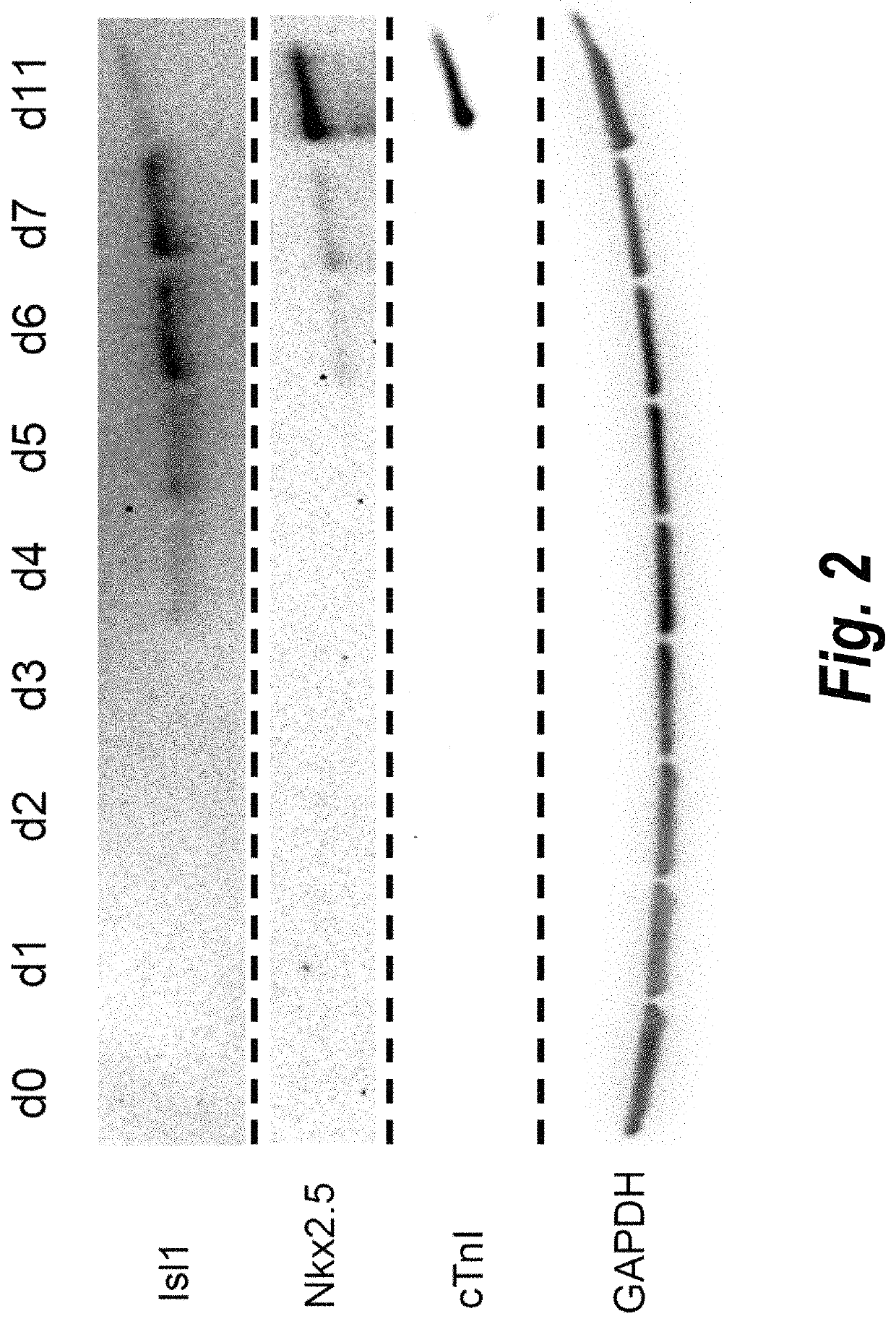
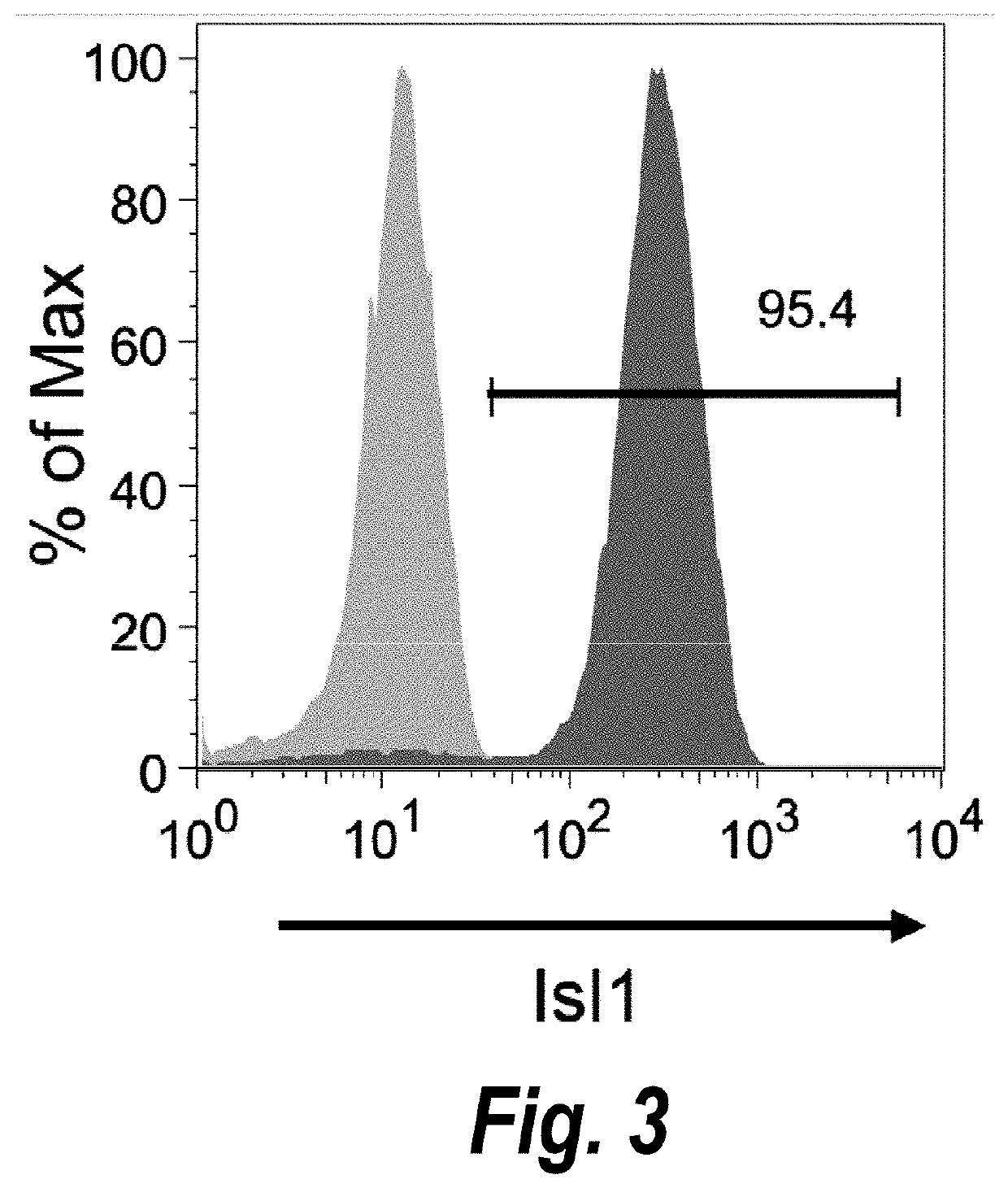
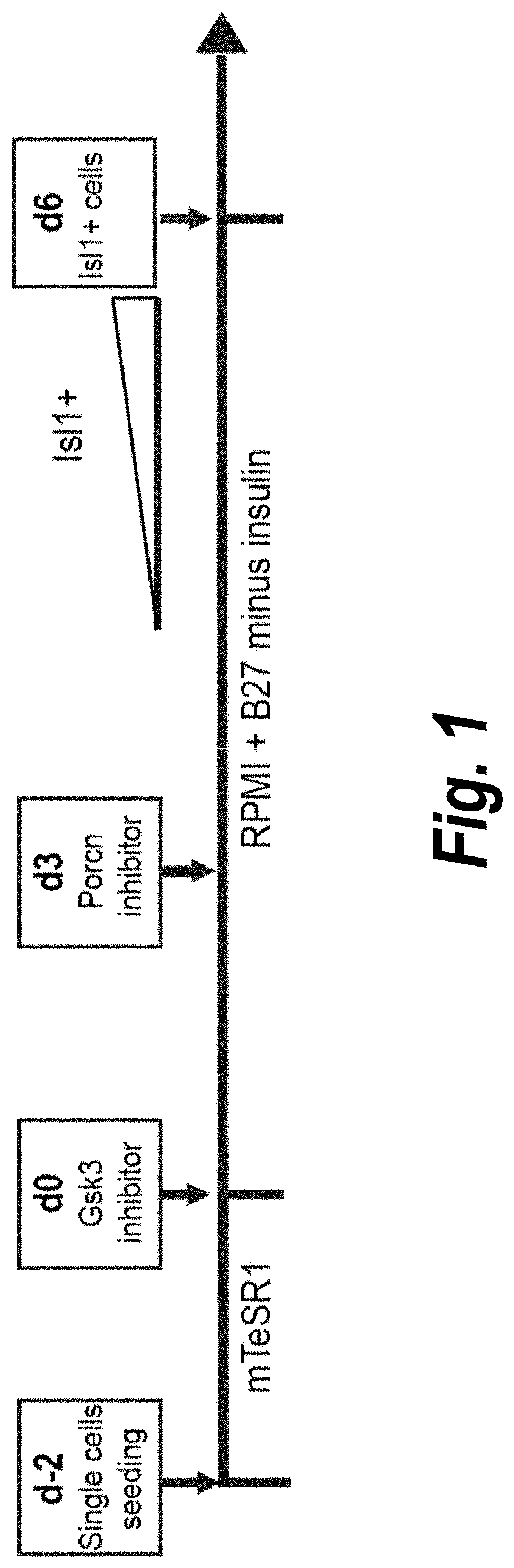
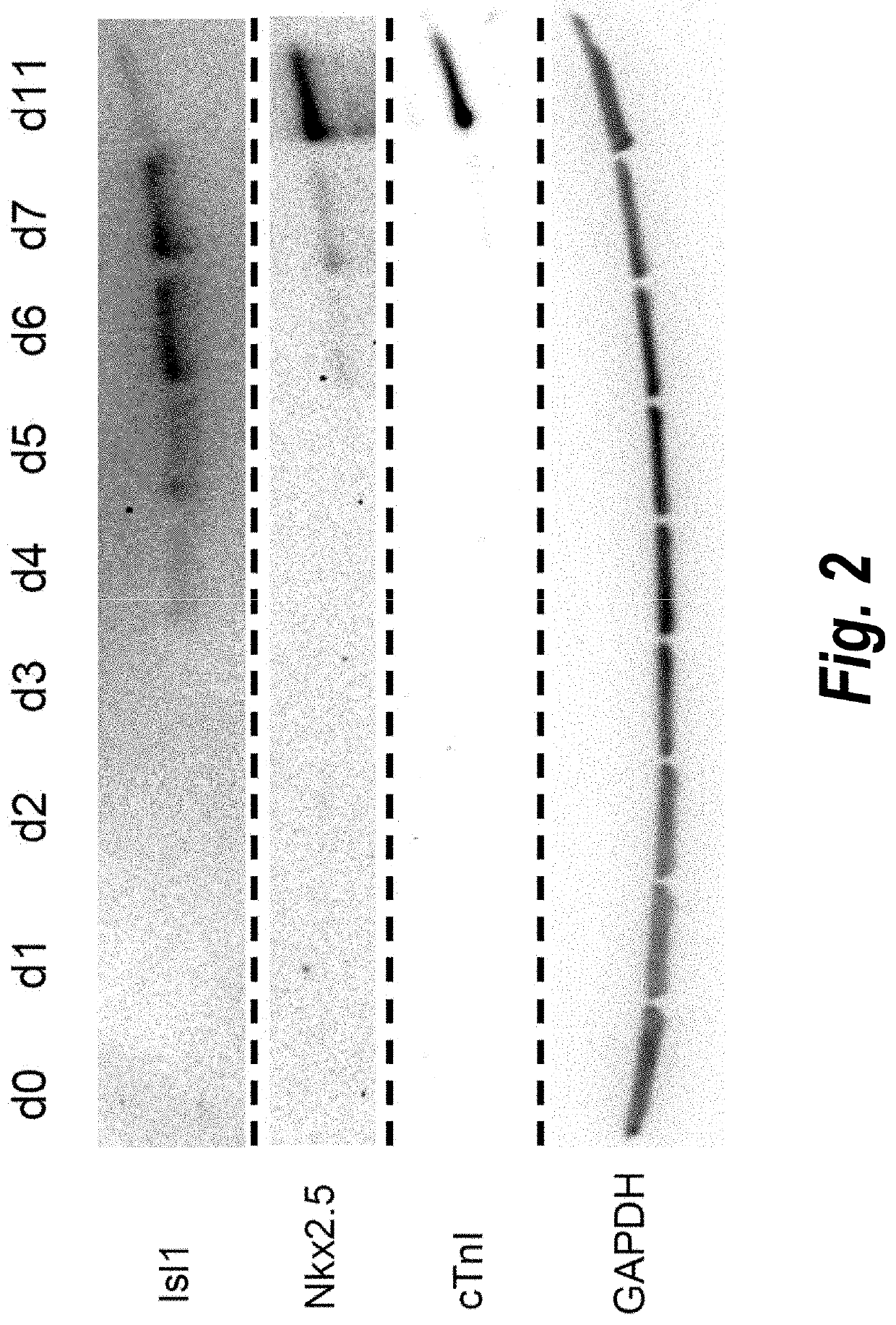
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Ventricular muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiac Physiology. The heart is composed of three major types of cardiac muscle: 1) atrial muscle, 2) ventricular muscle, and 3) specialized excitatory and conductive muscle fibers. The atrial and ventricular types of muscle contract in much the same manner as skeletal muscle fibers.
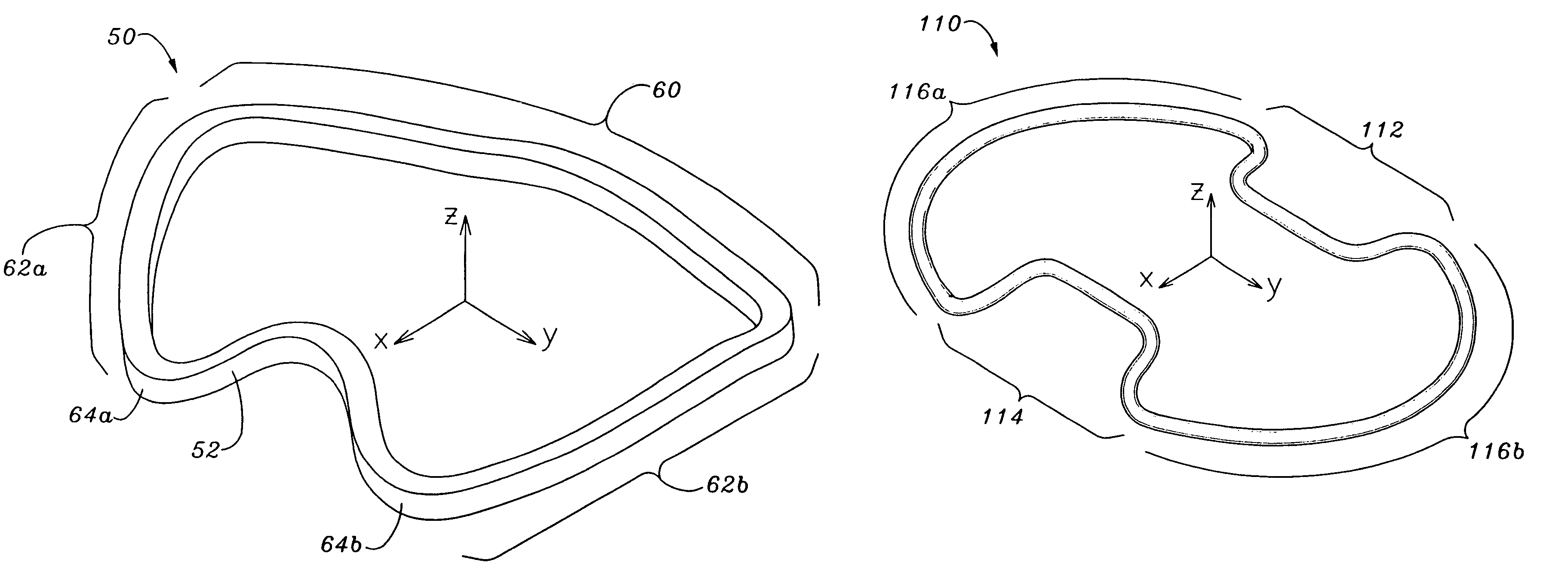
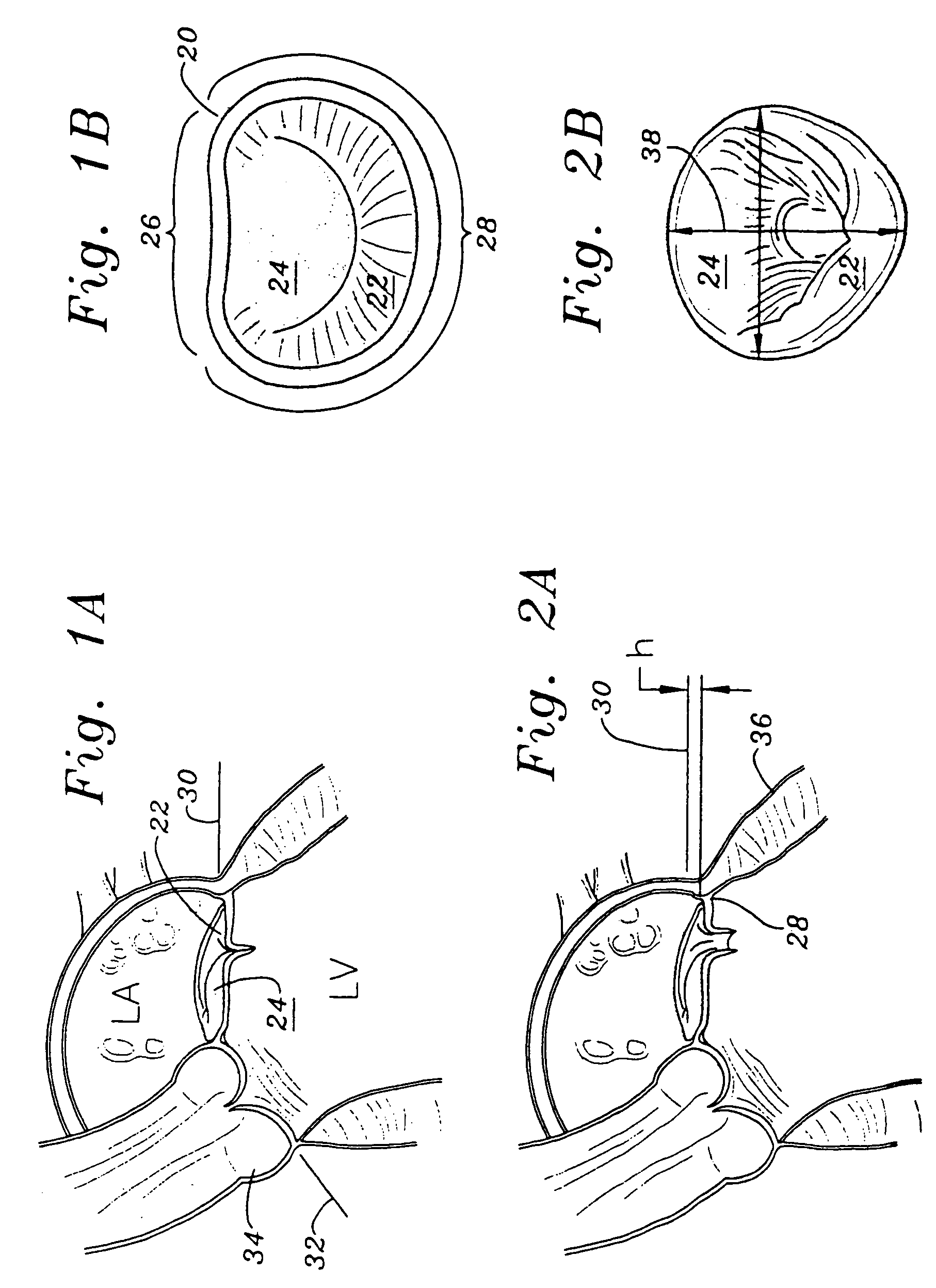
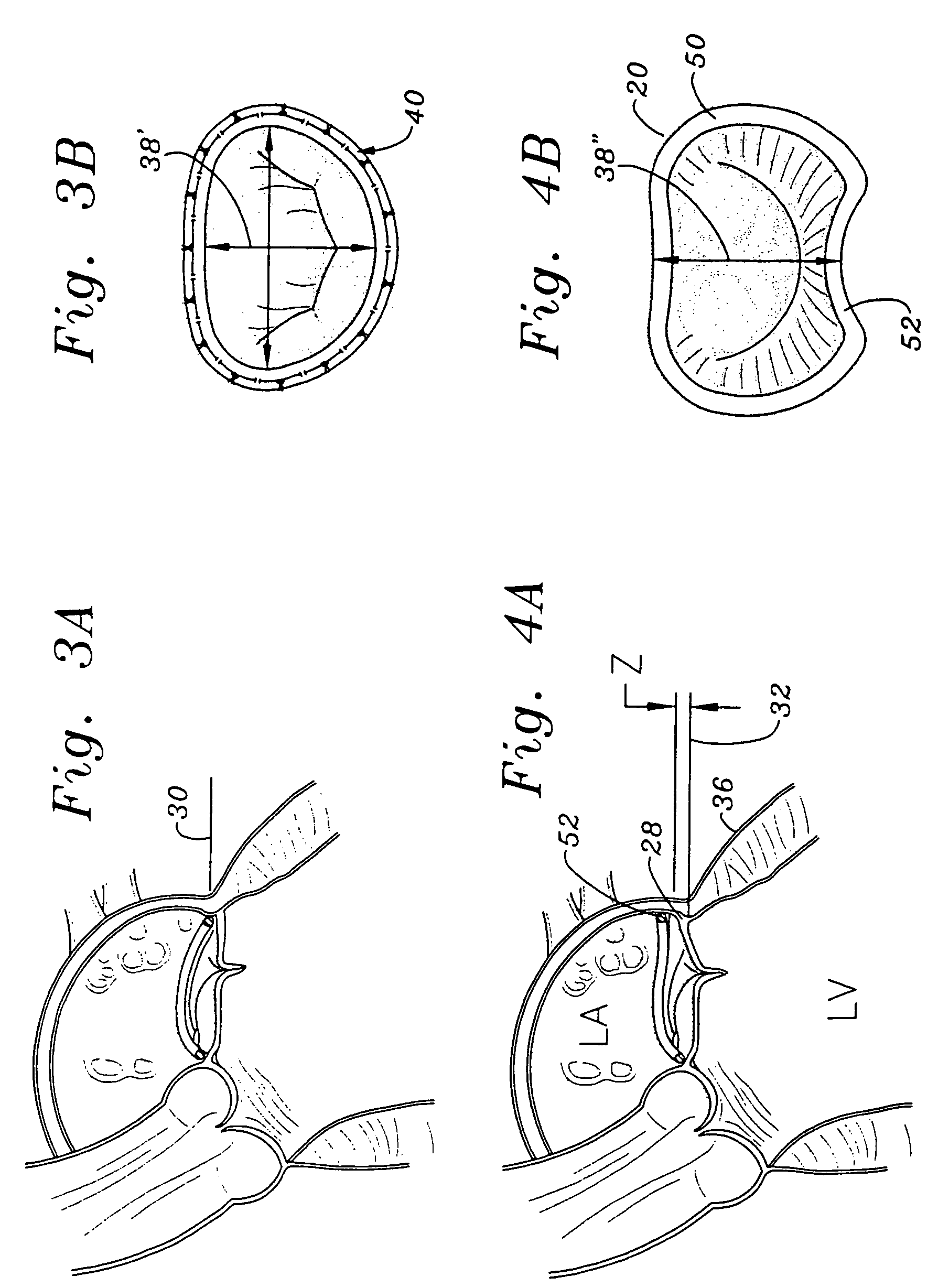
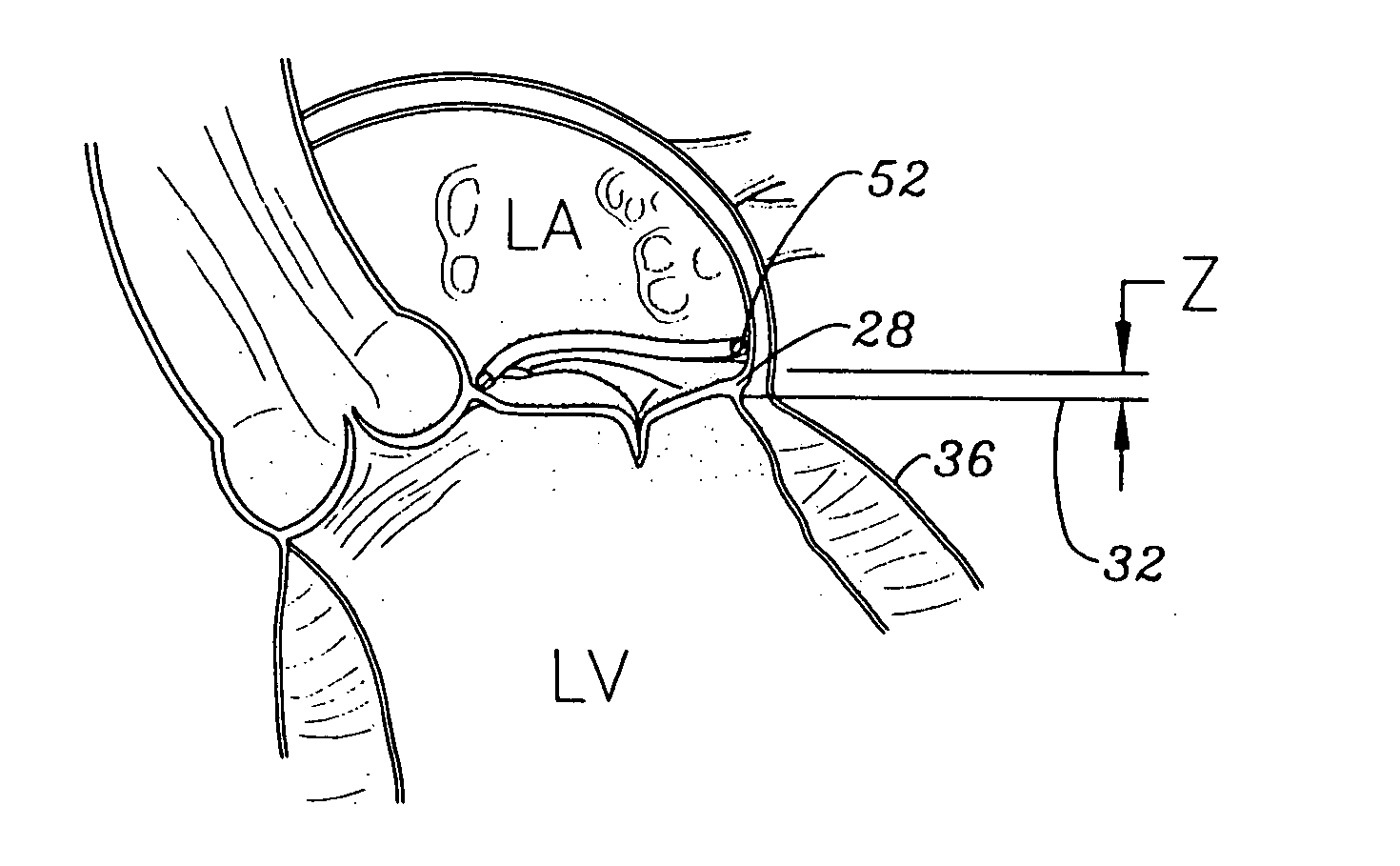
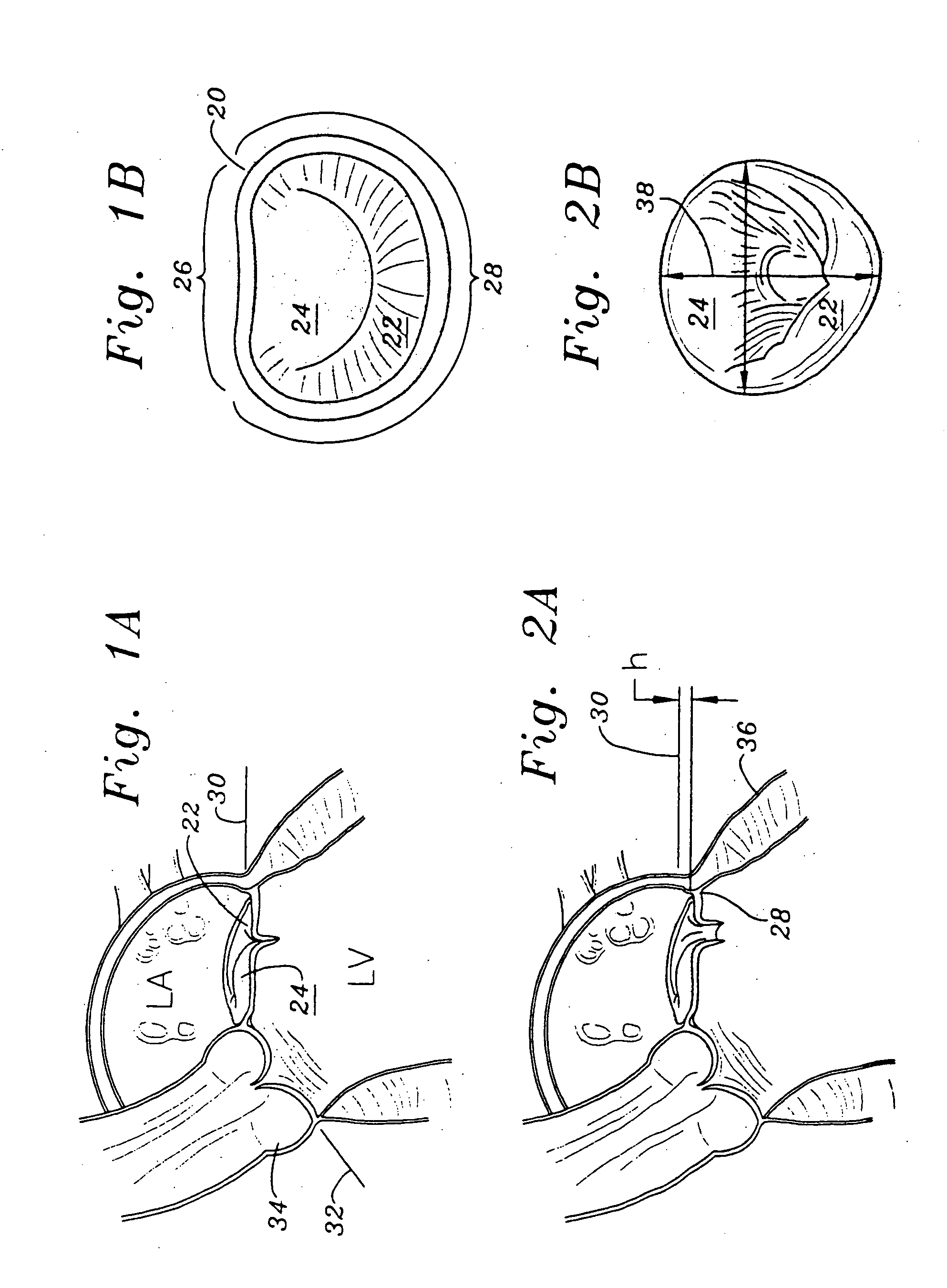
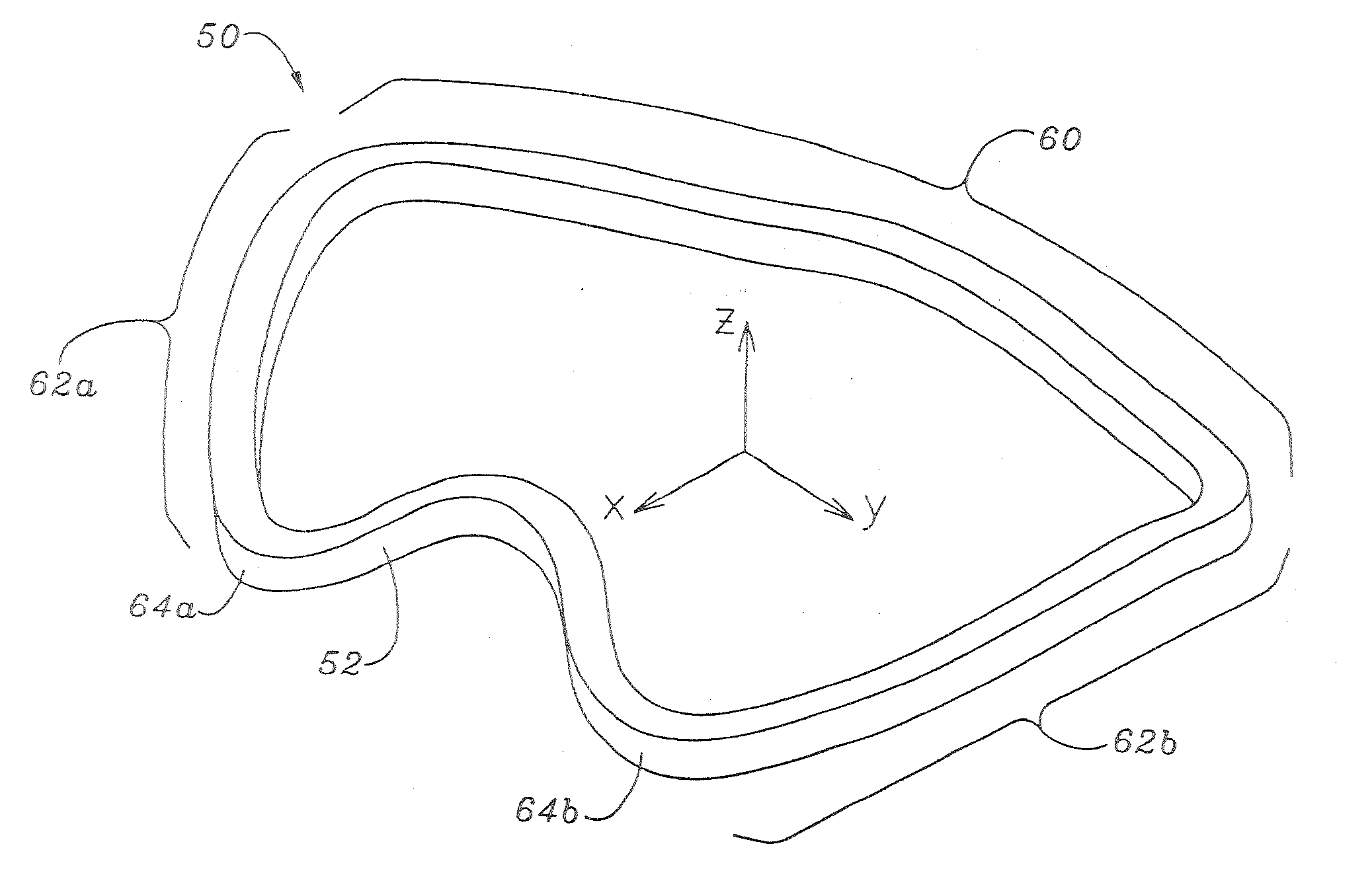
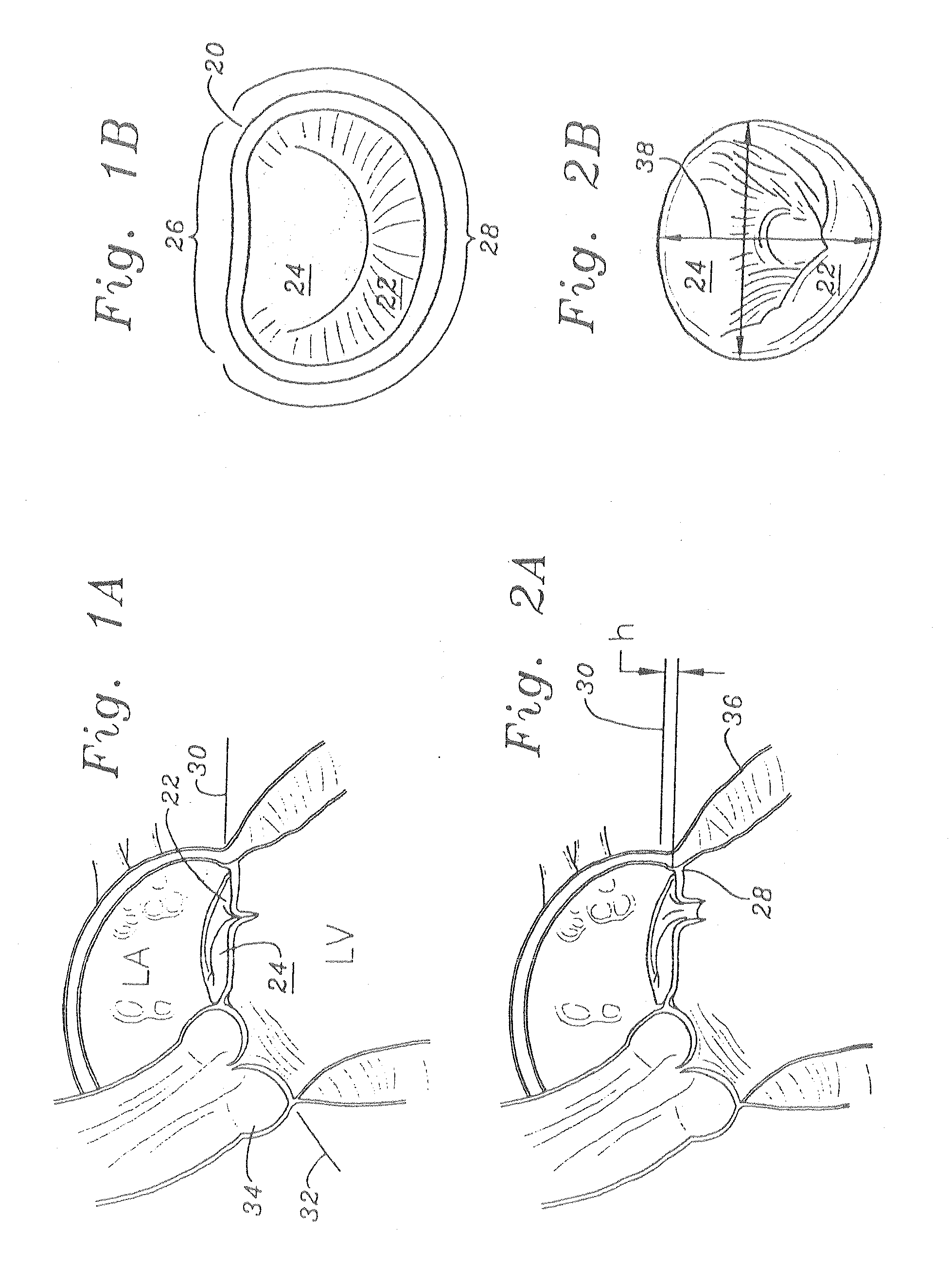
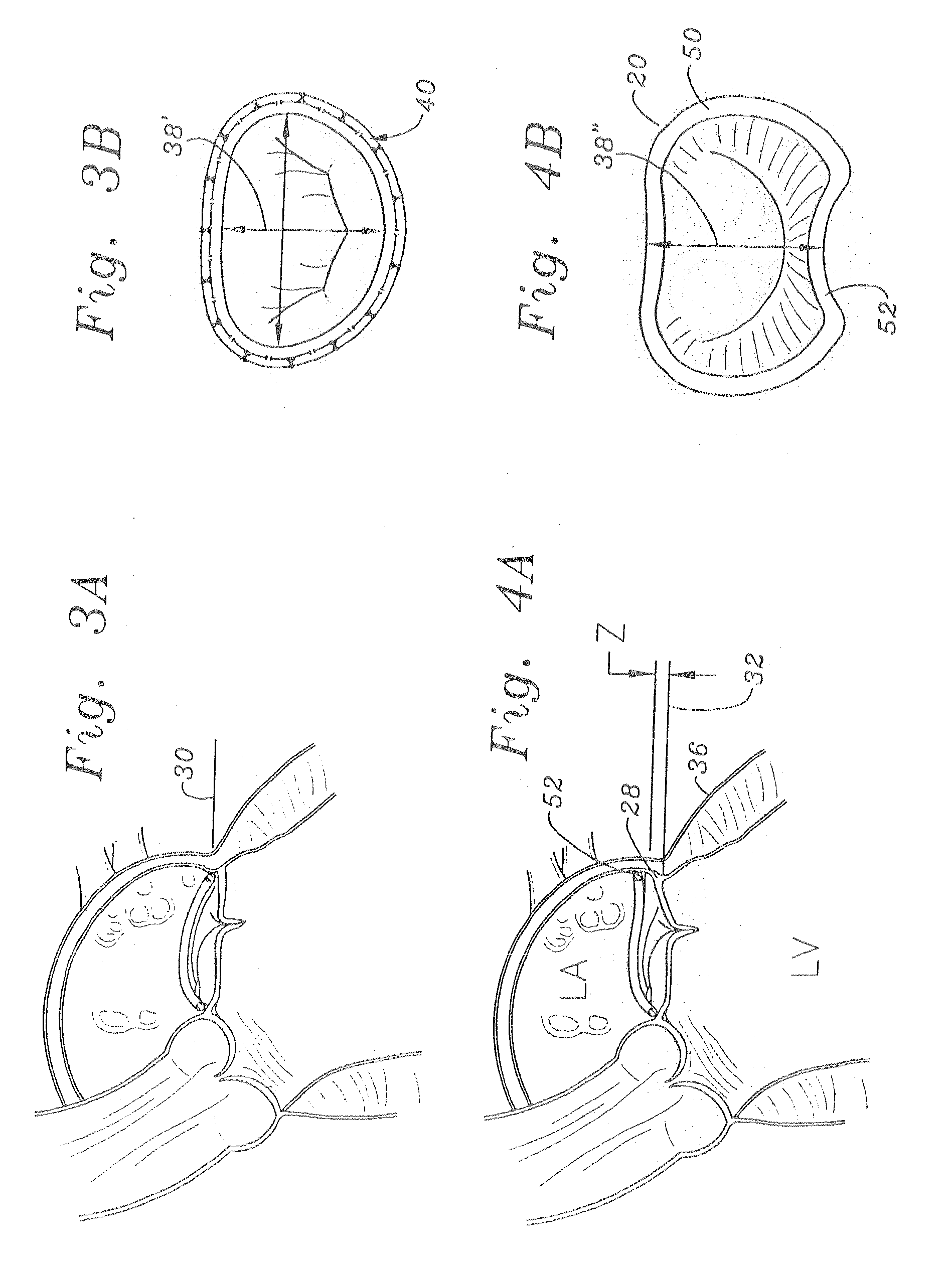
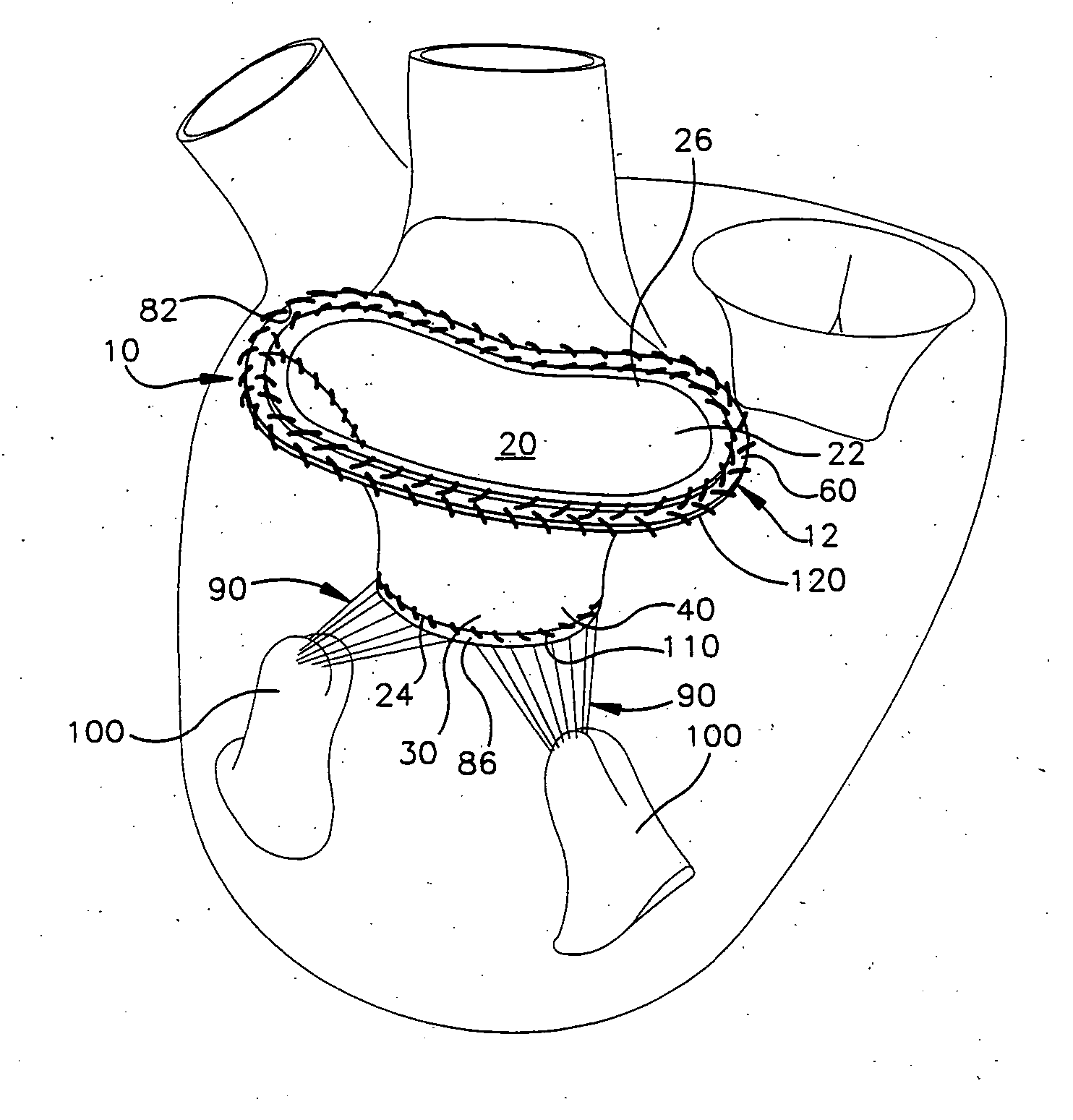
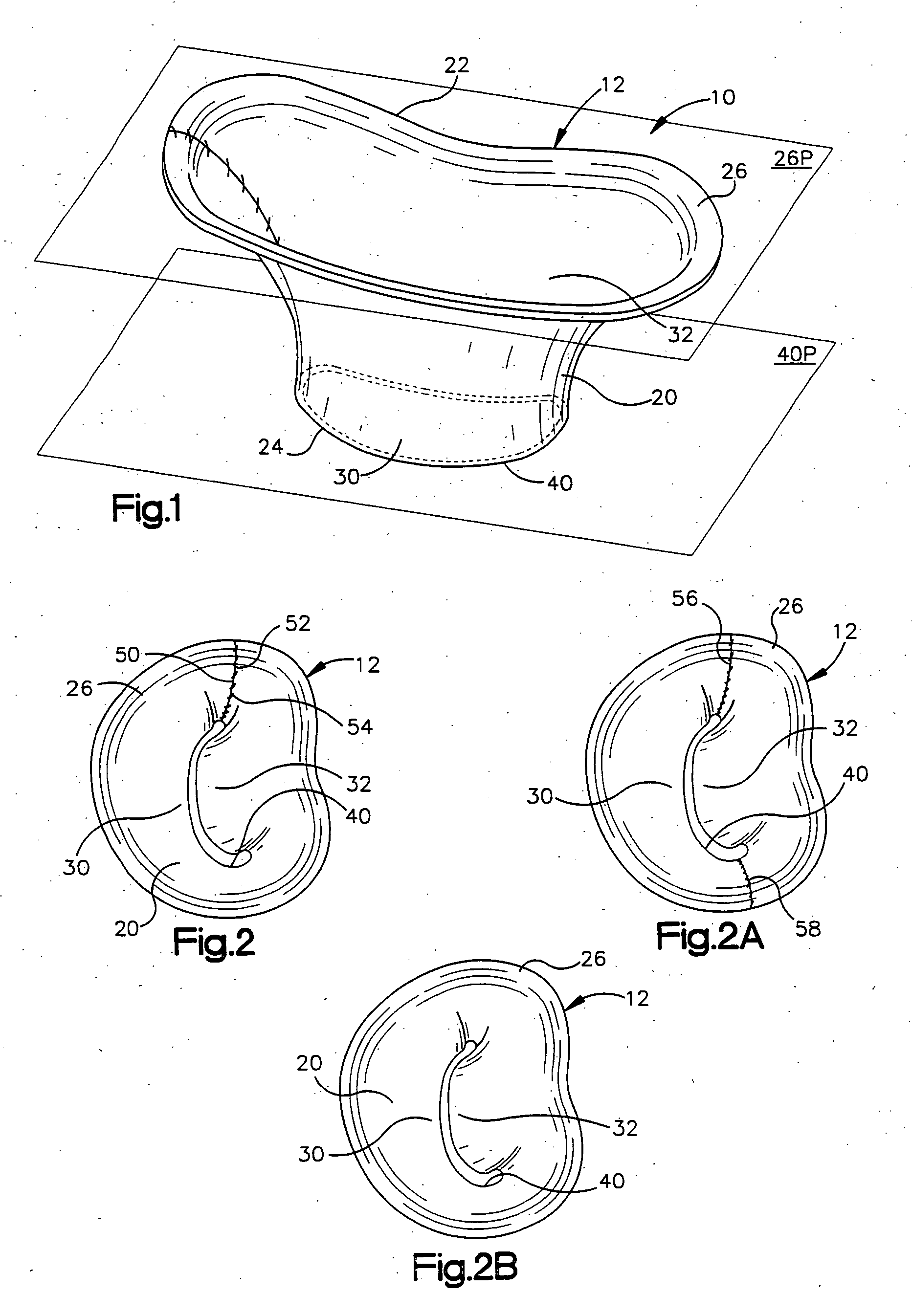
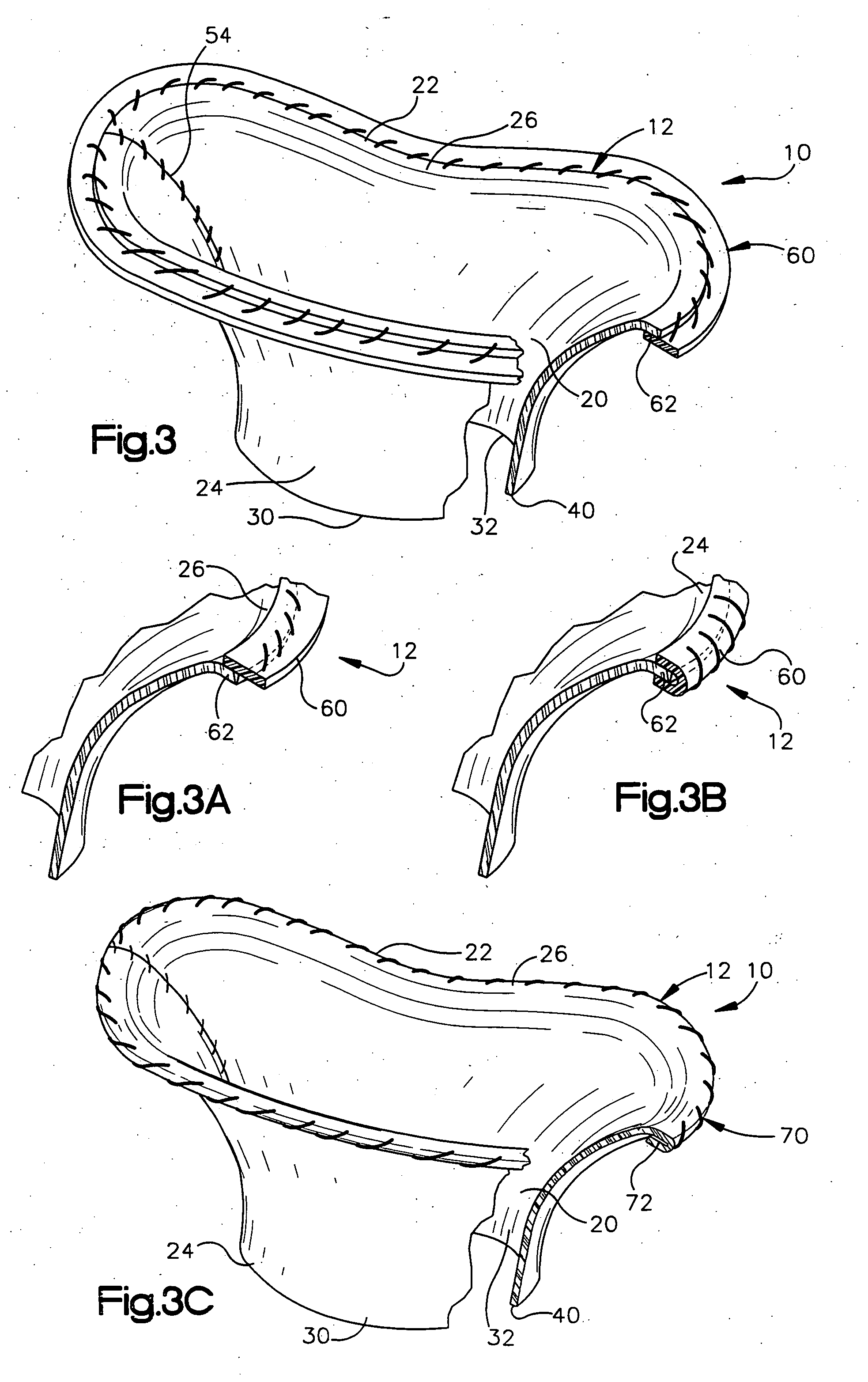
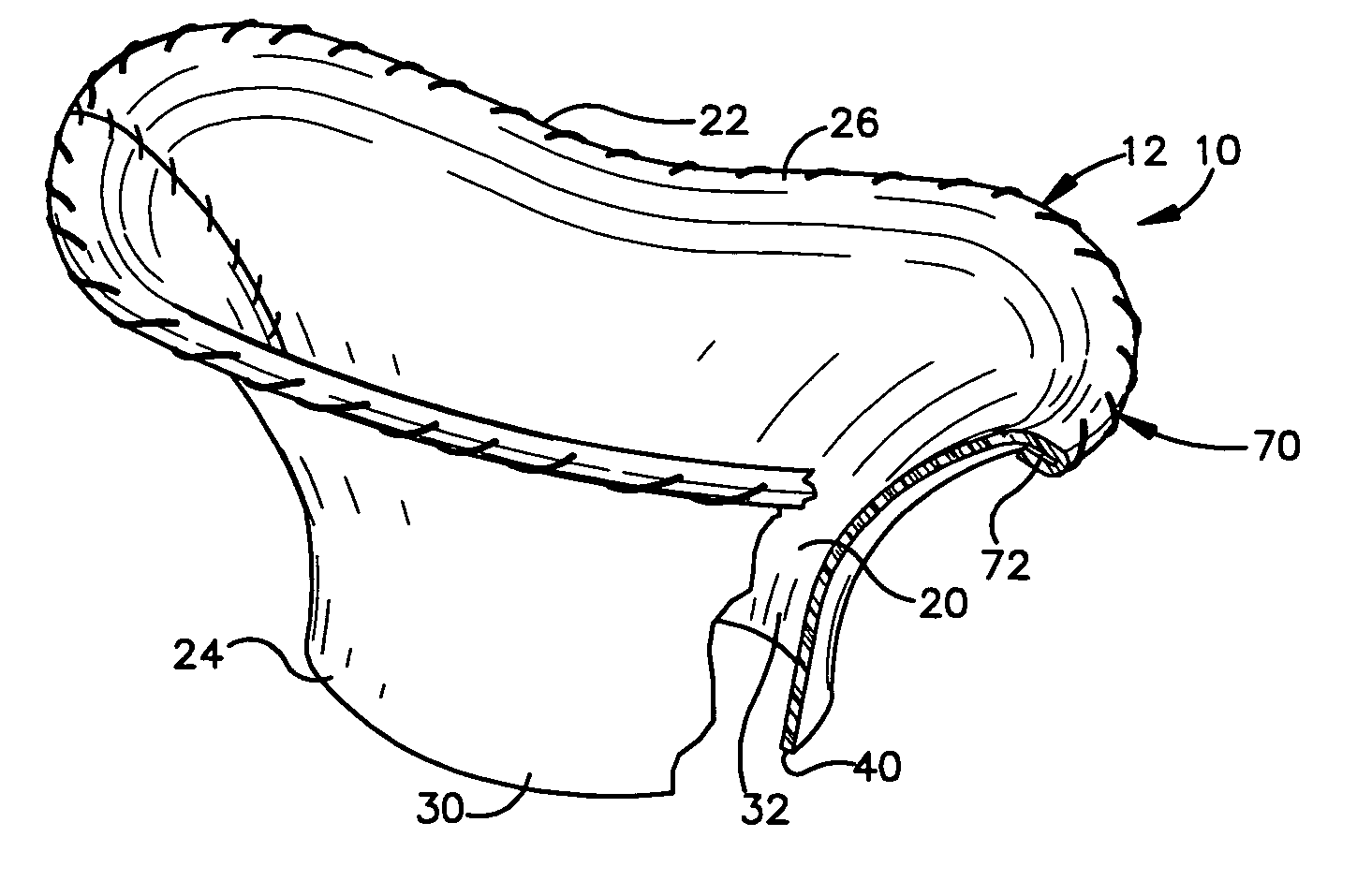
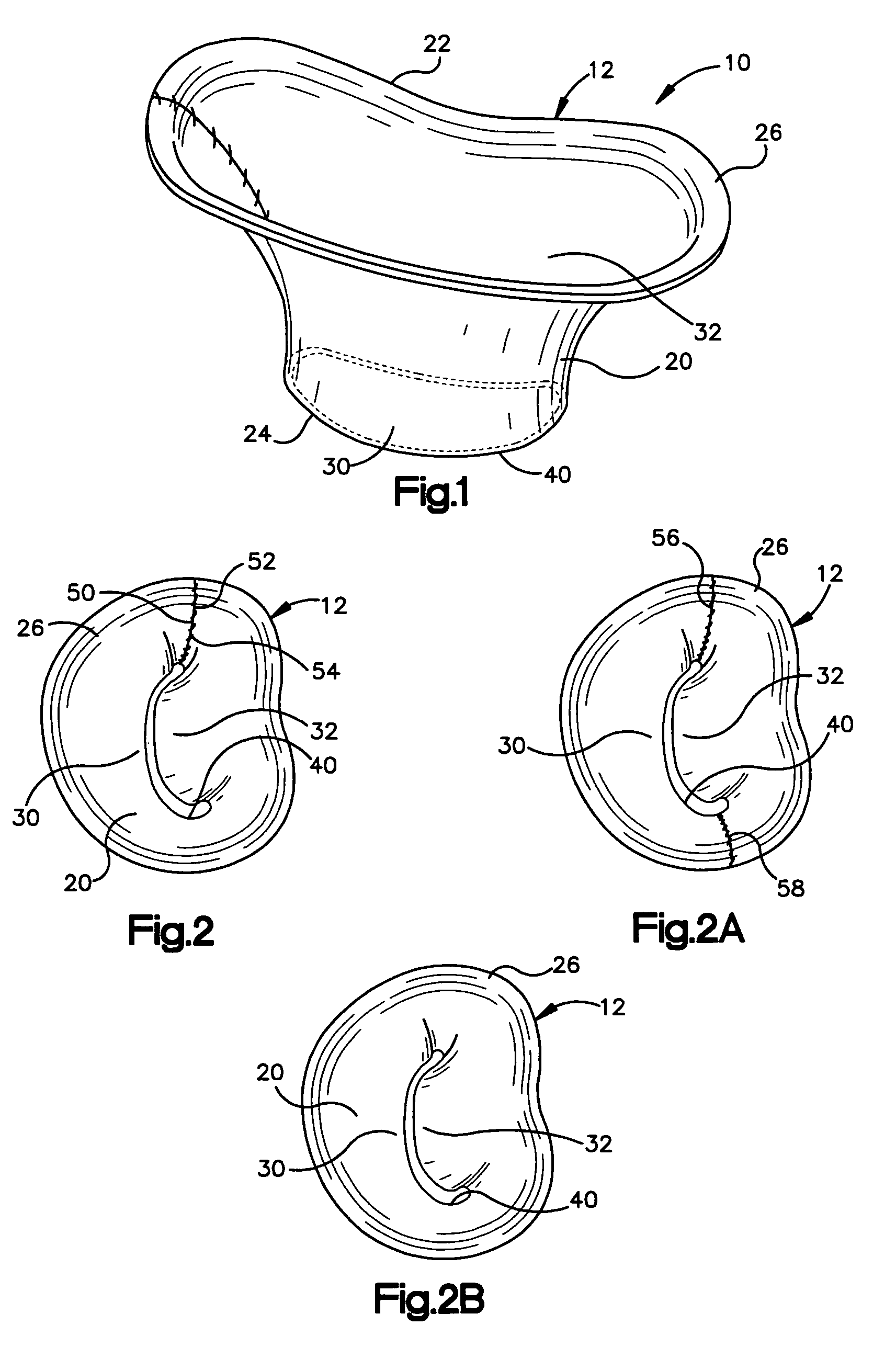
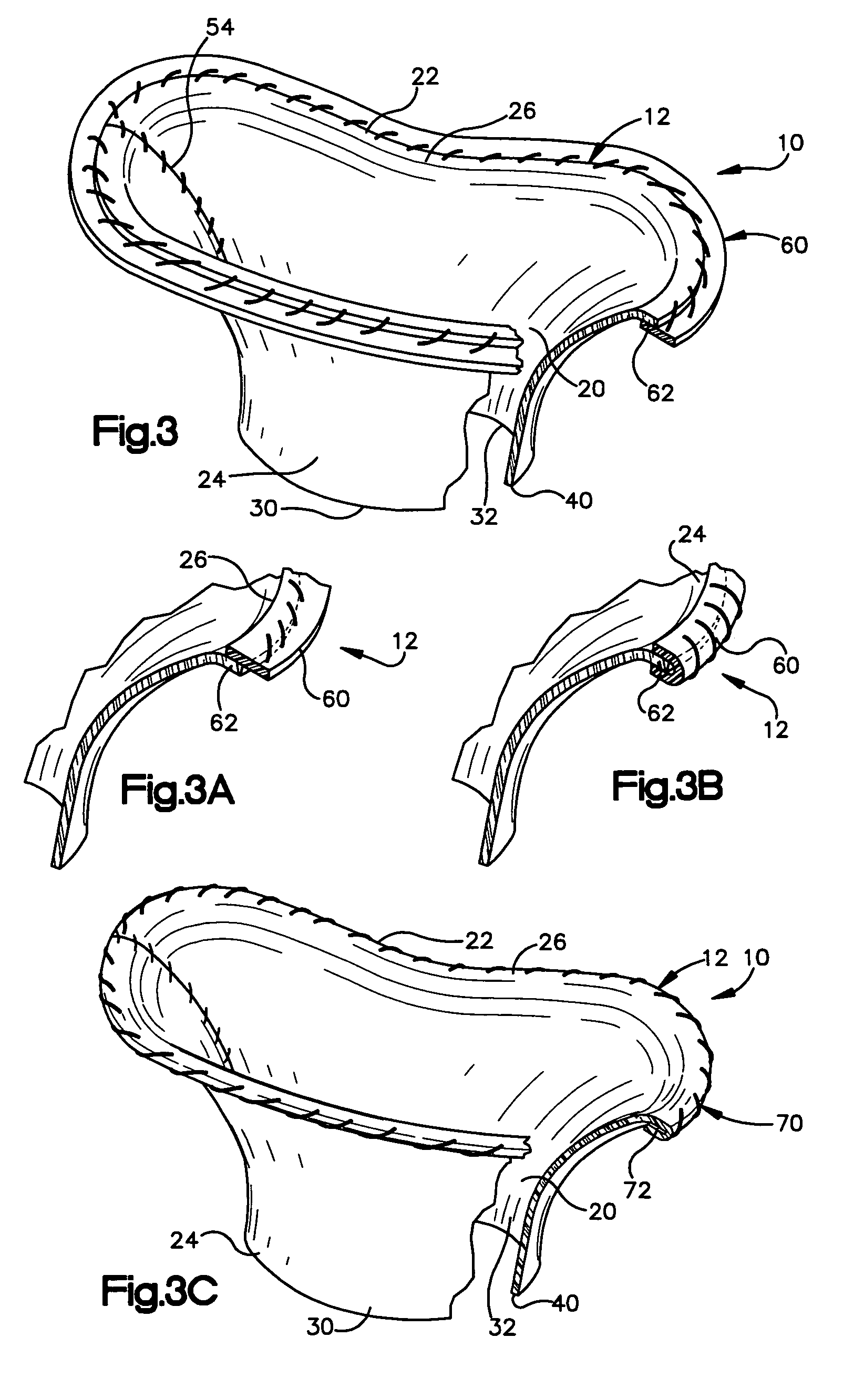
Methods of implanting a mitral valve annuloplasty ring to correct mitral regurgitation
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods of implanting a mitral valve annuloplasty ring to correct mitral regurgitation
ActiveUS20050049698A1Reduce the impactReduce impactBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsStellite alloyMitral annuloplasty ring
Methods of implanting an annuloplasty ring to correct maladies of the mitral annulus that not only reshapes the annulus but also reconfigures the adjacent left ventricular muscle wall. The ring may be continuous and is made of a relatively rigid material, such as Stellite. The ring has a generally oval shape that is three-dimensional at least on the posterior side. A posterior portion of the ring rises or bows upward from adjacent sides to pull the posterior aspect of the native annulus farther up than its original, healthy shape. In doing so, the ring also pulls the ventricular wall upward which helps mitigate some of the effects of congestive heart failure. Further, one or both of the posterior and anterior portions of the ring may also bow inward. The methods include securing the annuloplasty ring with the anterior portion against the annulus anterior aspect and the posterior portion against the annulus posterior aspect so that the ring posterior portion elevates and may also pull radially inward, the annulus posterior aspect and corrects the mitral regurgitation.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
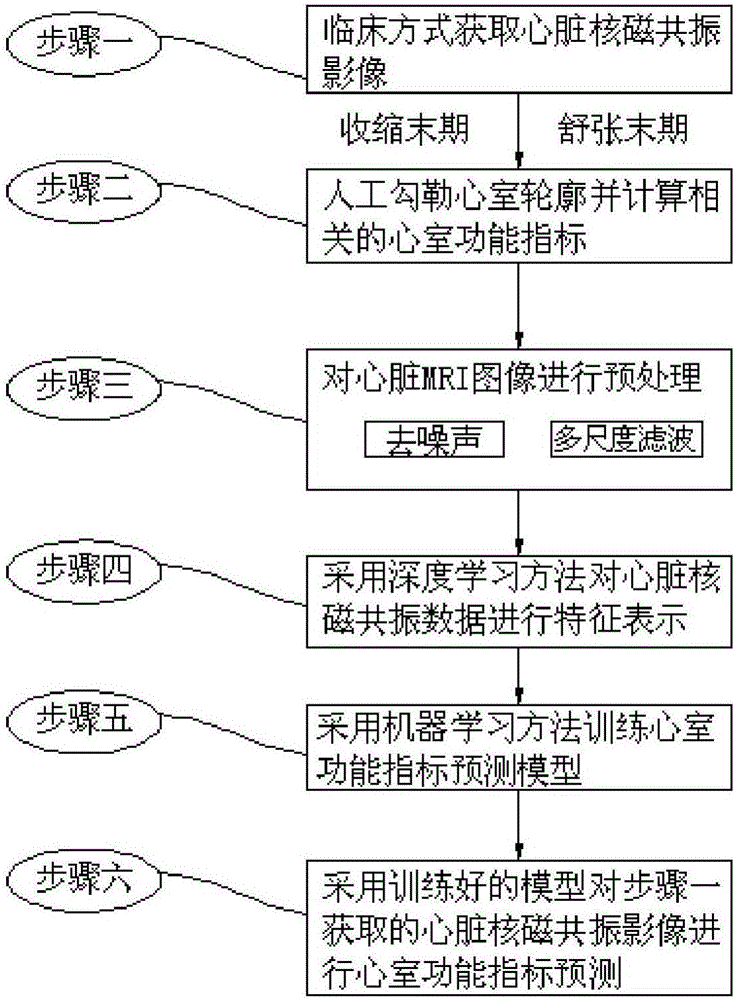
Deep learning and MRI image-based ventricular function index prediction method
InactiveCN106096632AFree laborAccurate diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningImaging processingPredictive methods
The invention discloses a deep learning and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) image-based ventricular function index prediction method and belongs to the field of medical image processing. A conventional ventricular index prediction method mainly depends on a process of artificially segmenting a ventricular muscle part of each phase and then performing measurement and calculation based on the artificial segmentation. The process needs to consume a large amount of manpower and time and has a serious artificial difference. The deep learning and MRI image-based ventricular function index prediction method is implemented by the following steps of clinically obtaining a heart MRI image; artificially drawing a ventricular outline and calculating related ventricular function indexes; preprocessing the heart MRI image; performing characteristic representation on heart MRI data by adopting a deep learning method; training a ventricular function index prediction model by adopting a machine learning method; and performing ventricular function index prediction on the heart MRI image obtained in the first step by adopting the trained model. According to the method, the ventricular function indexes can be quickly, accurately and automatically predicted to assist in diagnosis of clinical heart diseases.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
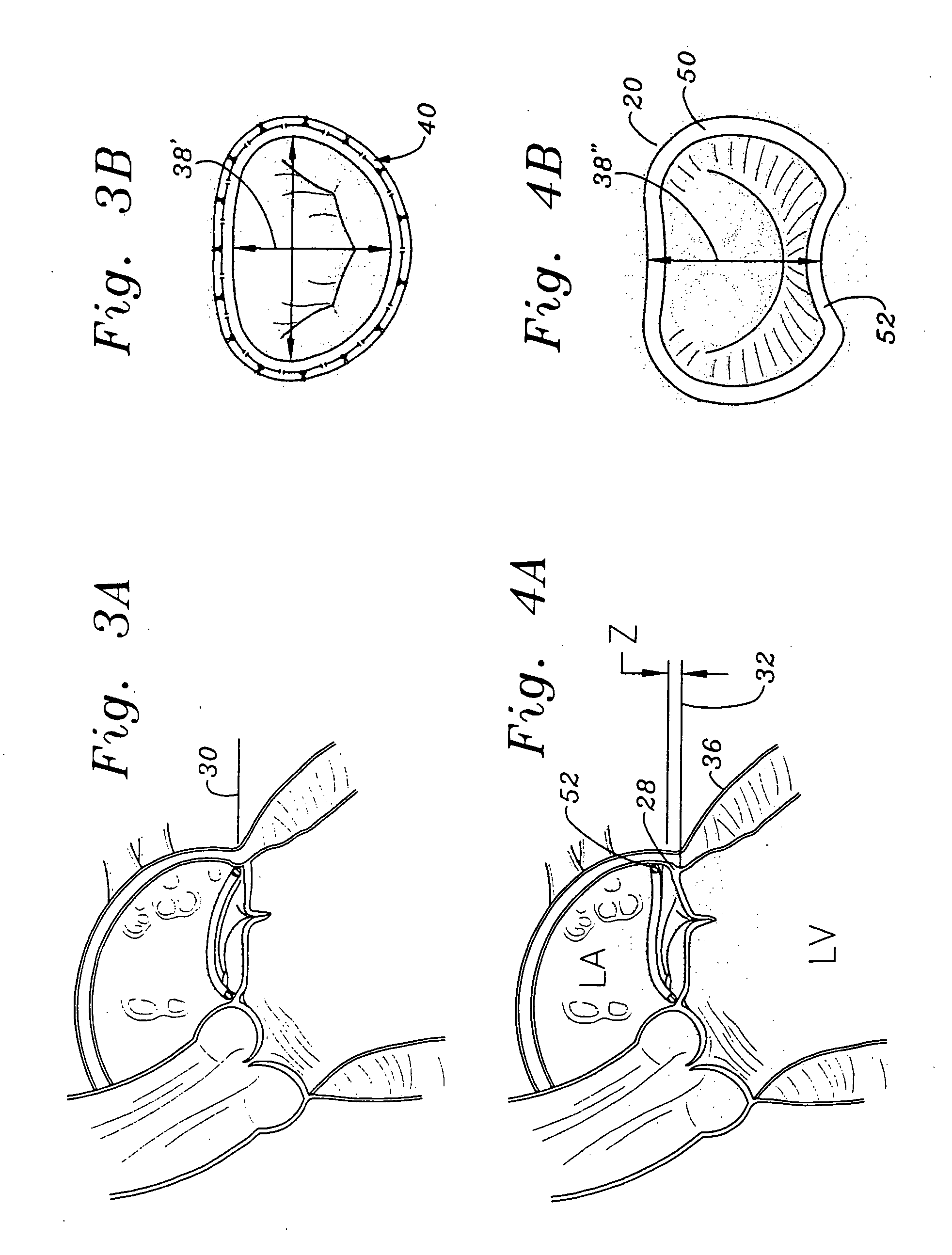
Mitral Annuloplasty Ring Having Upward Bows
Methods of implanting an annuloplasty ring to correct maladies of the mitral annulus that not only reshapes the annulus but also reconfigures the adjacent left ventricular muscle wall. The ring may be continuous and is made of a relatively rigid material, such as Stellite. The ring has a generally oval shape that is three-dimensional at least on the posterior side. A posterior portion of the ring rises or bows upward from adjacent sides to pull the posterior aspect of the native annulus farther up than its original, healthy shape. In doing so, the ring also pulls the ventricular wall upward which helps mitigate some of the effects of congestive heart failure. Further, one or both of the posterior and anterior portions of the ring may also bow inward. The methods include securing the annuloplasty ring with the anterior portion against the annulus anterior aspect and the posterior portion against the annulus posterior aspect so that the ring posterior portion elevates, and may also pull radially inward, the annulus posterior aspect and corrects the mitral regurgitation.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
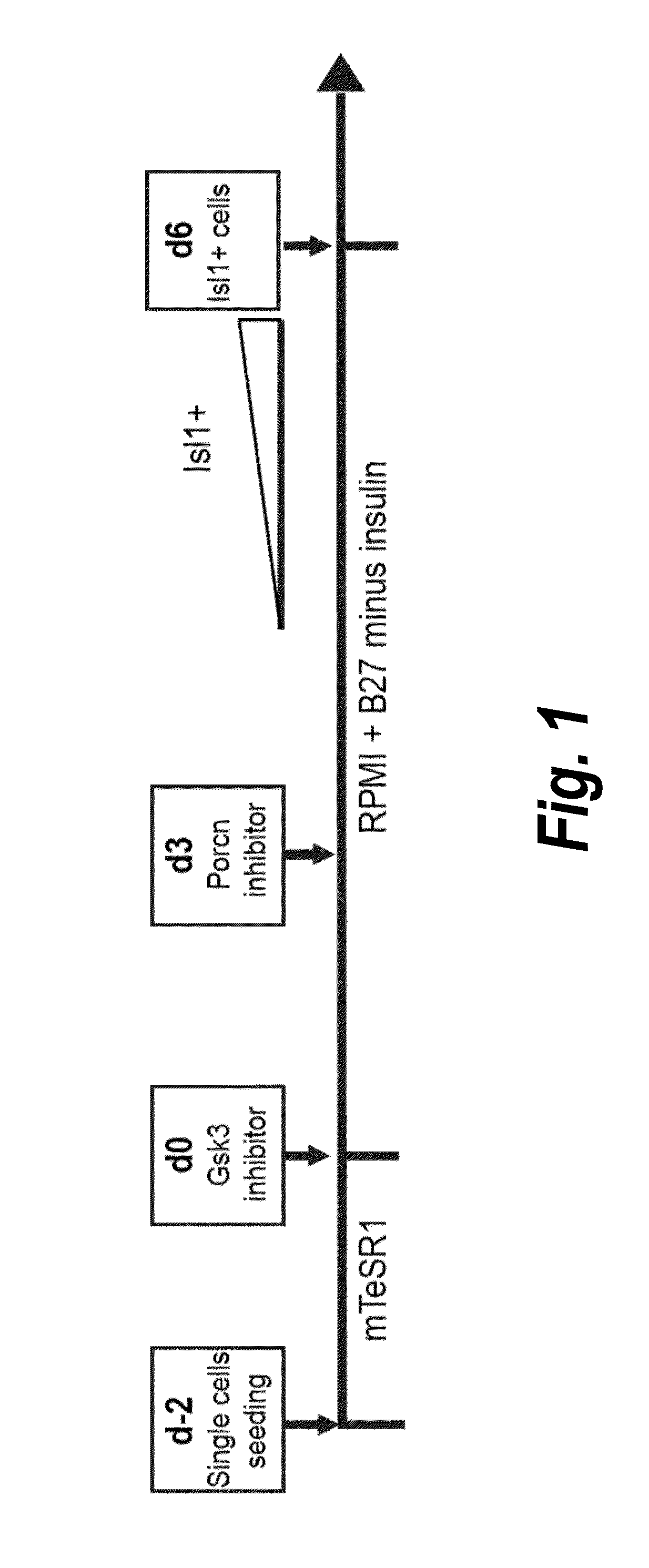
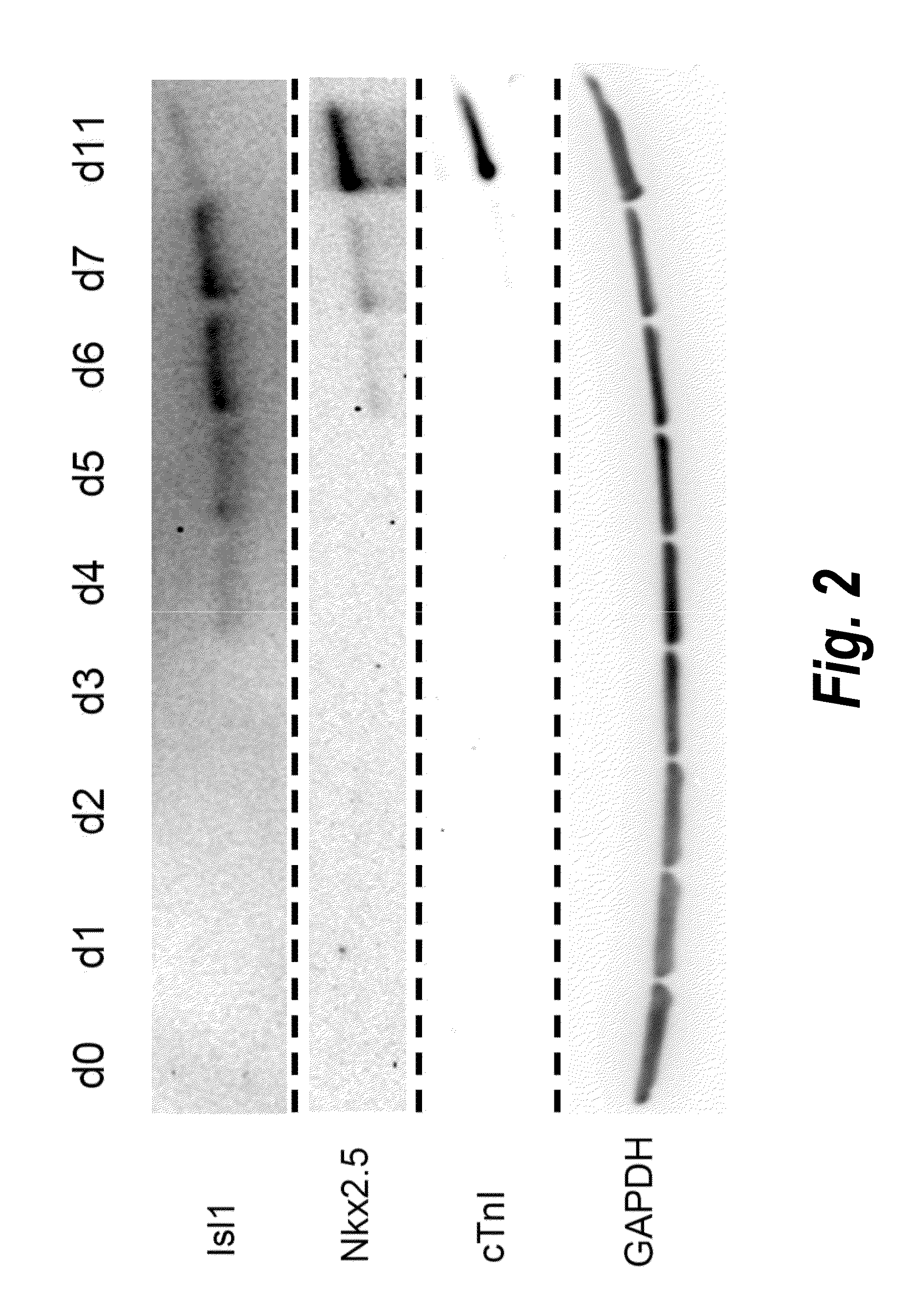
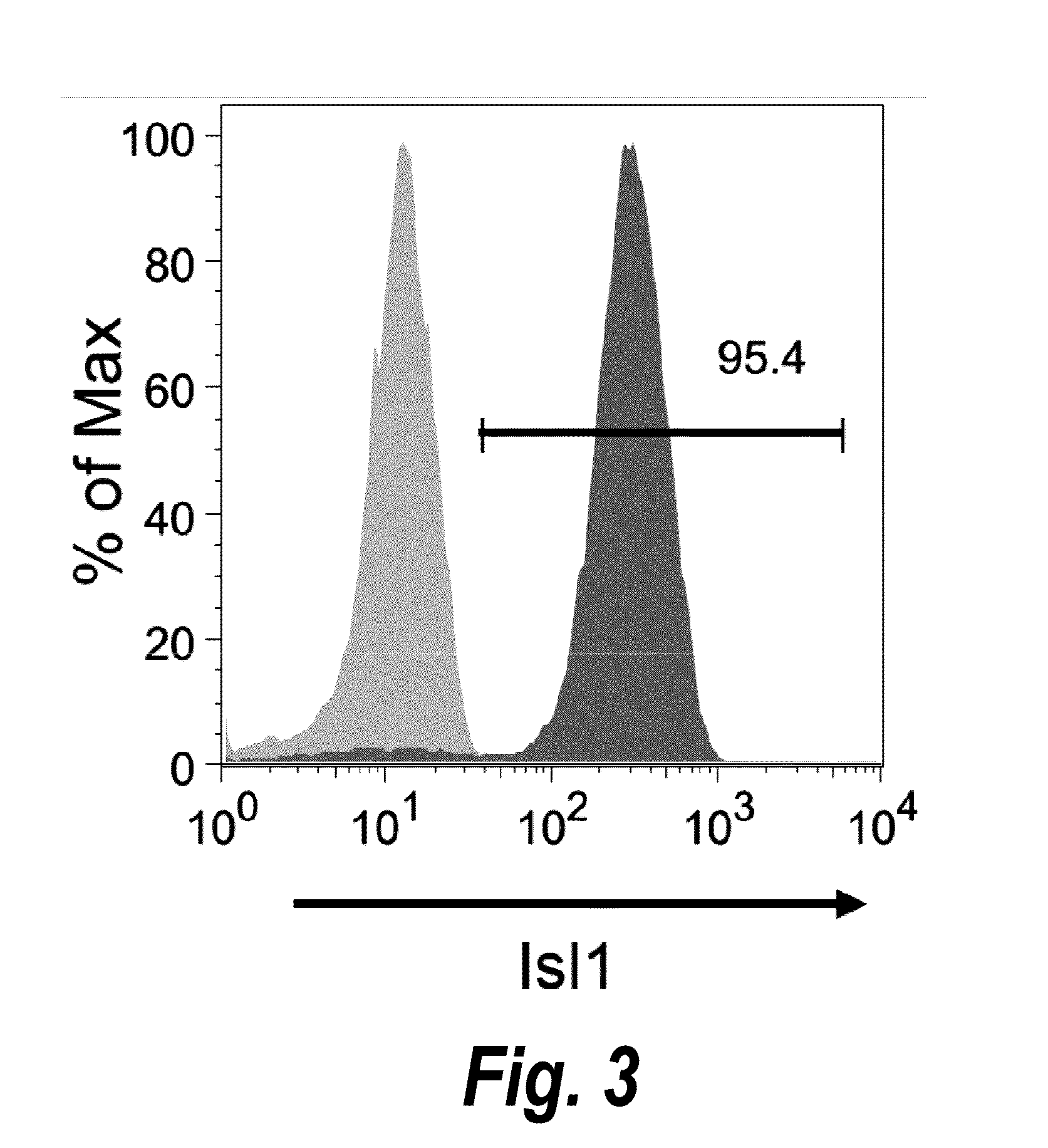
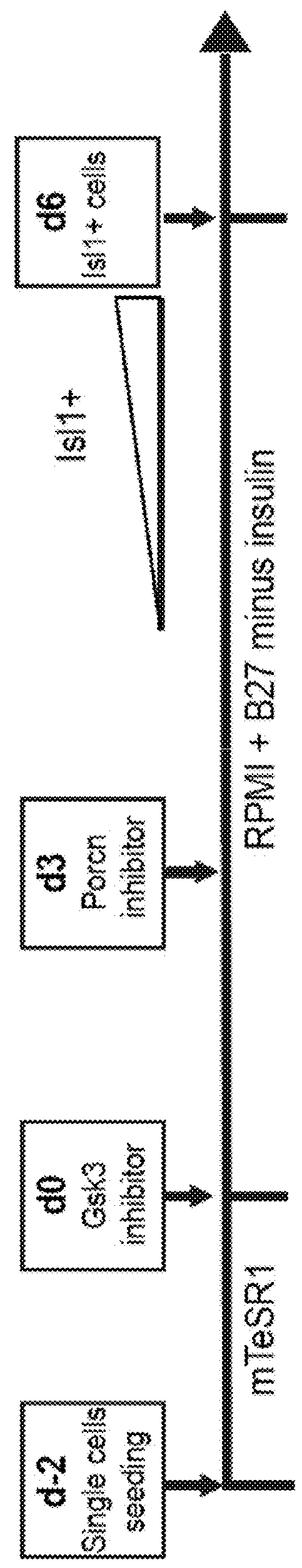
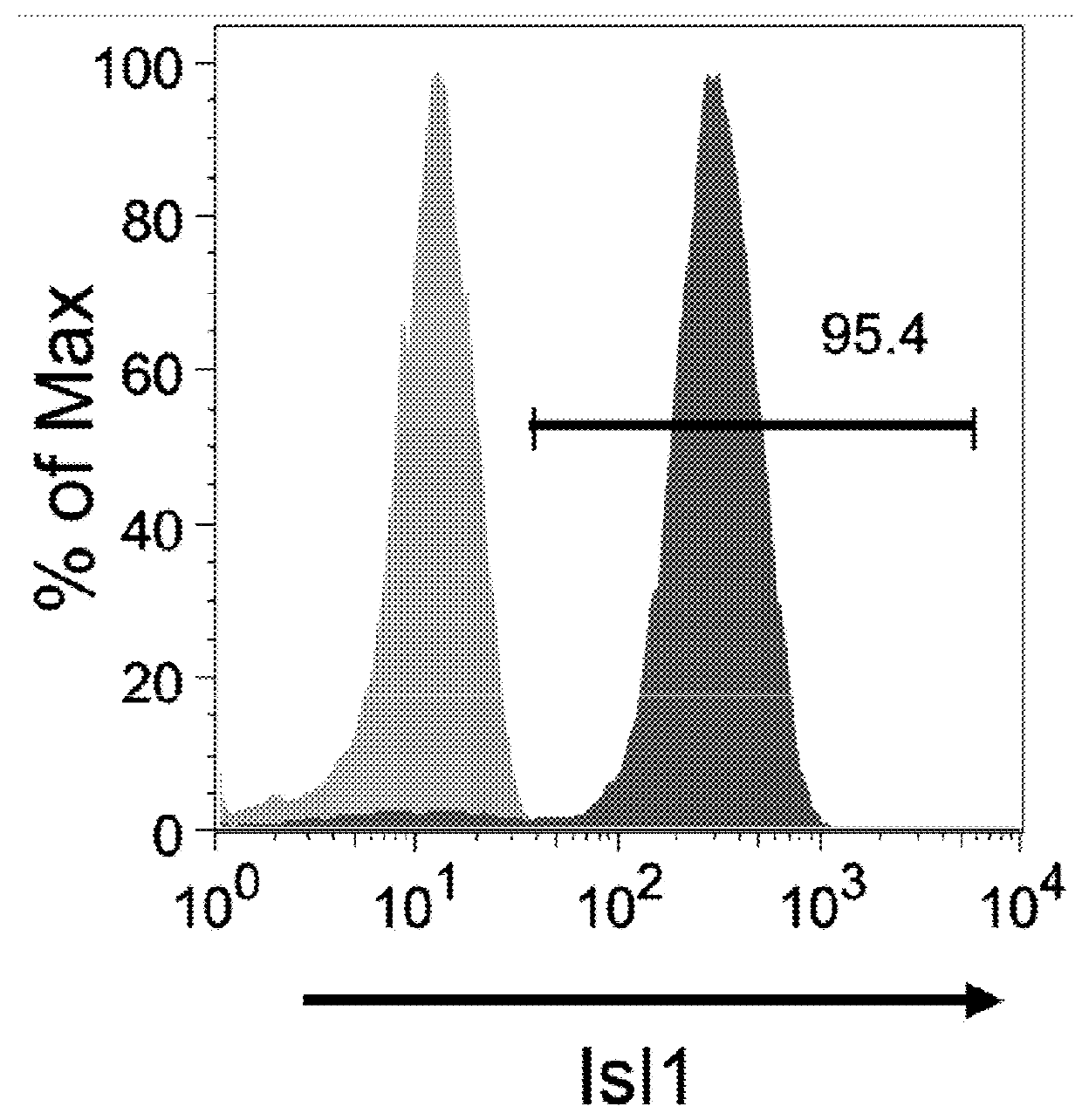
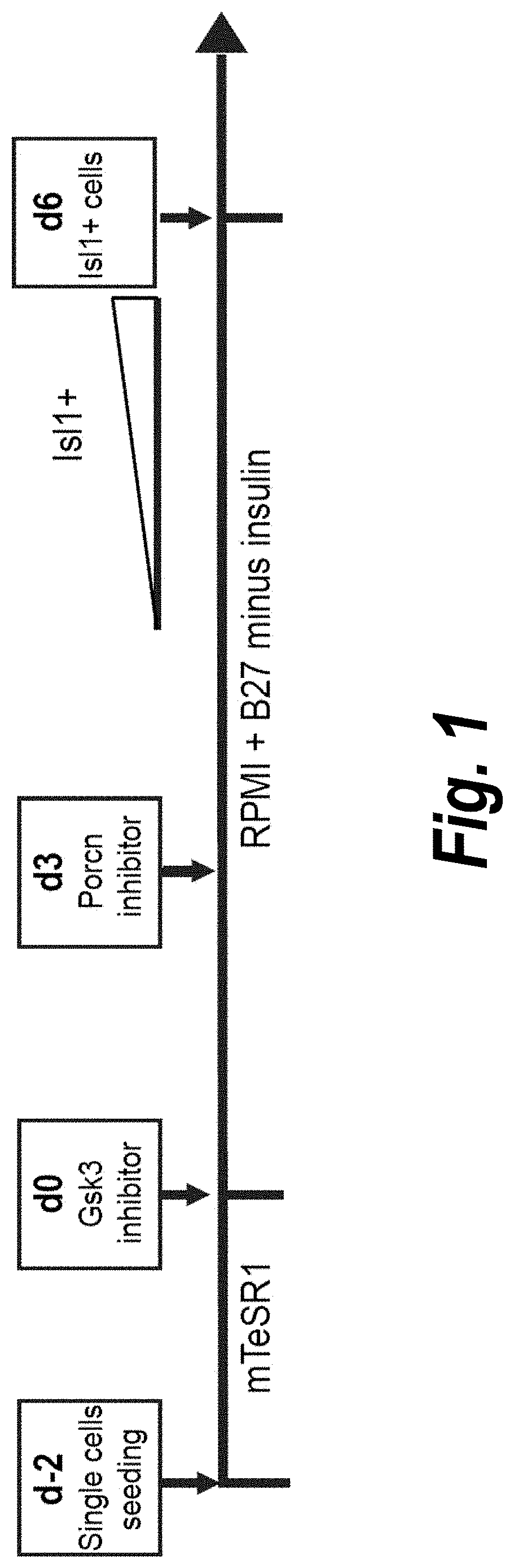
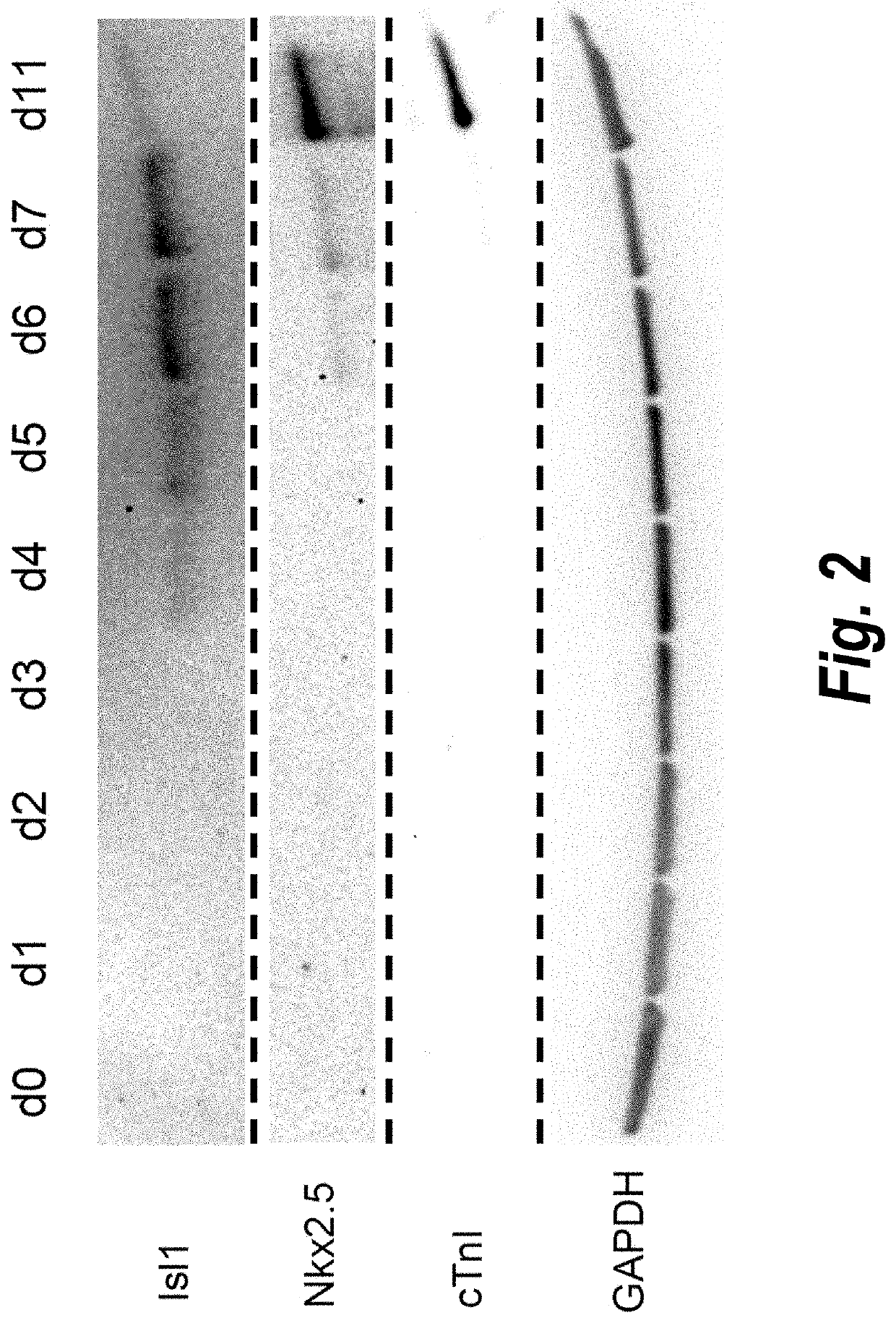
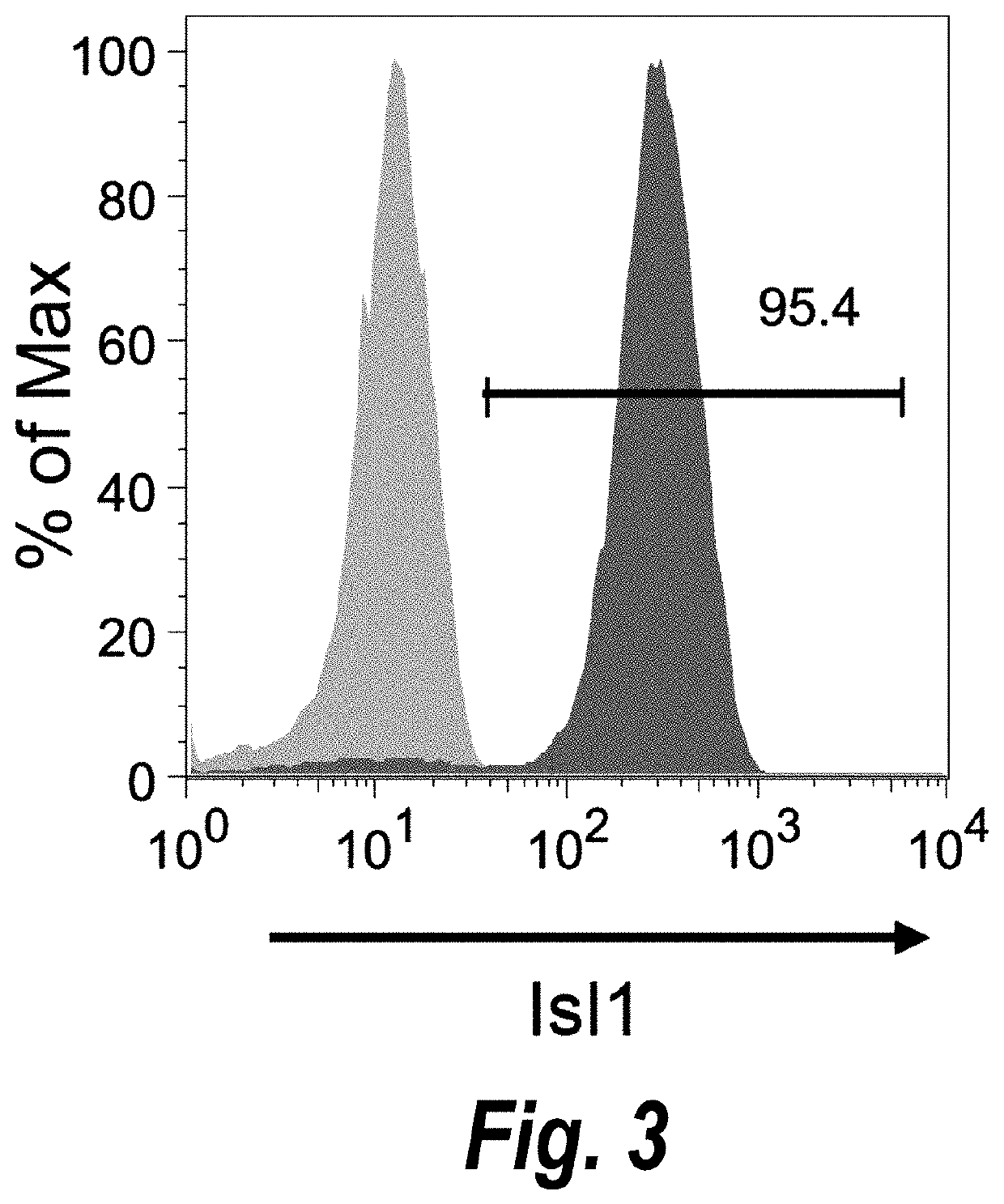
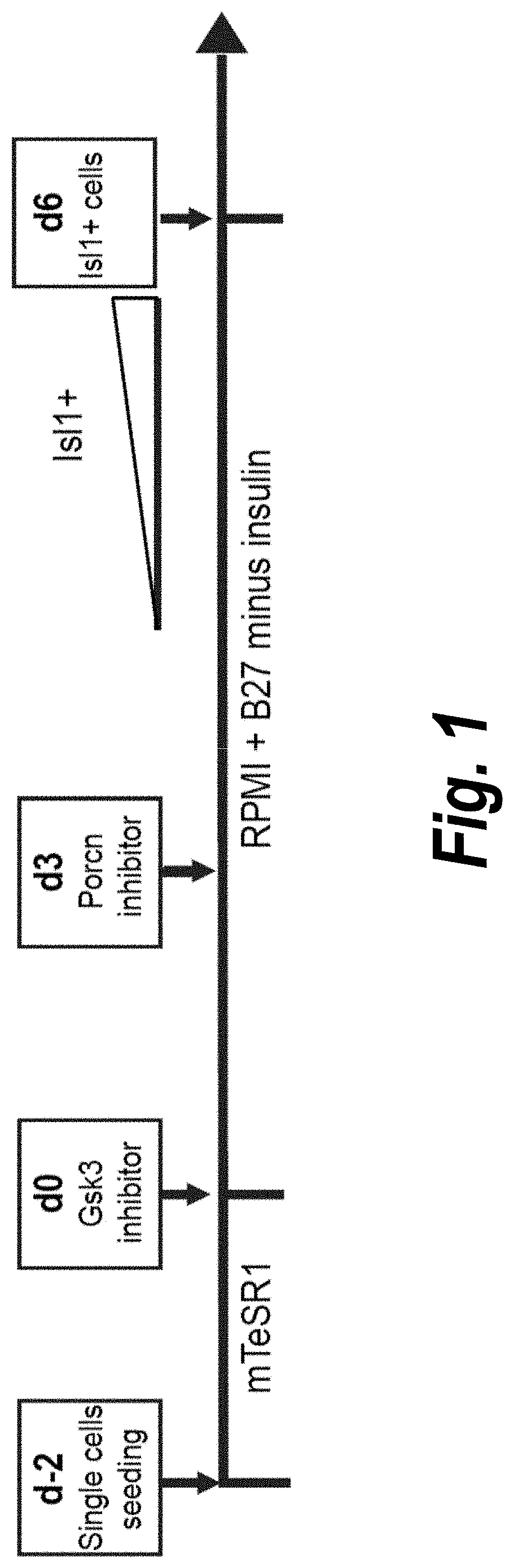
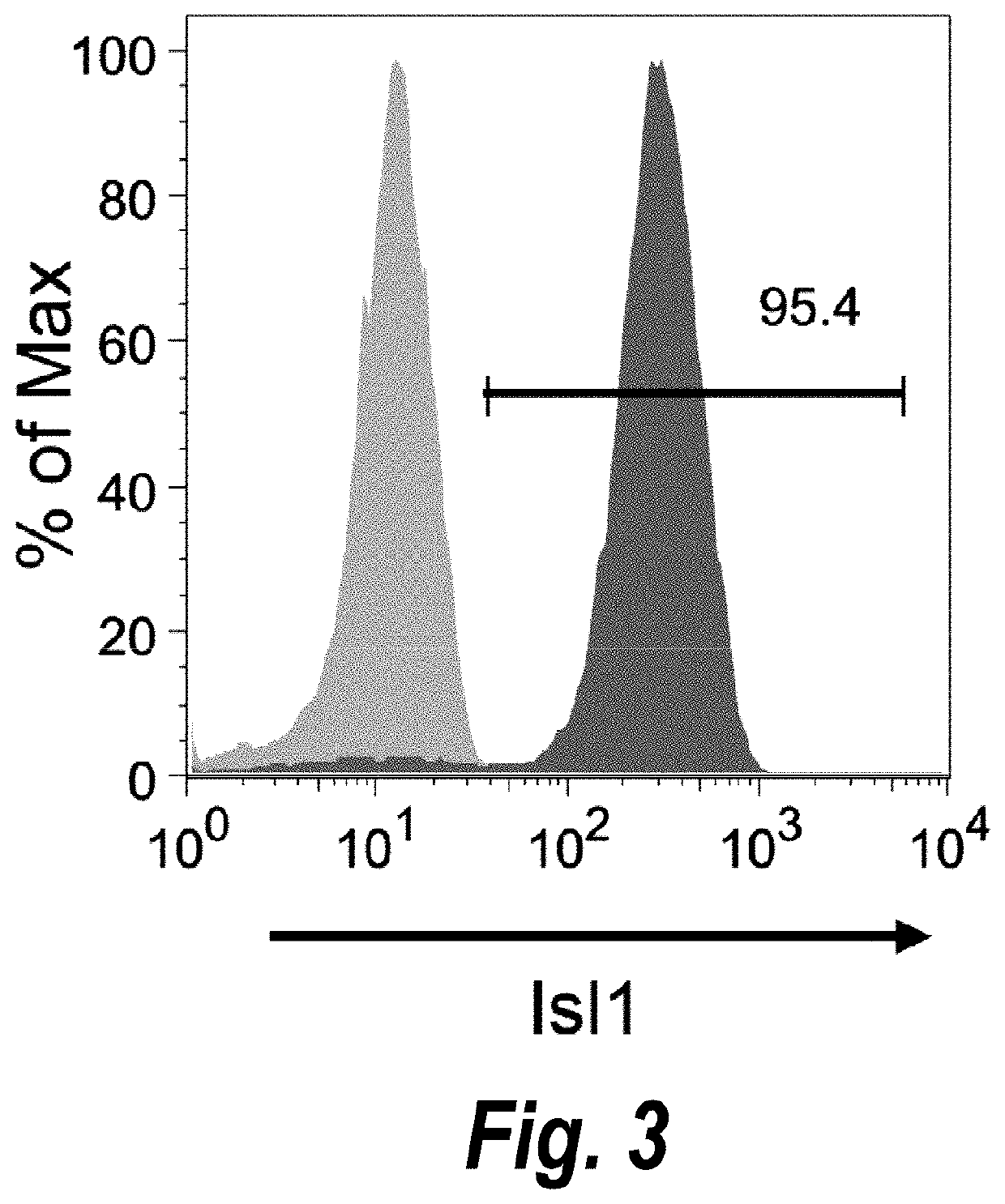
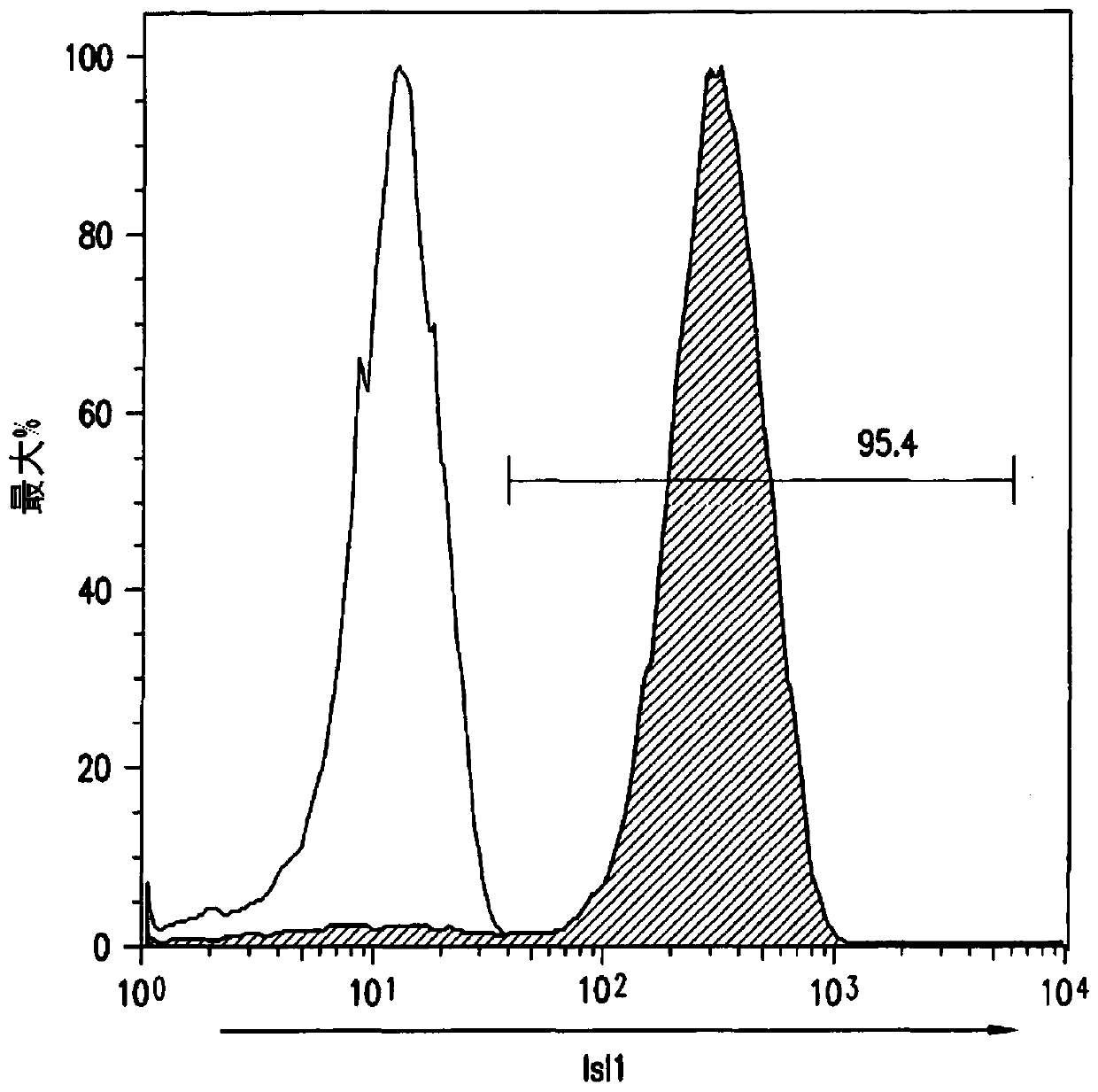
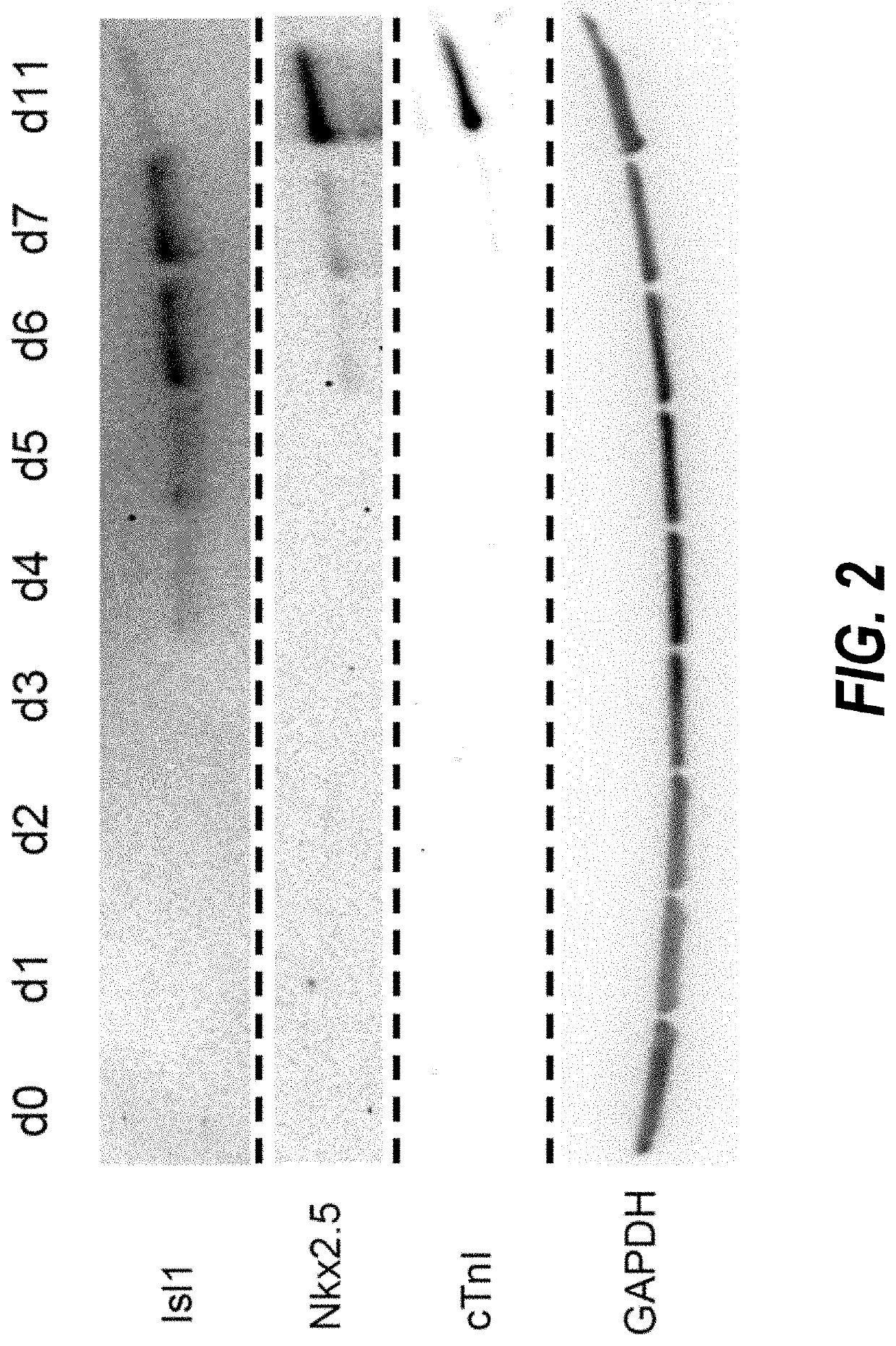
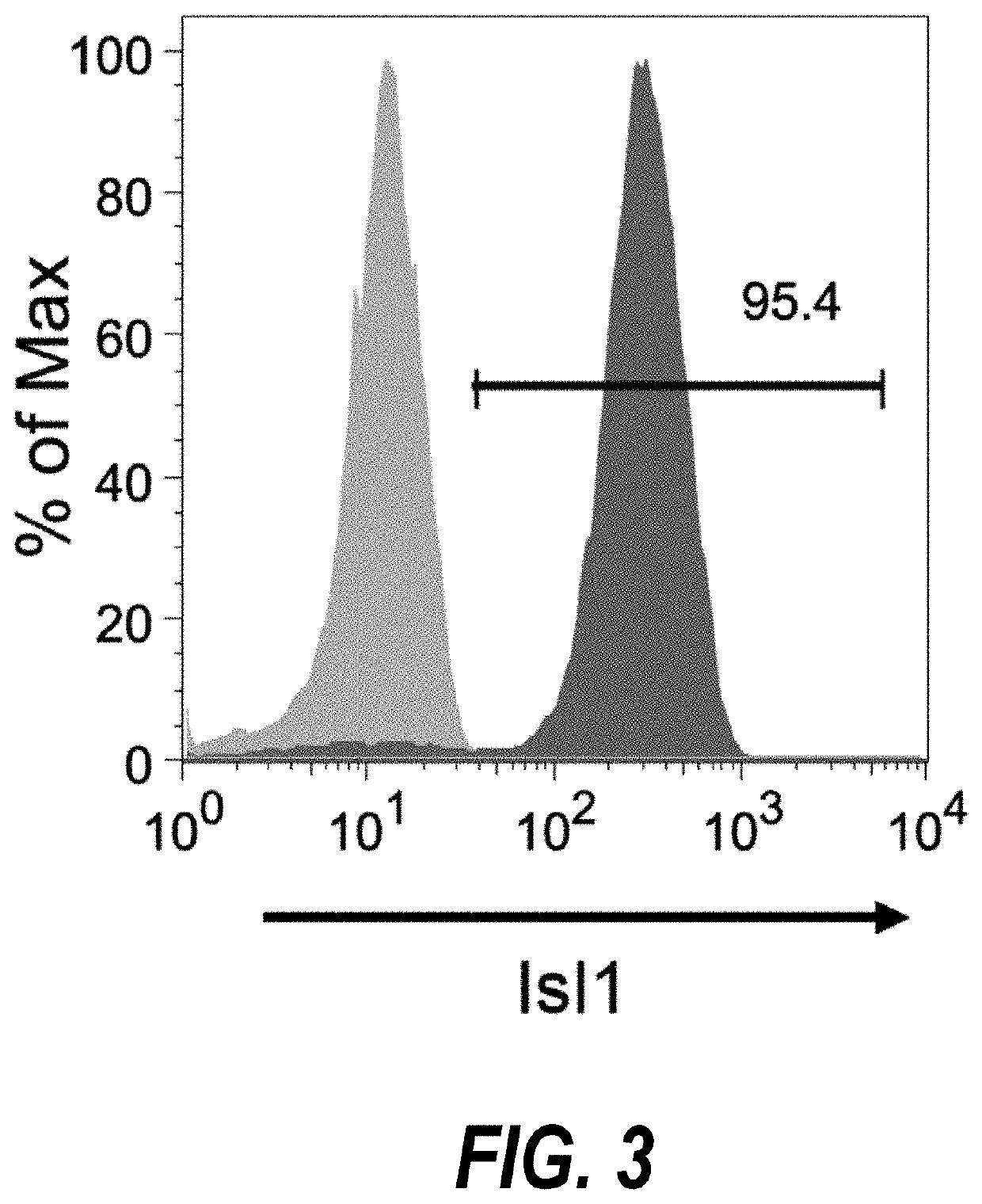
Use of lifr or fgfr3 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS20160108363A1Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseBiocideArtificial cell constructsSurface markerProgenitor
The present invention provides LIFR and FGFR3 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ LIFR+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / LIFR+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Use of jagged 1/frizzled 4 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS20160053229A1Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseBiocideDrug screeningSurface markerProgenitor
The present invention provides Jagged 1 and Frizzled 4 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ Jagged 1+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / Jagged 1+ / Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated Jagged 1+ and / or Frizzled 4+ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of Jagged 1+ and / or Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the Jagged 1+ and / or Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Method and apparatus for replacing a mitral valve with a stentless bioprosthetic valve
A stentless bioprosthetic valve includes at least one piece of biocompatible material comprising a bi-leaflet conduit. The conduit has a distal end, a proximal end defining a first annulus for suturing to the valve annulus of a heart, and leaflets extending between the proximal and distal ends. The distal end defines a second annulus having a profile substantially similar to a first annulus profile, at which the leaflets terminate. The second annulus is sutured to free edges of the leaflets of the native mitral valve that remain intact following resection of the native mitral valve. Therefore, the native chordae tendineae continue to provide prolapse prevention and left ventricular muscle support functions in addition to maintaining continuity between the valve annulus and the papillary muscles. The second annulus is spaced from the papillary muscles. A method for replacing the native mitral valve with a stentless bioprosthetic valve is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method and apparatus for replacing a mitral valve with a stentless bioprosthetic valve
ActiveUS7087079B2Impedes dilatationKeep movingHeart valvesBlood vesselsPosterior leafletLeft ventricular size
A stentless bioprosthetic valve includes at least one piece of biocompatible material comprising a bi-leaflet conduit. The conduit has a distal end and a proximal end that defines a first annulus for suturing to the valve annulus of a heart. The conduit further includes first and second leaflets that mimic the anterior and posterior leaflets of the native mitral valve. The first and second leaflets extend between the proximal and distal ends. The distal end defines a second annulus at which the first and second leaflets terminate. The second annulus is for suturing to free edges of the anterior and posterior leaflets of the native mitral valve that remain intact following resection of the native mitral valve so that the native chordae tendineae continue to provide prolapse prevention and left ventricular muscle support functions in addition to maintaining the continuity between the valve annulus and the papillary muscles. A method for replacing the native mitral valve with a stentless bioprosthetic valve is also provided.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Use of neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS20190062696A1Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseCulture processCell culture supports/coatingProgenitorSurface marker
The present invention provides NRP1 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells (HVPs), in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Additional HVP cell surface markers identified by single cell sequencing are also provided. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
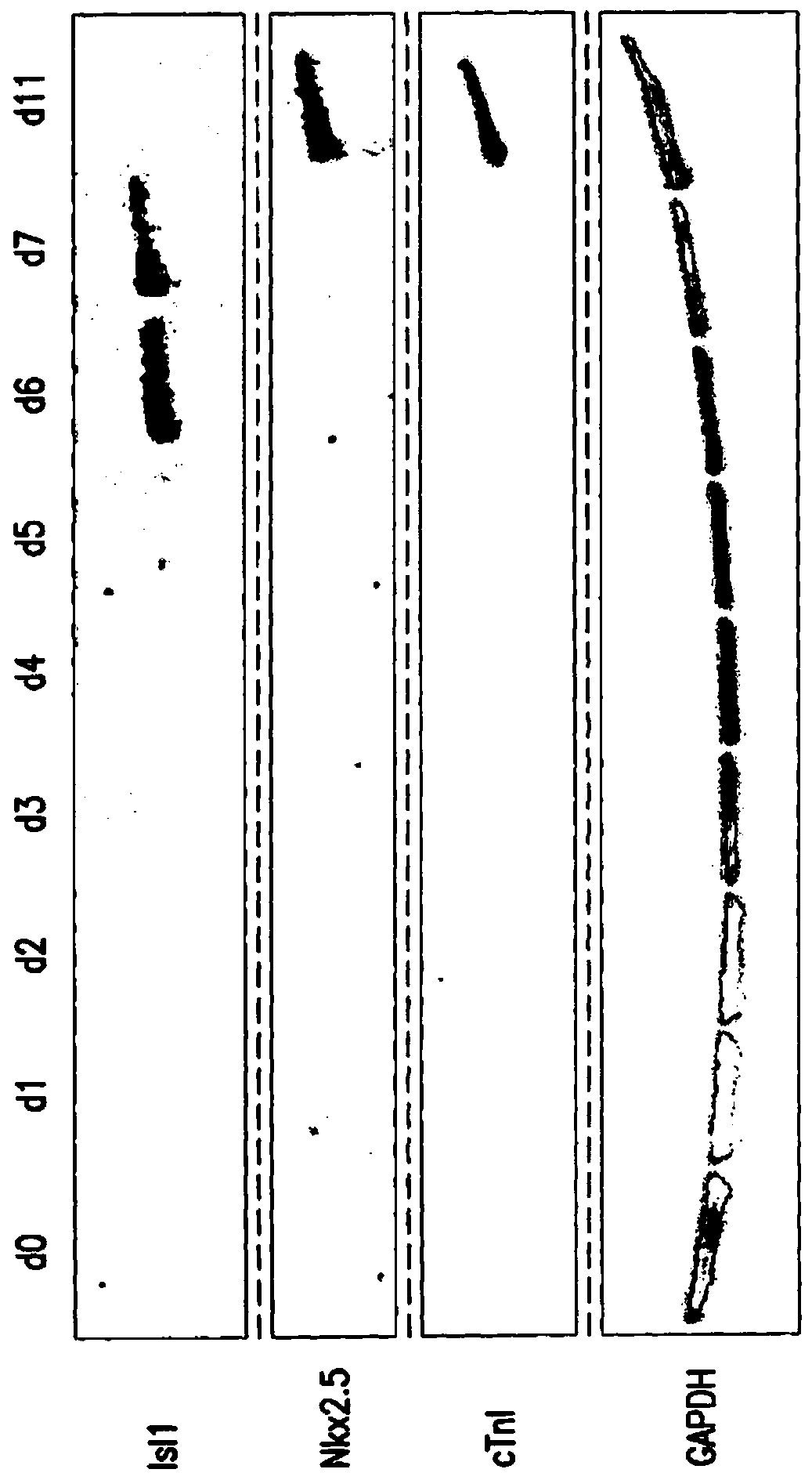
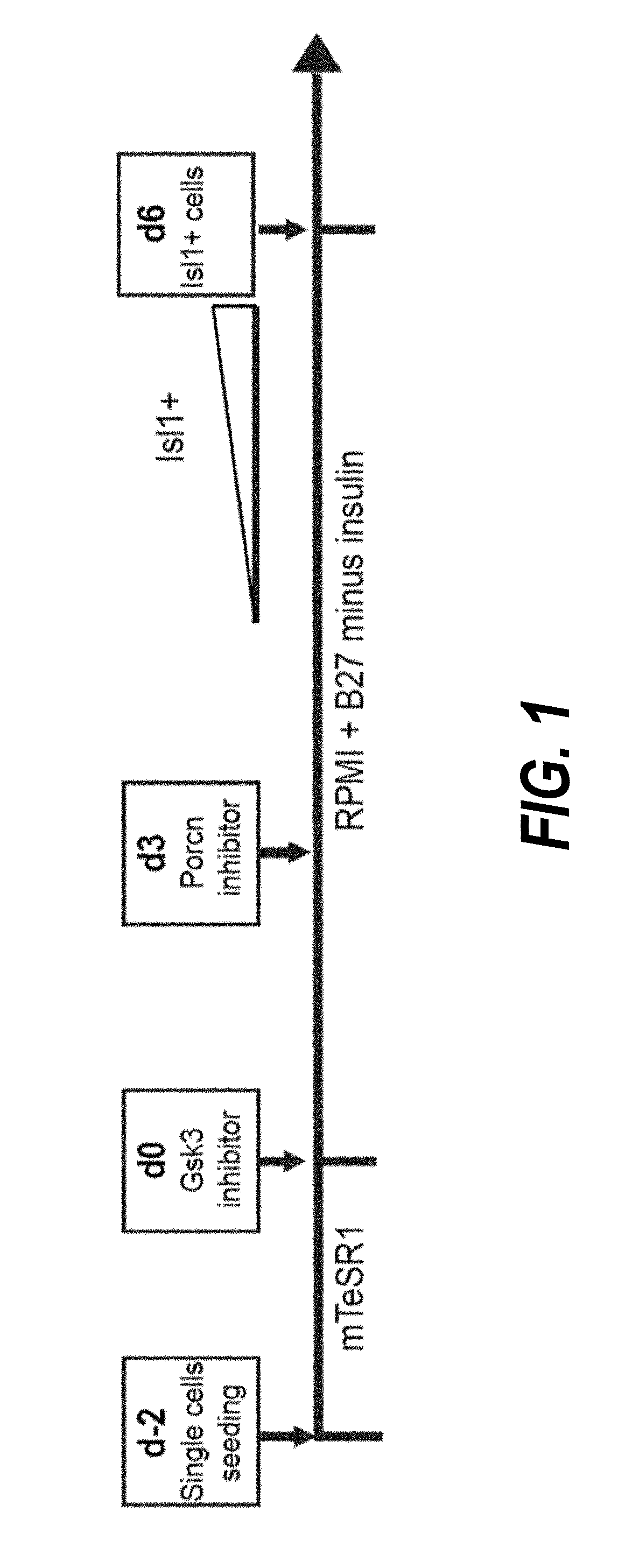
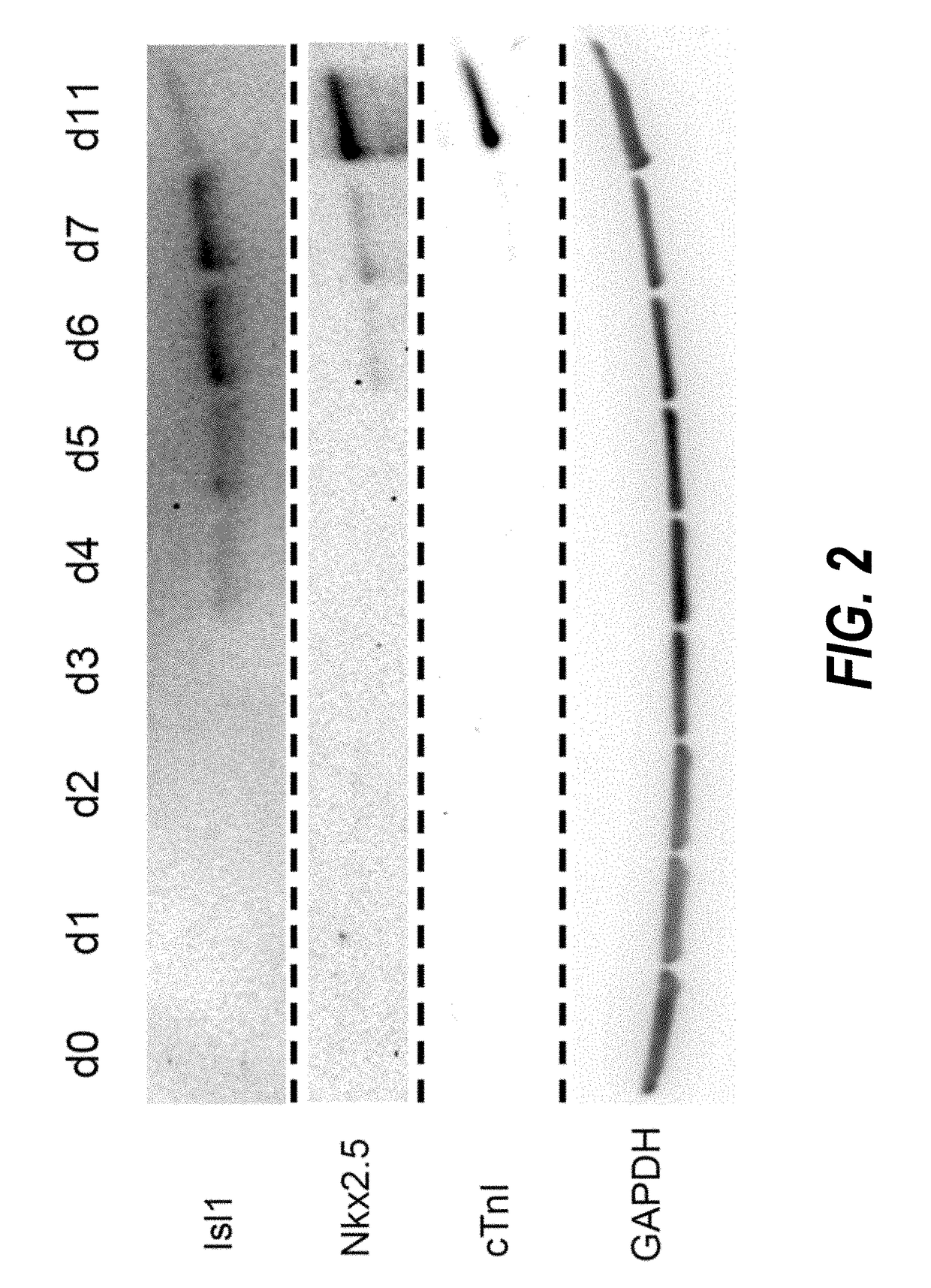
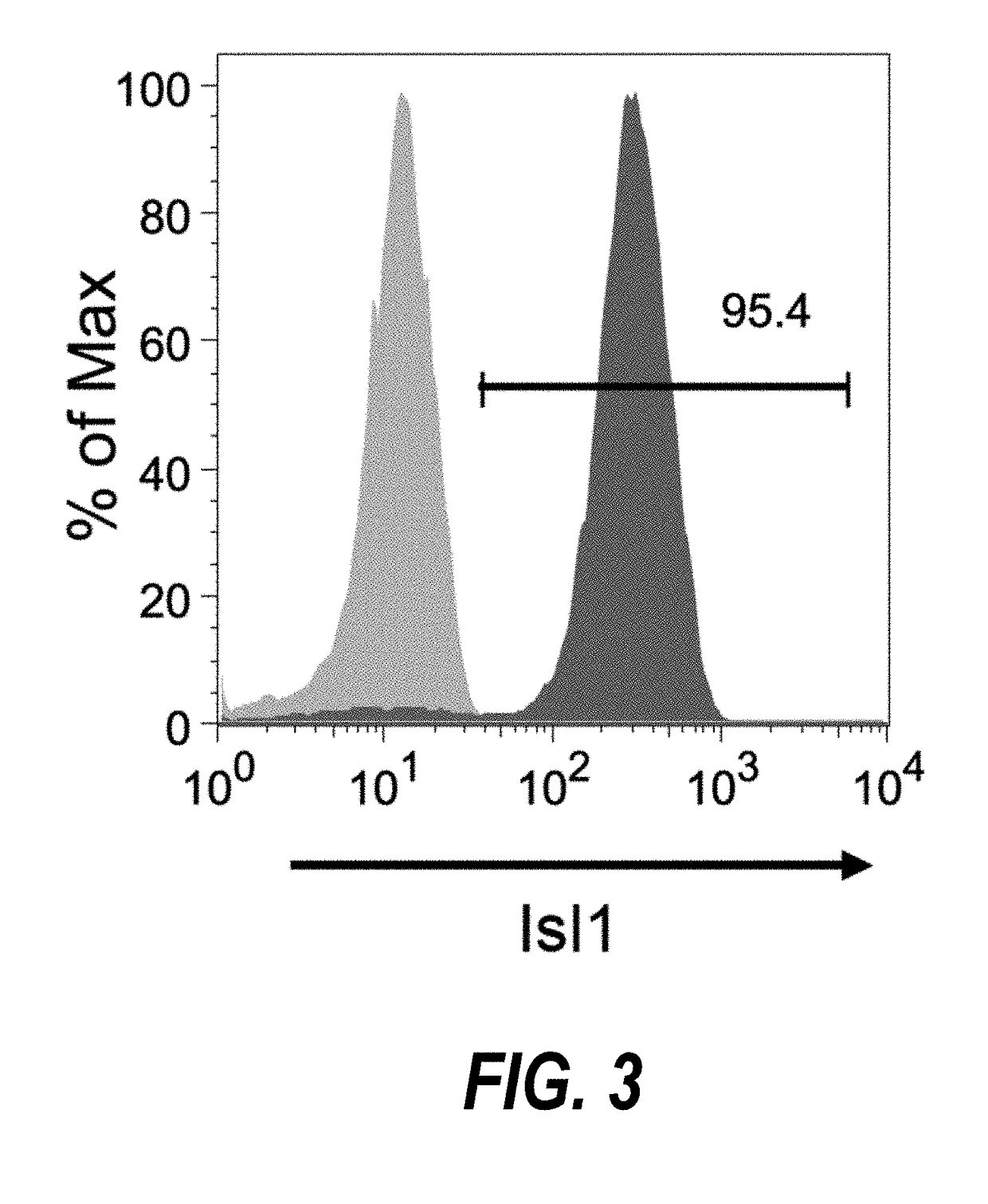
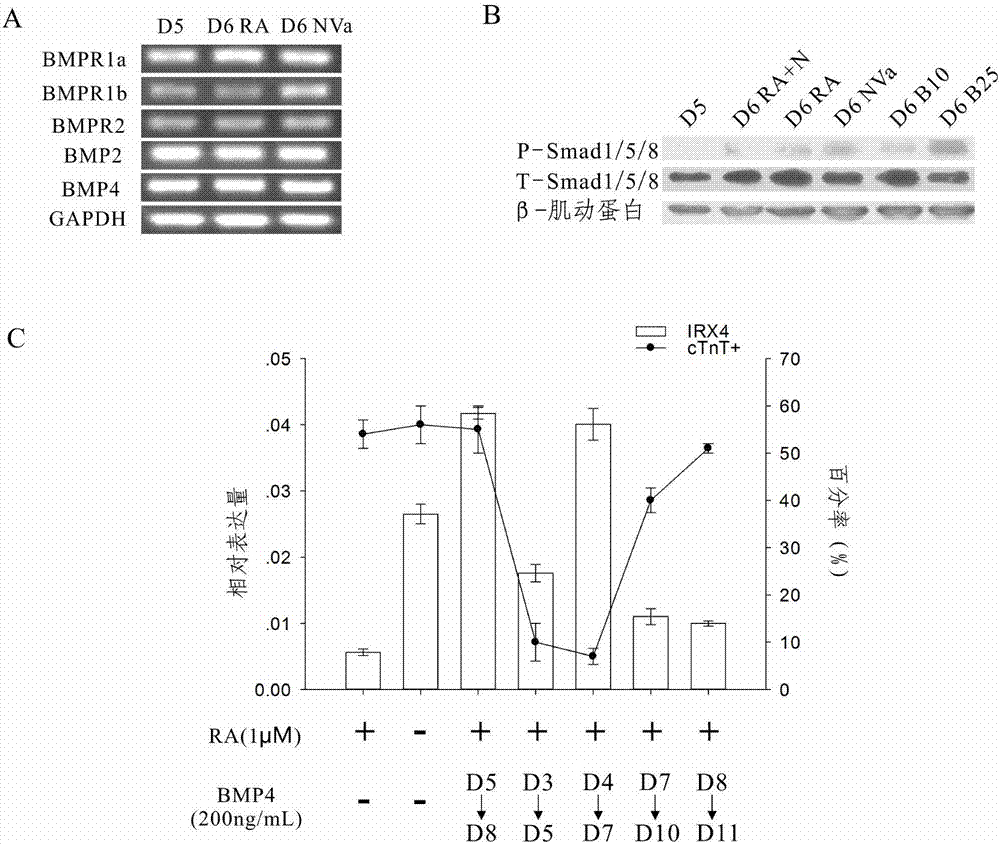
Method for differentiating as ventricular muscle cells by in-vitro induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN107460164AHigh purityDrug screeningSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCells transplantationHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
The invention provides a method for differentiating as ventricular muscle cells by in-vitro induced pluripotent stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: through maintaining, amplifying, and culturing pluripotent stem cells in vitro, in the metaphase of pluripotent stem cell cardiac muscle differentiation, namely the differentiation stage from mesoblastema or cardiac muscle precursor cells to the cardiac muscle cells, adding a substance for directly or indirectly activating an Smad1 / 5 / 8 signal channel to a culture medium, and enabling the stem cells to be directionally differentiated as the ventricular muscle cells. The ventricular muscle cells with the biology activity and function can be successfully obtained by using the method. A regulation mechanism in the differentiation process from the cardiac muscle precursor cells to the ventricular muscle cells is presented, and the human ventricular muscle cells obtained by the differentiation can be extensively applied for the myocardial infarction therapy by the cell transplantation and the cardiac toxicology analysis and the development of cardiac related drugs.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
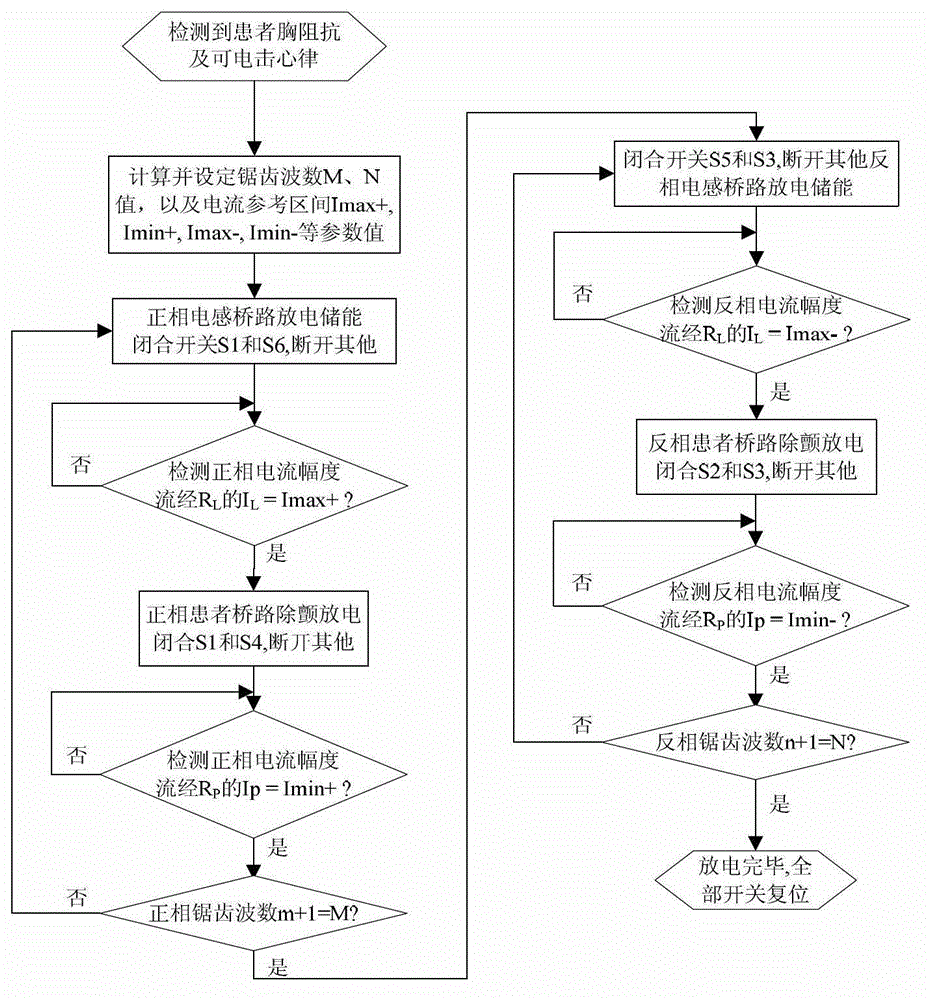
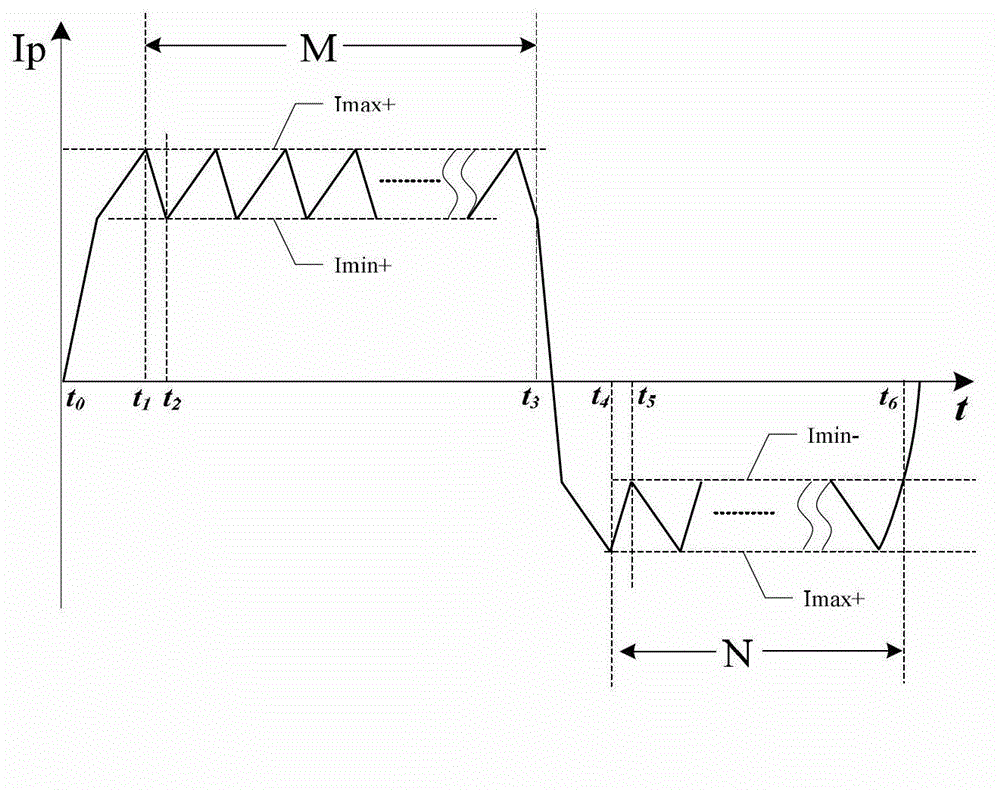
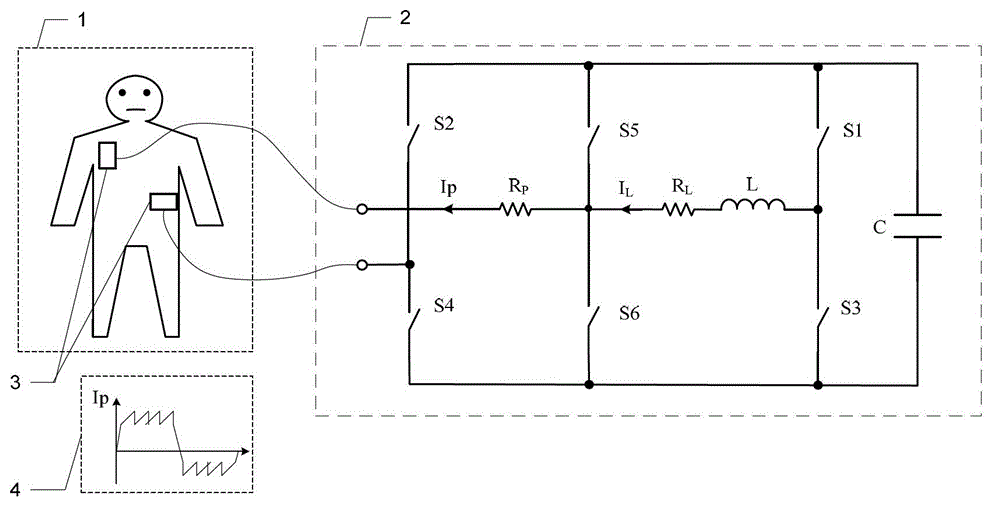
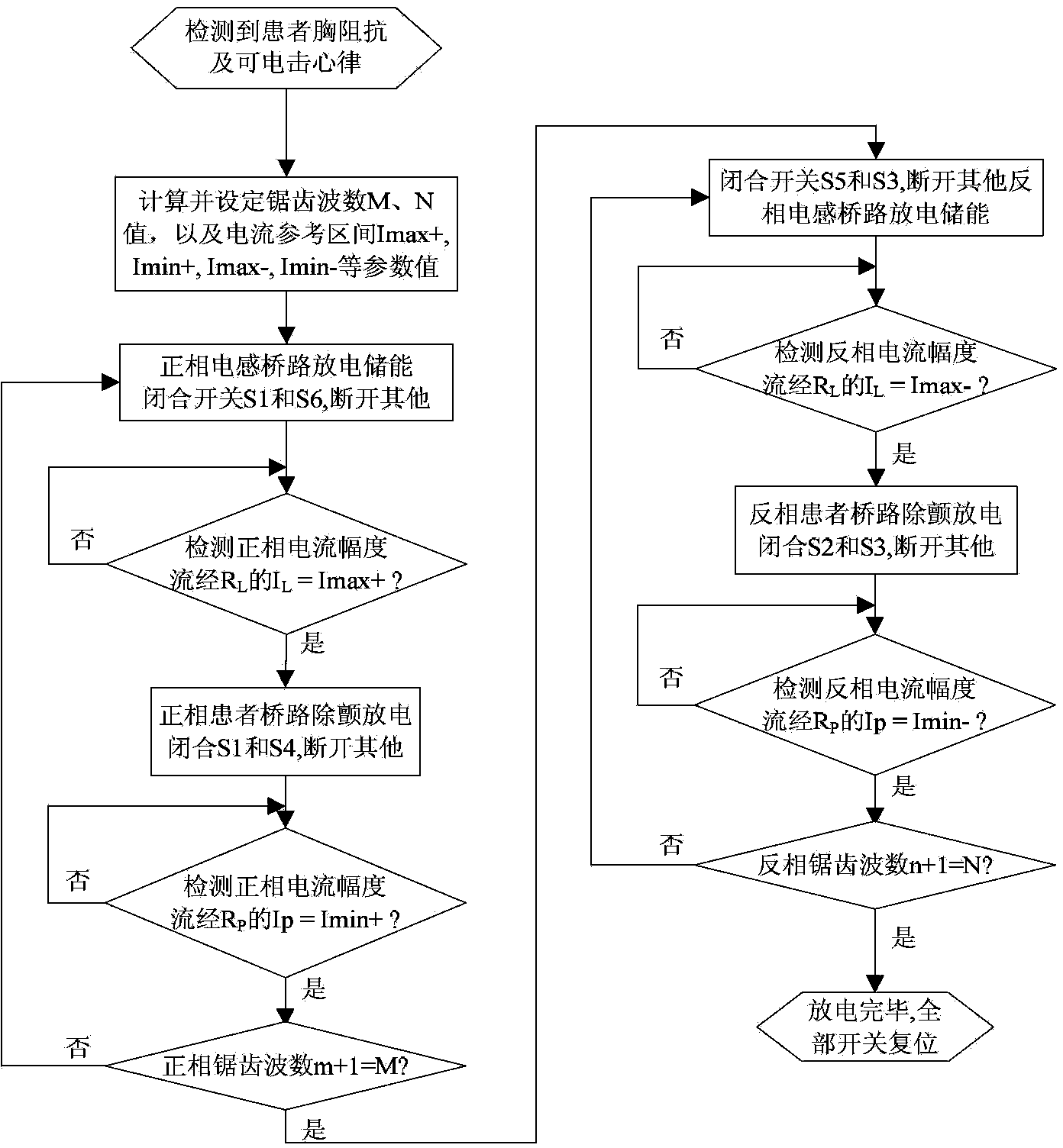
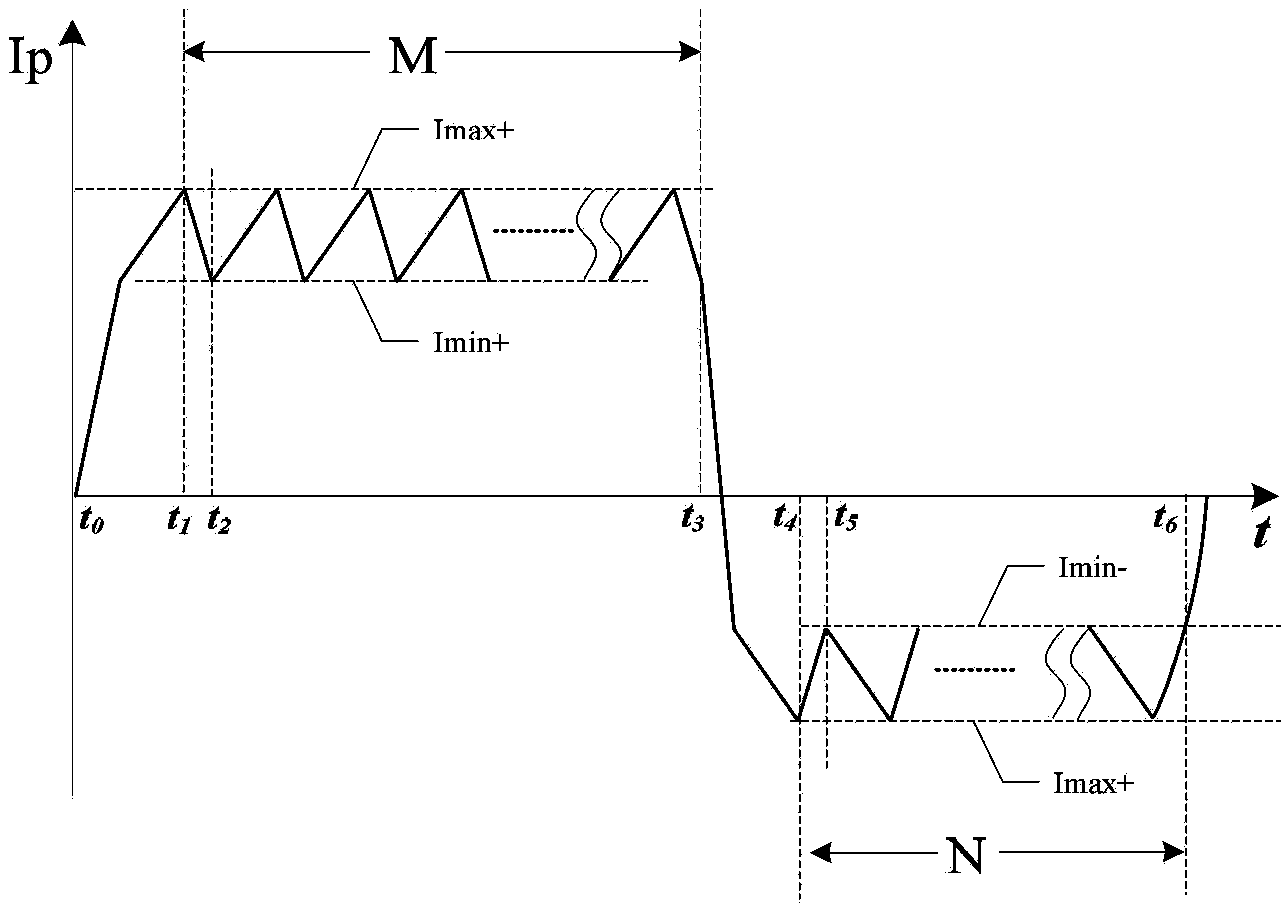
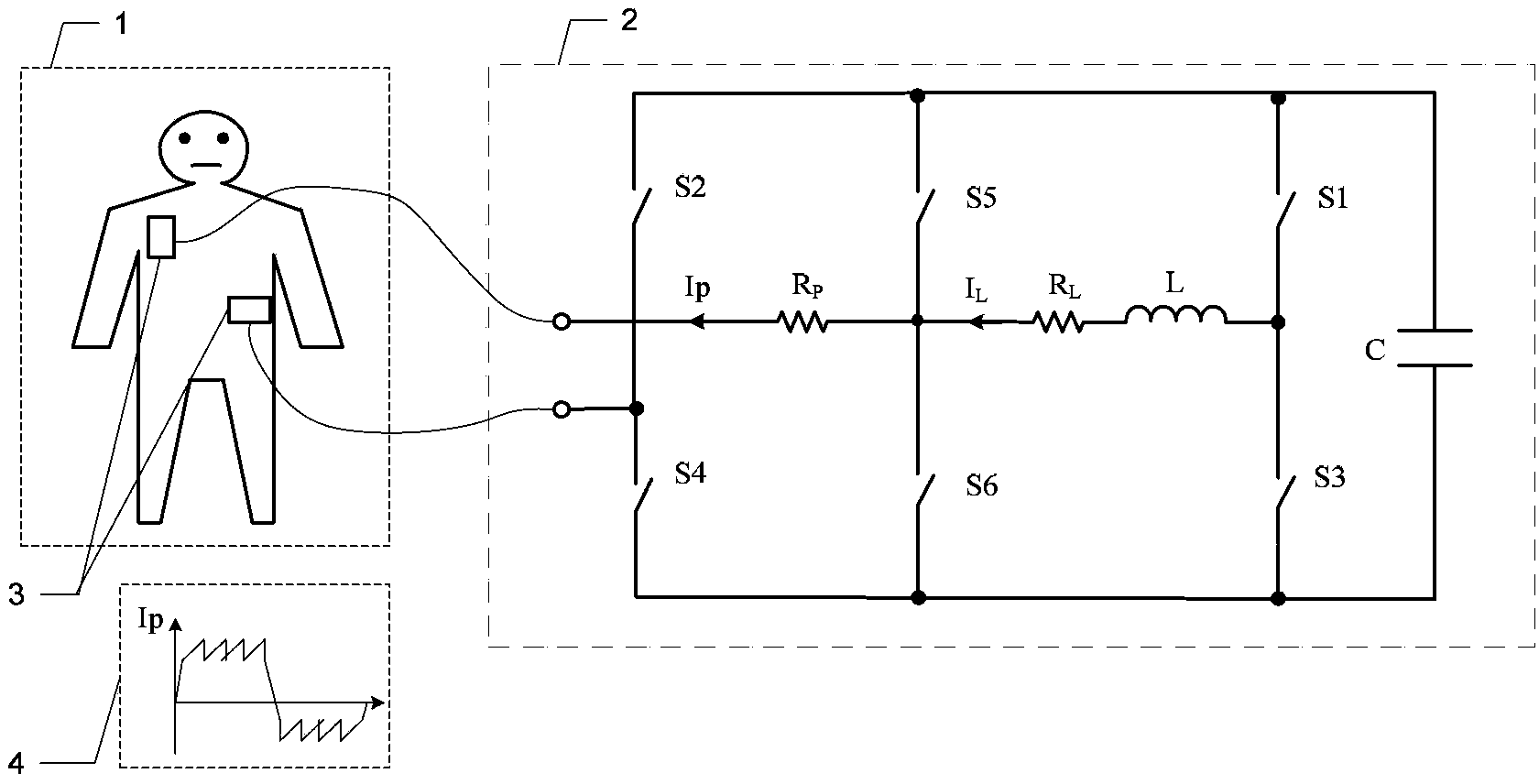
Defibrillator with extended H bridge circuit output stage and biphase sawtooth square wave high-voltage discharge method for defibrillating
ActiveCN102974040AHigh working reliabilityReduce myocardial damageHeart defibrillatorsCurrent sensorEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical electronics, and particularly discloses a defibrillator provided with an extended H bridge circuit output stage and a high-voltage discharge method based on an output stage circuit. The output stage circuit comprises an energy storage capacitor, an inductance coil, current sensors and a plurality of control switches, wherein the control switches are connected mutually to form an extended H bridge circuit switch with three vertical arm bridge circuits and two transverse arm bridge circuits. The high-voltage discharge method comprises the steps that electric energy in the capacitor and induction electric energy in the inductance coil are discharged at a high voltage onto a body of a patient by a defibrillation electrode in a biphase sawtooth waveform mode, so as to terminate fibrillation of a ventricular muscle and implement timely rescue of the patient via the output stage of the defibrillator according to a series of preset bridge circuit switch combinations and control strategies. The defibrillator and the high-voltage discharge method can lower the requirement on a high voltage characteristic of a discharge bridge circuit, individual and accurately-controlled defibrillation electric energy is provided for the patient, the success rate of electric shock defibrillation on a heart is increased, and injures to a cardiac muscle in a defibrillation process are reduced.
Owner:久心医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
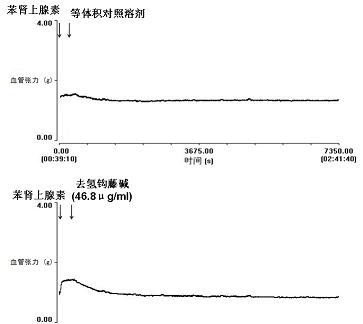
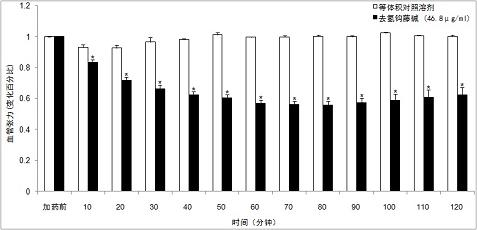
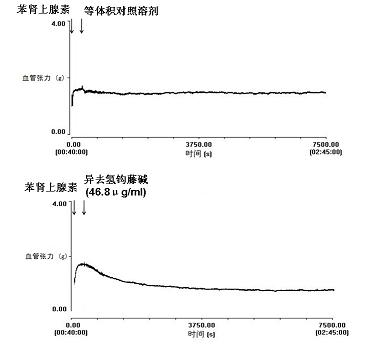
Corynoxeine and application of isomer thereof in preparing medicines
InactiveCN101991573ARaise the excitement thresholdAccurate massOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderVentricular tachycardiaAngina
The invention belongs to the traditional Chinese medicine field, and relates to corynoxeine and an application of an isomer of the corynoxeine in preparing medicines. In the invention, the results of animal experiments prove that the corynoxeine and the isomer thereof have the effects of expanding vessels and lowering blood pressure, and can be used for preparing the medicines for expanding the vessels and lowering the blood pressure; the corynoxeine and isocorynoxeine have the effects of expanding the vessels, lowering heart afterload, lightening heart burden and decreasing myocardial oxygen consumption, and can be used for preparing anti-angina pectoris medicines; the corynoxeine has the effects of negative myodynamia, directly decreasing the myocardial oxygen consumption, and doubly lowering the myocardial oxygen consumption; the corynoxeine and the isocorynoxeine have the effects of improving the ventricular muscle excited threshold and lowering the ventricular muscle contraction frequency, can be used for treating ventricular tachycardia, and can be used as a quality identification uncaria and tagged molecules of the ffective parts of the corynoxeine and the isocorynoxeine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
New application of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and guanfu base VIIII
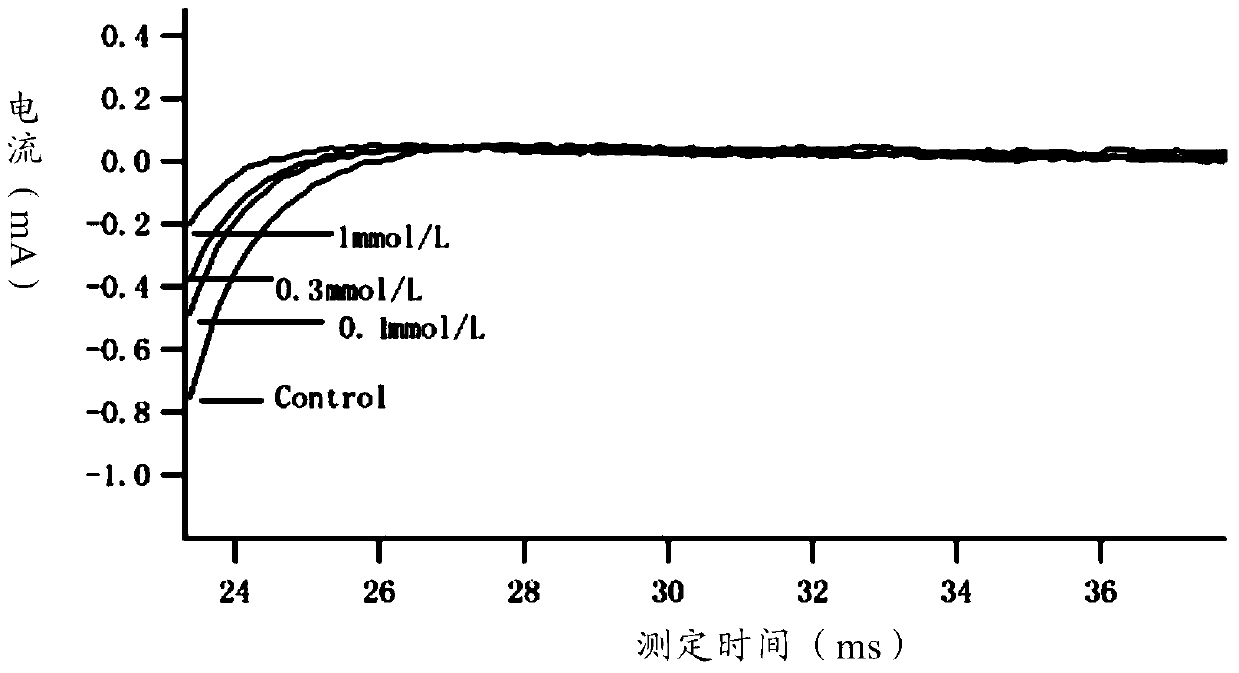
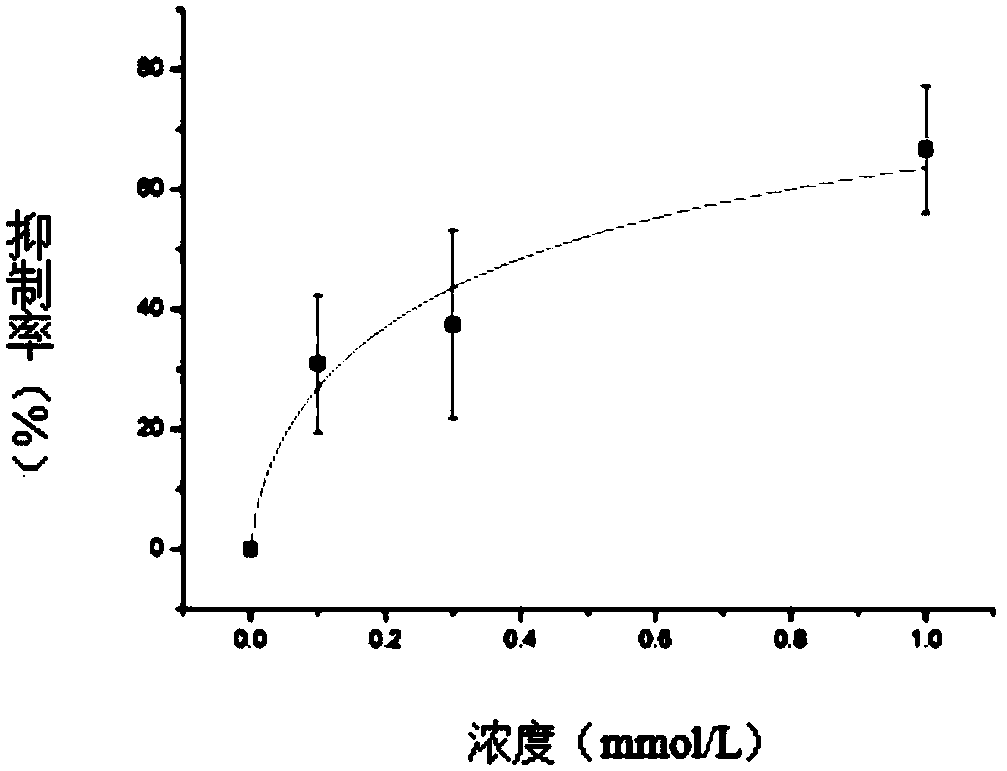
The invention provides a preparation method of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and applications in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent and preparing drugs for resisting arrhythmia. Both the Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and the guanfu base I are provided to have an effect for inhibiting slow sodium current of ventricular muscles of cavies. The invention particularly relates to an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a drug-metabolizing enzyme inhibitor. The invention also provides an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Novel application of Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicine
InactiveCN103156842ASmall contraction forceHeart rate slowing effectOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderSide effectAntiarrhythmic effect
The invention discloses a novel application of a traditional Chinese medicine extract product-Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicines. A research found that the Arctigenin has bidirectional anti-arrhythmia effect and can adjust arrhythmia caused by aconitine and ouabain. Arctigenin has an effect for reducing ventricular muscle contraction force. A pharmacological effect of the Arctigenin is bidirectional adjusted cardiac muscle cell inner calcium current, the cardiac muscle cell inner potassium current is increased, and the sodium current is inhibited. The invention shows that the Arctigenin has anti-arrhythmia effect, and especially has bidirectional adjusting on arrhythmia, the side-effect is smaller, the Arctigenin has application prospect for treating toxic arrhythmia and ischemic-reperfusion arrhythmia in aconitine and ouabain; and the Arctigenin with myocardial contractility reduction effect can be taken as an auxiliary treatment measurement for hypertensive disease.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
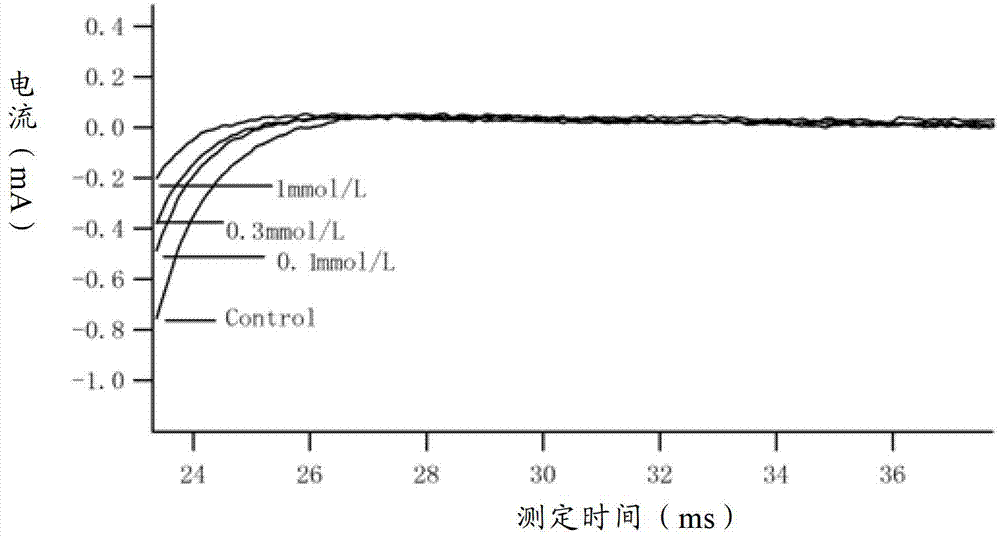
Method for recording Nav 1.5 sodium channel current by separating cavy ventricular muscle cells
InactiveCN102809595AHigh yieldImprove survival rateMaterial electrochemical variablesPower flowCardiac muscle
The invention provides a method for recording an Nav 1.5 sodium channel current by separating cavy ventricular muscle cells. The method comprises two steps of separating a single cavy ventricular muscle cell and recording the Nav 1.5 sodium channel current. According to the method, the yield rate and the survival rate of the separated cavy ventricular muscle cells are enhanced by improvement of a perfusate and a storage way, and the success rate and the stability of an experiment are increased by the prolonging of the stable time of the cell. The separated cavy ventricular muscle cell has a normal ion channel function and the method is suitable to research on a ventricular muscle physiological characteristic by a patch clamp technique; the experiment operation is easy to master, and the method for acutely separating the ventricular muscle cells is simple and efficient.
Owner:辉源生物科技(上海)有限公司
Method for recording L type calcium channel current by separating guinea pig ventricular muscle cells
InactiveCN103103245AFully cleanedAvoid influenceMicrobiological testing/measurementNervous systemAtrioventricular node
An L type calcium channel is mainly distributed in heart, blood vessels, endocrine and nervous systems, and plays a vitally important role in heart and smooth muscle excitation-contraction coupling, atrionector and atrioventricular node action potential conduction. The method that the influence of a compound on the L type calcium channel is observed through a patch clamp recording method so as to evaluate a hearth safety coefficient of the compound and the effect of treating the hypertension becomes an important research mode. According to the method for recording the L type calcium channel current by separating the guinea pig ventricular muscle cells, through improving a perfusate storage mode, the yield rate and the survival rate of separating the guinea pig ventricular muscle cells are increased, and the stabilization time of the cells is prolonged, and thus the success rate and the stability of experiments are increased.
Owner:辉源生物科技(上海)有限公司
Use of lifr or fgfr3 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
PendingUS20200268803A1Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUnknown materialsSurface markerCardiac functioning
The present invention provides LIFR and FGFR3 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ LIFR+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / LIFR+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Use of jagged 1/frizzled 4 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS10597637B2Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseDrug screeningSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSurface markerCardiac functioning
The present invention provides Jagged 1 and Frizzled 4 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ Jagged 1+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / Jagged 1+ / Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated Jagged 1+ and / or Frizzled 4+ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of Jagged 1+ and / or Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the Jagged 1+ and / or Frizzled 4+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Use of LIFR or FGFR3 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS10596200B2Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSurface markerCardiac functioning
The present invention provides LIFR and FGFR3 as cell surface markers for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells, in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Thus, the invention provides human ventricular progenitor (HVP) cells. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of Islet 1+ LIFR+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells and / or Islet 1+ / LIFR+ / FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the LIFR+ and / or FGFR3+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Use of neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveCN111133099ACulture processImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerCardiac functioning
The present invention provides NRP1 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells (HVPs), in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Additional HVP cell surface markers identified by single cell sequencing are also provided. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Use of Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS11186820B2Easy and rapid isolationFunction increaseCulture processImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerCardiac functioning
The present invention provides NRP1 as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiomyogenic ventricular progenitor cells (HVPs), in particular progenitor cells that preferentially differentiate into cardiac ventricular muscle cells. Additional HVP cell surface markers identified by single cell sequencing are also provided. The invention provides in vitro methods of the separation of NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells, and the large scale expansion and propagation thereof. Large clonal populations of isolated NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the NRP1+ ventricular progenitor cells for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
Total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani and novel use of Guanfu base I
The invention provides a preparation method of total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani as well as an application of the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani in preparing a slow sodium ion channel blocker and an antiarrhythmic medicine. Researches show that both the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani and Guanfu A hydrochlorate have an inhibiting effect on a slow sodium current of the ventricular muscle of a guinea pig. The invention particularly relates to an application of the Guanfu base I in preparing enzyme inhibitors for drug metabolism. The invention further provides an application of the Guanfu base A in preparing the slow sodium ion channel blocker.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Adjustable curved heart intracavity defibrillation catheter with inflatable air bag at head end
PendingCN110743102ACurved bigAvoid direct conflictBalloon catheterHeart defibrillatorsX-rayBlood vessel
The present invention discloses an adjustable curved heart intracavity defibrillation catheter with an inflatable air bag at a head end. The adjustable curved heart intracavity defibrillation cathetercomprises a handle and an outer surface of one end of the handle is provided with a balloon syringe interface and a defibrillation electrode tail circuit interface. A bending controller can enable the defibrillation catheter to accurately reach more heart intracavity spaces and to be better attached to ventricular muscles, so that lower-energy defibrillation is realized and use of a clinician isfacilitated. A defibrillation electrode can record electrical activity of each part in heart cavity and is conductive for the clinician to judge specific positions in the heart cavity. A head end balloon prevents risks of vascular rupture caused by mistake-entering of the catheter into small blood vessels, can increase contact area of the catheter head end with the heart, prevents the catheter from puncturing cardiac muscles to lead to cardiac rupture, can realize bedside blind sending of the defibrillation catheter into the heart cavity, reduces harms of X rays to body health, shortens rescuetime consumed by going to a heart catheter chamber, and can best master the best rescue time for patients.
Owner:YANTAI YUHUANGDING HOSPITAL
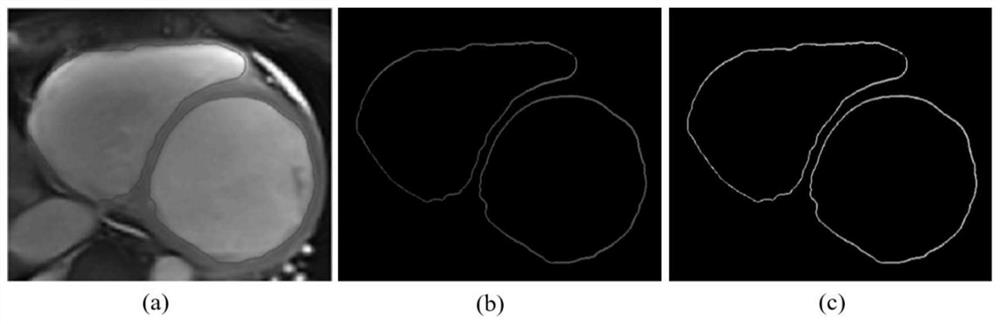
Automatic diagnosis system for human body dilated cardiomyopathy
ActiveCN113112473AAvoid errorsReduce manual involvementImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyOriginal data
The invention relates to the technical field of diagnosis of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), in particular to an automatic diagnosis system for human dilated cardiomyopathy. The system provided by the invention can realize the following diagnosis process: a heart image in a heart cycle is used as original data to be input, and a computer program can judge an end diastole image and an end systole image from the original data to segment a left ventricle and a right ventricle; and then heart parameters capable of reflecting the strain information of the left ventricle, the right ventricle and the ventricular muscle wall are calculated. After heart parameters are obtained, features of the heart parameters are input into a classifier, and DCM patients and non-DCM patients can be distinguished. The end-to-end full-automatic DCM diagnosis is realized, and compared with manual or semi-automatic diagnosis, the end-to-end full-automatic DCM diagnosis method has a good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
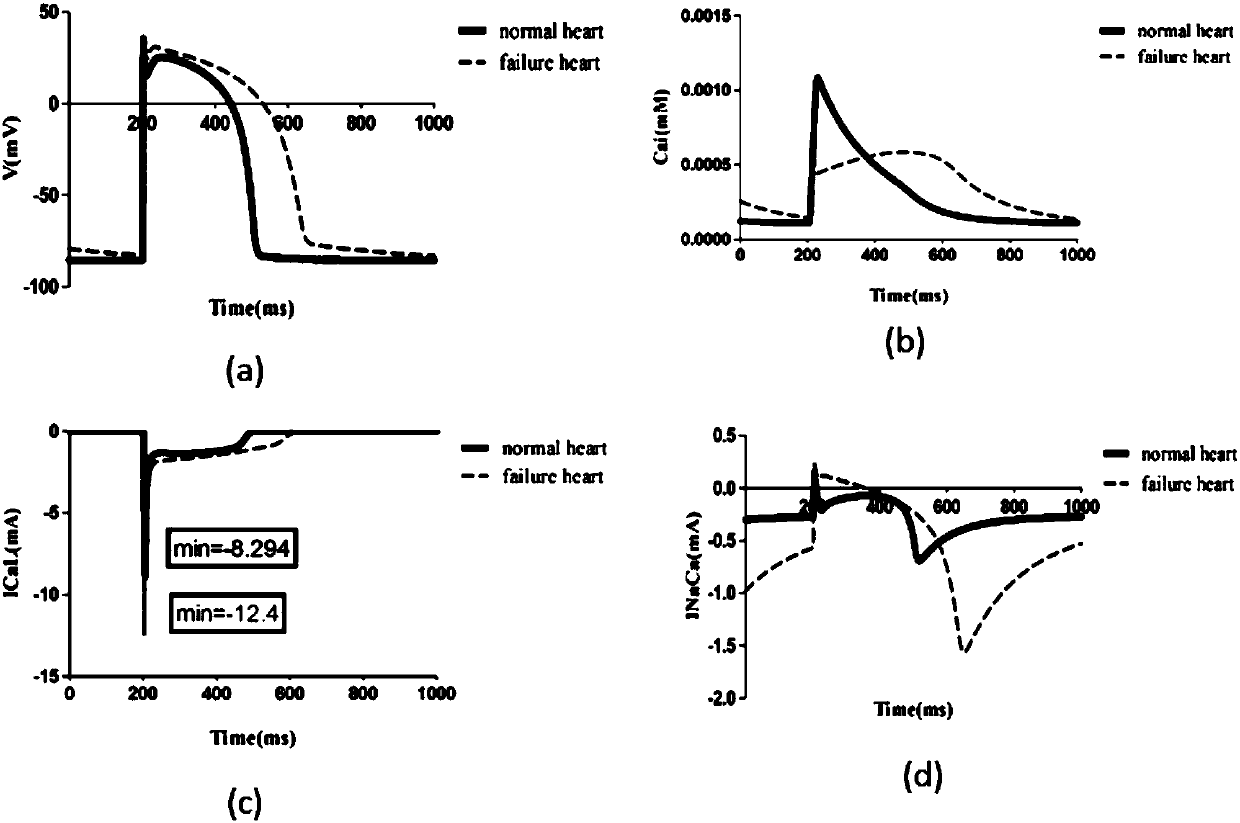
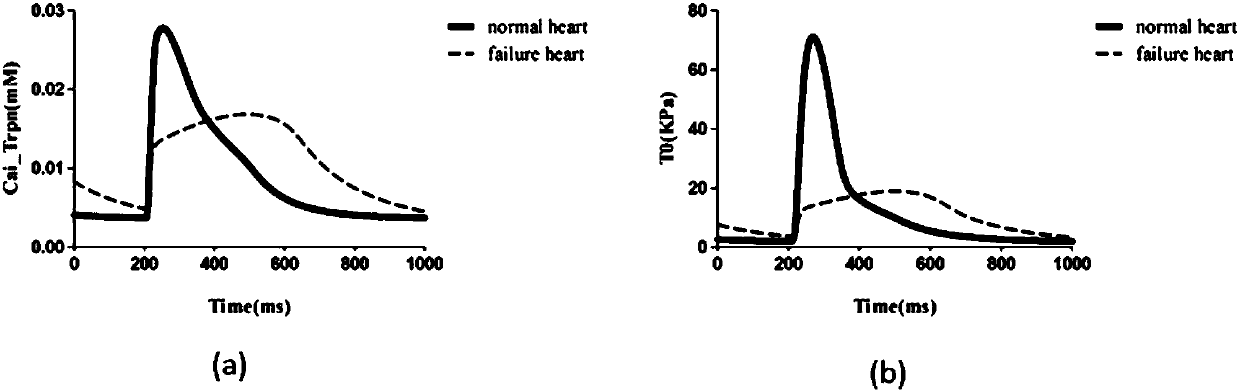
Design method for heart failure model of human ventricular muscle tissue
ActiveCN107273655ADeepen understandingGuaranteed simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyResearch Object
The invention discloses a design method for a heart failure model of a human ventricular muscle tissue, and belongs to the technical field of virtual human hearts. Heart failure is taken as a research object, and myocardial electrophysiological and mechanics characteristics and a spiral wave dynamics mechanism under heart excitation-contraction coupling are discussed to discover a relationship of interaction between the heart failure and arrhythmia. A TP06 model simulates a single ventricular muscle cell of a human body, then the TP06 model is coupled to an NHS08 model, and an ECC model is built; based on an improved TP06 model and existing data, a human ventricular heart failure muscle cell model is built, and the electrophysiological and mechanics characteristics of human ventricular muscle cells, an action potential duration restitution curve and an early afterdepolarization restitution curve under normal and heart failure conditions are compared; finally by adding coupling among the cells, a two-dimensional single-layer myocardial tissue action potential conduction model is successfully built, and spiral waves are induced by adopting a ''wave shearing method''; and then, dynamics characteristics of the spiral waves under the normal and heart failure conditions are compared.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
New application of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and guanfu base VIIII
The invention provides a preparation method of Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and applications in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent and preparing drugs for resisting arrhythmia. Both the Korean mondshood root total alkaloids and the guanfu base I are provided to have an effect for inhibiting slow sodium current of ventricular muscles of cavies. The invention particularly relates to an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a drug-metabolizing enzyme inhibitor. The invention also provides an application of guanfu base VIIII in preparing a slow sodium-ion passage blocking agent.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
New Application of Total Alkaloids of Guanbaifu and Guanfu Nonin
The invention provides a preparation method of total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani as well as an application of the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani in preparing a slow sodium ion channel blocker and an antiarrhythmic medicine. Researches show that both the total alkaloids of radix aconiti coreani and Guanfu A hydrochlorate have an inhibiting effect on a slow sodium current of the ventricular muscle of a guinea pig. The invention particularly relates to an application of the Guanfu base I in preparing enzyme inhibitors for drug metabolism. The invention further provides an application of the Guanfu base A in preparing the slow sodium ion channel blocker.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
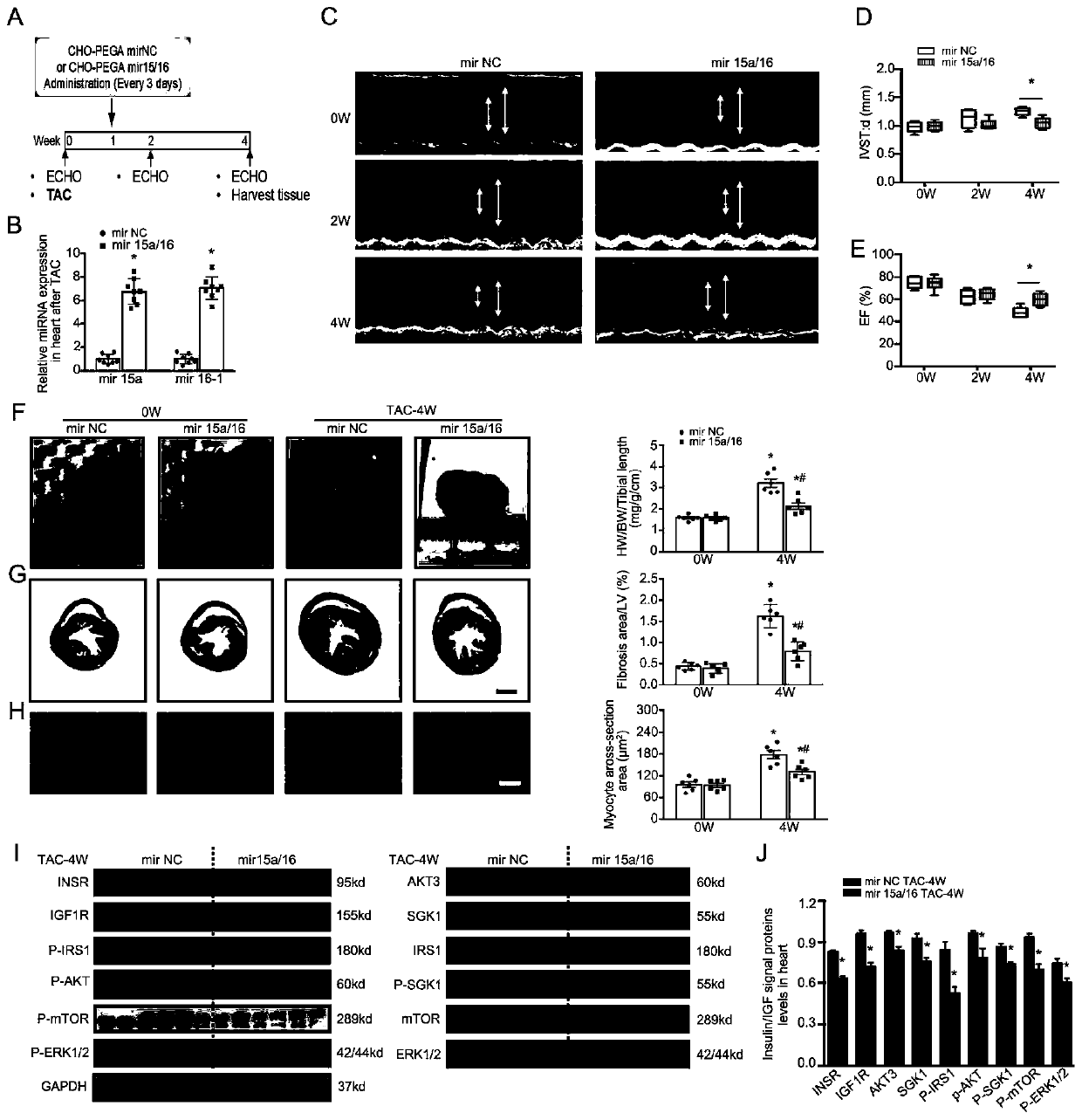
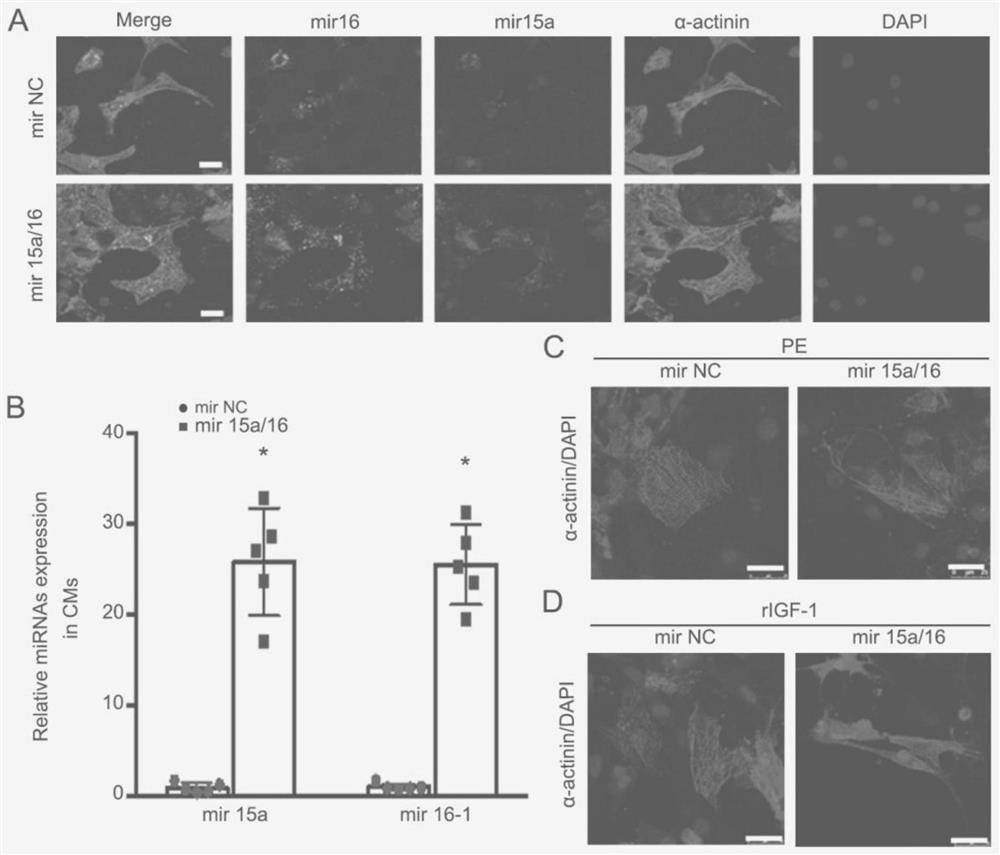
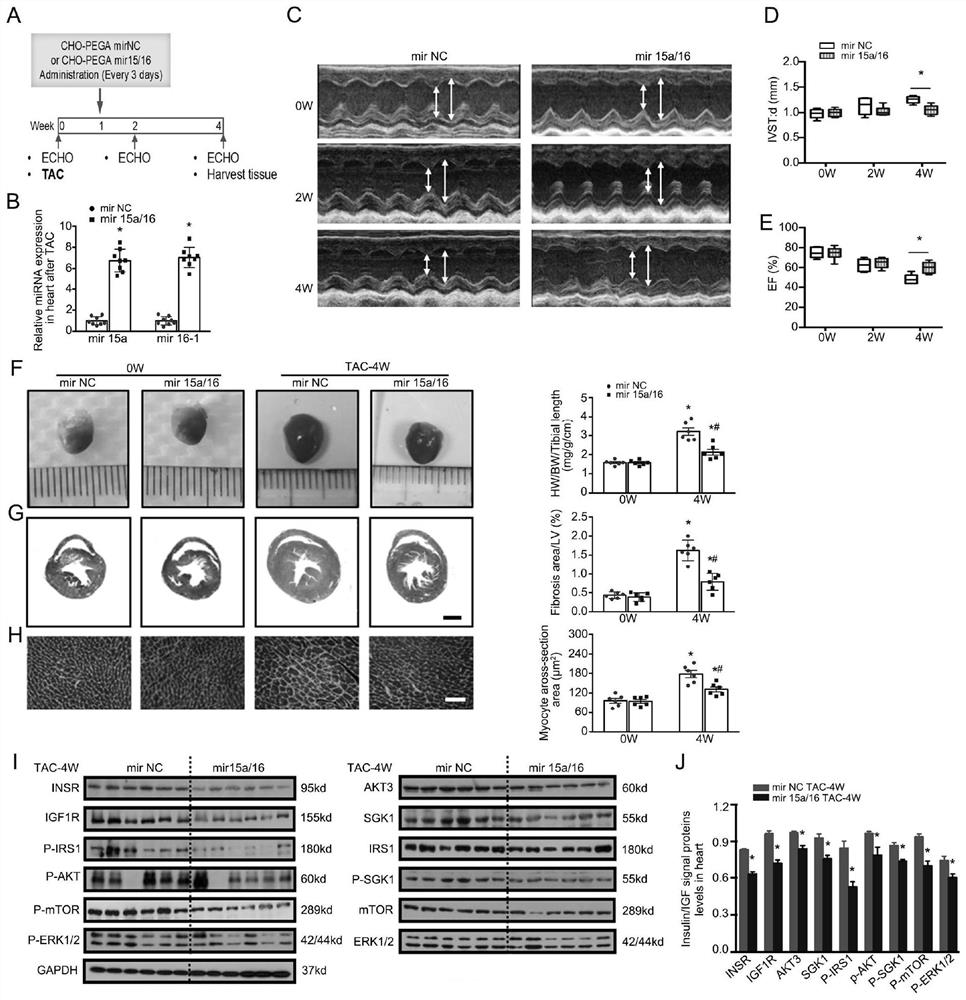
Application of miRNA in treating cardiac hypertrophy
ActiveCN111184734APrevent hypertrophyPrevent heart failureOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderNucleotideVentricular cavity
The invention relates to an application of miRNA in treating cardiac hypertrophy. Particularly, the miRNA is hsa-miR-15a-5p / hsa-miR-16-5p, and the nucleotide sequences of the miRNA are shown as SEQ IDNO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The cardiac hypertrophy refers to a pathophysiological process which is caused by overloading of a heart due to genetic factors, hypertension, myocardial infarction, valve diseases and the like and mainly takes thickening of ventricular muscles and narrowing of ventricular cavities as main characteristics. The invention also relates to an application of a complex loaded withthe hsa-miR-15a-5p / hsa-miR-16-5p in preparing a medicament for treating cardiac hypertrophy, wherein the complex is a CHO-PGEA-nucleic acid complex.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEART LUNG & BLOOD VESSEL DISEASES
Application of miRNA in the treatment of cardiac hypertrophy
The present invention relates to the application of miRNA in the treatment of myocardial hypertrophy. Specifically, the miRNA is hsa-miR-15a-5p / hsa-miR-16-5p, and its nucleotide sequences are respectively as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.1. Shown in ID NO.2. The cardiac hypertrophy refers to a pathophysiological process mainly characterized by thickening of the ventricular muscle and narrowing of the chamber caused by the overload of the heart caused by heredity, hypertension, myocardial infarction, valvular disease and the like. The present invention also relates to the application of the complex loaded with hsa-miR-15a-5p / hsa-miR-16-5p in the preparation of medicine for treating myocardial hypertrophy, the complex being CHO-PGEA-nucleic acid complex.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEART LUNG & BLOOD VESSEL DISEASES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com