Collagen binding protein compositions and methods of use
a collagen and protein technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of poor clinical outcome, permanent disability with limited motion or persistent pain in the affected joint, and bacterial arthritis acquired by the patient's hematogenous bacterial infection remains a serious medical problem,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
5.1 Example 1
Critical Residues In The Ligand Binding Site Of The S. Aureus CBP
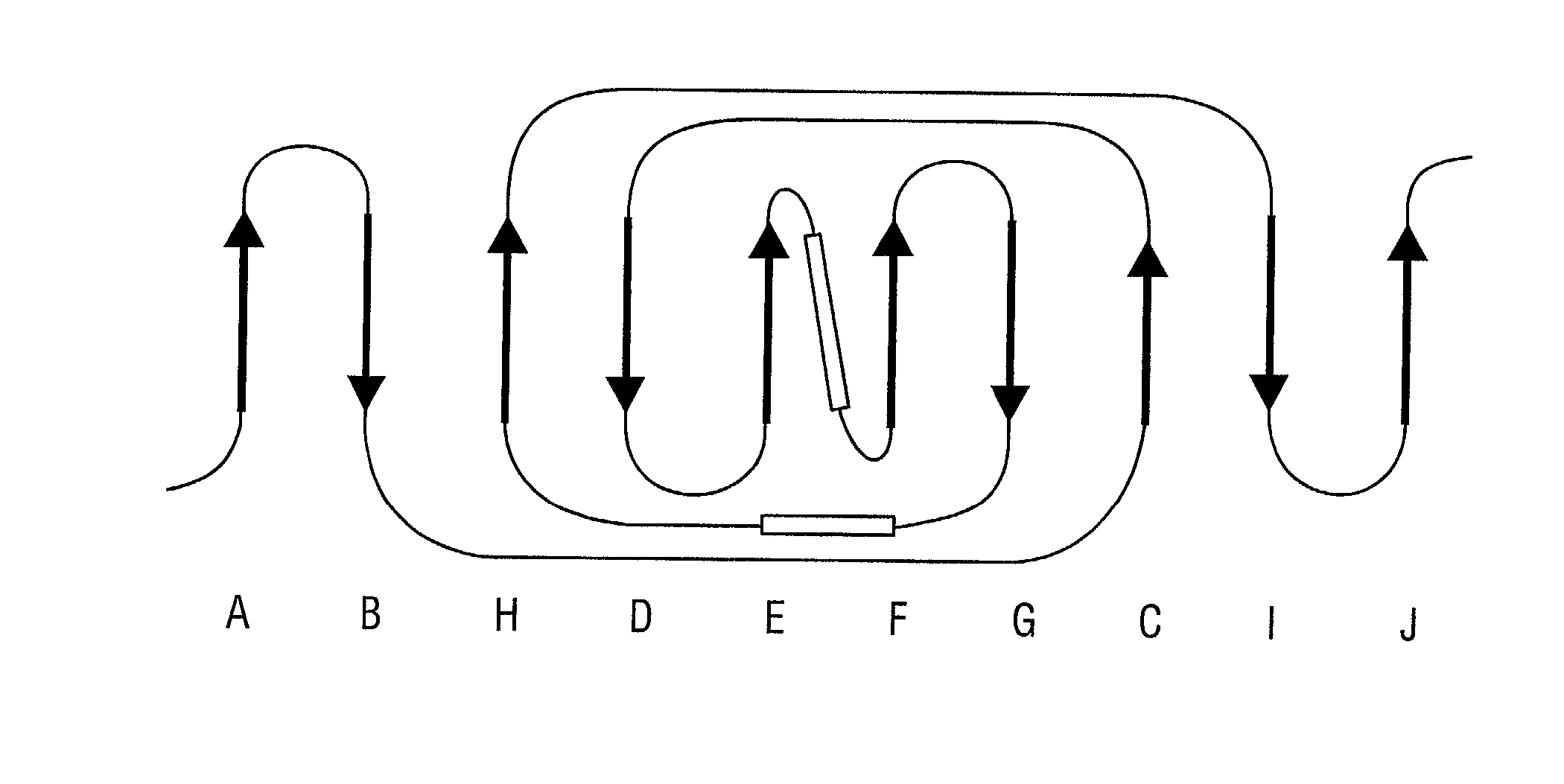
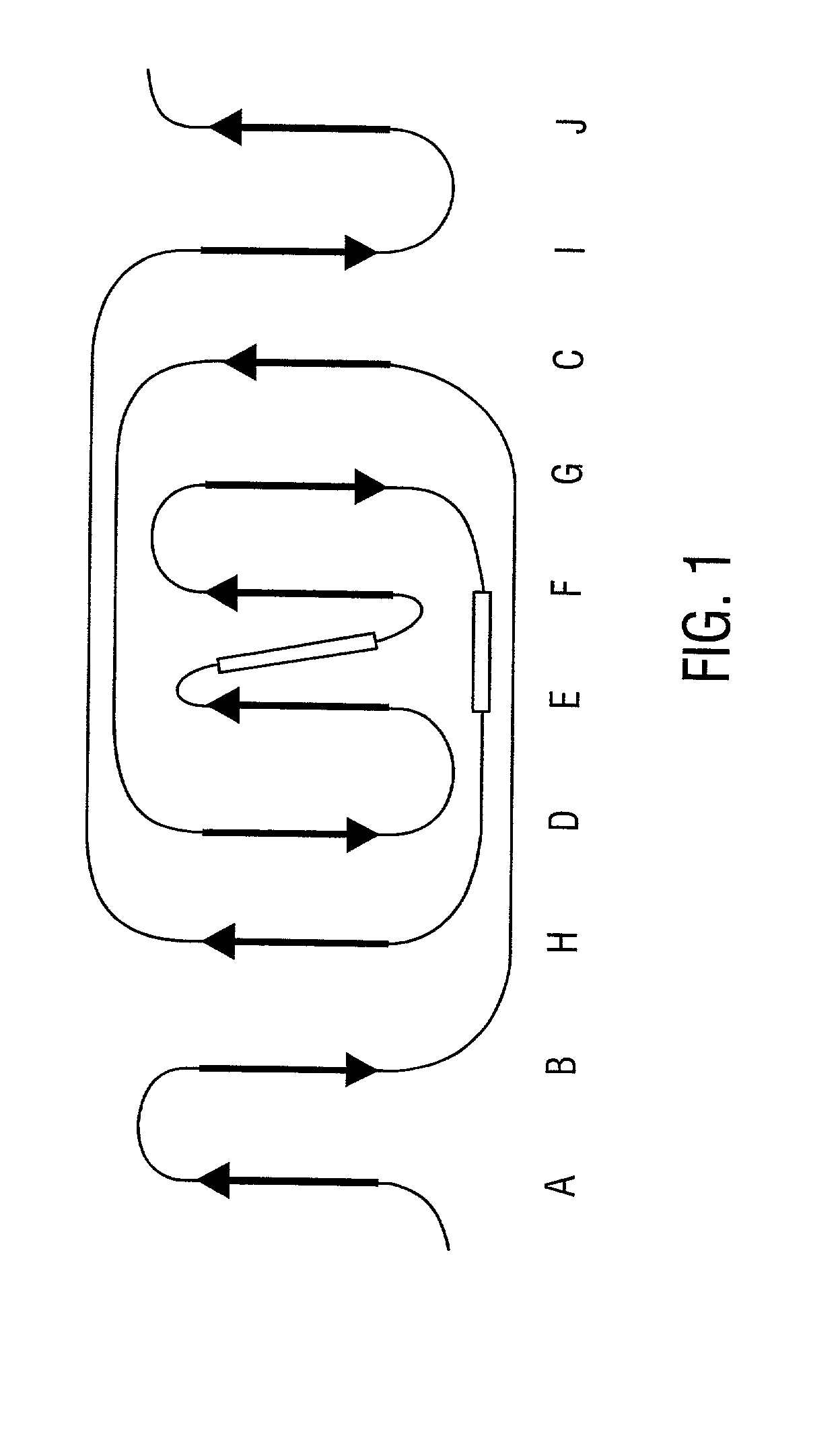
[0316] A discrete Col-binding site has been identified within the S. aureus Col adhesion that is located in a region between amino acids Asp.sup.209 and Tyr.sup.233. Polyclonal antibodies raised against a recombinant form of the Col adhesin inhibited the binding of type II Col to S. aureus. When overlapping synthetic peptides mimicking segments of the adhesion fragment were tested for their ability to neutralize the inhibitory activity of the antibody only one peptide, CBD4 was found to be active. CBD4 bound directly to Col and at high concentrations inhibited the binding of Col to S. aureus. A synthetic peptide derivative of CBD4 lacking 2 carboxyl-terrninal residues (Asn.sup.232, Tyr.sup.233) had minimal inhibitory activity. The importance of these residues for Col binding was confirmed by biospecific interaction analysis. Mutant adhesin proteins N.sup.232.fwdarw.A and Y.sup.233.fwdarw.A exhibited dramat...
example 2
5.2 EXAMPLE 2
Structure of the COL-binding Domain from the S. aureus CBP
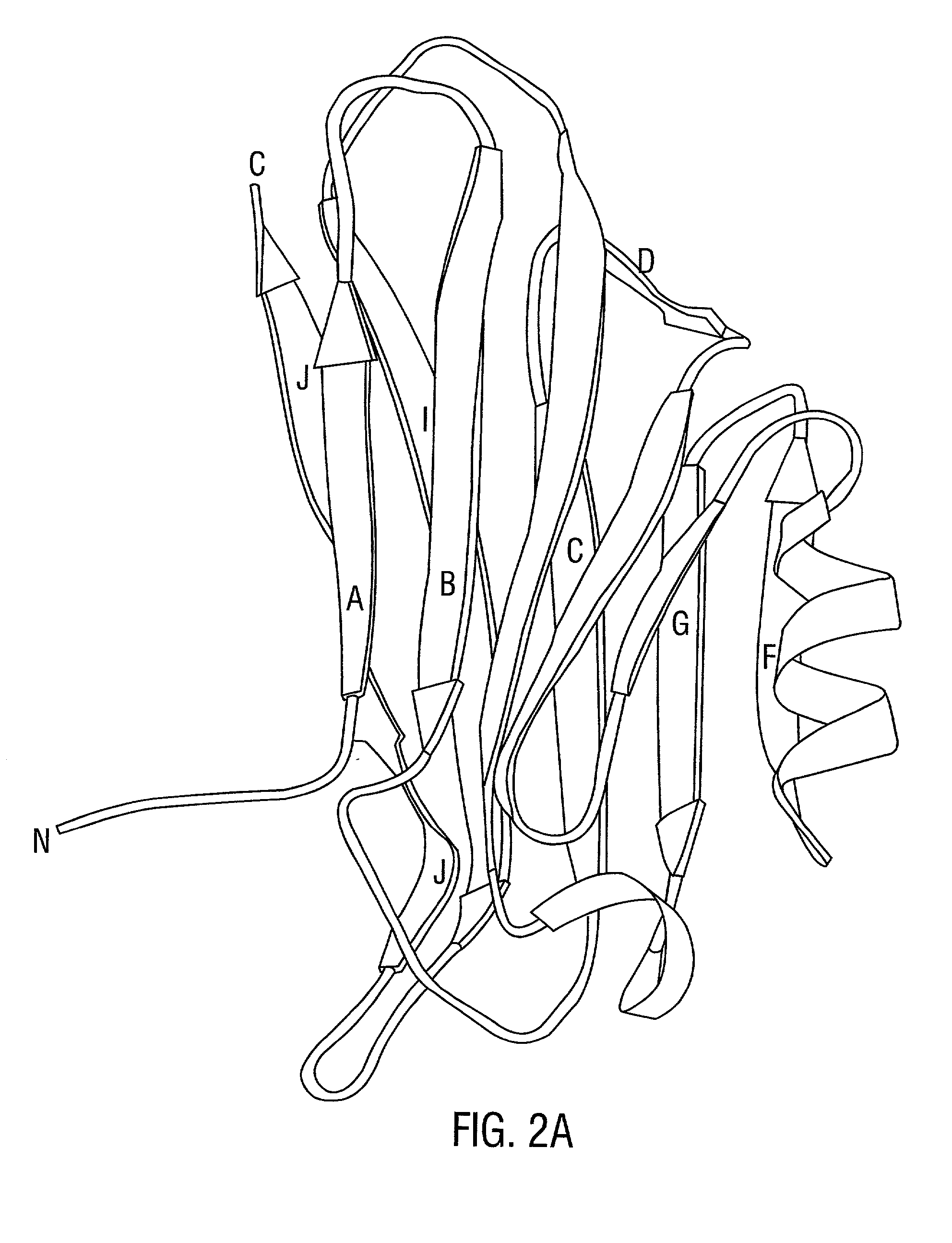
[0333] The structural basis for host tissue targeting by S. aureus presented here reveals that the Col-binding domain CBD(151-318) is well-designed to interact with triple-helical Col structures. The binding interface of the domain is built along a groove on a concave .beta.-sheet and has considerable geometrical and chemical complementarity to the Col helical segment containing four repeats of Gly-Pro-Hyp or Gly-Pro-Pro per chain. Mutational analysis has confined the putative Col binding site, and suggests that the simple docking model may have more general significance. In this model, the Col triple helix itself is a major recognition-element for the bacterial adhesin containing complementary binding site. This provides a structural explanation for the earlier observations of the MSCRAMM's specificity for triple-helical structures (Speziale et al., 1986). In addition, the suggested binding site on the adhesin a...
example 3
5.3 EXAMPLE 3
Passive Immunization Using Epitopes of MSCRAMMS
[0359] Underlined amino acids are encoded in the vector pQE.TM.-30 (Qiagen Inc. Chatsworth, Calif.)
4 5.3.1 S. AUREUS COL-BINDING MSCRAMM DERIVATIVE M17 (SEQ ID NO:2) MRGSHHHHHHGSITSGNKSTNVTVHKSEAGTSSVFYYKTGDMLPEDTTHV RWFLNINNEKSYVSKDITIKDQIQGGQQLDLSTLNINVTGTHSNYYSGQS AITDFEKAFPGSKITVDNTKNTIDVTIPQGYGSYNSFSINYKTKITNEQQ KEFVNNSQA (GenBank accession number of entire cna gene is M81736)
[0360]
5 5.3.2 S. AUREUS CBP EPITOPE M17 DNA (SEQ ID NO:1) ATAACATCTGGGAATAAATCAACGAATGTTACGGTTCATAAAAGTGAAGCGGGAACAAGTAGTGTTTTC TATTATAAAACGGGAGATATGCTACCAGAAGATACGACACATGTACGATGGTTTTTAAAT-ATTAACAAT GAAAAAAGTTATGTATCGAAAGATATTACTATAAAGGATCAGATTCAA-GGTGGACAGCAGTTAGATTTA AGCACATTAAACATTAATGTGACAGGTACACATAGC-AATTATTATAGTGGACAAAGTGCAATTACTGAT TTTGAAAAAGCCTTTCCAGGTTCT-AAAATAACTGTTGATAATACGAAGAACACAATTGATGTAACAATT CCACAAGGCTATGGGTCATATAATAGTTTTTCAATTAACTACAAAACCAAAATTACGAATGAACAGCAA AAAGAGTTTGTTAATAATTCACAAGCT
[0361]
6 5.3.3 S. AUREUS COL-BINDING MSCRAMM ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com