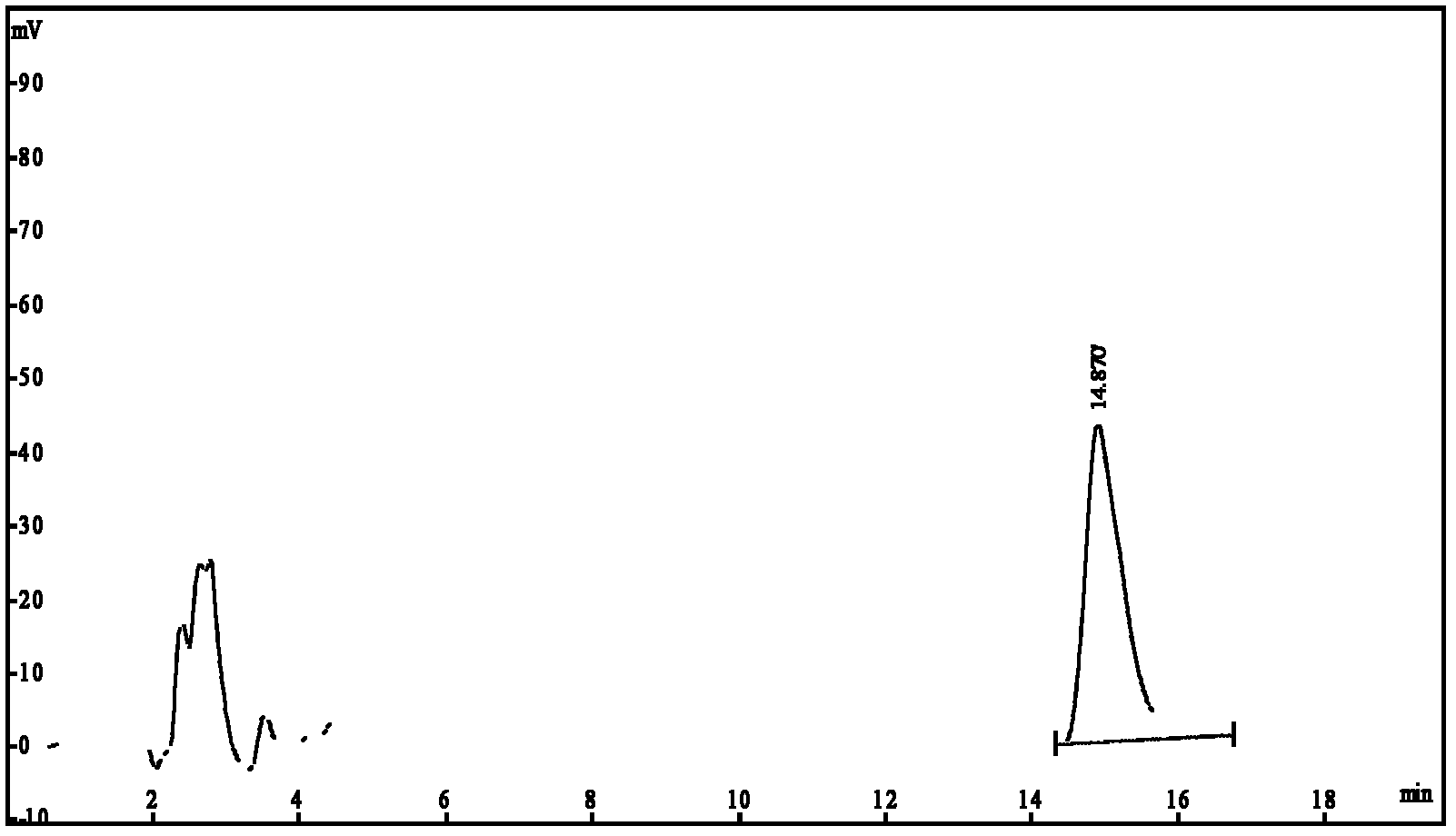
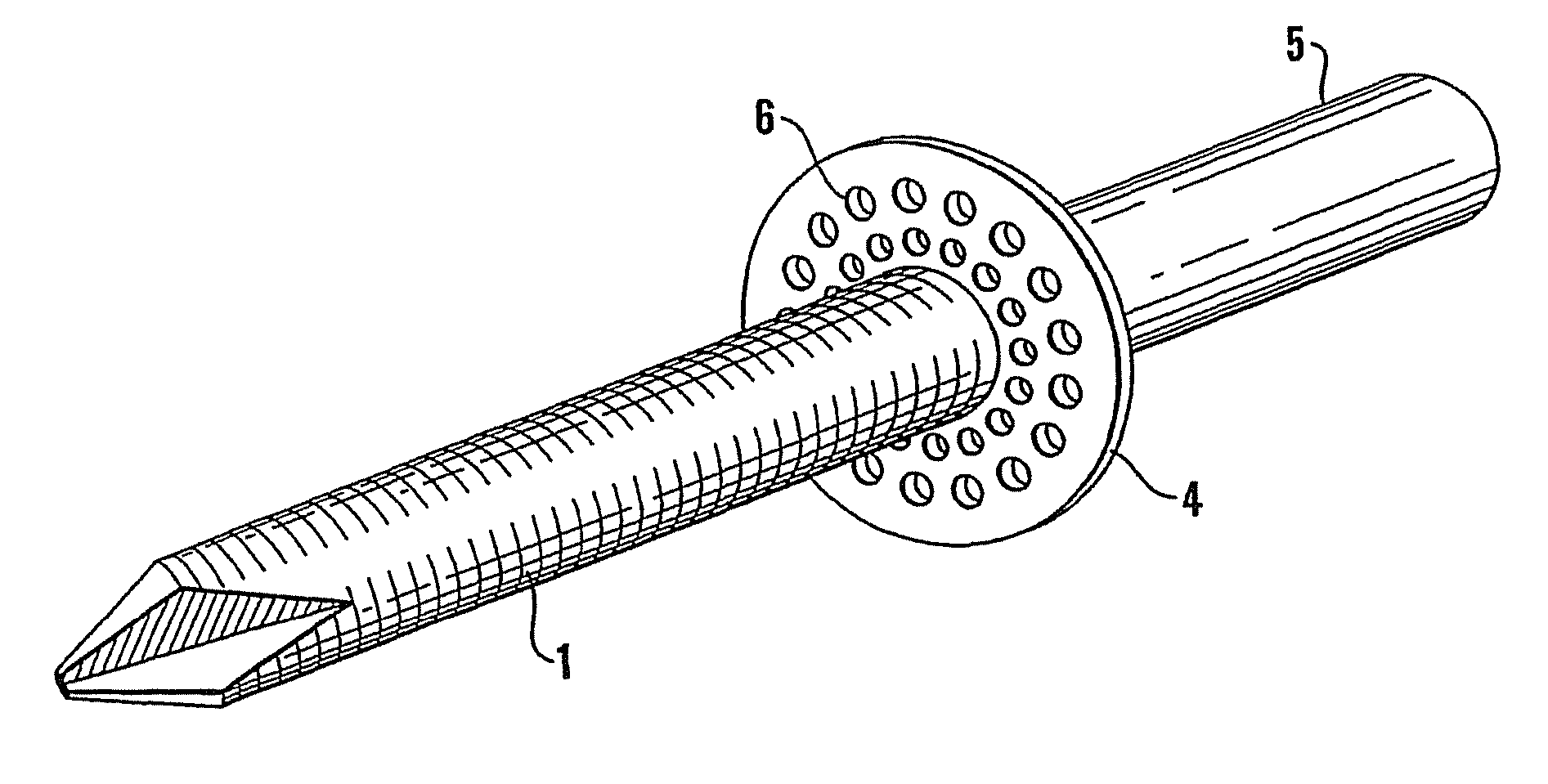
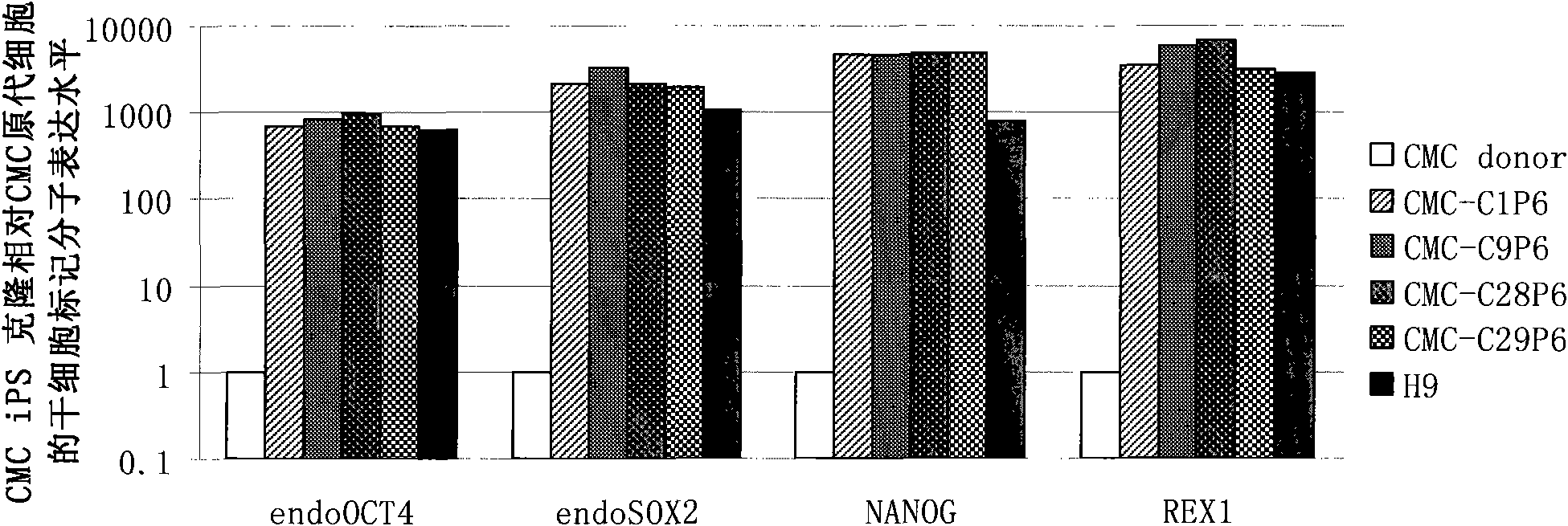
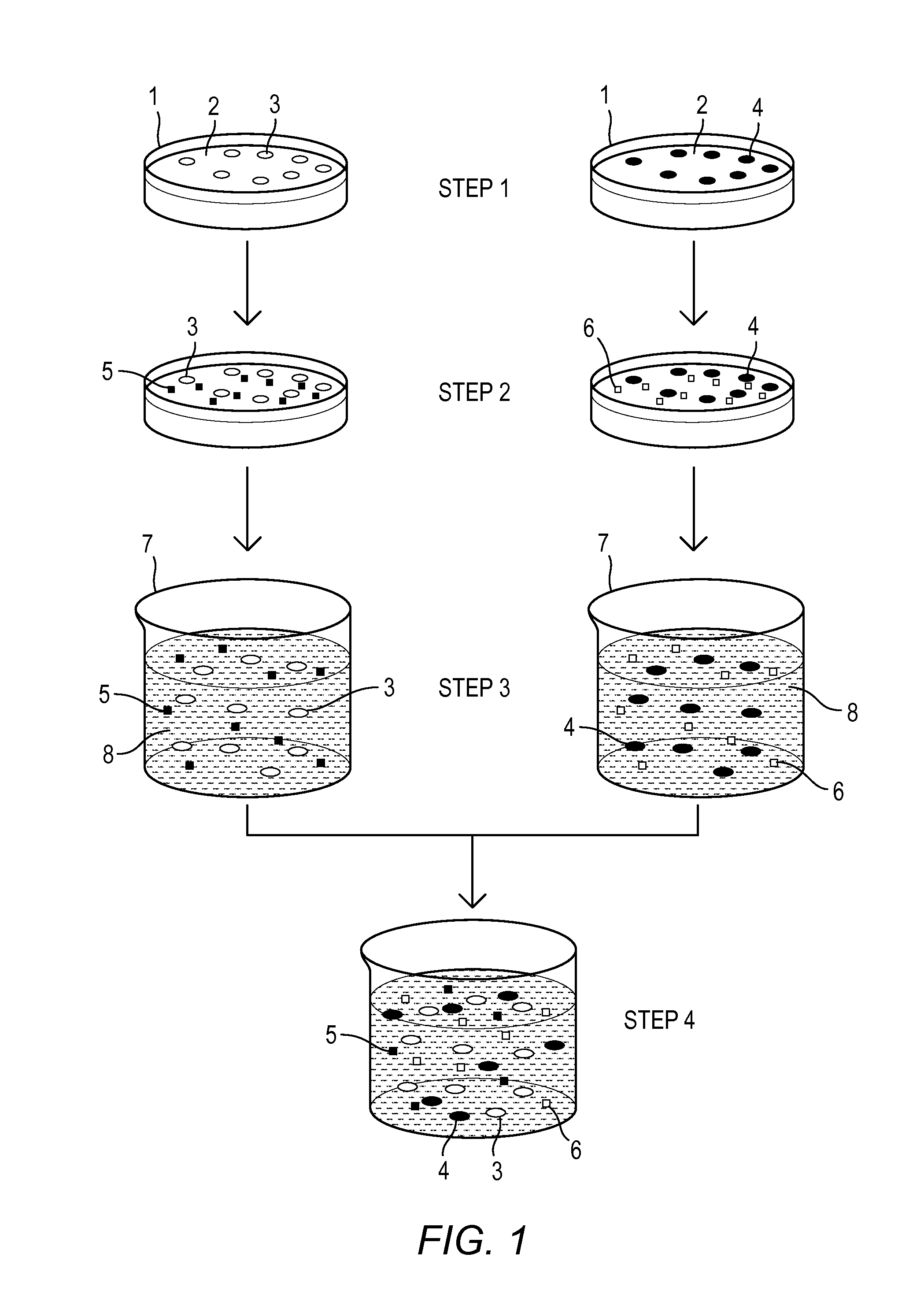
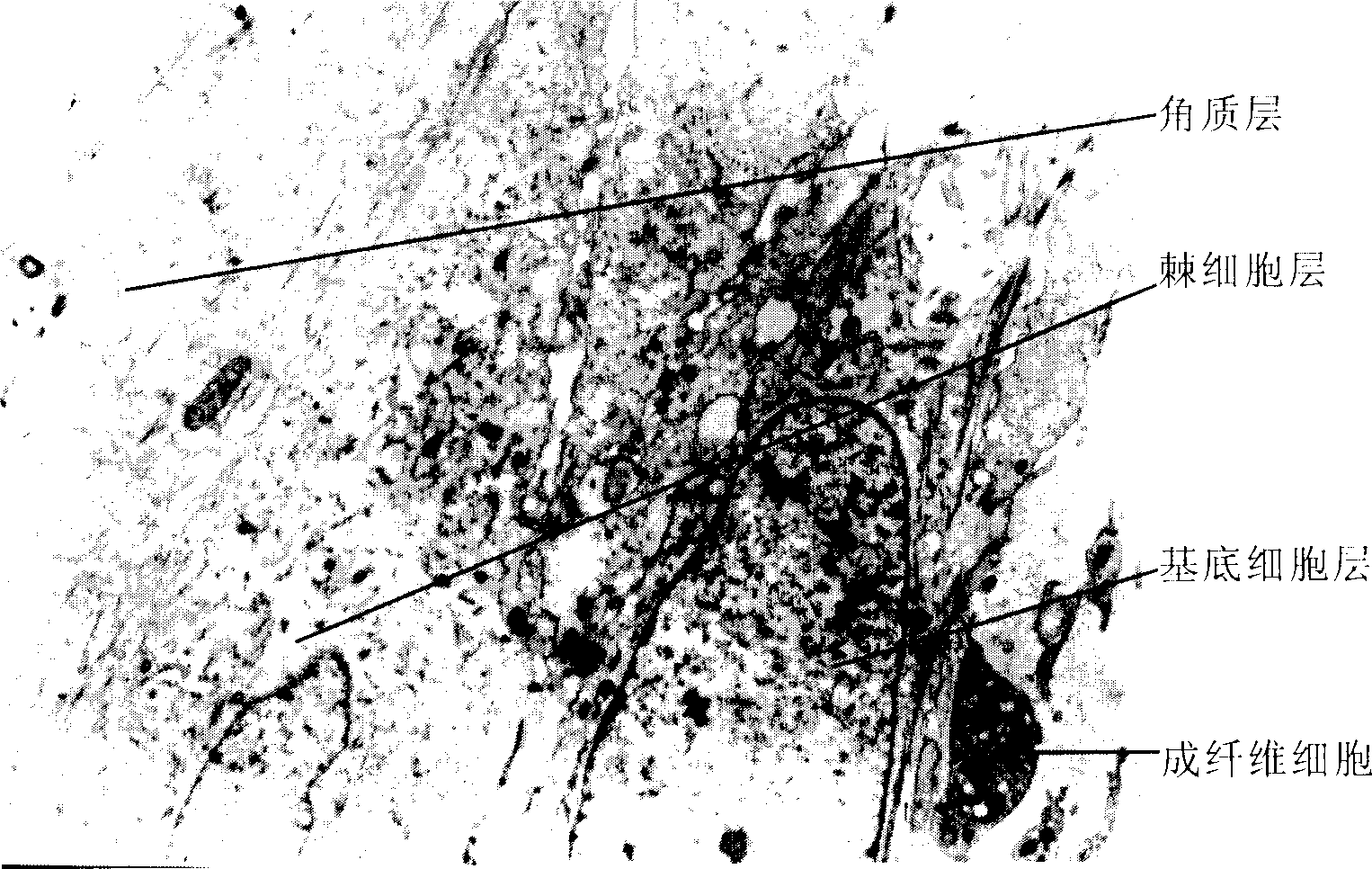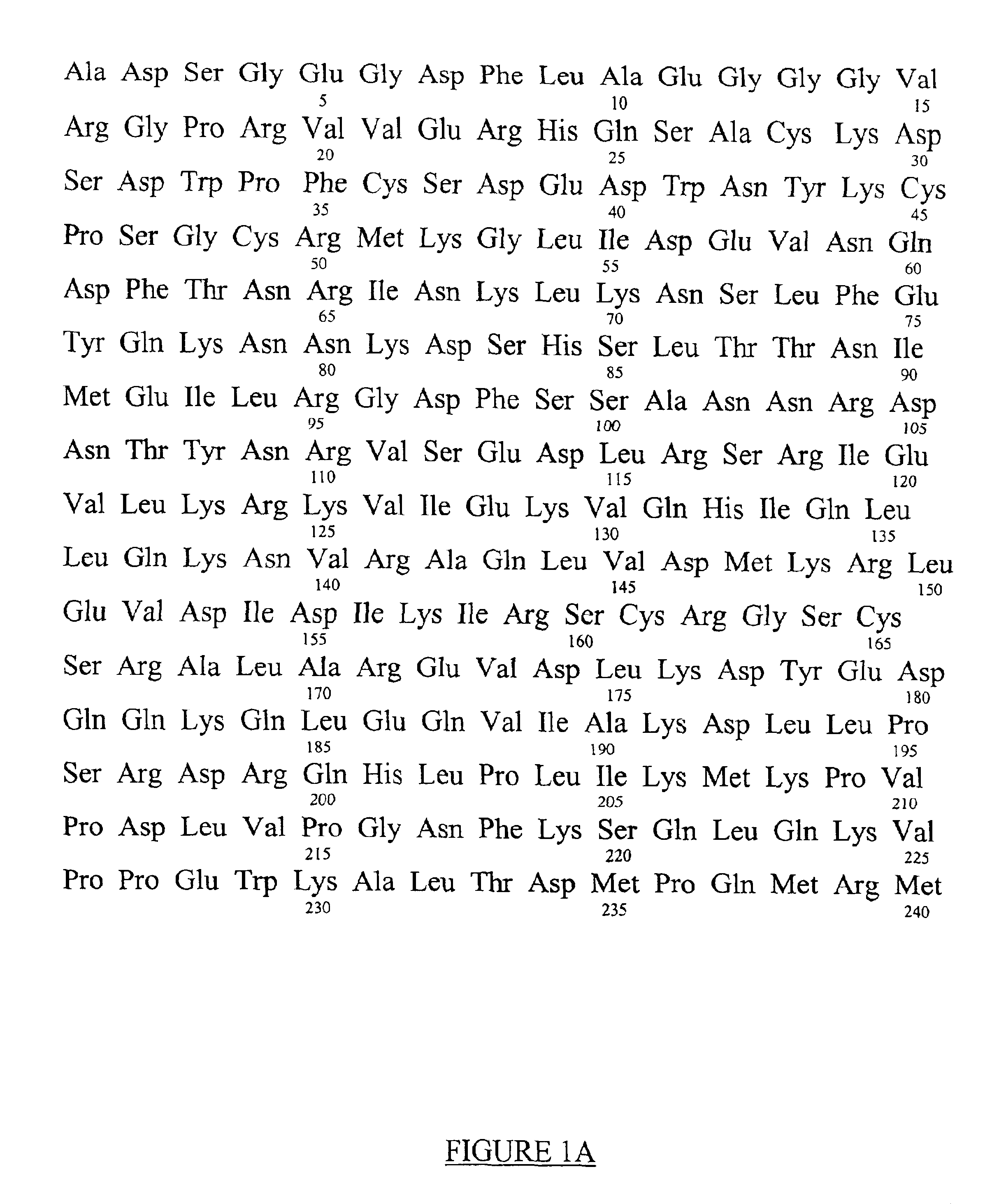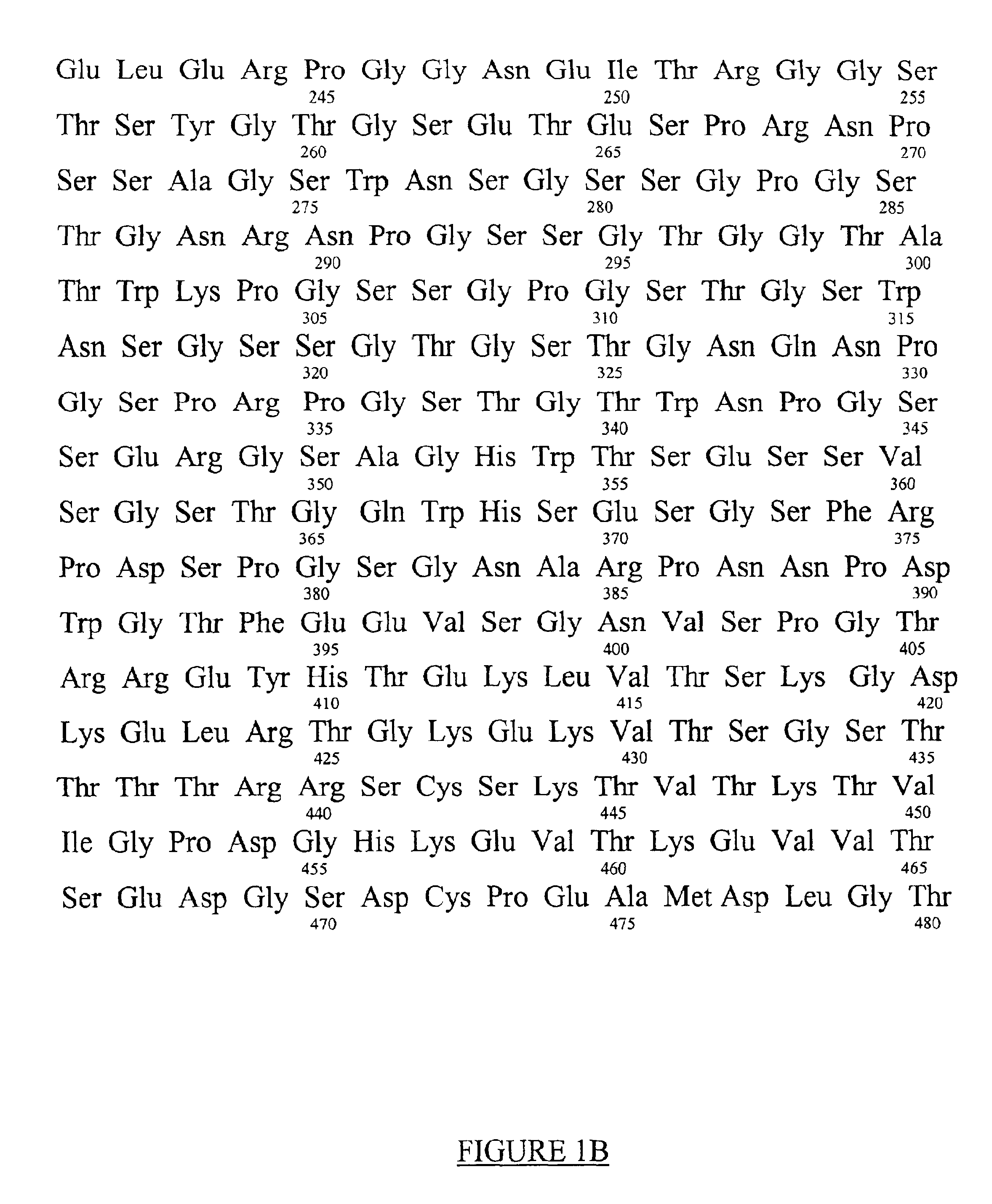Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
305 results about "Fibroblastic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fibroblast, the principal active cell of connective tissue. Fibroblasts are large, flat, elongated (spindle-shaped) cells possessing processes extending out from the ends of the cell body. The cell nucleus is flat and oval. Fibroblasts produce tropocollagen, which is the forerunner of collagen, and ground substance,...
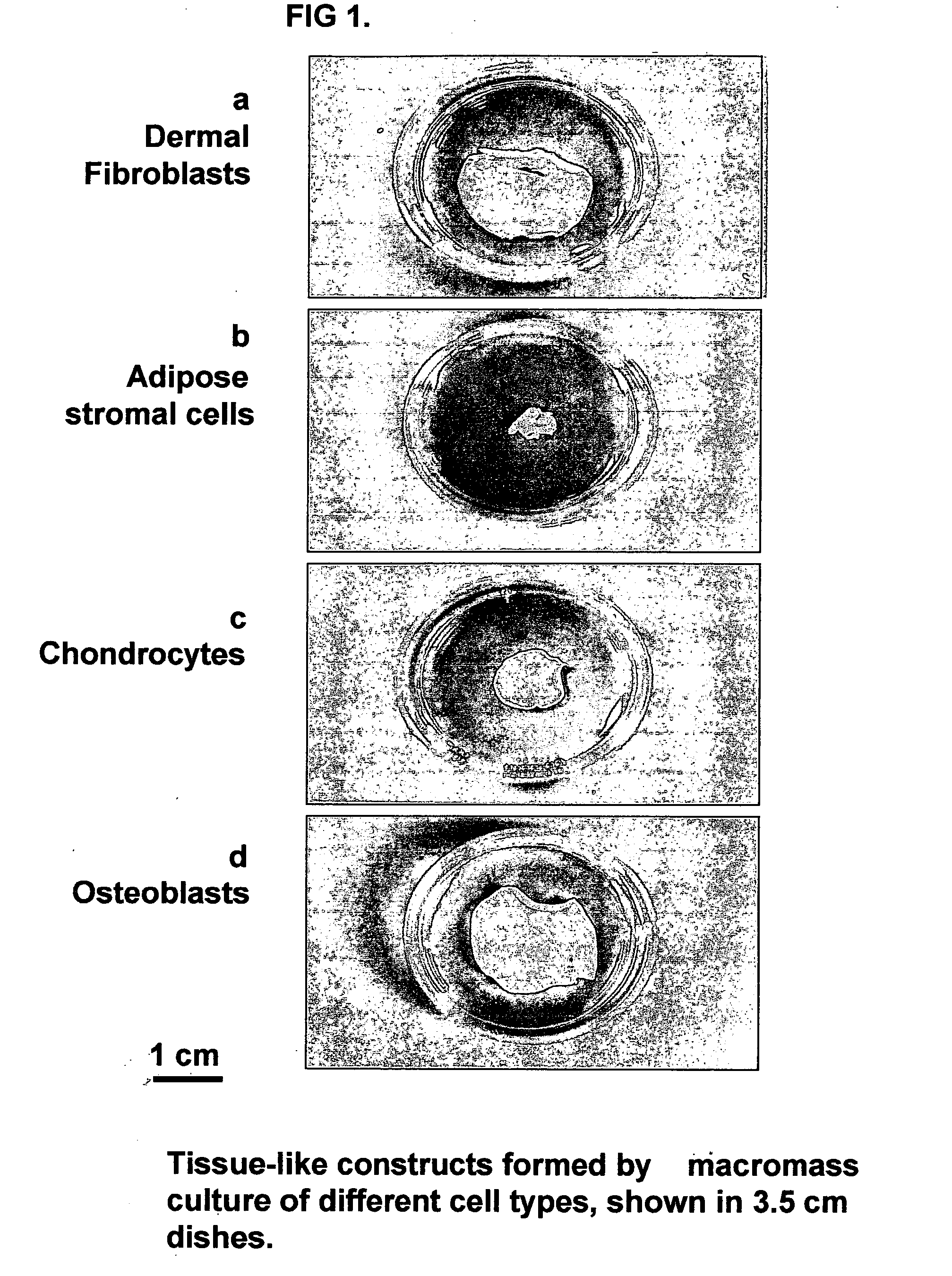
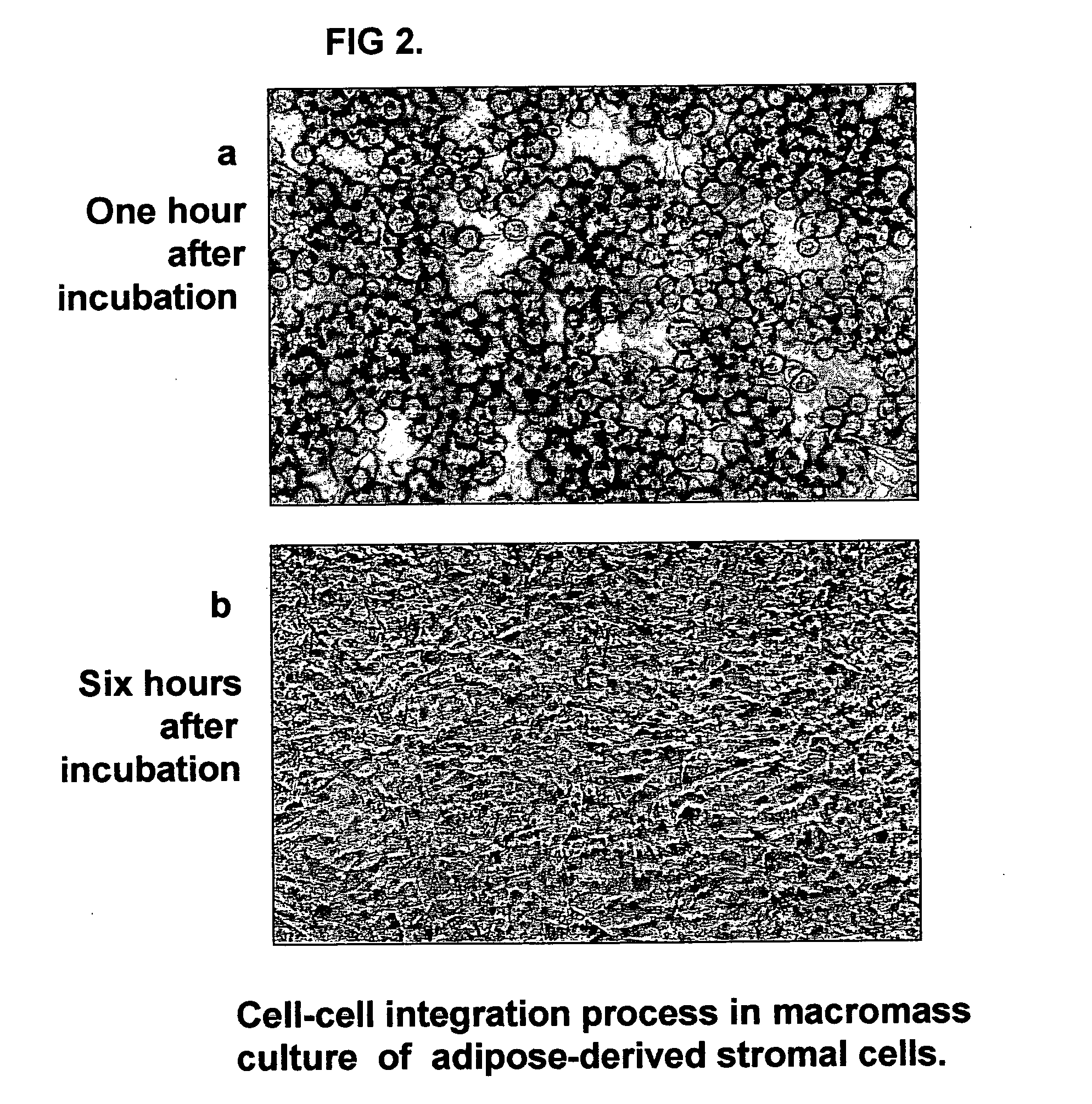
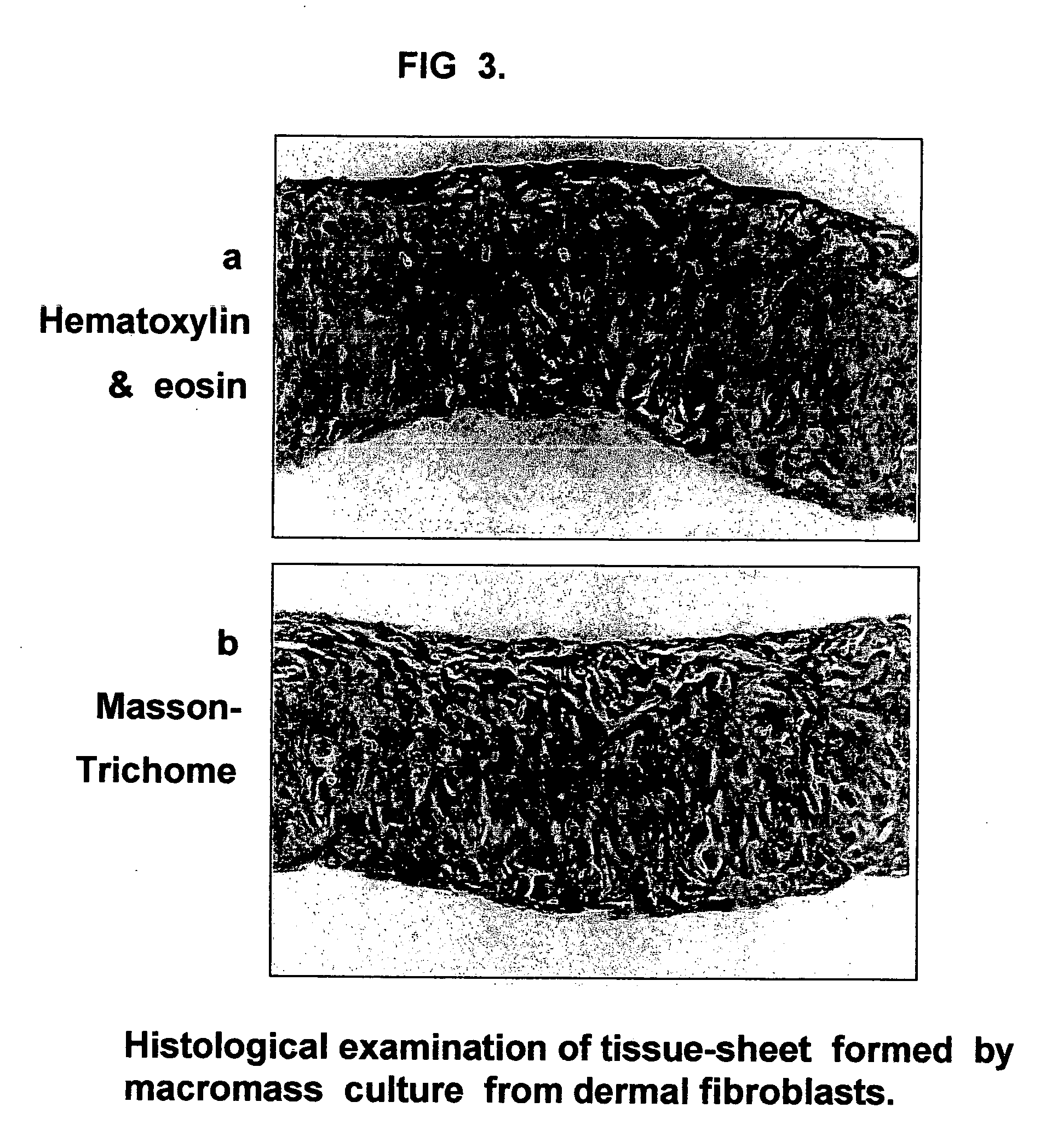
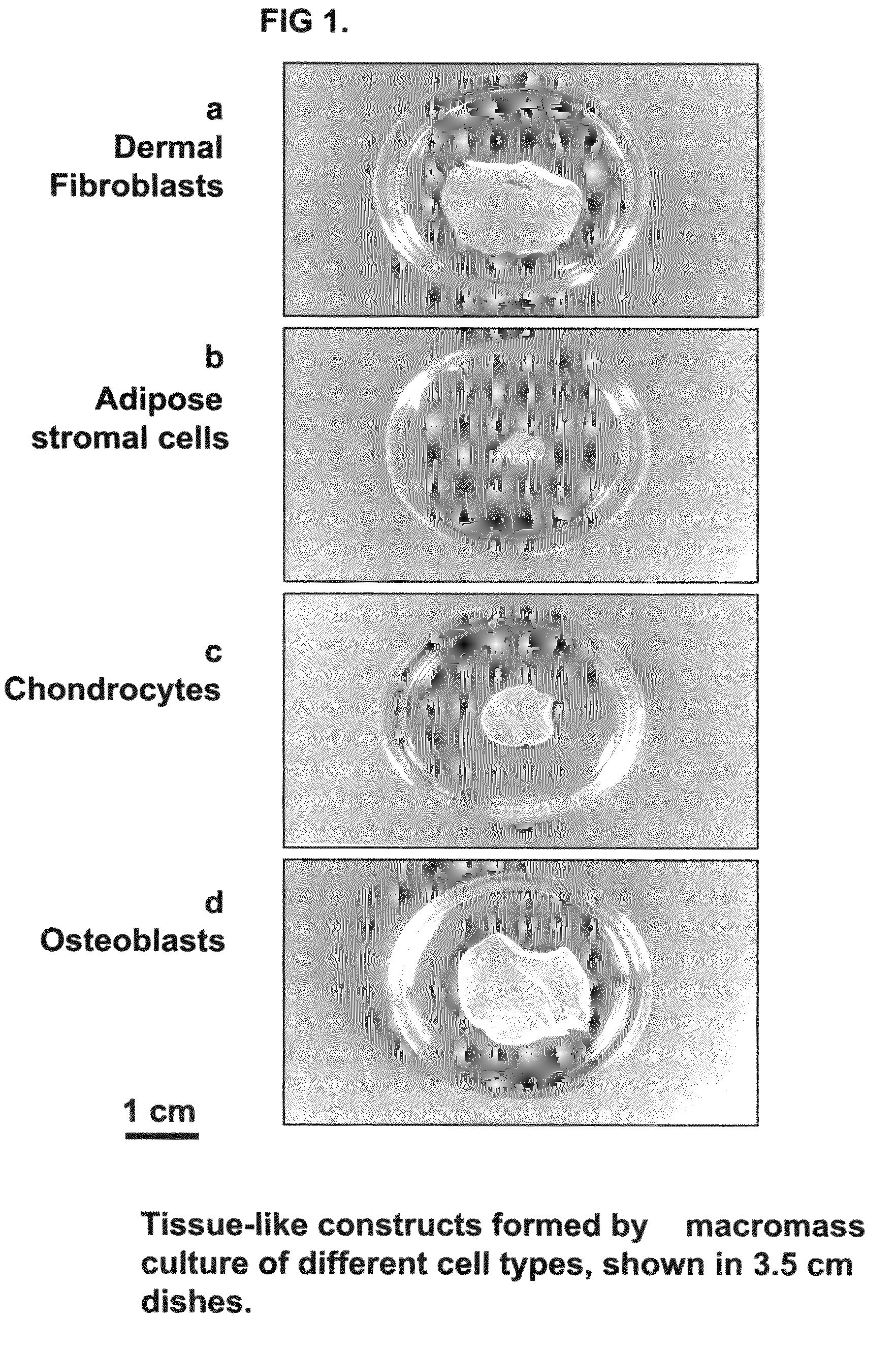
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells, and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20040082063A1Sectioned easilySmall sizeEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellFiber
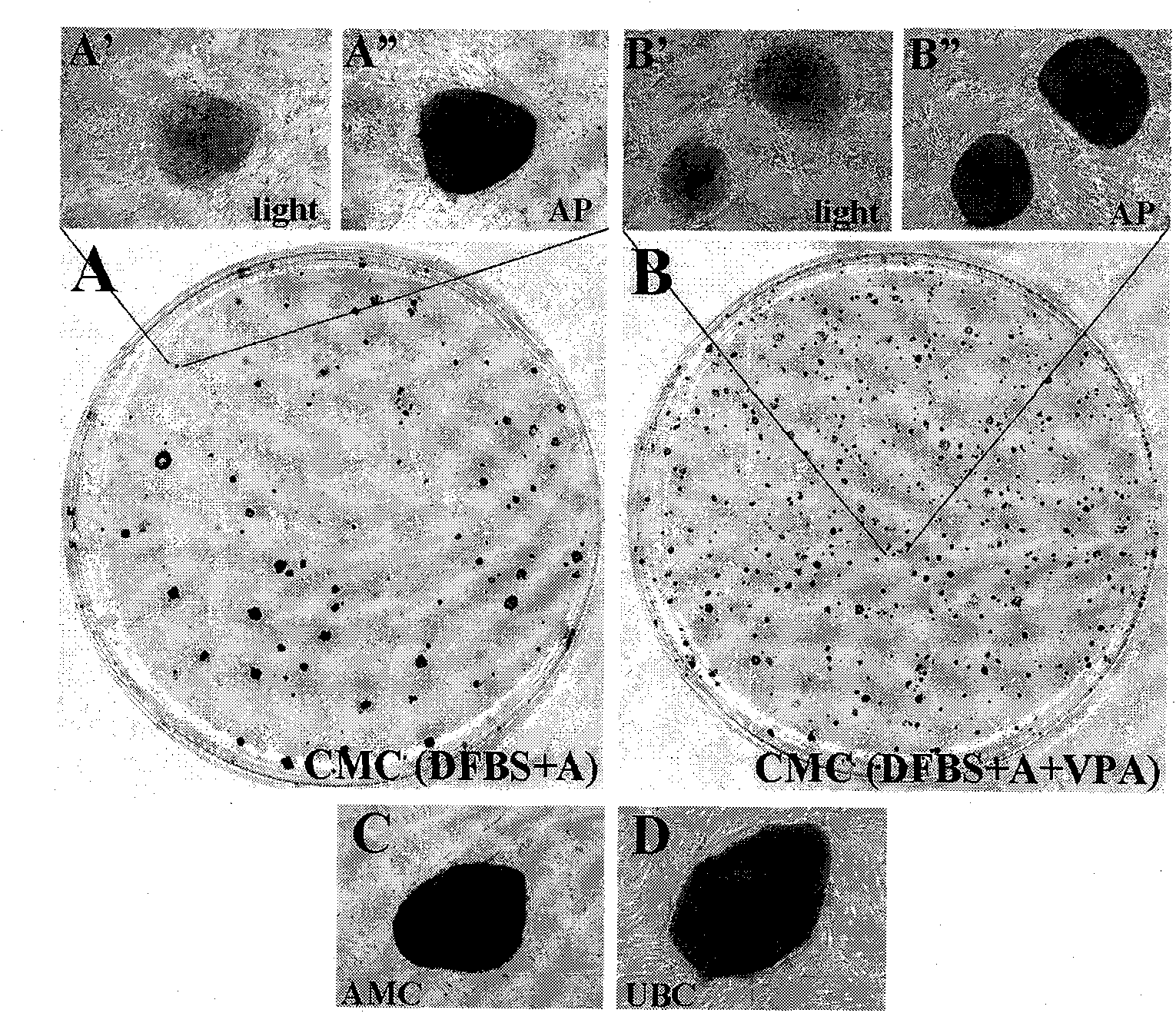
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
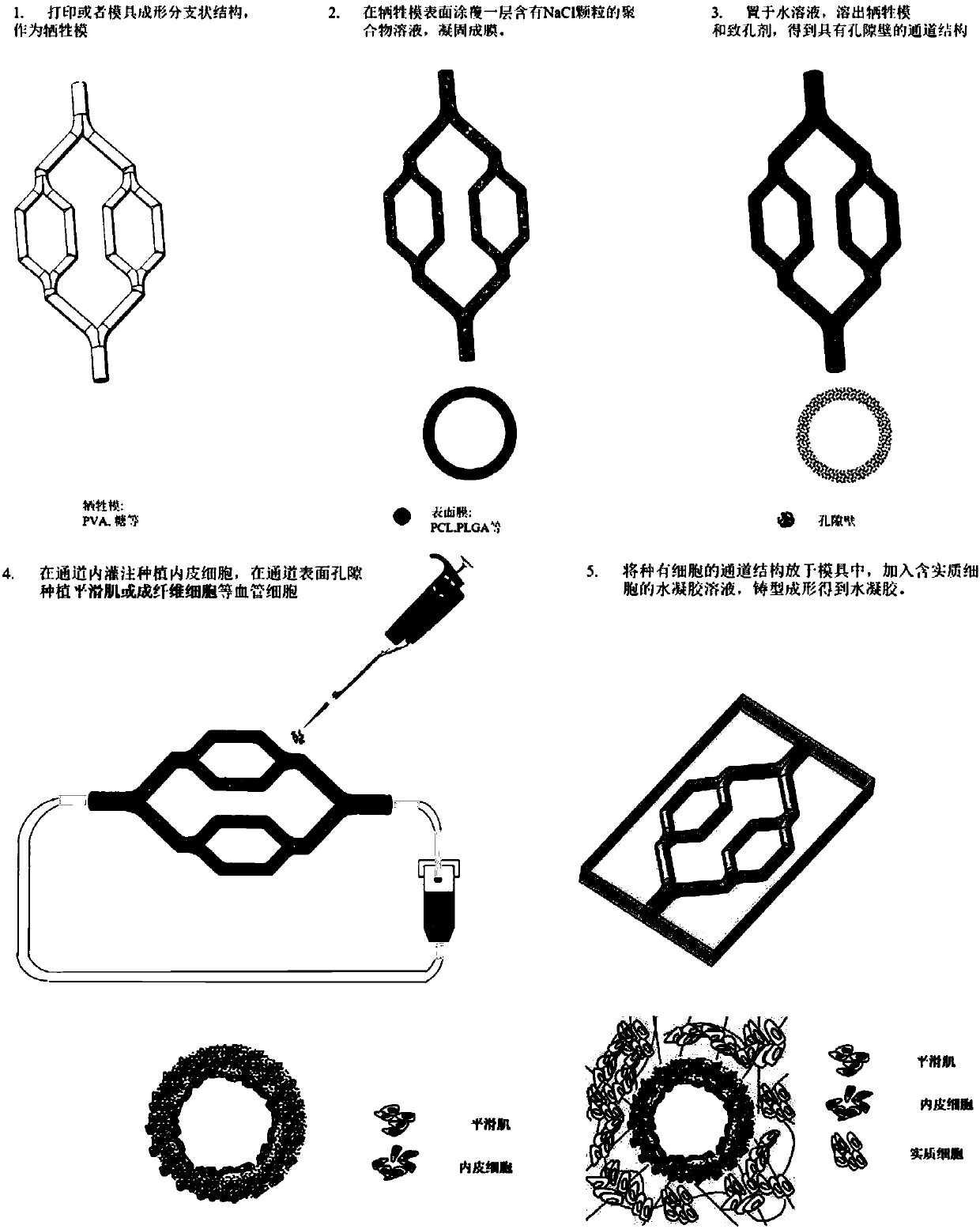
Bionic vascularized soft tissue with multilayer vascular structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107693846AAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsPolymer thin filmsPolymer solution
The invention discloses a bionic vascularized soft tissue with a multilayer vascular structure and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: employing a moulding process or 3D printing way to obtain a sacrificial membrane with a branched structure; coating or spraying a polymer solution containing a pore-foaming agent on the surface of the sacrificial membrane toobtain a polymer film; removing the treated sacrificial membrane of the structure and the pore-foaming agent to obtain a vascular channel-like structure with surface pores; conducting perfusion planting of endothelial cells in the channel of the vascular channel-like structure; planting smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts in the surface pores of the vascular channel-like structure; and placing thetreated vascular channel-like structure in a mold, adding an aquogel solution containing parenchymal cells, and conducting moulding so as to obtain the bionic vascularized soft tissue. The method provided by the invention can construct bionic blood vessels with a multilayer structure in artificial tissues.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods for producing induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20110306516A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsFibroblastReprogramming
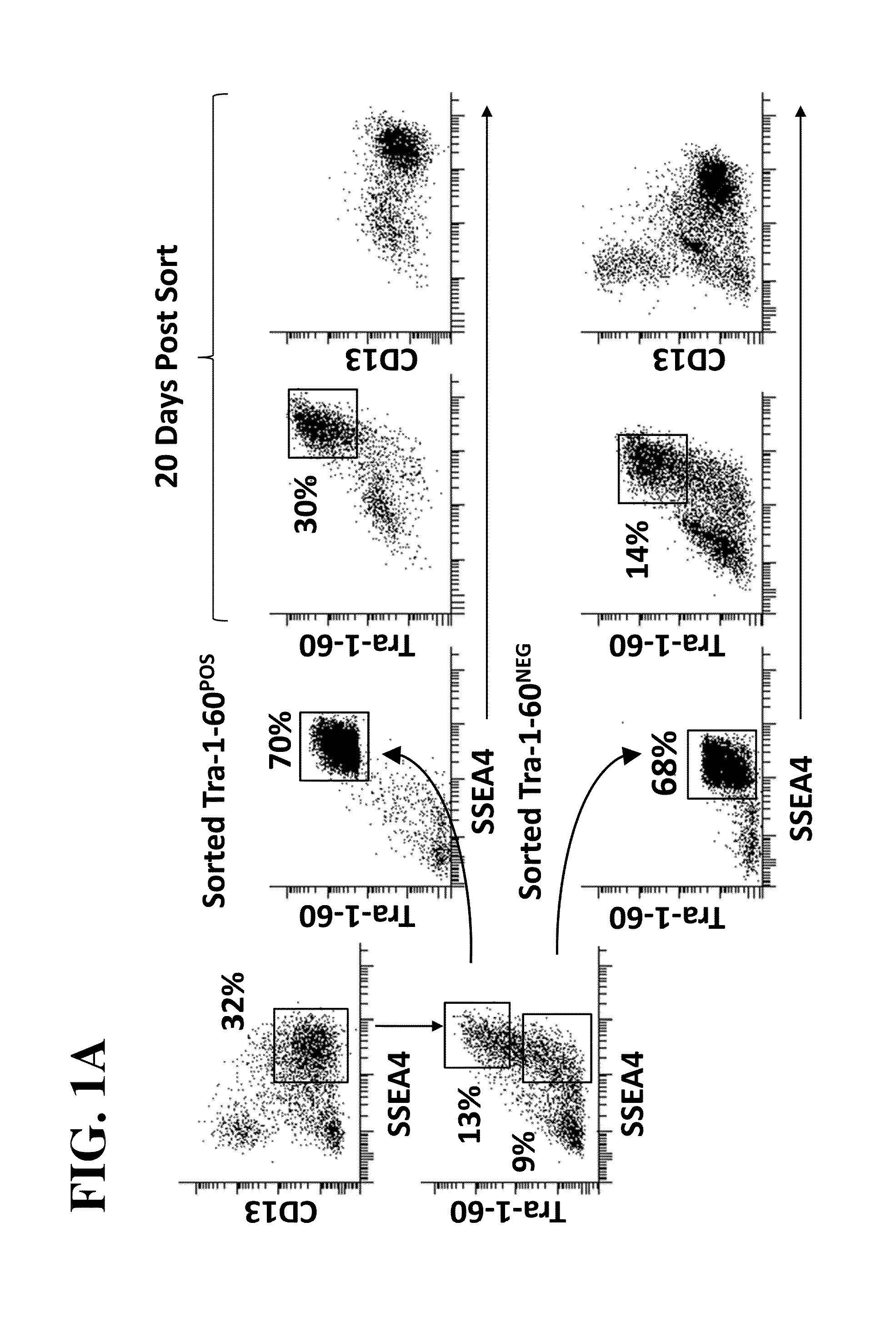
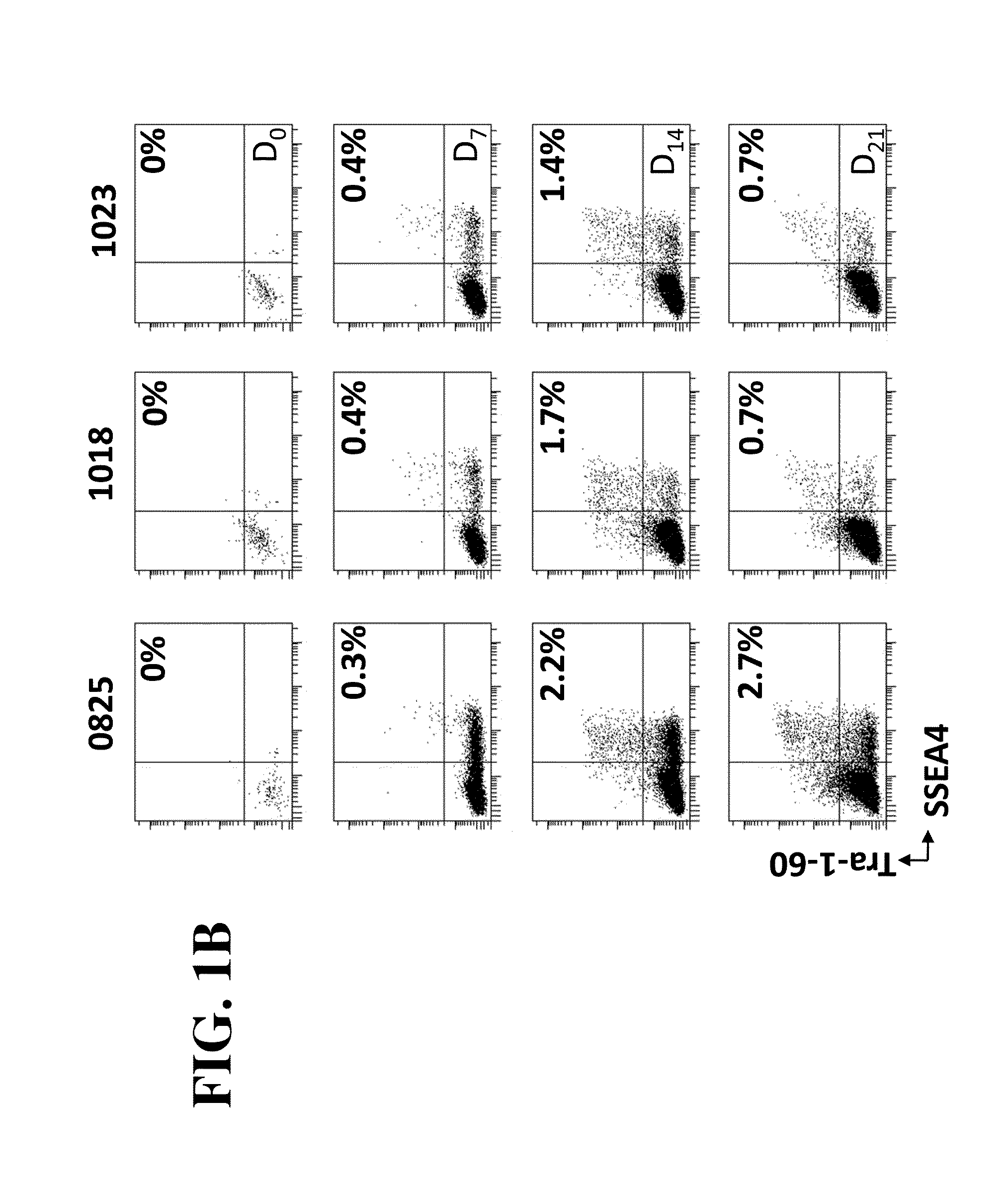
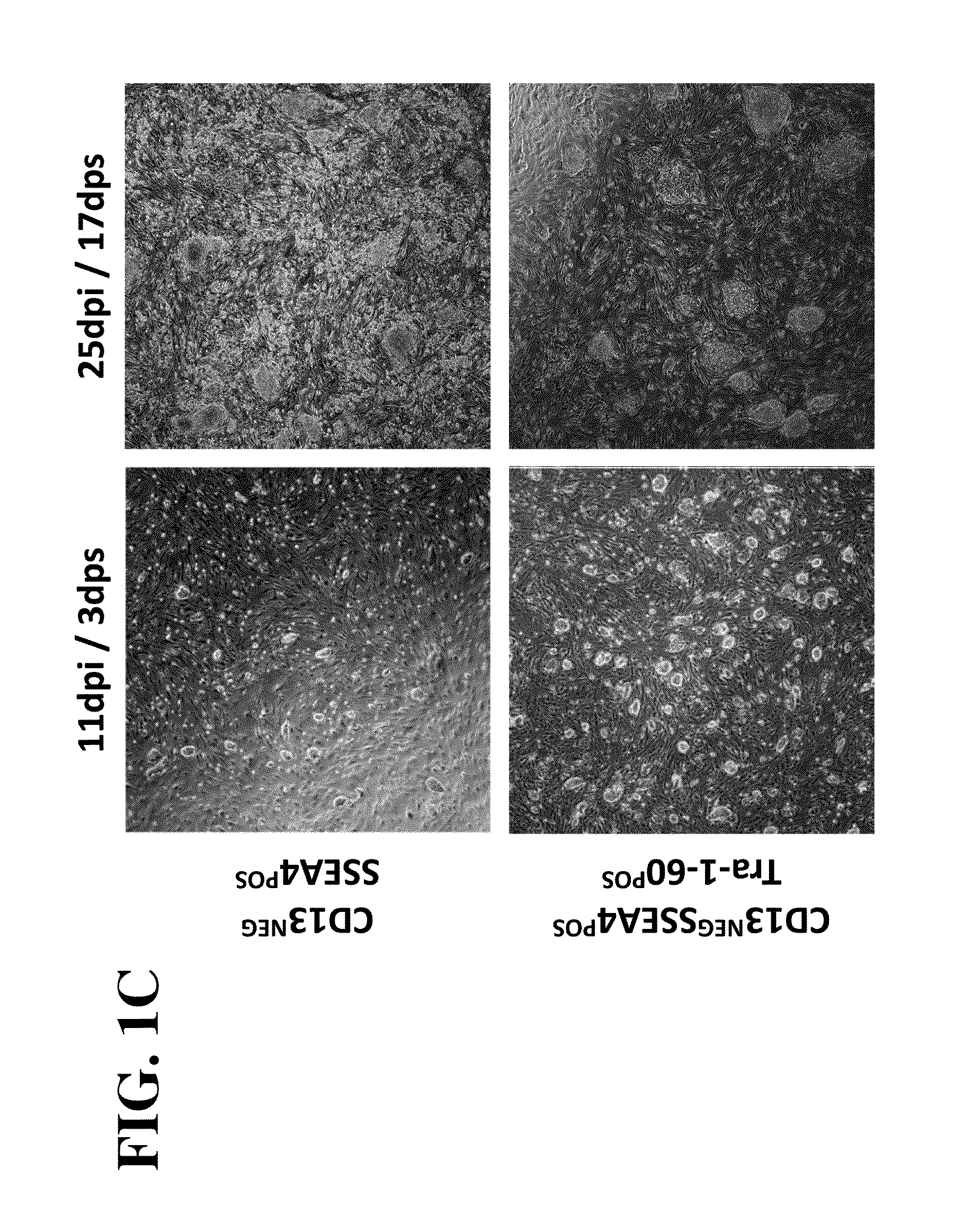
The invention provides improved methods for producing induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) from adult fibroblasts. The methods include contacting adult fibroblasts with a reprogramming composition suitable for reprogramming the adult fibroblasts to iPSC, under conditions effective for the reprogramming composition to penetrate the adult fibroblasts, followed by culturing the contacted fibroblasts for a time period sufficient for the cells to be reprogrammed. The cultured cells are then sorted to select cells based upon their expression of the cell membrane surface markers CD13NEG SSEA4POS Tra-1-60POS. iPSC colonies are then identified from the sorted cells.
Owner:NEW YORK STEM CELL FOUND INC
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Enriched stem cell and progenitor cell populations, and methods of producing and using such populations
InactiveUS8017389B2BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementIschemic heartFirst myocardial infarction
The present invention provides a novel method to isolate and expand pure progenitor / stem cells from a primary tissue explant, which produces a population enriched in multipotent functional progenitor / stem cells free of contaminating fibroblasts and other cell types. Cardiac progenitor / stem cells isolated by this method maintain their self-renewal and clonogenic character in vitro and differentiate into normal cells in myocardium, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, after transplantation into ischemic hearts. The present invention also includes substantially pure populations of multipotent progenitor / stem cells, e.g., cardiac progenitor / stem cells, and their use to treat and prevent diseases and injuries, including those resulting from myocardial infarction.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST A UNIV OF THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and apparatuses for growing cells
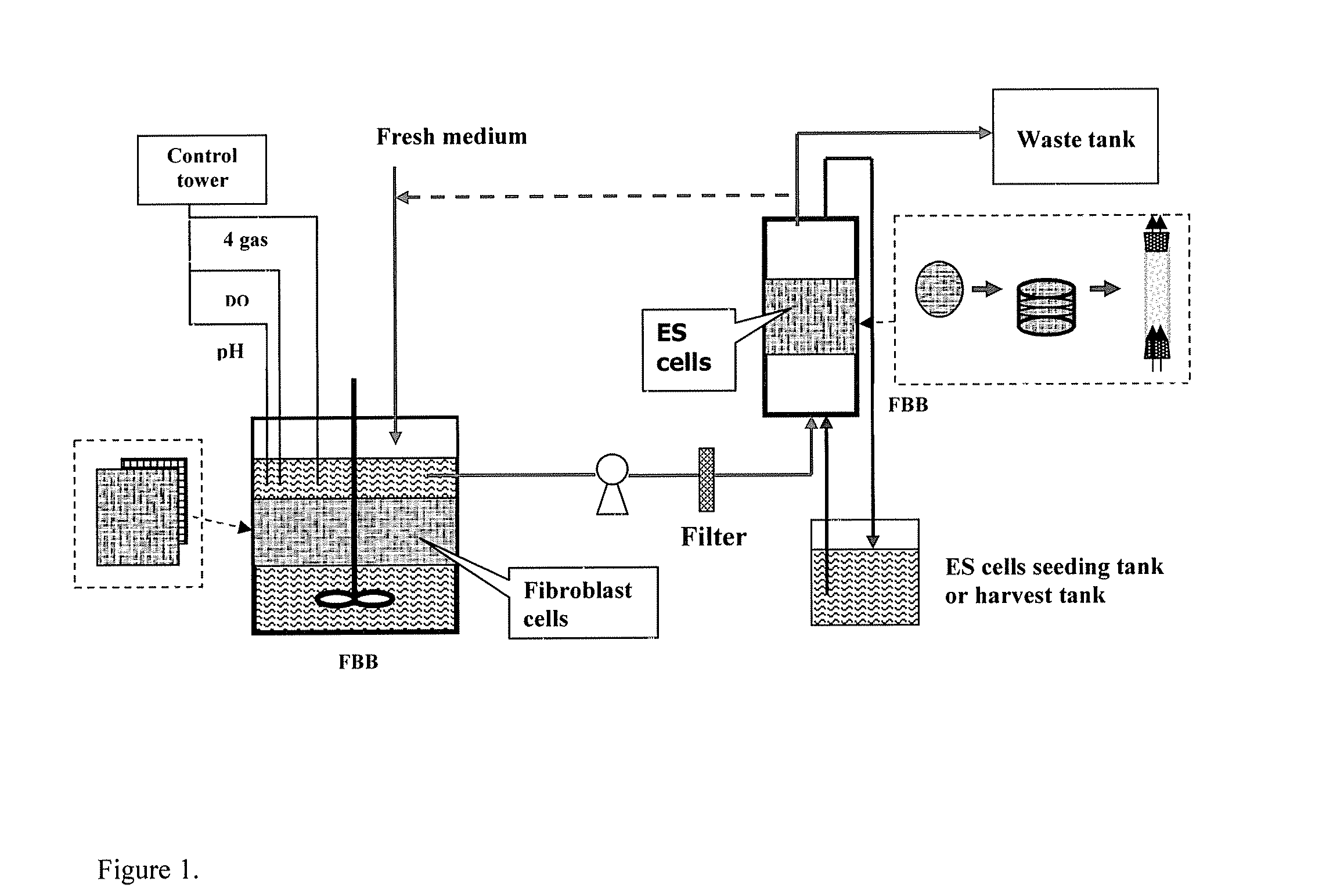
InactiveUS20070178586A1Increase flow rateEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCulture cellCell culture media
Methods of culturing stem cells including growing fibroblast cells on a three-dimensional scaffold, perfusing the fibroblast cells with a cell culture medium to form fibroblast cell-conditioned cell culture medium, and growing the stem cells on a three-dimensional scaffold perfused with the fibroblast cell-conditioned cell culture medium are presented. Multi-stage bioreactors for growing stem cells, comprising a first fibrous bed bioreactor in fluid communication with a second fibrous bed bioreactor are also presented.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Bioreactor for the Manufacture of Tissue Engineered Blood Vessels
InactiveUS20060286664A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBursting strengthBioreactor
The invention relates to bioreactors having an enclosed chamber, a sheet growth module, a rollable mandrel, and a clamp for holding the sheet to the mandrel for rolling for the manufacture of a tissue engineered blood vessel (TEBV). The TEBV is made from a cultured fibroblast sheet rolled into a multilayer vessel which has sufficient burst strength to withstand physiological blood pressure without the inclusion of smooth muscle cells or synthetic scaffolding.
Owner:NIGHTINGALE INC
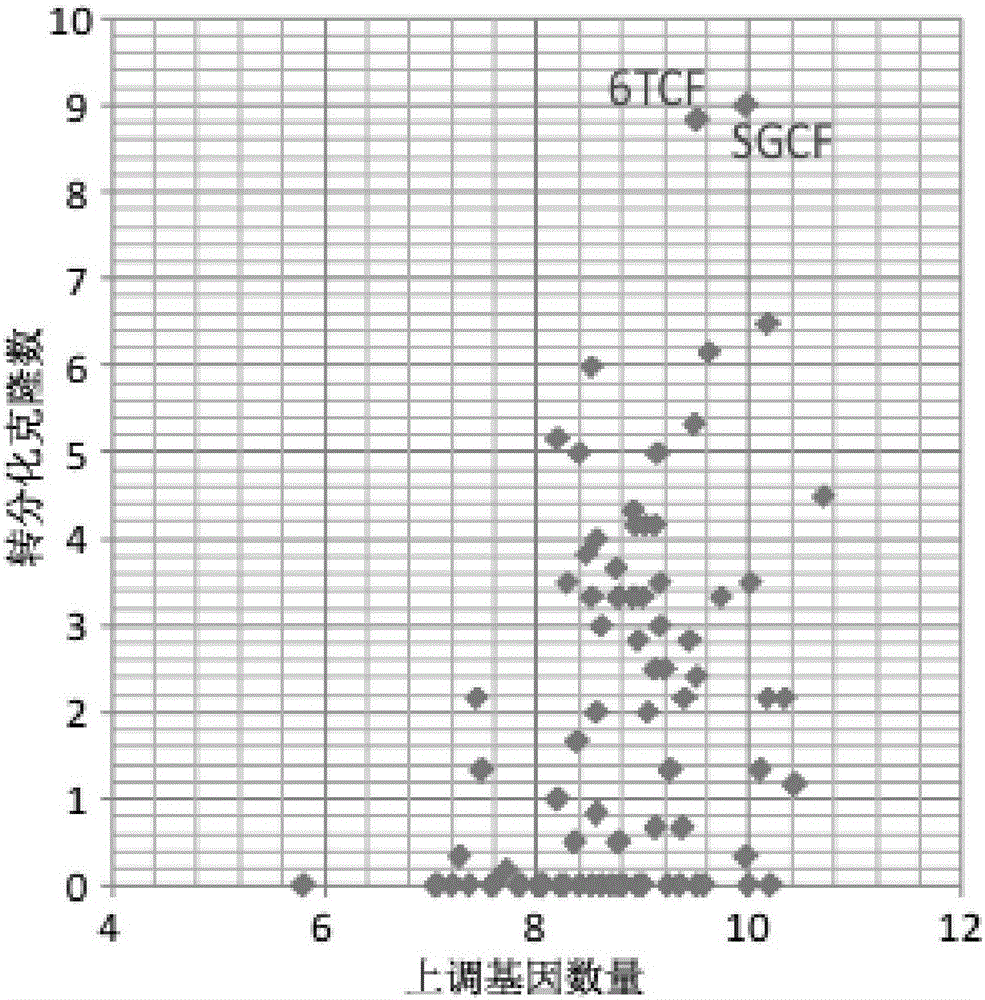
Inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells and application of inducing culture medium
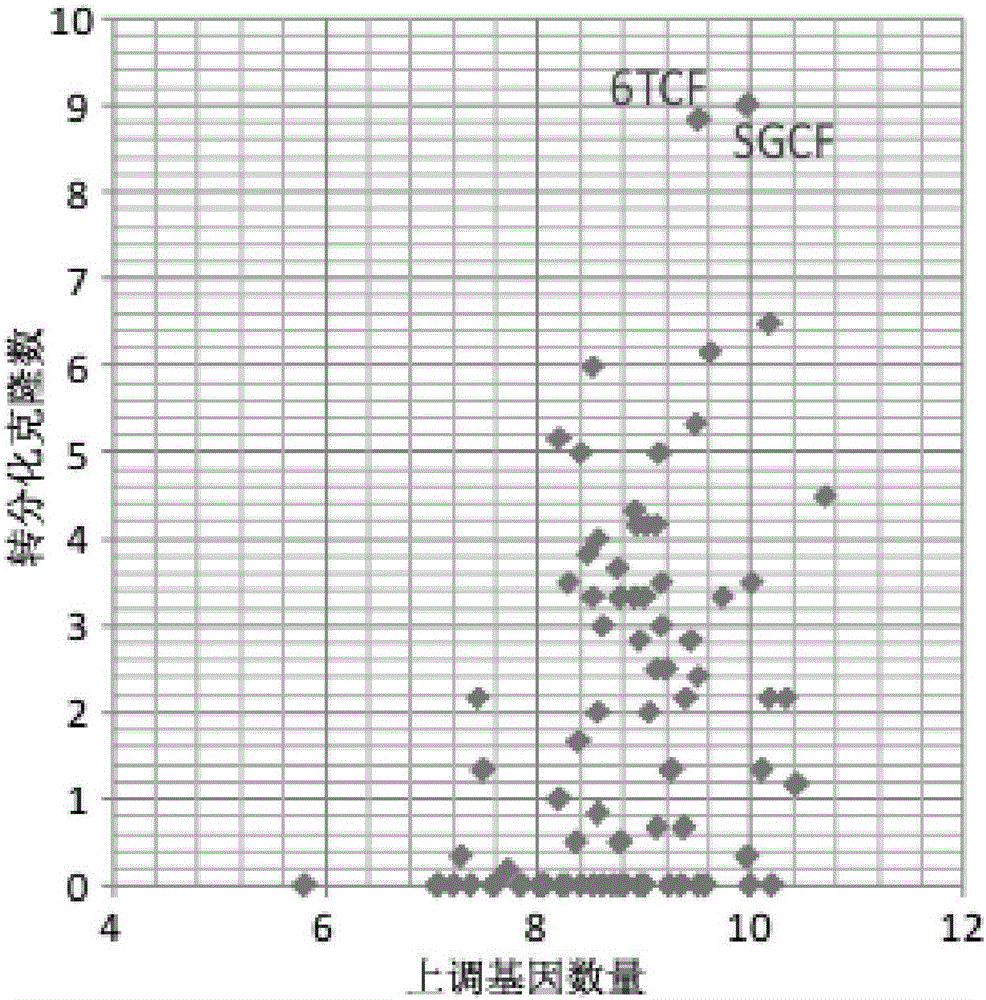
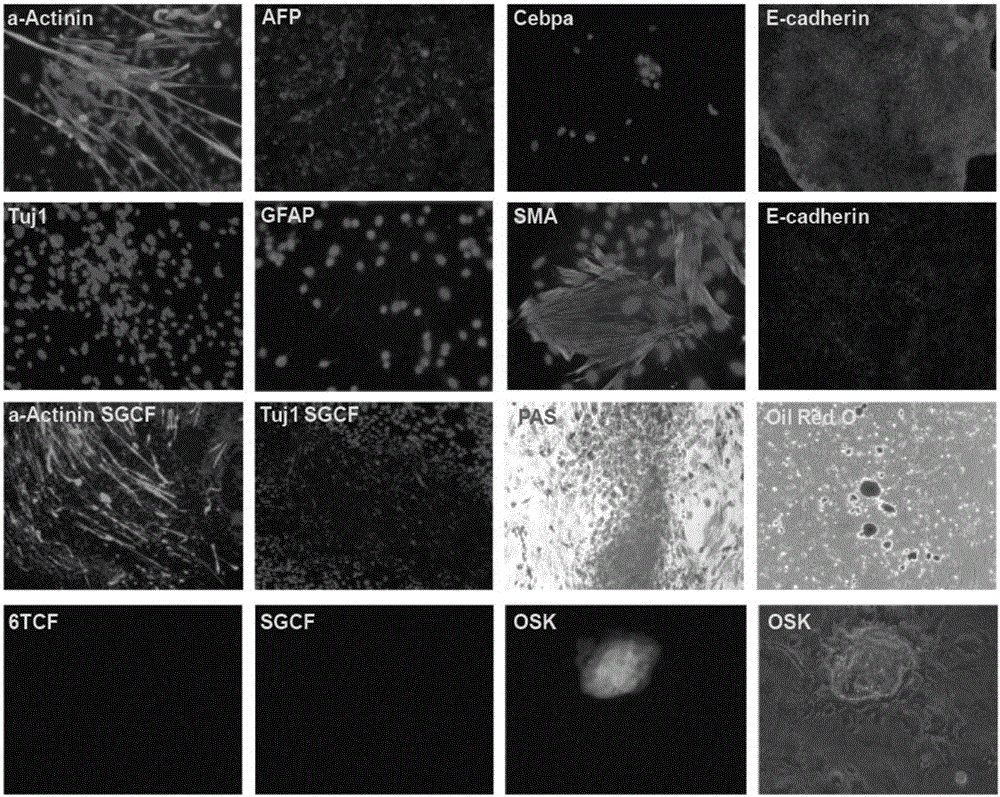
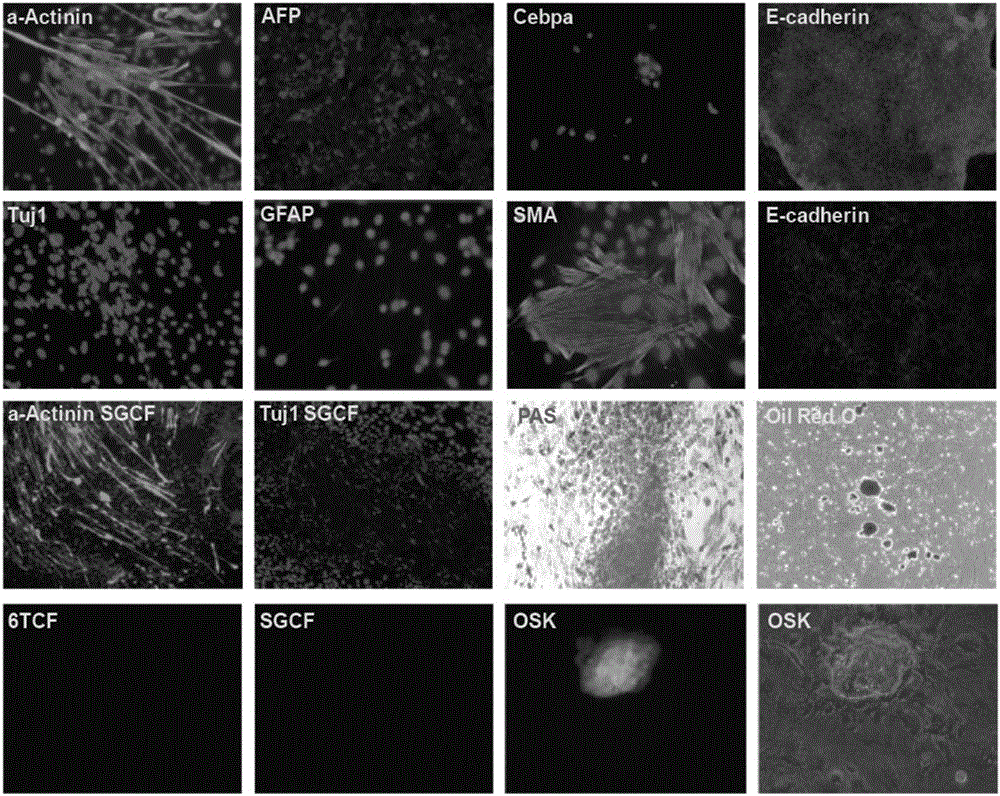
ActiveCN105861428ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsFibroblastCells fibroblast
The invention discloses an inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells, a method and an application of the inducing culture medium. The inducing culture medium comprises a basic culture medium and an inducing small molecular assembly which is 6TCFOW or SCFOV, wherein 6 is E61541, T is tranylcypromine, C is CHIR99021, F is forskolin, O is Dorsomorphin, W is IWR-I, S is SB431542, and V is valproic acid. The inducing culture medium can trans-differentiate the fibroblast into the cardiac muscle cells which have normal cardiac muscle cell specific molecular tags and a normal cardiac muscle function, so that a new way is provided for solving the cell source problem of the regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cornea edge stem cell tissue engineering composite body and its preparation method
InactiveCN1590541APromote cell differentiationPromote differentiationArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNon-embryonic pluripotent stem cellsBiological tissueLimbal stem cell
A tissue-engineered complex of human limbus stem cell and amnion for treating the limbus stem cell-deficiency eye diseases is disclosed. It is perpared through removing epithelium from amnion, using it as carrier, using fibroblast 3T3 as nutritive layer, culturing by cell suspension method, and promoting differentiation of cells by air-lifting technique.
Owner:天津医科大学眼科中心
Method for amplifying seed cells of skin tissue engineering
ActiveCN102086451APromote growthNo effect on growthSurgeryVertebrate cellsPhosphateCell culture media
The invention relates to a method for culturing seed cells of tissue engineering. The method for amplifying the seed cells of the tissue engineering comprises the following steps of: (1) adding a macroporous microcarrier into a bioreactor, hydrating and sterilizing and then adding 50 to 100ml of fibroblast culture medium, and adding fibroblasts for culturing; (2) inhibiting the fibroblasts from amplifying when the fibroblasts are attached to the microcarrier and the growth area is near 50 percent of surface area of the microcarrier, and standing and then pouring out culture solution; and (3) washing the obtained carrier by using sterile, calcium-free and magnesium-free phosphate buffered solution (PBS), then adding an epidermal cell culture medium and epidermal cells, and continuing to stir and culture until the cells overgrow the carrier to obtain the seed cells of skin tissue engineering. The quantity and function of the cells cultured by the method can both be apparently increased,the damage of the cells is reduced, the cells can be directly used as seed cells for skin construction of the tissue engineering, and the effect is superior to those of methods using epidermal cell suspension and epidermal cell patches.
Owner:韩春茂
Methods for Generating Cardiomyocytes
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Double-layered artificial skin and its prepn process
The present invention provides one kind of double-layered artificial skin implant comprising one hypodermal layer containing polyglycollic acid and other biodegradable material, fibroblast and matrix protein; and one epidermal layer on the hypodermal layer. The artificial skin has continuous epidermal cell growing on the surface of the fibroblast-PGA composite, well cell differentiation and obvious lamination. The slice shows the artificial skin has the tissue structure characteristic similar to that of normal body skin. The preparation process and use of the artificial skin is also provided.
Owner:上海组织工程研究与开发中心
Centella asiatica triterpenic acid single-glucopyranoside composition, its preparation method, its quantitative analysis method and its application
The invention relates to a centella asiatica triterpenic acid single-glucopyranoside composition which is composed of ursane madecassic acid single-glucopyranoside, madecassic acid single-glucopyranoside and oleanane chebuloside II, wherein the mass ratio of ursane madecassic acid single-glucopyranoside to madecassic acid single-glucopyranoside to oleanane chebuloside II is 1:0.5-2:0.1-1, and the sum of the mass percentage content of three components is not less than 50%. The composition takes a centella asiatica extract as a substrate, the centella asiatica extract is fermented and hydrolyzed by microbes of beta-glucosidase or microbes capable of generating beta-glucosidase, and extracted by n-butanol or separated and purified by macroporous adsorption resin. The invention also provides a quantitative analysis method which is a HPLC quantitative analysis for three components by adding a proper amount of mobile phase of beta-cyclodextrin. Experimental research of pharmacodynamics proves that the composition has substantial activity for inhibiting tumor cells and fibroblast, the composition can be used for treating tumor and scar hyperplasia.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Transcutaneous prosthesis
InactiveUS20090149966A1More powerAid adhesionDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBacterial AdhesionsProsthesis
A transcutaneous prosthesis includes a first component configured for attachment to a bone, the first component including flutes or grooves on a surface thereof for deterring rotation of the prosthesis within a bone; a second component adapted for location between the bone and the skin, the second component having a surface treatment for stimulation of fibroblastic cell proliferation and attachment of epithelial cells; and a third component adapted for location to extend from the skin surface and is adapted to extend directly from the skin surface in use, the third component having a coating of a non-stick material on an outer surface thereof, the coating having a surface energy that is lower than a surface energy of the first and second components and which is low enough to deter bacterial adhesion.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20080026461A1Sectioned easilySimple processEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellHuman body
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Tissue engineering composite skin material, and its preparing method
A composite skin material prepared by tissue engineering for skin implantation is composed of the hypoderminal cell layer and epithelial cell layer attached on fibrin scaffold. Its preparing process includes such steps as taking fibroblasts and epithelial stem cells from patient itself and foreign person, dispersing them in fibrinogen liquid, preparing serozyme solution, mixing them together, and coating the mixture on the surface of wound.
Owner:北京赛尔泰和生物医药科技有限公司
Induction medium for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into adipocyte and application thereof
The invention discloses an induction medium inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into adipocyte, an induction method and application thereof. The induction medium contains a basal culture medium and an induction micromolecule combination, wherein the induction micromolecule combination is SG or 6TF, S is SB431542, G is GSK126, 6 is E61541, T is tranylcypromine, and F is forskolin. The induction medium can induce and trans-differentiate the fibrolast into the adipocyte, the obtained adipocyte contains a normal adipocyte specificity molecular tag and has a normal fat adipogenesis function, and a new approach is provided for solving the cellular source problem of regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Targeting agent for cancer cell or cancer-associated fibroblast
InactiveUS20130210744A1Efficient deliverySuppression of activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsRetinoidTumor-Associated Fibroblasts
Disclosed are a novel therapeutic agent and a novel treatment method for cancer. Specifically disclosed are: a targeting agent for a cell selected from the group consisting of a cancer cell and a cancer-associated fibroblast, which comprises a retinoid and / or derivative thereof; a substance delivery carrier for the cell, which comprises the targeting agent; an anti-cancer composition utilizing the targeting agent or the carrier; an anticancer-associated fibroblast composition; and a method for treatment of cancer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Transcutaneous Prosthesis
InactiveUS20070073412A1Increase the outer surface areaMore powerDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBacterial AdhesionsProsthesis
A transcutaneous prosthesis includes a first component shaped for implantation into a bone, the first component including flutes or grooves on a surface thereof for deterring rotation of the prosthesis within a bone; a second component adapted for location between the bone and the skin, the second component having a surface treatment for stimulation of fibroblastic cell proliferation and attachment of epithelial cells; and a third component adapted for location to extend from the skin surface and is adapted to extend directly from the skin surface in use, the third component having a coating of a non-stick material on an outer surface thereof, the coating having a surface energy that is lower than a surface energy of the first and second components and which is low enough to deter bacterial adhesion.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Multilayer core-shell nano-fiber scaffold, and method for constructing tissue engineering material by using multilayer core-shell nano-fiber scaffold and melanocyte
ActiveCN105525385AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh strengthSynthetic fibresPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSpinningBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a multilayer core-shell structured nano-fiber scaffold, and a method for constructing a tissue engineering material by using the multilayer core-shell structured nano-fiber scaffold and melanocyte. The multilayer core-shell nano-fiber scaffold is prepared through electrostatic spinning, the external layer of the scaffold is a biocompatible material, the middle layer of the scaffold is a polymer barrier layer, and the core layer of the scaffold is a drug supported core material. The tissue engineering material can be formed by using the multilayer nano-fiber scaffold and the melanocyte, or using the multilayer nano-fiber scaffold, fibroblast and keratinocyte, and can be used to treat depigmentation (such as leucoderma). The multilayer core-shell structured nano-fiber scaffold has the advantages of good biocompatibility and mechanical performances, and realization of long-time controllable release of drugs, and the tissue engineering scaffold constructed by using the multilayer core-shell structured nano-fiber scaffold can effectively support growth, propagation and transplantation of melanocyte and co-culture cells.
Owner:HANGZHOU THIRD HOSPITAL +1
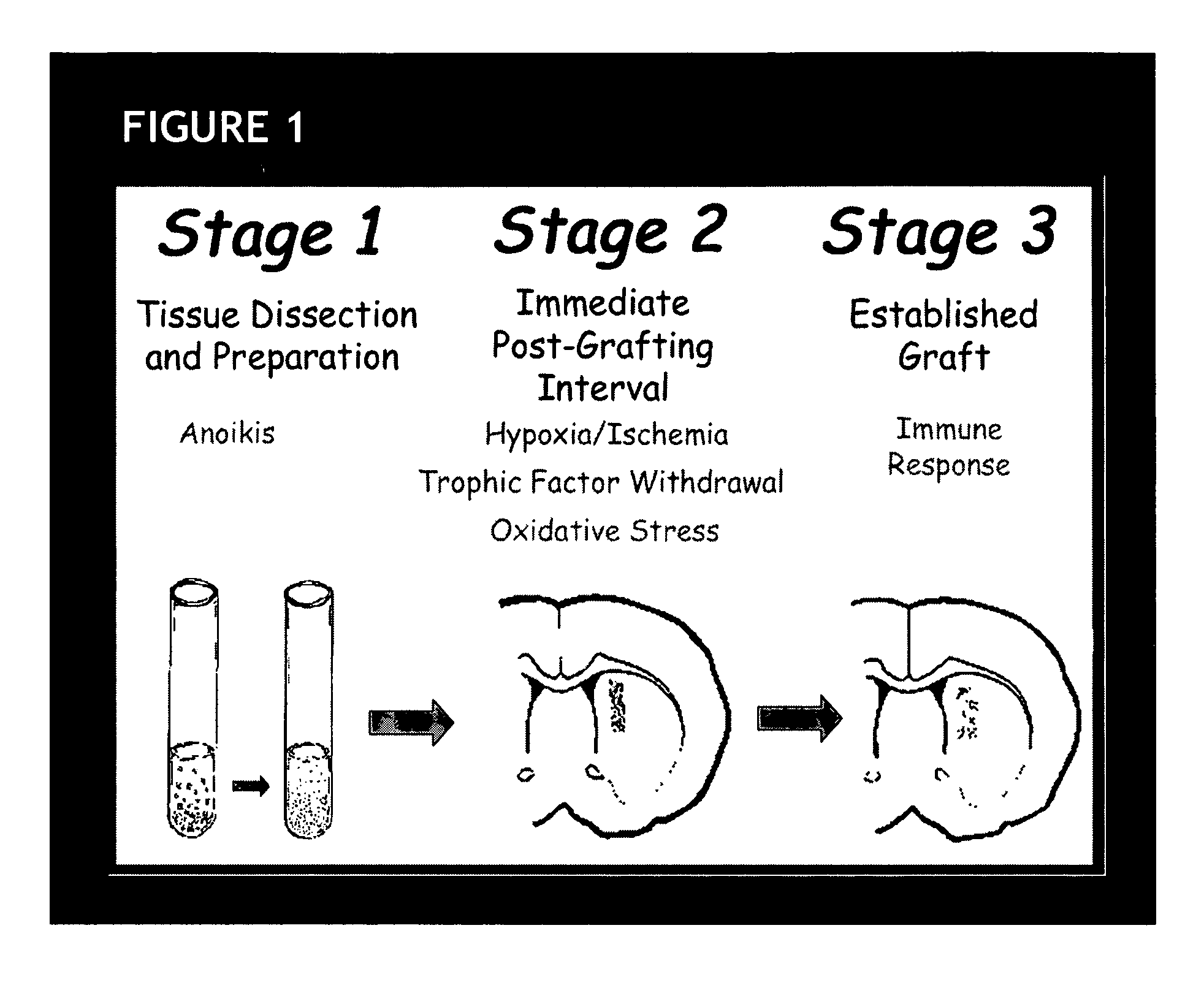
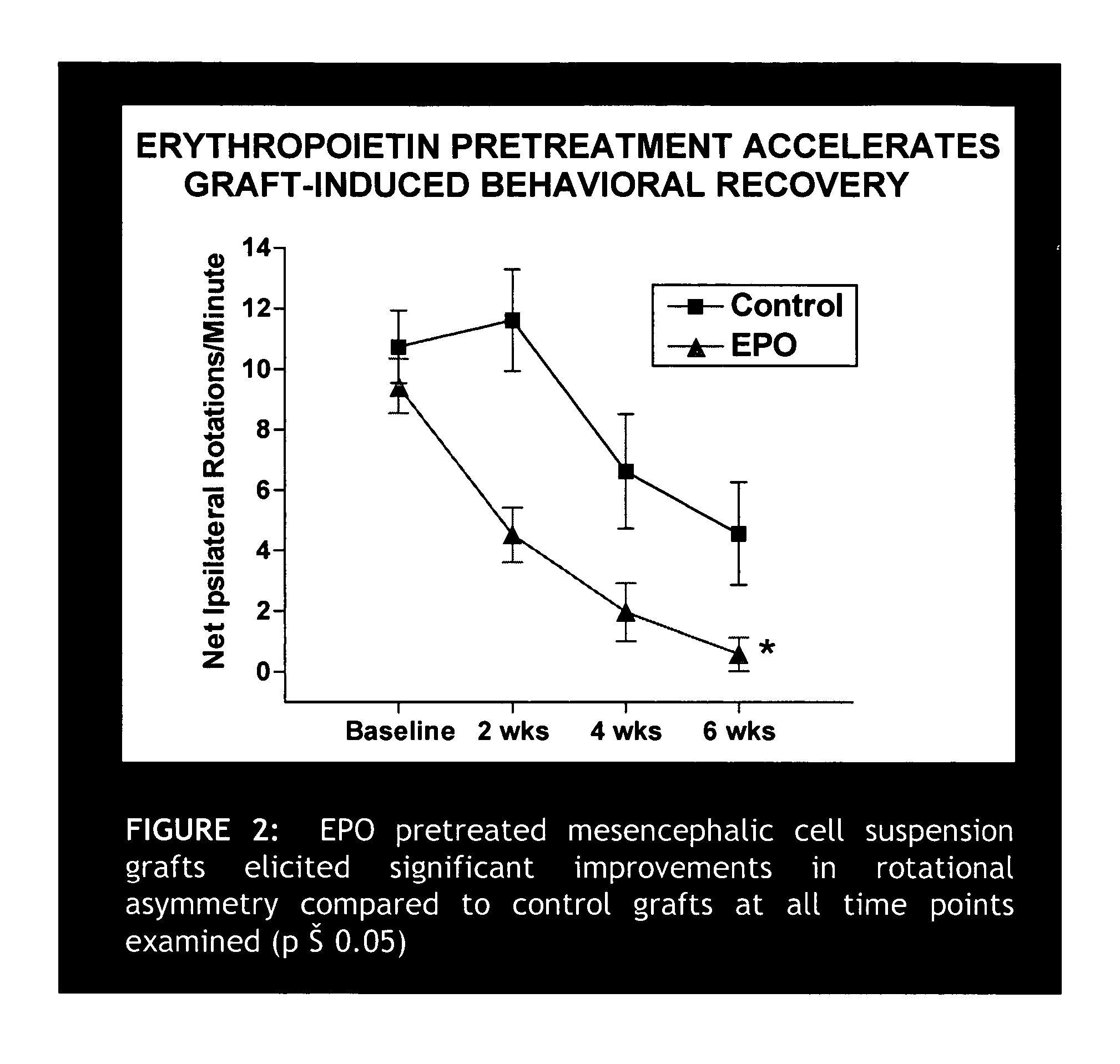
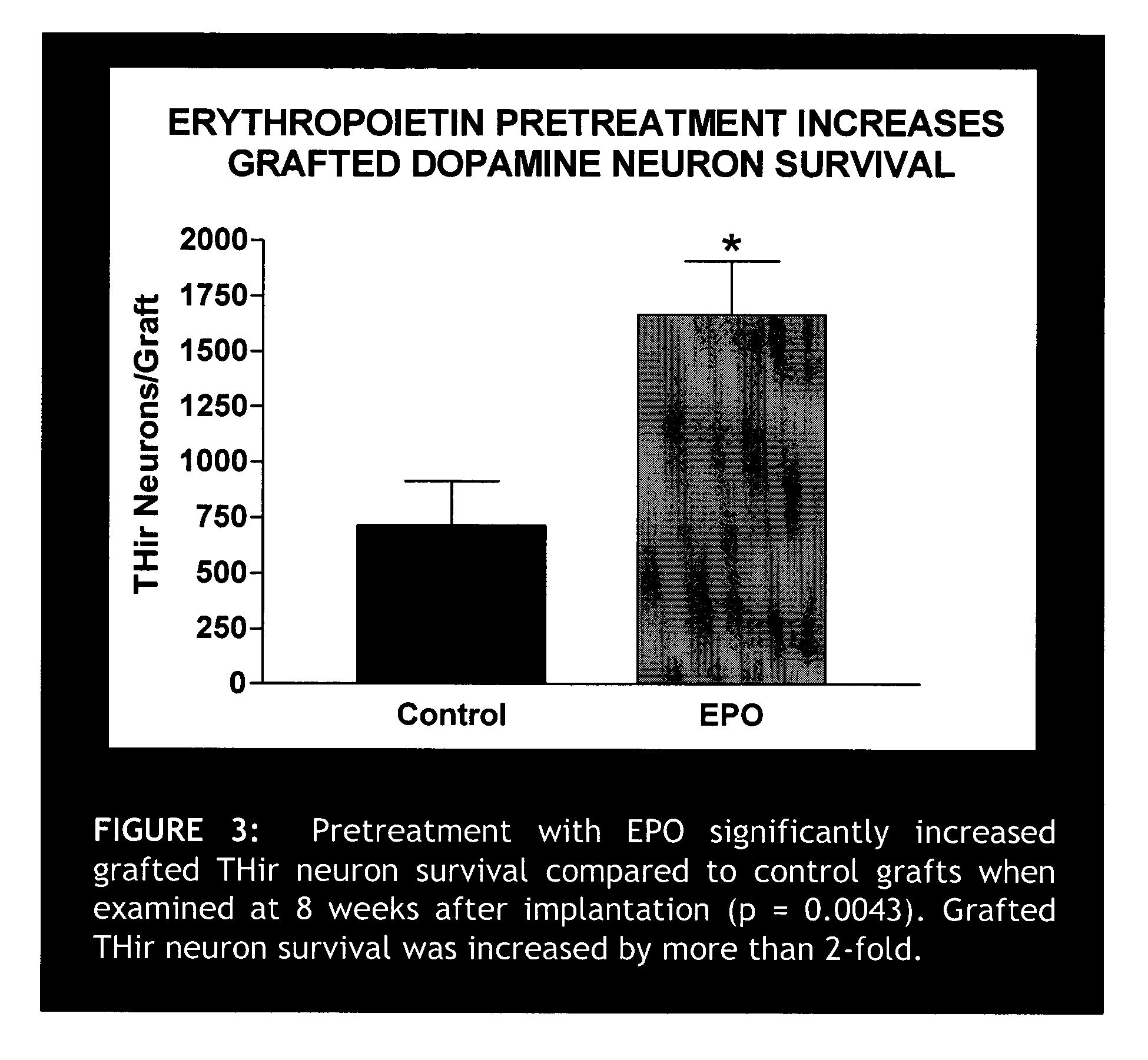
Erythropoietin administration to improve graft survival
ActiveUS7459152B2Enhance cell viabilityImprove survivalBiocideNervous disorderErythropoietinGraft survival
The present invention provides methods, compounds and kits for increasing the viability of cells. The methods involve treating cells that make up a tissue graft with erythropoietin before, during or after delivery or administration. The method can employ cells of different types, including cells of neural or paraneural origin, such as adrenal chromaffin cells. Also useful are cell lines grown in vitro. Cells not of neural or paraneural origin, such as fibroblasts, may also be used following genetic alteration to express a desired neural product such as a neurotransmitter or a neuronal growth factor. The method is used to treat neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, epilepsy, and traumatic brain or spinal cord injury.
Owner:RUSH UNIV MEDICAL CENT
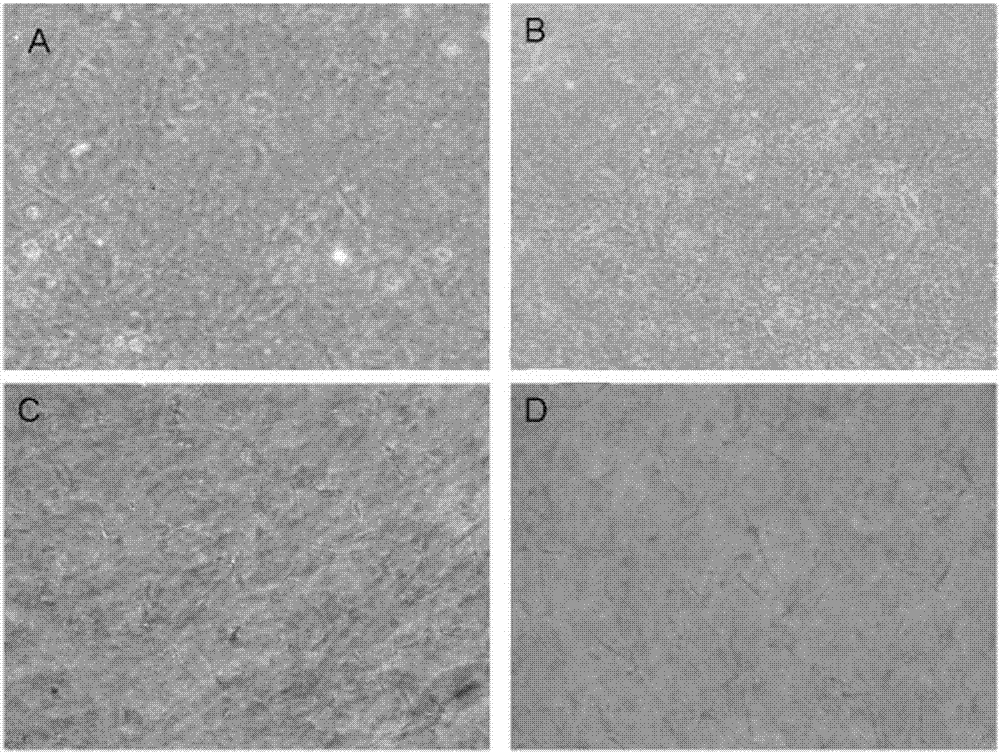
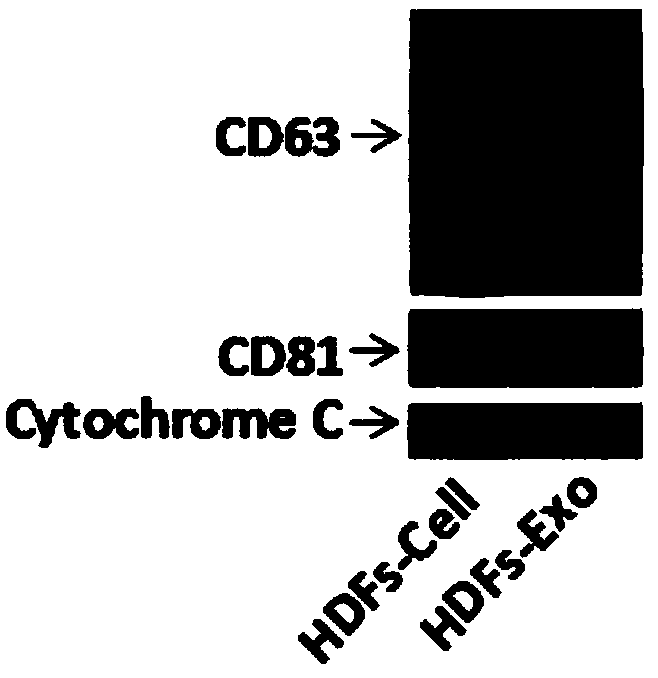
Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Containing a High Amount of Growth Factors
InactiveUS20190133922A1High levelImprove skin conditionCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsFibroblastGrowth factor
The present invention relates to exosomes with an increased amount of growth factors, which are obtained from stem cells cultured in a medium containing an epithelial growth factor (EGF) and / or a fibroblast growth factor (FGF). It is expected that the nano-sized exosomes isolated from a stem cell culture liquid can penetrate into the dermal layer of the skin and thereby increase their regenerative effect. In addition, since exosomes contain a large amount of various growth factors, they provide effects such as skin regeneration and anti-aging, promotion of collagen synthesis, hair growth, restoration of shrunken hair follicles, and wound healing through proliferation and activation of fibroblasts, which are skin component cells.
Owner:KANGSTEM BIOTECH
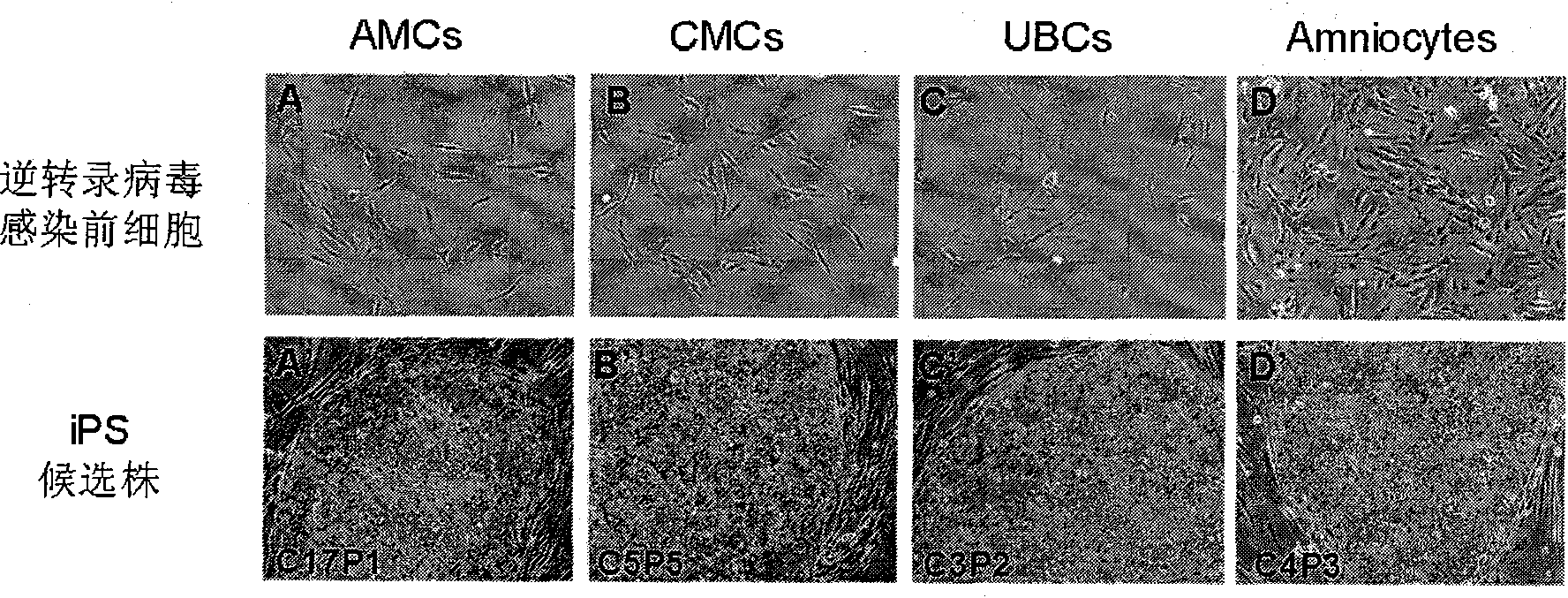
Cell type used for producing induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101984050AGreat therapeutic application prospectsGood pluripotencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionControl orientedDisease
The invention discloses four cell types which have wide heteroplastic transplantation application prospect and can be effectively induced into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. The origins of three cell types are placental tissue, namely amnion mesenchymal cell, chorion mesenchymal cell and umbilical cord mesenchymal cell; and the origin of the other one is amniotic fluid cell. Besides, the invention also discloses an induction reprogramming method for producing cells capable of producing induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by efficient induction, including the following steps: cDNA containing pluripotent stem cell factor is respectively introduced into the four primary culture cells; the four primary cells in which cDNA is introduced are respectively cultured on appropriate culture mediums, primary iPS is obtained and then quality of iPS is optimized on appropriate culture mediums, and cloning of pluripotent stem cell can be primarily evaluated. In the invention, three mesenchymal cells of placenta origin and amniotic fluid cell all can be induced into iPS, wherein the chorion mesenchymal cell is compared with fibroblast, efficiency of induction reprogramming is improved by over 100 times, efficiency is about 2.3%, and the efficiency is slightly higher than that of horny cell; and a means which is more effective and more pertinent is provided for building disease model, screening drug and controlling oriented differentiation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions derived from stem cell released molecules & methods for formulation thereof
InactiveUS20140205563A1Ensuring structureEnsure stabilityBiocideCosmetic preparationsFibroblastic cellCytokine
Compositions for use in treatment of a variety of tissue diseases include stem cells and stem cell released molecules (SRM's) suspended in an aqueous solution with a cellulosic material or other thickening agent. The stem cells and SRM's can be derived from one or more distinct cell lines. The SRM's can further include one or more mucins, cytokines, or growth factors. Exemplary formulations include stem cells and SRMs derived from epithelial stem cells, corneal limbal stem cells, and fibroblasts. Other compositions and methods for formulation thereof are described.
Owner:BIOREGENERATIVE SCI
Pro-inflammatory fibrinopeptide
InactiveUS6908899B2Cleaning systemEvaluate the effectiveness of existing compoundsFibrinogenAntipyreticGlycineArginine
Owner:VETERANS AFFAIRS U S DEPT OF
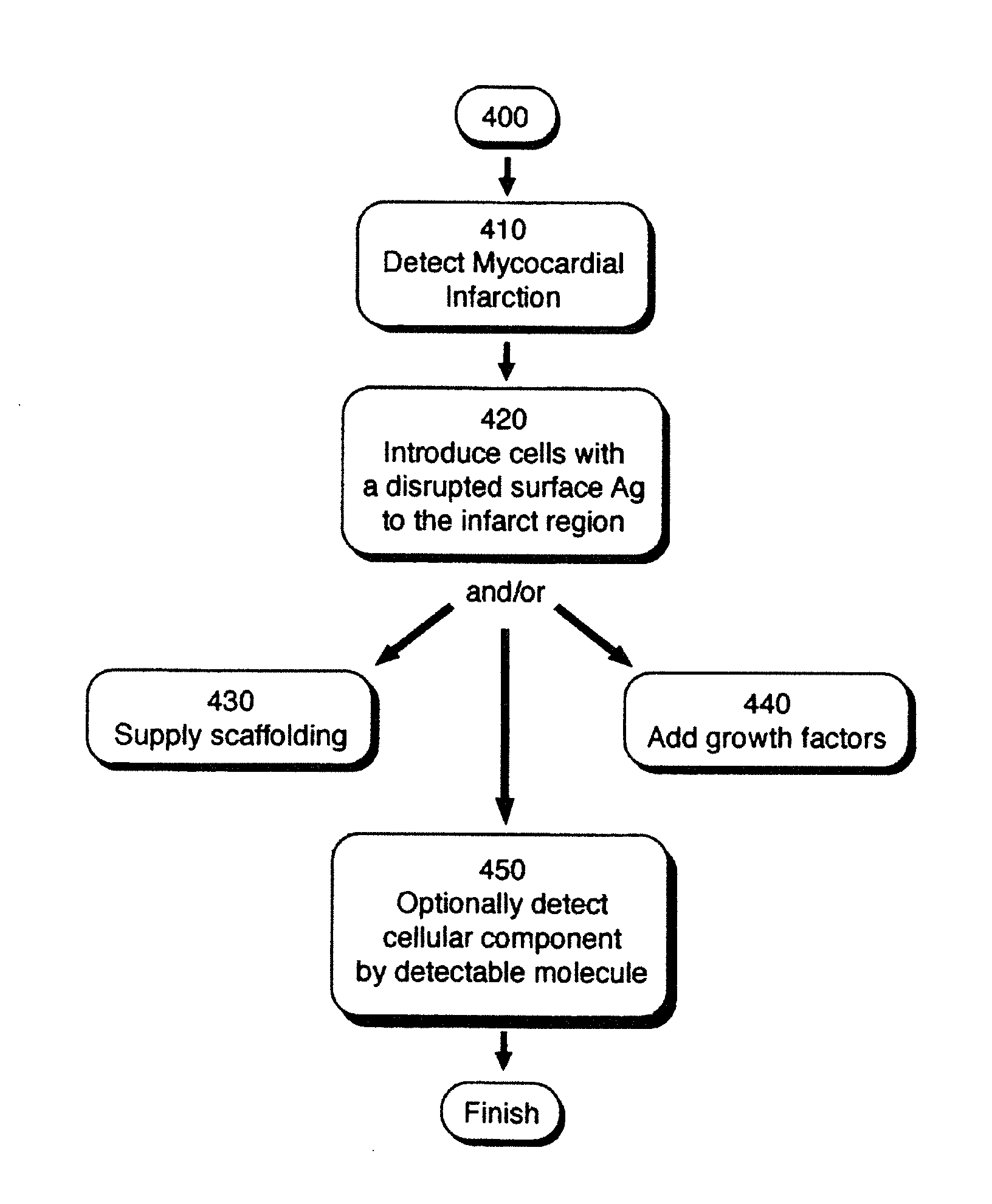
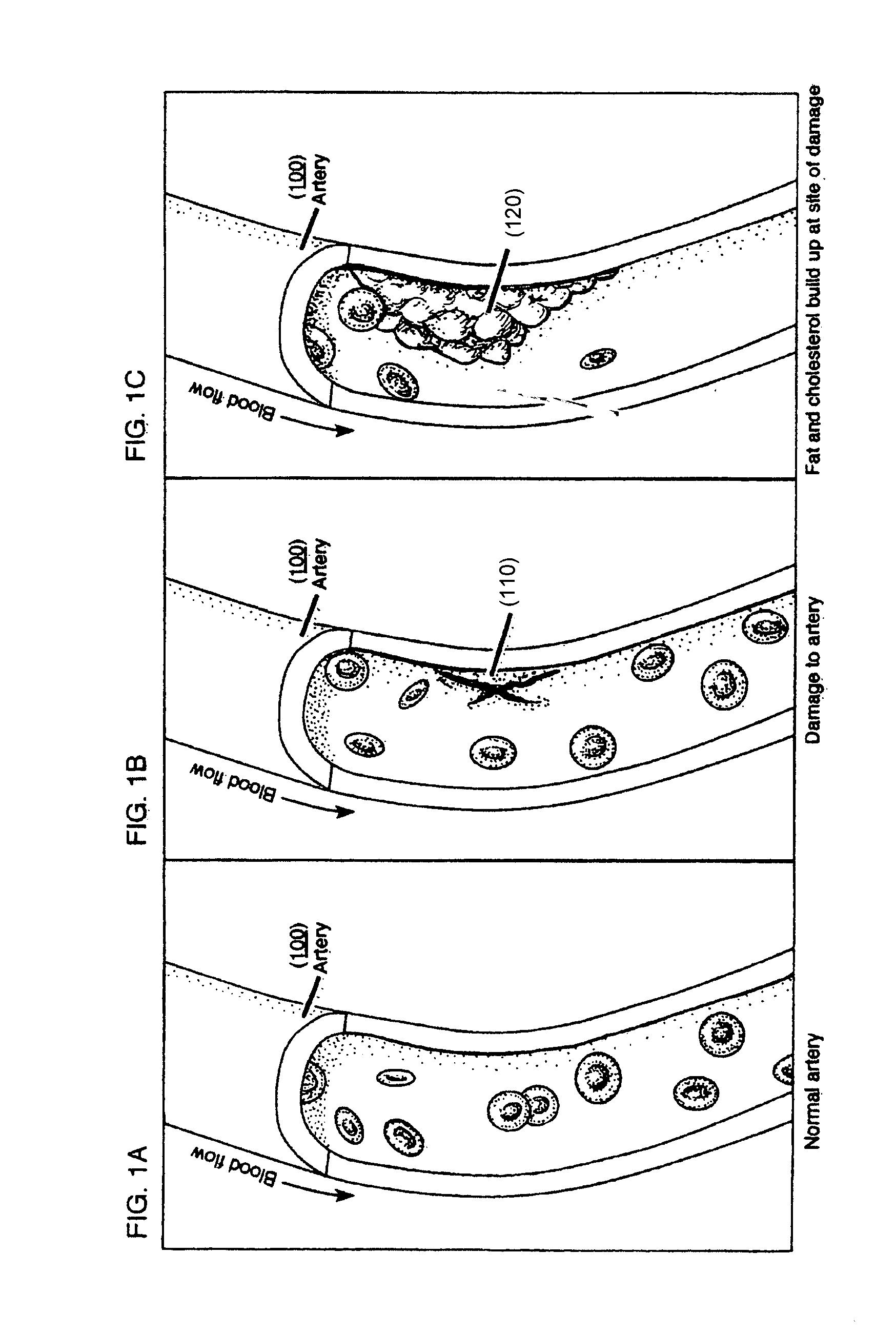
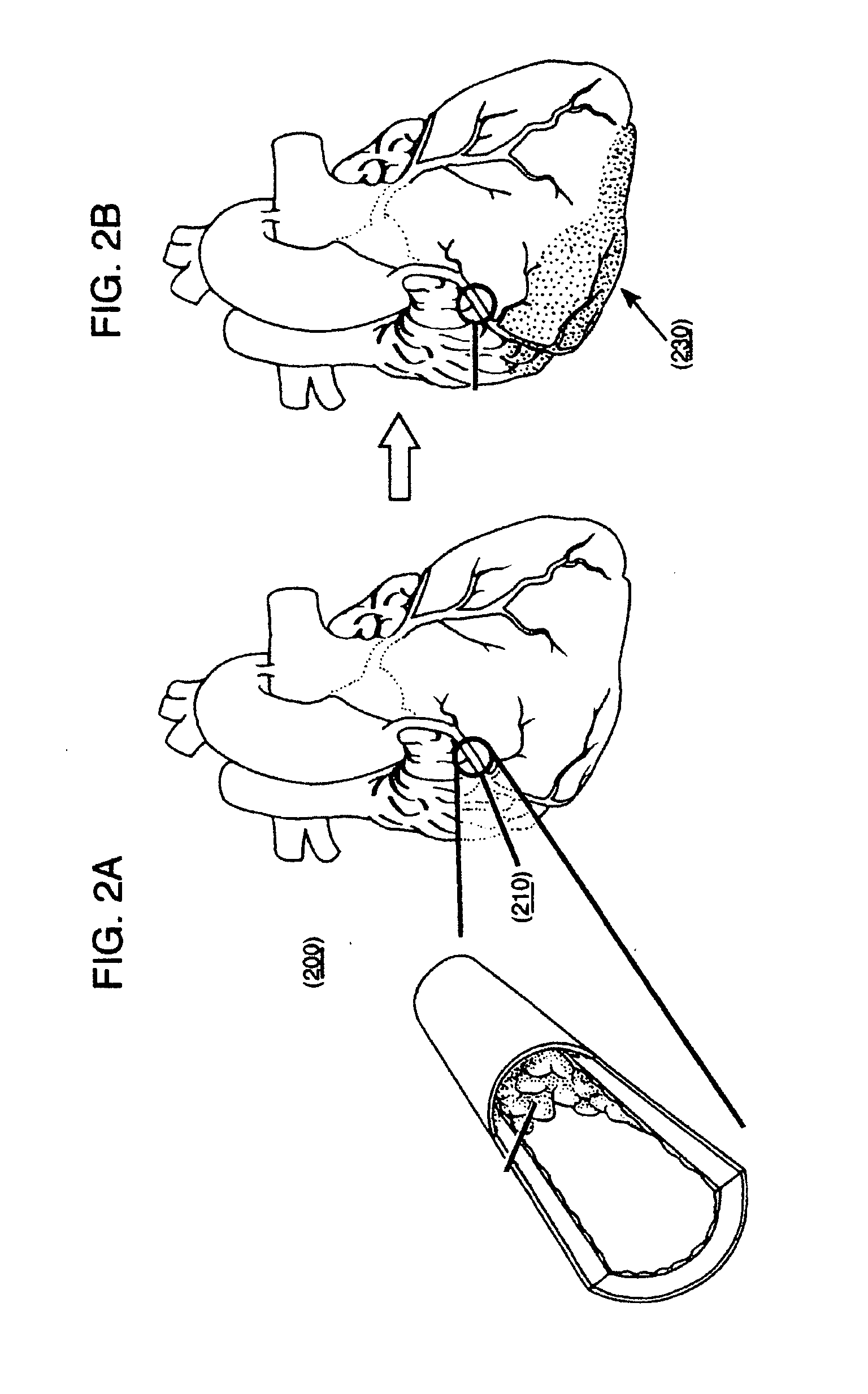
Methods and compositions to treat myocardial conditions
InactiveUS20150018747A1Reduce stimulationReduce stressSurgical adhesivesDrug photocleavageMultiple therapyElectric stimulation therapy
Methods, devices, kits and compositions to treat a myocardial infarction. In one embodiment, the method includes the prevention of remodeling of the infarct zone of the ventricle using a combination of therapies. The method may include the introduction of structurally reinforcing agents. In other embodiments, agents may be introduced into a ventricle to increase compliance of the ventricle. The prevention of remodeling may include the prevention of thinning of the ventricular infarct zone. Another embodiment includes the reversing or prevention of ventricular remodeling with electro-stimulatory therapy. The unloading of the stressed myocardium over time effects reversal of undesirable ventricular remodeling. These therapies may be combined with structurally reinforcing therapies. In other embodiments, the structurally reinforcing component may be accompanied by other therapeutic agents. These agents may include but are not limited to pro-fibroblastic and angiogenic agents.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for building three-dimensional skin model applied to anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy effect evaluation
ActiveCN107267441AVerify experimental stabilityVerify repeatabilityCompounds screening/testingEpidermal cells/skin cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixAir liquid interface
The invention provides a method for building a three-dimensional skin model. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing an extracellular matrix polymeric hydrogel solution; 2) mixing fibroblast and the extracellular matrix polymeric hydrogel solution, and culturing through a small culture chamber; and 3) inoculating cutin to form cells; performing air-liquid interface culture to obtain the three-dimensional skin model containing a corium layer, an epidermal layer and a cutin layer. The method is capable of effectively building the three-dimensional skin model; in addition, the preparation method is simple and convenient, and can be applied to the sieving of anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy skin drugs; and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Application and preparation method of autologous fibroblast-sourced freeze-dried exosome powder
InactiveCN109010247AImprove proliferative abilityEasy to synthesizeCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFreeze-dryingFibroblast
The invention relates to application and a preparation method of an autologous fibroblast-sourced freeze-dried exosome powder. The autologous fibroblast-sourced freeze-dried exosome powder is appliedinto wrinkle resistance and oxidation resistance, and the application method is as follows: normal saline is used for dissolving the autologous fibroblast-sourced freeze-dried exosome powder into 0.5percent by weight of solvent, so that injection is obtained, and the injection is injected deep into deep stratum of the dermis by a microneedle. The preparation method of the freeze-dried exosome powder comprises four steps, i.e., obtainingment of skin-sourced fibroblasts, cell amplification and cell identification, separation and identification of exosome and freeze-drying of exosome. Since theinvention adopts the autologously sourced exosome to resist wrinkles and oxidation, the autologous fibroblast-sourced freeze-dried exosome powder is easy to store and transport, ethical problems do not exist, moreover, safety is high, and the wrinkle-resistant and oxidation-resistant effect is good.
Owner:浙江卫未生物医药科技有限公司
Titanium net with fimbrin and its prepn and application
InactiveCN1739809AReduce complicationsPromote repairTissue cultureTubular organ implantsFiberBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention belongs to the field of tissue engineering and medical material technology, and is especially titanium net with fimbrin coating and its preparation process and application in reconstructing trachea default. The present invention prepares fimbrin-titanium net complex with medical titanium net as support material and fimbrin to form coating. Fimbrin has excellent biocompatibility and can promote the growth of fibroblast and mucosa cell, speed healing, reduce complications. Clinically, the present invention is used in repairing trachea default. The present invention is significant in the research of fimbrin in promoting repair of trachea mucosa, reconstructing trachea default and reducing complications during reconstructing trachea default.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
Asymmetric double-crosslinked composite material, as well as preparation method and application of same
The invention discloses an asymmetric double-crosslinked composite material, as well as a preparation method and the application of the material. The asymmetric double-crosslinked composite material is obtained by preparing sodium hyaluronate / chitosan composite material into an asymmetric surface material with a smooth surface and a spongy surface, has good hydrophilicity, water absorbency, water storability and breathability, has the functions of promoting growth of epithelial cells and endothelial cells and inhibiting growth of fibroblasts, has a wide antibacterial effect, and has a wide application prospect in the field of medical care.
Owner:佛山市领固胶粘科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com