Method for preparing sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material with high coercive force and high corrosion resistance
A high coercivity, permanent magnet material technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic material magnetism, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of grain shedding, overall alloy corrosion, etc., to achieve reduced corrosion resistance, good corrosion resistance, The effect of reducing the scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
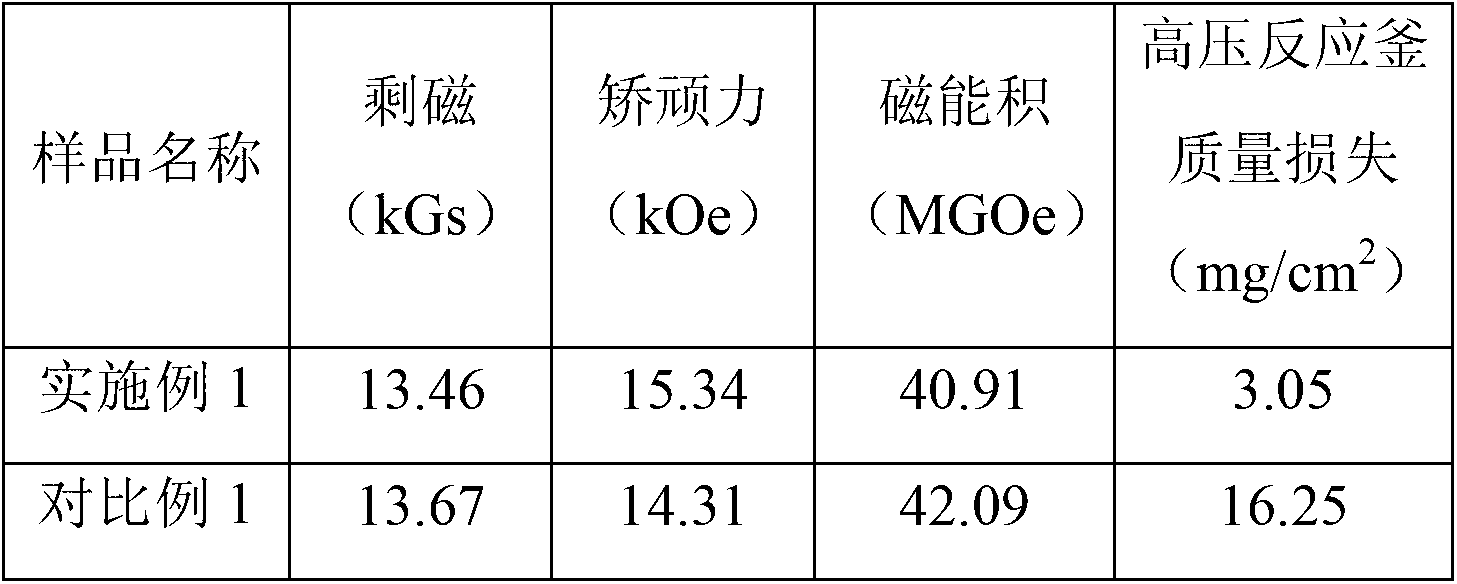
[0017] Use quick-setting technology to change the composition to Nd 13.5 Fe bal al 0.4 B 6 (atomic percent content) of the alloy is prepared as flakes, and then the powder is made into a powder with an average particle size of 3 microns by using a hydrogen crushing-jet milling process. Dysprosium-zinc alloy powder (DyZn 5 ) to the above initial powder, and use a mixer to mix the two powders evenly. The uniformly mixed powder was oriented in a magnetic field of 1.8T and pressed into shape. Then put the compact into a high-vacuum sintering furnace and heat up to 1060°C for sintering for 3 hours. Afterwards, secondary heat treatment is carried out, wherein the temperature of the primary heat treatment is 950° C. for 2 hours, and the temperature of the secondary heat treatment is 580° C. for 1 hour. That is, a sintered magnet was obtained.
[0018] Billy 1
[0019] Adopt the same process as embodiment 1 to prepare the Nd of undoped dysprosium-zinc alloy powder particle 13...
Embodiment 2
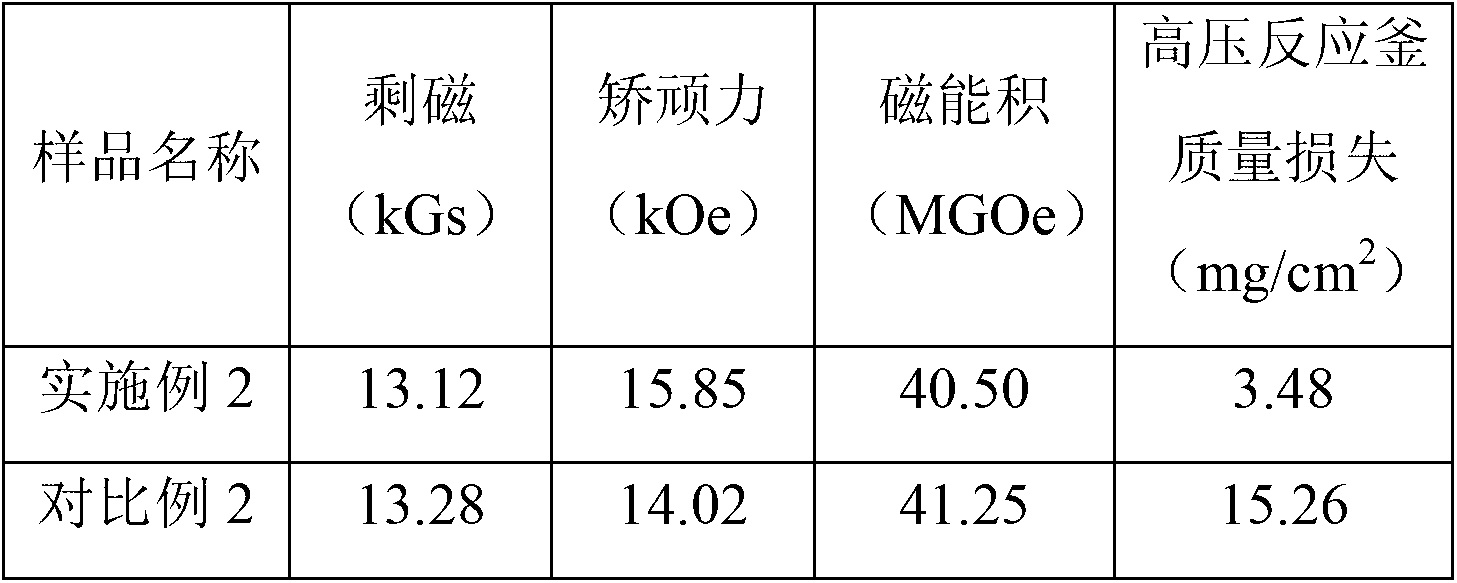
[0025] Use quick-setting technology to change the composition to Nd 12.5 Fe bal Al 0.5 Nb 0.2 B 6 (atomic percent) of the alloy is prepared as flakes, and then the powder is made into a powder with an average particle size of 5 microns by using a hydrogen crushing-jet milling process. Then, 1.0% by weight dysprosium-zinc alloy (DyZn) powder with an average particle size of 3 microns was added to the above initial powder, and the two powders were uniformly mixed by a mixer. The uniformly mixed powder was oriented in a magnetic field of 1.8T and pressed into shape. Then put the compact into a high-vacuum sintering furnace, and heat up to 1000°C for sintering for 4 hours. Then carry out secondary heat treatment, wherein the temperature of primary heat treatment is 900°C for 3 hours; the temperature of secondary heat treatment is 460°C for 2 hours. That is, a sintered magnet was obtained.
Embodiment 2 and comparative example 2
[0029] Table 2 Example 2 and Comparative Example 2 magnet magnetic properties and corrosion resistance comparison
[0030]
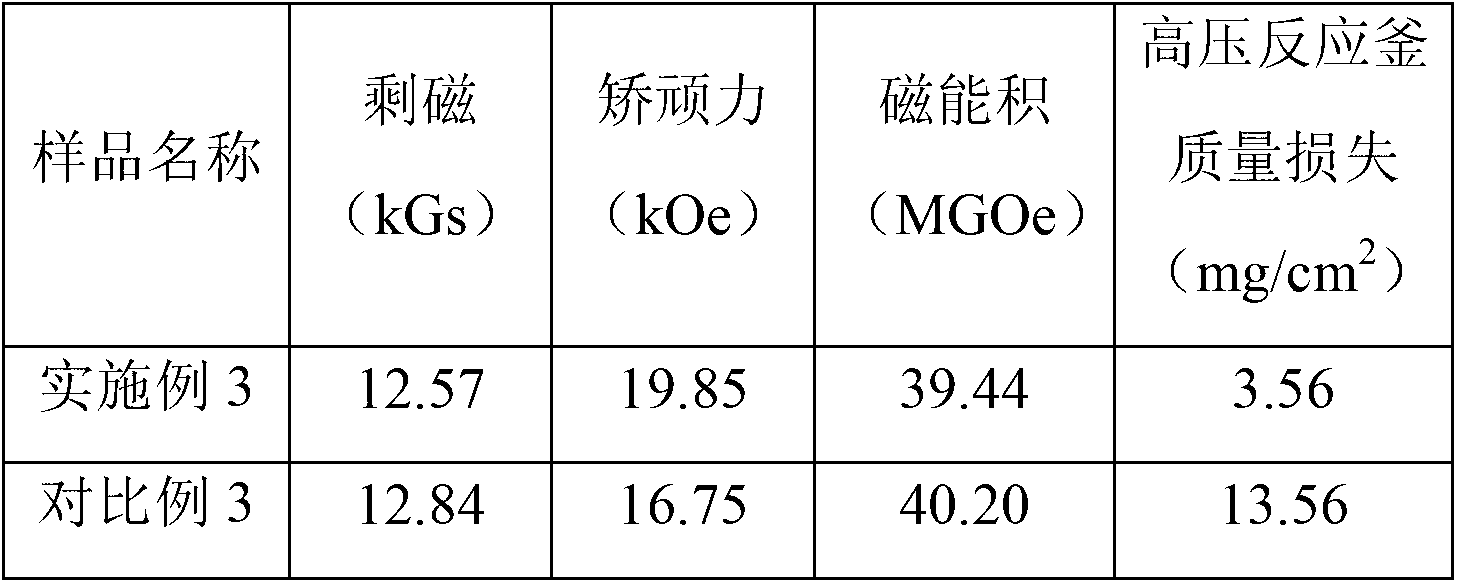
[0031] The above results illustrate that for sintered NdFeB magnets with the same composition, the coercive force of the magnet prepared by adding dysprosium-zinc alloy powder particles according to the present invention is significantly improved compared with that of the undoped magnet. In addition, the remanence and energy product of the two magnets are equivalent. The corrosion resistance of the magnet is significantly improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com