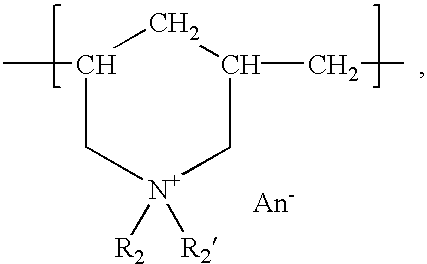
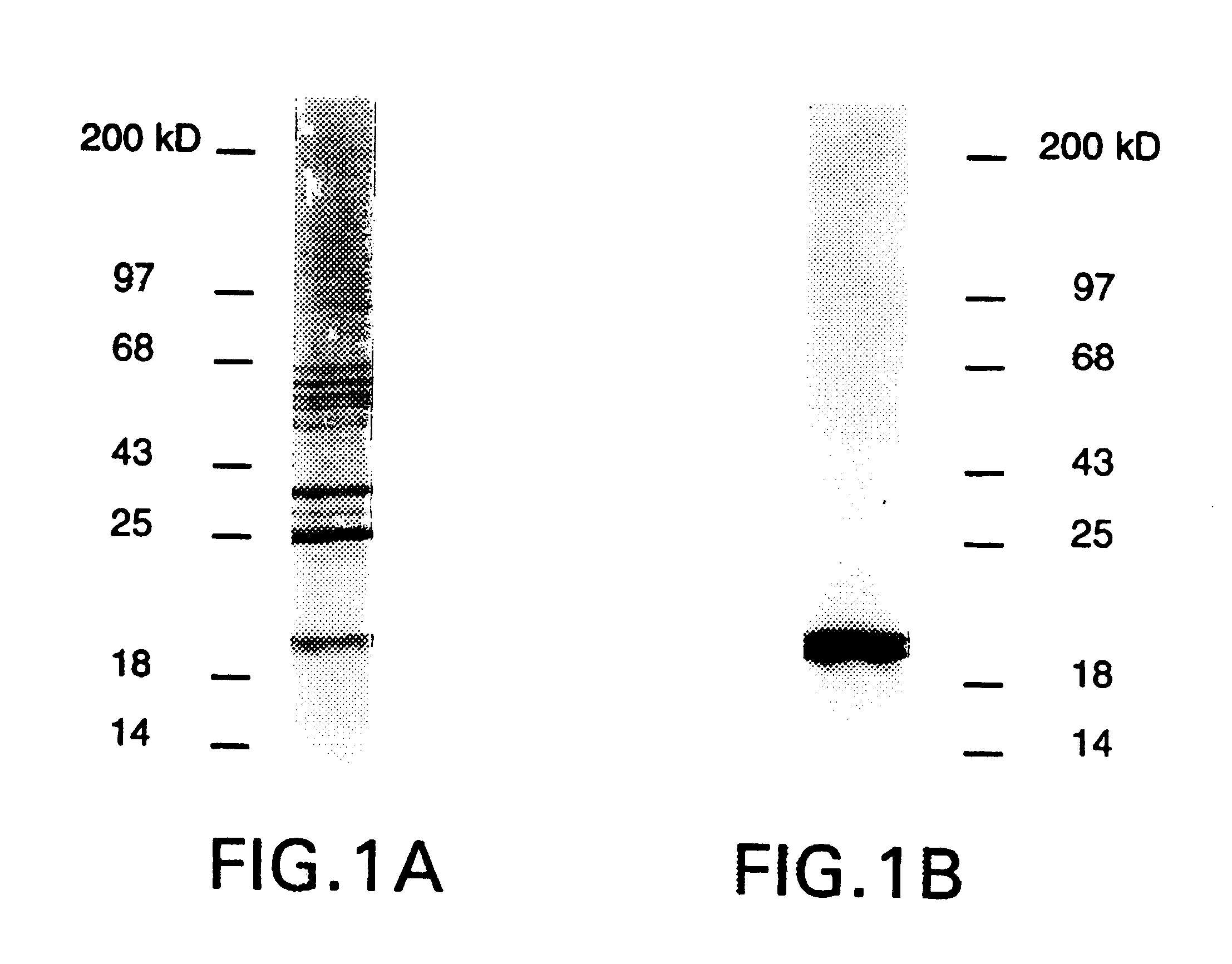
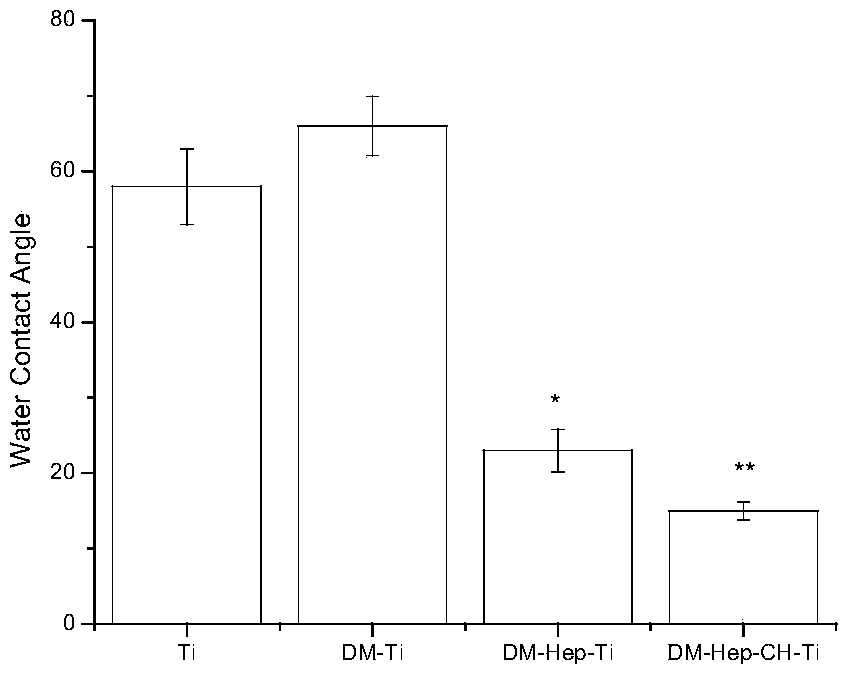
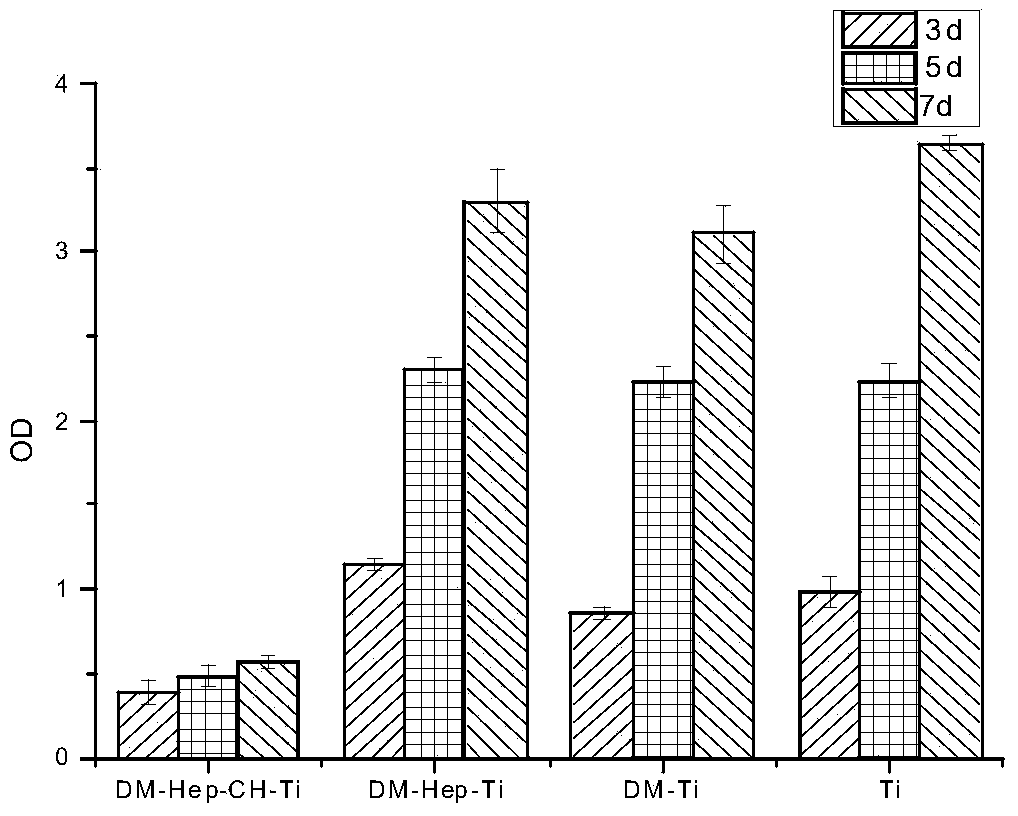
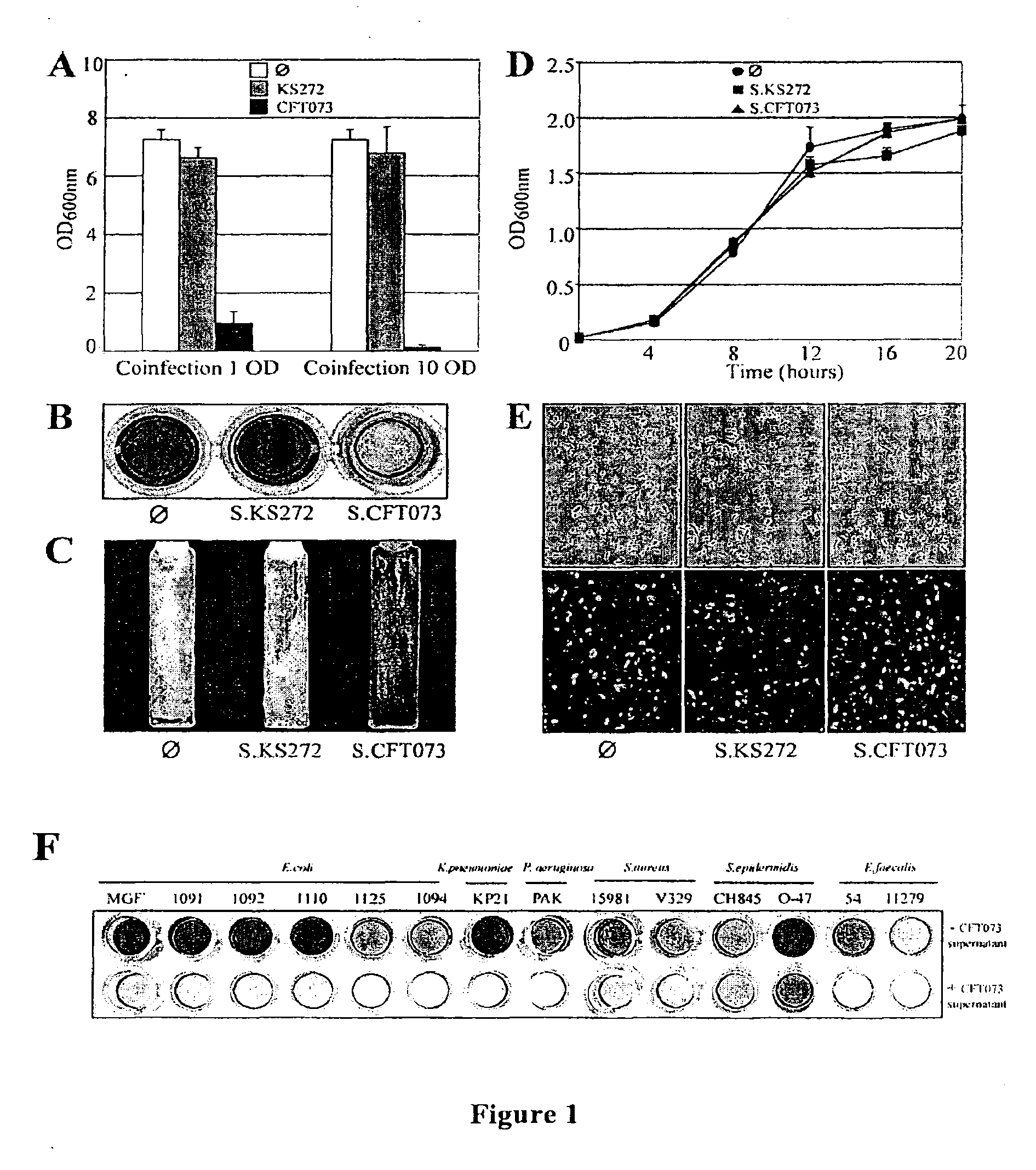
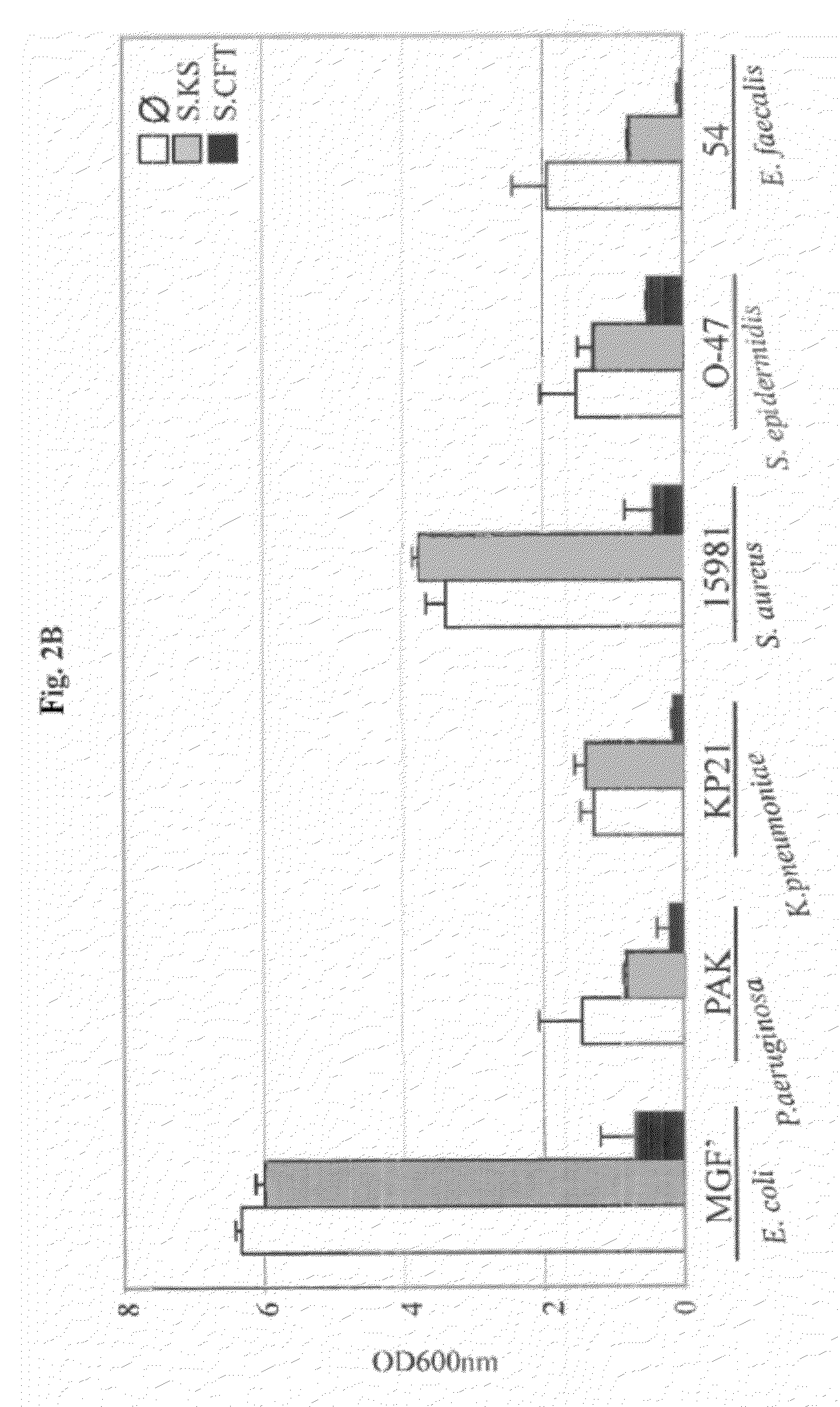
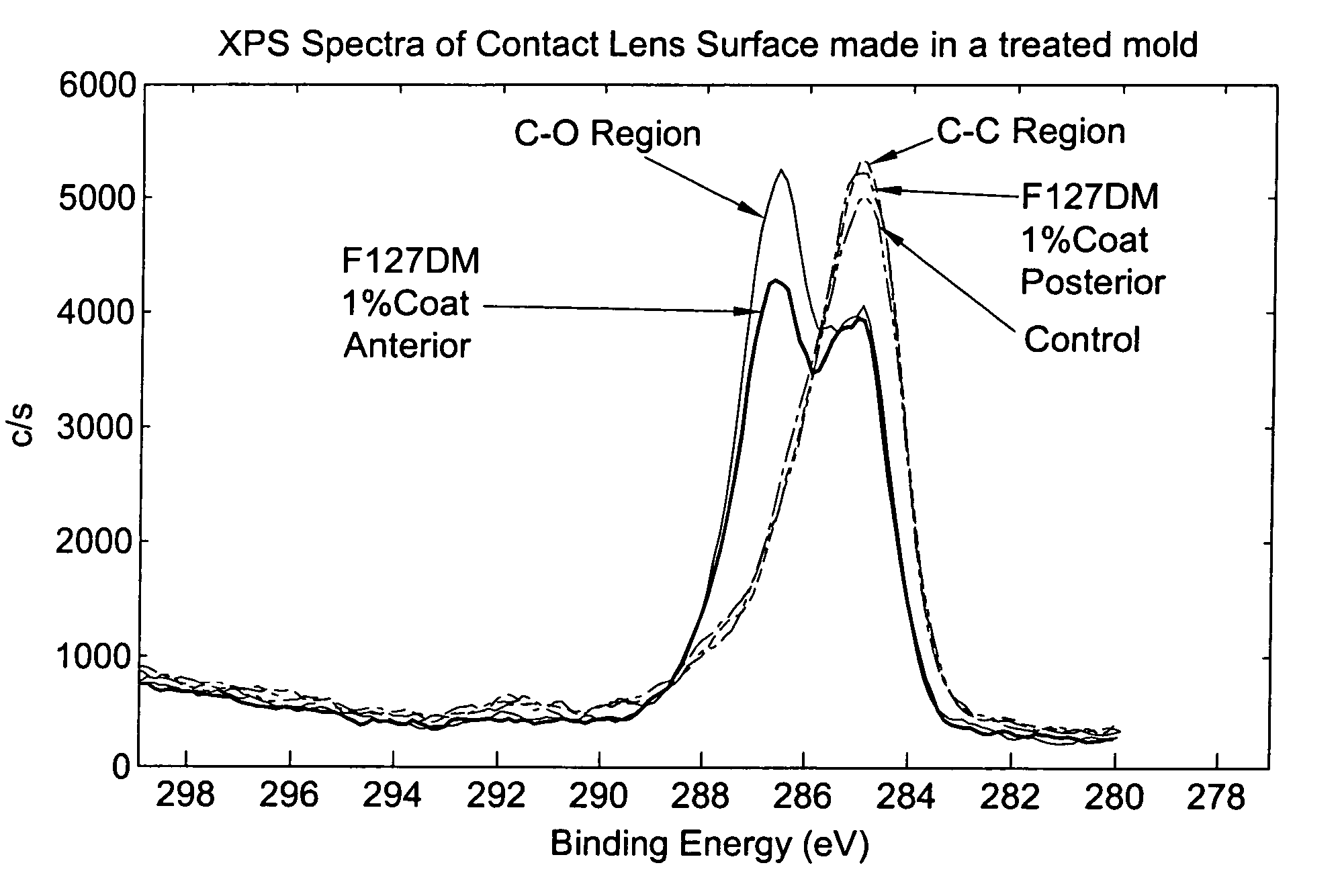
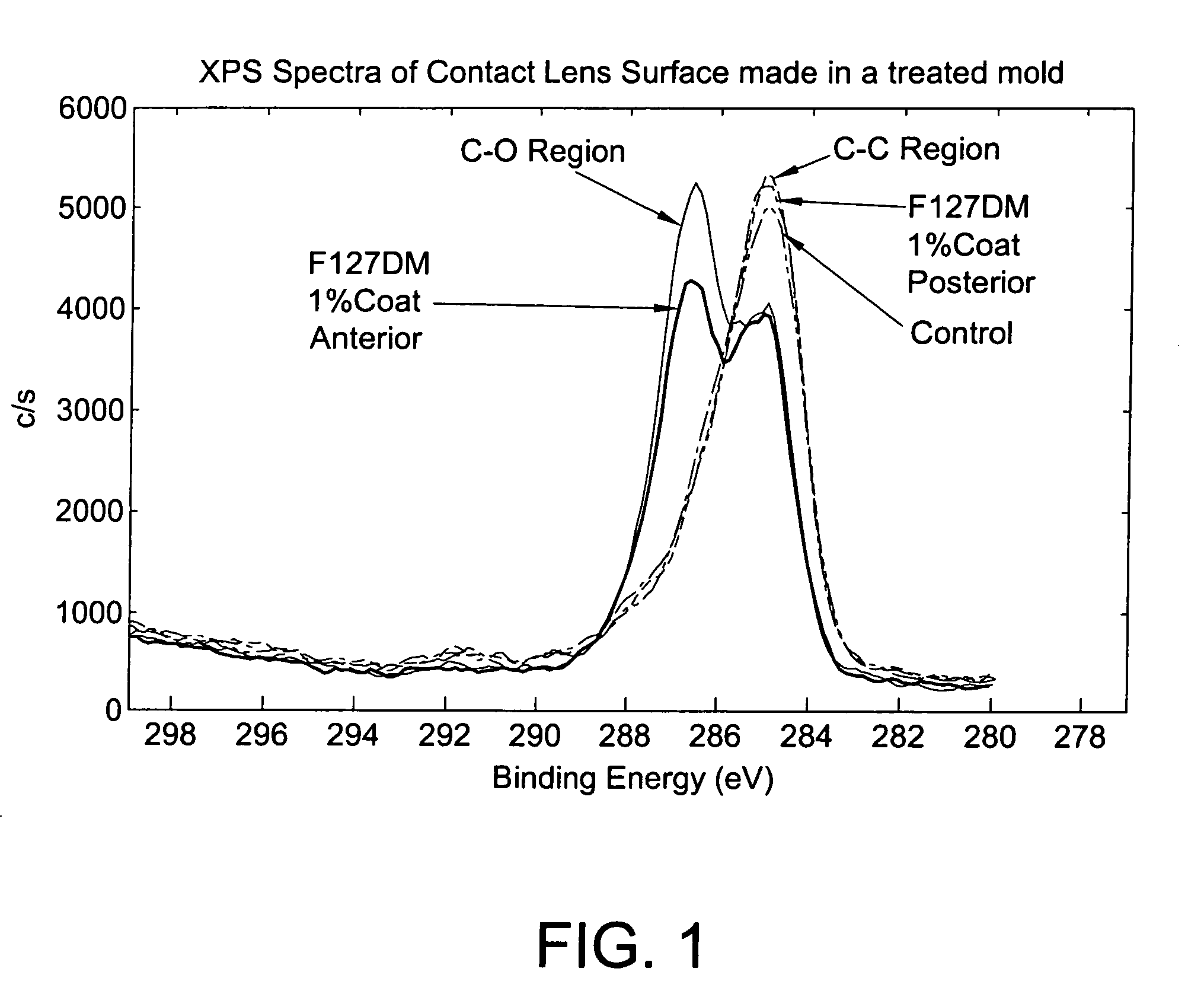
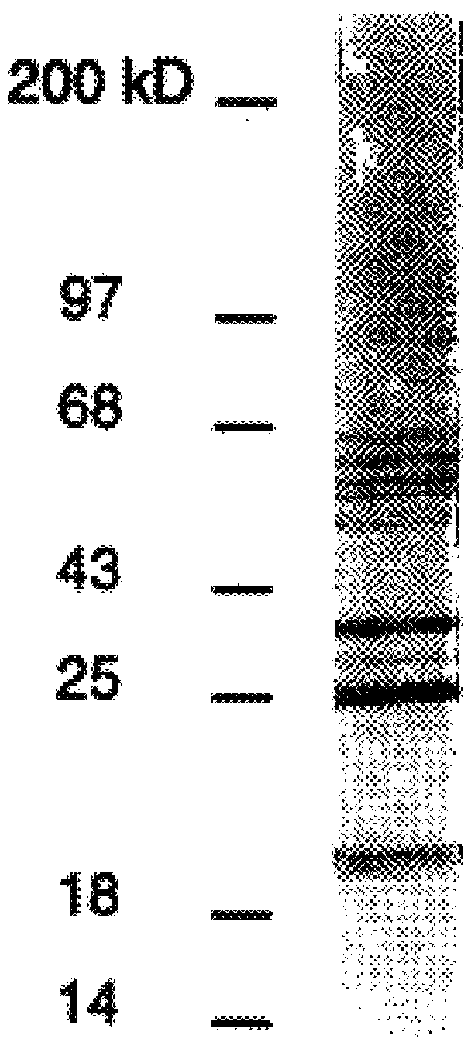
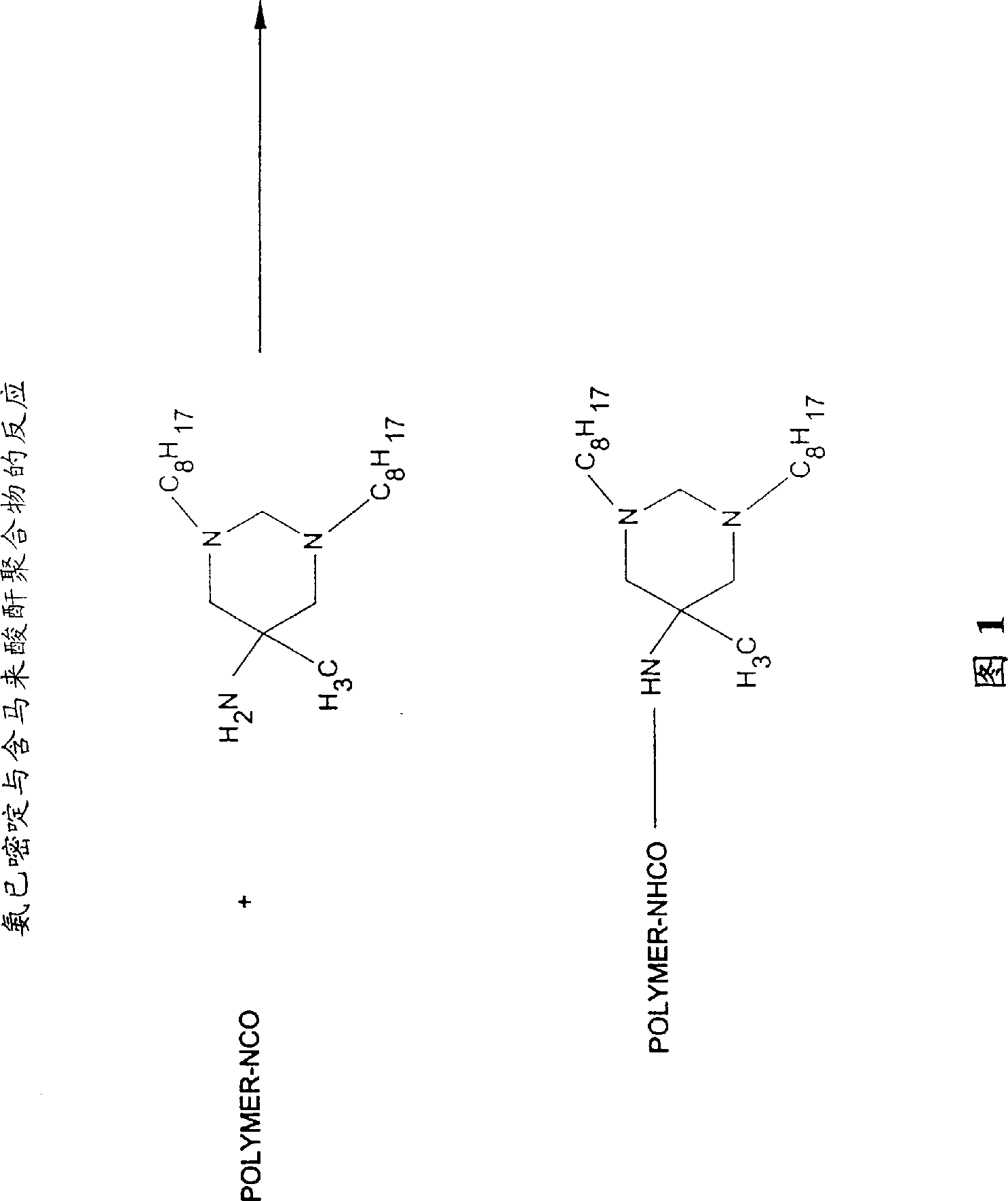
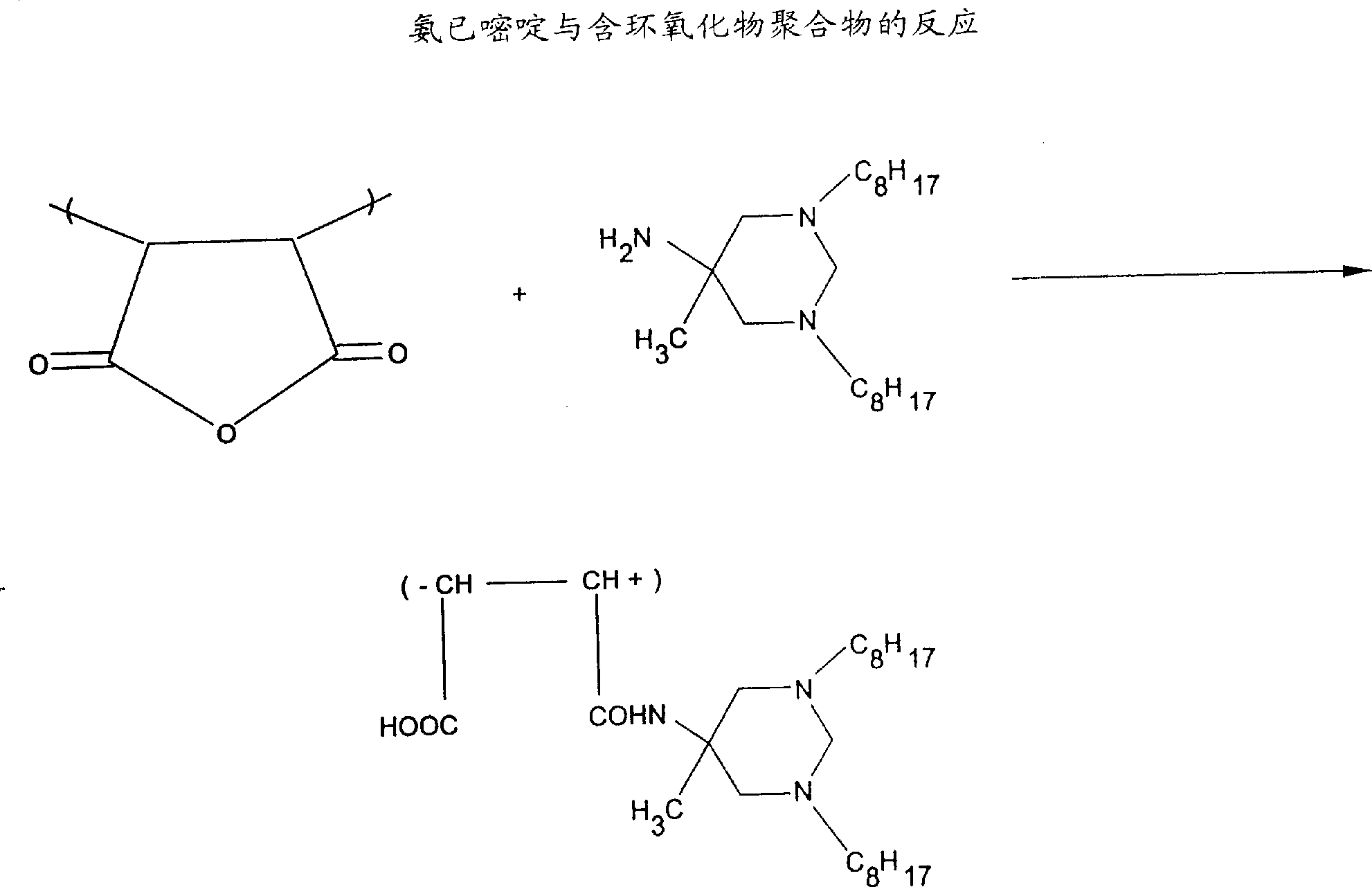
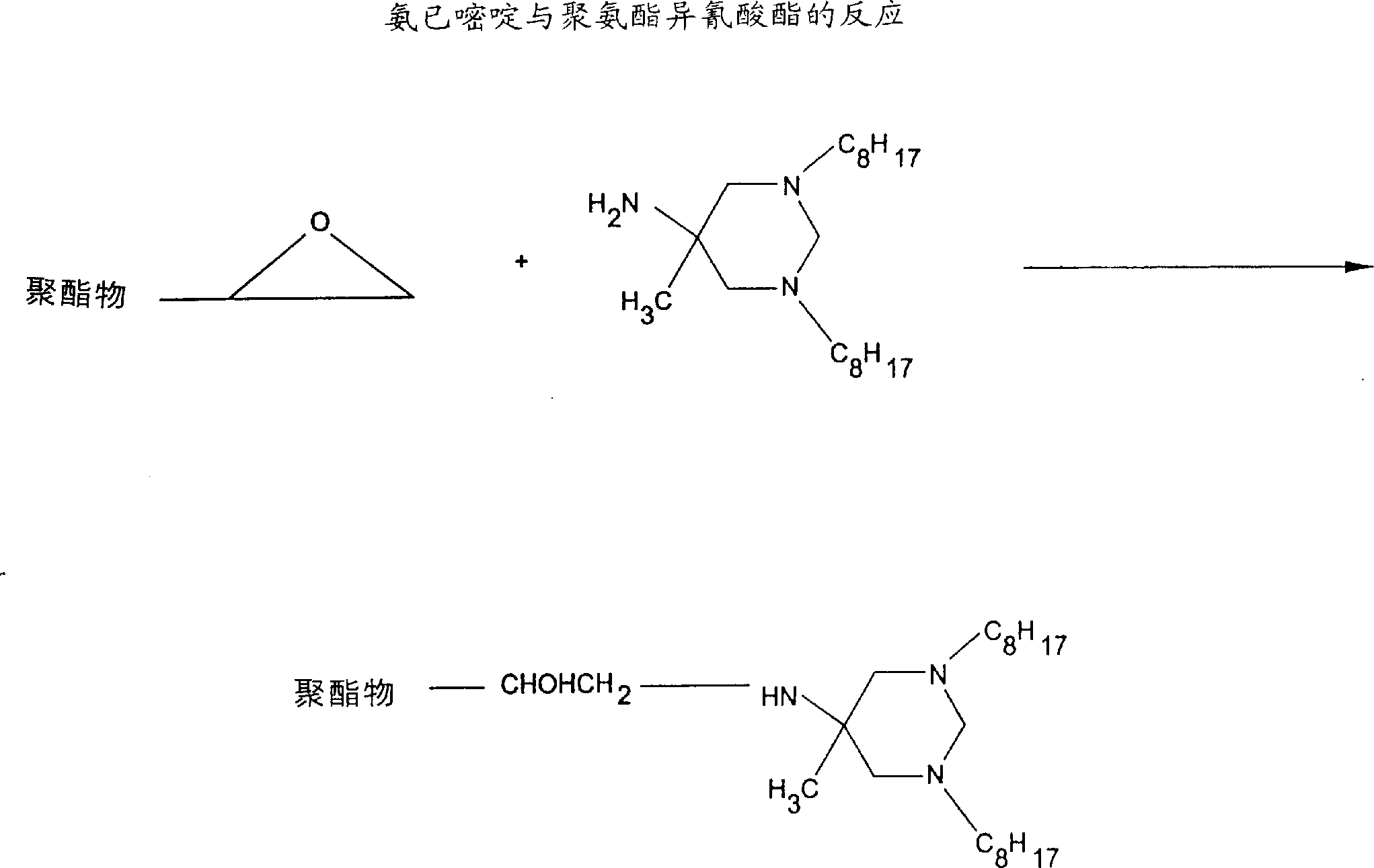
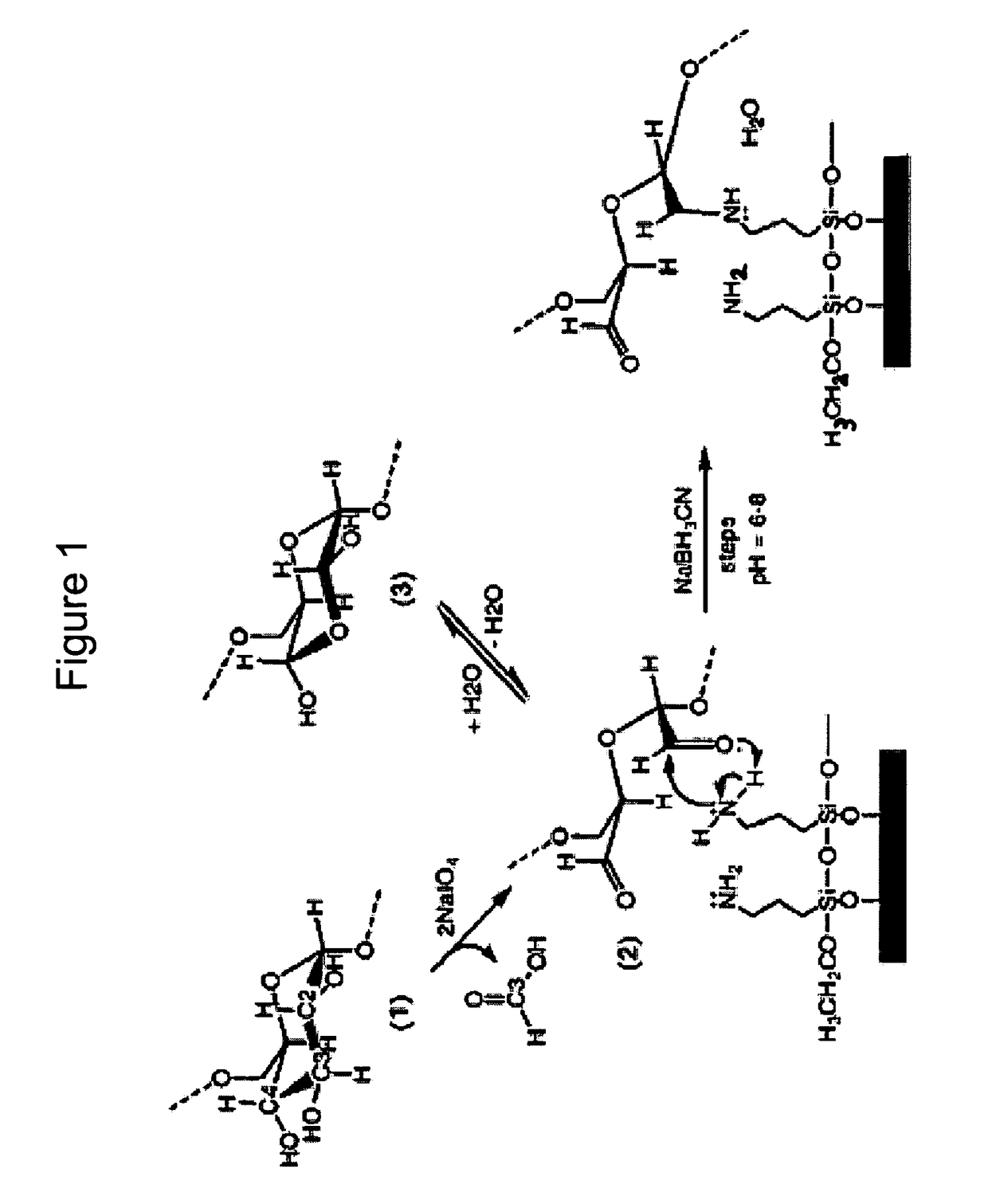
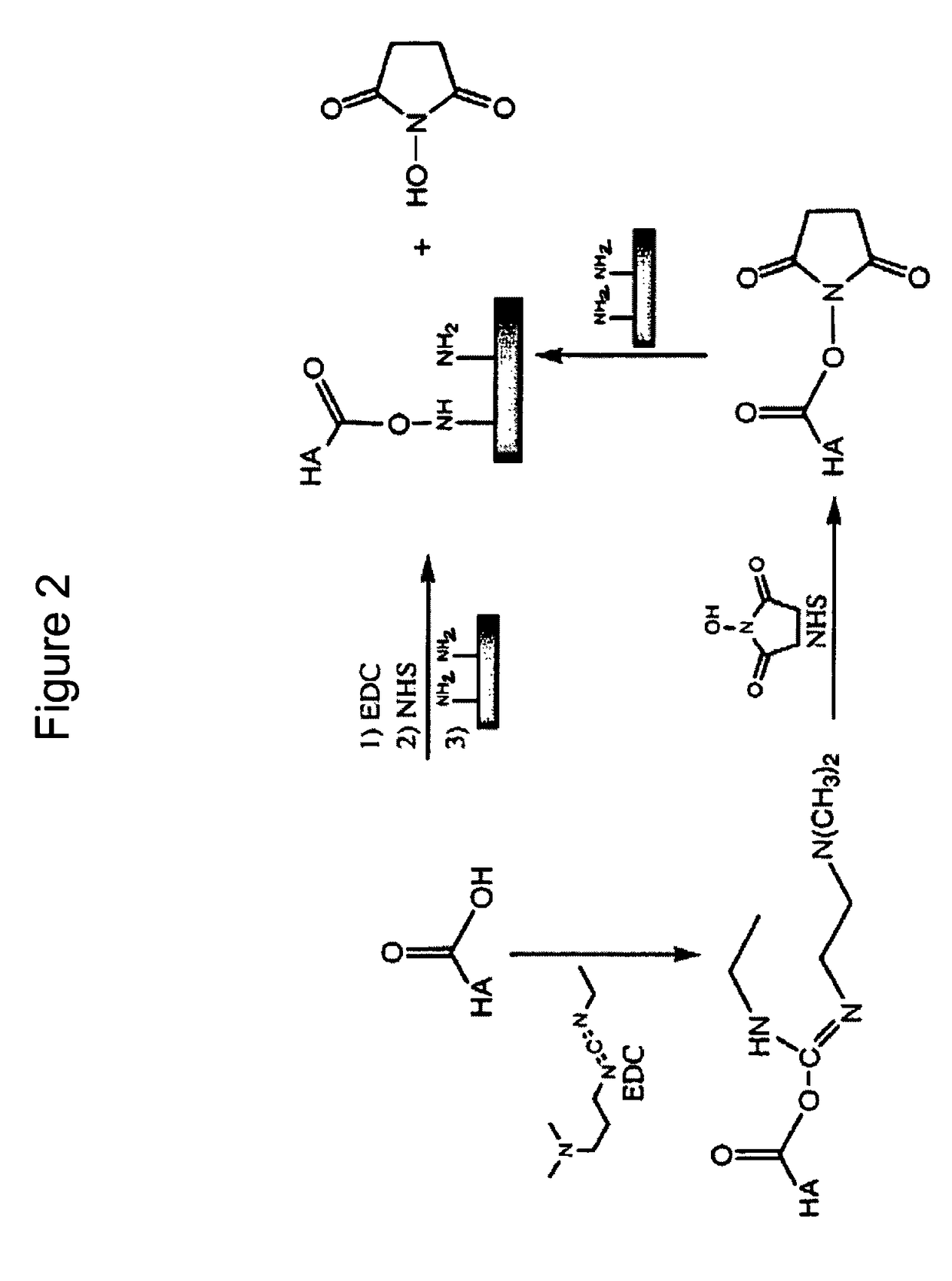
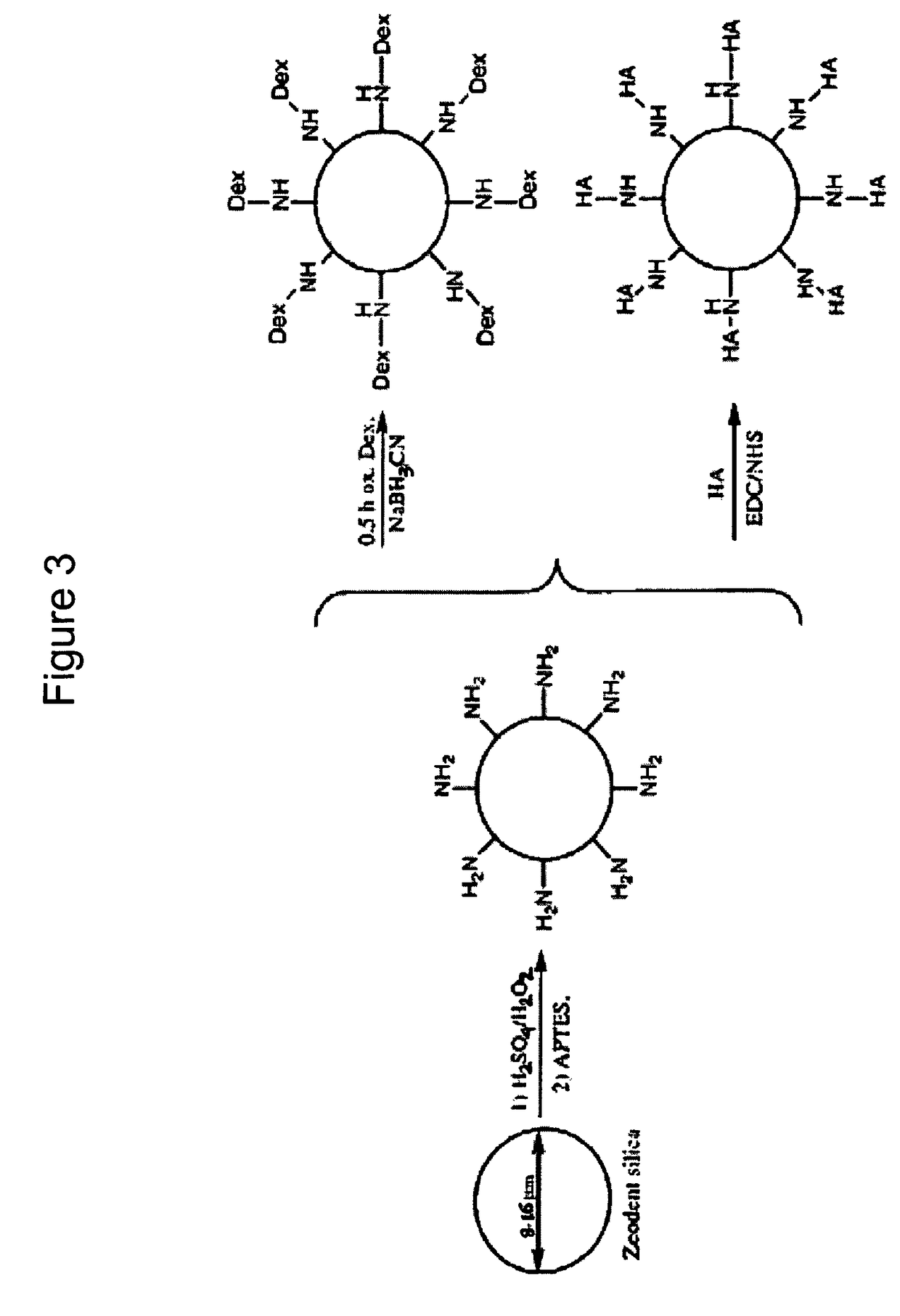
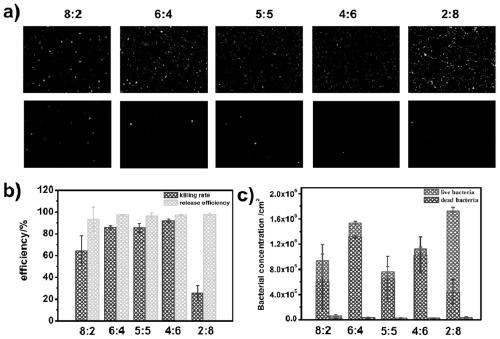
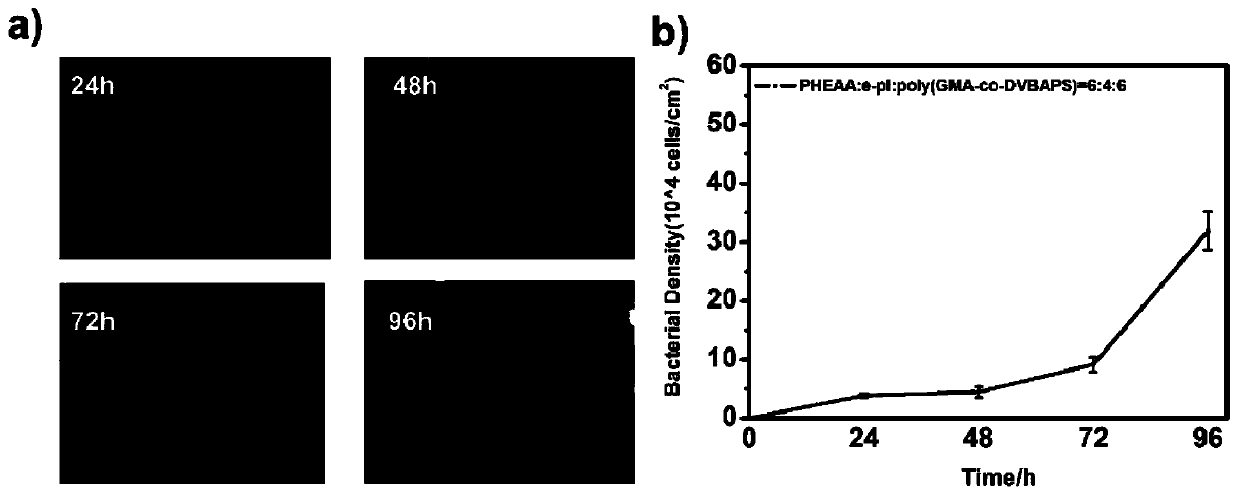
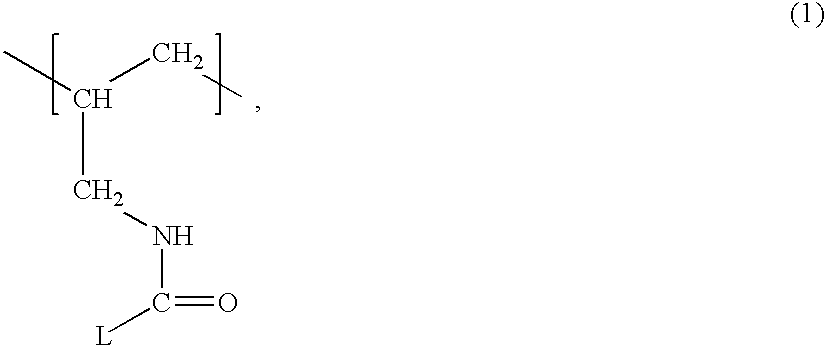Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
205 results about "Bacterial Adhesions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymeric articles having a lubricious coating and method for making the same
InactiveUS6940580B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove the lubrication effectSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsExtended wear contact lensesLens materials
The present invention provides a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens, which comprises a lubricious coating including a capping layer of polyvinylpyrrolidone and / or at least one layer of a lubricious coating material and one layer of a polyionic material having charges opposite of the charges of the lubricious coating material. The lubricious coating on the medical device of the invention has increased lubricity, preferably characterized by an averaged CoF of about 3.0 or less, increased hydrophilicity characterized by an averaged contact angle of about 80 degree or less, and increased bacterial adhesion resistance, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material. Such lenses are useful as extended-wear contact lenses. In addition, the invention provides a method for making a medical device, preferably a contact lens, having a lubricious coating thereon.
Owner:ALCON INC
Collagen binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6288214B1Prevent and lessen adhesionReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsCarrier protein
Disclosed are the cna gene and cna-derived nucleic acid segments from Staphylococcus aureus, and DNA segments encoding cna from related bacteria. Also disclosed are Col binding protein (CBP) compositions and methods of use. The CBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to Col. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(Col binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of bacterial colonization in an animal such as a human. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of S. aureus infection.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Antimicrobial coating for inhibition of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation
InactiveUS20080063693A1Increased coating antimicrobial efficacyPrevent bacterial adhesionBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsWater insolubleMetallic materials
The present invention provides antimicrobial coatings for coating substrate surfaces, particularly medical devices, for preventing bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation by inhibiting microbial growth and proliferation on the coating surface. The antimicrobial coatings are composed of a hydrogel and a bioactive agent including a substantially water-insoluble antimicrobial metallic material that is solubilized within the coating. Antimicrobial coating formulations for obtaining such coatings, and coating methods are also described.
Owner:BACTERIN
Coatings
ActiveUS20060150862A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCoated surfaceMedicine
This invention relates to coating a surface wherein the coated surface inhibits foulants such as cell and / or protein and / or prion adhesion or formation. In particular, the coated surface may be part of a medical device which inhibits bacterial adhesion and colonisation, thrombus formation and / or prion, blood protein and / or protein formation.
Owner:DUNDEE UNIV OF THE UNIV COURT OF THE
Method and apparatus for reducing intraocular pressure
ActiveUS20100057055A1Lower eye pressureFacilitate communicationEye surgeryWound drainsConjunctivaIntraocular pressure
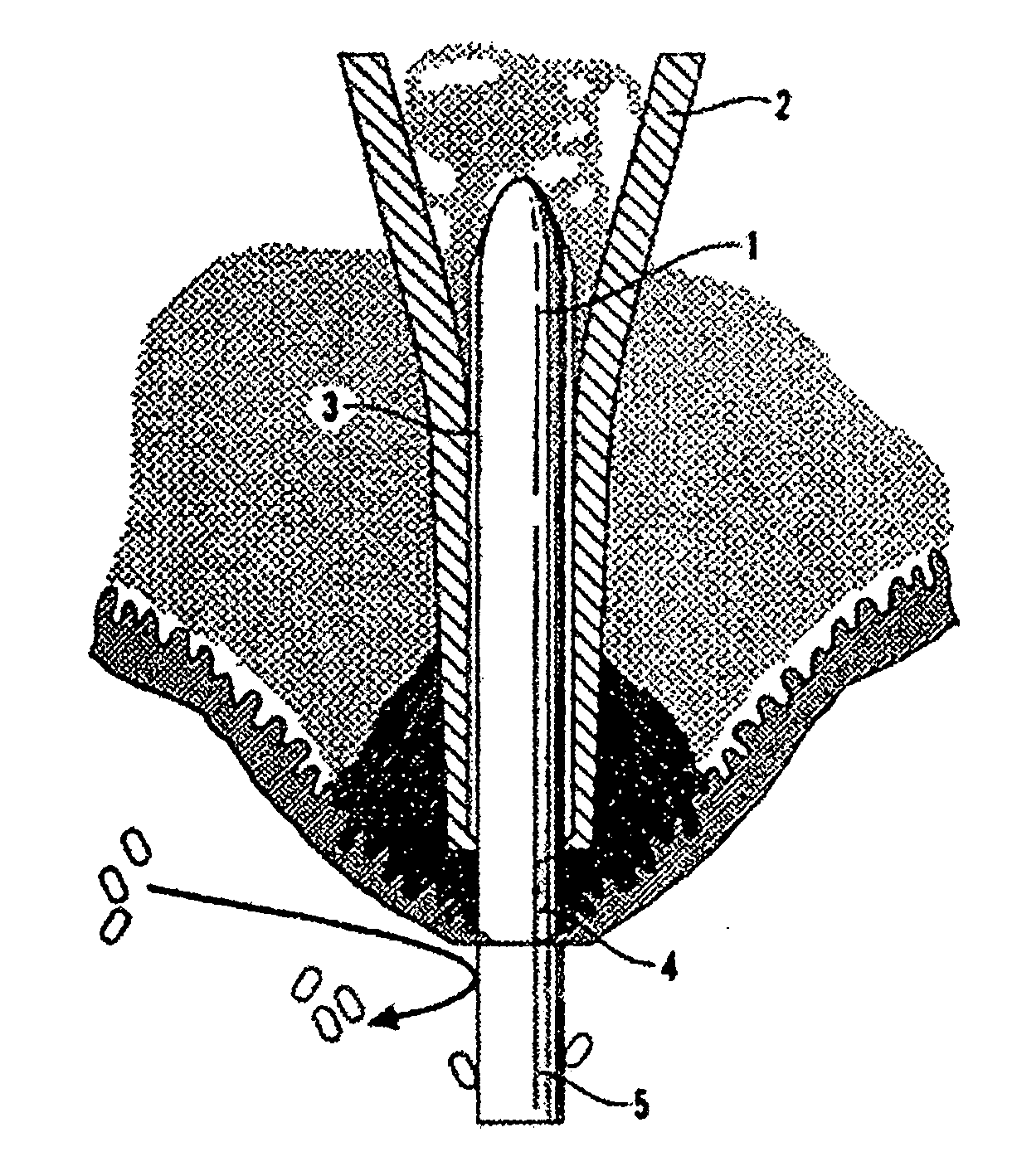
A drainage apparatus is disclosed to reduce intraocular pressure in an eyeball that includes an anterior chamber having aqueous humor disposed therein, a cornea and a surrounding marginal limbus by which the cornea is continuous with a scleral layer and a conjunctival layer disposed on an exposed surface of the eyeball and under eyelids, the apparatus comprising an inlet assembly configured to be disposed at the anterior chamber of the eyeball, an outlet assembly configured to be disposed at the external surface of the eyeball, the assembly having a central chamber, a tube extending between the inlet and outlet assemblies and configured to promote fluid communication between the inlet and outlet assemblies, and control means disposed within the outlet assembly for controlling a flow of aqueous humor through the tube from the anterior chamber of the eyeball to the external surface of the eyeball, the control means further comprising a replaceable filter disposed within the central chamber of the outer member to prevent intraocular infection, the filter having a medicinal agent applied thereto for preventing occlusion of the filter or bacterial contamination by inhibiting at least one of the formation of fibrotic membranes, inflammatory membrane, or bacterial adhesions or biofilms, thereby preventing increased of intraocular pressure or infection.
Owner:CAMRAS VISION
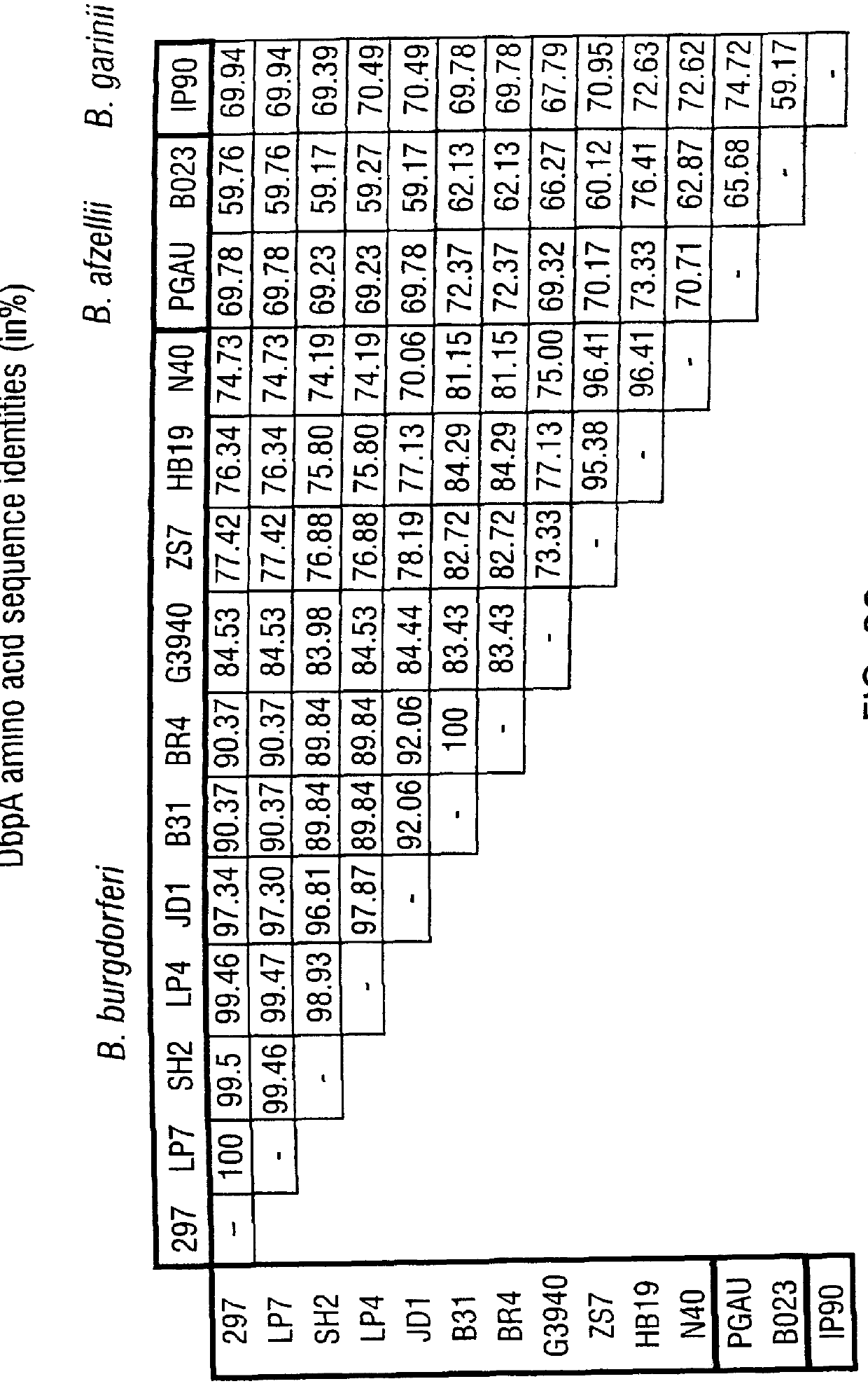
DbpA compositions and methods of use
Disclosed are the dbp gene and dbp-derived nucleic acid segments from Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiological agent of Lyme disease, and DNA segments encoding dbp from related borrelias. Also disclosed are decorin binding protein compositions and methods of use. The DBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological Borrelia infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to decorin. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(decorin binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of Borrelia colonization in an animal. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of Lyme disease.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Antibacterial and antitumor orthopaedic implantation material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an antibacterial and antitumor orthopaedic implantation material and a preparation method thereof. The implantation material is a medical pure titanium sheet with the surface modified by chitosan, methotrexate, heparin sodium, polylysine and dopamine. According to the material, dopamine serves as a bridge to allow polylysine and a heparin sodium particle to be bonded on the surface of titanium; heparin, as a good anticoagulant, can improve biocompatibility between the material and blood, and is bonded with chitosan and methotrexate with antibacterial and antitumor effects through an electrostatic effect. Physiological-biochemical characteristics of drugs are utilized ingeniously to form an orderly and uniform antibacterial and antitumor coating with high biocompatibility on the surface of the titanium, and the prepared implantation material has good antibacterial and antitumor activity, and can effectively prevent bacterial adhesion and reproduction, as well as recurrence and transfer of a cancer.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY COMMAND
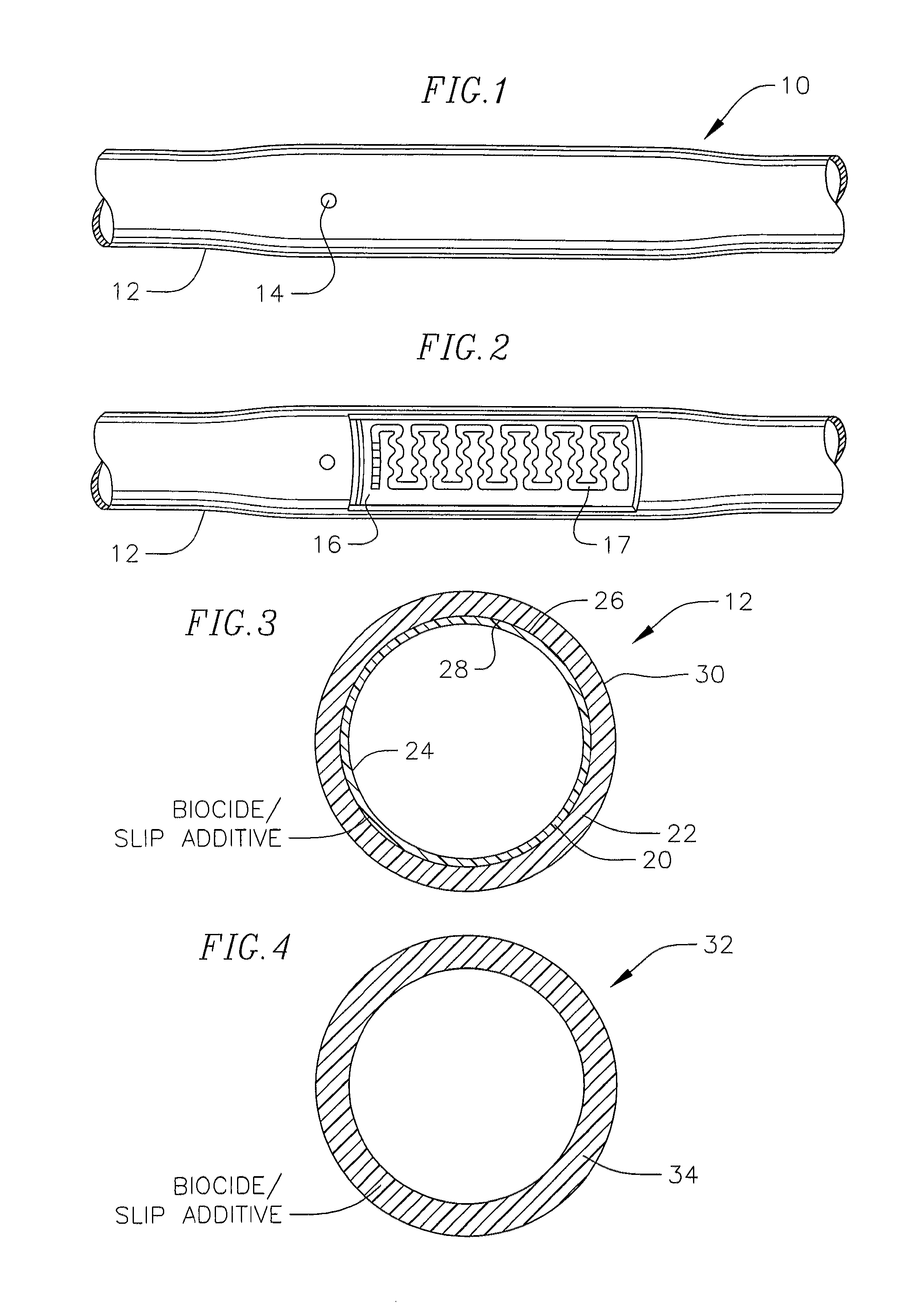
Prevention of bacterial adhesion irrigation conduits
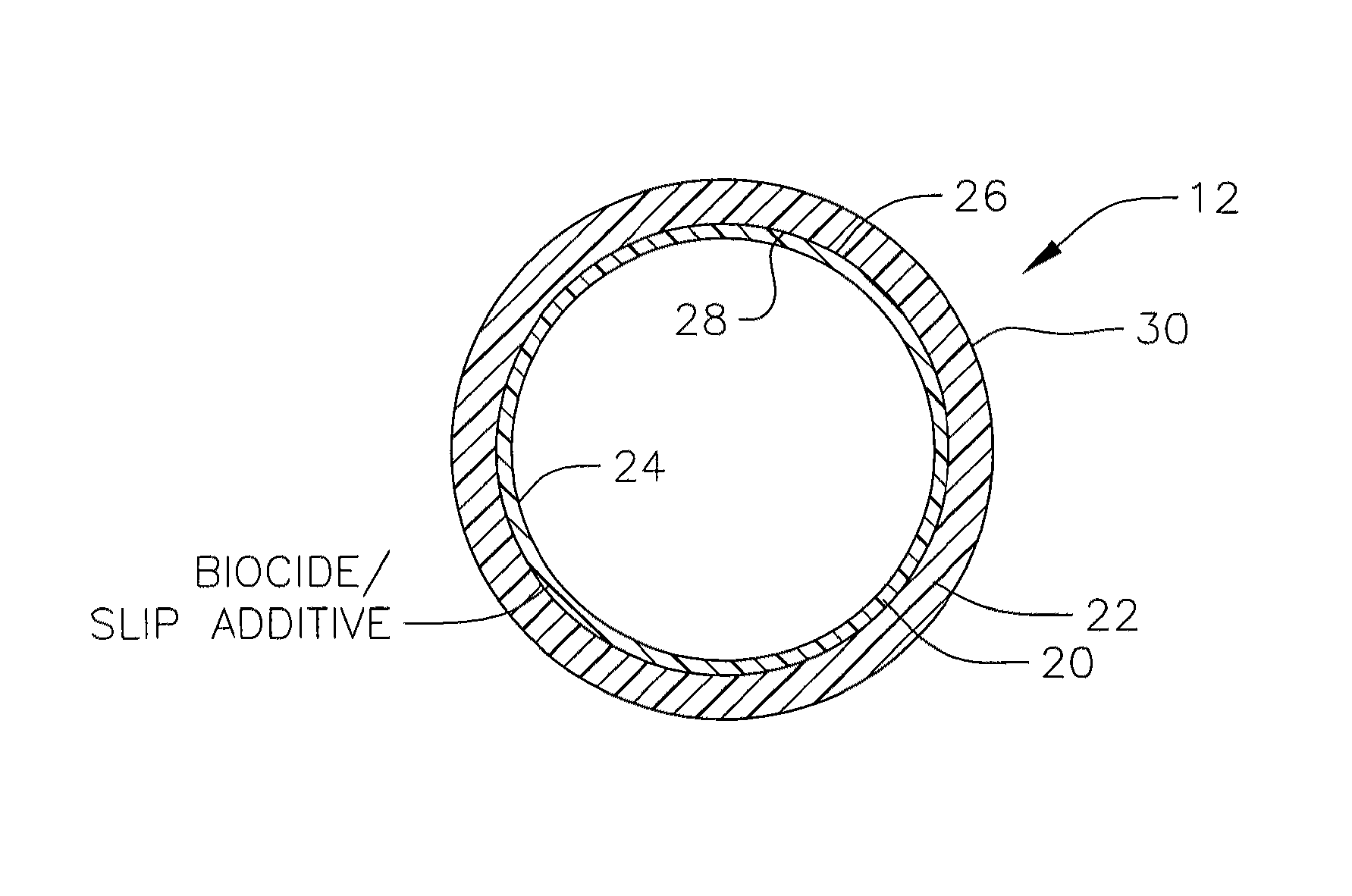
ActiveUS8286667B2Lower surfaceAvoid stickingHollow filament manufactureLayered productsBacterial AdhesionsDrip irrigation
A water transmission tubing for controlling the flow of water under pressure comprises a tubular inner liner of generally uniform cross-sectional configuration continuous with the length of the tubing and having an anti-bacterial agent for preventing the growth of bacteria on the inside wall of the tube. The inner liner contains a dispersed slip additive that forms a low friction surface inside the tubing for preventing adherence of slime to the inside of the tubing. The slip additive can comprise a fluoroelastomer, a fluoropolymer, a silicone resinous material, or mixtures thereof. The liner can be a separate inner layer of a multi-layer dripline, a monolayer form of the dripline or the inside of a drip irrigation emitter. The invention is particularly useful in subsurface treatment of wastewater.
Owner:CAST ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS LLC
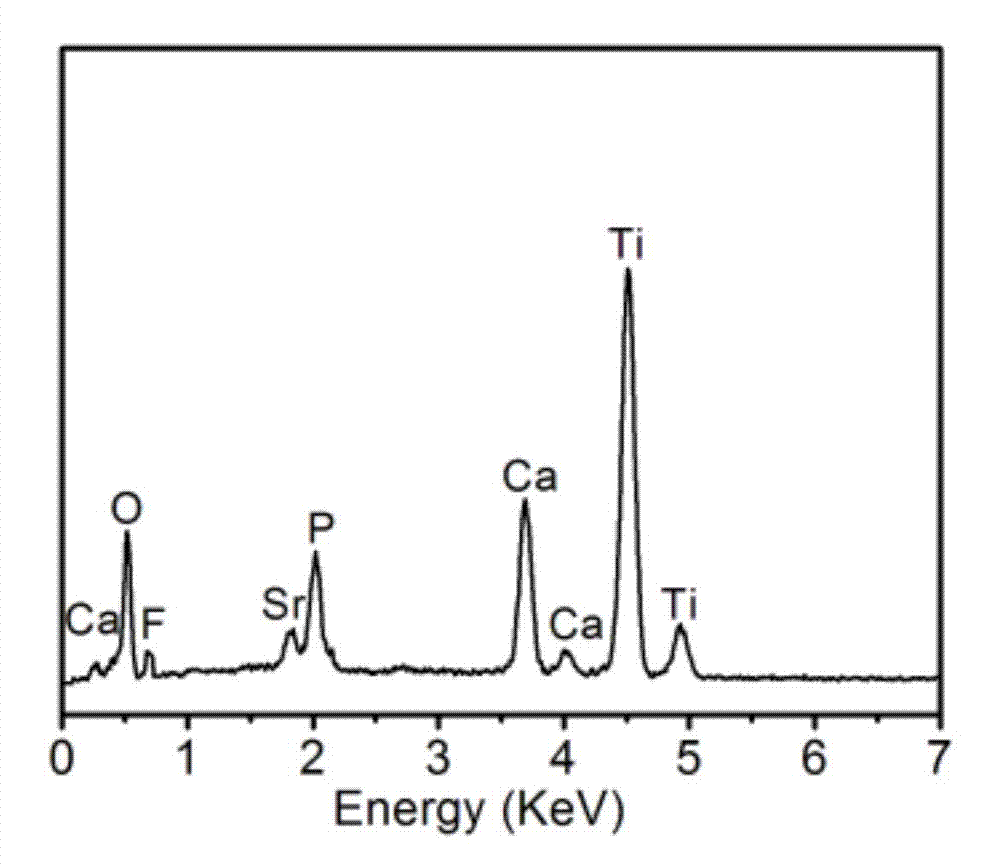
Titanium dioxide/strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104726921AEase of mass productionSimple and fast operationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisSolubilityPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention provides a titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an electrolyte containing calcium ions, strontium ions, fluorine ions and phosphate anions; and then by taking titanium or a titanium alloy as an anode and stainless steel as a cathode, directly preparing the titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating on the surface of a titanium or titanium alloy substrate by virtue of a micro-arc oxidation technology. The coating consists of an inner layer combined on the surface of the substrate and a surface layer combined on the surface of the inner layer, wherein the inner layer is a titanium dioxide layer in a form of a nano crystal and the surface layer is a nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer. No non-continuous interfaces are available between the coating and the substrate and the coating has high combining strength and structural stable performance; the coating is relatively small in solubility in a simulated body fluid, so that the coating is effectively implanted and used; and the nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer in the surface layer can remarkably promote the osteogenic function of the cells to form new bones and inhibit bacterial adhesion and growth.
Owner:宝鸡卡斯特医疗科技有限公司
Method for applying lubricious coating to a polymeric article
ActiveUS20050153056A1Improve hydrophilicityImprove the lubrication effectPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPretreated surfacesExtended wear contact lensesPolymer
The present invention provides a medical device, preferably an ophthalmic device, more preferably a contact lens, which comprises a lubricious coating including a capping layer of polyvinylpyrrolidone and / or at least one layer of a lubricious coating material and one layer of a polyionic material having charges opposite of the charges of the lubricious coating material. The lubricious coating on the medical device of the invention has increased lubricity, preferably characterized by an averaged CoF of about 3.0 or less, increased hydrophilicity characterized by an averaged contact angle of about 80 degree or less, and increased bacterial adhesion resistance, while maintaining the desired bulk properties such as oxygen permeability and ion permeability of lens material. Such lenses are useful as extended-wear contact lenses. In addition, the invention provides a method for making a medical device, preferably a contact lens, having a lubricious coating thereon.
Owner:ALCON INC
Oral compositions for prevention and reduction of bacterial adhesion to oral surfaces
ActiveUS20060134018A1Reduce interactionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAnti-Adhesion AgentAdditive ingredient
The present invention encompasses an oral composition containing an anti-adhesion agent, preferably a cysteine protease and most preferably ficin. In another aspect, the cysteine protease is in combination with one or more ingredients, such as antibacterial agent and surfactant. The anti-adhesion agent mitigates interaction between a subject oral cavity and plaque-forming materials.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Collagen binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20020102262A1Prevent diseaseSimple methodAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPassive ImmunizationsCarrier protein
Disclosed are the cna gene and cna-derived nucleic acid segments from Staphylococcus aureus, and DNA segments encoding cna from related bacteria. Also disclosed are Col binding protein (CBP) compositions and methods of use. The CBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to Col. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(Col binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of bacterial colonization in an animal such as a human. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of S. aureus infection.
Owner:HOOK MAGNUS +2
Transcutaneous prosthesis
InactiveUS20090149966A1More powerAid adhesionDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBacterial AdhesionsProsthesis
A transcutaneous prosthesis includes a first component configured for attachment to a bone, the first component including flutes or grooves on a surface thereof for deterring rotation of the prosthesis within a bone; a second component adapted for location between the bone and the skin, the second component having a surface treatment for stimulation of fibroblastic cell proliferation and attachment of epithelial cells; and a third component adapted for location to extend from the skin surface and is adapted to extend directly from the skin surface in use, the third component having a coating of a non-stick material on an outer surface thereof, the coating having a surface energy that is lower than a surface energy of the first and second components and which is low enough to deter bacterial adhesion.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Biological antibacterial and antifouling low surface energy coating with surface micro-structure and preparation method of biological antibacterial and antifouling low surface energy coating
ActiveCN104479487AGood weather resistanceImprove mechanical propertiesAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesMicro structureToxic material
The invention discloses a biological antibacterial and antifouling low surface energy coating with a surface micro-structure and a preparation method of the biological antibacterial and antifouling low surface energy coating. The antibacterial and antifouling coating comprises a microemulsionprepolymerizationsolution prepared from raw materials as follows: a fluorine-containinglow surface energy monomer, an acrylate monomer, a hydantoinderivative, an emulsifying agent, a co-emulsifier, an ammonia solution and tetraethoxysilane. The antifouling coating not only has anti-adhesion low surface energy hydrophobic nature, has a sterilization functionsimultaneously, can simultaneously resist protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion and has a double-protection function to delay formation of a biological film on the surface of a coating, so that growth and breeding of large-scale living organisms such as microalgae and the like on the coating surface are slowed down; the antifouling coating is prepared with a one-step microemulsion polymerizationmethod, can effectively prevent volatilization pollution of organic solvents, doesn't release toxic substances simultaneouslyand has the characteristics of environment-friendliness and safety; and the preparation method is simple and convenient, and film forming is fast.
Owner:广东洁科膜分离技术有限公司
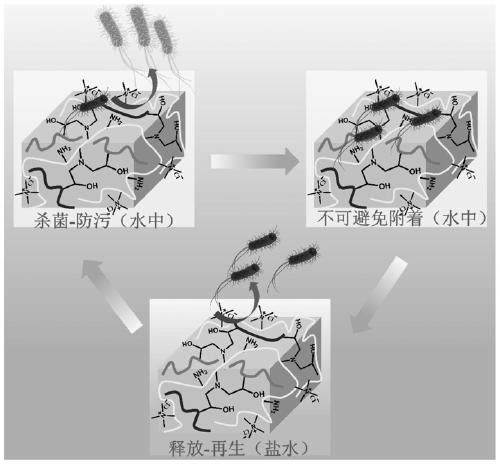
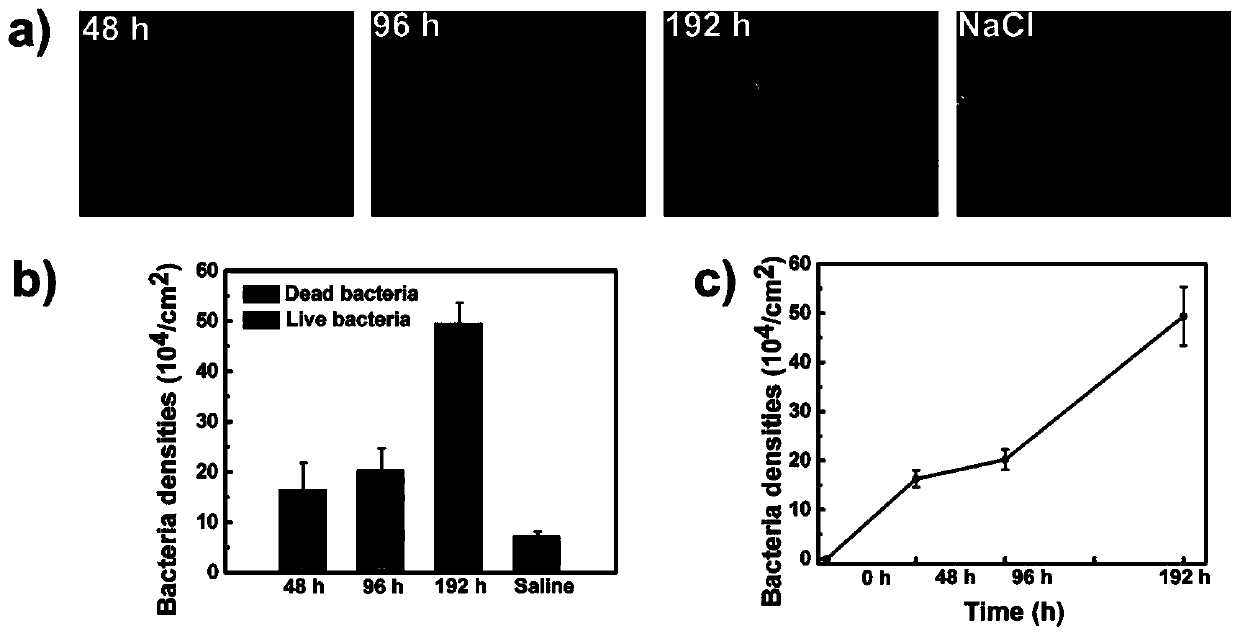
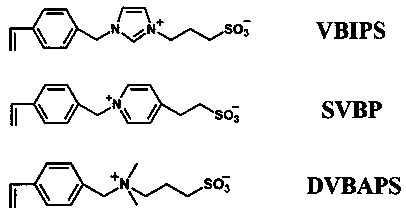
Antibacterial hydrogel with sterilization, low bacterial adhesion and bacterial release, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110330658AGood biocompatibilityOvercoming the problem of poor biocompatibilityBandagesWound dressingBacterial Adhesions
The invention belongs to the field of hydrogels, and particularly discloses a preparation method of an antibacterial hydrogel with sterilization, low bacterial adhesion and bacterial release, the method comprises the following steps: 1) mixing a response monomer and an epoxy monomer, and carrying out a free radical copolymerization reaction to obtain an epoxy group-containing response polymer; 2)mixing and dissolving the epoxy group-containing responsive polymer and an epoxy group-containing hydrophilic polymer in a solvent, and adding an amino group-containing bactericide to carry out epoxyring opening reaction to obtain the antibacterial hydrogel. The invention also discloses the antibacterial hydrogel with sterilization, low bacterial adhesion and bacterial release prepared by the preparation method and application thereof in wound dressing. The preparation process of the method is simple and efficient, the obtained hydrogel has comprehensive functions and good biocompatibility, has wide research prospects in the fields of biomedicine and tissue engineering, and provides a new idea for the preparation of functional materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Use of bacterial polysaccharides for biofilm inhibition
InactiveUS20120308632A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacterial AdhesionsBacterial polysaccharide
A method comprises preventing or inhibiting bacterial adhesion and / or bacterial biofilm development by treating a substrate with a composition of a soluble group II capsular polysaccharide obtained from a bacterial strain.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Enzyme-responsive intelligent bacterial adhesion resistant and bactericidal layer-by-layer self-assembled multi-layer film coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106853265AImprove adhesionImprove the bactericidal effectSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSpray coatingLayer by layer self assembly
The invention provides an enzyme-responsive intelligent bacterial adhesion resistant and bactericidal layer-by-layer self-assembled multi-layer film coating and a preparation method thereof. A surface-hydrophobic gel coating which is stable in a water environment is obtained through physical coating of chitosan, hyaluronic acid and a lysine solution, so that a material is endowed with bacterial adhesion resisting and contact sterilizing functions; polylysine improves the bacterial adhesion resistance of the material, so that the coating has the favorable gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial adhesion resisting and sterilizing capabilities. The preparation method is simple in process, quick, mild in condition, and easy for dip-coating, spin-coating, spray-coating and layer-by-layer self-assembly, can be implemented industrially, and has a wide application range, and the antibacterial performance, the bio-compatibility and the lubricity of the surface of medical devices can be effectively improved.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method for coating lens material
InactiveUS20070120279A1Desirable resultImprove wettabilityOptical articlesCoatingsBacterial AdhesionsMacromonomer
This invention relates generally to a method for treatment of lens surfaces by first coating the mold material with a reactive macromonomer and subsequently casting and curing the lens forming material along with the coating material present on the surface of the mold. The macromonomer reacts with the lens monomer mix and is covalently bound to the lens matrix. The modified lenses may ultimately show enhanced wettability, inhibition of bacterial adhesion and lower levels of protein and lipid deposition leading to increased comfort and longer wearing times.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
DbpA compositions
Disclosed are the dbp gene and dbp-derived nucleic acid segments from Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiological agent of Lyme disease, and DNA segments encoding dbp from related borrelias. Also disclosed are decorin binding protein compositions and methods of use. The DBP protein and antigenic epitopes derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the treatment of pathological Borrelia infections, and in particular, for use in the prevention of bacterial adhesion to decorin. DNA segments encoding these proteins and anti-(decorin binding protein) antibodies will also be of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of Borrelia colonization in an animal. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are contemplated for use in the preparation of vaccines and, also, for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations, and in the formulation of compositions for use in the prevention of Lyme disease.
Owner:MEDIMMUNIE +1
Biostatic coatings for reduction and prevention of bacterial adhesion
InactiveCN1282216AReduce coefficient of frictionNo reduction in antimicrobial propertiesBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsThiolBacterial Adhesions
The present invention relates to biostatic compositions, as well as coatings and methods for preparing biostatic articles using the same. The compositions contain a hydrophilic polymer possessing a functional group which covalently bonds to an amine, thiol, carboxyl, or hydroxyl active group of an antimicrobial agent. The functional group is capable of reacting with and covalently bonding to an antimicrobial agent without effectively reducing antimicrobial property of the antimicrobial agent below its capability of acting as a biostatic agent and without releasing the antimicrobial agent into a solution.
Owner:海德罗默公司
Particles that disrupt or impede bacterial adhesion, related compositions and methods
Oral care and other compositions comprising particles having cores attached to bioadhesive polymers for inhibition of pellicle formation, plaque formation, biofilm formation, biofouling, and microbial adhesion or attachment are described. Methods using said compositions to treat surfaces, such as oral surfaces.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Method for preparing broad-spectrum long-acting antibacterial anti-adhesive chitosan nano silver composite gel coating layer
InactiveCN105999407AImprove bond firmnessStable chemical structureSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolyvinyl alcoholSpray coating
The invention discloses a method for preparing a broad-spectrum long-acting antibacterial anti-adhesive chitosan nano silver composite gel coating layer, and is characterized in that with use of solutions of chitosan, silver nitrate and polyvinylpyrrolidone, the nano composite gel coating layer having hydrophilic surface and being stable in an aqueous environment is obtained by base material pretreatment, physical coating and in-situ reduction; the coating layer has excellent broad-spectrum bacterial adhesion resistance and sterilization abilities, and has excellent cellular biocompatibility. The method is simple and rapid in process, mild in conditions, easy to achieve by spin coating, dip coating, spray coating and other methods which can be implemented industrially, is wide in applicable scope, and can effectively improve antibacterial property, biocompatibility and lubricating property of surfaces of medical devices.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Stability-enhanced compound antibacterial coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
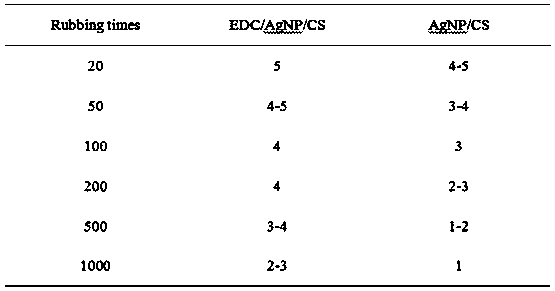
ActiveCN107899077AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove stabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsBacterial AdhesionsAqueous solution
The invention provides a preparation method of a stability-enhanced compound antibacterial coating. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a chitosan water solution is used for soaking a collagen substrate; then, water washing is performed to remove uncombined chitosan, wherein the molecular weight of the chitosan is 50 thousand to 500 thousand; (2) a nano-silver water solution is usedfor soaking the matter obtained in the step (1); then, water washing is performed to remove uncombined nano-silver; (3) an EDC and NHS mixed solution is used for soaking the matter obtained in the step (2); then, water washing is performed; next, drying is performed to obtain the stability-enhanced compound antibacterial coating. The obtained compound antibacterial coating has three kinds of antibacterial functions of resisting the bacterial adhesion, releasing bactericides for sterilization and realizing contact sterilization; the antibacterial performance is excellent; meanwhile, the compound antibacterial coating also has excellent stability, is applicable to various kinds of complicated environment and is particularly applicable to medical instrument surface anti-bacterium.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Engineered surfaces for reducing bacterial adhesion
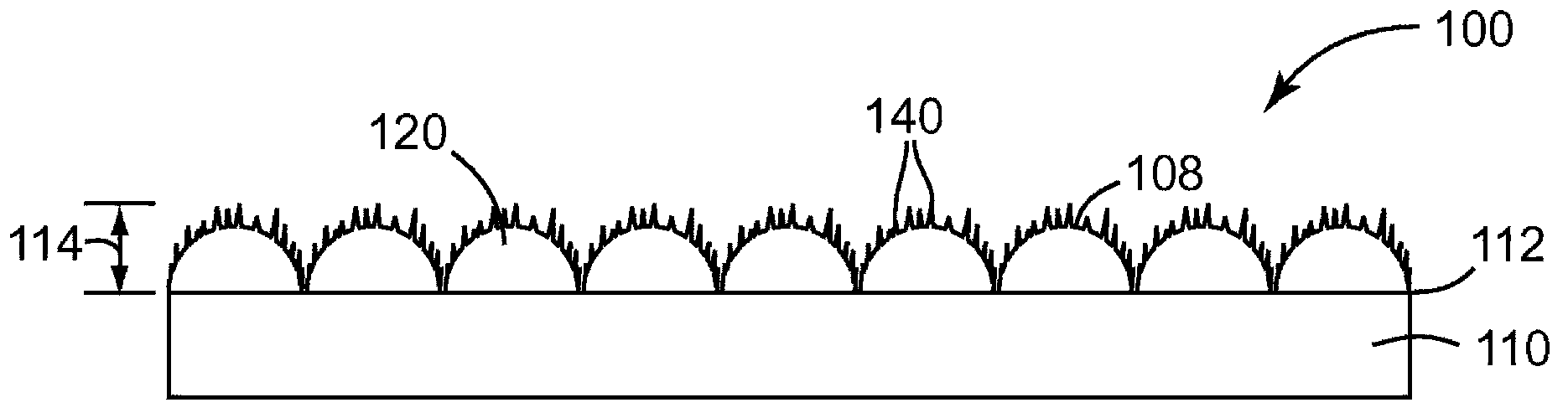
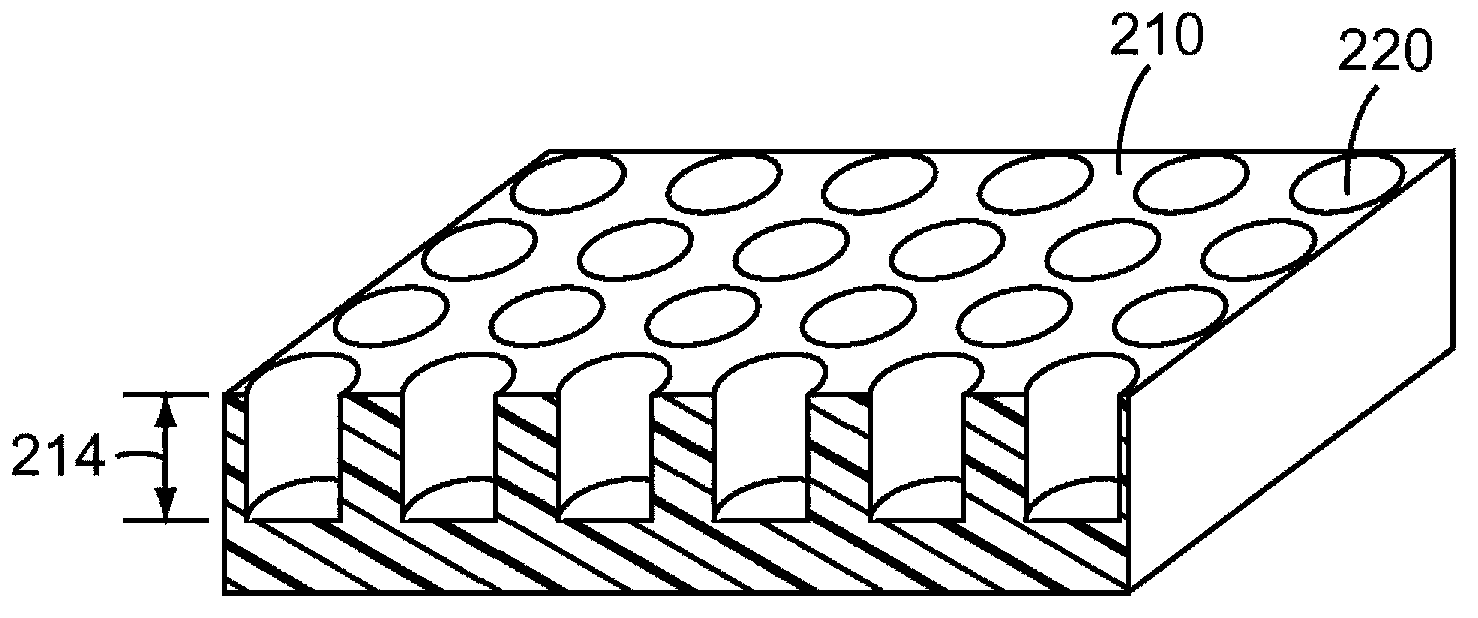
InactiveCN103180059ARetraction is predictable and more uniformGreat heat uniformityMaterial nanotechnologyFouling preventionBiofilmBacterial Adhesions
Disclosed are surfaces for resisting and reducing biofilm formation, particularly on medical articles (100). The surfaces include a plurality of microstructures (120) including a plurality of nanofeatures (140) arranged according to at least one unit cell. Also disclosed are methods for creating anti - adherent surfaces.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Transcutaneous Prosthesis
InactiveUS20070073412A1Increase the outer surface areaMore powerDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBacterial AdhesionsProsthesis
A transcutaneous prosthesis includes a first component shaped for implantation into a bone, the first component including flutes or grooves on a surface thereof for deterring rotation of the prosthesis within a bone; a second component adapted for location between the bone and the skin, the second component having a surface treatment for stimulation of fibroblastic cell proliferation and attachment of epithelial cells; and a third component adapted for location to extend from the skin surface and is adapted to extend directly from the skin surface in use, the third component having a coating of a non-stick material on an outer surface thereof, the coating having a surface energy that is lower than a surface energy of the first and second components and which is low enough to deter bacterial adhesion.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Preparation method of novel hydrogel with low bacterial adhesion and sterilization and regenerable functions
The invention discloses a preparation method of novel renewable hydrogel with low bacterial adhesion and sterilization and regenerable functions and belongs to the technical field of hydrogel preparation. The preparation method specifically comprises steps as follows: 1) a UV polymerization reaction; 2) an esterification reaction; 3) an ATRP reaction; 4) a sliver-supporting reaction. The preparation method is simple and feasible, a polymerization method guarantees the effectiveness and controllability of the length of a functional polymer brush, and the long-time antibacterial effect is realized through slow release of silver ions. The product has a remarkable inhibition effect on escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus; compared with an antibacterial product containing single components in the prior art, the product has greatly improved antibacterial efficiency. Besides, through the environmental responsibility of the functional polymer brush, shrinkage and extension of the polymerbrush due to the outside environment are changed, desorption of dead bacteria is further driven, and the regenerable antibacterial property of the hydrogel is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Medical macromolecular three-dimensional structural composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110029499AEvenly dispersedImprove stabilityVegetal fibresNatural fibresBiocompatibility TestingControllability
The invention provides a medical macromolecular three-dimensional structural composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that a degradable medical macromolecular polymer with the weight ratio of 1-10% is placed in an organic solvent and stirred for 2-12 hours; a mixed solution is prepared into a thin film with a three-dimensional structure; the three-dimensional structural material is placed in a dopamine solution for surface functionalization treatment; the three-dimensional structural material is taken out and placed in a zwitterionic polymerand collagen blended solution for a reaction of 12-48 hours; the three-dimensional structural material is taken out, washed with distilled water twice, dried under vacuum overnight and stored for use. The method is simple, feasible and high in controllability; the prepared composite material can resist bacterial adhesion, has good adhesion to cells and good biocompatibility, stability and mechanical properties, and is suitable for surface modification of three-dimensional stent materials.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Method for screening anti-adherent compounds on polymers for preventing biofilm formation
The instant invention provides a live labeling microorganism assay for screening a one-bead one-compound library to identify synthetic anti-adherent compounds for blocking biofilm formation. The compounds of libraries may be peptides, small molecules, nucleic acids, other types of molecules or a combination of the foregoing. The live labeling microorganisms are incubated with a one-bead one-compound library for a long period with fresh-labeled bacteria and nutrition replacement in regular intervals. Those beads without bacterial adhesion are transferred into nutritional agar for the culture. The true anti-adherent beads are isolated and the sequences of each isolated compound-bead are determined with sequencer. The anti-adherent compounds identified in this invention are proved to possess long-term effect of blocking bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Thus the instant invention provides a unique and powerful method to identify anti-adherent compounds from library more quickly and reliably than current state-of-the-art technology allows.
Owner:BIOPATH LAB DELAWARE
Method for constructing antifouling-sterilizing-releasing type surface coating by utilizing dopamine and product thereof
ActiveCN110484062A"Anti-pollution-sterilization-release" triple function is goodAvoid complexityAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesStimuli responsiveBacterial Adhesions
The invention discloses a method for constructing an antifouling-sterilizing-releasing type surface coating by using dopamine, which comprises the following steps: adding an epoxy group-containing stimuli-responsive polymer, a sterilization polymer and an anti-pollution polymer into a dopamine solution, and standing and co-depositing on a substrate to obtain the anti-pollution-sterilization-release surface coating. The method is simpler and more efficient and can be applied to any substrate, and the application range of antibacterial surfaces is greatly expanded. The invention further discloses the antifouling-sterilizing-releasing type surface coating prepared by the method, the coating can resist bacterial adhesion for a long time and kill bacteria, and when the adhesion amount of dead bacteria reaches a certain degree, the bacteria adhered to the surface can be released by changing external conditions, and functional regeneration is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com