank; the obtained square blank is subject to heat preservation for 2 hours to 4 hours at the temperature from (beta t-20) DEG C to (beta t-10) DEG C, second-heating forging is carried out, the obtained square blank is subject to free drawing until the deformation amount reaches 50% to 60% of the total deformation amount, and the square blank obtained after free drawing is obtained; the obtained square blank obtained after free drawing rotates by 45 degrees around the center axis of the length direction of the square blank, pressing is carried out, and the final square blank is obtained; and the macrostructure of the cross section of the forge blank obtained after machining is uniform, the grain boundary is clear, no special-shaped piebald defects exist, the microstructure is uniform and consistent, the whole is of a net basket structure or equal-axis structure, and the edge and heart structures have no difference.
Owner:西安赛特思迈钛业有限公司
Method for displaying metallurgical structure of ultralow-carbon cold roll annealed interstitial-free steel
ActiveCN101984334AClear grain boundariesAvoid erosionPreparing sample for investigationAqueous alcoholDistilled water
The invention relates to a method for displaying the metallurgical structure of ultralow-carbon cold roll annealed interstitial-free steel, which belongs to the technical field of physical detection. The invention is used for realizing the aims of clear display and easy operation of the metallurgical structure of ultralow-carbon cold roll annealed interstitial-free steel. The method comprises the following steps: a. coarse grinding; b. polishing; c. erosion by a first reagent: eroding the polished sample in the first reagent for 10-20 seconds, wherein the first reagent is 5.5-6.5% nitric acid alcohol; d. erosion by a second reagent: eroding the sample in the second reagent immediately after taking out the sample from the first reagent, until the sample surface is evenly black, wherein the second reagent is prepared from 3-7g of sodium pyrosulfite, 9-12g of anhydrous sodium thiosulfate and 70-100ml of distilled water; and e. sample detection: wiping the sample with the first reagent to remove black on the surface, rinsing with alcohol, and blow-drying so that people can observe the sample. The method has the advantages of simpleness, simplified steps, easy master, resource conservation and high efficiency; the obtained structure has the advantages of clear grain boundary and no double grain boundary, and can properly reflect the annealing situation; and thus, the method is very suitable for field usage, and performs important functions on reasonably controlling technological parameters and ensuring product performance in the production field.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
High-strength and fatigue-resistant titanium ring and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN107012364AHigh precisionImprove impact resistanceLaser beam welding apparatusIngotTitanium
The invention provides a high-strength and fatigue-resistant titanium ring and a preparing method thereof. The high-strength and fatigue-resistant titanium ring is Ti-Al-Mo-V-Cr series alloy, wherein Ti alloy comprises a primary alpha phase of which the transverse-to-longitudinal ratio is 1-3. The preparing method specifically comprises: adopting sponge titanium, pure Al, pure Cr, Al-Mo intermediate alloy, Al-V intermediate alloy and Ti-Mo intermediate alloy as raw materials, pressing the materials into a consumable electrode under the condition that the purity is larger than 99%, and making a Ti-Al-Mo-V-Cr alloy ingot through the two-times smelting of a vacuum consumable electro-arc furnace; then, through cogging, deforming and repeated upsetting and drawing which are carried out at temperature lowered to 750-820DEG C, making a Ti ingot bar or plate after the accommodated deformation quantity is larger than 70%; after forging, rolling, heat treatment, levelling and machining, making a titanium plate; washing the titanium plate to remove dirt on the surface; then, engraving the grid surface of the titanium plate by using laser, and rolling the engraved titanium plate into the titanium ring by using a rolling machine; and finally carrying out washing and drying to obtain the high-strength and fatigue-resistant titanium ring.
Owner:郭和谦
Manufacturing technology for rare earth-magnesium alloy
The invention belongs to the fields of metal materials and metallurgy, aims to solve the problems that impurities of alloy are hard to separate, ingredients are nonuniform, the utilization rate of rare earth element is low, precipitated rare earth phases are nonuniform, the segregation is more, and effects for the quality is great by adopting the manner that alloying, rare earth process, and casting are conducted in a pot during a conventional manufacturing technology process, and provides a manufacturing technology for rare earth-magnesium alloy. According to the manufacturing technology, conducting adding, refining, and degassing with hexachloroethane degassing agent of alloy element in a melting pot; and pouring into a second pot after standing for 30 min, adding rare earth, and standing and casing. A manufactured bar material has uniform and stable metallographic structure and clear crystal boundary; the product is without pore, shrinkage cavity and cold shut, and the surface is smooth and without rugosity; the purity, ingredients, and equilibrium of physical properties of the product are guaranteed, the grain size of the alloy is refined, very stable dispersed phase is precipitated, and the rigidity and the decay resistance of texture are improved; therefore, product performances are allowed to be superior to an ordinary alloy standard.
Owner:孝义市东义镁业有限公司 +1
Processing method for crystal patterns of titanium product
InactiveCN107215139AThe process steps are simpleEase of industrial productionDecorative surface effectsTitaniumMachining process
The invention provides a processing method for crystal patterns of a titanium product. The processing method comprises the following steps that firstly, the titanium product is heat-treated under the vacuum condition; secondly, the heat-treated titanium product is polished; and thirdly, the polished titanium product is acid-pickled, and thus the titanium product with the crystal patterns is obtained. The processing method has the following effects that (1), the method comprises the three steps of heat treatment, polishing and acid pickling, the technical steps are simple, and industrial production is facilitated; (2) abnormally-thick titanium crystal grains (the size of each crystal grain can reach 1-5 mm) are obtained through heat treatment firstly, then the crystal boundaries are corroded through the polishing and acid pickling technique, so that the grain boundaries among the crystal grains are clear and visible to naked eyes, the naked eyes can see the crystal patterns with metal luster through observation, and the product yield rate is high; and (3) technical parameters in the processing process are convenient to control, reagents are easy to obtain, and the processing cost is low.
Owner:湖南湘投金天钛金属股份有限公司
(Ba<x>Ca<1-x>)(Ti<y>M<1-y>)O3 system piezoelectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates a (Ba<x>Ca<1-x>)(Ti<y>M<1-y>)O3 system piezoelectric ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The piezoelectric ceramic material can be represented by the following general formula: (Ba<x>Ca<1-x>)(Ti<y>M<1-y>)O3, wherein M is one of Zr or Sn, 0<=x<=1 and 0<=y<=1. In the invention, a ceramic sample is prepared through a method of combination of liquid-phase mixing and solid-phase sintering. By means of the method, the raw materials can be mixed more uniformly. The prepared ceramic sample is more uniform in crystal grain size, is clear in crystal boundary and is uniform and compact in structure. The ceramic sample is better in piezoelectric performances and electrostrictive strain than those of a sample prepared through a conventional solid phase method.
Owner:南通双辉医疗器械科技有限公司
Metallographic corrosion solution and use method thereof
InactiveCN108220965AClear grain boundariesJudging the grain sizePreparing sample for investigationCrystalliteBarium dichloride
The invention provides a metallographic corrosion solution and a use method thereof, relates to a corrosion solution for metallographic analysis, and particularly relates to a metallographic corrosionsolution of a C276 corrosion resistant alloy and a use method thereof. The metallographic corrosion solution is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by weight: 2-2.5g of ferric trichloride, 1.0-1.5g of barium chloride, 20-25ml of glacial acetic acid, 70-75ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and 20-25ml of concentrated nitric acid. The metallographic corrosion solution is applicable to metallographic corrosion of a C276 corrosion resistant alloy board and capable of clearly showing a metallographic structure of a C276 corrosion resistant alloy sample, and thus clearphase boundary and grain boundary can be realized; the particle size can be conveniently determined and the structure in crystal grains can be conveniently observed during scientific research and production, thus the technical parameters of each process can be adjusted, and the foundation is provided to determine the product quality.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for preparing sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material with high coercive force and high corrosion resistance
ActiveCN103060657AImprove magnetic propertiesAccelerated corrosionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare earthDysprosium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material with high coercive force and high corrosion resistance, and belongs to the technical field of a magnetic material. The method comprises the steps of adding dysprosium zinc nano powder of which the mean grain size is 1-10 microns to neodymium iron boron powder with the grain size of 3-5 microns and evenly mixing, wherein the adding amount is 0.3-3.0%, and then orienting, pressing and molding in 1.8T magnetic field; putting in a vacuum sintering furnace, then heating and sintering at 1000-1100 DEG C for 3-5 hours, and finally carrying out thermal treatment by two levels, wherein the primary thermal treatment temperature is 850-950 DEG C; the time is 1-3 hours; the secondary thermal treatment temperature is 460-600 DEG C, and the time is 1-3 hours, finally obtaining the sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material with high coercive force and high corrosion resistance. The corrosion resistance of the magnetic body is greatly improved when the coercive force of the magnetic body is obviously improved, and the rare earth content is also reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Observing method of metallographic structure of equiatomic platinum-cobalt alloy
InactiveCN107727476AReduce risk of churnLower level requirementsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansPlatinumDenture base
The invention discloses an observing method of a metallographic structure of an equiatomic platinum-cobalt alloy. The observing method comprises the steps that 1, an equiatomic PtCo alloy sample is cut on a workpiece and fixed on denture base resin; 2, the alloy sample is ground by a grinding machine and then is ground level by level by sequentially adopting number 600 metallographic abrasive paper and number 1200 metallographic abrasive paper; the polished platinum-cobalt alloy sample is subjected to mechanical polishing, and the platinum-cobalt alloy sample without remarkable scratch and contamination point is obtained; 4, the platinum-cobalt alloy obtained after mechanical polishing is placed in a corrosive container filled with a corrosive solution for etching, after etching is completed, the platinum-cobalt alloy is placed under a metallographic microscope, and thus the metallographic structure of the equiatomic platinum-cobalt alloy is observed. The sample preparing method has low requirements for levels of experimental devices and operating personnel, is suitable for preparation of the equiatomic platinum-cobalt alloy in a normal laboratory, is quite low in alloy consumption, and greatly lowers the risk of loss and waste of precious metal.
Owner:西安诺博尔稀贵金属材料股份有限公司
Production method of ceramic polished brick and ceramic polished brick produced by it
A process for preparing the polished ceramic tile includes such steps as providing raw materials, shaping, calcining and polishing. It features that said raw materials including at least one fine powder (10-70 wt%) and at least one granular material (30-90 wt.%), which have different colors and mass feelings after calcined and polished.
Owner:陈继棉
5xxx series Al-Mg alloy grain boundary corrosive liquid and corrosion method
ActiveCN113358449AAccelerated corrosionClear grain boundariesPreparing sample for investigationAlcoholEmery paper
The invention relates to a corrosion method of a 5xxx series Al-Mg alloy grain boundary, which mainly comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a corrosion liquid which comprises the following components: 80-110 mL, 15-20 mL, 0.5-3.5 mL of HF, 0.5-3 mL of HCl and 2-5 g of HCl; 2, embedding an aluminum alloy sample; 3, polishing the embedded samples sequentially with abrasive paper from low meshes to high meshes; 4, polishing the ground sample; 5, cleaning the polished sample with absolute ethyl alcohol; 6, corroding the sample for 60-90 seconds by using the prepared corrosive liquid; and 7, after corrosion patterns appear on the surface of the sample, cleaning the sample with absolute ethyl alcohol and carrying out drying treatment. After the method is used for corroding the 5xxx series Al-Mg alloy, the grain boundary of the alloy can be clearly observed, and the method is low in equipment requirement, simple in operation step, capable of saving cost, good in stability and suitable for researching the grain morphology, the grain size, the microstructure performance and the like of the Al-Mg alloy.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Manufacturing method for austenitic stainless steel bar used for nuclear power reactor
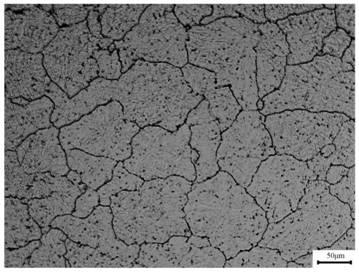
The invention provides a manufacturing method for an austenitic stainless steel bar used for a nuclear power reactor. The manufacturing method includes the following steps that firstly, first roller die drawing is conducted on the austenitic stainless steel bar, and a first drawing bar blank is obtained; secondly, first solid solution treatment is conducted on the first drawing bar blank; thirdly, second roller die drawing is conducted, and a second drawing bar blank is obtained; fourthly, the second drawing bar blank is subjected to fixed die drawing; fifthly, second solid solution treatment is conducted; and sixthly, electric heating stretcher straightening and roller type straightening are conducted, and the austenitic stainless steel bar used for the nuclear power reactor is obtained. According to the manufacturing method, the dimensional tolerance of the manufactured austenitic stainless steel bar used for the nuclear power reactor is not larger than 0.02 mm, linearity is not larger than 0.2 mm / m, the mechanical performance completely meets the requirement for ASTM A276 technology conditions, a microscopic structure is uniform and small, a crystal boundary is clear, and obvious carbide precipitation does not exist.
Owner:西安诺博尔稀贵金属材料股份有限公司
Rapid preparation method of gadolinium zirconate ceramics
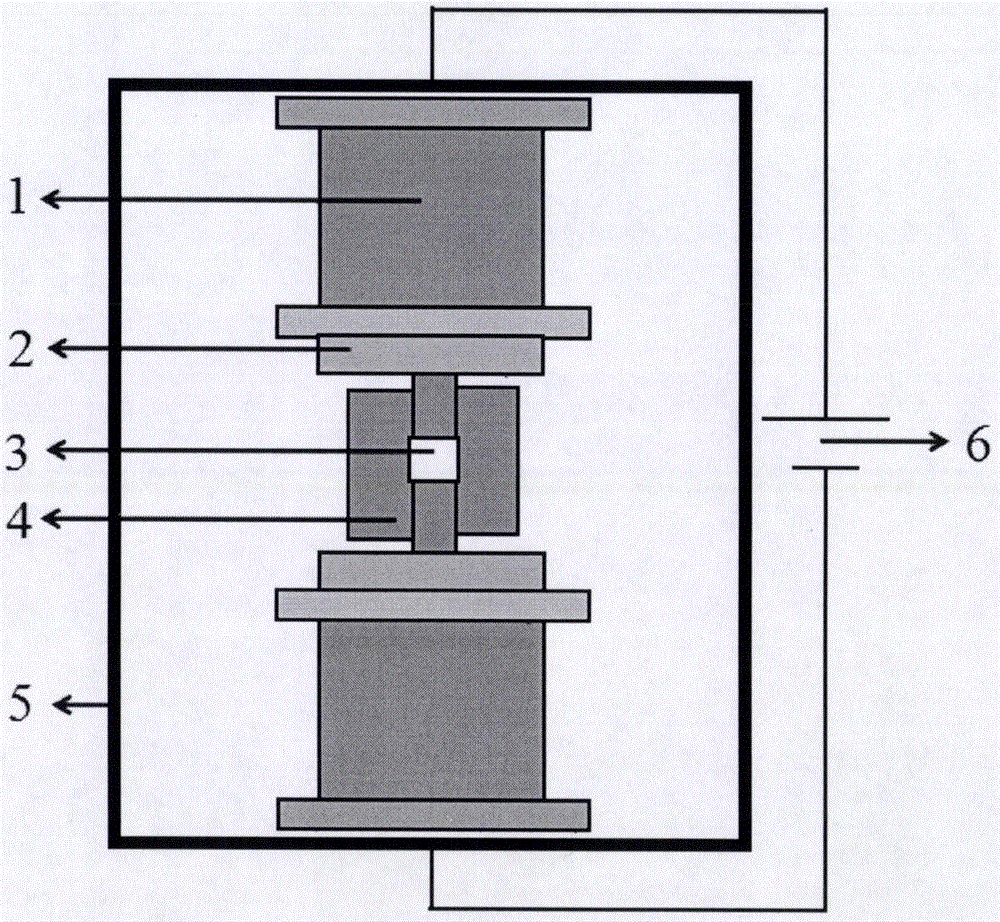
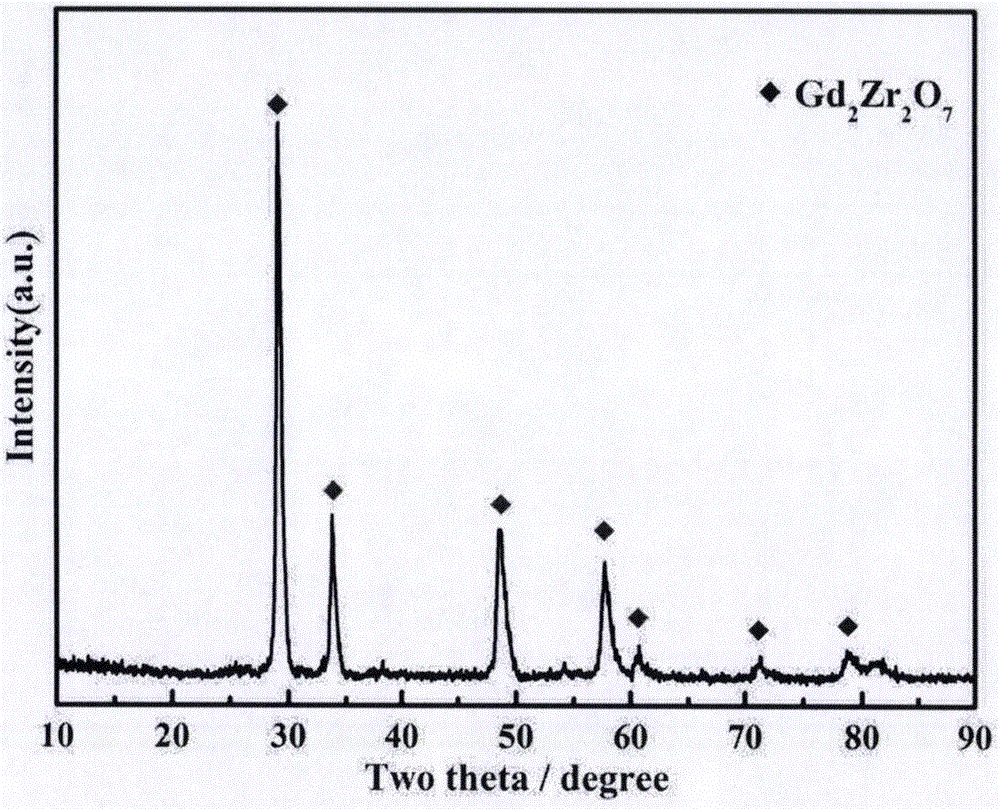
The invention discloses a rapid preparation method of gadolinium zirconate ceramics, and belongs to the field of chemical synthesis. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of mixing gadolinium oxide powder with zirconium oxide power, performing sufficient grinding to obtain mixture granules, applying a direct current pulse voltage to the mixture granules, and enabling the mixture granules to be subjected to a solid phase reaction, wherein after the reaction is completed, the gadolinium zirconate ceramics are obtained. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being high in temperature-rising rate, short in sintering time, simple in technological process, energy-saving, environmentally friendly, safe, reliable and the like. The samples of the prepared gadolinium zirconate ceramics are in single phases, and the gadolinium zirconate ceramics are high in crystallinity, high in density, clear in grain boundary, plump in crystal grains, and free from holes.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Metallographic corrosive agent for double-phase medium manganese steel and metallographic structure display method
ActiveCN112857950AGood corrosion effectEasy to knowPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansCopper chlorideAustenite
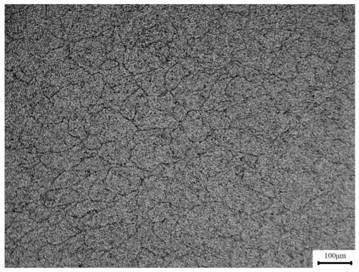
The invention provides a metallographic corrosive agent for double-phase medium manganese steel and a metallographic structure display method. The metallographic corrosive is a mixed solution formed by copper chloride dihydrate, concentrated hydrochloric acid, absolute ethyl alcohol, sodium chloride, concentrated sulfuric acid and water. The metallographic structure display method comprises the following steps: providing a double-phase medium manganese steel sample; manually grinding and mechanically polishing the double-phase medium manganese steel sample; immersing the polished medium manganese steel sample in a metallographic corrosive at the temperature of 20 to 30 DEG C, slightly rotating and stirring, corroding for 10 to 20 s and then taking out; and cleaning the corroded medium manganese steel sample with detergent, alcohol and clear water sequentially and blow-drying, and carrying out observation through a metallographic microscope. The metallographic corrosive is simple in preparation method and convenient to use, the corrosion effect is good through the method, and the austenite ferritic structure effect of the two-phase medium manganese steel material can be clearly analyzed.
Owner:沧州赛腾特种材料科技有限公司
TWIP (twinning induced plasticity) steel metallographic phase specimen preparation agent and use method thereof
InactiveCN102914465AClear grain boundariesEasy to organizePreparing sample for investigationTwipMegasonic cleaning
The invention discloses a TWIP (twinning induced plasticity) steel metallographic phase specimen preparation agent. The TWIP steel metallographic phase specimen preparation agent comprises an aggressive agent and a cleaning agent, wherein the aggressive agent is a mixed solution of nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and alcohol in volume ratio of (1-3):(0.2-0.5):100; the cleaning agent is hydrochloric acid solution in a volume ratio of (0.1-0.4):100. Polished metallographic phase grinding surface is dipped in the aggressive agent to keep for 40-80s; after the specimen is taken out, the specimen is directly put into a flask containing the cleaning agent; the specimen is put in a supersonic cleaner to oscillate and clean for 60-80s; the specimen is taken out and is cleaned for 20-40s in warm water with the temperature of 50-70 DEG C; and after the specimen is blown to be dry, an metallographic phase observation can be performed.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Corrosive for displaying austenitic stainless steel grain boundary of fine grains and method for preparing corrosive
ActiveCN102888608BAccelerated corrosionReduce corrosionPreparing sample for investigationAcetic acidThermal treatment
The invention discloses a corrosive for displaying austenitic stainless steel grain boundaries of fine grains and a method for preparing the corrosive. The corrosive is characterized by comprising the following components by weight: 80-150ml of H2O, 10-20ml of HCl, 15-25g of FeCl3, 10-15g of CuCl2 / H2O, 2.0-7.0ml of glacial acetic acid and 1-5 drops of benzalkonium bromide. The method comprises the steps of: placing CuCl2.H2O in a beaker; then adding FeCl3, and uniformly stirring after adding HCl and H2O; and uniformly mixing after adding glacial acetic acid and benzalkonium bromide finally. According to the corrosive for the austenitic stainless steel of the fine grains, the grain boundaries of the austenitic stainless steel of the fine grains in the original state and the thermal treatment state can be clearly displayed, the 100 times of rating on grain size can be easily performed, the grain boundaries are clear, the interference of a texture to the grain boundaries is small, and the corrosion effect is good.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOILER WORKS
Rock crystal structure rapid modeling method based on particle cluster substitution
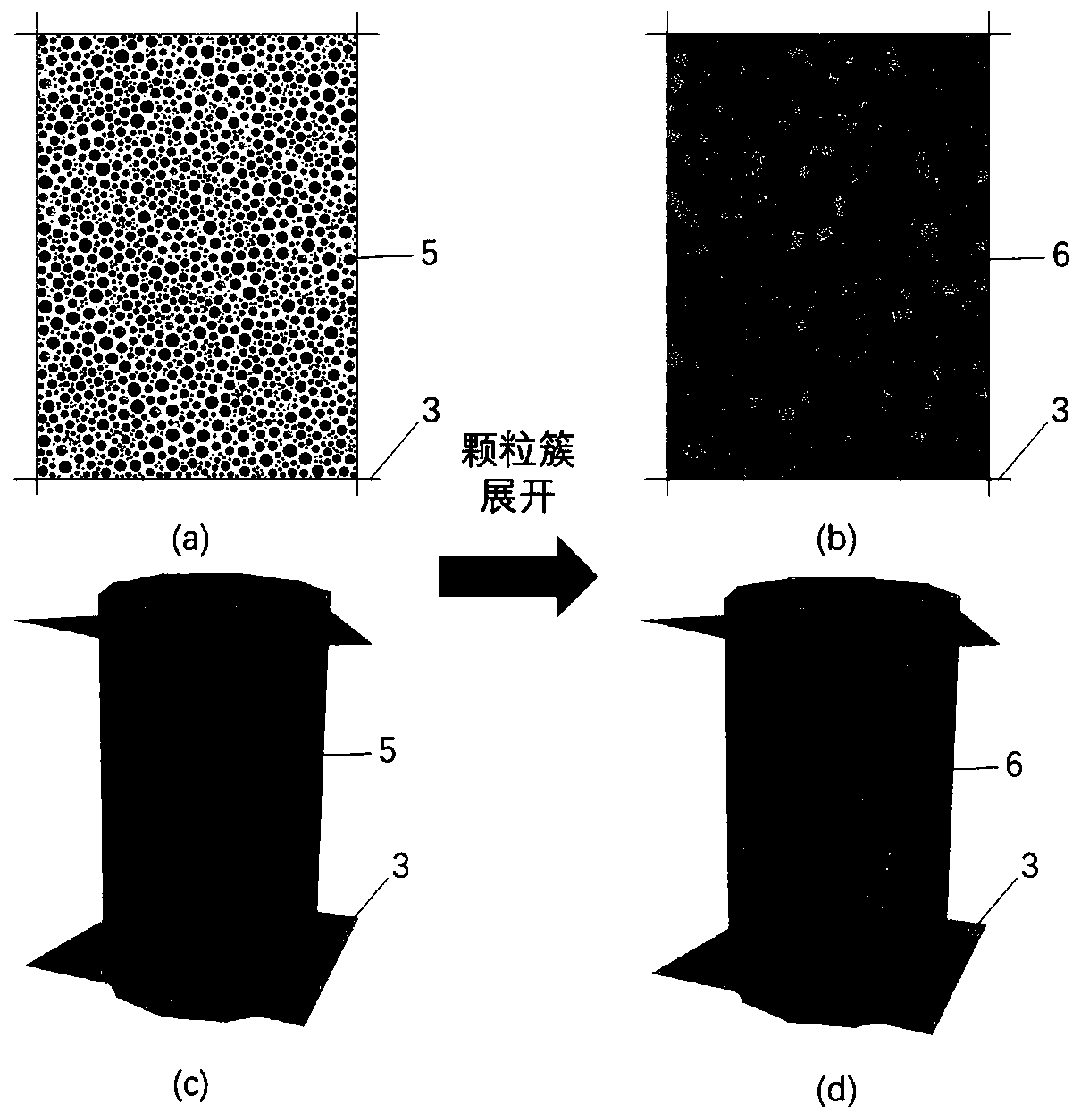
ActiveCN110990911ARealize the establishmentContains few particlesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationChemical physicsThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a rapid rock crystal structure modeling method based on particle cluster substitution, which comprises the following steps: firstly, specifying a model area in PFC (Power Factor Correction) software, establishing a boundary wall of a rock sample, analyzing and setting different put particle groups according to the crystal grain components of the sample, and endowing attribute parameters of a wall body and particles; generating particle clusters by adopting small balls with the radius reduced in equal proportion relative to the radius of original particles to replace theoriginal particles, compressing the particle clusters according to a certain proportion, and then deleting the original particles; after the particle clusters are generated, assigning attribute parameters of the particle clusters, and expanding the particle clusters into a crystal structure through expansion among particles; and finally, grouping the materials according to a contact identification method, and endowing corresponding contact model parameters to finish modeling. Compared with an existing method, rapid modeling of the rock crystal microstructure is achieved through the self-compiled FISH language function, the method is popularized to the three-dimensional space, and the method conforms to the physical process of rock crystal structure formation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com