Use of neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a cell surface marker for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
A technology of cardiac progenitor cells and progenitor cells, applied in the field of the ventricular region of the heart, can solve problems such as isolating a large number of living cells, and the target is out of reach
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0204] In another embodiment, the method includes:
[0205] administering a test compound to a non-human animal, wherein the non-human animal comprises NRP1+ human ventricular progenitor cells transplanted into an organ of the non-human animal; and
[0206] The effect of test compounds on NRP1+ human ventricular progenitor cells in non-human animals is assessed.
[0207] In one embodiment, for example, by measuring the effect of a test compound on the viability of human ventricular tissue or NRP1+ human ventricular progenitor cells in a non-human animal (compared to the viability of the tissue or progenitor cells in the absence of the test compound), To assess the cardiotoxicity of test compounds. Cell viability can be assessed by standard methods known in the art.
[0208] In another embodiment, for example, by measuring the effect of the test compound on the differentiation of human ventricular tissue or NRP1+ progenitor cells in a non-human animal (compared to the differe...
Embodiment 1
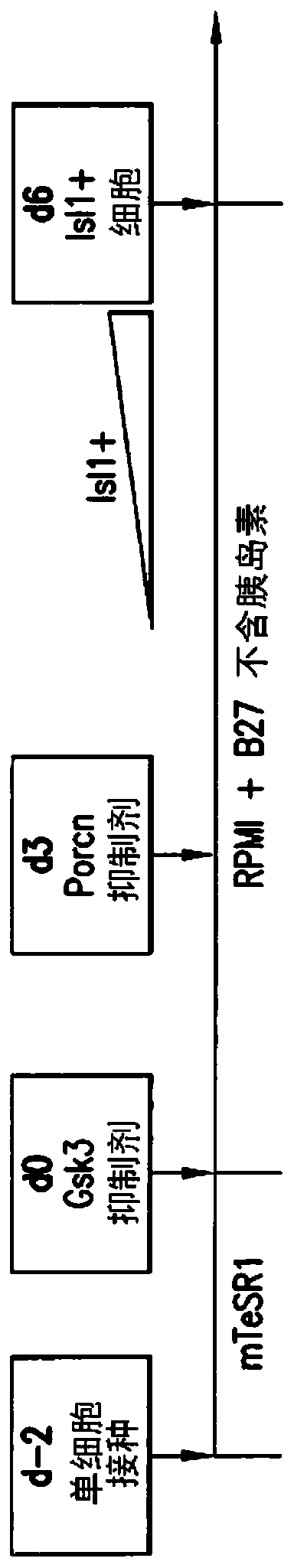
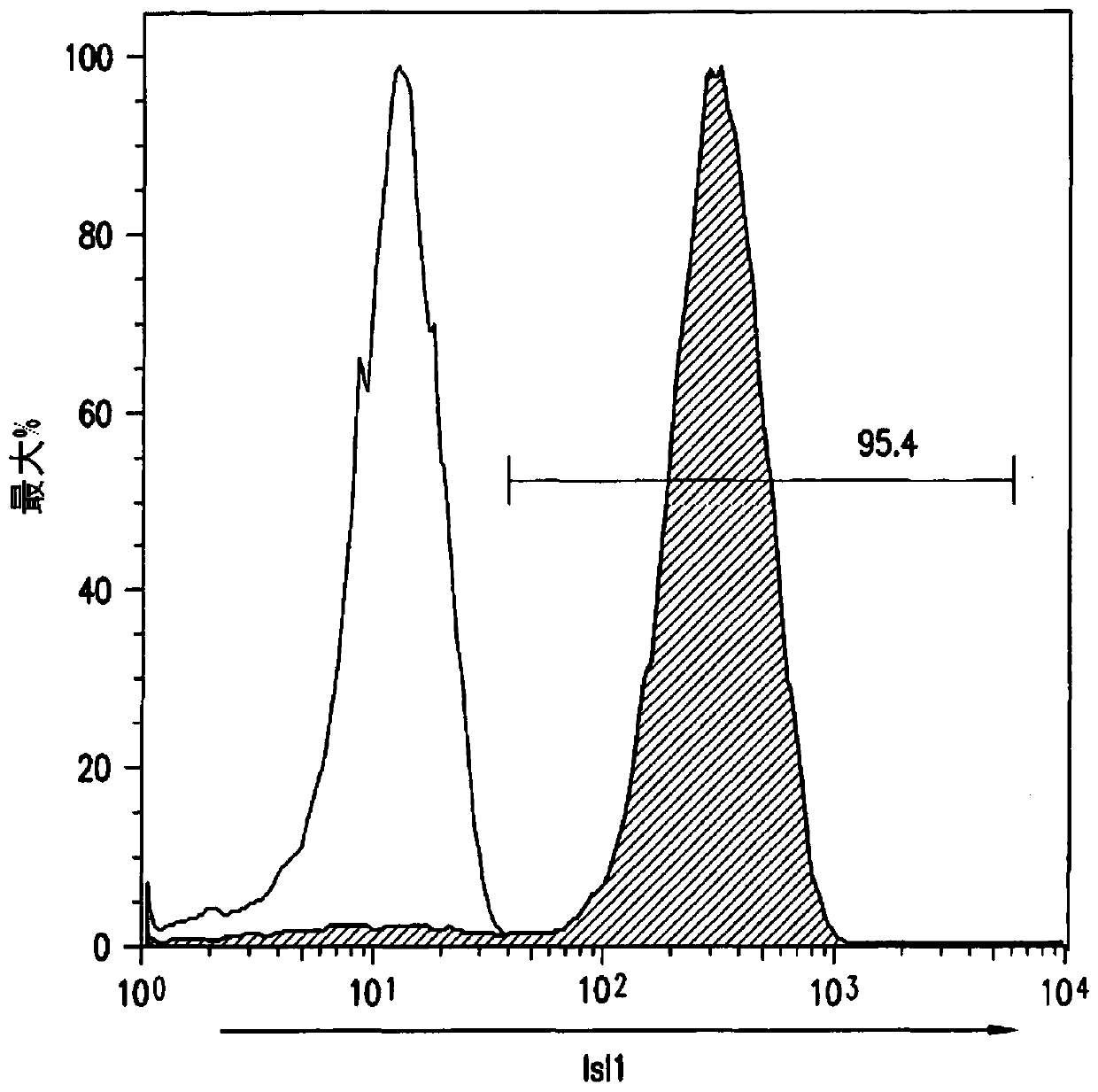
[0215] Example 1: Generation of human Isl1+ cardiomyocyte-derived progenitor cells by modulating Wnt signaling in human pluripotent stem cells
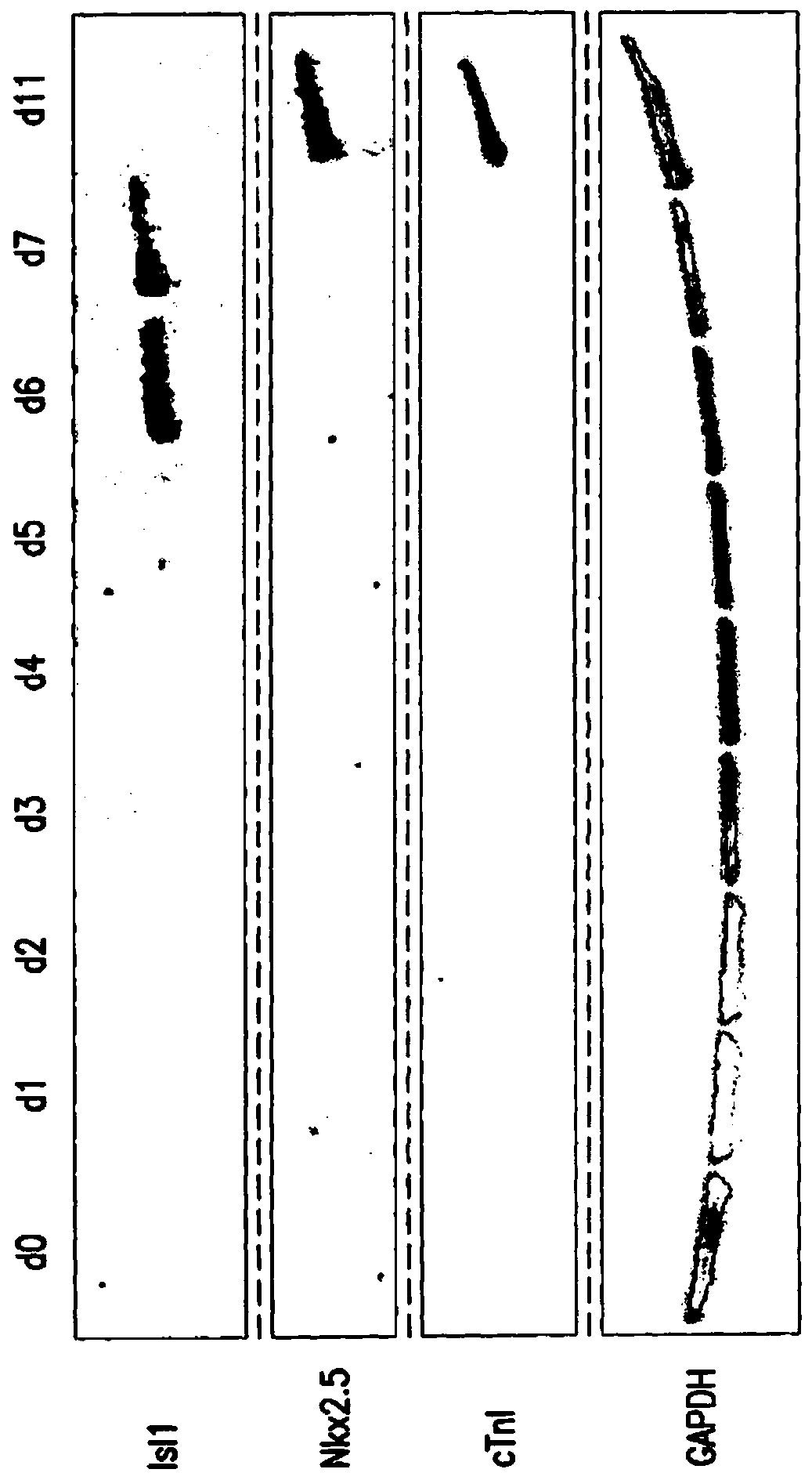
[0216] Temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling has been shown to be sufficient to generate functional cardiomyocytes in high yield and purity from many hPSC lines (Lian, X. et al. (2012) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109 : E1848-1857; Lian, X. et al. (2013) Nat. Protoc. 8:162-175). In this approach, Wnt / β-catenin signaling is first activated in hPSCs, followed by an incubation period followed by inhibition of Wnt / β-catenin signaling. In the initially published protocol, by combining with the Gsk3 inhibitor CHIR99021 (GSK-3α, IC 50 =10nM; GSK-3, βIC50=6.7nM) to achieve Wnt / β-catenin signaling activation by incubation with Porcn inhibitor IWP2 (IC 50 = 27 nM) to achieve Wnt / β-catenin signaling inhibition. Because we used Gsk3 inhibitors and Wnt production inhibitors for cardiac differentiation, this protocol was called the GiWi p...
Embodiment 2
[0224] Example 2: Identification of Jagged 1 as a cell surface marker for cardiac progenitor cells
[0225]To characterize the transcriptional changes that occur during cardiac differentiation at the genome-scale level, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was performed at various time points after differentiation to establish the cardiac developmental transcriptional environment. We performed RNA-seq experiments on samples from days 0 to 7, as well as samples from days 19 and 35 (two independent biological replicates for each time point). Two batches of RNA-seq (100bp and 50bp read lengths) were performed using the illumine Hiseq 2000 platform. A total of 20 samples were examined. Mapped our reads into the reference human genome (hg19) using Bowtie and Tophat and calculated per-gene expression (genes were annotated according to Refseq) using the RPKM method (reads per kilobase transcript per million reads) . The differentiation of hPSCs into cardiomyocytes involves five major cell typ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com